Page 1

EAP 9550
11N Multi-Function AP/Repeater
Page 2

Table of Content
1. Introduction.............................................................................................................................3
1.1. Features and Benefits...................................................................................................3
1.2. Package Contents......................................................................................................... 4
1.3. System Requirement....................................................................................................4
2. Modes.....................................................................................................................................5
2.1. Access Point................................................................................................................5
2.2. WDS Bridge................................................................................................................5
2.3. Universal Repeater....................................................................................................... 5
3. Web Configuration.................................................................................................................. 6
3.1. System.........................................................................................................................6
3.1.1. Operation Mode ...............................................................................................6
3.1.2. Status...............................................................................................................7
3.1.3. Schedule...........................................................................................................7
3.1.4. Event Log ........................................................................................................ 8
3.1.5. Monitor............................................................................................................ 8
3.2. Wireless..................................................................................................................... 10
3.2.1. AP.................................................................................................................. 10
3.2.2. WDS Bridge................................................................................................... 20
3.2.3. Universal Repeater (AP).................................................................................26
3.3. Network..................................................................................................................... 33
3.3.1. Status.............................................................................................................33
3.3.2. LAN............................................................................................................... 34
3.4. Management.............................................................................................................. 34
3.4.1. Admin............................................................................................................ 34
3.4.2. SNMP............................................................................................................ 35
3.4.3. Firmware........................................................................................................ 36
3.4.4. Configure.......................................................................................................36
3.4.5. Reset.............................................................................................................. 36
3.5. Tools.......................................................................................................................... 37
3.5.1. Time Setting................................................................................................... 37
3.5.2. Power Saving................................................................................................. 38
3.5.3. Diagnosis .......................................................................................................38
3.5.4. LED Control .................................................................................................. 39
3.6. Logout....................................................................................................................... 39
Appendix A – SPECIFICATIONS................................................................................................. 40
Appendix B – FCC INTERFERENCE STATEMENT................................................................... 41
Appendix C – IC Interference Statement....................................................................................... 42
Page 3
1. Introduction
Repeater. Smoke detector appearance will minimize visibility. So this model can work properly at Hotel or public area.
EAP9550
EAP9550 is a Wireless Network device that delivers up to 6x faster speeds and 7x extended coverage than 802.11g
devices. Product’s RF performance is finely tuned so it will bring best wireless signal for each client. EAP9550
supports home network with superior throughput, performance and unparalleled wireless range. To protect data during
wireless transmissions, EAP9550 encrypts all wireless transmissions through WEP data encryption and supports
WPA/WPA2. Its MAC address filter allows users to select stations with access to connect network. EAP9550 thus is the
best product to ensure network quality for hotspots.
is a powerful and multi-functioned 11n Access Point and it can act three modes AP/WDS/Universal
1.1. Features and Benefits
Features Benefits
High Speed Data Rate Up to 300Mbps Capable of handling heavy data payloads such as MPEG video
streaming
IEEE 802.11n draft Compliant and
backward compatible with 802.11b/g
Multi-modes selectable
Fully compatible with IEEE 802.11b/g/n devices
Allowing users to select AP/WDS/Universal Repeater mode in
various application
Point-to-point, Point-to-multipoint
Wireless Connectivity
WDS (Wireless Distributed System)
Universal Repeater The easiest way to your wireless network's coverage
Support Multi-SSID function (4 SSID)
in AP mode
WPA2/WPA Powerful data security
MAC address filtering in AP mode Ensuring secure network connection
User isolation support (AP mode) Protecting the private network between client users.
Power-over-Ethernet (IEEE802.3af) Flexible Access Point locations and saving cost
Keep personal setting Keeping the latest setting when firmware upgrade
SNMP Remote Configuration
Management
Allowing to transfer data from buildings to buildings
Making wireless AP and Bridge mode simultaneously as a wireless
repeater
Allowing clients to access different networks through a single
access point and to assign different policies and functions for each
SSID by manager
Helping administrators to remotely configure or manage the Access
Point easily
QoS (WMM) support Enhancing user performance and density
Page 4

1.2. Package Contents
The package contains the following items. In case of return, please keep the original box set, and
the complete box set must be included for full refund.
Ø 1 EAP 9550
Ø 1 12V/1A 100V~240V Power Adapter
Ø 1 CD-ROM with User’s Manual
Ø 1 Quick Guide
1.3. System Requirement
The following are the minimum system requirements in order to configure the device.
Ø PC/AT compatible computer with an Ethernet interface.
Ø Operating system that supports HTTP web-browser
Page 5

2. Modes
AP/WDS/Repeater
2.1. Access Point
In AP (Access Point) mode, your device acts as a communication hub for users with a
wireless device to connect to a wired LAN/WAN.
2.2. WDS Bridge
You can only connect to the device via Wireless Client
WDS (Wireless Distribution System) allows AP to communicate with one another wirelessly. This
capability is critical in providing a seamless experience for roaming clients and for managing
multiple wireless networks.
2.3. Universal Repeater
Repeater is used to regenerate or replicate signals that are weakened or distorted by transmission
over long distances and through areas with high levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Universal Repeater (AP) mode on one radio channel is usually configured along with Universal
Repeater (STA) mode on another radio channel.
Page 6

3. Web Configuration
3.1. System
3.1.1. Operation Mode
You are allowed to configure EAP 9550 into different modes: AP, WDS Bridge and
Universal Repeater.
Please refer to Chapter 2: Modes for operation under different modes.
Page 7
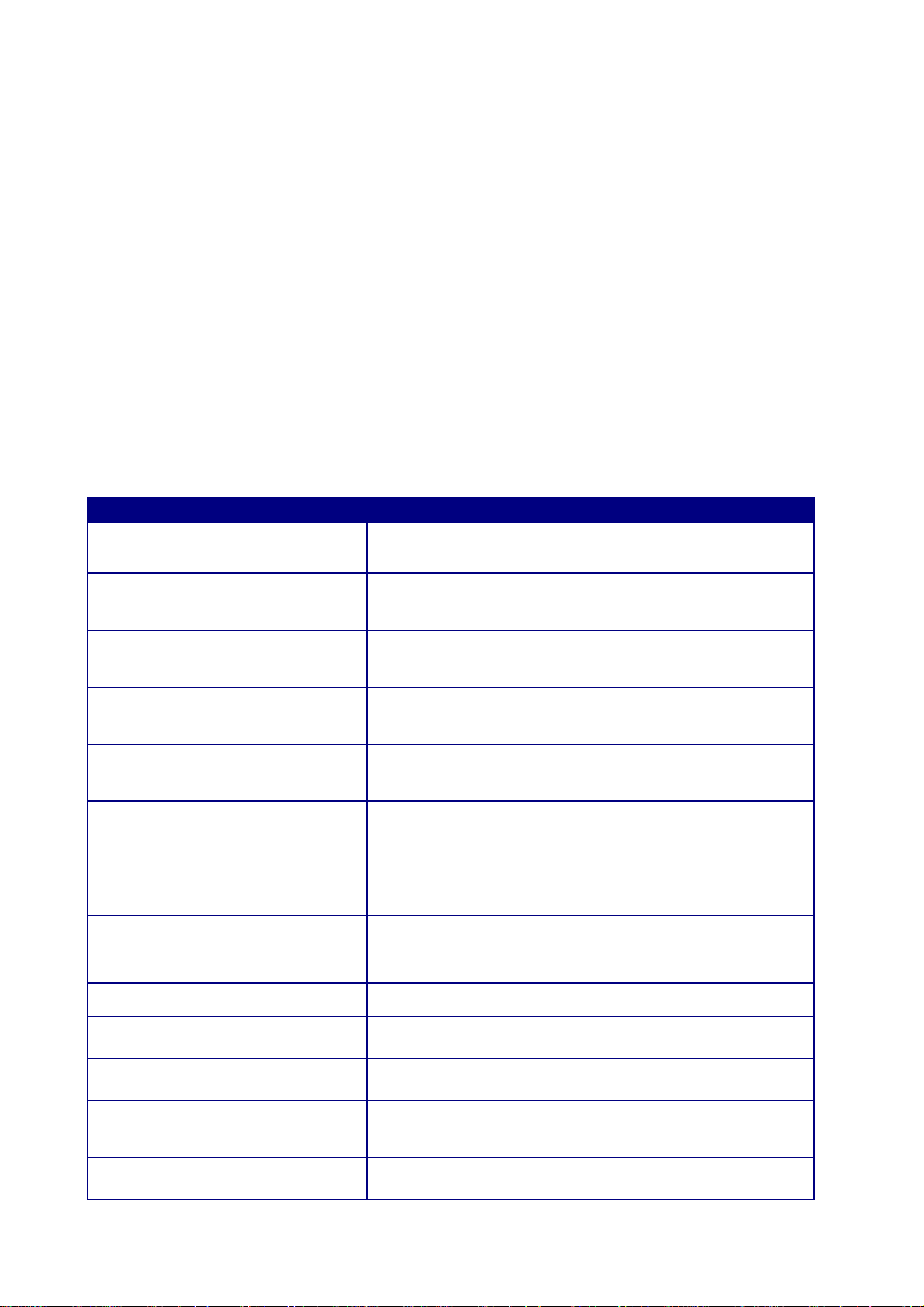
3.1.2. Status
Ø System: Basic information of the device.
Ø WLAN Settings: WLAN channel.
Ø SSID_1: SSID information.
3.1.3. Schedule
Page 8
3.1.4. Event Log
3.1.5. Monitor
The device will record the router transmission status in a time span.
Page 9
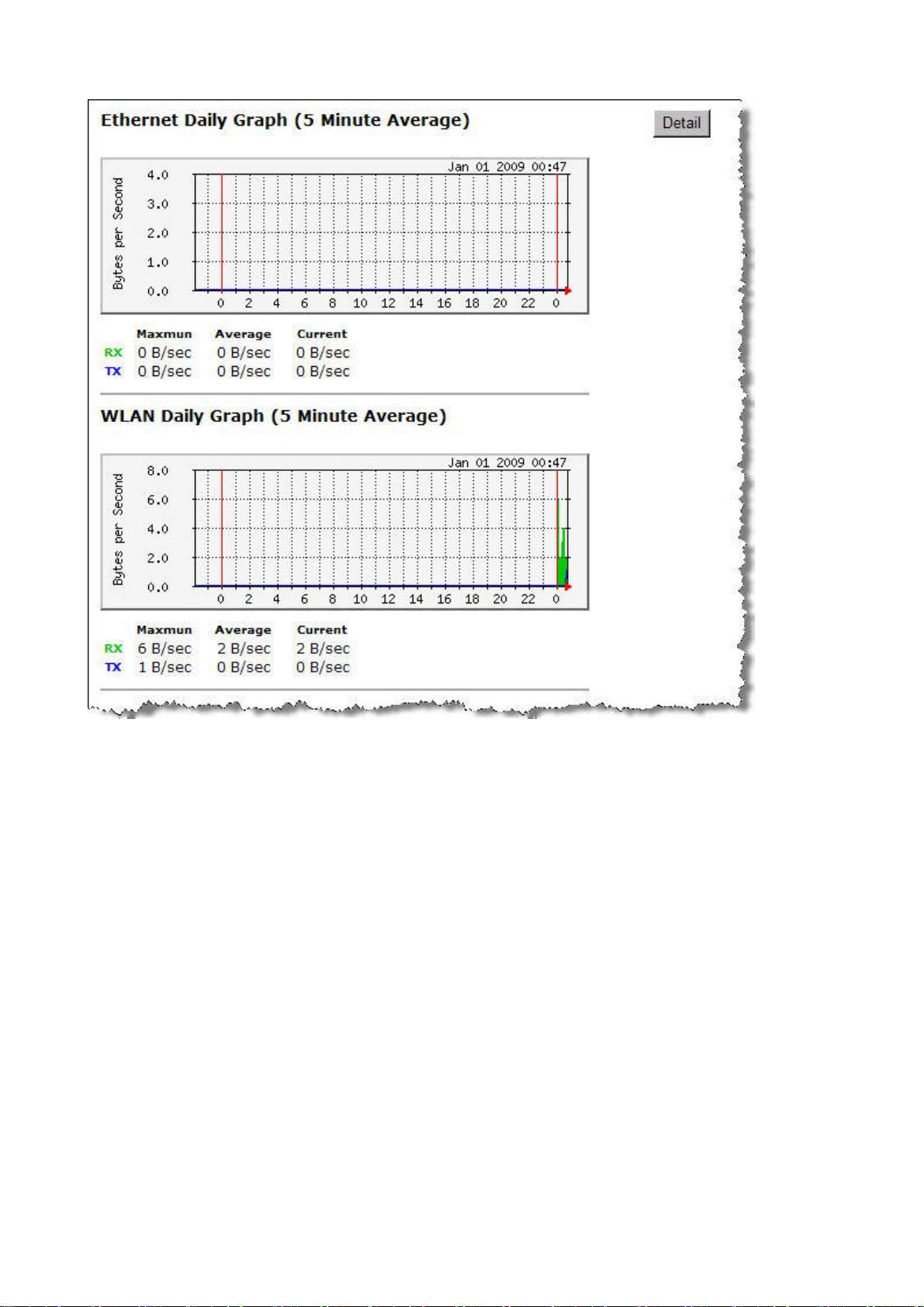
Ø Detail: Click into detail to see historical record.
Page 10
3.2. Wireless
3.2.1. AP
3.2.1.1. Status
Page 11

3.2.1.2. Basic
Ø Radio: To enable/disable radio frequency.
Ø Mode: Define AP in different modes. When in AP mode, the device works as regular AP, or WDS
mode to interlink with other AP devices You are allowed to set MAC address and encryption
algorithm (Please refer to 4.2.1.4 for encryption configuration)
ü AP
ü WDS
Ø Band: Configure the device into different wireless modes.
ü 2.4 GHz (B)
ü 2.4 GHz (N)
ü 2.4 GHz (B+G)
ü 2.4 GHz (G)
ü 2.4 GHz (B+G+N)
Page 12

Ø Enabled SSID#: The device allows you to add up to 4 unique SSID
Ø ESSID#: Description of each configured SSID
Ø Auto Channel: To enable/disable devices auto-detect channel used
Ø Check Channel Time (Channel): When Auto Channel is enabled; you can configure the channel
detection interval. When Auto Channel is disabled; you can manually configure a channel to be
used.
Ø MAC Address 1~4: To specify MAC address of other AP devices.
MAC address will only shows when configured in WDS AP mode.
Ø
Security: Please refer to 4.2.1.4 for encryption configuration
3.2.1.3. Advanced
Ø Fragment Threshold: Packets over the specified size will be fragmented in order to improve
performance on noisy networks. Specify a value between 256 and 2346. The default value is
2346.
Ø RTS Threshold: Packets over the specified size will use the RTS/CTS mechanism to maintain
performance in noisy networks and preventing hidden nodes from degrading the performance.
Specify a value between 0 and 2347. The default value is 2347.
Ø Beacon Interval: Beacons are packets sent by a wireless Access Point to synchronize wireless
devices. Specify a Beacon Interval value between 24 and 1024. The default value is set to 100
milliseconds.
Page 13
Ø DTIM Period: A DTIM is a countdown informing clients of the next window for listening to
broadcast and multicast messages. When the wireless Access Point has buffered broadcast or
multicast messages for associated clients, it sends the next DTIM with a DTIM Period value.
Wireless clients detect the beacons and awaken to receive the broadcast and multicast
messages. The default value is 1. Valid settings are between 1 and 10.
Ø Data rate: You may select a data rate from the drop-down list, however, it is recommended to
select auto. This is also known as auto-fallback.
Ø N Data Rate: You may select N data rate from the drop-down list, however, it is recommended to
select auto.
Ø Channel Bandwidth: Select channel bandwidth.
Ø Preamble Type: Select a short or long preamble. For optimum performance it is recommended
to also configure the client device as the same preamble type.
Ø CTS Protection: CTS (Clear to Send) can be always enabled, auto, or disabled. By enabled CTS,
the Access Point and clients will wait for a ‘clear’ signal before transmitting. It is recommended to
select auto.
Ø Tx Power: You may control the transmit output power of the device by selecting a value from the
drop-down list. This feature can be helpful in restricting the coverage area of the wireless network.
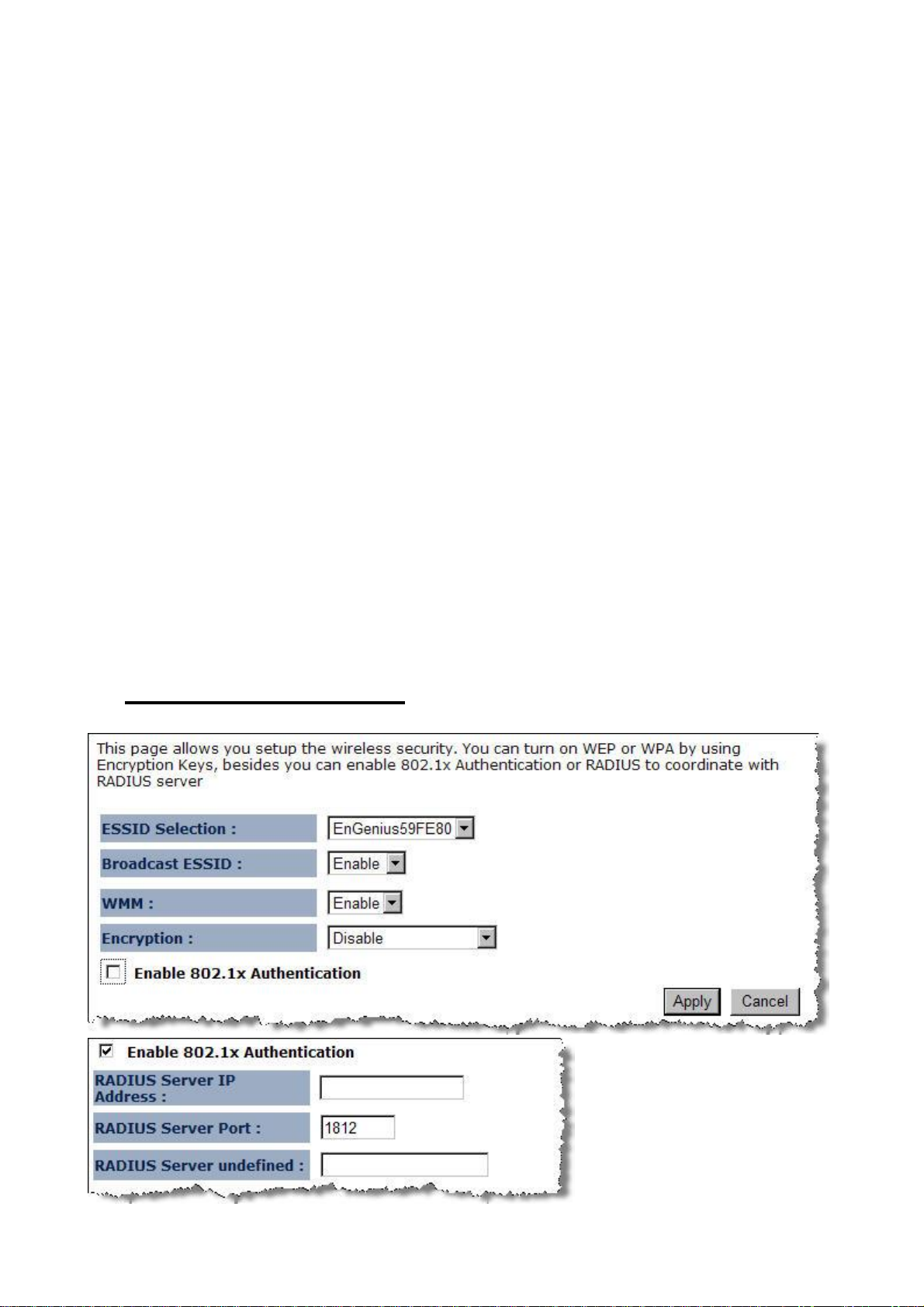
3.2.1.4. Security
Ø Encryption: Disabled
Page 14

Ø Encryption: WEP
Ø ESSID Selection: As this device supports multiple SSIDs, it is possible to configure a different
security mode for each SSID (profile). Select an SSID from the drop-down list.
Ø Broadcast SSID: Select Enable or Disable from the drop-down list. This is the SSID broadcast
feature.
range of your signal
this is disabled, you must enter the Wireless Network Name (SSID) on the client manually to
connect to the network.
Ø WMM: Choose to Enable or Disable WMM. This is the Quality of Service (QoS) feature for
prioritizing voice and video applications. This option can be further configured in WMM under the
Wireless drop-down menu.
Ø Encryption: Select WEP from the drop-down list.
Ø Authentication Type: Select Open System, Shared Key, or auto. Authentication method from
the drop-down list. An open system allows any client to authenticate as long as it conforms to any
MAC address filter policies that may have been set. All authentication packets are transmitted
without encryption. Shared Key sends an unencrypted challenge text string to any device
When this option is set to Enable, your wireless network name is broadcast to anyone within the
. If you're not using encryption then they could connect to your network. When
Page 15

attempting to communicate with the AP. The device requesting authentication encrypts the
challenge text and sends it back to the access point. If the challenge text is encrypted correctly,
the access point allows the requesting device to authenticate. It is recommended to select Auto if
you are not sure which authentication type is used.
Ø Key Length: Select a 64-bit or 128-bit WEP key length from the drop-down list.
Ø Key Type: Select a key type from the drop-down list. 128-bit encryption requires a longer key
than 64-bit encryption. Keys are defined by entering in a string in HEX (hexadecimal - using
characters 0-9, A-F) or ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange alphanumeric characters) format. ASCII format is provided so you can enter a string that is easier
to remember.
Ø Default Key: You may choose one of your 4 different WEP keys from below.
Ø Encryption Key 1-4: You may enter four different WEP keys.
Ø Enable 802.1x Authentication: Place a check in this box if you would like to use RADIUS
authentication. This option works with a RADIUS Server to authenticate wireless clients. Wireless
clients should have established the necessary credentials before attempting to authenticate to the
Server through this Gateway. Furthermore, it may be necessary to configure the RADIUS Server
to allow this Gateway to authenticate users. You will then be required to specify the RADIUS
Server’s IP address, port, and password.
Ø
Encryption: WPA pre-shared key
Ø ESSID Selection: As this device supports multiple SSIDs, it is possible to configure a different
security mode for each SSID (profile). Select an SSID from the drop-down list.
Ø Broadcast SSID: Select Enable or Disable from the drop-down list. This is the SSID broadcast
feature.
When this option is set to Enable, your wireless network name is broadcast to anyone within the
Page 16

range of your signal
this is disabled, you must enter the Wireless Network Name (SSID) on the client manually to
connect to the network.
Ø WMM: Choose to Enable or Disable WMM. This is the Quality of Service (QoS) feature for
prioritizing voice and video applications. This option can be further configured in WMM under the
Wireless drop-down menu.
Ø Encryption: Select WPA pre-shared key from the drop-down list.
Ø WPA Type: Select TKIP, AES, or WPA2 Mixed. The encryption algorithm used to secure the data
communication. TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) provides per-packet key generation and
is based on WEP. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a very secure block based encryption.
Note that, if the bridge uses the AES option, the bridge can associate with the access point only if
the access point is also set to use only AES.
Ø Pre-shared Key Type: The Key Type can be passphrase or Hex format.
Ø Pre-Shared Key: The key is entered as a pass-phrase of up to 63 alphanumeric characters in
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) format at both ends of the wireless
connection. It cannot be shorter than eight characters, although for proper security it needs to be
of ample length and should not be a commonly known phrase. This phrase is used to generate
. If you're not using encryption then they could connect to your network. When
session keys that are unique for each wireless client.
Ø
Encryption: WPA RADIUS
Ø ESSID Selection: As this device supports multiple SSIDs, it is possible to configure a different
security mode for each SSID (profile). Select an SSID from the drop-down list.
Ø Broadcast SSID: Select Enable or Disable from the drop-down list. This is the SSID broadcast
feature.
When this option is set to Enable, your wireless network name is broadcast to anyone within the
Page 17

range of your signal
this is disabled, you must enter the Wireless Network Name (SSID) on the client manually to
connect to the network.
Ø WMM: Choose to Enable or Disable WMM. This is the Quality of Service (QoS) feature for
prioritizing voice and video applications. This option can be further configured in WMM under the
Wireless drop-down menu.
Ø Encryption: Select WPA RADIUS from the drop-down list.
Ø WPA Type: Select TKIP, AES, or WPA2 Mixed. The encryption algorithm used to secure the data
communication. TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) provides per-packet key generation and
is based on WEP. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a very secure block based encryption.
Note that, if the bridge uses the AES option, the bridge can associate with the access point only if
the access point is also set to use only AES.
Ø RADIUS Server IP Address: Specify the IP address of the RADIUS server.
Ø RADIUS Server Port: Specify the port number of the RADIUS server, the default port is 1812.
Ø RADIUS Server Password: Specify the pass-phrase that is matched on the RADIUS Server.
. If you're not using encryption then they could connect to your network. When
3.2.1.5. Filter
Page 18

3.2.1.6. WPS
Ø WPS Current Status:
Ø Self Pin Code:
Ø SSID:
Ø Authentication Mode:
Ø Passphrase Key:
Ø WPS Via Push Button:
Ø WPS Via PIN:
3.2.1.7. Client List
Page 19

3.2.1.8. VLAN
Only Available in AP mode
Ø Virtual LAN: Choose to Enable or Disable the VLAN features.
Ø SSID1 Tag: Specify the VLAN tag.
3.2.1.9. WMM
Page 20

3.2.2. WDS Bridge
You can only connect to the device via Wireless Client
3.2.2.1. Status
3.2.2.2. Basic
Ø Radio: To enable/disable radio frequency.
Page 21

Ø Mode: WDS mode allows you to interlink with other AP devices. Setting MAC address and
encryption algorithm (Please refer to 4.2.1.4 for encryption configuration)
Ø Band: Configure the device into different wireless modes.
ü 2.4 GHz (B)
ü 2.4 GHz (N)
ü 2.4 GHz (B+G)
ü 2.4 GHz (G)
ü 2.4 GHz (B+G+N)
Ø Enabled SSID#: The device allows you to add up to 4 unique SSID
Ø ESSID#: Description of each configured SSID
Ø Channel: You can manually configure a channel to be used.
Ø MAC Address 1~4: To specify MAC address of other AP devices.
MAC address will only shows when configured in WDS AP mode.
Ø
Security: Please refer to 4.2.1.4 for encryption configuration
Ø Security: Disabled
Page 22

Ø Security: WEP
Ø Key Length: Select a 64-bit or 128-bit WEP key length from the drop-down list.
Ø Key Format: Select a key type from the drop-down list. 128-bit encryption requires a longer key
than 64-bit encryption. Keys are defined by entering in a string in HEX (hexadecimal - using
characters 0-9, A-F) or ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange alphanumeric characters) format. ASCII format is provided so you can enter a string that is easier
to remember.
Ø Default Tx Key: You may choose one of your 4 different WEP keys from below.
Ø Encryption Key 1-4: You may enter four different WEP keys.
Ø Security: WPS pre-shared key
Page 23

Ø WPA Type: Select TKIP, AES, or WPA2 Mixed. The encryption algorithm used to secure the data
communication. TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) provides per-packet key generation and
is based on WEP. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a very secure block based encryption.
Note that, if the bridge uses the AES option, the bridge can associate with the access point only if
the access point is also set to use only AES.
Ø Pre-shared Key Type: The Key Type can be passphrase or Hex format.
Ø Pre-Shared Key: The key is entered as a pass-phrase of up to 63 alphanumeric characters in
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) format at both ends of the wireless
connection. It cannot be shorter than eight characters, although for proper security it needs to be
of ample length and should not be a commonly known phrase. This phrase is used to generate
session keys that are unique for each wireless client.
3.2.2.3. Advanced
Ø Fragment Threshold: Packets over the specified size will be fragmented in order to improve
performance on noisy networks. Specify a value between 256 and 2346. The default value is
2346.
Ø RTS Threshold: Packets over the specified size will use the RTS/CTS mechanism to maintain
performance in noisy networks and preventing hidden nodes from degrading the performance.
Specify a value between 0 and 2347. The default value is 2347.
Page 24

Ø Beacon Interval: Beacons are packets sent by a wireless Access Point to synchronize wireless
devices. Specify a Beacon Interval value between 25 and 1000. The default value is set to 100
milliseconds.
Ø DTIM Period: A DTIM is a countdown informing clients of the next window for listening to
broadcast and multicast messages. When the wireless Access Point has buffered broadcast or
multicast messages for associated clients, it sends the next DTIM with a DTIM Period value.
Wireless clients detect the beacons and awaken to receive the broadcast and multicast
messages. The default value is 1. Valid settings are between 1 and 10.
Ø Data rate: You may select a data rate from the drop-down list, however, it is recommended to
select auto. This is also known as auto-fallback.
Ø N Data Rate: You may select N data rate from the drop-down list, however, it is recommended to
select auto.
Ø Channel Bandwidth: Select channel bandwidth.
Ø Preamble Type: Select a short or long preamble. For optimum performance it is recommended
to also configure the client device as the same preamble type.
Ø CTS Protection: CTS (Clear to Send) can be always enabled, auto, or disabled. By enabled CTS,
the Access Point and clients will wait for a ‘clear’ signal before transmitting. It is recommended to
select auto.
Ø Tx Power: You may control the transmit output power of the device by selecting a value from the
drop-down list. This feature can be helpful in restricting the coverage area of the wireless network.
Page 25

3.2.2.4. WMM
Page 26

3.2.3. Universal Repeater (AP)
3.2.3.1. Status
3.2.3.2. Basic
Page 27

Ø Radio: To enable/disable radio frequency.
Ø Mode: Universal Repeater
Ø Band: Configure the device into different wireless modes.
ü 2.4 GHz (B)
ü 2.4 GHz (N)
ü 2.4 GHz (B+G)
ü 2.4 GHz (G)
ü 2.4 GHz (B+G+N)
Ø Enabled SSID#: The device allows you to add up to 4 unique SSID
Ø ESSID#: Description of each configured SSID
Ø Channel: You can manually configure a channel to be used.
Ø Site Survey: List out all connected devices.
3.2.3.3. Advanced
Page 28

Ø Fragment Threshold: Packets over the specified size will be fragmented in order to improve
performance on noisy networks. Specify a value between 256 and 2346. The default value is
2346.
Ø RTS Threshold: Packets over the specified size will use the RTS/CTS mechanism to maintain
performance in noisy networks and preventing hidden nodes from degrading the performance.
Specify a value between 0 and 2347. The default value is 2347.
Ø Beacon Interval: Beacons are packets sent by a wireless Access Point to synchronize wireless
devices. Specify a Beacon Interval value between 25 and 1000. The default value is set to 100
milliseconds.
Ø DTIM Period: A DTIM is a countdown informing clients of the next window for listening to
broadcast and multicast messages. When the wireless Access Point has buffered broadcast or
multicast messages for associated clients, it sends the next DTIM with a DTIM Period value.
Wireless clients detect the beacons and awaken to receive the broadcast and multicast
messages. The default value is 1. Valid settings are between 1 and 10.
Ø Data rate: You may select a data rate from the drop-down list, however, it is recommended to
select auto. This is also known as auto-fallback.
Ø Preamble Type: Select a short or long preamble. For optimum performance it is recommended
to also configure the client device as the same preamble type.
Ø CTS Protection: CTS (Clear to Send) can be always enabled, auto, or disabled. By enabled CTS,
the Access Point and clients will wait for a ‘clear’ signal before transmitting. It is recommended to
select auto.
Ø
Tx Power: You may control the transmit output power of the device by selecting a value from the
drop-down list. This feature can be helpful in restricting the coverage area of the wireless network.
3.2.3.4. Security
Ø Encryption: Disabled
Page 29

Ø Encryption: WEP
Ø ESSID Selection: As this device supports multiple SSIDs, it is possible to configure a different
security mode for each SSID (profile). Select an SSID from the drop-down list.
Ø Broadcast SSID: Select Enable or Disable from the drop-down list. This is the SSID broadcast
feature.
range of your signal
this is disabled, you must enter the Wireless Network Name (SSID) on the client manually to
connect to the network.
Ø WMM: Choose to Enable or Disable WMM. This is the Quality of Service (QoS) feature for
prioritizing voice and video applications. This option can be further configured in WMM under the
Wireless drop-down menu.
Ø Encryption: Select WEP from the drop-down list.
Ø Authentication Type: Select Open System, Shared Key, or auto. Authentication method from
the drop-down list. An open system allows any client to authenticate as long as it conforms to any
MAC address filter policies that may have been set. All authentication packets are transmitted
without encryption. Shared Key sends an unencrypted challenge text string to any device
attempting to communicate with the AP. The device requesting authentication encrypts the
When this option is set to Enable, your wireless network name is broadcast to anyone within the
. If you're not using encryption then they could connect to your network. When
challenge text and sends it back to the access point. If the challenge text is encrypted correctly,
Page 30

the access point allows the requesting device to authenticate. It is recommended to select Auto if
you are not sure which authentication type is used.
Ø Key Length: Select a 64-bit or 128-bit WEP key length from the drop-down list.
Ø Key Type: Select a key type from the drop-down list. 128-bit encryption requires a longer key
than 64-bit encryption. Keys are defined by entering in a string in HEX (hexadecimal - using
characters 0-9, A-F) or ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange alphanumeric characters) format. ASCII format is provided so you can enter a string that is easier
to remember.
Ø Default Key: You may choose one of your 4 different WEP keys from below.
Ø Encryption Key 1-4: You may enter four different WEP keys.
Ø
Enable 802.1x Authentication: Place a check in this box if you would like to use RADIUS
authentication. This option works with a RADIUS Server to authenticate wireless clients. Wireless
clients should have established the necessary credentials before attempting to authenticate to the
Server through this Gateway. Furthermore, it may be necessary to configure the RADIUS Server
to allow this Gateway to authenticate users. You will then be required to specify the RADIUS
Server’s IP address, port, and password.
Ø Encryption: WPA pre-shared key
Ø ESSID Selection: As this device supports multiple SSIDs, it is possible to configure a different
security mode for each SSID (profile). Select an SSID from the drop-down list.
Ø Broadcast SSID: Select Enable or Disable from the drop-down list. This is the SSID broadcast
feature.
range of your signal
this is disabled, you must enter the Wireless Network Name (SSID) on the client manually to
connect to the network.
When this option is set to Enable, your wireless network name is broadcast to anyone within the
. If you're not using encryption then they could connect to your network. When
Page 31

Ø WMM: Choose to Enable or Disable WMM. This is the Quality of Service (QoS) feature for
prioritizing voice and video applications. This option can be further configured in WMM under the
Wireless drop-down menu.
Ø Encryption: Select WPA pre-shared key from the drop-down list.
Ø WPA Type: Select TKIP, AES, or WPA2 Mixed. The encryption algorithm used to secure the data
communication. TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) provides per-packet key generation and
is based on WEP. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a very secure block based encryption.
Note that, if the bridge uses the AES option, the bridge can associate with the access point only if
the access point is also set to use only AES.
Ø Pre-shared Key Type: The Key Type can be passphrase or Hex format.
Ø
Pre-Shared Key: The key is entered as a pass-phrase of up to 63 alphanumeric characters in
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) format at both ends of the wireless
connection. It cannot be shorter than eight characters, although for proper security it needs to be
of ample length and should not be a commonly known phrase. This phrase is used to generate
session keys that are unique for each wireless client.
3.2.3.5. Filter
Page 32

3.2.3.6. WPS
Ø WPS Current Status:
Ø Self Pin Code:
Ø SSID:
Ø Authentication Mode:
Ø Passphrase Key:
Ø WPS Via Push Button:
Ø WPS Via PIN:
3.2.3.7. Client List
Page 33

3.2.3.8. WMM
3.3. Network
3.3.1. Status
Page 34

3.3.2. LAN
Ø Bridge Type: Select Static IP or Dynamic IP from the drop-down list. If you select Static IP, you
will be required to specify an IP address and subnet mask. If Dynamic IP is selected, then the IP
address is received automatically from the external DHCP server.
Ø IP Address: Specify an IP address.
Ø IP Subnet Mask: Specify a subnet mask for the IP address.
Ø 802.1d Spanning Tree: Select Enable or Disable from the drop-down list. Enabling spanning tree
will avoid redundant data loops.
3.4. Management
3.4.1. Admin
Change current login password of the device. It is recommended to change the default
password for security reasons.
Page 35

3.4.2. SNMP
Allows you to assign the contact details, location, community name and trap settings for
SNMP. This is a networking management protocol used to monitor network-attached
devices. SNMP allows messages (called protocol data units) to be sent to various parts of a
network. Upon receiving these messages, SNMP-compatible devices (called agents) return
data stored in their Management Information Bases.
Ø SNMP Active: Choose to enable or disable the SNMP feature.
Ø SNMP Version: You may select a specific version or select All from the drop-down list.
Ø Read Community Name: Specify the password for access the SNMP community for read only
access.
Ø Set Community Name: Specify the password for access to the SNMP community with read/write
access.
Page 36

Ø System Location: Specify the location of the device.
Ø System Contact: Specify the contact details of the device.
Ø Trap Active: Choose to enable or disable the SNMP trapping feature. .
Ø Trap Manager IP: Specify the password for the SNMP trap community.
Ø Trap Community: Specify the name of SNMP trap community.
3.4.3. Firmware
Allows you to upgrade the firmware of the device in order to improve the functionality and
performance.
Ensure that you have downloaded the appropriate firmware from the vendor’s
website.
Connect the device to your PC using an Ethernet cable, as the firmware cannot be
upgraded with wireless interface.
3.4.4. Configure
This allows you to restore to factory default setting or backup/restore your current setting.
3.4.5. Reset
This will only reset you devices with current configuration unaffected.
Page 37

3.5. Tools
3.5.1. Time Setting
This feature allows you to configure, update, and maintain the correct time on the device’s
internal system clock as well as configure the time zone. The date and time of the device
can be configured manually or by synchronizing with a time server.
If the device losses power for any reason, it will not be able to keep its clock running,
and will not display the correct time once the device has been restarted. Therefore, you
must re-enter the correct date and time.
Ø Time Zone: Select time zone.
Page 38

Ø NTP Time Server: Specify the NTP server’s IP address for time synchronization.
Ø
Daylight Saving: To enable daylight savings time.
3.5.2. Power Saving
DDNS allows you to create a hostname that points to your dynamic IP or static IP address
or URL. The devices allows you redirecting the traffic to a specific DDNS providers for
dynamic domain name routing.
Ø Dynamic DNS: To enable/disable the DDNS service
Ø Server Address: List of DDNS Service providers
ü 3322
ü DHS
ü DynDNS
ü ZoneEdit
ü CyberGate
Ø Host Name: Host name to be redirected
Ø Username: User name for DDNS Service providers
Ø Password: Password for DDNS Service providers
3.5.3. Diagnosis
Check whether a network destination is reachable with ping service.
Page 39

3.5.4. LED Control
3.6. Logout
Page 40

Appendix A – SPECIFICATIONS
Frequency Band 2.400~2.484 GHz
Media Access Protocol
Modulation Technology
Operating Channels 11 for North America, 14 for Japan, 13 for Europe
Receive Sensitivity
(Typical)
Available transmit power
Antenna *3
Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA)
- OFDM: BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM
- DBPSK, DQPSK, CCK
- IEEE802.11n
MCS8 @ -90dBm
MCS15 @ -70dBm
- IEEE802.11g
6Mbps@ -92dBm
54Mbps@ -72dBm
- IEEE802.11b
1Mbps@ -93dBm
11Mbps@ -89dBm
- IEEE802.11n/g
18dBm@6~9 Mbps / MCS9
16dBm@12~18 Mbps / MCS11
14dBm@24~36 Mbps / MCS13
13dBm@48~54 Mbps / MCS15
- IEEE802.11b
17.5dBm@1, 11Mbps
Directional internal antenna
TNC type; Peak Gain = 5dBi
Page 41

Appendix B – FCC INTERFERENCE STATEMENT
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will
not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which
can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the
following measures:
l Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
l Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
l Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
l Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may
not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the
user's authority to operate this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment should
be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
We declare that the product is limited in CH1~CH11 by specified firmware controlled in the USA.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
Page 42

Appendix C – IC Interference Statement
Industry Canada statement:
This device complies with RSS-210 of the Industry Canada Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with IC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment
should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
This device has been designed to operate with an antenna having a maximum gain of 2 dBi. Antenna having a higher gain
is strictly prohibited per regulations of Industry Canada. The required antenna impedance is 50 ohms.
 Loading...
Loading...