Page 1

INSTRUCTIONS for
F-5884-U
July, 2005
C-58 MACHINE CUTTING TORCHES
CAUTION
!
These INSTRUCTIONS are for experienced operators. If you are not fully familiar with the principles of operation and safe practices for Oxy-Fuel gas
equipment, we urge you to read our booklet "Precautions and Safe Practices for Welding, Cutting, and Heating, "Form 2035. Do NOT permit untrained
persons to install, operate or maintain this equipment. Do NOT attempt to install or operate this equipment until you have read and fully understand
these instructions. If you do not fully understand these instructions, contact your supplier for further information.
The cutting torch covered by these instructions are listed by Underwriter's Laboratories only when using cutting nozzles and parts manufactured by
ESAB Welding & Cutting Products to the specifications on file with Underwriter's Laboratories, Inc. and when they are used in the gas service for
which they are designed and listed. The use of other cutting nozzles and parts that cause damage or failure to the equipment will void the manufacturer's
warranty.
SPECIFICATIONS
Cutting Capacity using acetylene ..................... 6-in. (150 mm)
Cutting Capacity using other fuel gases ........... 2-in. (50 mm)
Cutting Nozzles ........................................................ 1500 series
Torch-Hose Connections ........................... ."B" size (9/16"-18)
Overall Length.............................................. 12-1/2in. (318 mm)
Barrel Diameter ............................................... 1-3/8-in. (35 mm)
OPERA TING INSTRUCTIONS
CONNECTING
1. Attach regulators to the oxygen and fuel gas cylinders. Follow all instructions supplied with the regulators.
NOTE: If using the 3-hose C-58 torch, use two oxy-
gen cylinders-one for cutting oxygen and the
other for preheat oxygen.
2. Attach the oxygen and the fuel gas hoses to the regulators and to the proper connections on the torch, after making sure all metal seating surfaces are clean.
Tighten all connection nuts with a wrench.
3. Attach nozzle to torch head, and tighten connection
nut with a wrench.
4. Check throttle valve packing nuts for tightness.
Flashbacks can cause serious burns.
Be sure gas flow is sufficient for head or nozzle size.
Adjust regulators for proper psig pressures.
Adjust throttle valves properly.
Keep torch in good repair.
DO NOT throttle back gases to use large head or nozzle
on thin material.
ADJUSTING GAS PRESSURES
Fuel Gas: Open the fuel gas valve about one turn. Turn
in the pressure-adjusting screw on the fuel gas regulator until its delivery-pressure gauge registers the desired
pressure (see cutting chart on page 4). Then immediately close the fuel gas valve.
Oxygen: Open the cutting oxygen valve wide and turn
in the pressure-adjusting screw on the oxygen regulator until its delivery-pressure gauge registers the desired
cutting oxygen pressure (see cutting chart on page 4).
Then close the cutting oxygen valve.
If using the 3-hose C-58 torch, open the preheat oxygen valve two full turns and adjust regulator to the desired preheat oxygen pressure (see cutting chart on page
4). Then close the preheat oxygen valve.
NOTE: When gaugeless regulators are used, do not
open torch valves. Merely turn in the pressureadjusting screws to the desired pressure as indicated on the scales of the regulator caps.
TESTING FOR LEAKS
Every cutting outfit should be thoroughly tested for leaks
after it is first hooked up, and at regular intervals thereafter. After all connections have been made, make sure
all valves on the torch handle are closed. Then turn in
the regulator pressure-adjusting screws until the oxygen delivery-pressure gauge registers 60 psi and the
fuel gas delivery-pressure gauge registers 10 psi. Using Leak Test Solution, suitable for oxygen service, such
as P/N 998771 (8 oz. container), check for leaks at the
cylinder valves, the cylinder-to-regulator connections,
the regulator-to-hose connections, and the hose-to-torch
Be sure this information reaches the operator.
Y ou can get extra copies through your supplier.
Page 2

SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
These Safety Precautions are for your protection. They summarize precautionary information from the references listed
in Additional Safety Information section. Before performing any
installation or operating procedures, be sure to read and follow the safety precautions listed below as well as all other
manuals, material safety data sheets, labels, etc. Failure to observe Safety Precautions can result in injury or death.
PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS - Some
welding, cutting and gouging processes are
noisy and require ear protection. Hot metal can
cause skin burns and heat rays may injure
eyes. Training in the proper use of the processes and equipment is essential to prevent
accidents. Also:
1. Always wear safety glasses with side shields in any work area,
even if welding helmets, face shields, or goggles are also required.
2. Wear flameproof gauntlet type gloves, heavy long-sleeve shirt,
cuffless trousers, high-topped shoes, and a welding helmet or
cap for hair protection, to protect against hot sparks and hot
metal. A flameproof apron may also be desirable as protection
against radiated heat and sparks.
3. Hot sparks or metal can lodge in rolled up sleeves, trousers
cuffs, or pockets. Sleeves and collars should be kept buttoned,
and open pockets eliminated from the front of clothing.
4. Protect other personnel from hot sparks with a suitable nonflammable partition or curtains.
5. Use goggles over safety glasses when chipping slag or grinding. Chipped slag may be hot and can travel considerable distances. Bystanders should also wear goggles over safety
glasses.
FIRES AND EXPLOSIONS - Heat from a flame
can act as an ignition source. Hot slag or sparks
can also cause fires or explosions. Therefore:
1. Remove all combustible materials well away from the work
area or completely cover the materials with a protective nonflammable covering. Combustible materials include wood,
cloth, sawdust, liquid and gas fuels, solvents, paints and coatings, paper, etc.
2. Hot sparks or hot metal can fall through cracks or crevices in
floors or wall openings and cause a hidden smoldering fire on
the floor below. Make certain that such openings are protected
from hot sparks and metal.
3. Do not weld, cut, or perform any other hot work on materials,
containers, or piping until it has been completely cleaned so
that no substances on the material can produce flammable or
toxic vapors. Do not do hot work on closed containers. They
may explode.
4. Have fire extinguishing equipment handy for instant use, such
as a garden hose, a pail of water or sand, or portable fire
extinguisher. Be sure you are trained in its use.
5. After completing operations, inspect the work area to be sure
that there are no hot sparks or hot metal which could cause a
later fire. Use fire watchers when necessary.
6. For additional information, refer to NFPA Standard 51B, “Fire
Prevention in Use of Cutting and Welding Processes”, which
is available from the National Fire Protection Association,
Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
FUMES AND GASES - Fumes and gases, particularly in confined spaces, can cause discomfort or injury. Do not breathe fumes or
gases from welding or cutting, Therefore:
1. Always provide adequate ventilation in the work area by natural or mechanical ventilation means. Do not weld, cut, or gouge
on materials such as galvanized steel, stainless steel, copper,
zinc, lead, beryllium, or cadmium unless positive mechanical
ventilation is provided. Do not breathe fumes and gases from
these materials.
2. If you develop momentary eye, nose, or throat irritation while
operating, this is an indication that ventilation is not adequate.
Stop work at once and take necessary steps to improve ventilation in the work area. Do not continue to operate if physical
discomfort persists.
3. Refer to ANSI/ASC Standard Z49.1 listed below for specific
ventilation recommendations.
4. WARNING: This product, when used for welding or
1. Always have qualified personnel perform the installation,
troubleshooting, and maintenance work. Do not operate or
repair any equipment unless you are qualified to do so.
2. Keep all oxy-fuel equipment free of grease or oil. Grease, oil,
and other similar combustible materials, when ignited, can burn
violently in the presence of oxygen.
3. Do not abuse any equipment or accessories. Keep equipment
away from heat and wet conditions, oil or grease, corrosive
atmospheres and inclement weather.
4. Keep all safety devices in position and in good repair.
5. Use equipment for its intended purpose. Do not modify it in
any manner.
1. Use the proper gas for the process and use the proper pressure reducing regulator designed to operate from the compressed gas cylinder. Do not use adaptors to mount the regulator on the cylinder. Maintain hoses and fittings in good condition. Follow manufacturer’s operating instructions for mounting the regulator to the gas cylinder.
2. Always secure cylinders in an upright position by chain or strap
to suitable hand trucks, benches, walls, post, or racks. Never
secure cylinders to work tables or fixtures where they may
become part of an electrical circuit.
3. When not in use, keep cylinder valves closed. Have the valve
protection cap in place on top of the cylinder if no regulators is
installed. Secure and move cylinders by using suitable hand
trucks. Avoid rough handling of cylinders.
4. Locate cylinders away from heat, sparks, or flame of a welding, cutting, or gouging operation. Never strike an arc on a
cylinder.
5. For additional information, refer to CGA Standard P-1, “Precautions for Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders:, which is available from the Compressed Gas Association, 1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Arlington, VA 22202.
The following publications, which are available from the American
Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJuene Road, Miami, FL 33126, are
recommended to you:
1. ANSI/AWS Z49.1 - “Safety in Welding and Cutting”.
2. AWS F4.1 - “Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cutting of Containers and Piping That
Have Held Hazardous Substances”/
3. AWS SP - “Safe Practices” - Reprint, Welding Handbook.
2
cutting, produces fumes or gases which
contain chemicals known to the State of
California to cause birth defects and, in
some cases, cancer. (California Health &
Safety Code §25249.5 et seq.)
EQUIPMENT MAINTENANCE - Faulty or improperly maintained equipment, such as torches, hoses
and regulators, can result in poor work, but even
more important, it can cause injury or death
through fires. Therefore:
GAS CYLINDER HANDLING - Gas cylinders, if mishandled, can rupture or explode violently . Sudden
rupture of a cylinder, valve or relief device can injure or kill you. Therefore:
ADDITIONAL SAFETY INFORMATION - For more
information on safe practices for oxy-fuel welding
and cutting equipment, ask your distributor for a
copy of “Precautions and Safe Practices for Gas
Welding, Cutting, and Heating”, Form 2035. Gas
apparatus safety guidelines are also available on
video cassettes from your distributor.
MEANING OF SYMBOLS - As used throughout
this manual: Means Attention! Be Alert! Your
safety is involved.
Means immediate hazards which, if not avoided,
will result in immediate, serious personal in-
jury or loss of life.
Means potential hazards which could result in
personal injury or loss of life.
Means hazards which could result in minor
personal injury.
SP-GA 10/98
Page 3

connections. If bubbling at any point indicates leakage,
tighten the connection. If this does not stop the leakage, close the appropriate cylinder valve, open the corresponding torch valve to remove all pressure from the
line, and finally release the regulator pressure-adjusting
screw by turning it counterclockwise. Then break the
leaky connection, wipe metal seating surfaces with a
clean dry cloth, and examine them for nicks and
scratches. Remake the connection(s) and retest. Do
not try to light the torch until you are satisfied that all
connections are gas-tight.
5. If larger or smaller preheat flames are desired, alternately readjust fuel gas and preheat oxygen valve to
obtain the final flame setting.
SHUTTING OFF
Close the cutting oxygen valve. Then close the fuel gas
valve, and finally the preheat oxygen valve.
If operations are to be stopped for a half-hour or more,
all pressure should be released from the torch, hoses,
and regulators by doing the following.
After lighting the torch and adjusting flames, use leak
test solution to check for leakage at all torch valves and
at the nozzle nut.
LIGHTING AND FLAME ADJUSTMENT
CAUTION: Use friction lighter for lighting torch. Do NOT
use a match. Use of a match can seriously
burn you hand.
Using Acetylene
1. Open the acetylene valve on the torch about 1/2 turn,
and light the gas at the nozzle.
2. Slowly close the acetylene valve until the yellow flame
just starts to throw off black smoke.
3. Slowly open preheat oxygen valve on torch until neutral flames are obtained.
4. Finally, open the cutting oxygen valve and readjust
for neutral flames by turning preheat oxygen valve.
The flame now has the proper strength for any cutting
job. With this flame, acetylene is being consumed economically and the torch will be operating at best resistance to flashback. If greater preheat flame temperature is desired for faster starts or piercing, open the cutting oxygen valve and adjust the preheat oxygen valve
until the flame inner cones shorten about 10 percent and
become sharply pointed.
1. Close each cylinder or station valve.
2. Open torch valves.
3. After relieving the gases, back out the pressure-adjusting screw of each regulator and close the torch
valves.
OPERA TING PRECAUTIONS
Flow: There must be proper flow of gases for safe
operation and full performance. This requires the following three conditions: (1) the regulators that determine
the inlet pressure to the hoses must be set to the correct
pressure: (2) the hoses and their connectors must have
adequate capacity for the job (hoses that are too long,
too small or have connectors with small passageways
can cause problems); and (3) the throttle valves on the
torch must be adjusted with the procedure shown in
these instructions.
Note: Items (1) and (2) can be checked by measuring
the gas pressures at the torch. Gauge adaptors
are available for this purpose.
Backfire: Improper operation of the torch may cause
the flames to go out with a loud 'pop'. Such a backfire
may be caused by contact with the work, by spatter from
the work, by the use of incorrect gas pressures, or by
leakage at the cutting nozzle seats due to dirt or nicks
on seats or to a loose nozzle nut.
Using Fuel Gases except Acetylene
1. Crack the fuel gas valve and light the gas at the nozzle.
2. Open fuel gas valve until flame starts to leave the end
of the nozzle.
3. Slowly open preheat oxygen valve on torch until flame
stabilizes.
4. Open cutting oxygen valve and then adjust preheat
oxygen valve until preheat flames are at their shortest length.
Flashback: Under certain circumstances, the flame may
not 'pop' out (backfire) but instead burn back inside the
torch with a shrill hissing or squeal. This is called a
'flashback'. A flashback should never occur if (1) the
equipment is in good condition; (2) preheat ports on cutting nozzles or welding tips are cleaned frequently; (3)
operating pressures are correct; and (4) throttle valves
are adjusted properly. Should a flashback occur, IMMEDIATELY shut off the torch. Allow it to cool off for a
least a minute. Then check your nozzle or tip, gas pressures, readjust regulators if necessary, and relight the
torch. If flashback recurs, send the cutting torch with
nozzle to your distributor for repair.
3
Page 4
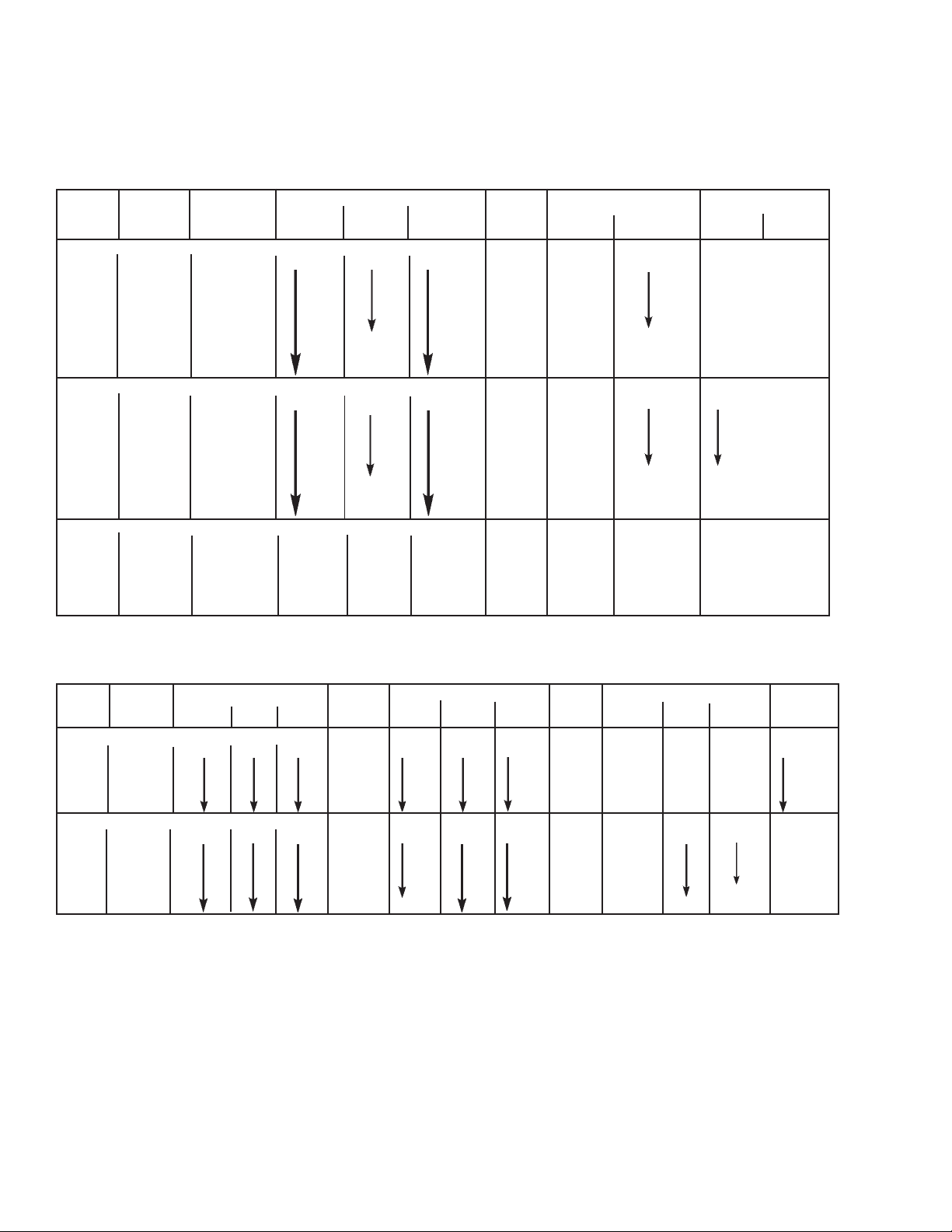
OPERATING DATA, CLEANING DATA, and PART NUMBERS
GENERAL NOTES:
1. Generally, 1/4-in. hoses up to 25-ft. long are adequate for
cutting steel up to 4-in. thick. If longer hoses are required
and if cutting thicker steel, 3/8-in. hoses should be used.
2. The table shown average values based on typical conditions. The type and quality of steel, its surface condition,
the purity of oxygen, etc. will always have a bearing on the
end results.
Acetylene Cutting Nozzles
Nozzle Steel Gas Pressure, psig Cutting Gas Consumption, cfh Cleaning Drill Size
Size Part No. in. Oxygen Oxygen Acetylene in./min. Oxygen Acetylene Preheat Cutting
1563 Series - High Speed, Low Gas Consumption, Machine Cutting
1/2" 639171 1/2 90 20-25 5-7 21-30 60-70 5-9
3/4" 639172 3/4 20-28 110-110
1" 639173 1 19-25 110-120
1-1/2" 639174 1-1/2 14-23 155-165
2" 639175 2 13-20 240-250
2-1/2 639176 2-1/2 25-30 12-19 250-265 6-12
4" 639177 3-4 8-17 265-300 6-12
6" 639178 6 7-10 405-420 8-12
1565 Series - General Purpose Cutting, Low Acetylene Consumption
1/8" 639182 1/8" 40 25-30 5-7 30-40 30-40 5-9 73 78
1/4" 639263 1/4" 20-30 35-40 69
1/2" 639264 1/2" 18-25 55-65 65
3/4" 639265 3/4" 15-24 60-70 61
1" 639266 1" 14-20 85-95 54
2" 639267 2" 10-14 155-165 8-12 70 51
3" 639268 3" 20-25 7-11 215-230 10-12 69 47
4" 639269 4" 25-30 5-9 340-360 15-20 65 40
1502 Series - General Purpose Cutting, Medium Preheat
1/4" 08Z67 1/4 20-25 20-25 5-7 17-25 35-45 6-8 69 68
1/2" 15Z17 1/2 30-35 20-25 5-7 15-23 65-75 8-10 66 60
1-1/2" 15Z18 3/4-1-1/2 30-45 20-25 5-7 11-21 120-170 14-20 65 53
4" 15Z19 2-4 25-45 20-30 6-8 6-14 185-285 16-22 61 46
8" 15Z20 6 35-45 25-30 6-10 3.5-6.5 395-460 20-25 57 39
Thickness Cutting Preheat Speed Total
Use Nozzle
Cleaning Kit
P/N 755F00
for cleaning
preheat and
cutting oxygen
orifices.
Fuel Gas Two-Piece Cutting Nozzles (Do NOT use with Acetylene)
Nozzle Nozzle Sleeve (External) Steel Gas Pressure, psig Cutting Gas Consumption, cfh Cleaning
Size (Internal) Thickness Cutting Preheat Speed Total Drill Size
Part No. in. Oxygen Oxygen Fuel Gas in/min. Oxygen FG-2 Nat. Gas Cutting
1566 HS Series - High Speed, High Preheat, machine Cutting
1/2" 639600 639322 998277 998557 1/2 90 20-25 3-5 21-26 60-80 5-10 20-25
3/4" 639601 3/4 20-25 110-130 5-10 20-25
1" 639602 1 18-23 120-140 5-10 25-30
1-1/2" 639603 1-1/2 13-18 175-195 8-15 25-30
2" 639604 2 12-17 265-285 8-15 35-40
1567 Series - High Preheat, General Purpose Cutting
1/8" 639614 639322 998277 998557 1/8 40 20-25 3-5 23-26 20-40 5-10 20-25 79
1/4 639615 1/4 20-25 45-65 69
1/2" 639616 1/2 18-25 65-85 65
3/4" 639617 3/4 15-24 70-90 61
1" 639618 1 14-20 95-115 25-30 54
2" 639619 2 10-14 175-200 8-15 30-35 51
Nat. Gas
Propane
Use where high preheat intensity is desired.
Consumption of MAPP or propane is approximately the same as FG-2.
Use soft-bristled brush (750F99) to clean preheat slots of internal nozzles.
Clean cutting oxygen bores with "HS" Cleaning Kit - P/N 755F00.
FG-2
MAPP
Part No.
FG-2
MAPP
4
Page 5

MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS
For all repairs other than those covered below, send
the torch to your ESAB welding equipment distributor or to ESAB Remanufacturing Center, Florence,
SC. Improperly repaired apparatus is hazardous.
Valves: Leakage around a throttle valve can usually be
corrected by tightening the packing nut slightly. If a valve
fails to shut off completely, remove the valve assembly
from the torch. With a clean cloth, wipe the ball in the
end of the stem. Then reinsert valve assembly and
tighten it several times with maximum force. If this does
not eliminate leakage, try a new throttle valve assembly.
If then the valve does not shut off completely, send the
torch to a repair station for reseating of the body.
the mixer locking screw. Finally, dislodge the mixer either by rapping the torch, held vertically, against a block
of soft wood, or by turning a long 10-32 machine screw
into the thread in the end of the mixer and pulling it out.
Reassemble the mixer in reverse order. Be sure the
mixer chamber plug is fitted with an O-ring in good condition.
Cleaning Cutting Nozzles: If the cutting nozzle does
not produce straight, uniform flames, or if any of the
nozzle orifices become clogged, clean them by hand
with the correct size twist drills shown in the table on
page 4, or with tip cleaners. (The relationship between
OXWELD tip cleaners and drill sizes is shown on the tip
cleaner case.)
After installing a new throttle valve assembly, tighten the
packing nut until the valve can be turned only with great
difficulty, and set the unit aside, for three or four hours at
least, to set the packing. Then back off the packing nut
until the valve turns readily.
Mixer: To remove the mixer for cleaning or replacement,
first unscrew the mixer chamber plug. Then unscrew
NOTE: If using a 1563 series nozzle, do NOT clean with
notched-type wires or twist drills since any metal
removal from the passages will destroy the precision cutting characteristics. Use the non-cutting wires and taper reamers included in the
OXWELD Nozzle Cleaning Kit (P/N 755F00).
Cleaning instructions are supplied with the kit.
5
Page 6

PARTS INFORMATION
All parts which can be replaced without breaking soldered or brazed joints are illustrated and listed below. When
ordering parts, please give both part number and description (including size where appropriate). Parts may be ordered
from your ESAB welding equipment distributor or from ESAB Welding & Cutting Systems, Customer Service Department, Florence, SC.
LEVER - 25Z22
PIN. SLOTTED SPRING
5/32" DIA. X 9/16"- 62350924
WASHER - 53Z61
PACKING - 73Z39
WASHER - 78Z03
SPRING - 28Z54
STEM/SEAT - 20624
NUT - 36Z07
7/8 - 20
(2) SCREW No. 6--32 x 1/4-in.
6102-7849
CAM-TYPE CUTTING VAL VE
ASS'Y - 32Y08
WASHER - 73Z36
CASING - 24Z68
(2) THROTTLE VALVE
ASS'Y - 33Y08
3/8 - 24
9/16 - 24
NUT - 33A56
MIXER (ACET.) - 01Y26
(2) SCREW - 35Z11
#6 - 32
RACK ASS'Y. - 50Y38
SCREW - 34Z15
O-RING - 86W85
PLUG - 134Z55
(2) SCREW - 6102-7851
C-58 (2-hose) Machine Cutting Torch - P/N 02X74 C-58 (3-hose) Machine Cutting Torch - P/N 02X44 (illus.)
6
Page 7

7
Page 8

ESAB Welding & Cutting Products, Florence, SC Welding Equipment
COMMUNICATION GUIDE - CUSTOMER SERVICES
A. CUSTOMER SERVICE QUESTIONS:
Order Entry Product Availability Pricing Delivery
Order Changes Saleable Goods Returns Shipping Information
Telephone: (800)362-7080 / Fax: (800) 634-7548
Telephone: (800)783-5360 / Fax: (800) 783-5362
Telephone: (800) 235-4012/ Fax: (888) 586-4670
B. ENGINEERING SERVICE: Telephone: (843) 664-4416 / Fax : (800) 446-5693
Welding Equipment Troubleshooting Hours: 7:30 AM to 5:00 PM EST
Warranty Returns Authorized Repair Stations
C. TECHNICAL SERVICE: Telephone: (800) ESAB-123/ Fax: (843) 664-4452
Part Numbers Technical Applications Hours: 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM EST
Performance Features Technical Specifications Equipment Recommendations
D. LITERATURE REQUESTS: Telephone: (843) 664-5562 / Fax: (843) 664-5548
E. WELDING EQUIPMENT REPAIRS: Telephone: (843) 664-4487 / Fax: (843) 664-5557
Repair Estimates Repair Status Hours: 7:30 AM to 3:30 PM EST
F. WELDING EQUIPMENT TRAINING:
Telephone: (843)664-4428 / Fax: (843) 679-5864
Training School Information and Registrations Hours: 7:30 AM to 4:00 PM EST
G. WELDING PROCESS ASSISTANCE:
Telephone: (800) ESAB-123 / Fax: (843) 664-4454 Hours: 7:30 AM to 4:00 PM EST
H. TECHNICAL ASST. CONSUMABLES:
Telephone : (800) 933-7070 Hours: 7:30 AM to 5:00 PM EST
Eastern Distribution Center
Central Distribution Center
Western Distribution Center
Hours: 7:30 AM to 4:00 PM EST
IF YOU DO NOT KNOW WHOM TO CALL
Telephone: (800) ESAB-123/ Fax: (843) 664-4452/ Web:http://www.esab.com
F-5884-U 7/2005 1M Printed in U.S.A.
Hours: 7:30 AM to 5:00 PM EST
 Loading...
Loading...