Page 1

GM
Innova 1998
GM CODE READER 1.6
SAVE TIME AND MONEY BY
IDENTIFYING ENGINE PROBLEMS YOURSELF
• COMPUTER SAFE
• NO BATTERY REQUIRED
FOR GENERAL MOTORS AND SATURN
VEHICLES FROM 1982 TO 1995
(EXCLUDING CADILLAC)
Page 2

Table of Contents
i GM
Paragraph Title Page No.
YOU CAN DO IT! ........................................................ ii
GENERAL INFORMATION
1.1 YOUR VEHICLE'S COMPUTER SYSTEM............... 1-1
1.2 ABOUT YOUR CODE READER................................. 1-2
1.3 TEST CONNECTOR LOCATIONS ............................ 1-2
1.4 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS........................................... 1-3
1.5 VEHICLE SERVICE MANUALS ............................... 1-3
1.6 PRELIMINARY VEHICLE DIAGNOSIS .................. 1-4
WORKSHEET
RETRIEVING ECM CODES
2.1 VEHICLES COVERED ............................................... 2-1
2.2 BEFORE YOU BEGIN ............................................... 2-2
2.3 RETRIEVING SERVICE CODES ............................. 2-3
2.4 ERASING SERVICE CODES ..................................... 2-6
2.5 ECM SERVICE CODES.............................................. 2-6
RETRIEVING ABS CODES
3.1 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEMS ................................ 3-1
3.2 APPLICATIONS ......................................................... 3-1
3.3 RETRIEVING SERVICE CODES ............................. 3-2
3.4 ERASING SERVICE CODES ..................................... 3-7
3.5 ABS SERVICE CODES............................................... 3-9
GLOSSARY
4.1 INTRODUCTION ........................................................ 4-1
4.2 GLOSSARY OF TERMS AND ................................... 4-1
ABBREVIATIONS
WARRANTY AND SERVICE
5.1 LIMITED ONE YEAR WARRANTY .......................... 5-1
5.2 SERVICE PROCEDURES .......................................... 5-1
Page 3
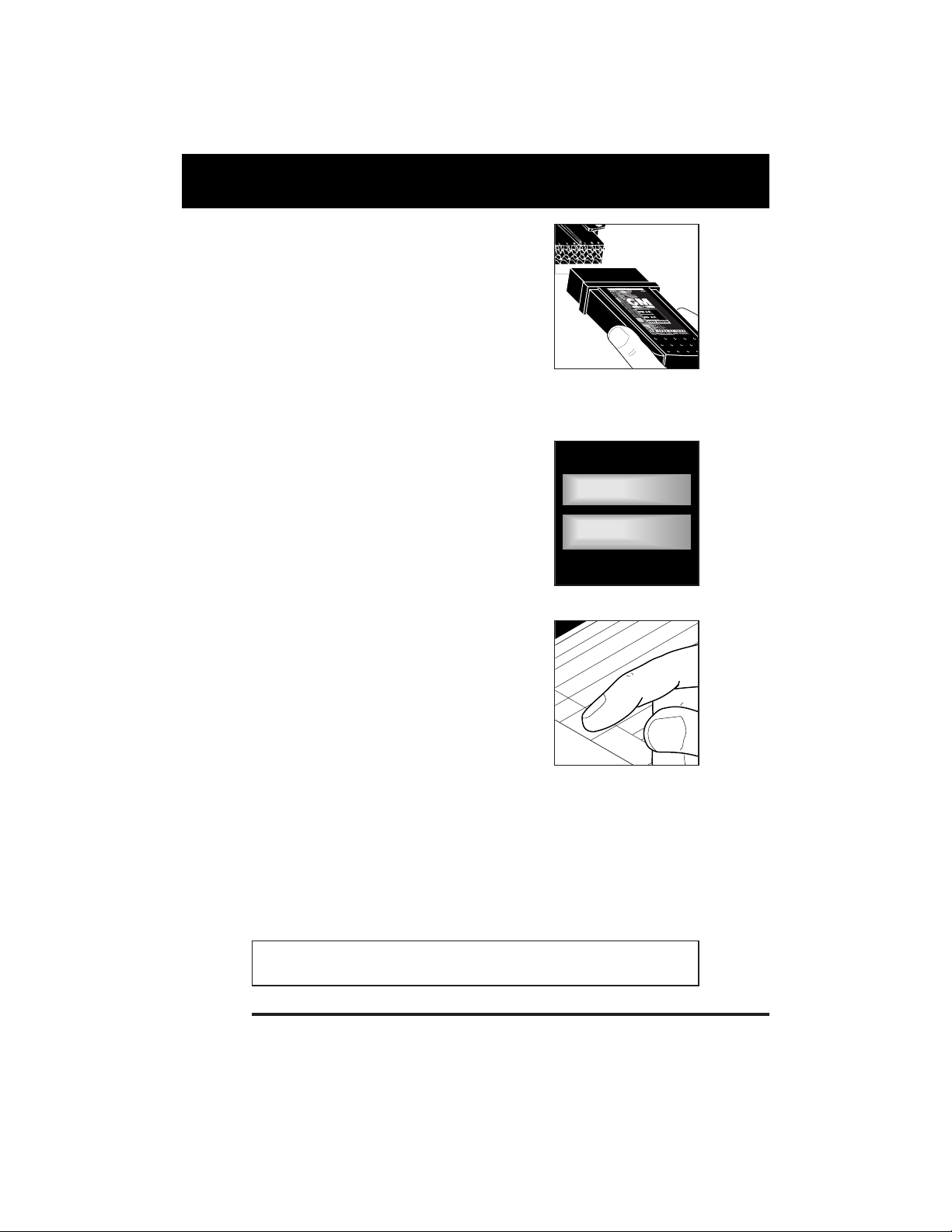
You Can Do It!
GM ii
Plug It In
•
Test connector usually found
under the left side of the
dashboard.
•
Set Selector switch to ECM A-B
position.
•
Make sure ignition is off. Plug
Code Reader into test connector.
Read Fault Codes
•
Turn on ignition. DO NOT
START ENGINE.
•
Read codes from flashing
"Check Engine" or "Service
Engine Soon" light.
Pinpoint Problems
•
Locate fault code(s) in the
appropriate Service Codes List.
1
CHECK ENGINECHECK ENGINE
SERVICESERVICE
ENGINEENGINE
SOONSOON
2
3
CODE DEFINITION
el Injector circuit is not working p
Ignition system fault - Intermittent 7X sign
loss of 58X signal or 6X signal (Saturn)
1 Throttle position sensor (TPS) - signal voltag
high during engine idle or deceleration
22 Throttle position sensor (TPS) - signal
low during engine idle
Fuel cutoff relay circuit - open
ground
23 Manifold air temperature (M
voltage is low or high
Throttle position senso
Mixture Control (M
circuit problems
Intake Air T
Vehicle sp
problem
Read manual for a complete description of the Code Reader and
it's proper use and operation.
Page 4
1
1-1 GM
1.1 YOUR VEHICLE'S COMPUTER SYSTEM
Today's vehicles are equipped with computer self-testing
abilities that can locate problems in your vehicle and store
them as service codes in the vehicle's onboard computer. The
Code Reader allows you access to the computer's memory and
recalls the service codes.
1.1.1 Instrument Panel Indicator Lights
Your vehicle's Instrument panel has several indicator lights, such
as the "Check Engine", "Service Engine Soon", "ABS", "Shift to
D2" and "Temperature" indicator lights. These lights do more
than tell you to check for engine, brake, or other component
malfunctions. They can also transmit the service codes in the
computer memory by blinking on and off.
NOTE:
If your instrument panel indicator lights do not come
on when you turn on the ignition, please refer to your
vehicle's service manual. You may have problems in
the car's circuitry. You must fix these problems before
you can obtain service codes from the vehicle's
onboard computer.
1.1.2 Service Codes
The service codes are also called "fault codes", "diagnostic
codes" or "trouble codes". These codes can be used to identify
systems or components which are malfunctioning.
The computer records codes for two types of problems:
"Hard" Codes. "Hard" codes are stored for problems
which are happening now. The instrument panel indicator
light will stay on when the engine is running.
■ "Intermittent" Codes or "Continuous Memory" Codes.
Intermittent service codes are stored in the computer's
memory for problems which occur intermittently, or for
problems which happened in the past but are not currently
present. Intermittent problems may cause the panel
indicator light to flicker or to turn on intermittently.
Intermittent codes are stored in the computer's memory for
a set period of time (usually 50 start cycles). If an
intermittent problem does not recur within this time
period, the computer automatically erases the related
intermittent fault code from it's memory.
CHECK ENGINECHECK ENGINE
SERVICESERVICE
ENGINEENGINE
SOONSOON
■
Page 5

General Information
GM 1-2
NOTE :
For Saturn vehicles, either the "Shift to D2" light or
the "Temperature" indicator light is used to transmit
Saturn Electronic Transmission codes.
1.2 ABOUT YOUR CODE READER
The Code Reader is a device which connects to your vehicle's
computer self-test connector. It allows the computer to output
the service codes through the vehicle's instrument panel
indicator lights. The Code Reader can be used to retrieve:
■ Engine/Electronic Transmission codes (ECM/PCM)
NOTE:
Unless otherwise indicated, any reference to ECM
throughout this manual also applies to PCM.
■ Anti-Lock Brake System codes (ABS)
1.2.1 Controls and Indicators
Selector Switch – Selects
operating mode for Code Reader:
■ ECM A-B – Use to retrieve ECM
codes
■ ABS A-H – Use to retrieve ABS
service codes
1.3 TEST CONNECTOR LOCATIONS
•
The gateway to your vehicle's onboard computer.
Your vehicle test connector also
known as the Assembly Line Data
Link (ALDL) connector or Assembly
Line Communication Link (ALCL)
connector is usually black in color
and is most likely found under the left side of the dashboard.
Some connectors can be found on the right kick panel, under
the center of the dashboard, on the side of the fuse block or
under the ashtray in the center console. The connector might
have a plastic cover on it labeled "Diagnostic Connector". If
you have any questions about the connector's location, please
refer to your vehicle's service manual for detailed information.
Page 6

1
1-3 GM
1.4 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
•
Always observe safety precautions whenever working on a
vehicle.
a. Always wear safety eye protection.
b. Only work on your vehicle in a well-ventilated area.
c. Put transmission in “park” (for automatic) or “neutral” (for
manual). Set parking brake.
d. Put blocks on drive wheels.
e. Avoid moving fan blades or any potentially moving parts.
f. Avoid hot engine parts.
g. Turn off ignition before connecting (or disconnecting) any
testing equipment.
h. Please read your vehicle’s service manual and follow it’s
safety procedure.
1.5 VEHICLE SERVICE MANUALS
It is recommended that you consult
the manufacturer’s instructions and
specifications in these service manuals before any test or tune-up
procedures are performed.
IMPORTANT: You MUST use the
wiring diagrams in your vehicle's
service manual to ensure proper
connections during testing.
Contact your local car dealership, auto parts store, bookstore
or public library for availability of these manuals. The
following companies publish valuable repair manuals:
■ General Motors Publications, Helm, Inc., 14310 Hamilton
Ave., Highland Park, MI 48203, Phone: (800) 782-4356
■ Haynes Publications, 861 Lawrence Drive, Newbury Park,
California 91320, Phone: (805) 498-6703, Fax: (805) 4982867
■ Mitchell International, 14145 Danielson St., Poway,
California 92064, Phone: (888) 724-6742
■ Motor Publications, 5600 Crooks Road, Troy, Michigan
48098, Phone: (800) 426-6867, Fax: (313) 828-0215
F8
PNK-BLK PNK-BLK
F/P FUSE
DK GRN-WHT
BLK-WHT
PNK-BLK
GRY
RED
FUEL PUMP
PRIME CONN
FUEL PUMP
6
2
4
1
3
TYPICAL WIRING
DIAGRAM
Page 7

General Information
GM 1-4
1.6 PRELIMINARY VEHICLE DIAGNOSIS WORKSHEET
The purpose of this form is to help you gather preliminary information
on your vehicle before you retrieve codes. By having a complete
account of your vehicle's current problem(s), you will be able to
systematically pinpoint the problem(s) by comparing your answers to
the fault codes you retrieve. You can also provide this information to
your mechanic to assist in diagnosis and help avoid costly and
unnecessary repairs. It is important for you to complete this form to help
you and/or your mechanic have a clear understanding of your vehicle's
problems.
NAME:
DATE:
VIN*:
YEAR:
MAKE:
MODEL:
ENGINE SIZE:
VEHICLE MILEAGE:
*VIN: Vehicle Identification Number, found at the base of the
windshield on a metallic plate, or at the driver door latch area (consult
your vehicle owner's manual for location).
TRANSMISSION:
❑ Automatic
❑ Manual
Please check all applicable items in each category.
DESCRIBE THE PROBLEM:
Page 8

1
1-5 GM
WHEN DID YOU FIRST NOTICE THE PROBLEM:
❑ Just Started
❑ Started Last Week
❑ Started Last Month
❑ Other:
LIST ANY REPAIRS DONE IN THE PAST SIX MONTHS:
PROBLEMS STARTING
ENGINE QUITS OR STALLS
IDLING CONDITIONS
RUNNING CONDITIONS
❑ No symptoms
❑ Will not crank
❑ Cranks, but will not start
❑ Starts, but takes a long time
❑ No symptoms
❑ Right after starting
❑ When shifting into gear
❑ During steady-speed driving
❑ Right after vehicle comes to a stop
❑ While idling
❑ During acceleration
❑ When parking
❑ No symptoms
❑ Is too slow at all times
❑ Is too fast
❑ Is sometimes too fast or too slow
❑ Is rough or uneven
❑ Fluctuates up and down
❑ No symptoms
❑ Runs rough
❑ Lacks power
❑ Bucks and jerks
❑ Poor fuel economy
❑ Hesitates or stumbles on
accelerations
❑ Backfires
❑ Misfires or cuts out
❑ Engine knocks, pings or rattles
❑ Surges
❑ Dieseling or run-on
Page 9

General Information
GM 1-6
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION PROBLEMS (if applicable)
PROBLEM OCCURS
❑ Morning ❑ Afternoon ❑ Anytime
ENGINE TEMPERATURE WHEN PROBLEM OCCURS
❑ Cold ❑ Warm ❑ Hot
DRIVING CONDITIONS WHEN PROBLEM OCCURS
DRIVING HABITS
GASOLINE USED
WEATHER CONDITIONS WHEN PROBLEM OCCURS
CHECK ENGINE LIGHT / DASH WARNING LIGHT
❑ Sometimes ON ❑ Always ON ❑ Never ON
PECULIAR SMELLS
STRANGE NOISES
❑ Short - less than 2 miles
❑ 2 ~ 10 miles
❑ Long - more than 10 miles
❑ Stop and go
❑ While turning
❑ While braking
❑ At gear engagement
❑ With A/C operating
❑ With headlights on
❑ During acceleration
❑ Mostly driving downhill
❑ Mostly driving uphill
❑ Mostly driving level
❑ Mostly driving curvy roads
❑ Mostly driving rough roads
❑ Mostly city driving
❑ Highway
❑ Park vehicle inside
❑ Park vehicle outside
❑ Drive less than 10 miles per day
❑ Drive 10 to 50 miles per day
❑ Drive more than 50 miles per day
❑ 87 Octane
❑ 89 Octane
❑ 91 Octane
❑ More than 91 Octane
❑ 32 ~ 55° F (0 ~ 13° C)
❑ Below freezing (32° F / 0° C)
❑ Above 55° F (13° C)
❑ "Hot"
❑ Sulfur ("rotten egg")
❑ Burning rubber
❑ Gasoline
❑ Burning oil
❑ Electrical
❑ Rattle
❑ Knock
❑ Squeak
❑ Other
❑ No symptoms
❑ Shifts too early or too late
❑ Changes gear incorrectly
❑ Vehicle does not move when in
gear
❑ Jerks or bucks
Page 10
2
2-1 GM
2.1 VEHICLES COVERED
This Code Reader may be used to retrieve engine service codes
from most General Motors (GM) and Saturn domestic cars and
trucks (EXCEPT Geo, Nova, and Sprint). Includes all models
EXCEPT Cadillacs and diesel vehicles. Specific makes and
models are listed below.
Model
Year Make Model
1982-93 Buick Century, Electra, Electra Wagon, Estate
Wagon, Le Sabre, Le Sabre Wagon, Park
Avenue, Reatta*, Regal, Grand National,
Riviera*, Roadmaster, Skyhawk, Skylark,
Somerset
Chevrolet Berreta, Camaro, Caprice, Cavalier, Cele-
brity, Chevette, Citation, Corisca, Corvette,
El Camino, Impala, Lumina, Monte Carlo
Oldsmobile Achieva, Calais, Custom Cruiser, Cutlass
Calais, Ciera, Cutlass Cruiser, Cruiser
Wagon, Cutlass Supreme, Supreme Classic,
Delta 88, Eighty-eight, Firenze, Ninetyeight, Omega, Toronado*, Touring Sedan,
Trofeo*
Pontiac 6000, 6000 STE, Bonneville, Fiero, Firebird,
Grand Am, Grand Prix, J 2000, Lemans,
J Parisienne, Phoenix, Safari, Safari Wagon,
Sunbird, T 1000
Saturn All models
Trucks All one ton capacity or less with gas
and Vans engines
1994 Buick Roadmaster 5.7 liter
Chevrolet Camaro 3.4 liter/5.7 liter, Caprice 5.7 liter,
Caprice 5.7 liter, Cavalier 3.1 liter,
Lumina 3.1 liter
Pontiac Firebird 3.4 liter/5.7 liter, Sunbird 2.0 liter/
3.1 liter
Saturn All models
Trucks All one ton capacity or less with gas
and Vans engines
Page 11
Retrieving ECM Codes
GM 2-2
* Not applicable to models equipped with climate control
computers
NOTE:
For 1994 and 1995 vehicles, only the models listed
above are compatible with the Code Reader.
The Code Reader
is not compatible with 1996 and
later model year vehicles.
2.1.1 Vehicle Test Connector
GM and Saturn vehicles use one of two types of test
connectors: 12-pin or 16-pin.
12-Pin Connector: The 12-pin
connector was phased out
completely in 1996. Some 1994
and 1995 vehicles still use the
12-pin connector, but because of changes in the ECM, the
Code Reader is not compatible with some of these systems
(see paragraph 2.1).
■ 16-Pin Connector: The new
16-pin connector was introduced
on some 1994 and 1995 models,
and was made standard
equipment on all 1996 and
subsequent model year vehicles.
The Code Reader will
not work on vehicles equipped with the 16-pin
connector.
2.2 BEFORE YOU BEGIN
•
Fix any known mechanical problems before performing
any test.
Make a thorough check before starting any test procedure.
Loose or damaged hoses, wiring, or electrical connectors are
often responsible for poor engine performance, and in some
cases they may cause a “false” fault code.
Model
Year Make Model
1995 Chevrolet Caprice 4.3 liter
Saturn All models
Trucks All one ton capacity or less with gas
and Vans engines (EXCEPT S/T Series vehicles)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
910111213141516
■
Page 12

2
2-3 GM
Please read your vehicle’s service manual for proper
connection of vacuum hoses, electrical wiring, and wiring
harness connectors. Check the following areas:
a. All fluid levels
b. Air cleaner and ducts
c. Belts
d. Mechanical linkage associated with sensor
e. Vacuum hoses
f. Spark plugs and wires
g. Electrical wiring
h. Electrical connectors
i. Proper battery voltage
j. Fuel system components
2.3 RETRIEVING SERVICE CODES
•
Always observe safety precautions before and during the
testing process.
•
Fix any known mechanical problems before this test.
•
Have pencil and paper handy.
1. Turn off ignition.
2. Connect the Code Reader to the vehicle test connector.
NOTE:
The Code Reader only fits into the connector one way.
3. Set Selector Switch to ECM A-B
position.
4. Turn on ignition. DO NOT
START THE ENGINE.
5. Read codes from the "Check Engine" or "Service Engine
Soon" light (from the "Shift to D2" light - 1991 and 1992
models or the "Temperature" indicator light - 1993 and
subsequent - for Saturn Electronic Transmission codes) on
your vehicle's instrument panel. Be sure to write the codes
down.
NOTE:
If the light does not blink, refer to your vehicle's
service manual for information on checking the
circuitry.
•
All codes are two digits.
Page 13

Retrieving ECM Codes
GM 2-4
•
Each code is transmitted three times before the next code
is sent.
•
Code sets will begin with Code 12 ("System Pass") even if
fault codes are present.
•
The codes will continue to be sent as long as the ignition is
on and the Code Reader is connected.
•
Count blinks to get the service codes:
•
Code 12 looks like:
NOTE:
Code 12 is not a fault code. Code 12 indicates the
computer's self-diagnostic system is functioning
properly (SYSTEM PASS). If code 12 is the only code
which displays when you perform the diagnostic test,
this means there are no fault codes stored in the
vehicle's computer. Consult your vehicle's repair
manual for "no codes" problems.
•
Code 22 looks like:
IMPORTANT: Any code that ends in zero ("0") is transmitted
as follows:
•
Code 30 looks like:
6. Next, erase service codes (see paragraph 2.4). This will
help you determine which codes are "hard" faults and
which codes are "intermittent" faults.
7. Turn on ignition, start engine, and observe "Service
Engine Soon" light; light should turn off. Run engine for
several minutes (to allow engine to reach normal
operating temperature), then observe "Service Engine
Soon" light:
■ If "Service Engine Soon" light turns on, turn off ignition
and repeat steps 2 through 5. This reveals "hard" fault
codes.
ABNORMALLY LONG PAUSE
BLINK BLINK
= Code 30
BLINK
BLINK
PAUSE
= Code 12
BLINK BLINK
BLINK BLINK
PAUSE
= Code 22
BLINK BLINK
Page 14

2
2-5 GM
NOTE:
It may be necessary to test drive the vehicle to
reset "hard" fault codes 13, 15, 24, 44, 45, and 55
after they have been erased.
■ If "Service Engine Soon" light does not turn on, the initial
stored fault codes were all "intermittent" fault codes.
(Refer to the "Diagnostic Procedures" section in the
manufacturer's service manual for your vehicle.)
8. Follow the testing and repair procedures outlined in the
manufacturer's service manual for your vehicle to correct
"hard" faults. Codes should be addressed and eliminated
in the order they were received, erasing and retesting
after each repair is made to be sure the fault was
eliminated. Code 12 will appear alone when no other fault
codes are present.
NOTE:
Whenever codes 51, 52, 54, or 55 are displayed with
other codes, troubleshoot and eliminate the "50
Series" codes first, then proceed with the lowernumbered codes.
9. Turn off ignition and remove the Code Reader.
2.3.1 Servicing Fault Codes
Diagnostic trouble codes indicate a problem in a circuit, not
necessarily a faulty component. DO NOT replace components
based only on trouble codes without first following the service
procedures described in your vehicle's repair manual. Most
faults (including those that set trouble codes) are caused by
damaged, shorted or open wiring, damaged or corroded
connections, improper voltages or grounds, or other
mechanical problems.
Sometimes a fault in one circuit or system will cause the
computer to set a fault code for a different circuit or system.
Example:
A defective spark plug wire can cause a "rich condition" fault
code to be set on the oxygen sensor circuit. In this case,
replacing any component in the oxygen sensor circuit will not
correct the fault, because the problem is caused by the
defective spark plug wire and not by the oxygen sensor circuit.
This is called a "false" code.
For this reason, it is
IMPORTANT that you make a thorough
inspection of all systems: wiring, hoses, vacuum, engine
mechanical, charging, ignition, power, ground, fuel, (some of
these systems are not connected to the computer system, but
Page 15

Retrieving ECM Codes
GM 2-6
will still affect it) before retrieving trouble codes. Refer to your
vehicle's service/repair manual for specifications and system
testing procedures which apply to your particular vehicle.
2.4 ERASING SERVICE CODES
•
Always observe safety precautions before and during
testing process.
1. Turn off ignition.
2. Remove ECM fuse from the fuse block or disconnect the
negative battery cable to disconnect power to the vehicle's
computer.
3. Wait fifteen seconds for codes to be erased from the
computer's memory.
4. Reconnect ECM fuse or reconnect negative battery cable.
NOTE:
Once the computer's memory has been erased your
vehicle may run rough for up to 40 miles while new
information is being saved in the vehicle's computer.
If the battery cable is removed, you will have to
reprogram your radio, clock and memory seat
position.
2.5 ECM SERVICE CODES
•
Consult your vehicle's service manual for detailed
meanings or definitions related to your vehicle.
Refer to the appropriate service codes table for your vehicle:
2.5.1 GM Engine/Electronic Transmission Service Codes;
Saturn Engine Service Codes
2.5.2 Saturn Electronic Transmission Service Codes
Refer to the "Diagnostic Charts" and "Diagnostic Aids" in your
vehicle's service manual to further assist in the fault isolation
and elimination process.
Page 16

2
2-7 GM
2.5.1 GM Engine/Electronic Transmission Service Codes; Saturn
Engine Service Codes
CODE SERVICE CODE DEFINITION
11 (Saturn vehicles ONLY): Indicates transmission service
codes will be displayed next on the "Shift to D2" light
(1991-92 models) or "Temperature" indicator light (1993
and later models)
12 Diagnostic mode; no distributor signal to Electronic
Control Module; System PASS
13 Oxygen sensor signal fault - signal too low / open left
oxygen sensor circuit (Dual sensor models)
14 Coolant sensor or circuit fault - signal voltage low or
shorted
15 Coolant temperature sensor or circuit fault - signal
voltage high
16 Battery or alternator problem - voltage too high or low
Direct ignition system (DIS) fault line open or shorted to
ground
Ignition system fault - loss of 2X or Low Resolution
Pulse signal
Transmission speed error
17 RPM signal problem
Camshaft sensor - circuit problems
Electronic Control Module (ECM) computer circuit
problem - Pull-up resistor (Saturn)
18 Camshaft or Crankshaft sensor - circuit problems
Fuel Injector circuit is not working properly - possible
blown fuel injector fuse
19 Ignition system fault - Intermittent 7X signal or loss of
58X signal or 6X signal (Saturn)
21 Throttle position sensor (TPS) - signal voltage is high
22 Throttle position sensor (TPS) - signal voltage is low
Fuel cutoff relay circuit - open or shorted to ground
23 Manifold air temperature (MAT) sensor - signal voltage
is low or high
Throttle position sensor (TPS) error
Mixture Control (M/C) solenoid - open or short circuit
problems
Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IAT) low
Page 17

Retrieving ECM Codes
GM 2-8
CODE SERVICE CODE DEFINITION
24 Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) - open or short circuit
problems or park/neutral switch circuit problem
25 Manifold air temperature (MAT) sensor - signal voltage
is low or high
Vacuum switching valve circuit open or shorted to
ground
ATS sensor - signal voltage is high or low
26 Quad-Driver module or Quad-driver No. 1 error
27 2nd gear switch problem
Quad-Driver module or Quad-driver No. 2 error
28 3rd gear switch
Quad-Driver module or Quad-driver No. 3 error
(Corvette)
(Transmission) Fluid pressure switch assembly - open or
short circuit problems
29 4th gear switch
Quad-Driver module or Quad-driver No. 3 error
Secondary air injection system - circuit problems
31 Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor - signal
voltage is low
Fuel injector
Park/Neutral switch - circuit problems
CAM sensor - circuit problems
Engine speed control governor malfunction (Van)
Turbocharger wastegate overboost
Wastegate electrical signal - open or shorted to ground
Purge solenoid voltage high (carburetor engines)
32 Barometric pressure (BARO) sensor circuit failure
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve diagnostic switch -
closed during engine start-up or open when EGR flow
requested by ECM
Electronic vacuum regulator valve (EVRV) error (EVRV
controls EGR vacuum)
Page 18

2
2-9 GM
CODE SERVICE CODE DEFINITION
33 Mass air flow (MAF) sensor - signal voltage or frequency
is high during engine idle
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor - signal
voltage is high during engine idle (Note: Engine misfire
or unstable idle may cause this code)
34 Mass air flow (MAF) sensor - signal voltage or frequency
is low during engine cruise
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor - signal
voltage is low during ignition on
Pressure sensor circuit - signal voltage too high or low
(carburetor engines)
35 Idle air control (IAC) system problem - can not set
desired RPM or idle speed actuator (ISA) carbureted
system problems
36 Mass air flow (MAF) sensor - burn-off circuit problem
Transmission shift problem (electronically controlled
transmissions only)
Direct ignition system (DIS) fault - loss of 24X signal or
extra or missing pulses in electronic spark timing (EST)
signal
Ignition system fault - loss of High Resolution Pulse
signal
37 Brake switch stuck"on"
38 Brake switch circuit fault
Knock sensor (KS) - open circuit problem
39 Torque converter clutch (TCC circuit fault)
Clutch switch circuit problems
Knock sensor (KS) - short circuit problem
41 Cam sensor (CAM) failure
Cylinder select error
Tach input error - no reference pulses during engine run
Electronic spark timing (EST) circuit - open or shorted
to ground during engine run
Direct ignition system (DIS) fault - bypass circuit open
or shorted to ground during engine run
Ignition system fault - loss of 1X Reference Pulse signal
Page 19

Retrieving ECM Codes
GM 2-10
CODE SERVICE CODE DEFINITION
42 Electronic spark timing (EST) circuit - open or shorted
Direct ignition system (DIS) fault - bypass circuit open
or shorted to ground during engine run
Fuel cutoff relay circuit - open or shorted to ground
43 Electronic spark timing (EST) circuit - low voltage
detected
Electronic spark control (ESC) - circuit problems
44 Lean exhaust indicated (Left side on dual oxygen models)
45 Rich exhaust indicated (Left side on dual oxygen
models)
46 Vehicle anti-theft system (VATS) failure
Power steering pressure switch failure
47 Circuit or component problem in ECM/PCM (communi-
cation error)
Knock sensor module error (inside computer)
48 Misfire symptom
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor - circuit error
49 RPM is high at idle (possible vacuum leak)
50 System voltage is low
51 Computer problem; faulty, wrong or incorrectly installed
PROM circuit; or ECM/PCM failure
52 Calibration Package Chip or ECM fault or oil tem-
perature sensor fault/low engine temperature
(Corvette); faulty or missing PROM/Calibration Package
Chip; ECM problem
System voltage high for a long period of time
53 System voltage too high (over 17.7 volts to ECM) or
EGR system fault or alternator voltage not normal or
Vehicle Anti-Theft System fault
54 Fuel pump circuit fault or Mixture Control (M/C)
solenoid fault or Electronic Control Module (ECM)
fault/EGR solenoid #2 failure (3.8L VIN1)
Fuel pump relay
55 Electronic Control Module (ECM) fault or oxygen sensor
circuit fault or EGR solenoid #3 failure (3.8L VIN1) or
fuel lean monitor (Corvette)
Page 20

2
2-11 GM
CODE SERVICE CODE DEFINITION
56 Vacuum sensor circuit fault or quad driver "B" fault
(3.8L VIN1)
Corrosivity/add coolant
57 Boost control problem (3.8L VIN1)
58 Vehicle Anti-Theft System fault (3.8L)
Transmission Temperature Sensor (TTS) - short circuit
Transmission fluid temp high
59 Transmission Temp Sensor (TTS) - open
Transmission fluid temp low
60 Transmission not in drive
61 Oxygen sensor signal fault or port throttle system fault
or on-board cruise control fault (vent solenoid circuit)
Air Conditioner (A/C) system performance problems
62 Engine oil temperature sensor fault or gear switch
signal circuit fault or on-board cruise control fault
(vacuum solenoid circuit)
63 EGR flow problem or on-board cruise control problem
Servo Position Sensor (SPS) circuit fault or Manifold
Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor fault or oxygen sensor
fault
64 EGR flow problem or on-board cruise control problem or
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor fault or
oxygen sensor fault
65 EGR flow problem or on-board cruise control problem
Servo Position Sensor (SPS) circuit fault or Manifold
Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor fault or oxygen sensor
fault or fuel injector current low
66 Electronic Control Module (ECM) computer circuit fault
or air conditioning pressure sensor circuit fault or low
air conditioning refrigerant charge
(Transmission) 3-2 shift control solenoid - circuit
problems
67 Cruise control - switch circuit problems
Air Conditioner (A/C) pressure sensor - circuit problems
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) solenoid - circuit
problems
Cruise control switches - circuit problems
Page 21

Retrieving ECM Codes
GM 2-12
CODE SERVICE CODE DEFINITION
68 On-board cruise control switch circuit problems Servo
Position Sensor (SPS) circuit fault or shorted A/C clutch
relay circuit (Corvette) or overdrive ratio error
69 Air conditioning head pressure switch circuit fault or air
conditioning pressure switch problem
Torque converter clutch stuck "on"
70 Air conditioning refrigerant pressure sensor circuit fault
(high pressure) or quad driver module error
71 Air conditioning evaporator temperature sensor circuit
fault (low temp.)
72 Gear select switch circuit fault - Corvette only
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) - loss of signal
73 Air conditioning evaporator temperature sensor circuit
fault (high temp.)
(Transmission) Pressure control solenoid - circuit
problems
74 Traction control circuit voltage low
75 Digital EGR fault - #1 solenoid or system voltage low
(charging system problem)
Transmission voltage low
76 Digital EGR fault - #2 solenoid
77 Digital EGR fault - #3 solenoid
Primary cooling fan relay driver circuit - circuit
problems
78 Secondary cooling fan relay driver circuit - circuit
problems
79 Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) - signal voltage too high
Transmission Temperature Sensor (TTS) - high
temperature
80 Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) - signal voltage too low;
transmission component fault
81 QDM Solenoid "B" monitored voltage differs from
commanded
Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) message fault (Saturn)
Brake switch circuit problems
Page 22

2
2-13 GM
CODE SERVICE CODE DEFINITION
82 Internal PCM communication fault (Saturn) or QDM
Solenoid "A" monitored voltage differs from commanded
Ignition system fault - 3X signal problem
83 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) solenoid - circuit
problems
Reverse Inhibit - open or short circuit in reverse inhibit
solenoid
84 3-2 Control solenoid - open or short circuit problems
Skip shift solenoid - open or short circuit problems
85 Programmable Read Only Memory error or undefined
gear ratio (input or output sensor failure)
Torque converter clutch (TCC) - TCC is mechanically
stuck on
86 Analogue/Digital Electronic Control Module (ECM)
error or shift Solenoid "B" stuck on
87 Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
(EEPROM) error or shift Solenoid "B" stuck off or high
gear ratio error
88 Electronic Control Module (ECM) computer circuit fault
89 Power Management fault
90 TCC error
91 Skip shift light - open or short circuit problems in skip
shift light circuit
93 Pressure control solenoid - transmission line pressure
not at desired level
95 Change oil light - wrong voltage is present in light
circuit for more than 26 seconds
96 Transmission voltage low - low system voltage possibly
caused by generator voltage supply circuit or power
train control module
Low oil light - wrong voltage is present in light circuit
for more than 26 seconds
97 Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) - output circuit problems
99 Tachometer output circuit problems
Page 23

Retrieving ECM Codes
GM 2-14
2.5.2 Saturn Electronic Transmission Service Codes
•
Transmission codes will be transmitted (if present) after
all engine codes are transmitted and code 11 has been
sent. Code 11 indicates that transmission codes are
present and will be transmitted on the "Shift to D2" light
(1991-92 models) or the "Temperature" indicator light
(1993 and later models).
CODE SERVICE CODE DEFINITION
13 Line pressure high
14 Line pressure low
15 Hot light
16 No 1st gear
Electrical variable orifice (EVO) fault
17, 18 No gears available
21 2nd gear stuck "on"
22 No 2nd gear
23 No 3rd gear
24 No 4th gear
25 No torque converter clutch
26 Torque converter clutch stuck "on"
27 Quick quad-driver output fault
31 Transaxle temperature circuit open
32 Transaxle temperature circuit grounded
34 Powertrain Control Module (PCM) - communication
failure
35 No turbine speed signal
36 Turbine speed signal noise
41 Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) circuit - no signal
42 Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) circuit - signal noise
43 Master relay - open or grounded
44 Master relay - shorted
45 Gear selector switch circuit problem - no signal
46 Gear selector switch circuit problem - invalid signal
47 Powertrain Control Module (PCM) computer circuit
problem - communication interrupt failure
Page 24

2
2-15 GM
CODE SERVICE CODE DEFINITION
48 Hold mode voltage is too low
Reference input intermittent
49 Gear selector error signal
51 Powertrain Control Module (PCM) computer circuit
problem
52 Hold mode stuck "on"
Battery voltage out of range
53 Hold mode stuck "off"
ESC (Knock present)
54 Powertrain Control Module (PCM) computer circuit
problem
5-volt reference ground
55 Transaxle temperature sensor failure
56 Generic Field-Effect Transistor (FET) driver failure
57 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
58 Battery voltage unstable
61 Possible open or intermittent in DIS module harness 6X
Signal fault
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
62 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
63 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
Option check sum error (set if tire size and options do
not compare with those stored)
64 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
65 Ignition voltage problem
66 Clamp shorted
67 Clamp open
Handwheel sensor circuit fault
68 Line circuit grounded or open
69 Line circuit shorted
71 2nd line circuit - grounded or open
Cooling system high temperature
72 2nd line circuit - shorted
Cooling system low temperature
Page 25

Retrieving ECM Codes
GM 2-16
CODE SERVICE CODE DEFINITION
73 3rd line circuit - grounded or open
Coolant sensor signal unstable
74 Coolant/Transmission temperature sensor ratio error
3rd line circuit - shorted
75 3rd gear stuck "on"
Air temperature sensor signal
76 4th line circuit - grounded or open
Throttle position sensor (TPS) to manifold absolute
pressure (MAP) sensor voltage out of range
77 4th line circuit - shorted
78 4th gear stuck "on"
79 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) circuit - grounded or
open
81 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) circuit - shorted
82 Transaxle temperature unstable
83 Transaxle temperature low
Low coolant
84 Brake switch stuck open
85 Brake switch stuck closed
86 Engine speed invalid
87 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) hold circuit - grounded
or open
88 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) hold circuit - shorted
89 Master relay stuck "on"
91 Assembly Line Diagnostic Link (ALDL)
92 Clamp circuit - intermittent fault
93 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) hold circuit -
intermittent fault
94 Master enable relay circuit intermittent fault
95 Line circuit - intermittent fault
96 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) circuit - intermittent
fault
97 2nd gear circuit - intermittent fault
98 3rd gear circuit - intermittent fault
99 4th gear circuit - intermittent fault
Page 26

3
3-1 GM
3.1 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEMS (ABS)
3.1.1 What is ABS?
The ABS system utilizes several mechanical, hydraulic, and
electric/electronic components to automatically control
hydraulic brake pressure to the rear, or front and rear wheels
(depending on the brake system) to prevent wheel lock-up
during hard braking.
3.1.2 What are the benefits of ABS?
By preventing wheel lock-up during hard braking, ABS helps
maintain vehicle directional stability, as well as driver control,
ensuring a safer and more controlled stop in the shortest
distance.
3.1.3 How does the ABS system work?
The ABS system utilizes a computer called an Electronic
Brake Control Module (EBCM). The system also employs
several sensors and switches which monitor and control wheel
speed and hydraulic brake pressure when hard braking is
applied. When the wheel speed sensor(s) detect a potential
lock-up condition, a signal is sent to the EBCM. The EBCM, in
turn, sends a signal to the hydraulic system to relieve brake
pressure at the affected wheels, preventing the lock-up
condition.
3.1.4 What is the purpose of the Code Reader?
Most ABS systems generate diagnostic service codes when a
fault in the system is detected. These service codes are stored
in the EBCM. The Code Reader allows you to access the
EBCM's memory and recalls the service codes. The EBCM
outputs the service codes through the "Anti-Lock" light on the
vehicle's instrument panel.
3.2 APPLICATIONS
GM vehicles use a variety of Anti-Lock Brake Systems. This
Code Reader may be used to retrieve ABS service codes from
the following vehicle models:
Page 27

Retrieving ABS Codes
GM 3-2
3.3 RETRIEVING SERVICE CODES
•
Always observe safety precautions before and during
testing process.
•
Fix any known mechanical problems before this test.
•
Have pencil and paper handy.
1. Determine your vehicle's ABS Type (paragraph 3.1) and
retrieve codes using the appropriate procedures:
Teves II Paragraph 3.3.1
Kelsey-Hayes RWAL Paragraph 3.3.2
Kelsey-Hayes 4WAL Paragraph 3.3.3
Bosch 2S Paragraph 3.3.4
Bosch 2U Paragraph 3.3.4
Be sure to write codes down.
Year Model ABS Type
1989-93 Astro, "G" Series Van, "R" and "V" Series Kelsey-Hayes
Trucks, Safari, Suburban RWAL
1987-94 Blazer, "C" and "K" Series Pickup, Sierra, Kelsey-Hayes
"S" and "T" Series Pickup (EXCEPT RWAL
93-94 4.3L M/T)
1989-90 Eldorado, Reatta, Riviera, Seville, Toro- Teves II
nado, Delta 88, Bonneville, DeVille,
Electra, Le Sabre, Ninety-Eight, Fleet-
wood, Park Avenue, Touring Sedan
(EXCEPT 1988 Eldorado, Reatta, Riviera,
Seville, Toronado)
1990-91 Corvette Bosch 2S
1990-92 Brougham Bosch 2U
1990-94 Astro, Bravada, Jimmy, Safari, Sierra, Kelsey-Hayes
Sonoma, Suburban, Cyclone, Typhoon, 4WAL
Yukon, "C" and "K" Series Blazer and
Pickup, "S" and "T" Series Blazer and
Pickup, "G" Series Van
1995 Astro, "C" and "K" Series Pickup, "G" Kelsey-Hayes
Series Van, Safari, Sierra, Suburban, 4WAL
Tahoe, Yukon
1991-92 Custom Cruiser, Eldorado, Seville, Bosch 2U
Reatta, Toronado, Trofeo
1991-93 Riviera, Roadmaster, Caprice Bosch 2U
1993 Eldorado, Seville Bosch 2U
ABS/TCS
Page 28

3
3-3 GM
2. After retrieving ABS fault codes, erase codes using the
appropriate procedures for your vehicle and ABS system
(paragraph 3.4).
3. Repeat the procedure to retrieve ABS fault codes (step 1,
above).
NOTE:
It may be necessary to perform a thorough test drive
to reset some fault codes.
4. In most cases, codes which reappear indicate "hard"
faults. Codes which DO NOT reappear are usually
"intermittent" faults.
5. Follow the testing and repair procedures outlined in the
manufacturer's service manual for your vehicle to correct
"hard" faults. Codes should be addressed and eliminated
in the order they were received, erasing and retesting
after each repair is made to be sure the fault was
eliminated.
3.3.1 Retrieving Service Codes for Teves II Systems
1.
Turn on ignition. DO NOT START THE ENGINE.
Observe "Anti-Lock" light:
■ If "Anti-Lock" light turns off within 30 seconds, no
ABS service codes have been stored.
■ If "Anti-Lock" light remains on longer than 30
seconds, continue to step 2 to retrieve ABS service
codes.
2. Turn off ignition.
3. Connect the Code Reader to the vehicle test connector.
NOTE:
The Code Reader only fits into the connector one way.
4. Set Selector Switch to ABS A-H
position.
5. Turn on ignition. DO NOT
START THE ENGINE.
6. Read codes from the "Anti-Lock"light on your vehicle's
instrument panel. Be sure to write the codes down.
NOTE:
If the light does not blink, refer to your vehicle's
service manual for information on checking the
circuitry.
Page 29

Retrieving ABS Codes
GM 3-4
•
All codes are two digits.
•
Count blinks to get the service codes:
•
First and second digits of code are separated by a 3 second
pause.
•
Second digit of service code is followed by a termination
code ("Anti-Lock" light remains steady on).
NOTE:
DO NOT count termination code as part of second
digit.
•
Code 13 looks like:
7. Up to seven codes can be stored by the EBCM. To check
for additional codes: with ignition still on, disconnect and
then reconnect Code Reader. Repeat this procedure until
all codes have been retrieved.
NOTE:
Service codes cannot be erased until all stored service
codes have been retrieved.
8. Turn off ignition and remove the Code Reader.
3.3.2 Retrieving Service Codes for Kelsey-Hayes RWAL Systems
1.
Turn off ignition.
2. Connect the Code Reader to the vehicle test connector.
NOTE:
The Code Reader only fits into the connector one way.
3. Set Selector Switch to ABS A-H
position.
4. Turn on ignition. DO NOT
START THE ENGINE.
NOTE:
There is a 20 second pause before service codes begin
to display.
5. Read codes from the "Brake" light on your vehicle's
instrument panel. Be sure to write the codes down.
NOTE:
If the light does not blink, refer to your vehicle's
service manual for information on checking the
circuitry.
BLINK
PAUSE
BLINK BLINK
= Code 13
BLINK
STEADY ON
TERMINATION
CODE
Page 30

3
3-5 GM
•
Count blinks to get the service codes.
•
Codes may be one or two digits.
•
Codes are displayed as a pattern of one long blink followed
by one or more short blinks. Count
ALL blinks to get code.
•
Code 3 looks like:
•
The EBCM stores only one service code at a a time, even
though it may detect more than one fault condition. The
first fault detected results in a stored service code. The
detected fault must be corrected, and the service code
must be erased from the computer's memory before
additional codes can be stored.
•
After the first fault is corrected and the service code is
erased, drive the vehicle at a speed greater than 35 mph
to set any additional service codes.
3.3.3 Retrieving Service Codes for Kelsey-Hayes 4WAL Systems
1.
Turn off ignition.
2. Connect the Code Reader to the vehicle test connector.
NOTE:
The Code Reader only fits into the connector one way.
3. Set Selector Switch to ABS A-H
position.
4. Turn on ignition. DO NOT
START THE ENGINE.
5. Read codes from the "Anti-Lock" light on your vehicle's
instrument panel. Be sure to write the codes down.
NOTE:
If the light does not blink, refer to your vehicle's
service manual for information on checking the
circuitry.
•
All codes are two digits.
•
Count blinks to get the service codes:
•
First and second digits of code are separated by a pause.
= Code 3
SHORT
BLINK
SHORT
BLINK
LONG
BLINK
Page 31

Retrieving ABS Codes
GM 3-6
•
Code 21 looks like:
NOTE:
Service codes will repeat as long as Code Reader is
connected.
6. Turn off ignition and remove the Code Reader.
3.3.4 Retrieving Service Codes for Bosch 2S and 2U Systems
1.
Turn off ignition.
2. Connect the Code Reader to the vehicle test connector.
NOTE:
The Code Reader only fits into the connector one way.
3. Set Selector Switch to ABS A-H
position.
4. Turn on ignition. DO NOT
START THE ENGINE.
5. Read codes from the "Service ABS" or "Anti-Lock" light on
your vehicle's instrument panel. Be sure to write the codes
down.
NOTE:
If the light does not blink, refer to your vehicle's
service manual for information on checking the
circuitry.
•
All codes are two digits.
•
Count blinks to get the service codes:
•
First and second digits of code are separated by a pause.
•
Code sequence will start with Code 12:
NOTE:
Code 12 is not a fault code. Code 12 indicates the
self-diagnostic system is functioning properly
(system pass).
•
Each code is repeated three times. After all codes have
been displayed, the entire code sequence is repeated.
NOTE:
Service codes will repeat as long as Code Reader is
connected.
6. Turn off ignition and remove the Code Reader.
BLINK
PAUSE
= Code 21
BLINKBLINK
BLINK
PAUSE
= Code 12
BLINK BLINK
Page 32

3
3-7 GM
3.4 ERASING SERVICE CODES
•
Always observe safety precautions before and during
testing process.
•
Erase codes only when all repairs have been completed.
Determine your vehicle's ABS Type (paragraph 3.2) and erase
codes using the appropriate procedures:
3.4.1 Teves II
3.4.2 Kelsey-Hayes RWAL
3.4.3 Kelsey-Hayes 4WAL
3.4.4 Bosch 2S
3.4.5 Bosch 2U
3.4.1 Erasing Service Codes for Teves II Systems
1.
Drive vehicle at a speed greater than 20 MPH. Service
codes will automatically be cleared.
2. Repeat procedure for retrieving service codes (paragraph
3.3.1) to make sure codes have been erased and no new
codes have been recorded.
3.4.2 Erasing Service Codes for Kelsey-Hayes RWAL Systems
A. For all vehicle models EXCEPT "C" and "K" 3500 Series
Heavy Duty (HD) (1992-93):
1.
Turn off ignition.
2. Remove STOP/HAZARD fuse from fuse block.
3. Wait 20 seconds, then reinstall STOP/HAZARD fuse.
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 for each code stored. For example: if
four codes were retrieved, remove and install
STOP/HAZARD fuse four times.
5. Repeat procedure for retrieving service codes (paragraph
3.3.2) to make sure codes have been erased.
B. For "C" and "K" 3500 Series Heavy Duty (HD) (1992-93)
vehicles ONLY:
1.
Turn off ignition.
2. Remove STOP/HAZARD fuse from fuse block.
3. Turn on ignition and observe
"Brake" light. If "Brake" light is
on, a code(s) is stored.
4. Set Selector Switch to ABS A-H
position.
Page 33

Retrieving ABS Codes
GM 3-8
5. Connect the Code Reader to the vehicle test connector for
one second, remove the Code Reader for one second,
reconnect the Code Reader for one second, then remove
the Code Reader.
6. Turn off ignition.
7. Reinstall STOP/HAZARD fuse in fuse block.
8. Repeat procedure for retrieving service codes (paragraph
3.3.2) to make sure codes have been erased.
3.4.3 Erasing Service Codes for Kelsey-Hayes 4WAL Systems
1.
Turn on ignition.
2. Set Selector Switch to ABS A-H
position.
3. Connect the Code Reader to the vehicle test connector for
two seconds, remove the Code Reader for one second,
reconnect the Code Reader for two seconds, then remove
the Code Reader.
4. The "Anti-Lock" and "Brake" light should BOTH light,
then turn off. This indicates service codes have been
erased.
5. Turn off ignition.
6. Repeat procedure for retrieving service codes (paragraph
3.3.3) to make sure codes have been erased.
3.4.4 Erasing Service Codes for Bosch 2S Systems
1.
Turn off ignition.
2. Set Selector Switch to ABS A-H
position.
3. Connect the Code Reader to the
vehicle test connector.
4. Turn on ignition. "Service ABS" light will begin displaying
service codes.
5. Remove the Code Reader for one second, then reconnect
the Code Reader for at least one second.
6. Repeat step 5 three more times (a total of four times)
within a ten second period.
LEAVE THE CODE
READER CONNECTED AFTER THE FOURTH
TIME.
Page 34

3
3-9 GM
7. The ""Service ABS" light should display code 12
continuously. If any other codes are displayed, repeat
steps 1 through 6.
8. Turn off ignition.
3.4.5 Erasing Service Codes for Bosch 2U Systems
1.
Turn on ignition and observe "Anti-Lock" light. "AntiLock" light should turn off within 3 to 4 seconds. If "AntiLock" light remains on, a fault is still present.
NOTE:
Service codes cannot be erased until all stored service
codes have been retrieved.
2. Set Selector Switch to ABS A-H
position.
3. Connect the Code Reader to the
vehicle test connector and
observe "Anti-Lock" light.
4. When "Anti-Lock" light turns on, disconnect Code Reader.
5. When "Anti-Lock" light turns off, reconnect Code Reader
and observe "Anti-Lock" light. When "Anti-Lock" light
turns on, disconnect Code Reader.
6. Repeat step 5.
7. When "Anti-Lock" light turns off, reconnect Code Reader.
"Anti-Lock" light will turn on. Disconnect Code Reader.
All service codes are now cleared.
8. Turn off ignition.
9. Repeat procedure for retrieving service codes (paragraph
3.3.4) to make sure codes have been erased.
3.5 ABS SERVICE CODES
•
Consult your vehicle's service manual for detailed
meaning related to your vehicle.
Determine your vehicle's ABS Type (paragraph 3.2) and refer
to the appropriate service codes table:
Teves II Paragraph 3.5.1
Kelsey-Hayes RWAL Paragraph 3.5.2
Kelsey-Hayes 4WAL Paragraph 3.5.3
Bosch 2S Paragraph 3.5.4
Bosch 2U Paragraph 3.5.5
Page 35

Retrieving ABS Codes
GM 3-10
3.5.1 Teves II System Service Codes
Code Service Code Definition
11 Electronic Brake Control Module (EBCM) fault
12 Electronic Brake Control Module (EBCM) fault
21 Main valve fault
22 Left front inlet valve fault
23 Left front outlet valve fault
24 Right front inlet valve
25 Right front outlet valve
26 Rear inlet valve
27 Rear outlet valve
31 Left front Wheel Speed Sensor (WSS)
32 Right front Wheel Speed Sensor
33 Right rear Wheel Speed Sensor
34 Left rear Wheel Speed Sensor
35 Left front Wheel Speed Sensor
36 Right front Wheel Speed Sensor
37 Right rear Wheel Speed Sensor
38 Left rear Wheel Speed Sensor
41 Left front Wheel Speed Sensor
42 Right front Wheel Speed Sensor
43 Right rear Wheel Speed Sensor
44 Left rear Wheel Speed Sensor
45 Left front sensors (2)
46 Right front sensors (2)
47 Rear sensors (2)
48 sensors (3)
51 Left front outlet valve
52 Right front outlet valve
53 Rear outlet valve
54 Rear outlet valve
55 Left front Wheel Speed Sensor
56 Right front Wheel Speed Sensor
57 Right rear Wheel Speed Sensor
58 Left rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Page 36

3
3-11 GM
3.5.2 Kelsey-Hayes RWAL System Service Codes
Code Service Code Definition
61 Electronic Brake Control Module loop circuit
71 Left front outlet valve
72 Right front outlet valve
73 Rear outlet valve
74 Rear outlet valve
75 Left front Wheel Speed Sensor
76 Right front Wheel Speed Sensor
77 Right rear Wheel Speed Sensor
78 Left rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Code Service Code Definition
1 Rear Wheel Anti-Lock (RWAL) Electronic Control Unit
(ECU) malfunction or improper voltage
2 Open isolation valve or faulty ECU
3 Open dump valve or faulty ECU
4 Grounded anti-lock valve reset switch circuit
5 Excessive actuation of the dump valve during an anti-lock
stop
6 Erratic speed signal
7 Shorted isolation valve circuit or faulty ECU
8 Shorted dump valve circuit or faulty ECU
9 Open or grounded circuit to the vehicle speed sensor
10 Brake lamp switch circuit fault
11 Rear Wheel Anti-Lock (RWAL) Electronic Control Unit
(ECU) malfunction or improper voltage
12 Rear Wheel Anti-Lock (RWAL) Electronic Control Unit
(ECU) malfunction or improper voltage
13 Rear Wheel Anti-Lock (RWAL) Electronic Control Unit
(ECU) malfunction
14 Rear Wheel Anti-Lock (RWAL) Electronic Control Unit
(ECU) malfunction
15 Rear Wheel Anti-Lock (RWAL) Electronic Control Unit
(ECU) malfunction
Page 37

Retrieving ABS Codes
GM 3-12
3.5.3 Kelsey-Hayes 4WAL System Service Codes
Code Service Code Definition
12 System Normal
13 System Normal (2WD)
14 System Normal (4WD/AWD)
15 System Normal (4WD/AWD)
21 Right front wheel sensor fault
22 Missing right front wheel sensor signal
23 Erratic right front speed sensor
25 Left front speed sensor fault
26 Missing left front speed signal
27 Erratic left front speed sensor
28 Simultaneous loss of both front sensor signals
29 Simultaneous drop out of all 4 sensors
31 Right rear speed sensor fault
32 Missing right rear speed signal
33 Erratic right rear speed sensor
35 Left rear speed sensor fault or VSS circuit open (1993)
36 Missing left rear speed signal or VSS signal missing (1993)
37 Erratic left rear speed signal or erratic VSS signal (1993)
38 Wheel speed error
41 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
42 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
43 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
44 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
45 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
46 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
47 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
48 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
49 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
50 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
51 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
52 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
53 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
54 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
Page 38

3
3-13 GM
3.5.4 Bosch 2S System Service Codes
Code Service Code Definition
55 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
56 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
57 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
58 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
59 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
60 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
61 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
62 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
63 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
64 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
65 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
66 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
67 Open motor circuit or shorted ECU output
68 Locked motor or shorted motor circuit
71 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
72 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
73 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
74 4 Wheel Anti-Lock (4WAL) control unit fault
81 Brake switch circuit shorted or open
85 Open anti-lock warning lamp
86 Shorted anti-lock warning lamp
88 Shorted brake warning lamp
Code Service Code Definition
12 Diagnostic system operational
21 Right front speed sensor fault
22 Right front toothed wheel frequency error
25 Left front speed sensor fault
26 Left front toothed wheel frequency error
31 Right rear speed sensor fault
32 Right rear toothed wheel frequency error
35 Left rear speed sensor fault
36 Left rear toothed wheel frequency error
Page 39

Retrieving ABS Codes
GM 3-14
3.5.5 Bosch 2U System Service Codes
Code Service Code Definition
41 Right front solenoid valve fault
45 Left front solenoid valve fault
55 Rear solenoid valve fault
61 Pump motor or motor relay fault
63 Solenoid valve relay fault
71 Electronic Brake Control Module (EBCM) fault
72 Serial data link fault
75 Lateral accelerometer fault; short to battery, ground or
open circuit
76 Lateral accelerometer fault, signal out of range or incorrect
Code Service Code Definition
12 Normal
21 Right front wheel sensor fault
22 Right front toothed wheel frequency error
25 Left front wheel sensor fault
26 Left front toothed wheel frequency error
35 Rear axle speed sensor fault
36 Rear axle toothed wheel frequency error
41 Right front solenoid valve fault
45 Left front solenoid valve fault
55 Rear wheels solenoid valve fault
61 Pump motor or motor relay fault
63 Solenoid valve relay fault
71 Electronic brake control module fault
72 Serial data line fault
Page 40

4
4-1 GM
4.1 INTRODUCTION
The Society of Automotive Engineers has issued a Standard
(SAE J1930) for Electrical/Electronic Systems Diagnostic
Terms, Definitions, Abbreviations, and Acronyms. However, at
the present time, this Standard is not in wide use by vehicle
manufacturers.
This Glossary contains definitions for abbreviations and terms
you may find in this manual or in your vehicle service manual.
These definitions
may not agree with those contained in SAE
J1930.
4.2 GLOSSARY OF TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
A/C – Air Conditioning.
AAC – Auxiliary Air Control Valve.
ABS – Anti-Lock Brake System.
ACC – Air Conditioning Clutch compressor signal input to
computer relating status of air conditioning clutch.
ACCS – Air Conditioning Cycling Switch.
ACD – Air Conditioner Demand switch.
ACT – Air Charge Temperature sensor or signal circuit.
ACV – Thermactor Air Control Valve.
AIR – Air Injector Reaction system, airflow from pump is
directed into engine reduce exhaust emissions.
AIR BPV – Thermactor Air Bypass Valve.
AIS – Automatic Idle Speed circuit and/or motor.
ALDL – Assembly Line Data Link. Diagnostic connector
under dash. Same as ALCL.
AM1 – Thermactor Air Management (TAB).
AM2 – Thermactor Air Management (TAD).
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE – Temperature of air
surrounding vehicle being serviced.
ANTI-BFV – Anti-Backfire Valve.
AOD – Automatic Over Drive transmission.
ATDC – After Top Dead Center.
AVOM – Analog Volt/Ohm Meter.
AWD – All Wheel Drive.
AXOD – Automatic Overdrive transaxle.
AXOD-E – Electronic Automatic Overdrive transaxle.
Page 41

Glossary
GM 4-2
BAC – Bypass Air Control valve.
BARO – Barometric Pressure.
BASE IDLE – Idle rpm determined by throttle switch with
idle speed control fully retracted.
BCM – Body Computer Module.
BOO – Brake On-Off input to the computer.
BOOST – Turbo charger boost solenoid or its control circuit.
BP – Barometric Pressure sensor. Used to compensate for
altitude variations.
BPMV – Brake Pressure Modulator Valve.
BTDC – Before Top Dead Center.
BVT – Back-pressure Variable Transducer.
CALPAC – A device used with fuel injection to allow fuel
delivery in the event of a PROM or PCM malfunction.
CANISTER – A container, in an evaporative emission system,
that contains charcoal to trap fuel vapors from the fuel system.
CANISTER PURGE SOLENOID – Electrical solenoid or its
control line. Solenoid opens a valve from fuel vapor canister
line to intake manifold when energized. Controls flow of
vapors between carburetor bowl vent and carbon canister.
CANP – Canister Purge solenoid.
CATALYTIC CONVERTER – Muffler like assembly placed
in exhaust system that contains a catalyst to change
hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide into water vapor and
carbon dioxide.
CCC – Climate Control Center.
CCC – Computer Command Control.
CCC – Converter Clutch Control solenoid or its circuit.
CCDIC – Climate Control/Driver Information Center.
CCO – Converter Clutch Override output from the computer
processor to the transmission.
CCS – Coast Clutch Solenoid or its circuit.
CEC – Computerized Emission Control.
CER – Cold Enrichment Rod.
CES – Clutch Engage Switch.
CFI – Central Fuel Injection.
CHECK ENGINE LIGHT – Dash panel light used either to
aid in identification and diagnosis of a system problems or to
indicate that maintenance is required.
Page 42

4
4-3 GM
CHECK VALVE – Valve that operates like a one-way gate.
CID – Cylinder Identification sensor or its circuit.
CKT – Circuit.
CL – Closed Loop.
CLC – Converter Lock-up Clutch.
CO – Carbon Monoxide.
COC – Conventional Oxidation Catalyst.
COMPUTER TIMING –Total spark advance in degrees
before top dead center.
CPS – Crankshaft Position Sensor. Provides the ECU with
engine speed and crankshaft angle (position).
CRT – Cathode Ray Tube. A device for displaying video
signals, similar to a television picture tube. Similar devices
used on General Motors vehicles are referred to as DID or VIC.
CTS – Coolant Temperature Sensor.
CURB IDLE – Computer controlled idle rpm.
CVR – Control Vacuum Regulator.
CWM – Cold Weather Modulator.
CYLINDER IDENTIFICATION SIGNAL (CID) – A signal
generated by crankshaft timing sensor, used to synchronize
ignition coils, due to the fact that some models use a 2 ignition
coil pack DIS system.
C3I – Computer Controlled Coil Ignition. Produces ignition
spark without aid of an ignition distributor.
DCL – Data Communications Link.
DERM – Diagnostic Energy Reserve Module and air bag (SIR)
controller.
DFS – Decel Fuel Shut-off.
DIC – Driver Information Center.
DID – Driver Information Display.
DIS – Direct Ignition System. Produces ignition spark without
aid of an ignition distributor. (Similar to C3I).
DLC – Data Link Connector.
DRA – Digital Ratio Adapter.
DRAB – Digital Ratio Adapter Buffer.
DRAC – Digital Ratio Adapter Calibrator.
DTC – Diagnostic Trouble Code.
Page 43

Glossary
GM 4-4
DUAL CATALYTIC CONVERTER – Combines 2 converters
in one shell. Controls NOx, HC and CO. Also called TWC.
DV TW – Delay Valve, 2 Way.
DVM (10 MEG) – Digital voltmeter with a minimum of 10
million ohms resistance. Allows measurement in circuit
without affecting the circuit operation.
DWELL – Amount of time (recorded on a dwell meter in
degrees) that current passes through a closed switch.
EAS – Electronic Air Switching, directs airflow to catalytic
converter or exhaust ports of the engine.
EBCM – Electronic Brake Control Module.
ECM – Engine Control Module properly call a Powertrain
Control Module.
ECT – Engine Coolant Temperature sensor or circuit.
ECU – Electronic Control Unit. To process input information
to trigger ignition control module.
EDF – Electro-Drive Fan relay or its circuit.
EECS – Evaporative Emission Control System.
EEGR – Electronic Exhaust Gas Recirculation valve (Sonic).
EEPROM – Electronically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory.
EET – Electronic Exhaust Gas Recirculation Transducer.
EFC – Electronic Feedback Carburetor. Utilizes an electronic
signal, generated by an exhaust gas oxygen sensor to precisely
control air/fuel mixture ratio in the carburetor.
EFI – Electronic Fuel Injection. Computer controlled fuel
injection system.
EGO – Exhaust Gas Oxygen sensor.
EGR – Exhaust Gas Recirculation system is designed to allow
flow of inert exhaust gases into combustion chamber to cool
combustion and reduce nitrous oxides in exhaust.
EHC – Exhaust Heat Control vacuum solenoid or its circuit.
EHCU - Electro-Hydraulic Control Unit.
EIC – Electronic Instrument Cluster.
ELECTRONIC SPARK CONTROL – Used to retard spark
advance if detonation occurs.
ELECTRONIC SPARK TIMING – PCM controlled timing of
the ignition spark.
EMI - Electro-Magnetic Interference.
Page 44

4
4-5 GM
EMR – Electronic Module Retard, controls spark retard.
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE – A microprocessor based
device which contains electronic circuitry to control and
monitor air/fuel and emission systems, and aid in diagnostics.
EPC – Electronic Pressure Control solenoid.
EPROM – Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory.
ERS – Engine RPM Sensor.
ESA – Electronic Spark Advance.
ESC – Electronic Spark Control.
EST – Electronic Spark Timing.
EVP – EGR Valve Position sensor or its circuit.
EVR – EGR Vacuum Regulator or its circuit.
EVRV – Electronic Vacuum Regulator Valve. Controls EGR
vacuum.
EXHAUST GAS OXYGEN SENSOR – Sensor that changes
its voltage output as exhaust gas oxygen content changes as
compared to oxygen content of the atmosphere. The constantly
changing electrical signal is used to control fuel mixture.
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION – Procedure where a
small amount of exhaust gas is re-admitted to combustion
chamber to reduce peak combustion temperatures, thus
reducing NOx.
FAIL SAFE – or Fail Soft: any attempt by a computer to
compensate for a fault or lost signal, usually by substituting
fixed replacement valves.
FEEDBACK CARBURETOR (FBC) – System of fuel control
employing a computer controlled solenoid that varies the
carburetors air/fuel mixture.
FMEM – Failure Mode Effects Management. Sometimes
referred to limp-in mode.
GND, GRD or GRND – Ground. Common line leading to the
negative side of the battery.
HALL EFFECT – Process where current is passed through a
small slice of semi-conductor material at the same time as a
magnetic field to produce a small voltage in the semiconductor.
HARD FAULT – Fault present during current engine
operating cycle. Opposite of an intermittent fault which does
not stay present.
HEDF – High-speed Electro-Drive Fan relay or its circuit.
HEGO – Heated Oxygen Sensor or its circuit.
HIC – Hot Idle Compensator.
Page 45

Glossary
GM 4-6
HPA - High Pressure Accumulator.
IAC – Idle Air Control.
IAS – Inlet Air Solenoid valve or its circuit.
IAT – Intake air temperature sensor, performs same function
as MAT sensor.
ICM – Integrated Control Module.
IDLE TRACKING SWITCH – An input device that sends a
signal to the computer to indicate a closed throttle condition.
IGN – Ignition.
INTERMITTENT FAULT – Fault which occurred during a
previous engine operating cycle. Intermittent fault may have
set a fault code which is still present in PCM memory.
ISA – Idle Speed Actuator. Extends or retracts to control
engine idle speed and to set throttle stop angle during
deceleration.
ISC – Idle Speed Control, either computer control motor, air
bypass valve, or any device used to control idle rpm.
ISO VALVE - Isolation Valve.
ITS – Idle Tracking Switch.
KAM – Keep Alive Memory. Battery power memory locations
in computer used to store failure codes and some diagnostic
parameters.
KAPWR – Keep Alive Power, used to power KAM circuit of
the processor.
KNOCK SENSOR (KS) – Input device that responds to spark
knock, caused by over advanced ignition timing.
LEAN MIXTURE – Air/fuel mixture that has excessive
oxygen left after all fuel in combustion chamber has burned, 1
part fuel to 15 or more parts air.
LED – Light Emitting Diode.
LOCK UP TORQUE CONVERTER – Converter with
internal mechanism that locks turbine to impeller when
engaged.
LPA - Low Pressure Accumulator.
LUS – Lock-Up Solenoid.
M/C – Mixture control or mixture control solenoid.
MAF – Mass Air Flow sensor, used to measure amount of
airflow through the throttle body.
MAP – Manifold Absolute Pressure sensor or its circuit.
MAT – Manifold Air Temperature.
Page 46

4
4-7 GM
MFI – Multi-port Fuel Injection.
MIL – Malfunction Indicator Light. Check engine light.
MIXTURE CONTROL SOLENOID – Device installed on
carburetor, that regulates the air/fuel ratio.
MLP – Manual (shift) Lever Position sensor or its circuit.
MPFI – Multi-Port Fuel Injection.
MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION – Individual injectors for
each cylinder mounted in intake manifold. Injectors are pulsed
in groups rather than individually.
NDS – Neutral Drive Switch.
NGS – Neutral Gear Switch or its circuit.
NON-VOLATILE MEMORY – Memory retained in block
learn cells (not affected by turning the ignition ON or OFF).
NOx – Nitrous Oxides.
NPS – Neutral Pressure Switch or its circuit.
OCT ADJ – Octane Adjust device which modifies ignition
spark.
OXYGEN SENSOR – Sensor that changes its voltage output
as exhaust gas oxygen content changes as compared to the
oxygen content of the atmosphere. The constantly changing
electrical signal is used to control fuel mixture.
PCM – Powertrain Control Module. Computer that controls
engine fuel, ignition and emission related functions.
PCV – Positive Crankcase Ventilation. System that controls
flow of crankshaft vapors into engine intake manifold where
they are burned in combustion rather then being discharged
into the atmosphere.
PFE – Pressure Feedback EGR sensor or its circuit.
PFI – Port Fuel Injection.
PORTED VACUUM SWITCH – Temperature actuated
switch that changes vacuum connections when the coolant
temperature changes.
POT – Potentiometer.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE – Same as ECM, but
also controls electronically controlled automatic transmission.
PROM – Programmable Read Only Memory.
PSPS – Power Steering Pressure Switch. Signal is used by
computer to compensate for power steering loads.
PVS – Ported Vacuum Switch.
PWM - Pulse Width Modulation.
Page 47

Glossary
GM 4-8
QUAD-DRIVER (QDM) – Computer chip, in the PCM,
capable of operating four separate outputs. Some have digital
and some have pulse width modulated outputs.
RAP – Retained Accessory Power.
RELAY – Switching device operated by a low current circuit,
which controls opening and closing of another higher current
circuit.
RELIEF VALVE – Pressure limiting valve located in exhaust
chamber of thermactor air pump. Relieves part of exhaust
airflow if pressure exceeds a calibrated value.
RICH MIXTURE – Air/fuel mixture that has more fuel than
can burn completely, 1 part fuel to 14 or less parts air.
SAW – Spark Advance Word, and also Spark Angle Word.
SCC – Spark Control Computer.
SES – Service Engine Soon light.
SEFI, SFI – Sequential Fuel Injection, type of MFI with
injectors pulsed individually based on engine firing order.
SIG RTN – Signal Return circuit for all sensors except HEGO.
SIL – Shift Indicator Light. Indicates to driver optimum time
to shift gears.
SIR – Supplemental Inflatable Restraint (SIR) system; air
bag.
SIS – Solenoid Idle Stop.
SOLENOID – Wire coil with a movable core which changes
position by means of electromagnetism when current flows
through the coil.
SPARK RETARD SOLENOID – Output device that receives
an output signal to bleed distributor’s vacuum advance when
spark knock occurs.
SSI – Solid State Ignition system.
T.V. – Throttle Valve.
TAB – Thermactor Air Bypass solenoid.
TACH INPUT – Engine rpm signal sent to computer from
ignition coil primary circuit.
TAD – Thermactor Air Diverter solenoid.
TBI – Throttle Body Injection (Fuel).
TCC – Torque Converter Clutch.
TCP – Temperature Compensating Pump.
Page 48

4
4-9 GM
TDC – Top Dead Center.
THERMACTOR AIR CONTROL VALVE – Combines
function of a normally closed air bypass valve and an air
diverter valve in one integral valve.
THERMACTOR AIR SYSTEM – Efficiency of catalytic
converter is dependent upon temperature and chemical
makeup of exhaust gases. These requirements are met by the
thermactor air supply system.
THREE-WAY CATALYST – Combines 2 converters in 1
shell. Controls NOx, HC and CO. Also called dual catalytic
converter.
TIMING – Relationship between spark plug firing and piston
position.
TKS – Throttle Kicker Solenoid, when energized, supplies
manifold vacuum to throttle kicker actuator as directed by
computer to compensate for engine loads. Also called idle-up
system.
TOT – Transmission Oil Temperature sensor.
TP or TPS – Throttle Position Sensor or its circuit. Used to
signal computer the position of the throttle plates.
TPI – Tuned Port Injection, a type of MFI with intake tubes
designed to be tuned for performance. Most TPI engines are
also SFI.
TTS – Transmission Temperature Switch.
TVS – Temperature Vacuum Switch.
TVV – Thermal Vent Valve.
TWC – Three-Way Catalyst.
VACUUM – A term to describe a pressure that is less than
atmospheric pressure.
VACUUM ADVANCE – Advances ignition timing with
relation to engine load or computer signals.
VAF – Vane Air-Flow sensor or its circuit.
VAT – Vane Air-Flow Temperature sensor.
VATS – Vehicle Anti-theft System.
VCM - Vehicle Control Module.
VM – Vane Meter or air flow meter.
VSS – Vehicle Speed Sensor.
WOT – Wide Open Throttle or Wide Open Throttle switch.
WSS - Wheel Speed Sensor.
Page 49

Glossary
GM 4-10
Page 50

5
5-1 GM
5.1 LIMITED ONE YEAR WARRANTY
The Manufacturer warrants to the original purchaser that this
unit is free of defects in materials and workmanship under
normal use and maintenance for a period of one (1) year from
the date of original purchase.
If the unit fails within the one (1) year period, it will be
repaired or replaced, at the Manufacturer's option, at no
charge, when returned prepaid to the Service Center with
Proof of Purchase. The sales receipt may be used for this
purpose. All replacement parts, whether new or remanufactured, assume as their warranty period only the
remaining time of this warranty.
This warranty does not apply to damage caused by improper
use, accident, abuse, improper voltage, service, fire, flood,
lightning, or other acts of God, or if the product was altered or
repaired by anyone other than the Manufacturer's Service.
The Manufacturer, under no circumstances shall be liable for
any consequential damages for breach of any written warranty
of this unit.
This warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may also
have rights which vary from state to state.
This manual is copyrighted with all rights reserved. No
portion of this document may be copied or reproduced by any
means without the express written permission of the
Manufacturer. THIS WARRANTY IS NOT TRANSFERABLE.
For service, send via U.P.S. (if possible) prepaid to
manufacturer.
Allow 3-4 weeks service time
5.2 SERVICE PROCEDURES
If you have any questions, please contact your local store,
distributor or the Manufacturer's Service Department.
USA & Canada:
(800) 544-4124 (9:00-4:00, Monday-Friday PST)
All others:
(714) 241-6802 (9:00-4:00, Monday-Friday PST)
FAX:
(714) 432-7910 (24 hr.)
Page 51

Warranty and Service
GM 5-2
Page 52

Innova 1998 GM
INNOVA ELECTRONICS CORPORATION
17287 Mt. Herrmann Street
Fountain Valley, CA 92708
USA
#3123
 Loading...
Loading...