Page 1

62-0392-03
Class 5000 Meter
ADVANCED KWH/DEMAND METER
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
E-Mon
850 Town Center Drive
Langhorne, PA 19047
(800) 334-3666
www.emon.com
info@emon.com
Page 2

CLASS 5000 METER
Dear Valued Customer,
We are pleased that you chose to buy one of our products, and want you to be just as
pleased with owning it. Before installing your new E-Mon product, please read the
information on the following pages carefully.
We believe that you will find the E-Mon D-Mon meters easy to install and to use for
monitoring and evaluating your electrical usage.
To be sure that you are 100% satisfied with your products, we provide toll-free
technical and sales support Monday through Friday, 8:00 am to 7:30 pm, EST:
(800) 334-3666. You may also reach us via email at info@emon.com.
If you have questions, we can handle them quickly and effectively with a telephone call.
Please let us try to help you BEFORE you remove your meter. And to help us help you,
we ask that you have all relevant information on hand when you call (model or part
numbers, nature of difficulty, etc.)
Be sure to forward this manual to the owner after installation is complete, so that they
may use it as a reference guide when reading the E-Mon D-Mon meter.
Thank you.
62-0392-03 2
Page 3

CLASS 5000 METER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section 1.0 Introduction 4
Section 2.0 Internal Electronic Assemblies 5
Section 2.1 Main Power Board 6
Section 2.2 Display Board 7
Section 2.3 Input Board 8
Section 2.4 Pulse Type and Value 9
Section 3.0 Meter Technical Specifications 9
Section 4.0 Safety Label Definitions and Information 12
Section 5.0 Precautionary/Safety Information 12
Section 6.0 Meter Installation 13
Section 6.1 Mounting the Class 5000 Meter 13
Section 6.2 Main Power Board Connections 13
Section 6.3 Phasing of Line Voltage 15
Section 6.4 Current Sensor Installation & Wiring 16
Section 6.5 Main Power & Current Sensor Wiring Diagram 19
Section 6.6 Line Voltage/Current Sensor Diagnostics 19
Section 6.7 RS-485 Wiring 21
Section 6.8 RS-232 Communications 23
Section 6.9 Modem Wiring 25
Section 6.10 Modbus RTU Wiring 29
Section 6.11 BACnet Wiring 29
Section 6.12 Connecting Class 5000 Meters to USB Key using RS485 30
Section 6.13 Ethernet Communications 31
Section 7.0 Multiple-Load Monitoring 32
Section 8.0 Preventative/Scheduled Maintenance 33
Section 9.0 Lithium Battery Replacement 35
Section 10.0 Class 5000 Meter Features 35
Section 10.1 Display Board Push Buttons 36
Section 10.2 Normal Mode Display Screens 37
Section 10.3 How to Program the Display Screens 43
Section 11.0 Frequently Asked Questions 45
Section 12.0 Protocol Descriptions 55
Section 13.0 High Voltage Metering 58
Section 14.0 Meter Limited Warranty 59
3 62-0392-03
Page 4

CLASS 5000 METER
CAUTION
WARNING
1.0 INTRODUCTION
The E-Mon D-Mon® Class 5000 meter is a 3-phase meter with communications. The
device is used to monitor electric power usage of individual loads after the utility meter
and store kW and kVAR data for automatic meter reading. The Class 5000 meter is
dual protocol capable and provides both RS485 and Ethernet communications.
Installation must only be performed by qualified personnel and in accordance with
these instructions and all applicable local and national electrical codes. E-Mon and its
representatives assume no responsibility for damages or injury resulting from the
improper installation of this meter.
Verify the input voltage rating and configuration on the unit panel label to ensure that it
is suitable for the intended electrical service. Class 5000 meters labeled for 120/208V
service MUST NOT be installed on service feeds of 277/480 volts or 347/600 and vice
versa. Verify that the Class 5000 meter’s current sensors are sized suitably for the load
to be monitored. Compare the color of the arrows on the current sensors to the chart
below to confirm the correct current sensor is being used.
Sensor Arrow Color Code Sensor Rating
Brown 100 A
Red 200 A
Yellow 400 A
Black 800 A
Blue 1600 A
White/Black 3200 A
Internal circuit card components are extremely sensitive to electrostatic
discharge. Prior to handling or touching internal circuitry, discharge any static
buildup on your person. To discharge yourself, touch a grounded metal object
such as conduit or an earth grounded metal enclosure.
Use of this instrument, Class 5000, in a manner inconsistent with this manual
or not specified by the manufacturer in writing, can cause permanent damage
to the unit and/or serious injury to the operator. The protection and safety
features provided by this equipment may become impaired or otherwise
compromised.
NOTE: If any trouble arises during installation or functional verification operations, do
62-0392-03 4
not immediately remove unit. Before removing the unit, contact E-Mon’s technical support department at (800) 334-3666. E-Mon’s technical department
will assist you in detailed troubleshooting of the Class 5000 installation.
Page 5

CLASS 5000 METER
MAIN POWER
BOARD
DISPLAY
BOARD
M33270
2.0 INTERNAL ELECTRONIC ASSEMBLIES
The unit is comprised of two major subassembly boards, the main power board and
the display board. Both circuit boards are mounted inside a NEMA 4X enclosure.
Fig. 1. Internal Electronic Assemblies.
5 62-0392-03
Page 6
CLASS 5000 METER
M33271
TB1
POSITIONS
POSITIONS
6-10
PHASE LOSS
TB42
J3
J4
J8
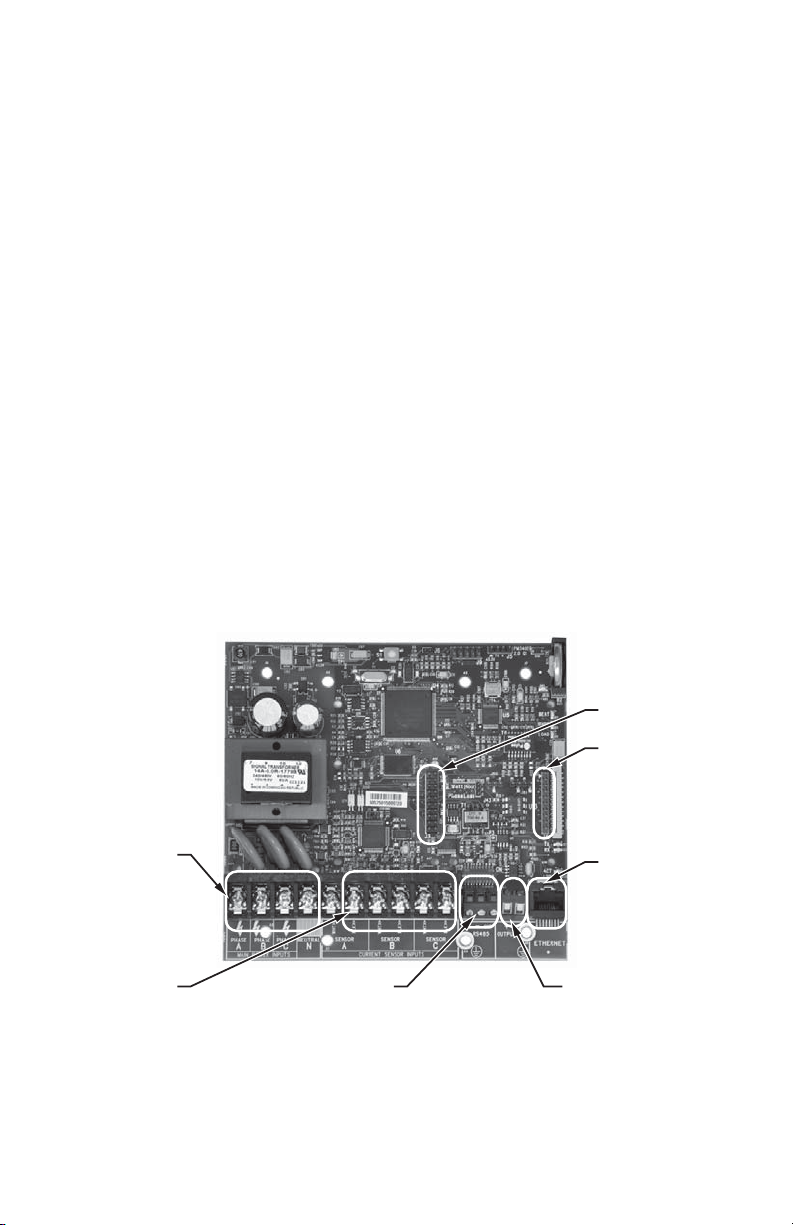
2.1 Main Power Board
Connections to this board include the MAIN Power Input and current sensors. The
MAIN Power Input terminals are positions one through four on the four position screw
terminal block, TB1. These terminals are covered with a protective shield for safety
purposes. The current sensor assemblies interface to the TB2, TB3 and TB4. Each
terminal block corresponds to an input voltage phase; care must be exercised to
ensure that each current sensor is connected to the correct terminal block. One three
terminal screw connector(TB42) is provided for RS-485 communications. One RJ-45
jack (J8) is provided for 10/100-base T Ethernet.
The contact is a solid-state switch for the phase-loss alarm function. Switching is
limited to 100 ma (0.1 amp) and voltage should not exceed 60 Volts AC or DC.
The (N.O.) contact closes within the meter due to the loss any one of the three lines of
voltage inputs to the meter. The contact closure may be used to activate an audible
alarm, light, control coil, or other indicator device. This alerts appropriate personnel to
the loss of voltage. An emergency phone dialer may also be programmed to send
notification automatically by phone, text, or pager. Alarming devices to be supplied by
others and are not included by with the E-Mon Class 5000 meter.
One two terminal screw connector provides phase loss alarming.
There are also two headers present for adding option cards. Header J3 is 20 positions
for use with an I/O board with up to two relays, two pulse inputs and two pulse out puts.
Header J4 is a 10 positions for use with modem and LonWorks TP/FT-10.
62-0392-03 6
Fig. 2. Main Power Board.
Page 7

CLASS 5000 METER
M33279
DOWN
UP
SELECT
MENU
2.2 Display Board
The display board connects to the main power board via a flex ribbon cable and the
board mounts on the inside of the housing door.
No additional connections to the display board are required. The display board’s LCD
readout indicates the metered values as well as errors associated with the Class 5000
meter, such as phase loss or sensor error conditions.
Fig. 3. Display Board.
7 62-0392-03
Page 8
CLASS 5000 METER
M33272
INPUT TERMINALS
CL5000 METER INPUT BOARD
INP1
+
+++
INP2 OUT1 OUT2
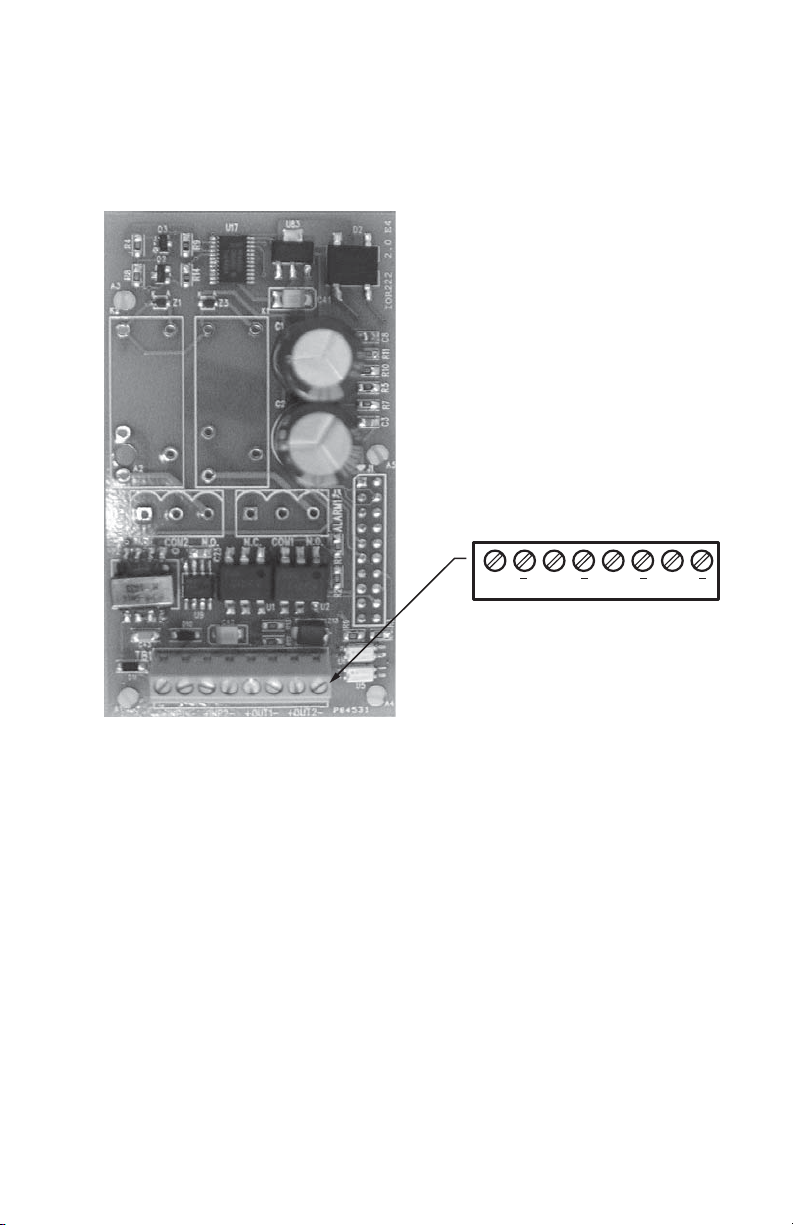
2.3 Input Board
The Class 5000 meter is supplied with an input board which allows it to accept pulses
(dry contact) from third party meters, such as gas, water, BTU, etc.
Fig. 4. Input Board.
The input terminals are used by the Class 5000 meter. The output terminals are not.
Connect metering devices with “dry contacts” only. If the contacts are from solid - state
(electronic) sources, polarity must be observed for proper operation.
62-0392-03 8
Page 9
CLASS 5000 METER
M33273
EXAMPLE:
E 50 208 400 R 05 KIT
CLASS 5000 METER
INPUT VOLTAGE (208V)
CURRENT RATING (400A)
ENCLOSURE (4X)
EZ7/BACnet IP/NO MODEM
E-MON
SPLIT CORE SENSORS
2.4 Pulse Type and Value
The pulse outputs provided by the Class 5000 meter are watt-hours and var-hours.
Output 1 is the watt-hour pulse and Output 2 is the var-hour pulse. The pulse value is
dependant on the amperage size of the meter. See the chart below for the values also
true for expansion board pulse output.
Meter Amps Watt-hours / pulse Var-hours / pulse
100 1.95313 1.95313
200 3.90625 3.90625
400 7.8125 7.8125
800 15.625 15.625
1800 31.25 31.25
3200 62.5 62.5
3.0 METER TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Ordering Information: Define brand, class, input voltage, current sensor rating,
enclosure, protocols/options, expanded feature package, and sensor type in the format
A-BB-CCC-DDDD-E-FF-G-HHH, where:
A = Brand: E for E-Mon
BB = designates Class: 3200 (32), 3400 (34), or 5000 (50) meter
CCC = input voltage: (208, 480, 600, 120 volt for high voltage applications only)
DDDD = current sensor rating: (100, 200, 400, 800, 1600, 3200, 25HV)
E = enclosure: J = metal (type 1), R = non-metallic (type 4X)
FF= protocol option:
G = Expanded Feature Package: package = X, no package = “blank”
(on Class 3400 only)
HHH= Sensor Type: kit=split-core, scs= solid-core, non-supplied blank”
“-SP ”= 1 or 2 Phase
9 62-0392-03
Page 10
CLASS 5000 METER
3.0 METER TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS (CONTINUED)
Input Voltage
Configuration
Mains Voltage Input Up To 480 VAC RMS Available
Input Power 6 VA Maximum Rating
Current Sensor
Rating
Power Factor 0.5 Leading Or Lagging
Line Frequency 50-60 Hz
Metering Accuracy Certified To ANSI C12.20
Voltage Operating
Range
Temperature Range -20 C To +50 C (Standard indoor enclosure):
Temperature Range -20 C To +70 CNEMA 4X (NEMA 4X outdoor enclosure)
Relative Humidity
Range
Altitude 2000 Meters Maximum
Voltage Overload +25% Continuously: +100% For 20 Cycles
Current Sensor
Overload
Pollution Degree Degree 2 In Accordance With IEC 664
Installation
(Overvoltage)
Category
Measurement
Category
Enclosure Material Indoor Housing Rating (Standard): NEMA 12
Display Readout KWh Accumulated,
Standards EN 61326-1:2006 IEC 61010-1:2001, 2nd Edition
Standard Ranges 4-Wire Wye, 120/208 VAC: 100, 200, 400, 800,1600,3200 Amp
3-wire (Delta) Or 4-wire (Wye)
Up To 3200 Amps RMS AC Available
+/-10% Of Rated Load
0-95% Non-condensing
100% For 1 Minute Without Damaging Meter
Category 111
Category 111
Outdoor Housing Rating (Optional): NEMA 4X
2 Phase, 120/240 VAC: 100, 200, 400, 800,1600,3200 Amp
4-Wire Wye, 277/480 VAC: 100, 200, 400, 800,1600,3200 Amp
3-Wire Delta, 220/240 VAC: 100, 200,400,800,1600,3200 Amp
3-Wire Delta, 480 VAC: 100, 200, 400, 800,1600,3200 Amp
62-0392-03 10
Page 11
CLASS 5000 METER
Modem Interface Cable: UL-listed Telephone Cord,
6-cond. 300 VAC, Stranded
Cond. 22-26 AWG.
Cable Connector: RJ-45 male IDC
Input/Output Voltage: +5 VDC/18 VAC
Ckt Input Isolation 5.3K VAC for 1 Minute
Baud Rate: 9600
IDR Interface Port Cable: UL-listed/rated Telephone
Cord. 4-cond.
Input/output Voltage: Ground-isolated +/-5.4VDC
Cable Connector: RF-45 Male IDC Or Screw
Terminal Termination
Circuit Input Isolation: 5.3kVAC
Circuit output Isolation: 21.5kVAC
Isolated Pulse/Alarm Outputs
(TB5, TB6):
Output Voltage Potential: 0 VDC to +5 VDC Logic Levels
Mating Plug Connector: Weidmuller PN: 152876
Signal Isolation Voltage: 5.3K VAC for 1 Minute
Recommended
In-line Fuse
Manufacturer: Littlefuse
Mfg. Part No: KLDR.100
Rating: 100mA, Time-delay, 600VAC
Cartridge Fuse
Battery Cell Description: Non-rechargeable Cell Used
For Memory Retention
Manufacturer: Panasonic
Mfg Part No: CR2032
Working Voltage: 3 VDC
Current Capacity 225 mAHr
Electrolyte: Manganese Dioxide Lithium
11 62-0392-03
Page 12
CLASS 5000 METER
CAUTION
WARNING
WARNING
4.0 SAFETY LABEL DEFINITIONS AND
INFORMATION
The 5000 meter may contain one or more of the following labels. Operator(s) should
familiarize themselves with the meaning of each label to minimize risk.
The presence of this label is a cautionary indicator identifying a
danger risk. The manual should be consulted prior to proceeding.
The presence of this label indicates an electrical shock hazard exists in
the location or area where the label is placed. Prior to proceeding, the
MAINS power must be disconnected and the manual consulted for
safety information.
5.0 PRECAUTIONARY AND SAFETY
INFORMATION
Internal circuit card components are extremely sensitive to electrostatic
discharge. Be careful not to touch internal circuitry prior to discharging any
static buildup on your person. To discharge yourself, touch a grounded metal
object such as conduit or an earth-grounded metal enclosure.
High voltages present on main PCB terminal block TB1 screw terminals. Risk
of serious injury and/or electrical shock exists. Prior to performing any wiring
operations, review all contents of the user manual and de-energize the MAINS
power switch. Only qualified personnel should perform installation wiring.
Installation wiring must comply with all local and national electrical codes.
NEVER open front panel of unit while unit has MAINS power applied. Failure to
comply can increase the risk of serious injury and/or electrical shock.
62-0392-03 12
Page 13
6.0 METER INSTALLATION
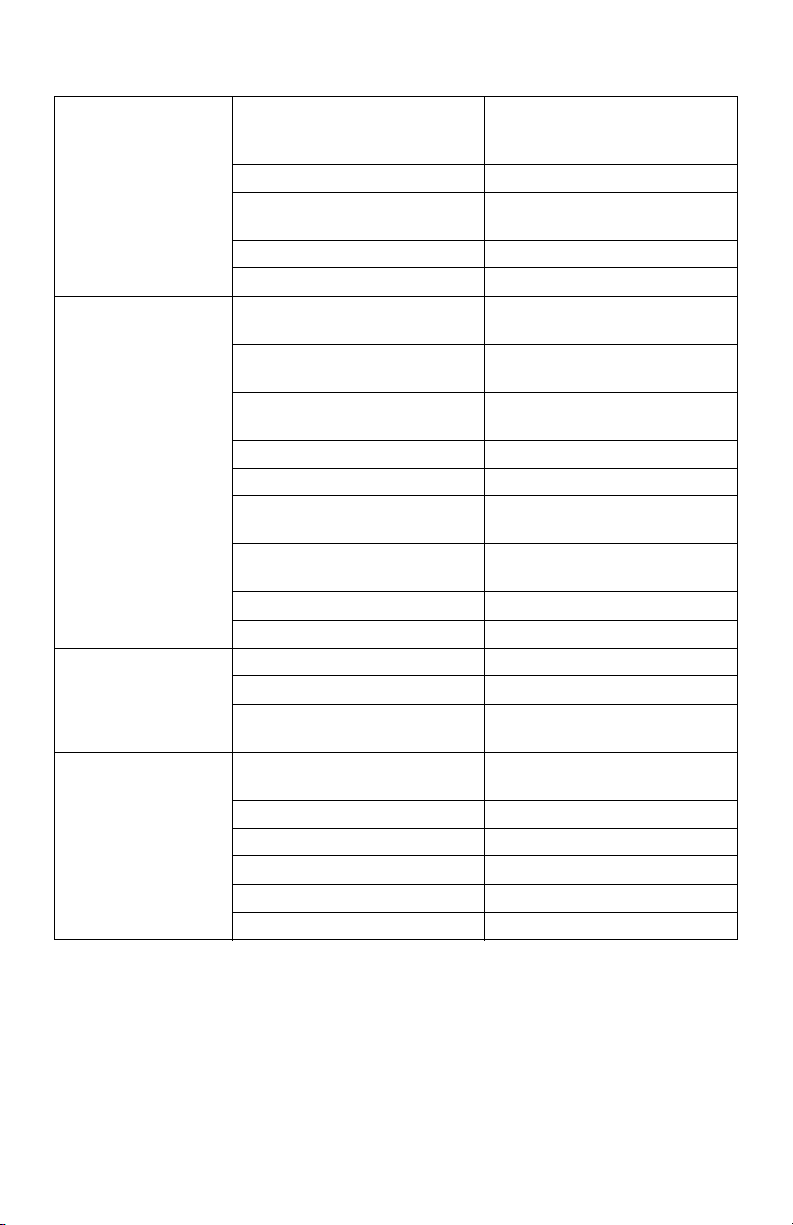
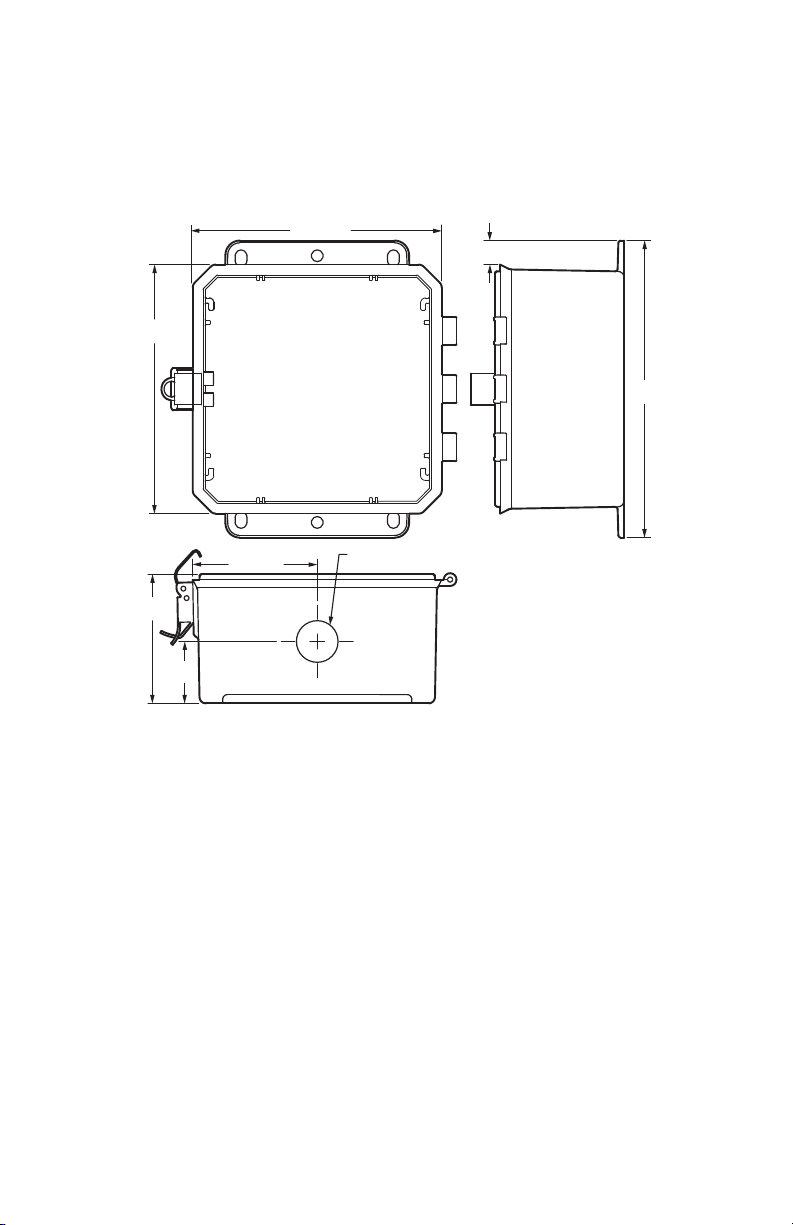
6.1 Mounting the Class 5000 Meter
6-35/64 (166)
5/8 (16)
6-35/64
(166)
CLASS 5000 METER
7-51/64
(198)
Ø 1-3/32 (28) THROUGH
NEAR SIDE ONLY
M34684
3-25/64
(86)
1-5/8
(41)
3-17/64 (83)
Fig. 5. Enclosure Dimensions
Use appropriately sized mounting hardware to fasten the meter enclosure to the
selected mounting surface.
The four housing mounting holes are centered 6.75” H x 4” W.
NOTE: Units housed in UL Type 1 enclosures must only be installed in indoor envi-
ronments, where they will not be affected by the elements.
13 62-0392-03
Page 14
CLASS 5000 METER
WARNING
6.2 Main Power Board Connections
1. Installing a temporary ground for ESD protection: With all circuits de-energized,
connect a temporary protective earth ground connection for ESD protection.
Prior to performing any unit wiring, be sure to discharge any static on your person.
2. Installing the Class 5000 protective earth ground: Connect an earth ground wire
to the Class 5000 protective earth ground lug with a torque of 7 N-m. * for meters
in metal enclosures.
Failure to attach the protective earth ground wire securely to the meter creates
a potential shock hazard. Do not operate the meter without a protective earth
ground connection securely installed.
3. Wire Entry: One 3/4” conduit opening is located on the bottom of the unit enclosure. This opening is used for bringing in MAINS power and for current sensor
wiring. Route the appropriate cabling to and through the respective enclosure
opening.
4. After installing the conduit fitting and conduit, verify that each conduit slip nut is
securely tightened to its respective conduit fitting. Any unused openings must be
sealed with a UL rated plugging device suitable for the rating of the enclosure
(check formatting).
NOTE: Metallic enclosure has one additional 1/2” conduit opening at top of unit.
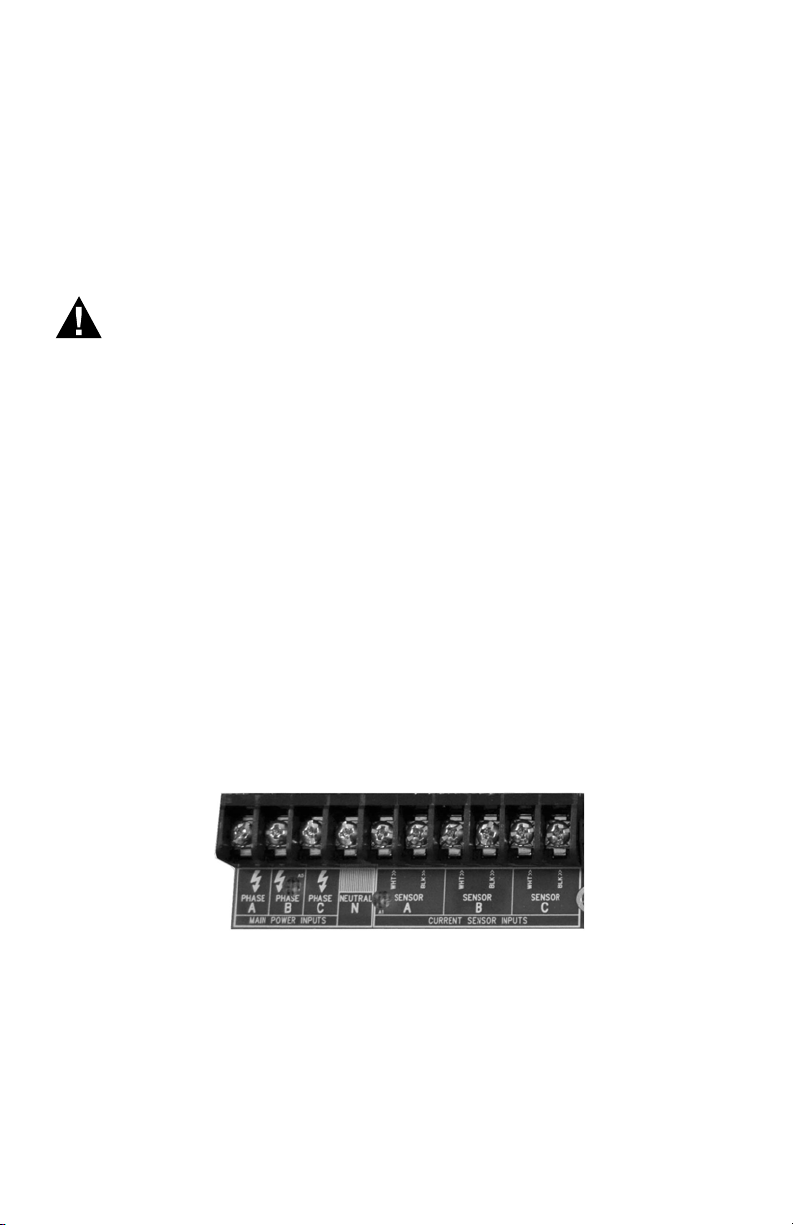
5. Unit MAINS wiring: The first four positions of terminal block TB1, located at the
bottom left corner of the main power board, are clearly labeled Phase A, B, C, N
(neutral). Earth Ground MUST be connected to the PCB mounting screw in the
lower right corner.
a. Connect the NEUTRAL wire to the appropriate terminal block position.
Fig. 6. Terminal Block TB1.
NOTE: For 3-wire delta-type applications, do NOT connect the NEUTRAL wire.
Remove the terminal block screw for this position.
b. Earth Ground. Connect the Earth Ground to the PCB mounting screw in the
lower right corner.
62-0392-03 14
Page 15
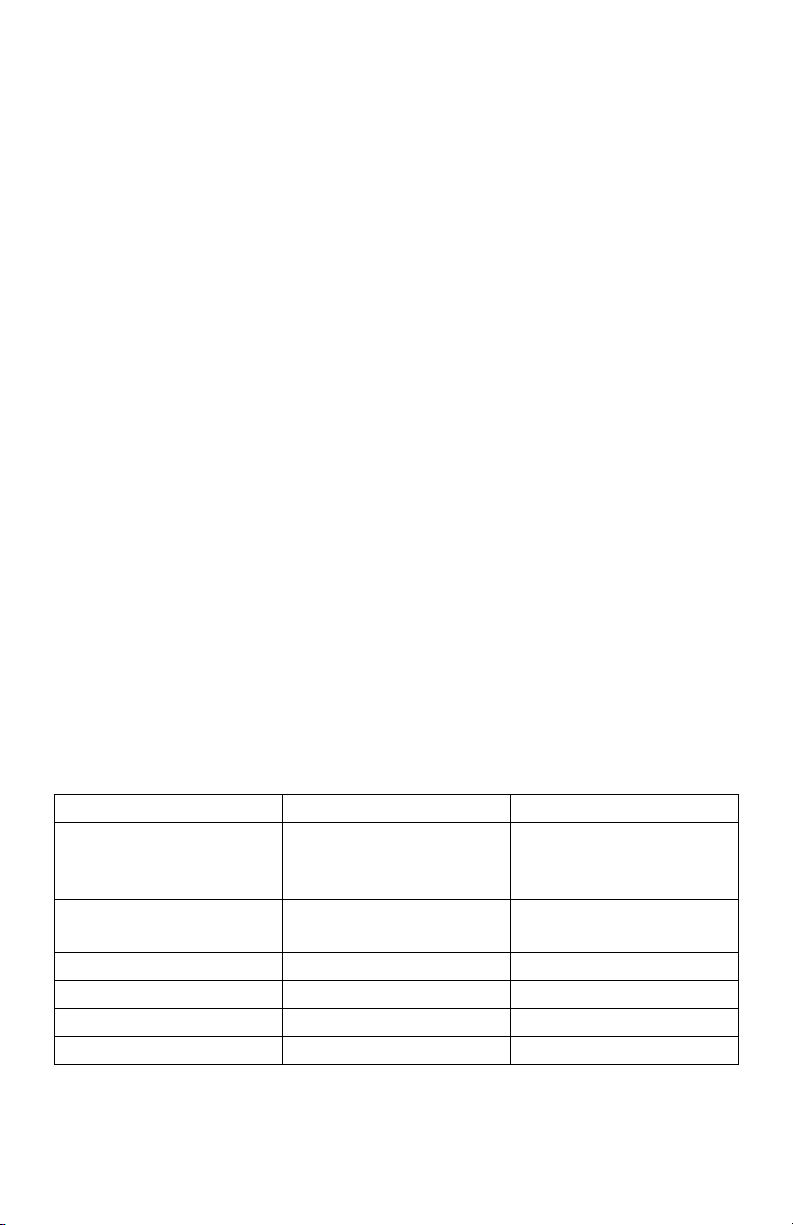
CLASS 5000 METER
c. External Switch Mechanism/In-Line Fuse Installation.
To ensure a safe installation, the Class 5000 meter requires an external
switch mechanism, such as a circuit breaker, be installed on the Class 5000
MAINS input wiring. The switch mechanism must be installed in close proximity to the meter and easily reachable for the operator. This device must
also be marked as the disconnecting device for the Class 5000 meter. Install
1/10 Amp Slow Activation in-line fuses with the suitable voltage rating for
each conductor phase at the MAINS input to the meter. The fuses must be
labeled to indicate voltage and current rating as well as element characteristics. The fuse element must be slow activating type.
d. Connect the three AC main power wires (Phases A, B and C) to their respec-
tive positions as labeled on terminal block TB1 and tighten to 7 in-lb. After all
conductors are connected to each of their respective terminal block positions
and tightened down, verify that each terminal block screw is securely fastened by gently tugging on each conductor.
NOTE: On Single phase connections: Connect two AC main power wires to
phases A and B - Connect jumper from B to C - factory installed for “-SP”
option. Verify that no conductor wires are frayed or shorting to adjacent terminal block positions.
e. Turn ON the AC main power input. The meter display will light up and scroll
through 7 displays. Each display is visible for 5 seconds. Display screens are
as follows:
Screen 1 - Total kilowatt-hours (kWh) consumed
Screen 2 - Peak demand (kW) with date & time stamp
Screen 3 - Actual load (kW) with preset date & time
Screen 4 - Average current (amps) per phase
Screen 5 - Average voltage (volts) per phase
Screen 6 - Average voltage (volts) phase to phase
Screen 7 - Power factor (PF) per phase
f. Verify the voltage readings on Screen 5 using an AC voltmeter. Typical read-
ings shown below are measured phase to neutral for 4 wire and phase to
phase for 3 wire. Readings should be +/- 10% of nominal.
Meter Type Nominal Voltage Limits (+/- 10%)
120/208V, 3ø, 4 Wire
120/240V, 1ø, 3 Wire
120V, 1ø, 2 Wire
277/480V, 3ø, 4 Wire
277V, 1ø, 2 Wire
240V, 3ø, 3 Wire 240 VAC (L-L) 216 to 264 VAC
400V, 3ø, 4 Wire 230 VAC (L-N) 207 to 253 VAC
480V, 3ø, 3 Wire 480 VAC (L-L) 432 to 528 VAC
600V, 3ø, 4 Wire 347 VAC (L-N) 312 to 380 VAC
NOTE: Meters are powered by phases A and B. The displayed voltages will be the
measured AC voltage between phases.
120 VAC (L-N) 108 to 132 VAC
277 VAC (L-N) 249 to 305 VAC
15 62-0392-03
Page 16

CLASS 5000 METER
6.3 Phasing of Line Voltage
The 3-phase AC power input must be in proper phase sequence. Single phase “-SP”
option - AC power input must be in proper phase sequence. If the sequence is
incorrect or a phase is missing, there will be a message on the meter’s display: “PH
Sequence Error” or “PH Missing:. (Refer to the section on Line Voltage Diagnostics if
this message is present.) When the line voltage is connected correctly, the meter’s
display will be blank (no message.)
Wait for the meter display to scroll to the voltage display. Verify that the meter reads
correct voltages on all three phases. Repeat Step 6.2.5.F.
Once the meter displays the correct line voltages and there are no error messages,
you are ready to connect the current sensors to the meter. Before continuing with the
installation, verify that the seven screens display as follows:
Screen 1 (kWh): Should read 0.0 kWh; if not, should be reset.
Screen 2 (kW Peak Demand): kW peak should read 0.0 kW. There will not be a
date/time stamp yet. If there is a kW peak recorded,
it should be reset later.
Screen 3 (Load/Clock Calendar): Should read 0.0 kW load.
Screen 4 (Amps per Phase): There should be 0.0 on all three phases. Or
in the SP option - 0.0 in A and B phases.
Screen 5 (Volts RMS Phase to Neutral): See the section 6.2.5.F.
Screen 6 (Volts RMS Phase to Phase): See the section 6.2.5.F.
Screen 7 (Power Factor Per Phase): There should be 0.0 PF on all three phases.
Or in the SP option - 0.0 in A and B phases.
NOTE: The meter will be reset later via the software during “startup” procedures.
62-0392-03 16
Page 17

CLASS 5000 METER
6.4 Current Sensor Installation & Wiring
Once the AC voltages have been confirmed to be within acceptable limits, you are
ready to install the current sensors. TB2 is the input for Phase A, TB3 is the input for
Phase B and TB4 is the Phase C input. For the SP option: use TB1 pos 5&6 are for the
A Phase - TB1 pos 7&8 are for the B phase -factory installed jumper wire on positions
9&10. Factory installed Jumper should not be removed.
The Class 5000 meter can be used with two types of current sensors:
1. Split-core current sensor. This sensor opens so that it can be attached around
the circuit being monitored without interrupting power. Unless otherwise specified, all Class 5000 meters are supplied with this sensor type.
2. Solid-core current sensor. This sensor does not open and requires the monitored
conductor to be removed from the circuit to install the current sensor. This type is
only supplied when specified at time of order.
6.4.1 Installing the Split-Core Current Sensor Assembly
1. Each phase being monitored will require one two-piece current sensor assembly.
Open the two-piece current sensor assembly by releasing the nylon clamp using
a fl at head screwdriver.
Fig. 7. Split Core Current Sensor.
2. Reassemble the current sensor assembly around the conductor(s) to be monitored. Ensure the current sensor halves marked “Load” are both facing the load
side of the conductor. The colored arrow will be on the source side of the conductor being monitored and MUST be pointed in a clockwise direction around
the conductor being monitored. Tighten the nylon clamp to complete the assembly.
17 62-0392-03
Page 18

CLASS 5000 METER
M33213
LOAD
SOURCE
Fig. 8. Installation of a Split Core Sensor.
IMPORTANT:
When looking from the source side of the conductor(s) being monitored, you
should see the arrow on the current sensor assembly. The arrow should be
pointing in a clockwise direction around the conductor(s) being monitored. If
the arrow is not positioned on the source side, inaccurate readings will result.
6.4.2 Current Sensor Wiring
Once the current sensors are installed onto their appropriate phase conductors, you
can begin terminating the current sensors onto the Class 5000 main board. The
current sensors can be extended up to 500 feet for remote monitoring applications. To
extend the length of the wires, use #22 AWG twisted-pair wire with one white and one
black wire.
The easiest way to connect the current sensors is to use the meter’s built-in current
sensor diagnostics. To do this, there must be at least 1% of the meter’s current rating
(amps) fl owing in each of the conductors being monitored. The Class 5000 meter’s
diagnostic program will provide data to ensure that the current sensor installation is
done properly.
The current sensor connection points are located at the bottom right of the main power
board. These are terminals 5 through 10 of terminal block TB1. Each sensor connects
to two terminals, one labeled “Black” and the other “White.” Current sensors should be
connected to the meter one at a time and verified using the current sensor diagnostic
program.
Connect one of the current sensors to TB1 terminals 5 and 6 (Phase A). Wait 5
seconds and look at the meter display.
62-0392-03 18
Page 19

CLASS 5000 METER
6.4.2 Current Sensor Wiring (continued)
If the meter displays an error message (see below), remove the wires from terminals 5
and 6 and install them on terminals 7 and 8 (Phase B). if an error message occurs with
the sensor attached to terminals 7 and 8, try again on terminals 9 and 10 (Phase C).
The “CT Error: * “message will disappear when the current sensor is connected to the
correct terminals (phase).
Error Messages: CT ERROR: A
NOTE: The 1-Phase option will only display errors for A and B.
Refer to the section on Current Sensor Diagnostics for assistance in troubleshooting
these errors.
CT ERROR: A B
CT ERROR: A C
6.4.3 Main Power
After the meter circuit wiring has been examined for correctness, power may be
applied to the circuit board. There are three LEDs located in the upper right corner of
the Meter Board labeled BEAT, STATUS and LOAD. The BEAT and STATUS LEDs will
blink once per second when the meter is operating normally, twice per second if there
is a problem. If the monitored circuit is under load the LOAD LED will actively blink. A
heavy load will cause the LED to blink faster than a light load. Very light loads will
result in an extended blink time.
19 62-0392-03
Page 20
CLASS 5000 METER
LINE VOLTAGE CURRENT SENSORS
ØA ØB ØC
W B W B W B
A B C N
LOAD SOURCE
A
B
C
N
TERMINAL BLOCK LOCATED INSIDE E-MON D-MON
®
METER
Ø Ø
Ø
M34291
RECOMMENDED FUSES OR CIRCUIT BREAKER PER THE NATIONAL
ELECTRICAL CODE (METER LOAD 6VA.)
NEUTRAL NOT USED IN DELTA SYSTEM.
SPLIT-CORE CURRENT SENSORS. INSTALL ACCORDING TO
INSTRUCTIONS.
1
2
3
1
1
1
2
3
3
3
6.5 Main Power & Current Sensor Wiring Diagram
Fig. 9. 3-Phase - 3-Wire or 3-Phase - 4-Wire Installation Diagram.
TERMINAL BLOCK LOCATED INSIDE METER
LINE VOLTAGE CURRENT SENSORS
Ø
A B N
W B W B W B
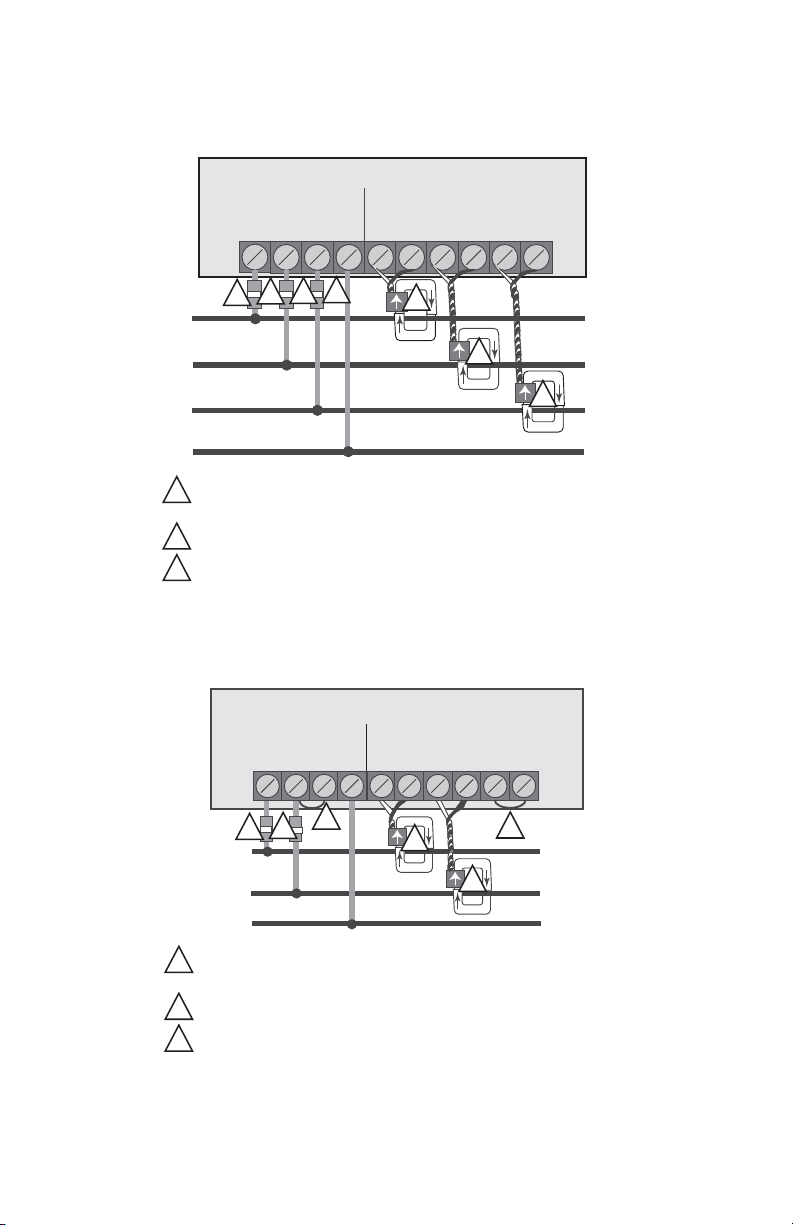
Fig. 10. Single-Phase, 3-Wire, 120/240, 120/208 or 277/480 Volt Installation Diagram
62-0392-03 20
1
2
3
1
RECOMMENDED FUSES OR CIRCUIT BREAKER PER THE NATIONAL
ELECTRICAL CODE (METER LOAD 6VA.)
CURRENT SENSORS INSTALLED ACCORDING TO INSTRUCTIONS.
INSTALL JUMPER WIRES.
ØC
Ø
3
1
LOAD SOURCE
ØA
2
ØB
2
ØC
3
A
B
N
M34842
Page 21

CLASS 5000 METER
6.6 Line Voltage/Current Sensor Diagnostics
Following is a list of diagnostic messages that may appear on the meter display.
DIAGNOSTIC MESSAGES SHOULD NOT BE ON CONTINUOUSLY WHEN THE
METER IS INSTALLED PROPERLY AND IS IN WORKING ORDER.
6.6.1 Line Voltage Diagnostics
The diagnostics program detects line voltage faults by displaying one of two
messages:
PH Missing: B C or Phase sequence error.
PH Missing: B C:
This message will appear whenever the power on either Phase B or Phase C is off.
Screen 5 (Voltage per Phase) will also indicate a loss of line voltage.
Phase sequence error
hooked up in the proper phase sequence. This message should never be seen
continuously on the display during normal operation. The meter will not display correct
electrical data in this condition. The phase sequence problem must be remedied in
order for the meter to work properly.
Indicates that the line voltage is missing on Phase B and/or Phase C.
: Indicates that the 1-phase or the 3-phase line voltage is not
21 62-0392-03
Page 22

CLASS 5000 METER
6.6.2 Current Sensor Diagnostics
The load current must be at least 1% of the meter’s rated load in order to use the
diagnostic function. Current sensor diagnostics can detect:
1. Reversed current sensors
2. Incorrect phase correspondence
3. Unusually low power factor (0.642 or lower)
CT Error: (ABC) is used to detect the swapping of current sensor phases. This
message could (in some rare cases) indicate a low (<65%) power factor condition. This
message may appear intermittently due to changes in line conditions. It should not be
on continuously.
NOTE: If you have connected the current sensor to all three terminals and the error
message is still appearing, reverse the black and white wires and repeat the
previous steps until the correct connection is found.
If the
CT Error:
however, the current sensor was not installed properly around the conductor, or the
sensor wires were extended and not spliced together correctly. Correct the sensor
installation, reconnect the black wire to the black terminal and the white wire to the
white terminal on the plug and reinstall the plug into the correct phase terminal for that
current sensor. The error message should disappear and the current sensor is now
installed properly.
If the
CT Error:
ways, check the AC voltage input from the current sensor between the black and white
wires using an AC voltmeter. It will read approximately zero volts indicating that the
load current is very small (or zero) or the current sensors are not secured properly
(tight connection between core halves or lead splices not secure.)
message disappears, you have found the correct sensor connection;
message does not disappear at any time while trying all 3 inputs both
Once the first current sensor is connected properly and the error message disappears,
repeat the previous procedure for the remaining two current sensors. When all error
messages have disappeared and all sensors are installed correctly, the meter is
operational.
62-0392-03 22
Page 23

CLASS 5000 METER
6.7 RS-485 Wiring
RS-485 communication allows a computer or modem to communicate with one or
more Class 5000 meters. You can connect as many as 52 meters along a 4000-foot
RS-485 cable run.
There are four communication protocols available through the Class 5000 RS-485
connection. They are EZ7, Modbus RTU, BACnet MS/TP, and Lonworks FT-10. The
protocol is chosen when ordering the Class 5000 meter. A second protocol is available
through the Ethernet port. The Ethernet protocol is also chosen when the meter is
ordered. See ordering information for the available choices.
Daisy-Chain Method
This is the simplest method for connecting meters together.
M32776
Fig. 11. Daisy-Chain Configuration.
1. Connect the +(high) terminal of PORT 1 of each meter together so that the + terminals on all meters are linked, + to + to +...
2. Connect the -(low) terminal of PORT 1 of each meter together so that the - terminals on all meters are linked, - to -...
3. Connect the GND terminals of PORT 1 of each meter so that the GND terminals
on all meters are linked, GND to GND to GND.
RS-485
TERMINAL
M33274
Fig. 12.
23 62-0392-03
Page 24

CLASS 5000 METER
6.7 RS-485 Wiring (continued)
After performing these steps, all of the meters will be connected in a daisy chain
configuration. This network of meters can then be connected to the RS-485 network
and communication can be established.
Internal Modem
An optional internal modem inside one meter will communicate with the others via the
RS-485 network. Simply connect one of the two telephone jacks on the modem to the
telephone line to complete the installation.
Local Computer
A local computer installed in the building can communicate with the RS-485 network.
The computer must be connected to an RS-232 key. The RS-232 key is then
connected to an available RS-485 jack in the meter using an RJ-11 cable.
NOTE: Don’t confuse the modem’s telephone jacks with the RS-485 jacks!!!
NOTE: When using one meter with an external modem, only the telephone line is
connected. RS-485 is not needed.
62-0392-03 24
Page 25

CLASS 5000 METER
CHANNEL 2
~
~
~
~
CHANNEL 3
UP TO 4000
FEET TOTAL
RS-232
KEY*
RS-232 SERIAL
PORT COM1
OR COM2
UP TO 52
CLASS 5000
METERS
M33275
UP TO 4000
FEET TOTAL
UP TO 52
CLASS 5000
METERS
CHANNEL 1
AC ADAPTER
PC
15 FEET MAX
6.8 RS-232 Communications
6.8.1 Hardwired System using the RS-232 Communication Key
The RS-232 communications key allows you to connect Class 5000 meters to a
personal computer that has the E-Mon Energy™ software installed. The computer
communicates with the meters through the RS-232 key.
The RS-232 key must be located within 15 feet of the host computer.
Fig. 13. RS-232 Configuration.
6.8.2 Connecting the RS-232 Key to the Computer
The RS-232 key is supplied with:
a. (1) 8-conductor cable fitted with RJ-45 plugs
b. (1) DB-9 serial COM port adapter
c. (1) AC adapter that converts 120VAC to 9VDC for powering the RS-232 key
Connection Steps:
1. Connect the 8-conductor cable to the left-side jack (labeled “RS232”) on the rear
panel of the RS-232 key.
2. Connect the appropriate COM port adapter (DB-9) to the serial port on the back
of the computer. Plug the 8-conductor cable from the RS-232 key into the COM
port adapter.
3. Connect the provided AC adapter into the rear panel input on the RS- 232 key.
Plug the adapter into a 120VAC outlet. On the front panel of the RS-232 key, two
LEDs (POWER ON and AC ON) will light up.
25 62-0392-03
Page 26

CLASS 5000 METER
NOTE: When the E-Mon Energy™ software is accessed on the computer, a third
LED (RS232 READY) will turn on. This indicator will light up as soon as the
E-Mon Energy software is booted up and the correct COM port is set up via
the settings provided in the software’s Locations menu.
6.8.3 Connecting Class 5000 Meters to the RS-232 Key using
RS-485
On the rear panel of the RS-232 key, there are three jacks labeled as channels A, B
and C. These are RS-485 serial communications ports used to connect the meters.
Each of these channels can be connected to as many as 52 individual meters over a
total cable distance of 4,000 feet. The channels are independent and must not be
connected to each other.
Modular Plug Method
This simple method requires using 4 stranded conductors inside a cable that is fitted
with an RJ-11 type plug for 4-conductor modular systems at each end of the cable.
*Do not use any pre-made telephone cables.
1. Plug the 4-wire RJ-11 cable/plug assembly into Channel A on the RS-232 key.
Connect the other end of this cable to the meter via the RS-485 port, (PORT 2)
at the bottom right of the Class 5000 meter main power board.
NOTE: The total combined cable length must not be more than 4000 feet.
2. Each meter has one yellow (TX) and one green (RX) LED located on the right
side of meter board just below the ribbon cable. If the system is properly wired,
these two LEDs will be OFF. These LEDs will fl ash when the computer and
meter are communicating.
62-0392-03 26
Page 27

6.9 Modem Wiring
CLASS 5000 METER
UP TO 4000
FEET TOTAL
UP TO 52
CLASS 5000
METERS PER
CHANNEL
UP TO 4000
FEET TOTAL
UP TO 52
CLASS 5000
METERS PER
CHANNEL
~
~
~
~
CHANNEL 2
M33276
PC OR WINDOWS
COMPATIBLE
TELEPHONE
LINK
RS-232 SERIAL
PORT COM1
THROUGH COM3
MAXIMUM 15 FEET
CHANNEL 1
LOCAL
MODEM
~
~
RS-232
KEY RM
AC ADAPTER
CHANNEL 3
Fig. 14. Modem Configuration.
6.9.1 Built-In Modem (RS-232 KEY RM)
The RS-232 key with built-in modem connects the entire RS-485 network of Class
5000 meters to a telephone line.
** Refer to Section 6.7 for RS-485 network connections.
On the back panel of the RS-232 key/modem, the left jack (RS232) is not used in most
cases since there is no local host computer.
The two jacks at the top center of the rear panel on the RS-232 key/modem are for
connecting the phone line. Connect either one of these two jacks to the telephone line.
IMPORTANT:
The telephone line should be dedicated exclusively to the automatic meter
reading system. Never connect to a telephone line used by other modems or
fax machines. If there are telephones connected to this phone line, the proprietor must be aware that all phones must be on “hook” in order for the modem
to work. A dedicated phone line is suggested for system reliability.
27 62-0392-03
Page 28

CLASS 5000 METER
6.9.2 External Modem
1. All meters should be connected to the RS-232 key as described in 6.8.2. 2.
2. DISCONNECT POWER TO THE RS-232 KEY. Remove the cover by removing
the 2 screws from the bottom of the enclosure.
3. On the circuit board, locate the blue jumpers J7 (MODEM) and J8 (ex-MODEM).
If these jumpers are set in the DIRECT position, you must move the jumpers so
they are set in the MODEM position. Re place the cover and secure the enclosure.
4. Connect the RS-232 key to the external modem using the supplied 8-conductor
fl at modular cable.
5. Connect the 9VDC adapter to the power input on the back of the RS-232 key
and plug it into a 120VAC outlet.
IMPORTANT:
The modem should use a phone line that is dedicated exclusively to the AMR
system. Do not use a phone line that is shared by another modem or fax
machine.
62-0392-03 28
Page 29

CLASS 5000 METER
6.9.3 Baud Rate Selection
The communication baud rate is selected by means of a jumper on the circuit board.
There are four (4) selections: 9600 (factory default), 19200, 38400, and 76800.
1. Select 9600 when using the Class 5000 meter with a modem.
2. The baud rate on the meter must always match the baud rate selected in the EMon Energy software; otherwise, communications will not work.
3. After a baud rate change, press CPU Reset to register the change.
4. All meters in the daisy-chain circuit must be set at the same baud rate.
5. The DIP switch is located above the RS-485 terminals.
6. Using other than 9600 BAUD will reduce the maximum cable length allowed for
communication.
NOTE: USE ONLY POSITIONS 3 AND 4 - DO NOT CHANGE ANY OTHER
POINTS.
The selections are noted below.
Fig. 15. Baud Rate Selection
3
4 Baud rate
ON ON 9600 (EZ-7, modbus RTU, BACnet MS/TP)
OFF ON 19200 (EZ-7, modbus RTU, BACnet MS/TP)
ON OFF 38400 (Modbus RTU, BACnet MS/TP)
OFF OFF 78600 (Bacnet MS-TP)
29 62-0392-03
Page 30

CLASS 5000 METER
6.9.4 Dip Switch Settings
COMMUNICATION
PROTOCOLS
Ethernet
Option
01 EZ7 EZ7 Modbus ON ON ON ON
02 Modbus RTU EZ7 Modbus OFF ON ON ON
03 BACnet MS/TPEZ7 BACnet
04 EZ7 Modbus
05 EZ7 BACnet IP BACnet IP ON OFF ON ON
06 Modbus RTU Modbus
07 LonWorks
08 LonWorks
09 EZ7 w/
10 EZ7 w/
11 EZ7 w/
RS-485 Port
TP/FT-10
TP/FT-10
Modem
Modem
Modem
Port SW1 SW2 SW3 SW4
TCP/IP
TCP/IP
EZ7 LonWorks X ON ON ON
Modbus
TCP/IP
EZ7 Modbus ON ON ON ON
Modbus
TCP/IP
BACnet IP BACnet IP ON OFF ON ON
Firmware
PN#
MS/TP
Modbus ON OFF ON ON
Modbus OFF OFF ON ON
LonWorks X OFF ON ON
Modbus ON OFF ON ON
PROTOCOL BAUD RATE
OFFONONOFF
NOTE: *Protocol selections are done via DIP Switch (S2); pos 1 for RS-485 and pos
NOTE: Pass Through Feature - S2 position 8 - to off - ethernet to RS485 pass
62-0392-03 30
2 for Ethernet. When the DIP switch is in the ON position, EZ7 protocol will be
active. Changing protocol setting requires restarting the CPU. DIP Switch
indicating by X means don’t care.
through - only valid with EZ7 protocol. -S2 position 8 - on - true dual protocol
settings.
Page 31

CLASS 5000 METER
RS-485
TERMINAL
6.10 Modbus RTU Wiring
The Class 5000 Modbus meter communicates with building automation equipment
over a 2-wire (3-conductor) RS-485 network using Modbus RTU protocol. The meters
are networked in a daisy-chain configuration (Section 6.7) with BELDEN 1120A cable
or equivalent. The cable rating of 600V allows the RS-485 network to be connected to
480-volt meters. Up to 52 meters can be installed on a network string. The maximum
combined length of all daisy-chained cables must not exceed 4000 feet.
The meter-to-network connection is through the 3-screw terminal which is located on
the Main Power Board of the meter.
Fig. 16. Modbus R Wiring.
The meter is shipped with a Modbus ID number of 01. This must be changed if the
network has more than one meter installed. The change must be done before the
meter is introduced into the network. The meter can be numbered from 1 to 247. There
can be no duplicate numbers on a network, so caution must be taken when assigning
a meter ID number prior to its installation on the RS-485 network.
SEE SECTION 10 FOR INSTRUCTIONS ON CHANGING ID AND IP ADDRESSES.
6.11 BACnet MS/TP Wiring
BACnet MS/TP wiring is the same as Modbus and EZ7 wiring. See Sections 10 and 11
for instructions on changing I.D. and IP addresses.
31 62-0392-03
Page 32

CLASS 5000 METER
PC WITH USB PORT
USB KEY
M33406
UP TO 52, CLASS 5000
METERS, ON RS485 CABLING
UP TO 4000 FEET TOTAL
RS485 CABLE LENGTH
6.12 Connecting Class 5000 Meters to the USB Key
using RS485
The USB Key plugs into the PC’s USB port and provides a termination point for the
RS485 wiring from the meters. Up to 52 meters can be “Daisy chained” with up to 4000
feet total RS485 wiring. The USB Key is labeled for “plus (+)”, “minus (-)“, and ground
and the wiring must match the same positions on the meters. If more than 52 meters
are to be monitored, additional USB Keys can be utilized to connect them to the PC.
Fig. 17. Connecting Class 5000 Meters to the USB Key using RS485.
62-0392-03 32
Page 33

CLASS 5000 METER
M32786
EMS OR
CONTROL UNIT
WITH MODBUS
COMMUNICATION
6.13 Ethernet Communications
Ethernet/IP communications connections are provided through an RJ-45
connector(J8) in the lower right corner of the main power board. This port can be
connected directly to a network port of a PC using a Cat. 5e crossover cable.
Two LEDs are provided directly above the connector. The LINK LED is yellow and
when lit, indicates ethernet connectivity. The ACT led is green and when lit, indicates
communication activity. The communication protocol for the Ethernet port is selected
when ordering the meter. The available choices are EZ7, Modbus TCP/IP and BACnet
IP. See the ordering information for the available choices in combination with the RS485 output.
Class 5000 Ethernet/IP Addressable meters can be tied into a local Ethernet network
individually, or a single Ethernet-connected meter can communicate with multiple RS485 daisy-chained conventional class 5000 meters using a single IP address. Each
device that is connected directly to the ethernet network requires a unique IP address.
SEE SECTION 10 FOR INSTRUCTIONS ON CHANGING ID AND IP ADDRESSES.
RS-485 DAISY CHAIN (SECTION 5.7)
Fig. 18. Ethernet/IP Communications.
33 62-0392-03
ETHERNET
NETWORK
M32787
Page 34

CLASS 5000 METER
7.0 MULTIPLE-LOAD MONITORING
The E-Mon D-Mon Class 5000 meter provides extreme flexibility by allowing additional
sets of current sensors to be used in parallel so multiple load locations can be
monitored by one meter. This feature allows a totalized display readout from two or
more load circuits.
You may use parallel sensors to monitor specific breakers from one panel, specific
breakers from more than one panel, two or more complete panels, etc. When
paralleling current sensors, the following rules must be followed for accurate readings:
1. Current sensors must be installed in complete sets of three, with a maximum of
three sensors installed in parallel per phase.
NOTE:-In 1-phase option - sensors must be installed in set of 2 with maximum of
three sensors per phase.
2. All sensors used in parallel must be of the same amperage rating (all 100-amp,
all 400-amp, etc.) The rating is determined by the current rating of the meter. For
example, a 200-amp meter must use extra sets of 200-amp current sensors.
3. All locations being monitored must have the same power source. A 480-volt
meter cannot monitor a 208-volt load, nor can a meter monitor two-480 volt loads
if they are from different originating power sources or from different transformers.
4. 4. Multiply the meter display readings by the number of sets of current sensors
installed. Example: Meter readings of 5 kWh with 2 sets of current sensors - 10
kWh is the actual usage. (5 x 2=10.)
NOTE: One set of current sensors equates to three sensors, one per phase. The
multiplier only applies when extra sets of current sensors are installed on one
meter. If you are using only one set of three current sensors, the multiplier is
not required.
LINE VOLTAGE CURRENT SENSORS
C N B W B W B W
1
1
LINE VOLTAGE LEADS
LOAD A
A
B
C
N
LOAD SOURCE (LINE)
LOAD B
A
B
C
N
LOAD SOURCE (LINE)
1
CURRENT
SENSOR
LEADS
CURRENT SENSOR LEADS
M34643
Fig. 19. Multiple-load Wiring Diagram.
62-0392-03 34
Page 35

Fig. 20. Single Phase Multiple Load Diagram.
CURRENT SENSORS
B W B W B W
Ø
AØBØC
N
LINE VOLTAGE
Ø
A
Ø
B
LOAD SOURCE
N
LOAD A
LOAD B
LOAD SOURCE
Ø
A
Ø
B
N
M34644
INSTALL JUMPER W IRE.
1
1
CLASS 5000 METER
8.0 PREVENTATIVE/SCHEDULED
MAINTENANCE
The unit is shipped in a calibrated and fully functional tested condition. Since the unit is
factory-calibrated using proprietary firmware algorithms, no internal unit adjustments
are necessary.
This unit contains no internal adjustments, so no preventative or scheduled
maintenance is required.
No cleaning or decontamination procedures are required for this instrument.
35 62-0392-03
Page 36

CLASS 5000 METER
WARNING
9.0 LITHIUM BATTERY REPLACEMENT
INSTRUCTIONS
The Class 5000 kWh/Demand meter has a Lithium Battery Cell, which is used to retain
the contents of SRAM and the RTC during power outages. The battery has a life
expectancy of greater than 5 years.
Nominal Working Voltage 3 Vdc Output
Nominal Current Capacity 225 mAHr
Cell Chemical Manganese Dioxide Lithium
Operating Temperature Range -30 to +60 Degrees Celsius
Manufacturer Panasonic
Manufacturer’s Part Number CR2032
Fig. 21. Battery Specifications at 25 Degrees Celsius.
Only replace battery with Panasonic part number CR2032 only. Use of another
battery may present a risk or explosion. See owners manual for safety
instructions. Internal circuit card components are extremely sensitive to
electrostatic discharge. Be careful not to touch internal circuitry prior to
discharging any static buildup on your person. To discharge yourself, touch a
grounded metal object such as conduit or a metal enclosure exterior.
62-0392-03 36
Page 37

CLASS 5000 METER
M33278
BATTERY
+
–
The battery cell is mounted in a coin cell on the upper right side of the main power
board. Replace the battery if the low battery warning is on display.
Fig. 22. Lithium Battery Cell.
Use the following procedure to replace the battery cell:
STEP 1: Disconnect power from the meter at the unit external circuit breaker.
STEP 2: Remove the battery from its holder and place on a non-conductive surface.
STEP 3: Install new battery into the battery holder.
NOTE: Care should be taken to insure that the replacement battery is installed the
same polarity as the battery that was removed. No damage to unit or battery
will occur if battery is inadvertently installed in the wrong direction.
STEP 4: Dispose of the used battery in accordance with the manufacturers’
(Panasonic) instructions.
37 62-0392-03
Page 38

CLASS 5000 METER
CL5000 M
Starting Up.....
110608TR
1A 38400 EZ7x EZ7x
MD 3P 208V 200A*
CF 1.057 1.056 1.057
DT 00000000 06.21.01
*1-Phase option will state:
MD 2P 208V 200A
10.0 CLASS 5000 METER
OPERATING MODES
The E-Mon D-Mon® Class 5000 meter is used to monitor electric power usage of
individual loads after the utility meter and store kW and kVAR data for automatic meter
reading.
10.1 Start Up Screens
When the meter starts up, the screen first
displays the meter name and firmware
image type.
After approximately 4 seconds, the screen
displays misc. information such as active
configurations, meter configurations,
phase, voltage, amperage, calibration
factors, serial number, Date/time and
firmware version.
62-0392-03 38
Page 39

CLASS 5000 METER
Screen 1: Total Kilowatt-Hours (kWh)
Delivered.
Screen 2: Peak Demand (kW)
with Date & Time Stamp
Screen 3: Actual Load (kW)
with Present Time
Screen 4: Average Current (amps)
Per Phase.
Note: 1-Phase option will only state:
PH-A and PH-B.
Screen 5: Average Voltage (volts)
Per Phase.
Note: 1-Phase option will only state:
PH-A and PH-B.
Screen 6: Average Voltage (volts)
Phase to Phase.
Note: 1-Phase option will only state:
P-AB and P-BA.
Screen 7: Power Factor (pf)
Per Phase.
Note: 1-Phase option will only state:
PH-A and PH-B.
10.2 Normal Mode Display Screens
The Class 5000 meter features seven Normal Mode Display Screens for monitoring
the meter. Each screen is displayed for 5 second intervals, before scrolling onto the
next screen.
You can “lock” the scrolling display on any one of the seven screens. This will be
explained in detail on following pages.
Explanations of the Normal Mode Display Screens are as follows:
39 62-0392-03
Page 40

CLASS 5000 METER
DOWN
UP
SELECT
MENU
M33279
Fig. 23. Push Buttons.
10.3 How to Program the Display Screens
The display information can be programed using four push buttons switches. The push
buttons (DOWN, UP, SELECT, MENU) are located at the top of the display board on
the inside front door of the meter. The buttons are used to program the following:
• Date & Time (This field sets the month, day, year, and time).
• Device ID (This field changes the default setting, which is 1A for EZ7 and 2 for
ModBus).
• IP Settings (This field allows you to select the DHCP or static IP address, mask and
gateway information).
• Reset KW/KWH Read (This field resets the Peak kW Demand to zero).
62-0392-03 40
Page 41

CLASS 5000 METER
—> DATE & TIME
DEVICE ID
IP SETTINGS
RESET KW/KWH READ
DATE: 02-16-2012
TIME: 01:57:36
Save changes: Y / N
10.3.1 Date & Time Display Screen
To change the date and time, complete the following steps:
1. Press the MENU button.
2. The following screen will appear:
3. Press the SELECT button. The Date and Time Screen will appear, and the 2
digit month will be blinking.
4. Use UP or DOWN button to make changes, press the SELECT button to
advance to the next setting. Repeat this step until all the date and time settings
have been updated.
5. If changes were made, you’ll be asked to save, press UP or DOWN to select Y or
N.
6. Press SELECT to save new settings. This will also return you to main menu. In
main menu, select EXIT to get out of programming mode and return to normal
display mode.
41 62-0392-03
Page 42

CLASS 5000 METER
—> DATE & TIME
DEVICE ID
IP SETTINGS
RESET KW/KWH READ
DATE & TIME
—> DEVICE ID
IP SETTINGS
RESET KW/KWH READ
EZ7 ID: 1A
MODBUS ID: 2
Save changes: Y / N
10.3.2 Device I.D. Display Screen
To change Device I.D., complete the following steps:
1. Press the MENU button.
2. The following screen will appear:
3. Use UP or DOWN button until the arrow is on the Device ID line.
4. Press the SELECT button. The Device ID Screen will appear.
5. Use UP or DOWN button to make changes, press the SELECT button to
advance to the next setting. Repeat this step until all the settings have been
updated.
6. If changes were made, you’ll be asked to save, press UP or DOWN to select Y or
N.
7. Press SELECT to save new settings. This will also return you to main menu. In
main menu, select EXIT to get out of programming mode and return to normal
display mode.
62-0392-03 42
Page 43

CLASS 5000 METER
—> DATE & TIME
DEVICE ID
IP SETTINGS
RESET KW/KWH READ
DATE & TIME
DEVICE ID
—> IP SETTINGS
RESET KW/KWH READ
ENABLE DHCP? N
IP: 192.168. 0.168
MSK: 255.255.255 0
GWY: 192.168. 0. 1
Save changes: Y / N
10.3.3 IP Setting Display Screen
To Change the IP settings, complete the following steps:
1. Press the MENU button.
2. The following screen will appear:
3. Use UP or DOWN button until the arrow is on the IP Setting line.
4. Press the SELECT button. The IP Setting Screen will appear.
5. Use UP or DOWN button to make changes, press the SELECT button to
advance to the next setting. Repeat this step until all the settings have been
updated.
6. If changes were made, you’ll be asked to save, press UP or DOWN to select Y or
N.
7. Press SELECT to save new settings. This will also return you to main menu. In
main menu, select EXIT to get out of programming mode and return to normal
display mode.
43 62-0392-03
Page 44

CLASS 5000 METER
DATE & TIME
DEVICE ID
IP SETTINGS
—> RESET KW/KWH READ
Reset kW only? N
Reset all? N
10.3.4 Peak Demand Reset
To reset the recorded peak kW demand, complete the following steps:
1. Press the MENU button until “Reset kW/kWh Read” is indicated by the arrow on
the display.
2. Press the SELECT button. The following screen will appear on the display.
3. Press the UP button to change the N to a Y after “Reset kW only?”.
4. The peak demand will be reset to zero and the meter will return to its normal
scrolling display mode.
62-0392-03 44
Page 45

CLASS 5000 METER
10.3.4 Display Hold Feature
You can “lock” the scrolling display so that it will stay locked on any one of the six
screens.
To stop the display from scrolling, complete the following steps:
1. Press the UP and DOWN buttons to choose which of the six screens you would
like to display.
2. Press the Select button. At the top of the display, you will see the message
HOLD1. This will lock the display for 1 HOUR.
NOTE: The display hold feature has different selectable time periods.
3. Pressing Select again will show the message HOLD6. This will lock the display
for 6 HOURS.
4. Continuing to press the Select button will provide additional timing choices:
HOLD12: Locks the display for 12 HOURS
HOLD24: Locks the display for 24 HOURS
HOLD: Locks the display indefinitely
To exit the HOLD mode:
Press the Select button as many times as needed until the HOLD message disappears from the display.
** Be sure to exit from the HOLD mode when you are done using this feature.
45 62-0392-03
Page 46

CLASS 5000 METER
11.0 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Q. When providing line voltage to the meter, can I tap off of the same breaker I am
monitoring?
A. Yes, the voltage can be pulled from the same breaker being monitored.
Q. Can the meter’s line voltage wires be run in the same conduit as the sensor leads?
A. Yes. There will be no effect if the sensor leads and line voltage wires are run in the
same conduit.
Q. Can the meter’s communication wires and line voltage be run in the same conduit?
A. It is not recommended to run these wires together due to noise concerns and their
effects on the communications signal integrity. Communications wires can be
routed separately using a 1/2” conduit port.
Q. How do I find the cost for kWh and kW to bill my tenants?
A. Your local utility bill should list the cost per kWh and kW. If not, simply call your
utility and ask them to provide you with the cost per kWh and kW.
Q. What size wire do I use for the line voltage leads?
A. These wires are normally sized at #14 AWG, but be sure to confirm this
requirement with your local and national electrical code requirements.
Q. What size wire should I use to extend the current sensor leads?
A. These wires are normally 14-22 AWG, twisted-pair arrangement. Consult your
electrical code for proper wiring requirements.
62-0392-03 46
Page 47

CLASS 5000 METER
Q. The load I need to monitor has parallel feeds. How do I install the current sensors
for this application?
A. There are two ways you can monitor parallel feeds. The easiest and preferred
method is to clamp the sensors around all feed wires for each phase. The second
way to monitor parallel feeds is to clamp the sensor around one of the feed wires for
each phase. When you read the Class 5000 meter, the final reading must be
multiplied by the number of feed wires for each phase.
Q. I have two subpanels I would like to monitor with one Class 5000 meter. These
subpanels are fed by different transformers in the building. Can I parallel sensors
and monitor both panels with one meter?
A. No. These panels cannot be monitored with one meter because they are different
power sources. When you parallel current sensors, all loads being monitored must
be from the same voltage source.
Q. I have 5 breakers in one subpanel I would like to monitor with one class 5000 meter.
Can this be done without having to parallel current sensors?
A. Yes. Simply run all the breaker wires through one set of current sensors. Make sure
all A-phase circuits are run through the A-phase sensor, and the same for B & C
phases. The meter should be sized by the highest amount of current being
monitored by one sensor.
Q. I’ve gone through the troubleshooting guides and I still can’t get my class 5000
meter to work. What should I do?
A. Before removing the unit, contact E-Mon’s technical services department at (800)
334-3666. E-Mon’s technical department will assist you in detailed troubleshooting
of the meter installation and assist you in getting the unit running without having to
remove and/or return it.
47 62-0392-03
Page 48

CLASS 5000 METER
12.0 PROTOCOL DESCRIPTIONS
ModBus Customer Point Map: CL5000
Address Registers Format Description Units
1
40001
40003
40005
40007
41001
41003
41005
41007
41009 2 Float Real power kW R
41011 2 Float Reactive power kVAR R
2 Integer Energy delivered Wh Pulse R/W
1
2 Integer Energy received Wh Pulse R/W
1
2 Integer Reactive energy delivered VARh Pulse R/W
1
2 Integer Reactive energy received VARh Pulse R/W
1
2 Float Energy delivered kWh R/W
1
2 Float Energy received kWh R/W
1
2 Float Reactive energy delivered kVARh R/W
1
2 Float Reactive energy received kVARh R/W
CL
5000
41013 2 Float Apparent power kVA R
41015 2 Float Power factor % PF R
41017 2 Float Peak demand kW R
41019 2 Float Current average Amps R
41021 2 Float Voltage line-neutral Volts-N R
41023 2 Float Voltage line-line Volts-L R
41025 2 Float Frequency Hz R
41027 2 Float Phase angle Degree R
41029 2 Float Real power, phase A kW R
41031 2 Float Real power, phase B kW R
41033 2 Float Real power, phase C kW R
62-0392-03 48
Page 49

CLASS 5000 METER
ModBus Customer Point Map: CL5000
Address Registers Format Description Units
41035 2 Float Reactive power, phase A kVAR R
41037 2 Float Reactive power, phase B kVAR R
41039 2 Float Reactive power, phase C kVAR R
41041 2 Float Apparent power, phase A kVA R
41043 2 Float Apparent power, phase B kVA R
41045 2 Float Apparent power, phase C kVA R
41047 2 Float Power factor, phase A % PF R
41049 2 Float Power factor, phase B % PF R
41051 2 Float Power factor, phase C % PF R
41053 2 Float Current, phase A Amps R
41055 2 Float Current, phase B Amps R
CL
5000
41057 2 Float Current, phase C Amps R
41059 2 Float Voltage, line to neutral, phase A-NVolts-N R
41061 2 Float Voltage, line to neutral, phase B-NVolts-N R
41063 2 Float Voltage, line to neutral, phase C-NVolts-N R
41065 2 Float Voltage, line to line, phase A-B Volts-L R
41067 2 Float Voltage, line to line, phase B-C Volts-L R
41069 2 Float Voltage, line to line, phase C-A Volts-L R
41071 2 Float Phase angle, phase A Degree R
41073 2 Float Phase angle, phase B Degree R
41075 2 Float Phase angle, phase C Degree R
49 62-0392-03
Page 50

CLASS 5000 METER
ModBus Customer Point Map: CL5000
CL
Address Registers Format Description Units
2
41083
41085
44001
44007
45501
46025
46049
2 Float External Input 1 Pulse R/W
2
2 Float External Input 2 Pulse R/W
3
6 Custom Interval Day Block R/W
4
1 per
Integer Interval Data Pulse R
interval
5
2 per day Custom Interval Data Headers R
6
8 Custom RTC Date/Time R/W
7
8 Custom EZ7 ID, ModBus ID, Serial
Number
5000
R/W
46057 8 Custom Recorder Info., Demand Interval R/W
46513 8 Custom Flags L1: Power Failure, Battery R
46521 8 Custom Flags L2: Power Failure Date R
1. To clear single meter kWh/kVARh, set multiple points at 40001 or 41001 for 8
points with data set to 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000.
2. External inputs are standard on Class 5000 meters and optional on Class 3400
meters (Part of Expanded Feature Package).
To clear external inputs, set multiple points at 41083 or 41085 for 2 points with data
set to 0000 0000. Jumper J6 must be closed. Remove J6 when changes have been
completed.
3. To set the interval data day block, set multiple points at 44001 for 6 points with data
set to 0C0I 0000 MMDD YYYY 0000 0000.
0C = Channel, 0I = Interval (0F = 15 minute intervals, 05 = 5 minute intervals)
4. Each register represents a 15 or 5 minute kWh pulse value based on the interval
day block. 96 registers max with 15 minute intervals. 288 registers max with 5 minute
intervals. The first interval data register 44007 represents the pulse count for the first
15 or 5 minute interval beginning at midnight.
5. The interval data headers represent days with available interval data. Each day
represents 2 registers. Format: MMDD YYYY.
6. To set the date and time, set multiple points at 46025 for 4 points with data set to
HHMM SSDW MMDD YYYY (DW=day of week)
7. To change the ModBus ID, set single point at 46050 with data set to new ModBus
ID (e.g. 1 to 247). Jumper J6 must be closed. Remove J6 when changes have been
completed.
62-0392-03 50
Page 51

Instance IDBACnet
Object Description Units
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
Analog
Input
Analog
Input
Analog
Input
Analog
Input
5 Analog
Input
6 Analog
Input
7 Analog
Input
8 Analog
Input
9 Analog
Input
10 Analog
Input
11 Analog
Input
12 Analog
Input
13 Analog
Input
14 Analog
Input
15 Analog
Input
16 Analog
Input
17 Analog
Input
18 Analog
Input
19 Analog
Input
CLASS 5000 METER
BACnet Object Descriptors: CL5000
BACnet
PropertyCL5000
Energy delivered kWh Present Value R
Energy received kWh Present Value R
Reactive energy delivered kVARh Present Value R
Reactive energy received kVARh Present Value R
Real power kW Present Value R
Reactive power kVAR Present Value R
Apparent power kVA Present Value R
Power factor % PF Present Value R
Peak demand kW Present Value R
Current average Amps Present Value R
Voltage line-neutral Volts-N Present Value R
Voltage line-line Volts-L Present Value R
Frequency Hz Present Value R
Phase angle Degree Present Value R
Real power phase A kW Present Value R
Real power phase B kW Present Value R
Real power phase C kW Present Value R
Reactive power phase A kVAR Present Value R
Reactive power phase B kVAR Present Value R
51 62-0392-03
Page 52

CLASS 5000 METER
Instance IDBACnet
Object Description Units
20 Analog
Input
21 Analog
Input
22 Analog
Input
23 Analog
Input
24 Analog
Input
25 Analog
Input
26 Analog
Input
27 Analog
Input
28 Analog
Input
29 Analog
Input
30 Analog
Input
31 Analog
Input
32 Analog
Input
33 Analog
Input
34 Analog
Input
35 Analog
Input
36 Analog
Input
37 Analog
Input
38 Analog
Input
BACnet Object Descriptors: CL5000
BACnet
PropertyCL5000
Reactive power phase C kVAR Present Value R
Apparent power phase A kVA Present Value R
Apparent power phase B kVA Present Value R
Apparent power phase C kVA Present Value R
Power factor phase A % PF Present Value R
Power factor phase B % PF Present Value R
Power factor phase C % PF Present Value R
Current phase A Amps Present Value R
Current phase B Amps Present Value R
Current phase C Amps Present Value R
Voltage line-neutral phase A-NVolts-N Present Value R
Voltage line-neutral phase B-NVolts-N Present Value R
Voltage line-neutral phase C-NVolts-N Present Value R
Voltage line-line phase A-B Volts-L Present Value R
Voltage line-line phase B-C Volts-L Present Value R
Voltage line-line phase C-A Volts-L Present Value R
Phase angle phase A Degree Present Value R
Phase angle phase B Degree Present Value R
Phase angle phase C Degree Present Value R
62-0392-03 52
Page 53

CLASS 5000 METER
BACnet Object Descriptors: CL5000
Instance IDBACnet
Object Description Units
39 Analog
Reserve A No units Present Value R
BACnet
PropertyCL5000
Input
40 Analog
Reserve B No units Present Value R
Input
41 Analog
Reserve C No units Present Value R
Input
42
43
2
2
Analog
Input
Analog
Input
External Input 1 Pulse Present Value R
External Input 2 Pulse Present Value R
1. To clear single meter kWh/kVARh, select reset kW/kWh on the display menu of the
meter. This function will also reset external inputs. Jumper J6 must be closed.
Remove J6 when changes have been completed.
2. External inputs are standard on Class 5000 meters and optional on Class 3400
meters (Part of Expanded Feature Package). To clear external inputs, select reset
kW/kWh on the display menu of the meter. This function will also reset kW/kVARh.
Jumper J6 must be closed. Remove J6 when changes have been completed.
53 62-0392-03
Page 54

CLASS 5000 METER
Instance ID BACnet Object BACnet Property CL5000
BACnet Device ID Device Object identifier R
BACnet Device ID Device Object name R
BACnet Device ID Device Object type R
BACnet Device ID Device System status R/W
BACnet Device ID Device Vendor name R
BACnet Device ID Device Vendor Identifier R
BACnet Device ID Device Model name R
BACnet Device ID Device Firmware revision R
BACnet Device ID Device Application software version R
BACnet Device ID Device Location R/W
BACnet Device ID Device Description R/W
BACnet Device ID Device Protocol version R
BACnet Device ID Device Protocol services supported R
BACnet Device ID Device Protocol object types supported R
BACnet Device ID Device Protocol revision R
BACnet Device ID Device Object list R
BACnet Device ID Device Max APDU length supported R
BACnet Device ID Device Segmentation supported R
BACnet Device ID Device Local time R
BACnet Device ID Device Local date R
BACnet Device ID Device APDU time out R/W
BACnet Device ID Device Number of APDU retries R/W
BACnet Device ID Device Device address binding R
62-0392-03 54
Page 55

CLASS 5000 METER
Lonworks SNVT Types Point Map: CL5000
Network Variable
Name SNVT Type Description Units CL5000
nvoKWh_Del
nvoKWh_Rec
nvoKVarh_Del
1
1
1
SNVT_count_inc_f Energy
delivered
SNVT_count_inc_f Energy
received
SNVT_count_inc_f Reactive
energy
kWh R
kWh R
kVARh R
delivered
nvoKVarh_Rec
1
SNVT_count_inc_f Reactive
energy
kVARh R
received
nvoReal_Pwr SNVT_count_inc_f Real power kW R
nvoReact_Pwr SNVT_count_inc_f Reactive
kVAR R
power
nvoAppar_Pwr SNVT_count_inc_f Apparent
kVA R
power
nvoPwr_Fact SNVT_pwr_fact_f Power factor % PF R
nvoPeak_Dem SNVT_count_inc_f Peak demand kW R
nvoCurrent_Avg SNVT_amp_f Current
Amps R
average
nvoVolt_LN SNVT_volt_f Voltage line-
Volts-N R
neutral
nvoVolt_LL SNVT_volt_f Voltage line-
Volts-L R
line
nvoFrequency SNVT_freq_f Frequency Hz R
nvoPhase_Angle SNVT_angle_f Phase angle Degree R
nvoReal_Pwr_PhA SNVT_count_inc_f Real power,
kW R
phase A
nvoReal_Pwr_PhB SNVT_count_inc_f Real power,
kW R
phase B
nvoReal_Pwr_PhC SNVT_count_inc_f Real power,
kW R
phase C
nvoReact_Pwr_PhA SNVT_count_inc_f Reactive
kVAR R
power, phase
A
nvoReact_Pwr_PhB SNVT_count_inc_f Reactive
kVAR R
power, phase
B
55 62-0392-03
Page 56

CLASS 5000 METER
Lonworks SNVT Types Point Map: CL5000
nvoReact_Pwr_PhC SNVT_count_inc_f Reactive
power, phase
C
nvoAppar_Pwr_PhA SNVT_count_inc_f Apparent
power, phase
A
nvoAppar_Pwr_PhB SNVT_count_inc_f Apparent
power, phase
B
nvoAppar_Pwr_PhC SNVT_count_inc_f Apparent
power, phase
C
nvoPwr_Fact_PhA SNVT_pwr_fact_f Power factor,
phase A
nvoPwr_Fact_PhB SNVT_pwr_fact_f Power factor,
phase B
nvoPwr_Fact_PhC SNVT_pwr_fact_f Power factor,
phase C
nvoCurrent_PhA SNVT_amp_f Current,
phase A
nvoCurrent_PhB SNVT_amp_f Current,
phase B
nvoCurrent_PhC SNVT_amp_f Current,
phase C
nvoVolt_LN_PhA_N SNVT_volt_f Voltage, line
to neutral,
phase A-N
nvoVolt_LN_PhB_N SNVT_volt_f Voltage, line
to neutral,
phase B-N
nvoVolt_LN_PhC_N SNVT_volt_f Voltage, line
to neutral,
phase C-N
nvoVolt_LL_PhA_B SNVT_volt_f Voltage, line
to line, phase
A-B
nvoVolt_LL_PhB_C SNVT_volt_f Voltage, line
to line, phase
B-C
nvoVolt_LL_PhC_A SNVT_volt_f Voltage, line
to line, phase
C-A
kVAR R
kVA R
kVA R
kVA R
% PF R
% PF R
% PF R
Amps R
Amps R
Amps R
Volts-N R
Volts-N R
Volts-N R
Volts-L R
Volts-L R
Volts-L R
62-0392-03 56
Page 57

CLASS 5000 METER
Lonworks SNVT Types Point Map: CL5000
nvoPhase_AngleA SNVT_angle_f Phase angle,
Degree R
phase A
nvoPhase_AngleB SNVT_angle_f Phase angle,
Degree R
phase B
nvoPhase_AngleC SNVT_angle_f Phase angle,
Degree R
phase C
nvoReserve_A SNVT_count_f Reserve A No units R
nvoReserve_B SNVT_count_f Reserve B No units R
nvoReserve_C SNVT_count_f Reserve C No units R
2
nvoExt_Input_1
nvoExt_Input_2
1. To clear single meter kWh/kVARh, select reset kW/kWh on the display menu of the
meter. This function will also reset external inputs. Jumper J6 must be closed.
Remove J6 after changes have been completed.
2. External inputs are standard on Class 5000 meters and optional on Class 3400
meters (Part of Expanded Feature Package). To clear external inputs, select reset
kW/kWh on the display menu of the meter. This function will also reset kW/kVARh.
Jumper J6 must be closed. Remove J6 after changes have been completed.
SNVT_count_f External
2
SNVT_count_f External
Input 1
Input 2
Pulse R
Pulse R
57 62-0392-03
Page 58

CLASS 5000 METER
13.0 HIGH VOLTAGE METERING
kWh Meter Installation Instructions for Use with E-Mon
Meters in High Voltage Applications
The E-Mon model # 12025HV kWh meter is designed to be used for monitoring high
voltage (2400, 4160, 13200, etc) circuits, either “stand alone” or in an AMR application.
This meter is intended to be used with the appropriate high voltage Potential
Transformers (PTs) and Current Transformers CTs) supplied by others. The meter
application is centered around a 120 VAC secondary output from the high voltage PTs
and a 5 amp secondary output from the high voltage CTs.
Items addressed by this document include the installation of the 12025HV meter on
high voltage circuits as well as the calculations to provide the correct meter multiplier
based on the PT and CT sizes used on the high voltage conductors.
Installation should be performed by qualified personnel and only according to all
applicable electrical codes.
High Voltage CTs (supplied by others) reduce the primary current (amps) to a directly
proportional 0~5 amp secondary output. As an example, a 0~400 amp primary
becomes a 0~5 amp proportional signal from the secondary output. In our application,
the high voltage CT secondary is installed as a continuous “loop”, with a single
conductor connected to both secondary terminals.
To convert the 0~5 amp signal to a 0~ 2 volt signal, E-Mon’s Current Sensors are
installed on the CT secondary conductor. A set of 25 amp sensors is used in this
application. These sensors have the high voltage CT secondary conductor passed
through them five (5) times (see below) by looping the secondary conductor as shown
in the drawing. The reason for this is so that the 5 amp secondary now appears to the
current sensor as a 0~25 amp signal. This creates a conversion of the CT’s primary
current to a directly proportional 0~ 2 volt signal which is utilized by the E-Mon meter.
The example from the first paragraph has now become a 400 amp to 2 volt device, by
this technique.
62-0392-03 58
Page 59

PASS #1
PASS #2
Fig. 24. High Voltage CTs.
CLASS 5000 METER
PASS #3
PASS #4
PASS #5
M34227
Fig. 25. Wiring Diagram For 3-wire High Voltage Circuits.
59 62-0392-03
M34228
Page 60

CLASS 5000 METER
This special high voltage meter installation shows the correct wiring procedure for 4wire high voltage circuits. In this application, the 3 element meter connection is used
on the secondary circuits of the user supplied high voltage PTs and CTs.
The E-Mon meter used in this application is the model 12025 HV.
Installation of these meters requires the use of three (3) current sensors mounted on
the secondaries of the high voltage Current Transformers. See the drawing above for
proper wiring. For correct operation, the meter must be installed correctly.
This special high voltage meter installation utilizes high voltage PTs (Potential
Transformers) and CTs (Current Transformers) supplied by others. The E-Mon meter is
installed using the secondary outputs of these devices.
High voltage PTs reduce the primary voltage (4160v, 13200v, etc.) to a Secondary
output of 120v. This secondary is connected to the E-Mon meter voltage inputs as
shown in the wiring diagram. High voltage CTs reduce the primary current (amps) to a
directly proportional 0~5 amp output. As an example, a 0~400 amp primary becomes a
0~5 amp proportional signal from the secondary output. This allows much smaller
wiring to be utilized in the meter hookup. The high voltage CT secondary is installed as
a continuous “loop”, with a single lead connected to both secondary terminals.
E-Mon meters accept a 0~2 volt signal from their Current Sensors. To convert the 0~5
amp signal, the Current Sensors are installed on the CT secondary lead. A set of 25
amp sensors is used in this application. These sensors have the high voltage CT
secondary lead passed through them five (5) times by looping the wire as shown in the
drawing. This allows a direct conversion of the CTs primary current to a directly
proportional 0~2 volt signal, which is used by the meter.
Since there is a signal ratio introduced by the high voltage CTs and PTs, it will be
necessary to multiply the number on the meter’s display for a correct reading. The
meter multiplier is calculated by using the CT ratio and the PT Ratio. [PTr x CTr /
Number of Secondary Lead Passes Through Sensor]. The E-Mon 25 amp HV kWh
meter with 5 wraps of the high voltage CT secondary will have its multiplier calculated
by the formula shown below.
EXAMPLE: CT = 400:5 = 80:1 (CTr = 80)
PT = 4200:120 = 35:1 (PTr = 35)
Wraps (Passes) = 5
METER MULTIPLIER
= PTr x (CTr/Wraps)
35 x (80/5)
35 x (16) = 560
62-0392-03 60
Page 61

CLASS 5000 METER
14.0 METER LIMITED WARRANTY
Subject to the exclusions listed below, E-Mon will either repair or replace (at its option)
any product that it manufactures and which contains a defect in material or
workmanship.
The following exclusions apply:
1. This Limited Warranty is only effective for a period of (5) five years following the
date of manufacture when installed in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions by qualified personnel.
2. E-Mon must be notified of the defect within ninety (90) days after the defect
becomes apparent or known.
3. Buyer’s remedies shall be limited to repair or replacement of the product or component which failed to conform to E-Mon’s express warranty set forth above.
4. Buyer shall be responsible for all freight costs and shall bear all risk of loss or
damage to returned goods while in transit.
5. This Limited Warranty does not cover installation, removal, reinstallation, or labor
costs, and excludes normal wear and tear. Buyer shall provide labor for the
removal of the defective component or item and installation of its replacement at
no charge to E-Mon.
6. This Limited Warranty does not cover any product if: (i) a product is altered or
modified from its original manufactured condition, (ii) any repairs, alterations or
other work has been performed by Buyer or others on such item, other than work
performed with E-Mon’s authorization and according to its approved procedures;
(iii) the alleged defect is a result of abuse, misuse, improper maintenance,
improper installation, accident or the negligence of any party; (iv) damaged as a
result of events beyond E-Mon’s control or other force majeure events or (v) used
in conjunction with equipment, components, accessories, parts or materials not
supplied or approved by E-Mon.
7. This Limited Warranty is limited to the obligation to repair or replace the manufactured product. This is the sole and exclusive remedy for any breach of warranty. IN
NO EVENT SHALL E-MON BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES (INCLUDING ANY DAMAGE
FOR LOST PROFITS) ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE FURNISHING OF PRODUCTS, PARTS OR SERVICES, OR THE PERFORMANCE, USE
OF, OR INABILITY TO USE ANY PRODUCTS, PARTS OR SERVICES, SALE OF
OR OTHERWISE, WHETHER BASED IN CONTRACT, WARRANTY, TORT,
INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, NEGLIGENCE, OR ANY OTHER LEGAL OR
EQUITABLE THEORY.
8. EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY PROVIDED HEREIN, E-MON MAKES NO WARRANTY
OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WITH RESPECT TO ANY PRODUCTS,
PARTS OR SERVICES PROVIDED BY E-MON INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. PRODUCTS OR COMPONENTS DISTRIBUTED, BUT NOT
MANUFACTURED, BY E-MON ARE NOT WARRANTED BY E-MON AND BUYER
MUST INSTEAD RELY ON THE REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES, IF ANY,
PROVIDED DIRECTLY TO THE BUYER BY THE MANUFACTURER OF SUCH
PRODUCT OR COMPONENT.
61 62-0392-03
Page 62

CLASS 5000 METER
62-0392-03 62
Page 63

CLASS 5000 METER
63 62-0392-03
Page 64

CLASS 5000 METER
E-Mon
850 Town Center Drive
Langhorne, PA 19047
www.emon.com
info@emon.com
® U.S. Registered Trademark
© 2013 E-Mon
62-0392-03 JPG Rev. 04-13
Printed in United States
 Loading...
Loading...