Page 1
TRADEMARK
All products and company names are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective holders.
These specifications are subject to change without notice.
Manual Revision 1.0
February 25, 2003
User’User’
User’User’
User’
ss
ss
s
ManualManual
ManualManual
Manual
An Intel SocAn Intel Soc
An Intel SocAn Intel Soc
An Intel Soc
kk
kk
k
et 478 Pret 478 Pr
et 478 Pret 478 Pr
et 478 Pr
ocessor Basedocessor Based
ocessor Basedocessor Based
ocessor Based
Mainboard (400/533/533+MHz)Mainboard (400/533/533+MHz)
Mainboard (400/533/533+MHz)Mainboard (400/533/533+MHz)
Mainboard (400/533/533+MHz)
SupporSuppor
SupporSuppor
Suppor
ts ts
ts ts
ts
PC1600/PC1600/
PC1600/PC1600/
PC1600/
21002100
21002100
2100
/2700/2700
/2700/2700
/2700
Memor Memor
Memor Memor
Memor
y Modulesy Modules
y Modulesy Modules
y Modules
(DDR-200/266/333/333+ Memor(DDR-200/266/333/333+ Memor
(DDR-200/266/333/333+ Memor(DDR-200/266/333/333+ Memor
(DDR-200/266/333/333+ Memor
y)y)
y)y)
y)
$ 2&
Page 2
DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTIES:
THERE ARE NO WARRANTIES WHICH EXTEND BEYOND THE
DESCRIPTION ON THE FACE OF THE MANUFACTURER LIMITED
WARRANTY. THE MANUFACTURER EXPRESSLY EXCLUDES ALL
OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING ITS
PRODUCTS; INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR
NONINFRINGEMENT. THIS DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTIES SHALL
APPLY TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED UNDER LOCAL LAWS IN THE
COUNTRY PURCHASED IN WHICH LOCAL LAWS DO NOT ALLOW
OR LIMIT THE EXCLUSION OF THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES.
Page 3
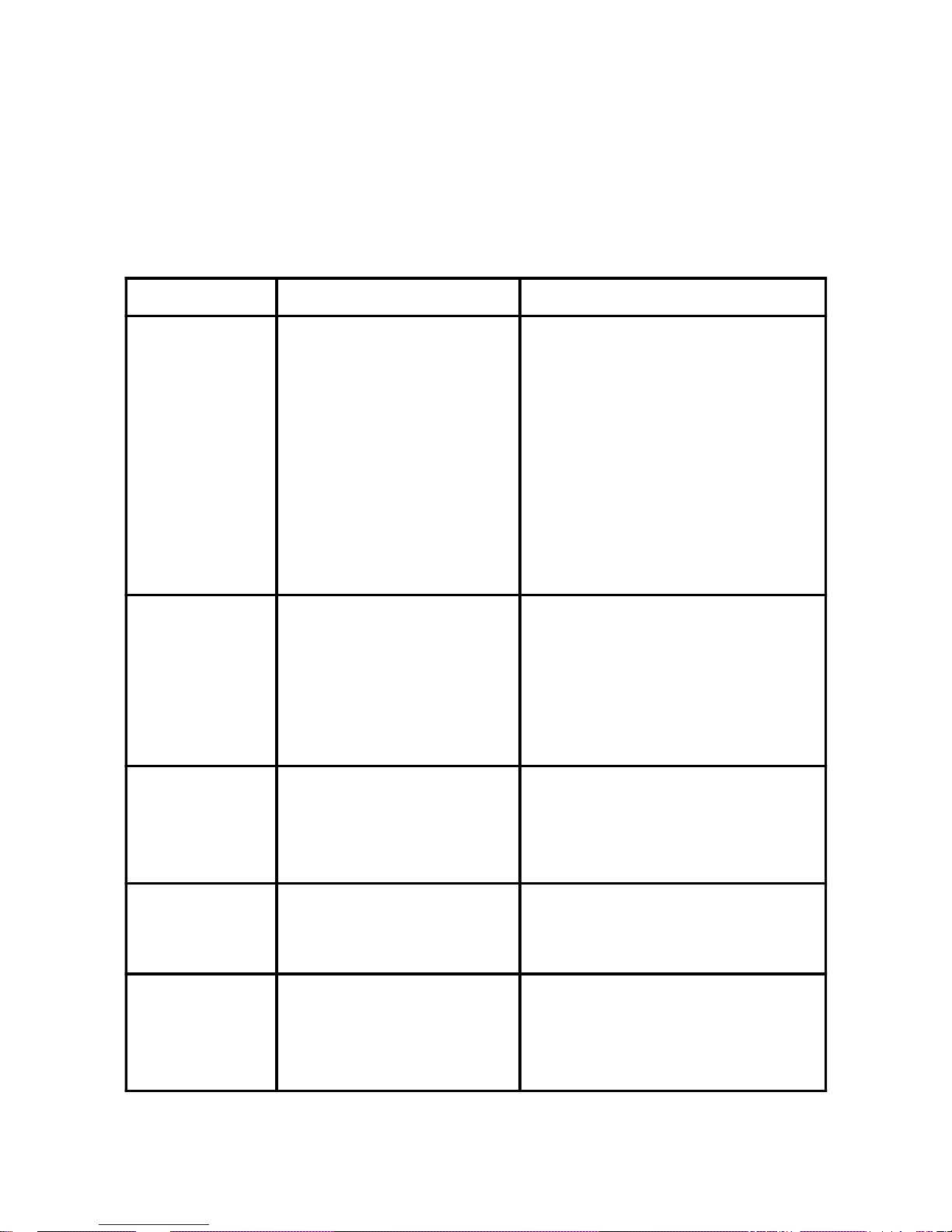
80 Port Frequently Asked Questions
Below is a list of some basic POST Codes, possible problems, and solutions. For
more detailed information about POST Codes, refer to Appendix E in this manual.
PO ST CODE Problem Soluti on
FFh or CFh 1.BIOS chip inserted
incorrectly
2. Incorrect BIOS update
version
3. M ainboard problem
4. Add-on card inserted
incorrectly.
1. Reinsert the BIOS
chip
2. Download the correct
BIOS version update
from the manufacturer's
Web site.
3. Replace mainboard
4. Remove and replace the
add-on card
C1h - C5h 1. Memory module
inserted incorrectly
2. M em ory compatibility
problem
3. M emory m odule
damaged
1. Reinsert memory
module
2. Replace memory
with correct type
3. Replace memory
module
2Dh 1. Error occured in VGA
BIOS
2. VGA card inserted
incorrectly
1. Replace VGA card
2. Reinsert the VGA
card
26h Overclock error Clear CMOS or press the insert
key to power on the system
07h - 1 2 h 1. Init keyboard
controller error
2. RTC error
1. Ensure that the keybo ard and
mouse are connected
correctly.
2. Replace the RTC battery.
Initial Keyboard
Page 4

T able of Contents
Section 1 Introduction
Components Checklist ............................................... 1-1
Overview
System Overview ....................................................... 1-2
Chipset Components.................................................. 1-3
Intel Pentium 4 Processors......................................... 1-4
Accelerated Graphics Port ......................................... 1-6
Ultra ATA66/100 ........................................................ 1-6
Hardware Monitoring................................................. 1-6
Mainboard Form-Factor ............................................. 1-7
I/O Shield Connector.................................................. 1-8
Power-On/Off (Remote) .............................................. 1-8
System Block Diagram ............................................... 1-9
Section 2 Features
Mainboard Features ................................................... 2-1
Section 3 Installation
Mainboard Layout ..................................................... 3-2
Easy Installation Procedure
CPU Installation ......................................................... 3-3
Jumper Settings.......................................................... 3-5
System Memory Configuration.................................. 3-6
Expansion slots .......................................................... 3-8
Device Connectors..................................................... 3-9
External Modem Ring-in Power ON and
Keyboard Power ON Function (KBPO) ..................... 3-15
STR (Suspend To RAM) Function .......................... 3-16
Supports AGP Card 3.3V Protection .......................... 3-17
Page
Page 5
Section 4 Award BIOS Setup
Main Menu ................................................................ 4-1
Standard CMOS Setup ............................................... 4-2
Advanced BIOS Features .......................................... 4-3
Advanced Chipset Features ...................................... 4- 8
Integrated Peripherals ................................................ 4-10
Power Management Setup ......................................... 4-15
PNP/PCI Configuration Setup .................................... 4-20
PC Health Status ........................................................ 4-22
Frequency/Voltage Control ........................................ 4-24
Defaults Menu ........................................................... 4-28
Supervisor/User Password Setting ............................4-29
Exit Selecting .............................................................. 4-30
Section 5 Driver Installation
Easy Driver Installation.............................................. 5-1
ALC650/655 Configuration Setup (6 Channel)........... 5-2
Appendix Appendix A
Realtek Media Player Users Guide ............................ A-1
Appendix B
Update Your System BIOS ......................................... B-1
Appendix C
EEPROM BOIS Remover ............................................ C-1
Appendix D
GHOST 7 Quick Users Guide (Optional) ................... D-1
Appendix E
POST Codes .............................................................. E-1
Page 6

Page Left Blank
Page 7
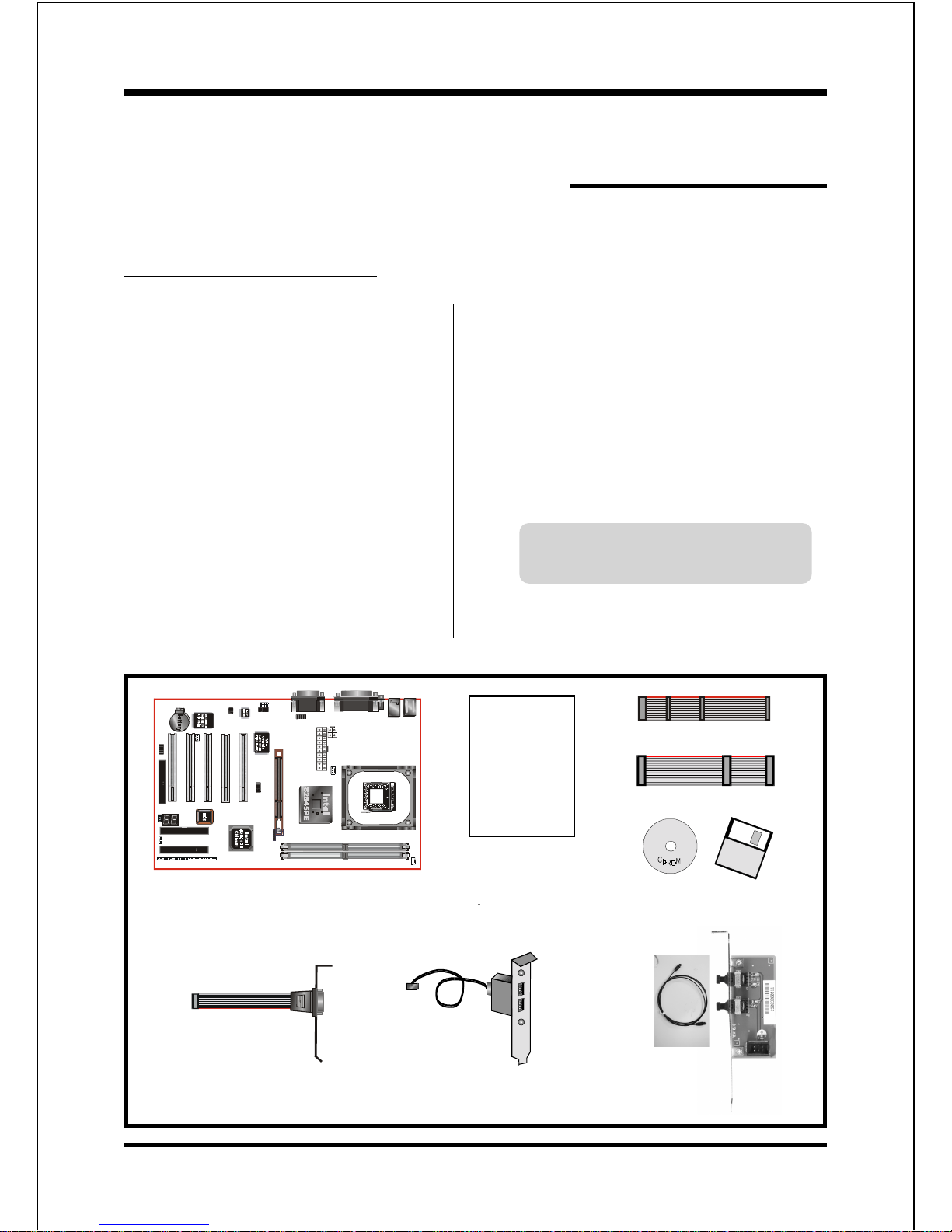
Introduction
Page 1-1
B
A
C
D
USERS
MANUAL
E
or
G
F
H
Section 1
INTRODUCTION
Package Contents
Contents
A.Mainboard
B. Users manual
C. Floppy disk drive cable
D. Hard disk drive cable
E. CD (drivers and utilities)
Deluxe Pack Items
F. COM2 port cable
G. USB port cable
Other Optional Items
H. SPD650 card
If you need the other optional item,
please contact dealer for assistance.
Page 8

Introduction
Page 1-2
System Overview
This board is designed with Intel® 845PE chipset. The Intel® 845PE chipset includes
MCH(FW82845PE), ICH4(FW82801DB) and FWH three chips. The Intel® 845PE
chipset is designed for Intels FC-PGA2 socket 478 package architecture and
support the 4X capability of the AGP 2.0 Interface Specification. A new chipset
component interconnect, the hub interface, is designed into the Intel® 845PE chipset
to provide more efficient communication between chipset components.
Support of AGP 4X, 266/333/333+MHz DDR SDRAM and the hub interface provides
a balanced system architecture for the Pentium® 4 in the Socket 478 architecture
processor minimizing bottlenecks and increasing system performance. By
increasing memory bandwidth to 2.128GB/s through the use of AGP 4X, the
Intel® 845PE chipset will deliver the data throughput necessary to take advantage
of the high performance provided by the powerful Pentium® 4 in the Socket 478
architecture processor.
The Intel® 845PE chipset architecture removes the requirement for the ISA
expansion bus that was traditionally integrated into the I/O subsystem of Intel
chipsets. This removes many of the conflicts experienced when installing
hardware and drivers into legacy ISA systems. The elimination of ISA will provide
true plug-and play for the Intel® 845PE platform.
Intel® 845PE chipset contains three core components: the Memory Controller
Hub (MCH), the I/O Controller Hub (ICH4) and the Firmware Hub (FWH). The
MCH integrates the data transfer rate of 400/533/533+MHz, Pentium® 4 processor
bus controller, AGP 2.0 controller, 266/333/333+MHz DDR SDRAM controller and a
high-speed hub interface for communication with the ICH4. The ICH4 integrates an
Ultra ATA/66/100 controller, USB host controller, LPC interface controller, FWH
interface controller, PCI interface controller, and a hub interface for communication
with the MCH. The Intel® 845PE chipset will provide the data buffering and
interface arbitration required to ensure that system interfaces operate efficiently and
provide the system bandwidth necessary to obtain peak performance the Pentium® 4
in the Socket 478 architecture.
Page 9
Introduction
Page 1-3
Chipset Components
The Intel® 845PE chipset consists of the Memory Controller Hub (MCH), the I/O
Controller Hub (ICH4) and the Firmware Hub (FWH).
!!
!!
! Memory Controller Hub (MCH)
The MCH provides the interconnect between the DDR SDRAM and the system
logic. It integrates:
- Support for single processor with a data transfer rate of 400/533/533+MHz.
- 200/266/333/333+MHz DDR SDRAM interface supporting 2GB of DDR SDRAM.
- 4X 1.5V AGP interface (Only support 1.5V on AGP interface).
- Downstream hub link for access to the ICH4.
!!
!!
! I/O Controller Hub (ICH4)
The I/O controller Hub provides the I/O subsystem with access to the rest of
the system. Additionally, it integrates many I/O functions. The ICH4 integrates:
- Upstream hub link for access to the MCH
- 2 Channel Ultra ATA/33/66/100 Bus Master IDE controller
- USB controller
- SMBus controller
- FWH interface
- LPC interface
- PCI 2.2 interface
- Integrated System Management Controller
!!
!!
! Firmware Hub (FWH)
The FWH component is a key element to enabling a new security and manageability infrastructure for the PC platform. The device operates under the FWH
interface and protocol. The hardware features of this device include a unique a
Random Number Generator (RNG), register-based locking, and hardwarebased locking.
Page 10

Introduction
Page 1-4
Intel Pentium 4 processors
Formally known as the Willamette, the PentiumTM 4 is the next PEneration IA-32
processor from Intel. This next generation design is based upon a new microarchitecture that brings higher clock speeds and performance than previous
processors could deliver. Among other advanced features the Pentium 4 offers
Streaming SIMD extensions 2, Advanced Dynamic Execution, Hyper Pipelined
Technology, and a data transfer rate of 400/533/533+MHz system bus.
Streaming SIMD Extensions 2
Building upon the foundations of core features of their previous line of processors the Pentium 4, this new version introduces Streaming SIMD Extensions 2
technology commonly referred to as SSE2. But what does this mean? SIMD stands
for Single Instruction Multiple Data. Usually, processors process one data
element in one instruction, called Single Instruction Single Data, or SISD. In
contrast, with Single Instruction Single Data (SISD), SIMD has the ability to
process more than one piece of data element during one instruction.
This technology is useful for 3D graphics applications that handle considerable
amounts of floating-point numbers. With SIMD applications such as 3D graphics
will be able to processor more data per instruction when equates to better
performance. This technology adds 144 new instructions to the CPU core that can
be used in a wide variety of applications. Software programmers can for example,
take advantage of these new instructions and write more optimized code that take
advantage of newer SIMD double-precision floating-point, integer, and cache
ability instructions. In theory, this will enable better next generation services such
as Interactive Digital TV to be produced.
Advanced Dynamic Execution
Advanced Dynamic Execution describes the improved implementation and
abilities over the older P6 processor lines out-of-order decoupled super scalar
execution. Dynamic execution allows instructions to the processor to be executed
without the need to do so in order. The ability to do this can add a significant
performance increase versus ordered execution.
Page 11
Introduction
Page 1-5
Hyper Pipelined Technology & 400/533/533+MHz System Bus
Hyper Pipelined Technology doubles the pipeline depth the Pentium 4 delivers to
20 stages. This significantly increases the performance and frequency capabilities.
Pentium 4 also introduces a 400/533/533+MHz system bus as opposed to the 100
and 133MHz bus seen in previous Pentium III processors. This allows 3.2Gbytes per
second of throughput while the Pentium III had a limited 1.06Gbyte/s throughput.
Willamette will reportedly be introduced in the 0.18-micron using aluminum.
Hyper-Threading Technology
Hyper-Threading Technology is a new features in the IA-32 Intel Architecture that
provides a performance boost for future Intel-32 processors based on the Intel
NetBurstTM micro architecture. This technology enables a single processor to run
two separate threads simultaneously, this arrangement looks like two processors.
Hyper-Threading Technology makes a single physical processor appear as multiple
logical processors, there is one copy of the architecture state for each logical
processor, and the logical processor share a single set of physical execution
resources. From a software or architecture perspective, this means operating
systems and user programs can schedule processors or threads to logical processors as they would on conventional physical processors in a multi-processor
system. From a micro architecture perspective , this means that instructions form
logical processors will persist and execute simultaneously on shared execution
resources.
For more information about all the new features the Pentium 4 delivers check
out the Intel website at http://www.intel.com
Page 12
Introduction
Page 1-6
Accelerated Graphics Por t (AGP or A.G.P.)
Typically, 3D graphics rendering requires a tremendous amount of memory, and
demands ever increasing throughput speed as well. As 3D products for the
personal computer become more and more popular, these demands will only
increase. This will cause a rise in costs for both end users and manufacturers.
Lowering these costs as well as improving performance is the primary motivation
behind AGP. By providing a massive increase in the bandwidth available between
the video card and the processor, it will assist in relieving some of these pressures
for quite sometime.
The board provides the AGP 2.0 interface. The AGP Interface Specification revision
2.0 enhances the functionality of the original AGP Interface Specification (revision
1.0) by allowing 4X data transfers (4 data samples per clock) and 1.5 volt (power
supply) operation. The AGP 2.0 interface, along with SDRAM memory technology,
allows graphics controllers to access main memory at over 1GB/s. In order to match
the 4X AGP Card. The board used the Universal AGP connector. (1.5 volt AGP Card
supports only).
Ultra ATA/66/100
The ICH4 provides two channel Ultra ATA/66/100 Bus Master IDE controllers, that
support Ultra ATA/66/100 protocols, perfect for such demanding applications as
real-time video, multimedia, and high performance operating system. A new IDE
cable is required for Ultra ATA/66/100. This cable is an 80 conductor cable;
however the connectors are, of course, backwards compatible with ATA/33.
Hardware Monitoring
Hardware monitoring allows you to monitor various aspects of your system
operations and status. The features include CPU temperature, voltage and RPM of
fan.
Page 13

Introduction
Page 1-7
Mainboard Form-Factor
The board is designed with ATX form factor - the latest industry standard of
chassis. The ATX form factor is essentially a Baby-AT baseboard rotated 90
degrees within the chassis enclosure and a new mounting configuration for the
power supply. With these changes the processor is relocated away from the
expansion slots, allowing them all to hold full length add-in cards. ATX defines
a double height aperture to the rear of the chassis which can be used to host a
wide range of onboard I/O. Only the size and position of this aperture is
defined, allowing PC manufacturers to add new I/O features (e.g.; TV input, TV
output, joystick, modem, LAN, audio, etc.) to systems. This will help systems
integrators differentiate their products in the marketplace, and better meet your
needs.
By integrating more I/O down onto the board and better positioning the
hard drive and floppy connectors material cost of cables and add-in cards is
reduced.
By reducing the number of cables and components in the system, manufac-
turing time and inventory holding costs are reduced and reliability will
increase.
By using an optimized power supply, it's possible to reduce cooling costs
and lower acoustical noise. An ATX power supply, which has a sidemounted fan, allows direct cooling of the processor and add-in cards making
a secondary fan or active heatsink unnecessary in most system applications.
Expandable I/O
Figure 2: Summary of ATX chassis features
CPU
Single chassis fan
for system
Floppy / IDE
connectors
5 1/4"
Bay
3 1/2"
Bay
AT X
Power
Supply
ATX 12V power
connector
PCI slots
AGP slot
ATX power
connector
Page 14
Introduction
Page 1-8
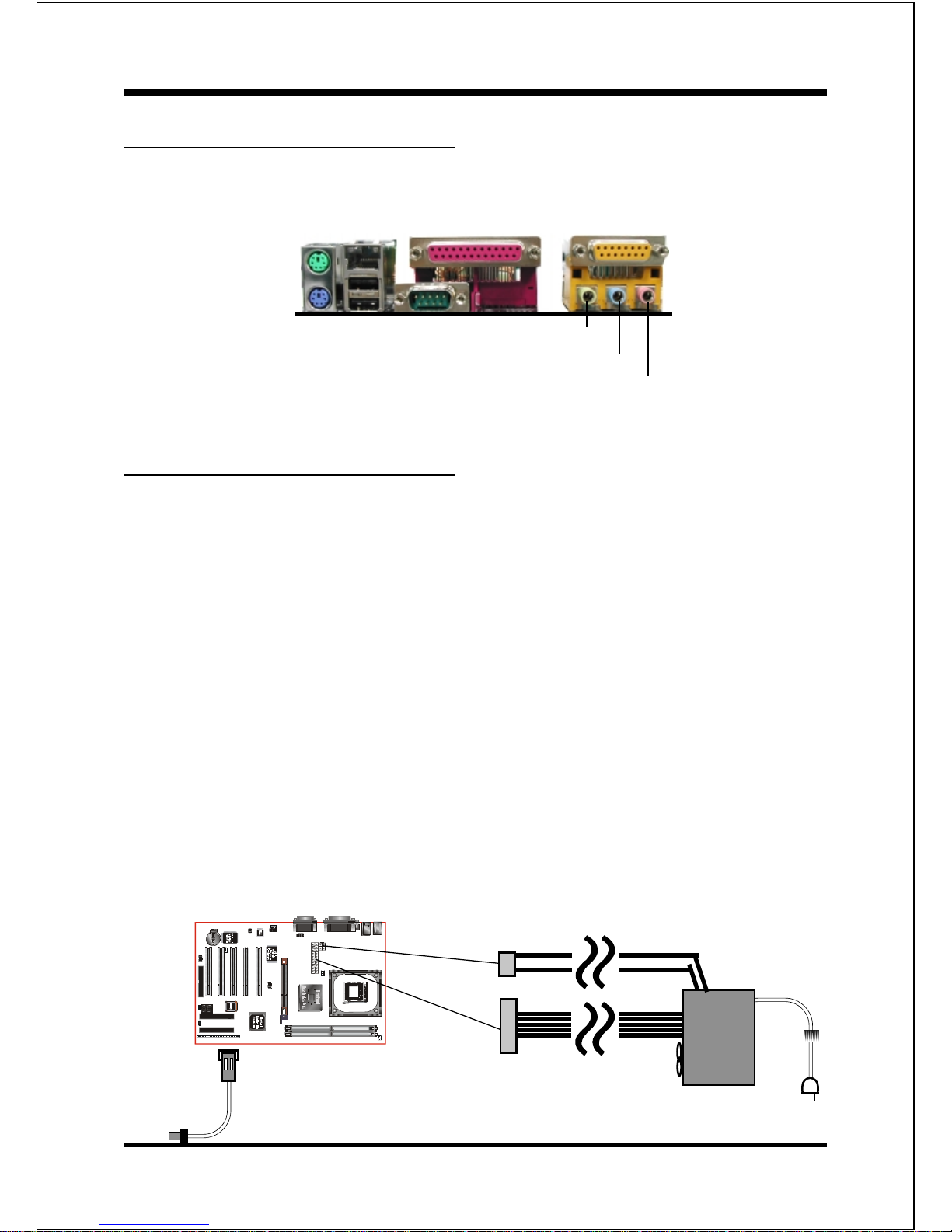
I/O Shield Connector
The board is equipped with an I/O back panel. Please use the appropriate I/O shield
(figure 3).
Power-On/Off (Remote)
The board has a single 20-pin ATX and 4-pin ATX12V connector for power supplies
(Figure 4). For power supplies that support the Remote On/Off feature, this should
be connected to the mainboard front panel PW_ON connector for the computer
power On/Off button.
The board has been designed with Soft Off" function. You can turn off the system
two ways: pressing the front panel power On/Off button, using the "Soft Off"
function (incorporated in the mainboards onboard circuit controller) that can be
controlled by an operating system such as Windows®XP/ME/2000/98.
Note: For maintaining the DDR SDRAM power during STR (ACPI S3) function, it is
strongly recommend to use power supplies that have a +5VSB current of (>=)
1A (1000mA). Please check the 5VSBs specification that has been printed on
the power supplys outer case.
Note: The board requires a minimum of 250 Watt power supply to operate. Your
system configuration (amount of memory, add-in cards, peripherals, etc.) may
exceed the minimum power requirement but to ensure that adequate power is
provided, use a 300 Watt (or greater) power supply.
J 3
Case (chassis) Power ON/OFF button (J 3)
Figure 3: I/O back panel layout
Mic-in/Center&Subwoofer
Line-out/Front out
Line-in/Rear out
PS/2 Mouse
PS/2 Keyboard
COM1
Parallel Port
RJ-45 LAN
(Optional)
USB2.0
ports
Joystick/Midi Port
12V 4-pin
20-pin
Figure 4: Simple ATX power ON/OFF controller
Page 15

Introduction
Page 1-9
Figure 5: System Block Diagram
System Block Diagram
Pentium 4
Processor
478 pin Package
MCH
(Memory
Controller
Hub)
ICH4
(I/O
Controller
Hub)
DDR SDRAM
200/266/333/333+ M zH
100/133MHz
66MHz
4X (1.5V only)
USB 1,2
USB 5,6
80 Port
FWH (Firm Ware Hub)
Flash memory
LPC I/O
Winbond
83627HF
Serial Port 1
Serial Port 2
LPT Port
PS/2 Mouse
PS/2 Keyboard
Game
IR
AC'97
Audio
PCI Slots
HDD
1,-
1,-
USB 3,4
Page 16
Introduction
Page 1-10
Page Left Blank
Page 17
.A=JKHAI
Page 2-1
Section 2
FEATURES
Mainboard Features
Processor
!
Socket 478 Intel® Pentium® 4 processor from 1.4 to 3.06GHz with 400/533/
533+MHz Front Side Bus
!
Supports Hyper-Threading Technology
Enabling the functionality of Hyper-Threading Technology for your
computer system requires ALL of the following platform Components:
"CPU: An Intel
®
Pentium® 4 Processor with HT Technology.
"Chipset: An Intel
®
Chipset that supports HT Technology.
"BIOS: A BIOS that supports HT Technology and has it enabled.
"OS: An operating system that supports HT Technology.
Chipset
!
Intel 82845PE Chipset (82845PE + ICH4)
Main Memory
!
Two 184-pin DDR DIMM sockets for PC1600/2100/2700 (DDR-200/266/333/
333+) DIMMs
!
Supports up to 2GB memory size
BIOS
!
Flash EEPROM with Award BIOS
- ACPI v2.0 compliant
- S3 (Suspend to DRAM) sleep-state support
- SMBIOS (System Management BIOS)v2.2 compliant
- Supports Power failure recovery
- Capable to waked the computer up from specific states by LAN, Power
switch, PME#, RTC alarm, USB, PS2 devices, Modem Ring-in COM#1
Page 18
.A=JKHAI
Page 2-2
Onboard PCI Devices
! LAN --> Embedded 10/100Mbps Fast Ethernet controller with
VIA 6105 LAN Chipset
! IDE --> Embedded IDE controller supports 2 IDE ports for up to 4
IDE devices
- Supports ATA-100 with up to 100Mbps bandwidth
Legacy IO Controller
! Winbond W83627HF LPC IO controller with floppy, printer, game,
serial and CIR/SIR interface
Audio
! Six channel audio with analog and digital output using ALC650/655 AC97
CODEC
- AC97 v2.2 compliant
- In 2-CH mode, supports Mic-In (Pink), Line-In (Blue) and Line-Out
(Green) at rear panel
- In 6-CH mode, supports Center/Subwoofer (Pink), Rear out (Blue),
Front out (Green) at rear panel
- Supports CD-In, Aux-In and S/PDIF-In/out interface
- Supports Line-out and Mic-In for front panel
Peripheral Interfaces
! PS/2 keyboard and mouse ports (at rear panel)
! One Parallel (printer) port (at rear panel)
! One RJ45 LAN connector (at rear panel)(Optional)
! Two Serial ports (1 at rear panel)
! One game port (at rear panel)
! One floppy drive interface
! Two IDE interfaces with up to ATA-100 support
! Six USB2.0 ports (2 at rear panel)
! Three Fan connectors
(Optional)
Page 19
.A=JKHAI
Page 2-3
Front Panel Controller
! Supports Reset & Soft-Off switches and KeyLock
! Supports HDD & Power LEDs
! Supports PC speaker
Expansion Slots
! One AGP slots supporting 1.5v 4X AGP cards
- AGP v2.0 compliant
! Five PCI bus sockets with Bus Master support
- PCI v2.2 compliant
Other Features
! Magic Health a H/W monitoring software utility, for voltages, tempera-
tures and fan-speeds sensing
! EZ Boot An easy way let end-user can choose to boot from hard drive,
CD-ROM, floppy,
! Excellent Over clocking capabilities by
- subtle voltage tuning on CPU, Memory, AGP
- subtle frequency tuning on FSB
- Supports complete FSB/Memory and FSB/AGP, PCI Asynchronous
scheme for over-clocking
! Supports AGP card 3.3V Protection
! P80P for system debugging
Form Factor
! 305 x 195 mm ATX size
Page 20

.A=JKHAI
Page 2-4
Page Left Blank
Page 21
Installation
Page 3-1
Section 3
INSTALLATION
Page 22

Installation
Page 3-2
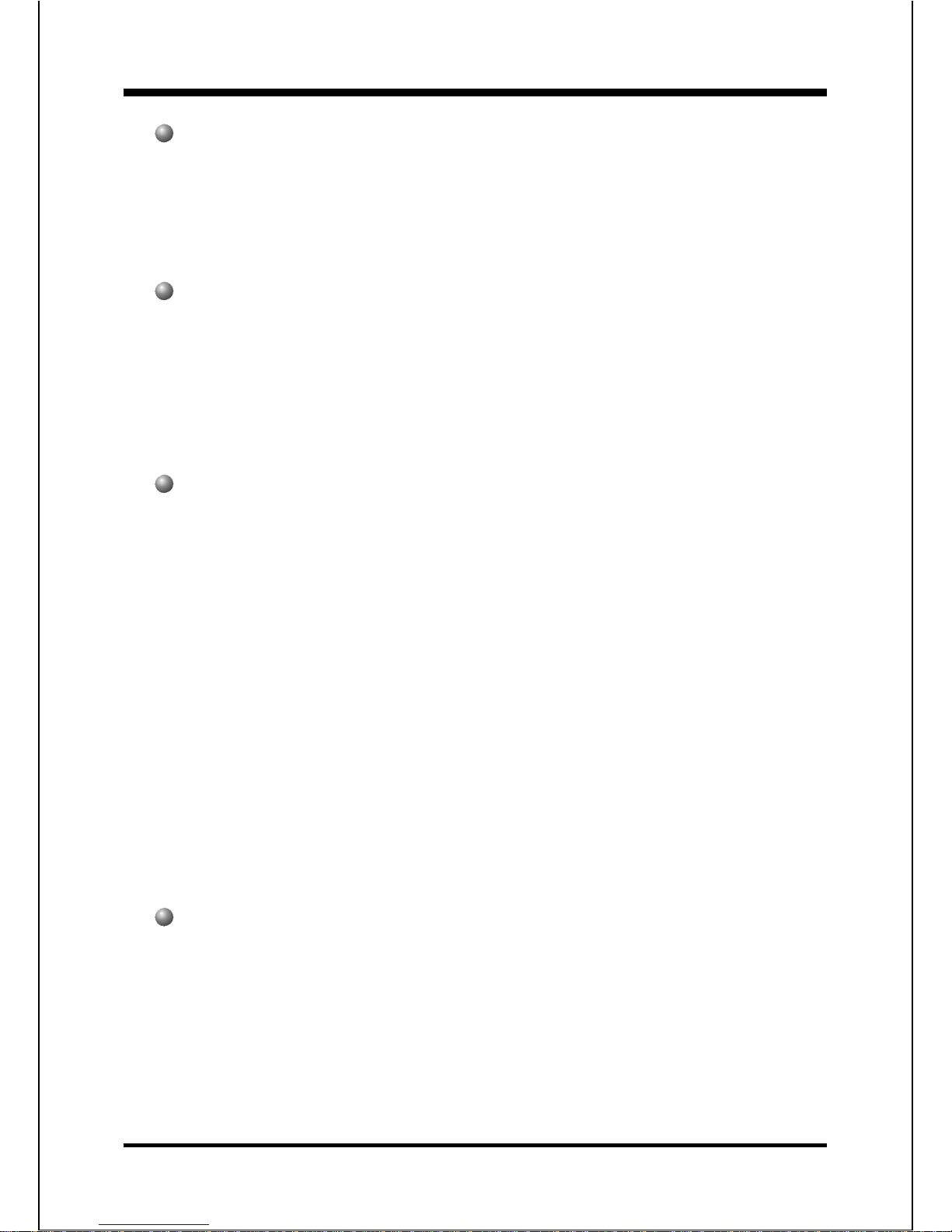
Mainboard Layout
Page 23
Installation
Page 3-3
Step 1
Open the socket by raising the actuation
lever.
Figure 1
Step 2
Align pin 1 on the CPU with pin 1 on
the CPU socket as shown in the
illustration above. The CPU is keyed to
prevent incorrect insertion. Dont
force the processor into the socket. If
it does not go in easily, check for misorientation and reinsert the CPU.
Make sure the processor is fully
inserted into the socket.
Figure 2
Pin 1
Easy Installation Procedure
The following must be completed before powering on your new system:
3-1. CPU Installation
3-2. Jumper Settings
3-3. System Memory Configuration
3-4. Expansion Slots
3-5. Device Connectors
Section 3-1
CPU Installation
Page 24

Installation
Page 3-4
Figure 3
Step 4
Apply thermal compound to the top of
the CPU and install the heatsink as
shown.
Step 5
Install the cooling fan assembly. Press
the two clips in the direction of the
arrows shown in Figure 5 to secure the
assembly to the CPU socket.
Step 6
Plug the CPU fan into the CPU fan connector (FAN1).
The installation is complete.
Figure 4
Figure 5 Figure 6
NOTES:
Damage to Intel Pentium
TM
4 processors might result if installed with
incorrect CPU fan and heatsink assemblies. Use Intels design thermal
solution shown in the illustrations above: an active heatsink; an extruded
aluminum heatsink base; and a fan attached to the top on the fin array.
Apply heatsink thermal compound or paste to the CPU to avoid CPU
overheating and damage.
In accordance with Intel Corp. specifications, do not install a CPU over
50 times to avoid bending the pins and damaging the CPU.
Step 3
Close the socket by lowering and
locking the actuation lever.
Page 25
Installation
Page 3-5
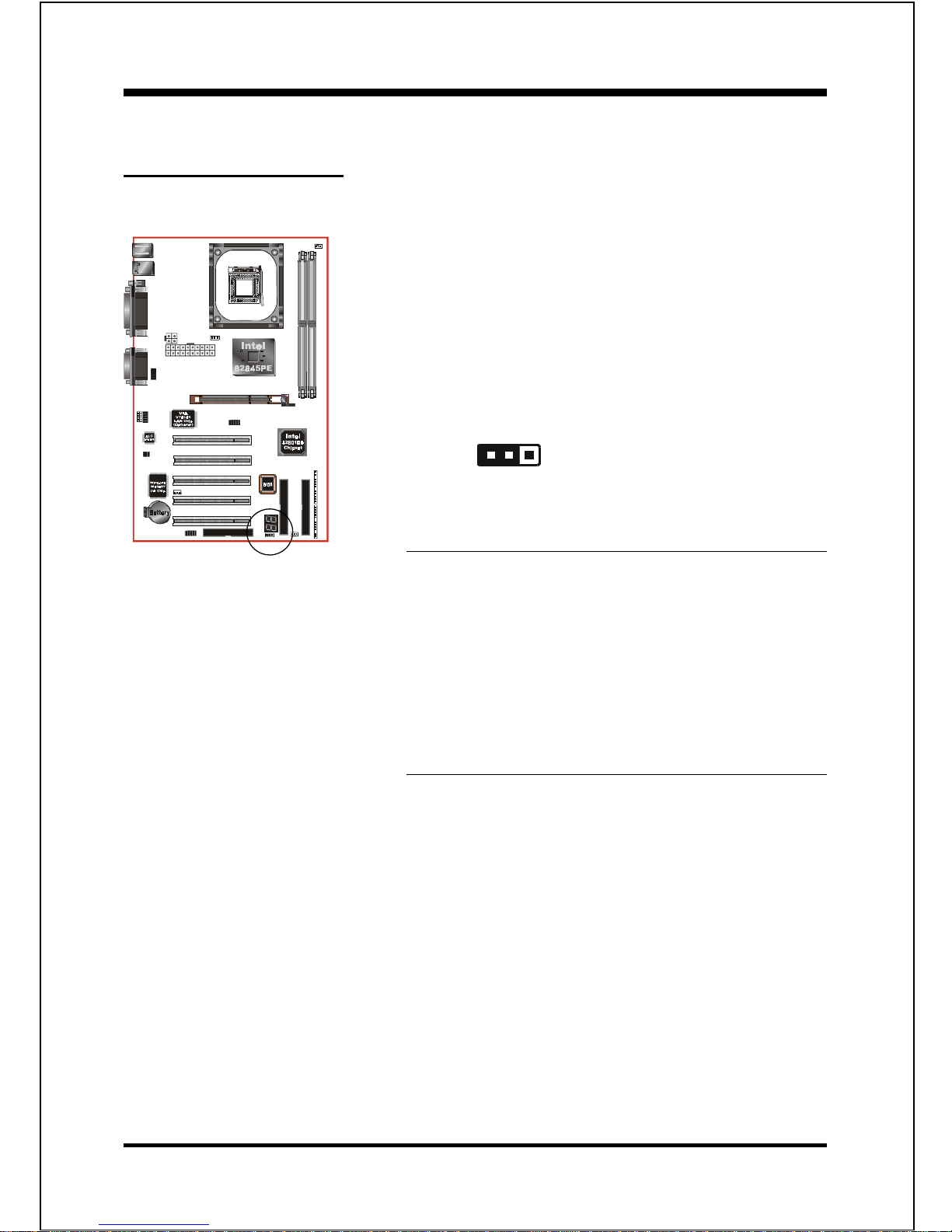
Section 3-2
Jumper Settings
JBAT1
Clear CMOS data Jumper
If the CMOS data becomes corrupted or you
forgot the supervisor or user password,
clear the CMOS data to reconfigure the
system back to the default values stored in
the ROM BIOS.
Settings:
1-2: Normal (Default)
2-3: Clear CMOS
To CMOS Clear data, please follow the steps below.
1. Turn off the system.
2. Change the jumper from 1-2 to 2-3 position
for a few seconds.
3. Replace the jumper on to the 1-2 position.
4. Turn of the system and hold down the <Del>
key to enter BIOS setup.
Page 26
Installation
Page 3-6
Section 3-3
System Memory Configuration
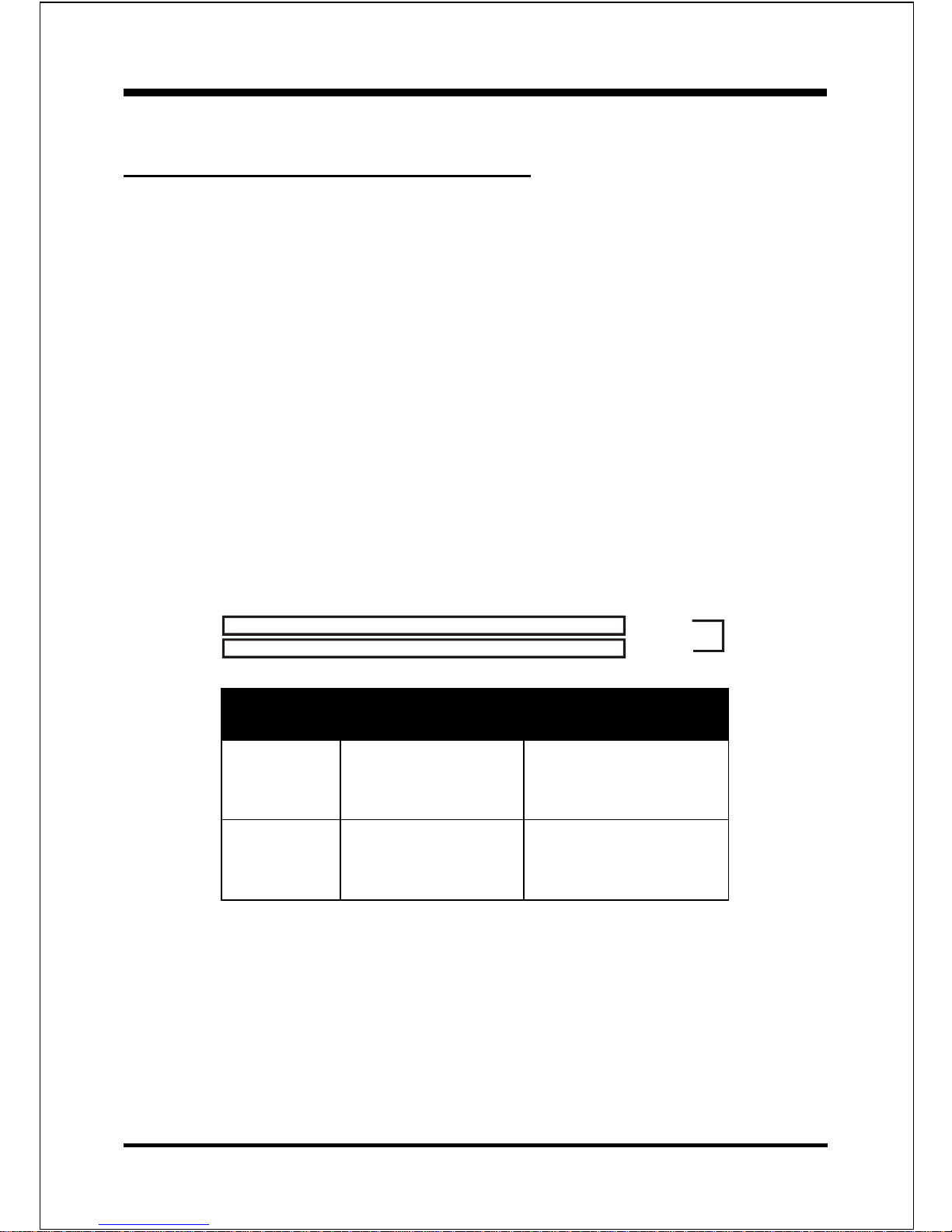
Memor y Layout
The mainboard accommodates two PC1600/2100/2700 184-pin DIMMs (Dual In-line
Memory Modules):
Supports up to 2.0GB of 200/266/333/333+MHz DDR SDRAM.
Supports up to 2 DDR DIMMs (refer to Table 1).
Supports unbuffered non-ECC DIMMs only.
Supports configurations defined in the JEDEC DDR DIMM specification
NOTE:The mainboard does not support double-sided x 16 DDR DIMMs. Use DDR
SDRAM (Double-Data-Rate Synchronous DRAM) modules only.
Figure 7 and Table 1 show several possible memory configurations.
NOTES:
_ Using non-compliant memory with higher bus speeds (overclocking) may
severely compromise the integrity of the system.
<Figure 7>
<Table 1>
* DDR SDRAM supports 64, 128, 256, 512MB and 1GB DIMM modules using
512Mb technology.
DDR DIMM 1
DDR DIMM 2
Bank 0/1
DDR
Synchronous
DRAM
Bank 2/3
yromeMlatoT
1MMIDRDD
)1/0knaB(
2MMIDRDD
)3/2knaB(
BG1=
mumixaM
*MARDSRDD
,BM652,BM821,BM46
1X*BG1,BM215
enoN
BG2=
mumixaM
*MARDSRDD
,BM652,BM821,BM46
1X*BG1,BM215
*MARDSRDD
,BM652,BM821,BM46
1X*BG1,BM215
Page 27
Installation
Page 3-7
DIMM Module Installation
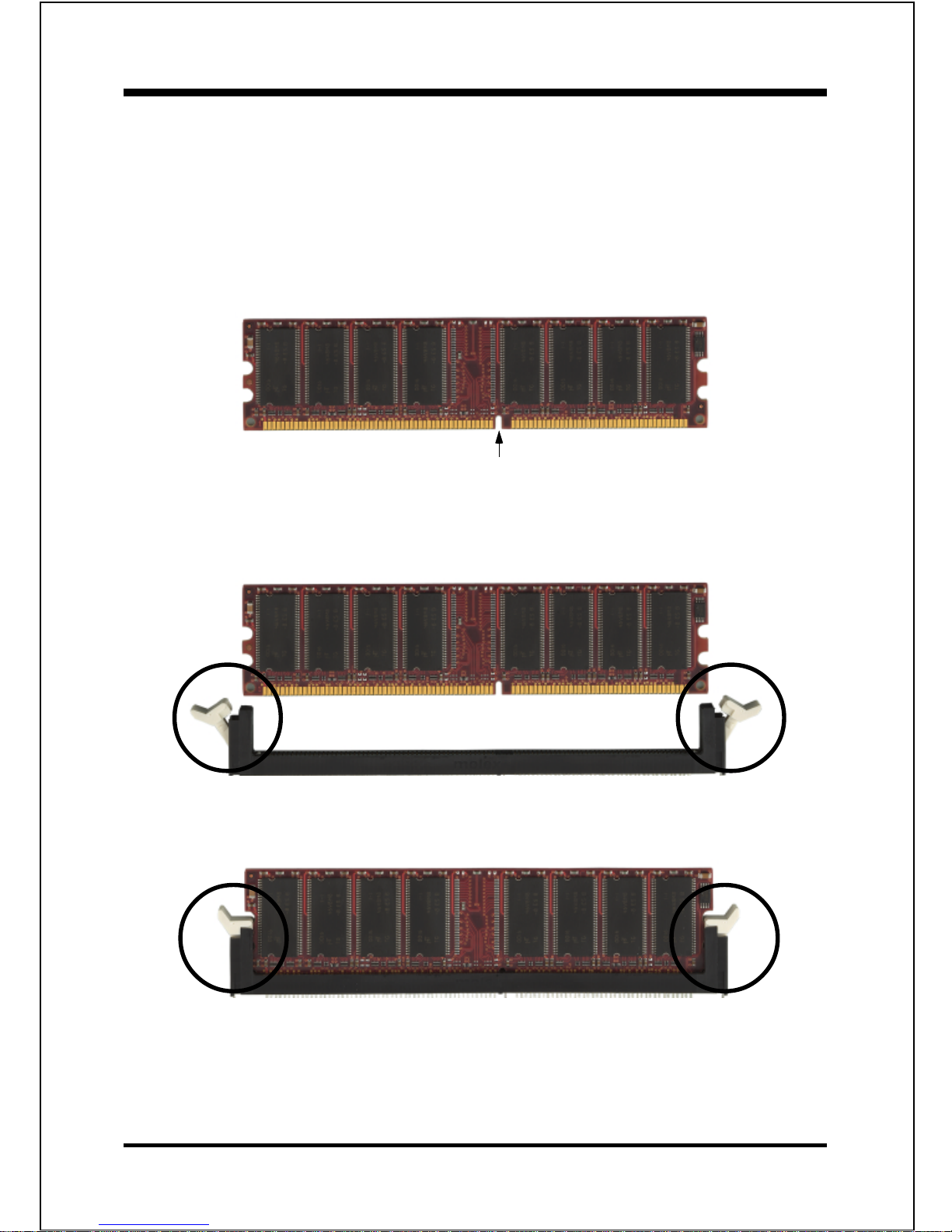
Figure 8 displays the notch on the DDR DIMM memory module.
DIMMs have 184 pins and one notch that matches with the DDR DIMM socket.
DIMM modules are installed by placing the chip firmly into the socket and
pressing straight down as shown in figure 9 until the white clips close and the
module fits tightly into the DIMM socket (figure 10).
Figure 8 - DIMM notch
Figure 10 - DIMM module clip after installation
To remove the DIMM module press down the white clips and the module is
released from the socket.
Figure 9 - DIMM module clips before installation
CENTER KEY ZONE
(2.5 V DRAM)
Page 28
Installation
Page 3-8
3-4 Expansion Slots
Installing an Expansion Card
The steps below assume that the mainboard is already installed in the system chassis.
1. Make sure the PC and all other peripheral devices connected to its has been
powered down.
2. Disconnect all power cords and cables.
3. Remove the system unit cover.
4. Remove the bracket of the slot that you intend to use. (You need to remove the
screw in order to remove the bracket.)
5. Align the card above the slot then press it down firmly until it is completely
seated in the slot.
6. Secure the card to the chassis with the screw you removed in step 4.
7. Replace the system unit cover.
8. Power on the PC.
9. Enter the BIOS step program to make the necessary settings.
10. Save the settings and restart the PC.
11. Install the software drivers of the expansion cards, if necessary.
AGP Slot
The mainboard is equipped with an AGP
slot. Make sure you install a card that
supports the 1.5V specification.
PCI Slots
The mainboard is equipped with 5 PCI
slots. It supports PCI cards that comply
with the PCI specification.
PCI Slots
AGP Slot
Page 29
Installation
Page 3-9
GND
PME
+5V Standby
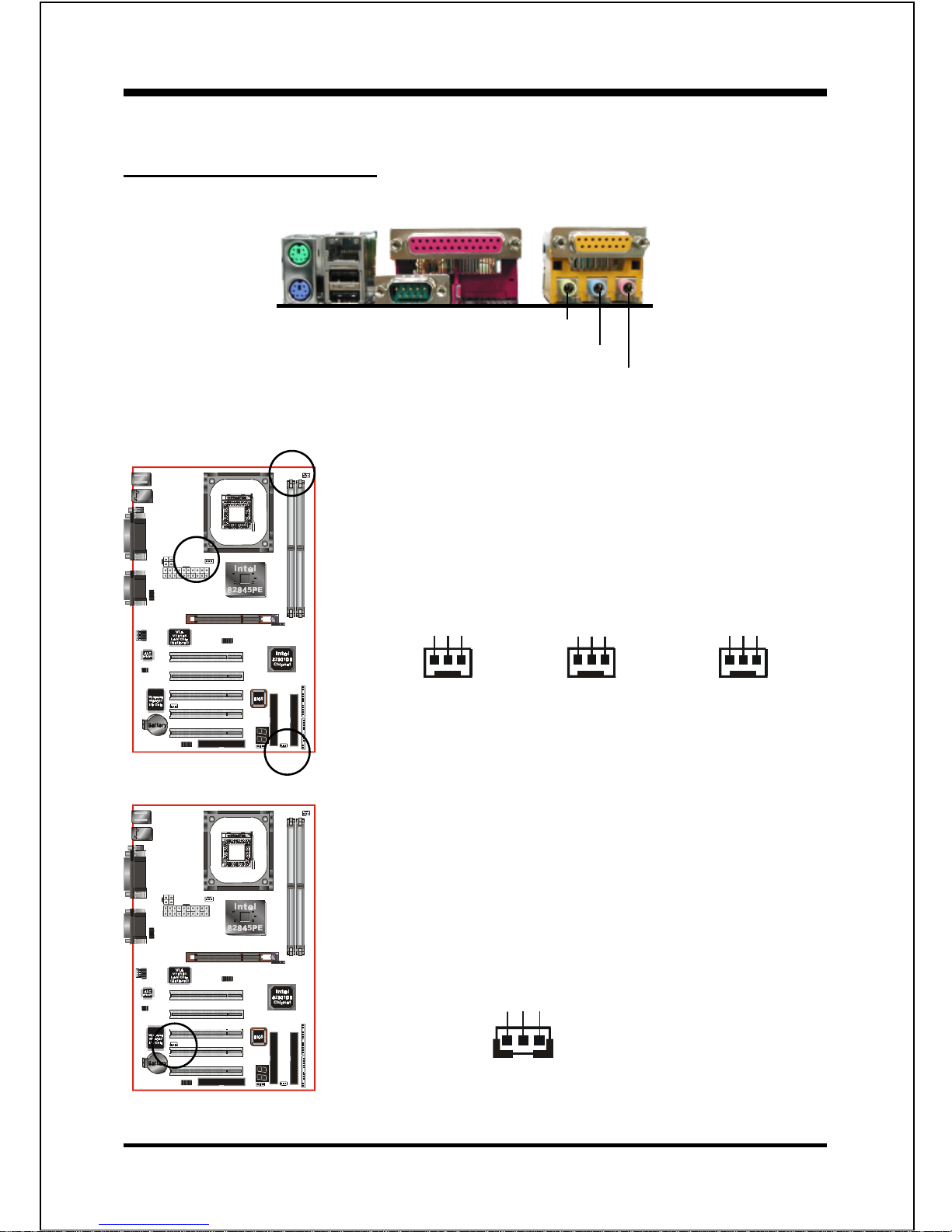
FAN1 / FAN2 / FAN3:
CPU/Power/Chassis Fan Power Connectors
FAN1:
CPU Fan
FAN2:
Power Fan
WOL1:WOL (Wake On LAN) Connector
Reserved for an NIC (Network Interface Card) to wake the system from
power saving mode.
GND
+12V
Rotation
FAN3:
Chassis Fan
GND
+12V
Rotation
GND
+12V
NC
FAN1
FAN3
FAN2
Figure 11 - I/O Ports
Mic-in/Center&Subwoofer
Line-out/Front out
Line-in/Rear out
PS/2 Mouse
PS/2 Keyboard
COM1
Parallel Port
RJ-45 LAN
(Optional)
USB2.0
ports
Joystick/Midi Port
Section 3-5
Device Connectors
Page 30

Installation
Page 3-10
ATX1
ATX2
IDE1/IDE2: Ultra DMA-66/100 Primary/Secondary
IDE Connector (Blue)
This mainboard is equipped with 2 IDE disk connectors for connecting up to 4 ATA-100 IDE drives. It
supports PIO and DMA mode operations for
maximum data transfer rate of 100Mbps per channel.
FLOPPY: Floppy Controller Connector (Black)
This mainboard is equipped with a floppy disk drive
connector for connecting up to 2 floppy disk drives.
40 39
2
1
IDE1/IDE2
34 33
2
1
FLOPPY
!!
!!
! When use two IDE drives, one must be set to Master
mode and the other one to Slave mode. Refer to your
disk drive users manual for information about selecting the proper drive switch settings.
FLOPPY
IDE2IDE1
ATX1: 20-pin ATX Power Connector
ATX2: 4-pin ATX12V Power Connector
The mainboard is equipped with a standard 20-pin
ATX main power connector and a 4-pin +12V
power connector for connecting an ATX12V
power supply. The plugs of the power cables are
designed to fit in only one orientation. Find the
proper orientation then insert the plugs into the
connectors until they fit in place.
Caution:
Be sure that the PW1 and PW12 Power Connector must be used
simultaneously or else boot-up may not be possible.
!!
!!
! The board requires a minimum of 250 Watt power
supply to operate. Your system configuration
(amount of memory, add-in cards, peripherals, etc.)
may exceed the minimum power requirement but to
ensure that adequate power is provided, use a 300
Watt (or greater) power supply.
!
-12V3.3V
Gronud+5V
PS-ON+5V
-5VPW-OK
+5V5VSB
+5V+12V
+12V+12V
"
3.3V3.3V
GronudGronud
GronudGronud
GronudGron ud
GronudGronud
ATX1
ATX2
Page 31

Installation
Page 3-11
CDIN1
AUXIN1
Settings
Pins (5-6) & (9-10) Short (default): Only the Onboard Rear
Audio Speaker can be used.
Pins (5-6) & (9-10) Open: Only Front Panel Audio Speaker
can be used.
FPCN1: Front Panel Audio Connector
When the jumpers are removed and this connector is used for front panel audio. The type
of front panel line-out phone jack is normal
close. Without phone plug inserted, the rear
panel audio is enabled. With phone plug
inserted, the rear panel audio is disabled.
!!
!!
! In 2-Channel audio mode, Mic-In is shared for both front panel and rear panel.
In 6-Channel audio mode, the Mic-In is dedicated for front panel used, and rear
panel Mic-In function will switch to Center and subwoofer support.
CDIN1 / AUXIN1: CD Audio_IN Connector
The CD-IN and AUX-IN connectors are used to
receive audio form a CD-ROM drive, TV tuner or
MPEG card.
CD_IN_Left
1
CD_IN_Right
CD_Reference
AUX_IN_Left
1
AUX_IN_Right
GND
CDIN1
AUXIN1
Page 32

Installation
Page 3-12
SPDIF1: Sony/Philips Digital Interface
This connector is the digital link between
the motherboard and your devices, such
as CD player, sampler or DAT recorder. It
allows the digital transmission of audio
data in SPDIF format.
1
5
2
6
VCC
NC
GND
SPDIF_IN
SPDIF_OUT
USB2/3: USB port header for four USB2.0 ports.
It will help your device more efficient for
the transfer speed up to 480Mbps.
#NIProloceriWemaNlangiStnemmoC
1deRccVrewoPelbaC
2kcalBdnuorGdnuorGesaC
3etihWataD-ataD
4kcalBdnuorGdnuorGelbaC
5neerGataD+ataD
6neerGataD+ataD
7kcalBdnuorGdnuorGelbaC
8etihWataD-ataD
9kcalBdnuorGdnuorGesaC
01deRccVrewoPelbaC
USB port header pin descriptions
VCC
VCC
GND
GND
-Data
-Data
+Data
+Data
'
USB3
USB2
CAUTION !
Please make sure the USB cable has the
same pin assignment. The different pin
assignment may be caused damage of
system.
If you need the USB cable, please contact
our retailer.
Page 33

Installation
Page 3-13
LED1: 80 Port Debug LED
Provides two digits LED light to show why
system boots failed for quick and easy
optimization.
80 Port Debug 7-segment LED display
(Refer to Appendix E for POST codes)
Page 34

Installation
Page 3-14
J3
J2
""
""
" Power On/Off
This is connected to the power button on the
case. Using the Soft-Off by Pwr-BTTN
feature, you can choose either Instant Off
(turns system off immediately), or 4 sec delay
(push the button for 4 seconds before the
system turns off). When the system is in 4
sec delay mode, suspend mode is enabled by
pushing the button momentarily.
""
""
" Turbo LED indicator
""
""
" IDE LED indicator
LED on when onboard PCI IDE Hard disks are
being accessed.
""
""
" IR Connector
1. VCC 4. GND
2. CIRRX 5. IRTX
3. IRRX
""
""
" KeyLock
Keyboard lock switch & power LED connector
1. Power LED(+) 4. KeyLock
2. N/C 5. GND
3. GND
""
""
" Speaker
Connect to the systems speaker for beeping
1. Speaker 3. GND
2. N/C 4. VCC
""
""
" Reset
Closed to restart system.
* The power LED lights when the
system is powered on and blinks
in SLEEP Mode or STR Mode.
Page 35

Installation
Page 3-15
NOTES:
Intel ATX version 2.0 specification recommends you use a power
supply that supplies >=1.0 A in 5.0 VSB. However, this mainboard
supports a 5.0 VSB standby power supply > = 1A .
We recommend you use the power supply with 1.0 A in 5.0 VSB, which
supports PCI 2.2 specification for remote power-on and wake-up
functions.
Section 3-6
Exter nal Modem Ring-in Power ON and
Keyboard Power ON Functions (KBPO)
Modem-Ring Power ON Function
The I/O chipset provides the two serial ports with the External Modem Ring-in
Power ON function. Once you connect an external modem to COM1 or COM2,
the mainboard enables you to turn on the system through remote and host dial-up
control.
Keyboard Power ON Function
The mainboard features a keyboard power on function that enables you to turn on
the power supply using a keypress. Follow these instructions to enable the Keyboard Power ON function .
Step : Use the Keyboard Power ON function (KBPO) to turn on the system by using
a key press, password, or hot key combination etc. as set in the BIOS Power
Management Setup menu (refer to the BIOS Power Management Setup for
details). The BIOS default setting is keyboard Hot key (<Ctrl> + <F1>). To
power off the system, use the soft-OFF function under Windows XP/ME/2000/
98. (refer to Windows online help).
Page 36

Installation
Page 3-16
3-7 STR (Suspend To RAM) Function
This mainboard supports the STR (Suspend To RAM) power management
scheme by maintaining the appropriate power states in the DDR SDRAM
interface signals. The power source to the DDR SDRAM must be kept active
during STR (ACPI S3). Advanced Configuration Power Interface (ACPI)
provides many Energy Saving Features for operating systems that support
Instant ON and QuickStartTM function.
1. Use the STR functionality to save system power, you are recommended to
confirm the following requirements:
a. Install ACPI qualified add-on cards (such as AGP, LAN, and modem cards).
b. In BIOS under Power Management Setup (refer to Section 4), select ACPI
Suspend Type: S3(STR) and USB Wake-Up From S3: Enabled (if you
have a USB mouse or keyboard device).
c. Install Windows® XP/2000/ME/98SE.
d. Restart the system.
e. Open the Control Panel Power Management application, and click the
Advanced tab. In the Power buttons section, select Stand By from the
drop-down lists.
2. To enable the STR function, click the START button and choose Shut Down. In
the Shut Down Windows dialog box, select the Stand By option to enter STR
mode.
The following lists the differences between STR power saving mode and Green
(or Suspend) mode:
a. STR is the most advanced Power Management mode.
b. STR cuts all the power supplied to peripherals except to memory - max.
power saving.
c. STR saves and keeps all on-screen data including any executed applications
to DDR SDRAM.
d. In STR mode, you must push the power button (connected to the onboard J3
pin), click your USB mouse buttons, or press your USB keyboard keys to
wake up your system to the last display.
NOTE: Clicking your PS/2 mouse or pressing a PS/2 keyboard key does not wake the
system from STR mode.
Page 37

Installation
Page 3-17
3-8 Supports AGP Card 3.3V Protection
The Intel® 845PE chipset supports 1.5 volt AGP graphics cards only. Using a 3.3
volt AGP card in an Intel® 845PE chipset-based board might damage the chipset on
an 845PE-equipped mainboard. However, this mainboard features a protection
function that prevents the system from powering on when a 3.3V AGP card is
inadvertently inserted into the AGP slot.
If this happens, we recommend you to follow these steps:
Step 1: Remove the 3.3V AGP card from the AGP slot.
Step 2: Unplug the ATX/ATX12V power cable.
Step 3: Insert a 1.5V AGP card into the AGP slot.
Step 4: Wait for 5 ~ 7 seconds and then plug in the ATX/ATX12V power
cord again (or turn on the ATX/ATX12V power switch) to turn on
your system.
Note: There should be an interval of 5 ~ 7 seconds between
unplugging and plugging in the power cord, or turning
the ATX/ATX12V power supply on and off.
Page 38

Installation
Page 3-18
Page Left Blank
Page 39

BIOS
Page 4-1
Section 4
AWARD BIOS SETUP
Main Menu
Awards ROM BIOS provides a built-in Setup program which allows user to modify
the basic system configuration and hardware parameters. The modified data is
stored in a battery-backed CMOS, so that data will be retained even when the power
is turned off. In general, the information saved in the CMOS RAM will stay unchanged unless there is a configuration change in the system, such as hard drive
replacement or a device is added.
It is possible for the CMOS battery to fail causing CMOS data loss. If this happens
you will need install a new CMOS battery and reconfigure your BIOS settings.
To enter the Setup Program :
Power on the computer and press the <Del> key during the POST (Power On Self
Test). The BIOS CMOS SETUP UTILITY opens. (Figure 1)
Figure 1: CMOS Setup Utility
Page 40

BIOS
Page 4-2
The main menu displays all the major selection items. Select the item you need to
reconfigure. The selection is made by moving the cursor (press any direction (arrow
key ) to the item and pressing the Enter key. An on-line help message is displayed
at the bottom of the screen as the cursor is moved to various items which provides a
better understanding of each function. When a selection is made, the menu of the
selected item will appear so that the user can modify associated configuration
parameters.
4-1 Standard CMOS Setup
Choose STANDARD CMOS FEATURES in the CMOS SETUP UTILITY Menu
(Figure 2). Standard CMOS Features Setup allows the user to configure system
settings such as the current date and time, type of hard disk drive installed, floppy
drive type, and display type. Memory size is auto-detected by the BIOS and
displayed for your reference. When a field is highlighted (use direction keys to move
the cursor and the <Enter> key to select), the entries in the field can be changed by
pressing the <PgDn> or the <PgUp> key.
Figure 2: Standard CMOS Setup
Page 41

BIOS
Page 4-3
Notes:
_ If the hard disk Primary Master/Slave and Secondary Master/Slave are
set to Auto, then the hard disk size and model will be auto-detected.
_ The Halt On: field is used to determine when to halt the system by the
BIOS if an error occurs.
_ Floppy 3 Mode support is a mode used to support a special 3.5-inch
drive used in Japan. This is a 3.5-inch disk that stores 1.2 MB. The
default setting for this is disabled.
4-2 Advanced BIOS Features
Selecting the ADVANCED BIOS FEATURES option in the CMOS SETUP UTILITY
menu allows users to change system related parameters in the displayed menu. This
menu shows all of the manufacturers default values for the board.
Pressing the [F1] key displays a help message for the selected item.
Figure 3: BIOS Features Setup
Page 42

BIOS
Page 4-4
Virus Warning
During and after system boot up, any attempt to write to the boot sector or partition
table of the hard disk drive halts the system and an error message appears.
You should then run an anti-virus program to locate the virus. Keep in mind that this
feature protects only the boot sector, not the entire hard drive. The default is
Disabled.
Enabled: Activates automatically when the system boots up causing a warning
message to appear when anything attempts to access the boot sector.
Disabled: No warning message appears when anything attempts to access the boot
sector.
Note: Many disk diagnostic programs that access the boot sector table can
trigger the virus warning message. If you plan to run such a program, we
recommend that you first disable the virus warning.
CPU L1 & L2 Cache
This controls the status of the processors internal Level One and Level Two cache.
The default is Enabled.
Enabled: This activates the processors internal cache thereby increasing
performance.
Disabled: This deactivates the processors internal cache thereby lowering
performance.
CPU Hyper-Threading
Enables the CPU Hyper-Threading Technology.
Options: Enables, Disabled.
Note: Recommends enabling Hyper-Threading Technology on system with
Windows XP and Linux 2.4 and disabling for legacy OS.
Quick Power On Self Test
This category speeds up the Power On Self Test (POST). The default is Enabled.
Enabled: This setting will shorten or skip of the items checked during POST.
Disabled: Normal POST.
APIC Mode
This item allows you to enable APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller)
functionality. APIC is an Intel chip that provides symmetric multiprocessing (SMP)
for its Pentium systems.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
Page 43

BIOS
Page 4-5
HDD S.M.A.R.T. Capability
The S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) system is a
diagnostics technology that monitors and predicts device performance. S.M.A.R.T.
Software resides on both the disk drive and the host computer.
The disk drive software monitors the internal performance of the motors, media, heads,
and electronics of the drive. The host software monitors the overall reliability status of
the drive. If a device failure is predicted, the host software, through the Client WORKS
S.M.A.R.T applet, warns the user of the impending condition and advises appropriate
action to protect the data. The default is Disabled.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
Boot Up NumLock Status
This controls the state of the NumLock key when the system boots. The default is On.
On: The keypad acts as a 10-key pad.
Off: The keypad acts like cursor keys.
Gate A20 Option
This refers to the way the system addresses memory above 1 MB (extended
memory). The default is Normal.
Normal: The A20 signal is controlled by the keyboard controller or chipset
hardware.
Fast: The A20 signal is controlled by Port 92 or chipset specific method.
Typematic Rate Setting
This determines the keystrokes repeat rate. The default is Disabled.
Enabled: Allows typematic rate and typematic delay programming.
Disabled: The typematic rate and typematic delay will be controlled by the keyboard
controller in your system.
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec)
This is the number of characters that will be repeated by a keyboard press. The
default is 6.
Options: 6 ~ 30 characters per second.
Typematic Delay (msec)
This setting controls the time between the first and the second character displayed
by typematic auto-repeat. The default is 250.
Options: 250/500/750/1000 msec.
Page 44

BIOS
Page 4-6
Security Option
This category allows you to limit access to the System and Setup, or just to Setup.
The default is Setup.
System: The system will not boot and access to Setup will be denied unless the
correct password is entered at the prompt.
Setup: The system will boot, but access to Setup will be denied unless the
correct password is entered at the prompt.
OS Select For DRAM > 64 MB
Some operating systems require special handling. Use this option only if your
system has greater than 64 MB of memory. The default is Non-OS2.
OS2: Select this if you are running the OS/2 operating system with greater
than 64 MB of RAM.
Non-OS2: Select this for all other operating systems and configurations.
Boot Seq & Floppy Setup
Scroll to Boot Seq & Floppy Setup and press <Enter>. The following screen
appears:
First /Second/Third/Other Boot Device
The BIOS attempts to load the operating system from the devices in the sequence
selected in these items.
Options: Floppy, LS120, HDD-0, SCSI, CDROM, HDD-1, HDD-2, HDD-3, ZIP100,
USB-FDD, USB-ZIP, USB-CDROM, USB-HDD, LAN, Disabled.
Boot Other Device
When enabled, the system searches all other possible locations for an operating
system if it fails to find one in the devices specified under the first, second, and
third boot devices. The default is Enabled.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
Page 45

BIOS
Page 4-7
Swap Floppy Drive
This will swap your physical drive letters A & B if you are using two floppy disks.
The default is Disabled.
Enabled:Floppy A & B will be swapped under the O/S.
Disabled: Floppy A & B will be not swapped.
Boot Up Floppy Seek
If this item is enabled, it checks the size of the floppy disk drives at start-up time.
You dont need to enable this item unless you have a legacy diskette drive with
360K capacity. The default is Disabled.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
Report No FDD For Win 95
If you are running a system with no floppy drive under Windows 95, select Yes for
this item to ensure compatibility with the Windows 95 logo certification.
Otherwise, select No.
Ye s: The system has no floppy drive when you are using Windows 95.
No: The system has an operating system other than Windows 95.
Page 46

BIOS
Page 4-8
4-3 Advanced Chipset Features
Choose the ADVANCED CHIPSET FEATURES option in the CMOS SETUP
UTILITY menu to display following menu.
Figure 4: Chipset Features Setup
DRAM Timing Selectable
For setting DRAM Timing, By SPD is follow Intel PC DDR SDRAM Serial Presence
Detect Specification.
Options: Manual, By SPD.
CAS Latency Time
Enables you to select the CAS latency time. The value is set at the factory depending
on the DRAM installed. Do not change the values in this field unless you change
specifications of the installed DRAM and DRAM clock from DRAM Timing Selectable.
The default is by DRAM SPD.
Options: 1.5, 2, and 2.5.
Active to Precharge Delay
This item specifies the number of clock cycles needed after a bank active command
before a precharge can occur (sets the minimum RAS pulse width.). The default is by
DRAM SPD.
Options: 5, 6, 7.
Page 47

BIOS
Page 4-9
DRAM RAS# to CAS# Delay
This item sets the timing parameters for the system memory such as the CAS (Column
Address Strobe) and RAS (Row Address Strobe). The default is by DRAM SPD.
Options: 2, 3.
DRAM RAS# Precharge
This item refers to the number of cycles required to return data to its original
location to close the bank or the number of cycles required to page memory before
the next bank activate command can be issued. The default is by DRAM SPD.
Options: 2, 3.
System BIOS Cacheable
This item allows the system to be cached in memory for faster execution.
Options: Disabled, Enabled.
Video BIOS Cacheable
This item allows the video to be cached in memory for faster execution.
Options: Disabled, Enabled.
Delayed Transaction
The mainboards chipset has an embedded 32-bit post write buffer to support delay
transactions cycles. Select Enabled to support compliance with PCI specification
version 2.2. The default is Enabled.
Options: Disabled, Enabled.
Command Per Clock
Enabling this item improves performance. The default is Auto.
Options: Auto, Enabled, Disabled.
Fast CS#
When set to Enabled and SDRAM is idle, CS# is asserted in the same time the
SDRAM tracking transitions to active state. The fast CS# timing is also applicable
for pipelined assertion that follows page hit cycle.
Auto: This selection will Auto detect.
Disabled: Normal CS# mode (CS# active two clocks after internal SDRAM-start
indication)
Enabled: Fast CS# mode (CS# active one clocks after internal SDRAM-start
indication)
Page 48

BIOS
Page 4-10
Delay Prior to Thermal
Set this item to enable the CPU Thermal function to engage after the specified time.
The default is 16 minutes.
Options: 4, 8, 16, 32 minutes.
AGP Aperture Size (MB)
This item defines the size of the aperture if you use an AGP graphics adapter. It
refers to a section of the PCI memory address range used for graphics memory.
Options: 32, 64, 128, 256 MB.
4-4 Integrated Peripherals
Figure 5: Integrated Peripherals
Notes:
If you do not use the Onboard IDE connector, then you will need to set that
Onboard Primary PCI IDE: Disabled and Onboard Secondary PCI IDE: Disabled
The Onboard PCI IDE cable should be equal to or less than 18 inches (45 cm.).
Init Display First
If two video cards are used (1 AGP and 1 PCI) this specifies which one will be the
primary display adapter. The default is PCI Slot.
Options: PCI Slot, AGP.
Page 49

BIOS
Page 4-11
VIA6105 Lan Boot ROM (Optional)
Enables and disables the onboard LAN Boot ROM. The default is Disabled.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
Onboard IDE Device Setup
Scroll to Onboard IDE Device Setup and press <Enter>. The following screen appears:
On-Chip Primary PCI IDE
The integrated peripheral controller contains an IDE interface with support for two
IDE channels. Select Enabled (default) to activate each channel separately.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave PIO
The four IDE PIO (Programmed Input/Output) fields let you set a PIO mode (0-4)
for each of the four IDE devices that the onboard IDE interface supports. From
Modes 0 to 4 provide successively increased performance. In Auto mode, the
system automatically determines the best mode for each device. The default is
Auto.
Options: Auto, Mode 0 ~ 4.
IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave UDMA
This allows you to select the mode of operation for the Ultra DMA-33/66/100
implementation is possible only if your IDE hard drive supports it and the operating environment includes a DMA driver (Windows 95 OSR2 or a third-party IDE
bus master driver). If your hard drive and your system software both support Ultra
DMA-33/66/100, select Auto to enable UDMA mode by BIOS or you can select
mode by manual.
Options: Auto, Disabled.
Page 50

BIOS
Page 4-12
IDE HDD Block Mode
IDE Block Mode allows the controller to access blocks of sectors rather than a
single sector at a time. The default is Enabled.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
Onboard PCI Device Setup
Scroll to Onboard PCI Device Setup and press <Enter>. The following screen appears:
USB Controller
Enables the all USB controller.
Options: Disabled, Enabled.
USB 2.0 Controller
Enables the EHCI (USB2.0) controller.
Options: Disabled, Enabled.
USB Keyboard Support
Your system contains a Universal Serial Bus (USB) controller and you have a USB
keyboard. The default is Auto detect.
Options: Auto, Enabled, Disabled.
USB Mouse Support
Your system contains a Universal Serial Bus (USB) controller and you have a USB
Mouse . The default is Disabled.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
AC97 Audio
This item allows you to decide to auto or disable the chipset family to support
AC97 Audio. The function setting AC97 Audio Codec states. The system default
is Auto.
Options: Auto, Disabled.
Page 51

BIOS
Page 4-13
Game Port Address
Select an address for the Game port.
Options: 201 (default), 209, Disabled.
Midi Port Address
Select an address for the Midi port.
Options: 290, 300, 330, Disabled (default).
Midi Port IRQ
Select an interrupt for the Midi port.
Options: 5, 10 (default).
Onboard LAN Device (Optional)
Enables the onboard LAN feature.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
Onboard I/O Chip Setup
Scroll to Onboard I/O Chip Setup and press <Enter>. The following screen appears:
Onboard FDC Controller
Select Enabled if your system has a floppy disk controller (FDC) installed on the
system board and you wish to use it. If you install add-in FDC or the system has
no floppy drive, select Disabled in this field.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
Onboard Serial Port 1/2
Select an address and corresponding interrupt for the first and second serial ports.
Options: 3F8/IRQ4, 2E8/IRQ3, 3E8/IRQ4, 2F8/IRQ3, Disabled, Auto.
Page 52

BIOS
Page 4-14
UART Mode Select
This filed allows the users to configure what IR mode the 2nd serial port should
use. The default is Normal.
Options: Normal, IrDA and ASKIR.
RxD, TxD Active
This field configures the receive and transmit signals generated from the IR port.
The default is Hi Lo (when UART Mode Select is not set to Normal).
Options: Hi Hi, Hi Lo, Lo Hi, and Lo Lo.
IR Transmission delay
This item allows you to enabled/disable IR transmission delay.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
UR2 Duplex Mode
This item allows you to select IR half/full duplex function.
Options: Half, Full.
Use IR Pins
This item allows you to select IR transmission routes, one is RxD2, TxD2 (COM
Port) and the other is IR-Rx2Tx2.
Options: IR-Rx2Tx2, RxD2, TxD2.
Onboard Parallel Port
This field allows the user to configure the LPT port.
Options: 378/IRQ7, 278/IRQ5, 3BC/IRQ7, Disabled.
Parallel Port Mode
This field allows the user to select the parallel port mode.
Options: SPP, EPP, ECP, ECP+EPP.
EPP Mode Select
This item allows you to determine the IR transfer mode of onboard I/O chip.
Options: EPP1.9, EPP1.7.
ECP Mode USE DMA
This field allows the user to select DMA1 or DMA3 for the ECP mode.
Options: DMA1, DMA3.
Page 53

BIOS
Page 4-15
4-5 Power Management Setup
Choose the POWER MANAGEMENT SETUP in the CMOS SETUP UTILITY to
display the following screen. This menu allows the user to modify the power
management parameters and IRQ signals. In general, these parameters should not be
changed unless its absolutely necessary.
Figure 6: Power Management
ACPI Suspend Type
This item allows you to select S1(POS) or S3(STR) function. When set to S3(STR)
or S1&S3 the following two fields become available.
Options: S1(POS), S3(STR), S1&S3.
Run VGABIOS if S3 Resume
This determines whether or not to enable the system to run the VGA BIOS when
resuming from S3(STR) or S1&S3.
Options: Auto, Yes, No.
Page 54

BIOS
Page 4-16
S3 KB Wake-up Function
This determines whether or not to enable keyboard/mouse activity to awaken the
system from S3(STR) or S1&S3.
Options: AnyKey or Mouse, By PowerOn Func., AnyKey, Mouse.
POWER ON Function
Enables computer power on by keyboard, mouse, or hotkey activity. The default is
Hot KEY.
Password: Requires you to enter a password when using the keyboard
to power on. Set the password in the next field KB Power ON
Password.
Hot KEY: Enables you to use a hot key combination to power on the
computer. Set the hot key combination in the Hot Key Power
ON field.
Any KEY: Enables you to set any keyboard activity to power on the
computer.
BUTTON ONLY: Requires you to push the computer power button to power on
the system.
Keyboard 98: Enables you to set the Windows 98 key to power on the system.
Keyboard Power ON Password
Press Enter to create a password that is required when you use the keyboard to
power on the system. You must set the POWER ON Function to Password to be
prompted for a password at power on.
Hot Key Power ON
Enables you to set a hot key combination to be used for powering on the system.
The default is Ctrl-F1.
Options: Ctrl-F1 ~ Ctrl F12.
PWRON After PWR-Fail
This item enables your computer to automatically restart or return to its last operating status after power returns from a power failure.
Off: The system stays off after a power failure.
Former-Sts: The system returns to the state it was in just prior to the power
failure.
Page 55

BIOS
Page 4-17
Power Management
Use this to select your Power Management selection. The default is User define.
Max. saving: Maximum power savings. Inactivity period is 1 minute in each mode.
Min. saving: Minimum power savings. Inactivity period is 1 hour in each mode.
User define: Allows user to define PM Timers parameters to control power saving
mode.
Video Off Method
This option allows you to select how the video will be disabled by the power
management. The default is V/H Sync + Blank
V/H Sync + Blank: System turns off vertical and horizontal synchronization ports
and writes blanks to the video buffer.
DPMS Support: Select this option if your monitor supports the Display Power
Management Signaling (DPMS) standard of the Video
Electronics Standards Association (VESA). Use the software
supplied for your video subsystem to select video power
management values.
Blank Screen: System only writes blanks to the video buffer.
Video Off In Suspend
Lets you enable the video to power off in suspend mode.
No: Video power off not controlled by power management.
Ye s: Video powers off after time shown in suspend mode setting.
Suspend Type
Determines CPU status during power saving mode.
Stop Grant: CPU goes into idle mode during power saving mode.
PwrOn suspend: CPU and system remain powered on in suspend mode.
MODEM Use IRQ
Name the interrupt request (IRQ) line assigned to the modem (if any) on your
system. Activity of the selected IRQ always awakens the system. Default is IRQ 3.
Options: N/A, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11
Suspend Mode
enabled and after the set time of system inactivity, all devices except the CPU will be
shut off.
Options: Disabled, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 20, 30, 40 Min and 1 Hour.
Page 56

BIOS
Page 4-18
HDD Power Down
When enabled and after the set time of system inactivity, the hard disk drive will be
powered down while all other devices remain active.
Options: Disabled, 1 ~ 15 Min.
Soft-Off by PWRBTN
Use this to select your soft-off function. The default is Instant Off.
Instant Off: Turns off the system instantly.
Delay 4 Second : Turns off the system after a 4 second delay. If momentary press
of button, the system will go into Suspend Mode. Press the
power button again to make system back to work.
CPU THRM-Throttling
This item sets the percentage of time that the CPU is idled if CPU throttling is
initiated by excess heat. The default setting is 50%.
Options: 12.5%, 25.0%, 37.5%, 50.0%, 62.5%, 75.0%, 87.5%.
PowerOn by PCI Card
An input signal form PME on the PCI card awakens the system from a soft off state.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
Power On by Ring or WOL
When enabled, any modem or LAN activity awakens the system from power savings
mode.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
USB Wake-Up From S3
When enabled, any USB activity awakens the system from power savings mode.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
RTC Alarm Resume
When enabled, you can set the date and time in the following two fields. Any event
occurring at the specified date or time awakens the system from power savings
mode.
Page 57

BIOS
Page 4-19
** Reload Global Timer Events **
Primary/Secondary IDE 0/1
Any activity occuring on these channels awakens the system from power savings
mode.
FDD, COM, LPT Port
When enabled, any event occurring on these ports awakens the system from power
savings mode.
PCI PIRQ[A-D]#
When enabled, any event occurring on these PCI slots awakens the system from
power savings mode.
Page 58

BIOS
Page 4-20
4-6 PNP/PCI Configuration
The PNP/PCI configuration program is for the user to modify the PCI/ISA IRQ
signals when various PCI/ISA cards are inserted in the PCI or ISA slots.
WARNING: Conflicting IRQs may cause the system to not find certain devices.
Figure 7: PNP/PCI Configuration Setup
Resources Controlled By
Determines what controls system PNP/PCI resources. The default is Auto (ESCD).
Manual: PNP Cards resources are controlled manually. The IRQ Resources field
becomes available and you can set which IRQ-X and DMA-X are
assigned to PCI/ISA PNP or Legacy ISA Cards.
Auto: If your ISA card and PCI cards are all PNP cards, BIOS assigns the
interrupt resource automatically.
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop
This item is designed to overcome problems that can be caused by some nonstandard
VGA cards. This board includes a built-in VGA system that does not require palette
snooping so you must leave this item disabled.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
Page 59

BIOS
Page 4-21
PCI Latency Timer (CLK)
The latency timer defines the minimum amount of time, in PCI clock cycles, that the
bus master can retain the ownership of the bus.
Options: 0-255.
AGP SLOT/ AC97/IPCI Slot 1 ~ Slot 5/Onboard LAN NT Assignment
This setting enables the user to specify what IRQ will be assigned to the AGP/
AC97/PCI Slot 1 ~ PCI Slot 5/Onboard LAN devices in the chosen slot.
Options: Auto, 3, 4, 5, 7,9 ,10, 11, 12, 14 & 15. The default is Auto.
Interrupt requests are shared as shown below:
IMPORTANT!
If using PCI cards on shared slots, make sure that the drivers support Shared IRQ
or that the cards dont need IRQ assignments. Conflicts will arise between the two
PCI groups that will make the system unstable or cards inoperable.
ATNIBTNICTNIDTNIETNIFTNIGTNIHTNI
tolSPGA
V
79CM/79CA
V
1tolS
V
2tolS
V
tolS3
V
tolS4
V
tolS5
V
)lanoitpO(NALdraobnO
V
1BSUdraobnO
V
2BSUdraobnO
V
3BSUdraobnO
V
0.2BSU
V
SUBMS
V
Page 60

BIOS
Page 4-22
4-7 PC Health Status
Figure 8: PC Health Status
Show PC Health in POST
When this function is enabled the PC Health information is displayed during the
POST (Power On Self Test).
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
CPU Warning Temperature
Sets the temperature at the time which the computer will respond to an overheating
CPU. The default is Disabled.
Options: Disabled, 50OC/122OF ~ 70OC/158OF.
Current CPU Temperature
Displays the current CPU temperature.
Current System Temperature
Displays the current system temperature.
Current CPU/Chassis/Power FAN Speed
Displays the current speed of the CPU, chassis, and power fan speed in RPMs.
Vagp (V)
The voltage level of Power supplied to AGP card.
33oC/91oF
59
o
C/138oF
0 RPM
1.50V
1.75V
2.50V
4.97V
12.12V
-12.28V
-5.09V
0 RPM
3.48V
4.89V
0 RPM
Page 61

BIOS
Page 4-23
Vcore (V)
The voltage level of the CPU(Vcore).
Vdimm(V)
The voltage level of the DRAM.
± 5V, ± 12V, VBAT(V), 5VSB(V)
The voltage level of the switching power supply.
ACPI Shutdown Temperature
This is the temperature that the computer will turn off the power to combat the
effects of an overheating system. (requires ACPI to be enabled in Power Management BIOS and ACPI compliant operating system.) The default is Disabled.
Options available are 60oC/140oF to 95oC/203oF in increments of 5oC.
Page 62

BIOS
Page 4-24
4-8 Frequency/Voltage Contr ol
Figure 9: Frequency/Voltage Control
CPU Clock Ratio
Use this item to select a multiplier for the system front side bus (FSB) frequency.
The value of the multiplier must be set so that:
Multiplier x Front side Bus Frequency = CPU Clock Speed
For example, if you have a processor that is rated to run at 800 MHz and the
system is running a front side bus frequency of 100 MHz, you should select a
multiplier of 8 so that:
8 (Multiplier) x 100 MHz (front side bus) = 800 MHz (CPU clock)
Key in the DEC (decimalism) number for the CPU Clock Ratio.
1.75V
1.75V
2.50V
[8X]
2.50V
1.50V
66
33
1.50V
Page 63

BIOS
Page 4-25
Watching-Dog Function
If you select enabled and overclock fail before POST code 26h, the system will reset
automatically by default configuration.
Options: Enabled, Disabled.
CPU FSB/SPEED
Enables you to set the CPU front side bus speed. The default is 100 MHz. Enables
you to adjust CPU clock 1MHz by step. Pressing Enter displays the following
screen:
Key in the DEC (decimalism) number for the CPU FSB/SPEED.
Note: Overclocking failure will cause system No display problem. At this
moment, please press Insert key to back to the initial or default
setting to boot up your system.
Memory Frequency
Enables you to select a ratio of the Double Data Rate Synchronous DRAM to match
the installed DRAM frequency 200/266/333/333+MHz. We recommend that you
leave this item at the default value.
When the FSB is 400MHz the options will display 1:1 =>DDR200, 3:4 =>DDR266, 4:5=>
DDR250, Auto =>DDR266.
When the FSB is 533MHz the options will display 1:1 =>DDR266, 3:4=>DDR354, 4:5 =>
DDR333, Auto =>DDR266.
When the FSB is 800MHz the options will display 1:1=>DDR400. (Use DDR400
memory to obtain the best CPU performance)
Page 64

BIOS
Page 4-26
AGP/PCI Clock
Enables you to set the host clock to work concurrently with the PCI bus or the AGP
bus. The default is AUTO.
AUTO: The system sets the item automatically.
AGP-FSB*2/3 PCI-FSB/3: The system sets the host clock to work with the PCI
and AGP bus.
By subtle tuning item: The system sets the host clock according to the
number produced by the subtle tuning item.
AGP/PCI subtle tuning
Enables you to set the AGP/PCI frequency, enables you to subtle tuning AGP clock
1MHz by step. The default is 66 MHz. Pressing Enter displays the following screen:
Key in the DEC (decimalism) number for the AGP/PCI subtle tuning.
In the following items, Default Voltage indicates the original factory value,
and New Voltage indicates the value that you assign.
CPU Vcore Voltage
This item allows you to set the CPU Vcore voltage. The default is -0.075V.
Options: -0.100V to +0.350V in 0.025V increments. We recommend that you leave this
at the default value.
AGP Voltage
This item allows you to set the AGP slot voltage. The default is +0.00V.
Options: +0.00V to +0.70V in 0.10V increments. We recommend that you leave this at
the default value.
Page 65

BIOS
Page 4-27
DIMM Voltage
This item allows you to set the DIMM slot voltage. The default is +0.00V.
Options: +0.00V to +0.70V in 0.10V increments. We recommend that you leave this at
the default value.
Clock Generation for EMI
Scroll to Clock Generation for EMI and press <Enter>. The following screen
appears:
Auto Detect PCI Clk
When enabled the mainboard automatically disables the clock source for a PCI
slot which does not have a module in it, reducing EMI (ElectroMagnetic
Interference). The default is Enabled.
Spread Spectrum Modulated
If you enable spread spectrum, it can significantly reduce the EMI
(ElectroMagnetic Interference) generated by the system.
Page 66

BIOS
Page 4-28
4-9 Defaults Menu
Selecting Defaults from the main menu shows you two options which are described below
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
When you press <Enter> on this item you get a confirmation dialog box:
Load Fail-Safe Defaults (Y/N) ? N
Pressing Y loads the BIOS default values for the most stable, minimal-performance
system operations.
Load Optimized Defaults
When you press <Enter> on this item you get a confirmation dialog box:
Load Optimized Defaults (Y/N) ? N
Pressing Y loads the default values that are factory settings for optimal performance system operations.
Page 67

BIOS
Page 4-29
4-10 Super visor/User Password Setting
These items are used to install a password. A Supervisor password takes precedence over a User password, and the Supervisor limits the activities of a User.
You can set either a supervisor or user password, or both of them:
Supervisor password: authorized to enter and change the options of the setup
menus.
User password: authorized to enter, but not authorized to change the
options of the setup menus.
When you select Set User/Supervisor Password, the following message appears
prompting you to type a password:
ENTER PASSWORD:
Type the password, up to eight characters in length, and press <Enter>. The password
typed now clears any previously entered password from CMOS memory. You will be
prompted to confirm the password. Type the password and press <Enter>. You may
also press <Esc> to abort the selection and not enter a password.
To disable a password, press <Enter> when you are prompted to enter the password.
A message will confirm the password is disabled:
PASSWORD DISABLED.
Once the password is disabled, the system will boot and you can enter Setup freely.
When a password has been enabled, you will be prompted to enter it every time you
try to enter Setup. This prevents an unauthorized person from changing any part of
your system configuration.
Additionally, when a password is enabled, you can also require the BIOS to request
a password every time your system is rebooted. This prevents unauthorized use of
your computer.
You determine when the password is required within the BIOS Features Setup menu
Security option. If the Security option is set to System, the password will be
required both at boot and at entry to Setup. If set to Setup, prompting only
occurs when trying to enter Setup.
Page 68

BIOS
Page 4-30
4-11 Exiting BIOS
Save & Exit Setup
Pressing <Enter> on this item asks for confirmation:
Save to CMOS and EXIT (Y/N)? Y
Pressing Y stores the selections made in the menus in CMOS a special section
of memory that stays on after you turn your system off. The next time you boot
your computer, the BIOS configures your system according to the Setup selections
stored in CMOS. After saving the values the system is restarted again.
Exit Without Saving
Pressing <Enter> on this item asks for confirmation:
Quit without saving (Y/N)? Y
This allows you to exit Setup without storing in CMOS any change. The previous
selections remain in effect. This exits the Setup utility and restarts your computer.
Page 69

Drivers Installation
Page 5-1
Section 5
Driver Installation
Easy Driver Installation
Insert the bundled CD-disk, the main menu screen will appear. The main menu
displays buttons that link you to the supported drivers, utilities and software.
Step 1 : Click INTEL CHIPSET INF FILES to install all components
recommended.
Step 2 : Click REALTEK AC97 SYSTEM SOFTWARE to install audio
driver.
Step 3 : Click VIA 6105 LAN DRIVER to install LAN driver. (Optional)
Step 4 : Click USB V2.0 DRIVER (README.HTM) for installation intro-
duction to install USB V2.0 driver.
ACROBAT READER
CD EXPLORER EXIT
INTEL 845G/845GL/845GE/845PE CHIPSET DRIVER
INTEL CHIPSET INF FILES
REALTEK AC97 SYSTEM SOFTWARE
VIA 6105 LAN DRIVER
USB V2.0 DRIVER (README.HTM)
(Optional)
OTHER
Page 70

Drivers Installation
Page 5-2
ALC650/655 Configuration Setup (6 Channel)
! To enable ALC650/655 Function
Sound Effect:
1. Right-click Sound Effect button in the tool bar display currently selected
Titles. Select Sound Manager.
2. Click Sound Effect button and select Environment from the drop-down
menu.
<Figure 2>
<Figure 1>
Page 71

Drivers Installation
Page 5-3
Equalizer:
Speak
Configutation:
<Figure 3>
3. Click Equalizer and setup the value of dB.
<Figure 4>
4. Click Line in and Mic in buttons to enable 6 channel function as this is
required for the ALC650/655.
Page 72

Drivers Installation
Page 5-4
<Figure 5>
5. The selected screen appears.
<Figure 6>
6. Click Speaker Test button and click on the speakers directly which show
on the screen to test it.
Speaker Test:
Speak
Configutation:
Page 73

Drivers Installation
Page 5-5
<Figure 7>
7. General Information for user reference.
General:
Page 74

Drivers Installation
Page 5-6
Page Left Blank
Page 75

Appendix
A-1
Appendix A
A-1 Realtek Media Player User’s Guide
Functional Descriptions
A. Playback Windows Display
Playback windows displays the following mode information:
1. Playback Time Display
2. Voice Cancellation Mode Display
3. Pitch Mode Display
4. Surround Sound Mode Display
Realtek
Media Player Platform
A
B
!
"
#
$
%
&
C
D
E
06-Reo Speedwagon - K 03:31
F
G
H
I
J
!
"
#
$
H
K
06 - Reo Speedwagon
Page 76

Appendix
A-2
B. Playback Function Controls
There are 8 selectable functions for the playback:
1. Volume control High/Low Adjustment Bar.
2. Pitch control 4-step High/Low Adjustment Bar.
3. Repeat mode Choice of Repeat, All Repeat, Random or No
Repeat Mode.
4. Mute Mute On/Off Mode select.
5. Voice cancellation Voice Cancellation On/Off Mode select for
Karaoke.
6. Surround mode A total of 26 Surround Sound mode select as
shown in the table below.
edomdnuorruSedomdnuorruS
cireneGrodirrocenotS
deddaPyellA
mooRtserroF
moorhtaBytiC
moorgniviLniatnuoM
enotSyrrauQ
muirotiduAnialP
trecnoCtolgnikraP
evaCepipreweS
anerAretawrednU
ragnaHgurD
tepraCyzziD
yawllaHlacigolohcysP
7. Skin change Media Player Skin Type select.
8. Open Open file formats including MP3, CDA, MDI, WAV
& WMA support.
C. Playback Controls
The playback controls include Play, Pause, Stop, Previous, Backward,
Forward, & Next.
Page 77

Appendix
A-3
D. Seeking bar
Display Animated Playback Status
E. Title/Play List Windows
Display Currently Selected Title(s)
F. Title/Play List Edit Controls
There title/play list controls include Add, Del, Clear, Load, & Store.
1. Add Add to the Title/Play List.
2. Del Remove form the Title/Play List.
3. Clear Clear the Title/Play List.
4. Load Load Title/Play List.
5. Store Save Title/Play List.
G. Title/Play List Scroll bar
Scroll Up/Down the Title/Play List.
H. Recording Function Controls
The recording function controls include Input, Save, New, Rec, Stop,
& Play.
1. Input Input soruce select.
2. Save Save to file.
3. New Open new file & select format includes Sampling
Rate, Sampling bit, Mono or Stereo.
4. Rec Start Rec.
5. Stop Stop Rec.
6. Play Playback Rec file.
I. REC/Playback Time Display
Displays REC/Playback Time.
Page 78

Appendix
A-4
J. Platform Display Panel Controls
The platform display panel control include Minimize & Close.
1. Minimize Minimize Platform Display Panel.
2. Close Close/Exit Platform Display Panel.
K. Equalizer Control Panel
The Equalizer Control Panel include On/Off & Preset.
1. On/Off Enable/Disable Equalizer.
2. Preset Clear Equalizer setting to default value.
Page 79

Appendix
B-1
Appendix B
B-1 Update Your System BIOS
Download the xxxxx.EXE file corresponding to your model form the our website to
an empty directory on your hard disk or floppy. Run the downloaded xxxxx.EXE
file and it will self extract. Copy these extracted files to a bootable DOS floppy
disk.
Note: The DOS floppy disk should contain NO device drivers or other programs.
1. Type A:\AWDFLASH and press <Enter> Key.
2. You will see the following setup on screen.
3. Please key in the xxxxx.bin BIOS file name.
4. If you want to save the previous BIOS data to the diskette, please key in [Y],
otherwise please key in [N].
xxxxx.bin
XXXX
XXXXX
XXXX
Page 80

Appendix
B-2
5. Key in File Name to save previous BIOS to file.
6. Are you sure to program (y/n), please key in [Y] to start the programming.
7. The programming is finished.
xxxxx.bin
F1 : Reset
F10 : Exit
XXXXX
XXXX
xxxxx.bin
xxxxx.bin
XXXXX
XXXX
xxxxx.bin
xxxxx.bin
XXXXX
XXXX
Page 81

Appendix
C-1
Appendix C
C-1 EEPROM BIOS Remover
Do not remove the BIOS chip, unless instructed by a technician and only with a
PLCC IC extractor tool.
The BIOS socket may be damaged if using an improper method to
replace the BIOS chip.
Page 82

Appendix
C-2
Page Left Blank
Page 83

Appendix
D-1
Appendix D
D-1 GHOST 7 Quick User’s Guide (Optional)
Installation is very easy. You only need to copy the Ghost7 folder or Ghost.exe to
your hard disk.
In which Disk indicates hard disk options
Partition indicates partition options
Check indicates check options
Description of Menu
Ghost clones and backs up Disk and Partition.
Main Menu
Disk
Page 84

Appendix
D-2
Disk To Disk (Disk Cloning)
1. Select the location of the Source drive.
2. Select the location of the Destination drive.
3. When cloning a disk or restoring the backup, set the required partition size as
shown in the following figure.
There are 3 hard disk functions:
1. Disk To Disk (disk cloning)
2. Disk To Image (disk backup)
3. Disk From Image (restore backup)
Important!
1. To use this function, the system must have at least 2 disks. Press the Tab key to
move the cursor.
2. When restoring to a destination disk, all data in that disk will be completely
destroyed.
4. Click OK to display the following confirmation screen. Select Yes to start.
Page 85

Appendix
D-3
Disk To Image (Disk Backup)
1. Select the location of the Source drive.
3. Click OK to display the following confirmation screen. Select Yes to start.
2. Select the location for storing the backup file.
Disk From Image(Restore Backup)
1. Select the Restoring file.
Page 86

Appendix
D-4
Partition
2. Select the Destination drive of the disk to be restored.
3. When restoring disk backup, set the required partition size as shown in the
following figure.
4. Click OK to display the following confirmation screen. Select Yes to start.
Page 87

Appendix
D-5
There are 3 partition functions:
1. Partition To Partition (partition cloning)
2. Partition To Image (partition backup)
3. Partition From Image (restore partition)
Partition To Partition (Partition Cloning)
The basic unit for partition cloning is a partition. Refer to disk cloning for the
operating method.
Partition To Image (Partition Backup)
1. Select the disk to be backed up.
2. Select the first partition to be backed up. This is usually where the operating
system and programs are stored.
3. Select the path and file name to store the backup file.
Page 88

Appendix
D-6
Partition From Image (Restore Partition)
1. Select the backup file to be restored.
2. Select the source partition.
5. Select Yes to start performing backup.
4. Is the file compressed? There are 3 options:
(1) No: do not compress data during backup
(2) Fast: Small volume compression
(3) High: high ratio compression. File can be compressed to its minimum, but
requiring longer execution time.
Page 89

Appendix
D-7
3. Select the disk to be restored.
4. Select the partition to be restored.
5. Select Yes to start restoring.
Check
This function is to check possible error caused by defective FAT or
track during backup or restoring.
Page 90

Appendix
D-8
How to Reinstall Windows in 2 Minutes
This chapter guides you how to setup your computer properly and, if
necessary, reinstall Windows in 2 minutes. Ghost provides different
methods to complete this task. The following two sections explain how to
create an emergency Recover Floppy and Recover CD:
Emergency Recover Floppy
Divide a hard disk into two partitions. The first partition is to store the
operating system and application programs. The second partition is to back
up the operating system and data. The size of the partition can be
determined according to the backup requirements. For example, the
Windows operating system needs 200MB of hard disk space, Plus
complete Office programs require 360MB. The remaining space can be
used to store data.
After installing Windows, use Ghost to create a backup area for the system
and to store the file (Image file) in drive D. The file is named Original.gho.
Then, create a recover floppy disk containing:
!" Bootable files (Command.com, Io.sys, and MSDOS.SYS )
!"Config.sys (configuration setup file)
!"Autoexec.bat (auto-execution batch file)
!"Ghost.exe (Ghost execution file)
There are two ways to create the content of the recover floppy for
restoring:
(1)To load Windows automatically after booting, store the Autoexec.
bat file with a command line:
Ghost.exe clone, mode=pload, src=d:\original.gho:2,dst=1:1 -fx -sure -rb
Command Description: Runs the restore function automatically with
the Image File. Stored in drive D. After execution, it will exit Ghost
and boots the system.
Refer to the [Introducing Ghosts Functions] for details.
Page 91

Appendix
D-9
(2) After booting, the screen displays the Menu. Select Backup or Restore:
Since the user may install other applications in the future, he/she may
alter Autoexec.bat file to back up or restore the user-defined Image
file as follows:
##
##
#
BackupBackup
BackupBackup
Backup
Back up Windows and application programs as a file (Recent.
gho). Command is:
Ghost clone,mode=pdump,src=1:1,dst=d:\Recent.gho -fx sure -rb
##
##
#
RestoreRestore
RestoreRestore
Restore
Restore types include [General Windows] and [Windows and
Application Programs]. If you select [General Windows],
the system is restored to the general Windows operation
condition. The command is:
Ghost.exe -clone,mode=pload,src=d:\Original.gho,dst=1:1 -fx
-sure -rb
If you select [Windows and Application Programs], the latest
backup file (Recent.gho) is restored, skipping the installation
and setup of application programs.
For description of related parameters, refer to [Introducing Ghosts
Functions].
For more information about menu design, refer to Config.sys and
Autoexec.bat under /Menu in the CD. You can also create a backup CD
containing Ghost.exe and these two files.
Page 92

Appendix
D-10
Recover CD
The following is a simple guide to create a recover CD:
1. First, create a recover floppy disk contains the following with any
copy program such as Easy CD Create (Note 2) :
Bootable files (Command.com and Io.sys and MSDOS.SYS)
Config.sys (Configuration setup file)
Autoexec.bat (Auto-execution batch file)
Mscdex.exe (CD-Rom execution file)
Ghost.exe (Ghost execution file)
Oakcdrom.sys (ATAPI CD-ROM compatible driver)
The content of Config.sys is:
DEVICE=Oakcdrom.sys /d:idecd001
The content of Autoexec.bat includes:
MSCDEX.EXE /D:IDECD001 /L:Z
Ghost.exe clone,mode=load,src=z:\original.gho,dst=1 -sure -rb
2. Write the backup image file (original.gho) of the entire hard disk or
partition into the recover CD. Use the Recover CD to boot up the
system and restore the backup files automatically.
For description of related parameters, refer to [Introducing Ghosts
Functions].
Note: For more details about copy the creation program and method to create a
recover CD, please refer to the releated software and its associated
operating manual.
Note: Ghost may be executed in interactive or in batch mode. Most of the Ghost
switches are used to assist in batch mode operation. To list switches, type
ghost.exe -h.
Page 93

Appendix
E-1
Appendix E
E-1 POST CODES (Optional)
POST (hex) DESCRIPTION
CFh Test CMOS R/W functionality.
C0h Early chipset initialization:
- Disable shadow RAM
- Disable L2 cache (socket 7 or below)
- Program basic chipset registers
C1h Detect memory
- Auto-detection of DRAM size, type and ECC.
- Auto-detection of L2 cache (socket 7 or below)
C3h Expand compressed BIOS code to DRAM
C5h Call chipset hook to copy BIOS back to E000 & F000 shadow RAM.
01h Expand the Xgroup codes locating in physical address 1000:0
02h Reserved
03h Initial Superio_Early_Init switch.
04h Reserved
05h 1. Blank out screen
2. Clear CMOS error flag
06h Reserved
07h 1. Clear 8042 interface
2. Initialize 8042 self-test
08h 1. Test special keyboard controller for Winbond 977 series Super I/O
chips.
2. Enable keyboard interface.
09h Reserved
0Ah 1. Disable PS/2 mouse interface (optional).
2. Auto detect ports for keyboard & mouse followed by a port &
interface swap (optional).
3. Reset keyboard for Winbond 977 series Super I/O chips.
0B-0Dh Reserved
0Eh Test F000h segment shadow to see whether it is R/W-able or not. If test
fails, keep beeping the speaker.
0Fh Reserved
10h Auto detect flash type to load appropriate flash R/W codes into the run
time area in F000 for ESCD & DMI support.
11h Reserved
12h Use walking 1s algorithm to check out interface in CMOS circuitry.
Also set real-time clock power status, and then check for override.
13h Reserved
14h Program chipset default values into chipset. Chipset default values are
MODBINable by OEM customers.
15h Reserved
16h Initial Early_Init_Onboard_Generator switch.
17h Reserved
Page 94

Appendix
E-2
18h Detect CPU information including brand, SMI type (Cyrix or Intel) and
CPU level (586 or 686).
19-1Ah Reserved
1Bh Initial interrupts vector table. If no special specified, all H/W
interrupts are directed to SPURIOUS_INT_HDLR & S/W
interrupts to SPURIOUS_soft_HDLR.
1Ch Reserved
1Dh Initial EARLY_PM_INIT switch.
1Eh Reserved
1Fh Load keyboard matrix (notebook platform)
20h Reserved
21h HPM initialization (notebook platform)
22h Reserved
23h 1. Check validity of RTC value:
e.g. a value of 5Ah is an invalid value for RTC minute.
2. Load CMOS settings into BIOS stack. If CMOS checksum fails, use
default value instead.
3. Prepare BIOS resource map for PCI & PnP use. If ESCD is valid,
take into consideration of the ESCDs legacy information.
4. Onboard clock generator initialization. Disable respective clock
resource to empty PCI & DIMM slots.
5. Early PCI initialization:
-Enumerate PCI bus number
-Assign memory & I/O resource
-Search for a valid VGA device & VGA BIOS, and put it into C000:0.
24-26h Reserved
27h Initialize INT 09 buffer
28h Reserved
29h 1. Program CPU internal MTRR (P6 & PII) for 0-640K memory
address.
2. Initialize the APIC for Pentium class CPU.
3. Program early chipset according to CMOS setup.
Example: onboard IDE controller.
4. Measure CPU speed.
5. Invoke video BIOS.
2A-2Ch Reserved
2Dh 1. Initialize multi-language
2. Put information on screen display, including Award title, CPU type,
CPU speed .
2E-32h Reserved
33h Reset keyboard except Winbond 977 series Super I/O chips.
34-3Bh Reserved
3Ch Test 8254
3Dh Reserved
3Eh Test 8259 interrupt mask bits for channel 1.
3Fh Reserved
40h Test 8259 interrupt mask bits for channel 2.
41h Reserved
42h Reserved
Page 95

Appendix
E-3
43h Test 8259 functionality.
44h Reserved
45-46h Reserved
47h Initialize EISA slot
48h Reserved
49h 1. Calculate total memory by testing the last double word of each 64K
page.
2. Program writes allocation for AMD K5 CPU.
4A-4Dh Reserved
4Eh 1. Program MTRR of M1 CPU
2. Initialize L2 cache for P6 class CPU & program CPU with proper
cacheable range.
3. Initialize the APIC for P6 class CPU.
4. On MP platform, adjust the cacheable range to smaller one in case
the cacheable ranges between each CPU are not identical.
4Fh Reserved
50h Initialize USB
51h Reserved
52h Test all memory (clear all extended memory to 0)
53-54h Reserved
55h Display number of processors (multi-processor platform)
56h Reserved
57h 1. Display PnP logo
2. Early ISA PnP initialization
-Assign CSN to every ISA PnP device.
58h Reserved
59h Initialize the combined Trend Anti-Virus code.
5Ah Reserved
5Bh (Optional Feature) Show message for entering AWDFLASH.EXE
from FDD (optional)
5Ch Reserved
5Dh 1. Initialize Init_Onboard_Super_IO switch.
2. Initialize Init_Onbaord_AUDIO switch.
5E-5Fh Reserved
60h Okay to enter Setup utility; i.e. not until this POST stage can users enter
the CMOS setup utility.
61-64h Reserved
65h Initialize PS/2 Mouse
66h Reserved
67h Prepare memory size information for function call: INT 15h ax=E820h
68h Reserved
69h Turn on L2 cache
6Ah Reserved
6Bh Program chipset registers according to items described in Setup & Auto-
configuration table.
6Ch Reserved
6Dh 1. Assign resources to all ISA PnP devices.
2. Auto assign ports to onboard COM ports if the corresponding item
in Setup is set to AUTO.
Page 96

Appendix
E-4
6Eh Reserved
6Fh 1. Initialize floppy controller
2. Set up floppy related fields in 40:hardware.
70-72h Reserved
73h (Optional Feature) Enter AWDFLASH.EXE if :
-AWDFLASH is found in floppy drive.
-ALT+F2 is pressed
74h Reserved
75h Detect & install all IDE devices: HDD, LS120, ZIP, CDROM..
76h Reserved
77h Detect serial ports & parallel ports.
78h-79h Reserved
7Ah Detect & install co-processor
7B-7Eh Reserved
7Fh 1. Switch back to text mode if full screen logo is supported.
-If errors occur, report errors & wait for keys
-If no errors occur or F1 key is pressed to continue:
!"Clear EPA or customization logo.
80h-81h Reserved
82h 1. Call chipset power management hook.
2. Recover the text fond used by EPA logo (not for full screen logo)
3. If password is set, ask for password.
83h Save all data in stack back to CMOS
84h Initialize ISA PnP boot devices
85h 1. USB final Initialization
2. NET PC: Build SYSID structure
3. Switch screen back to text mode
4. Set up ACPI table at top of memory.
5. Invoke ISA adapter ROMs
6. Assign IRQs to PCI devices
7. Initialize APM
8. Clear noise of IRQs.
86-92h Reserved
93h Read HDD boot sector information for Trend Anti-Virus code
94h 1. Enable L2 cache
2. Program boot up speed
3. Chipset final initialization.
4. Power management final initialization
5. Clear screen & display summary table
6. Program K6 write allocation
7. Program P6 class write combining
95h 1. Program daylight saving
2. Update keyboard LED & typematic rate
96h 1. Build MP table
2. Build & update ESCD
3. Set CMOS century to 20h or 19h
4. Load CMOS time into DOS timer tick
5. Build MSIRQ routing table.
FFh Boot attempt (INT 19h)
 Loading...
Loading...