
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13)
Configuration Guide
9033754-03


NOTICE
Enterasys Networks reserves the right to mak e cha nges in specifications and other information contained in this
document and its web site without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult Enterasys Networks to determine
whether any such changes have been made.
The hardware, firmware, or software described in this document is subject to change without notice.
IN NO EVENT SHALL ENTERASYS NETWORKS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT, SPECIAL,
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOST PR OFITS)
ARISING OUT OF OR RELATED TO THIS DOCUMENT, WEB SITE, OR THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN
THEM, EVEN IF ENTERASYS NETWORKS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF , KNEW OF, OR SHOULD HAVE KNOWN
OF, THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Enterasys Networks, Inc.
50 Minuteman Road
Andover, MA 01810
2003 Enterasys Networks, Inc. All rights reserved.
Printed in the United States of America.
Part Number: 9033754-03 May 2003
ENTERASYS NETWORKS, ENTERASYS MATRIX, LANVIEW, MATRIX, NETSIGHT, WEBVIEW, and any logos
associated therewith, are tra demarks or registered trademarks of Enterasys Networks, Inc. in the United States and other
countries.
All other product names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies.
Version: Information in this guide refers to Matrix E1 (1G694-13) firmware
version 1.2x.xx.

ENTERASYS NETWORKS, INC.
PROGRAM LICENSE AGREEMENT
BEFORE OPENING OR UTILIZING THE ENCLOSED PRODUCT,
CAREFULLY READ THIS LICENSE AGREEMENT.
This document is an agreement (“Agreement”) between the end user (“You”) and Enterasys Networks, Inc. on behalf of
itself and its Affiliates (as hereinafter defined) (“Enterasys”) that sets forth Your rights and obligations with respect to
the Enterasys software program (including any accompanying documentation, hardware or media) (“Program”) in the
package and prevails over any additional, conflicting or inconsistent terms and conditions appearing on any purchase
order or other document submitted by You. “Affiliate” means any person, partnership, corporation, limited liability
company, or other form of enterprise that directly or indirectly through one or more intermediaries, controls, or is
controlled by, or is under common control with the party specified. This Agreement constitutes the entire understanding
between the parties, and supersedes all prior discussions, representations, understandings or agreements, whether oral or
in writing, between the parties with respect to the subject matter of this Agreement. The Program may be contained in
firmware, chips or other media.
BY INST ALLING OR O THER WISE USING THE PR OGRAM, Y OU REPRESENT THAT YOU ARE A UTHORIZED
TO ACCEPT THESE TERMS ON BEHALF OF THE END USER (IF THE END USER IS AN ENTITY ON WHOSE
BEHALF YOU ARE AUTHORIZED TO ACT, “YOU” AND “YOUR” SHALL BE DEEMED TO REFER TO SUCH
ENTITY) AND THAT YOU AGREE THAT YOU ARE BOUND BY THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, WHICH
INCLUDES, AMONG OTHER PROVISIONS, THE LICENSE, THE DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTY AND THE
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY. IF YOU DO NOT AGREE TO THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT OR ARE NOT
AUTHORIZED TO ENTER INTO THIS AGREEMENT , ENTERASYS IS UNWILLING TO LICENSE THE
PROGRAM TO YOU AND YOU AGREE TO RETURN THE UNOPENED PRODUCT TO ENTERASYS OR YOUR
DEALER, IF ANY, WITHIN TEN (10) DAYS FOLLOWING THE DATE OF RECEIPT FOR A FULL REFUND.
IF YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS ABOUT THIS AGREEMENT, CONTACT ENTERASYS NETWORKS, LEGAL
DEPARTMENT AT (978) 684-1000.
You and Enterasys agree as follows:
1. LICENSE. You have the non-exclusive and non-transferable right to use only the one (1) copy of the Program
provided in this package subject to the terms and conditions of this Agreement.
2. RESTRICTIONS. Except as otherwise authorized in writing by Enterasys, You may not, nor may You permit any
third party to:
(i) Reverse engineer, decompile, disassemble or modify the Program, in whole or in part, including for reasons of
error correction or interoperability , except to the e xtent e xpressly permitte d by ap plicable la w and to the e xtent
the parties shall not be permitted by that applicable law, such rights are expressly excluded. Information
necessary to achieve interoperability or correct errors is available from Enter asys upon request and upon
payment of Enterasys’ applicable fee.
(ii) Incorporate the Program, in whole or in part, in any other product or create deriva tive works based on the
Program, in whole or in part.
(iii) Publish, disclose, copy, reproduce or transmit the Program, in whole or in part.
(iv) Assign, sell, license, sublicense, rent, lease, encumber b y way of security interest, pledge or otherwise transfer
the Program, in whole or in part.
(v) Remove any copyright, trademark, proprietary rights, disclaimer or warning notice includ ed on or embedded in
any part of the Program.

3. APPLICABLE LAW. This Agreement shall be interpreted and governed under the laws and in the state and federal
courts of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts without regard to its conflicts of laws provisions. You accept the personal
jurisdiction and venue of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts courts. None of the 1980 United Nations Convention on
Contracts for the International Sale of Goods, the United Nations Convention on th e Limitation Period in the International
Sale of Goods, and the Uniform Computer Information Transactions Act shall apply to this Agreement.
4. EXPORT RESTRICTIONS. You understand that Enterasys and its Affiliates are subject to regulation by agencies
of the U.S. Government, including the U.S. Department of Commerce, which prohibit export or di version of certain
technical products to certain countries, unless a license to export the Program is obtained from the U.S. Government or
an exception from obtaining such license may be relied upon by the exporting party.
If the Program is exported from the United States pursuant to the License Exception CIV under the U.S. Export
Administration Regulations, You agree that You are a civil end user of the Program and agree that You will use the
Program for civil end uses only and not for military purposes.
If the Program is exported from the United States pursuant to the License Exception TSR under the U.S. Export
Administration Regulations, in addition to the restriction on transfer set forth in Sections 1 or 2 of this Agreement, You
agree not to (i) reexport or release the Program, the source code for the Program or technology to a national of a country
in Country Groups D:1 or E:2 (Albania, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Bulgaria, Cambodia, Cuba, Estonia, Georgia,
Iraq, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Latvia, Libya, Lithuania, Moldova, North Korea, the People’s Republic of China,
Romania, Russia, Rwanda, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Vietnam, or such other countries as may be
designated by the United States Government), (ii) export to Country Groups D:1 or E:2 (as defined herein) the direct
product of the Program or the technology, if such foreign produced direct product is subject to national security controls
as identified on the U.S. Commerce Control List, or (iii) if the direct product of the technology is a complete plant or an y
major component of a plant, export to Country Groups D:1 or E:2 the direct product of the plant or a major component
thereof, if such foreign produced direct product is subject to national security controls as identified on the U.S. Commerce
Control List or is subject to State Department controls under the U.S. Munitions List.
5. UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS. The enclosed Program (i) was developed solely
at private expense; (ii) contains “restricted computer software” submitted with restricted rights in accordance with section
52.227-19 (a) through (d) of the Commercial Computer Software-Restricted Rights Clause and its successors, and (iii) in
all respects is proprietary data belonging to Enterasys and/or its suppliers. For Department of Defense units, the Program
is considered commercial computer software in accordance with DFARS section 227.7202-3 and its successors, and use,
duplication, or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions set forth herein.
6. DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTY. EXCEPT FOR THOSE WARRANTIES EXPRESSLY PROVIDED TO YOU
IN WRITING BY ENTERASYS, ENTERASYS DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EITHER EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
SATISFACTORY QUALITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, TITLE AND NON- INFRINGEMENT
WITH RESPECT TO THE PROGRAM. IF IMPLIED WARRANTIES MAY NOT BE DISCLAIMED BY
APPLICABLE LAW, THEN ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES ARE LIMITED IN DURATION TO THIRTY (30)
DAYS AFTER DELIVERY OF THE PROGRAM TO YOU.
7. LIMITATION OF LIABILITY. IN NO EVENT SHALL ENTERASYS OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR
ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF
BUSINESS, PROFITS, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF BUSINESS INFORMATION, SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR RELIANCE DAMAGES, OR OTHER LOSS) ARISING OUT OF THE USE
OR INABILITY TO USE THE PROGRAM, EVEN IF ENTERASYS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
OF SUCH DAMAGES. THIS FOREGOING LIMITATION SHALL APPLY REGARDLESS OF THE CAUSE OF
ACTION UNDER WHICH DAMAGES ARE SOUGHT.
THE CUMULATIVE LIABILITY OF ENTERASYS TO YOU FOR ALL CLAIMS RELATING TO THE PROGRAM,
IN CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, SHALL NOT EXCEED THE T OTA L AMOUNT OF FEES PAID TO
ENTERASYS BY YOU FOR THE RIGHTS GRANTED HEREIN.

8. AUDIT RIGHTS. You hereby acknowledge that the intellectual property rights associated with the Program are of
critical value to Enterasys and, accordingly, You hereby agree to maintain complete books, records and accounts showing
(i) license fees due and paid, and (ii) the use, copying and deployment of the Program. You also grant to Enterasys and
its authorized representatives, upon reasonable notice, the right to audit and examine during Your normal business hours,
Your books, records, accounts and hardware devices upon which the Program may be deployed to verify compliance with
this Agreement, including the verification of the license fees due and paid Enterasys and the use, copying and deployment
of the Program. Enterasys’ right of examination shall be exercised reasonably, in good faith and in a manner calculated
to not unreasonably interfere with Your business. In the event such audit discovers non-compliance with this Agreement,
including copies of the Program made, used or deployed in breach of this Agreement, You shall promptly pay to Enterasys
the appropriate license fees. Enterasys reserves the right, to be exercised in its sole discretion and without prior notice, to
terminate this license, effective immediately, for failure to comply with this Agreement. Upon any such termination, You
shall immediately cease all use of the Program and shall return to Enterasys the Program and all copies of the Program.
9. OWNERSHIP. This is a license agreement and not an agreement for sale. You acknowledge and agree that the
Program constitutes trade secrets and/or copyrighted material of Enterasys and/or its suppliers. You agree to implement
reasonable security measures to protect such trade secrets and copyrighted material. All right, title and interest in and to
the Program shall remain with Enterasys and/or its suppliers. All rights not specifically granted to You shall be reserved
to Enterasys.
10. ENFORCEMENT. You acknowledge and agree that any breach of Sections 2, 4, or 9 of this Agreement by You
may cause Enterasys irreparable damage for which recovery of money damages would be inadequate, and that Enterasys
may be entitled to seek timely injunctive relief to protect Enterasys’ rights under thi s Agreement in addition to any and
all remedies available at law.
11. ASSIGNMENT. You may not assign, transfer or sublicense this Agreement or any of Your rights or obligations
under this Agreement, except that You may assign this Agreement to any person or entity which acquires substantially all
of Your stock or assets. Enterasys may assign this Agreement in its sole discretion. This Agreement shall be binding upon
and inure to the benefit of the parties, their legal representatives, permitted transferees, successors and assigns as
permitted by this Agreement. Any attempted assignment, transfer or sublicense in violation of the terms of this Agreement
shall be void and a breach of this Agreement.
12. WAIVER. A waiver by Enterasys of a breach of any of the terms and conditions of this Agreement must be in
writing and will not be construed as a waiver of any subsequent breach of such term or condition. Enterasys’ failure to
enforce a term upon Your breach of such term shall not be construed as a waiver of Your breach or prevent enforcement
on any other occasion.
13. SEVERABILITY. In the event any provision of this Agreement is found to be invalid, illega l or unenforceable, the
validity, legality and enforceability of any of the remaining provisions shall not in any way be affected or impaired
thereby, and that provision shall be reformed, construed and enforced to the maximum extent permissible. Any such
invalidity, illegality or unenforceability in any jurisdiction shall not invalidate or render illegal or unenforceable such
provision in any other jurisdiction.
14. TERMINATION. Enterasys may terminate this Agreement immediately upon Your breach of any of the terms and
conditions of this Agreement. Upon any such termination, You shall immediately cease all use of the Program and shall
return to Enterasys the Program and all copies of the Program.

Contents
Figures ..........................................................................................................................................xiii
Tables............................................................................................................................................xiv
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Using This Guide............................................................................................................xv
Structure of This Guide .... ... ... .... ................................ ... ... .... ... ................................ ... ...xvi
Related Documents... .... ... ... ... .... ................................ ... ... .... ................................ ... ... ..xvii
Document Conventions.............................. ... ................................ .... ... ... ... ..................xvii
Typographical and Keystroke Conven tio ns.......................... ... ... ... .............................. xviii
1
2
3
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Overview.........................................................................................................1-1
1.2 Local Management Requirements..................................................................1-2
1.3 Getting Help....................................................................................................1-3
SETUP REQUIREMENTS
2.1 Connecting to a Console Port for Local Management ....................................2-1
2.1.1 What Is Needed...............................................................................2-2
2.1.2 Connecting to an IBM or Compatible Device...................................2-2
2.1.3 Connecting to a VT Series Terminal................................................2-3
2.1.4 Connecting to a Modem ..................................................................2-5
2.1.5 Adapter Wiring and Signal Assignments .................... ... ..................2-7
2.2 Using a Telnet Connection..............................................................................2-8
STARTUP AND GENERAL CONFIGURATION
3.1 Startup and General Configuration Summary.................................................3-1
3.1.1 Factory Default Settings .......................................................... ... ... ..3-1
3.1.2 “Command Defaults” Descriptions...................................................3-3
3.1.3 CLI Command Modes......................................................................3-4
3.1.4 Using WebView ...............................................................................3-4
3.1.5 Process Overview: CLI Startup and Gen er al Con fig u ra tion ............3-5
Contents v

3.1.6 Starting and Navigating the Command Line Interface.....................3-5
3.1.6.1 Using a Console Port Connection...................................3 -5
3.1.6.2 Logging in with a Default User Account ..........................3-6
3.1.6.3 Logging in With an Administratively Configured
User Account.... ... ... ................................ .... ... ... ...............3-7
3.1.6.4 Using a Telnet Conn e ctio n............ ... ... ... .... .....................3 -7
3.1.7 Getting Help with CLI Syntax...........................................................3-8
3.1.8 CLI Screen Scrolling Commands ....................................................3-8
3.1.9 Basic Line Editing Commands.........................................................3-9
3.2 General Configuration Command Set...........................................................3-10
3.2.1 Setting the Login Password...........................................................3-10
3.2.1.1 set password .................................................................3-10
3.2.2 Setting Basic System Information..................................................3-11
3.2.2.1 show system............................................... ... ... .............3-12
3.2.2.2 show time ............................ ... ... ................................. ...3-13
3.2.2.3 set time..........................................................................3-14
3.2.2.4 show version .......................... ... ................................. ...3-15
3.2.2.5 set system name...........................................................3-16
3.2.2.6 set system location........................................................3-17
3.2.2.7 set system contact.........................................................3-18
3.2.2.8 set terminal....................................................................3-19
3.2.2.9 set system baud............................................................3-20
3.2.2.10 show ip address .................................. ... .... ...................3 - 21
3.2.2.11 set ip address................................................................3-22
3.2.3 Downloading a Firmware Image.......... ... ... .... ... .............................3-23
3.2.3.1 Downloading via the Serial Port ....................................3-23
3.2.3.2 Downloading via TFTP.............. .... ... .............................3-24
3.2.4 Setting SNMP Community Names ................................................3-26
3.2.4.1 show community........... .... ................................ ... ... .......3-27
3.2.4.2 set community...............................................................3-28
3.2.4.3 clear community............................................................3-29
3.2.5 Setting SNMP Traps............................... ... ................................. ...3-30
3.2.5.1 show trap................... ... .... ... ................................ ... .......3-31
3.2.5.2 set trap ..........................................................................3-32
3.2.5.3 clear trap .......................................................................3-33
3.2.6 Closing the CLI..............................................................................3-33
3.2.6.1 exit.................................................................................3-34
vi Contents

4
PORT CONFIGURATION
4.1 Po rt Config u ra tio n Sum m a ry.................. .... ... ... ... .... ................................ ... ... ..4-1
4.1.1 Port Assignment Scheme........................ ... ... ... ...............................4-2
4.1.2 Port String Syntax Used in the CLI....................... ... ... ... ... ...............4-3
4.1.3 Process Overview: Port Configuration.............................................4-5
4.2 Po rt Config u ra tio n Co mm a nd Set .............................. ... ... .... ...........................4-6
4.2.1 Reviewing Port Status .....................................................................4-6
4.2.1.1 show port status ..............................................................4-7
4.2.1.2 show port counters..........................................................4-9
4.2.2 Disabling / Enabling Ports .............................................................4-11
4.2.2.1 set port disable..............................................................4-12
4.2.2.2 set port enable...............................................................4-13
4.2.3 Setting Port Auto-Negotiation.................. ... ................................ ...4-14
4.2.3.1 show port negotiation ....................................................4-15
4.2.3.2 set port negotiation........................................................4-16
4.2.4 Setting Flow Control ................................... ... ... .... ... ... ...................4- 17
4.2.4.1 show port flowcontrol.....................................................4-18
4.2.4.2 set port flowcontrol ........................................................4-19
4.2.5 Enabling / Disabling Jumbo Frame Support..................................4-20
4.2.5.1 show jumbo ...................................................................4-21
4.2.5.2 set jumbo.......................................................................4-22
4.2.6 Setting Port Traps.......................... ... ... ................................. ... ......4-23
4.2.6.1 show port trap................................................................4-24
4.2.6.2 set port trap...................................................................4-25
4.2.7 Overview: Port Mirroring................................................... .... ... ......4-26
4.2.8 Port Mirroring Commands .......................... ... ... .... .........................4-26
4.2.8.1 show port mirroring........................................................4-27
4.2.8.2 set port mirroring ...........................................................4-28
4.2.9 Overview: Port Trunking.......................... ... ... ................................4-29
4.2.10 Settin g Por t Tr un kin g.............. .... ................................ ... ... .............4-30
4.2.10.1 show trunk.....................................................................4-31
4.2.10.2 set trunk.........................................................................4-32
4.2.10.3 clear trunk......................................................................4-33
4.2.10.4 set trunk port .................................................................4-34
4.2.10.5 clear trunk port ..............................................................4-35
Contents vii

5
SPANNING TREE CONFIGURATION
5.1 Spanning Tree Configuration Summary..........................................................5-1
5.1.1 General............................................................................................5-1
5.1.2 Spanning Tree Features............... .... ... ... ... ................................. ... ..5-2
5.1.3 Process Overview: Spanning Tree Configuration............................5-2
5.2 Spanning Tree Configuration Command Set ..................................................5-3
5.2.1 Reviewing and Setting Spanning Tree Bridge Parameters .............5-3
5.2.1.1 show spantree stats ............................................... .... ... ..5-4
5.2.1.2 set spantree.....................................................................5-7
5.2.1.3 show spantree ver sion .................. ... ...............................5-8
5.2.1.4 set spantree version........................................................5-9
5.2.1.5 set spantree priority.......................................................5-10
5.2.1.6 set spantree hello..........................................................5-11
5.2.1.7 set spantree maxage.....................................................5-12
5.2.1.8 set spantree fwddelay ...................................................5-13
5.2.1.9 show spantree edg e po rt de la y .................... ... ... ... ... .... ...5-14
5.2.1.10 set spantree edgeportdelay...........................................5-15
5.2.1.11 show spantree legacypathcost............ ..........................5-16
5.2.1.12 set spantree legacypathcost..........................................5-17
5.2.1.13 show spantree tctrapsuppress ............... .... ... ................5- 18
5.2.1.14 set spantree tctrapsuppress..........................................5-19
5.2.1.15 show spantree rtmsgage............... ... ... ... .... ...................5 - 20
5.2.1.16 set spantree rtmsgage...................................................5-21
5.2.1.17 show spantree txholdcount............... .............................5-22
5.2.1.18 set spantree txholdcount...............................................5-23
5.2.2 Reviewing and Setting Spanning Tree Port Parameters...............5-24
5.2.2.1 set spantree portadmin..................................................5-25
5.2.2.2 show spantree bloc ke dp or ts.......... ... .............................5-26
5.2.2.3 show spantree por tp ri............. ................................ .... ...5-27
5.2.2.4 set spantree portpri .......................................................5-28
5.2.2.5 show spantree por tc ost ................. ... ... ... .... ... ................5- 29
5.2.2.6 set spantree portcost.....................................................5-30
5.2.2.7 show spantree adm in ed g e ............................................5-32
5.2.2.8 set spantree adminedge................................................5-33
5.2.2.9 show spantree adm in po i n t ..................... .... ... ... ... ... .......5-34
5.2.2.10 set spantree adminpoint................................................5-35
viii Contents

6
802.1Q VLAN CONFIGURATION
6.1 VLAN Configuration Summary........................................................................6-1
6.1.1 Port Assignment Scheme........................ ... ... ... ...............................6-1
6.1.2 Port String Syntax Used in the CLI....................... ... ... ... ..................6-1
6.1.3 Process Overview: 802.1Q VLAN Configuration.............................6-2
6.2 VLAN Configuration Command Set ................................................................6-3
6.2.1 Reviewing Existing VLANs ..............................................................6-3
6.2.1.1 show vlan ........................................................................6-4
6.2.1.2 show vlan static...............................................................6-6
6.2.2 Creating and Naming Static VLANs ................................................6-7
6.2.2.1 set vlan............................................................................6-8
6.2.2.2 set vlan name..................................................................6-9
6.2.2.3 clear vlan.......................................................................6-10
6.2.2.4 clear vlan name.............................................................6-11
6.2.3 Assigning Port VLAN IDs (PVIDs) and Ingress Filtering ...............6-12
6.2.3.1 show port vlan...............................................................6-13
6.2.3.2 set port vlan...................................................................6-14
6.2.3.3 clear port vlan................................................................6-15
6.2.3.4 show port ingress filter ..................................................6-16
6.2.3.5 set port ingress filter......................................................6-17
6.2.4 Configuring the VLAN Egress List.................................................6-18
6.2.4.1 set vlan egress..............................................................6-19
6.2.4.2 clear vlan egress...........................................................6-20
6.2.5 Setting the Host VLAN.......................................................... ... ... ...6-21
6.2.5.1 show host vlan...............................................................6-22
6.2.5.2 set host vlan ..................................................................6-23
6.2.5.3 clear host vlan...............................................................6-24
6.2.6 Enabling/Disabling GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protocol) ...6-25
6.2.6.1 show gvrp configuration ................................................6-27
6.2.6.2 set gvrp..........................................................................6-28
6.2.6.3 set gvrp timer.................................................................6-29
Contents ix

7
PORT PRIORITY CONFIGURATION
7.1 Port Priority Configuration Summary...............................................................7-1
7.1.1 Weighted Round Robin (WRR) Priority Queu e ing...... ... ... ... ... .... ... ..7-1
7.1.2 Process Overview: Port Priority Configuration ................................7-2
7.2 Port Priority Configuration Command Set.......................................................7-2
7.2.1 Configuring Port Priority ................................ ................................ ..7-2
7.2.1.1 show port priority........................................... ... ... ............7-3
7.2.1.2 set port priority.................................................................7-4
7.2.1.3 clear port priority..............................................................7-5
7.2.2 Configuring Priority to Transmit Queue Mapping ............................7-6
7.2.2.1 show priority que ue ................... .... ... ... ............................7-6
7.2.2.2 set priority queue.............................................................7-8
7.2.3 Configuring Quality of Service (QoS) ......................... ... ..................7-9
7.2.3.1 show port qos............... .... ... ................................ ... .......7-10
7.2.3.2 set port qos wrr..............................................................7-11
8
IGMP CONFIGURATION
8.1 Multic ast Filterin g Co nf igu ra tio n Sum m a ry ............................ .... .....................8 -1
8.1.1 Process Overview: IGMP Configura tion........ ... ... ... .... ... ... ...............8-1
8.2 IGMP Co nfig u ra tio n Co mm and Set.................................................. ... ... .... ... ..8-2
8.2.1 Enabling / Disabling IGMP...............................................................8-2
8.2.1.1 show igmp ........................... ... ... ................................. ... ..8-3
8.2.1.2 set igmp...........................................................................8-4
8.2.2 Setting IGMP Query Count and Report Delay.................................8-5
8.2.2.1 show igmp query count ...................................................8-6
8.2.2.2 set igmp query count.......................................................8-7
8.2.2.3 show igmp report delay ...................................................8-8
8.2.2.4 set igmp report delay.......................................................8-9
8.2.3 Reviewing IGMP Groups...............................................................8-10
8.2.3.1 show igmp groups .................................................. .... ...8-10
8.3 About IP Multicast Filtering ...........................................................................8-12
x Contents

9
NETWORK MANAGEMENT
9.1 Pro cess overview: Network Management..................... ................................ ..9-1
9.2 Network Management Command Set.............................................................9-1
9.2.1 Managing General Device Settings.................................................9-1
9.2.1.1 clear config......................................................................9-2
9.2.1.2 reset ................................................................................9-3
9.2.1.3 show cdp .........................................................................9-4
9.2.1.4 set cdp.............................................................................9-6
9.2.1.5 set cdp interval................................................................9-7
9.2.2 Monitoring Network Events and Status ...........................................9-8
9.2.2.1 show eventlog .................................................................9-9
9.2.2.2 clear eventlog................................................................9-10
9.2.2.3 history............................................................................9-11
9.2.2.4 repeat ............................................................................9-12
9.2.2.5 show history ..................................................................9-13
9.2.2.6 set history......................................................................9-14
9.2.2.7 show netstat..................................................................9-15
9.2.2.8 ping................................................................................9-17
9.2.2.9 show rmon stats ............................................................9-19
9.2.2.10 show users....................................................................9-22
9.2.2.11 disconnect.....................................................................9-23
9.2.3 Managing Network Addresses and Rou te s ...................... .............9-24
9.2.3.1 show arp........................................................................9-25
9.2.3.2 set arp ...........................................................................9-26
9.2.3.3 clear arp ........................................................................9-27
9.2.3.4 show ip route.................................................................9-28
9.2.3.5 set ip route.....................................................................9-29
9.2.3.6 clear ip route..................................................................9-30
9.2.3.7 show mac ......................................................................9-31
9.2.3.8 clear mac.......................................................................9-33
A
MATRIX E1 CLI QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE
A.1 Overview.........................................................................................................A-1
A.2 CLI Tasks, Commands and Syntax.................................................................A-1
INDEX
Contents xi

xii Contents

Figures
Figure Page
2-1 Connecting an IBM PC or Compatible Device ................................................................2-3
2-2 Co nn e ctin g a VT Serie s Term ina l .......................... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ................................ ..2-4
2-3 Connecting to a Modem ..................................................................................................2-6
3-1 Sample Command Default Description...........................................................................3-3
3-2 Console Port Initial Startup Screen Before User Authorization.......................................3-6
3-3 Startup Screen After User Authorization .........................................................................3-7
3-4 Using ? to Display Command Options ............................................................................3-8
4-1 Expansion Module and Fixed Front Panel Port Numbering Scheme..............................4-3
4-2 Optional 10-Gigabit Ethernet Expansion Modules ..........................................................4-3
6-1 Example of VLAN Propagation via GVRP.....................................................................6-26
Figures xiii

Tables
Table Page
3-1 Factory Default Device Settings....................................................................................3-1
3-2 Screen Scrolling Commands ........................................................................................3-8
3-3 Basic Line Editing Commands......................................................................................3-9
4-1 Optional Ethernet Expansion Modules, Compliance, and Physical Connection...........4-2
4-2 show port status Output Details....................................................................................4-8
4-3 show port counters Output Details..............................................................................4-11
5-1 show spantree stats Output Details ..............................................................................5-5
8-1 show igmp groups Output Details...............................................................................8-11
9-1 show cdp Output Details...............................................................................................9-5
9-2 show netstat Output Details........................................................................................9-16
9-3 show rmon stats Output Details................. .... ................................ ... ... .......................9-20
9-4 show ip route Output Details................... ... .... ... ... ................................ .... ... ................9-28
xiv Tables

About This Guide
Welcome to the Enterasys Networks Matrix E1 1G694-13 Configuration Guide. This manual
explains how to access the device’s Command Line Interface (CLI) and how to use it to configure
the Matrix E1 1G694-13 switch device.
Important Notice
Depending on the firmware version used in the Matrix E1 device, some features described in this
document may not be supported. Refer to the Release Notes shipped with the Matrix E1 device to
determine which features are supported.
USING THIS GUIDE
A general working knowledge of basic network operations and an understanding of CLI
management applications is helpful before configuring the Matrix E1 device.
This manual describes how to do the following:
• Access the Matrix E1 CLI
• Use CLI commands to perform network management and device configuration operations
• Establish and manage Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs)
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide xv

Structure of This Guide
STRUCTURE OF THIS GUIDE
The guide is organized as follows:
Chapter 1, Introduction, provides an overview of the tasks that can be accomplished using the
CLI interface, an overview of local manageme nt requirements, and information about obtaining
technical support.
Chapter 2, Setup Requirements, describes how to configure and connect a management terminal
or a modem to the SmartSwitch device, and how to Telnet to the device.
Chapter 3, Startup and General Configuration, provides and overview of the device’s factory
default settings and describes how to start the CLI interface, how to set basic system information,
how to set SNMP community names and traps, how to set the login password and how to exit the
CLI.
Chapter 4, Port Configuration, describes how to review port status, enable or disable ports,
enable or disable port auto-negotiation, set port flow control, set port traps and port mirroring, and
how to configure port trunking.
Chapter 5, Spanning Tree Configuration, describes how to review and set Spanning Tree
(802.1D and 802.1w) bridge parameters for the device, including bridge priority, hello time,
maximum aging time and forward delay, and how to review and set Spanning Tree port
parameters, including port priority and path costs.
Chapter 6, 802.1Q VLAN Configuration, describes how to create static VLANs, filter frames
according to VLAN, establish VLAN forwarding (egress) lists, route frames according to VLAN
ID, and configure ports on the switch as GVRP-aware ports.
Chapter 7, Port Priority Configuration, describes how set the transmit priority of each port,
display the current traffic class-mapping-to-priority or each port, and to set ports to transmit
frames according to selected priority transmit queues. It also describes how to configure Quality of
Service (QoS) settings.
Chapter 8, IGMP Configuration, describes how to configure Internet Group Management
Protocol (IGMP) settings for multicast filtering, including IGMP query count, IGMP report delay
and IGMP group status.
Chapter 9, Network Management, describes how to manage general device settings, how to
monitor network events and status, including the eventlog, command history, netstats and RMON
statistics, and how to manage network addresses and routes.
xvi Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Related Documents
RELATED DOCUMENTS
The following Enterasys Netw ork s documents may help you to set up, control, and manage the
Matrix E1 device:
• Ethernet Technology Guide
• Cabling Guide
• Matrix E1 1G694-13 Installation Guide
• Matrix E1 1G694-13 WebView User’s Guide
Documents listed above, can be obtained from the World Wide Web in Adobe Acrobat Portable
Document Format (PDF) at the following web site:
http://www.enterasys.com/
DOCUMENT CONVENTIONS
This guide uses the following conventions:
NOTE: Calls the reader’s attention to any item of information that may be of special
importance.
CAUTION: Contains information essential to avoid damage to the equipment.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide xvii

Typographical and Keystroke Conventions
TYPOGRAPHICAL AND KEYSTROKE CONVENTIONS
bold type Bold type indicates required user input, including command keywords,
that must be entered as shown for the command to exec ute.
RETURN Indicates either the ENTER or RETURN key, depending on your
keyboard.
ESC Indicates the keyboard Escape key.
SPACE bar Indicates the keyboard space bar key.
BACKSPACE Indicates the keyboard backspace key.
arrow keys Refers to the four keyboard arrow keys.
[-] Indicates the keyboard dash key.
DEL Indicates the keyboard delete key.
italic type When used in general text, italic type indicates complete document titles.
When used in CLI command syntax, italic type indicates a user-supplied
parameter, either required or optional, to be entered after the command
keyword(s).
n.nn A period in numerals signals the decimal point indicator (e.g., 1.75 equals
one and three fourths). Or, periods used in numerals signal the decimal
point in Dotted Decimal Notation (DDN) (e.g., 000.000.000.000 in an IP
address).
x A lowercase italic x indicates the generic use of a letter (e.g., xxx indicates
any combination of three alphabetic characters).
n A lowercase italic n indicates the generic use of a number (e.g., 19nn
indicates a four-digit number in which the last two digits are unknown).
[ ] Square brackets indicate optional parameters.
{ } Braces indicate required parameters. One or more parameters must be
entered.
| A bar indicates a choice in parameters.
[{ | }] Braces and vertical bars within square brackets indicate a required choice
within an optional element. Y ou do not need to select one. If you do, you have
some required choices.
xviii Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

1
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the tasks that may be accomplished using the Matrix E1
1G694-13 CLI interface, an introduction to in-band and out-of-band network management, and
information on how to contact Enterasys Networks for technical support.
Important Notice
Depending on the firmware version used in the Matrix E1 1G694-13 device, some feat ures
described in this document may not be supported. Refer to the Releas e Notes shipped with the
Matrix E1 device to determine which features are supported.
1.1 OVERVIEW
Enterasys Networks’ Matrix E1 CLI interface allows you to perform a variety of network
management tasks, including the following:
• Assign IP address and subnet mask.
• Select a default gateway.
• Assign a login password to the device for additional security.
• Download a new firmware image.
• Designate which network management workstations receive SNMP traps from the device.
• View switch, interface, and RMON statistics.
• Configure ports to perform load sharing using trunking commands.
• Clear NVRAM.
• Configure ports to perform load sharing using trunking commands.
• Configure 802.1D and 802.1w Spanning Trees.
• Set 802.1Q VLAN memberships and port configurations.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 1-1

Introduction
• Configure the device to operate as a Generic Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP) device to
dynamically create VLANs across a switched network.
There are five ways to manage the Matrix E1 device:
• Locally using a VT type terminal connected to the console port.
• Remotely using a VT type terminal connected through a modem.
• Remotely using an SNMP management station.
• In-band through a Telnet connection.
• Remotely using WebView, Enterasys Networks’ embedded web server.
NOTE: This guide describes configuring and managing the Matrix E1 device using CLI
commands. For details on using WebView for configuration and management tasks,
refer to the Matrix E1 1G694-13 WebView User’s Guide.
Chapter 2 provides setup instructions for connecting a terminal or modem to the Matrix E1 device.
1.2 LOCAL MANAGEMENT REQUIREMENTS
The Matrix E1 device provides one communication port, labeled console, which supports a
management terminal connection. To access the CLI management interface, connect one of the
following systems to the console port:
• IBM or compatible PC running a VT series emulation software package.
• Digital Equipment Corporation VT series terminal.
• VT type terminal running emulation programs for the Digital Equipment Corporation
VT series.
You can also access the CLI management interface using a Telnet connection through one of the
network ports of the Matrix E1 device.
NOTE: For details on the setup parameters for the console, how to connect a console
to the Matrix E1 device, or how to make a Telnet connection, refer to Chapter 2.
1-2 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Introduction
1.3 GETTING HELP
For additional support related to this device or document, contact Enterasys Networks using one of
the following methods:
World Wide Web http://www.enterasys.com/
Phone (603) 332-9400
Internet mail support@enterasys.com
To send comments or suggestions concerning this document, contact the Enterasys Networks
Technical Writing Department via the following email address: TechWriting@enterasys.com
Make sure to include the document Part Number in the email message.
Before calling Enterasys Networks, have the following information ready:
• Your Enterasys Networks service contract number
• A description of the failure
• A description of any action(s) already taken to resolve the problem
(e.g., changing mode switches, rebooting the unit, etc.)
• The serial and revision numbers of all involved Enterasys Networks products in the network
• A description of your network environment (layout, cable type, etc.)
• Network load and frame size at the time of trouble (if known)
• The device history (i.e., have you returned the device before, is this a recurring problem, etc.)
• Any previous Return Material Authorization (RMA) numbers
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 1-3


2
Setup Requirements
This chapter provides information concerning the following ways to access the Matrix E1
management interface:
• Connecting to a Console Port for Local Management (Section 2.1), which describes how to
connect a PC, a VT series terminal, or a modem to the Enterasys Networks host device.
• Using a Telnet Connection (Section 2.2), which provides guidelines when using a Telnet
connection to access the CLI management interface.
2.1 CONNECTING TO A CONSOLE PORT FOR LOCAL
MANAGEMENT
To access local management on the Matrix E1 device, connect one of the following systems to the
console port:
• IBM or compatible PC running a VT series emulation software package (Section 2.1.2).
• Digital Equipment Corporation VT series terminal; or VT type terminal running emulation
programs for the Digital Equipment Corporation VT series (Section 2.1.3).
• A modem (Section 2.1.4).
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 2-1

Setup Requirements
What Is Needed
2.1.1 What Is Needed
One RJ45-to-DB9 female adapter (supplied with the switch).
The following is a list of the user-supplied parts that may be needed depending on the connection:
• UTP cable with RJ45 connectors
• RJ45-to-DB25 female adapter (PN 9372110)
• RJ45-to-DB25 male adapter (PN 9372112)
Using a UTP cable with RJ45 connectors and RJ45-to-DB9 adapter, you can connect products
equipped with an RJ45 console port to an IBM or compatible PC running a VT series emulation
software package.
Using a UTP cable and an optional RJ45-to-DB25 female ad apter (PN 9372110), you can connect
products equipped with an RJ45 console port to a VT series terminal or VT type terminals running
emulation programs for the VT series.
Using a UTP cable and an optional RJ45-to-DB25 male adapter (PN 9372112), you can connect
products equipped with an RJ45 console port to a Hayes compatible modem that supports
9600 baud.
2.1.2 Connecting to an IBM or Compatible Device
To connect an IBM PC, or compatible device, running the VT terminal emulation, to an Enterasys
Networks module console port (Figure 2-1), proceed as follows:
1. Connect the RJ45 connector at one end of the cable (not supplied) to the console port on the
Enterasys Networks device.
2. Plug the RJ45 connector at the other end of the cable into the RJ45-to-DB9 adapter (supplied
with the switch). Refer to Section 2.1.5 for adapter wiring and signal assignments.
3. Connect the RJ45-to-DB9 adapter to the communications port on the PC.
4. Turn on the PC and configure your VT emulation package with the following parameters:
Parameter Setting
Mode 7 Bit Control
Transmit Transmit=9600
Bits Parity 8 Bits, No Parity
Stop Bit 1 Stop Bit
2-2 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Connecting to a VT Series Terminal
5. When these parameters are set, the Matrix E1 startup screen will display.
Figure 2-1 Connecting an IBM PC or Compatible Device
1G694-13
Setup Requirements
CPUPWR
Reset
Console
1
Á
Ã
Â
À
3712_20
PC
➀
RJ45-to-DB9 PC Adapter
➁
UTP Cable with RJ45 Connectors
➂
RJ45 Console Port
➃
2.1.3 Connecting to a VT Series Terminal
To connect a VT series terminal to an Enterasys Networks switch console port (Figure 2-2), use a
UTP cable with RJ45 connectors and an optional RJ45-to-DB25 female adapter (PN 9372110),
and proceed as follows:
1. Connect the RJ45 connector at one end of the cable to the console port on the Enterasys
Networks device.
2. Plug the RJ45 connector at the other end of the cable into the RJ45-to-DB25 female adapter.
Refer to Section 2.1.5 for adapter wiring and signal assignments.
3. Connect the RJ45-to-DB25 adapter to the port labeled COMM on the VT terminal.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 2-3

Setup Requirements
Connecting to a VT Series Terminal
4. Turn on the terminal and access the setup directory. Set the following parameters on your
terminal:
Parameter Setting
Mode 7 Bit Control
Transmit Transmit=9600
Bits Parity 8 Bits, No Parity
Stop Bit 1 Stop Bit
5. When these parameters are set, the Matrix E1 startup screen will display.
Figure 2-2 Connecting a VT Series Terminal
À
VT Series Terminal
➀
RJ45-to-DB25 VT Adapter
➁
Á
1G694-13
Â
UTP Cable with RJ45 Connectors
➂
RJ45 Console Port
➃
Reset
CPUPWR
Console
1
Ã
3712_18
2-4 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Setup Requirements
Connecting to a Modem
2.1.4 Connecting to a Modem
To connect a modem to an Enterasys Networks device modem port (Figure 2-3), use a UTP cable
with RJ45 connectors and an optional RJ45-to-DB25 male adapter (PN 9372112), and proceed as
follows:
1. Connect the RJ45 connector at one end of the cable to the modem port on the Enterasys
Networks device.
2. Plug the RJ45 connector at the other end of the cable into the RJ45-to-DB25 male adapter.
Refer to Section 2.1.5 for adapter wiring and signal assignments.
3. Connect the RJ45-to-DB25 adapter to the communications port on the modem.
4. Turn on the modem and configure your VT emulation package with the following parameters:
Parameter Setting
Mode 7 Bit Control
Transmit Transmit=9600
Bits Parity 8 Bits, No Parity
Stop Bit 1 Stop Bit
5. When these parameters are set, the Matrix E1 startup screen will display.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 2-5

Setup Requirements
Connecting to a Modem
Figure 2-3 Connecting to a Modem
1G694-13
CPUPWR
RJ45 Modem Port
➀
Modem
➁
À
Á
RJ45-to-DB25 Modem Adapter
➂
UTP Cable with RJ45 Connectors
➃
Â
Ã
Reset
RJ45 Console Port
➄
Console
Ä
1
3712_19
2-6 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Adapter Wiring and Signal Assignments
2.1.5 Adapter Wiring and Signal Assignments
Console Port Adapter Wiring and Signal Diagram
RJ45 DB9
Pin Conductor Pin Signal
1 Blue 2 Receive (RX)
4 Red 3 Transmit (TX)
5 Green 5 Ground (GRD)
2 Orange 7 Request to Send (RTS)
6 Yellow 8 Clear to Send (CTS)
Setup Requirements
Pins
RJ45 Connector (Female)
81
045905
DB9 Connector (Female)
Pins
15
69
045904
VT Series Port Adapter Wiring and Signal Diagram
RJ45 DB25
Pin Conductor Pin Signal
4 Red 2 Transmit (TX)
1 Blue 3 Receive (RX)
6 Yellow 5 Clear to Send (CTS)
5 Green 7 Ground (GRD)
2 Orange 20 Data Terminal Ready
Pins
RJ45 Connector (Female)
81
045905
13 1
25
DB25 Connector (Female)
Pins
14
045906
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 2-7

Setup Requirements
Adapter Wiring and Signal Assignments
Modem Port Adapter Wiring and Signal Diagram
RJ45 DB25
Pin Conductor Pin Signal
1 Blue 2 Transmit (TX)
2 Orange 8 Data Carrier Detect (DCD)
4 Red 3 Receive
5 Green 7 Ground (GRD)
6 Yellow 20 Data Terminal Ready (DTR)
8 Gray 22 Ring Indicator
Pins
81
RJ45 Connector (Female)
045905
DB25 Connector (Male)
Pins
131
2514
045907
2.2 USING A TELNET CONNECTION
Once the Matrix E1 device has a valid IP address, you can establish a Telnet session from any
TCP/IP based node on the network.
For information about setting the IP address, refer to Section 3.2.2.11.
Refer to the instructions included with the Telnet application for information about establishing a
Telnet session.
2-8 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

3
Startup and General Configuration
This chapter describes factory default settings and the Startup and General Configuration set of
commands.
3.1 STARTUP AND GENERAL CONFIGURATION SUMMARY
At startup, the Matrix E1 device is configured with many defaults and standard features. The
following sections provide information on how to review and change factory defaults, and how to
customize basic system settings to adapt to your work environment.
3.1.1 Factory Default Settings
Table 3-1 lists factory default device settings available on the Matrix E1.
.
Table 3-1 Factory Default Device Settings
Device Feature Default Setting
CDP Auto enabled on all ports.
CDP interval Transmit frequency of CDP messages set to 60 seconds.
Community name Public.
GVRP Globally disabled. Enabled on all ports.
GVRP timer Join timer set to 20, leave timer set to 60, leaveall timer set to 1000
(centiseconds).
Host VLAN Assigned to default (VID 1) VLAN.
IGMP Disabled.
IP mask Set to 255.255.0.0.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-1

Startup and General Configuration
Factory Default Settings
Table 3-1 Factory Default Device Settings (Continued)
Device Feature Default Setting
Password None configured. User must press ENTER at password prompt to
access CLI.
Port auto-negotiation Disabled.
Port enable/disable Enabled.
Port trap Link traps for all ports are enabled.
QoS weighted
Set to 25% for weighted queues (0 through 3).
round-robin (WRR)
Spanning Tree Enabled (globally and on all ports).
Spanning Tree edge
Enabled.
port administrative
status
Spanning Tree edge
Enabled.
port delay
Spanning Tree forward
Set to 15 seconds.
delay
Spanning Tree hello
Set to 2 seconds.
interval
Does not apply to MATRIX
Spanning Tree ID
Set to 1.
(SID)
Spanning Tree legacy
Enabled.
path cost
Spanning Tree
Set to 20 seconds.
maximum aging time
Spanning Tree port cost Se t to 1 for both 1-Gigabit and 10-Gigabit Ethernet ports.
Spanning Tree port
priority
All 1-Gigabit ports are set to 128 (medium priority). The 10-Gigabit
uplink port is set to 112.
Spanning Tree priority Bridge priority is set to 32768.
3-2 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Table 3-1 Factory Default Device Settings (Continued)
Device Feature Default Setting
Startup and General Configuration
“Command Defaults” Descriptions
Spanning Tree tran smit
Set to 3.
hold count
Spanning Tree version. Set to rstp (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol).
System baud rate Set to 9600 baud.
System contact Set to sysContact.
System location Set to sysLocation.
System name Set to sysName.
Terminal CLI display set to 80 columns and 24 rows.
VLAN ID All ports use a VLAN identifier of 1, and are included on the host
VLAN ID 1 port VLAN list.
WebView Enabled.
WebView port Set at TCP port number 80.
3.1.2 “Command Defaults” Descriptions
Each command description in this guide includes a section entitled “Command Defaults” which
contains different information than the factory default settings on the device as described in
Table 3-1. The command defaults section defines CLI behavior if the user enters a command
without optional parameters (indicated by square brackets [ ]). For commands without optional
parameters, the defaults section lists “None”. For commands with optional parameters, this section
describes how the CLI responds if the user opts to enter only the k eyword s of the command syntax.
Figure 3-1 provides an example.
Figure 3-1 Sample Command Default Description
show port status [port_string]
Command Defaults
If port_string is not specified, status information for all ports
will be displayed.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-3

Startup and General Configuration
CLI Command Modes
3.1.3 CLI Command Modes
Each command description in this guide includes a section entitled “Command Mode” which states
whether the command is executable in Read-Write or Read-Only mode. Users with Read-Only
access will only be permitted to view Read-Only (show) commands. Users with Read-Write access
will be able to modify all modifiable parameters in set and show commands, as well as view
Read-Only commands.
3.1.4 Using WebView
NOTE: This guide describes configuring and managing the Matrix E1 device using CLI
commands. For details on using WebView (Enterasys Networks’ embedded web server)
for configuration and management tasks, refer to the Matrix E1 1G694-13 WebView
User’s Guide.
By default WebView is enabled on TCP port number 80 of the Matrix E1 device. You can verify
WebView status, enable or disable WebView, and reset the WebView port as described below.
Displaying WebView status:
To display WebView status, enter show webview at the CLI command prompt.
This example shows that WebView is enabled on TCP port 80, the default port number.
Matrix>show webview
Webview is currently enabled on port 80.
Enabling / disabling WebView:
To enable or disable WebView, enter set webview {enable | disable} at the CLI command prompt.
This example shows how to enable WebView.
Matrix>set webview enable
Webview enabled.
Setting the WebView port:
To set a different TCP port through which to run WebView, enter set webvi ew port webview_port
at the CLI command prompt. Webview_port must be a number value from 1 to 65535 specifying
the WebView TCP port.
3-4 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Startup and General Configuration
Process Overview: CLI Startup and General Configuration
This example shows how to set the WebView port to 100.
Matrix>set webview port 100
Webview port set to 100.
3.1.5 Process Overview: CLI Startup and General Configuration
Use the following steps as a guide to the startup and general configuration process:
1. Starting and navigating the Command Line Interface (CLI) (Section 3.1.6)
2. Setting the login password (Section 3.2.1)
3. Setting basic system information (Section 3.2.2)
4. Setting SNMP community names (Section 3.2.4)
5. Setting SNMP traps (Section 3.2.5)
6. Closing the CLI (Section 3.2.6)
3.1.6 Starting and Navigating the Command Line Interface
3.1.6.1 Using a Console Port Connection
NOTE: By default, this Matrix E1 Series device is configured with two user login
accounts: ro for Read-Only access, and rw for Read-Wr i te ac ce ss. The default
password is set to a blank string (carriage return). For information on changing these
default settings, refer to Section 3.2.1.1.
Once you have connected a terminal to the local console port as described in Chapter 2, the initial
startup screen, Figure 3-2, will display. You can now start the Command Line Interface (CLI) by
• Using a default user account, as described in Section 3.1.6.2, or
• Using an administratively-assigned user account as described in Section 3.1.6.3.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-5

Startup and General Configuration
Starting and Navigating the Command Line Interface
3.1.6.2 Logging in with a Default User Account
If this is the first time your are logging in to the Matrix E1 Series device, or if the default user
accounts have not been administratively changed, proceed as follows:
1. At the Username login prompt, enter one of the following default user names:
• ro for Read-Only access,
• rw for Read-Write access.
2. Press ENTER. The Password prompt displays.
Leave this string blank and press ENTER. The notice of authorization and the Matrix prompt
displays as shown in Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-2 Console Port Initial Startup Screen Before User Authorization
(c)Copyright ENTERASYS Networks, Inc. 2001
Matrix 1G694-13
POST Version ver 01.00.08
Loading primary functional image ... PASSED
Application image loaded to CPU SDRAM.
Starting Application ...
1G694-13
Switch init start...
Switch SOC init...
Switch 10G PHY init...
Starting Boot......Press Ctrl-c to enter Diagnostics mode
Initializing hardware ...
Switch clear VLAN table...
Switch init finished...
Initializing databases...
Username:
3-6 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Startup and General Configuration
Starting and Navigating the Command Line Interface
3.1.6.3 Logging in With an Administratively Configured
User Account
If the device’s default user account settings have been changed, proceed as follows:
1. At the Username login prompt, enter your administratively-assigned user name and press
ENTER.
2. At the Password prompt, enter your password and press ENTER.
The notice of authorization and the Matrix prompt displays as shown in Figure 3-3.
3.1.6.4 Using a Telnet Connection
Once the Matrix E1 device has a valid IP address, you can establish a Telnet session from any
TCP/IP based node on the network as follows.
1. Telnet to the device’s IP address.
2. Enter login (user name) and passwor d information in one of the following ways:
• If the device’s default login and password settings have not been changed, follow the steps
listed in Section 3.1.6.2, or
• Enter an administratively-configured user name and password.
The notice of authorization and the Matrix prompt displays as shown in Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-3 Startup Screen After User Authorization
Username:rw
Password:
waiting for authorization......
****************************************
* *
* Matrix 1G694-13 *
* *
* Enterasys Networks, Inc. *
* P.O. Box 5005 *
* Rochester, NH 03866-5005 USA *
* *
****************************************
Matrix>
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-7

Startup and General Configuration
Getting Help with CLI Syntax
For information about setting the IP address, refer to Section 3.2.2.11.
Refer to the instructions included with the Telnet application for information about establishing a
Telnet session.
3.1.7 Getting Help with CLI Syntax
As shown in Figure 3-4, you can display command options, such as syntax details and a list of
commands that share the same initial keywords, by entering a question mark (?) in the CLI
command string. This feature is useful if you are unsure of all the keywords in a command, or what
other commands complete a configuration step.
Figure 3-4 Using ? to Display Command Options
This example shows how to use the ? to display commands beginning with show priority:
Matrix>show priority ?
classification
queue
Matrix>show priority
3.1.8 CLI Screen Scrolling Commands
CLI commands that require more than one screen to display will prompt you to enter the following
keystrokes to return to the command prompt or to continue displaying output .
Table 3-2 Screen Scrolling Commands
Key Sequence Command
Ctrl+C Return to the command prompt.
S Scroll through the output.
M Show “more” -- the next screen in the command output.
3-8 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Startup and General Configuration
Basic Line Editing Commands
3.1.9 Basic Line Editing Commands
The CLI supports EMACs-like line editing commands. Table 3-3 lists some commonly used
commands.
Table 3-3 Basic Line Editing Commands
Key Sequence Command
Ctrl+A Move cursor to beginning of line.
Ctrl+B Move cursor back one character.
Ctrl+C Abort command.
Ctrl+D Delete character.
Ctrl+E Move cursor to end of line.
Ctrl+F Move cursor forward one character.
Ctrl+H Delete character to left of cursor.
Ctrl+I or TAB key Command completion.
Ctrl+K Delete all characters after cursor.
Ctrl+L or Ctrl+R Re-display line.
Ctrl+N Scroll to next command in command history (use the CLI show history
command to display the history.)
Ctrl+P Scroll to previous command in command history.
Ctrl+T Transpose characters.
Ctrl+U Erase entire line.
Ctrl+W Delete word to the left of cursor.
Ctrl+X Delete all characters before the cursor.
Ctrl+Y Restore the most recently deleted item.
Ctrl+Z Delete all characters before the cursor.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-9

Startup and General Configuration
Setting the Login Password
3.2 GENERAL CONFIGURATION COMMAND SET
3.2.1 Setting the Login Password
Purpose
To change the login password on the CLI.
Command
The command needed to set the login password is listed below and described in the associated
section as shown.
• set password (Section 3.2.1.1)
3.2.1.1 set passwor d
Use this command to set the login password on the CLI.
set password {rw | ro}
Syntax Description
rw | ro Sets the password to Read-Write or Read-Only.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Example
This example shows how to set an initial Read-Write password:
Matrix>set password rw
Enter old password: ********
Enter new password: ********
Retype new password: ********
Password changed.
3-10 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Startup and General Configuration
Setting Basic System Information
3.2.2 Setting Basic System Information
Purpose
To display and set the basic system information, including time, contact name, terminal output,
baud rate and version information, to display or set the local host IP address, and to download a
new firmware image to the device.
Commands
The commands needed to set basic system information are listed below and described in the
associated section as shown.
•show system (Section 3.2.2.1)
•show time (Section 3.2.2.2)
• set time (Section 3.2.2.3)
• show version (Section 3.2.2.4)
• set system name (Section 3.2.2.5)
• set system location (Section 3 .2.2.6)
• set system contact (Section 3.2.2.7)
• set terminal (Section 3.2.2.8)
• set system baud (Section 3.2.2.9)
• show ip address (Section 3.2.2.10)
• set ip address (Section 3.2.2.11)
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-11

Startup and General Configuration
Setting Basic System Information
3.2.2.1 show system
Use this command to display system information.
show system
Syntax Description
None.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Only.
Example
This example shows how to display system information:
Matrix>show system
Power Supply Status
-----------------------PS1 - Operational
PS2 - Operational
System Baud : 9600.
System Uptime : 15 days, 9 hours, 43 minutes, 10 seconds
System Name System Location System Contact
------------------------ ------------------------ -----------------------sysName sysLocation sysContact
3-12 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Startup and General Configuration
Setting Basic System Information
3.2.2.2 show time
Use this command to display the current time of day in the system clock.
show time
Syntax Description
None.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Only.
Example
This example shows how to display the current time:
Matrix>show time
Thu 11/06/2001 08:24:28
The output shows the day of the week, month, day, year, hour, minutes, and
seconds.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-13

Startup and General Configuration
Setting Basic System Information
3.2.2.3 set time
Use this command to change the time of day on the system clock.
set time [day_of_week][mm/dd/yyyy][hh:mm:ss]
Syntax Description
day_of_week (Optional) Specifies the day of the week.
mm/dd/yyyy (Optional) Specifies the month, day, and year.
hh:mm:ss (Optional) Specifies the current time in 24-hour format.
Command Defaults
This command has no default setting.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Example
This example shows how to set the system clock to Saturday, October 31, 2003, 7:50 a.m:
Matrix>set time sat 10/31/2003 7:50
Sat Oct 31 1998, 07:50:00
3-14 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Startup and General Configuration
Setting Basic System Information
3.2.2.4 show version
Use this command to display hardware and firmware information. Refer to Section 3.2.3 for
instructions on how to download a firmware image.
show version
Syntax Description
None.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Only.
Example
This example shows how to display version information:
Matrix>show version
Slot Ports Model Serial Number HW Version FW Version
---- ----- --------- ------------- ---------- ---------- 0 12 1G694-13 01310004900a 2 01.02.03
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-15

Startup and General Configuration
Setting Basic System Information
3.2.2.5 set system name
Use this command to configure a name for the system.
set system name “name_string”
Syntax Description
name_string Specifies a text string that identifies the system. A name
string containing a space in the text must be enclosed in
quotes as shown in the example below.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Usage Guidelines
None.
Example
This example shows how to set the system name to Information Systems:
Matrix>set system name “Information Systems”
System name set.
3-16 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

3.2.2.6 set system location
Use this command to identify the location of the system.
set system location “location_string”
Syntax Description
location_string Specifies a text string that indicates where the system is
located. A location string containing a space in the text
must be enclosed in quotes as shown in the example
below.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Startup and General Configuration
Setting Basic System Information
Example
This example shows how to set the system location string:
Matrix>set system location “Bldg N32-04 Closet 9 Alpha Sierra”
System location set.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-17

Startup and General Configuration
Setting Basic System Information
3.2.2.7 set system contact
Use this command to identify a contact person for the system.
set system contact “contact_string”
Syntax Description
contact_string Specifies a text string that contains the name of the
person to contact for system administration. A contact
string containing a space in the text must be enclosed in
quotes as shown in the example below.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Example
This example shows how to set the system contact string:
Matrix>set system contact “Joe Smith”
System contact set.
3-18 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Startup and General Configuration
Setting Basic System Information
3.2.2.8 set terminal
Use this command to set the number of columns and rows of the terminal connected to the console
port of the device. This information is used to control the output of the CLI itself.
set terminal {rows num_rows | cols num_cols}
Syntax Description
rows Specifies the number of terminal rows to be set.
num_rows Specifies the number of terminal rows to be set. Integer
must be greater than 1.
cols Specifies the number of terminal columns to be set.
num_cols Specifies the number of terminal columns to be set. Integer
must be greater than 1.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Example
This example shows how to set the terminal columns to 50:
Matrix>set terminal cols 50
Terminal width set to 50.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-19

Startup and General Configuration
Setting Basic System Information
3.2.2.9 set system baud
Use this command to set the console port baud rate.
set system baud rate
Syntax Description
rate Specifies the console baud rate. Valid rates are 9600, 19200,
2400, 4800 and 38400.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Example
This example shows how to set the system baud rate to 19200:
Matrix>set system baud 19200
System console port baud rate set to 19200.
3-20 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Startup and General Configuration
Setting Basic System Information
3.2.2.10 show ip address
Use this command to display the local host port IP address and the system mask.
show ip address
Syntax Description
None.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Only.
Example
This example shows how to display the host port IP address and the system mask.
Matrix>show ip address
System IP - 10.1.10.1
System Mask - 255.255.128.0
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-21

Startup and General Configuration
Setting Basic System Information
3.2.2.11 set ip address
Use this command to set the local host IP address and subnet mask.
set ip address ip_addr [ip_mask]
Syntax Description
ip_addr Specifies the IP address to be set as the local host.
ip_mask (Optional) Specifies the IP mask of the local host.
Command Defaults
If not specified, ip_mask will be set to 255.255.0.0.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Example
This example shows how to set the host port IP address to
Matrix>set ip address 172.29.78.111 255.255.0.0
Local IP address set.
System mask set.
172.29.78.111:
3-22 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Startup and General Configuration
Downloading a Firmware Image
3.2.3 Downloading a Firmware Image
You can upgrade the operational firmwa re in the Matrix E1 without physically opening the device
or being in the same location. The software storage sector in the flash memory of the device is
reprogrammed, allowing you to easily download firmware feature enhancements and problem
fixes to the device from a local or remote location.
Firmware can be downloaded to the device in two ways:
• V ia the serial (console) port. This procedure is an out-of-band operation that copies the f irmware
through the serial port to the device. This operation takes approximately three minutes and
requires minimal configuration.
• Via TFTP download. This procedure uses a TFTP server connected to the network and
downloads the f irmware using the TFTP protocol. A TFTP download is much f aster than a serial
download, requiring only a few seconds, and can be used to upgrade a device that is not
physically in the area. The disadvantage is that this method requires a TFTP server and
additional setup.
3.2.3.1 Downloading via the Serial Port
A serial download is the easiest method to upgrade the de vice f irmw are, requiring the least amount
of equipment and configuration.
To download device firmware via the serial port, proceed as follows:
1. Reset the device’s dip switch 6 as detailed in Appendix B: “Mode Switch Bank Settings” in the
Matrix E1 1G694-13 Installation Guide.
2. With the console port connected, reset the device by powering the device off and then on.
3. After the power-on hardware and software tests are complete, the system initialization screen
displays the following message:
Starting Serial X-modem download.
Switch console baud rate to 115200.
Press RETURN to continue, CTRL-C to abort ...
4. Change your terminal baud rate to 115200 bps and press ENTER. The following message is
displayed:
Ready to receive image via X-modem download ...
Downloading image ...................................
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-23

Startup and General Configuration
Downloading a Firmware Image
5. Send the file using the XMODEM protocol from your computer application (the procedure
varies depending upon the application used).
6. When the XMODEM procedure finishes, the following messages are displayed:
Performing checksum of received image ............... PASSED
Programming primary functional image to flash ....... PASSED
Programming secondary functional image to flash ..... PASSED
7. Change your baud rate back to 9600 and press ENTER. The new image will be loaded and
started.
3.2.3.2 Downloading via TFTP
To perform a TFTP download, you must first set the device’s IP address (as detailed in
Section 3.2.2.11). You then use the dload command to enter the IP address of th e TFTP serv er a nd
the name of the image file.
dload
Use this command to download a new firmware image from a TFTP server to the device.
dload ip_address filename [noreboot]
Syntax Description
ip_address Specifies the address of the TFTP server from which the
new image file will be downloaded.
filename Specifies the TFTP server path and file name of the new
image.
noreboot (Optional) Specifies that the device will not reboot after
completing the download of an image file. The device
will continue using the existing firmware image and will
store the new image in FLASH memory. The next time
the device is reset or powered-up, it will boot from
FLASH memory using the new image.
Command Defaults
If noreboot is not entered, the device will reboot automatically using the new
image.
3-24 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide
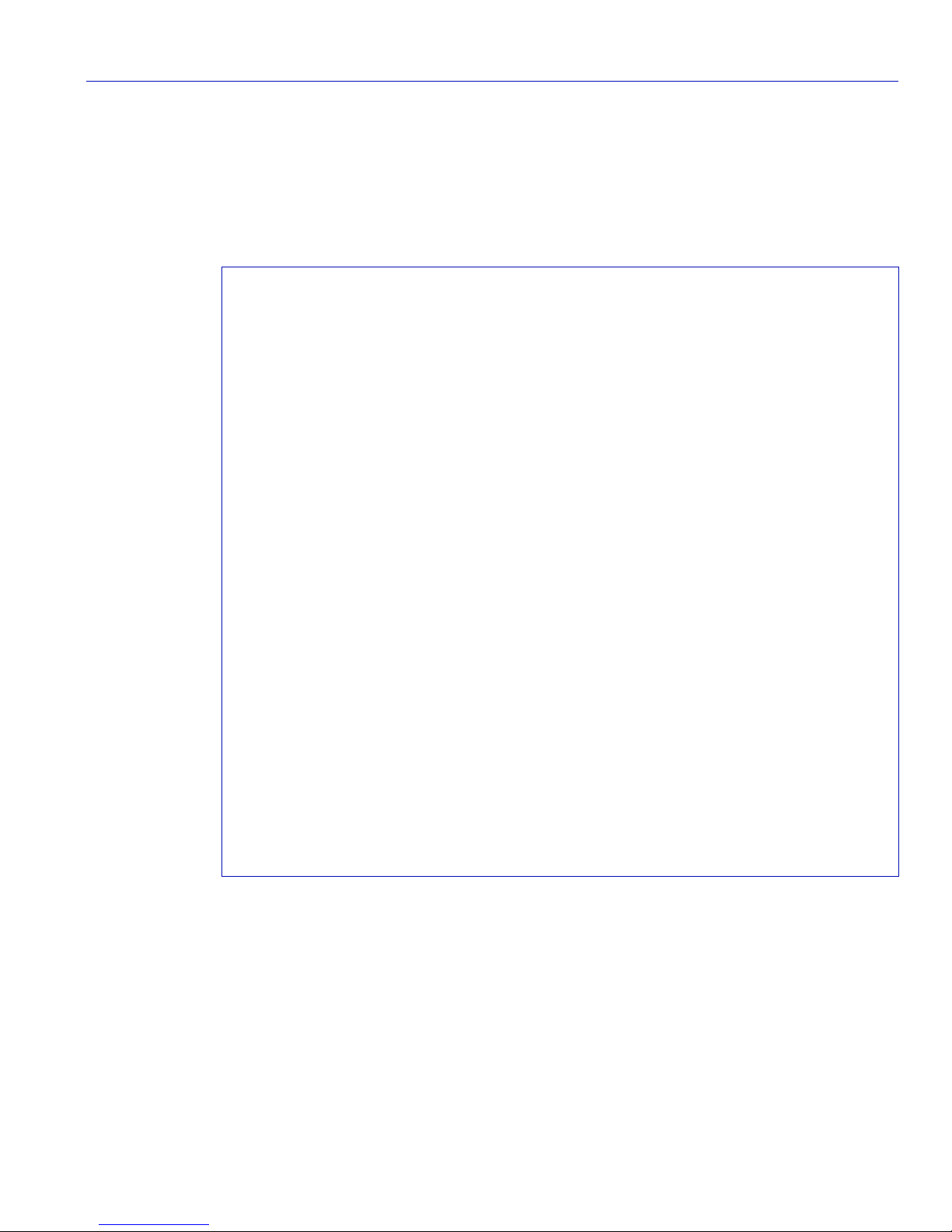
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Example
This example shows how to download a new firmware image:
Matrix>dload 172.101.50.87 d:\images\xfiles\010000.09
File downloaded successfully.
Updating flashROM image at 0xFF200000 ...
Image update successful.
Updating flashROM image at 0xFF500000 ...
Image update successful.
Restarting system...
Saving persistent data
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
(c)Copyright ENTERASYS Networks, Inc. 2001
Matrix 1G694-13
POST Version 01.00.00
Application image found in Flash memory.
Loading functional image ...
Application image loaded to CPU SDRAM.
Start Application ...
1G694-13
Switch init start...
Switch Budget init...
Initializing hardware...
Switch clear VLAN table...
Initializing databases...
Username:
Startup and General Configuration
Downloading a Firmware Image
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-25

Startup and General Configuration
Setting SNMP Community Names
3.2.4 Setting SNMP Community Names
Purpose
To set SNMP Management community names and access policies. Community names act as
passwords to remote SNMP management. Access is controlled by enacting either of two levels of
security authorization (read-only or read-write.)
NOTE: Read-write access gives the user full management privileges, allows existing
passwords to be changed, and all modifiable MIB objects to be edited.
Commands
The commands needed to set community names are listed below and described in the associated
section as shown.
• show community (Section 3.2.4.1)
• set community (Section 3.2.4.2)
• clear community (Section 3.2.4.3)
3-26 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Startup and General Configuration
Setting SNMP Community Names
3.2.4.1 show community
Use this command to display SNMP community names and access policies.
show community
Syntax Description
None.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Only.
Example
This example shows how to display community names and access policies:
Matrix>show community
Community Name Permissions
------------------ ----------Public Read-Write
Private Read-Write
Read-Only
Read-Only
Read-Only
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-27

Startup and General Configuration
Setting SNMP Community Names
3.2.4.2 set community
Use this command to set SNMP community names and access policies.
set community community_name access_ policy
Syntax Description
community_name Specifies the name through which a user will access
SNMP management. Up to 5 community names can be
set.
access_ policy Specifies the access permission accorded each
community name. The available access levels are:
• read-only (ro): This community name gives the user
read-only access to the device MIB objects, and
excludes access to security-protected fields of
read-write authorization.
• read-write (rw): This community name gives the user
read-write access to the device MIB objects and also
allows the user to change all modifiable parameters,
including community names, IP addresses, traps and
SNMP objects.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-write.
Example
This example shows how to set the community name “green” for read-write access.
Matrix>set community green rw
Community record added.
3-28 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

3.2.4.3 clear community
Use this command to delete SNMP community names.
clear community community_name
Syntax Description
community_name Specifies the SNMP management user access name to be
deleted.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Startup and General Configuration
Setting SNMP Community Names
Example
This example shows how to delete the community name “green.”
Matrix>clear community green
Community record cleared.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-29

Startup and General Configuration
Setting SNMP Traps
3.2.5 Setting SNMP Traps
Purpose
To assign IP addresses where SNMP traps will be sent. The device can send messages to multiple
network management stations to alert users of status changes. For details on the types of traps this
device supports, refer to the appropriate Matrix E1 Release Notes.
Commands
The commands needed to set SNMP traps are listed below and described in the associated section
as shown.
•show trap (Section 3.2.5.1)
• set trap (Section 3.2.5.2)
• clear trap (Section 3.2.5.3)
3-30 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Startup and General Configuration
Setting SNMP Traps
3.2.5.1 show trap
Use this command to display SNMP trap configuration information.
show trap
Syntax Description
None.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Only
Example
This example shows how to use the show trap command. It shows that there are two SNMP traps
enabled. One is assigned to the “orange” community at IP address 1.2.3.4. Another is assigned to
the “blue” community at IP address 100.54.5.112.
Matrix>show trap
Community Name IP Address Status
-------------------- --------------- --------
orange 1.2.3.4 enabled
blue 100.54.5.112 enabled
public 0.0.0.0 disabled
public 0.0.0.0 disabled
public 0.0.0.0 disabled
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-31

Startup and General Configuration
Setting SNMP Traps
3.2.5.2 set trap
Use this command to configure an SNMP trap assigned to an IP address.
set trap ip_ address community_name {enable | disable}
Syntax Description
ip_address Specifies the IP address of the trap to be set.
community_name Specifies the community name of the trap to be set.
enable | disable Enables or disables the trap.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Example
This example shows how to enable a trap on IP address 172.29.65.123 in the “blue” community:
Matrix>set trap 172.29.65.123 blue enable
Trap set successfully.
3-32 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Startup and General Configuration
3.2.5.3 clear trap
Use this command to clear an SNMP trap assigned to an IP address.
clear trap ip_address
Syntax Description
ip_address Specifies the IP address of the trap to be cleared.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write
Example
This example show s how to clear the trap assigned to IP address 172.29.65.123.
Closing the CLI
Matrix>clear trap 172.29.65.123
Trap cleared.
3.2.6 Closing the CLI
Purpose
To close your CLI session.
Command
The command used to close the CLI session is listed below and described in the associated section
as shown.
• exit (Section 3.2.6.1)
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 3-33

Startup and General Configuration
Closing the CLI
3.2.6.1 exit
Use this command to leave a CLI session.
exit
NOTE: Device timeout occurs after five minutes of user inactivity, automatically closing
your CLI session.
Syntax Description
None.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Only.
Example
This example shows how to exit a CLI session:
Matrix>exit
Connection closed by foreign host.
3-34 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Port Configuration
This chapter describes the Port Configuration set of commands and how to us e them.
4.1 PORT CONFIGURATION SUMMARY
The Matrix E1 1G694-13 features a fixed front panel of twelve 1-Gigabit Ethernet ports and an
optional expansion module slot with one 10-Gigabit Ethernet uplink port.
1-Gigabit Ethernet Ports
The 1-Gigabit Ethernet ports consist of
• eight fixed MT-RJ style ports that are 1000BASE-SX compliant, and
4
• four port slots that support optional hot-swappable Mini-GBICs.
As of the printing of this manual, there were three Mini-GBIC models available: two that comply
with standard 1000BASE-SX; one that complies with 1000BASE-LX.
10-Gigabit Ethernet Port
The 10-Gigabit Ethernet port is an expansion slot for a 10-Gigabit Ethernet Expansion Module.
Depending on the Ethernet Expansion Module inst alled, the uplink can be via different connectors
and media that support 10-Gigabit Ethernet operation.
At the time that this manual was printed, there were two Ethernet Expansion Module models
available: ZPIM1-01 and ZPIM-06. Table 4-1 lists the standards these modules comply with and
their physical connection types. Refer to the Matrix E1 1G694-13 Installation Guide for cable
specifics.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-1

Port Configuration
Port Assignment Scheme
Table 4-1 Optional Ethernet Expansion Modules, Compliance, and Physical Connection
Ethernet Expansion Module Compliant to Physical Connection
ZPIM1-01 10-Gigabit Ethernet One fixed SC connector
ZPIM1-06 10-Gigabit Ethernet One slot for an optional
10-Gigabit Ethernet (10 GbE)
module with one fiber optic SC
connector. This module must
conform to the XENPAK 10
GbE standard.
4.1.1 Port Assignment Scheme
The expansion module and fixed front panel port numbering scheme used when configuring
Matrix E1 1G694-13 port functionality is shown in Figure 4-1. Ports 1 through 12 are designated
as 0 for being fixed ports on the front panel. In this numbering scheme, front panel port 8 is
expressed as 0.8 in the CLI syntax.
The device’s optional 10-Gigabit Ethernet expansion module slot (location 1) is designated as 1.1
in the CLI syntax. Figure 4-2 shows the expansion modules available at the time of this printing.
For information on how this device’s port assignment scheme is expressed in CLI syntax, refer to
Section 4.1.2.
4-2 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Port Configuration
1G694-13
Console
Port String Syntax Used in the CLI
Figure 4-1 Expansion Module and Fixed Front Panel Port Numbering Scheme
1G694-13
CPUPWR
Reset
1223 4 5 6 7 8
Console
1
9 10 11 12
12
0
1
3754_03
Figure 4-2 Optional 10-Gigabit Ethernet Expansion Modules
ZPIM1-01
RX TX
1
TX
1
RX
ZPIM1-06
3754_21
4.1.2 Port String Syntax Used in the CLI
Commands requiring a port_string parameter use the following syntax to designate port type and
location:
port type.slot location.port number
Where port type can be:
ge, for Gigabit Ethernet, or
tg for 10-Gigabit Ethernet
Slot location can be:
0, for the fixed front panel port,
1, for the expansion module slot,
Port number can be:
Any port number in a port location.
The highest port number that can be entered is dependent on the number of ports in a slo t location.
For example: The Matrix E1 1G694-13 has 12 front panel ports (location 0), and 1 port in the
expansion module (slot location 1).
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-3

Port Configuration
Port String Syntax Used in the CLI
Examples
This example shows the port_string syntax for specifying Gigabit Ethernet port 3 in the device’s
fixed front panel.
ge.0.3
This example shows the port_string syntax for specifying Gigabit Ethernet ports 1 through 10 in
the device’s fixed front panel.
ge.0.1-10
This example shows the port_string syntax for specifying Gigabit Ethernet ports 1, 3, 7, 8, 9 and
10 in the device’s left expansion module slot.
ge.1.1,ge.1.3,ge.1.7-10
This example shows the port_string syntax for specifying the 10-Gigabit Ethernet port 1 in the
device’s expansion module slot.
tg.1.1
This example shows the port_string syntax for specifying all Gigabit Ethernet ports in the device.
ge.*.*
This example shows the port_string syntax for specifying all ports (of any interface type) in the
device.
*.*.*
4-4 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Process Overview: Port Configuration
4.1.3 Process Overview: Port Configuration
Use the following steps as a guide in the port configuration process:
1. Reviewing port status (Section 4.2.1)
2. Disabling / enabling ports (Section 4.2.2)
3. Setting auto negotiation (Section 4.2.3)
4. Setting flow control (Section 4.2.4)
5. Enabling / disabling jumbo frame support (Section 4.2.5)
6. Setting port traps (Section 4.2.6)
7. Setting port mirroring (Section 4.2.7)
8. Setting port trunking (Section 4.2.9)
Port Configuration
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-5

Port Configuration
Reviewing Port Status
4.2 PORT CONFIGURATION COMMAND SET
4.2.1 Reviewing Port Status
Purpose
To display port operating status, duplex mode, speed and port type, and statistical information
about traffic received and transmitted through one port or all ports on the device.
Commands
The commands needed to review port status are listed below and described in the associated
sections as shown.
• show port status (Section 4.2.1.1)
• show port counters (Section 4.2.1.2)
4-6 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

4.2.1.1 show port status
Use this command to display port status information.
show port status [port_string]
Syntax Description
port_string (Optional) Specifies the port(s) for which status will be
displayed. For a detailed description of possible port_string
values, refer to Section 4.1.2.
Command Defaults
If port_string is not specified, status information for all ports will be displayed.
Command Mode
Read-Only.
Port Configuration
Reviewing Port Status
Example
This example shows how to display status information for Gigabit Ethernet front panel ports 8
through 11:
Matrix>show port status ge.0.8-11
Port Oper Admin Duplex Speed Type
Status Status
-----------------------------------------------------
ge.0.1 up up full 1000 1000base-SX
ge.0.2 down up full 1000 1000base-SX
ge.0.3 down up full 1000 1000base-SX
ge.0.4 down up full 1000 1000base-SX
ge.0.5 down up full 1000 1000base-SX
ge.0.6 down up full 1000 1000base-SX
ge.0.7 down up full 1000 1000base-SX
ge.0.8 down up full 1000 1000base-SX
ge.0.9 down up full 1000 GBIC
ge.0.10 down up full 1000 GBIC
ge.0.11 down up full 1000 GBIC
ge.0.12 down up full 1000 GBIC
Table 4-2 provides an explanation of the command output.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-7

Port Configuration
Reviewing Port Status
Table 4-2 show port status Output Details
Output What It Displays...
Port Port designation. For a detailed description of possible
Oper Status Whether the port has a valid link. Oper status will be down
Admin Status Whether the port is enabled (up) or disabled (down).
Duplex Duplex mode of the port.
Speed Operational speed in Mbps (1000 or 10000) of the port.
Type Port type as:
port_string values, refer to Section 4.1.2
until a link is established to an external device and the port is
enabled.
• 1000SX: 1000Base-SX
• 1000LX: 1000Base-LX
• GBIC
• 10Gig: 10-Gigabit
4-8 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Port Configuration
Reviewing Port Status
4.2.1.2 show port counters
Use this command to display counter statistics detailing traffi c through the switch device and
through all MIB2 network devices.
show port counters [port_string] [mib2 | switch]
Syntax Description
port_string (Optional) Specifies the port(s) for which counter statistics
will be displayed. For a detailed description of possible
port_string values, refer to Section 4.1.2.
mib2 | switch (Optional) Shows MIB2 or switch statistics. Switch
statistics detail performance of the Matrix E1 switch
device. MIB2 interface statistics detail performance of all
network devices.
Command Defaults
If port_string is not specified, counter statistics will be displayed for all ports. If
mib2 or switch is not specified, all counter statistics will be displayed for the
specified port(s).
Command Mode
Read-Only.
Examples
This example shows how to display all counter statistics, including MIB2 network traffic and
traffic through the switch device for Gigabit Ethernet front panel port 1:
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-9

Port Configuration
Reviewing Port Status
Matrix>show port counters ge.0.1
Port: ge.0.1 Bridge Port: 1
--------------------------------------MIB2 Interface Counters:
In Octets: 0
In Unicast Pkts: 0
In Multicast Pkts: 0
In Broadcast Pkts: 0
In Discards: 0
In Errors: 0
In Unknown Protocol: 0
Out Octets: 0
Out Unicast Pkts: 0
Out Multicast Pkts: 0
Out Broadcast Pkts: 0
Out Discards: 0
Out Errors: 0
Out Queue Length: 0
802.1Q Switch Counters:
Frames Received: 0
Frames Transmitted: 0
This example shows how to display all port counter statistics related to traffic through the switch
device.
Matrix>show port counters ge.0.1 switch
Port: ge.0.1 Bridge Port: 1
802.1Q Switch Counters:
---------------------Frames Received: 0
Frames Transmitted: 0
Table 4-3 provides an explanation of the command output.
4-10 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Port Configuration
Disabling / Enabling Ports
Table 4-3 show port counters Output Details
Value What It Displays...
Port Port designation. For a detailed description of possible
port_string values, refer to Section 4.1.2.
Bridge Port Bridge port designation.
802.1Q Switch
Counts of frames received and transmitted.
Counters
4.2.2 Disabling / Enabling Ports
Purpose
To disable and re-enable one or more ports. By default, all ports are enabled at device startup. You
may need to disable ports in the event of network problems or to put ports “off-line” during certain
configuration procedures.
Commands
The commands needed to enab le and dis able po rts are listed belo w and descri bed in the associated
section as sho wn.
• set port disable (Section 4.2.2.1)
• set port enable (Section 4.2.2.2)
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-11

Port Configuration
Disabling / Enabling Ports
4.2.2.1 set port disable
Use this command to administrativ e ly disable one or more ports.
set port disable port_string
Syntax Description
port_string Specifies the port to disable. For a detailed description of
possible port_string values, refer to Section 4.1.2.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Example
This example shows how to disable Gigabit Ethernet front panel port 1:
Matrix>set port disable ge.0.1
Port ge.0.1 is administratively disabled.
4-12 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

4.2.2.2 set port enable
Use this command to administratively enable one or more ports.
set port enable port_string
Syntax Description
port_string Specifies the port to enable. For a detailed description of
possible port_string values, refer to Section 4.1.2.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Port Configuration
Disabling / Enabling Ports
Example
This example shows how to enable Gigabit Ethernet front panel port 1:
Matrix>set port enable ge.0.1
Port ge.0.3 is administratively enabled.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-13

Port Configuration
Setting Port Auto-Negotiation
4.2.3 Setting Port Auto-Negotiation
Purpose
To determine whether auto-negotiation is enabled or disabled for the specific port and to set the
state, and to display or set a port’ s advertised mode of operation. During auto-negotiation, the port
“tells” the device at the other end of the segment what its capabilities are.
Commands
The commands needed to configure auto-negotiation are listed below and described in the
associated section as shown.
• show port negotiation (Section 4.2.3.1)
• set port negotiation (Section 4.2.3.2)
4-14 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Setting Port Auto-Negotiation
4.2.3.1 show port negotiation
Use this command to display the status of auto-negotiation for one or more ports.
show port negotiation [port_string]
Syntax Description
port_string (Optional) Specifies the port(s) for which
auto-negotiation status will be displayed. For a detailed
description of possible port_string values, refer to
Section 4.1.2.
Command Defaults
If port_string is not specified, auto-negotiation status for all ports will be
displayed.
Port Configuration
Command Mode
Read-Only.
Example
This example shows how to display auto-negotiation status on the Gigabit Ethernet front panel
port 5:
Matrix>show port negotiation ge.0.5
Auto negotiation enabled for port ge.0.5
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-15

Port Configuration
Setting Port Auto-Negotiation
4.2.3.2 set port negotiation
Use this command to enable or disable auto-negotiation on one or more ports.
set port negotiation port_string {disable | enable}
Syntax Description
port_string Specifies the port(s) for which auto-negotiation will be
enabled or disabled. For a detailed description of possible
port_string values, refer to Section 4.1.2.
disable | enable Disables or enables auto-negotiation.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Example
This example shows how to disable auto-negotiation on Gigabit Ethernet front panel port 11:
Matrix>set port negotiation ge.0.11 disable
Auto negotiation disabled for port ge.0.11.
4-16 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Port Configuration
Setting Flow Control
4.2.4 Setting Flow Control
Purpose
To display, enable or disable flow control. Flow control is used to manage the transmission
between two devices as specified by IEEE 802.3x to prevent receiving ports from being
overwhelmed by frames from transmitting devices.
Commands
The commands needed to set flow control are listed below and described in the associated section
as shown.
• show port flowcontrol (Section 4.2.4.1)
• set port flowcontrol (Section 4.2.4.2)
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-17

Port Configuration
Setting Flow Control
4.2.4.1 show port flowcontrol
Use this command to display the flow control state for one or more ports.
show port flowcontrol [port_string]
Syntax Description
port_string (Optional) Specifies the port(s) for which flow control
state will be displayed. For a detailed description of
possible port_string values, refer to Section 4.1.2.
Command Defaults
If port_string is not specif ied, flow control statistics for all ports will be displayed.
Command Mode
Read-Only.
Example
This example shows how to display the port flow control state for Gigabit Ethernet front panel
ports 1 through 4. It shows that auto-negotiation is enabled on ports 1 and 4 (therefore, flow
control cannot be enabled on these ports). It also shows that flow control is disabled on port 2, and
enabled on port 3.
Matrix>show port flowcontrol ge.0.15-18
Port ge.0.1 flow control state is auto negotiate.
Port ge.0.2 flow control state is disabled.
Port ge.0.3 flow control state is enabled.
Port ge.0.4 flow control state is auto negotiate.
4-18 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

4.2.4.2 set port flowcontrol
Use this command to enable or disable flow control for one or more ports.
set port flowcontrol port_string {disable | enable}
Syntax Description
port_string Specifies the port(s) for which flo w control will be enabled
or disabled. For a detailed description of possible
port_string values, refer to Section 4.1.2.
disable | enable Disables or enables flow control.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Port Configuration
Setting Flow Control
Example
This example shows how to enable flow control on Gigabit Ethernet front panel ports 1 through 4:
Matrix>set port flowcontrol ge.0.1-4 enable
Port flow control enabled for port ge.0.1.
Port flow control enabled for port ge.0.2.
Port flow control enabled for port ge.0.3.
Port flow control enabled for port ge.0.4.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-19

Port Configuration
Enabling / Disabling Jumbo Frame Support
4.2.5 Enabling / Disabling Jumbo Frame Support
Purpose
To review, enable, and disable jumbo frame support on the device. This allows switch ports to
transmit and receive frames up to 9 KB in size.
Commands
The commands needed to review, enable and disable jumbo frame support are listed below and
described in the associated section as shown.
• show jumbo (Section 4.2.5.1)
• set jumbo (Section 4.2.5.2)
NOTE: Jumbo frame support is available on Matrix E1 1G694-13 devices equipped
with hardware version 2 and higher. Earlier hardware versions will display the jumbo
frame commands, but will not allow jumbo frames to be enabled. To determine your
device’s hardware version, use the show version command as described in
Section 3.2.2.4.
4-20 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Enabling / Disabling Jumbo Frame Support
4.2.5.1 show jumbo
Use this command to display the status of jumbo frame support on the device.
show jumbo
Syntax Description
None.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Only.
Example
This example shows how to display the status of jumbo frame support:
)
Port Configuration
Matrix>show jumbo
Jumbo frames are currently disabled.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-21

Port Configuration
Enabling / Disabling Jumbo Frame Support
4.2.5.2 set jumbo
Use this command to enable or disable jumbo frame support on the device.
set jumbo {enable | disable}
Syntax Description
enable | disable Enables or disables jumbo frame support.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Example
This example shows how to enable jumbo frame support on the device:
Matrix>set jumbo enable
Jumbo frames enabled.
4-22 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Port Configuration
Setting Port Traps
4.2.6 Setting Port Traps
Purpose
To display the status, and to enable or disable an SNMP link trap on one or more ports. This
operation is typically used to alert the system manager of a change in the link status of the port.
Command
The commands needed to disp lay, enable or disable port traps are listed below and descri bed in the
associated section as shown.
• show port trap (Section 4.2.6.1)
• set port trap (Section 4.2.6.2)
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-23

Port Configuration
Setting Port Traps
4.2.6.1 show port trap
Use this command to display the status of an SNMP link trap on one or more ports.
show port trap [port_string]
Syntax Description
port_string (Optional) Specifies the port(s) for which trap status will be
displayed. For a detailed description of possible port_string
values, refer to Section 4.1.2.
Command Defaults
If no port_string is specified, the trap status for all ports is displayed.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Examples
This example show s how to display SNMP link trap status for Gigabit Ethernet front panel ports 1
through 3:
Matrix>show port trap ge.0.1-3
Port State
--------- --------ge.0.1 enabled
ge.0.2 enabled
ge.0.3 enabled
This example shows how to display SNMP link trap status for all ports:
Matrix>show port trap
Port State Port State Port State
--------- --------- --------- --------- --------- --------ge.0.1 enabled ge.0.2 enabled ge.0.3 enabled
ge.0.4 enabled ge.0.5 enabled ge.0.6 enabled
ge.0.7 enabled ge.0.8 enabled ge.0.9 enabled
ge.0.10 enabled ge.0.11 enabled ge.0.12 enabled
4-24 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

4.2.6.2 set port trap
Use this command to enable or disable an SNMP link trap on one or more ports.
set port trap port_string {enable | disable}
Syntax Description
port_string Specifies the port(s) for which a trap will be enabled on
disabled. For a detailed description of possible port_string
values, refer to Section 4.1.2.
enable | disable Enables or disables a trap on the specified port.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Port Configuration
Setting Port Traps
Example
This example shows how to disable the SNMP link trap for Gigabit Ethernet front panel port 3:
Matrix>set port trap ge.0.3 disable
SNMP link traps disabled for port ge.0.3
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-25

Port Configuration
Overview: Port Mirroring
4.2.7 Overview: Port Mirroring
CAUTION: Port mirroring configuration should be per formed only b y personnel who are
knowledgeable about the effects of port mirroring and its impact on network operation.
The Matrix E1 allows you to mirror the traffic being switched on a po rt for the purposes of
network traffic analysis and connection assurance. When port mirroring is enabled, one port
becomes a monitor port for another port within the switch. When configuring port mirroring on
this device, note that
• Only one mirror is allowed per device;
• Only one mirroring session is allowed at a time;
• Traffic mirrored includes both received and transmitted packets;
• Unknown protocol packets and broadcast packets can be forwarded out the monitor port when
mirroring is enabled.
For details on how to specify port designation in the CLI syntax, refer to Section 4.1.2.
4.2.8 Port Mirroring Commands
Purpose
To display or set a source and target port for port mirroring on the device.
Commands
The commands needed to conf igu re port mirroring are listed belo w and described in the associated
section as shown.
• show port mirroring (Section 4.2.8.1)
• set port mirroring (Section 4.2.8.2)
4-26 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Port Configuration
Port Mirroring Commands
4.2.8.1 show port mirroring
Use this command to display the source and target ports for mirroring, and whether mirroring is
currently enabled or disabled for those ports.
show port mirroring
Syntax Description
None.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Only.
Example
This example shows that Gigabit Ethernet front panel port 4 is configured as a source port, that
port 11 is configured as the targ et port to monitor all of port 4’s activity, and that mirroring is
disabled.
Matrix>show port mirroring
Port Mirroring
==============
Source Port = ge.0.4
Target Port = ge.0.11
Port mirroring status disabled.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-27

Port Configuration
Port Mirroring Commands
4.2.8.2 set port mirroring
Use this command to designate a single port pair (source and target ports) for mirroring.
set port mirroring port_string port_string {disable | enable}
Syntax Description
port_string Specifies the port designations for source port and target
port. The first port_string specifies the source on which
the traffic will be monitored. The second port_string
specifies the target port that will duplicate or “mirror” all
the traffic on the monitored port. Since only one port
mirror is allowed per device, it is not necessary to specify
port string when disabling mirroring. For a detailed
description of possible port_string values, refer to
Section 4.1.2.
disable | enable Disables or enables mirroring on the specified ports.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-write.
Examples
This example shows ho w to enable port mirroring w ith ge.0.4 as the source po rt and ge.0.11 as the
target port.
Matrix>set port mirroring ge.0.4 ge.0.11 enable
Port ge.0.4 and port ge.0.11 are enabled for Port Mirroring.
This example shows how to disable port mirroring:
Matrix>set port mirroring disable
Port Mirroring disabled.
4-28 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

Port Configuration
Overview: Port Trunking
4.2.9 Overview: Port Trunking
Port trunks can be used to increase the bandwidth of a network connection and to ensure fault
recovery. The Matrix 1G694-13 allows you to configure up to six trunks (of tw o ports per trunk)
on the device. It also allows you to configure all 12 Gigabit Ethernet ports into an aggregate
connection. Besides balancing the load across each port in the trunk, the additional ports provide
redundancy by taking over the load if another port in the trunk should fail. However, before
making any physical connections between devices, use the set trunk command to specify the
trunk on the devices at both ends. When using a port trunk, note that:
• Ports can only be assigned to one trunk.
• 10-Gigabit ports cannot be part of a trunk.
• The ports at both ends of a connection must be enabled and configured as trunk ports.
• The ports at both ends of a trunk must be configured in an identical manner, including speed,
duplex mode, and VLAN assignments.
• None of the ports in a trunk can be configured as a mirror source port or mirror target port.
• All the ports in a trunk have to be treated as a whole when mov ed from/to, added or deleted from
a VLAN.
• The Spanning Tree Algorithm will treat all the ports in a trunk as a whole.
• Before removing a port trunk via CLI commands, you must remove all network cables.
Otherwise, a loop may be created.
• To disable a single link within a port trunk, you should first remove the network cable, and then
disable both ends of the link. This allows the traf f i c passin g across that link t o be automa tically
distributed to the other links in that trunk, without losing any significant amount of traffic.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-29

Port Configuration
Setting Port Trunking
4.2.10 Setting Port Trunking
Purpose
To display trunking information, to create and delete trunks on the device, and to display and
configure port settings for a particular trunk.
Commands
The commands needed to configure port trunking are listed below and described in the associated
section as shown.
• show trunk (Section 4.2.10.1)
• set trunk (Section 4.2.10.2)
• clear trunk (Section 4.2.10.3)
• set trunk port (Section 4.2.10.4)
• clear trunk port (Section 4.2.10.5)
4-30 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

4.2.10.1 show trunk
Use this command to display trunking information for the device.
show trunk [trunk_name]
Syntax Description
trunk_name (Optional) Specifies the name of the trunk port for which
information will be displayed.
Command Defaults
If trunk_name is not specified, information for all trunks will be displayed.
Command Mode
Read-Only.
Port Configuration
Setting Port Trunking
Example
This example shows how to display trunking information for the “blue” trunk:
Matrix>show trunk blue
trunk port: 7
trunk port: 8
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-31

Port Configuration
Setting Port Trunking
4.2.10.2 set trunk
Use this command to create, enable and disable trunks.
set trunk trunk_name {create | disable | enable}
Syntax Description
trunk_name Specifies the name of the trunk port to be created,
disabled or enabled.
create | disable |
enable
Creates, disables or enables a trunk with the specified
name.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Example
This example shows how to create a trunk named “blue”:
Matrix>set trunk blue create
Successful trunking operation for blue.
4-32 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide

4.2.10.3 clear trunk
Use this command to delete a specific trunk from the switch.
clear trunk trunk_name
Syntax Description
trunk_name Specifies the name of the trunk to be deleted.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Example
This example shows how to delete the “green” trunk from the device
Port Configuration
Setting Port Trunking
:
Matrix>clear trunk green
Trunk green deleted.
Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide 4-33

Port Configuration
Setting Port Trunking
4.2.10.4 set trunk port
Use this command to add a trunk port to an existing trunk.
set trunk port trunk_name port_string
Syntax Description
trunk_name Specifies the name of the trunk to which the trunk port
will be added.
port_string Specifies the designation of the port to be added to the
trunk. For a detailed description of possible port_string
values, refer to Section 4.1.2.
Command Defaults
None.
Command Mode
Read-Write.
Example
This example shows how to add Gigabit Ethernet front panel ports 3 through 6 to the “blue” trunk.
Matrix>set trunk port blue ge.0.3-6
Port ge.0.3 added to trunk blue.
Port ge.0.4 added to trunk blue.
Port ge.0.5 added to trunk blue.
Port ge.0.6 added to trunk blue.
4-34 Matrix E1 Series (1G694-13) Configuration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...