Page 1

Page 2

Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION
WHAT IS OBD?
YOU CAN DO IT! ............................................................................................ 2
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
SAFETY FIRST!
ABOUT THE SCAN TOOL
VEHICLES COVERED
BATTERY REPLACEMENT ............................................................... 6
ADJUSTMENTS AND SETTINGS .................................................... 7
SCAN TOOL CONTROLS
CONTROLS AND INDICATORS
DISPLAY FUNCTIONS ........................................................................ 12
ONBOARD DIAGNOSTICS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCs)
PREPARATION FOR TESTING
PRELIMINARY VEHICLE DIAGNOSTIC WORKSHEET
BEFORE YOU BEGIN ......................................................................... 20
VEHICLE SERVICE MANUALS ........................................................ 21
USING THE SCAN TOOL
CODE RETRIEVAL PROCEDURE
THE ENHANCED MAIN MENU ......................................................... 28
VIEWING ABS DTCs ............................................................................ 29
VIEWING ENHANCED DTCs ............................................................ 32
ERASING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCs)................. 40
I/M READINESS TESTING ................................................................ 41
LIVE DATA MODE
VIEWING LIVE DATA
CUSTOMIZING LIVE DATA (PIDs) .................................................. 48
RECORDING (CAPTURING) LIVE DATA ..................................... 49
LIVE DATA PLAYBACK ...................................................................... 53
O2 SENSOR TEST ............................................................................... 55
NON-CONTINUOUS TEST ................................................................ 57
SYSTEM TEST ...................................................................................... 58
VEHICLE INFORMATION ................................................................... 59
GENERIC (GLOBAL) OBD2 PID LIST ..................................................... 61
GLOSSARY
GLOSSARY OF TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
WARRANTY AND SERVICING
LIMITED ONE YEAR WARRANTY
SERVICE PROCEDURES .................................................................. 69
..................................................................................... 1
..................................................................................... 3
......................................................................... 5
...................................................... 11
..................................... 15
........... 17
.................................................. 22
.......................................................................... 47
....................... 66
.................................................. 69
i OBD2
Page 3

Introduction
WHAT IS OBD?
WHAT IS OBD?
The Enhanced OBD2 Scan Tool is designed to work on all OBD2
compliant vehicles. All 1996 and newer vehicles (cars, light trucks
One of the most exciting improvements in the
automobile industry was the addition of onboard diagnostics (OBD) on vehicles, or in more
basic terms, the computer that activates the
vehicle’s “CHECK ENGINE” light. OBD1 was
designed to monitor manufacturer-specific
systems on vehicles built from 1981 to 1995.
Then came the development of OBD2, which is
on all 1996 cars and light trucks sold in the U.S. Like its predecessor,
OBD2 was adopted as part of a government mandate to lower vehicle
emissions. But what makes OBD2 unique is its universal application for
all late model cars and trucks - domestic and import. This sophisticated
program in the vehicle’s main computer system is designed to detect
failures in a range of systems, and can be accessed through a universal
OBD2 port, which is usually found under the dashboard. For all OBD
systems, if a problem is found, the computer turns on the “CHECK
ENGINE” light to warn the driver, and sets a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) to identify where the problem occurred. A special diagnostic tool,
such as the Enhanced OBD2 Scan Tool, is required to retrieve these
codes, which consumers and professionals use as a starting point for
repairs.
The Enhanced OBD2 Scan Tool provides the additional ability to
retrieve enhanced DTCs from most Chrysler/Jeep, General Motors,
Ford, Mazda and Isuzu vehicles. The types of enhanced data available
depends on the vehicle make. Chrysler/Jeep, Ford/Mazda, GM/Izusu,
Honda/Acura and Toyota/Lexus vehicles, as well as Anti-Lock Brake
System (ABS) DTCs and vehicle information. The types of enhanced
data available depends on the vehicle make.
and SUVs) sold in the United States are OBD2 compliant.
OBD2 1
Page 4

You Can Do It!
EASY TO USE - EASY TO VIEW - EASY TO DEFINE
Easy To Use . . . .
Connect the Scan Tool to the vehicle’s
test connector.
Turn the ignition key "On.”
Press the LINK button.
Easy To View . . . .
The Scan Tool retrieves stored codes,
Freeze Frame data and I/M Readiness
status.
Codes, I/M Readiness status and
Freeze Frame data are displayed on the
Scan Tool’s display screen. System
status is indicated by LED indicators.
Easy To Define . . . .
Read code definitions from the Scan
Tool’s display.
View Freeze Frame data.
View Live Data.
2 OBD2
Page 5

Safety Precautions
SAFETY FIRST!
SAFETY FIRST!
To avoid personal injury, instrument damage and/or
damage to your vehicle; do not use the OBD2 Scan Tool
This manual describes common test procedures used
by experienced service technicians. Many test procedures
require precautions to avoid accidents that can result in
personal injury, and/or damage to your vehicle or test
equipment. Always read your vehicle's service manual and
follow its safety precautions before and during any test or
service procedure. ALWAYS observe the following general
safety precautions:
When an engine is running, it produces carbon monoxide,
a toxic and poisonous gas. To prevent serious injury or
death from carbon monoxide poisoning, operate the
vehicle ONLY in a well-ventilated area.
To protect your eyes from propelled objects as well as hot
or caustic liquids, always wear approved safety eye
protection.
before reading this manual.
When an engine is running, many parts (such as the
coolant fan, pulleys, fan belt etc.) turn at high speed. To
avoid serious injury, always be aware of moving parts.
Keep a safe distance from these parts as well as other
potentially moving objects.
Engine parts become very hot when the engine is running.
To prevent severe burns, avoid contact with hot engine
parts.
Before starting an engine for testing or troubleshooting,
N
R
P
make sure the parking brake is engaged. Put the
D
L
transmission in park (for automatic transmission) or
neutral (for manual transmission). Block the drive wheels
with suitable blocks.
Connecting or disconnecting test equipment when the
ignition is ON can damage test equipment and the
vehicle's electronic components. Turn the ignition OFF
before connecting the Scan Tool to or disconnecting the
Scan Tool from the vehicle’s Data Link Connector (DLC).
OBD2 3
Page 6

Safety Precautions
SAFETY FIRST!
To prevent damage to the on-board computer when taking
vehicle electrical measurements, always use a digital
multimeter with at least 10 megOhms of impedance.
Fuel and battery vapors are highly flammable. To prevent
an explosion, keep all sparks, heated items and open
flames away from the battery and fuel / fuel vapors. DO
NOT SMOKE NEAR THE VEHICLE DURING TESTING.
Don't wear loose clothing or jewelry when working on an
engine. Loose clothing can become caught in the fan,
pulleys, belts, etc. Jewelry is highly conductive, and can
cause a severe burn if it makes contact between a power
source and ground.
4 OBD2
Page 7
About the Scan Tool
VEHICLES COVERED
VEHICLES COVERED
The Enhanced OBD2 Scan Tool is designed to work on all OBD2
compliant vehicles. All 1996 and newer vehicles (cars and light trucks)
sold in the United States are OBD2 compliant.
Federal law requires that all 1996 and newer cars and light
trucks sold in the United States must be OBD2 compliant; this
includes all Domestic, Asian and European vehicles.
Some 1994 and 1995 vehicles are OBD2 compliant. To find out if a
1994 or 1995 vehicle is OBD2 compliant, check the following:
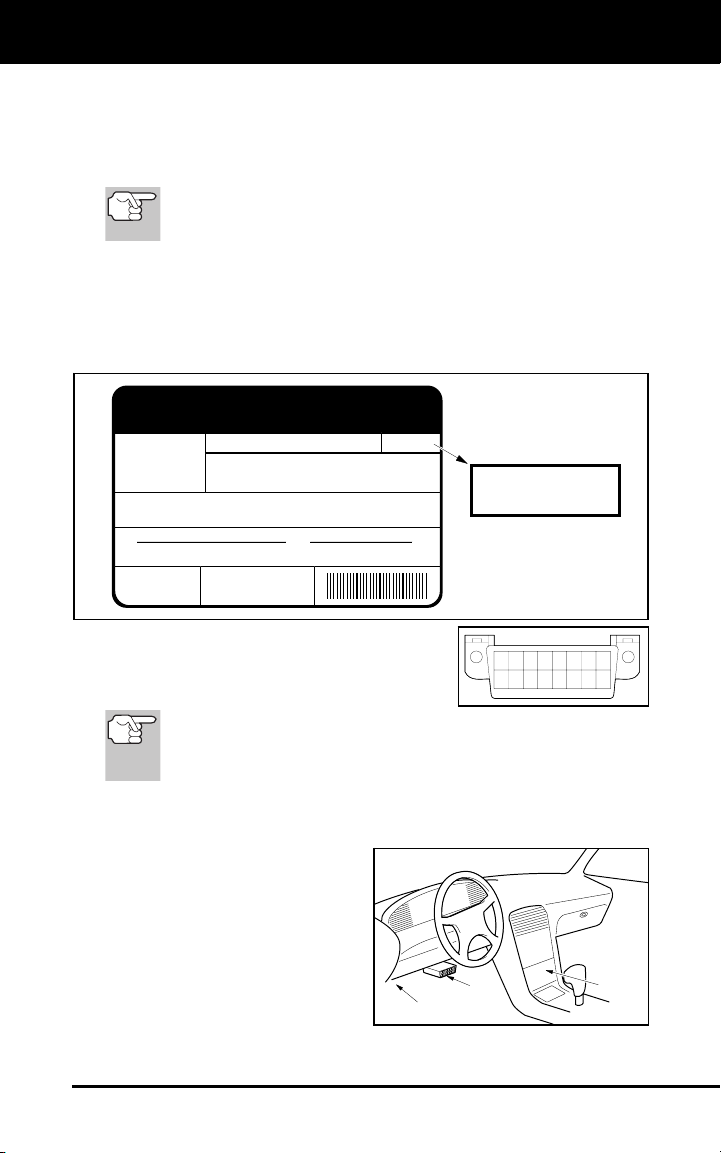
1. The Vehicle Emissions Control Information (VECI) Label. This
label is located under the hood or by the radiator of most vehicles. If
the vehicle is OBD2 compliant, the label will state “OBD II
Certified.”
VEHICLE EMISSION CONTROL INFORMATION
ENGINE FAMILY EFN2.6YBT2BA
VEHICLE
MANUFACTURER
REFER TO SERVICE MANUAL FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
TUNE-UP CONDITIONS: NORMAL OPERATING ENGINE TEMPERATURE,
ACCESSORIES OFF, COOLING FAN OFF, TRANSMISSION IN NEUTRAL
EXHAUST EMISSIONS STANDARDS STANDARD CATEGORY
CERTIFICATION
IN-USE
SPARK PLUG
TYPE NGK BPRE-11
GAP: 1.1MM
DISPLACEMENT 2.6L
THIS VEHICLE CONFORMS TO U.S. EPA AND STATE
OF CALIFORNIA REGULATIONS APPLICABLE TO
1999 MODEL YEAR NEW TLEV PASSENGER CARS.
CATALYST
TLEV
TLEV INTERMEDIATE
OBD II
CERTIFIED
OBD II
CERTIFIED
2. Government Regulations require that all
OBD2 compliant vehicles must have a
“common” sixteen-pin Data Link
Connector (DLC).
12345678
9 10111213141516
Some 1994 and 1995 vehicles have 16-pin connectors but are
not OBD2 compliant. Only those vehicles with a Vehicle
Emissions Control Label stating “OBD II Certified” are OBD2
compliant.
Data Link Connector (DLC) Location
The 16-pin DLC is usually
located under the instrument
panel (dash), within 12 inches
(300 mm) of center of the panel,
on the driver’s side of most
vehicles. It should be easily
accessible and visible from a
kneeling position outside the
vehicle with the door open.
LEFT CORNER
OF DASH
NEAR
CENTER
OF DASH
BEHIND
ASHTRAY
OBD2 5
Page 8
About the Scan Tool
BATTERY REPLACEMENT
On some Asian and European vehicles the DLC is located
behind the “ashtray” (the ashtray must be removed to
access it) or on the far left corner of the dash. If the DLC
cannot be located, consult the vehicle’s service manual for
the location.
BATTERY REPLACEMENT
Replace batteries when the battery symbol is visible on display
and/or the 3 LEDS are all lit and no other data is visible on screen.
1. Locate the battery cover on the back of the Scan Tool.
2. Slide the battery cover off (use your fingers).
3. Replace batteries with three AA-size batteries (for longer life, use
Alkaline-type batteries).
4. Reinstall the battery cover on the back of the Scan Tool.
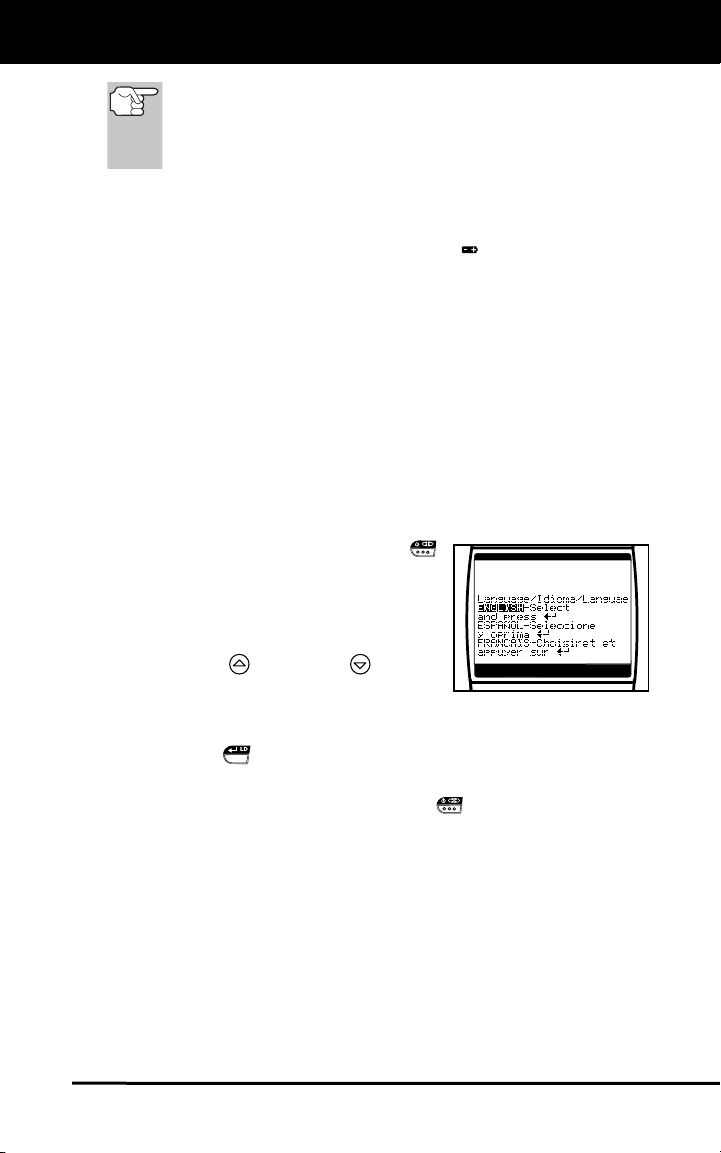
Language Selection After Battery Installation
The first time the Scan Tool is turned on, you must select the desired
display language (English, French or Spanish). Select the display
language as follows:
1. Press and hold the POWER/LINK
button for approximately 3 seconds to
turn the Scan Tool “ON.”
The Select Language screen dis-
plays.
2. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight the desired
display language.
3. When the desired display language is selected, press the
ENTER/LD
The display shows the "To Link" message in the selected display
language. Press the POWER/LINK
Tool "off."
After the initial language selection is performed, it as well as
other settings can be changed as desired. See ADJUSTMENTS
AND SETTINGS on page 7 for further instructions.
and DOWN buttons,
button to confirm your selection.
button to turn the Scan
6 OBD2
Page 9
About the Scan Tool
ADJUSTMENTS AND SETTINGS
ADJUSTMENTS AND SETTINGS
The OBD2 Scan Tool lets you make several adjustments and settings to
configure the Scan Tool for your particular needs. The following
adjustments and settings are available:
Adjust Brightness: Adjusts the brightness of the display screen.
DTC Library - Library of OBD2 DTC definitions.
Display Backlight: Turns the display backlight on and off.
Select Language: Sets the display language for the Scan Tool to
English, French or Spanish.
Unit of Measurement: Sets the Unit of Measurement for the Scan
Tool’s display to USA or metric.
Adjustments and settings can be made only when the Scan
Tool is NOT connected to a vehicle.
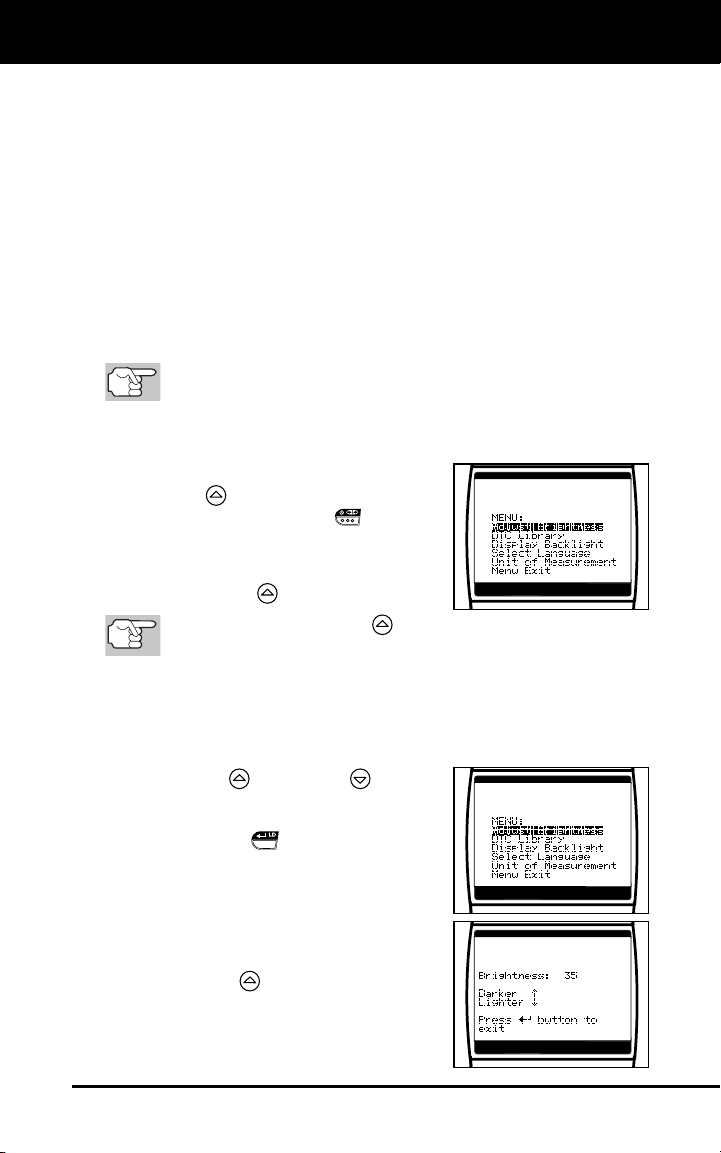
To enter the MENU Mode:
1. With the Scan Tool “off”, press and hold
the UP
release the POWER/LINK
The adjustments and setting MENU
displays.
2. Release the UP
3. Make adjustments and settings as described in the following
paragraphs.
button, then press and
DO NOT release the UP
settings MENU is visible on the display.
button.
button.
button until the adjustments and
Adjusting Display Brightness
1. Use the UP
and DOWN buttons,
as necessary, to highlight Adjust
Brightness in the MENU, then press
the ENTER/LD
The Adjust Brightness screen
button.
displays.
The Brightness field shows the
current brightness setting, from 0 to
43.
2. Press the UP
button to decrease the
brightness of the display (make the
display darker).
OBD2 7
Page 10
About the Scan Tool
ADJUSTMENTS AND SETTINGS
3. Press the DOWN button to increase the brightness of the display
(make the display lighter).
4. When the desired brightness is obtained, press the ENTER/LD
button to save your changes and return to the MENU.
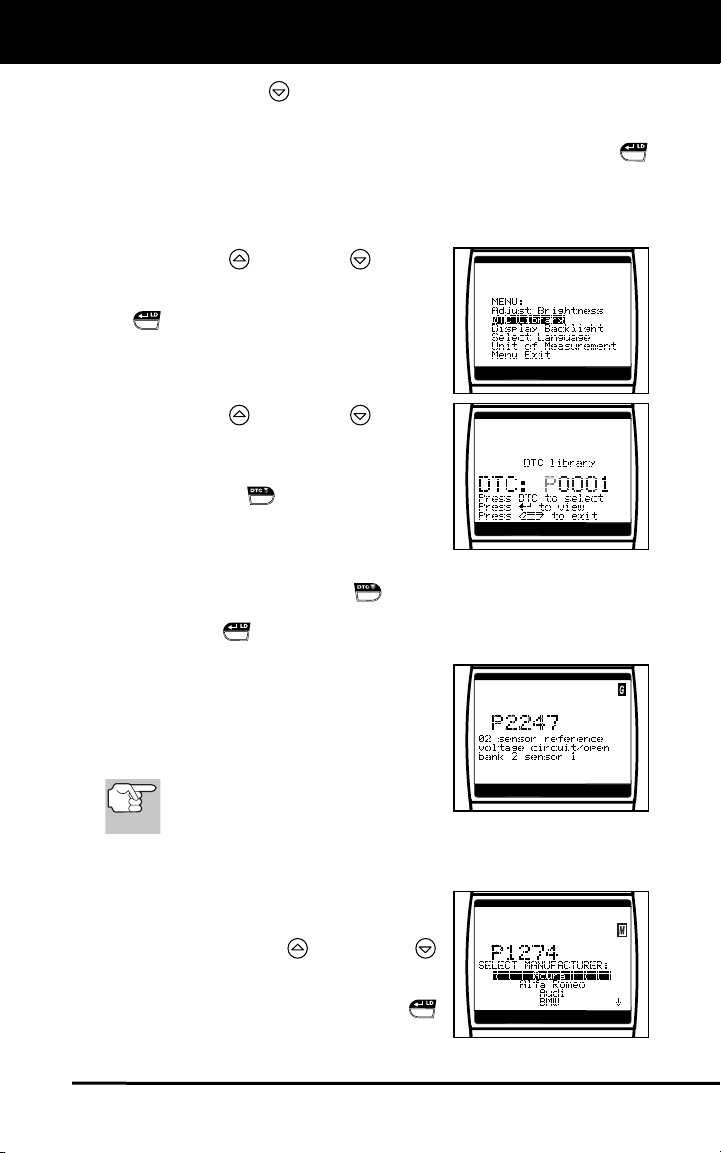
Searching for a DTC Definition Using the DTC Library
1. Use the UP
and DOWN buttons,
as necessary, to highlight DTC Library
in the MENU, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
The Enter DTC screen displays. The
screen shows the code “P0001”,
with the “P” flashing.
2. Use the UP
and DOWN buttons,
as necessary, to scroll to the desired
DTC type (P=Powertrain, U=Network,
B=Body, C=Chassis), then press the
DTC SCROLL
The selected character displays “solid”,
button.
and the next character begins flashing.
3. Select the remaining characters in the DTC in the same way,
pressing the DTC SCROLL button to confirm each character.
When you have selected all the DTC characters, press the
ENTER/LD
If you entered a “Generic” DTC
button to view the DTC definition.
(DTCs that start with “P0”, “P2” and
some “P3”):
- The selected DTC and DTC
definition (if available) show on
the Scan Tool’s display.
If a definition for the DTC you
entered is not available, the “To
Link” screen displays.
If you entered a “Manufacturer-Specific” DTC (DTCs that start
with “P1” and some “P3”):
- The “Select Manufacturer” screen
displays.
- Use the UP
and DOWN
buttons, as necessary, to highlight the appropriate manufacturer,
then press the ENTER/LD
button to display the correct DTC
for your vehicle.
8 OBD2
Page 11
About the Scan Tool
ADJUSTMENTS AND SETTINGS
If a definition for the DTC you
entered is not available, an
advisory message shows on the
CanOBD2 Scan Tool’s display.
4. If you wish to view definitions for
additional DTCs, press the ENTER/LD
button to return to the Enter DTC
screen, and repeat steps 2 and 3.
5. When all desired DTCs have been viewed, press the ERASE
button to exit the DTC Library.
Using the Backlight
1. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight Display
Backlight in the MENU, then press the
ENTER/LD
The Display Backlight screen dis-
plays.
2. Press the UP
as necessary, to select the desired
backlight mode, either ON or OFF.
3. When the desired backlight mode is
selected, press the ENTER/LD
button to save your changes.
The display returns to the MENU,
and the backlight turns “on” or “off”
as selected.
and DOWN buttons,
button.
or DOWN button,
Selecting the Display Language
1. Use the UP
and DOWN buttons,
as necessary, to highlight Select
Language in the MENU, then press the
ENTER/LD button.
The Select Language screen dis-
plays.
The currently selected display
Language is highlighted.
2. Press the UP
or DOWN button,
as necessary, to highlight the desired
display language.
3. When the desired display language is
highlighted, press the ENTER/LD
button to save your changes and return
to the MENU (shown in the selected
display language).
OBD2 9
Page 12
About the Scan Tool
ADJUSTMENTS AND SETTINGS
Setting the Unit of Measurement
1. Use the UP
and DOWN buttons,
as necessary, to highlight Unit of
Measurement in the MENU, then press
the ENTER/LD
2. Press the UP
button.
or DOWN button,
as necessary, to highlight the desired
Unit of Measurement.
3. When the desired Unit of Measurement
value is selected, press the ENTER/LD
button to save your changes.
Exiting the MENU Mode
1. Use the UP
Menu Exit in the MENU, then press the ENTER/LD
The display returns to the DTC screen (if data is currently stored
and DOWN buttons, as necessary, to highlight
button.
in the Scan Tool) or to the "To Link" message (if no data is
currently stored in the Scan Tool).
10 OBD2
Page 13
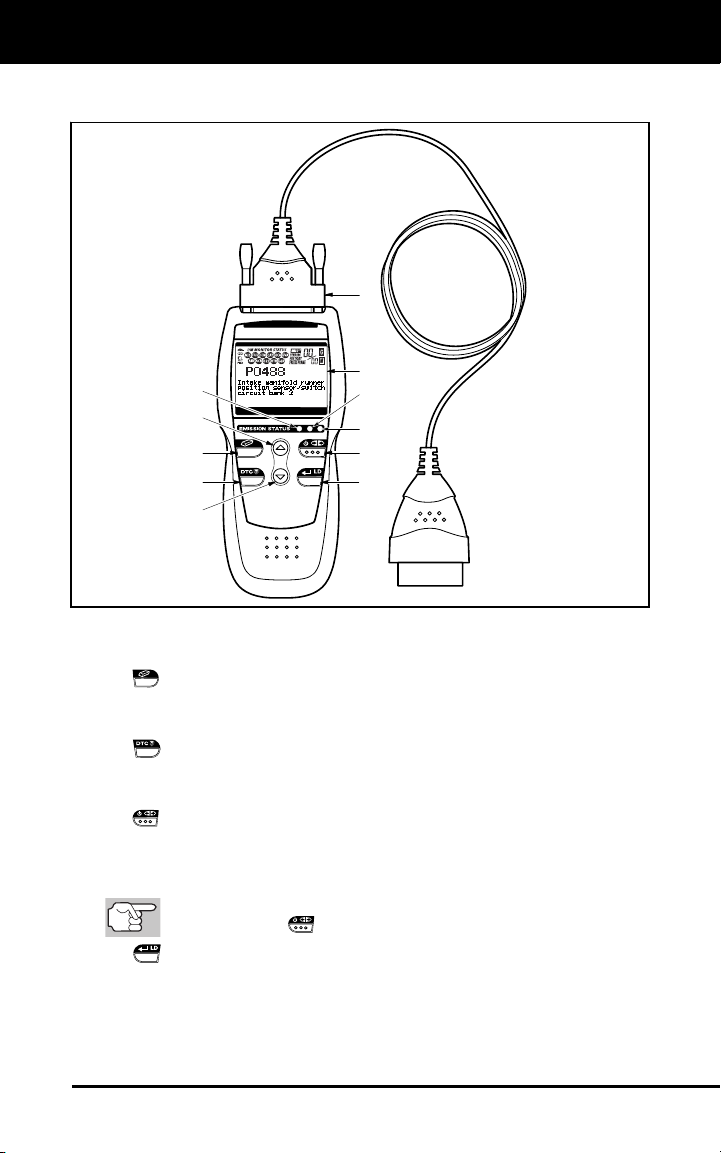
Scan Tool Controls
CONTROLS AND INDICATORS
CONTROLS AND INDICATORS
7
6
1
2
5
11
10
8
9
3
4
Figure 1. Controls and Indicators
See Figure 1 for the locations of items 1 through 11, below.
ERASE button - Erases Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), and
1.
“Freeze Frame” data from your vehicle’s computer, and resets
Monitor status.
DTC SCROLL button - Displays the DTC View screen and/or
2.
scrolls the display to view DTCs when more than one DTC is
present.
POWER/LINK button - When the Scan Tool IS NOT connected
3.
to a vehicle, turns the Scan Tool “On” and “Off”. When the Scan
Tool is connected to a vehicle, links the Scan Tool to the vehicle’s
PCM to retrieve diagnostic data from the computer’s memory.
To turn the Scan Tool "On", you must press and hold the
POWER/LINK
ENTER/LIVE DATA button - When in MENU mode, confirms
4.
button for approximately 3 seconds.
the selected option or value. When linked to a vehicle, places the
Scan Tool in "Live Data" mode.
OBD2 11
Page 14
Scan Tool Controls
DISPLAY FUNCTIONS
5. DOWN button - When in MENU mode, scrolls DOWN through
the menu and submenu selection options. When LINKED to a
vehicle, scrolls DOWN through the current display screen to display
any additional data.
UP button - When in MENU mode, scrolls UP through the menu
6.
and submenu selection options. When LINKED to a vehicle, scrolls
UP through the current display screen to display any additional data.
7. GREEN LED - Indicates that all engine systems are running
normally (all Monitors on the vehicle are active and performing their
diagnostic testing, and no DTCs are present).
8. YELLOW LED - Indicates there is a possible problem. A “Pending”
DTC is present and/or some of the vehicle’s emission monitors have
not run their diagnostic testing.
9. RED LED - Indicates there is a problem in one or more of the
vehicle’s systems. The red LED is also used to show that DTC(s)
are present. DTCs are shown on the Scan Tool’s display. In this
case, the Multifunction Indicator (“Check Engine”) lamp on the
vehicle’s instrument panel will light steady on.
10. Display - Displays settings Menu and submenus, test results, Scan
Tool functions and Monitor status information. See DISPLAY
FUNCTIONS, following, for more details.
11. CABLE - Connects the Scan Tool to the vehicle’s Data Link
Connector (DLC).
DISPLAY FUNCTIONS
12 13
21
3
4
5
6
7
8
11
15
16
14
10
9
Figure 2. Display Functions
See Figure 2 for the locations of items 1 through 16, following.
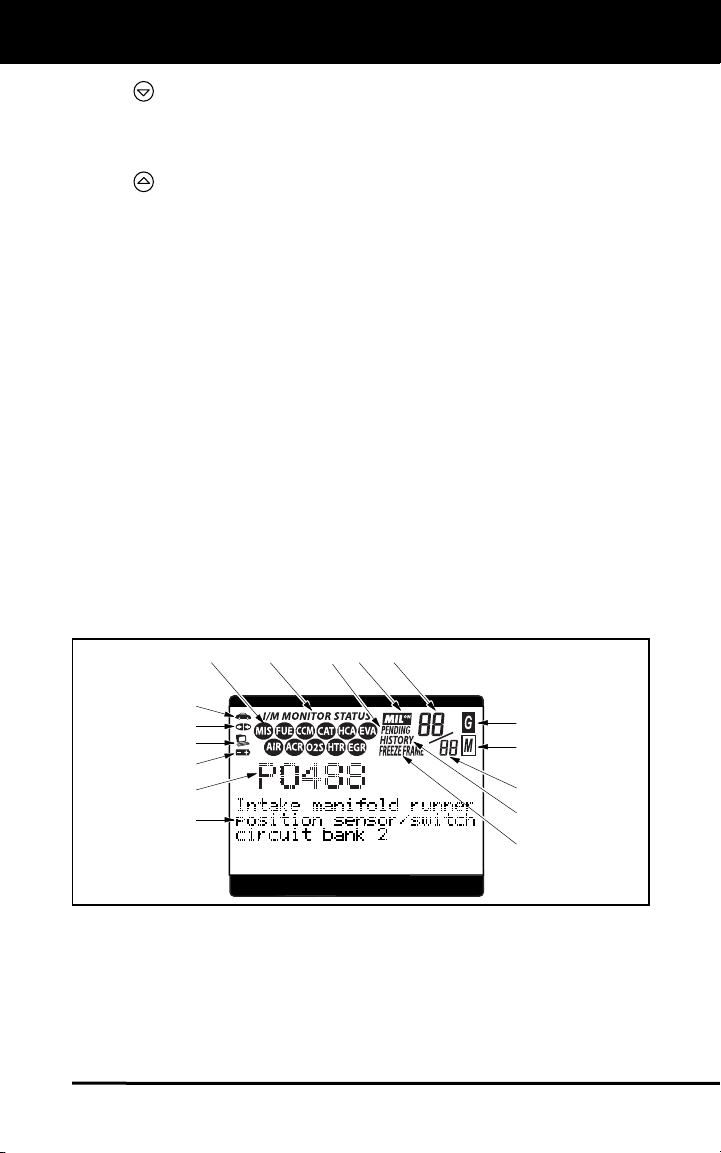
1. I/M MONITOR STATUS field - Identifies the I/M Monitor status area.
12 OBD2
Page 15

Scan Tool Controls
DISPLAY FUNCTIONS
2. Monitor icons - Indicate which Monitors are supported by the
vehicle under test, and whether or not the associated Monitor has
run its diagnostic testing (Monitor status). When a Monitor icon is
solid, it indicates that the associated Monitor has completed its
diagnostic testing. When a Monitor icon is flashing, it indicates that
the vehicle supports the associated Monitor, but the Monitor has not
yet run its diagnostic testing.
3.
Vehicle icon - Indicates whether or not the Scan Tool is being
properly powered through the vehicle’s Data Link Connector (DLC).
A visible icon indicates that the Scan Tool is being powered through
the vehicle’s DLC connector.
Link icon - Indicates whether or not the Scan Tool is
4.
communicating (linked) with the vehicle’s on-board computer. When
visible, the Scan Tool is communicating with the computer. If the
Link icon is not visible, the Scan Tool is not communicating with the
computer.
Computer icon - When this icon is visible it indicates that the
5.
Scan Tool is linked to a personal computer. An optional “PC Link
Kit” is available that makes it possible to upload retrieved data to a
personal computer.
6.
Scan Tool Internal Battery icon - When visible, indicates the
Scan Tool batteries are “low” and should be replaced. If the
batteries are not replaced when the battery symbol
LEDs will light up as a last resort indicator to warn you that the
batteries need replacement. No data will be displayed on screen
when all 3 LEDs are lit.
7. DTC Display Area - Displays the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
number. Each fault is assigned a code number that is specific to that
fault.
8. Test Data Display Area - Displays DTC definitions, Freeze Frame
data, Live Data and other pertinent test information messages.
9. FREEZE FRAME icon - Indicates that there is Freeze Frame data
from “Priority Code” (Code #1) stored in the vehicle’s computer
memory.
10. HISTORY icon - Indicates the currently displayed DTC is a “History”
code.
11. PENDING icon - Indicates the currently displayed DTC is a
“Pending” code.
12. MIL icon - Indicates the status of the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL). The MIL icon is visible only when a DTC has commanded the
MIL on the vehicle’s dashboard to light.
13. Code Number Sequence - The Scan Tool assigns a sequence
number to each DTC that is present in the computer’s memory,
starting with “01.” This number indicates which code is currently
displayed. Code number “01” is always the highest priority code,
and the one for which “Freeze Frame” data has been stored.
is "on", all 3
OBD2 13
Page 16

Scan Tool Controls
DISPLAY FUNCTIONS
If “01” is a “Pending” code, there may or may not be “Freeze
Frame” data stored in memory.
14. Code Enumerator - Indicates the total number of codes retrieved
from the vehicle’s computer.
15.
Generic DTC icon - When visible, indicates that the currently
displayed DTC is a “generic” or universal code.
Manufacturer Specific DTC icon - When visible, indicates that
16.
the currently displayed DTC is a Manufacturer Specific Code.
14 OBD2
Page 17
Onboard Diagnostics
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCs)
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are
meant to guide you to the proper
service procedure in the vehicle’s
service manual. DO NOT replace parts
based only on DTCs without first
Diagnostic Trouble
Codes (DTCs) are
codes that identify a
specific problem area.
consulting the vehicle’s service manual
for proper testing procedures for that
particular system, circuit or component.
DTCs are alphanumeric codes that are used to identify a
problem that is present in any of the systems that are
monitored by the on-board computer (PCM). Each trouble
code has an assigned message that identifies the circuit,
component or system area where the problem was found.
OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes are made up of five characters:
The 1st character is a letter. It identifies the “main system” where
the fault occurred (Body, Chassis, Powertrain, or Network).
The 2nd character is a numeric digit. It identifies the “type” of code
(Generic or Manufacturer-Specific).
Generic DTCs are codes that are used by all vehicle
manufacturers. The standards for generic DTCs, as well as
their definitions, are set by the Society of Automotive
Engineers (SAE).
Manufacturer-Specific DTCs are codes that are controlled by
the vehicle manufacturers. The Federal Government does not
require vehicle manufacturers to go beyond the standardized
generic DTCs in order to comply with the new OBD2
emissions standards. However, manufacturers are free to
expand beyond the standardized codes to make their systems
easier to diagnose.
The 3rd character is a numeric digit. It identifies the specific
system or sub-system where the problem is located.
The 4th and 5th characters are numeric digits. They identify the
section of the system that is malfunctioning.
DTCs and MIL Status
When the vehicle’s on-board computer detects
a failure in an emissions-related component or
system, the computer’s internal diagnostic
program assigns a diagnostic trouble code
(DTC) that points to the system (and subsystem)
where the fault was found. The diagnostic
program saves the code in the computer’s
memory. It records a “Freeze Frame” of
conditions present when the fault was found, and lights the Malfunction
Indicator Lamp (MIL). Some faults require detection for two trips in a row
before the MIL is turned on.
OBD2 15
Page 18
Onboard Diagnostics
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCs)
The “Malfunction Indicator Lamp” (MIL) is the accepted term
used to describe the lamp on the dashboard that lights to warn
the driver that an emissions-related fault has been found.
Some manufacturers may still call this lamp a “Check Engine”
or “Service Engine Soon” light.
P0201 - Injector Circuit Malfunction, Cylinder 1
OBD2 DTC EXAMPLE
B
-
Body
C
-
Chassis
P
-
Powertrain
U
-
Network
-
Generic
0
-
Manufacturer Specific
1
-
Generic
2
-
Includes both Generic and Manufacturer
3
Specific Codes
Identifies the system where the
problem is located:
1
-
Fuel and Air Metering
2
-
Fuel and Air Metering (injector circuit
malfunction only)
3
-
Ignition System or Misfire
4
-
Auxiliary Emission Control System
5
-
Vehicle Speed Control and Idle Control
System
6
-
Computer Output Circuits
7
-
Transmission
8
-
Transmission
Identifies what section of the system
is malfunctioning
P 0 2 0 1
16 OBD2
Page 19
Preparation for Testing
PRELIMINARY VEHICLE DIAGNOSTIC WORKSHEET
PRELIMINARY VEHICLE DIAGNOSTIC WORKSHEET
The purpose of this form is to help you gather preliminary information on
your vehicle before you retrieve codes. By having a complete account of
your vehicle's current problem(s), you will be able to systematically
pinpoint the problem(s) by comparing your answers to the fault codes
you retrieve. You can also provide this information to your mechanic to
assist in diagnosis and help avoid costly and unnecessary repairs. It is
important for you to complete this form to help you and/or your
mechanic have a clear understanding of your vehicle's problems.
NAME:
DATE:
VIN*:
YEAR:
MAKE:
MODEL:
ENGINE SIZE:
VEHICLE MILEAGE:
*VIN: Vehicle Identification Number, found at the base of the windshield
on a metallic plate, or at the driver door latch area (consult your vehicle
owner's manual for location).
TRANSMISSION:
❏ Automatic
❏ Manual
Please check all applicable items in each category.
DESCRIBE THE PROBLEM:
OBD2 17
Page 20

Preparation for Testing
PRELIMINARY VEHICLE DIAGNOSTIC WORKSHEET
WHEN DID YOU FIRST NOTICE THE PROBLEM:
❏ Just Started
❏ Started Last Week
❏ Started Last Month
❏ Other:
m
LIST ANY REPAIRS DONE IN THE PAST SIX MONTHS:
PROBLEMS STARTING
❏ No symptoms
❏ Will not crank
ENGINE QUITS OR STALLS
❏ No symptoms
❏ Right after starting
❏ When shifting into gear
❏ During steady-speed
driving
❏ Cranks, but will not start
❏ Starts, but takes a long
time
❏ Right after vehicle
comes to a stop
❏ While idling
❏ During acceleration
❏ When parking
IDLING CONDITIONS
❏ No symptoms
❏ Is too slow at all times
❏ Is too fast
❏ Is sometimes too fast or
too slow
❏ Is rough or uneven
❏ Fluctuates up and down
RUNNING CONDITIONS
❏ No symptoms
❏ Runs rough
❏ Lacks power
❏ Bucks and jerks
❏ Poor fuel economy
❏ Hesitates or stumbles on
❏ Backfires
❏ Misfires or cuts out
❏ Engine knocks, pings or
rattles
❏ Surges
❏ Dieseling or run-on
accelerations
18 OBD2
Page 21

Preparation for Testing
PRELIMINARY VEHICLE DIAGNOSTIC WORKSHEET
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION PROBLEMS (if applicable)
❏ No symptoms
❏ Shifts too early or too late
❏ Changes gear incorrectly
PROBLEM OCCURS
❏ Morning ❏ Afternoon ❏ Anytime
ENGINE TEMPERATURE WHEN PROBLEM OCCURS
❏ Cold ❏ Warm ❏ Hot
DRIVING CONDITIONS WHEN PROBLEM OCCURS
❏ Short - less than 2 miles
❏ 2 - 10 miles
❏ Long - more than 10 miles
❏ Stop and go
❏ While turning
❏ While braking
❏ At gear engagement
❏ With A/C operating
DRIVING HABITS
❏ Mostly city driving
❏ Highway
❏ Park vehicle inside
❏ Park vehicle outside
GASOLINE USED
❏ 87 Octane
❏ 89 Octane
WEATHER CONDITIONS WHEN PROBLEM OCCURS
❏ 32 - 55° F (0 - 13° C)
❏ Below freezing (32° F / 0° C)
CHECK ENGINE LIGHT / DASH WARNING LIGHT
❏ Sometimes ON ❏ Always ON ❏ Never ON
PECULIAR SMELLS
❏ "Hot"
❏ Sulfur ("rotten egg")
❏ Burning rubber
STRANGE NOISES
❏ Rattle
❏ Knock
❏ Vehicle does not move
when in gear
❏ Jerks or bucks
❏ With headlights on
❏ During acceleration
❏ Mostly driving downhill
❏ Mostly driving uphill
❏ Mostly driving level
❏ Mostly driving curvy
roads
❏ Mostly driving rough
roads
❏ Drive less than 10 miles per day
❏ Drive 10 to 50 miles per day
❏ Drive more than 50 miles per
day
❏ 91 Octane
❏ More than 91 Octane
❏ Above 55° F (13° C)
❏ Gasoline
❏ Burning oil
❏ Electrical
❏ Squeak
❏ Other
OBD2 19
Page 22

Preparation for Testing
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
The Enhanced OBD2 Scan Tool
aids in monitoring electronicand emissions-related faults in
your vehicle and retrieving fault
codes related to malfunctions in
these systems. Mechanical
problems such as low oil level or
damaged hoses, wiring or electrical connectors can cause poor engine
performance and may also cause a fault code to set. Fix any known
mechanical problems before performing any test. See your vehicle’s
service manual or a mechanic for more information.
Check the following areas before starting any test:
Check the engine oil, power steering fluid, transmission fluid (if
applicable), engine coolant and other fluids for proper levels. Top off
low fluid levels if needed.
Make sure the air filter is clean and in good condition. Make sure all
air filter ducts are properly connected. Check the air filter ducts for
holes, rips or cracks.
Make sure all engine belts are in good condition. Check for cracked,
torn, brittle, loose or missing belts.
Make sure mechanical linkages to engine sensors (throttle, gearshift
position, transmission, etc.) are secure and properly connected. See
your vehicle’s service manual for locations.
Check all rubber hoses (radiator) and steel hoses (vacuum/fuel) for
leaks, cracks, blockage or other damage. Make sure all hoses are
routed and connected properly.
Make sure all spark plugs are clean and in good condition. Check
for damaged, loose, disconnected or missing spark plug wires.
Make sure the battery terminals are clean and tight. Check for
corrosion or broken connections. Check for proper battery and
charging system voltages.
Check all electrical wiring and harnesses for proper connection.
Make sure wire insulation is in good condition, and there are no bare
wires.
Make sure the engine is mechanically sound. If needed, perform a
compression check, engine vacuum check, timing check (if
applicable), etc.
20 OBD2
Page 23

Preparation for Testing
VEHICLE SERVICE MANUALS
VEHICLE SERVICE MANUALS
Always refer to the manufacturer’s service manual for your vehicle
before performing any test or repair procedures. Contact your local car
dealership, auto parts store or bookstore for availability of these
manuals. The following companies publish valuable repair manuals:
Haynes Publications
861 Lawrence Drive
Newbury Park, California 91320
Phone: 800-442-9637
Mitchell International
14145 Danielson Street
Poway, California 92064
Phone: 888-724-6742
Motor Publications
5600 Crooks Road, Suite 200
Troy, Michigan 48098
Phone: 800-426-6867
FACTORY SOURCES
Ford, GM, Chrysler, Honda, Isuzu, Hyundai and Subaru Service
Manuals
Helm Inc.
14310 Hamilton Avenue
Highland Park, Michigan 48203
Phone: 800-782-4356
OBD2 21
Page 24

Using the Scan Tool
CODE RETRIEVAL PROCEDURE
CODE RETRIEVAL PROCEDURE
Retrieving and using Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) for
troubleshooting vehicle operation is only one part of an
Never replace a part based only on the DTC definition.
Each DTC has a set of testing procedures, instructions and
flow charts that must be followed to confirm the location of
the problem. This information is found in the vehicle's
service manual. Always refer to the vehicle's service manual
for detailed testing instructions.
Check your vehicle thoroughly before performing
any test. See BEFORE YOU BEGIN on page 20 for
details.
ALWAYS observe safety precautions whenever working on a
vehicle. See SAFETY PRECAUTIONS on page 3 for more
information.
1. Turn the ignition off.
2. Locate the vehicle's 16-pin Data Link
Connector (DLC). See page 5 for
connector location.
Some DLCs have a plastic cover
that must be removed before
connecting the Scan Tool cable
connector.
If the Scan Tool is ON, turn it OFF
by pressing the POWER/LINK
button BEFORE connecting the
Scan Tool to the DLC.
3. Connect the Scan Tool cable connector to the vehicle’s DLC. The
cable connector is keyed and will only fit one way.
If you have problems connecting the cable connector to the DLC,
rotate the connector 180° and try again.
If you still have problems, check the DLC on the vehicle and on
the Scan Tool. Refer to your vehicle’s service manual to properly
check the vehicle’s DLC.
4. When the Scan Tool’s cable connector
is properly connected to the vehicle’s
DLC, the unit automatically turns ON,
and the display shows instructions for
linking to the vehicle’s on-board
computer.
overall diagnostic strategy.
22 OBD2
Page 25

Using the Scan Tool
CODE RETRIEVAL PROCEDURE
If the unit does not power on automatically when connected to
the vehicle’s DLC connector, it usually indicates there is no
power present at the vehicle’s DLC connector. Check your fuse
panel and replace any burned-out fuses.
If replacing the fuse(s) does not correct the problem, consult
your vehicle’s repair manual to identify the proper computer
(PCM) fuse/circuit, and perform any necessary repairs before
proceeding.
5. Turn the ignition on. DO NOT start the engine.
6. Press and release the Scan Tool’s POWER/LINK
The Scan Tool will automatically
start a check of the vehicle’s
computer to determine which type of
communication protocol it is using.
When the Scan Tool identifies the
computer’s communication protocol,
a communication link is established.
The protocol type used by the
vehicle’s computer is shown on the
display.
A PROTOCOL is a set of rules and procedures for
regulating data transmission between computers, and
between testing equipment and computers. As of this
writing, five different types of protocols (ISO 9141, Keyword
2000, J1850 PWM, J1850 VPW and CAN) are in use by
vehicle manufacturers. The Scan Tool automatically
identifies the protocol type and establishes a
communication link with the vehicle’s computer.
7. After approximately 10~60 seconds, the Scan Tool will retrieve and
display any Diagnostic Trouble Codes, Monitor Status and Freeze
Frame Data retrieved from the vehicle’s computer memory.
If the Scan Tool fails to link to the
vehicle’s computer a “Linking
Failed” message shows on the Scan
Tool’s display.
- Verify the connection at the DLC,
and verify the ignition is ON.
- Turn the ignition OFF, wait 5
seconds, then turn back ON to
reset the computer.
- Ensure your vehicle is OBD2 compliant. See VEHICLES
COVERED on page 5 for vehicle compliance verification
information.
button.
OBD2 23
Page 26

Using the Scan Tool
CODE RETRIEVAL PROCEDURE
The Scan Tool will display a code
only if codes are present in the
vehicle’s computer memory. If no
codes are present, a “No DTC’s or
Freeze Frame data presently stored
in the vehicle’s computer” message
is displayed.
- If the ENTER/LD
pressed from the “no DTCs”
screen, the message “No
Powertrain DTCs or Freeze
Frame Data is presently stored in
the Scan Tool’s memory. Press
the DTC button to view your
Enhanced or ABS DTC’s”
displays. Press the DTC SCROLL
button to enter the
“enhanced” mode (see THE
ENHANCED MAIN MENU on page 28).
The Scan Tool is capable of retrieving and storing up to 32
codes in memory, for immediate or later viewing.
8. To read the display:
Refer to DISPLAY FUNCTIONS on page 12 for a description
of display elements.
A visible icon indicates that the Scan Tool is being powered
through the vehicle’s DLC connector.
A visible icon indicates that the Scan Tool is linked to
(communicating with) the vehicle’s computer.
The I/M Monitor Status icons indicate the type and number of
Monitors the vehicle supports, and provides indications of the
current status of the vehicle’s Monitors. A solid Monitor icon
indicates the associated Monitor has run and completed its
testing. A blinking Monitor icon indicates the associated Monitor
has not run and completed its testing.
The upper right hand corner of the
display shows the number of the
code currently being displayed, the
total number of codes retrieved, the
type of code (G = Generic; M =
Enhanced or Manufacturer specific),
and whether or not the displayed
code commanded the MIL on. If the
code being displayed is a PENDING
code, the PENDING icon is shown.
The Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and related code definition
are shown in the lower section of the display.
button is
24 OBD2
Page 27

Using the Scan Tool
CODE RETRIEVAL PROCEDURE
In the case of long code definitions, or when viewing Freeze
Frame and Live Data, a small arrow is shown in the
upper/lower right-hand corner of the Scan Tool display area to
indicate the presence of additional information. Use the
buttons, as necessary, to view the additional informa-
and
tion.
If a definition for the currently displayed code is not available,
an advisory message shows on the Scan Tool’s display.
9. Read and interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes/system condition
using the display and the green, yellow and red LEDs.
The green, yellow and red LEDs are used (with the display) as
visual aids to make it easier to determine engine system
conditions.
Green LED – Indicates that all
engine systems are “OK” and
operating normally. All monitors
supported by the vehicle have run
and performed their diagnostic
testing, and no trouble codes are
present. A zero will show on the
Scan Tool’s display, and all Monitor
icons will be solid.
Yellow LED – Indicates one of the
following conditions:
A. A PENDING CODE IS PRESENT –
If the yellow LED is illuminated, it
may indicate a Pending code is
present. Check the Scan Tool’s
display for confirmation. A Pending
code is confirmed by the presence
of a numeric code and the word
PENDING on the Scan Tool’s
display.
B. MONITOR NOT RUN STATUS – If
the Scan Tool’s display shows a
zero (indicating there are no DTC’s
present in the vehicle’s computer
memory), but the yellow LED is
illuminated, it may be an indication
that some of the Monitors
supported by the vehicle have not
yet run and completed their
diagnostic testing. Check the Scan
Tool’s display for confirmation. All Monitor icons that are
blinking have not yet run and completed their diagnostic
testing; all Monitor icons that are solid have run and
completed their diagnostic testing.
OBD2 25
Page 28

Using the Scan Tool
CODE RETRIEVAL PROCEDURE
Red LED – Indicates there is a
problem with one or more of the
vehicle’s systems. The red LED is
also used to indicate that DTC(s)
are present (displayed on the Scan
Tool’s screen). In this case, the
Multifunction Indicator (Check
Engine) lamp on the vehicle’s
instrument panel will be illuminated.
DTC’s that start with “P0”, “P2” and some “P3” are
considered Generic (Universal). All Generic DTC definitions
are the same on all OBD2 equipped vehicles. The Scan Tool
automatically displays the code definitions (if available) for
Generic DTC’s.
If the definition for the currently
displayed code is not available,
an advisory message shows on
the Scan Tool’s LCD display.
DTC’s that start with “P1” and some
“P3” are Manufacturer specific codes
and their code definitions vary with
each vehicle manufacturer. When a
Manufacturer specific DTC is
retrieved, the LCD display shows a
list of vehicle manufacturers. Use the
and DOWN buttons, as
UP
necessary, to highlight the
appropriate manufacturer, then press
the ENTER/LD button to display
the correct code definition for your
vehicle.
If the manufacturer for your vehicle is not listed, use the UP
and DOWN
manufacturer and press the ENTER/LD
additional DTC information.
If the Manufacturer Specific definition for the currently displayed
code is not available, an advisory
message shows on the Scan
Tool’s display.
10. If more than one DTC was retrieved,
and to view Freeze Frame Data, press
and release the DTC SCROLL
button, as necessary.
Each time the DTC SCROLL button is pressed and
released, the Scan Tool will scroll and display the next DTC in
sequence until all DTCs in its memory have displayed.
buttons, as necessary, to select Other
button for
26 OBD2
Page 29

Using the Scan Tool
CODE RETRIEVAL PROCEDURE
Freeze Frame Data (if available) will display after DTC #1.
Whenever the Scroll function is used to view additional
DTCs and Freeze Frame Data, the Scan Tool's
communication link with the vehicle's computer
disconnects. To re-establish communication, press the
POWER/LINK
In OBD2 systems, when an
emissions-related engine malfunction occurs that causes a DTC to set,
a record or snapshot of engine
conditions at the time that the
malfunction occurred is also saved
in the vehicle’s computer memory.
The record saved is called Freeze
Frame data. Saved engine
conditions include, but are not limited to: engine speed, open or
closed loop operation, fuel system commands, coolant
temperature, calculated load value, fuel pressure, vehicle speed,
air flow rate, and intake manifold pressure.
If more than one malfunction is present that causes more than
one DTC to be set, only the code with the highest priority will
contain Freeze Frame data. The code designated “01” on the
Scan Tool display is referred to as the PRIORITY code, and
Freeze Frame data always refers to this code. The priority
code is also the one that has commanded the MIL on.
Retrieved information can be uploaded to a Personal
Computer (PC) with the use of an optional “PC Link Kit.” (see
instructions included with PC-Link program for more
information).
11. When the last retrieved DTC has been displayed and the DTC
SCROLL
“enhanced” mode.
See VIEWING ENHANCED DTCs on page 32 to view enhanced
DTCs for your vehicle.
If you do not wish to view enhanced DTCs, press the DTC
SCROLL
If a Manufacturer specific DTC was retrieved during the
code retrieval process, and the manufacturer selected for
the code was not Chrysler, Jeep, Ford, Mazda, General
Motors or Isuzu, pressing the DTC SCROLL
after display of the last retrieved DTC returns the screen to
the first retrieved DTC (the Enhanced DTC menu is not
displayed).
12. Determine engine system(s) condition by viewing the Scan Tool’s
display for any retrieved Diagnostic Trouble Codes, code definitions,
Freeze Frame data and Live Data, interpreting the green, yellow and
red LEDs.
button again.
button is pressed, the Scan Tool enters the
button to return to the OBD2 DTC screen.
button
OBD2 27
Page 30

Using the Code Reader
THE ENHANCED MAIN MENU
If DTC’s were retrieved and you are going to perform the repairs
yourself, proceed by consulting the Vehicle’s Service Repair
Manual for testing instructions, testing procedures, and flow
charts related to retrieved code(s).
If you plan to take the vehicle to a professional to have it
serviced, complete the PRELIMINARY VEHICLE DIAGNOSTIC
WORKSHEET on page 17 and take it together with the retrieved
codes, freeze frame data and LED information to aid in the
troubleshooting procedure.
To prolong battery life, the Scan Tool automatically shuts “Off”
approximately three minutes after it is disconnected from the
vehicle. The DTCs retrieved, captured Live Data Information,
Monitor Status and Freeze Frame data (if any) will remain in the
Scan Tool’s memory, and may be viewed at any time by turning
the unit “On”. If the Scan Tool’s batteries are removed, or if the
Scan Tool is re-linked to a vehicle to retrieve codes/data, any
prior codes/data in its memory are automatically cleared.
THE ENHANCED MAIN MENU
Following the code retrieval procedure (see CODE RETRIEVAL
PROCEDURE on page 22), when the last retrieved DTC has been
displayed and the DTC SCROLL
enters the “enhanced” mode. The “enhanced” mode provides the ability
to retrieve enhanced DTCs from most Chrysler/Jeep, Ford/Mazda,
GM/Isuzu, Honda/Acura and Toyota/Lexus vehicles. The types of
enhanced data available depends on the vehicle make. You can also
retrieve Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) DTCs.
ABS DTCs are available for Chrysler/Jeep, Ford and GM
vehicles only.
The screen shown when the Scan Tool enters the “enhanced” mode
depends on the type(s) of DTC(s) returned during the code retrieval process:
If no DTCs were retrieved, or only
generic DTCs were retrieved, the
Enhanced Main Menu displays. Use the
UP
necessary, to highlight the desired
option, then press the ENTER/LD
button to view the selected information,
or, press the DTC SCROLL
to return to the OBD2 DTC screen.
and DOWN buttons, as
button is pressed, the Scan Tool
button
- When View ABS DTCs or View
Enhanced DTCs is selected, the
Select Manufacturer screen displays.
Use the UP
and DOWN
buttons, as necessary, to highlight
the appropriate manufacturer, then
press the ENTER/LD
button to
view the selected information.
28 OBD2
Page 31

Using the Code Reader
VIEWING ABS DTCs
If the manufacturer of the
vehicle from which codes were
retrieved is not listed, press
the DTC SCROLL
to return to the OBD2 DTC
screen. Enhanced data is not
available for your vehicle.
If a Manufacturer specific DTC was
retrieved, and the manufacturer selected
for the code was Chrysler, Jeep, Ford,
Mazda, General Motors, Isuzu, Honda,
Acura, Toyota or Lexus, the Select Data
menu displays. Use the UP
DOWN
highlight the desired option, then press
the ENTER/LD
the DTC SCROLL
If a Manufacturer specific DTC was retrieved, and the manufacturer
selected for the code was not Chrysler, Jeep, Ford, Mazda, General
Motors, Isuzu, Honda, Acura, Toyota or Lexus the “enhanced” mode
is bypassed, and the OBD2 DTC screen shows the first code
retrieved. Enhanced data is not available for your vehicle.
To view ABS DTCs: Select View ABS
DTCs from the Enhanced Main Menu (then
choose the appropriate manufacturer if
prompted). Refer to VIEWING ABS DTCs on
page 29 to view ABS DTCs for your vehicle.
buttons, as necessary, to
button
and
button to view the selected information, or, press
button to return to the OBD2 DTC screen.
To view Enhanced DTCs: Select View
Enhanced DTCs from the Enhanced Main
Menu (then choose the appropriate
manufacturer if prompted). Refer to
VIEWING ENHANCED DTCs on page 32 to
view enhanced DTCs for your vehicle.
VIEWING ABS DTCs
When View ABS DTCs is selected from the
Enhanced Main Menu (and the appropriate
vehicle manufacturer is selected, if
prompted), the ABS Menu for the appropriate vehicle manufacturer displays. You may
choose to “Read ABS DTCs” or “Erase ABS
DTCs.”
OBD2 29
Page 32

Using the Code Reader
VIEWING ABS DTCs
Reading ABS DTCs
1. Use the UP and DOWN buttons, as necessary, to highlight
Read ABS DTCs, then press the ENTER/LD
A "One moment please" message
displays while the Scan Tool
retrieves the selected DTCs.
If the Scan Tool fails to link to the
vehicle’s computer, a "Linking
Failed" message shows on the Scan
Tool’s display.
- Verify the ignition is ON, then
press the ENTER/LD
If the vehicle does not support ABS communication, an advisory
message shows on the Scan Tool’s display. Press the
ENTER/LD
2. To read the display:
Refer to DISPLAY FUNCTIONS on page 12 for a description
of LCD display elements.
A visible icon indicates that the Scan Tool is being powered
through the vehicle’s DLC connector.
A visible icon indicates that the Scan Tool is linked to
(communicating with) the vehicle’s computer.
The upper right hand corner of the
display shows the number of the
code currently being displayed, the
total number of codes retrieved.
The Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
and related code definition are
shown in the lower section of the
LCD display.
I/M MONITOR STATUS icons are not displayed when viewing
ABS DTCs.
In the case of long code definitions, a small arrow is shown in
the upper/lower right-hand corner of the code display area to
indicate the presence of additional information. Use the UP
and DOWN
information.
The Scan Tool will display a code
only if codes are present in the
vehicle’s computer memory. If no
codes are present, a "No ABS
DTC’s are presently stored in the
vehicle’s computer" is displayed.
Press the ENTER/LD
return to the ABS Menu.
button.
button to continue.
button to return to exit.
buttons, as necessary, to view the additional
button to
30 OBD2
Page 33

Using the Code Reader
VIEWING ABS DTCs
3. If more than one code was retrieved press the DTC SCROLL
button, as necessary, to display additional codes one at a time.
Whenever the scroll function is used to view additional codes,
the Scan Tool’s communication link with the vehicle’s computer
disconnects. To re-establish communication, press the LINK
button again.
4. When the last retrieved DTC has been displayed and the DTC SCROLL
button is pressed, the Scan Tool returns to the ABS Menu.
To exit the enhanced mode, use the UP and DOWN
buttons, as necessary, to select Exit from the ABS Menu, then
press the ENTER/LD
the OBD2 DTC screen.
Erasing ABS DTCs
If you plan to take the vehicle to a Service Center for repair, DO NOT
erase the ABS DTCs from the vehicle’s computer. If the codes are
erased, valuable information that might help the technician troubleshoot
the problem will be erased.
1. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight Erase ABS
DTCs, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
2. A confirmation message shows on the
LCD display.
If you are sure you want to proceed, press the ERASE
button to erase the ABS DTCs from the vehicle’s computer.
If you do not want to continue with the erase process, press the
POWER/LINK
the ABS Menu.
3. If you chose to erase ABS DTCs, a
progress screen displays while ion is in
progress.
If the erase was successful, a
confirmation message shows on the
LCD display. Press the ENTER/LD
button to return to the ABS Menu.
and DOWN buttons,
button. The Code Reader returns to
button to exit the erase mode and return to
If the erase was not successful, an
advisory message shows on the
LCD display. Verify that the Scan
Tool is properly connected to the
vehicle’s DLC and that the ignition is
on, then repeat steps 2 and 3, above.
OBD2 31
Page 34

Using the Scan Tool
VIEWING ENHANCED DTCs
Erasing ABS DTCs does not fix the problem(s) that caused the
code(s) to be set. If proper repairs to correct the problem(s)
that caused the code(s) to be set are not made, the code(s)
will appear again as soon as the vehicle is driven long enough
for the problem to recur.
VIEWING ENHANCED DTCs
Refer to the appropriate paragraph to view enhanced data for your
vehicle:
Chrysler/Jeep......................................... page 32
Ford/Mazda............................................ page 33
GM/Isuzu................................................ page 35
Honda/Acura.......................................... page 37
Toyota/Lexus ......................................... page 38
Chrysler/Jeep Enhanced DTCs
When View Enhanced DTCs is selected from the Enhanced Main
Menu (and Chrysler/Jeep is selected, if prompted), the Chrysler
Enhanced menu displays. You may view either “Engine DTCs” or
“Transmission DTCs.”
1. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight the desired
option, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
Transmission DTCs are not supported on most Chrysler/Jeep vehicles manufactured prior to 2002.
A “One moment please” message displays while the Scan Tool
retrieves the selected DTCs.
If the Scan Tool fails to link to the
vehicle’s computer, a “Linking
Failed” message shows on the Scan
Tool’s display.
- Verify the ignition is ON, then
press the ENTER/LD
to continue.
2. To read the display:
Refer to DISPLAY FUNCTIONS on page 12 for a description
of LCD display elements.
A visible icon indicates that the Scan Tool is being powered
through the vehicle’s DLC connector.
A visible icon indicates that the Scan Tool is linked to
(communicating with) the vehicle’s computer.
and DOWN buttons,
button
32 OBD2
Page 35

Using the Scan Tool
VIEWING ENHANCED DTCs
The upper right hand corner of the
display shows the number of the
code currently being displayed, the
total number of codes retrieved.
The Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
and related code definition are
shown in the lower section of the
LCD display.
I/M MONITOR STATUS icons are not displayed when
viewing enhanced DTCs.
In the case of long code definitions, or when viewing
Freeze Frame data, a small arrow is shown in the
upper/lower right-hand corner of the code display area
to indicate the presence of additional information. Use
the
additional information.
The Scan Tool will display a code only
if codes are present in the vehicle’s
computer memory. If no codes are
present, a “No Enhanced DTC’s are
presently stored in the vehicle’s
computer” is displayed. Press the
ENTER/LD
Chrysler Enhanced menu.
3. If more than one code was retrieved press the DTC SCROLL
button, as necessary, to display additional codes one at a time.
Whenever the Scroll function is used to view additional codes,
the Scan Tool’s communication link with the vehicle’s computer
disconnects. To re-establish communication, press the LINK
button again.
4. When the last retrieved DTC has been displayed and the DTC
SCROLL
Chrysler Enhanced menu.
To view additional enhanced DTCs, repeat steps 1 through 4, above.
To exit the enhanced mode, use the UP and DOWN
buttons, as necessary, to select Exit from the Chrysler
Enhanced menu, then press the ENTER/LD
Scan Tool returns to the OBD2 DTC screen.
button is pressed, the Scan Tool returns to the
and buttons, as necessary, to view the
button to return to the
button. The
Ford/Mazda Enhanced DTCs
Mazda Enhanced DTCs are available for Mazda-branded
Ford vehicles only.
OBD2 33
Page 36

Using the Scan Tool
VIEWING ENHANCED DTCs
When View Enhanced DTCs is selected from the Enhanced Main
Menu (and Ford/Mazda is selected, if prompted), the Ford/Mazda
Enhanced menu displays. You may view DTCs for either the
“Continuous Memory Test”, “KOEO (Key On Engine Off) Test” or
“KOER (Key On Engine Running) Test.”
1. Use the UP
necessary, to highlight the desired option,
then press the ENTER/LD
When choosing to view KOER
Test DTCs, start the vehicle’s
engine before making your
selection.
A “One moment please” message
displays, while the Scan Tool
retrieves the selected DTCs.
If the Scan Tool fails to link to the
vehicle’s computer, a “Linking
Failed” message shows on the Scan
Tool’s Display.
- Verify the ignition is ON, then press the ENTER/LD
button to continue.
If the KOER Test was selected, and
the vehicle’s engine is not running,
an advisory message shows on the
Scan Tool’s display.
- Start the vehicle’s engine, then
press the ENTER/LD
to continue.
2. To read the display:
Refer to DISPLAY FUNCTIONS on page 12 for a description
of LCD display elements.
A visible icon indicates that the Scan Tool is being powered
through the vehicle’s DLC connector.
A visible icon indicates that the Scan Tool is linked to
(communicating with) the vehicle’s computer.
The upper right hand corner of the
display shows the number of the
code currently being displayed, the
total number of codes retrieved.
The Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
and related code definition are shown in
the lower section of the LCD display.
I/M MONITOR STATUS icons are not displayed when
viewing enhanced DTCs.
and DOWN buttons, as
button.
button
34 OBD2
Page 37

Using the Scan Tool
VIEWING ENHANCED DTCs
In the case of long code definitions, or when viewing
Freeze Frame data, a small arrow is shown in the
upper/lower right-hand corner of the code display area
to indicate the presence of additional information. Use
the
additional information.
The Scan Tool will display a code only if
codes are present in the vehicle’s
computer memory. If no codes are
present, a “No Enhanced DTC’s are
presently stored in the vehicle’s
computer” is displayed. Press the
ENTER/LD
Ford/Mazda Enhanced menu.
3. If more than one code was retrieved press the DTC SCROLL
button, as necessary, to display additional codes one at a time.
Whenever the Scroll function is used to view additional codes,
the Scan Tool’s communication link with the vehicle’s computer
disconnects. To re-establish communication, press the LINK
button again.
4. When the last retrieved DTC has been displayed and the DTC
SCROLL
Ford/Mazda Enhanced menu.
To view additional enhanced DTCs, repeat steps 1 through 4,
above.
To exit the enhanced mode, use the UP and DOWN
buttons, as necessary, to select Exit from the Ford/Mazda
Enhanced menu, then press the ENTER/LD
Scan Tool returns to the OBD2 DTC screen.
button is pressed, the Scan Tool returns to the
and buttons, as necessary, to view the
button to return to the
button. The
General Motors/Isuzu Enhanced DTCs
When View Enhanced DTCs is selected from the Enhanced Main
Menu (and General Motors/Isuzu is selected, if prompted), the
GM/Isuzu Enhanced menu displays. You may view the “MIL DTC”,
“Current DTC”, “Fail Since Clear DTC” or “History DTC.”
1. Use the UP
and DOWN buttons,
as necessary, to highlight the desired
option, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
A “One moment please” message
displays while the Scan Tool
retrieves the selected DTCs.
OBD2 35
Page 38

Using the Scan Tool
VIEWING ENHANCED DTCs
If the Scan Tool fails to link to the
vehicle’s computer, a “Linking
Failed” message shows on the Scan
Tool’s display.
- Verify the ignition is ON, then
press the ENTER/LD
to continue.
2. To read the display:
Refer to DISPLAY FUNCTIONS on page 12 for a description
of LCD display elements.
A visible icon indicates that the Scan Tool is being powered
through the vehicle’s DLC connector.
A visible icon indicates that the Scan Tool is linked to
(communicating with) the vehicle’s computer.
The upper right hand corner of the
display shows the number of the
code currently being displayed, the
total number of codes retrieved.
The Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
and related code definition are
shown in the lower section of the
LCD display.
I/M MONITOR STATUS icons are not displayed when
viewing enhanced DTCs.
In the case of long code definitions, or when viewing
Freeze Frame data, a small arrow is shown in the
upper/lower right-hand corner of the code display area
to indicate the presence of additional information. Use
the
additional information.
The Scan Tool will display a code
only if codes are present in the
vehicle’s computer memory. If no
codes are present, a “No Enhanced
DTC’s are presently stored in the
vehicle’s computer” is displayed.
Press the ENTER/LD
return to the GM Enhanced menu.
3. If more than one code was retrieved press the DTC SCROLL
button, as necessary, to display additional codes one at a time.
Whenever the Scroll function is used to view additional codes,
the Scan Tool’s communication link with the vehicle’s computer
disconnects. To re-establish communication, press the LINK
button again.
button
and buttons, as necessary, to view the
button to
36 OBD2
Page 39

Using the Scan Tool
VIEWING ENHANCED DTCs
4. When the last retrieved DTC has been displayed and the DTC
SCROLL
GM/Isuzu Enhanced menu.
To view additional enhanced DTCs, repeat steps 1 through 4,
above.
To exit the enhanced mode, use the UP and DOWN
buttons, as necessary, to select Exit from the GM/Isuzu
Enhanced menu, then press the ENTER/LD
Scan Tool returns to the OBD2 DTC screen.
Honda/Acura Enhanced DTCs
When View Enhanced DTCs is selected from
the Enhanced Main Menu (and Honda/Acura
is selected, if prompted), the Honda Acura
Enhanced menu displays. Depending on the
protocol used to communicate with your
vehicle, the Honda/Acura Enhanced menu
provides options to view:
Permanent DTCs or Temporary DTCs
Confirmed DTCs or History DTCs
1. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight the desired
option, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
A “One moment please” message
displays while the Scan Tool
retrieves the selected DTCs.
If the Scan Tool fails to link to the
vehicle’s computer, a “Linking
Failed” message shows on the Scan
Tool’s display.
- Verify the ignition is ON, then press the ENTER/LD
2. To read the display:
Refer to DISPLAY FUNCTIONS on page 12 for a description
of LCD display elements.
A visible icon indicates that the Scan Tool is being powered
through the vehicle’s DLC connector.
A visible icon indicates that the
Scan Tool is linked to (communicating with) the vehicle’s computer.
The upper right hand corner of the
display shows the number of the
code currently being displayed, the
total number of codes retrieved.
button is pressed, the Scan Tool returns to the
button to continue.
button. The
and DOWN buttons,
OBD2 37
Page 40

Using the Scan Tool
VIEWING ENHANCED DTCs
The Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and related code definition
are shown in the lower section of the LCD display.
I/M MONITOR STATUS icons are not displayed when
viewing enhanced DTCs.
In the case of long code definitions, or when viewing
Freeze Frame data, a small arrow is shown in the
upper/lower right-hand corner of the code display area
to indicate the presence of additional information. Use
the
additional information.
The Scan Tool will display a code only
if codes are present in the vehicle’s
computer memory. If no codes are
present, a “No Enhanced DTC’s are
presently stored in the vehicle’s
computer” is displayed. Press the
ENTER/LD
Honda/Acura Enhanced menu.
3. If more than one code was retrieved press the DTC SCROLL
button, as necessary, to display additional codes one at a time.
Whenever the Scroll function is used to view additional codes,
the Scan Tool’s communication link with the vehicle’s computer
disconnects. To re-establish communication, press the LINK
button again.
4. When the last retrieved DTC has been displayed and the DTC
SCROLL
Honda/Acura Enhanced menu.
To view additional enhanced DTCs, repeat steps 1 through 4, above.
To exit the enhanced mode, use the UP and DOWN
buttons, as necessary, to select Exit from the Honda/Acura
Enhanced menu, then press the ENTER/LD
Scan Tool returns to the OBD2 DTC screen.
button is pressed, the Scan Tool returns to the
and buttons, as necessary, to view the
button to return to the
button. The
Toyota/Lexus Enhanced DTCs
When View Enhanced DTCs is selected
from the Enhanced Main Menu (and
Toyota/Lexus is selected, if prompted), the
Toyota/Lexus Enhanced menu displays.
Depending on the protocol used to communicate with your vehicle, the Toyota/Lexus
Enhanced menu provides options to view:
Current DTCs, History DTCs or Pending
DTCs
38 OBD2
Page 41

Using the Scan Tool
VIEWING ENHANCED DTCs
Current DTCs, Historical DTCs or
Readiness DTCs
1. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight the desired
option, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
A “One moment please” message
displays, while the Scan Tool
retrieves the selected DTCs.
If the Scan Tool fails to link to the
vehicle’s computer, a “Linking
Failed” message shows on the Scan
Tool’s Display.
- Verify the ignition is ON, then
press the ENTER/LD
to continue.
2. To read the display:
Refer to DISPLAY FUNCTIONS on page 12 for a description
of LCD display elements.
A visible icon indicates that the Scan Tool is being powered
through the vehicle’s DLC connector.
A visible icon indicates that the Scan Tool is linked to
(communicating with) the vehicle’s computer.
The upper right hand corner of the
display shows the number of the
code currently being displayed, the
total number of codes retrieved.
The Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
and related code definition are shown in
the lower section of the LCD display.
I/M MONITOR STATUS icons are not displayed when
viewing enhanced DTCs.
In the case of long code definitions, or when viewing
Freeze Frame data, a small arrow is shown in the
upper/lower right-hand corner of the code display area
to indicate the presence of additional information. Use
the
additional information.
The Scan Tool will display a code only
if codes are present in the vehicle’s
computer memory. If no codes are
present, a “No Enhanced DTC’s are
presently stored in the vehicle’s
computer” is displayed. Press the
ENTER/LD
Toyota/Lexus Enhanced menu.
and DOWN buttons,
button
and buttons, as necessary, to view the
button to return to the
OBD2 39
Page 42

Using the Scan Tool
ERASING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCs)
3. If more than one code was retrieved press the DTC SCROLL
button, as necessary, to display additional codes one at a time.
Whenever the Scroll function is used to view additional codes,
the Scan Tool’s communication link with the vehicle’s computer
disconnects. To re-establish communication, press the LINK
button again.
4. When the last retrieved DTC has been displayed and the DTC
SCROLL
Toyota/Lexus Enhanced menu.
To view additional enhanced DTCs, repeat steps 1 through 4,
above.
To exit the enhanced mode, use the UP and DOWN
buttons, as necessary, to select Exit from the Toyota/Lexus
Enhanced menu, then press the ENTER/LD
Scan Tool returns to the OBD2 DTC screen.
ERASING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCs)
When the Scan Tool’s ERASE function is used to erase
DTCs from the vehicle's on-board computer, "Freeze
Frame" data and manufacturer-specific enhanced data are
also erased.
If you plan to take the vehicle to a Service Center for repair, DO NOT
erase the codes from the vehicle's computer. If the codes are erased,
valuable information that might help the technician troubleshoot the
problem will also be erased.
Erase DTCs from the computer's memory as follows:
When DTCs are erased from the vehicle's computer memory,
the I/M Readiness Monitor Status program resets the status of
all Monitors to a not run "flashing" condition. To set all of the
Monitors to a DONE status, an OBD2 Drive Cycle must be
performed. Refer to your vehicle's service manual for
information on how to perform an OBD2 Drive Cycle for the
vehicle under test.
The Scan Tool must be connected
to the vehicle’s DLC to erase the
codes from the computer’s memory.
If you press the ERASE
when the Scan Tool is not
connected to the vehicle’s DLC, the
erase instruction screen displays.
The Erase function can be performed only from the OBD2
DTC screen. The Erase function cannot be performed while
the Scan Tool is in “enhanced” mode.
button is pressed, the Scan Tool returns to the
button. The
button
40 OBD2
Page 43

Using the Scan Tool
I/M READINESS TESTING
1. If not connected already, connect the
Scan Tool to the vehicle's DLC, and turn
the ignition "On.” (If the Scan Tool is
already connected and linked to the
vehicle's computer, proceed directly to
step 4. If not, continue to step 2.)
2. Turn the ignition on. DO NOT start the engine.
Press and release the POWER/LINK
button to establish communication with the
vehicle's computer.
3. Press and release the ERASE
button. A confirmation message shows
on the display.
- If you are sure you want to proceed
press the ERASE
erase DTCs from the vehicle’s computer.
- If you do not want to continue with
the erase process, press the
POWER/LINK
erase mode.
4. If you chose to erase DTCs, a progress screen displays while the
erase function is in progress.
If the erase was successful, a
confirmation message shows on the
display. Press the DTC SCROLL
button to return to the DTC
screen.
If the erase was not successful, an
advisory message shows on the
display. Verify that the Scan Tool is
properly connected to the vehicle’s
DLC and that the ignition is on, then
repeat steps 2 and 3, above.
Erasing DTCs does not fix the
problem(s) that caused the code(s)
to be set. If proper repairs to
correct the problem that caused
the code(s) to be set are not made,
the code(s) will appear again (and the check engine light will
illuminate) as soon as the vehicle is driven long enough for its
Monitors to complete their testing.
button again to
button to exit the
I/M READINESS TESTING
I/M is an Inspection and Maintenance program legislated by the
Government to meet federal clean-air standards.
OBD2 41
Page 44

Using the Scan Tool
I/M READINESS TESTING
The program requires that a vehicle be taken periodically to an
Emissions Station for an "Emissions Test" or "Smog Check,” where the
emissions-related components and systems are inspected and tested
for proper operation. Emissions Tests are generally performed once a
year, or once every two years.
On OBD2 systems, the I/M program is enhanced by requiring vehicles
to meet stricter test standards. One of the tests instituted by the Federal
Government is called I/M 240. On I/M 240, the vehicle under test is
driven under different speeds and load conditions on a dynamometer for
240 seconds, while the vehicle's emissions are measured.
Emissions tests vary depending on the geographic or regional
area in which the vehicle is registered. If the vehicle is
registered in a highly urbanized area, the I/M 240 is probably
the type of test required. If the vehicle is registered in a rural
area, the stricter “dynamometer type” test may not be required.
I/M Readiness Monitors
I/M Readiness shows whether the various emissions-related systems on
the vehicle are operating properly and are ready for Inspection and
Maintenance testing.
State and Federal Governments enacted Regulations, Procedures and
Emission Standards to ensure that all emissions-related components
and systems are continuously or periodically monitored, tested and
diagnosed whenever the vehicle is in operation. It also requires vehicle
manufacturers to automatically detect and report any problems or faults
that may increase the vehicle's emissions to an unacceptable level.
The vehicle's emissions control system consists of several components
or sub-systems (Oxygen Sensor, Catalytic Converter, EGR, Fuel
System, etc.) that aid in reducing vehicle emissions.
To have an efficient Vehicle Emission Control System, all the emissionsrelated components and systems must work correctly whenever the
vehicle is in operation.
To comply with State and Federal Government regulations, vehicle
manufacturers designed a series of special computer programs called
"Monitors" that are programmed into the vehicle's computer. Each of
these Monitors is specifically designed to run tests and diagnostics on a
specific emissions-related component or system (Oxygen Sensor,
Catalytic Converter, EGR Valve, Fuel System, etc.) to ensure their
proper operation. Currently, there are a maximum of eleven Monitors
available for use.
Each Monitor has a specific function to test and diagnose only
its designated emissions-related component or system. The
names of the Monitors (Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Catalyst
Monitor, EGR Monitor, Misfire Monitor, etc.) describe which
component or system each Monitor is designed to test and
diagnose.
42 OBD2
Page 45

Using the Scan Tool
I/M READINESS TESTING
Emissions Inspection and Maintenance (I/M) Readiness
Monitor Status Information
I/M Readiness Monitor Status shows which of the vehicle's Monitors
have run and completed their diagnosis and testing, and which ones
have not yet run and completed testing and diagnosis of their
designated sections of the vehicle's emissions system.
If a Monitor was able to meet all the conditions required to enable it
to perform the self-diagnosis and testing of its assigned engine
system, it means the monitor "HAS
If a Monitor has not yet met all the conditions required for it to
perform the self-diagnosis and testing of its assigned engine system;
it means the Monitor "HAS NOT
The Monitor Run/Not Run status does not show whether
or not a problem exists in a system. Monitor status only
indicates whether a particular Monitor has or has not run
and performed the self-diagnosis and testing of its
associated system.
RUN.”
RUN.”
Performing I/M Readiness Quick Check
When a vehicle first comes from the factory, all Monitors
indicate a “HAVE RUN” status. This indicates that all Monitors
have run and completed their diagnostic testing. The “HAVE
RUN” status remains in the computer's memory, unless the
Diagnostic Trouble Codes are erased or the vehicle's
computer memory is cleared.
The Scan Tool allows you to retrieve Monitor/System Status Information
to help you determine if the vehicle is ready for an Emissions Test
(Smog Check). In addition to retrieving Diagnostic Trouble Codes, the
Scan Tool also retrieves Monitor Run/Not Run status. This information is
very important since different areas of the state/country have different
emissions laws and regulations concerning Monitor Run/Not Run status.
Before an Emissions Test (Smog Check) can be performed, your
vehicle must meet certain rules, requirements and procedures legislated
by the Federal and state (country) governments where you live.
1. In most areas, one of the requirements that must be met before a
vehicle is allowed to be Emissions Tested (Smog Checked) is that
the vehicle does not have any Diagnostic Trouble Codes present
(with the exception of PENDING Diagnostic Trouble Codes).
2. In addition to the requirement that no Diagnostic Trouble Codes be
present, some areas also require that all the Monitors that a
particular vehicle supports indicate a "Has Run" status condition
before an Emissions Check may be performed.
3. Other areas may only require that some (but not all) Monitors
indicate a "Has Run" status before an Emissions Test (Smog Check)
may be performed.
OBD2 43
Page 46

Using the Scan Tool
I/M READINESS TESTING
Monitors with a "Has Run" status indicate that all the
required conditions they needed to perform diagnosis and
testing of their assigned engine area (system) have been
met, and all diagnostic testing has completed successfully.
Monitors with a "Has Not Run" status have not yet met the
conditions they need to perform diagnosis and testing of
their assigned engine area (system), and have not been
able to perform diagnostic testing on that system.
The green, yellow and red LEDs provide a quick way to help you
determine if a vehicle is ready for an Emissions Test (Smog Check).
Follow the instructions below to perform the Quick Check.
Perform the CODE RETRIEVAL PROCEDURE as described on page
22, then interpret the LED indications as follows:
Interpreting I/M Readiness Test Results
1. GREEN LED - Indicates that all engine
systems are "OK" and operating
normally (all Monitors supported by the
vehicle have run and performed their
self-diagnostic testing). The vehicle is
ready for an Emissions Test (Smog
Check), and there is a good possibility
that it can be certified.
2. YELLOW LED - Determine from the CODE RETRIEVAL
PROCEDURE (page 22) which of the two possible conditions is
causing the yellow LED to light.
If a "PENDING" Diagnostic Trouble
Code is causing the yellow LED to
light, it is possible that the vehicle
will be allowed to be tested for
emissions and certified. Currently,
most areas (states / countries) will
allow an Emissions Test (Smog
Check) to be performed if the only
code in the vehicle's computer is a
"PENDING" Diagnostic Trouble
Code.
If the illumination of the Yellow LED
is being caused by monitors that
“have not run” their diagnostic
testing, then the issue of the vehicle
being ready for an Emissions Test
(Smog Check) depends on the
emissions regulations and laws of
your local area.
44 OBD2
Page 47

Using the Scan Tool
I/M READINESS TESTING
- Some areas require that all Monitors indicate a "Has Run"
status before they allow an Emissions Test (Smog Check) to
be performed. Other areas only require that some, but not all,
Monitors have run their self-diagnostic testing before an
Emissions Test (Smog Check) may be performed.
- From the code retrieval procedure, determine the status of
each Monitor (a solid Monitor icon shows Monitor "Has Run"
status, a flashing Monitor icon indicates "Has Not Run" status).
Take this information to an emissions professional to
determine (based on your test results) if your vehicle is ready
for an Emissions Test (Smog Check).
3. RED LED - Indicates there is a problem
with one or more of the vehicle's systems.
A vehicle displaying a red LED is definitely
not ready for an Emissions Test (Smog
Check). The red LED is also an indication
that there are Diagnostic Trouble Code(s)
present (displayed on the Scan Tool's
screen). The Multifunction Indicator (Check
Engine) Lamp on the vehicle's instrument
panel will light steady. The problem that is
causing the red LED to light must be repaired before an Emissions Test
(Smog Check) can be performed. It is also suggested that the vehicle be
inspected/repaired before driving the vehicle further.
If the Red LED was obtained, there is a definite problem present in
the system(s). In these cases, you have the following options.
Repair the vehicle yourself. If you are going to perform the
repairs yourself, proceed by reading the vehicle service manual
and following all its procedures and recommendations.
Take the vehicle to a professional to have it serviced. The
problem(s) causing the red LED to light must be repaired before
the vehicle is ready for an Emissions Test (Smog Check).
Using the I/M Readiness Monitor Status to Confirm a Repair
The I/M Readiness Monitor Status function can be used (after repair of a
fault has been performed) to confirm that the repair has been performed
correctly, and/or to check for Monitor Run Status. Use the following
procedure to determine I/M Readiness Monitor Status:
1. Using retrieved Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and code
definitions as a guide, and following manufacturer's repair
procedures, repair the fault or faults as instructed.
2. After the fault or faults have been repaired, connect the Scan Tool to
the vehicle's DLC and erase the code or codes from the vehicle's
computer memory.
See page 40 for procedures for ERASING DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLE CODES (DTCs) from the vehicle's on-board computer.
Write the codes down on a piece of paper for reference before
erasing.
OBD2 45
Page 48

Using the Scan Tool
I/M READINESS TESTING
3. After the erase procedure is performed, most of the Monitor icons on
the Scan Tool’s display will be flashing. Leave the Scan Tool
connected to the vehicle, and perform a Trip Drive Cycle for each
"flashing" Monitor:
Misfire, Fuel and Comprehensive Component Monitors run
continuously and their icons will always be on solid, even after
the erase function is performed.
Each DTC is associated with a specific Monitor. Consult the
vehicle's service manual to identify the Monitor (or Monitors)
associated with the faults that were repaired. Follow the
manufacturer's procedures to perform a Trip Drive Cycle for the
appropriate Monitors.
While observing the Monitor icons on the Scan Tool’s display,
perform a Trip Drive Cycle for the appropriate Monitor or
Monitors.
If the vehicle needs to be driven in order to perform a Trip
Drive Cycle, ALWAYS have a second person help you.
One person should drive the vehicle while the other
person observes the Monitor icons on the Scan Tool for
Monitor RUN status. Trying to drive and observe the Scan
Tool at the same time is dangerous, and could cause a
serious traffic accident.
4. When a Monitor's Trip Drive Cycle is performed properly, the Monitor
icon on the Scan Tool’s display changes from "flashing" to "solid,”
indicating that the Monitor has run and finished its diagnostic testing.
If, after the Monitor has run, the MIL on the vehicle's dash is not lit, and
no stored or pending codes associated with that particular Monitor are
present in the vehicle's computer, the repair was successful.
If, after the Monitor has run, the MIL on the vehicle's dash lights
and/or a DTC associated with that Monitor is present in the
vehicle's computer, the repair was unsuccessful. Refer to the
vehicle's service manual and recheck repair procedures.
46 OBD2
Page 49

Live Data Mode
VIEWING LIVE DATA
The OBD2 Scan Tool is a special diagnostic tool that communicates
with the vehicle's computer. The Scan Tool lets you view and/or
"capture" (record) "real-time" Live Data. This information includes values
(volts, rpm, temperature, speed etc.) and system status information
(open loop, closed loop, fuel system status, etc.) generated by the
various vehicle sensors, switches and actuators.
In effect the Scan Tool lets you view, in "real time", the same
signal values generated by the sensors, actuators, switches and/or
vehicle system status information used by the vehicle's computer
when calculating and conducting system adjustments and corrections.
The real time (Live Data) vehicle operating information (values/status)
that the computer supplies to the Scan Tool for each sensor, actuator,
switch, etc. is called Parameter Identification (PID) Data.
Each PID (sensor, actuator switch, status, etc.) has a set of operating
characteristics and features (parameters) that serve to identify it. The
Scan Tool displays this information for each sensor, actuator, switch or
status that is supported by the vehicle under test.
WARNING: If the vehicle must be driven in order to perform a
troubleshooting procedure, ALWAYS have a second person
help you. One person should drive the vehicle while the other
person observes the Scan Tool data. Trying to drive and
operate the Scan Tool at the same time is dangerous, and
could cause a serious traffic accident.
VIEWING LIVE DATA
1. Follow steps 1 through 7 of the CODE RETRIEVAL PROCEDURE
(page 22) to place the Scan Tool in "Code Retrieval" mode.
2. Press and release the ENTER/LD
button to place the Scan Tool in "Live
Data" mode.
3. Real-time Live Data (PID) information
supported by the vehicle under test
displays.
Remember, what you are viewing is "real-time" Live Data. The
values (volts, rpm, temperature, vehicle speed, system status
etc) for the various PIDS displayed may change as the
vehicle's operating conditions change.
4. A vehicle usually supports several PIDs, however, only a limited
amount of PID data can be displayed on the screen at one time. If
additional PID data is available, a small arrow will be shown on the
display. Use the the UP
and DOWN buttons, as necessary,
to scroll up or down to view all available PID data.
OBD2 47
Page 50

Live Data Mode
CUSTOMIZING LIVE DATA (PIDs)
If communication with the vehicle is
lost while viewing Live Data, a
Communication Lost" message
shows on the Scan Tool's display.
5. If you experience vehicle problems,
view and/or compare the Live Data (PID)
information displayed on the Scan Tool
to specifications in the vehicle's repair
manual.
If desired, you can "customize" the Live Data display to show only
those PIDs you are interested in viewing. See Customizing Live
Data (PIDs) below for details. You may also choose to "capture"
(record) Live Data for later viewing. See RECORDING
(CAPTURING) LIVE DATA on page 49for details.
6. You can toggle back and forth between the DTC screen (to view
DTCs) and Live Data screen (to view PIDs) by alternately pressing
and releasing the DTC SCROLL
buttons once (the unit will stay linked to the vehicle while toggling
between modes). If the DTC SCROLL
then the screen will scroll to the next DTC and the tool will be taken
out of link.
When toggling from the Live Data to the DTC screen a “one
moment please...” message will temporarily display, followed
by the DTC screen.
and the ENTER/LD
button is pressed twice,
CUSTOMIZING LIVE DATA (PIDs)
This feature lets you customize the Scan Tool display to show only
those PIDs that are of interest at the current time. You can customize
the Live Data display by placing the Scan Tool in "Custom Live Data"
mode and selecting only the PIDs that you wish to display. To customize
the Live Data display, proceed as follows:
1. With the Scan Tool in "Live Data" mode
(see VIEWING LIVE DATA on page 47
for details), press and hold the
ENTER/LD
button until the "Mode
Selection Menu" appears.
2. Use the UP
and DOWN buttons,
as necessary, to highlight “Live Data
Menu”, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
The "Live Data Menu" displays.
3. Use the UP
and DOWN buttons,
as necessary, to highlight “Custom Live
Data”, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
48 OBD2
Page 51

Live Data Mode
RECORDING (CAPTURING) LIVE DATA
The "Custom Live Data" menu displays, with the first PID in the
menu highlighted.
4. Use the UP
to scroll through the available PIDs.
When the PID you wish to display is
highlighted, press the ENTER/LD
button to select it (a "checkmark" will
show in the checkbox to the right of the
PID to confirm your selection). Repeat
the procedure until only the PIDs you
want to display have all been selected.
To deselect a currently selected PID, highlight the PID, then
press the ENTER/LD
removed from the checkbox.
5. When you are finished making your selection(s), scroll to the end of
the PID list and highlight the word DONE, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
The Scan Tool is now in "Custom Live Data" mode. Only the
PIDs you selected are shown on the Scan Tools display.
To toggle between the "Custom Live Data" display and the full
Live Data display, momentarily press the ENTER/LD
6. To exit the "Custom Live Data" mode, press and hold the
ENTER/LD
and DOWN buttons
button until the “Mode Selection Menu” displays.
button. The checkmark will be
button.
RECORDING (CAPTURING) LIVE DATA
You can record and save several frames of Live Data information for
each PID supported by the vehicle in the Scan Tool's memory.
Recorded Live Data can serve as valuable information to help you in the
troubleshooting of vehicle problems.
There are two ways that the Scan Tool can "record" Live Data:
Record by DTC Trigger
Record by Manual Trigger
If the POWER/LINK
button is pressed at any time while in
Live Data mode, any stored (recorded) Live Data will be
cleared (erased) from the Scan Tool’s memory.
Record by DTC Trigger
This function automatically records (captures) Live Data information
when a DTC sets and saves it in the Scan Tool’s memory. The recorded
(captured) data can be a valuable troubleshooting aid, particularly if you
are experiencing a fault that is causing a DTC to set.
OBD2 49
Page 52

Live Data Mode
RECORDING (CAPTURING) LIVE DATA
1. With the Scan Tool in "Live Data" mode
(see VIEWING LIVE DATA on page 47
for details), press and hold the
ENTER/LD
Selection Menu" appears.
2. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight “Live Data
Menu”, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
The "Live Data Menu" displays.
3. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight “Record Live
Data”, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
The "Record Live Data Menu" dis-
plays.
4. Use the UP and DOWN buttons,
as necessary, to highlight Record by
DTC trigger, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
5. When the "Record by DTC Trigger" screen displays, select the
desired trigger point as follows:
The Scan Tool is capable of recording approximately 20
frames of Live Data. Record by DTC trigger lets you select the
point in time at which you wish the Scan Tool to begin
recording Live Data. You can set the trigger point to record the
20 frames of data before an event (when the DTC sets), after
the event, or in the middle (10 frames before and 10 frames
after the event.
Beginning - records approximately
20 frames of Live Data after the
DTC sets.
Middle - records approximately 10
frames of Live Data before and 10
frames after the DTC sets.
End - records approximately 20 frames
of Live Data before the DTC sets.
6. Use the UP
as necessary, to select the desired
trigger point, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
A "One moment please. . ." message
shows on the display. When the Scan
Tool is ready to record Live Data, the
"Record Live Data" screen displays.
button until the "Mode
and DOWN buttons,
and DOWN buttons,
and DOWN buttons,
50 OBD2
Page 53

Live Data Mode
RECORDING (CAPTURING) LIVE DATA
7. Put the engine in the operating condition that causes the DTC to set.
If necessary, drive the vehicle until you reach the vehicle speed
at which the problem occurs.
8. When the Scan Tool detects a fault that causes a DTC to set, it
automatically records and saves approximately 20 frames of Live
Data information in its memory (according to your trigger selection)
for each PID supported by the vehicle.
All three LEDs will blink for three
seconds to indicate that Live Data is
being recorded, and a "One moment
please..." message shows on the
display.
When recording is complete, a
confirmation screen displays, asking
if you would like to view the
recorded data. Use the UP
DOWN
select Yes or No, as desired, then
press the ENTER/LD button.
If Yes is selected, the Scan Tool
enters "Playback" mode from
which you can view a frame-byframe playback of recorded Live Data (see LIVE DATA
PLAYBACK on page 53 for details). If No is selected, the
display returns to the "Live Data View" mode.
9. You can exit the "Record Live Data Mode" at any time by pressing
and holding the ENTER/LD
Menu" displays.
If desired, you can transfer the recorded Live Data information
to a personal computer using the optional PC-LINK program
(see instructions included with PC-Link for more information).
buttons, as necessary, to
and
button until the "Mode Selection
Record by Manual Trigger
This option lets you select the precise time at which the Live Data
recording will occur. Record by Manual Trigger can be a very valuable
diagnostic tool when troubleshooting intermittent problems that do not
meet the requirements for a DTC to set. Even though a DTC is not
present, the intermittent problems will sometimes manifest themselves
briefly, for a few fractions of a second and/or only at certain vehicle
speeds or vehicle operating conditions.
1. With the Scan Tool in "Live Data" mode
(see VIEWING LIVE DATA on page 47
for details), press and hold the
ENTER/LD
button until the "Mode
Selection Menu" appears.
OBD2 51
Page 54

Live Data Mode
RECORDING (CAPTURING) LIVE DATA
2. Use the UP and DOWN buttons,
as necessary, to highlight “Live Data
Menu”, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
The "Live Data Menu" displays.
3. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight “Record Live
Data”, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
The "Record Live Data Menu" dis-
plays.
4. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight “Record by
manual trigger”, then press the
ENTER/LD button.
5. When the "Record by Manual Trigger" screen displays, select the
desired trigger point as follows:
The Scan Tool is capable of recording approximately 20
frames of Live Data. Record by DTC trigger lets you select the
point in time at which you wish the Scan Tool to begin
recording Live Data. You can set the trigger point to record the
20 frames of data before an event (when the DTC was set),
after the event, or in the middle (10 frames before and 10
frames after the event.
Beginning - records approximately
20 frames of Live Data after the
ENTER/LD
Middle - records approximately 10
frames of Live Data before and 10
frames after the ENTER/LD
button was pressed.
End - records approximately 20 frames of Live Data before the
ENTER/LD
6. Use the UP
desired trigger point, then press the ENTER/LD
A "One moment please. . ."
message shows on the display.
When the Scan Tool is ready to
record Live Data, the "Record Live
Data" screen displays.
7. Put the engine in the operating condition
where the problem manifests itself.
and DOWN buttons,
and DOWN buttons,
button was pressed.
button was pressed.
and DOWN buttons, as necessary, to select the
button.
52 OBD2
Page 55

Live Data Mode
LIVE DATA PLAYBACK
If necessary, drive the vehicle until you reach the vehicle speed
at which the problem occurs.
8. When the problem occurs, press and
release the ENTER/LD
All three LEDs will blink for three
seconds to indicate that Live Data is
being recorded, and a "One moment
please. . ." message shows on the
display.
When recording is complete, a confirmation screen displays,
asking if you would like to view the recorded data. Use the UP
as desired, then press the ENTER/LD
If Yes is selected, the Scan Tool enters "Playback" mode from
which you can view a frame-by-frame playback of recorded
Live Data (see LIVE DATA PLAYBACK on page 53 for details).
If No is selected, the display returns to the "Live Data View"
mode.
9. You can exit the "Record Live Data Mode" at any time by pressing
and holding the ENTER/LD
Menu" displays.
If desired, you can transfer the recorded Live Data information
to a personal computer using the optional PC-LINK program
(see instructions included with PC-Link for more information).
button.
and DOWN buttons, as necessary, to select Yes or No,
button.
button until the "Mode Selection
Important Information
1. When Live Data capture is initiated, the green, yellow and red LEDs
on the Scan Tool will flash three times to indicate that Live Data is
being saved to the Scan Tool's memory.
2. When you are LINKED to a vehicle and you are in the “Live Data
View mode”, you can toggle between “Live Data View” mode and
“DTC view” mode by alternately pressing and releasing the DTC
SCROLL
or the ENTER/LD buttons. The Scan Tool will
stay linked to the vehicle’s computer during this process. However, if
the DTC SCROLL
button is pressed twice the DTC screen will
be advanced to the next DTC screen and the Scan Tool will be
taken out of link.
LIVE DATA PLAYBACK
Once Live Data has been recorded, it is saved in the Scan Tool's
memory. You can view recorded Live Data immediately after recording
by selecting Yes from the Record Live Data confirmation screen (see
RECORDING (CAPTURING) LIVE DATA on page 49 for more
information), or you can view it later using the "Playback" function.
OBD2 53
Page 56

Live Data Mode
LIVE DATA PLAYBACK
1. With the Scan Tool not connected to a vehicle, press the
POWER/LINK
The "To Link" screen shows on the
Scan Tool's display.
2. Press the ENTER/LD
place the Scan Tool in "Live Data
Playback" mode.
The display shows the recorded
Live Data, beginning with the
"trigger" frame.
When you select Yes from the Record Live Data confirmation
screen, the Scan Tool enters the "Live Data Playback" mode,
and the display shows the recorded Live Data, beginning with
the "trigger" frame.
A vehicle usually supports several PIDs, however, only a limited
amount of PID data can be displayed on the screen at one time.
If additional PID data is available, a small arrow will be shown on
the display. Use the UP
necessary, to scroll up or down to view all available PID data.
When viewing recorded Live Data, look for any irregularities in
any of the PID values/signal information (LTFT %, RPM, MAP,
TEMP, etc.). If any PIDs are not within specification, or
irregularities are detected, follow the procedures in the vehicle's
service repair manual to perform additional troubleshooting and
repair.
When recorded Live Data is played back, all available PIDs
are shown, even if you have customized the Live Data
selections.
If there is no Live Data currently stored in the Scan Tool's
memory, an advisory message shows on the display. Press
the DTC SCROLL
mode.
3. When you have viewed all PID information for the current frame of
Live Data, use the DOWN
list. Highlight Next Frame or Previous Frame, as desired, then press
the ENTER/LD
4. When you have finished viewing the recorded Live Data, exit the
“Live Data Playback” mode using the appropriate procedure shown
below:
If the Scan Tool is connected to a vehicle, use the DOWN
button to scroll to the end of the PID list, highlight Exit Playback,
then press the ENTER/LD
If the Scan Tool is not connected to a vehicle, press the DTC
SCROLL
button.
button to
and DOWN buttons, as
button to exit the "Live Data Playback"
button to scroll to the end of the PID
button.
button.
button.
54 OBD2
Page 57

Additional Tests
O2 SENSOR TEST
In addition to retrieving Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and viewing
Live Data, you can use the Scan Tool to perform additional diagnostic
tests, and to view diagnostic and vehicle information stored in your
vehicle's on-board computer.
Additional tests are accessed through the
"Mode Selection Menu." To access the
"Mode Selection Menu", place the Scan
Tool in "Live Data" mode (see VIEWING
LIVE DATA on page 47 for details), then
press and hold the ENTER/LD
until the "Mode Selection Menu" appears.
The following functions are available from the "Mode Selection Menu":
Live Data Menu - Displays the "Live Data Menu" from which you
can choose to record, customize and play back Live Data (see the
Live Data Mode section beginning on page 47 for more information)
O2 Sensor Test - Retrieves and displays O2 sensor monitor test
esults from your vehicle's on-board computer.
Non-Continuous Test - Retrieves and displays test results for
emission-related powertrain components and systems that are not
continuously monitored.
System Test - Performs a leak test for the vehicle's EVAP system.
Vehicle Information - Retrieves the vehicle's VIN number,
calibration ID(s) and other related information, and lets you view a
listing of available modules for the vehicle.
button
O2 SENSOR TEST
OBD2 regulations require that applicable vehicles monitor and test
operation of the oxygen (O2) sensors to identify problems that can affect
fuel efficiency and vehicle emissions. These tests are performed
automatically when engine operating conditions are within predefined
limits. Results of these tests are stored in the on-board computer's
memory.
The O2 Sensor Test function lets you retrieve and view O2 sensor
monitor test results for the most recently completed tests from your
vehicle's on-board computer.
Vehicles are equipped with multiple O2 sensors. O2 sensors are
installed both upstream of (before) and downstream of (after) the
exhaust system Catalytic Converters. The name of an O2 sensor
identifies its location in the exhaust system. The name of each O2
sensor is made up of three parts:
O2S XX YY -or- O2S X Y
O2S -this is the basic designation for all O2 sensors.
OBD2 55
Page 58

Additional Tests
O2 SENSOR TEST
X or XX - These characters identify the location of the O2 sensor in
relation to a cylinder bank. An O2 sensor for cylinder bank 1 is
identified by the designation “1” or "B1"; a sensor for cylinder bank 2
is identified as “2” or "B2."
”Bank One” indicates the side of the engine where cylinder
number one is located (V-type engines). Bank Two is opposite
of Bank One.
Y or YY - These characters identity the location of the O2 sensor in
relation to the exhaust system catalyst. An O2 sensor located
upstream of the catalyst is identified by the designation”1” or "S1", a
sensor located downstream of the Catalytic Converter is identified
as “2” or "S2."
For example, O2S12 or O2SB1S2 is the designation for the
downstream O2 sensor for cylinder bank 1.
The Scan Tool does not perform O2 sensor tests, but retrieves
results from the most recently performed O2 sensor tests from
the on-board computer's memory. You may retrieve O2 sensor
test results for only one test of one sensor at any given time.
1. From the "Mode Selection Menu", use
the UP
necessary, to highlight O2 Sensor Test,
then press the ENTER/LD
The "Select Sensor" screen displays.
The screen shows all O2 sensors
applicable to the vehicle under test.
If O2 sensor tests are not
supported by the vehicle under
test, an advisory message shows
on the Scan Tool's display. Press
the ENTER/LD
return to "Live Data" mode.
2. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight the O2 sensor
for which you wish to view test results,
then press the ENTER/LD button.
3. A "One moment please..." message
displays while the request is sent to the
vehicle's on-board computer.
4. When test results have been retrieved,
data for the selected sensor test will
show on the Scan Tool's display.
5. When you have finished viewing the retrieved test data, scroll to the
end of the display to select Exit, then press the ENTER/LD
button to return to the "Select Test" screen.
and DOWN buttons, as
button.
button to
and DOWN buttons,
56 OBD2
Page 59

Additional Tests
NON-CONTINUOUS TEST
NON-CONTINUOUS TEST
The Non-Continuous Test function retrieves and displays test results
for emission-related powertrain components and systems that are not
continuously monitored. The tests available are determined by the
vehicle manufacturer.
The Scan Tool does not perform non-continuous test, but
retrieves results from the most recently performed tests from
the on-board computer’s memory. You may retrieve noncontinuous test results for only one test at any given time.
1. From the "Mode Selection Menu", use
the UP
necessary, to highlight Non-
Continuous Test, then press the
ENTER/LD
The “Select Test” screen displays.
The screen shows all tests
applicable to the vehicle under test.
Refer to the vehicle’s service repair
manual for information related to
non-continuous tests.
If non-continuous tests are not
supported by the vehicle under test,
an advisory message shows on the
Scan Tool's display. Press the
ENTER/LD
the Mode Selection menu.
2. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight the desired
test, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
3. A “One moment please. . .” message
diplays while the request is sent to the
vehicle’s on-board computer.
4. When test results have been retrieved, data for the selected test will
show on the Scan Tool’s display. The display shows the following
information:
Test ID number
Module ID number
Component ID number
Min or Max test limit
Test Value and status
and DOWN buttons, as
button.
button to return to
and DOWN buttons,
Only one test limit, either Min
or Max, is shown for any given
test.
OBD2 57
Page 60

Additional Tests
SYSTEM TEST
Status is calculated by the Scan Tool by comparing the Test
Value against the displayed test limit (either Min or Max).
Status is shown as either Low, High or OK.
5. When you have finished viewing the retrieved test data, scroll to the
end of the display to select Exit, then press the ENTER/LD
button to return to the “Select Test” screen.
SYSTEM TEST
The System Test function lets you initiate a leak test for the vehicle's
EVAP system.
The Scan Tool does not perform the leak test, but signals to
vehicle's on-board computer to initiate the test. The vehicle
manufacturer determines the criteria and method for stopping
the test once it has been started. BEFORE using the System
Test function, refer to the vehicle's service repair manual to
determine the procedures necessary to stop the test.
1. From the "Mode Selection Menu", use
the UP
necessary, to highlight System Test,
then press the ENTER/LD
The "System Test Menu" displays.
2. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight EVAP Leak
Test, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
3. A "One moment please..." message
displays while the request is sent to the
vehicle's on-board computer.
Some vehicle manufacturers do
not allow Scan Tools or other
external devices to control vehicle
systems. If the EVAP Leak Test is
not supported by the vehicle under
test, an advisory message shows
on the Scan Tool's display. Press
the ENTER/LD
return to the System Test menu.
4. When the EVAP leak test has been
initiated by the vehicle's on-board
computer, a confirmation message
shows on the Scan Tool's display. Press
the ENTER/LD
"Live Data" mode.
and DOWN buttons as
button.
and DOWN buttons,
button to
button to return to
58 OBD2
Page 61

Additional Tests
VEHICLE INFORMATION
VEHICLE INFORMATION
The Vehicle Information function offers two options for retrieving
reference information for the vehicle under test; Vehicle ID and
Available Modules.
Retrieving Vehicle ID Information
The Vehicle ID function is applicable to model year 2000 and
newer OBD2-compliant vehicles.
The Scan Tool can retrieve a list of information (provided by the vehicle
manufacturer), unique to the vehicle under test, from the vehicle's onboard computer. This information may include:
The vehicle's VIN number
The control module identification number
The vehicle's calibration ID(s). These IDs uniquely identify the
software version(s) for the vehicle's control module(s).
The Vehicle's Calibration Verification Number(s) (CVNs) required by
ODB2 regulations. CVNs are used to determine if emission-related
calibrations for the vehicle under test have been changed. One or
more CVNs may be returned by the vehicle's computer.
1. From the “Mode Selection Menu”, use
the UP
necessary, to highlight Vehicle
Information, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
The “Vehicle Information Menu” dis-
plays.
If the Vehicle Information function is not supported by the vehicle
under test, an advisory message
shows on the Scan Tool’s display.
Press the ENTER/LD
to return to the Mode Selection
menu.
2. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight Vehicle ID,
then press the ENTER/LD
and DOWN buttons, as
button
and DOWN buttons,
button.
3. A "One moment please..." message
displays while the requested information
is retrieved from the vehicle's computer.
The first time the Vehicle ID function is used, it may take
several minutes
to retrieve the information from the vehicle's
computer.
OBD2 59
Page 62

Additional Tests
VEHICLE INFORMATION
4. When the retrieval process is completed,
the vehicle ID information is shown on
the Scan Tool's display. Use the UP
and DOWN
to view the entire list.
5. When you have finished viewing the
retrieved vehicle ID information, press
the ENTER/LD
"Live Data" mode.
Viewing Available Modules
The Scan Tool can retrieve a list of modules supported by the vehicle
under test.
1. From the “Mode Selection Menu”, use
the UP
necessary, to highlight Vehicle
Information, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
The “Vehicle Information Menu” dis-
plays.
If the Vehicle Information function is not supported by the vehicle
under test, an advisory message
shows on the Scan Tool’s display.
Press the ENTER/LD
to return to the “Live Data” mode.
2. Use the UP
as necessary, to highlight Available
Modules, then press the ENTER/LD
button.
3. A "One moment please..." message
displays while the requested information
is retrieved from the vehicle's computer.
4. When the retrieval process is completed,
a complete list of modules supported by
the vehicle under test is shown on the
Scan Tool's display. Use the UP
DOWN
view the entire list.
5. When you have finished viewing the list
of available modules, press the
ENTER/LD
Data" mode.
buttons, as necessary,
button to return to
and DOWN buttons, as
button
and DOWN buttons,
and
buttons, as necessary, to
button to return to "Live
60 OBD2
Page 63

Generic (Global) OBD2 PID List
The following is a list of Generic (Global) PIDs and their descriptions.
Tool
Display
ACC Pedal D % XXX.X Accelerator Pedal Position D
ACC Pedal E % XXX.X Accelerator Pedal Position E
ACC Pedal F % XXX.X Accelerator Pedal Position F
Air Status - UPS, DNS,
Ambient *C /
Aux Input
Status
BARO kPa
Calc LOAD % XXX.X Calculated LOAD Value
CAT Temp 11 *C /
CAT Temp 12 *C /
CAT Temp 21 *C /
CAT Temp 22 *C /
Command
EGR
Command
EVAP
Command
TAC
Dist DTC Clr km
Dist MIL ON km
ECT *C /
ECU Volts V XX.XXX Control Module Voltage
EGR Error % XXX.X EGR Error
Eng RPM min XXXXX Engine RPM
EQ Ratio - X.XXX Commanded Equivalence Ratio
EQ Ratio 11 - X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 1 Equivalence
EQ Ratio 12 - X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 2 Equivalence
EQ Ratio 13 - X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 3 Equivalence
EQ Ratio 14 - X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 4 Equivalence
Unit Value PID Description
OFF
XXX Ambient Air Temperature
*F
- On / Off Auxiliary Input Status
XXX /
/inHg
XX.X
XXXX.X Catalyst Temperature Bank 1-
*F
XXXX.X Catalyst Temperature Bank 1-
*F
XXXX.X Catalyst Temperature Bank 2-
*F
XXXX.X Catalyst Temperature Bank 2-
*F
% XXX.X Commanded EGR
% XXX.X Commanded Evaporative Purge
% XXX.X Commanded Throttle Actuator
XXXXX Distance since DTC Cleared
/mile
XXXXX Distance Traveled while MIL ON
/mile
s
XXX / XXX Engine Coolant Temp
*F
Commanded Secondary Air Status
Barometric Pressure
Sensor 1
Sensor 2
Sensor 1
Sensor 2
Ratio
Ratio
Ratio
OBD2 61
Page 64

Generic (Global) OBD2 PID List
Tool
Display Unit Value PID Description
EQ Ratio 21 - X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 1 Equivalence
EQ Ratio 22 - X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 2 Equivalence
EQ Ratio 23 - X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 3 Equivalence
EQ Ratio 24 - X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 4 Equivalence
EVAP Press Pa
H2O
FP / Vac kPa
/PSI
Fuel Level % XXX.X Fuel Level Input
Fuel Press kPa
/PSI
Fuel Press kPa
/PSI
Fuel Sys 1 - OL Fuel System 1 Status
Fuel Sys 1 - CL Fuel System 1 Status
Fuel Sys 1 - OL-Drive Fuel System 1 Status
Fuel Sys 1 - OL-Fault Fuel System 1 Status
Fuel Sys 1 - CL-Fault Fuel System 1 Status
Fuel Sys 2 - OL Fuel System 2 Status
Fuel Sys 2 - CL Fuel System 2 Status
Fuel Sys 2 - OL-Drive Fuel System 2 Status
Fuel Sys 2 - OL-Fault Fuel System 2 Status
Fuel Sys 2 - CL-Fault Fuel System 2 Status
IAT *C /
LOAD Value % XXX.X Absolute Load Value
LTFT B1 % XXX.X Long Term Fuel Trim-Bank 1
LTFT B2 % XXX.X Long Term Fuel Trim-Bank 2
LTFT B3 % XXX.X Long Term Fuel Trim-Bank 3
LTFT B4 % XXX.X Long Term Fuel Trim-Bank 4
MAF g/s ;l
b/min
MAP kPa
/PSI
MIL On Time hrs,
min
Monitor Status - ICONS on
O2S B1 S1 V X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 1
O2S B1 S1 mA X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 1 O2S Current
62 OBD2
XXXX.XX
/in
/XX.XXX
XXXX.XXX
/XXX.X
XXX /
XX.X
XXXXX
/XXXX.X
XXX / XXX Intake Air Temperature
*F
XXX.XX
/XXXX.X
XXX /
XX.X
XXXX, XX Engine Run Time while MIL ON
Display
Ratio
Ratio
Ratio
Ratio
Ratio
Evap System Vapor Pressure
Fuel Rail Pressure relative
toVacuum
Fuel Rail Pressure
Fuel Rail Pressure
Air Flow Rate from Mass Air Flow
Sensor
Intake Manifold Absolute Pressure
Monitor Status this Driving Cycle
Page 65

Generic (Global) OBD2 PID List
Tool
Display Unit Value PID Description
mA
O2S B1 S1 V V X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 1 O2S Voltage
O2S B1 S2 V X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 2
O2S B1 S2
mA
O2S B1 S2 V V X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 2 O2S Voltage
O2S B1 S3 V X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 3
O2S B1 S3
mA
O2S B1 S3 V V X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 3 O2S Voltage
O2S B1 S4 V X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 4
O2S B1 S4
mA
O2S B1 S4 V V X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 4 O2S Voltage
O2S B2 S1 V X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 1
O2S B2 S1
mA
O2S B2 S1 V V X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 1 O2S Voltage
O2S B2 S2 V X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 2
O2S B2 S2
mA
O2S B2 S2 V V X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 2 O2S Voltage
O2S B2 S3 V X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 3
O2S B2 S3
mA
O2S B2 S3 V V X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 3 O2S Voltage
O2S B2 S4 V X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 4
O2S B2 S4
mA
O2S B2 S4 V V X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 4 O2S Voltage
O2S Location - O2S11 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 1, Sensor 1
O2S Location - O2S12 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 1, Sensor 2
O2S Location - O2S13 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 1, Sensor 3
O2S Location - O2S14 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 1, Sensor 4
O2S Location - O2S21 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 2, Sensor 1
O2S Location - O2S22 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 2, Sensor 1
O2S Location - O2S23 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 2, Sensor 3
O2S Location - O2S24 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 2, Sensor 4
O2S Location - O2S11 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 1, Sensor 1
O2S Location - O2S12 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 1, Sensor 2
O2S Location - O2S21 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 2, Sensor 1
O2S Location - O2S22 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 2, Sensor 2
O2S Location - O2S31 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 3, Sensor 1
O2S Location - O2S32 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 3, Sensor 2
O2S Location - O2S41 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 4, Sensor 1
O2S Location - O2S42 Oxygen Sensor, Bank 4, Sensor 2
mA X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 2 O2S Current
mA X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 3 O2S Current
mA X.XXX Bank 1 - Sensor 4 O2S Current
mA X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 1 O2S Current
mA X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 2 O2S Current
mA X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 3 O2S Current
mA X.XXX Bank 2 - Sensor 4 O2S Current
OBD2 63
Page 66

Generic (Global) OBD2 PID List
Tool
Display Unit Value PID Description
OBD Support - OBD2 OBD Requirements
OBD Support - OBD OBD Requirements
OBD Support - OBD and
OBD Support - OBD1 OBD Requirements
OBD Support - No OBD OBD Requirements
OBD Support - EOBD OBD Requirements
OBD Support - EOBD and
OBD Support - EOBD and
OBD Support - EOBD,
OBD Support - JOBD OBD Requirements
OBD Support - JOBD and
OBD Support - JOBD and
OBD Support - JOBD,
PTO Status - On / Off Power Take Off Status
Rel TPS % XXX.X Relative Throttle Position
Spark Adv deg XX Ignition Timing Advance #1
STFT B1 % XXX.X Short Term Fuel Trim-Bank 1
STFT B1 S1 % XXX.X Bank 1 - Sensor 1
STFT B1 S2 % XXX.X Bank 1 - Sensor 2
STFT B1 S3 % XXX.X Bank 1 - Sensor 3
STFT B1 S4 % XXX.X Bank 1 - Sensor 4
STFT B2 % XXX.X Short Term Fuel Trim-Bank 2
STFT B2 S1 % XXX.X Bank 2 - Sensor 1
STFT B2 S2 % XXX.X Bank 2 - Sensor 2
STFT B2 S3 % XXX.X Bank 2 - Sensor 3
STFT B2 S4 % XXX.X Bank 2 - Sensor 4
STFT B3 % XXX.X Short Term Fuel Trim-Bank 3
STFT B4 % XXX.X Short Term Fuel Trim-Bank 4
Time DTC Clr hrs,
min
Time Since
sec XXXX Time Since Engine Start
Start
TPS % XXX.X Absolute Throttle Position
TPS B % XXX.X Absolute Throttle Position B
TPS C % XXX.X Absolute Throttle Position C
OBD2
OBD2
OBD
OBD and
OBD2
OBD2
EOBD
EOBD and
OBD2
XXXX, XX Time since DTC Cleared
OBD Requirements
OBD Requirements
OBD Requirements
OBD Requirements
OBD Requirements
OBD Requirements
OBD Requirements
Cylinder
64 OBD2
Page 67

Generic (Global) OBD2 PID List
Tool
Display Unit Value PID Description
Veh Speed km/h
mph
Warm-up DTC
Clr
XXX / XXX Vehicle Speed Sensor
/
- XXX # Warm-ups since DTC Cleared
OBD2 65
Page 68

Glossary
GLOSSARY OF TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
GLOSSARY OF TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
CARB – California Air Resources Board
CCM – Central Control Module
Computer Control System – An electronic control system, consisting
of an on-board computer and related sensors, switches and actuators,
used to ensure peak performance and fuel efficiency while reducing
pollutants in the vehicle’s emissions.
DIY – Do-It-Yourself
DLC – Data Link Connector
Drive Cycle – An extended set of driving procedures that takes into
consideration the various types of driving conditions encountered in real
life.
Driving Condition – A specific environmental or operation condition
under which a vehicle is operated; such as starting the vehicle when
cold, driving at steady speed (cruising), accelerating, etc.
DTC(s) – Diagnostic Trouble Code(s)
EGR – Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EPA – Environmental Protection Agency
EVAP – Evaporative Emissions System
Fault Code – See DTCs
Freeze Frame – A digital representation of engine and/or emissions
system conditions present when a fault code was recorded.
FTP – Fuel Tank Pressure
Generic Code – A DTC that applies to all OBD2 compliant vehicles.
I/M Readiness – An indication of whether or not a vehicle’s emissions-
related system are operating properly and are ready for Inspection and
Maintenance testing.
I/M Test / Emissions Test / Smog Check – A functional test of a
vehicle to determine if tailpipe emissions are within Federal/State/Local
requirements.
LCD – Liquid Crystal Display
LED – Light Emitting Diode
LTFT – Long Term Fuel Trim, is a program in the vehicle’s computer
designed to add or subtract fuel from the vehicle to compensate for
operating conditions that vary from the ideal A/F ratio (long term).
Manufacturer Specific Code – A DTC that applies only to OBD2
compliant vehicles made by a specific manufacturer.
MIL – Malfunction Indicator Lamp (also referred to as “Check Engine”
light
OBD1 – On-Board Diagnostics Version 1 (also referred to as “OBD I”)
66 OBD2
Page 69

Glossary
GLOSSARY OF TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
OBD2 – On-Board Diagnostics Version 2 (also referred to as “OBD II”)
On-Board Computer – The central processing unit in the vehicle’s
computer control system.
PCM – Powertrain Control Module
Pending Code – A code recorded on the “first trip” for a “two-trip” code.
If the fault that caused the code to be set is not detected on the second
trip, the code is automatically erased.
PID – Parameter Identification
STFT – Short Term Fuel Trim, is a program in the vehicle’s computer
designed to add or subtract fuel from the vehicle to compensate for
operating conditions that vary from the ideal A/F ratio. The vehicle uses
this program to make minor fuel adjustments (fine tune) on a short-term
basis.
Trip Drive Cycle – Vehicle operation that provides the necessary
driving condition to enable a vehicle Monitor to run and complete its
diagnostic testing.
VECI – Vehicle Emission Control Information Decal
OBD2 67
Page 70

Notes
68 OBD2
Page 71

Warranty and Servicing
LIMITED ONE YEAR WARRANTY
The Manufacturer warrants to the original purchaser that this unit is free
of defects in materials and workmanship under normal use and
maintenance for a period of one (1) year from the date of original
purchase.
If the unit fails within the one (1) year period, it will be repaired or
replaced, at the Manufacturer’s option, at no charge, when returned
prepaid to the Service Center with Proof of Purchase. The sales receipt
may be used for this purpose. Installation labor is not covered under this
warranty. All replacement parts, whether new or remanufactured,
assume as their warranty period only the remaining time of this warranty.
This warranty does not apply to damage caused by improper use,
accident, abuse, improper voltage, service, fire, flood, lightning, or other
acts of God, or if the product was altered or repaired by anyone other
than the Manufacturer’s Service Center.
The Manufacturer, under no circumstances shall be liable for any
consequential damages for breach of any written warranty of this unit.
This warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have
rights, which vary from state to state. This manual is copyrighted with all
rights reserved. No portion of this document may be copied or
reproduced by any means without the express written permission of the
Manufacturer. THIS WARRANTY IS NOT TRANSFERABLE. For
service, send via U.P.S. (if possible) prepaid to Manufacturer. Allow 3-4
weeks for service/repair.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
If you have any questions, require technical support or information on
UPDATES and OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES, please contact your local
store, distributor or the Service Center.
USA & Canada:
(800) 544-4124 (5:00 AM-6:00 PM, Monday-Friday PST)
All others: (714) 241-6802 (5:00 AM-6:00 PM, Monday-Friday PST)
FAX: (714) 432-7511 (24 hr.)
Web: www.CanOBD2.com
OBD2 69
Page 72

®
Innova Electronics Corp.
17291 Mt. Herrmann Street
Fountain Valley, CA 92708
Printed in Taiwan
Instruction MRP
Copyright © 2008 IEC. All Rights Reserved.
#93-0230
© 2008
 Loading...
Loading...