
Emotron VS10 and VS30
AC drive
Operation instruction
Valid from software vers ion 04.01.xx.xx

2 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Contents
1. General information ..................................................................................................................... 13
1.1. Read first, then start ........................................................................................................................ 13
2. Safety instructions ........................................................................................................................ 14
2.1. Basic safety measures...................................................................................................................... 14
2.2. Residual hazards .............................................................................................................................. 15
2.3. Application as directed .................................................................................................................... 15
3. Mounting ..................................................................................................................................... 16
3.1. Important notes ............................................................................................................................... 16
3.2. Electrical installation ....................................................................................................................... 17
3.2.1. 1-phase mains connection 230/240 V ..................................................................................... 17
3.2.1.1. Connection plan ............................................................................................................... 17
3.2.1.2. Fusing and terminal data ................................................................................................. 18
3.2.2. 1/3-phase mains connection 230/240 V ................................................................................. 20
3.2.2.1. Connection plan ............................................................................................................... 20
3.2.2.2. Fusing and terminal data ................................................................................................. 21
3.2.3. 3-phase mains connection 400 V............................................................................................. 23
3.2.3.1. Connection plan ............................................................................................................... 23
3.2.3.2. Fusing and terminal data ................................................................................................. 24
3.2.4. 3-phase mains connection 480 V............................................................................................. 27
3.2.4.1. Connection plan ............................................................................................................... 27
3.2.4.2. Fusing and terminal data ................................................................................................. 28
3.2.5. CANopen/Modbus RTU ........................................................................................................... 31
4. Commissioning ............................................................................................................................. 32
4.1. Important notes ............................................................................................................................... 32
4.2. Operating interfaces ........................................................................................................................ 33
4.2.1. Keypad ..................................................................................................................................... 33
2.2. Engineering tool »Emotron EASY Starter« .............................................................................. 34
4.
4.2.2.1. Generate a connection between inverter and »Emotron Easy starter« ......................... 35
4.3. Parameter setting ............................................................................................................................ 37
4.3.1. General notes on parameters .................................................................................................. 37
4.3.2. Basic inverter settings.............................................................................................................. 39
4.3.3. Basic motor settings ................................................................................................................ 42
4.3.4. Function assignment of the inputs and outputs ..................................................................... 43

4.4. Keypad parameter list ..................................................................................................................... 46
4.5. Save parameter settings in the memory module ............................................................................ 73
4.5.1. Save parameter settings with keypad ..................................................................................... 73
4.5.2. Save parameter settings with »Emotron Easy starter« ........................................................... 73
5. Diagnostics and fault elimination .................................................................................................. 74
5.1. LED status display ............................................................................................................................ 74
5.2. Diagnostics parameter ..................................................................................................................... 75
5.2.1. Logbook ................................................................................................................................... 76
5.2.2. Error history buffer .................................................................................................................. 77
5.2.3. Inverter diagnostics ................................................................................................................. 81
5.2.4. Network diagnostics ................................................................................................................ 85
5.2.4.1. CANopen diagnostics ....................................................................................................... 86
5.2.4.2. Modbus diagnostics ......................................................................................................... 89
5.2.5. Diagnostics of the inputs and outputs ..................................................................................... 90
5.2.5.1. Digital inputs and outputs ............................................................................................... 90
5.2.5.2. Analog inputs and outputs .............................................................................................. 91
5.2.6. Wireless-LAN diagnostics......................................................................................................... 93
5.2.7. Setpoint diagnostic .................................................................................................................. 94
5.2.8. Process controller status ......................................................................................................... 95
5.2.9. Sequencer diagnostics ............................................................................................................. 96
5.2.10. Device identification ................................................................................................................ 97
5.2.11. Device overload monitoring (i*t) ............................................................................................. 98
5.2.12. Heatsink Temperature Monitoring .......................................................................................... 99
5.2.13. Life-diagnosis ........................................................................................................................... 99
5.3. Error handling ................................................................................................................................ 100
5.3.1. Error types ............................................................................................................................. 100
5.3.2. E
rror configuration ................................................................................................................ 101
5.3.3. Error reset .............................................................................................................................. 101
5.3.4. Keypad error messages ......................................................................................................... 102
5.4. Data handling ................................................................................................................................. 103
6. Basic setting ............................................................................................................................... 106
6.1. Mains voltage ................................................................................................................................ 106
6.2. Control source selection ................................................................................................................ 108
6.3. Selection of setpoint source .......................................................................................................... 109
6.3.1. Keypad setpoint default setting ............................................................................................ 113
6.4. Starting/stopping performance ..................................................................................................... 114
6.4.1. Starting performance ............................................................................................................ 114
6.4.2. Stopping performance ........................................................................................................... 116
4 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

6.5. Frequency limits and ramp times .................................................................................................. 117
6.6. Quick stop ...................................................................................................................................... 120
6.7. S-shaped ramps ............................................................................................................................. 122
6.8. Optical device identification .......................................................................................................... 123
7. Motor control ............................................................................................................................. 124
7.1. Motor data ..................................................................................................................................... 125
7.1.1. Manual setting of the motor data ......................................................................................... 125
7.2. Motor control selection ................................................................................................................. 126
7.2.1. V/f characteristic control (VFC) ............................................................................................. 127
7.2.1.1. Linear V/f characteristic ................................................................................................. 128
7.2.1.2. Square-law V/f characteristic ........................................................................................ 130
7.2.1.3. User-definable V/f characteristic ................................................................................... 132
7.2.1.4. V/f characteristic control energy-saving (VFC Eco) ....................................................... 133
7.2.2. Sensorless vector control (SLVC) ........................................................................................... 134
7.2.3. Sensorless control for synchronous motors (SL-PSM) ........................................................... 137
7.2.3.1. Stall monitoring ............................................................................................................. 140
7.3. Optimisation of motor control ...................................................................................................... 141
7.3.1. V/f voltage boost ................................................................................................................... 142
7.3.2. Skip frequencies..................................................................................................................... 143
7.3.3. Optimising the stalling behaviour.......................................................................................... 145
7.3.4. Slip compensation ................................................................................................................. 147
7.3.5. Oscillation damping ............................................................................................................... 149
7.3.6. Synchronous motor: Pole position identification (PPI) ......................................................... 150
7.3.6.1. Pole position identification (PPI) without movement ................................................... 151
7.4. Optimisation of the control loops .................................................................................................. 152
7.4.1. Options for optimized motor tuning ..................................................................................... 155
7.4.1.1. Tu
ning of the motor and the speed controller .............................................................. 156
7.4.1.2. Automatic motor identification (energized) .................................................................. 157
7.4.1.3. Automatic motor calibration (non-energized) ............................................................... 158
7.4.2. Inverter Characteristics .......................................................................................................... 159
7.4.3. Motor equivalent circuit diagram data .................................................................................. 160
7.4.4. Motor controller settings ....................................................................................................... 161
7.4.4.1. Current controller .......................................................................................................... 161
7.4.4.2. Field controller ............................................................................................................... 161
7.4.4.3. Field weakening controller ............................................................................................ 162
7.4.4.4. Field weakening controller (advanced) ......................................................................... 162
7.4.4.5. Imax controller ............................................................................................................... 163

7.4.4.6. Flying restart controller ................................................................................................. 164
7.4.4.7. SLVC controller .............................................................................................................. 164
7.4.4.8. Torque control w/ freq. limit ......................................................................................... 165
7.4.4.9. Slip controller ................................................................................................................. 169
7.4.5. 7Speed controller .................................................................................................................. 170
7.5. Motor rotating direction ................................................................................................................ 171
7.6. Switching frequency changeover ................................................................................................... 172
7.7. Motor protection ........................................................................................................................... 173
7.7.1. Motor overload monitoring (i²*t) .......................................................................................... 173
7.7.1.1. Speed compensation for protecting motors at low speed ............................................ 175
7.7.2. Current limits ......................................................................................................................... 177
7.7.3. Overcurrent monitoring ......................................................................................................... 179
7.7.4. Motor phase failure detection ............................................................................................... 180
7.7.5. Motor speed monitoring ....................................................................................................... 181
7.7.6. Motor torque monitoring ...................................................................................................... 182
8. Configuring the network ............................................................................................................. 183
8.1. General network settings ............................................................................................................... 184
8.2. Predefined process data words ..................................................................................................... 202
8.2.1. Device profile CiA 402 ............................................................................................................ 203
8.2.2. AC Drive Profile ...................................................................................................................... 204
8.2.2.1. Customer specific configurations .................................................................................. 205
8.2.3. Further process data .............................................................................................................. 206
8.3. Parameter access monitoring (PAM) ............................................................................................. 211
8.4. Acyclic data exchange .................................................................................................................... 212
5. CANopen ........................................................................................................................................ 213
8.
8.5.1. CANopen introduction ........................................................................................................... 213
8.5.2. CANopen node address ......................................................................................................... 214
8.5.3. CANopen baud rate ............................................................................................................... 214
8.5.3.1. CANopen initialisation ................................................................................................... 215
8.5.4. CANopen diagnostics ............................................................................................................. 216
8.5.5. CANopen emergency telegram .............................................................................................. 217
8.5.6. CANopen heartbeat protocol ................................................................................................ 217
8.5.7. CANopen process data objects .............................................................................................. 219
8.5.8. CANopen data mapping ......................................................................................................... 224
8.5.9. CANopen service data objects ............................................................................................... 227
8.5.10. CANopen error responses ...................................................................................................... 229
8.5.11. CANopen diagnostic counter ................................................................................................. 230
8.5.12. CANopen LED status displays ................................................................................................. 231
6 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

8.5.13. Resetting the CANopen interface .......................................................................................... 232
8.5.14. CANopen short setup ............................................................................................................ 233
8.6. Modbus RTU .................................................................................................................................. 236
8.6.1. Modbus RTU introduction ..................................................................................................... 236
8.6.2. Modbus RTU node address.................................................................................................... 236
8.6.3. Modbus RTU baud rate .......................................................................................................... 237
8.6.4. Modbus RTU data format ...................................................................................................... 238
8.6.5. Modbus RTU time-out monitoring ........................................................................................ 238
8.6.6. Modbus RTU diagnostics ....................................................................................................... 238
8.6.7. Modbus RTU function codes.................................................................................................. 241
8.6.8. Modbus RTU data mapping ................................................................................................... 242
8.6.9. Modbus RTU LED status displays ........................................................................................... 246
8.6.10. Reset Modbus RTU interface ................................................................................................. 246
8.6.11. Modbus RTU response time .................................................................................................. 246
8.6.12. Short setup of Modbus RTU .................................................................................................. 247
9. Configuring the process controller ............................................................................................... 249
9.1. Basic process controller settings .................................................................................................... 250
9.2. Process controller idle state and rinse function ............................................................................ 256
9.2.1. Process controller idle state .................................................................................................. 256
9.2.2. Process controller rinse function ........................................................................................... 257
10. Additional functions ................................................................................................................ 258
10.1. Device Commands ..................................................................................................................... 259
10.1.1.1. 10.1.1 Reset parameters to default ............................................................................... 259
10.1.1.2. Details ............................................................................................................................ 259
1.2. Saving/loading the parameter settings .................................................................................. 260
10.
10.1.2.1. 10.1.3 Device commands for parameter change-over .................................................. 263
10.1.3. Delete logbook ....................................................................................................................... 264
10.2. Keypad ....................................................................................................................................... 265
10.2.1. Keypad language selection .................................................................................................... 265
10.2.2. Keypad setpoint increment.................................................................................................... 265
10.2.3. Keypad scaling of speed display ............................................................................................ 265
10.2.4. Keypad status display............................................................................................................. 265
10.2.5. Keypad Configuration of R/F and CTRL buttons .................................................................... 266
10.3. Wireless LAN (WLAN) ................................................................................................................ 269
10.3.1. WLAN LED status displays ...................................................................................................... 269
10.3.2. WLAN basic settings ............................................................................................................... 270
10.3.2.1. Resetting WLAN settings to default setting ................................................................... 272
10.3.3. WLAN access point mode ...................................................................................................... 273

10.3.3.1. Establishing a direct WLAN connection between Emotron Easy starter PC and inverter
274
10.3.4. WLAN client mode ................................................................................................................. 276
10.4. DC braking .................................................................................................................................. 278
10.4.1. Example 1: Automatic DC braking when the motor is started .............................................. 280
10.4.2. Example 2: Automatic DC braking when the motor is stopped ............................................. 281
10.5. Brake energy management ........................................................................................................ 283
10.5.1. Stopping the deceleration ramp function generator ............................................................. 284
10.5.2. Inverter motor brake ............................................................................................................. 285
10.6. Load loss detection .................................................................................................................... 286
10.7. Access protection ...................................................................................................................... 287
10.7.1. Write access protection ......................................................................................................... 287
10.7.1.1. Write access protection in the »Emotron Easy starter« ............................................... 289
10.7.1.2. Write access protection in the keypad .......................................................................... 292
10.7.1.3. Configuring the write access protection with the keypad ............................................. 293
10.8. Favorites .................................................................................................................................... 296
10.8.1. Accessing the "Favorites" with the keypad ............................................................................ 296
10.8.2. Favorites parameter list (default setting) .............................................................................. 297
10.8.3. Configuring the "Favorites" ................................................................................................... 299
10.9. Parameter change-over ............................................................................................................. 302
10.9.1. Example: Selective control of several motors with one inverter ........................................... 313
10.10. Device profile CiA 402 ................................................................................................................ 315
10.11. Holding brake control ................................................................................................................ 318
10.11.1. Basic setting ....................................................................................................................... 319
10.
11.2. "Automatic" brake mode (automatic operation) .............................................................. 320
10.11.3. Brake holding load ............................................................................................................. 322
10.11.3.1. General mode of operation ........................................................................................... 323
10.11.4. Brake closing level.............................................................................................................. 324
10.11.5. Manual release of the holding brake ................................................................................. 326
10.12. Flying restart circuit ................................................................................................................... 327
10.13. Timeout für fault reaction ......................................................................................................... 329
10.14. Automatic restart ....................................................................................................................... 330
10.15. Mains failure control .................................................................................................................. 331
10.15.1. Activating the mains failure control................................................................................... 333
10.15.2. Restart protection .............................................................................................................. 334
10.15.3. Fast mains recovery ........................................................................................................... 334
10.15.4. Commissioning the mains failure control .......................................................................... 335
10.16. Process data ............................................................................................................................... 336
8 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

10.16.1. Position counter ................................................................................................................. 336
10.17. Firmware download ................................................................................................................... 337
10.17.1. Firmware download with »Emotron Easy starter (Firmware loader)« .............................. 337
10.18. Additive voltage impression ...................................................................................................... 338
10.18.1. Example: Using the function with a 400-V inverter ........................................................... 339
10.19. Parameter for engineering tools ................................................................................................ 340
11. Sequencer ............................................................................................................................... 343
11.1. Segment configuration .............................................................................................................. 346
11.2. Sequence configuration ............................................................................................................. 356
11.3. Sequencer basic settings ............................................................................................................ 371
12. Flexible I/O configuration ........................................................................................................ 374
12.1. Control source change-over ....................................................................................................... 375
12.1.1. Example 1: Change-over from terminal control to keypad control ....................................... 378
12.1.2. Example 2: Change-over from terminal control to network control ..................................... 379
12.2. Start / stop motor ...................................................................................................................... 380
12.2.1. Example 1: Start/stop (1 signal) and reversal ........................................................................ 386
12.2.2. Example 2: Start forward/start reverse/stop (edge-controlled) ............................................ 387
12.2.3. Example 3: Run forward/Run reverse/stop (status-controlled) ............................................. 389
12.2.4. Example 4: Quick stop ........................................................................................................... 391
12.2.5. Example 5: Jog forward/Jog reverse ...................................................................................... 393
12.2.6. Example 6: Enable inverter .................................................................................................... 395
12.3. Setpoint change-over ................................................................................................................. 396
3.1. Priority of the setpoint sources ............................................................................................. 398
12.
12.3.2. Analog input setpoint source ................................................................................................. 398
12.3.3. Keypad setpoint source ......................................................................................................... 401
12.3.4. Network setpoint source ....................................................................................................... 403
12.3.5. Setpoint source of preset setpoints ....................................................................................... 404
12.3.6. Motor potentiometer setpoint source (MOP) ....................................................................... 409
12.3.7. Setpoint source segment setpoints ....................................................................................... 413
12.4. Reset error ................................................................................................................................. 415
12.5. Activating DC braking manually ................................................................................................. 417
12.6. Releasing holding brake manually ............................................................................................. 419
12.7. Activating ramp 2 manually ....................................................................................................... 421
12.8. Triggering a user-defined fault .................................................................................................. 423
12.9. Functions for parameter change-over ....................................................................................... 424
12.9.1. Example 1: Activation via command (only when disabled) ................................................... 426
12.9.2. Example 2: Activation via command (immediately) .............................................................. 428
12.9.3. Example 3: Activation if the selection is changed (only if the inverter is disabled) .............. 429

12.9.4. Example 4: Activation if the selection is changed (immediately) .......................................... 431
12.10. Process controller function selection ........................................................................................ 433
12.11. Sequencer control functions ...................................................................................................... 436
12.12. Frequency threshold for "Frequency threshold exceeded" trigger ........................................... 441
12.13. Configuration of digital inputs ................................................................................................... 443
12.14. Configuration of analog inputs .................................................................................................. 444
12.14.1. Analog input 1.................................................................................................................... 444
12.14.1.1. Example 1: Input range 0 ... 10 V ≡ setting range 0 ... 50 Hz ....................................... 446
12.14.1.2. Example 2: Input range 0 ... 10 V ≡ setting range -40 ... +40 Hz .................................. 446
12.14.1.3. Example 3: Error detection ............................................................................................ 447
12.14.2. Analog input 2.................................................................................................................... 448
12.15. Configuration of digital outputs ................................................................................................ 450
12.15.1. Relay .................................................................................................................................. 450
12.15.2. Digital output 1 .................................................................................................................. 454
12.15.3. NetWordOUT1 status word ............................................................................................... 454
12.16. Configuration of analog outputs................................................................................................ 459
12.16.1. Analog output 1 ................................................................................................................. 459
12.16.1.1. Example 1: Output voltage 0 ... 10 V ≡ output frequency 0 ... 100 Hz ........................ 461
12.16.1.2. Example 2: Output voltage 2 ... 10 V ≡ output frequency 30 ... 60 Hz ........................ 461
13. Technical data ......................................................................................................................... 462
13.1. Standards and operating conditions .......................................................................................... 462
13.1.1. Protection of persons and device protection ........................................................................ 462
13.1.2. EMC data................................................................................................................................ 462
13.1.3. Motor connection .................................................................................................................. 462
13.1.4. E
nvironmental conditions ...................................................................................................... 463
13.1.5. Electrical supply conditions ................................................................................................... 463
13.2. 1-phase mains connection 230/240 V ....................................................................................... 464
13.2.1. Rated data .............................................................................................................................. 464
13.3. 1/3-phase mains connection 230/240 V ................................................................................... 465
13.3.1. Rated data .............................................................................................................................. 465
13.4. 3-phase mains connection 400 V ............................................................................................... 466
13.4.1. Rated data .............................................................................................................................. 466
13.5. 3-phase mains connection 480 V ............................................................................................... 468
13.5.1. Rated data .............................................................................................................................. 468
14. Appendix ................................................................................................................................ 470
14.1. Operate and parameterise the inverter with keypad ................................................................ 470
14.1.1. Keypad operating mode ........................................................................................................ 471
14.1.1.1. Keypad status display ..................................................................................................... 471
10 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

14.1.1.2. Function of keypad keys in operating mode .................................................................. 472
14.1.1.3. Error reset with keypad ................................................................................................. 473
14.1.2. Keypad parameterisation mode ............................................................................................ 474
14.1.2.1. Parameter groups .......................................................................................................... 474
14.1.2.2. Function of the keypad keys in the parameterisation mode ......................................... 475
14.1.2.3. Save parameter settings with keypad ............................................................................ 476
14.1.2.4. Display of status words on keypad ................................................................................ 477
14.2. Error codes ................................................................................................................................. 478
14.3. Parameter attribute list .............................................................................................................. 488

12 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation
1. General information
1.1. Read first, then start
WARNING!
Read this documentation thoroughly before carrying out the installation and commissioning.
Please observe the safety instructions!
Information and tools with regard to the CG products can be found on the
Internet:
http://www.emotron.com Download
2. Safety instructions
2.1. Basic safety measures
Disregarding the following basic safety measures may lead to severe personal injury and
dam age to material assets!
The product
• must only be used as directed.
• must never be commissioned if they display signs of damage.
• must never be technically modified.
• must never be commissioned if they are not fully mounted.
• must never be operated without required covers.
Connect/disconnect all pluggable terminals only in deenergised condition. Only remove
the product from the installation in the deenergised state.
Insulation resistance tests between 24 V control potential and PE: According to EN
61800−5−1, the maximum test voltage must not exceed 110 V DC.
Observe all specifications of the corresponding documentation supplied. This is the
precondition for safe and trouble-free operation and for obtaining the product features
specified.
The procedural notes and circuit details described in this document are only proposals. It
is up to the user to check whether they can be adapted to the particular applications.
Drives & Automation does not take any responsibility for the suitability of the procedures
and circuit proposals described.
The product must only be used by qualified personnel. IEC 60364 or CENELEC HD 384
define the skills of these persons:
• They are familiar with installing, mounting, commissioning, and operating the product.
• They have the corresponding qualifications for their work.
• They know and can apply all regulations for the prevention of accidents, directives, and
laws applicable at the place of use.
Please observe the specific notes in the other chapters!
Notes used:
DANGER!
This note refers to an imminent danger which, if not avoided, may result in death or serious injury.
WARNING!
This note refers to a danger which, if not avoided, may result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION!
This note refers to a danger which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury.
NOTICE
This note refers to a danger which, if not avoided, may result in damage to property.
14 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

2.2. Residual hazards
The user must take the residual hazards mentioned into consideration in the risk
assessment for his/her machine/system.
If the above is disregarded, this can lead to severe injuries to persons and damage to
material assets!
Product
Observe the warning labels on the product!
Icon Description
Electrostatic sensitive devices:
Before working on the product, the staff must ensure to be free of electrostatic charge!
Dangerous electrical voltage
Before working on the product, check if no voltage is applied to the power terminals!
After mains disconnection, the power terminals carry the hazardous electrical voltage given on the product!
High leakage current:
Carry out fixed installation and PE connection in compliance with EN 61800−5−1 or EN 60204−1!
Hot surface:
Use personal protective equipment or wait until devices have cooled down!
Motor
If there is a short circuit of two power transistors, a residual movement of up to
180°/number of pole pairs can occur at the motor! (For 4-pole motor: residual movement
max. 180°/2 = 90°).
2.3. Application as directed
• The product must only be operated under the operating conditions prescribed in this
documentation.
• The product meets the protection requirements of 2014/35/EU: Low-Voltage Directive.
• The product is not a machine in terms of 2006/42/EC: Machinery Directive.
• Commissioning or starting the operation as directed of a machine with the product is
not permitted until it has been ensured that the machine meets the regulations of the
EC Directive 2006/42/EC: Machinery Directive; observe EN 60204−1.
• Commissioning or starting the operation as directed is only allowed when there is
compliance with the EMC Directive 2014/30/EU.
• The harmonised standard EN 61800−5−1 is used for the inverters.
• The product is not a household appliance, but is only designed as component for
commercial or professional use in terms of EN 61000−3−2.
• The product can be used according to the technical data if drive systems have to
comply with categories according to EN 61800−3.
In residential areas, the product may cause EMC interferences. The operator is
responsible for taking interference suppression measures.

3. Mounting
3.1. Important notes
DANGER!
Dangerous electrical voltage
Possible consequence: death or severe injuries
All work on the inverter must only be carried out in the deenergised state.
After switching off the mains voltage, wait for at least 3 minutes before you start working.
16 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

3.2. Electrical installation
3.2.1. 1-phase mains connection 230/240 V
3.2.1.1. Connection plan
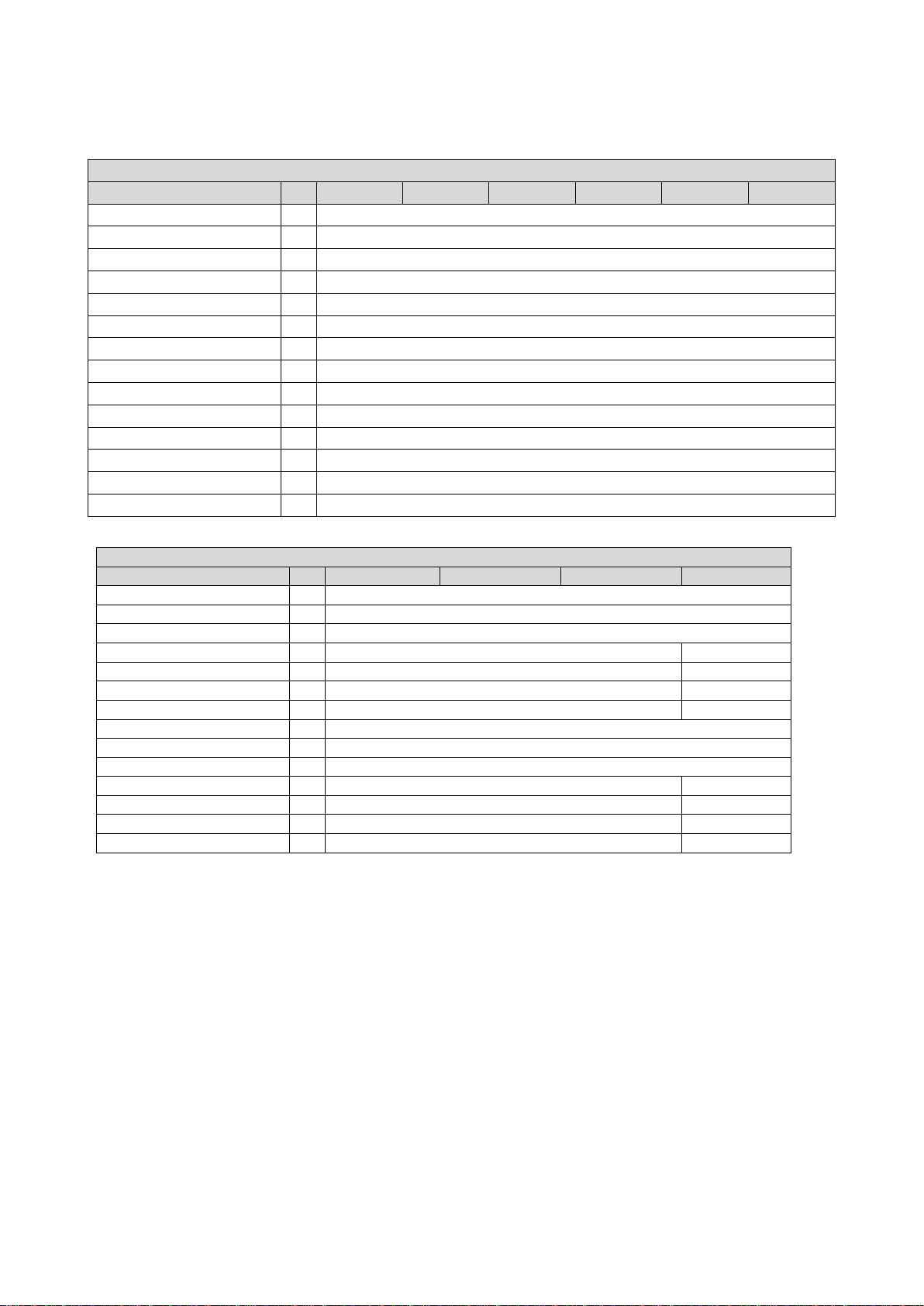
The wiring diagram is valid for Emotron VS10 inverters.
Fig. 1: Wiring example
S1 Run/Stop
Fx Fuses
Q1 Mains contactor
--Dashed line = options
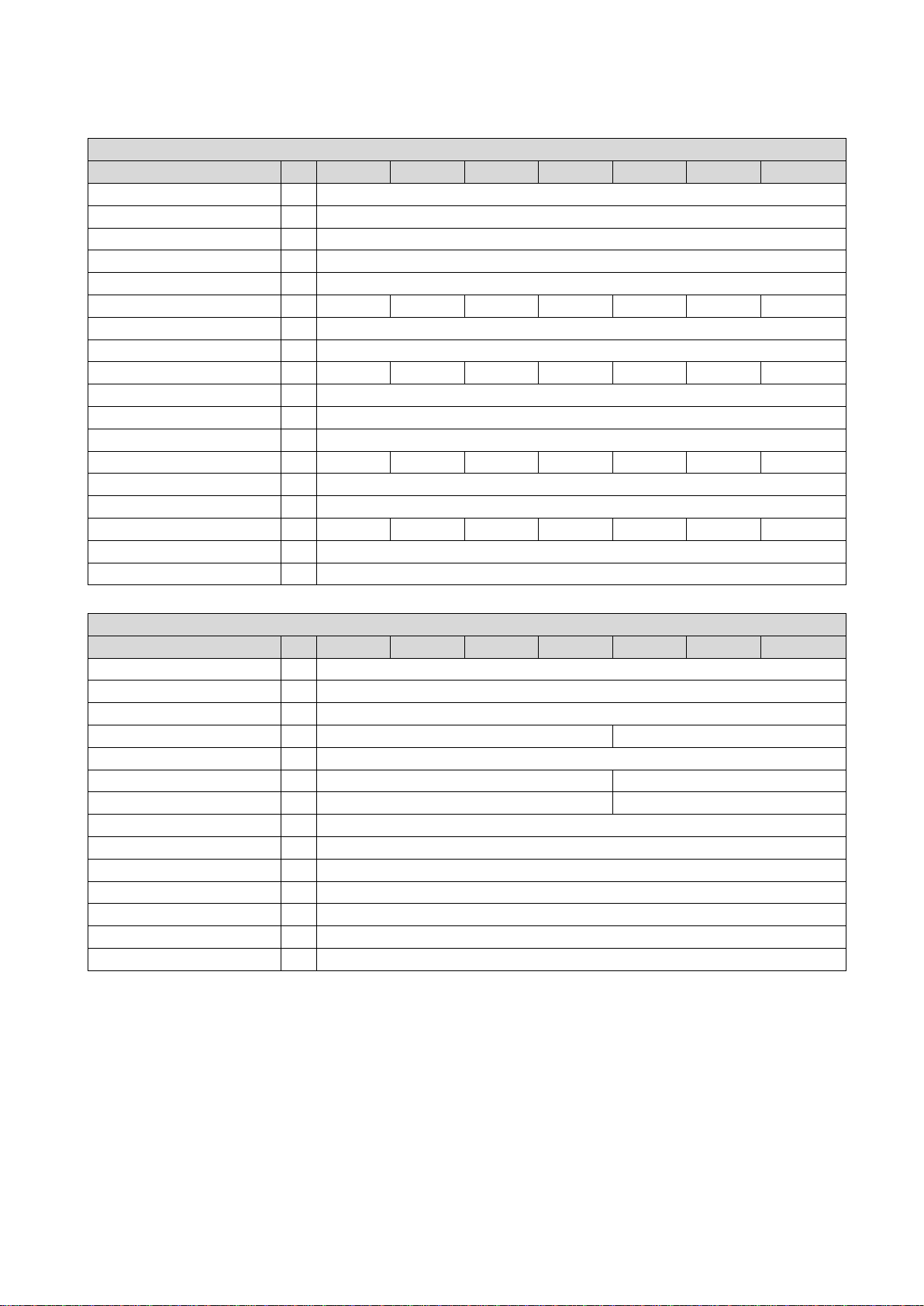
3.2.1.2. Fusing and terminal data
Fuse data
Inverter
Cable installation in compliance with
EN 60204-1
Laying system
B2
Fuse
Characteristics
gG/gL or gRL
Max. rated current
A
10
10
16
16
25
25
25
Circuit breaker
Max. rated current
A
10
10
16
16
25
25
25
operation
with mains choke
Fuse
Characteristics
gG/gL or gRL
10 10 16 16 25 25 25
Circuit breaker
Characteristics
B
Max. rated current
A
10
10
16
16
25
25
25
Earth-leakage circuit breaker
Mains connection
Inverter
Connection
X100
Min. cable cross-section
mm² 1 Max. cable cross-section
mm²
2.5
6
Stripping length
mm 8 Tightening torque
Nm
0.5
0.7
Connection
PE
Connection type
PE screw
Min. cable cross-section
mm² 1 Max. cable cross-section
mm²
6
Tightening torque
Nm
1.2
Required tool
0.8 x 5.5
VS10-23-1P7 VS10-23-2P4 VS10-23-3P2 VS10-23-4P2 VS10-23-6P0 VS10-23-7P0 VS10-023-9P6
operation
Characteristics
Max. rated current
1-phase mains connection
without mains choke
B
A
≥ 30 mA, type A or B
VS10-23-1P7 VS10-23-2P4 VS10-23-3P2 VS10-23-4P2 VS10-23-6P0 VS10-23-7P0 VS10-023-9P6
Connection type
Required tool
Stripping length
mm
0.5 x 3.0
pluggable screw terminal
0.6 x 3.5
10
18 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation
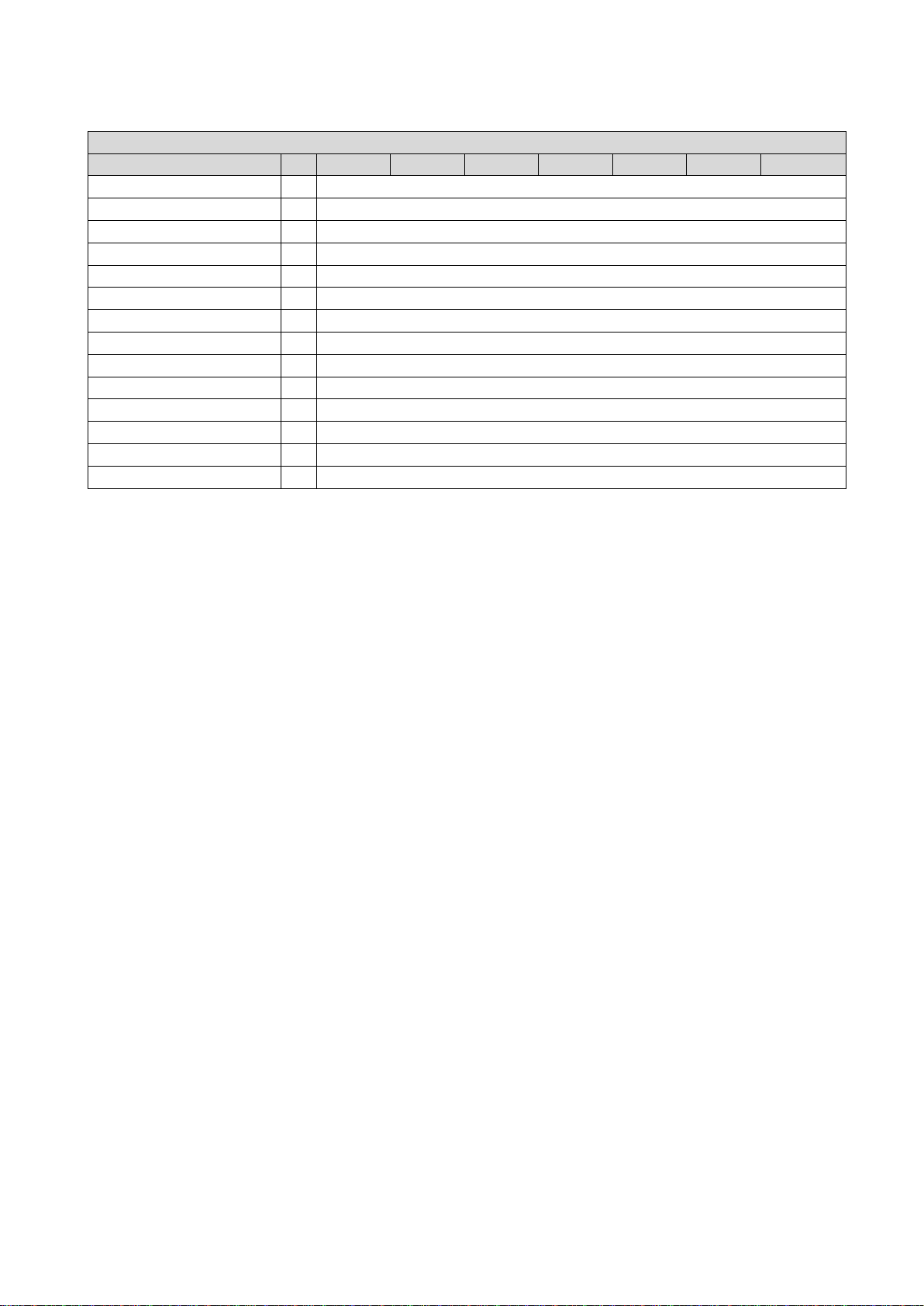
Motor connection
Connection
X105
Connection type
pluggable screw terminal
Min. cable cross-section
mm² 1 Max. cable cross-section
mm²
2.5
Tightening torque
Nm
0.5
Required tool
0.5 x 3.0
Connection
PE
Connection type
PE screw
Max. cable cross-section
mm²
6
Stripping length
mm
10
Tightening torque
Nm
1.2
Required tool
0.8 x 5.5
Inverter
Stripping length
Min. cable cross-section
VS10-23-1P7 VS10-23-2P4 VS10-23-3P2 VS10-23-4P2 VS10-23-6P0 VS10-23-7P0 VS10-023-9P6
mm
mm²
8
1

3.2.2. 1/3-phase mains connection 230/240 V
Emotron VS30-23 inverters do not have an integrated EMC filter in the AC mains
supply.
In order to comply with the EMC requirements according to EN 61800−3, an external
EMC filter according to IEC EN 60939 has to be used.
The user must prove that the EN 61800−3 requirements for conformity are fulfilled.
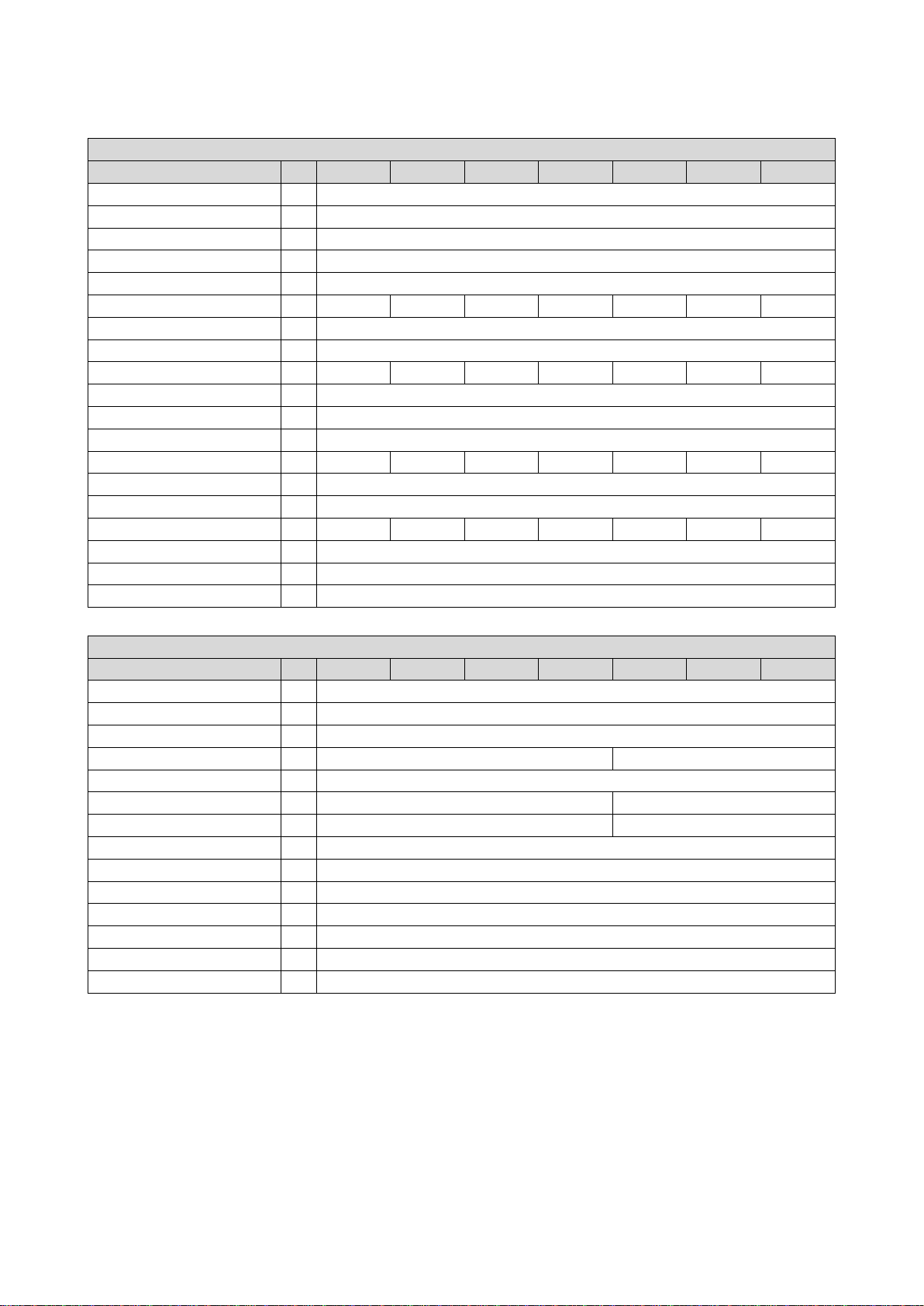
3.2.2.1. Connection plan
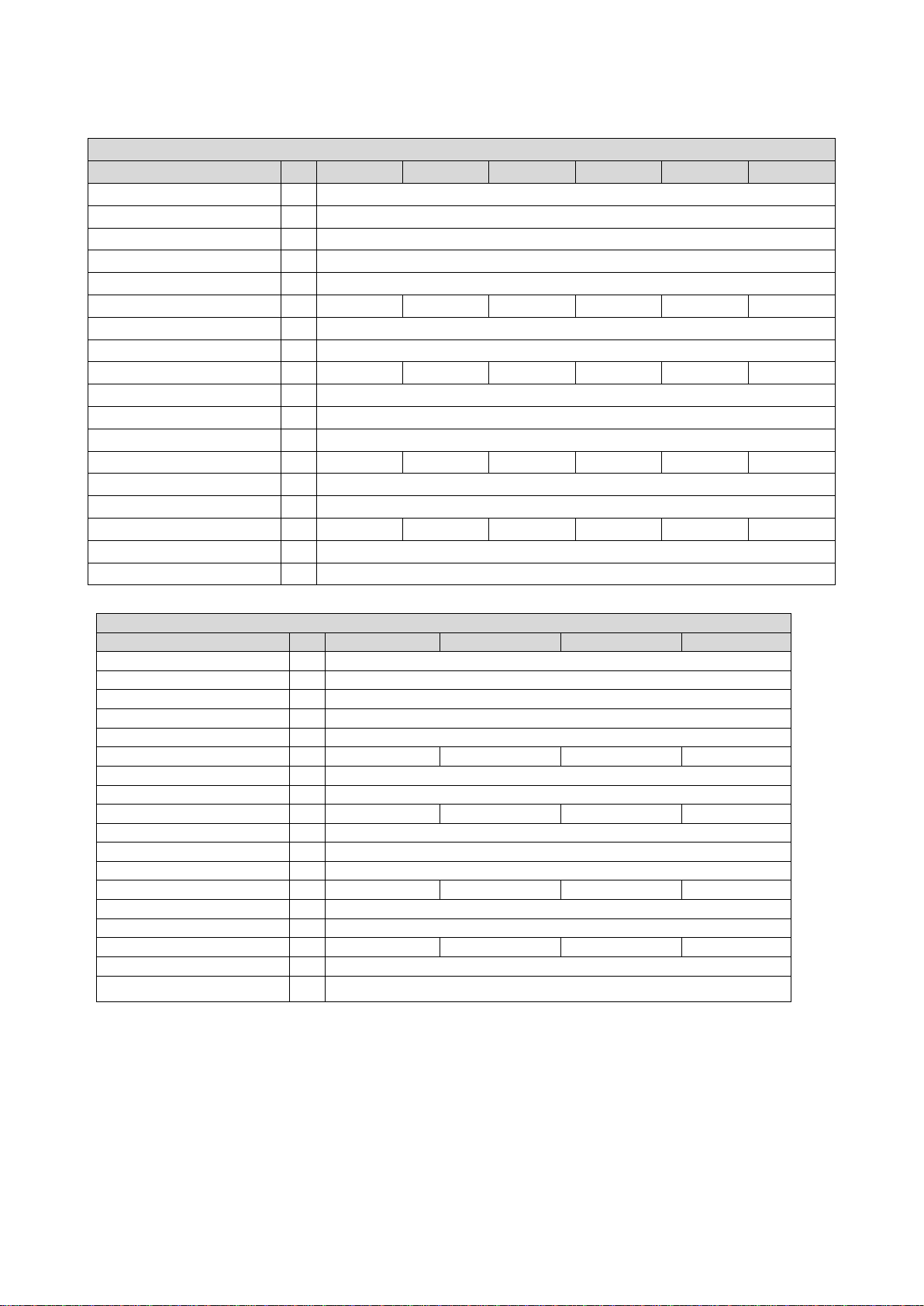
The wiring diagram is valid for Emotron VS30 inverters.
Fig. 2: Wiring example
S1 Run/Stop
Fx Fuses
Q1 Mains contactor
--Dashed line = options
20 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation
3.2.2.2. Fusing and terminal data
Fuse data
Inverter
Cable installation in compliance with
EN 60204-1
Laying system
B2
Fuse
Characteristics
gG/gL or gRL
Max. rated current
A
10
10
16
16
25
25
25
Circuit breaker
Max. rated current
A
10
10
16
16
25
25
25
operation
with mains choke
Fuse
Characteristics
gG/gL or gRL
10 10 16 16 25 25 25
Circuit breaker
Characteristics
B
Max. rated current
A
10
10
16
16
25
25
25
Earth-leakage circuit breaker
3-phase mains connection
≥ 30 mA, type B
Mains connection
Inverter
Connection type
pluggable screw terminal
Min. cable cross-section
mm² 1 Max. cable cross-section
mm²
2.5
6
Stripping length
mm
8
Required tool
0.5 x 3.0
0.6 x 3.5
Connection
PE
Connection type
PE screw
Min. cable cross-section
mm²
1
Stripping length
mm
10
Tightening torque
Nm
1.2
Required tool
0.8 x 5.5
VS30-23-1P7 VS30-23-2P4 VS30-23-3P2 VS30-23-4P2 VS30-23-6P0 VS30-23-7P0 VS30-23-9P6
operation
Characteristics
Max. rated current
1-phase mains connection
Connection
without mains choke
B
A
≥ 30 mA, type A or B
VS30-23-1P7 VS30-23-2P4 VS30-23-3P2 VS30-23-4P2 VS30-23-6P0 VS30-23-7P0 VS30-23-9P6
X100
Tightening torque
Max. cable cross-section
Nm
mm²
0.5
0.7
6
Motor connection
Connection
X105
Connection type
pluggable screw terminal
Min. cable cross-section
mm² 1 Max. cable cross-section
mm²
2.5
Tightening torque
Nm
0.5
Required tool
0.5 x 3.0
Connection
PE
Connection type
PE screw
Max. cable cross-section
mm²
6
Stripping length
mm
10
Tightening torque
Nm
1.2
Required tool
0.8 x 5.5
Inverter
Stripping length
Min. cable cross-section
VS30-23-1P7 VS30-23-2P4 VS30-23-3P2 VS30-23-4P2 VS30-23-6P0 VS30-23-7P0 VS30-23-9P6
mm
mm²
8
1
22 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

3.2.3. 3-phase mains connection 400 V
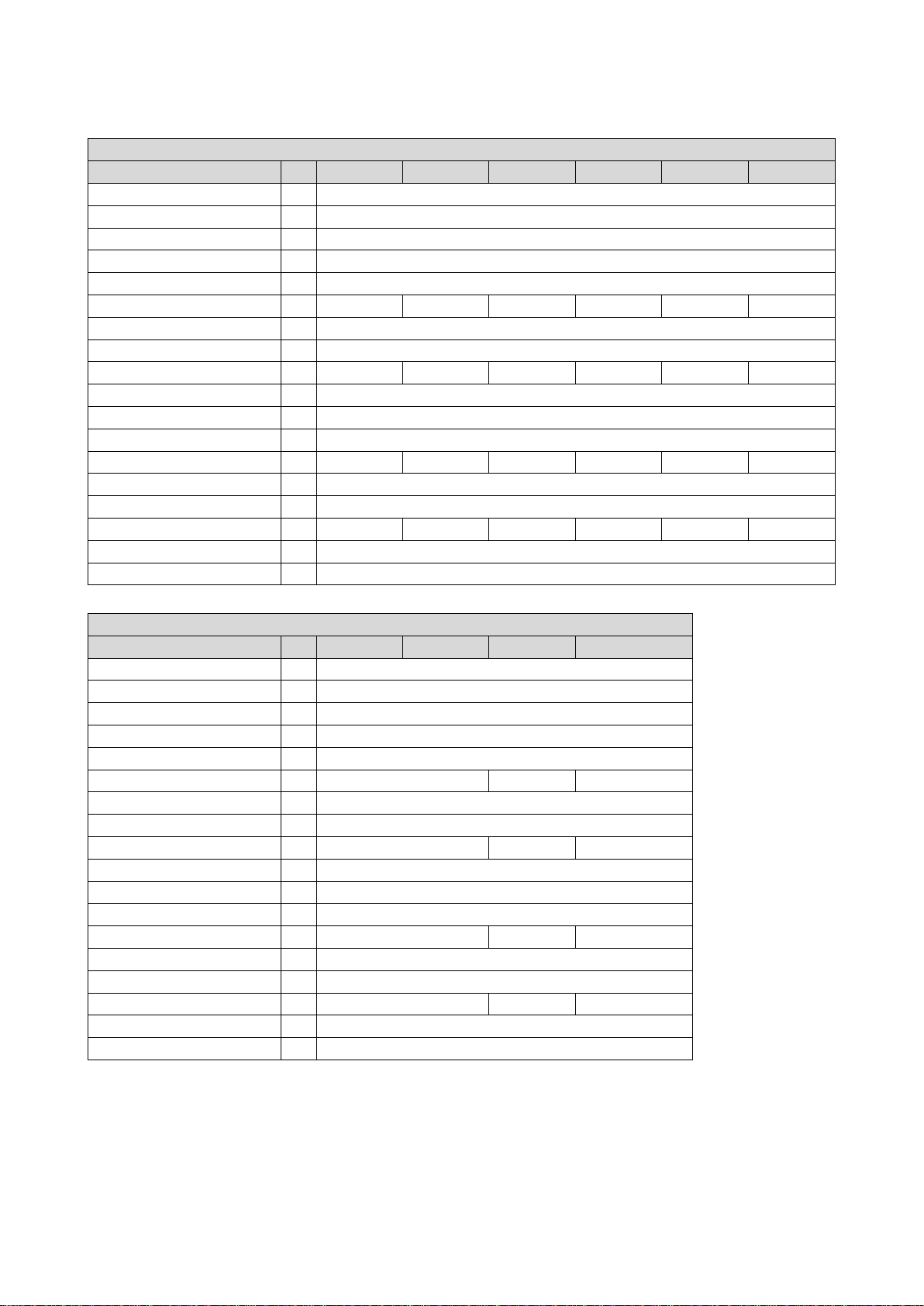
3.2.3.1. Connection plan
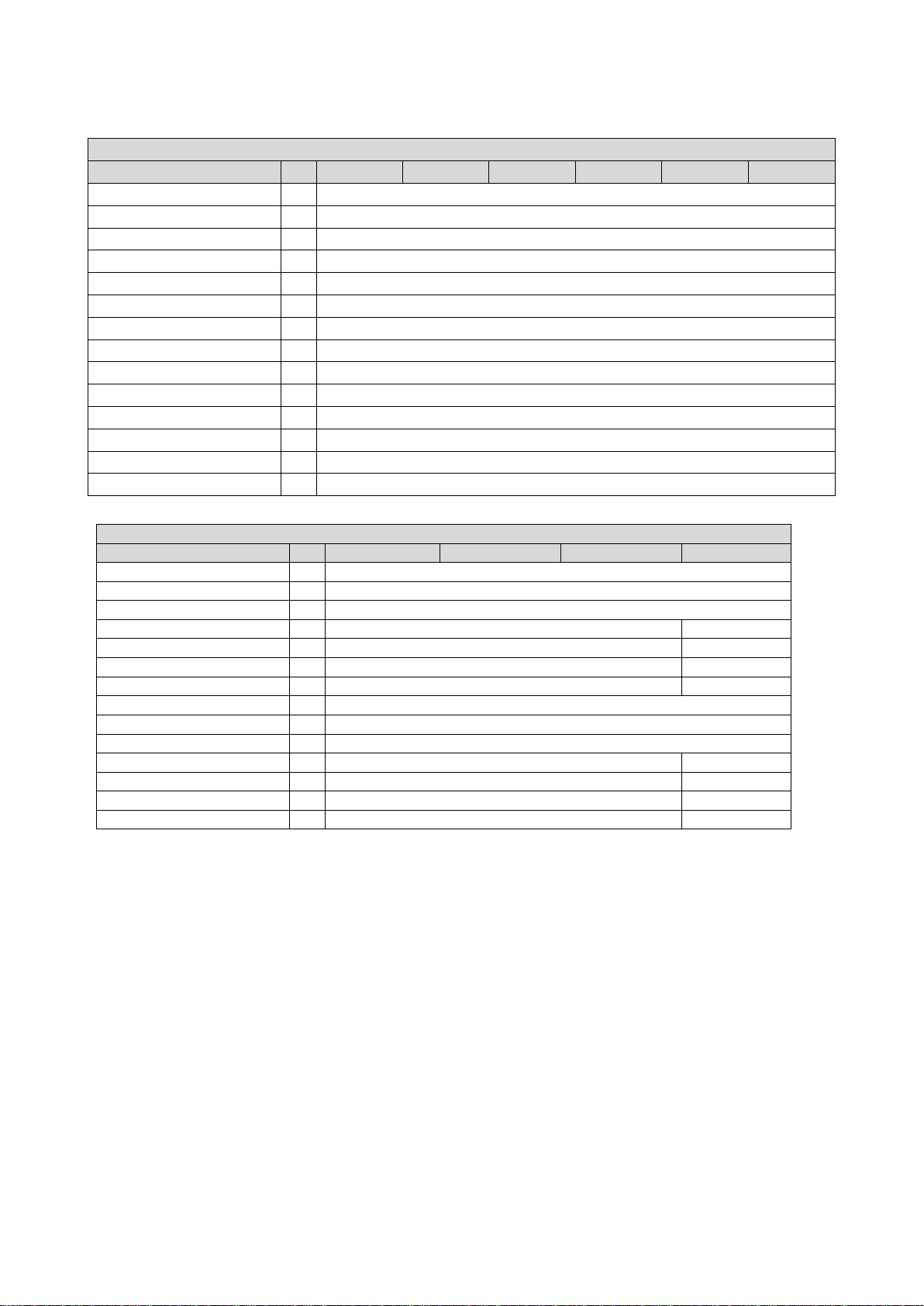
The wiring diagram is valid forEmotron VS30 inverters.
Fig. 3: Wiring example
S1 Run/Stop
Fx Fuses
Q1 Mains contactor
--Dashed line = options
3.2.3.2. Fusing and terminal data
Fuse data
Inverter
Cable installation in compliance with
EN 60204-1
Laying system
B2
Fuse
Characteristics
gG/gL or gRL
Max. rated current
A
10
10
10
16
16
16
Circuit breaker
Max. rated current
A
10
10
10
16
16
16
operation
with mains choke
Fuse
Characteristics
gG/gL or gRL
10 10 10 16 16 16
Circuit breaker
Characteristics
B
Max. rated current
A
10
10
10
16
16
16
Earth-leakage circuit breaker
Fuse data
Inverter
Cable installation in compliance with
E N 60204-1
B2
operation
without mains choke
Fuse
Characteristics
gG/gL or gRL
Max. rated current A 6
16
35
Characteristics
B
Max. rated current A 6
16
35
operation
with mains choke
Fuse
gG/gL or gRL
Max. rated current A 6
16
35
Circuit breaker
Characteristics
B
Max. rated current A 6
16
35
3-phase mains connection
≥ 30 mA, type B
VS30-40-1P3 VS30-40-1P8 VS30-40-2P4 VS30-40-3P2 VS30-40-3P9 VS30-40-5P6
operation
Characteristics
Max. rated current
3-phase mains connection
without mains choke
B
A
≥ 30 mA, type B
VS30-40-7P3 VS30-40-9P5 VS30-40-013 VS30-40-016
Laying system
Circuit breaker
Characteristics
Earth-leakage circuit breaker
24 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation
Mains connection
Inverter
Connection
X100
Connection type
pluggable screw terminal
Max. cable cross-section
mm²
2.5
Stripping length
mm
8
Tightening torque
Nm
0.5
Required tool
0.5 x 3.0
Connection type
PE screw
Min. cable cross-section
mm²
1
Max. cable cross-section
mm² 6 Stripping length
mm
10
Required tool
0.8 x 5.5
Mains connection
Inverter
Connection
X100
Connection type
Screw terminal
Min. cable cross-section
mm²
1.5
Max. cable cross-section
mm²
6
16
Tightening torque
Nm
0.5
1.2
Required tool
0.6 x 3.5
0.8 x 4.0
Connection type
PE-screw
Min. cable cross-section
mm²
1.5
Max. cable cross-section
mm²
6
16
Stripping length
mm
10
11
Tightening torque
Nm
1.2
3.4
Required tool
0.8 x 5.5
PZ2
VS30-40-1P3 VS30-40-1P8 VS30-40-2P4 VS30-40-3P2 VS30-40-3P9 VS30-40-5P6
Min. cable cross-section
Connection
Tightening torque
mm²
Nm
1
PE
1.2
VS30-40-7P3 VS30-40-9P5 VS30-40-013 VS30-40-016
Stripping length mm 9 11
Connection
PE
Motor connection
Inverter
Connection
X105
Connection type
pluggable screw terminal
Min. cable cross-section
mm² 1 Max. cable cross-section
mm²
2.5
Stripping length
mm 8 Tightening torque
Nm
0.5
Required tool
0.5 x 3.0
Connection
PE
Connection type
PE screw
Min. cable cross-section
mm² 1 Max. cable cross-section
mm² 6 Stripping length
mm
10
Tightening torque
Nm
1.2
Required tool
0.8 x 5.5
Motor connection
Inverter
X105
Connection type
Screw terminal
Min. cable cross-section
mm²
1.5
Max. cable cross-section
mm²
6
16
Stripping length
mm
9
11
Tightening torque
Nm
0.5
1.2
Required tool
0.6 x 3.5
0.8 x 4.0
Connection
PE
Connection type
PE screw
Min. cable cross-section
mm²
1.5
16
Stripping length
mm
10
11
Tightening torque
Nm
1.2
3.4
Required tool
0.8 x 5.5
PZ2
VS30-40-1P3 VS30-40-1P8 VS30-40-2P4 VS30-40-3P2 VS30-40-3P9 VS30-40-5P6
VS30-40-7P3 VS30-40-9P5 VS30-40-013 VS30-40-016
Connection
Max. cable cross-section mm² 6
26 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

3.2.4. 3-phase mains connection 480 V
3.2.4.1. Connection plan
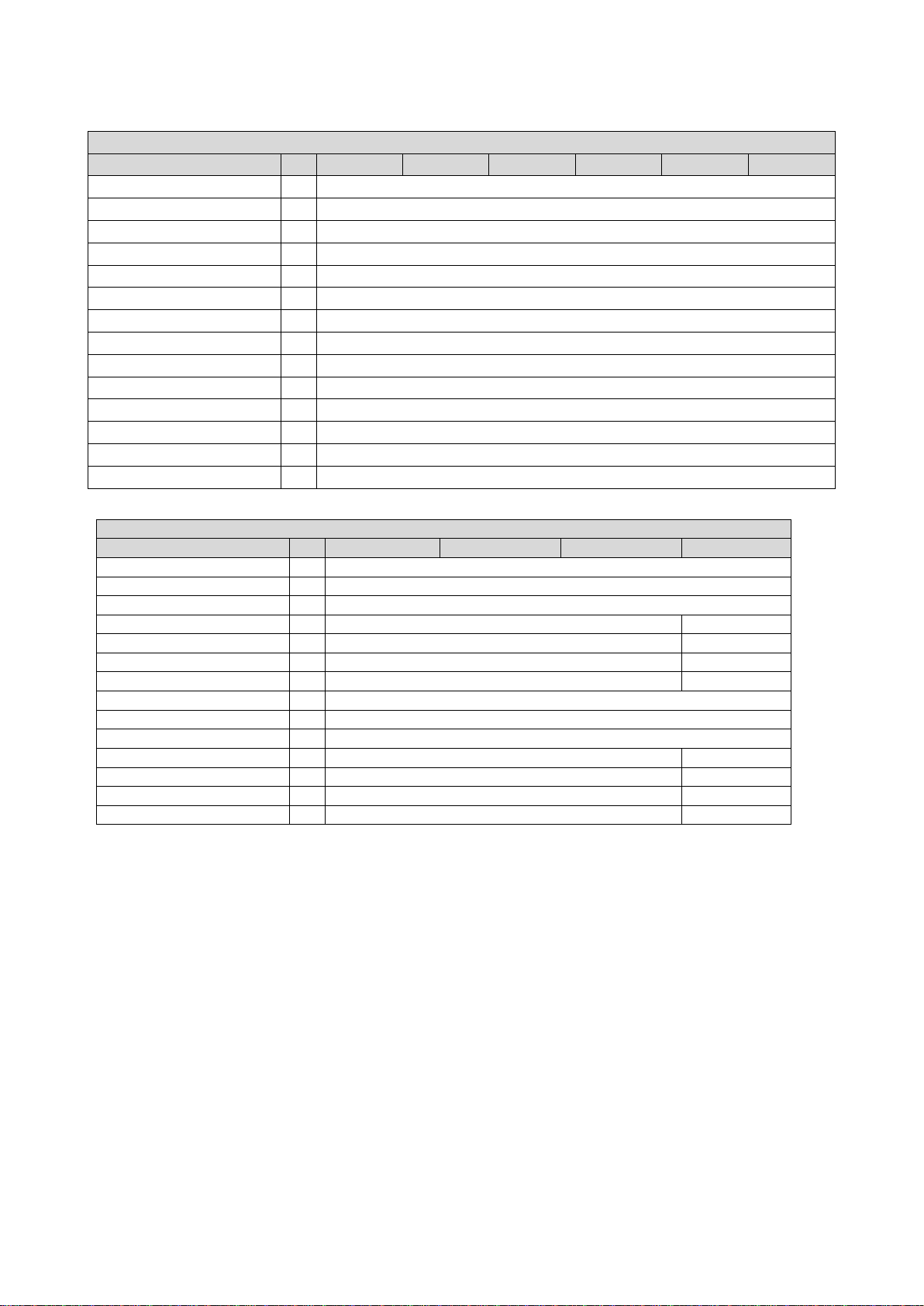
The wiring diagram is valid for Emotron VS30 inverters.
Fig. 4: Wiring example
S1 Run/Stop
Fx Fuses
Q1 Mains contactor
--Dashed line = options
3.2.4.2. Fusing and terminal data
Fuse data
Inverter
Cable installation in compliance with
EN 60204-1
Laying system
B2
Fuse
Characteristics
gG/gL or gRL
Max. rated current
A
10
10
10
16
16
16
Circuit breaker
Max. rated current
A
10
10
10
16
16
16
operation
with mains choke
Fuse
Characteristics
gG/gL or gRL
10 10 16 16 16
Circuit breaker
Characteristics
B
Max. rated current
A
10
10
10
16
16
16
Earth-leakage circuit breaker
Fuse data
Inverter
VS30-40-7P3
VS30-40-9P5
VS30-40-013
VS30-40-016
Cable installation in compliance with
EN 60204-1
Laying system
B2
without mains choke
Fuse
Characteristics
gG/gL or gRL
Circuit breaker
Characteristics
B
Max. rated current
A
25
25
25
32
operation
with mains choke
Fuse
Characteristics
gG/gL or gRL
Circuit breaker
Characteristics
B
Earth-leakage circuit breaker
3-phase mains connection
≥ 30 mA, type B
VS30-40-1P3 VS30-40-1P8 VS30-40-2P4 VS30-40-3P2 VS30-40-3P9 VS30-40-5P6
operation
Characteristics
Max. rated current
3-phase mains connection
without mains choke
B
A
10
≥ 30 mA, type B
operation
Max. rated current A 25 25 25 32
Max. rated current A 25 25 25 32
Max. rated current A 25 25 25 32
28 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation
Mains connection
Inverter
Connection
X100
Connection type
pluggable screw terminal
Max. cable cross-section
mm²
2.5
Stripping length
mm
8
Tightening torque
Nm
0.5
Required tool
0.5 x 3.0
Connection type
PE screw
Min. cable cross-section
mm²
1
Max. cable cross-section
mm² 6 Stripping length
mm
10
Required tool
0.8 x 5.5
Mains connection
Inverter
Connection
X100
Connection type
Screw terminal
Min. cable cross-section
mm²
1.5
Max. cable cross-section
mm²
6
16
Tightening torque
Nm
0.5
1.2
Required tool
0.6 x 3.5
0.8 x 4.0
Connection type
PE-screw
Min. cable cross-section
mm²
1.5
Max. cable cross-section
mm²
6
16
Stripping length
mm
10
11
Tightening torque
Nm
1.2
3.4
Required tool
0.8 x 5.5
PZ2
VS30-40-1P3 VS30-40-1P8 VS30-40-2P4 VS30-40-3P2 VS30-40-3P9 VS30-40-5P6
Min. cable cross-section
Connection
Tightening torque
mm²
Nm
1
PE
1.2
VS30-40-7P3 VS30-40-9P5 VS30-40-013 VS30-40-016
Stripping length mm 9 11
Connection
PE
Motor connection
Connection
X105
Connection type
pluggable screw terminal
Min. cable cross-section
mm² 1 Max. cable cross-section
mm²
2.5
Tightening torque
Nm
0.5
Required tool
0.5 x 3.0
Connection
PE
Connection type
PE screw
Max. cable cross-section
mm²
6
Stripping length
mm
10
Tightening torque
Nm
1.2
Required tool
0.8 x 5.5
Motor connection
Inverter
Connection
X105
Screw terminal
Min. cable cross-section
mm²
1.5
Max. cable cross-section
mm²
6
16
11
Tightening torque
Nm
0.5
1.2
Required tool
0.6 x 3.5
0.8 x 4.0
Connection
PE
Connection type
PE screw
Min. cable cross-section
mm²
1.5
Max. cable cross-section
mm²
6
16
11
Tightening torque
Nm
1.2
3.4
Required tool
0.8 x 5.5
PZ2
Inverter
Stripping length
Min. cable cross-section
Connection type
VS30-40-1P3 VS30-40-1P8 VS30-40-2P4 VS30-40-3P2 VS30-40-3P9 VS30-40-5P6
mm
mm²
VS30-40-7P3 VS30-40-9P5 VS30-40-013 VS30-40-016
8
1
Stripping length mm 9
Stripping length mm 10
30 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

3.2.5. CANopen/Modbus RTU
Line
Terminal description
CANopen/Modbus
Connection
X216
Connection type
pluggable spring
terminal
Min. cable cross-section
mm²
0.5
Max. cable cross-section
mm²
2.5
Stripping length
mm
10
Required tool
0.4 x 2.5
Typical topologies
Tightening torque
Nm
-
Basic network settings
1. Select network CANopen or Modbus using the switch on the front of the inverter
2. Set node address and baud rate via the corresponding parameters.
The network must be terminated with a 120 Ω resistor at the physically first and last
node.
Connect resistor to terminals CH/TB and CL/TA.

4. Commissioning
4.1. Important notes
WARNING!
Incorrect wiring can cause unexpected states during the commissioning phase.
Possible consequence: death, severe injuries or damage to property
Check the following before switching on the mains voltage:
Is the wiring complete and correct?
Are there no short circuits and earth faults?
Is the motor circuit configuration (star/delta) adapted to the output voltage of the inverter?
Is the motor connected in-phase (direction of rotation)?
Does the "emergency stop" function of the entire plant operate correctly?
WARNING!
Incorrect settings during commissioning may cause unexpected and dangerous motor and system movements.
Possible consequence: death, severe injuries or damage to property
Clear hazardous area.
Observe safety instructions and safety clearances.
32 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

4.2. Operating interfaces
Commissioning the inverter requires an operator-process interface.
4.2.1. Keypad
The keypad is an easy means for the local operation, parameterisation, and diagnostics of
the inverter.
• The keypad is simply connected to the diagnostic interface on the front of the inverter.
• The keypad can also be connected and removed during operation.
Detailed information on the keypad can be found in the appendix:
Operate and parameterise the inverter with keypad
446

4.2.2. Engineering tool »Emotron EASY Starter«
The »Emotron Easy starter« is a PC software that is especially designed for the
commissioning and maintenance of the inverter.
The »Emotron Easy starter« PC software can be found on the Internet:
http://easystarter.emotron.com
Sample screenshot:
34 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

4.2.2.1. Generate a connection between inverter and »Emotron Easy starter«
For commissioning the inverter with the »Emotron Easy starter«, a communication link
with the inverter is required. This can be established in a wired or wireless manner via
WLAN.
Preconditions
• For the wired communication with the inverter, the USB module and a USB 2.0 cable (A
plug on Micro-B plug) are required.
• For the wireless communication with the inverter, the WLAN module is required.
Moreover, the PC on which the »Emotron Easy starter« is installed must be wirelessenabled.

Details
The following instructions describe the connection establishment via the USB module.
• Parameterising without motor operation does not require a mains voltage: If you
connect the inverter directly to the PC without a hub, The USB interface of the PC is
sufficient for the voltage supply.
•
Instructions for the connection establishment via the WLAN module can be found in
251
the chapter "Wireless LAN (WLAN)".
How to establish a communication to the inverter via USB:
Preconditions for commissioning:
• The functional test described in the mounting and switch-on instructions has been
completed successfully (without any errors or faults).
• The inverter is ready for operation (mains voltage is switched on).
Accessories required for commissioning:
• USB module
• USB 2.0 cable (A-plug on micro B-plug)
• PC with installed »Emotron Easy starter« software
1. Plug the USB module onto the front of the inverter (interface X16).
2. Use a USB cable to connect the inverter to the PC on which »Emotron Easy starter« is
installed:
• Plug the micro B plug of the USB cable into the socket of the USB module.
• Plug the other end into a free USB type A-socket of the PC.
3. Start »Emotron Easy starter«.
• The "Add devices" dialog is shown.
4. Select the "
USB - USB with module 01-6180-00" connection:
5. Click the Insert button.
»Emotron Easy starter« searches for connected devices via the communication path
selected. When the connection has been established successfully, the inverter is displayed
in the device list of »Emotron Easy starter«. The inverter parameters can now be accessed
via the tabs of »Emotron Easy starter«.
36 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

4.3. Parameter setting
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
Index:Subindex
Parameter designation
•
Optional information with regard to the parameter.
Explanations & notes with regard to the parameter.
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
Index:Subindex
Parameter designation
•
Optional information with regard to the parameter.
Explanations & notes with regard to the parameter.
set. Other values are not permissible.
0
Designation of selection 0
Optionally: Explanations & notes with regard to the corresponding
1
Designation of selection 1
As a part of a machine with a speed-variable drive system, the inverter must be adapted
to its drive task. The adaptation process of the inverter is carried out by changing
parameters.
Optionally these parameters can be accessed by means of the keypad or »Emotron Easy
starter«. If the inverter is provided with a network option, access can also be effected by a
higher-level Controller via the corresponding network.
Certain device commands or settings which might cause a critical state of the drive
behaviour can only be carried our when the inverter is inhibited.
4.3.1. General notes on parameters
Each parameter features a 16-bit index as address. Under this address, the parameter is
stored in the object directory of the inverter.
• Parameters that belong together functionally are combined in a data set. These
parameters are additionally provided with an 8-bit subindex.
• The colon is used as a separator between the index and subindex Example:
"0x2540:001"
• There are parameters the setting of which can be changed, and (diagnostic) parameters
which can only be read.
Parameterisation using the keypad
• All parameters which can be accessed by means of the keypad are provided with a
"Display code", the first digit of the display code specifying the group in which the
parameter can be found on the keypad.
• In the documentation, the display code — if available — is specified in brackets behind
the address. Example: "0x2915 (P210.00)".
Keypad parameterisation mode
450
Structure of the parameter descriptions in this documentation
• The parameter descriptions in this documentation are structured in table form.
• The representation distinguishes parameters with a setting range, text, selection list,
and bit-coded display.
• The default setting of parameters with a write access feature is shown in bold.
• The display code as well as the short keypad designation of the parameter which is
limited to 16 characters, are — if available — shown in brackets.
Example: parameters with a setting range
(display code)
(abbreviated keypad designation)
Minimum value ... [default setting] ... maximum value
Example: parameters with a selection list
(display code)
(abbreviated keypad designation)
2 Designation of selection 2
Note: The corresponding selection number (here 0, 1, or 2) must be
selection.
The default selection is shown in bold.

Example: parameters with a bit-coded display
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
Index:Subindex
Parameter designation
•
Optional information with regard to the parameter.
Explanations & notes with regard to the parameter.
Bit 1
Designation of bit 1
Bit 2
Designation of bit 2
...
...
Bit 15
Designation of bit 15
(display code)
(abbreviated keypad designation)
Bit 0 Designation of bit 0
Optionally: Explanations & notes with regard to the corresponding bit.
Parameter overview lists in this documentation
Keypad parameter list: for the parameterisation using the keypad, contains a list of all
•
parameters which can also be accessed by means of the keypad.
•
Parameter attribute list: contains a list of all inverter parameters. This list in particular
38
includes some information that is relevant for the reading and writing of parameters
464
via the network.
38 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

4.3.2. Basic inverter settings
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
inhibi
ted.
0
230 Veff
1
400 Veff 2
0x2838:001
Start/stop configuration: Start method
ted.
Behaviour after start command.
0
Normal
After start command, the standard ramps are active.
•
Deceleration time 1 can be set in 0x2918 (P221.00).
1
DC braking
After start command, the "DC braking" function is active for the time set
2
Flying restart circuit
After the start command, the flying restart circuit is active.
0x2838:002
Start/stop configuration: Start at power-up
(Start/stop confg: Start at powerup)
Starting performance after switching on the mains voltage.
0
Off
No automatic start after switching on mains voltage. In addition to the
inverter enable, a renewed start command is always required to start the
motor.
1
On
Automatic start of the motor after switching on the mains voltage if the
inverter is enabled and a start command exists.
0x2838:003
Start/stop configuration: Stop method
(Start/stop confg: Stop method)
Behaviour after the "Stop" command.
0
Coasting
The motor becomes torqueless (coasts down to standstill).
1
Standard ramp
The motor is brought to a standstill with deceleration time 1 (or
0x283A
Limitation of rotation
(Limit. rotation)
Optional restriction of the rotating direction.
0
Only clockwise (CW)
The motor can only be rotated clockwise (CW). The transfer of negative
for this rotating direction.
1
Both rotation directions
Check the following basic settings of the inverter and adapt them, if required.
0x2540:001
(P208.01)
(P203.01)
(P203.02)
Mains settings: Rated mains voltage
(Mains settings: Mains voltage)
Setting can only be changed if the inverter is
•
480 Veff
(Start/stop confg: Start method)
Setting can only be changed if the inverter is
•
inhibi
Selection of the mains voltage for actuating the inverter.
•
Acceleration time 1 can be set in 0x2917 (P220.00).
in 0x2B84:002 (P704.02).
DC braking
262
The flying restart function makes it possible to restart a coasting motor
during operation without speed feedback. Synchronicity between the
inverter and motor is coordinated so that the transition to the rotating
motor is effected without jerk at the time of connection.
Flying restart circuit
311
(P203.03)
(P304.00)
2 Quick stop ramp
deceleration time 2, if activated).
•
Deceleration time 1 can be set in 0x2918 (P221.00).
•
Deceleration time 2 can be set in 0x291A (P223.00).
Frequency limits and ramp times
100
The motor is brought to a standstill with the deceleration time set for
the "Quick stop" function.
•
Deceleration time for quick stop can be set in 0x291C (P225.00).
The "quick stop" function can also be activated manually, for instance
•
via a digital input.
Quick stop
103
frequency and PID setpoints to the motor control is prevented.
This function takes effect after the "Invert rotation" function
•
(0x2631:013 (P400.13)).
Since this function only prevents negative setpoints, counter-
•
clock
wise rotation (CCW) is possible if the motor has been wired
Both directions of motor rotation are enabled.

Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x2860:001
Frequency control: Default setpoint source
Selection of the standard setpoint source for operating mode "MS:
1
Keypad
The setpoint is specified locally by the keypad.
2
Analog input 1
The setpoint is defined as analog signal via the analog input 1.
3
Analog input 2
The setpoint is defined as analog signal via the analog input 2.
5
Network
The setpoint is defined as process data object via the network.
11
Frequency preset 1
For the setpoint selection, preset values can be parameterised and
12
Frequency preset 2
14
Frequency preset 4
15
Frequency preset 5
16
Frequency preset 6
17
Frequency preset 7
19
Frequency preset 9
20
Frequency preset 10
21
Frequency preset 11
22
Frequency preset 12
24
Frequency preset 14
25
Frequency preset 15
31
Segment preset 1
For the setpoint selection, the segment presets parameterised for the
32
Segment preset 2
34
Segment preset 4
35
Segment preset 5
36
Segment preset 6
37
Segment preset 7
50
Motor potentiometer
The setpoint is generated by the "motor potentiometer" function. This
0x2911:001
Frequency setpoint presets: Preset 1
0.0 ... [20.0] ... 599.0 Hz
Parameterisable frequency setpoints (presets) for operating mode
0.0 ... [40.0] ... 599.0 Hz
0x2911:003
Frequency setpoint presets: Preset 3
Device for 60-Hz mains: 0.0 ... [60.0] ... 599.0 Hz
(P201.01)
(Stnd. setpoints: Freq. setp. src.)
13 Frequency preset 3
18 Frequency preset 8
Velocity mode".
The selected standard setpoint source is always active in the
•
operat
ing mode 0x6060 (P301.00) = "MS: Velocity mode [-2]"
when no setpoint change-over to another setpoint source via
corresponding triggers/functions is active.
Setpoint change-over
Default setting: 0x2601:001 (P202.01)
•
•
Use the
and
378
navigation keys to change the keypad
setpoint (also during running operation).
Analog input 1
Analog input 2
Configuring the network
423
427
166
selected.
Setpoint source of preset setpoints
386
23 Frequency preset 13
(from version 03.00)
(from version 03.00)
33 Segment preset 3 (from versi on 03.00)
(from version 03.00)
(from version 03.00)
(from version 03.00)
(from version 03.00)
38 Segment preset 8 (from versi on 03.00)
(P450.01)
0x2911:002
(P450.02)
(P450.03)
(Freq. presets: Freq. preset 1)
Frequency setpoint presets: Preset 2
(Freq. presets: Freq. preset 2)
(Freq. presets: Freq. preset 3)
Device for 50-Hz mains: 0.0 ... [50.0] ... 599.0 Hz
"sequencer" function can be selected as well.
Sequencer
327
function can be used as an alternative setpoint control which is
controlled via two signals: "MOP setpoint up" and "MOP setpoint
down".
Motor potentiometer setpoint source (MOP)
392
"MS: Velocity mode".
40 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x2915
(P210.00)
Minimum frequency
0.0 ... [0.0] ... 599.0 Hz
Lower limit value for all frequency setpoints.
0x2916
Maximum frequency
Device for 60-Hz mains: 0.0 ... [60.0] ... 599.0 Hz
Upper limit value for all frequency setpoints.
0x291C
Quick stop deceleration time
Quick stop deceleration time for the operating mode "MS: Velocity
(Min. frequency)
(P211.00)
0x2917
(P220.00)
0x2918
(P221.00)
(P225.00)
(Max. frequency)
Device for 50-Hz mains: 0.0 ... [50.0] ... 599.0 Hz
Acceleration time 1
(Accelerat.time 1)
0.0 ... [5.0] ... 3600.0 s
Deceleration time 1
(Decelerat.time 1)
0.0 ... [5.0] ... 3600.0 s
(QSP dec. time)
0.0 ... [1.0] ... 3600.0 s
Acceleration time 1 for the operating mode "MS: Velocity mode".
The acceleration time set refers to the acceleration from standstill
•
to
the maximum frequency set. In the case of a lower setpoint
selection, the actual acceleration time is reduced accordingly.
Setting is not effective in the operating mode 0x6060
•
(P301.00) =
299
Deceleration time 1 for the operating mode "MS: Velocity mode".
The deceleration time set refers to the deceleration from the
•
maxi
actual frequency, the actual deceleration time is reduced
accordingly.
Setting is not effective in the operating mode 0x6060
•
(P301.00) =
299
mode".
If the "Quick stop" function is activated, the motor is brought
•
to a
The deceleration time set refers to the deceleration from the
•
maxi
actual frequency, the actual deceleration time is reduced
accordingly.
Setting is not effective in the operating mode 0x6060
•
(P301.00) =
299
"CiA: Velocity mode [2]".
mum frequency set to standstill. In the case of a lower
"CiA: Velocity mode [2]".
standstill within the deceleration time set here.
mum frequency set to standstill. In the case of a lower
"CiA: Velocity mode [2]".
Device profile CiA 402
Device profile CiA 402
Device profile CiA 402
All possible basic settings are described in the "
Basic setting
" chapter.
89

4.3.3. Basic motor settings
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
* Default setting depending on the size.
* Default setting depending on the size.
0x2C00
Motor control mode
Selection of the motor control type.
3
Sensorless control (SL PSM)
This control type is used for the sensorless control of a synchronous
4
Sensorless vector control (SLVC)
This control type is used for sensorless vector control of an
6
V/f characteristic control (VFC open loop)
This control mode is used for the speed control of an asynchronous
0x2C01:010
Motor parameters: Motor name
The name (e.g. " 1") can be freely selected by the user.
here (example: "MDSKA080-22, 70").
Check the following default settings for the motor and motor control and adapt them, if
required.
Drive behaviour by default
By default, the V/f characteristic control with a linear characteristic is preset as motor
control for asynchronous motors. The V/f characteristic control is a motor control for
conventional frequency inverter applications. It is based on a simple and robust control
mode for the operation of asynchronous motors with a linear or square-law load torque
characteristic (e.g. fan). Because of the minimal parameterisation effort, such applications
can be commissioned easily and quickly.
The default settings of the parameters ensure that the inverter is ready for operation
immediately and the motor works adequately without further parameterization if an
inverter and an asynchronous motor* Hz asynchronous machine with matching
performances are assigned to each other.
* Depending on the device/mains frequency either 50-Hz asynchronous motor or 60-Hz
asynchronous motor.
0x2B01:001
(P303.01)
0x2B01:002
(P303.02)
(P300.00)
0x6075
(P323.00)
V/f shape data: Base voltage
(V/f shape data: Base voltage)
0 ... [230]* ... 5000 V
V/f shape data: Base frequency
(V/f shape data: Base frequency)
Device for 50-Hz mains: 0 ... [50]* ... 1500 Hz
Device for 60-Hz mains: 0 ... [60]* ... 1500 Hz
(Motor ctrl mode)
Setting can only be changed if the inverter is
•
inhibi
ted.
(from
version 02.00)
Motor rated current
(Motor current)
0.001 ... [1.700]* ... 500.000 A
* Default setting depending on the size.
Setting can only be changed if the inverter is
•
inhibi
ted.
Base voltage and base frequency define the V/f ratio and thus the
gradient of the V/f characteristic.
The V/f base voltage is usually set to the rated motor
•
voltage
0x2C01:007 (P320.07).
The V/f base frequency is usually set to the rated motor
•
frequency
motor.
Sensorless control for synchronous motors (SL-PSM)
asynchronous motor.
Sensorless vector control (SLVC)
motor via a V/f characteristic and is the simplest control mode.
V/f characteristic control (VFC)
If the motor in the engineering tool has been selected from the
"motor catalog", the respective motor name is automatically entered
The rated motor current to be set here serves as a reference value for
different parameters with a setting/display of a current value in
percent.
Example:
Motor rated current = 1.7 A
•
Max current 0x6073 (P324.00) = 200 % Motor rated current = 3.4 A
•
0x2C01:005 (P320.05).
118
115
110
All possible settings with regard to the motor and motor control are described in the
107
"Motor control" chapter.
42 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

4.3.4. Function assignment of the inputs and outputs
Parameter
Name
Default setting
Control functions
② 0x2631:004 (P400.04)
Reset fault
Digital input 2 [12]
③ 0x2631:013 (P400.13)
Invert rotation
Digital input 3 [13]
④ 0x2631:018 (P400.18)
Activate preset (bit 0)
Digital input 4 [14]
⑤ 0x2631:019 (P400.19)
Activate preset (bit 1)
Digital input 5 [15]
⑥ 0x2634:001 (P420.01)
Relay
Ready for operation [51]
⑦ 0x2634:002 (P420.02)
Digital output 1
Release holding brake [115]
⑧ 0x2634:003 (P420.03)
Digital output 2 (only for application I/O)
Error active [56]
Settings for the frequency setpoint
⑩ 0x2911:001 (P450.01)
Frequency setpoint presets: Preset 1
20 Hz ⑪
0x2911:002 (P450.02)
Frequency setpoint presets: Preset 2
40 Hz ⑫
0x2911:003 (P450.03)
Frequency setpoint presets: Preset 3
50 Hz ⑬
0x2917 (P220.00)
Acceleration time 1
5.0 s
The inverter control can be adapted individually to the respective application. This is
basically effected by assigning digital control sources ("triggers") to functions of the
inverter.
By default, the inverter can be controlled via the I/O terminals as follows:
①
0x2631:002 (P400.02) Run Digital input 1 [11]
Configuration of digital outputs
⑨
0x2860:001 (P201.01) Frequency control: Default setpoint source Analog input 1 [2]
⑭
0x2918 (P221.00) Deceleration time 1 5.0 s

Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x2631:002
Function list: Run
Assignment of a trigger for the "Run" function.
reverse) have been connected to triggers, no keypad control is active and
[1]",
•
The stop method can be selected in 0x2838:003 (P203.03).
(P400.02)
11
Digital input 1
State of X3/DI1, taking an inversion set in 0x2632:001 (P411.01) into
consideration.
0x2631:004
Function list: Reset fault
Assignment of a trigger for the "Reset fault" function.
12
Digital input 2
State of X3/DI2, taking an inversion set in 0x2632:002 (P411.02) into
consideration.
0x2631:013
Function list: Invert rotation
Assignment of a trigger for the "Invert rotation" function.
13
Digital input 3
State of X3/DI3, taking an inversion set in 0x2632:003 (P411.03) into
consideration.
0x2631:018
Function list: Activate preset (bit 0)
Assignment of a trigger for the "Activate preset (bit 0)" function.
14
Digital input 4
State of X3/DI4, taking an inversion set in 0x2632:004 (P411.04) into
consideration.
consideration.
(Function list: Run)
Setting can only be changed if the inverter is
•
inhibi
ted.
For further possible settings, see parameter
•
0x2631:001 (P400.01).
364
Function 1: Start / stop motor (default setting)
Function 1 is active if no further start commands (start forward/start
no network control is active.
Trigger = TRUE: Let motor rotate forward (CW).
Trigger = FALSE: Stop motor.
Notes to function 1:
If "Enable inverter" 0x2631:001 (P400.01) is set = "Constant TRUE
•
the only permissible trigger for this function is a digital input in order
that the motor can be stopped again any time.
•
The stop method can be selected in 0x2838:003 (P203.03).
•
The function also serves to realise an automatic start after switch-on.
Starting performance
97
Function 2: Start enable/stop motor
Function 2 is active if further start commands have been connected to
triggers, keypad control is active or network control is active.
Trigger = TRUE: Start commands of the active control source are
enabled.
Trigger = FALSE: Stop motor.
Notes to function 2:
If no separate start enable is required for the application, the trigger
•
"Constant TRUE [1]" must be set.
(P400.04)
(P400.13)
(P400.18)
(Function list: Reset fault)
For further possible settings, see parameter
•
0x2631:001 (P400.01).
364
(Function list: Invert rotation)
Setting can only be changed if the inverter is
•
inhibi
ted.
For further possible settings, see parameter
•
0x2631:001 (P400.01).
364
(Function list: Setp: Preset b0)
For further possible settings, see parameter
•
0x2631:001 (P400.01).
364
0x2631:019
(P400.19)
Function list: Activate preset (bit 1)
(Function list: Setp: Preset b1)
For further possible settings, see parameter
•
0x2631:001 (P400.01).
364
Trigger = FALSE↗TRUE (edge): Active error is reset (acknowledged) if
the
error condition is not active anymore and the error is resettable.
Trigger = FALSE: no action.
Trigger = TRUE: the setpoint specified is inverted (i. e. the sign is inverted).
Trigger = FALSE: no action / deactivate function again.
Selection bit with the valency 20 for the bit-coded selection and activation of a parameterised setpoint (preset value).
Trigger = FALSE: selection bit = "0".
Trigger = TRUE: selection bit = "1".
Assignment of a trigger for the "Activate preset (bit 1)" function.
Selection bit with the valency 21 for the bit-coded selection and activa-
tion of a parameterised setpoint (preset value).
Trigger = FALSE: selection bit = "0".
Trigger = TRUE: selection bit = "1".
44 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation
15 Digital input 5
State of X3/DI5, taking an inversion set in 0x2632:005 (P411.05) into

Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x2634:001
(P420.01)
Digital outputs function: Relay
Assignment of a trigger to the relay.
here.
and DC-bus voltage ok). Otherwise FALSE.
0x2634:002
Digital outputs function: Digital output 1
Assignment of a trigger to digital output 1.
here.
115
Release holding brake
Trigger signal for releasing the holding brake (TRUE = release holding
(Dig.out.function: Relay function)
For further possible settings, see parameter
•
0x2634:001 (P420.01).
429
Trigger = FALSE: X9/NO-COM open and NC-COM closed.
Trigger = TRUE: X9/NO-COM closed and NC-COM open.
Notes:
An inversion set in 0x2635:001 (P421.01)is taken into consideration
•
(P420.02)
51 Ready for operation
(Dig.out.function: DO1 function)
For further possible settings, see parameter
•
0x2634:001 (P420.01).
429
TRUE if inverter is ready for operation (no error active, no STO active
Trigger = FALSE: X3/DO1 set to LOW level.
Trigger = TRUE: X3/DO1 set to HIGH level.
Notes:
An inversion set in 0x2635:002 (P421.02) is taken into consideration
•
brake).
Note!
If this trigger is assigned to the relay or a digital output, the deceleration
times set for the respective output are not effective (are internally set to
"0"). Only the deceleration time set in 0x2820:012 (P712.12) for closing
the holding brake influences in this case the time-dependent behaviour
of the output.
Holding brake control
All functional possible settings for controlling the inverter are described in the "
configuration
" chapter.
487
302
Flexible I/O

4.4. Keypad parameter list
Parameter
Group name
Description
current actual values, and status messages.
P2xx
Group 2 Basic setting
Setting of the mains voltage, selection of the control and setpoint source,
P3xx
Group 3 Motor control
Configuration of the motor and motor control
P4xx
Group 4 I/O setting
Function assignment and configuration of the inputs and outputs
P5xx
Group 5 Network setting
Configuration of the network (if available)
P6xx
Group 6 Process controller
Configuration of the process controller
P7xx
Group 7 Additional functions
Parameterisable additional functions
P8xx
Group 8 Sequencer
The "sequencer" function serves to define a programmed sequence of speed
For commissioning or diagnostics using the keypad, all parameters of the inverter that can
also be accessed by means of the keypad are listed in the following "Keypad parameter
list".
• The keypad parameter list is sorted in ascending order in compliance with the "display
code" (Pxxx).
• In order to provide for quick access, all parameters of the inverter are divided into
different groups according to their function.
• Group 0 contains the configurable "Favorites". In the default setting these are the
most common parameters for the solution of typical applications. Favorites 401
• Based on the hundreds digit of the display code (Pxxx) you can quickly see in which
group the parameter is to be found on the keypad:
P1xx Group 1 Diagnostics Diagnostic/display parameters for displaying device-internal process factors,
starting and stopping performance, frequency limits and ramp times.
Basic setting
116
Motor control
Flexible I/O configuration
Configuring the network
Configuring the process controller
Additional functions
setpoints, PID setpoints or torque setpoints for the motor control. Switching to
the next setpoint can be executed in a time-based or event-based manner.
Sequencer
134
487
197
350
359
456
A complete overview of all parameter indexes can be found in the annex in the
Parameter attribute list. 623
46 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Frequently used abbreviations in the short keypad designations of the parameters:
Abbreviation
Meaning
AI
Analog input
AO
Analog output
B0, B1, ...
Bit 0, bit 1, ...
DI
Digital input
DO
Digital output
LU
Undervoltage
MOP
Motor potentiometer
OU
overvoltage
PID
Process controller
PU
Power unit
QSP
Quick stop
WD
Watchdog
Column
Meaning
Display code
Parameter number on the keypad. Format: Number.Subindex
Short designation
Short keypad designation limited to 16 characters.
Default setting
Default setting of the parameter.
Format: minimum value ... maximum value [unit]
Address
Address of the parameter in the object directory. Format: Index:Subindex
CU Control unit
NET Network
Setp Setpoint
How to read the keypad parameter list:
Setting range Possible setting range for the parameter.
Category Functional assignment of the parameter, for example "motor control" or "CANopen".

Keypad parameter list (short overview of all parameters with display code)
Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
P101.00
Scaled act value
x Units
(Read only)
0x400D
general
P102.00
Freq. setpoint
x.x Hz
(Read only)
0x2B0E
general
P103.00
Current actual
x.x %
(Read only)
0x6078
general
P104.00
Motor current
x.x A
(Read only)
0x2D88
general
P106.00
Motor voltage
x VAC
(Read only)
0x2D89
general
P107.00
Torque actual
x.x %
(Read only)
0x6077
general
P108.xx
Output power
└ P108.01
Effective power
x.xxx kW
(Read only)
0x2DA2:001
general
P109.xx
Output energy
└ P109.01
Motor
x.xx kWh
(Read only)
0x2DA3:001
general
└ P109.02
Generator
x.xx kWh
(Read only)
0x2DA3:002
general
P110.xx
AI1 diagnostics
└ P110.02
AI1 scaled freq.
x.x Hz
(Read only)
0x2DA4:002
general
└ P110.03
AI1 scaled PID
x.xx PID unit
(Read only)
0x2DA4:003
general
└ P110.04
AI1 scaled torq.
x.x %
(Read only)
0x2DA4:004
general
└ P110.16
AI1 status
- (Read only)
0x2DA4:016
general
└ P111.01
AI2 terminal %
x.x %
(Read only)
0x2DA5:001
general
└ P111.02
AI2 scaled freq.
x.x Hz
(Read only)
0x2DA5:002
general
└ P111.03
AI2 scaled PID
x.xx PID unit
(Read only)
0x2DA5:003
general
└ P111.04
AI2 scaled torq.
x.x %
(Read only)
0x2DA5:004
general
P112.xx
AO1 diagnostics
└ P112.01
AO1 Voltage
x.xx V
(Read only)
0x2DAA:001
general
└ P112.02
AO1 Current
x.xx mA
(Read only)
0x2DAA:002
general
P117.xx
Heatsink temp.
P118.00
Digital inputs
- (Read only)
0x60FD
general
P119.00
Keypad status
- (Read only)
0x2DAC
general
P120.00
Int. HW states
- (Read only)
0x2DAD
general
P121.xx
└ P121.02
PID process var.
x.xx PID unit
(Read only)
0x401F:002
general
└ P121.03
PID status
- (Read only)
0x401F:003
general
P123.00
Mot. i2t utilis.
x %
(Read only)
0x2D4F
general
P125.xx
Inverter diag.
└ P125.02
Active setpoint
- (Read only)
0x282B:002
general
└ P125.03
Keypad LCD stat.
-
(Read only)
0x282B:003
general
└ P125.04
Drive mode
-
(Read only)
0x282B:004
general
└ P125.05
Netw. contr.reg.
-
(Read only)
0x282B:005
general
* Default setting depending on the size. Firmware version 04.00.00.00
P100.00
P105.00
└ P108.02 Apparent power
└ P110.01 AI1 terminal %
P111.xx
Output frequency
DC-bus voltage
AI2 diagnostics
x.x Hz
x V
x.xxx kVA
x.x %
(Read only)
(Read only)
(Read only)
(Read only)
0x2DDD
0x2D87
0x2DA2:002
0x2DA4:001
general
general
general
general
└ P111.16 AI2 status
└ P117.01 Heatsink temp.
└ P121.01 PID setpoint
└ P125.01 Active control
-
x.x °C
x.xx PID unit
-
(Read only)
(Read only)
(Read only)
(Read only)
0x2DA5:016
0x2D84:001
0x401F:001
0x282B:001
general
general
general
general
48 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P125.06
Netw. setp.reg.
-
(Read only)
0x282B:006
general
P126.xx
└ P126.01
Cause of disable
- (Read only)
0x282A:001
general
└ P126.02
Cause of QSP
- (Read only)
0x282A:002
general
└ P126.03
Cause of stop
- (Read only)
0x282A:003
general
└ P126.05
Device status
- (Read only)
0x282A:005
general
└ P135.04
ixt utilisation
x %
(Read only)
0x2D40:004
general
└ P135.05
Error response
Fault [3]
Selection list
0x2D40:005
general
P140.xx
Sequencer diag
└ P140.01
Active Step
- (Read only)
0x2DAE:001
general
└ P140.03
StepTime remain
x.x s
(Read only)
0x2DAE:003
general
└ P140.04
Steps complete
- (Read only)
0x2DAE:004
general
└ P140.05
Steps remain
- (Read only)
0x2DAE:005
general
└ P140.06
Active sequence
- (Read only)
0x2DAE:006
general
└ P140.08
SeqTime remain %
x %
(Read only)
0x2DAE:008
general
└ P140.09
SeqTime remain
x.x s
(Read only)
0x2DAE:009
general
P150.00
Error code
- (Read only)
0x603F
general
P151.xx
Life-diagnosis
└ P151.02
Power-on time
x s
(Read only)
0x2D81:002
general
└ P151.03
CU oper. time
x ns
(Read only)
0x2D81:003
general
└ P151.04
Switching cycles
- (Read only)
0x2D81:004
general
└ P151.05
Relay cycles
- (Read only)
0x2D81:005
general
└ P151.07
Earthfault count
- (Read only)
0x2D81:007
general
└ P151.08
Clamp active
- (Read only)
0x2D81:008
general
└ P151.09
Fan oper. time
x s
(Read only)
0x2D81:009
general
P155.xx
Fault memory
P190.xx └ P190.01
Product code
- (Read only)
0x2000:001
general
└ P190.02
Serial number
- (Read only)
0x2000:002
general
└ P190.04
CU firmware ver.
- (Read only)
0x2000:004
general
└ P190.06
CU bootlder ver.
- (Read only)
0x2000:006
general
└ P190.07
CU bootlder type
- (Read only)
0x2000:007
general
└ P190.08
OBD version
- (Read only)
0x2000:008
general
└ P190.10
PU firmware ver.
- (Read only)
0x2000:010
general
└ P190.12
PU bootlder ver.
- (Read only)
0x2000:012
general
└ P190.13
PU bootlder type
- (Read only)
0x2000:013
general
P191.00
Device name
My Device
Text
0x2001
general
P197.00
Protect. status
- (Read only)
0x2040
general
P200.00
Control select.
Flexible I/O [0]
Selection list
0x2824
general
Status words
P135.xx
└ P140.02 StepTime elapsed
└ P140.07 Active segment
└ P151.01 Operating time
└ P151.06 Short-circ.count
Device utilisat.
x.x s
-
x s
-
(Read only)
(Read only)
(Read only)
(Read only)
0x2DAE:002
0x2DAE:007
0x2D81:001
0x2D81:006
general
general
general
general
└ P155.00 Error memory
└ P190.05 CU firmware type
└ P190.11 PU firmware type
P198.00
Status load. par
-
-
-
-
(Read only)
(Read only)
(Read only)
(Read only)
0x2006:000
0x2000:005
0x2000:011
0x2827
general
general
general
general

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
P201.xx
Stnd. setpoints
└ P201.01 Freq. setp. src.
└ P201.02
PID setp. src.
Keypad [1]
Selection list
0x2860:002
general
└ P201.03
Torque setp.src.
Analog input 1 [2]
Selection list
0x2860:003
general
P202.xx
Keypad setpoints
└ P202.01
KP freq.setpoint
20.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2601:001
general
└ P202.03
KP torq.setpoint
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x2601:003
general
P203.xx
Start/stop confg
└ P203.01
Start method
Normal [0]
Selection list
0x2838:001
general
└ P203.02
Start at powerup
Off [0]
Selection list
0x2838:002
general
P208.xx
Mains settings
└ P208.01
Mains voltage
230 Veff [0]
Selection list
0x2540:001
general
└ P208.02
LU warn. thresh.
0 V *
0 ... 800 V
0x2540:002
general
└ P208.03
LU error thresh.
x V
(Read only)
0x2540:003
general
└ P208.05
OU warn. thresh.
0 V *
0 ... 800 V
0x2540:005
general
└ P208.06
OU error thresh.
x V
(Read only)
0x2540:006
general
└ P208.07
OU reset thresh.
x V
(Read only)
0x2540:007
general
P210.00
Min. frequency
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2915
general
60.0 Hz
P220.00
Accelerat.time 1
5.0 s
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
0x2917
general
P221.00
Decelerat.time 1
5.0 s
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
0x2918
general
P223.00
Decelerat.time 2
5.0 s
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
0x291A
general
P224.00
Ramp 2 thresh.
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x291B
general
P225.00
QSP dec. time
1.0 s
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
0x291C
general
P226.xx
S-ramp char.
P230.xx
Optical tracking
└ P230.01
Start detection
Stop [0]
Selection list
0x2021:001
general
└ P230.02
Blink. duration
5 s
0 ... 3600 s
0x2021:002
general
P300.00
Motor ctrl mode
VFC open loop [6]
Selection list
0x2C00
general
P302.00
V/f charac.shape
Linear [0]
Selection list
0x2B00
general
P303.xx
V/f shape data
└ P303.01
Base voltage
230 V *
0 ... 5000 V
0x2B01:001
MCTRL
└ P303.02
Base frequency
Device for 50-Hz mains:
60 Hz *
0 ... 1500 Hz
0x2B01:002
MCTRL
└ P303.04
Midpoint freq
0 Hz
0 ... 1500 Hz
0x2B01:004
MCTRL
P304.00
Limit. rotation
Both directions [1]
Selection list
0x283A
general
P305.00
Switching freq.
0 *
Selection list
0x2939
general
P308.xx
Motor overload
Analog input 1 [2]
Selection list
0x2860:001
general
└ P202.02 KP PID setpoint
└ P203.03 Stop method
└ P208.04 LU reset thresh.
P211.00
P222.00
Max. frequency
Accelerat.time 2
0.00 PID unit
Standard ramp [1]
x V
Device for 50-Hz mains:
50.0 Hz
Device for 60-Hz mains:
5.0 s
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
Selection list
(Read only)
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
0x2601:002
0x2838:003
0x2540:004
0x2916
0x2919
general
general
general
general
general
P301.00
50 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation
└ P226.01 Smoothing factor
Modes of op.
└ P303.03 Midpoint voltage
0.0 %
MS: Velocitymode [-2]
50 Hz
Device for 60-Hz mains:
0 V
0.0 ... 100.0 %
Selection list
0 ... 5000 V
0x291E:001
0x6060
0x2B01:003
general
general
MCTRL

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P308.01
Max.load.for 60s
150 %
30 ... 200 %
0x2D4B:001
general
└ P308.02 Speed comp.
└ P308.03
Response
Fault [3]
Selection list
0x2D4B:003
general
P310.xx
Mot.phase.fail.
└ P310.01
Response
No response [0]
Selection list
0x2D45:001
general
└ P310.02
Current thresh.
5.0 %
1.0 ... 25.0 %
0x2D45:002
general
P315.xx
Slip compens.
└ P315.01
Slip: gain
100.00 %
-200.00 ... 200.00 %
0x2B09:001
general
└ P315.02
Filter time
5 ms
1 ... 6000 ms
0x2B09:002
general
P316.xx
V/f boosts
└ P316.02
Dynam. V/f boost
0.0 %
0.0 ... 20.0 %
0x2B12:002
general
P317.xx
Skip frequencies
└ P317.01
Skip frequency 1
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x291F:001
general
└ P317.02
Skip bandwidth 1
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 10.0 Hz
0x291F:002
general
└ P317.04
Skip bandwidth 2
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 10.0 Hz
0x291F:004
general
└ P317.05
Skip frequency 3
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x291F:005
general
└ P317.06
Skip bandwidth 3
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 10.0 Hz
0x291F:006
general
P318.xx
Oscillat. damp.
└ P318.02
Filter time
5 ms
1 ... 600 ms
0x2B0A:002
MCTRL
P319.00
Field weak thold
0.0 Hz
-599.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2B0C
general
P320.xx
Motor parameters
└ P320.04
Rated speed
Device for 50-Hz mains:
1750 rpm
50 ... 50000 rpm
0x2C01:004
MCTRL
└ P320.05
Rated frequency
Device for 50-Hz mains:
60.0 Hz
1.0 ... 1000.0 Hz
0x2C01:005
MCTRL
└ P320.06
Rated power
0.25 kW *
0.00 ... 655.35 kW
0x2C01:006
MCTRL
└ P320.07
Rated voltage
230 V *
0 ... 65535 V
0x2C01:007
MCTRL
P322.00
Max motor speed
6075 rpm
0 ... 480000 rpm
0x6080
general
P323.00
Motor current
1.700 A *
0.001 ... 500.000 A
0x6075
MCTRL
P324.00
Max current
200.0 %
0.0 ... 3000.0 %
0x6073
general
P325.00
Motor torque
1.650 Nm *
0.001 ... 1000.000 Nm
0x6076
MCTRL
└ P327.04
Identify mot.
0
0 ... 1
0x2822:004
general
└ P327.05
Calibrate mot.
0
0 ... 1
0x2822:005
general
P329.xx
MaxTrq.Monitor
└ P329.01
Response
No response [0]
Selection list
0x2D67:001
MCTRL
P330.xx
VFC-ECO
└ P330.01
Min. voltage
20 %
20 ... 100 %
0x2B0D:001
MCTRL
P332.xx
Speed controller
└ P332.01
Gain
0.00193 Nm/rpm *
0.00000 ...
20000.00000 Nm/rpm
0x2900:001
MCTRL
On [0]
Selection list
0x2D4B:002
general
└ P310.03 Voltage thresh.
└ P316.01 Fixed V/f boost
└ P317.03 Skip frequency 2
└ P318.01 Gain
10.0 V
2.5 % *
0.0 Hz
20 %
1450 rpm
Device for 60-Hz mains:
0.0 ... 100.0 V
0.0 ... 20.0 %
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
-100 ... 100 %
0x2D45:003
0x2B12:001
0x291F:003
0x2B0A:001
general
MCTRL
general
MCTRL
P326.00
└ P320.08 Cosine phi
Max torque
└ P329.02 Triggering delay
50.0 Hz
Device for 60-Hz mains:
0.80
250.0 %
0.000 s
0.00 ... 1.00
0.0 ... 3000.0 %
0.000 ... 10.000 s
0x2C01:008
0x6072
0x2D67:002
MCTRL
general
MCTRL

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P332.02
Reset time
80.0 ms *
1.0 ... 6000.0 ms
0x2900:002
MCTRL
P333.xx
└ P333.01
Gain
0.284 Hz/A *
0.000 ... 1000.000 Hz/A
0x2B08:001
MCTRL
└ P333.02
Reset time
2.3 ms *
1.0 ... 2000.0 ms
0x2B08:002
MCTRL
P334.xx
Current contr.
└ P334.01
Gain
42.55 V/A *
0.00 ... 750.00 V/A
0x2942:001
MCTRL
P335.xx
Moment of inert.
└ P335.01
Motor inertia
3.70 kg cm² *
0.00 ... 20000000.00 kg cm²
0x2910:001
MCTRL
└ P335.02
Load inertia
3.70 kg cm² *
0.00 ... 20000000.00 kg cm²
0x2910:002
MCTRL
└ P336.02
Ramp time
1.0 s
0.0 ... 60.0 s
0x2948:002
general
└ P337.01
Pos. torqlim src
Max torque [0]
Selection list
0x2949:001
general
└ P337.02
Neg. torqlim src
(-) Max torque [0]
Selection list
0x2949:002
general
└ P337.03
Act postorqlim
x.x %
(Read only)
0x2949:003
general
└ P337.04
Act negtorqlim
x.x %
(Read only)
0x2949:004
general
└ P340.01
Upper limit
0 vel. unit
-480000 ... 480000 vel. unit
0x2946:001
general
└ P340.02
Lower limit
0 vel. unit
-480000 ... 480000 vel. unit
0x2946:002
general
└ P340.03
Uppspeed lim src
Max. frequency [0]
Selection list
0x2946:003
general
└ P340.04
Lowspeed lim src
(-) Max. freq. [0]
Selection list
0x2946:004
general
60.0 Hz
└ P340.06
Lower freq.limit
Device for 50-Hz mains:
-60.0 Hz
-1000.0 ... 1000.0 Hz
0x2946:006
general
└ P340.07
Act uppspeed lim
x.x Hz
(Read only)
0x2946:007
general
P350.xx
Overspeed monit.
└ P350.01
Threshold
8000 rpm
50 ... 50000 rpm
0x2D44:001
general
└ P350.02
Response
Fault [3]
Selection list
0x2D44:002
general
P351.xx
ASM motor par.
└ P351.02
Mutual induct.
381.9 mH *
0.0 ... 50000.0 mH
0x2C02:002
MCTRL
└ P351.03
Magn. current
0.96 A *
0.00 ... 500.00 A
0x2C02:003
MCTRL
└ P351.04
Slip frequency
x.x Hz
(Read only)
0x2C02:004
general
P352.xx
PSM motor par.
P353.xx
Overcurr. monit.
└ P353.01
Threshold
6.8 A *
0.0 ... 1000.0 A
0x2D46:001
general
└ P353.02
Response
Fault [3]
Selection list
0x2D46:002
general
P354.00
Voltage reserve
5 %
1 ... 20 %
0x29E4
general
└ P400.01
Enable inverter
TRUE [1]
Selection list
0x2631:001
general
└ P400.02
Run
Digital input 1 [11]
Selection list
0x2631:002
general
└ P400.03
Quick stop
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:003
general
└ P400.04
Reset fault
Digital input 2 [12]
Selection list
0x2631:004
general
V/f Imax contr.
└ P334.02 Reset time
P337.xx
P340.xx
└ P340.05 Upper freq.limit
Speed limitation
4.50 ms *
Device for 50-Hz mains:
50.0 Hz
Device for 60-Hz mains:
-50.0 Hz
Device for 60-Hz mains:
0.01 ... 2000.00 ms
-1000.0 ... 1000.0 Hz
0x2942:002
0x2946:005
MCTRL
general
└ P340.08 Act lowspeed lim
└ P351.01 Rotor resistance
└ P352.01 BEMF constant
P400.xx
Function list
x.x Hz
8.8944 Ω *
41.8 V/1000rpm
(Read only)
0.0000 ... 200.0000 Ω
0.0 ... 100000.0 V/1000rpm 0x2C03:001
0x2946:008
0x2C02:001
general
MCTRL
MCTRL
52 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P400.05
DC braking
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:005
general
└ P400.06 Start forward
└ P400.07
Start reverse
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:007
general
└ P400.08
Run forward
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:008
general
└ P400.09
Run reverse
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:009
general
└ P400.10
Jog foward
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:010
general
└ P400.12
Keypad control
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:012
general
└ P400.13
Invert rotation
Digital input 3 [13]
Selection list
0x2631:013
general
└ P400.14
Setp: AI1
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:014
general
└ P400.15
Setp: AI2
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:015
general
└ P400.17
Setp: Network
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:017
general
└ P400.18
Setp: Preset b0
Digital input 4 [14]
Selection list
0x2631:018
general
└ P400.19
Setp: Preset b1
Digital input 5 [15]
Selection list
0x2631:019
general
└ P400.20
Setp: Preset b2
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:020
general
└ P400.23
MOP up
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:023
general
└ P400.24
MOP down
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:024
general
└ P400.25
Setp: MOP
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:025
general
└ P400.26
Setp: Segment b0
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:026
general
0x2631:027
└ P400.28
Setp: Segment b2
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:028
general
└ P400.29
Setp: Segment b3
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:029
general
└ P400.30
Seq: Run/abort
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:030
general
└ P400.31
Seq: Start
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:031
general
0x2631:032
└ P400.33
Seq: Pause
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:033
general
└ P400.34
Seq: Suspense
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:034
general
└ P400.35
Seq: Stop
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:035
general
└ P400.36
Seq: Abort
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:036
general
0x2631:037
└ P400.39
Activ. ramp 2
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:039
general
└ P400.40
Load param.set
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:040
general
└ P400.41
Sel. paramset b0
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:041
general
└ P400.42
Sel. paramset b1
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:042
general
0x2631:043
└ P400.44
Fault 2
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:044
general
└ P400.45
PID off
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:045
general
└ P400.46
PID output=0
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:046
general
└ P400.47
PID-I inhibited
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:047
general
0x2631:048
└ P400.49
Release brake
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:049
general
└ P400.50
Seq: Select. b0
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:050
general
└ P400.51
Seq: Select. b1
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:051
general
└ P400.52
Seq: Select. b2
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:052
general
0x2631:053
└ P400.54
PosCounter reset
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:054
general
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2631:006
general
└ P400.11 Jog reverse
└ P400.16 Setp: Keypad
└ P400.21 Setp: Preset b3
└ P400.27 Setp: Segment b1 Not connected [0] Selection list
└ P400.32 Seq: Next step Not connected [0] Selection list
Not connected [0]
Not connected [0]
Not connected [0]
Selection list
Selection list
Selection list
0x2631:011
0x2631:016
0x2631:021
general
general
general
general
general
└ P400.37 Network control Not connected [0] Selection list
└ P400.43 Fault 1 Not connected [0] Selection list
└ P400.48 PID-Inf ramp on TRUE [1] Selection list
└ P400.53 Seq: Select. b3 Not connected [0] Selection list
general
general
general
general

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
P410.xx
DI settings
└ P410.02 Input function
P411.xx
DI inversion
└ P411.01
DI1 inversion
Not inverted [0]
Selection list
0x2632:001
general
└ P411.02
DI2 inversion
Not inverted [0]
Selection list
0x2632:002
general
└ P411.03
DI3 inversion
Not inverted [0]
Selection list
0x2632:003
general
└ P411.05
DI5 inversion
Not inverted [0]
Selection list
0x2632:005
general
P412.00
Freq. threshold
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x4005
general
P413.00
MOP startmode
Last value [0]
Selection list
0x4003
general
P414.xx
MOP start value
└ P414.02
PID value
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x4004:002
general
└ P414.03
Torque
0.0 %
0.0 ... 1000.0 %
0x4004:003
general
P420.xx
Dig.out.function
└ P420.01
Relay function
Rdy for operat. [51]
Selection list
0x2634:001
general
└ P420.10
NetWordOUT1.00
Rdy for operat. [51]
Selection list
0x2634:010
general
└ P420.11
NetWordOUT1.01
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2634:011
general
└ P420.12
NetWordOUT1.02
Operat. enabled [52]
Selection list
0x2634:012
general
└ P420.13
NetWordOUT1.03
Error [56]
Selection list
0x2634:013
general
└ P420.15
NetWordOUT1.05
Quick stop [54]
Selection list
0x2634:015
general
└ P420.16
NetWordOUT1.06
Running [50]
Selection list
0x2634:016
general
└ P420.17
NetWordOUT1.07
Device warning [58]
Selection list
0x2634:017
general
└ P420.18
NetWordOUT1.08
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0x2634:018
general
0x2634:019
└ P420.20
NetWordOUT1.10
Speed setp=act [72]
Selection list
0x2634:020
general
└ P420.21
NetWordOUT1.11
At current limit [78]
Selection list
0x2634:021
general
└ P420.22
NetWordOUT1.12
Actual speed=0 [71]
Selection list
0x2634:022
general
└ P420.23
NetWordOUT1.13
Rot.dir.reversed [69]
Selection list
0x2634:023
general
0x2634:024
└ P420.25
NetWordOUT1.15
Safe Torque Off [55]
Selection list
0x2634:025
general
P421.xx
DO inversion
└ P421.01
Relay inverted
Not inverted [0]
Selection list
0x2635:001
general
└ P421.02
DO1 inversion
Not inverted [0]
Selection list
0x2635:002
general
└ P430.01
AI1 input range
0 ... 10 VDC [0]
Selection list
0x2636:001
general
└ P430.02
AI1 freq @ min
0.0 Hz
-1000.0 ... 1000.0 Hz
0x2636:002
general
└ P430.03
AI1 freq @ max
Device for 50-Hz mains:
60.0 Hz
-1000.0 ... 1000.0 Hz
0x2636:003
general
└ P430.04
AI1 PID @ min
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x2636:004
general
└ P430.05
AI1 PID @ max
100.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x2636:005
general
└ P430.06
AI1 filter time
10 ms
0 ... 10000 ms
0x2636:006
general
└ P430.07
AI1 dead band
0.0 %
0.0 ... 100.0 %
0x2636:007
general
└ P430.09
AI1 monit.cond.
IN < threshold [0]
Selection list
0x2636:009
general
Digital Input [0]
Selection list
0x2630:002
general
└ P411.04 DI4 inversion
└ P414.01 Frequency
└ P420.02 DO1 function
└ P420.14 NetWordOUT1.04
└ P420.19 NetWordOUT1.09 Not connected [0] Selection list
Not inverted [0]
0.0 Hz
Release brake [115]
Not connected [0]
Selection list
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
Selection list
Selection list
0x2632:004
0x4004:001
0x2634:002
0x2634:014
general
general
general
general
general
P430.xx
54 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation
└ P420.24 NetWordOUT1.14 Release brake [115] Selection list
Analog input 1
50.0 Hz
Device for 60-Hz mains:
└ P430.08 AI1 monit.level
0.0 %
-100.0 ... 100.0 %
0x2636:008
general
general

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P430.10
AI1 error resp.
Fault [3]
Selection list
0x2636:010
general
└ P430.11 Min. torque
└ P430.12
Max. torque
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x2636:012
general
P431.xx
Analog input 2
└ P431.01
AI2 input range
0 ... 10 VDC [0]
Selection list
0x2637:001
general
└ P431.02
AI2 freq @ min
0.0 Hz
-1000.0 ... 1000.0 Hz
0x2637:002
general
60.0 Hz
└ P431.04
AI2 PID @ min
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x2637:004
general
└ P431.05
AI2 PID @ max
100.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x2637:005
general
└ P431.07
AI2 dead band
0.0 %
0.0 ... 100.0 %
0x2637:007
general
└ P431.08
AI2 monit.level
0.0 %
-100.0 ... 100.0 %
0x2637:008
general
└ P431.09
AI2 error resp.
IN < threshold [0]
Selection list
0x2637:009
general
└ P431.10
AI2 error resp.
Fault [3]
Selection list
0x2637:010
general
└ P431.12
Max. torque
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x2637:012
general
P440.xx
Analog output 1
└ P440.01
AO1 outp. range
0 ... 10 VDC [1]
Selection list
0x2639:001
general
└ P440.02
AO1 function
Outp. frequency [1]
Selection list
0x2639:002
general
└ P440.04
AO1 max. signal
1000
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x2639:004
general
P450.xx
Freq. presets
└ P450.01
Freq. preset 1
20.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2911:001
general
└ P450.02
Freq. preset 2
40.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2911:002
general
60.0 Hz
0x2911:003
└ P450.04
Freq. preset 4
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2911:004
general
└ P450.05
Freq. preset 5
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2911:005
general
└ P450.06
Freq. preset 6
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2911:006
general
0x2911:007
└ P450.08
Freq. preset 8
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2911:008
general
└ P450.09
Freq. preset 9
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2911:009
general
└ P450.10
Freq. preset 10
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2911:010
general
└ P450.11
Freq. preset 11
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2911:011
general
0x2911:012
└ P450.13
Freq. preset 13
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2911:013
general
└ P450.14
Freq. preset 14
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2911:014
general
└ P450.15
Freq. preset 15
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2911:015
general
P451.xx
PID presets
└ P451.02
PID preset 2
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x4022:002
general
└ P451.03
PID preset 3
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x4022:003
general
└ P451.04
PID preset 4
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x4022:004
general
└ P451.05
PID preset 5
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x4022:005
general
0.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x2636:011
general
└ P431.03 AI2 freq @ max
└ P431.06 AI2 filter time
└ P431.11 Min. torque
└ P440.03 AO1 min. signal
└ P450.03 Freq. preset 3 Device for 50-Hz mains:
Device for 50-Hz mains:
50.0 Hz
Device for 60-Hz mains:
10 ms
0.0 %
0
50.0 Hz
Device for 60-Hz mains:
-1000.0 ... 1000.0 Hz
0 ... 10000 ms
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x2639:003
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2637:003
0x2637:006
0x2637:011
general
general
general
general
general
└ P450.07 Freq. preset 7 0.0 Hz 0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
└ P450.12 Freq. preset 12 0.0 Hz 0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
└ P451.01 PID preset 1
└ P451.06 PID preset 6
0.00 PID unit
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x4022:001
0x4022:006
general
general
general
general

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P451.07
PID preset 7
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x4022:007
general
└ P451.08 PID preset 8
P452.xx
Torque presets
└ P452.01
Torque preset 1
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x2912:001
general
└ P452.02
Torque preset 2
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x2912:002
general
└ P452.03
Torque preset 3
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x2912:003
general
└ P452.05
Torque preset 5
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x2912:005
general
└ P452.06
Torque preset 6
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x2912:006
general
└ P452.07
Torque preset 7
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x2912:007
general
└ P452.08
Torque preset 8
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x2912:008
general
└ P500.01
Active module ID
- (Read only)
0x231F:001
general
└ P500.02
Module ID conn.
- (Read only)
0x231F:002
general
P505.xx
NetWordIN1 fct.
└ P505.01
NetWordIN1.00
Not active [0]
Selection list
0x400E:001
general
└ P505.03
NetWordIN1.02
Quick stop [3]
Selection list
0x400E:003
general
└ P505.04
NetWordIN1.03
Not active [0]
Selection list
0x400E:004
general
└ P505.05
NetWordIN1.04
Run forward [8]
Selection list
0x400E:005
general
└ P505.06
NetWordIN1.05
Setp: Preset b0 [18]
Selection list
0x400E:006
general
└ P505.08
NetWordIN1.07
Reset error [4]
Selection list
0x400E:008
general
└ P505.09
NetWordIN1.08
Not active [0]
Selection list
0x400E:009
general
└ P505.10
NetWordIN1.09
DC braking [5]
Selection list
0x400E:010
general
└ P505.11
NetWordIN1.10
Not active [0]
Selection list
0x400E:011
general
└ P505.13
NetWordIN1.12
Invert rotation [13]
Selection list
0x400E:013
general
└ P505.14
NetWordIN1.13
Not active [0]
Selection list
0x400E:014
general
└ P505.15
NetWordIN1.14
Not active [0]
Selection list
0x400E:015
general
└ P505.16
NetWordIN1.15
Not active [0]
Selection list
0x400E:016
general
0x2300
P508.00
Modbus comm.
No action [0]
Selection list
0x2320
Modbus RTU
P509.00
CANopen switch
-
(Read only)
0x2303
CANopen
P509.00
Modbus switch
-
(Read only)
0x2323
Modbus RTU
P510.xx
CANopen sett.
└ P510.02
Baud rate
500 kbps [5]
Selection list
0x2301:002
CANopen
└ P510.03
Slave/Master
Slave [0]
Selection list
0x2301:003
CANopen
└ P510.04
Start rem. delay
3000 ms
0 ... 65535 ms
0x2301:004
CANopen
└ P510.05
SDO2 channel
Not active [0]
Selection list
0x2301:005
CANopen
P510.xx
Modbus sett.
└ P510.01
Node ID
1
1 ... 247
0x2321:001
Modbus RTU
└ P510.02
Baud rate
Automatic [0]
Selection list
0x2321:002
Modbus RTU
└ P510.03
Data format
Automatic [0]
Selection list
0x2321:003
Modbus RTU
P511.xx
CANopen diag.
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x4022:008
general
└ P452.04 Torque preset 4
P500.xx
└ P505.02 NetWordIN1.01
└ P505.07 NetWordIN1.06
└ P505.12 NetWordIN1.11
Module ID
100.0 %
Not active [0]
Setp: Preset b1 [19]
Not active [0]
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
Selection list
Selection list
Selection list
0x2912:004
0x400E:002
0x400E:007
0x400E:012
general
general
general
general
P508.00 CANopen comm. No action [0] Selection list
└ P510.01 Node ID
└ P510.06 COB-ID Config
└ P510.04 Min. resp. time
1
Base + node-ID [0]
0 ms
1 ... 127
Selection list
0 ... 1000 ms
0x2301:001
0x2301:006
0x2321:004
CANopen
CANopen
CANopen
Modbus RTU
56 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P511.01
Active node ID
- (Read only)
0x2302:001
CANopen
└ P511.02 Active baud rate
P511.xx
Modbus diag.
└ P511.01
Active node ID
- (Read only)
0x2322:001
Modbus RTU
└ P511.02
Active baud rate
- (Read only)
0x2322:002
Modbus RTU
└ P511.03
Data format
- (Read only)
0x2322:003
Modbus RTU
P515.xx
Modbus monit.
└ P515.01
Resp. Time-out
Fault [3]
Selection list
0x2858:001
Modbus RTU
└ P515.02
Time-out time
2.0 s
0.0 ... 300.0 s
0x2858:002
Modbus RTU
P516.00
CANopen status
- (Read only)
0x2308
CANopen
P518.00
CAN errorcounter
- (Read only)
0x230B
CANopen
P520.xx
Cons. heartbeat
└ P520.00
Highest subindex
- (Read only)
0x1016:000
CANopen
└ P520.01
Cons. heartbeat1
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0x00FFFFFF
0x1016:001
CANopen
└ P520.03
Cons. heartbeat3
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0x00FFFFFF
0x1016:003
CANopen
└ P520.04
Cons. heartbeat4
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0x00FFFFFF
0x1016:004
CANopen
P522.00
Prod. heartbeat
0 ms
0 ... 65535 ms
0x1017
CANopen
P530.xx
Para. mapping
└ P530.02
Parameter 2
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:002
Modbus RTU
└ P530.03
Parameter 3
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:003
Modbus RTU
└ P530.04
Parameter 4
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:004
Modbus RTU
└ P530.05
Parameter 5
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:005
Modbus RTU
└ P530.07
Parameter 7
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:007
Modbus RTU
└ P530.08
Parameter 8
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:008
Modbus RTU
└ P530.09
Parameter 9
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:009
Modbus RTU
└ P530.10
Parameter 10
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:010
Modbus RTU
└ P530.12
Parameter 12
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:012
Modbus RTU
└ P530.13
Parameter 13
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:013
Modbus RTU
└ P530.14
Parameter 14
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:014
Modbus RTU
└ P530.15
Parameter 15
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:015
Modbus RTU
└ P530.17
Parameter 17
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:017
Modbus RTU
└ P530.18
Parameter 18
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:018
Modbus RTU
└ P530.19
Parameter 19
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:019
Modbus RTU
└ P530.20
Parameter 20
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:020
Modbus RTU
0x232B:021
└ P530.22
Parameter 22
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:022
Modbus RTU
└ P530.23
Parameter 23
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:023
Modbus RTU
└ P530.24
Parameter 24
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x232B:024
Modbus RTU
P531.xx
Reg. assigned
└ P531.02
Register 2
- (Read only)
0x232C:002
Modbus RTU
-
(Read only)
0x2302:002
CANopen
P515.00
P517.00
└ P520.02 Cons. heartbeat2
└ P530.01 Parameter 1
└ P530.06 Parameter 6
Time-out status
CAN contr.status
-
-
0x00000000
0x00000000
0x00000000
(Read only)
(Read only)
0x00000000 ... 0x00FFFFFF 0x1016:002
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00 0x232B:001
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00 0x232B:006
0x2307
0x2309
CANopen
CANopen
CANopen
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU
└ P530.11 Parameter 11
└ P530.16 Parameter 16
└ P530.21 Parameter 21 0x00000000 0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
└ P531.01 Register 1
0x00000000
0x00000000
-
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00 0x232B:011
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00 0x232B:016
(Read only)
0x232C:001
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P531.03
Register 3
- (Read only)
0x232C:003
Modbus RTU
└ P531.04 Register 4
└ P531.05
Register 5
- (Read only)
0x232C:005
Modbus RTU
└ P531.06
Register 6
- (Read only)
0x232C:006
Modbus RTU
└ P531.07
Register 7
- (Read only)
0x232C:007
Modbus RTU
└ P531.08
Register 8
- (Read only)
0x232C:008
Modbus RTU
└ P531.10
Register 10
- (Read only)
0x232C:010
Modbus RTU
└ P531.11
Register 11
- (Read only)
0x232C:011
Modbus RTU
└ P531.12
Register 12
- (Read only)
0x232C:012
Modbus RTU
└ P531.13
Register 13
- (Read only)
0x232C:013
Modbus RTU
└ P531.15
Register 15
- (Read only)
0x232C:015
Modbus RTU
└ P531.16
Register 16
- (Read only)
0x232C:016
Modbus RTU
└ P531.17
Register 17
- (Read only)
0x232C:017
Modbus RTU
└ P531.18
Register 18
- (Read only)
0x232C:018
Modbus RTU
└ P531.20
Register 20
- (Read only)
0x232C:020
Modbus RTU
└ P531.21
Register 21
- (Read only)
0x232C:021
Modbus RTU
└ P531.22
Register 22
- (Read only)
0x232C:022
Modbus RTU
└ P531.23
Register 23
- (Read only)
0x232C:023
Modbus RTU
P532.00
Verificationcode
- (Read only)
0x232D
Modbus RTU
P540.xx
RPDO1 config.
└ P540.01
COB-ID
0x00000200
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFFFF
0x1400:001
CANopen
└ P540.02
Transm. type
255
0 ... 255
0x1400:002
CANopen
P541.xx
RPDO2 config.
└ P541.01
COB-ID
0x80000300
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFFFF
0x1401:001
CANopen
└ P541.02
Transm. type
255
0 ... 255
0x1401:002
CANopen
└ P541.05
Event timer
100 ms
0 ... 65535 ms
0x1401:005
CANopen
└ P542.01
COB-ID
0x80000400
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFFFF
0x1402:001
CANopen
└ P542.02
Transm. type
255
0 ... 255
0x1402:002
CANopen
└ P542.05
Event timer
100 ms
0 ... 65535 ms
0x1402:005
CANopen
P550.xx
TPDO1 config.
└ P550.02
Transm. type
255
0 ... 255
0x1800:002
CANopen
└ P550.03
Inhibit time
0.0 ms
0.0 ... 6553.5 ms
0x1800:003
CANopen
└ P550.05
Event timer
20 ms
0 ... 65535 ms
0x1800:005
CANopen
P551.xx
TPDO2 config.
└ P551.02
Transm. type
255
0 ... 255
0x1801:002
CANopen
└ P551.03
Inhibit time
0.0 ms
0.0 ... 6553.5 ms
0x1801:003
CANopen
└ P551.05
Event timer
0 ms
0 ... 65535 ms
0x1801:005
CANopen
P552.xx
TPDO3 config.
└ P552.02
Transm. type
255
0 ... 255
0x1802:002
CANopen
-
(Read only)
0x232C:004
Modbus RTU
└ P531.09 Register 9
└ P531.14 Register 14
└ P531.19 Register 19
└ P531.24 Register 24
└ P540.05 Event timer
-
-
-
-
100 ms
(Read only)
(Read only)
(Read only)
(Read only)
0 ... 65535 ms
0x232C:009
0x232C:014
0x232C:019
0x232C:024
0x1400:005
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU
CANopen
P542.xx
└ P550.01 COB-ID
└ P551.01 COB-ID
└ P552.01 COB-ID
RPDO3 config.
0x40000180
0xC0000280
0xC0000380
0x00000001 ... 0xFFFFFFFF 0x1800:001
0x00000001 ... 0xFFFFFFFF 0x1801:001
0x00000001 ... 0xFFFFFFFF 0x1802:001
CANopen
CANopen
CANopen
58 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P552.03
Inhibit time
0.0 ms
0.0 ... 6553.5 ms
0x1802:003
CANopen
└ P552.05 Event timer
P580.xx
CAN statistics
└ P580.01
PDO1 received
- (Read only)
0x230A:001
CANopen
└ P580.02
PDO2 received
- (Read only)
0x230A:002
CANopen
└ P580.03
PDO3 received
- (Read only)
0x230A:003
CANopen
└ P580.06
PDO2 transmitted
- (Read only)
0x230A:006
CANopen
└ P580.07
PDO3 transmitted
- (Read only)
0x230A:007
CANopen
└ P580.09
SDO1 counter
- (Read only)
0x230A:009
CANopen
└ P580.10
SDO2 counter
- (Read only)
0x230A:010
CANopen
└ P580.01
Mess. received
- (Read only)
0x232A:001
Modbus RTU
└ P580.02
Val. mess. rec.
- (Read only)
0x232A:002
Modbus RTU
└ P580.03
Mess. w. exc.
- (Read only)
0x232A:003
Modbus RTU
└ P580.04
Mess. w. errors
- (Read only)
0x232A:004
Modbus RTU
P583.xx
Rx data diagn.
└ P583.01
Rx data offset
0
0 ... 240
0x232E:001
Modbus RTU
└ P583.02
Last RxD byte0
- (Read only)
0x232E:002
Modbus RTU
└ P583.03
Last RxD byte1
- (Read only)
0x232E:003
Modbus RTU
└ P583.05
Last RxD byte3
- (Read only)
0x232E:005
Modbus RTU
└ P583.06
Last RxD byte4
- (Read only)
0x232E:006
Modbus RTU
└ P583.07
Letzt RxD-Byte5
- (Read only)
0x232E:007
Modbus RTU
└ P583.08
Last RxD byte6
- (Read only)
0x232E:008
Modbus RTU
└ P583.10
Last RxD byte8
- (Read only)
0x232E:010
Modbus RTU
└ P583.11
Last RxD byte9
- (Read only)
0x232E:011
Modbus RTU
└ P583.12
Last RxD byte10
- (Read only)
0x232E:012
Modbus RTU
└ P583.13
Last RxD byte11
- (Read only)
0x232E:013
Modbus RTU
└ P583.15
Last RxD byte13
- (Read only)
0x232E:015
Modbus RTU
└ P583.16
Last RxD byte14
- (Read only)
0x232E:016
Modbus RTU
└ P583.17
Last RxD byte15
- (Read only)
0x232E:017
Modbus RTU
P585.xx
Tx data diagn.
└ P585.02
Last TxD byte0
- (Read only)
0x232F:002
Modbus RTU
└ P585.03
Last TxD Byte1
- (Read only)
0x232F:003
Modbus RTU
└ P585.04
Last TxD byte2
- (Read only)
0x232F:004
Modbus RTU
└ P585.05
Last TxD byte3
- (Read only)
0x232F:005
Modbus RTU
└ P585.07
Last TxD byte5
- (Read only)
0x232F:007
Modbus RTU
└ P585.08
Last TxD byte6
- (Read only)
0x232F:008
Modbus RTU
└ P585.09
Last TxD byte7
- (Read only)
0x232F:009
Modbus RTU
└ P585.10
Last TxD byte8
- (Read only)
0x232F:010
Modbus RTU
└ P585.12
Last TxD byte10
- (Read only)
0x232F:012
Modbus RTU
0 ms
0 ... 65535 ms
0x1802:005
CANopen
└ P580.05 PDO1 transmitted
P580.xx
└ P580.05 Messages sent
└ P583.04 Last RxD byte2
└ P583.09 Last RxD byte7
Modbus statistic
-
-
-
-
(Read only)
(Read only)
(Read only)
(Read only)
0x230A:005
0x232A:005
0x232E:004
0x232E:009
CANopen
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU
└ P583.14 Last RxD byte12
└ P585.01 Tx data offset
└ P585.06 Last TxD byte4
└ P585.11 Last TxD byte9
-
0
-
-
(Read only)
0 ... 240
(Read only)
(Read only)
0x232E:014
0x232F:001
0x232F:006
0x232F:011
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P585.13
Last TxD byte11
- (Read only)
0x232F:013
Modbus RTU
└ P585.14 Last TxD byte12
0x232F:014
└ P585.15
Last TxD byte13
-
(Read only)
0x232F:015
Modbus RTU
└ P585.16
Last TxD byte14
-
(Read only)
0x232F:016
Modbus RTU
└ P585.17
Last TxD byte15
-
(Read only)
0x232F:017
Modbus RTU
P590.xx
NetWordINx
└ P590.02
NetWordIN2
0x0000
0x0000 ... 0xFFFF
0x4008:002
general
└ P590.03
NetWordIN3
0.0 %
0.0 ... 100.0 %
0x4008:003
general
└ P590.04
NetWordIN4
0.0 %
0.0 ... 100.0 %
0x4008:004
general
P591.xx
NetWordOUTx
└ P591.02
NetWordOUT2
- (Read only)
0x400A:002
general
P592.xx
Process data IN
└ P592.01
AC control word
0x0000
0x0000 ... 0xFFFF
0x400B:001
general
└ P592.02
LECOM ctrl word
0x0000
0x0000 ... 0xFFFF
0x400B:002
general
└ P592.04
Net.setp. speed
0 rpm
0 ... 50000 rpm
0x400B:004
general
└ P592.05
Net.freq. 0.01
0.00 Hz
0.00 ... 599.00 Hz
0x400B:005
general
└ P592.06
Veloc. mode setp
0.0 Hz
-599.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x400B:006
general
└ P592.07
PID setpoint
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x400B:007
general
└ P592.09
Torque scaling
0
-128 ... 127
0x400B:009
general
└ P592.11
PID feedback
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x400B:011
general
└ P592.12
NetSetfreq0.02Hz
0 Hz
-29950 ... 29950 Hz
0x400B:012
general
P593.xx
Process data OUT
└ P593.02
LECOM stat. word
- (Read only)
0x400C:002
general
└ P593.03
Frequency (0.1)
x.x Hz
(Read only)
0x400C:003
general
└ P593.04
Motor speed
x rpm
(Read only)
0x400C:004
general
└ P593.05
Drive status
- (Read only)
0x400C:005
general
└ P593.07
Torque scaled
- (Read only)
0x400C:007
general
└ P593.08
Frequency 0.02Hz
Hz
(Read only)
0x400C:008
general
P595.xx
PAM monitoring
└ P595.02
Keep alive reg.
0
0 ... 65535
0x2552:002
general
└ P595.04
Reaction
No response [0]
Selection list
0x2552:004
general
└ P595.05
Action
No action [0]
Selection list
0x2552:005
general
└ P595.06
PAM status
- (Read only)
0x2552:006
general
P600.xx
PID setup
└ P600.02
PID process var.
Analog input 1 [1]
Selection list
0x4020:002
general
└ P600.03
PID speed range
100 %
0 ... 100 %
0x4020:003
general
└ P600.04
PID line speed
w/o speed.add. [0]
Selection list
0x4020:004
general
└ P600.05
Min speed lim
-100.0 %
-100.0 ... 100.0 %
0x4020:005
general
P601.00
PID P-component
5.0 %
0.0 ... 1000.0 %
0x4048
general
-
(Read only)
Modbus RTU
└ P590.01 NetWordIN1
└ P591.01 NetWordOUT1
└ P592.03 Net.freq. 0.1
└ P592.08 Torque mode setp
└ P593.01 AC status word
0x0000
-
0.0 Hz
0 Nm
-
0x0000 ... 0xFFFF
(Read only)
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
-32768 ... 32767 Nm
(Read only)
0x4008:001
0x400A:001
0x400B:003
0x400B:008
0x400C:001
general
general
general
general
general
└ P593.06 Frequency 0.01
└ P595.03 Time-out time
└ P600.01 Operating mode
└ P600.06 Max speed lim
x.xx Hz
10.0 s
Inhibited [0]
100.0 %
(Read only)
0.0 ... 6553.5 s
Selection list
-100.0 ... 100.0 %
0x400C:006
0x2552:003
0x4020:001
0x4020:006
general
general
general
general
60 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
P602.00
PID Icomponent
400 ms
10 ... 6000 ms
0x4049
general
P603.00
P604.00
PID setp.ramp
20.0 s
0.0 ... 100.0 s
0x404B
general
P605.xx
PID setp. limit
└ P605.01
Minimum setpoint
-300.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x404E:001
general
└ P605.02
Maximum setpoint
300.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x404E:002
general
└ P606.01
Accel. time
1.0 s
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
0x4021:001
general
└ P606.02
Decel. time
1.0 s
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
0x4021:002
general
P607.xx
PID influence
└ P607.01
Show time
5.0 s
0.0 ... 999.9 s
0x404C:001
general
P608.xx
PID alarms
└ P608.01
MIN alarm thrsh.
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x404D:001
general
└ P608.02
MAX alarm thrsh.
100.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x404D:002
general
└ P608.03
Bandw. feedback
2.00 %
0.00 ... 100.00 %
0x404D:003
general
└ P610.01
Activation
Disabled [0]
Selection list
0x4023:001
general
└ P610.02
Stop method
Coasting [0]
Selection list
0x4023:002
general
└ P610.03
Freq. thresh.
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x4023:003
general
└ P610.04
Feedback thresh.
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x4023:004
general
└ P610.06
Recovery
Setp. > P610.3 [0]
Selection list
0x4023:006
general
└ P610.07
Bandwidth
0.00 PID unit
0.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x4023:007
general
└ P610.08
Recovery thresh.
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x4023:008
general
P615.xx
Auto-rinsing
└ P615.02
Rinse interval
30.0 min
0.0 ... 6000.0 min
0x4024:002
general
└ P615.03
Rinse speed
0.0 Hz
-599.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x4024:003
general
└ P615.04
Rinse period
0.0 s
0.0 ... 6000.0 s
0x4024:004
general
P700.xx
Device commands
└ P700.03
Save user data
Off / ready [0]
Selection list
0x2022:003
general
└ P700.04
Load user data
Off / ready [0]
Selection list
0x2022:004
general
└ P700.05
Load OEM data
Off / ready [0]
Selection list
0x2022:005
general
└ P700.06
Save OEM data
Off / ready [0]
Selection list
0x2022:006
general
└ P700.08
Load par. set 2
Off / ready [0]
Selection list
0x2022:008
general
└ P700.09
Load par. set 3
Off / ready [0]
Selection list
0x2022:009
general
└ P700.10
Load par. set 4
Off / ready [0]
Selection list
0x2022:010
general
└ P700.11
Save par. set 1
Off / ready [0]
Selection list
0x2022:011
general
└ P700.13
Save par. set 3
Off / ready [0]
Selection list
0x2022:013
general
└ P700.14
Save par. set 4
Off / ready [0]
Selection list
0x2022:014
general
└ P700.15
Delete logbook
Off / ready [0]
Selection list
0x2022:015
general
P701.00
KP setp. incr.
1
1 ... 100
0x2862
general
P703.00
KP status displ.
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x2864
general
PID D-component
0.0 s
0.0 ... 20.0 s
0x404A
general
P606.xx
└ P607.02 Mask out time
P610.xx
└ P610.05 Delay time
└ P615.01 Rinsing in idle
PID speed op.
PID sleep mode
5.0 s
0.0 s
Inhibited [0]
0.0 ... 999.9 s
0.0 ... 300.0 s
Selection list
0x404C:002
0x4023:005
0x4024:001
general
general
general
└ P700.01 Load def. sett.
└ P700.07 Load par. set 1
└ P700.12 Save par. set 2
P702.00
Scal.speed fact.
Off / ready [0]
Off / ready [0]
Off / ready [0]
0.00
Selection list
Selection list
Selection list
0.00 ... 650.00
0x2022:001
0x2022:007
0x2022:012
0x4002
general
general
general
general

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
P704.xx
DC braking
└ P704.01 Current
└ P704.02
Hold time autom.
0.0 s
0.0 ... 1000.0 s
0x2B84:002
general
└ P704.03
Threshold autom.
0.0 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2B84:003
general
└ P704.04
Demagnet. time
100 %
0 ... 150 %
0x2B84:004
general
└ P704.05
Def. demag. time
x ms
(Read only)
0x2B84:005
general
P706.xx
Brake management
└ P706.01
Operating mode
Rfg stop (RFGS) [1]
Selection list
0x2541:001
general
└ P706.02
Active threshold
x V
(Read only)
0x2541:002
general
└ P706.03
Red. threshold
0 V
0 ... 100 V
0x2541:003
general
└ P706.05
Del.overr.time
2.0 s
0.0 ... 60.0 s
0x2541:005
general
P708.xx
Keypad setup
└ P708.01
CTRL&F/R keys
CTRL&F/R Enable [1]
Selection list
0x2602:001
general
└ P708.02
Rotation setup
Forward [0]
Selection list
0x2602:002
general
P710.xx
Load loss detect
└ P710.01
Threshold
0.0 %
0.0 ... 200.0 %
0x4006:001
general
└ P710.02
Deceleration
0.0 s
0.0 ... 300.0 s
0x4006:002
general
P711.xx
Position counter
└ P711.02
Reset mode
Rising edge [0]
Selection list
0x2C49:002
general
└ P711.03
Actual position
- (Read only)
0x2C49:003
general
P712.xx
Brake control
└ P712.01
Brake mode
Off [2]
Selection list
0x2820:001
general
└ P712.03
Opening time
100 ms
0 ... 10000 ms
0x2820:003
general
└ P712.07
Closing thresh.
0.2 Hz
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2820:007
general
└ P712.08
Holding load
0.0 %
-500.0 ... 500.0 %
0x2820:008
general
└ P712.12
ClosingThr delay
0 ms
0 ... 10000 ms
0x2820:012
general
└ P712.15
Brake status
- (Read only)
0x2820:015
general
P718.xx
Flying restart
└ P718.01
Current
30 %
0 ... 100 %
0x2BA1:001
MCTRL
└ P718.02
Start frequency
20.0 Hz
-599.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2BA1:002
MCTRL
└ P718.08
Fl.res.frequency
x.x Hz
(Read only)
0x2BA1:008
MCTRL
P721.xx
Mains fail. ctrl
└ P721.01
Enable function
Disabled [0]
Selection list
0x2D66:001
general
└ P721.02
DC-bus act.level
0 % *
60 ... 90 %
0x2D66:002
general
└ P721.04
Res. time V-ctrl
20 ms
5 ... 2000 ms
0x2D66:004
general
└ P721.05
DC voltage setp.
100 %
80 ... 110 %
0x2D66:005
general
└ P721.06
Setp. ramp
20 ms
1 ... 16000 ms
0x2D66:006
general
└ P721.07
Clear time
20 ms
1 ... 60000 ms
0x2D66:007
general
└ P721.09
RERT:Status
- (Read only)
0x2D66:009
general
0.0 %
0.0 ... 200.0 %
0x2B84:001
general
P705.00
└ P706.04 Add.frequency
└ P708.03 Keypad Full Ctrl
└ P711.01 Signal source
└ P712.02 Closing time
KP language
English [1]
0.0 Hz
Off [0]
Disbled [0]
100 ms
Selection list
0.0 ... 10.0 Hz
Selection list
Selection list
0 ... 10000 ms
0x2863
0x2541:004
0x2602:003
0x2C49:001
0x2820:002
general
general
general
general
general
└ P712.13 HoldLoad ramptim
└ P718.03 Restart time
└ P721.03 Gain V-ctrl
└ P721.08 Restart level
0 ms
5911 ms *
0.01000 Hz/V
0.0 Hz
0 ... 100 ms
1 ... 60000 ms
0.00001 ... 0.50000 Hz/V
0.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x2820:013
0x2BA1:003
0x2D66:003
0x2D66:008
general
MCTRL
general
general
62 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
P730.00
PIN1 protection
0
-1 ... 9999
0x203D
general
P731.00
P732.00
Auto-Save EPM
Inhibit [0]
Selection list
0x2829
general
P740.xx
Favorites sett.
└ P740.01
Parameter 1
0x2DDD0000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:001
general
└ P740.02
Parameter 2
0x60780000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:002
general
└ P740.04
Parameter 4
0x603F0000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:004
general
└ P740.05
Parameter 5
0x28240000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:005
general
└ P740.06
Parameter 6
0x28600100
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:006
general
└ P740.07
Parameter 7
0x28380100
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:007
general
└ P740.09
Parameter 9
0x25400100
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:009
general
└ P740.10
Parameter 10
0x29150000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:010
general
└ P740.11
Parameter 11
0x29160000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:011
general
└ P740.12
Parameter 12
0x29170000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:012
general
└ P740.14
Parameter 14
0x2C000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:014
general
└ P740.15
Parameter 15
0x2B000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:015
general
└ P740.16
Parameter 16
0x2B010100
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:016
general
└ P740.17
Parameter 17
0x2B010200
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:017
general
0x261C:018
└ P740.19
Parameter 19
0x29390000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:019
general
└ P740.20
Parameter 20
0x2D4B0100
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:020
general
└ P740.21
Parameter 21
0x2B120100
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:021
general
└ P740.22
Parameter 22
0x60730000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:022
general
0x261C:023
└ P740.24
Parameter 24
0x26310200
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:024
general
└ P740.25
Parameter 25
0x26310300
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:025
general
└ P740.26
Parameter 26
0x26310400
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:026
general
└ P740.27
Parameter 27
0x26310500
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:027
general
0x261C:028
└ P740.29
Parameter 29
0x26310700
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:029
general
└ P740.30
Parameter 30
0x26310800
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:030
general
└ P740.31
Parameter 31
0x26310900
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:031
general
└ P740.32
Parameter 32
0x26310D00
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:032
general
0x261C:033
└ P740.34
Parameter 34
0x26311300
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:034
general
└ P740.35
Parameter 35
0x26311400
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:035
general
└ P740.36
Parameter 36
0x26340100
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:036
general
└ P740.37
Parameter 37
0x26340200
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:037
general
0x261C:038
└ P740.39
Parameter 39
0x26360200
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:039
general
└ P740.40
Parameter 40
0x26360300
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:040
general
└ P740.41
Parameter 41
0x26390100
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:041
general
└ P740.42
Parameter 42
0x26390200
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:042
general
0x261C:043
└ P740.44
Parameter 44
0x26390400
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:044
general
PIN2 protection
0
-1 ... 9999
0x203E
general
└ P740.03 Parameter 3
└ P740.08 Parameter 8
└ P740.13 Parameter 13
└ P740.18 Parameter 18 0x283A0000 0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
└ P740.23 Parameter 23 0x26310100 0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x2D890000
0x28380300
0x29180000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00 0x261C:003
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00 0x261C:008
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00 0x261C:013
general
general
general
general
general
└ P740.28 Parameter 28 0x26310600 0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
└ P740.33 Parameter 33 0x26311200 0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
└ P740.38 Parameter 38 0x26360100 0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
└ P740.43 Parameter 43 0x26390300 0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
general
general
general
general

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P740.45
Parameter 45
0x29110100
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:045
general
└ P740.46 Parameter 46 0x29110200 0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:046
└ P740.47
Parameter 47
0x29110300
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:047
general
└ P740.48
Parameter 48
0x29110400
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:048
general
└ P740.49
Parameter 49
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:049
general
└ P740.50
Parameter 50
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x261C:050
general
└ P750.01
Parameter 1
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:001
general
└ P750.02
Parameter 2
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:002
general
└ P750.03
Parameter 3
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:003
general
└ P750.04
Parameter 4
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:004
general
└ P750.06
Parameter 6
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:006
general
└ P750.07
Parameter 7
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:007
general
└ P750.08
Parameter 8
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:008
general
└ P750.09
Parameter 9
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:009
general
└ P750.11
Parameter 11
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:011
general
└ P750.12
Parameter 12
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:012
general
└ P750.13
Parameter 13
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:013
general
└ P750.14
Parameter 14
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:014
general
└ P750.16
Parameter 16
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:016
general
└ P750.17
Parameter 17
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:017
general
└ P750.18
Parameter 18
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:018
general
└ P750.19
Parameter 19
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:019
general
0x4041:020
└ P750.21
Parameter 21
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:021
general
└ P750.22
Parameter 22
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:022
general
└ P750.23
Parameter 23
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:023
general
└ P750.24
Parameter 24
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:024
general
0x4041:025
└ P750.26
Parameter 26
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:026
general
└ P750.27
Parameter 27
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:027
general
└ P750.28
Parameter 28
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:028
general
└ P750.29
Parameter 29
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:029
general
0x4041:030
└ P750.31
Parameter 31
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:031
general
└ P750.32
Parameter 32
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
0x4041:032
general
P751.xx
Par. value set 1
└ P751.01
Set 1 Value 1
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:001
general
└ P751.03
Set 1 Value 3
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:003
general
└ P751.04
Set 1 Value 4
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:004
general
└ P751.05
Set 1 Value 5
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:005
general
└ P751.06
Set 1 Value 6
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:006
general
└ P751.08
Set 1 Value 8
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:008
general
general
P750.xx
└ P750.05 Parameter 5
└ P750.10 Parameter 10
└ P750.15 Parameter 15
└ P750.20 Parameter 20 0x00000000 0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
Param.set setup
0x00000000
0x00000000
0x00000000
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00 0x4041:005
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00 0x4041:010
0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00 0x4041:015
general
general
general
general
└ P750.25 Parameter 25 0x00000000 0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
└ P750.30 Parameter 30 0x00000000 0x00000000 ... 0xFFFFFF00
└ P751.02 Set 1 Value 2
└ P751.07 Set 1 Value 7
0
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4042:002
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4042:007
general
general
general
general
64 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P751.09
Set 1 Value 9
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:009
general
└ P751.10 Set 1 Value 10
└ P751.11
Set 1 Value 11
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:011
general
└ P751.12
Set 1 Value 12
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:012
general
└ P751.13
Set 1 Value 13
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:013
general
└ P751.14
Set 1 Value 14
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:014
general
└ P751.16
Set 1 Value 16
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:016
general
└ P751.17
Set 1 Value 17
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:017
general
└ P751.18
Set 1 Value 18
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:018
general
└ P751.19
Set 1 Value 19
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:019
general
└ P751.21
Set 1 Value 21
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:021
general
└ P751.22
Set 1 Value 22
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:022
general
└ P751.23
Set 1 Value 23
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:023
general
└ P751.24
Set 1 Value 24
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:024
general
└ P751.26
Set 1 Value 26
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:026
general
└ P751.27
Set 1 Value 27
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:027
general
└ P751.28
Set 1 Value 28
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:028
general
└ P751.29
Set 1 Value 29
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:029
general
└ P751.31
Set 1 Value 31
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:031
general
└ P751.32
Set 1 Value 32
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4042:032
general
P752.xx
Par. value set 2
└ P752.01
Set 2 Value 1
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:001
general
└ P752.03
Set 2 Value 3
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:003
general
└ P752.04
Set 2 Value 4
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:004
general
└ P752.05
Set 2 Value 5
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:005
general
└ P752.06
Set 2 Value 6
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:006
general
0x4043:007
└ P752.08
Set 2 Value 8
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:008
general
└ P752.09
Set 2 Value 9
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:009
general
└ P752.10
Set 2 Value 10
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:010
general
└ P752.11
Set 2 Value 11
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:011
general
0x4043:012
└ P752.13
Set 2 Value 13
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:013
general
└ P752.14
Set 2 Value 14
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:014
general
└ P752.15
Set 2 Value 15
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:015
general
└ P752.16
Set 2 Value 16
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:016
general
0x4043:017
└ P752.18
Set 2 Value 18
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:018
general
└ P752.19
Set 2 Value 19
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:019
general
└ P752.20
Set 2 Value 20
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:020
general
└ P752.21
Set 2 Value 21
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:021
general
0x4043:022
└ P752.23
Set 2 Value 23
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:023
general
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4042:010
general
└ P751.15 Set 1 Value 15
└ P751.20 Set 1 Value 20
└ P751.25 Set 1 Value 25
└ P751.30 Set 1 Value 30
└ P752.02 Set 2 Value 2
0
0
0
0
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4042:015
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4042:020
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4042:025
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4042:030
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4043:002
general
general
general
general
general
└ P752.07 Set 2 Value 7 0 -2147483648 ... 2147483647
└ P752.12 Set 2 Value 12 0 -2147483648 ... 2147483647
└ P752.17 Set 2 Value 17 0 -2147483648 ... 2147483647
└ P752.22 Set 2 Value 22 0 -2147483648 ... 2147483647
general
general
general
general

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P752.24
Set 2 Value 24
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:024
general
└ P752.25 Set 2 Value 25 0 -2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:025
└ P752.26
Set 2 Value 26
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:026
general
└ P752.27
Set 2 Value 27
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:027
general
└ P752.28
Set 2 Value 28
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:028
general
└ P752.29
Set 2 Value 29
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:029
general
0x4043:030
└ P752.31
Set 2 Value 31
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:031
general
└ P752.32
Set 2 Value 32
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4043:032
general
P753.xx
Par. value set 3
└ P753.01
Set 3 Value 1
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:001
general
└ P753.03
Set 3 Value 3
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:003
general
└ P753.04
Set 3 Value 4
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:004
general
└ P753.05
Set 3 Value 5
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:005
general
└ P753.06
Set 3 Value 6
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:006
general
└ P753.08
Set 3 Value 8
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:008
general
└ P753.09
Set 3 Value 9
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:009
general
└ P753.10
Set 3 Value 10
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:010
general
└ P753.11
Set 3 Value 11
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:011
general
└ P753.13
Set 3 Value 13
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:013
general
└ P753.14
Set 3 Value 14
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:014
general
└ P753.15
Set 3 Value 15
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:015
general
└ P753.16
Set 3 Value 16
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:016
general
└ P753.18
Set 3 Value 18
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:018
general
└ P753.19
Set 3 Value 19
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:019
general
└ P753.20
Set 3 Value 20
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:020
general
└ P753.21
Set 3 Value 21
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:021
general
└ P753.23
Set 3 Value 23
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:023
general
└ P753.24
Set 3 Value 24
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:024
general
└ P753.25
Set 3 Value 25
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:025
general
└ P753.26
Set 3 Value 26
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:026
general
└ P753.28
Set 3 Value 28
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:028
general
└ P753.29
Set 3 Value 29
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:029
general
└ P753.30
Set 3 Value 30
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:030
general
└ P753.31
Set 3 Value 31
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4044:031
general
0x4044:032
P754.xx
Par. value set 4
└ P754.01
Set 4 Value 1
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:001
general
└ P754.02
Set 4 Value 2
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:002
general
└ P754.03
Set 4 Value 3
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:003
general
└ P754.05
Set 4 Value 5
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:005
general
general
└ P752.30 Set 2 Value 30 0 -2147483648 ... 2147483647
└ P753.02 Set 3 Value 2
└ P753.07 Set 3 Value 7
└ P753.12 Set 3 Value 12
└ P753.17 Set 3 Value 17
0
0
0
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4044:002
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4044:007
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4044:012
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4044:017
general
general
general
general
general
└ P753.22 Set 3 Value 22
└ P753.27 Set 3 Value 27
└ P753.32 Set 3 Value 32 0 -2147483648 ... 2147483647
└ P754.04 Set 4 Value 4
0
0
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4044:022
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4044:027
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4045:004
general
general
general
general
66 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P754.06
Set 4 Value 6
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:006
general
└ P754.07 Set 4 Value 7
└ P754.08
Set 4 Value 8
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:008
general
└ P754.09
Set 4 Value 9
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:009
general
└ P754.10
Set 4 Value 10
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:010
general
└ P754.11
Set 4 Value 11
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:011
general
└ P754.13
Set 4 Value 13
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:013
general
└ P754.14
Set 4 Value 14
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:014
general
└ P754.15
Set 4 Value 15
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:015
general
└ P754.16
Set 4 Value 16
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:016
general
└ P754.18
Set 4 Value 18
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:018
general
└ P754.19
Set 4 Value 19
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:019
general
└ P754.20
Set 4 Value 20
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:020
general
└ P754.21
Set 4 Value 21
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:021
general
└ P754.23
Set 4 Value 23
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:023
general
└ P754.24
Set 4 Value 24
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:024
general
└ P754.25
Set 4 Value 25
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:025
general
└ P754.26
Set 4 Value 26
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:026
general
└ P754.28
Set 4 Value 28
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:028
general
└ P754.29
Set 4 Value 29
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:029
general
└ P754.30
Set 4 Value 30
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:030
general
└ P754.31
Set 4 Value 31
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647
0x4045:031
general
P755.00
PSet activation
On op. disabled [0]
Selection list
0x4046
general
P756.xx
PSet error msg.
└ P756.01
Status
- (Read only)
0x4047:001
general
└ P756.02
List entry
- (Read only)
0x4047:002
general
└ P760.02
Restart delay
3.0 s
0.0 ... 1000.0 s
0x2839:002
general
└ P760.03
Restart counter
5
0 ... 255
0x2839:003
general
└ P760.04
Tro.count r.time
5.0 s
0.1 ... 3600.0 s
0x2839:004
general
└ P760.05
Trouble counter
- (Read only)
0x2839:005
general
P781.00
Target velocity
0 rpm
-32768 ... 32767 rpm
0x6042
general
P782.00
Velocity demand
x rpm
(Read only)
0x6043
general
P783.00
Velocity actual
x rpm
(Read only)
0x6044
general
P784.xx
Vel. min max
└ P784.02
Vel. max amount
2147483647 rpm
0 ... 2147483647 rpm
0x6046:002
general
P785.xx
Vel.acceleration
└ P785.01
Delta speed
3000 rpm
0 ... 2147483647 rpm
0x6048:001
general
└ P785.02
Delta time
10 s
0 ... 65535 s
0x6048:002
general
└ P786.01
Delta speed
3000 rpm
0 ... 2147483647 rpm
0x6049:001
general
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4045:007
general
└ P754.12 Set 4 Value 12
└ P754.17 Set 4 Value 17
└ P754.22 Set 4 Value 22
└ P754.27 Set 4 Value 27
└ P754.32 Set 4 Value 32
0
0
0
0
0
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4045:012
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4045:017
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4045:022
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4045:027
-2147483648 ... 2147483647 0x4045:032
general
general
general
general
general
P760.xx
P780.00
└ P784.01 Vel. min amount
P786.xx
Fault config.
CiA: Statusword
Vel.deceleration
-
0 rpm
(Read only)
0 ... 480000 rpm
0x6041
0x6046:001
general
general

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P786.02
Delta time
10 s
0 ... 65535 s
0x6049:002
general
P788.00
P789.00
Supported modes
- (Read only)
0x6502
general
P790.00
Quick stop dec.
546000 pos. unit/s²
0 ... 2147483647 pos. unit/s²
0x6085
general
P791.00
Fault reaction
Coasting [0]
Selection list
0x605E
general
P800.00
Sequencer mode
Disabled [0]
Selection list
0x4025
general
└ P801.01
Frequency setp.
0.0 Hz
-599.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x4026:001
general
└ P801.02
Accel./decel.
5.0 s
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
0x4026:002
general
└ P801.03
Time
0.0 s
0.0 ... 100000.0 s
0x4026:003
general
└ P801.04
Digital outp.
0
0 ... 255
0x4026:004
general
└ P801.06
PID setp.
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x4026:006
general
└ P801.07
Torque setp.
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x4026:007
general
P802.xx
Segment 2
└ P802.01
Frequency setp.
0.0 Hz
-599.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x4027:001
general
└ P802.03
Time
0.0 s
0.0 ... 100000.0 s
0x4027:003
general
└ P802.04
Digital outp.
0
0 ... 255
0x4027:004
general
└ P802.05
Analog outp.
0.00 VDC
0.00 ... 10.00 VDC
0x4027:005
general
└ P802.06
PID setp.
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x4027:006
general
P803.xx
Segment 3
└ P803.01
Frequency setp.
0.0 Hz
-599.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x4028:001
general
└ P803.02
Accel./decel.
5.0 s
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
0x4028:002
general
└ P803.03
Time
0.0 s
0.0 ... 100000.0 s
0x4028:003
general
└ P803.05
Analog outp.
0.00 VDC
0.00 ... 10.00 VDC
0x4028:005
general
└ P803.06
PID setp.
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x4028:006
general
└ P803.07
Torque setp.
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x4028:007
general
P804.xx
Segment 4
└ P804.02
Accel./decel.
5.0 s
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
0x4029:002
general
└ P804.03
Time
0.0 s
0.0 ... 100000.0 s
0x4029:003
general
└ P804.04
Digital outp.
0
0 ... 255
0x4029:004
general
└ P804.05
Analog outp.
0.00 VDC
0.00 ... 10.00 VDC
0x4029:005
general
└ P804.07
Torque setp.
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x4029:007
general
P805.xx
Segment 5
└ P805.01
Frequency setp.
0.0 Hz
-599.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x402A:001
general
└ P805.02
Accel./decel.
5.0 s
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
0x402A:002
general
└ P805.04
Digital outp.
0
0 ... 255
0x402A:004
general
└ P805.05
Analog outp.
0.00 VDC
0.00 ... 10.00 VDC
0x402A:005
general
└ P805.06
PID setp.
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x402A:006
general
└ P805.07
Torque setp.
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x402A:007
general
└ P806.01
Frequency setp.
0.0 Hz
-599.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x402B:001
general
Modes of op. dis
-
(Read only)
0x6061
general
P801.xx
└ P801.05 Analog outp.
└ P802.02 Accel./decel.
└ P802.07 Torque setp.
└ P803.04 Digital outp.
Segment 1
0.00 VDC
5.0 s
100.0 %
0
0.00 ... 10.00 VDC
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0 ... 255
0x4026:005
0x4027:002
0x4027:007
0x4028:004
general
general
general
general
└ P804.01 Frequency setp.
└ P804.06 PID setp.
└ P805.03 Time
P806.xx
Segment 6
0.0 Hz
0.00 PID unit
0.0 s
-599.0 ... 599.0 Hz
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0.0 ... 100000.0 s
0x4029:001
0x4029:006
0x402A:003
general
general
general
68 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P806.02
Accel./decel.
5.0 s
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
0x402B:002
general
└ P806.03 Time 0.0 s 0.0 ... 100000.0 s
0x402B:003
└ P806.04
Digital outp.
0
0 ... 255
0x402B:004
general
└ P806.05
Analog outp.
0.00 VDC
0.00 ... 10.00 VDC
0x402B:005
general
└ P806.06
PID setp.
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x402B:006
general
└ P806.07
Torque setp.
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x402B:007
general
└ P807.01
Frequency setp.
0.0 Hz
-599.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x402C:001
general
└ P807.02
Accel./decel.
5.0 s
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
0x402C:002
general
└ P807.03
Time
0.0 s
0.0 ... 100000.0 s
0x402C:003
general
└ P807.04
Digital outp.
0
0 ... 255
0x402C:004
general
└ P807.06
PID setp.
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x402C:006
general
└ P807.07
Torque setp.
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x402C:007
general
P808.xx
Segment 8
└ P808.01
Frequency setp.
0.0 Hz
-599.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x402D:001
general
└ P808.03
Time
0.0 s
0.0 ... 100000.0 s
0x402D:003
general
└ P808.04
Digital outp.
0
0 ... 255
0x402D:004
general
└ P808.05
Analog outp.
0.00 VDC
0.00 ... 10.00 VDC
0x402D:005
general
└ P808.06
PID setp.
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x402D:006
general
P820.00
StartOfSeq. mode
Restart sequencr [0]
Selection list
0x4040
general
P822.xx
End segment
└ P822.01
Frequency setp.
0.0 Hz
-599.0 ... 599.0 Hz
0x402E:001
general
└ P822.02
Accel./decel.
5.0 s
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
0x402E:002
general
└ P822.04
Digital outp.
0
0 ... 255
0x402E:004
general
└ P822.05
Analog outp.
0.00 VDC
0.00 ... 10.00 VDC
0x402E:005
general
└ P822.06
PID setp.
0.00 PID unit
-300.00 ... 300.00 PID unit
0x402E:006
general
└ P822.07
Torque setp.
100.0 %
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0x402E:007
general
P830.xx
Sequence 1
└ P830.01
Step 1
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4030:001
general
└ P830.02
Step 2
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4030:002
general
└ P830.03
Step 3
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4030:003
general
└ P830.05
Step 5
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4030:005
general
└ P830.06
Step 6
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4030:006
general
└ P830.07
Step 7
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4030:007
general
└ P830.08
Step 8
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4030:008
general
└ P830.10
Step 10
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4030:010
general
└ P830.11
Step 11
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4030:011
general
└ P830.12
Step 12
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4030:012
general
└ P830.13
Step 13
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4030:013
general
└ P830.15
Step 15
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4030:015
general
general
P807.xx
└ P807.05 Analog outp.
└ P808.02 Accel./decel.
└ P808.07 Torque setp.
└ P822.03 Time
Segment 7
0.00 VDC
5.0 s
100.0 %
0.0 s
0.00 ... 10.00 VDC
0.0 ... 3600.0 s
-400.0 ... 400.0 %
0.0 ... 100000.0 s
0x402C:005
0x402D:002
0x402D:007
0x402E:003
general
general
general
general
P824.00
└ P830.04 Step 4
└ P830.09 Step 9
└ P830.14 Step 14
End of seq. mode
Keep running [0]
Skip step [0]
Skip step [0]
Skip step [0]
Selection list
Selection list
Selection list
Selection list
0x402F
0x4030:004
0x4030:009
0x4030:014
general
general
general
general

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P830.16
Step 16
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4030:016
general
P831.00
P835.xx
Sequence 2
└ P835.01
Step 1
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4032:001
general
└ P835.02
Step 2
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4032:002
general
└ P835.03
Step 3
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4032:003
general
└ P835.05
Step 5
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4032:005
general
└ P835.06
Step 6
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4032:006
general
└ P835.07
Step 7
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4032:007
general
└ P835.08
Step 8
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4032:008
general
0x4032:009
└ P835.10
Step 10
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4032:010
general
└ P835.11
Step 11
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4032:011
general
└ P835.12
Step 12
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4032:012
general
└ P835.13
Step 13
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4032:013
general
0x4032:014
└ P835.15
Step 15
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4032:015
general
└ P835.16
Step 16
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4032:016
general
P836.00
Cycl. sequence 2
1
1 ... 65535
0x4033
general
P840.xx
Sequence 3
└ P840.02
Step 2
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4034:002
general
└ P840.03
Step 3
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4034:003
general
└ P840.04
Step 4
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4034:004
general
└ P840.05
Step 5
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4034:005
general
└ P840.07
Step 7
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4034:007
general
└ P840.08
Step 8
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4034:008
general
└ P840.09
Step 9
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4034:009
general
└ P840.10
Step 10
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4034:010
general
└ P840.12
Step 12
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4034:012
general
└ P840.13
Step 13
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4034:013
general
└ P840.14
Step 14
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4034:014
general
└ P840.15
Step 15
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4034:015
general
P841.00
Cycl. sequence 3
1
1 ... 65535
0x4035
general
P845.xx
Sequence 4
└ P845.01
Step 1
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4036:001
general
└ P845.02
Step 2
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4036:002
general
└ P845.04
Step 4
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4036:004
general
└ P845.05
Step 5
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4036:005
general
└ P845.06
Step 6
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4036:006
general
└ P845.07
Step 7
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4036:007
general
└ P845.09
Step 9
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4036:009
general
Cycl. sequence 1
1
1 ... 65535
0x4031
general
└ P835.04 Step 4
└ P835.09 Step 9 Skip step [0] Selection list
└ P835.14 Step 14 Skip step [0] Selection list
└ P840.01 Step 1
└ P840.06 Step 6
Skip step [0]
Skip step [0]
Skip step [0]
Selection list
Selection list
Selection list
0x4032:004
0x4034:001
0x4034:006
general
general
general
general
general
└ P840.11 Step 11
└ P840.16 Step 16
└ P845.03 Step 3
└ P845.08 Step 8
Skip step [0]
Skip step [0]
Skip step [0]
Skip step [0]
Selection list
Selection list
Selection list
Selection list
0x4034:011
0x4034:016
0x4036:003
0x4036:008
general
general
general
general
70 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P845.10
Step 10
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4036:010
general
└ P845.11 Step 11
└ P845.12
Step 12
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4036:012
general
└ P845.13
Step 13
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4036:013
general
└ P845.14
Step 14
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4036:014
general
└ P845.15
Step 15
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4036:015
general
P846.00
Cycl. sequence 4
1
1 ... 65535
0x4037
general
P850.xx
Sequence 5
└ P850.01
Step 1
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4038:001
general
└ P850.02
Step 2
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4038:002
general
└ P850.04
Step 4
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4038:004
general
└ P850.05
Step 5
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4038:005
general
└ P850.06
Step 6
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4038:006
general
└ P850.07
Step 7
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4038:007
general
0x4038:008
└ P850.09
Step 9
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4038:009
general
└ P850.10
Step 10
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4038:010
general
└ P850.11
Step 11
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4038:011
general
└ P850.12
Step 12
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4038:012
general
0x4038:013
└ P850.14
Step 14
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4038:014
general
└ P850.15
Step 15
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4038:015
general
└ P850.16
Step 16
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4038:016
general
P851.00
Cycl. sequence 5
1
1 ... 65535
0x4039
general
└ P855.01
Step 1
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403A:001
general
└ P855.02
Step 2
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403A:002
general
└ P855.03
Step 3
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403A:003
general
└ P855.04
Step 4
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403A:004
general
└ P855.06
Step 6
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403A:006
general
└ P855.07
Step 7
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403A:007
general
└ P855.08
Step 8
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403A:008
general
└ P855.09
Step 9
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403A:009
general
└ P855.11
Step 11
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403A:011
general
└ P855.12
Step 12
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403A:012
general
└ P855.13
Step 13
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403A:013
general
└ P855.14
Step 14
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403A:014
general
└ P855.16
Step 16
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403A:016
general
P856.00
Cycl. sequence 6
1
1 ... 65535
0x403B
general
P860.xx
Sequence 7
└ P860.01
Step 1
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403C:001
general
└ P860.03
Step 3
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403C:003
general
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x4036:011
general
└ P845.16 Step 16
└ P850.03 Step 3
└ P850.08 Step 8 Skip step [0] Selection list
└ P850.13 Step 13 Skip step [0] Selection list
P855.xx
Sequence 6
Skip step [0]
Skip step [0]
Selection list
Selection list
0x4036:016
0x4038:003
general
general
general
general
└ P855.05 Step 5
└ P855.10 Step 10
└ P855.15 Step 15
└ P860.02 Step 2
Skip step [0]
Skip step [0]
Skip step [0]
Skip step [0]
Selection list
Selection list
Selection list
Selection list
0x403A:005
0x403A:010
0x403A:015
0x403C:002
general
general
general
general

Display code
Short designation
Default setting
Setting range
Address
Category
└ P860.04
Step 4
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403C:004
general
└ P860.05 Step 5
└ P860.06
Step 6
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403C:006
general
└ P860.07
Step 7
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403C:007
general
└ P860.08
Step 8
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403C:008
general
└ P860.09
Step 9
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403C:009
general
└ P860.11
Step 11
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403C:011
general
└ P860.12
Step 12
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403C:012
general
└ P860.13
Step 13
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403C:013
general
└ P860.14
Step 14
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403C:014
general
└ P860.16
Step 16
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403C:016
general
P861.00
Cycl. sequence 7
1
1 ... 65535
0x403D
general
P865.xx
Sequence 8
└ P865.01
Step 1
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403E:001
general
└ P865.03
Step 3
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403E:003
general
└ P865.04
Step 4
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403E:004
general
└ P865.05
Step 5
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403E:005
general
└ P865.06
Step 6
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403E:006
general
0x403E:007
└ P865.08
Step 8
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403E:008
general
└ P865.09
Step 9
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403E:009
general
└ P865.10
Step 10
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403E:010
general
└ P865.11
Step 11
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403E:011
general
0x403E:012
└ P865.13
Step 13
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403E:013
general
└ P865.14
Step 14
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403E:014
general
└ P865.15
Step 15
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403E:015
general
└ P865.16
Step 16
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403E:016
general
0x403F
Skip step [0]
Selection list
0x403C:005
general
└ P860.10 Step 10
└ P860.15 Step 15
└ P865.02 Step 2
└ P865.07 Step 7 Skip step [0] Selection list
└ P865.12 Step 12 Skip step [0] Selection list
Skip step [0]
Skip step [0]
Skip step [0]
Selection list
Selection list
Selection list
0x403C:010
0x403C:015
0x403E:002
general
general
general
general
general
P866.00 Cycl. sequence 8 1 1 ... 65535
general
* Default setting depending on the size. Firmware version 04.00.00.00
72 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

4.5. Save parameter settings in the memory module
4.5.1. Save parameter settings with keypad
If one parameter setting has been changed with the keypad but has not been saved in the
memory module with mains failure protection, the SET display is blinking.
In order to save parameter settings in the user memory of the memory module, press the
keypad enter key longer than 3 s.
4.5.2. Save parameter settings with »Emotron Easy starter«
If a parameter setting has been changed with the »Emotron Easy starter« but not yet
saved in the memory module with mains failure protection, the status line of the
»Emotron Easy starter« displays the note "The parameter set was changed".
In order to save parameter settings in the user memory of the memory module,
• click the button in the toolbar of the »Emotron Easy starter«
• press the function key <F6> or
• execute the device command "Save user data": 0x2022:003 (P700.03) = "On / start [1]".
or

5. Diagnostics and fault elimination
"RDY" LED (blue)
"ERR" LED (red)
Status/meaning
off
off
No supply voltage.
on
on
Initialisation (inverter is started.)
off
Safe torque off (STO) active.
blinking fast (4 Hz)
Safe torque off (STO) active, warning active.
off
Inverter inhibited.
Inverter disabled, warning active.
Inverter disabled, error active.
short time
Inverter inhibited, no DC-bus voltage.
every 1 s
USB module is connected, 5-V supply voltage for the USB module is available.
off
Inverter enabled.
The motor rotates according to the specified setpoint or quick stop active.
blinking fast (4 Hz)
Inverter enabled, warning active.
Inverter enabled, quick stop as response to fault active.
mode
Firmware update active.
synchronous mode
"Visual tracking" function is active.
5.1. LED status display
The "RDY" and "ERR" LED status displays on the front of the inverter provide some quick
information about certain operating states.
blinking (1 Hz)
blinking (2 Hz)
blinking fast (4 Hz)
on
lit every 1.5 s for a
on for a short time
on
blinking (1 Hz)
Both LEDs are blinking in a rapidly alternating
Safe torque off (STO)
Error handling
Error handling 111
The motor rotates according to the specified setpoint or quick stop active.
Error handling
Firmware download 449
486
111
111
Both LEDs are blinking in a very rapidly
Optical device identification 133
74 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

5.2. Diagnostics parameter
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
•
set.
0x2B0B
Frequency setpoint
•
From version 03.00
Display of the actual frequency setpoint that is internally transferred
0x2B0E
Frequency setpoint
Display of the frequency setpoint currently assigned.
from the current output frequency 0x2DDD (P100.00).
0x2B0F
VFC output frequency
•
Read only: x.x Hz
Display of the current output frequency at V/f operation.
0x2D4F
Motor utilisation (i²*t)
•
Read only: x %
Display of the current thermal motor utilisation.
0x2D87
DC-bus voltage
•
Read only: x V
Display of the current DC-bus voltage.
•
Read only: x.x A
•
Read only: x VAC
•
Read only: x.xxx kW
0x2DA2:002
Output power: Apparent power
•
Read only: x.xxx kVA
Display of the apparent output power for an energy analysis in the
0x2DA3:001
Output energy: Motor
•
Read only: x.xx kWh
Display of the output power in motor mode for an energy analysis in
0x2DA3:002
Output energy: Generator
•
Read only: x.xx kWh
Display of the output power in generator mode for an energy analysis
0x2DDD
Output frequency
•
Read only: x.x Hz
Display of the current output frequency for diagnostics of the control.
0x400D
Scaled actual value
•
Read only: x Units
Display of the current speed in application units.
0x6077
Torque actual value
•
Read only: x.x %
Display of the current torque.
0x6078
Current actual value
•
Read only: x.x %
Display of the present motor current.
The inverter provides many diagnostic parameters which are helpful for operation,
maintenance, error diagnosis, error correction, etc.
• In the following overview the most common diagnostic parameters are listed. For the
keypad you can find these diagnostic parameters in group 1.
• Further parameters for more specific diagnostic purposes are described in the following
subchapters.
• The diagnostic parameters can only be read and cannot be written to.
0x2030
(P102.00)
(P123.00)
(P105.00)
0x2D88
(P104.00)
0x2D89
(P106.00)
0x2DA2:001
(P108.01)
(P108.02)
CRC parameter set
Read only
•
Read only: x.x Hz
(Freq. setpoint)
Read only: x.x Hz
•
(Mot. i2t utilis.)
(DC-bus voltage)
Motor current
(Motor current)
Motor voltage
(Motor voltage)
Output power: Effective power
(Output power: Effective power)
(Output power: Apparent power)
Display of the 32-bit hash sum for the integrity check of the parameter
to the motor control (after scaling and ramp generator).
Depending on the present operating conditions, this value may
•
differ
Display des present current-r.m.s. value.
Display of the current motor voltage.
Display of the active output power for an energy analysis in the
respective application.
respective application.
(P109.01)
(P109.02)
(P100.00)
(P101.00)
(P107.00)
(P103.00)
(Output energy: Motor)
(Output energy: Generator)
(Output frequency)
(Scaled act value)
(Torque actual)
(Current actual)
the respective application.
in the respective application.
100 % ≡ Motor rated torque 0x6076 (P325.00)
•
100 % ≡ Motor rated current 0x6075 (P323.00)
•

5.2.1. Logbook
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x2022:015
Device commands: Delete logbook (Device
inhibited.
1 = delete all entries in the logbook.
0
Off / ready
1
On / start
For diagnostic purposes, the logbook contains the last 32 error messages and warning
signals of the inverter, which have occurred during operation.
Preconditions
The logbook can only be accessed
• via the user interface of »Emotron Easy starter« ("Diagnostics" tab) or
• via network.
Details
In contrast to the error history buffer, the logbook additionally protocols the following
events:
• Fault messages
• Change-over from normal to setup mode (and vice versa)
• Execution of device commands
• Avoidance of safety functions
The logbook entries are saved persistently in the inverter. If all 32 memory units are
occupied, the oldest entry is deleted for a new entry. By means of the "Delete logbook"
device command, all logbook entries can be deleted.
Accessing the logbook with »Emotron Easy starter«
• Select the inverter on the left side in the »Emotron Easy starter« device list.
• Change to the "Diagnostics" tab.
• Click the
icon to open the logbook.
Observe that the logbook only presents a snapshot at the time the data are read out. If a
new event occurs, the logbook must be read out again so that the new event becomes
visible.
Accessing the logbook via network
The logbook can also be accessed via network from a higher-level controller or a
visualisation. The structure of the diagnostic messages complies with the "ETG.1020"
standard of the EtherCAT Technology Group (ETG).
See chapter 13.3 of document "ETG.1020 Protocol Enhancements" provided
by the EtherCAT Technology Group (ETG) for detailed information on the
structure of the diagnostic messages.
(P700.15)
commands: Delete logbook)
Setting can only be changed if the inverter is
76 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

5.2.2. Error history buffer
For purposes of diagnostics, the error history buffer contains the last 32 error and warning
messages of the inverter, which have occurred during operation. The error history buffer
can be read out using the keypad via P155.00 and provides a limited view on the logbook.
Details
• For each event that is recorded, the error history buffer contains the message text, the
error code, the time of occurrence as well as a counter for successive, identical events.
If an event that has already been recorded occurs repeatedly, only the counter is
incremented.
• The error history buffer can be reset by the user. In order to prevent the buffer from
being reset by the user, this function can be protected by means of a password.
• Observe that the error history buffer only presents a snapshot at the time the data are
read out. If a new event occurs, the error history buffer must be read out again via
P155.00 so that the new event becomes visible.

Accessing the error history buffer with the keypad
1. Use the key in the operating mode to navigate to the
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Information displayed (page 1):
① Message text
② No. of the entry (01 = latest event)
③ Response (W = warning, T = trouble, F = fault)
④ Error code
Information displayed (page 2):
⑤ Time of occurrence
⑥ No. of the entry (01 = latest event)
⑦ Counter for successive, identical events
Note:
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
Read only
0x2006:001
Error history buffer: Maximum number of messages
Read only
Display of the maximum number of messages which can be stored in
the history buffer (from subindex 6).
0x2006:002
Error history buffer: Latest message
Read only
Display of the subindex of the most recent message.
0x2006:003
Error history buffer: Latest acknowledgement
0 ... [0] ... 37
0 = delete all entries in the error history buffer.
0x2006:004
Error history buffer: New message
Read only
Reserved for future extensions.
Bit 0
Send emergency message
Bit 1
Disable info message
Bit 2
Disable warning message
Bit 3
Disable error message
Bit 5
Message overwritten
0x2006:006
Error history buffer: Message 0
Read only
Error history buffer entry 01 (latest event)
parameterization mode one level below.
You are now in the group level. All parameters of the
inverter are divided into different groups according to
their function.
Note: By using the
upwards again anytime.
Use the navigation key to select group 1
("Diagnostics").
Use the
You are now in the parameter level of the group
selected.
Use the
Use the key to navigate to one level below.
You are now in the error history buffer.
Use the
through the error history buffer entries.
Use the key, you can switch over the display.
key you can navigate one level
key to navigate to one level below.
and
select the P155.00 parameter.
and
navigation keys you can now scroll
0x2006:000
(P155.00)
Error history buffer: Keypad display (Fault memory:
Error memory)
message
0x2006:005 Error history buffer: Buffer overflow 0 ... [1] ... 65535 Bit 0 ... bit 4 = 0.
Bit 4 Mode selection
By using the
Display of the error history buffer on the keypad.
Bit 5 = 1 ≡ overflow (after recording the 33rd event in the error history
buffer.
key you can exit the error history buffer again.
78 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x2006:007
Error history buffer: Message 1
Read only
Error history buffer entry 02
0x2006:008
Error history buffer: Message 2
Read only
Error history buffer entry 03
0x2006:009
Error history buffer: Message 3
Read only
Error history buffer entry 04
0x2006:010 Error history buffer: Message 4
Read only
0x2006:011
Error history buffer: Message 5
Read only
Error history buffer entry 06
Read only
0x2006:013
Error history buffer: Message 7
Read only
Error history buffer entry 08
Read only
0x2006:015
Error history buffer: Message 9
Read only
Error history buffer entry 10
Read only
0x2006:017
Error history buffer: Message 11
Read only
Error history buffer entry 12
0x2006:018
Error history buffer: Message 12
Read only
Error history buffer entry 13
0x2006:019
Error history buffer: Message 13
Read only
Error history buffer entry 14
0x2006:020
Error history buffer: Message 14
Read only
Error history buffer entry 15
0x2006:021
Error history buffer: Message 15
Read only
Error history buffer entry 16
0x2006:022
Error history buffer: Message 16
Read only
Error history buffer entry 17
0x2006:023
Error history buffer: Message 17
Read only
Error history buffer entry 18
0x2006:024
Error history buffer: Message 18
Read only
Error history buffer entry 19
0x2006:025
Error history buffer: Message 19
Read only
Error history buffer entry 20
0x2006:026
Error history buffer: Message 20
Read only
Error history buffer entry 21
0x2006:027
Error history buffer: Message 21
Read only
Error history buffer entry 22
0x2006:028
Error history buffer: Message 22
Read only
Error history buffer entry 23
0x2006:029
Error history buffer: Message 23
Read only
Error history buffer entry 24
0x2006:030
Error history buffer: Message 24
Read only
Error history buffer entry 25
0x2006:031
Error history buffer: Message 25
Read only
Error history buffer entry 26
0x2006:032
Error history buffer: Message 26
Read only
Error history buffer entry 27
0x2006:033
Error history buffer: Message 27
Read only
Error history buffer entry 28
0x2006:034
Error history buffer: Message 28
Read only
Error history buffer entry 29
0x2006:035
Error history buffer: Message 29
Read only
Error history buffer entry 30
0x2006:036
Error history buffer: Message 30
Read only
Error history buffer entry 31
Read only
Error history buffer entry 05
0x2006:012 Error history buffer: Message 6
0x2006:014 Error history buffer: Message 8
0x2006:016 Error history buffer: Message 10
Error history buffer entry 07
Error history buffer entry 09
Error history buffer entry 11
0x2006:037 Error history buffer: Message 31
Error history buffer entry 32

Structure of the messages
Message:
00E010431201990000520B0473FC0100050001
00E01043
1201
9900
00520B0473FC0100
0500
01
Meaning:
Diag code
Message type
Text ID
Time stamp in [ns]
Flag param. 1
Parameter 1
Hex value:
0x4310 E000
0x0112
0x0099
0x0001 FC73 040B 5200
0x0005
0x01
The following example shows the detailed structure of one of the following messages
(parameter 0x2006:006 ... 0x2006:037):
Data type: U32 U16 U16 U64 U16 U8
Notes:
• The upper 16 bits of the "Diag Code" contain the error code (in the example "0x4310").
• Bit 0 ... 3 of the message type contain the error type (0: Info, 1: Warning, 2: Trouble, 3:
Fault).
• Convert time stamp: 0x0001 FC73 040B 5200 = 559045896000000 ns = 6 days, 11
hours, 17 minutes, 25 seconds
• The flag for parameter 1 has no meaning for decoding the message.
• The parameter 1 contains the counter for successive, identical events.
80 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

5.2.3. Inverter diagnostics
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x2040
Access protection status (Protect. status)
Read only
Bit-coded display of the active access protection after login by PIN1/
Bit 1
Only favorites changeable
0x2827
Currently loaded parameter settings (Status load.
Display of the parameter settings currently loaded.
0
User settings
User parameter settings of the memory module
1
Reset 60 Hz setting
Delivery status (default setting) for 50-Hz device
2
Reset 50 Hz setting
Delivery status (default setting) for 60-Hz device
3
OEM default settings
OEM parameter settings of the memory module
Read only
Bit 0
Flexible I/O configuration
1 ≡ the inverter was disabled by the trigger set in 0x2631:001 (P400.01).
Bit 1
Network
1 ≡ the inverter was disabled via network.
Bit 6
Fault DC-bus
1 ≡ the inverter was inhibited due to a DC-bus error.
Bit 7
Drive not ready
1 ≡ the inverter was disabled internally since the drive was not ready for
Defect device hardware
Bit 8
Quick stop active
1 ≡ the inverter has been disabled by the "Quick stop" function.
Bit 9
Motor data identification
1 ≡ the inverter was disabled by the "Automatic identification of the
motor data" function.
Bit 10
Automatic holding brake control
1 ≡ the inverter was disabled by the "Holding brake control" function.
Bit 12
CiA402 Inverter disabled
1 ≡ the inverter was disabled by the internal state machine.
command.
Bit 13
CiA402 Quick stop option code 2
1 ≡ the inverter has been disabled by the "Quick stop" function.
Bit 14
Safe torque off (STO)
1 ≡ the inverter has been disabled by the integrated safety system.
Bit 15
CiA402 operation mode 0
1 ≡ the inverter has been disabled because the selection "No mode
change/no mode assigned [0]" is set in 0x6060 (P301.00).
The following parameters supply some information about the current operating status of
the inverter.
This includes the following information:
• Active access protection after log-in by means of PIN1/PIN2
• Currently loaded parameter settings
• Cause(s) for disable, quick stop and stop.
• Active control source and active setpoint source
• Active operating mode
• Keypad status
• Status of the internal motor control
Some of the following parameters contain bit-coded status words. Each single bit has a
certain meaning.
Display of status words on keypad
453
(P197.00)
(P198.00)
0x282A:001
(P126.01)
PIN2.
Bit 0 No write access
par)
Read only
Status words: Cause of disable (Status words: Cause
of disable)
Bit 2 Axis command 1 ≡ the inverter was disabled via axis command 0x2822:001.
Datenhandling 113
Saving/loading the parameter settings
Bit-coded display of the cause(s) for disabled inverter.
operation.
Possible causes:
Under/overvoltage in the DC bus
361
The bit is only set if
operating mode 0x6060 (P301.00) = "CiA: Velocity mode [2]" and
state machine in the "Switch on disabled" state and
the state change has not been carried out via the "Disable operation"

Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x282A:002
(P126.02)
Status words: Cause of quick stop (Status words:
Read only
Bit coded display of the cause(s) of quick stop.
Bit 0
Flexible I/O configuration
1 ≡ quick stop was activated by the trigger set in 0x2631:003 (P400.03).
Bit 1
Network
1 ≡ quick stop was activated via network.
Bit 2
Axis command
1 ≡ quick stop was activated via axis command 0x2822:001.
0x282A:003
Status words: Cause of stop (Status words: Cause of
Read only
Bit coded display of the cause(s) of stop.
Bit 0
Flexible I/O: Start disabled
1 ≡ stop was activated by the trigger set in 0x2631:002 (P400.02).
Bit 1
Flexible I/O: Run forward
1 ≡ stop has been activated due to cancellation of the command "Run
forward (CW)".
Bit 2
Flexible I/O: Run reverse
1 ≡ stop has been activated due to cancellation of the command "Run
reverse (CCW)".
Bit 3
Flexible I/O: Jog forward
1 ≡ stop has been activated due to cancellation of the command "Jog
foward (CW)".
Bit 4
Flexible I/O: Jog reverse
1 ≡ stop has been activated due to cancellation of the command "Jog
reverse (CCW)".
Bit 5
Network
1 ≡ stop was activated via network.
Bit 7
Control mode transition
1 ≡ stop has been activated due to a change of the operating mode.
Bit 8
End of sequence
1 ≡ stop was activated by the "sequencer" function since the sequence
mode0x402F (P824.00) is set ="Stop [1]" or "Stop and abort [2]".
Bit 15
Waiting for start
1 ≡ Stop is active as a start command is not yet available (e.g. after
enabling the inverter).
Read only
Bit 8
Reversal
1 ≡ reversal active.
Bit 10
Safe torque off (STO) active
1 ≡ "Safe torque off (STO)" function has been triggered by the
integrated safety system.
Read only
0
Initialisation
2
Not ready to switch on
4
Ready to switch on
5
Switched on
6
Operation enabled
7
Disable operation
9
Quick stop active
10
Fault reaction active
11
Fault
0x282B:001
Inverter diagnostics: Active control source (Inverter
Read only
Display of the control source that is currently active.
0
Flexible I/O configuration
1
Network
2
Keypad
Cause of QSP)
Bit 6 Error response 1 ≡ quick stop has been activated as a response to an error.
(P126.03)
0x282A:004 Status words: Extended status word
0x282A:005
(P126.05)
stop)
Bit 6 Keypad 1 ≡ stop was activated via keypad.
Status words: Device status (Status words: Device
status)
is completed.
The bit is only set after the sequence is completed if End of sequence
Bit-coded status word.
Display of the current inverter device state.
3 Switch on disabled
8 Shut down
(P125.01)
diag.: Active control)
8 Keypad full control
82 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x282B:002
(P125.02)
Inverter diagnostics: Active setpoint source (Inverter
Read only
Display of the setpoint source that is currently active.
0
Not selected
1
Analog input 1
2
Analog input 2
4
HTL input
5
Network Setpoint
11
Setpoint preset 1
12
Setpoint preset 2
14
Setpoint preset 4
15
Setpoint preset 5
16
Setpoint preset 6
17
Setpoint preset 7
19
Setpoint preset 9
20
Setpoint preset 10
21
Setpoint preset 11
22
Setpoint preset 12
24
Setpoint preset 14
25
Setpoint preset 15
31
Segment preset 1
32
Segment preset 2
34
Segment preset 4
35
Segment preset 5
36
Segment preset 6
37
Segment preset 7
39
Last segment
50
Motor potentiometer
51
PID setpoint
From version 04.00
0x282B:003
Inverter diagnostics: Keypad LCD status (Inverter
Read only
Bit-coded state of the keypad status displays.
Bit 1
REM
1 ≡ remote control via terminals, network, etc. active.
Bit 2
MAN
1 ≡ manual setpoint selection via keypad active.
Bit 3
Auto
1 ≡ automatic setpoint selection via terminals, network, etc. active.
Bit 4
Set
1 ≡ a parameter setting has been changed but not been saved yet in the
memory module with mains failure protection.
0x282B:004
Inverter diagnostics: Active drive mode (Inverter
Read only
Display of the active drive mode.
1
PID control
PID control active.
2
Torque mode
From version 03.00
"Torque mode" active.
diag.: Active setpoint)
3 Keypad Setpoint
13 Setpoint preset 3
18 Setpoint preset 8
23 Setpoint preset 13
(P125.03)
(P125.04)
33 Segment preset 3
38 Segment preset 8
diag.: Keypad LCD stat.)
Bit 0 LOC 1 ≡ local keypad control active.
diag.: Drive mode)
0 Velocity mode "Velocity mode" active.

Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info 4 Jog operation
"Jog foward (CW)" or "Jog reverse (CCW)" function active.
0x2831 Inverter status word
Read only
Bit 1
Speed 1 limited
1 ≡ input of speed controller 1 in limitation.
Bit 3
Torque limited
1 ≡ setpoint torque in limitation.
Bit 4
Current limited
1 ≡ setpoint current in limitation.
Bit 5
Speed 2 limited
1 ≡ input of the speed controller 2 in "torque mode" in limitation.
Bit 6
Upper speed limit active
1 ≡ in "torque mode", the speed is limited to upper speed limit
0x2946:001 (P340.01).
Bit 7
Lower speed limit active
1 ≡ in "torque mode", the speed is limited to lower speed
limit0x2946:002 (P340.02).
Bit 10
Output frequency limited
1 ≡ setpoint frequency with V/f operation in limitation.
Bit 11
Magnetisation completed
1 ≡ during V/f operation, the factor 7 rotor time constant has passed
current for the first time). Otherwise 0.
Bit 12
Motor phase error
1 ≡ motor phase failure detection active.
Bit 14
Error reset blocking time active
1 ≡ the fault can only be reset when the blocking time has elapsed.
0x2833
Inverter status word 2
Read only
Bit-coded status word 2 of the inverter.
Bit 2
Manual control active
1 ≡ manual control active.
Bit 6
DC braking active
1 ≡ DC braking active.
0x2DAC
Keypad status (Keypad status)
Read only
Bit-coded display of the keypad status.
Bit 0
Start Key
1 ≡ keypad start key pressed.
Bit 1
Stop Key
Bit 2
Up arrow
1 ≡ keypad up-arrow key pressed.
Bit 4
Enter Key
1 ≡ keypad enter key pressed.
Bit 5
Back key
1 ≡ keypad back key pressed.
0x2DAD
Internal hardware states (Int. HW states)
Read only
Bit-coded display of internal hardware states.
Bit 0
Relay
0 ≡ X9/NO-COM open and NC-COM closed. 1 ≡ X9/NO-COM closed and
NC-COM open.
Bit 1
Digital output 1
0 ≡ LOW level, 1 ≡ HIGH level.
Bit 2
Digital output 2
Bit 10
Charge Relay
1 ≡ precharging of the DC bus via charge relay is active.
(P150.00)
Read only
Bit 2 Speed limited 1 ≡ output of speed controller 1 in limitation.
Bit 1 Manual test mode active 1 ≡ manual test mode active.
(P119.00)
Bit-coded status word of the internal motor control.
(calculated from the time at which the inverter was enabled without
restart on the fly and with a total motor current of 20 % rated motor
(P120.00)
0x603F
1 ≡ keypad stop key pressed.
Bit 3 Down arrow 1 ≡ keypad down-arrow key pressed.
Error code (Error code)
Error message
84 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

5.2.4. Network diagnostics
0x282B:005
Inverter diagnostics: Most recently used control
Read only
Display of the network register for the control that was accessed last
The lowest byte is always 0x00.
0x282B:006
Inverter diagnostics: Most recently used setpoint
Read only
Display of the network register for setpoint selection that was accessed
The lowest byte is always 0x00.
0x400B:006
Process input data: Velocity mode setpoint (Process
Mappable parameter for defining the setpoint for operating mode "MS:
determined by the sign of the setpoint.
0x400B:007
Process input data: PID setpoint (Process data IN: PID
Mappable parameter for defining the setpoint for the PID control via
"Network [5]" must be set in 0x2860:002 (P201.02).
0x400B:008
Process input data: Torque mode setpoint (Process
Mappable parameter for defining the setpoint for operating mode "MS:
Scaled torque setpoint = 345 [Nm] / 23 = 43.125 [Nm]
0x231F:001
Module ID: Active module ID (Module ID: Active
Default setting depending on the size.
Display of the network options currently configured in the inverter.
48
No network
71 80 82 84
87
Modbus
0x231F:002
Module ID: Module ID connected (Module ID:
Display of the network option currently available in the inverter.
0x400B:009
Process input data: Torque scaling (Process data IN:
From version 02.00
Scaling factor for torque setpoint 0x400B:008 (P592.08) and actual
The following parameters show some general information with regard to the network
option available and the network.
Further fieldbus-specific diagnostic parameters are described in the following subchapters.
Parameter Name / value range / [default setting] Info
(P125.05)
(P125.06)
(P592.06)
(P592.07)
(P592.08)
register
(Inverter diag.: Netw. contr.reg.)
register
(Inverter diag.: Netw. setp.reg.)
data IN: Veloc. mode setp)
-599.0 ... [0.0] ... 599.0 Hz
setpoint)
-300.00 ... [0.00] ... 300.00 PID unit
data IN: Torque mode setp)
-32768 ... [0] ... 32767 Nm
(e. g. 0x6040 or 0x400B:1).
Format: 0xiiiiss00 (iiii = hexadecimal index, ss = hexadecimal subindex)
last (e. g. 0x6042 or 0x400B:3).
Format: 0xiiiiss00 (iiii = hexadecimal index, ss = hexadecimal subindex)
Velocity mode" via network.
If this parameter is to be used as standard setpoint source, the selec
"Network [5]" must be set in 0x2860:001 (P201.01).
If this bipolar setpoint is used, the direction of rotation cannot be
controlled via the network control word. The direction of rotation is
network.
If this parameter is to be used as standard setpoint source, the selec
Torque mode" via network.
If this parameter is to be used as standard setpoint source, the selec
"Network [5]" must be set in 0x2860:003 (P201.03).
The scaling factor can be set in 0x400B:009 (P592.09).
Scaled torque setpoint = torque setpoint (0x400B:008) / 2
Example:
Torque setpoint (0x400B:008) = 345 [Nm]
Scaling factor (0x400C:009) = 3
scaling factor
tion
tion
tion
(P500.01)
(P500.02)
(P592.09)
module ID); Read only
67 CANopen
86
Module ID conn.)
Read only
For the meaning of the display see parameter
0x231F:001 (P500.01)
Torque scaling)
-128 ... [0] ... 127
.
199
Related topics
Configuring the network
166
With the help of this module ID, the keypad only shows the
communication parameters relevant to the respective network.
Note!
When switched on, the inverter checks whether the parameter settings
saved in the memory module match the inverter hardware and
firmware. In case of an incompatibility, a corresponding error message
is output. For details see chapter "Datenhandling" (section "Hardware
and firmware updates/downgrades"). 113
Note!
When switched on, the inverter checks whether the parameter
settings saved in the memory module match the inverter hardware
and firmware. In case of an incompatibility, a corresponding error
message is
"Hardware and
torque value 0x400C:007 (P593.07) via network.
With the setting 0, no scaling takes place.
output. For details see chapter "Datenhandling" (section
firmware updates/downgrades"). 113

5.2.4.1. CANopen diagnostics
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x1000
Device type
CANopen device profile according CANopen specification CiA 301/ CiA
0x02030192 ≡ stepper double axis
0x1001
Error register
Bit-coded error status.
Bit 7: Manufacturer-specific error
Read only
0x1009
Manufacturer hardware version
Read only
Display of the manufacturer hardware version.
Read only
0x1018:001
Identity object: Vendor ID
Display of the manufacturer's identification number.
Automation e. V." is "0x0000003B".
0x1018:002
Identity object: Product code
Read only
Display of the product code of the inverter.
0x1018:003
Identity object: Revision number
Read only
Display of the main and subversion of the firmware.
0x1018:004
Identity object: Serial number
Read only
Display of the serial number of the inverter.
0x2302:001
Active CANopen settings: Active node ID (CANopen
Read only
Display of the active node address.
0x2302:002
Active CANopen settings: Active baud rate (CANopen
Read only
Display of the active baud rate.
0
Automatic
From version 03.00
2
50 kbps
3
125 kbps
4
250 kbps
5
500 kbps
7
1 Mbps
The following parameters serve to diagnose the CANopen interface and communication
via CANopen.
Preconditions
Control unit (CU) of the inverter is provided with CANopen.
Read only
Read only
0x1008 Manufacturer device name
0x100A Manufacturer software version
Read only
402.
Specifies the axis type:
0x01010192 ≡ single axis
0x02010192 ≡ double axis
0x01020192 ≡ servo single axis
0x02020192 ≡ servo double axis
0x01030192 ≡ stepper single axis
Bit 0 is set if an error is active.
The other bits signalise which group the active error belongs to:
Bit 1: Current error
Bit 2: Voltage error
Bit 3: Temperature error
Bit 4: Communication error
Bit 5: Device profile-specific error
Bit 6: Reserved (always 0)
Display of the manufacturer device name.
Display of the manufacturer software version.
The identification number allocated to CG by the organisation "CAN in
(P511.01)
(P511.02)
diag.: Active node ID)
diag.: Active baud rate)
1 20 kbps
6 800 kbps
86 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x2307
(P515.00)
CANopen time-out status (Time-out status)
Read only
Bit-coded status display of the CAN time monitoring functions.
Bit 0
RPDO1-Timeout
1 ≡ RPDO1 was not received within the monitoring time or not with the
Setting of monitoring time for RPDO1 in 0x1400:005 (P540.05).
Bit 1
RPDO2-Timeout
1 ≡ RPDO2 was not received within the monitoring time or not with the
Setting of monitoring time for RPDO2 in 0x1401:005 (P541.05).
Bit 2
RPDO3-Timeout
1 ≡ RPDO3 was not received within the monitoring time or not with the
Setting of monitoring time for RPDO3 in 0x1402:005 (P542.05).
Bit 8
Heartbeat-Timeout Consumer 1
1 ≡ within the "Heartbeat Consumer Time", no heartbeat telegram was
"Heartbeat Consumer Time" setting in 0x1016:001 (P520.01).
Bit 9
Heartbeat-Timeout Consumer 2
1 ≡ within the "Heartbeat Consumer Time", no heartbeat telegram was
"Heartbeat Consumer Time" setting in 0x1016:002 (P520.02).
Bit 10
Heartbeat-Timeout Consumer 3
1 ≡ within the "Heartbeat Consumer Time", no heartbeat telegram was
"Heartbeat Consumer Time" setting in 0x1016:003 (P520.03).
Bit 11
Heartbeat-Timeout Consumer 4
1 ≡ within the "Heartbeat Consumer Time", no heartbeat telegram was
"Heartbeat Consumer Time" setting in 0x1016:004 (P520.04).
0x2308
CANopen status (CANopen status)
Read only
Display of the current fieldbus state
0
Initialisation
Fieldbus initialisation active.
automatically adopts the "Pre-Operational" state.
1
Reset node
"Reset Node" NMT command active.
relevant parameters).
2
Reset communication
"Reset Communication" NMT command active.
Initialisation of all CAN-relevant parameters with the values stored.
4
Stopped
Only network management telegrams can be received.
5
Operational
Parameter data and process data can be received. If defined, process
data is sent as well.
127
Pre-Operational
Parameter data can be received, process data are ignored.
0x2309
CANopen controller status (CAN contr.status)
Read only
Status display of the internal CANopen controller.
1
Error active
The inverter is a fully-fledged communication node at the CANopen
network. It is able to transmit and receive data and to report faults.
2
Error passive
The inverter can only passively indicate faulty reception via the ACK
field.
3
Bus off
The inverter is electrically separated from the CANopen network. In
automatic restart is implemented.
0x230A:001
CANopen statistics: PDO1 received (CAN statistics:
Read only
Display of the number of PDO1 telegrams received.
0x230A:002
CANopen statistics: PDO2 received (CAN statistics:
Read only
Display of the number of PDO2 telegrams received.
0x230A:003
CANopen statistics: PDO3 received (CAN statistics:
Read only
Display of the number of PDO3 telegrams received.
sync configured.
Status is reset automatically after the RPDO has been received again.
sync configured.
Status is reset automatically after the RPDO has been received again.
sync configured.
Status is reset automatically after the RPDO has been received again.
received from node 1 to be monitored.
Status can only be reset by mains switching or error reset.
received from node 2 to be monitored.
Status can only be reset by mains switching or error reset.
received from node 3 to be monitored.
Status can only be reset by mains switching or error reset.
received from node 4 to be monitored.
Status can only be reset by mains switching or error reset.
(P516.00)
(P517.00)
(P580.01)
The initialisation is started automatically at mains connection. During
this phase, the inverter us not involved in the data exchange process on
the CAN bus.
All CAN-relevant parameters are initialised with the saved settings.
When the initialisation process has been completed, the inverter
All parameters are initialised with the saved settings (not only the CAN-
order to exit this state, the CANopen interface must be reset. An
PDO1 received)
(P580.02)
(P580.03)
PDO2 received)
PDO3 received)

Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x230A:005
(P580.05)
CANopen statistics: PDO1 transmitted (CAN statistics:
Read only
Display of the number of PDO1 telegrams sent.
0x230A:006
CANopen statistics: PDO2 transmitted (CAN statistics:
Read only
Display of the number of PDO2 telegrams sent.
0x230A:007
CANopen statistics: PDO3 transmitted (CAN statistics:
Read only
Display of the number of PDO3 telegrams sent.
0x230A:009
CANopen statistics: SDO1 telegrams (CAN statistics:
Read only
Display of the number of SDO1 telegrams.
0x230A:010
CANopen statistics: SDO2 telegrams (CAN statistics:
Read only
Display of the number of SDO2 telegrams.
0x230B
(P518.00)
CANopen error counter (CAN errorcounter)
Read only
Display of the total number of CAN faults that have occurred.
PDO1 transmitted)
(P580.06)
(P580.07)
(P580.09)
(P580.10)
Related topics
CANopen
PDO2 transmitted)
PDO3 transmitted)
SDO1 counter)
SDO2 counter)
198
88 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

5.2.4.2. Modbus diagnostics
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x2322:001
Active Modbus settings: Active node ID (Modbus
Read only
Display of the active node address.
Read only
0x2322:003
Active Modbus settings: Data format (Modbus diag.:
Read only
Display of the active data format.
0x232A:001
Modbus statistics: Messages received (Modbus
Display of the total number of messages received.
"0".
0x232A:002
Modbus statistics: Valid messages received (Modbus
Read only
Display of the number of valid messages received.
"0".
"0".
"0".
Read only
"0".
The following parameters serve to diagnose the Modbus interface and communication via
Modbus.
Preconditions
Control unit (CU) of the inverter is provided with Modbus.
(P511.01)
0x2322:002
(P511.02)
(P511.03)
(P580.01)
(P580.02)
0x232A:003
(P580.03)
0x232A:004
(P580.04)
0x232A:005
(P580.05)
Related topics
diag.: Active node ID)
Active Modbus settings: Active baud rate (Modbus
diag.: Active baud rate)
Data format)
statistic: Mess. received)
Read only
statistic: Val. mess. rec.)
Modbus statistics: Messages with exceptions
(Modbus statistic: Mess. w. exc.)
Read only
Modbus statistics: Messages with errors (Modbus
statistic: Mess. w. errors)
Read only
Modbus statistics: Messages sent (Modbus statistic:
Messages sent)
Display of the active baud rate.
This counter counts both valid and invalid messages.
After the maximum value has been reached, the counter starts again
After the maximum value has been reached, the counter starts again
Display of the number of messages with exceptions that have been
received.
After the maximum value has been reached, the counter starts again
Display of the number of messages received with a faulty data integrity
(parity, CRC).
After the maximum value has been reached, the counter starts again
Display of the total number of messages sent.
After the maximum value has been reached, the counter starts again
Modbus RTU
220

5.2.5. Diagnostics of the inputs and outputs
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x60FD
Digital inputs
•
Read only
Bit coded display of the current state of the digital inputs
Bit 16
Level of digital input 1
0 ≡ LOW level, 1 ≡ HIGH level.
Bit 17
Level of digital input 2
Bit 18
Level of digital input 3
Bit 19
Level of digital input 4
Bit 21
Level of digital input 6
(not supported)
Bit 22
Level of digital input 7
Bit 25
Internal interconnection of digital inputs
0 ≡ digital input terminals are set to HIGH level via pull-up resistors.
1 ≡ digital input terminals are set to LOW level via pull-down resistors.
0x4016:005
Digital output 1: Terminal state
•
Read only
Display of the logic state of output terminal X3/DO1.
0
FALSE 1
0x4016:006
Digital output 1: Trigger signal state
•
Read only
Display of the logic state of the trigger signal for digital output 1
0
FALSE 1
0x4018:005
Relay: Relay state
•
Read only
Display of the logic state of the relay.
0
FALSE
1
TRUE
0x4018:006
Relay: Trigger signal state
•
Read only
Display of the logic state of the trigger signal for the relay (without
0
FALSE
1
TRUE
5.2.5.1. Digital inputs and outputs
The following parameters serve to diagnose the digital inputs and outputs of the inverter.
(P118.00)
(Digital inputs)
Bit 20 Level of digital input 5
TRUE
(without taking a ON/OFF delay set and inversion into consideration).
TRUE
Related topics
Configuration of digital inputs
Configuration of digital outputs
422
429
taking a ON/OFF delay set and inversion into consideration).
90 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

5.2.5.2. Analog inputs and outputs
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
•
0x2DA4:002
Diagnostics of analog input 1: Frequency value (AI1
Display of the current input value at X3/AI1 scaled as a frequency value.
"MS: Velocity mode [-2]" is selected in 0x2860:001 (P201.01).
0x2DA4:003
Diagnostics of analog input 1: Process controller
Display of the current input value at X3/AI1 scaled as a process
selected in 0x2860:002 (P201.02).
0x2DA4:004
Diagnostics of analog input 1: Torque value (AI1
Display of the current input value at X3/AI1 scaled as a percentage
"MS: Torque mode [-1]" is selected in 0x2860:003 (P201.03).
0x2DA4:016
Diagnostics of analog input 1: Status (AI1 diagnostics:
From version 04.00
Bit-coded display of the status of analog input 1 (X3/AI1).
Bit 0
Mode 0: 0 ... 10 VDC active
Bit 2
Mode 2: 2 ... 10 VDC active
Bit 3
Mode 3: -10 ... 10 VDC active
Bit 4
Mode 4: 4 ... 20 mA active
Bit 5
Mode 5: 0 ... 20 mA active
Bit 7
Calibration successful
Bit 8
Monitoring threshold exceeded/not
reached
Bit 9
Input current too low (mode 4)
Bit 10
Input voltage too low (mode 2)
Bit 11
Input voltage too high (mode 4)
0x2DA5:001
Diagnostics of analog input 2: Value in percent (AI2
Read only: x.x %
Display of the current input value at X3/AI2 scaled as a value in percent.
0x2DA5:002
Diagnostics of analog input 2: Frequency value (AI2
Read only: x.x Hz
Display of the current input value at X3/AI2 scaled as a frequency value.
"MS: Velocity mode [-2]" is selected in 0x2860:001 (P201.01).
selected in 0x2860:002 (P201.02).
0x2DA5:004
Diagnostics of analog input 2: Torque value (AI2
Read only: x.x %
Display of the current input value at X3/AI2 scaled as a percentage
100 % ≡ permissible maximum torque 0x6072 (P326.00)
The following parameters serve to diagnose the analog inputs and outputs of the inverter.
0x2DA4:001
(P110.01)
(P110.02)
(P110.03)
(P110.04)
(P110.16)
Diagnostics of analog input 1: Value in percent (AI1
diagnostics: AI1 terminal %)
Read only: x.x %
diagnostics: AI1 scaled freq.)
Read only: x.x Hz
value (AI1 diagnostics: AI1 scaled PID)
Read only: x.xx PID unit
diagnostics: AI1 scaled torq.)
Read only: x.x %
AI1 status)
Read only
Bit 1 Mode 1: 0 ... 5 VDC active
Bit 6 24 V supply OK
Display of the current input value at X3/AI1 scaled as value in percent.
100 % ≡ 10 V or 20 mA or 5
V
The standard setpoint source for operating mode
controller value.
The standard setpoint source for the reference value of PID control is
torque value.
100 % ≡ permissible maximum torque 0x6072 (P326.00)
The standard setpoint source for operating mode
0x6060 (P301.00)
0x6060 (P301.00)
=
=
(P111.01)
(P111.02)
0x2DA5:003
(P111.03)
(P111.04)
diagnostics: AI2 terminal %)
diagnostics: AI2 scaled freq.)
Diagnostics of analog input 2: Process controller
value (AI2 diagnostics: AI2 scaled PID)
Read only: x.xx PID unit
diagnostics: AI2 scaled torq.)
100 % ≡ 10 V or 20 mA or 5 V
The standard setpoint source for operating mode
Display of the current input value at X3/AI2 scaled as a process
controller value.
The standard setpoint source for the reference value of PID control is
torque value.
0x6060 (P301.00)
=

Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x2DA5:016
(P111.16)
Diagnostics of analog input 2: Status (AI2 diagnostics:
From version 04.00
Bit-coded display of the status of analog input 2 (X3/AI2).
Bit 1
Mode 1: 0 ... 5 VDC active
Bit 2
Mode 2: 2 ... 10 VDC active
Bit 3
Mode 3: -10 ... 10 VDC active
Bit 4
Mode 4: 4 ... 20 mA active
Bit 6
24 V supply OK
Bit 7
Calibration successful
Bit 8
Monitoring threshold exceeded/not
reached
Bit 9
Input current too low
Bit 10
Input voltage too low
Bit 11
Input voltage too high
0x2DAA:001
Diagnostics of analog output 1: Voltage (AO1
Read only: x.xx V
Display of the current output voltage at X3/AO1.
0x2DAA:002
Diagnostics of analog output 1: Current (AO1
Read only: x.xx mA
Display of the present output current at X3/AO1.
AI2 status)
Read only
Bit 0 Mode 0: 0 ... 10 VDC active
Bit 5 Mode 5: 0 ... 20 mA active
(P112.01)
(P112.02)
diagnostics: AO1 Voltage)
diagnostics: AO1 Current)
Related topics
Configuration of analog inputs
Configuration of analog outputs
423
437
92 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

5.2.6. Wireless-LAN diagnostics
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x2442:001
Active WLAN settings: Active IP address
From version 02.00
Display of the active IP address.
configured static IP address of the device.
0x2442:002
Active WLAN settings: Active netmask
From version 02.00
Display of the active netmask.
0x2442:003
Active WLAN settings: Active gateway
From version 02.00
Display of the active gateway IP address.
0x2442:004
Active WLAN settings: Active module mode
From version 02.00
Display of the active data source for the WLAN settings.
inverter or from the WLAN module.
1
Standalone
The WLAN settings saved in the WLAN module are used.
0x2442:005
Active WLAN settings: MAC address
From version 02.00
Display of the MAC address of the WLAN module.
0x2448:001
WLAN status: Connection time
From version 02.00
Display of the connection time in [s] since the current connection was
network.
From version 02.00
0x2448:004
WLAN status: Error statistics
From version 02.00
Display of the quality of the WLAN connection. A display value > 0
0x2449
WLAN error
From version 02.00
Bit coded display of WLAN errors.
Bit 2
WLAN error
Bit 3
Memory problem
Bit 4
WLAN connection problem
Bit 9
Client mode off
Bit 12
TCP/IP configuration error
Bit 13
Password length
Bit 14
Access denied
The following parameters serve to diagnose the WLAN module and the WLAN
communication.
Preconditions
WLAN module has been plugged onto the interface X16 on the front of the inverter.
Read only
Read only
Read only
Read only
0 Inverter The WLAN settings saved in the inverter are used.
Read only
Read only
0x2448:002 WLAN status: Number of connections
Read only
From version 02.00
0x2448:003 WLAN status: Rx frame counter
Read only
Read only
If DHCP is activated, the active IP address usually derives from the
This parameter indicates whether the settings used come from the
established.
In access point mode: Display of the number of currently connected
clients.
In client mode: 0 ≡ not connected; 1 ≡ connected with external WLAN
Display of the number of request received via WLAN.
indicates communication problemsn.
Read only
Bit 7 WLAN off
Related topics
Wireless LAN (WLAN)
251

5.2.7. Setpoint diagnostic
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
•
From version 03.00
0x282B:009
Inverter diagnostics: Actual frequency setpoint
•
From version 03.00
Display of the currently selected frequency setpoint that is internally
0x282B:010
Inverter diagnostics: Default PID setpoint
•
From version 03.00
Display of the PID control value of the standard setpoint source set in
0x282B:011
Inverter diagnostics: Preset PID setpoint
Display of the preset PID setpoint selected via the four functions
•
From version 03.00
•
100 % ≡ Motor rated torque 0x6076 (P325.00)
0x282B:013
Inverter diagnostics: Preset torque setpoint
Display of the preset torque setpoint selected via the four functions
0x2948:001
Actual torque setpoint
•
From version 03.00
Display of the currently selected torque setpoint that is internally
•
100 % ≡ Motor rated torque 0x6076 (P325.00)
0x2DAE:010
Sequencer diagnostics: Frequency setpoint
•
From version 03.00
Display of the current frequency setpoint of the "sequencer" function.
0x2DAE:011
Sequencer diagnostics: PID setpoint
•
From version 03.00
Display of the current PID control value of the "sequencer" function.
0x2DAE:012
Sequencer diagnostics: Torque setpoint
Display of the current torque setpoint of the "sequencer" function.
0x4009:004
MOP values saved: Frequency setpoint
•
Read only: x.x Hz
Display of the last MOP value saved internally for the operating mode
"MS: Velocity mode".
0x4009:005
MOP values saved: PID setpoint
•
Read only: x.xx PID unit
Display of the last MOP value saved internally for the reference value
of the PID control.
•
Read only: x.x %
"MS: Torque mode".
The following parameters show the current setpoints of different setpoint sources.
0x282B:007
0x282B:008
0x282B:012
Inverter diagnostics: Default frequency setpoint
•
Read only: x.x Hz
Inverter diagnostics: Preset frequency setpoint
•
Read only: x.x Hz
From version 03.00
•
•
Read only: x.x Hz
•
Read only: x.xx PID unit
•
Read only: x.xx PID unit
From version 03.00
•
Inverter diagnostics: Default torque setpoint
•
Read only: x.x %
•
Read only: x.x %
From version 03.00
•
•
Read only: x.x %
•
Read only: x.x Hz
Display of the frequency setpoint of the standard setpoint source set
in 0x2860:001 (P201.01).
Display of the preset frequency setpoint selected via the four
functions "Activate preset (bit 0)" ... " Activate preset (bit 3)".
Setpoint source of preset setpoints
386
transferred to the motor control.
0x2860:002 (P201.02).
"Activate preset (bit 0)" ... " Activate preset (bit 3)".
Setpoint source of preset setpoints
386
Display of the torque setpoint of the standard setpoint source set in
0x2860:003 (P201.03).
"Activate preset (bit 0)" ... " Activate preset (bit 3)".
Setpoint source of preset setpoints
386
transferred to the motor control.
Sequencer
327
•
Read only: x.xx PID unit
•
Read only: x.x %
From version 03.00
•
0x4009:006
MOP values saved: Torque setpoint
Related topics
Selection of setpoint source
Setpoint change-over
378
93
Sequencer
•
100 % ≡ Motor rated torque 0x6076 (P325.00)
Sequencer
327
327
Display of the last MOP value saved internally for the operating mode
94 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

5.2.8. Process controller status
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
•
Read only: x.xx PID unit
•
Read only: x.xx PID unit
0x401F:003
Status
•
Read only
Bit-coded status display of the process controller.
Bit 0
Process controller off
Bit 1
PID output set to 0
Bit 2
PID I-component inhibited
Bit 4
Setpoint = actual value
Bit 5
Idle state active
Bit 6
Reserved
Bit 7
Reserved
•
From version 03.00
•
From version 03.00
0x401F:006
PID output value
•
Display of the current process controller setpoint that is internally
value).
0x401F:007
PID error value
•
From version 03.00
Display of the difference between reference value (setpoint) and fed
The following parameters serve to diagnose the process controller.
0x401F:001
(P121.01)
0x401F:002
(P121.02)
(P121.03)
0x401F:004
0x401F:005
Current setpoint
(PID setpoint)
Current process variable
(PID process var.)
(PID status)
Bit 3 PID influence shown
PID control value
•
Read only: x.x Hz
PID Feedforward value
•
Read only: x.x Hz
•
Read only: x.x Hz
From version 03.00
Display of the current reference value (setpoint) for the process
controller.
Display of the current controlled variable (actual value) fed back for
the process controller.
Display of the output frequency after the PID controller, but without
any influencing factor.
Display of the feedforward control value for the process controller.
transferred to the motor control (considering the feedforward control
•
Read only: x.xx PID unit
Related topics
Configuring the process controller
232
back variable (actual value) of the process controller.

5.2.9. Sequencer diagnostics
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
From version 03.00
0x2DAE:002
Sequencer diagnostics: Step time elapsed
From version 03.00
Display of the time that has passed since the start of the current step.
0x2DAE:003
Sequencer diagnostics: Step time remaining
From version 03.00
Display of the residual time for the current step.
0x2DAE:004
Sequencer diagnostics: Steps complete
From version 03.00
Display of the number of steps that have been made since the start of
0x2DAE:005
Sequencer diagnostics: Steps remaining
From version 03.00
Display of the residual number of steps until the current sequence is
0x2DAE:006
Sequencer diagnostics: Active sequence
From version 03.00
Display of the active sequence.
0x2DAE:007
Sequencer diagnostics: Active segment
From version 03.00
Display of the active segment.
From version 03.00
0x2DAE:009
Sequencer diagnostics: Absolute sequence time
From version 03.00
Display of the residual time of the sequence in [s].
The following parameters serve to diagnose the "sequencer" function.
0x2DAE:001
(P140.01)
(P140.02)
(P140.03)
(P140.04)
(P140.05)
(P140.06)
(P140.07)
0x2DAE:008
(P140.08)
Sequencer diagnostics: Active step
(Sequencer diag: Active Step)
Read only
(Sequencer diag: StepTime elapsed)
Read only: x.x s
(Sequencer diag: StepTime remain)
Read only: x.x s
(Sequencer diag: Steps complete)
Read only
(Sequencer diag: Steps remain)
Read only
(Sequencer diag: Active sequence)
Read only
(Sequencer diag: Active segment)
Read only
Sequencer diagnostics: Relative sequence time
remaining
(Sequencer diag: SeqTime remain %)
Read only: x %
Display of the active step.
0 ≡ no sequence active.
the sequence.
completed. This includes the current step.
0 ≡ no sequence active.
0 ≡ no sequence active.
255 ≡ final sequence active.
Display of the residual time of the sequence in [%].
(P140.09)
remaining
(Sequencer diag: SeqTime remain)
Read only: x.x s
Related topics
Sequencer
Sequencer control functions
327
416
96 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

5.2.10. Device identification
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
Read only
0x2000:002
Serial number
Read only
Serial number of the complete device.
0x2000:004
CU firmware version
Read only
Firmware version of the control unit.
0x2000:005
CU firmware type
Read only
Firmware type of the control unit.
0x2000:006
CU bootloader version
Read only
Bootloader version of the control unit.
Read only
0x2000:008
Object directory version
Read only
Example: "108478"
0x2000:010
PU firmware version
Read only
Firmware version of the power unit.
0x2000:011
PU firmware type
Read only
Firmware type of the power unit.
0x2000:012
PU bootloader version
Read only
Bootloader version of the power unit.
Read only
0x2001
Device name
["My Device"]
Any device name (e.g. "Wheel drive") can be set in this object for the
The following parameters show some general information about the inverter.
0x2000:001
(P190.01)
(P190.02)
(P190.04)
(P190.05)
(P190.06)
0x2000:007
(P190.07)
(P190.08)
(P190.10)
(P190.11)
(P190.12)
Product code
(Product code)
(Serial number)
(CU firmware ver.)
(CU firmware type)
(CU bootlder ver.)
CU bootloader type
(CU bootlder type)
(OBD version)
(PU firmware ver.)
(PU firmware type)
(PU bootlder ver.)
Product code of the complete device.
Example: "VS10-23-1P7-20"
Example: "0000000000000000XYZXYZ"
Example: "01.00.01.00"
Example: "IOFW51AC10"
Example: "00.00.00.13"
Bootloader type of the control unit.
Example: "IOBL51AOnn"
Example: "00202"
Example: "IDFW5AA"
0x2000:013
(P190.13)
(P191.00)
PU bootloader type
(PU bootlder type)
(Device name)
Bootloader type of the power unit.
purpose of device identification.

5.2.11. Device overload monitoring (i*t)
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x2D40:002
Device utilisation (i*t): Warning threshold
If the device utilisation exceeds the threshold set, the inverter outputs
•
0x2D40:004
Device utilisation (i*t)
•
Read only: x %
Display of the current device utilisation.
0x2D40:005
Device utilisation (i*t): Error response
Selection of the response to be executed when the device overload
•
9090 | 0x2382 I*t error
2
Trouble
Error types
3
Fault
0x2DDF:001
Axis information: Rated current
•
Read only: x.xx A
Display of the rated current of the axis.
The inverter calculates the i*t utilisation in order to protect itself against thermal
overload. In simple terms: a higher current or an overcurrent that continues for a longer
time causes a higher i*t utilisation.
DANGER!
Uncontrolled motor movements by pulse inhibit.
When the device overload monitoring function is activated, pulse inhibit is set and the motor becomes torqueless. A
load that is connected to motors without a holding brake may therefore cause uncontrolled movements! Without a
load, the motor will coast.
Only operate the inverter under permissible load conditions.
Details
The device overload monitoring function primarily offers protection to the power section.
Indirectly, also other components such as filter chokes, circuit-board conductors, and
terminals are protected against overheating. Short-time overload currents followed by
recovery periods (times of smaller current utilisation) are permissible. The monitoring
function during operation checks whether these conditions are met, taking into
consideration that higher switching frequencies and lower stator frequencies as well as
higher DC voltages cause a greater device utilisation.
• If the device utilisation exceeds the warning threshold set in 0x2D40:002 (default
setting: 95 %), the inverter outputs a warning.
• If the device utilisation exceeds the permanent error threshold 100 %, the inverter is
disabled immediately and any further operation is stopped.
Device overload monitoring enables operation of the inverter under the following load
conditions:
• Continuous current load with up to 100 % rated current.
• 3-minute cycle: 150 % rated current for 60 s, recovery phase 120 s with 75 % rated
current.
• 15-second cycle: 200 % rated current for 3 s, recovery phase 12 s with 75 % rated
current.
(P135.04)
(P135.05)
0 ... [95] ... 101 %
(Device utilisat.: ixt utilisation)
(Device utilisat.: Error response)
a warning.
With the setting 0 % or ≥ 100 %, the warning is deactivated.
monitoring function is triggered.
Associated error code:
84
98 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation

5.2.12. Heatsink Temperature Monitoring
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x2D84:001
Heatsink temperature
•
Read only: x.x °C
Display of the current heatsink temperature.
0x2D84:002
Heatsink temperature: Warning threshold 50.0 ...
Warning threshold for temperature monitoring.
Parameter
Name / value range / [default setting]
Info
0x2D81:001
Life-diagnosis: Operating time (Life-diagnosis:
Read only: x s
Display showing for how long the inverter has been running so far
0x2D81:002
Life-diagnosis: Power-on time (Life-diagnosis: Power-
Read only: x s
Display showing for how long the inverter has been supplied with mains
0x2D81:003
Life-diagnosis: Control unit operating time (Life-
Display showing for how long the control unit has been supplied with
supplied with an external 24 V voltage.
0x2D81:004
Life-diagnosis: Main switching cycles (Life-diagnosis:
Read only
Display of the number of switching cycles of the mains voltage.
0x2D81:005
Life-diagnosis: Relay switching cycles (Life-diagnosis:
Read only
Display of the number of switching cycles of the relay.
Read only
0x2D81:007
Life-diagnosis: Earth fault counter (Life-diagnosis:
Read only
Display of the number of earth faults that have occurred.
0x2D81:008
Life-diagnosis: Clamp active (Life-diagnosis: Clamp
Display of the number of "Imax: Clamp responded too often" errors that
current limit shown in 0x2DDF:002 is reached.
0x2D81:009
Life-diagnosis: Fan operating time (Life-diagnosis: Fan
Read only: x s
Display showing for how long the internal fan has been running so far.
(P117.01)
(Heatsink temp.: Heatsink temp.)
[80.0]* ... 100.0 °C
* Default setting depending on the size.
•
If the heatsink temperature exceeds the threshold set here, the
inverter outputs a warning.
•
The warning is reset with a hysteresis of approx. 5 °C.
•
If the heatsink temperature increases further and exceeds the
nonadjustable error threshold (100 °C), the inverter changes to
the "Fault" device status. The inverter is disabled and thus any
further operation is stopped.
5.2.13. Life-diagnosis
The following parameters provide some information about the use of the inverter. This
includes the following information:
• Operating and power-on time of the inverter/control unit
• Operating time of the internal fan
• Number of switching cycles of the mains voltage
• Number of switching cycles of the relay
• Number of short-circuits and earth faults that have occurred
• Display of the number of "Imax: Clamp responded too often" errors that have occurred.
(P151.01)
(P151.02)
(P151.03)
(P151.04)
(P151.05)
0x2D81:006
(P151.06)
(P151.07)
(P151.08)
(P151.09)
Operating time)
on time)
diagnosis: CU oper. time)
Read only: x ns
Switching cycles)
Relay cycles)
Life-diagnosis: Short-circuit counter (Life-diagnosis:
Short-circ.count)
Earthfault count)
active)
Read only
oper. time)
"Operation enabled" device state).
voltage so far.
voltage so far. This includes the external 24-V supply and voltage supply
via USB module.
This also includes the time within which the control unit has only been
Display of the number of short circuits that have occurred.
have occurred.
"Clamp" = short-time inhibit of the inverter in V/f operation when the

5.3. Error handling
Error type
Logging in the
Display in the
(P780.00)
Inverter disable
Motor stop
Error reset is
"ERR" LED (red)
No response
No
No
No
No
No
off
blinking fast (4 Hz)
immediately.
coasting.
blinking (1 Hz)
454
Many functions integrated in the inverter can
• detect errors and thus protect inverter and motor from damages,
• detect an operating error of the user,
• output a warning or information if desired.
5.3.1. Error types
In the event of an error, the inverter response is determined by the error type defined for
the error.
In the following, the different error types are described.
Error type "No response"
The error is completely ignored (does not affect the running process).
Error type "Warning"
A warning does not severely affect the process and may be also ignored in consideration
of safety aspects.
Error type "Fault"
The motor is brought to a standstill with the quick stop ramp.
•
The inverter will only be disabled after the quick stop is executed (motor at standstill)
or after the time-out time set in 0x2826 has been elapsed.
reaction
•
Exception:
313
In case of a serious fault, the inverter is disabled immediately. The motor
becomes torqueless (coasts). For details see the table "Error codes".
Timeout für fault
454
Error type "Trouble"
Just like "Fault", but the error state will be left automatically if the error condition is not
active anymore.
•
Exception:
becomes torqueless (coasts). For details see the table "Error codes".
•
The restart behaviour after trouble can be configured. Automatic restart
In case of a severe trouble, the inverter is disabled immediately. The motor
454
314
In the operating mode 0x6060 (P301.00) = "CiA: Velocity mode [2]", the behaviour in
case of "Trouble" is just like in case of "Fault"!
Comparison of the error types
The following table compares the main differences of the error types:
Error history buf-
fer / Logbook
CiA 402 status
word 0x6041
required
Warning Yes yes, bit 7 No No No
Trouble Yes yes, bit 3
Error Yes yes, bit 3
after quick stop or
For details see table "Error codes".
quick stop ramp or
No
Yes
on
100 01-6203-01R3, CG Drives & Automation
 Loading...
Loading...