EnerSys PowerSafe RL Series, PowerSafe RM Series, PowerSafe RN Series, PowerSafe RH-420, PowerSafe RH Series Installation, Operating And Maintenance Instruction
Page 1
1 Publication No: EN-GAZ-Standard-IOM 001 Dec 2012
INSTALLATION, OPERATING
MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS
type RL …, RM …, RN …, RH …
Battery voltage: Capacity (5 h):
T
y
pe of cell: Number of cells:
Assembled and commissioned by: Date:
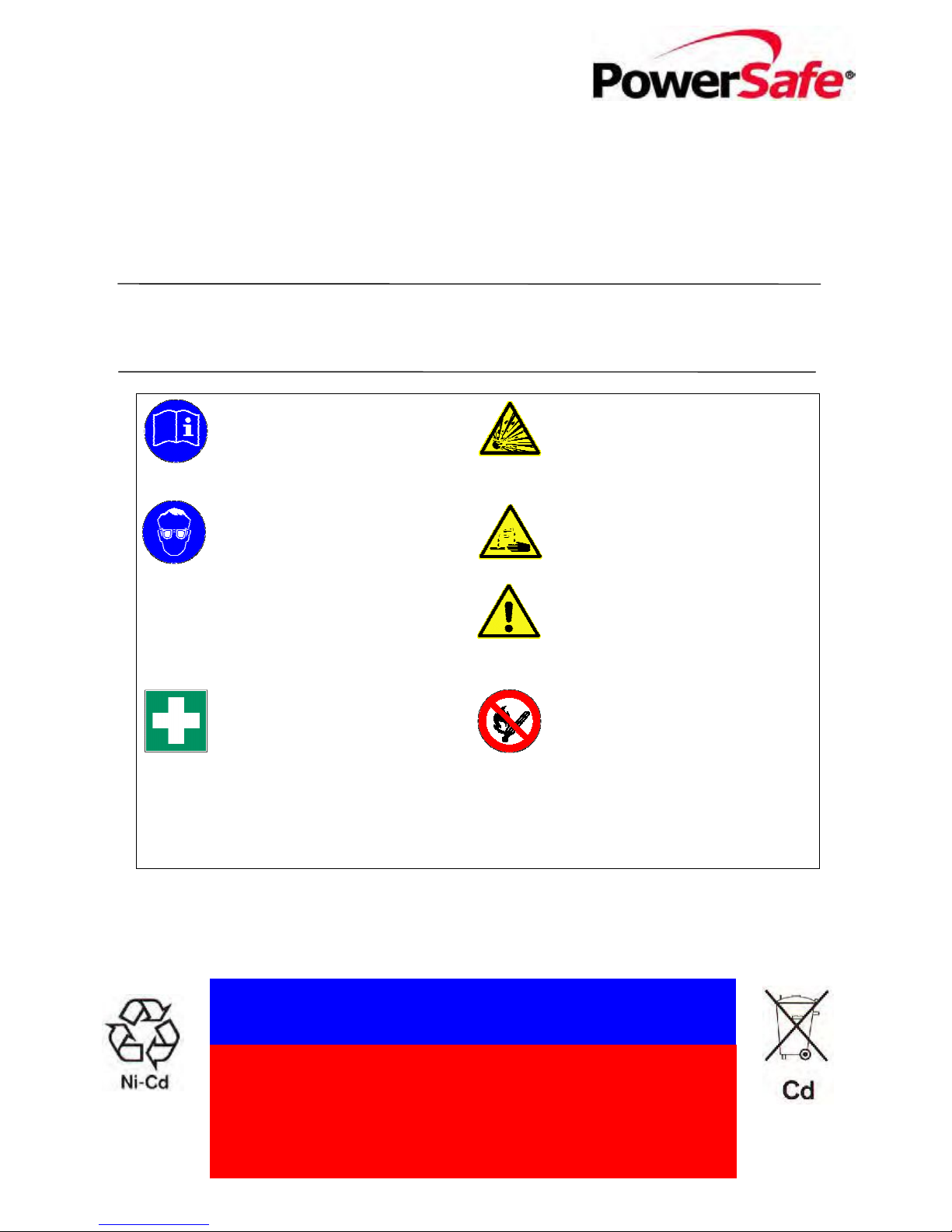
Warning!
The gases emitted during charging are explosive. The electrolyte (potassium hydroxide, KOH) is highly
co
rrosive. Exposed metal parts of the battery always conduct a voltage and are electrically active parts.
Precautions in accordance with DIN EN 50272, Part 2 have to be observed.
Observe the instructions for use and
place them visibly close to the
battery! Work only on batteries after
receiving instruction from qualified
personnel!
Warning: Risk of fire, explosion, or
burns! Avoid any short circuit!
Metallic parts under voltage on the
battery, do not place tools or items
on top of the battery!
Electrolyte is highly corrosive!
When working on batteries wear
safety glasses and protective
clothing. All metallic personal
objects, such as rings, watches,
bracelets etc. shall be removed
before starting work on the battery!
Only use insulated tools! Comply
strictly with the accident prevention
regulations and your national Health
and Safety standards as well as DIN
EN 50272, Part 1.
Cells are heavy!
Make sure they are safely
installed!
Only use suitable transport
equipment!
Electrolyte is harmful to skin and
eyes. Therefore, after an accidental
contact with the electrolyte flood the
eyes immediately with large
quantities of clean water for an
extended period of time of at least
15 minutes. In all cases, consult a
doctor immediately!
Clothing contaminated with
electrolyte should be washed in
water immediately!
No smoking! Do not allow naked
flames, embers or sparks near the
battery due to the risk of explosion
or fire!
The Installation, Operation and Handling Instructions must be strictly observed. Non-compliance
with the Maintenance and Handling Instructions, replacing with unoriginal spares, usage other
than specified, use of additives to the electrolyte and unauthorized tampering will invalidate any
entitlement to warranty.
Used batteries with this symbol are reusable products and have to be
put into a recycling system. Used batteries must be disposed of as
special waste in accordance with all standards.
WARNING!
Never use sulphuric acid or acidic
water.
Acid will damage the battery!
Page 2
2 Publication No: EN-GAZ-Standard-IOM 001 Dec 2012
1. Receiving the battery
The cells are not to be stored in
packaging, therefore, unpack the battery
immediately after arrival. Do not overturn
the package. The battery cells are
equipped with a blue plastic transport plug.
The battery can be delivered:
- Filled and charged/ the battery
is ready for installation. Replace
the transport plug with the vent
cap included in our accessories
just before use;
- Filled and discharged/ Replace
the transport plug with the vent
cap included in our accessories
just before use; or
- Unfilled and discharged/ do not
remove the transport plug until
ready to fill the battery.
The battery must not be charged with
the transport plug in the cells as this
can damage the battery.
2. Storage
The rooms provided for storing the
batteries must be clean, dry, cool (+10 °C
to 30 °C - in compliance with IEC 60623)
and well ventilated. The cells are not to be
stored in closed packaging and must not
be exposed to direct sunlight or UVradiation.
If the cells are delivered in plywood
boxes, open the boxes before storage
and remove the packing material on the
top of the cells. If the cells are delivered
on pallets remove the packing material
on the top of the cells.
2.
1 Uncharged and unfilled cells
Provided the correct storage conditions
are met then the cells and batteries can be
stored for long periods without damage if
they are deeply discharged, drained and
well sealed. It is very important that the
cells are sealed with the plastic transport
plug tightly in place. It is necessary to
check after receipt and at least every year.
Leaky plugs allow the carbon dioxide from
the atmosphere to infiltrate the cell, which
will result in carbonation of the plates. This
may influence the capacity of the battery.
2.2 Charged and filled cells/
discharged and filled cells
Filled cells can be stored for up to 12
months from the time of delivery. Storage
of filled cells at a temperature above
+30 °C results in loss of capacity of
approximately 5% per 10% year. It is very
important that the cells are sealed with the
plastic transport plugs tightly in place. In
case of loss of electrolyte during
transportation, refill the cell with distilled
water to the “MAX” mark before storage.
3. Installation
EN 50272-2:2001 “Accumulators and
battery installations, stationary battery
installations” is binding for the setting up
and operation of battery installations. For
non stationary installations specific
standards are valid.
3.1 Location
Install the battery in a dry and clean room.
Avoid direct sunlight and heat in all cases.
The battery will give the optimal
performance and maximum service life if
the ambient temperature lies between
+ 10 °C and + 30 °C.
3.2 Ventilation
During the last part of charging the battery,
gases (oxygen and hydrogen mixture) are
emitted. At normal float charge the gas
evolution is very small but some ventilation
is necessary. Special regulations for
ventilation might be required in your
area for certain applications. If no
regulations are fixed DIN EN 50272,
Part 2:2001 should be met.
3.3 Setting up
Always follow the assembly drawings,
circuit diagrams and other separate
instructions. The transport plugs have to
be replaced by the vent caps included in
the accessories. If batteries are supplied
“filled and charged” , all the electrolyte
levels should be checked and, if
necessary, topped up as described in
point 3.4.
Cell connectors and/or flexible cables
should be checked to ensure they are
tightly seated. Terminal nuts, screws and
connectors must be tightly seated. If
necessary, tighten with a torque wrench.
Torque loading for:
M10: 8 Nm
M16: 20 Nm
M20: 25 Nm
Female thread:
M 8: 20 – 25 Nm
M10: 25 – 30 Nm
The connectors and terminals should be
corrosion-protected by coating with a thin
layer of anti-corrosion grease.
3.4 Electrolyte
The electrolyte for NiCd batteries consists
of diluted caustic potash solution (specific
gravity 1.20 kg/litre ± 0.01 kg/litre) with
a lithium hydroxide component, in
accordance with IEC 60993. The caustic
potash solution is prepared in accordance
with factory regulations. The specific
gravity of the electrolyte does not allow
any conclusion to be drawn on the
charging state of the battery. It changes
only slightly during charging and
discharging and is only minimally related
to the temperature.
-
Battery delivered unfilled and
discharged/ if the electrolyte is
supplied dry, it is to be mixed to
the enclosed mixing instruction.
Remove the transport plugs from
the cell just before filling. Fill the
cells up to 20 mm above the
lower level mark “MIN”. Steel
cased cells have to be filled up to
the top edge of the plates. When
using battery racks fill cells before
installing. Only use genuine
electrolyte.
- Battery delivered filled and
charged or discharged/ check
electrolyte level. It should not be
less than 20 mm below the upper
level mark “MAX” (see 5.2).
3.5 Commissioning
A good commissioning is very important.
The following instructions are valid for
commissioning while 20 °C to 30 °C. For
different conditions please contact the
manufacturer. Charging at constant
current is preferable. If a site test is
requested it has to be carried out in
accordance with IEC 60623.
According to IEC 60623, 0.2 C5 A is also
expressed as 0.2 It A. The reference test
current It is expressed as:
It A = Cn Ah
1 h
Example:
0.2 ItA means:
20 A for a 100 Ah battery or
100 A for a 500 Ah battery
3.5.1 Commissioning with constant
current
Battery delivered unfilled and
discharged /after a period of 5 hours from
filling the electrolyte, the battery should be
charged for 15 hours at the rated charging
current 0.2 It A. Approximately 4 hour after
the end of charging, the electrolyte level
should be adjusted to the upper electrolyte
level mark “MAX” by using only genuine
electrolyte. For cells with steel cases, the
electrolyte level should be adjusted to the
maximum level according to the
“Instruction for the control of electrolyte
level”. During the charge the electrolyte
level and temperature should be
observed (see point 5.4). The
electrolyte level should never fall below
the “MIN” mark.
Battery delivered filled and discharged
/the battery should be charged for 15
hours at the rated charging current 0.2 It A.
Approximately 4 hours after the end of
charging, the electrolyte level should be
adjusted to the upper electrolyte level
mark “MAX” by using distilled or deionized
water in accordance with IEC 60993. For
cells with steel cases, the electrolyte level
should be adjusted to the maximum level
according to the “Instruction for the control
of electrolyte level”.
Page 3

3 Publication No: EN-GAZ-Standard-IOM 001 Dec 2012
During the charge the electrolyte level
and temperature should be observed
(see point 5.4). The electrolyte level
should never fall below the “MIN” mark.
Battery delivered filled and charged
and stored for more than 12 months/
the battery should be charged for 15 hours
at the rated charging current 0.2 It A.
Approximately 4 hours after the end of
charging, the electrolyte level should be
adjusted to the upper electrolyte level
mark “MAX” by using distilled or deionized
water in accordance with IEC 60993. For
cells with steel cases, the electrolyte level
should be adjusted to the maximum level
according to the “Instruction for the control
of electrolyte level”. During the charge
the electrolyte level and temperature
should be observed (see point 5.4). The
electrolyte level should never fall below
the “MIN” mark.
Battery delivered filled and charged/
a 5
hour charge at the rated charging current
0.2 It A must be carried out before putting
the battery into operation. Approximately 4
hours after the end of charging, the
electrolyte level should be adjusted to the
upper electrolyte level mark “MAX” by
using distilled or deionized water in
accordance with IEC 60993. For cells with
steel cases, the electrolyte level should be
adjusted to the maximum level according
to the “Instruction for the control of
electrolyte level”. During the charge the
electrolyte level and temperature
should be observed (see point 5.4). The
electrolyte level should never fall below
the “MIN” mark.
3.5.2 Commissioning with constant
voltage
If the charger´s maximum voltage setting
is too low to supply constant current
charging, divide the battery into two parts
that will be charged individually.
Battery delivered unfilled and
discharged / after a period of 5 hours
from filling the electrolyte, the battery
should be charged for 30 hours at the
rated charging voltage of 1.65 V/cell. The
current limit should be 0.2 It A maximum.
Approximately 4 hours after the end of
charging, the electrolyte level should be
adjusted to the upper electrolyte level
mark “MAX” by using only genuine
electrolyte. For cells with steel cases, the
electrolyte level should be adjusted to the
maximum level according to the
“Instruction for the control of electrolyte
level”. During the charge the electrolyte
level and temperature should be
observed (see point 5.4). The
electrolyte level should never fall below
the “MIN” mark.
Battery delivered filled and discharged
/
the battery should be charged for 30
hours at the rated charging voltage of 1.65
V/cell. The current limit should be 0.2 It A
maximum. Approximately 4 hours after the
end of charging, the electrolyte level
should be adjusted to the upper
electrolyte level mark “MAX” by using
distilled or deionized water in accordance
with IEC 60993. For cells with steel cases,
the electrolyte level should be adjusted to
the maximum level according to the
“Instruction for the control of electrolyte
level. During the charge the electrolyte
level and temperature should be
observed (see point 5.4). The
electrolyte level should never fall
below the “MIN” mark.
Ba
ttery delivered filled and charged
and stored for more than 12 months/
the battery should be charged for 30 hours
at the rated charging voltage of 1.65
V/cell. The current limit should be 0.2 It A
maximum. Approximately 4 hours after the
end of charging, the electrolyte level
should be adjusted to the upper electrolyte
level mark “MAX” by using distilled or
deionized water in accordance with IEC
60993. For cells with steel cases, the
electrolyte level should be adjusted to the
maximum level according to the
“Instruction for the control of electrolyte
level”. During the charge the electrolyte
level and temperature should be
observed (see point 5.4). The
electrolyte level should never fall below
the “MIN” mark.
Battery delivered filled and charged/ a
10 hour charge at the rated charging
voltage of 1.65 V/cell must be carried out
before putting the battery into operation.
The current limit should be 0.2 It A
ma
ximum. Approximately 4 hours after the
end of charging, the electrolyte level
should be adjusted to the upper electrolyte
level mark “MAX” by using distilled or
deionized water in accordance with IEC
60993. For cells with steel cases, the
electrolyte level should be adjusted to the
maximum level according to the
“Instruction for the control of electrolyte
level”. During the charge the electrolyte
level and temperature should be
observed (see point 5.4). The
electrolyte level should never fall below
the “MIN” mark.
4. Charging in Operation
4.1 Continous battery power supply
(with occasional battery discharge)
Recommended charging voltage for
ambient temperatures + 20 °C to + 25 °C.
Do not remove the vent caps during float-,
boost charge and buffer operation. The
current limit should be 0.3 It A maximum in
ge
neral.
4.
1.2 Two level charge
Floating: 1.40 – 1.42 V/cell
Boost charge: 1.55 – 1.70 V/cell
A high voltage will increase the speed and
efficiency of recharging the battery.
4.1.3 Single level charge
1.45 – 1.50 V/cell
4.2 Buffer operation
Where the load exceeds the charger
rating.
1.45 – 1.55 V/cell
5. Periodic Maintenance
The battery must be kept clean using only
water. Do not use a wire brush or solvents
of any kind. Vent caps can be rinsed in
clean water if necessary but must be dried
before using them again.
Check regularly (approximately every 6
months) that all connectors, nuts and
screws are tightly fastened. Defective vent
caps and seals should be replaced. All
metal parts of the battery should be
corrosion-protected by coating with a thin
layer of anti-corrosion grease. Do not
coat any plastic part of the battery, for
example cell cases!
Check the charging voltage. If a battery is
parallel connected it is important that the
recommended charging voltage remains
unchanged. The charging current in the
strings should also be checked to ensure it
is equal. These checks have to be carried
out once a year. High water consumption
of the battery is usually caused by
improper voltage setting of the charger.
5.
1 Equalizing charge
It is recommended to carry out an
equalizing charge once a year to maintain
capacity and to stabilize the voltage levels
of the cells. The equalizing charge can be
carried out for 15 hours at 0.2 It A or with
the boost charging stage in conformity with
the characteristic curve of the available
charging equipment. The electrolyte level
must be checked after an equalizing
charge.
In order to equalize the floating derating
effect, it is recommended to charge the
battery once a year for 15 hours at the
rated charging current 0.2 It A. Then
discharge the battery down to 1.0 V/cell
and charge again for 8 hours at the rated
charging current 0.2 It A.
Page 4

4 Publication No: EN-GAZ-Standard-IOM 001 Dec 2012
5.2 Electrolyte check an
d topping
up
Check the electrolyte level and never let
the level fall below the lower level mark
“MIN”. Use only distilled or deionized water
to top-up the cells in accordance with IEC
60993. Experience will tell the time interval
between topping-up. Refilling with
electrolyte is only permissible if spilled
electrolyte has to be replaced. If during
refilling or topping up electrolyte has been
splashed onto the cell cover or between
the cell cases, clean this off and then dry
the area.
NOTE: Once the battery has been
filled with the correct electrolyte
either at the factory or during the
battery commissioning, there is no
need to check the electrolyte
density periodically. Interpretation
of density measurements is difficult
and could lead to
misunderstandings.
5.3 Replacing of electrolyte
In most stationary applications the
electrolyte will retain its effectiveness for
the total lifetime of the battery. However,
under special battery operating conditions,
if the electrolyte is found to be carbonated,
the battery performance can be restored by
replacing the electrolyte. Only use
genuine electrolyte!
It is recommended to change the
electrolyte when reaching a carbonate
content of 75 g/litre. It is possible to test
the electrolyte in the manufacturer’s
laboratory. For this, a minimum quantity of
0.2 litres of electrolyte in a clean glass or
polyethylene container should be sent in,
paying strict attention to the valid
dangerous goods regulations. The sample
of electrolyte should be taken half an hour
after charging has ended and from several
cells of the battery. Do not take the
samples immediately after topping up. The
electrolyte sample and the cells should be
closed immediately after the electrolyte has
been taken.
CAUTION – caustic potash solution is
highly corrosive!
5.4 Electrolyte temperature
The temperature of the electrolyte should
never exceed 45 °C as higher
temperatures have a detrimental effect on
the function and duration of the cells. In the
course of charging, aim for an electrolyte
temperature of
≤ 35 °C. On exceeding
45 °C the charging should be temporarily
interrupted until the electrolyte temperature
falls down to 35 °C. The temperature
measurements are to be made on one of
the cells in the middle of the battery. Low
ambient or electrolyte temperatures down
to –25 °C do not have any detrimental
effect on the battery. They just cause a
temporary reduction in capacity.
6. Additional Warning notes
NiCd batteries must not be installed or
stored in the same room as lead acid
batteries. In addition to this, the charging
gases from lead acid batteries must be
kept away from Ni-Cd batteries by suitable
precautions such as ventilation or hermetic
isolation of the rooms. Tools for lead acid
batteries must not be used for NiCd
batteries.
Do not place electrically conductive objects
such as tools, etc. on the battery!
Risk of short circuit and fire!
No rings or metal bracelets should be worn
during the assembly of the battery – Risk
of injury!
Open the doors of the battery cabinet
during charging so that the charging gases
can escape. The charging gases from
batteries are explosive. Do not allow open
fire or ember in the vicinity of the battery!
Risk of explosion!
Caution – potassium hydroxide
(KOH) solution is highly corrosive!
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution is
used as electrolyte. Potassium
hydroxide (KOH) solution is a highly
corrosive liquid which can cause severe
damage to health if it comes into contact
with the eyes or the skin (risk of blinding). If
even small quantities are swallowed there
is a possibility of internal injuries.
When working with electrolyte and on
cells / batteries rubber gloves, safety
goggles with side guards and protective
clothing must always be worn!
Contact with the eyes: Flush out
immediately with abundant amounts of
water for 10 – 15 minutes. If necessary
consult an eye clinic.
Contact with the skin: Remove splashed
clothing immediately and wash the affected
skin areas with abundant amounts of
water. For any discomforts consult a
doctor.
Swallowing: Rinse out the mouth
immediately with abundant amounts of
water and keep drinking large amounts of
water. Do not provoke vomiting. Call an
emergency doctor immediately.
In the event of injuries: Rinse thoroughly
for a long period under running water.
Consult a doctor immediately.
 Loading...
Loading...