Page 1

STS16-20 User's Guide
Page 2

Page 3

Notice
Enterasys Networks reserves the right to make changes in speciÞcations and other information
contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult Enterasys
Networks to determine whether any such changes have been made.
The hardware, Þrmware, or software described in this manual is subject to change without notice.
IN NO EVENT SHALL ENTERASYS NETWORKS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT,
SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED
TO LOST PROFITS) ARISING OUT OF OR RELATED TO THIS MANUAL OR THE INFORMATION
CONTAINED IN IT, EVEN IF ENTERASYS NETWORKS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF, KNOWN, OR
SHOULD HAVE KNOWN, THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Virus Disclaimer
Enterasys has tested its software with current virus checking technologies. However, because no antivirus system is 100% reliable, we strongly caution you to write protect and then verify that the
Licensed Software, prior to installing it, is virus-free with an anti-virus system in which you have
conÞdence.
Enterasys Networks makes no representations or warranties to the effect that the Licensed Software is
virus-free.
Copyright © 2000 by Enterasys Networks. All rights reserved.
Printed in the United States of America.
Order Number: 9033047-02 April 2000
Enterasys Networks, Inc.
P.O. Box 5005
Rochester, NH 03866-5005
Enterasys , NetSight , and Matrix E7 are trademarks of Enterasys Networks.
SPECTRUM , MiniMMAC , FNB , Multi Media Access Center , and DNI are registered trademarks,
and Portable Management Application , IRM , IRM2 , IRM3 , IRBM , ESXMIM , ETSMIM , EMME ,
EMM-E6 , ETWMIM , FDMMIM , FDCMIM , MicroMMAC , MRXI , MRXI-24 , NB20E , NB25E , NB30 ,
NB35E , NBR , SEHI , STHI , TRBMIM , TRMM , TRMM-2 , TRMM-4 , TRMMIM , TRXI , Media
Interface Module , MIM , and Flexible Network Bus are trademarks of Enterasys Networks, Inc.
UNIX and OPENLOOK are trademarks of Unix System Laboratories, Inc. OSF/Motif and Motif are
trademarks of the Open Software Foundation, Inc. X Window System is a trademark of X Consortium,
Inc. Ethernet and XNS are trademarks of Xerox Corporation. Apple and AppleTalk are registered
trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc. Banyan is a registered trademark of Banyan Systems, Inc.
DECnet is a registered trademark of Digital Equipment Corporation. Novell is a registered trademark
of Novell, Inc. CompuServe is a registered trademark of CompuServe. Sun Microsystems is a
registered trademark, and Sun , SunNet , and OpenWindows are trademarks of Sun Microsystems,
Inc.
i
Page 4

Restricted Rights Notice
(Applicable to licenses to the United States Government only.)
1. Use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in
subparagraph (c) (1) (ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFARS
252.227-7013.
Enterasys Networks, Inc., 35 Industrial Way, Rochester, New Hampshire 03867-0505.
2. (a) This computer software is submitted with restricted rights. It may not be used, reproduced, or
disclosed by the Government except as provided in paragraph (b) of this Notice or as otherwise
expressly stated in the contract.
(b) This computer software may be:
(1) Used or copied for use in or with the computer or computers for which it was acquired,
including use at any Government installation to which such computer or computers may
be transferred;
(2) Used or copied for use in a backup computer if any computer for which it was acquired
is inoperative;
(3) Reproduced for safekeeping (archives) or backup purposes;
(4) Modified, adapted, or combined with other computer software, provided that the
modified, combined, or adapted portions of the derivative software incorporating
restricted computer software are made subject to the same restricted rights;
(5) Disclosed to and reproduced for use by support service contractors in accordance with
subparagraphs (b) (1) through (4) of this clause, provided the Government makes such
disclosure or reproduction subject to these restricted rights; and
(6) Used or copied for use in or transferred to a replacement computer.
(c) Notwithstanding the foregoing, if this computer software is published copyrighted computer
software, it is licensed to the Government, without disclosure prohibitions, with the minimum
rights set forth in paragraph (b) of this clause.
(d) Any other rights or limitations regarding the use, duplication, or disclosure of this computer
software are to be expressly stated in, or incorporated in, the contract.
(e) This Notice shall be marked on any reproduction of this computer software, in whole or in part.
ii
Page 5

Chapter 1 Introduction
Using the STS16-20 UserÕs Guide ............................................................................... 1-2
Related Manuals............................................................................................................ 1-3
Conventions................................................................................................................... 1-3
Common Window Fields...................................................................................... 1-4
Using Window Buttons......................................................................................... 1-5
Using the Mouse ....................................................................................................1-5
Getting Help .................................................................................................................. 1-6
Using On-Line Help ..............................................................................................1-6
Accessing On-line Documentation...................................................................... 1-7
Getting Help from the Global Technical Assistance Center ............................ 1-7
Contents
Chapter 2 Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
Viewing Chassis Information...................................................................................... 2-2
Viewing Front Panel Information........................................................................ 2-2
Menu Structure....................................................................................................... 2-4
Selecting a Port Status Display ............................................................................ 2-6
Port Status Display Color Codes .................................................................. 2-8
Displaying MIBs and MIB Components............................................................. 2-9
Viewing Hardware Descriptions ......................................................................... 2-9
Viewing the Device Type............................................................................... 2-9
Viewing the Interface Description.............................................................. 2-10
Viewing System Group Information................................................................. 2-10
Viewing I/F Summary Information.................................................................. 2-12
Displaying Interface Performance Statistics and Bar Graphs ................2-13
Viewing Interface Detail Statistics.............................................................. 2-15
Making Sense of Detail Statistics......................................................... 2-17
Chapter 3 Configuring ATM Connections
ConÞguring Permanent Virtual Circuits ............................................................ 3-3
Adding a Permanent Virtual Circuit............................................................ 3-4
Deleting a Permanent Virtual Circuit .......................................................... 3-4
Index
iii
Page 6

Contents
iv
Page 7

Chapter 1
Introduction
How to use the STS16-20 User’s Guide; related manuals; software conventions; getting help
Welcome to NetSight Element Manager STS16-20 UserÕs Guide . We have
designed this guide to serve as a reference for using NetSight Element Manager to
monitor and manage the family of SmartSTACK Token Ring STS16-20 switches.
The STS16-20 is a high performance, intelligent 20-port Token Ring switch that
provides switching intelligence to network backbones, workgroups, and desktop
connections.
The STS16-20 complies to IEEE 802.5 and supports 802.1D bridging. The STS16-20
provides half or full duplex connections, auto-conÞguration, enhanced bridging
capabilities, port-based VLANs, and four groups of RMON.
The STS16-20 devices include the STS16-20D, STS16-20R, STS16-20RM, and
STS16-20FRM. These devices are functionally identical, except for the
conÞguration of ports.
¥ The STS16-20D has 20 built-in RJ-45 ports Ñ16 workstation ports and 4
network ports.
¥ The STS16-20R has 20 built-in RJ-45 ports; a RI/RO-like connection is available
on all ports.
¥ The STS16-20RM has 20 built-in RJ-45 ports and supports two slots for
optional SmartSTACK Interface Modules (SSIMs). A RI/RO-like connection is
available on ports 19 and 20 and when a Þber expansion module is installed.
¥ The STS16-20FRM has 20 built-in Þber VF-45 ports and supports two slots for
optional SmartSTACK Interface Modules (SSIMs). A RI/RO-like connection is
available on all ports.
NOTE
For the STS16-20D, ports 1 through 16 are workstation ports, which support a single
MAC address per port; ports 17 through 20 are network ports, which provide full network
connectivity without a limitation on the number of MAC addresses that can be learned
per port. Refer to your hardware documentation for more information.
1-1
Page 8

Introduction
The STS16-20RM and STS16-20FRM provide two slots for optional expansion
SmartSTACK Interface Modules (SSIMs). Several types of SSIMs are available
which provide either standard 4/16 Mbps Token Ring connectivity, or high speed
connectivity via 155 Mbps ATM, 100 Mbps High-Speed Token Ring, and 100
Mbps Fast Ethernet, as described below:
¥ The Token Ring SSIMs (T5-04 and T8-04) provide 4 additional 4/16 Mbps ports
of Token Ring connectivity via twisted-pair with RJ-45-type connectors or
multimode Þber with ST-type connectors.
¥ The ATM SSIMs (A2-01 and A8-01) provide 1 port of 155 Mbps high-speed
connectivity to an ATM backbone via twisted pair with RJ-45-type connectors
or multimode Þber with duplex SC-type connectors.
¥ The HSTR SSIMs (R2-02 and R8-02) provide 2 ports of 100 Mbps High-Speed
Token Ring connectivity via twisted pair with RJ-45-type connectors or
multimode Þber and VF-45-type connectors. The HSTR SSIMs integrate Token
Ring networks with High-Speed Token Ring servers or backbones.
¥ The Fast Ethernet SSIM (H2-02) is a translational switch that provides 2 ports
of 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet connectivity via twisted pair with RJ-45-type
connectors. The Fast Ethernet SSIM integrates Token Ring and Ethernet
networks.
Depending on the type of SSIMs installed in the STS16-20FRM and STS16-20RM,
NOTE
the management options available will vary. If you have an ATM SSIM (A2-01 and
A8-01) installed, the ATM Connections option will be available from the Device menu.
Using the STS16-20 User’s Guide
Each chapter in this guide describes one major functionality or a collection of
several smaller functionalities of the STS16-20, which are accessed directly from
the device icon. Additional management information about tools and features
common to many devices can also be found in the NetSight Element Manager
UserÕs Guide , the NetSight Element Manager Tools Guide , and the Remote
Administration Tools UserÕs Guide .
Because the SmartSTACK Token Ring switches ÑSTS16-20RM, STS16-20FRM,
STS16-20D, and STS16-20RÑ share much of their functionality, the devices will be
jointly referred to as the STS16-20 throughout this guide. The options available
and the information displayed in some of the windows may differ slightly,
depending on the type of STS16-20 device being managed.
The following is a description of the chapters contained in this guide. While we
provide as much background information as we can, we do assume that you are
familiar with Token Ring networks and general network management concepts.
1-2 Using the STS16-20 User’s Guide
Page 9

Introduction
¥ Chapter 1, Introduction , provides a list of related documentation, describes
certain software conventions, and shows you how to contact Global Technical
Assistance Center.
¥ Chapter 2, Using the STS16-20 Chassis View , describes the visual display of
the Chassis View and explains how to use the mouse to access management
applications. Also described in this chapter are device and port level
monitoring functions.
¥ Chapter 3, ConÞguring ATM Connections , describes how to conÞgure
Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs). The ATM Connections option will only be
available if you have an ATM SSIM installed in your device.
In addition to providing its own management capabilities, NetSight Element
Manager enables you to access the SmartStack Manager for Windows 95/NT. The
SmartStack Manager is a conÞguration and device management application that
provides network managers with device conÞguration, performance monitoring,
and troubleshooting capabilities. For more information about the SmartStack
Manager, see the
SmartStack Manager - Installation and UserÕs Guide.
Related Manuals
The STS16-20 UserÕs Guide is only part of a complete document set designed to
provide comprehensive information about the features available to you through
NetSight Element Manager. Use the following documents to supplement the
procedures and other technical information provided in this manual:
NetSight Element Manager UserÕs Guide
NetSight Element Manager Tools Guide
NetSight Element Manager Remote Administration Tools UserÕs Guide
NetSight Element Manager Remote Monitoring (RMON) UserÕs Guide
NetSight Element Manager Alarm and Event Handling UserÕs Guide
Network Troubleshooting Guide
For more information about the capabilities of the STS16-20, consult the
appropriate hardware documentation.
For more information on the features of the SmartSTACK Manager, refer to
SmartSTACK Manager - Installation and UserÕs Guide.
Conventions
NetSight Element ManagerÕs device user interface contains a number of elements
which are common to most windows and which operate the same regardless of
the window in which they appear. A brief description of some of the most
common elements appears below.
Related Manuals 1-3
Page 10
Introduction
Common Window Fields
Similar descriptive information is displayed in the Þelds at the top of most
device-speciÞc windows in NetSight Element Manager, as shown in
Figure 1-1.
IP Address
Device
Name
Figure 1-1. Common Window Fields
Device Name
Displays the user-deÞned name of the device. The device name is entered and
can be changed via the System Group window; see Viewing System Group
Information in Chapter 2, or the Generic SNMP UserÕs Guide for details.
Location
MAC
Address
IP Address
Displays the deviceÕs IP (Internet Protocol) address. This is the IP address used
to deÞne the device icon. IP addresses are assigned via Local Management; they
cannot be changed via NetSight Element Manager.
Location
Displays the user-deÞned location of the device. The location is entered and can
be changed via the System Group window; see Viewing System Group
Information , in Chapter 2, or the Generic SNMP UserÕs Guide for details.
MAC Address
Displays the manufacturer-set MAC address that is associated with the IP address
used to deÞne the device icon when it is added to NetSight Element Manager.
This address is factory-set and cannot be altered.
1-4 Conventions
Page 11

Uptime
Displays the amount of time that the STS16-20 has been running since the last
start-up, displayed in an X day(s) hh:mm:ss format.
Using Window Buttons
The Cancel button that appears at the bottom of most windows allows you to exit
a window and terminate any unsaved changes you have made. You may also
have to use this button to close a window after you have made any necessary
changes and set them by clicking on the OK , Set , or Apply button.
An OK , Set , or Apply button appears in windows that have conÞgurable values;
it allows you to conÞrm and set changes you have made to those values. In some
windows, you may have to use this button to conÞrm each individual set; in other
windows, you can set several values at once and conÞrm the sets with one click
on the button.
Introduction
The
current window; see Getting Help , page 1-6, for details.
The command buttons, for example Bridge, display a menu listing the windows
available for that selection.
Any menu topic followed by ... (three dots) Ñ for example Statistics... Ñ launches
a window associated with that selection.
Using the Mouse
This document assumes that you are using a Windows-compatible mouse with
two buttons; if you are using a three button mouse, you should ignore the
operation of the middle button when following procedures in this document.
Procedures within NetSight Element Manager document set refer to these buttons
as follows.
Left Mouse Button
Help button brings up a Help text box with information speciÞc to the
Right Mouse Button
Figure 1-2. Mouse Buttons
Conventions 1-5
Page 12

Introduction
For many mouse operations, this document assumes that the left (primary) mouse
button is to be used, and references to activating a menu or button will not
include instructions about which mouse button to use.
However, in instances in which right (secondary) mouse button functionality is
available, instructions will explicitly refer to right mouse button usage. Also, in
situations where you may be switching between mouse buttons in the same area
or window, instructions will also explicitly refer to both left and right mouse
buttons.
Instructions to perform a mouse operation include the following terms:
¥ Pointing means to position the mouse cursor over an area without pressing
either mouse button.
¥ Clicking means to position the mouse pointer over the indicated target, then
press and release the appropriate mouse button. This is most commonly used
to select or activate objects, such as menus or buttons.
¥ Double-clicking means to position the mouse pointer over the indicated
target, then press and release the mouse button two times in rapid succession.
This is commonly used to activate an objectÕs default operation, such as
opening a window from an icon. Note that there is a distinction made between
Òclick twiceÓ and Òdouble-click,Ó since Òclick twiceÓ implies a slower motion.
¥ Pressing means to position the mouse pointer over the indicated target, then
press and hold the mouse button until the described action is completed. It is
often a pre-cursor to Drag operations.
¥ Dragging means to move the mouse pointer across the screen while holding
the mouse button down. It is often used for drag-and-drop operations to copy
information from one window of the screen into another, and to highlight
editable text.
Getting Help
This section describes different methods of getting help for questions or concerns
you may have while using NetSight Element Manager.
Using On-Line Help
You can use the Help button in the STS16-20 windows to obtain information
speciÞc to the device. When you click on a Help button, a window will appear
which contains context-sensitive on-screen documentation that will assist you in
the use of the window and its associated command and menu options. Note that
if the Help button is grayed out, on-line help has not yet been implemented for
the associated window.
1-6 Getting Help
Page 13

From the Help menu accessed from the Chassis View window menu bar, you can
launch on-line help speciÞc to the Chassis View window, as well as bring up the
Chassis Manager window for reference.
All of the on-line help windows use the standard Microsoft Windows help facility. If you
NOTE
are unfamiliar with this feature of Windows, you can select Help from the Windows
Start menu, or Help Ñ> How to Use Help from the primary NetSight Element
Manager window, or consult your Microsoft Windows product UserÕs Guide.
Accessing On-line Documentation
The complete suite of documents available for NetSight Element Manager
can be accessed via a menu option from the primary window menu bar:
Help Ñ> Online Documents. If you chose to install the documentation when you
installed NetSight Element Manager, selecting this option will launch AdobeÕs
Acrobat Reader and a menu Þle which provides links to all other available
documents.
Introduction
If you have not yet installed the documentation, the Online Documents option will
TIP
not be able to access the menu Þle. In order to activate this option, you must run the
setup.exe again to install the documentation component. See your Installation Guide
for details.
Getting Help from the Global Technical Assistance Center
If you need technical support related to NetSight Element Manager, contact the
Global Technical Assistance Center via one of the following methods:
By phone: (603) 332-9400
24 hours a day, 365 days a year
By fax: (603) 337-3075
By mail: Enterasys Networks
Technical Support
35 Industrial Way
Rochester, NH 03867
By e-mail: support@enterasys.com
FTP: ftp.ctron.com (134.141.197.25)
Login anonymous
Password your email address
By BBS: (603) 335-3358
Modem Setting 8N1: 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, No parity
Getting Help 1-7
Page 14

Introduction
NOTE
Send your questions, comments, and suggestions regarding NetSight
documentation to NetSight Technical Communications via the following e-mail
address:
Netsight_docs@enterasys.com
To locate product speciÞc information, refer to the Enterasys Web site at the
following address:
http://www.enterasys.com
For the highest Þrmware versions successfully tested with NetSight Element Manager
2.2.1, refer to the Readme Þle available from the NetSight Element Manager program
group. If you have an earlier version of Þrmware and experience problems, contact the
Global Technical Assistance Center.
1-8 Getting Help
Page 15

Chapter 2
Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
Navigating through the Chassis View; viewing Chassis information; using source address functions
The STS16-20 Chassis View window is the main screen that immediately informs
you of the current condition of individual ports on your switch via a color-coded
graphical display. The Chassis View window serves as a single point of access to
all applications and windows which are discussed in the following sections and
chapters.
To access the STS16-20 Chassis View window:
1. In any map, list, or tree view, double-click on the device icon of the STS16-20
you wish to manage.
Figure 2-1. SmartSTACK Icon
or
1. In any map, list, or tree view, click the left mouse button once to select the
STS16-20 you wish to manage.
2. Select Manage—>Node from the main NetSight Element Manager window
menu bar, or select the Manage Node toolbar button.
or
1. In any map, list, or tree view, click the right mouse button once to select the
STS16-20 you wish to manage.
2. On the resulting menu, click Manage.
2-1
Page 16

Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
Viewing Chassis Information
The Chassis View window (Figure 2-2) provides a graphical representation of the
STS16-20, including a color-coded port status display which immediately informs
you of the current conÞguration and status of the device and its ports. You can
access the menus that lead to more detailed device- and port- level windows by
clicking in the designated areas of the graphical display, or by using the menu bar
at the top of the Chassis View window.
The color-coded Port Status Display
lets you view the status of the device’s
ports, according to the parameters
selected from the Port Status menu.
The Menu Bar contains
Device, Port Status, Utilities,
and Help menus.
The Fr ont Panel displa ys status
information about the device.
Figure 2-2. The STS16-20 Chassis View Window
When you move the mouse cursor over a management Òhot spotÓ the cursor icon will
TIP
change into a hand symbol to indicate that clicking in the current location will bring up a
management option.
Viewing Front Panel Information
The Front Panel section provides the following device information:
Connection Status
This color-coded icon indicates the current state of communication between
NetSight Element Manager and the STS16-20:
¥ Green indicates a valid connection; the STS16-20 is responding to device polls.
2-2 Viewing Chassis Information
Page 17

Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
¥ Magenta indicates a temporary stand-by mode, while the STS16-20 responds
to a physical change in the switch.
¥ Blue indicates an unknown contact status; polling has not yet been established
with the STS16-20.
¥ Red indicates that the STS16-20 is not responding to device polls (the device is
off line, or device polling has failed across the network).
Up Time
The amount of time that the STS16-20 has been running without interruption
since the last start-up, displayed in an X day(s) hh:mm:ss format.
Port Status
Indicates the Port Status display selection currently in effect; see Selecting a Port
Status Display, page 2-6, for details. The default port status display is Admin; if
you have not changed the port status selection since launching the Chassis View,
this Þeld will display Default.
MAC
The physical layer address assigned to the interface associated with the IP
Address used to deÞne the device icon when it was added to NetSight Element
manager. MAC addresses are hard-coded into the device, and are not
conÞgurable.
NOTE
Boot Prom
The revision of BOOT PROM installed in the STS16-20.
Firmware
The revision of device Þrmware installed in the switchÕs ßash memory.
Time
The current time set in the internal clock of the STS16-20, displayed in a
24-hour hh:mm:ss format.
Date
The current date set in the internal clock of the STS16-20, displayed in a
mm/dd/yyyy format.
For some Þrmware versions, the Time, Date, and Boot Prom Þelds will display as N/A
(not available).
IP Address
The IP (Internet Protocol) address assigned to the device will appear in the title
bar of the Chassis View.
Viewing Chassis Information 2-3
Page 18

Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
Menu Structure
By clicking on various areas of the STS16-20 Chassis View, you can access menus
with device and port level options, as well as utility applications which apply to
the device. Figure 2-3 displays the menu structure for the STS16-20, and indicates
how to use the mouse to access the various menus.
Figure 2-3. Sample Chassis View Menu Structure (STS16-20RM with an ATM SSIM)
Depending on the type of SSIM(s) installed in the STS16-20FRM and STS16-20RM,
NOTE
the options available will vary. If you have an ATM SSIM (A2-01 and A8-01) installed,
the ATM Connections option will be available from the Device menu. For this release,
additional management support is not provided for the Token Ring SSIMs (T5-04 and
T8-04), the HSTR SSIMs (R2-02 and R8-02), and the Fast Ethernet SSIM (H2-02).
The Device Menu
From the Device menu of the Chassis View menu bar, you can access the
following selections:
¥ Device Type displays a hardware description of the device; see Viewing the
Device Type, page 2-9, for details.
2-4 Viewing Chassis Information
Page 19

Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
¥ System Group allows you to manage the STS16-20 by providing direct access
via SNMP to MIB II variables. Refer to the Generic SNMP UserÕs Guide for
more information on SNMP, or see Viewing System Group Information,
page 2-10, to edit the name, contact, and location Þelds.
¥ I/F Summary displays statistics for the trafÞc processed by each network
interface on the device, including a detailed transmit and receive trafÞc
breakdown; see Viewing I/F Summary Information, page 2-12, for details.
¥ ATM Connections lets you conÞgure Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs) on
the device. The ATM Connections option will only appear if you have an ATM
SSIM (A2-01 or A8-01) installed in the STS16-20RM or STS16-20FRM; see
Chapter 3, ConÞguring ATM Connections, for details.
¥ Exit closes the STS16-20 Chassis View window.
The Port Status Menu
The Port Status menu allows you to select the status information that will be
shown in the Chassis ViewÕs port status display.
¥ Status allows you to select one of two status types: Admin, or Operator.
NOTE
NOTE
¥ Load displays the portion of network load processed per polling interval by
each interface as a percentage of the theoretical maximum load (4 or 16 Mbps).
For this release, the Load port status option will display three dashes and maintain the
color code of the most recently selected option for any unlinked ports (i.e. ports for which
the Operator status is OFF).
¥ Errors displays the number of errors detected per polling interval by each
interface as a percentage of the total number of valid packets processed by the
interface.
¥ I/F Mapping displays the interface value associated with each port on the
STS16-20.
¥ I/F Speed displays the speed (4 or 16 Mbps) of the network segment attached
to each port.
For this release, the I/F Speed port status option will display a zero and maintain the
color code of the most recently selected option for any unlinked ports (i.e. ports for which
the Operator status is OFF).
¥ I/F Type displays the interface type of each port: TR for Token Ring.
Viewing Chassis Information 2-5
Page 20

Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
The Utilities Menu
From the Utilities menu, you can select the following options:
¥ MIB Tools provides direct access to the deviceÕs Management Information
Bases (MIBs); refer to the Tools Guide for more information.
¥ SmartStack Manager launches the Windows 95/NT SmartStack Manager,
which provides device conÞguration, performance monitoring, and
troubleshooting options. This selection will appear only if the SmartStack
Manager is installed on your NetSight workstation; refer to the SmartStack
Manager - Installation and UserÕs Guide for more information.
¥ RMON allows you to distribute network monitoring functions through your
network to smart devices; refer to the Remote Monitoring (RMON) UserÕs
Guide for more information.
The MIB Tools and RMON selections are also available from the Tools menu at
the top of the primary NetSight Element Manager window.
The Help Menu
The Help menu has the following three selections:
¥ MIBs Supported opens the Chassis Manager window which displays the
MIBs, RFCs, and MIB Components contained on the device; see Displaying
MIBs and MIB Components, page 2-9, for details.
¥ Chassis Manager Help opens a help window with information speciÞcally
related to using the Chassis Manager and Chassis View windows.
¥ About Chassis Manager opens a version window for the Chassis Manager
application in use.
The Port Menus
The Port menu offers the following selections:
¥ Description displays a hardware description of the selected port; see Viewing
the Interface Description, page 2-10, for details.
¥ I/F Statistics displays transmit and receive packets for the selected port; see
Viewing Interface Detail Statistics, page 2-15, for details.
Selecting a Port Status Display
The port status display graphically depicts all interfaces supported by the
STS16-20. When you open the Chassis View, each port on the STS16-20 will
display its Admin status (see page 2-7). To change the port status display, select
one of the options on the Port Status menu, as described in the following section.
2-6 Viewing Chassis Information
Page 21

NOTE
Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
The Port Status options allow you to display status information for the 20 built-in
Token Ring ports. The Port Status options do not display status information for any
SSIMs installed in the STS16-20RM and STS16-20FRM.
To change the port status display:
1. Click on Port Status in the Chassis View menu bar to access the Port Status
menu.
2. Click to select the status information you want to display; the appropriate
status information will be shown in the port status display.
The port status options available as follows:
Status
Displays bridge status information for each port, as determined by the selected
submenu option:
NOTE
¥ Admin displays each bridge portÕs administrative status:
-ON (Green) Ñ The port has been enabled by management and has a valid
link.
- OFF (Red) Ñ The port has not been enabled or it has been disabled
through a management action.
- N/A (Blue) Ñ The administrative status is not available.
¥ Operator displays each bridge portÕs actual operational state:
- ON (Green) Ñ The port is currently forwarding packets.
- OFF (Red) Ñ The port is not currently forwarding packets.
- N/A (Blue) Ñ The operator status is not available.
The Admin status provides the state requested by management; the Operator status
provides the actual state of the port. Depending on the circumstances, the Operator
status may or may not match the Admin status currently requested by management. For
example, ports which are administratively ON but not yet connected would display an
Operator status of OFF, since no packets are being forwarded.
Load
Displays the percentage of network load processed by each port during the last
polling interval. This percentage reßects the network load generated per polling
interval by devices connected to the port compared to the theoretical maximum
load (4 or 16 Mbps) of the network.
Viewing Chassis Information 2-7
Page 22

Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
For this release, the Load port status option will display three dashes and maintain the
NOTE
color code of the most recently selected Port Status option for any unlinked ports (i.e.
ports for which the Operator status is OFF).
Errors
Displays the percentage of the total number of valid packets processed by each
port during the last polling interval that were error packets. This percentage
reßects the number of errors generated during the last polling interval by devices
connected to that port compared to the total number of valid packets processed
by the port.
The polling interval is set via the Tools Ñ> Options window from the primary window
NOTE
menu bar. Refer to the NetSight Element Manager UserÕs Guide for more
information on setting device polling intervals.
I/F Mapping
Displays the index value associated with each port on the STS16-20.
I/F Speed
Displays the speed (4 or 16 Mbps) of the network segment connected to each port.
For this release, the I/F Speed port status option will display a zero and maintain the
NOTE
color code of the most recently selected Port Status option for any unlinked ports (i.e.
ports for which the Operator status is OFF).
I/F Type
Displays the interface type of each port on the STS16-20: TR for Token Ring.
Port Status Display Color Codes
The port status display options incorporate color coding schemes. For the Admin,
and Operator display options the color coding scheme is described above.
For all other port status display selections Ñ Load, Errors, I/F Mapping,
I/F Speed, and I/F Type Ñ color codes will reßect the most recently selected
option which incorporates its own color coding scheme.
2-8 Viewing Chassis Information
Page 23

Displaying MIBs and MIB Components
Like most networking devices, the STS16-20 draws its functionality from a
collection of proprietary MIBs, and IETF RFCs. The MIB data is organized into a
series of Òcomponents,Ó which is a logical grouping of MIB data with each group
controlling a deÞned set of objects. There is no one-to-one correspondence
between MIBs and MIB components. A single MIB component might contain
objects from several different proprietary MIBs and RFCs.
The Chassis Manager window (Figure 2-4) is a read-only window that displays
the MIBs and the MIB components Ñ and, therefore, the functionality Ñ
supported by the currently monitored device.
To open the Chassis Manager window:
1. Click on Help in the Chassis View menu bar to access the Help menu.
2. Click on MIBs Supported. The Chassis Manager window, Figure 2-4, will
appear.
The MIBs which provide the
functionality for the STS16-20
— both proprietary and IETF
RFCs — are listed here.
Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
The MIB Components are
listed here. Note, there is no
one-to-one correspondence
between MIBs and MIB
Components.
Figure 2-4. Chassis Manager Window
Viewing Hardware Descriptions
Menu options available at the device and port levels provide speciÞc information
about the physical characteristics of the STS16-20 and its ports.
Viewing the Device Type
The Device Type window displays a hardware description of the device.
To open the Device Type window:
1. Click on Device in the Chassis View menu bar to access the Device menu.
2. Click on Device T ype. A Device Type window, similar to the one shown in
Figure 2-5, will appear.
Viewing Chassis Information 2-9
Page 24

Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
Figure 2-5. Sample Device Type Window
Viewing the Interface Description
The Interface Description window displays a text description, which includes the
product name and hardware version number.
To open the Interface Description window:
1. Click on the port of interest to access the Port menu.
2. Click on Description; an Interface Description window, similar to the
examples shown in Figure 2-6, will appear.
Figure 2-6. Sample Interface Description Windows
Viewing System Group Information
The System Group window allows you to view and modify the contact, name,
and location for your STS16-20. The System Group window also provides direct
access via SNMP to MIB II variables; refer to the Generic SNMP UserÕs Guide for
more information.
2-10 Viewing Chassis Information
Page 25

Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
To open the System Group window:
1. Click on Device in the Chassis View menu bar to access the Device menu.
2. Click on System Group. The System group window, as shown in Figure 2-7,
will appear.
Figure 2-7. System Group Window
The System Group window contains the following Þelds:
Contact
Displays the user-deÞned name of the contact person responsible for the device.
Name
Displays the user-deÞned name of the device.
Location
Displays the user-deÞned location of the device.
Services
Displays the level of OSI service supported by the device.
To add or modify System Group information:
1. Click on the I-bar button in the Contact, Name, or Location fields. A text
window will appear which allows you to add or modify the entry.
2. Enter the new or modified contact, name, or location information.
3. Click OK to accept the changes or Cancel to exit without saving changes.
Viewing Chassis Information 2-11
Page 26

Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
Viewing I/F Summary Information
The I/F Summary option displays statistics for the trafÞc processed by each
network interface on your device. The I/F Summary window also provides access
to a detailed statistics window via the Detail button that breaks down transmit
and receive trafÞc for each interface.
To open the I/F Summary window:
1. Click on Device on the Chassis View menu bar to access the Device menu.
2. Click on I/F Summary. The I/F Summary window, as shown in Figure 2-8, will
appear.
You can select the
type of statistic and
the unit of measure
displayed.
Base Unit displays
the statistical unit as
Load, Raw Counts,
or Rate.
The Detail button launches
the I/F Statistics window.
The I/F Display section lets you view descriptive information for each interface.
The two drop-down lists (in the upper right corner) are used to display interface
performance statistics and, where applicable, bar graphs. The Detail button
provides additional statistics on the transmit and receive trafÞc for each interface.
The I/F Display section for the STS16-20 lists interface information for each of the 20
NOTE
built-in ports, followed by any installed SSIMs, and internal interfaces. When two or
more STS16-20 SmartSTACK switches are stacked together, the I/F Display section will
list the interfaces for each switch in the stack as described previously.
Measurement
parameter displays
the selected
statistical unit.
The I/F Display section lets you view
descriptive information for each interface.
Figure 2-8. I/F Summary Window
2-12 Viewing Chassis Information
Page 27

Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
The following descriptive information is provided for each interface:
Index
The index value assigned to each interface on the device.
Type
The type of the interface, distinguished by the physical/link protocol(s) running
immediately below the network layer: Token Ring for the built-ports; other
values, such as ATM , will display for the installed SSIMs.
Description
A text description of the interface: the device type (e.g. STS-16-20RM) will display
for the 20 built-in Token Ring ports; the SSIM type (e.g. SSIM-A8-01) will display
for any installed SSIMs; and other values will display for any internal interfaces.
Physical Status
The current physical statusÑor operational stateÑof the interface: Online or
Ofßine.
Logical Status
The current logical statusÑor administrative stateÑof the interface: Up or Down.
Displaying Interface Performance Statistics and Bar Graphs
The statistical values (and, where available, the accompanying bar graphs)
provide a quick summary of interface performance. You can select the type of
statistical value and the unit to be displayed by using the two drop-down lists
directly above the I/F Display section, as follows:
1. From the right-most drop-down list of the I/F Summary window, click on the
unit in which you wish to display the selected statistic: Load, Raw Counts, or
Rate.
2. Once you have selected the base unit, click on the left-most drop-down list to
specify the display statistic. Note that the options available from this menu will
vary depending on the base unit you have selected.
Bar graphs are only available when Load is the selected base unit; if you select Raw
NOTE
Counts or Rate, the Bar Graph column will be removed from the interface display.
After you select a new display mode, the statistics (and bar graphs, where
applicable) will refresh to reßect the current mode, as described below.
Viewing Chassis Information 2-13
Page 28

Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
Raw Counts
The total count of network trafÞc received or transmitted on the selected interface
since device counters were last reset. Raw counts are provided for the following
parameters:
¥ In Octets Ñ for octets received on the interface, including framing characters.
¥ In Packets Ñ for packets (both unicast and non-unicast) received by the device
interface and delivered to a higher-layer protocol.
¥ In Discards Ñ for packets received by the device interface that were discarded
even though no errors prevented them from being delivered to a higher layer
protocol (e.g., to free up buffer space in the device).
¥ In Errors Ñ for packets received by the device interface containing errors that
prevented them from being delivered to a higher-layer protocol.
¥ In Unknown Ñ for packets received by the device interface that were
discarded because of an unknown or unsupported protocol.
¥ Out Octets Ñ for octets transmitted by the interface, including framing
characters.
¥ Out Packets Ñ for packets transmitted, at the request of a higher level
protocol, by the device interface to a subnetwork address (both unicast and
non-unicast).
¥ Out Discards Ñ for outbound packets that were discarded by the device
interface even though no errors were detected that would prevent them from
being transmitted. A possible reason for discard would be to free up buffer
space in the device.
¥ Out Errors Ñ for outbound packets that could not be transmitted by the device
interface because they contained errors.
Load
The number of bytes processed by the selected interface during the last poll
interval in comparison to the theoretical maximum load for the selected interface
type (4 or 16 Mbps for the built-in Token Ring ports; 100 Mbps for the high-speed
Token Ring and Ethernet SSIMs; and 155 Mbps for the ATM SSIMs).
Load is further deÞned by the following parameters:
¥ In Octets Ñ the number of bytes received by this interface, expressed as a
percentage of the theoretical maximum load.
¥ Out Octets Ñ the number of bytes transmitted by this interface, expressed as
a percentage of the theoretical maximum load.
When you select this option, a Bar Graph Þeld will be added to the I/F Display
section; this Þeld is only available when Load is the selected base unit.
2-14 Viewing Chassis Information
Page 29

Rate
The count for the selected statistic during the last poll interval. The parameters for
Rate are the same as those provided for Raw Counts; for a complete description,
see Raw Counts, page 2-14.
Viewing Interface Detail Statistics
The Interface Statistics window provides detailed trafÞc statistics for each
individual interface, including counts for both transmit and receive packets, and
error and buffering information. Color-coded pie charts graphically display
statistics for both received and transmitted unicast, multicast, discarded, and
error packets.
The I/F Statistics window can be accessed from the I/F Summary window and
from the individual Port menus.
To open the Interface Statistics window from the I/F Summary window:
1. Click to select the interface for which you would like to view more detailed
statistics. The selected interface will be highlighted blue.
Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
2. Click on the Detail button; the I/F Statistics window, as shown in Figure 2-9,
will appear.
To open the Interface Statistics window from a Port menu:
1. From the Chassis View’s port status display, click to select the port of interest
to access the Port menu.
2. Click on I/F Statistics; the I/F Statistics window, as shown in Figure 2-9, will
appear.
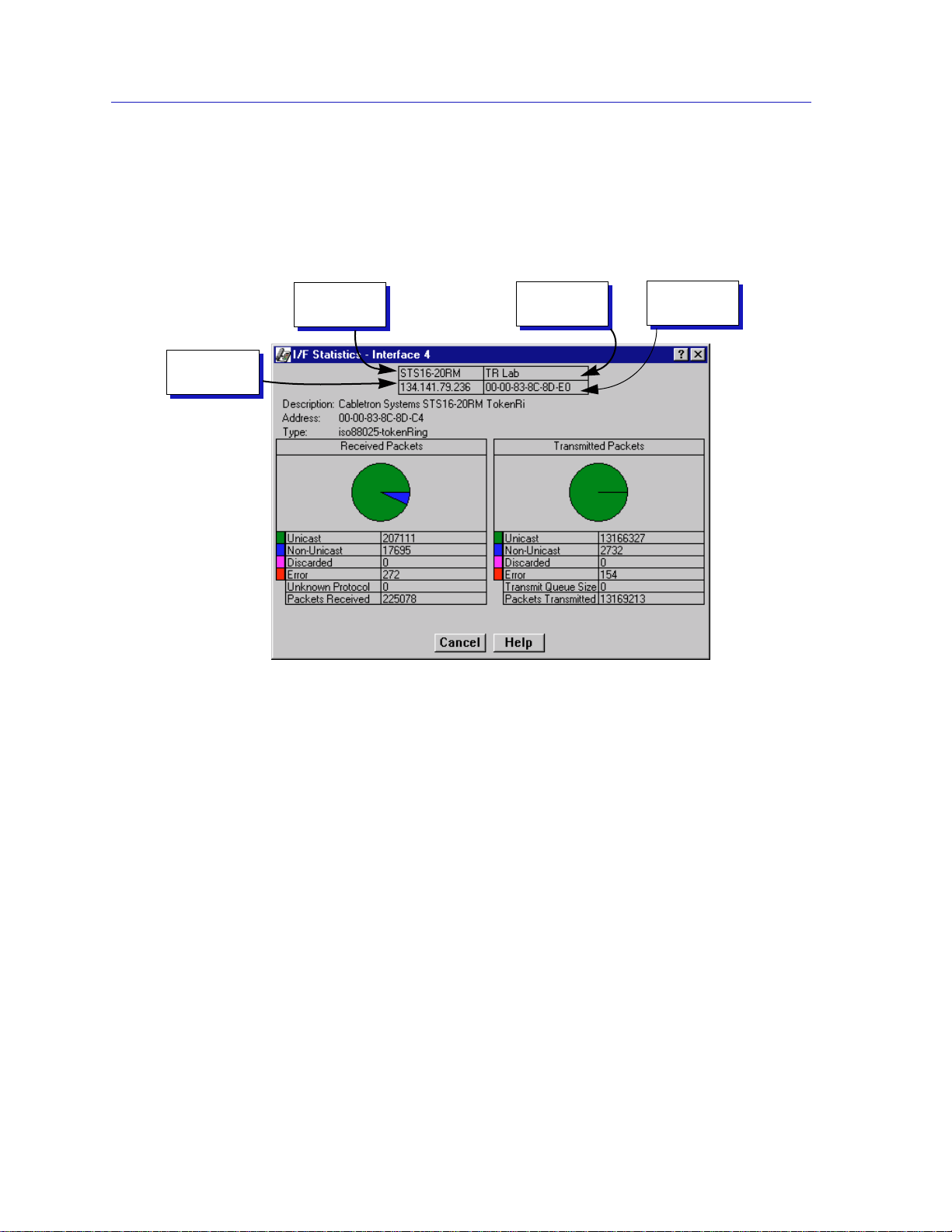
Figure 2-9. Interface Statistics Window
Viewing Chassis Information 2-15
Page 30

Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
The following three informational Þelds appear in the upper portion of the
window:
Description
The interface description for the currently selected interface.
Address
The MAC (physical) address of the selected interface.
Type
The interface type of the selected port.
The lower portion of the window provides the following transmit and receive
statistics. The Þrst four statistics are also displayed in pie charts.
Unicast
The number of packets transmitted to or received from this interface that had a
single, unique destination address. These statistics are displayed in the pie chart,
color-coded green.
Non-Unicast
The number of packets transmitted to or received from this interface that had a
destination address that is recognized by more than one device on the network
segment. The multicast Þeld includes a count of broadcast packetsÑthose that are
recognized by all devices on a segment. These statistics are displayed in the pie
chart, color-coded dark blue.
Discarded
The number of packets which were discarded even though they contained no
errors that would prevent transmission. These statistics are displayed in the pie
chart, color-coded magenta.
Good packets are typically discarded to free up buffer space when the network
becomes very busy. If this occurs routinely, it usually indicates that network trafÞc
is overwhelming the device. To solve this problem, you may need to reconÞgure
your bridging parameters, or perhaps reconÞgure your network to add additional
bridges or switches. Refer to the Network Troubleshooting Guide for details.
Error
The number of packets received or transmitted that contained errors. These
statistics are displayed in the pie chart, color-coded red.
Unknown Protocol
The number of packets received which were discarded because they were created
under an unknown or unsupported protocol.
Packets Received
The number of packets received by the selected interface.
(Received Packets only)
(Received Packets only)
2-16 Viewing Chassis Information
Page 31

Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
Transmit Queue Size
(Transmit Packets only)
The number of packets currently queued for transmission from this interface. The
amount of device memory devoted to buffer space and the trafÞc level on the
target network determines how large the output packet queue can expand before
the module will begin to discard packets.
Packets T ransmitted
(Transmit Packets only)
The number of packets transmitted by this interface.
Making Sense of Detail Statistics
By using a few simple calculations, the I/F Statistics window can give you a good
sense of the activity level and performance of the selected interface:
To calculate the percentage of input errors:
Received Errors /Packets Received
To calculate the percentage of output errors:
Transmitted Errors /Packets Transmitted
To calculate the total number of inbound and outbound discards:
Received Discards + Transmitted Discards
NOTE
To calculate the percentage of inbound packets that were discarded:
Received Discards /Packets Received
To calculate the percentage of outbound packets that were discarded:
Transmit Discards /Packets Transmitted
Unlike the Interface Detail window, which this window replaces, the Interface
Statistics window does not offer Disable or Test options. These options are
available in the Interface Group window, accessed via the System Group window
(DeviceÑ>System Group). Refer to your Generic SNMP UserÕs Guide for
more information on the System Group and Interface Group windows.
Viewing Chassis Information 2-17
Page 32

Using the STS16-20 Chassis View
2-18 Viewing Chassis Information
Page 33

Configuring ATM Connections
Viewing connection data; adding and deleting Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs)
The ATM Connections window is available when an ATM SSIM is installed in
the STS16-20RM or STS16-20FRM. An ATM SSIM allows you to integrate the
STS16-20 with an ATM backbone.
An ATM network uses two types of virtual channels or circuits: Switched Virtual
Circuits (SVCs) and Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs). SVCs are created and
dismantled dynamically on an as-needed basis, and require no management
deÞnition. By contrast, PVCs must be individually and manually conÞgured.
The ATM Connections window lets you view and modify Permanent Virtual
Circuits established at the device.
Chapter 3
NOTE
To access the ATM Connections window:
1. Click on Device in the Chassis View menu bar to display the Device menu.
2. Click on ATM Connections. The Current ATM Connections window, as shown
in Figure 3-1, will appear.
The ATM Connections option will only be available when at least one ATM SSIM (A2-01
or A8-01) is installed in the device.
3-1
Page 34

Configuring ATM Connections
Figure 3-1. Current ATM Connections Windows
The Current ATM Connections window provides the following information about
the deviceÕs ATM connections:
Connection Data
The Connection Data list box displays the conÞguration parameters for each ATM
interface available on the device.
I/F The index number assigned to each ATM SSIM installed in the
STS16-20. If an ATM SSIM is installed in the left hand slot, the
value in this Þeld will be 21; if an ATM SSIM is installed in the
right hand slot, the value in this Þeld will be 25.
Maximum The maximum number of connections allowed by the current
Connections version of Þrmware.
Current The maximum number of connections the port will keep active at
ConÞgured one time; the default value is 2048.
3-2
Page 35

Configuring ATM Connections
Settings
The Settings group box contains information about each of the currently
conÞgured PVCs, as well as the Þelds used to conÞgure new connections.
I/F The device interface index on which the PVC was conÞgured. An
ATM SSIM installed in the left hand slot will have an I/F value of
21; an ATM SSIM installed in the right hand slot will have an I/F
value of 25.
VPI The Virtual Path IdentiÞer assigned to the connection. Allowable
values are 0 - 3. VPIs are used to group virtual connections,
allowing for channel trunking between ATM switches. Each VPI
can be conÞgured to carry many different channels (designated
by Virtual Channel IdentiÞers) between two points.
VCI The Virtual Channel IdentiÞer assigned to the connection.
Allowable values are 0 - 1023 for each VPI. Each assigned VCI
must be unique within its deÞned VPI. However, you can assign
the same VCI to multiple VPIs (e.g., VPI 0/VCI 14, VPI 1/VCI 14,
VPI 2/VCI 14, etc.). Remember, it is the combined VPI and VCI
designations assigned to a channel that create the grouping of
virtual connections.
Encapsulation The method used to encapsulate LAN packets on the selected
Type circuit. Current versions of ATM SSIM Þrmware use VC MUX
802.5 LANE as the encapsulation method.
Status The current administrative status of the connection: Enabled or
Disabled.
UpTime The length of time the selected connection has been enabled.
Configuring Permanent Virtual Circuits
You can use the Add, Delete, or Refresh command buttons at the bottom of the
Current ATM Connections window to add or delete a Permanent Virtual Circuit
(PVC), or refresh the window.
¥ Add Ñ adds a new connection or modiÞes an existing connection, using the
parameters entered in the Þelds below the Settings list box. A conÞrmation
window will appear for additions and modiÞcations.
¥ Delete Ñ deletes the selected connection; a conÞrmation window requires that
you conÞrm the deletion.
¥ Refresh Ñ refreshes the connection information displayed in the window.
3-3
Page 36

Configuring ATM Connections
Adding a Permanent Virtual Circuit
To conÞgure a new Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC), enter the following
information in the Þelds which appear just below the Settings list box:
1. From the I/F menu, select the interface for which you wish to configure a
connection. All available ATM interfaces will be listed in this menu. The I/F
menu will display 21 if an ATM SSIM is installed in the left hand slot and/or 25
if an ATM SSIM is installed in the right hand slot of the switch.
2. In the VPI text box, enter the Virtual Path Identifier you wish to assign to this
connection. Allowable values are 0 to 3. The VPI you assign will be used to
group virtual connections, allowing for channel trunking between ATM
switches.
3. In the VCI text box, enter the Virtual Channel Identifier you wish to assign to
this connection. Allowable values are 0 to 1023
you could assign the same channel identifier as many as four times: once with
a VPI of 0, once with a VPI of 1, and so on. Remember that it is the
combination of VPI and VCI that will be used to direct cells through the
intermediate switches between the source and destination.
4. From the Encapsulation T ype menu, select the desired encapsulation type;
the STS16-20 uses VC MUX 802.5 LANE as the encapsulation method.
for each VPI
. For example,
5. Click on the Add button; the parameters for the new P ermanent Virtual Circuit
will be added to the Settings list box.
The circuit is automatically enabled, and will remain in place until it is manually
deleted.
Deleting a Permanent Virtual Circuit
Permanent Virtual Circuits remain in place until they are manually removed
using the Current ATM Connections window.
To delete an existing PVC:
1. In the Settings list box, click to select the Permanent Virtual Circuit you wish
to delete. The selected PVC will be highlighted blue.
2. Click on the Delete button. A confirmation window will appear, listing the
parameters assigned to the connection and asking you to verify the action.
3. Click OK to proceed with the deletion; the selected PVC will be deleted.
3-4
Page 37

Index
A
Admin status 2-7
Apply Button 1-5
ATM Connections
Configuring 3-3
ATM SSIM 1-2, 2-4, 3-1
B
Boot Prom 2-3
C
Cancel Button 1-5
Channel Trunking 3-3
Connection Status 2-2
Contact 2-11
D
Date 2-3
Description 2-10
Device Menu 2-4
Device Name 1-4
Discarded 2-16
H
Help Button 1-5
Help Menu 2-6
HSTR SSIM 1-2
I
I/F Mapping 2-8
I/F Speed 2-8
I/F Summary 2-12
I/F Type 2-8
Interface Statistics 2-15
IP Address 1-4, 2-3
L
Load 2-7, 2-14
Location 1-4, 2-11
Logical Status 2-13
M
MAC 2-3
MAC Address 1-4
Mouse Usage 1-5
E
Encapsulation Type 3-3
Errors 2-8
F
Fast Ethernet SSIM 1-2
Firmware 2-3
Firmware Versions 1-8
G
Getting Help 1-6
Global Technical Assistance Center 1-7
Grouping Virtual Connections 3-3
N
Name 2-11
Non-Unicast (Multicast) 2-16
O
OK Button 1-5
Operator status 2-7
P
Packets Received 2-16
Packets Transmitted 2-17
Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs) 3-1
Physical Status 2-13
Port Description 2-10
Port Menus 2-6
Port Status 2-3
Index-1
Page 38

Index
Port Status Display
Selecting 2-7
Port Status Menu 2-5
PVC 3-1
R
Rate 2-15
Readme 1-8
S
Set Button 1-5
SmartSTACK Manager 1-3, 2-6
SmartStack Manager 1-3
SSIM 2-4
STS16-20FRM 3-1
STS16-20RM 3-1
SVC 3-1
Switched Virtual Circuits (SVCs) 3-1
System Group 2-10
Editing 2-11
T
technical support 1-7
Time 2-3
Token Ring SSIM 1-2
Transmit Queue Size 2-17
Troubleshooting Guide 2-16
Type 2-13
U
Unicast 2-16
Unknown Protocol 2-16
Up Time 2-3
Uptime 1-5
Utilities Menu 2-6
V
VC MUX 802.5 LANE 3-3, 3-4
VCI 3-3
Virtual Channel IdentiÞer (VCI) 3-3
Virtual Path IdentiÞer (VPI) 3-3
VPI 3-3
Index-2
 Loading...
Loading...