Page 1

62-0389-05
Class 2000 Meter
KWH & KWH/DEMAND METER
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
E-Mon
850 Town Center Drive
Langhome, PA 19047
(800)334-3666
www.emon.com
Page 2

CLASS 2000 METER
Dear Valued Customer,
We are pleased that you chose to buy one of our products, and want you to be just as
pleased with owning it. Before installing your new E-Mon product, please read the
information on the following pages carefully.
We believe that you will find the E-Mon D-Mon meters easy to install and to use for
monitoring and evaluating your electrical usage.
To be sure that you are 100% satisfied with your products, we provide toll-free
technical and sales support Monday through Friday, 8:00 am to 7:30 pm, EST: (800)
334-3666. You may also reach us via e-mail at info@emon.com.
If you have questions, we can handle them quickly and effectively with a telephone call.
Please let us try to help you BEFORE you remove your meter. And to help us help you,
we ask that you have all relevant information on hand when you call (model or part
numbers, nature of difficulty, etc.)
Be sure to forward this manual to the owner after installation is complete, so that they
may use it as a reference guide when reading the E-Mon D-Mon meter.
Thank you.
62-0389-05 2
Page 3

CLASS 2000 METER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section 1.0 Pre-Installation Information 4
Section 2.0 Safety Label Definitions and Information 6
Section 3.0 Precautionary and Safety Information 7
Section 4.0 Meter Installation 8
Section 4.1 Mounting the Meter 8
Section 4.2 Main Power Board Connections 8
Section 4.3 Current Sensor Installation & Wiring 11
Section 4.4 MAINS Line Voltage & Current Sensor Wiring
Diagrams
Section 4.5 Installation Overview 15
Section 4.6 Check Polarity of the Current Sensor 15
Section 5.0 Monitoring Multiple Loads with One Meter 19
Section 6.0 KWh Meter Features & Functions 21
Section 6.1 KWh Meter Display Features 21
Section 6.2 How to Read the kWh Meter 22
Section 6.3 KWh Meter Hardware Functions 23
Section 6.4 Class 1000 and Class 2000 Pulse Output Removable
Two-Screw Terminal Plug
Section 7.0 KWh/Demand Meter Features & Functions* 26
Section 7.1 KWh/Demand Meter Display Functions 26
Section 7.2 How to Read the kWh/Demand Meter 27
Section 7.3 Demand Display Set-Up 28
Section 7.4 Demand Reset 30
Section 7.5 Test Mode 32
Section 8.0 Preventative/Scheduled Maintenance 34
Section 9.0 Lithium Battery Replacement Instructions 35
Section 10.0 Troubleshooting Guide 37
Section 10.1 Line Voltage Diagnostics 38
Section 11.0 High Voltage Metering 41
Section 12.0 Frequently Asked Questions 44
Section 13.0 Meter Technical Specifications 46
Section 14.0 Meter Limited Warranty 49
* Applies to meters equipped with the Demand option.
14
24
3 62-0389-05
Page 4
CLASS 2000 METER
1.0 PRE-INSTALLATION INFORMATION
The E-Mon D-Mon® Class 2000 kWh/Demand meter is a 3-element meter used to
monitor electric power usage of individual loads after the utility meter. Installation
must only be performed by qualified personnel and in accordance with these
instructions and all applicable local and national electrical codes. E-Mon or its
representatives assume no responsibility for damages or injury resulting from the
improper installation of this meter.
Meters are supplied in a UL Type 1 steel enclosure appropriate for indoor installation
where it will not be affected by the elements, such as moisture and extreme
temperatures.
Units designated by the “R” suffix on the model number have an extended
environmental operating range and are enclosed in a NEMA 4X enclosure to
accommodate outdoor environments.
Verify the input voltage rating and configuration on the meter label to ensure it is
suitable for the intended electrical services. For example, Class 2000 meters labeled
for 208V service MUST NOT be installed on service feeds of 480V and vice versa.
Verify the current sensors are sized suitably for the load to be monitored. Compare the
color of the arrows on the current sensors to the chart below to confirm the correct
current sensor is being used.
Sensor Arrow Color Code Sensor Rating
Brown 100 Amp
Red 200 Amp
Yellow 400 Amp
Black 800 Amp
Blue 1600 Amp
White/Black 3200 Amp
Meter Labeled: Works On:
120/240V 120/240V, 1 Phase
208V 208V, 3 Phase
240V 240V, 3 Phase
400V (380, 415) 400V, 3 Phase
480V 480V, 3 Phase
600V 600V, 3 Phase
62-0389-05 4
Page 5
CLASS 2000 METER
CAUTION
WARNING
M33177
MAIN POWER
BOARD
DISPLAY AND
KEYBOARD
Internal circuit card components are extremely sensitive to electrostatic
discharge. Prior to handling or touching internal circuitry, discharge any
static buildup on your person. To discharge yourself, touch a grounded
metal object such as conduit or an earth grounded metal enclosure.
Use of this instrument, Class 2000, in a manner inconsistent with this
manual or not specified by the manufacturer in writing, can cause
permanent damage to the unit and/or serious injury to the operator. The
protection and safety features provided by this equipment may become
impaired or otherwise compromised.
NOTE: If any trouble arises during installation or functional verification opera-
tions, do not immediately remove unit. Before removing the unit, contact E-Mon’s technical support department at (800) 334-3666. E-Mon’s
technical department will assist you in detailed troubleshooting of the
Class 2000 installation.
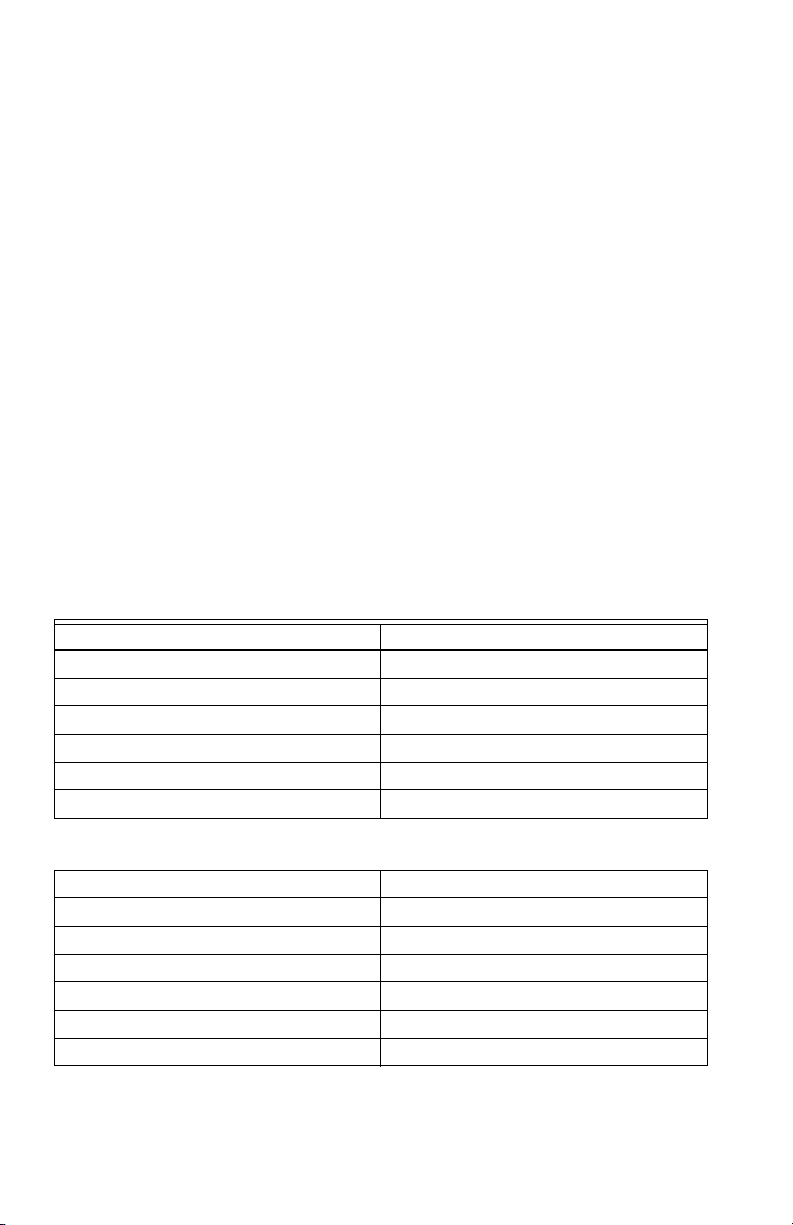
1.1 Internal Electronic Assemblies
The unit is comprised of a Main Power Board, Display Board and Keyboard. All circuit
cards are mounted inside a UL Type 1 (standard) or NEMA 4X (optional) enclosure.
Fig. 1. Power Supply Board and Display Board.
NOTE: Units are supplied in a UL Type 1 metal enclosure suitable for indoor
applications only. Units supplied in the optional NEMA 4X fiberglass
enclosure are suitable for either indoor or outdoor applications, within
the defined specifications. Refer to Section 12.0 for a definition of suitable environmental conditions for indoor and outdoor units.
5 62-0389-05
Page 6
CLASS 2000 METER
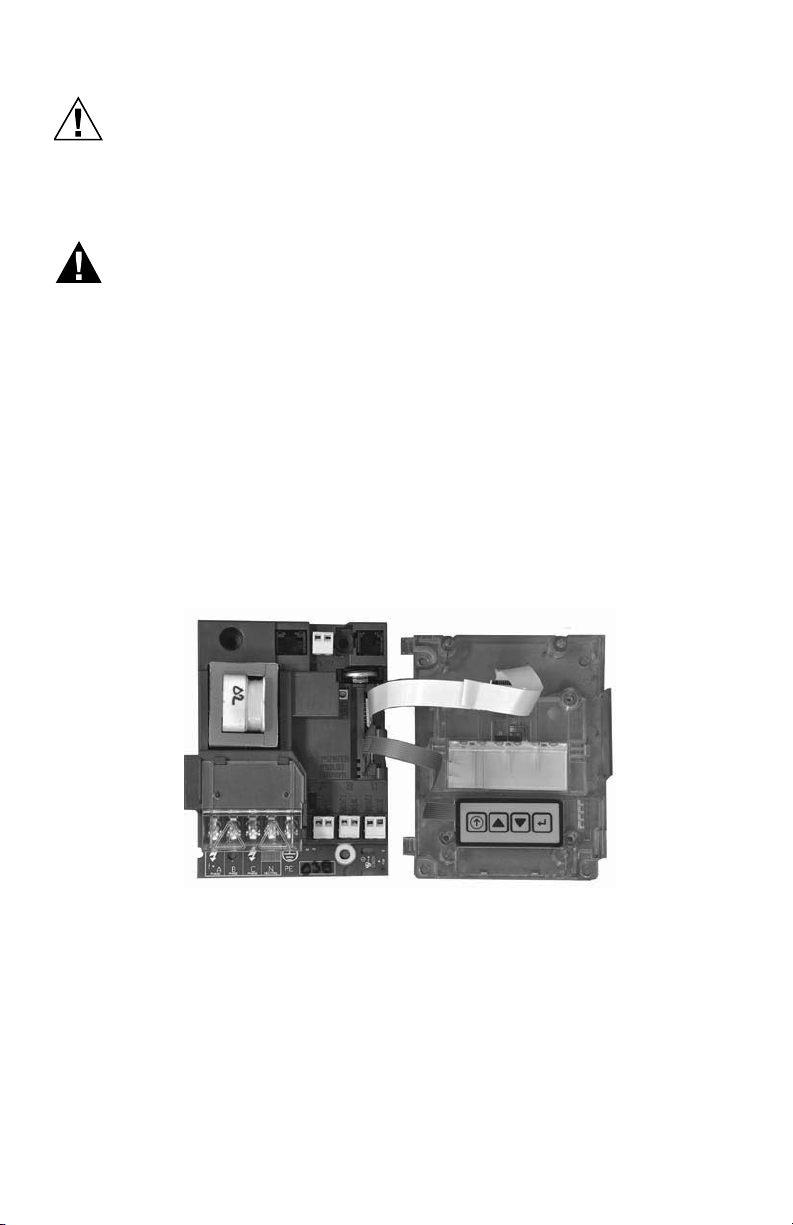
1.1.1 Main Power Board
Connections to this board include the MAINS Input Voltage, Current Sensors, external
IDR interface and Isolated Pulse Output. The MAINS input terminals are covered with
a protective shield for safety purposes. The current sensor assemblies interface to
three header connectors, labeled A, B, and C along with conductor color indication.
Each header connector input corresponds to an input voltage phase, so care must be
taken to ensure each current sensor is connected to the correct input header.
TB3
TB1
Fig. 2. Standard Configuration.
TB2
TB4
M33178
1.1.2 Display Board
The display connects to the main power board via a flex-ribbon cable and is mounted
on the inside of the enclosure door. The LCD readout indicates the cumulative kWh
and instantaneous kW value on kWh meters. The LCD readout indicates cumulative
kWh, peak demand and instantaneous kW values on kWh/ Demand meters).
2.0 SAFETY LABEL DEFINITIONS AND INFORMATION
The Green Class meter may contain one or more of the following labels. Operator(s)
should familiarize themselves with the meaning of each label to minimize risk.
The presence of this label is a cautionary indicator identifying a
danger risk. The manual should be consulted prior to proceeding.
The presence of this label indicates an electrical shock hazard exists
in the location or area where the label is placed. Prior to proceeding,
the MAINS power must be disconnected and the manual consulted for
safety information.
62-0389-05 6
Page 7

CLASS 2000 METER
CAUTION
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
3.0 PRECAUTIONARY AND SAFETY INFORMATION
Internal circuit card components are extremely sensitive to electrostatic
discharge. Be careful not to touch internal circuitry prior to discharging
any static buildup on your person. To discharge yourself, touch a
grounded metal object such as conduit or an earth-grounded metal
enclosure.
High voltages present on main PCB terminal block TB1 screw terminals.
Risk of serious injury and/or electrical shock exists. Prior to performing
any wiring operations, review all contents of the user manual and deenergize the MAINS power switch. Only qualified personnel should
perform installation wiring. Installation wiring must comply with all local
and national electrical codes.
Failure to ground the enclosure creates a possible shock hazard. Do not
operate the Class 2000 meter without a protective earth wire attached
securely to the PE terminal screw. After installing protective earth wiring,
secure the screw tightly (7in-lb torque.)
NEVER open front panel of unit while unit has MAINS power applied.
Failure to comply can increase the risk of serious injury and/or electrical
shock.
7 62-0389-05
Page 8
CLASS 2000 METER
3 (76)
7-1/2
(191)
M33627
6 (152)
4 (102)
6-3/4
(171)
4.0 METER INSTALLATION
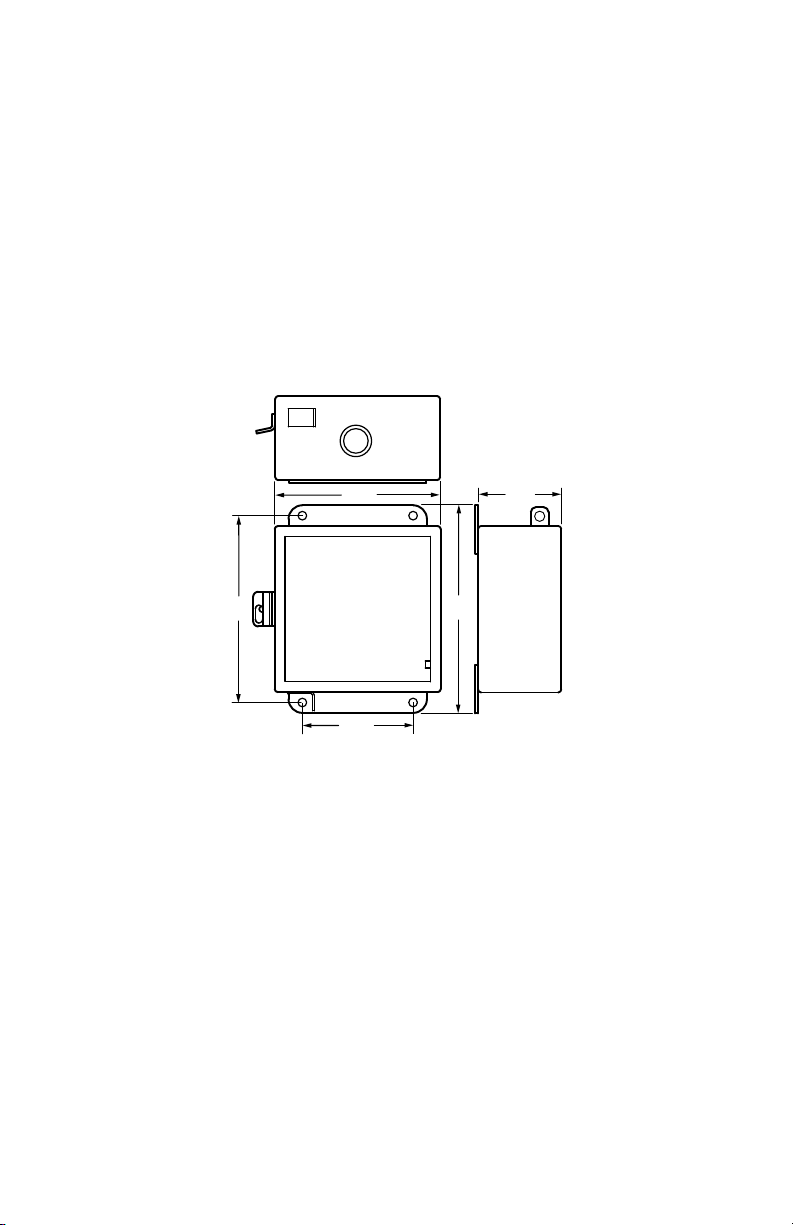
4.1 Mounting the Meter
Using the appropriate sized mounting hardware, fasten the Class 2000 meter
enclosure to the selected mounting surface. The four mounting holes are centered
6.75” H x 4” W. The mounting hole spacing is identical for either the UL Type 1 or
NEMA 4X enclosure.
NOTE: Only the NEMA 4X plastic enclosed unit is suitable for outdoor environ-
mental conditions. Units housed in UL Type 1 JIC steel enclosures must
only be installed in indoor environments where it will not be affected by
the elements, such as moisture and extreme temperatures.
Fig. 3. Enclosure Dimensions.
4.2 Main Power Board Connections
1. Install a temporary ground for ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) protection. With all
circuits de-energized, connect a temporary protective earth ground connection
for ESD protection. Prior to performing any unit wiring, be sure to discharge any
static on your person.
2. Install the Class 2000 Protective Earth Ground. Connect an earth ground wire to
the Class 2000 protective earth ground terminal screw located on the right side
of the line voltage terminal block. After installing the protective earth ground wire,
securely fasten the protective earth ground screw.
62-0389-05 8
Page 9

CLASS 2000 METER
WARNING
Failure to attach the protective earth ground wire securely to the
enclosure creates a potential shock hazard. Do not operate the Class
2000 meter without a protective earth ground connection securely
installed.
3. Wire Entry.
a. Two openings exist on the unit enclosure, one for 1/2” conduit and one for 3/
4” conduit. The 3/4” conduit opening located on the bottom of the enclosure
is used to bring in MAINS Power (voltage lines to power meter) and current
sensor wiring. The 1/2” conduit opening located on the top of the enclosure
is used to interface low voltage signals, such as the IDR interface and isolated pulse output. (Outdoor enclosures equipped with one 3/4” conduit
opening on bottom of enclosure only.)
b. Route the appropriate cabling to and through the respective enclosure open-
ing. The conduit and fittings interfacing the enclosure entrances must be UL
listed and properly sized to the enclosure port diameter, The interfacing fitting must use a gasket seal ring to interface between the conduit fitting and
the enclosure entry point. After installing the conduit fitting and conduit, verify
that the conduit fittings are aligned properly to their respective enclosure
entrance ports and tightened securely to prevent moisture entry. VERIFY
that each conduit slip nut is securely tightened to its respective conduit fitting.
c. Outdoor applications require the use of the optional 4X enclosure. The same
principles outlined for indoor meter installations as defined in the aforementioned paragraph carry over and apply to outdoor installations with one
exception. The exception is that the conduit and fittings for outdoor installations require an outdoor material rating and approval for 4X applications.
4. Unit MAINS Wiring (Voltage Wiring Connections)
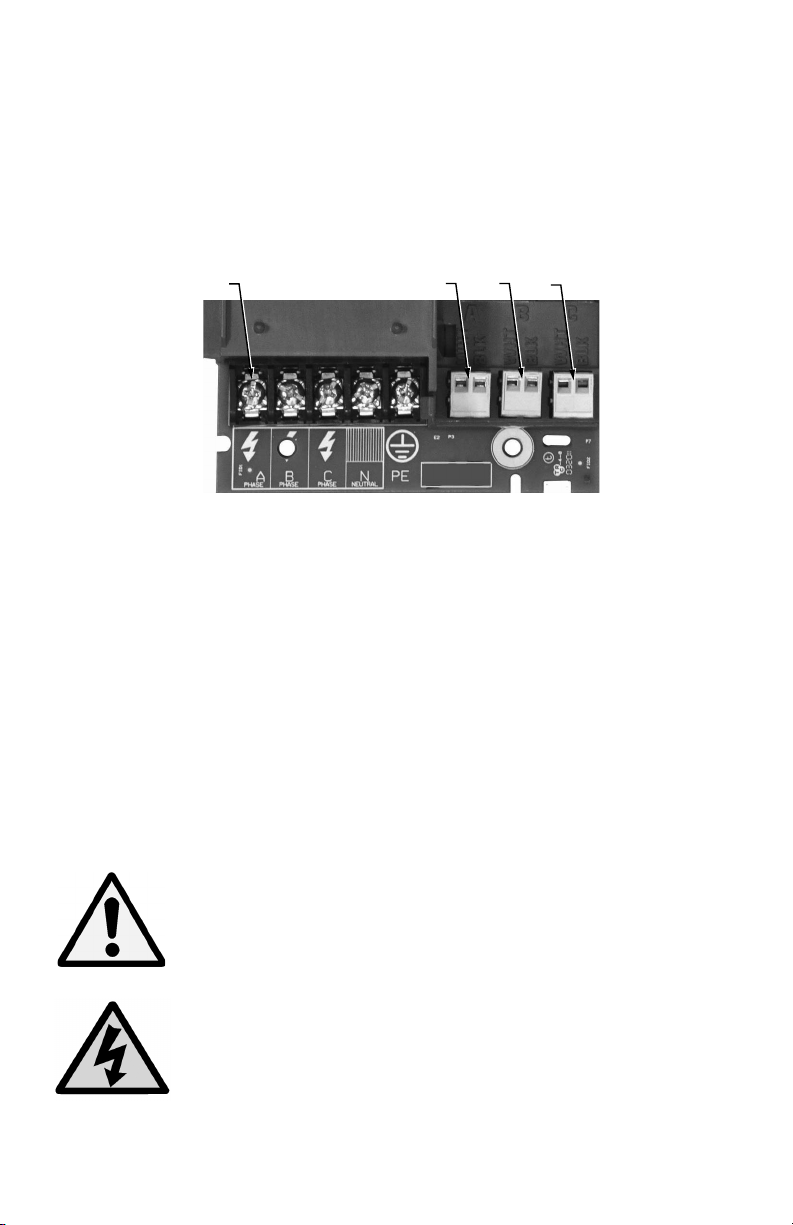
a. Remove the shield located over the phase A,B and C screw terminals on the
main power board. This shield can be removed by pulling back on the latch
on the right side of the shield and lifting up on the front. Wire each connection to the terminal block with stranded wire 14-12 AWG, rated at 600 VAC.
b. Strip back all wire insulation to expose between 1/4” and 3/8” of the copper
conductors. Gently twist each wire to prevent fraying. Insert the conductors
into their respective terminal block position and tighten down the terminal
block screw to securely fasten the conductor. The terminal block is clearly
labeled PHASE A, PHASE B, PHASE C and NEUTRAL.
c. Connect the NEUTRAL wire to the appropriate terminal block position.
NOTE: For Delta MAINS input wiring, DO NOT connect the NEUTRAL wire.
Remove the terminal block screw for this position.
9 62-0389-05
Page 10
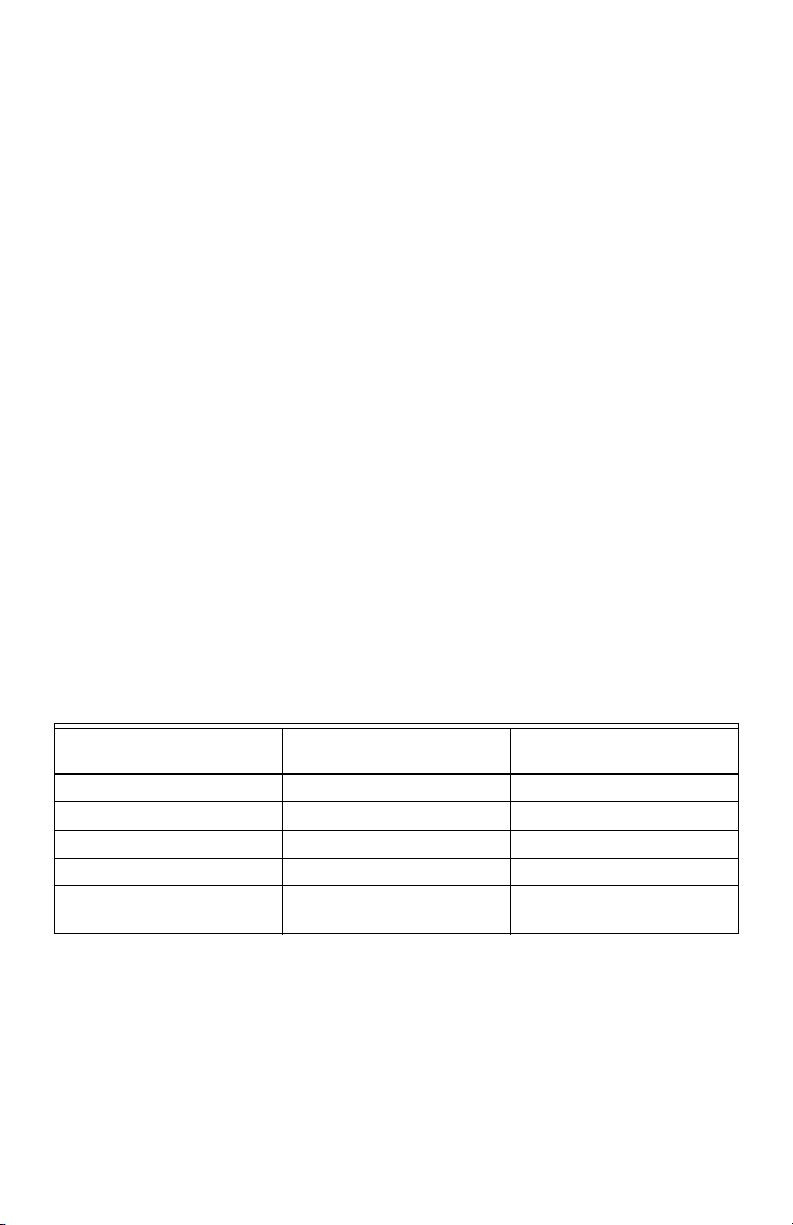
CLASS 2000 METER
d. Connect the AC mains power wires (Phase A, Phase B and Phase C) to their
respective positions as labeled on terminal block.Tighten the screws to 7 inlb of torque.
e. After all conductors are connected to their respective terminal block positions
and tightened down, verify that each terminal block screw is securely fastened by gently tugging on each conductor. Verify no conductor wires are
frayed or are shorting to adjacent terminal block positions.
5. External Switch Mechanism/In-Line Fuse Installation
a. To ensure a safe installation, the Class 2000 meter requires an external
switch mechanism, such as a circuit breaker, be installed on the Class 2000
MAINS input wiring. The switch mechanism must be installed in close proximity to the meter and easily reachable for the operator. This device must
also be marked as the disconnecting device for the Class 2000 meter.
b. Install 1/10 Amp Slow Activation in line fuses with the suitable voltage rating
for each conductor phase at the MAINS input to the meter. The fuses must
be labeled to indicate voltage and current rating as well as element characteristics. The fuse element must be slow activating type.
6. Once the MAINS wiring is complete, replace the clear Lexan protective shield
over terminal block TB1 and close the enclosure front panel. Secure the enclosure cover using the locking mechanism. Activate the external circuit breaker or
equivalent switch to apply AC MAINS power to the unit.
7. The Class 2000 meter display should turn on and indicate total kWh accumulation reading.
NOTE: On demand meters (meters ordered with "-D-") the unit display, clock
and other critical configuration parameters will be set once the unit
installation and wiring is complete.
8. Using an AC Voltmeter, verify the input voltage readings are within the limits
specified below.
Meter Input Voltage
Configuration Nominal Voltage Limits (+/- 10%)
120/208V, 3 Ph, 4 Wire 120 VAC (L-N) 108 to 132 VAC
277/480V, 3 Ph, 4 Wire 277 VAC (L-N) 249 to 305 VAC
240V, 3 Ph, 3 Wire 240 VAC (L-L) 216 to 264 VAC
480V, 3 Ph, 3 Wire 480 VAC (L-L) 432 to 528 VAC
347/600V, 3 Ph, 4 Wire
347 VAC (L-N) 540 to 660 VAC
(WYE Only)
9. Remove power from the unit by de-energizing the external switch.
NOTE: For 3-Wire systems, the voltages are measured Phase to Phase. On 4-
Wire systems the voltages are measured Phase to Neutral.
62-0389-05 10
Page 11

CLASS 2000 METER
4.3 Current Sensor Installation & Wiring
Once the AC voltages have been confirmed to be within acceptable limits, you are
ready to install the current sensors. The MAIN power board contains three header
connectors located at the bottom right of the board. The connectors are labeled A, B,
and C along with conductor color indication. This format must be followed in order for
the meter to function correctly.
The Class 2000 meter will be used with one of two basic types of current sensors:
a. Split-Core Current Sensor: This sensor opens so that it can be attached
around the circuit conductor being monitored without interrupting power.
Unless otherwise specified, all Class 2000 meters are supplied with this
sensor type.
b. Solid-Core Current Sensor: This sensor does not open and requires the
monitored conductor be removed from the circuit to install the current sensor.
This type is only supplied when specified at time of order.
NOTE: The unit serial label specifies if the unit is set up for split or solid core
current sensors. See ordering information for details.
Both types of current sensors output a 0-2 VAC signal proportional to the current being
measured.
The current sensors must be matched with the voltage phases. The A phase sensor
must be monitoring the same phase as the A phase voltage. B & C phase sensors
must also monitor the same phase as their respective voltage inputs.
11 62-0389-05
Page 12

CLASS 2000 METER
M33213
LOAD
SOURCE
4.3.1 Installing the Split-Core Current Sensor Assembly
Each phase being monitored will require one two-piece current sensor assembly.
Therefore, a three-phase meter will require three (3) assemblies. Open the two-piece
current sensor assembly by releasing the nylon clamp using a flat head screwdriver.
Fig. 4. Split-Core Current Sensor Assembly.
1. Reassemble the current sensor assembly around the conductor(s) to be moni-
tored. Ensure the current sensor halves marked “Load” are both facing the load
side of the conductor. The colored arrow will be on the source side of the conductor being monitored and MUST be pointed in a clockwise direction around
the conductor being monitored. Tighten the nylon clamp to complete the assembly.
Fig. 5. Arrow On The Current Sensor Assembly.
IMPORTANT:
When looking from the source side of the conductor(s) being monitored, you
should see the arrow on the current sensor assembly. The arrow should be
pointing in a clockwise direction around the conductor(s) being monitored. If
the arrow is not positioned on the source side, inaccurate readings will result.
62-0389-05 12
Page 13

CLASS 2000 METER
4.3.2 Installing the Solid-Core Current Sensor Assembly
The optional solid-core current sensors can be installed in the same applications as
the standard split-core units, however, the conductors that they are monitoring must
first be disconnected.
NOTE: Under no circumstances is this operation to take place without shutting
off the power to the conductor(s) being monitored.
With the power off, disconnect the conductor from its breaker or terminal. Slide the
solid-core current sensor over the conductor, making sure that the indicator on the
sensor is pointing in the direction of the load. After this is done, reconnect the
conductor and verify that it is properly installed.
Run the black and white wires from the solid-core current sensors and install them
according to the standard installation diagram. When this is completed, the power to
the monitored conductor can be turned back on.
Fig. 6. Solid-core Current Sensor.
4.3.3 Current Sensor Wiring
Once all the current sensors are installed on their appropriate phase conductors, you
can begin terminating the current sensors on to the Class 2000 main power board.
The current sensor leads can be extended up to 2,000 feet (using #14-22 AWG wire)
for remote monitoring applications. Consult your local electrical codes for proper wire
sizing (#22 AWG twisted pair wire with a black and white conductor, rated for 600 VAC
recommended.)
The current sensor connection points are located on the bottom right of the main
power board. Three removable plugs exist, one for each current sensor phase input.
The header portions of the connectors are labeled A, B and C. Text on the plastic cover
of each of the connectors instruct you which terminal of the plug is for the white
conductor and which terminal is wired to the black conductor. Once each current
sensor is wired to its respective plug, insert each plug into the appropriate header,
verifying polarity as they are installed (see section 4.6).
13 62-0389-05
Page 14
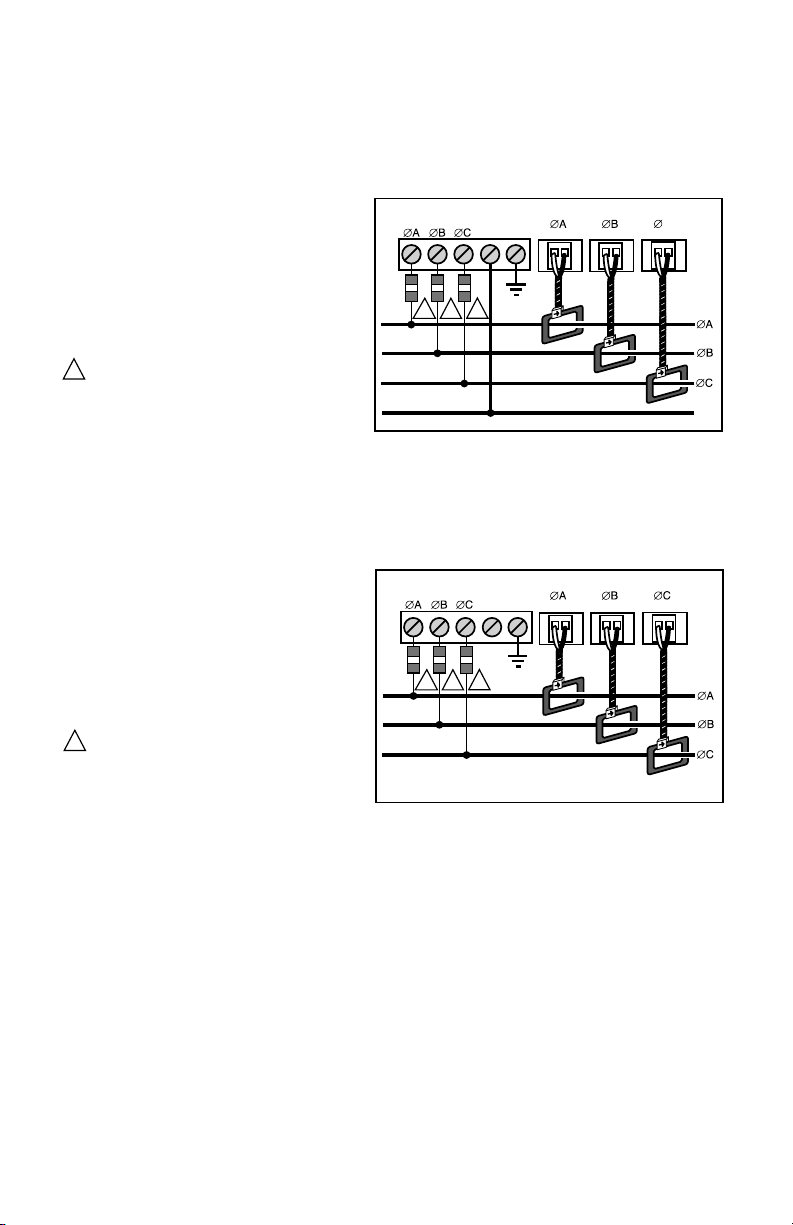
CLASS 2000 METER
LINE VOLTAGE
CURRENT SENSORS
N
LOAD SOURCE
M33185
3-PHASE, 4-WIRE INSTALLATION DIAGRAM
NOTES:
LINE VOLTAGE CONNECTIONS: #14-12 AWG
SENSOR CONNECTIONS: B = BLACK LEAD W = WHITE LEAD
NEUTRAL NOT USED IN DELTA SYSTEM. REMOVE NEUTRAL TERMINAL
BLOCK SCREW FOR DELTA SYSTEMS.
1/10A 600 VAC INLINE FUSE PER CONDUCTOR. LITTLEFUSE PART
NUMBER KLDR.100.
1
1
1
1
C
W B W B
N
PE
W B
LINE VOLTAGE
CURRENT SENSORS
LOAD SOURCE
M33186
3-PHASE, 3-WIRE INSTALLATION DIAGRAM
NOTES:
LINE VOLTAGE CONNECTIONS: #14-12 AWG
SENSOR CONNECTIONS: B = BLACK LEAD W = WHITE LEAD
NEUTRAL NOT USED IN DELTA SYSTEM. REMOVE NEUTRAL TERMINAL
BLOCK SCREW FOR DELTA SYSTEMS.
1/10A 600 VAC INLINE FUSE PER CONDUCTOR. LITTLEFUSE PART
NUMBER KLDR, 100.
1
1
1
1
W B W B
N
PE
W B
4.4 MAINS Line Voltage & Current Sensor Wiring Diagrams
Fig. 7. 3-Phase, 4-Wire Installation Diagram.
Fig. 8. 3-Phase, 3-Wire Installation Diagram.
62-0389-05 14
Page 15

CLASS 2000 METER
M34224
METER TERMINAL
BLOCK CONNECTIONS
CURRENT SENSOR AND
VOLTAGE CONNECTIONS
4.5 Installation Overview
Fig. 9. Install Overview.
4.6 Check Polarity of the Current Sensor.
Verify all phases are loaded by at least 1% of meter rated load, check the polarity of
the sensors.
Test the sensors wires one pair at a time, verifying polarity, phase rotation and
correspondence to line input.
The A/C line voltage power may be left on to the meter as long as the protective clear
shield is installed to cover the line side meter power supply terminals for safety. Extra
care must be taken when working around live circuits.
15 62-0389-05
Page 16

CLASS 2000 METER
1. Disconnect the Gray current sensor plugs for current sensor B and C phase
inputs (see Fig. 10).
POWER LED
PULSE LED
ERROR LED
M34955
Fig. 10. Error LED
With only the A sensor wires connected to the sensor A input verify if the error LED is
clear (Green LED is off).
If Error LED is clear then the A sensor input leads polarity is correct.
If the Error LED does not clear, then disconnect the gray plug and reverse the input
leads for A sensor by putting the white leads on the black input and the black leads on
the white input, (swapped polarity). If it clears, the “Sensor Error” then mark this pair
with a piece of masking tape as the A sensor and note polarity. Next disconnect the
gray plug for the A input. Marking them with tape as A and noting the polarity.
62-0389-05 16
Page 17

CLASS 2000 METER
Repeat the process for the B sensor gray plug. Connect only the B sensor plug to the B
phase current senor input terminal with the correct polarity (white to white and black to
black) the sensor error remains clears then the B sensor input leads polarity is correct
(see Fig. 11).
POWER LED
PULSE LED
ERROR LED
M34957
Fig. 11. Error LED
If the Error LED illuminates then reverse the input leads for B sensor by putting the
white leads on the black input and the black leads on the white input, (swapped
polarity). If it clears, the Error LED then tag as the B phase plug and take the gray plug
off the input marking them as B and note polarity to identify them later.
17 62-0389-05
Page 18

CLASS 2000 METER
POWER LED
PULSE LED
ERROR LED
M34958
Repeat the process for the C sensor gray plug. With only the C sensor plug connected
if the sensor error remains clear then the C sensor input and the polarity is correct (see
Fig. 12).
Fig. 12. The green power LED blinks this is normal.
If the Error LED illuminates disconnect the plug and reverse the wires for C sensor by
putting the white leads on the black input and the black leads on the white input,
(swapped polarity). When Error LED is clear leave the sensor C plug plugged into “C”
phase current sensor input C.
Reconnect sensor A and sensor B plugs as you had previously identified them for
phase and polarity.
The error should now be clear.
Class 2000 meters may only use one or two sensors depending on the applications.
Please see the appropriate installation manual for wiring configurations in these type
applications. “Check Install” message will always be present in single phase
applications on a Class 2000 meter and will not affect the meter accuracy.
62-0389-05 18
Page 19

CLASS 2000 METER
5.0 MONITORING MULTIPLE LOADS WITH ONE METER
The Class 2000 meter provides extreme flexibility by allowing additional sets of current
sensors to be used in parallel so that multiple load locations can be monitored by one
meter. This feature allows a totalized display readout from two or more load circuits.
You may use parallel sensors to monitor specific breakers from one panel, specific
breakers from more than one panel, two or more complete panels, etc.
When paralleling current sensors, the following rules must be followed for accurate
readings:
Rule 1: Current sensors must be installed in complete sets of three, with a maximum of
three sensors installed in parallel per phase.
Rule 2: All sensors used in parallel must be of the same amperage rating (i.e. 100
amp, 200 amp, etc.) The rating is determined by the current rating (amperage) of the
Class 2000 meter. For example, a 200 amp meter must use extra sets of 200 amp
current sensors.
Rule 3: All locations being monitored must have the same power source. A 480 volt
meter cannot monitor a 208 volt load nor can a meter monitor two 480 or 208 volt loads
if they are from different originating power sources or from different transformers.
Rule 4: The display readings must be multiplied by the number of sets of current
sensors installed. E.g. meter reading of 5 kWh with 2 sets of current sensors....5 x 2 =
10 kWh (actual usage.)
NOTE: One set of current sensors equates to three sensors, one per phase.
The multiplier only applies when extra sets of current sensors are
installed on one meter. Therefore, if you are using only one set of three
sensors (one per phase) the multiplier is not required.
19 62-0389-05
Page 20

CLASS 2000 METER
LINE VOLTAGE
Ø
A
Ø
B
LOAD SOURCE
N
LOAD A
LOAD B
CURRENT SENSORS
LOAD SOURCE
Ø
A
Ø
B
N
M33187
ØC
ØC
Ø
AØBØC
ØAØBØ
C
W B W B W BN
PE
Fig. 13. Multiple Loads with one Meter.
62-0389-05 20
Page 21

CLASS 2000 METER
6.0 KWH METER FEATURES & FUNCTIONS
6.1 KWh Meter Display Features
Fig. 14. Normal Mode (kWh Reading).
The Class 2000 kWh meter display requires no multiplier and shows kilowatt-hours
consumed. See section 6.2 for information on calculating cost based on kWh usage.
Fig. 15. KW Load Mode (Current Load in kW).
The Class 2000 kWh meter LOAD display shows the present circuit load in kilowatts.
.
Fig. 16. Start Up Mode.
When initially powered on, the Class 2000 meter will display the startup screens.
This screen indicates the meter voltage, amps and service configuration. It will remain
on for approximately five seconds before switching to the version screen, after which
the meter enters the normal operating mode.
21 62-0389-05
Page 22

CLASS 2000 METER
6.2 How to Read the kWh Meter
Fig. 17. Readings are Displayed in Whole Numbers.
The Class 2000 kWh meter displays readings in whole numbers, there are no
decimals.
To find the dollar cost for the power used by the load(s) being monitored, you must first
find out what the cost per kWh is in your area (this cost can be found on your utility
electric bill, or call your local utility and ask for their cost per kilowatt hour.) Simply
multiply the cost per kWh by the kWh reading from the E-Mon D-Mon meter. The
resultant figure is the dollar cost for power used by the load(s) being monitored by this
meter.
Example:
8-digit display reading 00000017
Cost per kWh from utility $0.12100
17 x $0.121 = $2.06
NOTE: THE FOLLOWING ONLY APPLIES TO METERS USING MORE THAN ONE
SET OF CURRENT SENSORS. For meters using parallel current sensors
you must multiply the kWh display reading by the number of sets of current sensors installed.
Example: 250 (meter display reading) x 2 (sets of sensors in parallel) = 500 kWh 500
kWh x $0.121 (utility cost per kWh) = $60.50
62-0389-05 22
Page 23

CLASS 2000 METER
M33212
ERROR
LED
METER
PULSE LED
POWER
ON LED
IDR JACK
PULSE OUTPUT
CALIBRATION
JACK
SEE
DESCRIPTIONS
ABOVE
HEADER
CONNECTOR
(CURRENT
SENSORS)
MAIN
POWER
TERMINAL
BLOCK
RESET BUTTON
6.3 KWh Meter Hardware Functions
IDR Jack 8-pin RJ-45-used to connect kWh meter to the E-Mon
Energy automatic meter reading system.
Pulse Output Optically isolated output pulse for connection to BAS or
peripheral equipment.
Calibration Jack Connector J11 is for factory calibration only, and is not
a user accessible port. Silicon plug is not to be
removed.
Reset Resets kWh and kW demand.
Power On LED When lit, indicates power to meter is on.
Meter Pulse LED Blinks to show the meter load. Blink rate increases with
load.
Error LED When lit, indicates that the current sensor is backwards
or on the incorrect phase.
Fig. 18. Hardware Functions.
23 62-0389-05
Page 24

CLASS 2000 METER
6.4 Fixed Pulse Value guide for Class 1000 & 2000,
kWh & or kW Demand Meter
Color Code Key of Sensor Arrow Must Match the Amperage of Meter:
Purple White Brown Red Yellow Black Blue Two Blue
25 Amp 50 Amp 100 Amp 200 Amp 400 Amp 800 Amp 1600 Amp 3200 Amp
Watt Hours per Pulse
0.48828 0.97656 1.95312 3.90625 7.81250 15.6250 31.2500 62.500
Pulse output signal is a 50/50 duty cycle. This means that whatever the time is
between pulses (based on load) the ON time will be 50% of that time. As an example,
if there were 9 seconds between pulses, the ON time would be 4.5 seconds. The OFF
time would be of the same amount.
TWO-POSITION REMOVEABLE
SCREW TERMINAL PLUG
(FIXED PULSE OUTPUT)
M34959
Fig. 19. Two-position removable screw terminal plug
(Fixed Pulse Output).
There is no voltage on the output of the pulse connection. It is referred to as a “dry”
contact. It is, however, not a physical contact. As an electronic contact equivalent,
there is a polarity associated with it because it is designed to function with a DC signal
from the BAS. The interface range is from 4.5 to 28 VDC, with a maximum of 50 mA.
62-0389-05 24
Page 25

Fig. 20. Hardware Functions.
M33183
MENU
UP
DOWN
SELECT
CLASS 2000 METER
25 62-0389-05
Page 26

CLASS 2000 METER
7.0 KWH/DEMAND METER FEATURES & FUNCTIONS*
(*Applies to meters equipped with the Demand Option [-D-],
for example: E20-208400-J-D-KIT.)
7.1 KWh/Demand Meter Display Functions
The Class 2000 kWh/Demand meter has a single display window that cycles through
the energy data screens. The meter will cycle through five (5) separate screens. The
screens are described below.
KWh display shows the amount of energy
consumed in kilowatt hours (kWh). Reading is
in whole numbers, there are no decimals and
the meter requires no multipliers.
LOAD display shows the present circuit load
in kilowatts.
KW display shows the electrical Demand in
kilowatts (kW). Demand interval is either 15
minutes, 30 minutes or 60 minutes. (Default is
15 minutes.)
Time display shows the time of the day that
the demand peak occurred.
Date display shows the date of the demand
(kW) peak.
Fig. 21. KWh/Demand Meter Display Functions.
62-0389-05 26
Page 27

CLASS 2000 METER
7.2 How to Read the kWh/Demand Meter
Fig. 22. KWh Reading.
The Class 2000 kWh meter displays readings in whole numbers, there are no
decimals.
To find the dollar cost for the power used by the load(s) being monitored, you must first
find out what the cost per kWh is in your area (this cost can be found on your utility
electric bill, or call your local utility and ask for their cost per kilowatt hour.) Simply
multiply the cost per kWh by the kWh reading from the E-Mon D-Mon meter. The
resultant figure is the dollar cost for power used by the load(s) being monitored by this
meter.
Example:
8-digit display reading 00000017
Cost per kWh from utility $0.12100
17 x $0.121 = $2.06
Fig. 23. KW (Demand) Reading.
The kW (Demand) reading is the peak usage over a specified time period (15 minute
standard, 30 minute and 60 minute optional). While kWh costs are interpreted as
cents, Kilowatt costs are usually represented in dollars, and interpretation of demand
costs are based on your utility’s tariff and rate structures. You will need to contact your
utility to see how your utility structures their kilowatt demand charges to ensure proper
allocation of costs utilizing data from the E-Mon D-Mon meter.
NOTE: THE FOLLOWING ONLY APPLIES TO METERS USING MORE THAN ONE
SET OF CURRENT SENSORS.
For meters using parallel current sensors you must multiply the kWh display reading by
the number of sets of current sensors installed. With Demand meters, the PEAK
Demand is also multiplied by the number of sets of current sensors installed.
Example:
17(meter display reading) x 2 (sets of sensors in parallel) = 34 kWh
34 kWh x $0.121 (utility cost per kWh) = $4.12
27 62-0389-05
Page 28

CLASS 2000 METER
HOME
DOWN
ENTER
UP
7.3 Demand Display Set-Up
The demand meter display is set-up using the four buttons located on the meter
display board which is mounted on the door inside the meter enclosure.
STEP 1: Press the HOME button to enter the menu screen.
STEP 2: Press the DOWN button to enter the setup screen.
STEP 3: Press the ENTER button to enter the DATE screen.
STEP 4: Press the Enter button to cycle between the day, month, and year. Press the
UP and DOWN buttons to change their respective numbers.
STEP 5: When the numbers have been changed, press ENTER again to save the
changes.
62-0389-05 28
Page 29

CLASS 2000 METER
STEP 6: Press the DOWN button to access the TIME screen.
STEP 7: Press ENTER to cycle between the hour, minutes, and day of week selection
Use the UP and DOWN buttons to change the selection.
STEP 8:When the changes are completed press the ENTER button to save the
changes.
STEP 9: Press ENTER to enter the DEMAND INTERVAL screen.
STEP 10: Press ENTER again to access the interval selection screen. Use the UP and
DOWN buttons to select the appropriate interval time. (default is 15 min.)
STEP 11:When the appropriate demand interval has been chosen, press ENTER to
save the changes.
29 62-0389-05
Page 30

CLASS 2000 METER
STEP 12: Press the HOME button to return to the setup screen.
STEP 13: Press the UP arrow to display the MENU screen.
STEP 14: Press the ENTER button to enter the normal display screen.
7.4 Demand RESET
STEP 1: Press the HOME button to access the Series 2000 MENU screen.
62-0389-05 30
Page 31

CLASS 2000 METER
STEP 2: Use the UP and DOWN buttons to access the CHECKOUT screen.
STEP 3: Press the ENTER button to access the kw RESET screen.
STEP 4: Press ENTER to access the RESET select screen. Use the UP and DOWN
buttons to select “yes” or “no”. Press ENTER to save the selection. “Change stored”
will be displayed after pressing ENTER.
STEP 5: Press the HOME button to return to the menu screens. Use UP and Down to
select the STATUS screen.
STEP 6: Press ENTER to return to the normal display.
31 62-0389-05
Page 32

CLASS 2000 METER
MENU
UP
DOWN
SELECT
7.5 Test Mode
Fig. 24. Press and release both the Up and Down
arrow buttons simultaneously to activate the Test Mode.
Test Mode activates a 3-screen auto scrolling display. Each of the 3-screens will
display for five-seconds then returning the LCD to normal scrolling mode kWh and kW
LOAD displays.
1. Test Mode screen one: LCD Segment Test (32 zeros)
0000000000000000
0000000000000000
2. Test Mode screen two: Calibration Parameters
(example Model E20-208100-JKIT display 208V 100A)
0000000000000000
0000000000000000
3. Test Mode screen three: Firmware Version (Class 2000 V1.03)
0000000000000000
0000000000000000
62-0389-05 32
Page 33

CLASS 2000 METER
M33183
MENU
UP
DOWN
SELECT
7.5.1 Test Mode Menu, Setup, And Checkout Features
A delay of twenty-seconds between any button choice and the screen will
automatically return to normal kWh and kW LOAD mode.
Press and release Menu Button displays MENU.
CL2000
MENU
Press and release Down Button displays SETUP.
CL2000
SETUP
Press & release the Down Button again displays CHECKOUT.
CL2000
CHECKOUT
Press & release the left Select Button displays CHECKOUT VOLTS A.
CHECKOUT
VOLTS A 121.3V
Press & release the Down Button displays CHECKOUT VOLTS B.
CHECKOUT
VOLTS B 0.3V
Press & release the Down Button displays CHECKOUT VOLTS C.
CHECKOUT
VOLTS C 0.2V
33 62-0389-05
Page 34

CLASS 2000 METER
Press & release Down Button again displays CHECKOUT AMPS A.
CHECKOUT
AMPS A 0.2V
Press & release Down Button again displays CHECKOUT AMPS B.
CHECKOUT
AMPS B 0.2V
Press & release Down Button again displays CHECKOUT AMPS C.
CHECKOUT
AMPS C 0.2V
This concludes the Class 2000 kWh meter advanced display features and instructions.
8.0 PREVENTATIVE/SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE
The Class 2000 kWh/Demand meter is shipped in a calibrated, tested and fully
functional condition.
- No field adjustments are required.
- No preventative or scheduled maintenance is required.
- No cleaning or decontamination procedures are required for this instrument.
62-0389-05 34
Page 35

CLASS 2000 METER
BATTERY
M33208
9.0 LITHIUM BATTERY REPLACEMENT INSTRUCTIONS
(*Applies to meters equipped with the Demand Option [-D-],
for example: E20-208400-J-D-KIT.)
The Class 2000 kWh/Demand meter has a Lithium Battery Cell, which is used to retain
the contents of SRAM and the RTC during power outages. The battery has a life
expectancy of greater than 5 years.
Fig. 25. Battery Location.
Nominal Working Voltage 3 Vdc Output
Nominal Current Capacity 225 mAHr
Cell Chemical Manganese Dioxide Lithium
Operating Temperature Range -30 to +60 Degrees Celsius
Manufacturer Panasonic
Manufacturer’s Part Number CR2032
Fig. 26. Battery Specifications at 25 Degrees Celsius.
35 62-0389-05
Page 36

CLASS 2000 METER
WARNING
WARNING: Only replace battery with Panasonic part number CR2032
only. Use of another battery may present a risk or explosion. See owners
manual for safety instructions. Internal circuit card components are
extremely sensitive to electrostatic discharge. Be careful not to touch
internal circuitry prior to discharging any static buildup on your person.
To discharge yourself, touch a grounded metal object such as conduit or
a metal enclosure exterior.
The battery cell is mounted in a coin cell on the upper right side of the main power
board. Replace the battery if the low battery warning is on display.
Fig. 27. Low Battery Display.
Use the following procedure to replace the battery cell
STEP 1: Disconnect power from the meter at the unit external circuit breaker.
STEP 2: Remove the battery from its holder and place on a non-conductive surface.
STEP 3: Install new battery into the battery holder.
NOTE: Care should be taken to insure that the replacement battery is installed
with the plus (+) symbol on the battery facing down. No damage to unit
or battery will occur if battery is inadvertently installed in the wrong
direction.
STEP 4: Dispose of the used battery in accordance with the manufacturers’
(Panasonic) instructions.
62-0389-05 36
Page 37

CLASS 2000 METER
10.0 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
The Class 2000 kWh/Demand meter is calibrated and tested at the factory before
being packaged and shipped. If installed properly and in accordance with these
installation instructions, your Class 2000 meter should provide years of trouble free
service. If the meter should not function, the following guide will assist in
troubleshooting the installation.
Problem Procedure to follow
1. Display window is blank. Check wiring to voltage terminals.
Check circuit breakers or fuses.
Verify that the power is turned on.
Test source for correct voltage.
2. Display shows incomplete figures or
numbers other than zeros when power is
turned on.
3. Display reading all zeros (00000000) Determine if load is sufficient to update
4. Display reads only a fraction of
consumption
Press RESET button located on door
inside meter enclosure (5 sec.)
the display.
Check RESET button to ensure there are
no wires or other objects pressing against
it when the door is closed.
Check the current sensors for installation
and polarity.
Be sure the current and voltage inputs
have the proper phase relationship.
Check wiring to voltage terminals.
Check circuit breaker or fuses.
Test source for correct voltage.
Check the supply voltage to be sure that it
is on continuously 24 hrs/day.
Check the current sensors for installation
and polarity.
Check sensor wiring to the terminal strip
in meter (color coding B & W.)
NOTE: If you still need assistance after performing the above troubleshooting
procedures, do not remove the unit. Before removing the unit, contact
E-Mon’s technical support department at (800) 334-3666, our support
experts will assist you in detailed troubleshooting of the meter installation and assist you in getting the unit operating correctly
37 62-0389-05
Page 38

CLASS 2000 METER
CAUTION
10.1 Line Voltage Diagnostics
E-Mon meters detect the direction of rotation of three-phase power. The proper phase
sequence must be A-B-C.
The AC power input must be in proper phase sequence A, B, C. If incorrect, the display
will read “Check Install.” See Fig. 28.
Fig. 28. Check Install Error.
How to Verify & Resolve a Phase Sequence Error
Dangerous voltage is present inside the meter!
The following steps are for Qualified Electrical Service Personnel only.
1. Have the electrician unplug or disconnect all three current sensors at the meter
input terminal.
2. If the meter still displays “Check Install” without any sensors connected the
utility power or transformer is connected counter clockwise (CBA) reverse phase
rotation.
3. Disconnect the power to the meter line voltage inputs. Swap A & C line inputs.
Power up the meter and verify there is not a “Check Install” displayed on the LCD
screen.
4. If reverse rotation line condition was present in step 2 and corrected in step 3
then swap the sensor inputs plugs A and C. Plug sensor “A” plug into the sensor
“C” input and plug sensor “C” plug into the “A” input. This will now match the line
phase correspondence.
NOTE: A light load or no load can cause the “Check Install” message to be dis-
played.
62-0389-05 38
Page 39

CLASS 2000 METER
A light load or circuit with no load will cause the “Check Install” to be displayed, for
example a transformer with no load. The meter must have at least 1% load for each
current sensor. For example model number E20-208200-(J or R)-KIT is 200 amp rated;
each of the current sensors must have at least two amps flowing though them to verify
installation. If the “Check Install” message goes off with 1% or more load, then there is
no issue with installation. “Check Install” was due to a light load; this is normal and will
turn back on during light load condition.
Intermittent “Check Install” message displays for a while and then goes off? This is
very typical with air conditioning monitoring applications. With modern air conditioning
systems a condenser coil-cooling fan runs on single-phase power and the compressor
runs off three-phase power. The “Check Install” displays when the fan is running and
will remain on until the compressor motor cycles back on. This is to be expected and is
normal.
“Check Install” display is still on with 1% load and phase rotation sequence A-B-C
verified in steps 1-4, then check for correct Current Sensor Installation.
Is the Current Sensor(s) clamped around the wire backwards?
Assemble the current sensor halves around the conductor(s) to be monitored. Ensure
each of the current sensor halves marked “Load” (Load Side is shown with two arrows
see Fig. 29) are both facing the load side of the conductor. (The load is the side of
the conductor where the equipment you are monitoring is located.)
When removing the spit-core Current Sensor halves, DO NOT cut the tie wrap! The
head of the cable tie has a release tab. Push down on the tab to release the green
colored core.
39 62-0389-05
Page 40

CLASS 2000 METER
How do I know line from load?
Generally speaking, “line” is the power coming in or “upstream” to a circuit breaker/
fuse/disconnect/etc. “Load is the power going out (“downstream”) of the device that
interrupts power. If you put a voltage meter on each side (presuming that your switch/
breaker/fuse/whatever is working correctly), then when you switch it on and off, the
load side is what goes on and off and the line side is what stays hot no matter what
(see Fig. 29).
Fig. 29. Line/Load
62-0389-05 40
Page 41

CLASS 2000 METER
11.0 HIGH VOLTAGE METERING
kWh Meter Installation Instructions for Use with E-MON Meters in High Voltage Applications
The E-MON model number containing “12025HV” kWh meter is designed to be used
for monitoring high voltage (2400, 4160, 13200, etc) circuits, either “stand alone” or in
an AMR application.
This meter is intended to be used with the appropriate high voltage Potential
Transformers (PTs) and Current Transformers CTs) supplied by others. The meter
application is centered around a 120 VAC secondary output from the high voltage PTs
and a 5 amp secondary output from the high voltage CTs.
Items addressed by this document include the installation of meters with model
number containing “12025HV” on high voltage circuits as well as the calculations to
provide the correct meter multiplier based on the PT and CT sizes used on the high
voltage conductors.
Installation should be performed by qualified personnel and only according to all
applicable electrical codes.
High Voltage CTs (supplied by others) reduce the primary current (amps) to a directly
proportional 0~5 amp secondary output. As an example, a 0~400 amp primary
becomes a 0~5 amp proportional signal from the secondary output. In our application,
the high voltage CT secondary is installed as a continuous “loop”, with a single
conductor connected to both secondary terminals.
To convert the 0~5 amp signal to a 0~ 2 volt signal, E-MON’s Current Sensors are
installed on the CT secondary conductor. A set of 25 amp sensors is used in this
application. These sensors have the high voltage CT secondary conductor passed
through them five (5) times (see below) by looping the secondary conductor as shown
in the drawing. The reason for this is so that the 5 amp secondary now appears to the
current sensor as a 0~25 amp signal. This creates a conversion of the CT’s primary
current to a directly proportional 0~ 2 volt signal which is utilized by the E-MON meter.
The example from the first paragraph has now become a 400 amp to 2 volt device, by
this technique.
41 62-0389-05
Page 42

CLASS 2000 METER
M34227
Fig. 30. High Voltage CTs.
Fig. 31. Wiring Diagram For 3-wire High Voltage Circuits.
62-0389-05 42
M34228
Page 43

CLASS 2000 METER
This special high voltage meter installation shows the correct wiring procedure for 3wire high voltage circuits. In this application, the 2 element meter connection is used
on the secondary circuits of the user supplied high voltage PTs and CTs.
The E-MON meter used in this application is the model containing “12025 HV”.
Installation of these meters requires the use of two (2) current sensors mounted on the
secondaries of the high voltage Current Transformers. See the drawing above for
proper wiring. For correct operation, the meter must be installed correctly.
This special high voltage meter installation utilizes high voltage PTs (Potential
Transformers) and CTs (Current Transformers) supplied by others. The E-MON meter
is installed using the secondary outputs of these devices.
High voltage PTs reduce the primary voltage (4160v, 13200v, etc.) to a Secondary
output of 120v. This secondary is connected to the E-MON meter voltage inputs as
shown in the wiring diagram. High voltage CTs reduce the primary current (amps) to a
directly proportional 0~5 amp output. As an example, a 0~400 amp primary becomes a
0~5 amp proportional signal from the secondary output. This allows much smaller
wiring to be utilized in the meter hookup. The high voltage CT secondary is installed as
a continuous “loop”, with a single lead connected to both secondary terminals.
E-MON meters accept a 0~2 volt signal from their Current Sensors. To convert the 0~5
amp signal, the Current Sensors are installed on the CT secondary lead. A set of 25
amp sensors is used in this application. These sensors have the high voltage CT
secondary lead passed through them five (5) times by looping the wire as shown in the
drawing. This allows a direct conversion of the CTs primary current to a directly
proportional 0~2 volt signal, which is used by the meter.
Since there is a signal ratio introduced by the high voltage CTs and PTs, it will be
necessary to multiply the number on the meter’s display for a correct reading. The
meter multiplier is calculated by using the CT ratio and the PT Ratio. [PTr x CTr /
Number of Secondary Lead Passes Through Sensor]. The E-MON 25 amp HV kWh
meter with 5 wraps of the high voltage CT secondary will have its multiplier calculated
by the formula shown below.
EXAMPLE: CT = 400:5 = 80:1 (CTr = 80)
PT = 4200:120 = 35:1 (PTr = 35)
Wraps (Passes) = 5
METER MULTIPLIER = PTr x (CTr/Wraps)
35 x (80/5)
35 x (16) = 560
43 62-0389-05
Page 44

CLASS 2000 METER
12.0 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Q. When providing line voltage to the meter, can I tap off of the same breaker I am
monitoring?
A. Yes, the voltage can be pulled from the same breaker being monitored.
Q. Can the meter’s line voltage wires be run in the same conduit as the sensor leads?
A. Yes, there will be no effect on the meter if the sensor leads and line voltage wires
are run in the same conduit.
Q. Can the meter communication wires and line voltage wires be run in the same
conduit?
A. It is NOT recommended to run these wires together due to noise concerns and their
effects on the communications signal integrity. Communication wires can be routed
separately using the 1/2” conduit port.
Q. How do I find the cost for kWh and kW to bill my tenants?
A. Your local utility bill should list the cost per kWh and kW. If not, simply call your utility
and ask them to provide you with the cost per kWh and kW.
Q. What size wire do I use for the line voltage leads?
A. These wires are normally #14 AWG, but be sure to consult your local electrical
codes for proper sizing requirements.
Q. What size wire should I use to extend the current sensor leads?
A. These wires are normally sized at #14-22 AWG, twisted pair arrangement. Consult
your local electrical codes for proper sizing requirements.
62-0389-05 44
Page 45

CLASS 2000 METER
Q. The load I need to monitor has parallel feeds. How do I install the current sensors
for this application?
A. There are two ways you can monitor parallel feeds. One method is to clamp the
sensors around all feed wires for each phase (no additional reading multiplier
required). The second way to monitor parallel feeds is to clamp the sensor around one
of the feed wires for each phase, and when you read the kWh meter the final reading
must be multiplied by the number of feed wires for each phase.
Q. I have two subpanels I would like to monitor with one meter. These subpanels are
fed by different transformers in the building. Can I parallel sensors and monitor both
panels with one meter?
A. No. These panels cannot be monitored by one meter because they are different
power sources. When you parallel current sensors, all loads must be from the same
voltage source.
Q. I have 5 breakers in one subpanel I would like to monitor with one meter. Can this
be done without having to parallel current sensors?
A. Yes. Simply run all the breaker wires through one set of current sensors. Make sure
all A phase circuits are run through the A phase sensor, and the same for B & C
phases. The meter should be sized by the highest amount of current being monitored
by one sensor.
Q. I’ve gone through the troubleshooting guides and I still can’t get my meter to work.
What should I do?
A. Before removing the unit, contact E-Mon’s technical support department at (800)
334-3666. Our technical support experts will assist you in detailed troubleshooting of
the meter installation and assist you in getting the meter functional without having to
remove and return the unit.
45 62-0389-05
Page 46

CLASS 2000 METER
13.0 METER TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Ordering Information: Define brand, class, input voltage, current sensor
amperage, enclosure type, and sensor type in the format A-BB-CCC-DDDD-E-FGGG where:
A = Brand: E for E-Mon
BB = Class: 20 for Class 2000
CCC = Input Voltage: 120, 208, 480 or 600
DDDD = Amperage: 100, 200,400,800,1600, or 3200
E = Enclosure Type: J = standard metal, R= 4X raintite, M = MMU
F = Demand Option: D for Demand “blank” for kWh meter
GGG = sensor type: KIT = split-core, SCS= solid core “blank” = none supplied
EXAMPLE:
E-MON
CLASS 2000 METER
INPUT VOLTAGE (480V)
AMPERAGE (100 AMPS)
ENCLOSURE TYPE (STANDARD METAL)
DEMAND METER
SENSOR TYPE (SPLIT CORE)
E 20 480 100 J D KIT
M34230
62-0389-05 46
Page 47

CLASS 2000 METER
Input Voltage
3-wire (Delta) Or 4-wire (Wye)
Configuration
Mains Voltage Input Up To 480 VAC RMS Available
Input Power 6 VA Maximum Rating
Current Sensor
Up To 3200 Amps RMS AC Available
Rating
Power Factor 0.5 Leading Or Lagging
Line Frequency 50-60 Hz
Metering Accuracy Meets ANSI C12.20
Voltage Operating
+/-10% Of Rated Load
Range
Temperature Range -20 C To +50 C (Standard indoor enclosure):
Temperature Range -20 C To +70 CNEMA 4X (NEMA 4X outdoor enclosure)
Relative Humidity
0-95% Non-condensing
Range
Altitude 2000 Meters Maximum
Voltage Overload +25% Continuously: +100% For 20 Cycles
Current Sensor
100% For 1 Minute Without Damaging Meter
Overload
Pollution Degree Degree 2 In Accordance With IEC 664
Installation
Category 111
(Overvoltage)
Category
Measurement
Category 111
Category
Enclosure Material Indoor Housing Rating (Standard): NEMA 12
Outdoor Housing Rating (Optional): NEMA 4X
Display Readout KWh Accumulated
Standard Ranges 4-Wire Wye, 120/208 VAC: 100, 200, 400, 800,1600,3200 Amp
2 Phase, 120/240 VAC: 100, 200, 400, 800,1600,3200 Amp
4-Wire Wye, 277/480 VAC: 100, 200, 400, 800,1600,3200 Amp
3-Wire Delta, 220/240 VAC: 100, 200,400,800,1600,3200 Amp
3-Wire Delta, 480 VAC: 100, 200, 400, 800,1600,3200 Amp
4-Wire Wye, 600 VAC: 100, 200, 400, 800,1600 Amp
47 62-0389-05
Page 48

CLASS 2000 METER
Modem Interface Cable: UL-listed Telephone Cord,
6-cond. 300 VAC, Stranded
Cond. 22-26 AWG.
Cable Connector: RJ-45 male IDC
Input/Output Voltage: +5 VDC/18 VAC
Ckt Input Isolation 5.3K VAC for 1 Minute
Baud Rate: 9600
IDR Interface Port Cable: UL-listed/rated Telephone
Cord. 4-cond.
Input/output Voltage: Ground-isolated +/-5.4VDC
Cable Connector: RF-45 Male IDC Or Screw
Terminal Termination
Circuit Input Isolation: 5.3kVAC
Circuit output Isolation: 21.5kVAC
Isolated Pulse/Alarm Outputs
(TB5, TB6):
Output Voltage Potential: 0 VDC to +5 VDC Logic Levels
Mating Plug Connector: Weidmuller PN: 152876
Signal Isolation Voltage: 5.3K VAC for 1 Minute
Recommended
In-line Fuse
Manufacturer: Littlefuse
Mfg. Part No: KLDR.100
Rating: 100mA, Time-delay, 600VAC
Cartridge Fuse
Battery Cell Description: Non-rechargeable Cell Used
For Memory Retention
Manufacturer: Eagle-Picher
Mfg Part No: LTC-3PN-S2
Working Voltage: 3.5VDC
Current Capacity 350mAhr
Electrolyte: Lithium Thionyl Nitrate
62-0389-05 48
Page 49

CLASS 2000 METER
14.0 LIMITED METER WARRANTY
Subject to the exclusions listed below, E-Mon will either repair or replace (at its option)
any product that it manufactures and which contains a defect in material or
workmanship.
The following exclusions apply:
1. This Limited Warranty is only effective for a period of (5) five years following the
date of manufacture when installed in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions by qualified personnel.
2. E-Mon must be notified of the defect within ninety (90) days after the defect
becomes apparent or known.
3. Buyer’s remedies shall be limited to repair or replacement of the product or component which failed to conform to E-Mon’s express warranty set forth above.
4. Buyer shall be responsible for all freight costs and shall bear all risk of loss or
damage to returned goods while in transit.
5. This Limited Warranty does not cover installation, removal, reinstallation, or labor
costs, and excludes normal wear and tear. Buyer shall provide labor for the
removal of the defective component or item and installation of its replacement at
no charge to E-Mon.
6. This Limited Warranty does not cover any product if: (i) a product is altered or
modified from its original manufactured condition, (ii) any repairs, alterations or
other work has been performed by Buyer or others on such item, other than work
performed with E-Mon’s authorization and according to its approved procedures;
(iii) the alleged defect is a result of abuse, misuse, improper maintenance,
improper installation, accident or the negligence of any party; (iv) damaged as a
result of events beyond E-Mon’s control or other force majeure events or (v) used
in conjunction with equipment, components, accessories, parts or materials not
supplied or approved by E-Mon.
7. This Limited Warranty is limited to the obligation to repair or replace the manufactured product. This is the sole and exclusive remedy for any breach of warranty. IN NO EVENT SHALL E-MON BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT,
INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES
(INCLUDING ANY DAMAGE FOR LOST PROFITS) ARISING OUT OF OR IN
CONNECTION WITH THE FURNISHING OF PRODUCTS, PARTS OR SERVICES, OR THE PERFORMANCE, USE OF, OR INABILITY TO USE ANY
PRODUCTS, PARTS OR SERVICES, SALE OF OR OTHERWISE, WHETHER
BASED IN CONTRACT, WARRANTY, TORT, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, NEGLIGENCE, OR ANY OTHER LEGAL OR EQUITABLE THEORY.
8. EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY PROVIDED HEREIN, E-MON MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WITH RESPECT TO ANY
PRODUCTS, PARTS OR SERVICES PROVIDED BY E-MON INCLUDING, BUT
NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. PRODUCTS OR COMPONENTS
DISTRIBUTED, BUT NOT MANUFACTURED, BY E-MON ARE NOT WARRANTED BY E-MON AND BUYER MUST INSTEAD RELY ON THE REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES, IF ANY, PROVIDED DIRECTLY TO THE
BUYER BY THE MANUFACTURER OF SUCH PRODUCT OR COMPONENT.
49 62-0389-05
Page 50

CLASS 2000 METER
62-0389-05 50
Page 51

CLASS 2000 METER
51 62-0389-05
Page 52

CLASS 2000 METER
E-Mon
850 Town Center Drive
Langhorne, PA 19047
www.emon.com
info@emon.com
® U.S. Registered Trademark
© 2014 E-Mon
62-0389—05 M.S. Rev. 01-14
Printed in United States
 Loading...
Loading...