Page 1

VERTICAL HORIZON
VH-8G
GIGABIT ETHERNET SWITCH
MANAGEMENT GUIDE
9033640
Page 2

Page 3

Notice
Only qualified personnel should perform installation
procedures.
NOTICE
Enterasys Networks reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information
contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult Enterasys
Networks to determine whether any such changes have been made.
The hardware, firmware, or software described in this manual is subject to change without notice.
IN NO EVENT SHALL ENTERASYS NETWORKS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING BUT
NOT LIMITED TO LOST PROFITS) ARISING OUT OF OR RELATED TO THIS MANUAL OR
THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN IT, EVEN IF ENTERASYS NETWORKS HAS BEEN
ADVISED OF, KNOWN, OR SHOULD HAVE KNOWN, THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES.
2000 by Enterasys Networks, P.O. Box 5005, Rochester, NH 03866-5005
All Rights Reserved
Printed in Taiwan, R.O.C.
Order Number: 9033640 November 2000
Enterasys, Enterasys Networks, and Vertical Horizon are trademarks or registered trademarks of
Enterasys Networks, Inc.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows 95, Windows 98, and Windows NT are either trademarks or registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Netscape and Netscape Navigator are trademarks of Netscape Communications Corporation.
All other product names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective companies.
9033640 i
Page 4

Notice
ii 9033640
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Configuration Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Required Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Console Port (Out-of-Band) Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
In-Band Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
2. VH-8G USER INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
User Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Factory Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Main Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
System Information Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Displaying System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Displaying Switch Version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Management Setup Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Changing the Network Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
IP Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
IP Connectivity Test (Ping) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
HTTP Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Configuring the Serial Port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Assigning SNMP Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Console Login Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Downloading System Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Saving the System Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Configuring Management Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Configuring the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Configuring Port Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Viewing the Current Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Using the Spanning Tree Algorithm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Viewing the Current Spanning Tree Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Using a Mirror Port for Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Configuring Port Trunks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
IGMP Multicast Filtering. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Configuring Broadcast Storm Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Configuring Bridge MIB Extensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Configuring Traffic Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Configuring Virtual LANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Multicast Router Port Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Static Multicast Router Port Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
IGMP Member Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Port Security Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Monitoring the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Displaying Port Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Displaying RMON Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Displaying the Unicast Address Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
9033640 Table of Contents iii
Page 6

Displaying the IP Multicast Registration Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Configuring Static Unicast Addresses. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Resetting the System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Logging Off the System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
3. CONFIGURING & MONITORING THE SWITCH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Common Tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Setting Password Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Assigning an IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Checking Network Configuration Status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Connecting via Telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Setting SNMP Management Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Viewing Switch Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Configuring Port Mirroring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Downloading a Software Upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Downloading Via the Serial Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Downloading Via TFTP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Configuring Spanning Tree Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Configuring VLANs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Configuring Class of Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Configuring Port Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Configuring the Unicast Address Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Setting a Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Configuring BootP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Configuring Port Trunks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
4. SNMP MANAGEMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
The SNMP Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
MIB Objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
RFC 1213 (MIB-II). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
RFC 1573 (Interfaces Evolution MIB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
RFC 1643 (Ethernet-Like MIB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
RFC 1493 (Bridge MIB). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
RFC 1757 (RMON MIB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
IEEE 802.1Q (Q-MIB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Enterasys Proprietary MIB Extensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Compiling MIB Extensions: Enterasys Website . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
APPENDIX A. SPANNING TREE CONCEPTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Spanning Tree Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Spanning Tree Protocol in a Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Spanning Tree Protocol Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Spanning Tree Protocol Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Communicating Between Bridges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Selecting a Root Bridge and Designated Bridges. . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Selecting Designated Ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Handling Duplicate Paths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Remapping Network Topology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
iv Table of Contents VH-8G
Page 7

APPENDIX B. VIRTUAL LANS (VLANS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
VLANs and Frame Tagging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
VH-8G VLAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Assigning Ports to VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Forwarding Tagged/Untagged Frames . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Automatic VLAN Registration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Forwarding Traffic with Unknown VLAN Tags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
APPENDIX C. CLASS OF SERVICE. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
APPENDIX D. IP MULTICAST FILTERING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
IGMP Snooping and IP Multicast Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
INDEX
9033640 Table of Contents v
Page 8

vi Table of Contents VH-8G
Page 9

1. MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW
Configuration Options
For advanced management capability, the Enterasys Networks’ Vertical
Horizon VH-8G provides a menu-driven system configuration program.
This program can be accessed by a direct connection to the serial port on
the switch’s rear panel (out-of-band), or by a Telnet connection over the
network (in-band).
The switch’s management is based on SNMP (Simple Network
Management Protocol). SNMP permits a switch to be managed from any
PC in the network using in-band management software.
The switch’s internal management also includes an embedded HTTP
Web server. This Web server can be accessed using a standard Web
browser from any computer attached to the network. Refer to the VH-8G
Web Management Guide for more information.
The system configuration program and SNMP support management
functions such as:
• Enable/disable any port
• Set the communication mode for any port
• Configure SNMP parameters
• Select RMON options
• Display system information or statistics
• Configure the switch to join a Spanning Tree
• Download system firmware
• Restart the system
Required Connections
Console Port (Out-of-Band) Connections
Attach a VT100 compatible terminal or a PC running a terminal emulation
program to the serial port on the switch’s rear panel. Use the null-modem
cable provided with this package, or use a null-modem connection that is
compatible with the console port pin assignments shown in Appendix A of
the VH-8G User Guide.
When attaching to a PC, set terminal emulation type to VT100, specify the
port used by your PC (i.e., COM 1~4), and then set communications to 8
data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity, and 19200 bps (for initial configuration).
Also be sure to set flow control to “none.” (Refer to “Configuring the Serial
Port” on page 17 for a complete description of configuration options.)
9033640 Management Overview 1
Page 10

In-Band Connections
Prior to accessing the switch via a network connection, you must first
configure it with a valid IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
using an out-of-band connection or the BootP protocol.
Telnet Connection
Prior to accessing the switch via an in-band Telnet connection, you must
first configure it with a valid IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
using an out-of-band connection or BootP protocol. After configuring the
switch’s IP parameters, you can access the on-board configuration
program from anywhere within the attached network.
Use the Network Configuration menu to specify the
maximum number of simultaneous Telnet sessions that
are supported by the system.
In-Band Network Connection
The on-board configuration program can be accessed using Telnet from
any computer attached to the network. The switch can also be managed
by any computer using a Web browser (Internet Explorer 4.0 or above, or
Netscape Navigator 4.0 or above), or from a network computer using
network management software.
2 Management Overview VH-8G
Page 11
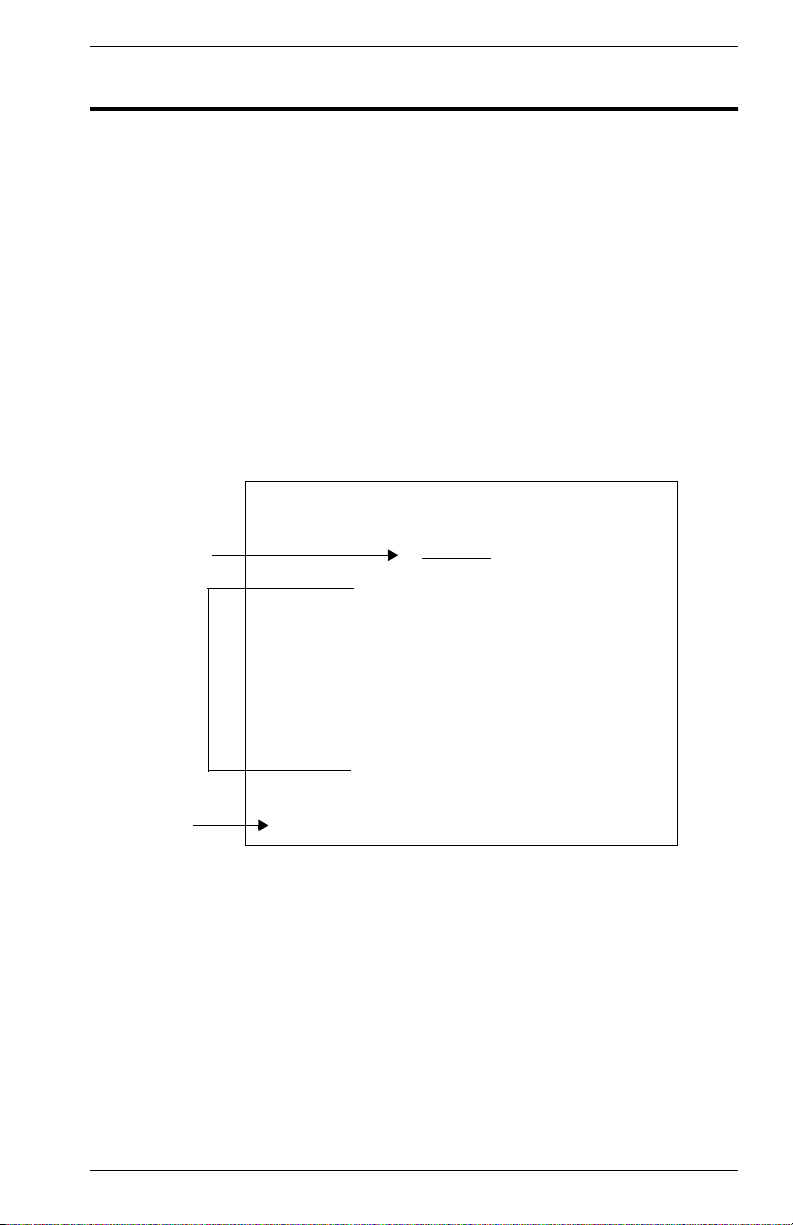
2. VH-8G USER INTERFACE
Overview
Access is gained to the console menus by directly connecting a terminal
to the console port with a null-modem cable connection, or using Telnet
to access the switch over the network. These menus allow you to
reconfigure the switch, as well as to monitor the status and performance
of the switch. The menus have a layout similar to the sample Main Menu
shown in Figure 2-1. The information is divided into the following parts:
• Menu Name (includes access privileges)
• Selectable Items
• Screen Prompt for menu selections and entry of field parameters,
and Message Area for display of parameters or error messages.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Menu name
Selectable
Items
Screen prompt
and message
area
Main Menu
System Information Menu...
Management Setup Menu...
Device Control Menu...
Network Monitor Menu...
System Restart Menu...
Exit
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Figure 2-1. Sample Main Menu
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 3
Page 12

User Access
Once a direct connection to the console port or a Telnet connection is
established, the login screen for the on-board configuration program
appears. You may need to press Enter a few times to display the screen.
The default user names are “admin” and “guest,” with no passwords. The
administrator has Read/Write access, which allows you to read and
modify switch information. The guest has Read Only access to the
management program, which allows you to view switch information, but
not modify any operating parameters.
You should define a new administrator password, record it and put it in a
safe place. From the Main Menu, select Management Setup Menu /
Console Login Configuration, and enter a new password for the
administrator. Passwords can consist of up to 11 alphanumeric
characters and are not case sensitive.
To use the console menus, do the following:
1. Use the cursor keys to highlight the desired option.
If the selected item is a submenu title, the submenu is displayed
when you press the Enter key.
2. Follow the screen prompts to specify the parameter requested.
If the selected item is a parameter, the system displays a prompt for
you to enter a new value. If the value entered is invalid, a message
displays, requesting you to enter a valid value.
A user is allowed three attempts to enter the correct
password; on the third failed attempt the current
connection is terminated.
4 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 13

Factory Defaults
Table 2-1 lists the default settings for switch configuration parameters.
Each parameter can be changed via the console menus or Telnet.
Parameter Default Value
Multicast Filtering
GMRP Disabled
IGMP Multicast Filtering Disabled
Port Configuration
Flow Control Disabled
Speed and Duplex Auto
Admin Enabled
Broadcast Storm Control Enabled - 500 pps
Port Priority
Default Ingress User Priority 0
Spanning Tree Algorithm
Active Aging Time 300
Bridge Priority 32768
Forward Delay 15
Hello Time 2
Max Age 20
Path Cost 4 - 1000Mbps ports
Port Priority 128
Spanning Tree Protocol Enabled
System Configuration
Management VLAN All
BootP Enable Disabled
Password <none>
Screen Timeout 10 min
Send Authentication Fail Traps Enabled
SNMP Community Name public, private
Terminal Baud Rate Auto
User Names admin, guest
Table 2-1. Factory Default Settings
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 5
Page 14

Parameter Default Value
Virtual LANs
Acceptable VLAN Frame Type All
Configurable PVID Tagging Yes
GVRP Disabled
Untagged VLAN Group Assignment 1
VLAN Ingress Filtering False
VLAN Learning SVL
6 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 15
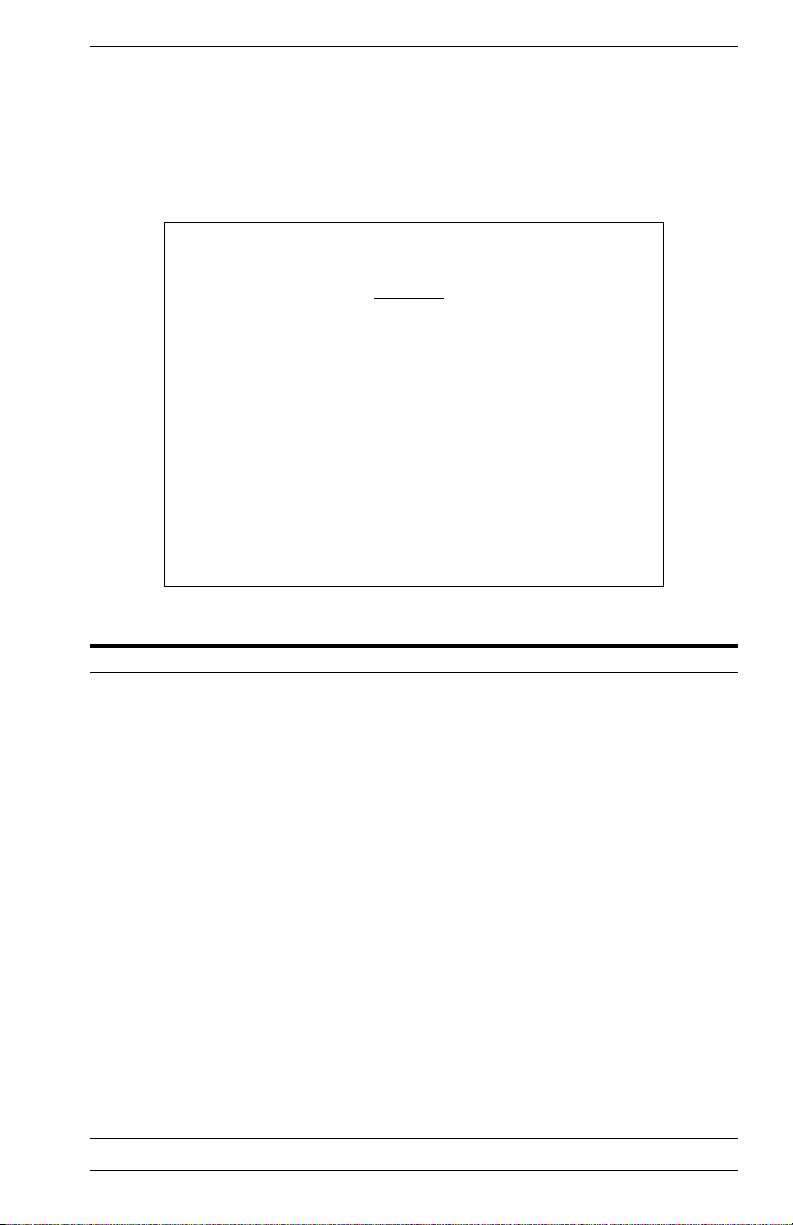
Main Menu
The Main Menu is the first screen seen after successfully logging into the
system. Figure 2-2 shows the Main Menu and the accompanying table
describes the Main Menu.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Main Menu
System Information Menu...
Management Setup Menu...
Device Control Menu...
Network Monitor Menu...
System Restart Menu...
Exit
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Figure 2-2. Main Menu
Selection Description
System Information Menu
System Information Provides basic system description, including contact
Switch Information Shows hardware/firmware version numbers and power
Management Setup Menu
Network Configuration Includes IP setup, Ping facility, HTTP (Web server) setup,
Serial Port
Configuration
SNMP Configuration Activates traps; and configures communities and trap
Console Login
Configuration
TFTP Download Downloads new version of firmware to update your system
Configuration Save &
Restore
Management
Configuration
information.
status of the switch.
Telnet configuration, and MAC address.
Sets communication parameters for the serial port, including
management mode, baud rate, console time-out, and screen
data refresh interval.
managers.
Sets user names and passwords for system access, as well
as the invalid password threshold and lockout time.
(in-band).
Saves the switch configuration to a file on a TFTP server.
This file can be later downloaded to restore the configuration.
Specifies if management access to the switch is available
from all VLANs or restricted to one VLAN.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 7
Page 16

Selection Description
Device Control Menu
Port Configuration Enables any port, enables/disables flow control, and sets
communication mode to auto-negotiation, full duplex or half
duplex.
Port Information Displays operational status, including link state, flow control
method, and duplex mode.
Spanning Tree
Configuration
Enables Spanning Tree Algorithm; also sets parameters for
hello time, maximum message age, switch priority, and
forward delay; as well as port priority and path cost.
Spanning Tree
Information
Mirror Port
Displays full listing of parameters for the Spanning Tree
Algorithm.
Sets the source and target ports for mirroring.
Configuration
Port Trunking
Specifies ports to group into aggregate trunks.
Configuration
BStorm Control
Configuration
Allows you to enable broadcast storm control and set the
packet-per-second threshold.
IGMP Configuration Configures IGMP multicast filtering.
Extented Bridge
Configuration
Displays/configures extended bridge capabilities provided by
this switch, including support for traffic classes, GMRP
multicast filtering, and VLAN extensions.
802.1P Configuration Configures default port priorities and queue assignments.
802.1Q VLAN
Base Information
802.1Q VLAN Current
Displays basic VLAN information, such as VLAN version
number and maximum VLANs supported.
Displays VLAN groups and port members.
Table Information
802.1Q VLAN Static
Table Configuration
Configures VLAN groups via static assignments, including
setting port members, or restricting ports from being
dynamically added to a port by the GVRP protocol.
Port Assignment
VLAN Configuration
Multicast Router Port
Information
Static Multicast Router
Port Cfg
IGMP Member Port
Configuration
Port Security
Configuration
Displays/configures port-specific VLAN settings, including
PVID, ingress filtering, and 802.1Q trunks.
Displays the ports on the switch attached to a neighboring
multicast router/switch for each VLAN ID.
Assigns ports that are attached to a neighboring multicast
router/switch.
Assigns ports that are attached to hosts who want to receive
a specific multicast service.
Allows you to enable and configure port security for the
switch.
Network Monitor Menu
Port Statistics Displays statistics on network traffic passing through the
selected port.
RMON Statistics Displays detailed statistical information for the selected port
such as packet type and frame size counters.
Unicast Address Table Provides full address listing, as well as search and clear
functions.
8 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 17
Selection Description
IP Multicast
Registration Table
Static Unicast Address
Table Configuration
System Restart Restarts system with options to use POST, or to retain
Exit Exits the configuration program.
Displays all the multicast groups active on this switch,
including multicast IP addresses and corresponding VLAN
IDs.
Used to manually configure host MAC addresses in the
unicast table.
factory defaults, IP settings, or user authentication settings.
System Information Menu
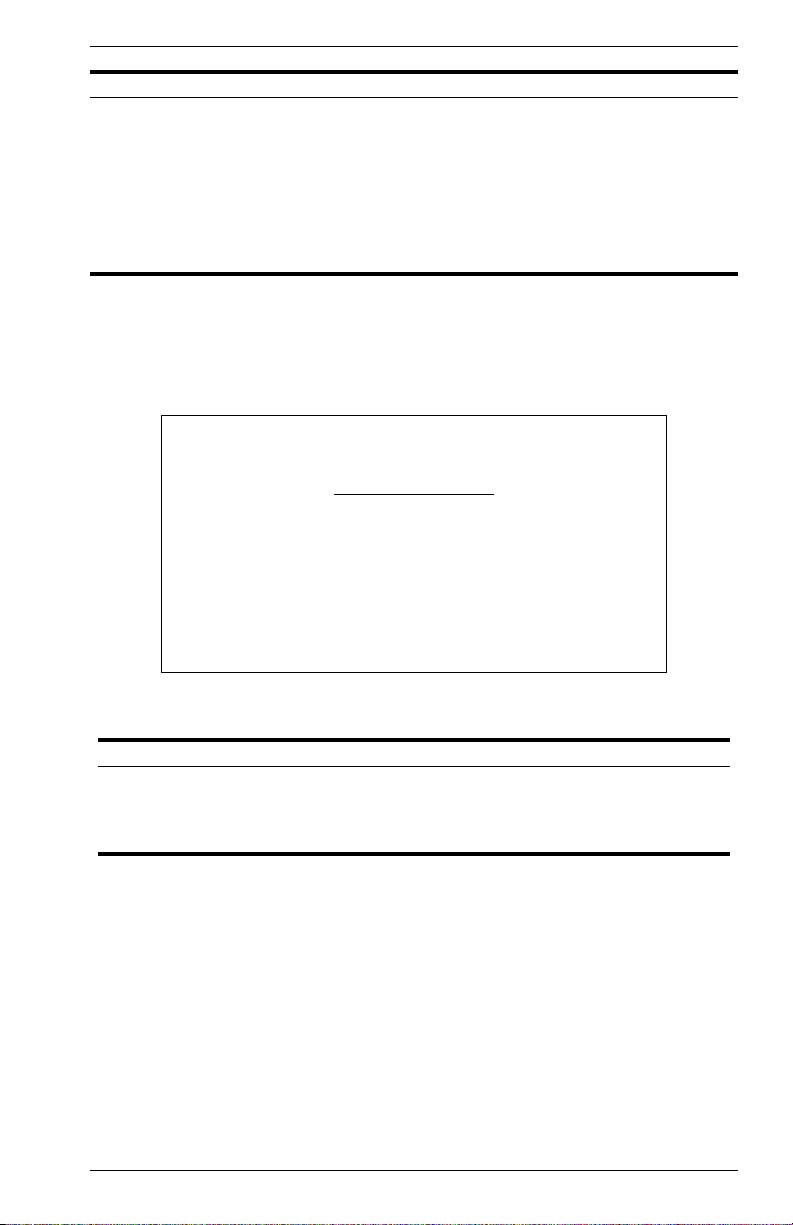
Use the System Information Menu to display a basic description of the
switch, including contact information, and hardware/firmware versions.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
System Information Menu
System Information ...
Switch Information ...
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
<OK>
Figure 2-3. System Information Menu
Selection Description
System Information Provides basic system description, including contact
Switch Information Shows hardware/firmware version numbers and power status
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 9
information.
of the switch.
Page 18
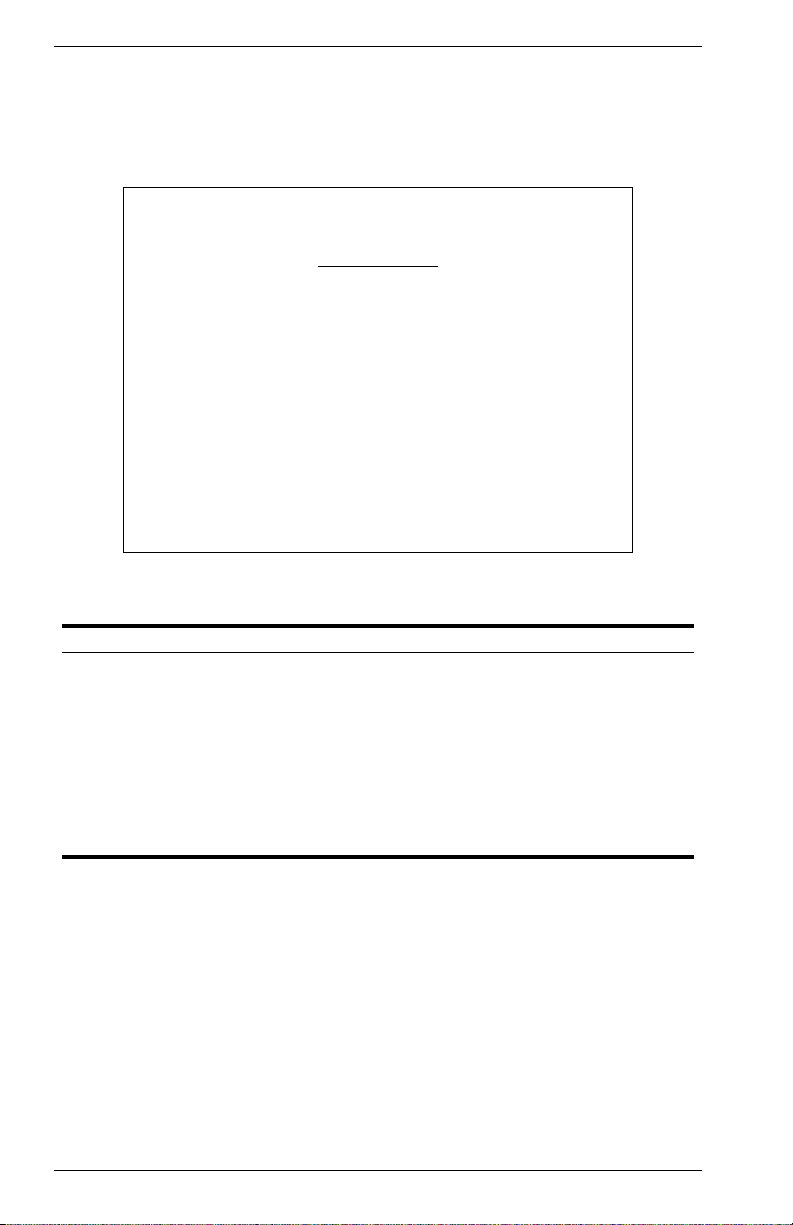
Displaying System Information
Use the System Information screen to display descriptive information
about the switch, or for quick system identification as shown in the
following figure and table.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
System Information
System Description : Vertical Horizon VH-8G
System Object ID : 1.3.6.1.4.1.5624.2.1.9
System Up Time : 48067 (0 day, 1 hr, 2min, 34 sec)
System Name : DEFAULT SYSTEM NAME
System Contact : DEFAULT SYSTEM CONTACT
System Location : DEFAULT SYSTEM LOCATION
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Figure 2-4. System Information
Parameter Description
System Description System hardware description.
System Object ID MIB II object identifier for switch’s network management
System Up Time Length of time the current management agent has been
System Name
*
System Contact
System Location
*
Maximum string length is 255, but the screen only displays 45 characters. You
can use the arrow keys to browse the whole string.
subsystem.
running. (Note that the first value is 1/100 seconds.)
Name assigned to the switch system.
*
Contact person for the system.
*
Specifies the area or location where the system resides.
10 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 19
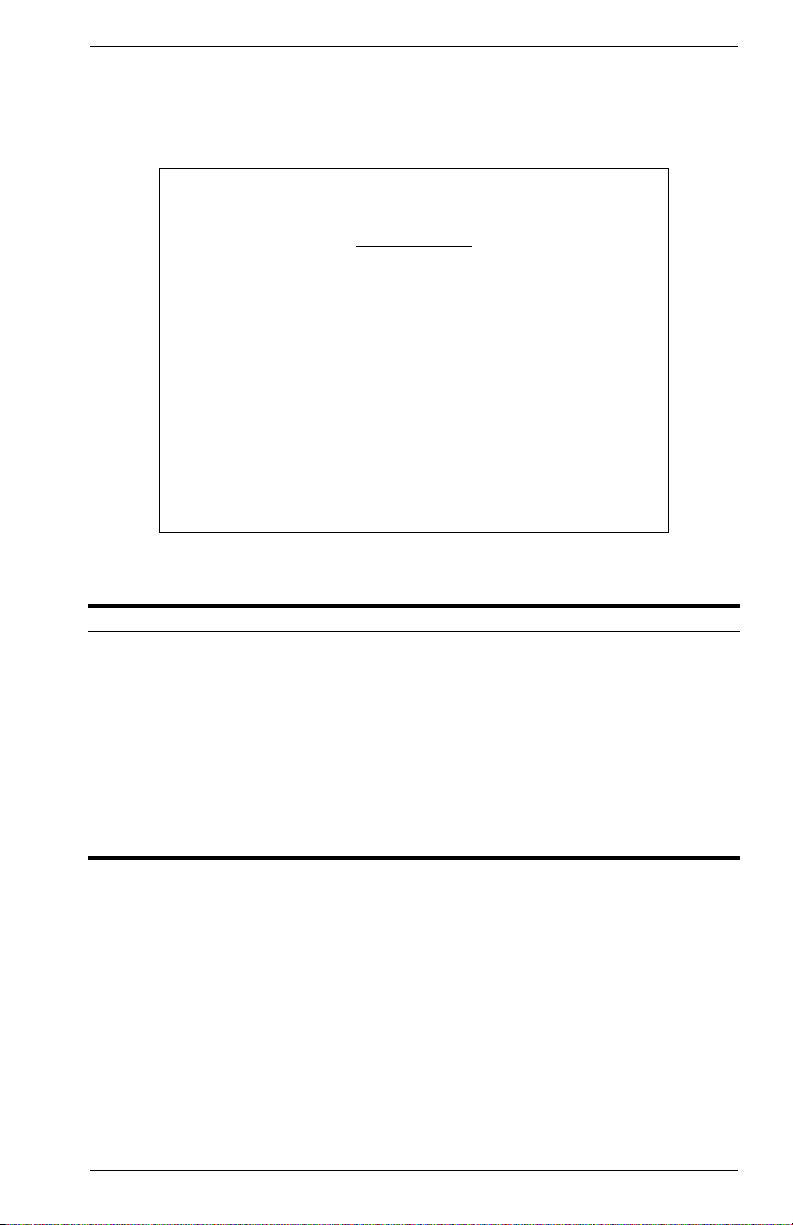
Displaying Switch Version
Use the Switch Information screen to display hardware/firmware version
numbers for the switch, as well as the power status of the system.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Switch Information
Main Board
Hardware Version : V0.0 (860 CPU)
Firmware Version : 02.04.00.00
POST ROM Version : V1.02
Serial Number : 00-E0-63-76-F3-00
Port Number : 8
Internal Power Status : Active
Redundant Power Status : Inactive
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
<OK>
Figure 2-5. Switch Information
Parameter Description
Main Board
Hardware Version Hardware version of the main board.
Firmware Version System firmware version in ROM.
POST ROM Version Power-On Self-Test version number.
Serial Number MAC address associated with the main board.
Port Number Number of ports on the switch.
Internal Power Status Power status for the switch.
Redundant Power
Status
Redundant power status for the switch.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 11
Page 20
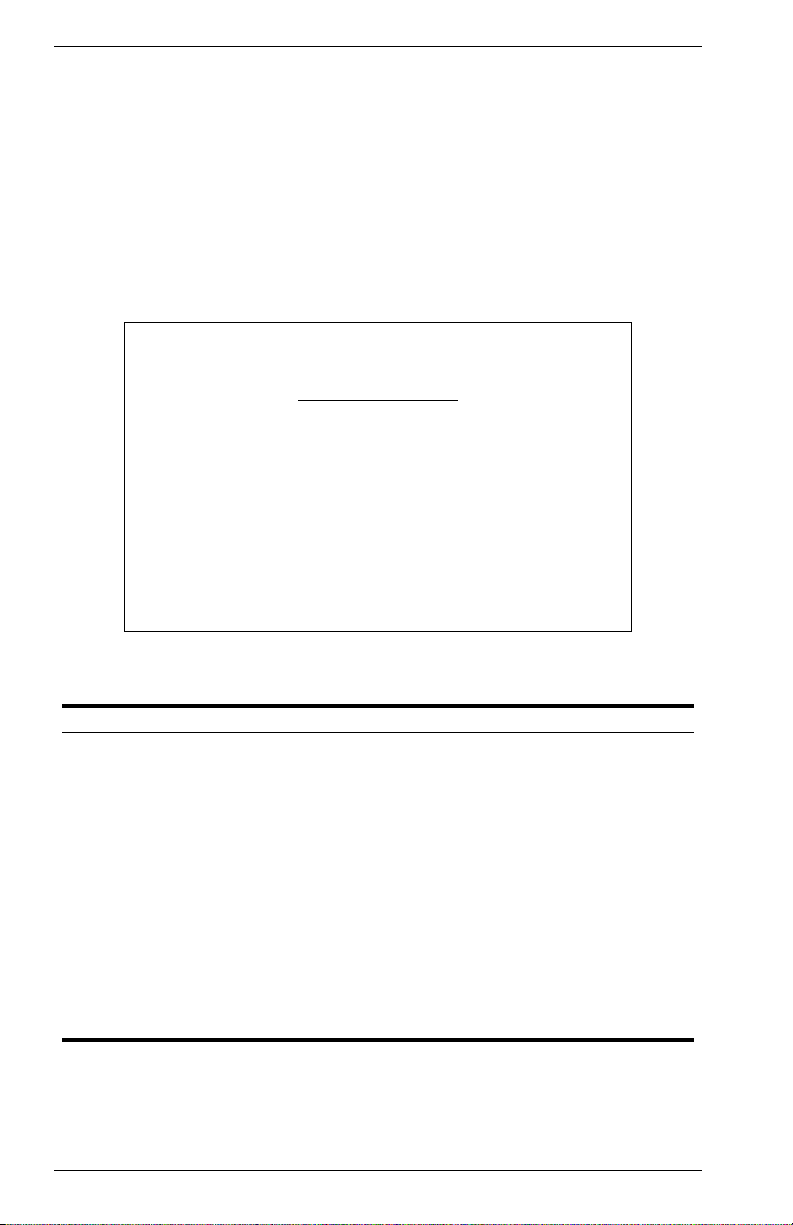
Management Setup Menu
After initially logging onto the system, adjust the communication
parameters for your console to ensure a reliable connection (Serial Port
Configuration). Specify the IP addresses for the switch (Network
Configuration / IP Configuration), and then set the Administrator and User
passwords (Console Login Configuration). Remember to record them in a
safe place. Also set the community string which controls SNMP access to
the switch via in-band management software (SNMP Configuration). The
items provided by the Management Setup Menu are described in the
following sections.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Management Setup Menu
Network Configuration ...
Serial Port Configuration ...
SNMP Configuration ...
Console Login Configuration ...
TFTP Download ...
Configuration Save & Restore ...
Management Configuration ...
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
<OK>
Figure 2-6. Management Setup Menu
Selection Description
Network
Configuration
Serial Port
Configuration
SNMP Configuration Activates traps; and configures communities and trap managers.
Console Login
Configuration
TFTP Download Downloads new version of firmware to update your system (in-
Configuration Save &
Restore
Management
Configuration
Includes IP setup, Ping facility, HTTP (Web server) setup, Telnet
configuration, and MAC address.
Sets communication parameters for the serial port, including
management mode, baud rate, console time-out, and screen
data refresh interval.
Sets user names and passwords for system access, as well as
the invalid password threshold and lockout time.
band).
Saves the switch configuration to a file on a TFTP server. This file
can be later downloaded to restore the configuration.
Specifies if management access to the switch is available from all
VLANs or restricted to one VLAN.
12 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 21
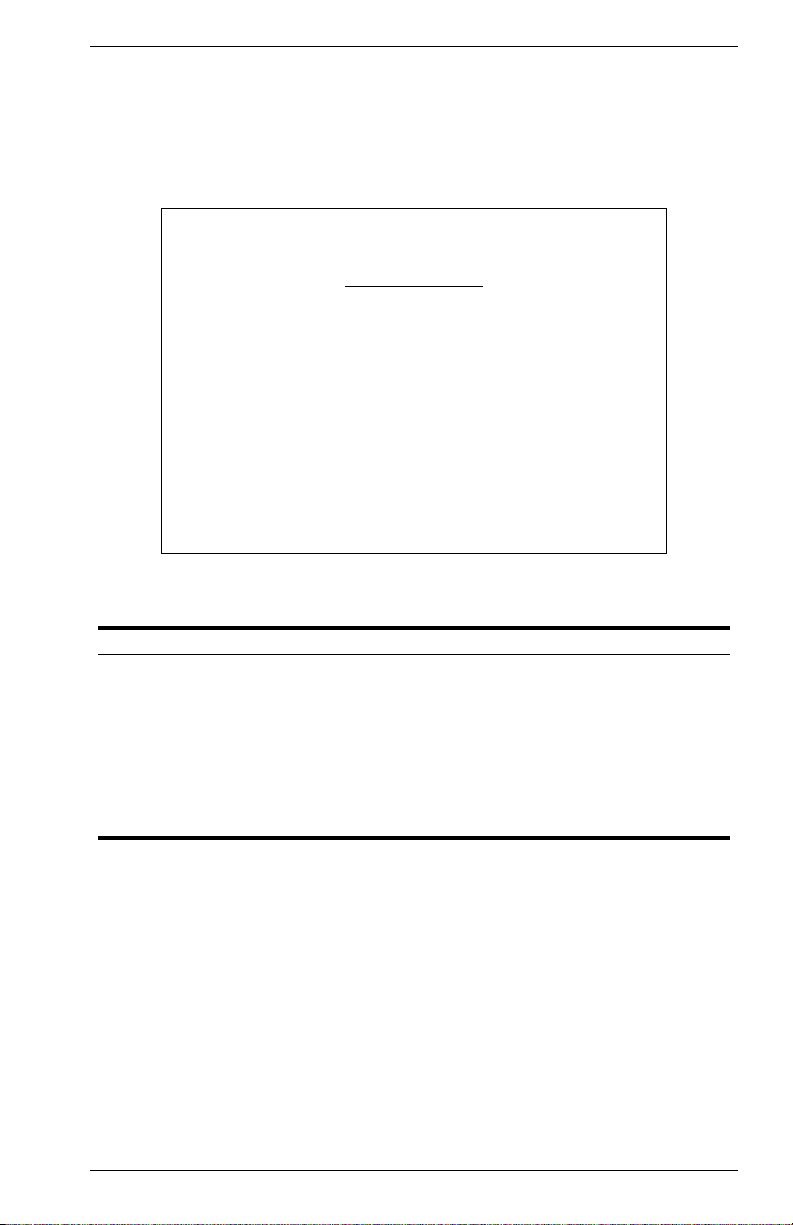
Changing the Network Configuration
Use the Network Configuration menu to set the bootup option, configure
the switch’s Internet Protocol (IP) parameters, enable the on-board Web
server, or to set the number of concurrent Telnet sessions allowed. The
screen shown below is described in the following table.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Network Configuration
IP Configuration ...
IP Connectivity Test (Ping) ...
HTTP Configuration ...
MAX Number of allowed Telnet sessions (1 -4) : 4
Physical Address : 00-E0-29-52-28-00
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Figure 2-7. Network Configuration
Parameter Description
IP Configuration Screen used to set the bootup option, or configure the switch’s IP
IP Connectivity Test Screen used to test IP connectivity to a (Ping) specified device.
HTTP Configuration Screen used to enable the Web server.
MAX Number of
Allowed Telnet
Sessions
Physical Address MAC address of the switch.
parameters.
The maximum number of Telnet sessions allowed to
simultaneously access the switch.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 13
Page 22
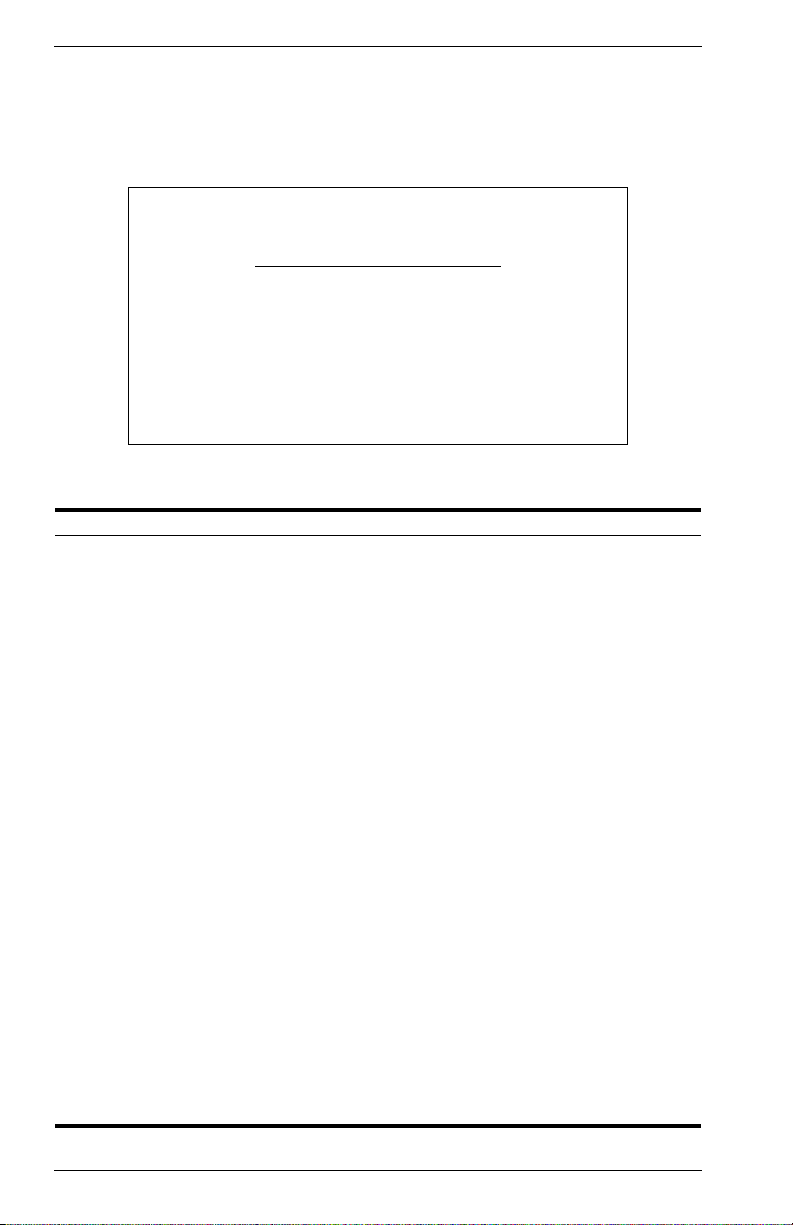
IP Configuration
Use the IP Configuration screen to set the bootup option, or configure the
switch’s IP parameters. The screen shown below is described in the
following table.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Network Configuration: IP Configuration
Interface Type : Ethernet
IP Address : 10.1.0.1
Subnet Mask : 255.255.0.0
Gateway IP : 10.1.0.254
IP State : USER-CONFIG
Figure 2-8. IP Configuration
Parameter Default Description
Interface Type Ethernet Indicates IP over Ethernet.
IP Address 10.1.0.1 IP address of the switch you are managing when
Subnet Mask 255.255.0.0 Subnet mask of the switch. This mask identifies the host
Default
0.0.0.0 Gateway used to pass trap messages from the switch’s
Gateway
IP State USER-
CONFIG
accessing it over the network. The switch supports SNMP
over UDP/IP transport protocol. In this environment, all
systems on the Internet, such as network interconnection
devices and any PC accessing the switch (or running
management software) must have an IP address.
Valid IP addresses consist of four numbers, of 0 to 255,
and separated by periods. Anything outside of this format
will not be accepted by the configuration program.
address bits used for routing to specific subnets.
agent to the management station. Note that the gateway
must be defined if the management station is located in a
different IP segment.
Specifies whether IP functionality is enabled via manual
configuration, or set by Boot Protocol (BootP). Options
include:
USER-CONFIG - IP functionality is enabled based on the
default or user specified IP
configuration.
BOOTP Get IP - IP is enabled but will not function until a
BootP reply has been received. BootP
requests will be periodically broadcast
by the switch in an effort to learn its IP
address. (BootP values can include the
IP address, default gateway, and
subnet mask.)
14 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 23
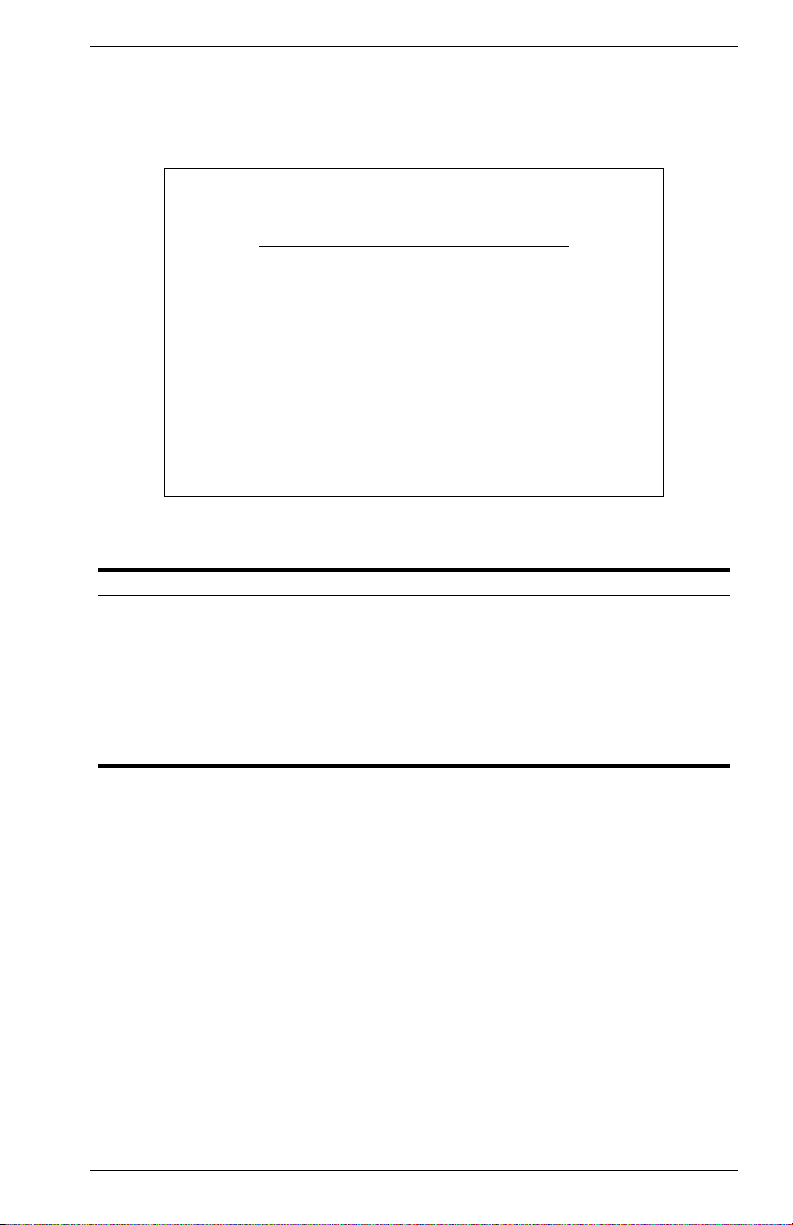
IP Connectivity Test (Ping)
Use the IP Connectivity Test to see if another site on the Internet can be
reached. The screen shown below is described in the following table.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Network Configuration: IP Connectivity Test (Ping)
IP Address : 200.123.211.109
Test Times : 1 Interval : 3
Success : 0 Failure : 0
[Start]
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
<OK>
Figure 2-9. IP Connectivity Test
Parameter Description
IP Address IP address of the site you want to ping.
Test Times The number of ICMP echo requests to send to the specified site.
Range: 1~1000
Interval The interval (in seconds) between pinging the specified site.
Range: 1~10 seconds
Success/Failure The number of times the specified site has responded or not to
pinging.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 15
Page 24
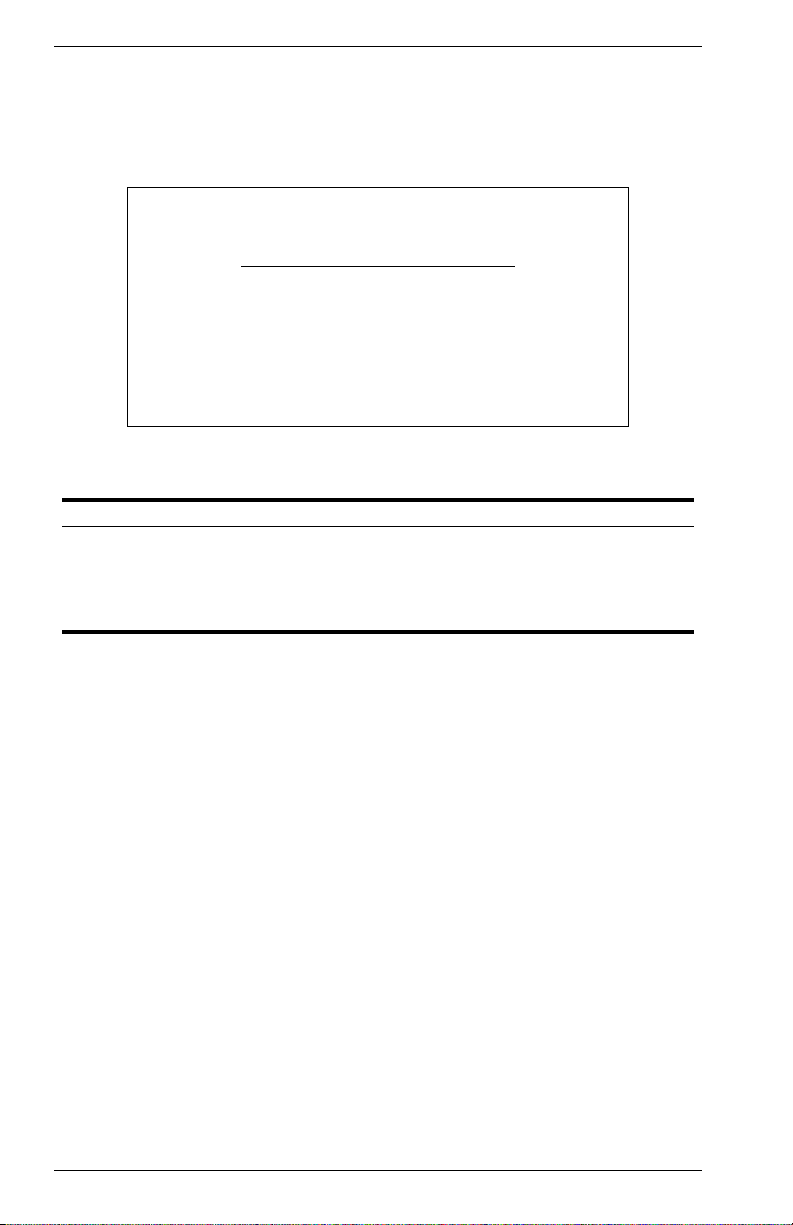
HTTP Configuration
Use the HTTP Configuration screen to enable/disable the on-board Web
server, and to specify the TCP port that will provide HTTP service. The
screen shown below is described in the following table.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Network Configuration : HTTP Configuration
HTTP Server : ENABLED
HTTP Port Number : 80
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
Figure 2-10. HTTP Configuration
Parameter Description
HTTP Server Enables/disables access to the on-board Web server.
HTTP Port Number Specifies the TCP port that will provide HTTP service.
Range : 0~65535
Default : Port 80
(Telnet Port 23 is prohibited.)
16 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 25
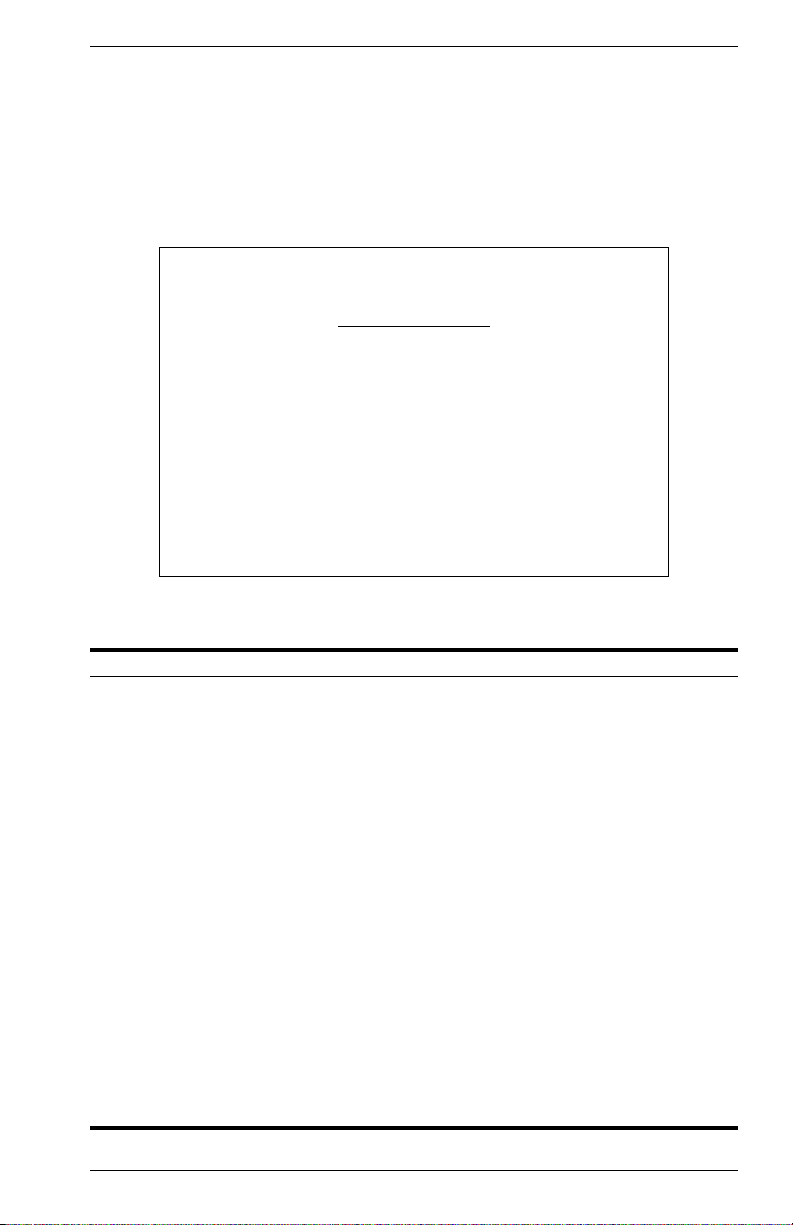
Configuring the Serial Port
You can access the on-board configuration program by attaching a VT100
compatible device to the switch’s serial port. (For more information on
connecting to this port, see “Required Connections” on page 1.) The
communication parameters for this port can be accessed from the Serial
Port Configuration screen shown below and described in the following
table.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Serial Port Configuration
Management Mode : CONSOLE MODE
Databits : 8
Parity : NONE
Time-Out (in minutes) : 10
Auto Refresh (in seconds) : 5
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
Baudrate : 19200
Stopbits : 1
Figure 2-11. Serial Port Configuration
Parameter Default Description
Management Mode Console Mode Indicates that the console port settings are for
Baud Rate Auto The rate at which data is sent between devices.
Databits 8 bits Sets the data bits of the RS-232 port.
Stopbits 1 bit Sets the stop bits of the RS-232 port.
Parity none Sets the parity of the RS-232 port.
Time-Out 10 minutes If no input is received from the attached device
Auto Refresh 5 seconds Sets the interval before a console session will
direct console connection.
Options : 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200 bps, and Auto
detection
Options : 7, 8
Options : 1, 2
Options : none/odd/even
after this interval, the current session is
automatically closed.
Range : 0 - 100 minutes; 0: disabled
auto refresh the console information, such as
Spanning Tree Information, Port Configuration,
Port Statistics, and RMON Statistics.
Range : 5-255 seconds; 0: disabled
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 17
Page 26
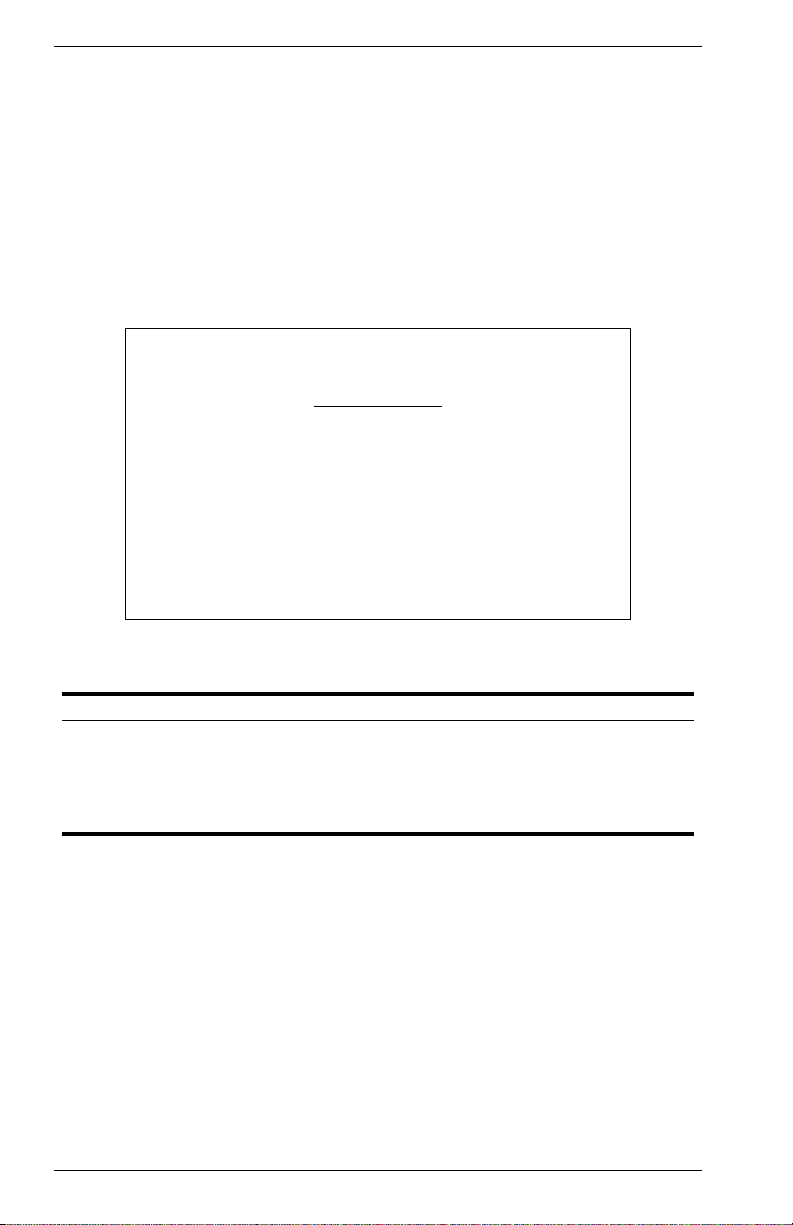
Assigning SNMP Parameters
Use the SNMP Configuration screen to display and modify parameters for
the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). The switch includes
an SNMP agent which monitors the status of its hardware, as well as the
traffic passing through its ports. A computer attached to the network,
called a Network Management Station (NMS), can be used to access this
information. Access rights to the switch are controlled by community
strings. To communicate with the switch, the NMS must first submit a valid
community string for authentication. The options for configuring
community strings and related trap functions are described in the
following sections.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
SNMP Configuration
Send Authentication Fail Traps : ENABLED
SNMP Communities ...
IP Trap Managers ...
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
Figure 2-12. SNMP Configuration
Parameter Description
Send Authentication
Fail Traps
SNMP Communities Assigns SNMP access based on specified strings.
IP Trap Managers Specifies management stations that will receive authentication
18 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Issue a trap message to specified IP trap managers whenever
authentication of an SNMP request fails. (The default is enabled.)
failure messages or other trap messages from the switch.
Page 27

Configuring Community Names
The following figure and table describe how to configure the community
strings authorized for management access. Up to 5 community names
may be entered.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
SNMP Configuration : SNMP Communities
Community Name Access Status
2. private READ/WRITE ENABLED
3.
4.
5.
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
1. public READ ONLY ENABLED
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Figure 2-13. SNMP Communities
Parameter Description
Community Name A community entry authorized for management access.
Maximum string length : 20 characters
Access Management access is restricted to Read Only or Read/Write.
Status Sets administrative status of entry to enabled or disabled.
Note: The default community strings are “public” with Read Only access, and
“private” with Read/Write access.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 19
Page 28
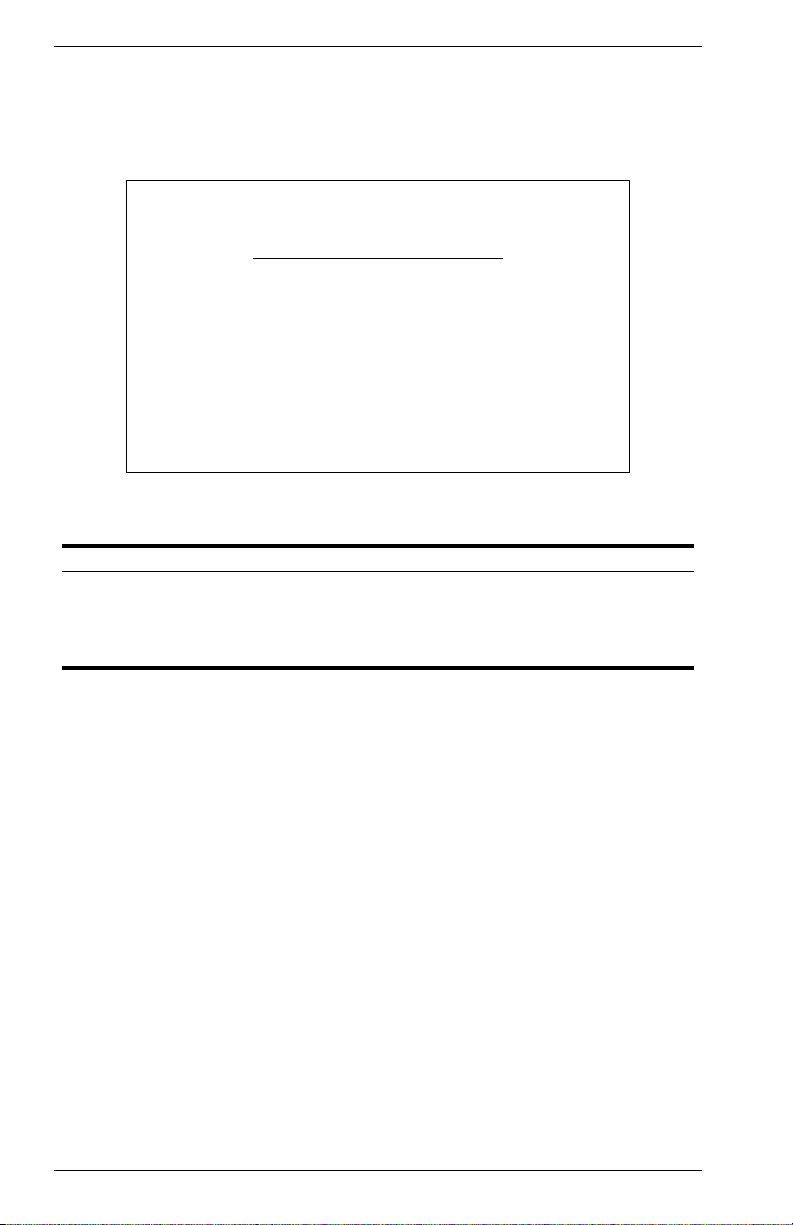
Configuring IP Trap Managers
The following figure and table describe how to specify management
stations that will receive authentication failure messages or other trap
messages from the switch. Up to 5 trap managers may be entered.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
SNMP Configuration : IP Trap Managers
IP Address Community Name Status
2.
3.
4.
5.
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
1. 10.1.0.23 public DISABLED
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Figure 2-14. IP Trap Managers
Parameter Description
IP Address IP address of the trap manager.
Community Name A community specified for trap management access.
Status Sets administrative status of selected entry to enabled or
disabled.
20 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 29
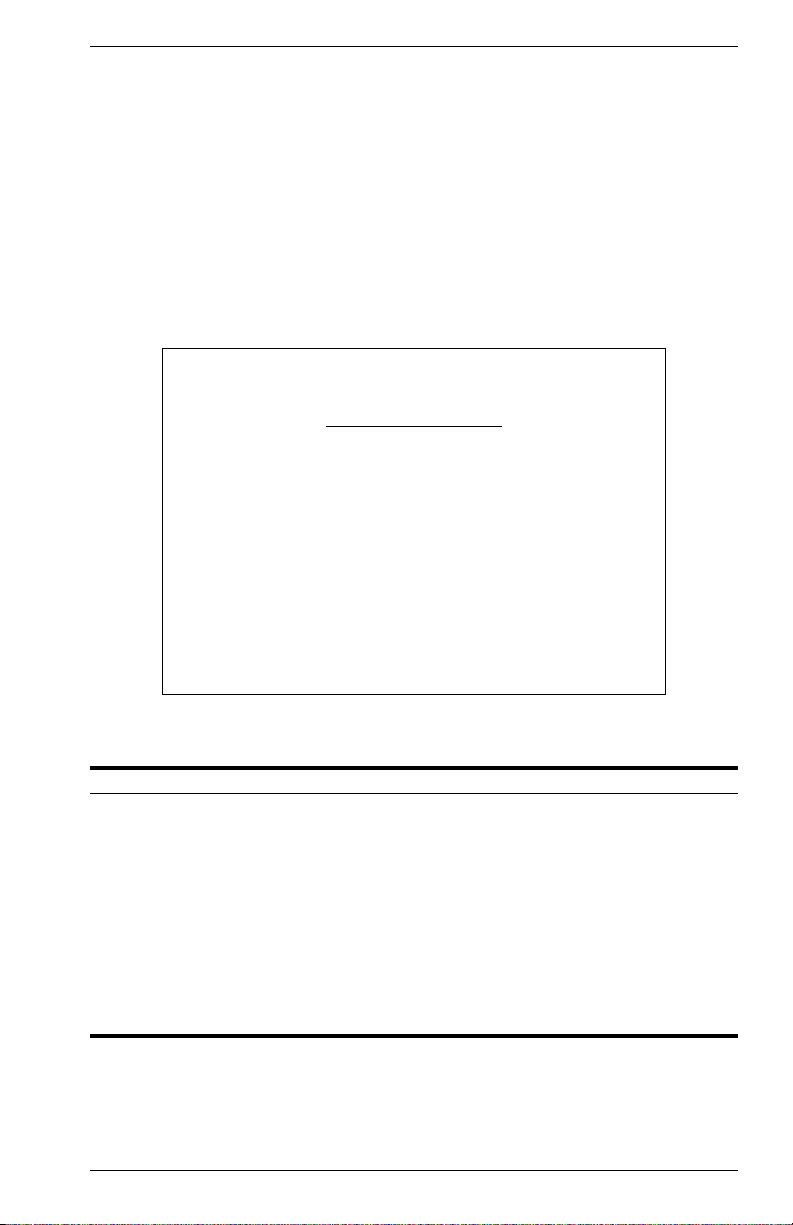
Console Login Configuration
Use the Management Setup: Console Login Configuration to restrict
management access based on specified user names and passwords, or
to set the invalid password threshold and timeout. There are only two user
types defined, ADMIN (Administrator) and GUEST, but you can set up to
five different user names and passwords. Only Administrators have write
access for parameters governing the switch. You should therefore assign
a user name and password to the default Administrator as soon as
possible, and store it in a safe place. (If for some reason your password
is lost, or you cannot gain access to the system configuration program,
contact Enterasys Technical Support for assistance.) The parameters
shown on this screen are indicated in the following figure and table.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Console Login Configuration
Lock-out Time (in minutes) : 0
User Type User Name Password
------------------------------------------------
1. ADMIN admin
2. GUEST guest
3.
4.
5.
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Password Threshold : 3
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Figure 2-15. Console Login Configuration
Parameter Default Description
Password Threshold 3 Sets the password intrusion threshold which limits
Lock-out Time 0 The time (in seconds) the management console
Admin* name: admin
password: null
Guest* name: guest
password: null
* Passwords can consist of up to 11 alphanumeric characters and are not case
sensitive.
the number of failed logon attempts.
Range : 0~65535
will be disabled, due to an excessive number of
failed logon attempts.
Range : 0~65535
Administrator has access privilege of Read/Write
for all screens.
Guest has access privilege of Read Only for all
screens.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 21
Page 30
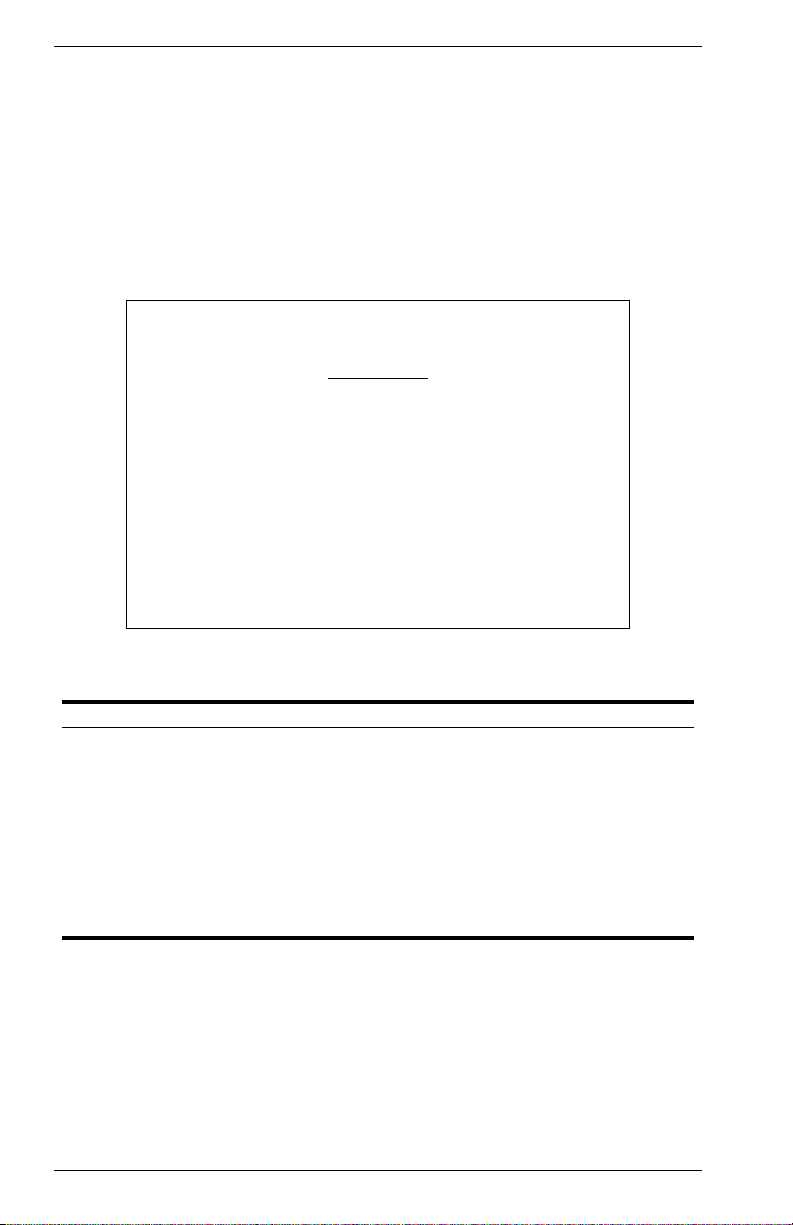
Downloading System Software
Using TFTP Protocol to Download Over the Network
Use the TFTP Download menu to load software updates into the switch.
The download file should be an VH-8G file from Enterasys; otherwise the
switch will not accept it. The success of the download operation depends
on the accessibility of the TFTP server and the quality of the network
connection. After downloading the new software, the switch will
automatically restart itself. Parameters shown on this screen are
indicated in the following figure and table.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
TFTP Download
Download Server IP : 0.0.0.0
Agent Software Upgrade : ENABLED
Download Filename : agent-v2.04
Download Mode : PERMANENT
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
[Process TFTP Download]
Download Status : Complete
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Figure 2-16. TFTP Download
Parameter Description
Download Server IP IP address of a TFTP server.
Agent Software
Upgrade
Download
Filename
Download Mode Indicates a download to permanent flash ROM.
[Process TFTP
Download]
Download Status Indicates if a download is “Complete” or “In Progress.”
Indicates that the switch is enabled for software upgrades.
The binary file to download to the switch.
Issues a request to the TFTP server to download the specified
file.
22 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 31

Saving the System Configuration
Use the Configuration Save & Restore menu to save the switch
configuration settings to a file on a TFTP server. The file can be later
downloaded to the switch to restore the switch’s settings. The success of
the operation depends on the accessibility of the TFTP server and the
quality of the network connection. Parameters shown on this screen are
indicated in the following figure and table.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Configuration Upload
Upload Server IP :
Upload Filename :
[Process TFTP Upload]
Upload status : Complete
Configuration Download
Download Server IP :
Download Filename :
[Process TFTP Download]
Download status : Complete
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Figure 2-17. Configuration Save & Restore
Parameter Description
Configuration Upload
Upload Server IP IP address of a TFTP server.
Upload Filename The name of the file to contain the switch configuration settings.
[Process TFTP
Upload]
Issues a request to upload the configuration settings to the
specified file on the TFTP server.
Upload Status Indicates if an upload is “Complete” or “In Progress.”
Configuration Download
Download Server IP IP address of a TFTP server.
Download Filename The name of the file that contains the switch configuration
settings you wish to restore.
[Process TFTP
Download]
Issues a request to the TFTP server to download the specified
file.
Download Status Indicates if a download is “Complete” or “In Progress.”
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 23
Page 32

Configuring Management Access
Use the Management Configuration menu to define which VLAN has
management access to the switch. Parameters shown on this screen are
indicated in the following figure and table.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Management Configuration
Management VLAN : ALL
VLAN : 1
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
Figure 2-18. Management Configuration
Parameter Default Description
Management VLAN All Select ALL to give all VLANs access to switch
VLAN 1 Specifies the VLAN ID that has access to switch
management, or ONE to restrict access to a
specified VLAN. If you select just one VLAN, you
must specify its VLAN ID on the following line.
management.
24 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 33

Configuring the Switch
The Device Control menu is used to control a broad range of functions,
including port configuration, Spanning Tree support for redundant
switches, port mirroring, multicast filtering, and Virtual LANs. Each of the
setup screens provided by these configuration menus is described in the
following sections.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Port Configuration ... Extended Bridge Configuration ...
Port Information ... 802.1P Configuration ...
Spanning Tree Configuration ... 802.1Q VLAN Base Information ...
Spanning Tree Information ... 802.1Q VLAN Current Table Information ...
Mirror Port Configuration ... 802.1Q VLAN Static Table Configuration ...
Port Trunking Configuration ... Port Assigment VLAN Configuration ...
IGMP Configuration ... Multicast Router Port Information ...
BStorm Control Configuration ... Static Multicast Router Port Cfg ...
Port GARP Configuration ... IGMP Member Port Configuration ...
Port GMRP Configuration ... Port Security Configuration ...
Device Control Menu
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
<OK>
Figure 2-19. Device Control Menu
Selection Description
Port Configuration Sets communication parameters for ports.
Port Information Displays current port settings and port status.
Spanning Tree
Configuration
Spanning Tree
Information
Mirror Port
Configuration
Port Trunking
Configuration
IGMP Configuration Configures IGMP multicast filtering.
BStorm Control
Configuration
Port GARP
Configuration*
Port GMRP
Configuration*
Extended Bridge
Configuration
802.1P Configuration Configures default port priorities and queue assignments.
Configures the switch, its ports and modules to participate in a
local Spanning Tree.
Displays the current Spanning Tree configuration for the switch,
its ports and modules.
Sets the source and target ports for mirroring.
Specifies ports to group into aggregate trunks.
Allows you to enable broadcast storm control and set the packetper-second threshold.
Configures generic attribute settings used in the spanning tree
protocol, VLAN registration, multicast filtering.
Configures GMRP multicast filtering.
Displays/configures extended bridge capabilities provided by this
switch, including support for traffic classes, and VLAN extensions.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 25
Page 34

Selection Description
802.1Q VLAN
Base Information
802.1Q VLAN
Displays basic VLAN information, such as VLAN version number
and maximum VLANs supported.
Displays VLAN groups and port members.
Current Table
Information
802.1Q VLAN Static
Table Configuration
Configures VLAN groups via static assignments, including setting
port members, or restricting ports from being dynamically added
to a port by the GVRP protocol.
Port Assignment
VLAN Configuration
Multicast Router Port
Information
Static Multicast
Router Port Cfg
IGMP Member Port
Configuration
Port Security
Displays/configures port-specific VLAN settings, including PVID,
ingress filtering, and 802.1Q trunks.
Displays the ports on the switch attached to a neighboring
multicast router/switch for each VLAN ID.
Assigns ports that are attached to a neighboring multicast router/
switch.
Assigns ports that are attached to hosts who want to receive a
specific multicast service.
Allows you to enable and configure port security for the switch.
Configuration
* Not implemented in the current firmware release.
26 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 35

Configuring Port Parameters
Use the Port Configuration menus to set or display communication
parameters for any port on the switch.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Port Configuration
Port Type Admin Flow Speed and
Control Duplex
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Flow Control on all ports : [Enable] [Disable]
1. 1000SX ENABLED ENABLED 1000-HALF
2. 1000SX ENABLED ENABLED 1000-FULL
3. 1000SX ENABLED ENABLED AUTO
4. 1000SX ENABLED ENABLED AUTO
5. 1000SX ENABLED ENABLED 1000-FULL
6. 1000SX ENABLED ENABLED 1000-HALF
7. 1000SX ENABLED ENABLED AUTO
8. 1000SX ENABLED ENABLED AUTO
Use <TAB> or arrows keys to move. <Space> to scroll options.
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
: Port 1 - 8
Figure 2-20. Port Configuration
Parameter Default Description
Flow Control on all
ports
Type Shows port type as 1000SX (1000Base-SX)
Admin ENABLED Allows you to disable a port due to abnormal
Flow Control DISABLED Used to enable or disable flow control. Flow
Speed and Duplex AUTO Used to set the current port speed, duplex mode,
DISABLED Allows you to enable or disable flow control for all
ports on the switch.
behavior (e.g., excessive collisions), and then reenable it after the problem has been resolved.
You may also disable a port for security reasons.
control can eliminate frame loss by “blocking”
traffic from end stations or segments connected
directly to the switch when its buffers fill. Back
pressure is used for half duplex and IEEE 802.3x
for full duplex.
and auto-negotiation.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 27
Page 36

Viewing the Current Port Configuration
The Port Information screen displays the port type, status, link state, and
flow control in use, as well as the communication speed and duplex mode.
To change any of the port settings, use the Port Configuration menu. .
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Port Information
Port Type Operational Link FlowControl Speed and
InUse Duplex InUse
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. 1000SX YES DOWN ----------------- ----------------
2. 1000SX YES DOWN ----------------- ----------------
3. 1000SX YES UP 802.3x 1000-FULL
4. 1000SX YES DOWN ----------------- ----------------
5. 1000SX YES DOWN ----------------- ----------------
6. 1000SX YES UP NONE 1000-HALF
7. 1000SX YES UP 802.3x 1000-FULL
8. 1000SX YES UP BACK_PRESSURE 1000-HALF
Use <TAB> or arrows keys to move. <Enter> to select.
: Port 1 - 8
<OK>
Figure 2-21. Port Information
Parameter Description
Type Shows port type as 1000SX (1000Base-SX)
Operational Shows if the port is functioning or not.
Link Indicates if the port has a valid connection to an external device.
FlowControl InUse Shows the flow control type in use. Flow control can eliminate
Speed and
DuplexInUse
frame loss by “blocking” traffic from end stations connected
directly to the switch. Back pressure is used for half duplex and
IEEE 802.3x for full duplex.
Displays the current port speed and duplex mode used.
Page 37

Using the Spanning Tree Algorithm
The Spanning Tree Algorithm can be used to detect and disable network
loops, and to provide backup links between switches, bridges or routers.
This allows the switch to interact with other bridging devices (that is, an
STA-compliant switch, bridge or router) in your network to ensure that
only one route exists between any two stations on the network. For a
more detailed description of how to use this algorithm, refer to Appendix
A, “Spanning Tree Concepts” on page 83.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Spanning Tree Configuration : Selection Menu
STA Bridge Configuration ...
STA Port Configuration ...
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Figure 2-22. Spanning Tree Configuration
Configuring Bridge STA
The following figure and table describe Bridge STA configuration.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Spanning Tree Configuration : Bridge STA Configuration
Spanning Tree Protocol : ENABLED
Priority : 32768
Hello Time (in seconds) : 2
Max Age (in seconds) : 20
Forward Delay (in seconds) : 15
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options,
Figure 2-23. Bridge STA Configuration
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 29
Page 38

Parameter Default Description
Spanning Tree
Protocol
Enabled Enable this parameter to participate in an STA
compliant network.
Priority 32,768 Device priority is used in selecting the root device,
root port, and designated port. The device with
the highest priority becomes the STA root device.
However, if all devices have the same priority, the
device with the lowest MAC address will then
become the root device.
Enter a value from 0 - 65535.
Remember that the lower the numeric value, the
higher the priority.
Hello Time 2 Time interval (in seconds) at which the root device
transmits a configuration message.
The minimum value is1.
The maximum value is
the lower of 10 or [(Max. Message Age / 2) -1].
Max (Message) Age 20 The maximum time (in seconds) a device can wait
without receiving a configuration message before
attempting to reconfigure. All device ports (except
for designated ports) should receive configuration
messages at regular intervals. Any port that ages
out STA information (provided in the last
configuration message) becomes the designated
port for the attached LAN. If it is a root port, a new
root port is selected from among the device ports
attached to the network.
The minimum value is
the higher of 6 or [2 x (Hello Time + 1)].
The maximum value is
the lower of 40 or [2 x (Forward Delay - 1)].
Forward Delay 15 The maximum time (in seconds) the root device
will wait before changing states (i.e., listening to
learning to forwarding). This delay is required
because every device must receive information
about topology changes before it starts to forward
frames. In addition, each port needs time to listen
for conflicting information that would make it
return to a blocking state; otherwise, temporary
data loops might result.
The maximum value is 30.
The minimum value is
the higher of 4 or [(Max. Message Age / 2) + 1].
30 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 39

Configuring STA for Ports
The following figure and table describe STA configuration for ports.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Fast forwarding mode of all ports : [Enable] [Disable]
--------------------------------------------------- 1 1000SX 128 4 ENABLED
2 1000SX 128 4 ENABLED
3 1000SX 128 4 ENABLED
4 1000SX 128 4 ENABLED
5 1000SX 128 4 ENABLED
6 1000SX 128 4 ENABLED
7 1000SX 128 4 ENABLED
8 1000SX 128 4 ENABLED
Spanning Tree Port Configuration : Port 1 - 8
Port Type Priority Cost FastForwarding
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Figure 2-24. Spanning Tree Port Configuration
Parameter Default Description
Fast forwarding mode
of all ports
Type Shows the port type as 1000SX (1000Base-SX).
Priority 128 Defines the priority for the use of a port in the STA
(Path) Cost 100/19/4 This parameter is used by the STA algorithm to
ENABLED Allows you to enable or disable fast forwarding for
all ports on the switch.
algorithm. If the path cost for all ports on a switch
are the same, the port with the highest priority
(i.e., lowest value) will be configured as an active
link in the spanning tree. Where more than one
port is assigned the highest priority, the port with
lowest numeric identifier will be enabled.
The range is 0 - 255.
determine the best path between devices.
Therefore, lower values should be assigned to
ports attached to faster media, and higher values
assigned to ports with slower media.
(Path cost takes precedence over port priority.)
The default and recommended range is:
Ethernet: 100 (50~600)
Fast Ethernet: 19 (10~60)
Gigabit Ethernet: 4 (3~10)
The full range is 0 - 65535.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 31
Page 40

Parameter Default Description
FastForwarding ENABLED This parameter is used to enable/disabled the
Fast Spanning Tree mode for the port. In this
mode, ports skip the Blocked, Listening and
Learning states and proceed straight to
Forwarding.
FastForwarding enables end-node workstations
and servers to overcome time-out problems when
the Spanning Tree Algorithm is implemented in a
network. Therefore, FastForwarding should only
be enabled for ports that are connected to an endnode device.
Viewing the Current Spanning Tree Configuration
The Spanning Tree Information screen displays a summary of the STA
information for the overall bridge or for a specific port. To make any
changes to the parameters for the Spanning Tree, use the Spanning Tree
Configuration menu.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Spanning Tree Information : Selection Menu
STA Bridge Information ...
STA Port Information ...
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Figure 2-25. Spanning Tree Information
<OK>
32 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 41

Displaying the Current Bridge STA
The parameters shown in the following figure and table describe the
current Bridge STA Information.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Spanning Tree Information : Bridge STA Information
Priority : 32768
Hello Time (in seconds) : 2
Max Age (in seconds) : 20
Forward Delay (in seconds) : 15
Hold Time (in seconds) : 1
Designated Root : 0.0000E800E800
Root Cost : 4
Root Port : 1
Configuration Changes : 2
Topology Up Time : 48069 (0 day, 1 hr, 2min, 34 sec)
<OK>
Use <Tab> or arrow keys to move, <Enter> to select.
Figure 2-26. Bridge STA Information
Parameter Description
Priority Device priority is used in selecting the root device, root port, and
Hello Time The time interval (in seconds) at which the root device transmits a
Max Age The maximum time (in seconds) a device can wait without receiving a
Forward Delay The maximum time (in seconds) the root device will wait before
Hold Time The minimum interval between the transmission of consecutive
Designated Root The priority and MAC address of the device in the spanning tree that
Root Cost The path cost from the root port on this switch to the root device.
Root Port The number of the port on this switch that is closest to the root. This
Configuration
Changes
Topology Up Time The time since the spanning tree was last reconfigured.
designated port. The device with the highest priority becomes the STA
root device. However, if all devices have the same priority, the device
with the lowest MAC address will then become the root device.
configuration message.
configuration message before attempting to reconfigure.
changing states (i.e., listening to learning to forwarding).
Configuration BPDUs.
this switch has accepted as the root device.
switch communicates with the root device through this port. If there is
no root port, then this switch has been accepted as the root device of
the spanning tree network.
The number of times the spanning tree has been reconfigured.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 33
Page 42

Displaying the Current STA for Ports
The parameters shown in the following figure and table are for port STA
Information.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Spanning Tree Port Information
Port Type Status Designated Designated Designated
Cost Bridge Port
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. 1000SX FORWARDING 4 0.0000E800E800 128.3
2. 1000SX FORWARDING 4 32768.00E029522800 128.1
3. 1000SX FORWARDING 4 32768.00E029522800 128.1
4. 1000SX FORWARDING 4 32768.00E029522800 128.5
5. 1000SX LISTENING 4 32768.00E029522800 128.6
6. 1000SX LEARNING 4 32768.00E029522800 128.3
7. 1000SX FORWARDING 4 32768.00E029522800 128.3
8. 1000SX FORWARDING 4 32768.00E029522800 128.3
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrows keys to move. <Enter> to select.
: Port 1 - 8
Figure 2-27. Spanning Tree Port Information
Parameter Description
Type Shows port type as 1000SX (1000Base-SX).
Status Displays the current state of this port within the spanning tree:
Broken There is no valid link on the port.
Disabled Port has been disabled by the user or has failed
Blocking Port receives STA configuration messages, but does
Listening Port will leave blocking state due to topology change,
Learning Has transmitted configuration messages for an
Forwarding The port forwards packets, and continues learning
diagnostics.
not forward packets.
starts transmitting configuration messages, but does
not yet forward packets.
interval set by the Forward Delay parameter without
receiving contradictory information. Port address
table is cleared, and the port begins learning
addresses.
addresses.
34 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 43

Parameter Description
The rules defining port status are:
• A port on a network segment with no other STA-compliant
bridging device is always forwarding.
• If two ports of a switch are connected to the same segment
and there is no other STA device attached to this segment,
the port with the smaller ID forwards packets and the other is
blocked.
• All ports are blocked when the switch is booted, then some
of them change state to listening, to learning, and then to
forwarding.
Designated Cost The cost for a packet to travel from this port to the root in the
current spanning tree configuration. The slower the media, the
higher the cost.
Designated Bridge
(ID)
The priority and MAC address of the device through which this
port must communicate to reach the root of the spanning tree.
Designated Port (ID) The priority and number of the port on the designated bridging
device through which this switch must communicate with the root
of the spanning tree.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 35
Page 44

Using a Mirror Port for Analysis
You can mirror traffic from any source port to a target port for real-time
analysis. You can then attach a logic analyzer or RMON probe to the
target port and study the traffic crossing the source port in a completely
unobtrusive manner. When mirroring port traffic, note that the target port
must be configured in the same VLAN as the source port (see Configuring
Virtual LANs on page 47).
You can use the Mirror Port Configuration screen to designate a single
port pair for mirroring as shown below:
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Mirror Port Configuration
Mirror Source Port : Port 1
Mirror Target Port : Port 2
Status : DISABLED
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Figure 2-28. Mirror Port Configuration
Parameter Description
Mirror Source Port The port whose traffic will be monitored.
Mirror Target Port The port that will duplicate or “mirror” all the traffic happening on
Status Enables or disables the mirror function.
36 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
the monitored port.
Page 45

Configuring Port Trunks
Port trunks can be used to increase the bandwidth of a network
connection or to ensure fault recovery. You can configure up to four trunk
connections (combining 2~4 ports into a fat pipe) between any two VH-8G
switches. However, before making any physical connections between
devices, use the Trunk Configuration menu to specify the trunk on the
devices at both ends. When using a port trunk, note that:
• Ports can only be assigned to one trunk.
• The ports at both ends of a connection must be configured as trunk
ports.
• The ports at both ends of a trunk must be configured in an identical
manner, including duplex mode, and VLAN assignments.
• None of the ports in a trunk can be configured as a mirror source port
or mirror target port.
• All the ports in a trunk have to be treated as a whole when moved
from/to, added or deleted from a VLAN.
• The Spanning Tree Algorithm will treat all the ports in a trunk as a
whole.
• Enable the trunk prior to connecting any cable between the switches
to avoid creating a loop.
• Disconnect all trunk port cables or disable the trunk ports before
removing a port trunk to avoid creating a loop.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 37
Page 46

You can use the Port Trunking Configuration screen set up port trunks as
shown below:
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Port Trunking Configuration
Trunk ID Status Member List
1 2 3 4
------------- ------------- ---------------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------------
Port : -- Port : -- Port : -- Port : --
Port : -- Port : -- Port : -- Port : --
Port : -- Port : -- Port : -- Port : --
Trunk ID : 1 Trunk ID : 1 Member Port : 1
[Show] [More]
[Enable] [Disable] [Add] [Delete]
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
<OK>
Figure 2-29. Port Trunking Configuration
Parameter Description
Trunk ID Configure up to four trunks per switch (ID of 1~4).
Port Select from 2~4 ports per trunk.
[Show] Displays trunk settings, where the first trunk listed is specified by
[More] Scrolls through the list of configured trunks.
[Enable] [Disable] Enables/disables the selected trunk.
“Sorted by Trunk ID.”
38 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 47

IGMP Multicast Filtering
Multicasting is used to support real-time applications such as video
conferencing or streaming audio. A multicast server does not have to
establish a separate connection with each client. It merely broadcasts its
service to the network, and any hosts which want to receive the multicast
register with their local multicast switch/router. Although this approach
reduces the network overhead required by a multicast server, the
broadcast traffic must be carefully pruned at every multicast switch/router
it passes through to ensure that traffic is only passed on the hosts which
subscribed to this service.
This switch uses IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) to query
for any attached hosts who want to receive a specific multicast service.
The switch looks up the IP Multicast Group used for this service and adds
any port which received a similar request to that group. It then propagates
the service request on to any neighboring multicast switch/router to
ensure that it will continue to receive the multicast service. (For more
information, see “IGMP Snooping and IP Multicast Filtering” on page 95.)
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 39
Page 48

Configuring IGMP
This protocol allows a host to inform its local switch/router that it wants to
receive transmissions addressed to a specific multicast group. You can
use the IGMP Configuration screen to configure multicast filtering shown
below:
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
IGMP Configuration
IGMP Status : DISABLED
Act as IGMP Querier : DISABLED
IGMP Query Count : 2
IGMP Report Delay (Seconds) : 10
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
Figure 2-30. IGMP Configuration
Parameter Description
IGMP Status If enabled, the switch will monitor network traffic to determine
Act as IGMP Querier If enabled, the switch can serve as the “querier,” which is
IGMP Query Count The maximum number of queries issued for which there has been
IGMP Report Delay The time (in seconds) between receiving an IGMP Report for an
Note: The default values are indicated in the sample screen.
which hosts want to receive multicast traffic.
responsible for asking hosts if they want to receive multicast
traffic.
no response before the switch takes action to solicit reports.
(Range: 1 - 10.)
IP multicast address on a port before the switch sends an IGMP
Query out of that port and removes the entry from its list.
(Range: 5 - 30.)
40 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 49

Configuring Broadcast Storm Control
Use the Broadcast Storm Control Configuration screen to enable
broadcast storm control for any port on the switch, as shown below:
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Broadcast Storm Control Configuration
Broadcast control on all ports : [Enable] [Disable]
Port Threshold Broadcast Control
------------------------------------------------------ 1 500 ENABLED
2 500 ENABLED
3 500 ENABLED
4 500 ENABLED
5 500 ENABLED
6 500 ENABLED
7 500 ENABLED
8 500 ENABLED
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
: Port 1 - 8
Figure 2-31. Broadcast Storm Control Configuration
Parameter Description
Broadcast Control on
All Ports
Threshold The packet-per-second threshold for broadcast packets on the
Broadcast Control Enables/disables broadcast control for the port. When enabled,
Allows you to enable/disable broadcast storm control for all ports
on the switch.
port. (Default is 500 pps.)
the switch drops all broadcast packets if the packet-per-second
threshold is exceeded. (Default is Enabled.)
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 41
Page 50

Configuring Bridge MIB Extensions
The Bridge MIB includes extensions for managed devices that support
Traffic Classes, Multicast Filtering and Virtual LANs. To configure these
extensions, use the Extended Bridge Configuration screen as shown
below:
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Extended Bridge Configuration
Extended Multicast Filtering Services: NO
Static Entry Individual Port : YES
Bridge Settings :
Traffic Class : TRUE
Bridge Capability : (Read Only)
Traffic Classes : YES
Configurable PVID Tagging : YES
Local VLAN Capable : NO
VLAN Learning : SVL
GMRP : DISABLED
GVRP : DISABLED
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Space> to scroll options.
Figure 2-32. Extended Bridge Configuration
Parameter Description
Bridge Capability
Extended Multicast
Filtering Services
Traffic Classes Indicates that the switch provides mapping of user priorities to
Static Entry
Individual Port
Configurable
PVID Tagging
Local VLAN
Capable
Indicates that the switch does not support the filtering of individual
multicast addresses based on GMRP (GARP Multicast
Registration Protocol). Note that this function is not implemented
for the current firmware release.
multiple traffic classes. (Refer to 802.1P Configuration.)
Indicates that the switch allows the static filtering for unicast and
multicast addresses. (Refer to Network Monitor Menu / Static
Unicast Address Table Configuration and Static Multicast
Address Table Configuration.)
Indicates that the switch allows you to override the default PVID
setting (Port VLAN ID used in frame tags) and its egress status
(VLAN-Tagged or Untagged) on each port. (Refer to Port
Assignment VLAN Configuration.)
This switch does not support multiple local bridges (that is,
multiple Spanning Trees).
42 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 51

Parameter Description
Bridge Settings
Traffic Class* Multiple traffic classes are supported by this switch as indicated
under Bridge Capabilities. However, you can disable this function
by setting this parameter to False.
VLAN Learning As default this switch uses Shared VLAN Learning (SVL),
whereby all ports share one VLAN filtering database. However,
you can set the switch to use Independent VLAN Learning (IVL),
where each port maintains its own filtering database.
Note that when you change from one method to the other, the
switch will automatically reset and the current VLAN configuration
will be lost.
GMRP* GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP) allows network
devices to register endstations with multicast groups.
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is currently
used by this switch to provide automatic multicast filtering.
GVRP* GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) defines a way for
switches to exchange VLAN information in order to register
necessary VLAN members on ports across the network. This
function should be enabled to permit VLANs groups which extend
beyond the local switch.
* Not implemented in the current firmware release.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 43
Page 52

Configuring Traffic Classes
IEEE 802.1p defines up to 8 separate traffic classes. This switch supports
Quality of Service (QoS) by using two priority queues, with weighted fair
queuing for each port. You can use the 802.1P Configuration menu to
configure the default priority for each port, or to display the mapping for
the traffic classes as described in the following sections. Also, refer to
Appendix C, “Class of Service” on page 93. .
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
802.1P Configuration : Selection Menu
802.1P Port Priority Configuration ...
802.1P Port Traffic Class Information ...
Use <TAB> or arrows keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Figure 2-33. 802.1P Configuration
<OK>
44 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 53

Port Priority Configuration
The default priority for all ingress ports is zero. Therefore, any inbound
frames that do not have priority tags will be placed in the low priority
output queue. Default priority is only used to determine the output queue
for the current port; no priority tag is actually added to the frame. You can
use the 802.1P Port Priority Configuration menu to adjust default priority
for any port as shown below:
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
802.1P Port Priority Configuration :
User Priority Traffic Class
--------------------------------------------------------- 1 0 2
5 0 2
6 0 2
Port Default Ingress Number of Egress
2 0 2
3 0 2
4 0 2
7 0 2
8 0 2
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Port 1 - 8
Figure 2-34. 802.1P Port Priority Configuration
Parameter Description
Port Numeric identifier for switch port.
Default Ingress User
Priority
Number of Egress
Traffic Classes
Default priority can be set to any value from 0~7, where 0~3
specifies the low priority queue and 4~7 specifies the high priority
queue.
Indicates that this switch supports two priority output queues.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 45
Page 54

802.1P Port Traffic Class Information
This switch provides two priority levels with weighted fair queuing for port
egress. This means that any frames with a default or user priority from
0~3 are sent to the low priority queue “0” while those from 4~7 are sent to
the high priority queue “1” as shown in the following screen:
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
802.1P Port Traffic Class Information
Port User Priority
----------------------------------------------------------------- 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
5 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
2 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
3 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
4 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
6 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
7 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
8 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
<OK>
: Port 1 - 8
Figure 2-35. 802.1P Port Traffic Class Information
Parameter Description
Port Numeric identifier for switch port.
User Priority Shows that user priorities 0~3 specify the low priority queue and
4~7 specify the high priority queue.
46 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 55

Configuring Virtual LANs
You can use the VLAN configuration menu to assign any port on the
switch to any of up to 256 LAN groups. In conventional networks with
routers, broadcast traffic is split up into separate domains. Switches do
not inherently support broadcast domains. This can lead to broadcast
storms in large networks that handle a lot of IPX and NetBeui traffic. By
using IEEE 802.1Q compliant VLANs and GARP VLAN Registration
Protocol, you can organize any group of network nodes into separate
broadcast domains, confining broadcast traffic to the originating group.
This also provides a more secure and cleaner network environment. For
more information on how to use VLANs, see Appendix B, “Virtual LANs
(VLANs)” on page 89. The VLAN configuration screens are described in
the following sections.
802.1Q VLAN Base Information
The 802.1Q VLAN Base Information screen displays basic information on
the VLAN type supported by this switch.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
802.1Q VLAN Base Information
VLAN Version Number : 1
MAX VLAN ID : 2048
MAX Supported VLANs : 256
Current Number of 802.1Q VLANs Configured : 2
<OK>
Return to previous panel.
<Enter> to select.
Figure 2-36. 802.1Q VLAN Base Information
Parameter Description
VLAN Version
Number
MAX VLAN ID Maximum VLAN ID recognized by this switch.
MAX Supported
VLANs
Current Number of
VLANs Configured
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 47
The VLAN version used by this switch as specified in the IEEE
802.1Q standard.
Maximum number of VLANs that can be configured on this
switch.
The number of VLANs currently configured on this switch.
Page 56

802.1Q VLAN Current Table Information
This screen shows the current port members of each VLAN and whether
or not the port supports VLAN tagging. Ports assigned to a large VLAN
group that crosses several switches should use VLAN tagging. However,
if you just want to create a small port-based VLAN for one or two switches,
you can assign ports to the same untagged VLAN (page 51). The current
configuration is shown in the following figure.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
802.1Q VLAN Current Table Information
Current Egress Ports Current Untagged Ports
11111111 11111111
Sorted by VID : 1
[Show] [More]
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Deleted VLAN Entry Counts : 0
VID Creation Time Status
------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 0 (0 day 0 hr 0 min 0 sec) Dynamic GVRP
Port 1 Port 8
<OK>
Figure 2-37. 802.1Q VLAN Current Table Information
Parameter Description
Deleted VLAN Entry
Counts
VID The ID for the VLAN currently displayed.
Creation Time The value of sysUpTime (System Up Time) when this VLAN was
Status Shows how this VLAN was added to the switch:
Current Egress Ports Shows the ports which have been added to the displayed VLAN
Current Untagged
Ports
[Show] Displays the members for the VLAN indicated by the “Sorted by
[More] Displays any subsequent VLANs if configured.
The number of times a VLAN entry has been deleted from this
table.
created.
Dynamic GVRP: Automatically learned via GVRP.
Permanent: Added as a static entry.
group, where “1” indicates that a port is a member and “0” that it
is not.
If a port has been added to the displayed VLAN (see Current
Egress Ports), its entry in this field will be “1” if the port is
untagged or “0” if tagged.
VID” field.
48 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 57

802.1Q VLAN Static Table Configuration
Use this screen to create a new VLAN or modify the settings for an
existing VLAN. You can add/delete port members for a VLAN, or prevent
a port from being automatically added to a VLAN via the GVRP protocol.
(Also, note that all ports can only belong to one untagged VLAN. This is
set to VLAN 1 by default, but can be changed via the Port Assignment
VLAN Configuration screen on page 51.)
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
1Q VLAN Static Table Configuration
VID VLAN Name Status
-------------------------------------1 Active
Egress Ports Forbidden Egress Ports
11111111 000 0 00 00
Untagged Ports
11111111 VID : 1
[Show]
[More]
[New]
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
<Enter> to select.
Figure 2-38. 802.1Q VLAN Static Table Configuration
Parameter Description
VID The ID for the VLAN currently displayed.
Range: 1-2048
VLAN Name A user-specified symbolic name for this VLAN.
String length: Up to 8 alphanumeric characters
Status Sets the current editing status for this VLAN as:
Not in Service, Destroy, or Active.
Egress Ports Set the entry for any port in this field to “1” to add it to the
Forbidden Egress
Ports
Untagged Ports Set the entry for any port in this field to “1” to add it to the
[Show] Displays settings for the specified VLAN.
[More] Displays consecutively numbered VLANs.
[New] Sets up the screen for configuring a new VLAN.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 49
displayed VLAN, or “0” to remove it from the VLAN.
Prevents a port from being automatically added to this VLAN via
GVRP.
displayed VLAN as an untagged port.
Page 58

For example, the following screen displays settings for VLAN 2, which
includes tagged ports 1-4, and forbidden port 8.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8GVH-8G
1Q VLAN Static Table Configuration
VID VLAN Name Status
-------------------------------------2 Active
Egress Ports Forbidden Egress Ports
1111 0000 0 00 0 00 01
Untagged Ports
00000000 VID : 2
[Show]
[More]
[New]
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
<Enter> to select.
Figure 2-39. 802.1Q VLAN Static Table Configuration Example
50 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 59

Port Assignment VLAN Configuration
Use this screen to configure port-specific settings for IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
features.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Port Assignment VLAN Configuration
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Port ID : 1 [Show]
[More]
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
Port PVID 802.1Q Trunk Ingress Filter
1 3 NO TRUE
2 3 NO TRUE
3 1 NO FALSE
4 1 NO FALSE
5 1 NO FALSE
6 1 NO FALSE
7 1 NO FALSE
8 1 NO FALSE
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Figure 2-40. Port Assignment VLAN Configuration
Parameter Description
PVID The VLAN ID assigned to untagged frames received on this port.
802.1Q Trunk Used to enable/disable the VLAN trunk status for the port. A
Ingress Filter* If set to “True,” incoming frames for VLANs which do not include
[Show] Displays settings for the specified port.
[More] Displays consecutively numbered ports.
* This control does not affect VLAN independent BPDU frames, such as GVRP or
STP. However, it does affect VLAN dependent BPDU frames, such as GMRP.
Use the PVID to assign ports to the same untagged VLAN.
VLAN Trunk link between two VLAN-aware switches will carry
traffic from all VLANs, allowing VLAN tagged frames to maintain
their VLAN ID across multiple switches. When enabled, a port
joins all configured VLANs and the untagged port VLAN ID
(PVID) is set to 4000, a reserved VLAN ID for trunk ports.
this port in their member set will be discarded at the inbound port.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 51
Page 60

Multicast Router Port Information
You can use the Multicast Router Port Information screen to display the
ports on this switch attached to a neighboring multicast router/switch for
each VLAN ID.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Multicast Router Port Information
Dynamic Router Port List Static Router Port List
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
11000000 00000000
Sorted by VID : 1
[Show] [More]
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
Figure 2-41. Multicast Router Port Information
Parameter Description
Dynamic Router Port
List
Static Router Port List The switch ports that have been manually listed as being
Sorted by VID The VLAN ID number used to sort the list.
[Show] Displays settings for the specified VLAN ID.
[More] Displays consecutively numbered VLAN IDs.
The switch ports that have been automatically listed as being
attached to a neighboring multicast router/switch.
attached to a neighboring multicast router/switch.
<OK>
52 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 61

Static Multicast Router Port Configuration
You can use the Static Multicast Router Port Configuration screen to
assign ports that are attached to a neighboring multicast router/switch.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Static Multicast Router Port Configuration
Static Multicast Router Port List
--------------------------------------------------- 00000010
Sorted by VID : 1 Port : 1
[Show] [More] [Add] [Delete]
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
Figure 2-42. Static Multicast Router Port Configuration
Parameter Description
Static Multicast
Router Port List
Sorted by VID The VLAN ID number used to sort the list.
[Show] Displays settings for the specified VLAN ID.
[More] Displays consecutively numbered VLAN IDs.
[Add] Adds a new router port to the current list.
[Delete] Removes a router port from the current list.
A list of the switch ports that have been manually configured as
being attached to a neighboring multicast router/switch.
<OK>
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 53
Page 62

IGMP Member Port Configuration
You can use the IGMP Member Port Configuration screen to assign ports
that are attached to hosts who want to receive a specific multicast service.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
IGMP Member Port Configuration
Dynamic IGMP Member Port List Static IGMP Member Port List
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VID :
Multicast IP : Port : 1
[Show] [More] [Add] [Delete]
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
Figure 2-43. IGMP Member Port Configuration
Parameter Description
Dynamic IGMP
Member Port List
Static IGMP Member
Port List
VID The VLAN ID number used to sort the list.
Multicast IP The IP address for a specific multicast service that is used to sort
[Show] Displays settings for the specified VLAN ID.
[More] Displays consecutively numbered VLAN IDs.
[Add] Adds a new host port to the current list.
[Delete] Removes a host port from the current list.
A list of the switch ports that have been automatically configured
as being attached to a IGMP host.
A list of the switch ports that have been manually configured as
being attached to a IGMP host.
the list.
<OK>
54 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 63

Port Security Configuration
Use the Port Security Configuration screen to enable and configure port
security for the switch. Port security allows you to configure each port with
a list of MAC addresses of devices that are authorized to access the
network through that port.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Port Security Configuration
MAC Address MAC Address
--------------------------------------------------------------
Secure address count = 0
Port : 1 MAC : 00-00-00-00-00-00
[Show] [More] [Add] [Delete]
Mode:DISABLE [Apply] [Clear]
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
Figure 2-44. Port Security Configuration
Parameter Description
MAC Address A list of the authorized MAC addresses that can access the
network through the specified port.
Secure Address Count The number of authorized MAC addresses for the specified
port.
Port The port number on the unit.
[Show] Displays authorized MAC addresses for the specified port.
[More] Displays more MAC addresses for the port.
Mode Port security can set to three states; Static, Disable, or
Learning. When set to Static, the switch will drop packets from
the port if the source MAC address does not match one of the
addresses in the MAC Address list. If set to Learning, the
switch will use the last valid source address to filter packets
from the port.
[Apply] Applies a change of Mode to the port.
MAC A specific MAC address to be added or deleted from the list.
[Add] Adds a new MAC address to the current list.
[Delete] Removes a MAC address from the current list.
[Clear] Clears all the MAC addresses for the current port.
<OK>
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 55
Page 64

Monitoring the Switch
The Network Monitor Menu provides access to port statistics, RMON
statistics, IP multicast addresses, and the static (unicast) address table.
Each of the screens provided by these menus is described in the following
sections.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Port Statistics ...
RMON Statistics ...
Unicast Address Table ...
Multicast Address Registration Table ...
IP Multicast Registration Table ...
Static Unicast Address Table Configuration ...
Static Multicast Address Table Configuration...
Network Monitor Menu
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
<OK>
Figure 2-45. Network Monitor Menu
Parameter Description
Port Statistics Displays statistics on network traffic passing through the selected
RMON Statistics Displays detailed statistical information for the selected port such
Unicast
Address Table
Multicast Address
Registration Table*
IP Multicast
Registration Table
Static Unicast
Address Table
Configuration
Static Multicast
Address Table
Configuration*
* Not implemented in the current firmware release.
port.
as packet type and frame size counters.
Provides full listing of all unicast addresses stored in the switch,
as well as sort, search and clear functions.
Displays the ports that belong to each GMRP Muticast group.
Displays the ports that belong to each IP Muticast group.
Allows you to display or configure static unicast addresses.
Allows you to display or configure static GMRP multicast
addresses.
56 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 65

Displaying Port Statistics
Port Statistics display key statistics from the Ethernet-like MIB for each
port. Error statistics on the traffic passing through each port are displayed.
This information can be used to identify potential problems with the switch
(such as a faulty port or unusually heavy loading). The values displayed
have been accumulated since the last system reboot.
Select the required port. The statistics displayed are indicated in the
following figure and table.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Port Statistics :
EtherLike Counter:
Alignment Errors :0 Late Collisions :0
FCS Errors :0 Excessive Collisions :0
Single Collision Frames :0 Internal MAC Transmit Errors:0
Multiple Collision Frames:0 Carrier Sense Errors :0
SQE Test Errors :0 Frames Too Long :0
Deffered Transmissions :0 Internal MAC Receive Errors :0
[Refresh Counters] [Reset Counters]
<OK> <PREV PORT> <NEXT PORT>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Port 1
Figure 2-46. Port Statistics
Parameter Description
Alignment Errors The number of frames received that are not an integral number of
FCS Errors The number of frames received that are an integral number of
Single Collision
Frames*
Multiple Collision
Frames*
SQE Test Errors* A count of times that the SQE TEST ERROR message is
Deferred
Transmissions*
Late Collisions The number of times that a collision is detected later than 512 bit-
Excessive Collisions* The number of frames for which transmission failed due to
Internal Mac
Transmit Errors*
octets in length and do not pass the FCS check.
octets in length but do not pass the FCS check.
The number of successfully transmitted frames for which
transmission is inhibited by exactly one collision.
A count of successfully transmitted frames for which transmission
is inhibited by more that one collision.
generated by the PLS sublayer.
A count of frames for which the first transmission attempt on a
particular interface is delayed because the medium was busy.
times into the transmission of a packet.
excessive collisions.
The number of frames for which transmission failed due to an
internal MAC sublayer transmit error.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 57
Page 66

Parameter Description
Carrier Sense Errors* The number of times that the carrier sense condition was lost or
never asserted when attempting to transmit a frame.
Frames Too Long The number of frames received that exceed the maximum
permitted frame size.
Internal Mac
Receive Errors*
The number of frames for which reception failed due to an internal
MAC sublayer receive error.
* The reported values will always be zero because these statistics are not
supported by the internal chip set.
Displaying RMON Statistics
Use the RMON Statistics screen to display key statistics for each port
from RMON group 1. (RMON groups 2, 3 and 9 can only be accessed
using SNMP management software.) The following screen displays the
overall statistics on traffic passing through each port. RMON statistics
provide access to a broad range of statistics, including a total count of
different frame types and sizes passing through each port. Values
displayed have been accumulated since the last system reboot.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
RMON Statistics :
Drop Events :0 Jabbers :0
Received Bytes :199299 Collisions :0
Received Frames :15746 64 Byte Frames :37837
Broadcast Frames :3249 65-127 Byte Frames :674356
Multicast Frames :0 128_255 Byte Frames :45430
CRC/Alignment Errors:0 256-511 Byte Frames :20447
Undersize Frames :0 512-1023 Byte Frames :3740
Oversize Frames :0 1024_1518 Byte Frames :35696
Fragments :0
[Refresh Counters] [Reset Counters]
<OK> <PREV PORT> <NEXT PORT>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Port 1
Figure 2-47. RMON Statistics
58 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 67

Parameter Description
Drop Events The total number of events in which packets were dropped due to
lack of resources.
Received Bytes Total number of bytes of data received on the network. This
statistic can be used as a reasonable indication of Ethernet
utilization.
Received Frames The total number of frames (bad, broadcast and multicast)
received.
Broadcast Frames The total number of good frames received that were directed to
the broadcast address. Note that this does not include multicast
packets.
Multicast Frames The total number of good frames received that were directed to
this multicast address.
CRC/Alignment
Errors
The number of frames received with CRC/alignment errors (FCS
or alignment errors).
Undersize Frames The total number of frames received that were less than 64 octets
long (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) and were
otherwise well formed.
Oversize Frames The total number of frames received that were longer than 1518
octets (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) and were
otherwise well formed.
Fragments The total number of frames received that were less than 64 octets
in length (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) and
had either an FCS or alignment error.
Jabbers The total number of frames received that were longer than 1518
octets (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets), and had
either an FCS or alignment error.
Collisions The best estimate of the total number of collisions on this
Ethernet segment.
64 Byte Frames The total number of frames (including bad packets) received and
transmitted that were 64 octets in length (excluding framing bits
but including FCS octets).
65-127 Byte Frames The total number of frames (including bad packets) received and
transmitted that were between 65 and 127 octets in length
inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
128-255 Byte Frames The total number of packets (including bad packets) received and
transmitted that were between 128 and 255 octets in length
inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
1024-1518 Byte
Frames
The total number of packets (including bad packets) received and
transmitted that were between 1024 and 1518 octets in length
inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 59
Page 68

Displaying the Unicast Address Table
The Address Table contains the MAC addresses and VLAN identifier
associated with each port (that is, the source port associated with the
address and VLAN), sorted by MAC address or VLAN ID. You can search
for a specific address, clear the entire address table, or information
associated with a specific address, or set the aging time for deleting
inactive entries. The information displayed in the Address Table is
indicated in the following figure and table.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Aging Time: 300 Dynamic Counts: 139 Static Counts: 0
Unicast Address Table
MAC VID Port Status MAC VID Port Status
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------00-00-00-AA-AA-06 1 1 D 00-00-E8-00-00-96 1 1 D
00-00-65-0D-00-D5 1 1 D 00-00-E8-00-01-01 1 1 D
00-00-C0-A4-63-F9 1 1 D 00-00-E8-00-01-02 1 1 D
00-00-E2-12-F9-F8 1 1 D 00-00-E8-00-E8-03 1 1 D
00-00-E2-20-C3-D5 1 1 D 00-00-E8-10-00-01 1 1 D
00-00-E8-00-00-00 1 1 D 00-00-E8-10-00-AB 1 1 D
00-00-E8-00-00-02 1 1 D 00-00-E8-10-DE-F1 1 1 D
Sorted by : MAC + VID Cleared by : MAC + VID
VLAN ID : 1 VLAN ID : 1
MAC : 00-00-00-00-00-00 MAC : 00-00-00-00-00-00
[Show] [More] [Clear] [Clear Dynamic]
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Figure 2-48. Unicast Address Table
Parameter Description
Aging Time Time-out period in seconds for aging out dynamically learned
Dynamic Counts The number of dynamically learned addresses in the table.
Static Counts The number of static addresses in the table.
MAC The MAC address of a node.
VID The VLAN(s) associated with this address or port.
Port The port whose address table includes this MAC address.
Status Indicates address status as:
[Show] Displays the address table based on specified VLAN ID, and
[More] Scrolls through the entries in the address table.
[Clear] Clears the specified MAC address.
[Clear Dynamic] Clears all dynamically learned MAC addresses in the table.
forwarding information.
Range: 10 - 65534 seconds; Default: 300 seconds
D: Dynamically learned, or
P: Fixed permanently by SNMP network management software.
sorted by primary key MAC or VID.
60 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 69

Displaying the IP Multicast Registration Table
Use the IP Multicast Registration Table to display all the multicast groups
active on this switch, including multicast IP addresses and the
corresponding VLAN ID.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
IP Multicast Registration Table
VID Multicast IP Dynamic Port Lists Learned by
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 224.0.0.2 00000001 IGMP
1 224.0.0.9 00000001 IGMP
1 224.0.1.22 00000001 IGMP
1 224.0.1.24 00000001 IGMP
1 224.1.2.9 00000010 IGMP
Sorted by : VID + Multicast IP
VID : 1
Multicast IP : 224.0.0.2
[Show] [More]
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
<OK>
Figure 2-49. IP Multicast Registration Table
Parameter Description
VID VLAN ID assigned to this multicast group.
Multicast IP IP address for specific multicast services.
Dynamic Port Lists The switch ports registered for the indicated multicast service.
Learned by Indicates if the ports were learned dynamically or via IGMP.
[Show] Displays the address table sorted on VID and then Multicast IP.
[More] Scrolls through the entries in the address table.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 61
Page 70

Configuring Static Unicast Addresses
Use the Static Unicast Address Table Configuration screen to manually
configure host MAC addresses in the unicast table. You can use this
screen to associate a MAC address with a specific VLAN ID and switch
port as shown below.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
Static Unicast Address Table Configuration
VID MAC Address Port Status
------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 00-00-00-E8-43-12 1 Permanent
Sorted by : VID + MAC VID : 1 MAC: 00-00-00-00-00-00
VID : 1 Port : 1
MAC : 00-00-00-00-00-00 Status : Permanent
[Show] [More] [Set]
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
Figure 2-50. Static Unicast Addreeess Table Configuration
Parameter Description
VID The VLAN group this port is assigned to.
MAC Address The MAC address of a host device attached to this switch.
Port The port the host device is attached to.
Status The status for an entry can be set to:
Permanent: This entry is currently in use and will remain
DeleteOnReset: This entry is currently in use and will remain
Invalid: Removes the corresponding entry.
DeleteOnTimeOut: This entry is currently in use and will remain
Other: This entry is currently in use but the
[Show] Displays the static address table sorted on VID as the primary key
and MAC address as secondary key.
[More] Scrolls through entries in the static address table.
[Set] Adds the specified entry to the static address table, such as
shown in the following example:
VID : 1 MAC : 00-00-00-e8-34-22
Port : 1
Status : Permanent
<OK>
so after the next reset of the switch.
so until the next reset.
so until it is aged out. (Refer to Address Table
Aging Time on page 60.)
conditions under which it will remain so differ
from the preceding values.
62 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 71

Resetting the System
Select the System Restart Menu under the Main Menu to reset the switch.
The reset screen includes options as shown in the following figure and
table.
Vertical Horizon Local Management -- VH-8G
System Restart Menu
Restart Option :
POST : YES
Reload Factory Defaults : NO
Keep IP Setting : NO
Keep User Authentication : NO
[Restart]
Parameter Description
POST Runs the Power-On Self-Test
Reload Factory
Defaults
Keep IP Setting Retains the settings defined in the IP Configuration menu.
Keep User
Authentication
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
Figure 2-51. System Restart Menu
Reloads the factory defaults
Retains the user names and passwords defined in the Console
Login Configuration menu.
Logging Off the System
Use the Exit command under the Main Menu to exit the configuration
program and terminate communications with the switch for the current
session.
9033640 VH-8G User Interface 63
Page 72

64 VH-8G User Interface VH-8G
Page 73

3. CONFIGURING & MONITORING THE SWITCH
Common Tasks
The switch console menus allow you to modify default switch settings and
configure the switch for network management. They also allow you to
monitor switch performance and status. See Section 2, “VH-8G User
Interface,” for an overview of the menu hierarchy and a description of all
menus. The following sections describe common tasks in setting up and
operating the VH-8G switch using the console menus.
To begin, set operating parameters and make sure the network
connections are correct by performing these tasks:
• Setting password protection for the switch to prevent unauthorized
access to console menus
• Assigning an IP address for the switch if you plan to manage the
switch using SNMP, or if you use Telnet to access the switch
• Checking network configuration status and verifying that network
connections are correct
After the switch is installed and operating, you may want to perform any
of the following tasks:
• Connecting via Telnet for in-band access to the console menus
• Setting SNMP parameters for management access
• Viewing switch statistics to monitor and evaluate switch performance
and traffic patterns on the network
• Configuring port mirroring
• Downloading a software upgrade
• Configuring Spanning Tree parameters
• Configuring VLANs
• Configuring Class of Service
• Configuring IGMP multicast filtering
• Configuring port operation (enable/disable, full/half duplex and flow
control)
• Configuring port trunks
• Configuring broadcast storm control
• Configring the Unicast Address table
• Setting a default gateway
• Configuring BootP
9033640 Configuring & Monitoring the Switch 65
Page 74

Setting Password Protection
The VH-8G switch is factory-configured with administrator access rights
to the console menus set to READ/WRITE. This setting allows anyone to
use the console menus to modify any operational parameter. To protect
the configuration of the switch from unauthorized modification, you should
enable password protection to the console menus.
To enter a password, do the following:
1. Select Management Setup Menu from the Main Menu and press
[Enter].
2. Select Console Login Configuration and press [Enter].
3. For the default “ADMIN” user type, enter a password containing up to
11 alphanumeric characters. Note that the password is not case
sensitive.
By factory default, there is no password configured. This means that at
the login: prompt, all you have to do is type “admin” for the user name and
press [Enter] to gain READ/ WRITE access to the console menus. When
you configure the password parameter, the factory default setting is
deactivated and the new password governs access to the console menus.
If you forget your password, contact your Enterasys Networks Support
Representative.
You are automatically logged out from the console menus
based on the Lock-out Time setting in the Console Login
Configuration Menu. A setting of “0” permits the console
menus to remain available indefinitely.
66 Configuring & Monitoring the Switch VH-8G
Page 75

Assigning an IP Address
To assign an IP address to the switch, do the following:
1. Select Management Setup Menu from the Main menu.
2. Select Network Configuration and then IP Configuration.
3. Highlight the IP address field and enter the IP address. Press [Enter].
The IP address is now set. To set the subnet mask, highlight Subnet Mask
and enter the appropriate mask.
Checking Network Configuration Status
To check connection status for the network, do the following:
1. Select Device Control Menu from the Main Menu.
2. Select Port Information and press [Enter].
If a network cable is properly connected to a port, the Link for the port
reads UP. If no cable is connected to the port, or if the cable or port
is faulty, the Link for the port reads DOWN.
3. If you see a DOWN status for a connected port, plug the cable into
another port on the switch or try another cable.
Connecting via Telnet
You can connect to the VH-8G switch from a remote location using the
Telnet application. This application allows you to establish in-band access
to the console menus.
To connect to the VH-8G switch via Telnet, do the following:
1. Assign an IP address using the Network Configuration Menu.
2. Set a password using the Console Login Configuration Menu.
3. Login to the VH-8G switch via Telnet using the configured IP address
and the password.
9033640 Configuring & Monitoring the Switch 67
Page 76

Setting SNMP Management Access
Access to the VH-8G switch through SNMP is controlled by community
names. The community names set for the switch must match those used
by the SNMP management station for successful communication to
occur. Access for community names can be set to READ/WRITE or
READ ONLY access. The default “Public” community name allows READ
ONLY access to the device via SNMP, whereas the default “Private”
community name allows READ/WRITE access.
The VH-8G switch can send SNMP messages called traps to SNMP
management stations when an important event occurs with the switch.
The switch allows up to five destinations to be configured for these trap
messages to be sent.
To configure SNMP access for the switch, do the following:
1. Select Management Setup Menu from the Main Menu.
2. Select SNMP Configuration Menu.
3. Select SNMP Communities from the menu. Enter the desired
community names (you are permitted to enter from one to 20
characters) and set access to READ/WRITE or READ ONLY.
4. Select IP Trap Managers from the SNMP Configuration Menu.
5. Enter appropriate IP addresses for the Trap destinations.
6. For each Trap destination entered, a corresponding access
community name should be entered.
Viewing Switch Statistics
To view switch statistics, do the following:
1. Select Network Monitor Menu from the Main Menu.
2. Select Port Statistics. Then select the port number to display the
main statistical counts for the port.
3. Select RMON Statistics. Then select the port number to display
detailed statistical counts for the port.
4. On any of the statistics screens, select Reset Counters to clear (zero)
the displayed statistical counts and Refresh Counters to refresh
(update) the displayed statistical counts.
68 Configuring & Monitoring the Switch VH-8G
Page 77

Configuring Port Mirroring
You can mirror the traffic being switched on any port for the purposes of
network traffic analysis and connection assurance. When Port Mirroring
is enabled, one port becomes a monitor port for any other port on the
switch. Note that the source and target ports must be configured within
the same VLAN and be operating at the duplex mode.
To configure port mirroring, do the following:
1. Select Device Control Menu from the Main Menu.
2. Select Mirror Port Configuration.
3. For the Mirror Source Port, select the port number.
4. For the Mirror Target Port, select the port number.
5. Set the Status field to ENABLED.
6. Connect a traffic analyzer or RMON probe to the mirroring port.
Downloading a Software Upgrade
You can upgrade the operational software in the VH-8G switch without
physically opening the switch or being in the same location. The software
storage sector in the flash memory of the switch is reprogrammable,
allowing you to easily download software feature enhancements and
problem fixes to the switch from a local or remote location.
Software can be downloaded to the switch in two ways:
• Via the serial port. This procedure is an out-of-band operation that
copies the software through the serial port to the switch. This
operation takes approximately 10 minutes and requires minimal
configuration.
• Via TFTP download. This procedure uses a TFTP server connected
to the network and downloads the software using the TFTP protocol.
A TFTP download is usually much faster than a serial download,
requiring only a few seconds, and can be used to upgrade an VH-8G
switch that is not physically proximate. The disadvantage is that this
method requires a TFTP server and additional setup.
9033640 Configuring & Monitoring the Switch 69
Page 78

Downloading Via the Serial Port
A serial download is the easiest method to upgrade the VH-8G switch
software, requiring the least amount of equipment and configuration.
To download switch software via the serial port, do the following:
1. With the console port connected, reset the switch by powering the
switch off and then on.
2. After the power-on hardware and software tests are complete, the
system initialization screen displays the following message:.
(D)ownload System Image or (S)tart Application: [S]
3. Press “D” to download system firmware. The following message
appears:
Select the Firmware Type to Download (1)Runtime
(2)POST [1]:
4. Select “1” to download the management software. The following
messages appear:
Your Selection: Runtime Code
Change Baud Rate to 115200 and Press <ENTER> to
Download.
5. Change your baud rate to 115200 bps and press [Enter]. Send the
file using the XMODEM protocol from your computer application (the
procedure varies depending upon the application used).
When the XMODEM procedure finishes, the following messages are
displayed:
XModem Download to DRAM buffer area 0x00200000: ...
SUCCESS !
Verifying image in DRAM download buffer
0x00200000... SUCCESS !
Update FlashROM Image at 0x02880000 ... SUCCESS !
(D)ownload another Image or (S)tart Application:
[S] s
Change Baud Rate to 19200 and Press <ENTER>.
6. Press “S” to start the user interface, change your baud rate to back
to 19200 bps and press [Enter]. The user interface logon screen will
then appear.
70 Configuring & Monitoring the Switch VH-8G
Page 79

Downloading Via TFTP
To perform a TFTP download, you must first configure the VH-8G switch.
This consists of programming the switch with an IP address, if this has not
already been done, and entering the IP address of the TFTP server and
the name of the upgrade file. To program the switch IP address, select the
Management Setup Menu from the Main Menu screen, then select
Network Configuration.
To download switch software via TFTP, do the following:
1. Select Download Server IP Address from the TFTP Download Menu.
2. Enter the TFTP server IP address and press [Enter].
3. Select Download Filename and enter the file name to be downloaded
from the TFTP server.
For a TFTP download, the path to the file must be included in
its name. For example, if the upgrade file name is
filename.bin and it resides in the directory /usr/tftp on the
TFTP server, then you must enter the TFTP file name as:
“/usr/tftp/filename.bin”.
4. If necessary, configure the address of an IP gateway to reach the
server from the switch using the Gateway IP field in the Network
Configuration: IP Configuration menu.
5. Configure the TFTP server by copying the download file from the
upgrade disk to an appropriate directory and starting the server.
6. Select Process TFTP Download and press [Enter].
To verify that the TFTP download has been successfully completed,
note the software version level displayed on the Switch Information
screen accessible from the System Information Menu. This number
should match the version number that appears on the upgrade disk.
9033640 Configuring & Monitoring the Switch 71
Page 80

Configuring Spanning Tree Parameters
The VH-8G switch supports the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol.
This protocol allows redundant connections to be created between LAN
segments for purposes of fault tolerance. Two or more physical paths
between different segments can be created through the switch, with the
Spanning Tree Protocol choosing a single path at any given time and
disabling all others.
If the chosen path fails for any reason, a disabled alternative is activated,
thereby maintaining the connection. See Appendix A, “Spanning Tree
Concepts” on page 83 for further information on using the Spanning Tree
Protocol in a network.
Configuring Spanning Tree parameters from their default
can cause serious deterioration of network performance.
To configure Spanning Tree Parameters, do the following:
1. Select the Device Control Menu from the Main Menu.
2. Select the Spanning Tree Configuration Menu and then STA Bridge
Configuration.
3. Turn the switch Spanning Tree operation on by setting the Spanning
Tree Protocol field to ENABLED.
4. Form the Spanning Tree Configuration Menu, select STA Port
Configuration.
The Spanning Tree Port Configuration Menu displays. Change the
parameters that display in this menu as required.
72 Configuring & Monitoring the Switch VH-8G
Page 81

Configuring VLANs
A virtual LAN (VLAN) is a group of devices on one or more LANs that are
configured such that they can communicate as if they were attached to
the same wire. Because VLANs are based on logical instead of physical
connections, they are extremely flexible.
The most fundamental benefit of VLAN technology is the ability to create
workgroups based on function rather than on physical location or media.
For further information, see Appendix B, “Virtual LANs (VLANs)” on page
89.
To configure VLANs, do the following:
1. Select the Device Control Menu from the Main Menu.
2. Select 802.1Q VLAN Static Table Configuration Menu.
3. In the VID and VLAN Name fields, enter an ID number (1-2048) and
a symbolic alphanumeric name (up to 8 characters) to indentify the
VLAN.
4. Set the Status field to Active.
5. Under Egress Ports, select ports by entering “1,” or enter “0” to
remove it from the VLAN.
6. Under Forbidden Egress Ports, enter a “1” to prevent a port from
being automatically added to this VLAN via GVRP.
Note that you can enable or disable GVRP for the switch from the
Extended Bridge Configuration screen on the Device Control Menu.
7. To configure other VLANs, select New and press [Enter].
Configuring Class of Service
You can configure Class of Service parameters using the 802.1P Port
Priority Configuration screen. This screen permits you to configure two
priority levels for traffic being forwarded through the switch. During
periods of congestion, Class of Service settings ensure that traffic which
has been assigned high priority is forwarded through the switch ahead of
normal priority traffic. For further information, see Appendix C, “Class of
Service” on page 93.
To configure Class of Service, do the following:
1. Select Device Control Menu from the Main Menu.
2. Select 802.1P Configuration, then 802.1P Port Priority Configuration.
3. Set individual port priorities by entering 0-3 for the low priority queue
or 4-7 for the high priority queue.
Note that the default for all ingress ports is zero.
9033640 Configuring & Monitoring the Switch 73
Page 82

Configuring Port Operation
You can configure switch ports for operational parameters such as autonegotiation, duplex mode, and flow control. The 1000Base-SX fiber ports
always operate at 1000Mbps speed. Therefore, this parameter is not
configurable.
To configure port operation, do the following:
1. Select Device Control Menu from the Main Menu.
2. Select Port Configuration and press [Enter].
3. Select the port number to configure.
4. In the Admin column, select ENABLED. You can also disable the port
due to abnormal behavior or for security reasons.
5. In the Flow Control column, select ENABLED to enable flow control
or DISABLED to disable it. When enabled, the switch uses back
pressure for half duplex and IEEE 802.3x for full duplex. These flow
control methods can also be set directly by selecting
BACK_PRESSURE or 802.3X.
6. In the Speed and Duplex column, select AUTO to enable Autonegotiation for the port, or select 1000_FULL or 1000_HALF.
If Auto-negotiation is not enabled, the duplex mode needs to
be configured.
74 Configuring & Monitoring the Switch VH-8G
Page 83

Configuring the Unicast Address Table
The Unicast Address Table allows you to designate forwarding treatment
through the switch for specific MAC addresses, allowing you to maintain
the efficiency and security of your network. You can search for a specific
MAC address, clear the entire table, or information associated with a
specific address, or set the Aging Time for deleteing inactive entries. The
switch learns addresses dynamically from incoming packets and builds a
table of these addresses along with their associated ports. There are two
types of MAC addresses in the forwarding table:
• Dynamic MAC addresses, which are dynamically learned and
removed by the switch based on a time period defined using the
Aging Time option.
• Static MAC addresses, which are entered manually, stored in
nonvolatile memory and automatically placed in the address table.
There are five types of status that can be configured for each address in
the table:
• Permenant, which means that the MAC address is in use and will
remain so after the next switch reset.
• Delete On Reset, which means that the MAC address is in use and
will remain so until the next switch reset.
• Invalid, which will remove the entry.
• Delete On Time Out, which means that the MAC address is in use
and will remain so until it is aged out.
• Other, which means that the MAC address is in use but the
conditions under which it will remain so differ from the preceding
values.
To configure the Unicast Address Table, do the following:
1. Select Network Monitor Menu from the Main Menu.
2. Select Unicast Address Table.
3. As desired, set the Aging Time for the table, or view, search or clear
entries by MAC address or VLAN ID.
To configure a specific MAC address in the table, do the following:
1. From the Network Monitor Menu, select Static Unicast Address Table
Configuration.
2. For the MAC address, specify the VLAN ID, switch port and the
Status (Permanent, Delete On Reset, Invalid, Delete On Time Out, or
Other).
3. Highlight the Set field and press [Enter].
9033640 Configuring & Monitoring the Switch 75
Page 84

Setting a Default Gateway
The default Gateway parameter defines the IP address of a router or other
network device to which IP packets are to be sent if destined for a subnet
outside of that which the switch is operating.
To set a default gateway, do the following:
1. Select Management Setup Menu from the Main Menu.
2. Select Network Configuration and then IP Configuration.
3. In the field Gateway IP,enter the IP address and press [Enter].
Configuring BootP
The BootP protocol allows you to automatically configure the switch’s IP
address information. Enabling this feature greatly speeds up device
configuration, especially when a large number of devices are installed.
A BootP server must be operating on the network and be properly
configured for this option to work. When this option is enabled, the switch
tries to obtain an IP address from the BootP server.
To configure BootP, do the following:
1. Select Management Setup Menu from the Main Menu.
2. Select Network Configuration and then IP Configuration.
3. In the IP State field, select BOOTP-GET-IP.
This selection toggles between BOOTP-GET-IP and USER-CONFIG
(the default setting).
76 Configuring & Monitoring the Switch VH-8G
Page 85

Configuring Port Trunks
You can configure up to four port trunks on the VH-8G switch. Each trunk
can combine up to four ports into an aggregate connection with up to
8Gbps of bandwidth when operating at full duplex. Besides balancing the
load across each port in the trunk, the additional ports provide
redundancy by taking over the load if another port in the trunk should fail.
To configure the port trunks, do the following:
1. Select the Device Control Menu from the Main Menu.
2. Select Port Trunking Configuration.
3. Enter a Trunk ID number from 1 to 4 to identify the trunk.
4. Select up to four ports to configure as one trunk. You can configure
up to four trunks per switch unit.
Note that ports at both ends of a trunk must be configured in an
identical manner, including duplex mode and VLAN assignments.
5. For each Trunk ID, select Enable to enable the trunk.
Note that it is advisable to enable the trunk prior to connecting any
cable between the switches to avoid creating a loop.
When using port trunks, remember that:
• Before removing a port trunk via the configuration menu, you must
disable all the ports in the trunk or remove all the network cables.
Otherwise, a loop may be created.
• To disable a single link within a port trunk, you should first remove the
network cable, and then disable both ends of the link via the
configuration menu. This allows the traffic passing across that link to
be automatically distributed to the other links in the trunk, without
losing any significant amount of traffic.
9033640 Configuring & Monitoring the Switch 77
Page 86

78 Configuring & Monitoring the Switch VH-8G
Page 87

4. SNMP MANAGEMENT
The SNMP Protocol
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a communication
protocol designed specifically for the purpose of managing devices or
other elements on a network. Network equipment commonly managed
with SNMP includes hubs, switches, routers, and host computers. SNMP
is typically used to configure these types of devices for proper operation
in their network environment, as well as to monitor them to evaluate their
performance and detect potential problems.
Managed entities supporting SNMP typically contain software, which runs
locally on the device and is referred to as an agent. In Figure 4-1, software
in an VH-8G switch functions as an agent, monitoring and controlling the
functionality of the switch.
Figure 4-1. VH-8G Switches Managed by an
SNMP Management Workstation
A defined set of variables, referred to as managed objects, is maintained
by the agent and used to manage the device. These objects are defined
in a Management Information Base (MIB) which allows for a standard
presentation of the information controlled by the agent over the network.
The software used to access the information maintained by the SNMP
agents across a network is referred to as the SNMP Manager, and
typically runs on a workstation.
The SNMP manager software uses a MIB specification, equivalent to that
which the agent maintains, to read and write objects controlled by the
agent for purposes of configuring and monitoring the device. SNMP
defines the format of the MIB specifications and the protocol used to
access this information.
9033640 SNMP Management 79
Page 88

There are three main operations defined in SNMP:
• GET operations read information from the managed device, such as
those used to obtain status or statistical data.
• SET operations change a functional parameter on the device, such
as those used to configure Port Speed or to initiate a software
download. GET and SET operations are initiated only by the
manager software, and result in a response by the agent.
• TRAP operations allow the agent to send an unsolicited message to
the manager. This operation is typically used as an alert of a potential
problem or a change of status with the device. The Trap Destination
parameter in the SNMP Configuration Menu is used to configure the
IP addresses of the SNMP Manager to which VH-8G trap messages
are sent.
MIB Objects
A number of standard MIB specifications have been defined for managing
network equipment. SNMP compliant devices typically support one or
more standard MIBs defined by the Internet Engineering Task Force
(IETF), in the form of Request for Comments (RFC) documents.
These MIBs provide a common method of managing devices, such as
hubs and switches, and network interfaces, such as Ethernet and token
ring. The primary standard MIB, referred to as MIB-II, provides an overall
view of the managed agent and must be supported, at least in part, by all
SNMP agents. In addition, proprietary MIB extensions are defined by
commercial vendors for managing device-specific functions of their
products.
The VH-8G switch supports six standard MIBs:
• RFC 1213 - Management Information Base for Network
Management of TCP/IP based Internets (MIB-II)
• RFC 1573 - Evolution of the Interfaces Group of MIB-II
• RFC 1643 - Definitions of Managed Objects for the Ethernet-like
Interface Types (Ethernet-Like MIB)
• RFC 1493 - Definitions of Managed Objects for Bridges
• RFC 1757 - Remote Network Monitoring Management Information
Base
• IEEE 802.1Q - VLAN Bridge Management (Q-MIB)
The VH-8G switch also supports Enterasys proprietary MIB extensions.
RFC 1213 (MIB-II)
RFC 1213 provides management of system-level parameters, including
TCP/IP protocol-related statistics, IP addressing, and interface statistics
for each switch port. MIB-II is the standard MIB defined by RFC 1213. All
agent devices operating SNMP are required to support at least part of
MIB-II.
80 SNMP Management VH-8G
Page 89

This MIB reports information about the protocols and network interfaces
supported on the agent itself, as well as other general information. The
MIB is divided into a number of groups, each of which corresponds to a
specific protocol or set of information. Some groups are defined in other
RFC documents.
The groups specifically defined in RFC 1213 and supported by the VH-8G
switch system software are as follows:
• System – General information about the agent system
• Interfaces – Information about the network interfaces of the system
• Address Translation – Interface address information, both MAC level
and network (IP) level
• IP – Statistics and information related to the IP protocol
• ICMP – Statistics and information related to the ICMP protocol
• TCP – Statistics and information related to the TCP protocol
• UDP – Statistics and information related to the UDP protocol
• Transmission – Statistics and information related to the physical
network medium to which the system interfaces (e.g. Ethernet, token
ring, etc.).
• SNMP – Statistics and information related to the SNMP protocol
RFC 1573 (Interfaces Evolution MIB)
RFC 1573 clarifies and extends the managed objects of the “Interfaces”
group of MIB-II. This MIB takes account of the evolution in interface types
and speeds employed in today’s networks.
RFC 1643 (Ethernet-Like MIB)
RFC 1643 provides management and monitoring for the Ethernet-specific
aspects of each port on the switch. This is the Ethernet-specific statistics
subgroup of the MIB-II Transmission group. This group provides a set of
statistics related to Ethernet’s physical level operation. Specifically, error
and collision-related statistics are presented.
RFC 1493 (Bridge MIB)
RFC 1493 is a group defined under MIB-II. This MIB deals with the
operation of the system as an 802.1D-compliant bridge. Areas of
functionality supported by this group include Spanning Tree and
forwarding table information and configuration.
RFC 1757 (RMON MIB)
RFC 1757 is a group defined under MIB-II. This MIB provides
management for the RMON aspects of the switch. The
VH-8G switch supports four of the nine groups of RMON defined for
Ethernet networks on a per port basis.
9033640 SNMP Management 81
Page 90

IEEE 802.1Q (Q-MIB)
This MIB includes the set of managed objects as defined in the IEEE
802.1Q VLAN standard. This MIB provides management for the VLAN
aspects of the switch.
Enterasys Proprietary MIB Extensions
Areas of VH-8G switch functionality not covered by the standard RFC
MIBs are specified in the Enterasys private MIB. This MIB definition is
specified separately from MIB-II. Areas covered in this MIB include
various system, switch, and port level information.
Compiling MIB Extensions: Enterasys Website
The MIBs supported by the VH-8G switch must be compiled into the
SNMP network management platform before the switch can be managed.
The supported MIBs are available using Enterasys’s website at:
http://www.enterasys.com
The four standard MIB specifications listed above with which the VH-8G
switch is compliant are generally available with the SNMP management
platform.
82 SNMP Management VH-8G
Page 91

APPENDIX A. SPANNING TREE CONCEPTS
General
The IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol resolves the problems of
physical loops in a network by establishing one primary path between any
two switches in a network. Any duplicate paths are barred from use and
become standby or blocked paths until the original path fails, at which
point they can be brought into service.
Spanning Tree Features
The VH-8G switch meets the requirements of the Spanning Tree Protocol
(STP) by performing the following functions:
• Creates a single spanning tree from any arrangement of switching or
bridging elements.
The term “switch” is used as an equivalent to “bridge” in
this document.
• Compensates automatically for the failure, removal, or addition of
any device in an active data path.
• Achieves port changes in short time intervals, which establishes a
stable active topology quickly with a minimum of network
disturbance.
• Uses a minimum amount of communications bandwidth to
accomplish the operation of the Spanning Tree Protocol.
• Reconfigures the active topology in a manner that is transparent to
stations transmitting and receiving data packets.
• Manages the topology in a consistent and reproducible manner
through the use of Spanning Tree Protocol parameters.
9033640 Spanning Tree Concepts 83
Page 92

Spanning Tree Protocol in a Network
Figure A-1 illustrates the use of an VH-8G switch to establish an effective
Spanning Tree configuration. Switches A, B and C are connected
together in a redundant topology (more than one path between two
points). If the connection between A and B goes down, the link between
A and C becomes active, thereby establishing a path between A and B
through switch C. Additionally, if the connection between B and C goes
down, the link between A and C becomes active, establishing a path
between B and C through switch A.
Figure A-1. Spanning Tree Using an VH-8G Switch
84 Spanning Tree Concepts VH-8G
Page 93

Spanning Tree Protocol Parameters
Several configuration parameters control the operation of the Spanning
Tree Protocol. Table A-1 describes the parameters and lists the VH-8G
switch default settings for each parameter.
You can cause serious network performance degradation
if you do not fully understand Spanning Tree concepts. Be
sure to consult personnel experienced with this process
prior to configuring Spanning Tree parameters.
Table A-1. Spanning Tree Protocol Defaults
Parameter Description Default Value
Bridge Group
Address
Bridge Identifier
Port Identifier Port Identifier Identifies each port of each bridge, with
Port Priority Indicates the priority of a specific port in relation to
Cost Component of Each
Port
Unique MAC group address, recognized by all bridges in the network.
Identifier for each bridge. This parameter consists of
two parts: a 16-bit bridge priority and a 48-bit network
adapter address. Ports are numbered in absolute
numbers starting from 1 regardless of their bridge attachment. The network adapter address is the same
address as the first port of the bridge.
an incremental default value given for each port.
Port 1 -32768
Port 2 -32769
Port 3 -32770
Port 4 -32771
Port 5 -32772
Port 6 -32773
Port 7 -32774
Port 8 -32775
other ports.
The Spanning Tree Protocol calculates and ensures
that an active topology generates minimal cost paths.
A value of 100 is generally used for 10Mbps Ethernet
networks, a value of 19 for 100Mbps Fast Ethernet,
and a value of 4 for 1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet.
32768 (bridge
priority)
128
4
For detailed information on the operation of the Spanning Tree Protocol,
consult Section 4 of IEEE Standard 802.1D, ISO/IEC 10038:1993.
9033640 Spanning Tree Concepts 85
Page 94

Spanning Tree Protocol Operation
When the Spanning Tree Protocol is enabled for the first time or when
there is a change in the network topology, such as a failure or the addition
or removal of a component, the Spanning Tree Protocol automatically
sets up the active topology of the current network.
Communicating Between Bridges
Periodically, all devices running the Spanning Tree Protocol on a network
transmit packets to each other “in care of” the Bridge Group Address
which all bridges share. When a bridge receives a frame sent to the
Bridge Group Address, the bridge’s Spanning Tree Protocol processes
the packet. Application software and other LAN segments ignore the
packet. Bridges communicate between each other in order to determine
the Root Bridge.
Selecting a Root Bridge and Designated Bridges
During communication between bridges, one bridge is determined to
have the lowest bridge identifier. This bridge becomes the Root Bridge.
After the Root Bridge has been selected, each LAN segment looks for the
bridge that has the lowest cost relative to the Root Bridge. These bridges
become Designated Bridges.
Selecting Designated Ports
Each Designated Bridge selects a Designated Port. This port is
responsible for forwarding packets to the Root Bridge.
Handling Duplicate Paths
When the active topology of the network is determined, all packets
between any two nodes in the network use only one path. Where a
duplicate path exists, the non-designated port is put into a blocking state.
Remapping Network Topology
If there is a change in the network topology due to a failure or the removal
or addition of any active components, the active topology also changes.
This may trigger a change in the state of some blocked ports.
86 Spanning Tree Concepts VH-8G
Page 95

There are five (5) states that the ports can be in for spanning tree:
• Blocking: A port in this state does not participate in the transmission
of frames, thus preventing duplication arising through multiple paths
existing in the active topology of the bridged LAN.
• Listening: A port in this state is preparing to participate in the
transmission of frames. The transmission of frames is temporarily
disabled in order to prevent temporary loops, which may occur in a
bridged LAN during the lifetime of this state as the active topology of
the bridged LAN changes.
• Learning: A port in this state is preparing to participate in the
transmission of frames.
• Forwarding: A port in this state is participating in the transmission of
frames.
• Disabled: A port in this state does not participate in the transmission
of frames or the operation of the spanning tree process.
9033640 Spanning Tree Concepts 87
Page 96

88 Spanning Tree Concepts VH-8G
Page 97

APPENDIX B. VIRTUAL LANS (VLANS)
VLANs and Frame Tagging
The VH-8G switch supports IEEE 802.1Q-compliant virtual LANs
(VLANs). This capability provides a highly efficient architecture for
establishing VLANs within a network and for controlling broadcast/
multicast traffic between workgroups. Central to this capability is an
explicit frame tagging approach for carrying VLAN information between
interconnected network devices.
With frame tagging, a four byte data tag field is appended to frames that
cross the network. The tag identifies which VLAN the frame belongs to.
The tag may be added to the frame by the end station itself or by a
network device, such as a switch. In addition to VLAN information, the
relative priority of the frame in the network can specified by the tag (see
Appendix C, “Class of Service”).
VLANs provide greater network efficiency by reducing broadcast traffic,
but also allow you to make network changes without having to update IP
addresses or IP subnets. VLANs inherently provide a high level of
network security, since traffic must pass through a Layer 3 switch or a
router to reach a different VLAN.
This switch supports the following VLAN features:
• Up to 256 VLANs based on the IEEE 802.1Q standard
• Distributed VLAN learning across multiple switches using explicit or
implicit tagging and GARP/GVRP protocol
• Port overlapping, allowing a port to participate in multiple VLANs
• End stations can belong to multiple VLANs
• Passing traffic between VLAN-aware and VLAN-unaware devices
• Two-level priority tagging
• Port trunking with VLANs
9033640 Virtual LANs (VLANs) 89
Page 98

VH-8G VLAN Configuration
VLAN operation on the VH-8G is enabled by default. Therefore, all frames
are transferred internally through the switch with a VLAN tag. This tag
may already be on the frame entering the switch, or added to the frame
by the switch. VLAN information already existing on frames entering the
switch is automatically handled by the switch. The VH-8G learns VLAN
information from tagged frames and appropriately switches frames out
the proper ports based on this information. The configuration of VLANs for
frames entering the switch without tags must be made by the user of the
switch. This configuration can be made either through the console
interface or via SNMP.
Assigning Ports to VLANs
Before enabling VLANs for the switch, you must first assign each port to
the VLAN groups it will participate in. By default all ports are assigned to
VLAN 1 as untagged ports. You should add a port as a tagged port (that
is, a port attached to a VLAN-aware device) if you want it to carry traffic
for one or more VLANs and the device at the other end of the link also
supports VLANs. Then assign the port at the other end of the link to the
same VLANs. However, if you want a port on this switch to participate in
one or more VLANs, but the device at the other end of the link does not
support VLANs, then you must add this port as an untagged port (that is,
a port attached to a VLAN-unaware device).
Port-based VLANs are tied to specific ports. The switch’s forwarding
decision is based on the destination MAC address and its associated port.
Therefore, to make valid forwarding and flooding decisions, the switch
learns the relationship of the MAC address to its related port—and thus to
the VLAN—at run-time.
VLAN Classification
When the switch receives a frame, it classifies the frame in one of two
ways:
• If the frame is untagged, the switch assigns the frame to an
associated VLAN based on the PVID of the receiving port.
• If the frame is tagged, the switch uses the tagged VLAN ID to identify
the port broadcast domain of the frame.
Port Overlapping
Port overlapping can be used to allow access to commonly shared
network resources among different VLAN groups, such as file servers or
printers. Note that if you implement VLANs which do not overlap, but still
need to communicate, you must connect them using a router or Layer 3
switch.
Page 99

Forwarding Tagged/Untagged Frames
Ports can be assigned to multiple tagged or untagged VLANs. Each port
on the switch is therefore capable of passing tagged or untagged frames.
To forward a frame from a VLAN-aware device to a VLAN-unaware
device, the switch first decides where to forward the frame, and then strips
off the VLAN tag. However, to forward a frame from a VLAN-unaware
device to a VLAN-aware device, the switch first decides where to forward
the frame, and then inserts a VLAN tag reflecting this port’s default VID.
The default PVID is VLAN 1, but this can be changed (see “Port
Assignment VLAN Configuration” on page 51). .
Figure B-1. Multi-Switch VLAN Configuration
Automatic VLAN Registration
GVRP defines a system whereby the switch can automatically learn the
VLANs each endstation should be assigned to. If an endstation (or its
network adapter) supports the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN standard, it can be
configured to broadcast a message to your network indicating the VLAN
groups it wants to join. When this switch receives these messages, it will
automatically place the receiving port in the specified VLANs, and then
forward the message to all other ports. When the message arrives at
another switch that supports GVRP, it will also place the receiving port in
the specified VLANs, and pass the message on to all other ports. VLAN
requirements are propagated in this way throughout the network. This
allows GVRP-compliant devices to be automatically configured for VLAN
groups based solely on endstation requests.
9033640 Virtual LANs (VLANs) 91
Page 100

Forwarding Traffic with Unknown VLAN Tags
This switch only supports 256 VLANs with VLAN IDs ranging from 1 to
2048, but the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN standard allows for VLAN IDs from 1 to
4094. Therefore, if this switch is attached to endstations that issue VLAN
registration requests, it will have to forward unknown VLAN tags. This
traffic can only be propagated to the rest of the network if automatic VLAN
registration is enabled on the switch.
92 Virtual LANs (VLANs) VH-8G
 Loading...
Loading...