Page 1
User Guide
SM-EtherCAT
Unidrive SP
Affinity
Digitax ST
Commander SK
Mentor MP
Part Number: 0471-0128-02
Issue: 2
www.controltechniques.com
Page 2

General Information
The manufacturer accepts no liability for any consequences resulting from inappropriate, negligent or
incorrect installation or adjustment of the optional parameters of the equipment or from mismatching the
variable speed drive with the motor.
The contents of this guide are believed to be correct at the time of printing. In the interests of commitment
to a policy of continuous development and improvement, the manufacturer reserves the right to change the
specification of the product or its performance, or the content of the guide without notice.
All rights reserved. No parts of this guide may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means,
electrical or mechanical including, photocopying, recording or by an information storage or retrieval system,
without permission in writing from the publisher.
Environmental Statement
Control Techniques is committed to minimising the environmental impacts of its manufacturing operations
and of its products throughout their life cycle. To this end, we operate an Environmental Management
System (EMS) which is certified to the International Standard ISO 14001. Further information on the EMS,
our Environment Policy and other relevant information is available on request, or can be found at
www.greendrives.com.
The electronic variable speed drives manufactured by Control Techniques have the potential to save
energy and (through increased machine/process efficiency) reduce raw material consumption and scrap
throughout their long working lifetime. In typical applications, these positive environmental effects far
outweigh the negative impacts of product manufacture and end-of-life disposal.
Nevertheless, when the products eventually reach the end of their useful life, they must not be discarded
but should instead be recycled by a specialist recycler of electronic equipment. Recyclers will find the
products easy to dismantle into their major component parts for efficient recycling. Many parts snap
together and can be separated without the use of tools, whilst other parts are secured with conventional
fasteners. Virtually all parts of the product are suitable for recycling.
Product packaging is of good quality and can be re-used. Large products are packed in wooden crates,
while smaller products come in strong cardboard cartons which themselves have a high-recycled fibre
content. If not re-used, these containers can be recycled. Polythene, used on the protective film and bags
from wrapping product, can be recycled in the same way. Control Techniques' packaging strategy favours
easily recyclable materials of low environmental impact, and regular reviews identify opportunities for
improvement.
When preparing to recycle or dispose of any product or packaging, please observe local legislation and
best practice.
Software Statement
This Solutions Module (SM) is supplied with the latest software version. When retro-fitting to an existing
system, all software versions should be verified to confirm the same functionality as Solutions Modules of
the same type already present. This also applies to products returned from a Control Techniques Service
Centre or Repair Centre. If there is any doubt please contact the supplier of product.
The software version of the Solutions Module can be identified by looking at Pr MM.02 and Pr MM.51,
where MM is the relevant menu number for the Solutions Module slot being used.
See Pr MM.02 and Pr MM.51 description later in this manual for more information.
The software version takes the form of xx.yy.zz, where Pr MM.02 displays xx.yy and Pr MM.51 displays zz
(e.g. for software version 01.01.00 Pr 15.02 will display 1.01 and Pr 15.51 will display 0).
REACH legislation
EC Regulation 1907/2006 on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and restriction of Chemicals
(REACH) requires the supplier of an article to inform the recipient if it contains more than a specified
proportion of any substance which is considered by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) to be a
Substance of Very High Concern (SVHC) and is therefore listed by them as a candidate for compulsory
authorisation.
For current information on how this requirement applies in relation to specific Control Techniques products,
please approach your usual contact in the first instance. Control Techniques position statement can be
viewed at:
http://www.controltechniques.com/REACH
Copyright : © March 2009 Control Techniques Ltd.
Issue Number : 2
Page 3

Contents
1 Safety Information ..........................................................5
1.1 Warnings, cautions and notes ...................................................................... 5
1.2 Electrical safety - general warning ...............................................................5
1.3 System design and safety of personnel ....................................................... 5
1.4 Environmental limits .....................................................................................6
1.5 Compliance with regulations ........................................................................6
1.6 Motor ............................................................................................................6
1.7 Adjusting parameters ...................................................................................6
1.8 General safety considerations for remote operation .................................... 7
2 Introduction ....................................................................8
2.1 Features .......................................................................................................8
2.2 Introduction to SM-EtherCAT ....................................................................... 8
2.3 What is EtherCAT? ......................................................................................8
2.4 Solution module identification ......................................................................8
2.5 Conventions used in this guide ....................................................................9
3 Mechanical Installation ................................................10
3.1 General Installation ....................................................................................10
4 Electrical Installation ...................................................11
4.1 SM-EtherCAT module information ............................................................. 11
4.2 Module grounding ...................................................................................... 11
4.3 Network topology ....................................................................................... 12
4.4 Minimum node-to-node cable length .......................................................... 12
5 Getting Started .............................................................13
5.1 Quick start guide ........................................................................................13
5.2 Quick start flowchart ..................................................................................17
5.3 Saving parameters to the drive ..................................................................18
5.4 Re-initialising the SM-EtherCAT ................................................................18
5.5 Re-initialise all Solutions Modules ............................................................. 18
6 Protocols .......................................................................19
6.1 CANopen over EtherCAT (CoE) ................................................................19
7 Drive profile (DSP-402) support ..................................28
7.1 0x6040 Controlword ................................................................................... 28
7.2 0x6041 Statusword .................................................................................... 29
7.3 Common profile features ............................................................................29
7.4 Interpolated position mode ......................................................................... 39
7.5 vl velocity mode .........................................................................................41
7.6 Profile Torque mode ..................................................................................46
7.7 Homing Mode ............................................................................................. 47
8 Advanced features .......................................................55
8.1 Distributed clocks .......................................................................................55
8.2 SM-EtherCAT protocol support .................................................................. 55
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 3
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Page 4

9 Diagnostics ...................................................................56
9.1 Module identification parameters ...............................................................56
9.2 Network configuration objects ....................................................................57
9.3 Diagnostic parameters ............................................................................... 58
9.4 Drive trip display codes .............................................................................. 59
9.5 SM-EtherCAT module temperature ........................................................... 59
9.6 SM-EtherCAT serial number ......................................................................59
9.7 SM-EtherCAT error codes ......................................................................... 60
9.8 Critical task % free .....................................................................................61
9.9 Worst case critical task % free ...................................................................61
9.10 FLASH file system % free .......................................................................... 61
9.11 Updating SM-EtherCAT firmware .............................................................. 61
10 Quick Reference ...........................................................62
11 Glossary Of Terms .......................................................65
4 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 5
1 Safety Information
Information
Safety
1.1 Warnings, cautions and notes
A Warning contains information, which is essential for avoiding a safety hazard.
WARNING
A Caution contains information, which is necessary for avoiding a risk of damage to the
product or other equipment.
CAUT ION
NOTE
A Note contains information, which helps to ensure correct operation of the product.
1.2 Electrical safety - general warning
The voltages used in the drive can cause severe electrical shock and/or burns, and
could be lethal. Extreme care is necessary at all times when working with or adjacent to
the drive.
Specific warnings are given at the relevant places in this user guide.
1.3 System design and safety of personnel
The drive is intended as a component for professional incorporation into complete
equipment or a system. If installed incorrectly, the drive may present a safety hazard.
The drive uses high voltages and currents, carries a high level of stored electrical
energy, and is used to control equipment which can cause injury.
Close attention is required to the electrical installation and the system design to avoid
hazards, either in normal operation or in the event of equipment malfunction. System
design, installation, commissioning / start up and maintenance must be carried out by
personnel who have the necessary training and experience. They must read this safety
information and this user guide carefully.
The STOP and SECURE DISABLE / SAFE TORQUE OFF functions of the drive do not
isolate dangerous voltages from the output of the drive or from any external option unit.
The supply must be disconnected by an approved electrical isolation device before
gaining access to the electrical connections.
With the sole exception of the SECURE DISABLE / SAFE TORQUE OFF function,
none of the drive functions must be used to ensure safety of personnel, i.e. they
must not be used for safety-related functions.
The SECURE DISABLE / SAFE TORQUE OFF function is only available as standard on
the Unidrive SP / Digitax ST. The Affinity, Commander SK and Mentor MP drives do not
have such a feature.
The SECURE DISABLE function on Unidrive SP and the SAFE TORQUE OFF function
of the Digitax ST meet the requirements of EN954-1 category 3 for the prevention of
unexpected starting of the drive. They may be used in a safety-related application. The
system designer is responsible for ensuring that the complete system is safe and
designed correctly according to the relevant safety standards.
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
Index
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 5
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Page 6

Careful consideration must be given to the functions of the drive which might result in a
hazard, either through their intended behavior or through incorrect operation due to a
fault. In any application where a malfunction of the drive or its control system could lead
to or allow damage, loss or injury, a risk analysis must be carried out, and where
necessary, further measures taken to reduce the risk - for example, an over-speed
protection device in case of failure of the speed control, or a fail-safe mechanical brake
in case of loss of motor braking.
1.4 Environmental limits
Instructions in the Unidrive SP User Guide, Mentor MP User Guide, Affinity User Guide,
Commander SK Getting Started Guide, Commander SK Technical Data Guide, Digitax
ST Getting Started Guide and Digitax ST Technical Data Guide regarding transport,
storage, installation and use of the drive must be complied with, including the specified
environmental limits. Drives must not be subjected to excessive physical force.
1.5 Compliance with regulations
The installer is responsible for complying with all relevant regulations, such as national
wiring regulations, accident prevention regulations and electromagnetic compatibility
(EMC) regulations. Particular attention must be given to the cross-sectional areas of
conductors, the selection of fuses or other protection, and protective ground
connections.
The Unidrive SP User Guide, Mentor MP User Guide, Affinity User Guide, Commander
SK
Technical Data Guide and Digitax ST Technical Data Guide contain instructions for
achieving compliance with specific EMC standards.
Within the European Union, all machinery in which this product is used must comply
with all relevant safety and EMC directives applicable to the installation.
1.6 Motor
Ensure the motor is installed in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Ensure the motor shaft is not exposed.
Standard squirrel cage induction motors are designed for single speed operation. If it is
intended to use the capability of the drive to run a motor at speeds above its designed
maximum, it is strongly recommended that the manufacturer is consulted first.
Low speeds may cause the motor to overheat because the cooling fan becomes less
effective. The motor should be installed with a protection thermistor. If necessary, an
electric forced vent fan should be used.
The values of the motor parameters set in the drive affect the protection of the motor.
The default values in the drive should not be relied upon.
It is essential that the correct value is entered in the motor rated current parameter,
Pr
5.07 (or Pr 0.46 in Unidrive SP, Mentor MP, Affinity and Digitax ST, or Pr 0.06 in
Commander SK). This affects the thermal protection of the motor.
1.7 Adjusting parameters
Some parameters and/or objects have a profound effect on the operation of the drive.
They must not be altered without careful consideration of the impact on the controlled
system. Measures must be taken to prevent unwanted changes due to error or
tampering especially if a remote user can access the drive parameters.
6 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 7

1.8 General safety considerations for remote operation
SM-EtherCAT enables the possibility of remotely controlling a machine from a distance.
It is vital that when connecting to a machine remotely, adequate safety procedures are
implemented to prevent damage to the machine or injury to personnel.
Any connection to a live system has the possibility of altering the state of the machine,
adequate procedures must be implemented to cover this situation.
It is the responsibility of the machine builder to ensure that such a system is safe
and complies with current legislation.
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 7
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
Index
Page 8
2 Introduction
2.1 Features
• Standard RJ45 connectivity with support for shielded twisted pair.
• Dual 100Mbps EtherCAT interfaces for use in line topologies i.e. daisy chaining.
• Supports the Unidrive SP drives range, Mentor MP, Affinity, Digitax ST and
Commander SK.
• Control loop synchronisation.
• Control cycle times down to 250µs.
• CANopen over EtherCAT (CoE) which includes:
• Support of CANopen DSP-402 (Device Profile for Drives and Motion)
• Interpolated position mode
• Velocity mode
• Profile torque mode
• Two transmit and two receive PDOs.
• SDO access to all profile objects and drive parameters.
2.2 Introduction to SM-EtherCAT
SM-EtherCAT is a Solutions Module that enables the Control Techniques range of
variable speed drives to be connected to an EtherCAT network as a slave device. It can
be used in a variety of applications, from those requiring accurate synchronization and
precise motion control, to those where ease of use and open loop control are
appropriate.
2.3 What is EtherCAT?
EtherCAT is an open high performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system that overcomes
the system limitations of other Ethernet solutions. The Ethernet packet is no longer
received, then interpreted and copied as process data at every connection; instead the
Ethernet frame is processed on the fly. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply
Ethernet to automation applications that require short data update times (also called
cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low
hardware costs. Typical application fields for EtherCAT are machine controls (e.g.
semiconductor tools, metal forming, packaging, injection moulding, assembly systems,
printing machines, robotics and many others).
2.4 Solution module identification
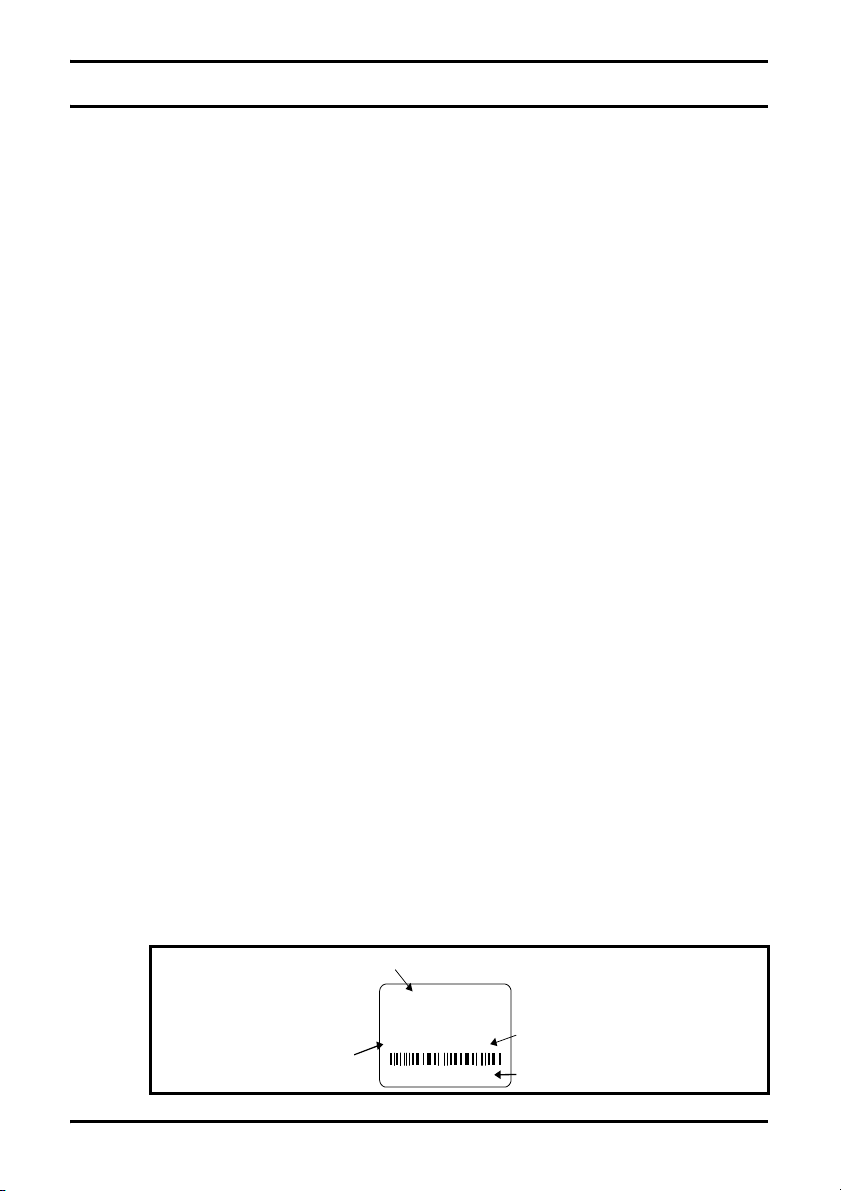
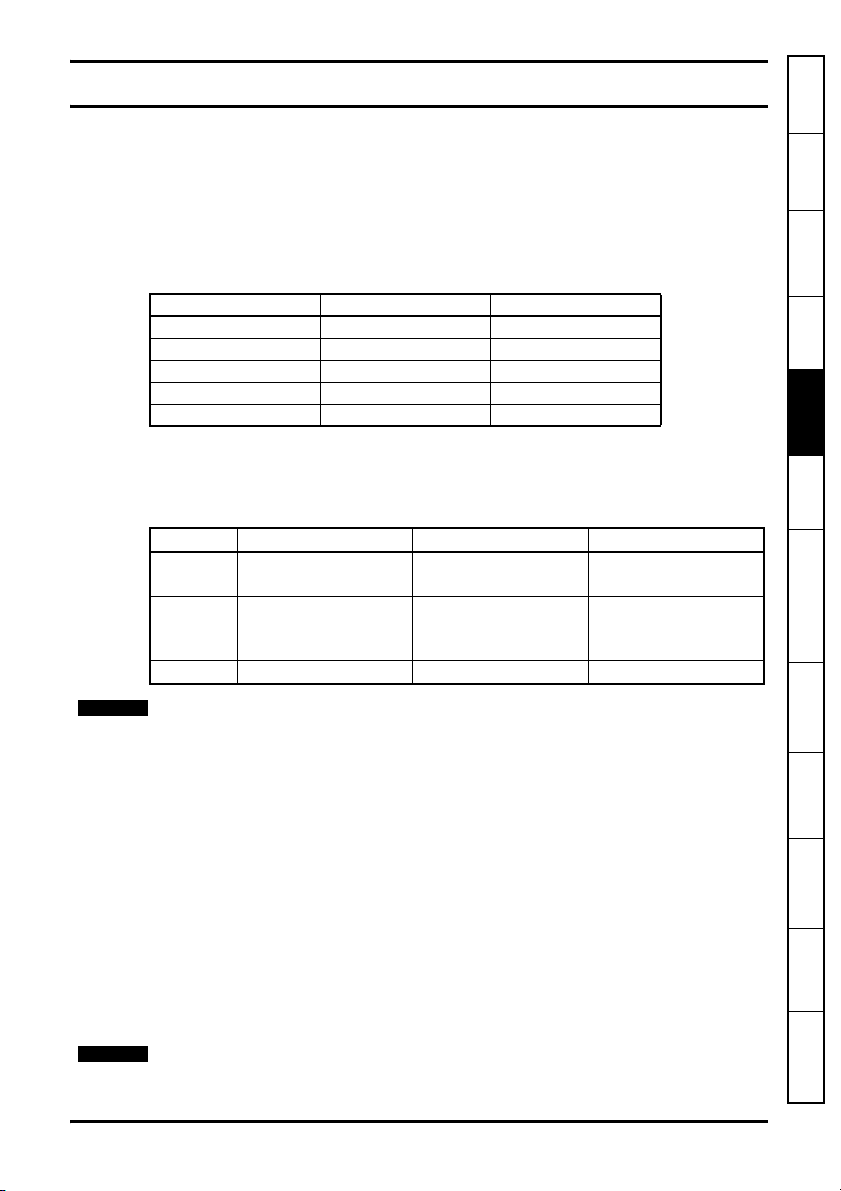
The SM-EtherCAT can be identified by:
1. The label located on the underside of the Solutions Module.
2. The colour coding across the front of the SM-EtherCAT (brown-red).
Figure 2-1 SM-EtherCAT label
Solutions Module
name
SM-Ether CAT
Hardware
issue
number
Revisio n:0 stdJ41
Ser N o : 3000005001
Customer
and date code
Serial number
8 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 9

2.4.1 Date code format
The date code is split into two sections: a letter followed by a number.
The letter indicates the year and the number indicates the week number (within the
year) in which the Solutions Module was built.
The letters are alphabetical in order, starting with A in 1991 (B in 1992, C in 1993 etc.).
Example:
A date code of Q46 would correspond to week 46 of year 2007.
2.5 Conventions used in this guide
The configuration of the host drive and Solutions Module is done using menus and
parameters. A menu is a logical collection of parameters that have similar functionality.
In the case of a Solutions Module, the parameters will appear in menu 15 for the
Commander SK, in menu 15 or 16 for Affinity and in menu 15, 16 or 17 for the Unidrive
SP, Digitax ST and Mentor MP depending on the slot the module is fitted into. The menu
is determined by the number before the decimal point. The method used to determine
the menu or parameter is as follows:
•Pr xx.00 - signifies any menu and parameter number 00.
•Pr MM.xx - where MM signifies the menu allocated to the Solution Module
(this could be 15, 16 or 17 on the Unidrive SP, Digitax ST or Mentor MP, 15 or
16 on the Affinity, but will always be 15 on the Commander SK) and xx
signifies the parameter number.
NOTE
All references in this manual to SM-Applications/Plus should also extend to SM-Applications Lite/Lite V2. The exceptions to this are references to SM-Applications/Plus input/
output, CTSync or the RS485 port, as these are not supported on SM-Applications Lite/
Lite V2. For full details of the differences see the SM-Applications Modules and Motion
Processors User Guide.
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
NOTE
It is strongly recommended that the latest firmware be used where possible to ensure
that all features are supported.
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 9
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
features
Reference
Te rm s
Advanced
Diagnostics
Quick
Glossary Of
Index
Page 10
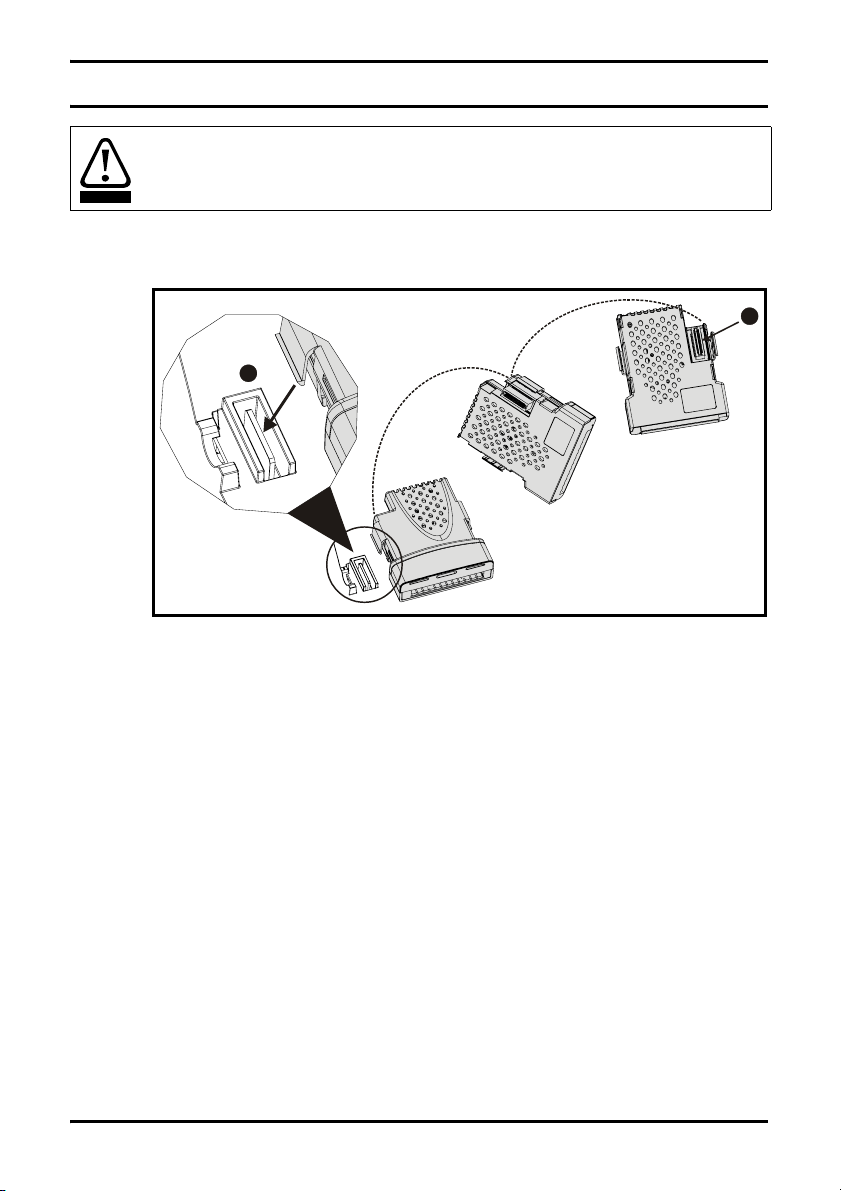
3 Mechanical Installation
Before installing or removing a Solutions Module in any drive, ensure the AC supply has
been disconnected for at least 10 minutes and refer to
WARNING
3.1 General Installation
page 5. If using a DC bus supply ensure this is fully discharged before working on any
drive or Solutions Module.
The installation of a Solutions Module is illustrated in Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1 Fitting a Solutions Module
2
The Solutions Module connector is located on the underside of the module (1). Push
this into the Solutions Module slot located on the drive until it clicks into place (2). Note
that some drives require a protective tab to be removed from the Solutions Module slot.
For further information, refer to the appropriate drive manual.
Chapter 1 Safety Information on
1
10 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 11

4 Electrical Installation
Information
Safety
4.1 SM-EtherCAT module information
4.1.1 Bus media
The SM-EtherCAT option module incorporates two x 100 BASE-TX RJ45 interfaces.
4.1.2 Cabling considerations
To ensure long-term reliability it is recommended that any cables used to connect a
system together be tested using a suitable Ethernet cable tester, this is of particular
importance when cables are constructed on site.
4.1.3 Cable
Cables should be shielded and as a minimum, meet TIA Cat 5e requirements.
NOTE
4.1.4 Maximum network length
NOTE
Cabling issues are the single biggest cause of network downtime. Ensure cabling is
correctly routed, wiring is correct, connectors are correctly fitted and any switches or
routers used are rated for industrial use. Office grade Ethernet equipment does not
generally offer the same degree of noise immunity as equipment intended for industrial
use.
The main restriction imposed on Ethernet cabling is the length of a single segment of
cable. The SM-EtherCAT module has two 100BASE-TX Ethernet ports, which support
segment lengths of up to 100m. This means that the maximum cable length which can
be used between one SM-EtherCAT port and another 100BASE-TX port is 100m
however it is not recommended that the full 100m cable length is used. The total
network length is not restricted by the Ethernet standard but depends on the number of
devices on the network and the transmission media (copper, fiber optic, etc.).
The EtherCAT system designer must consider the impact that the selected network
structure will have on performance.
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting
Star ted
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
4.2 Module grounding
SM-EtherCAT is supplied with a grounding tag on the module that should be connected
to the closest possible grounding point using the minimum length of cable. This will
greatly improve the noise immunity of the module.
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 11
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Ter m s
Index
Page 12

4.3 Network topology
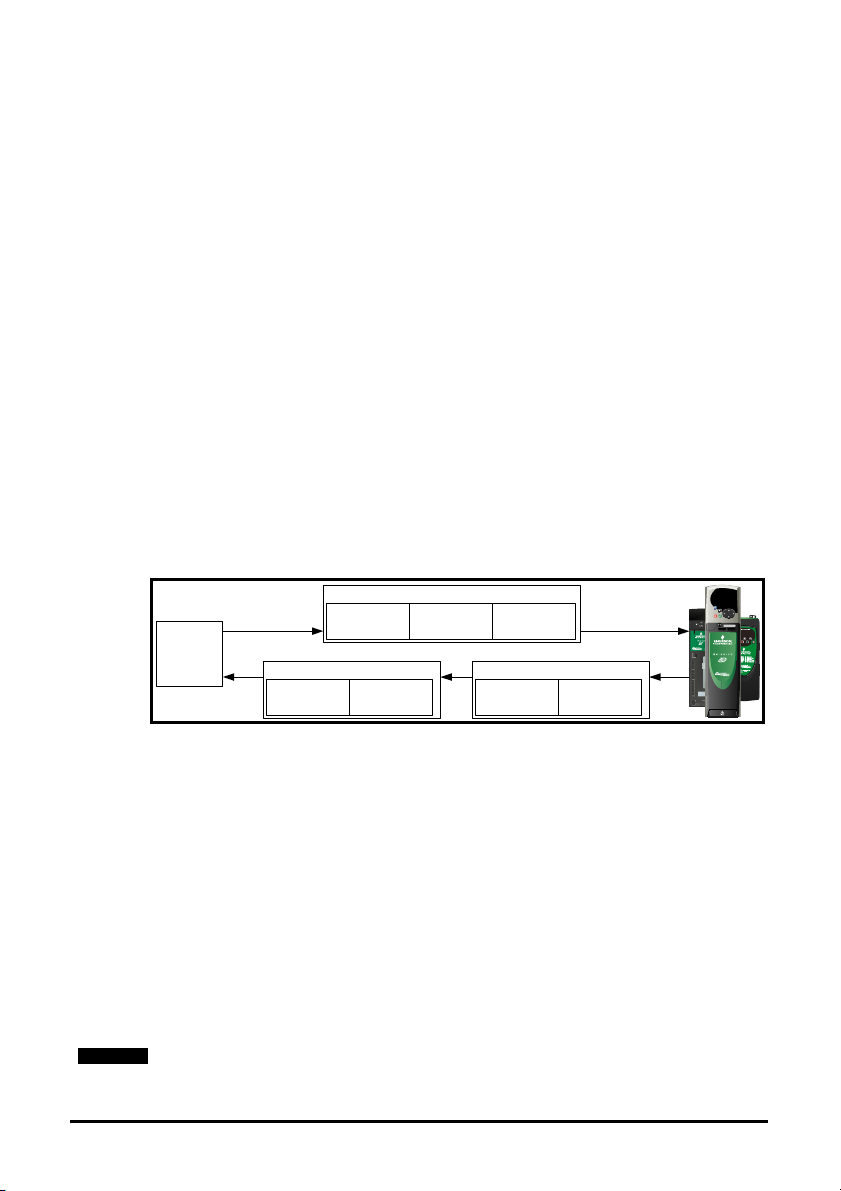
Control Techniques recommend implementing daisy chaining on EtherCAT networks
(see
Figure 4-1). Other Ethernet network topologies can be used but care must be taken
to ensure that the system still operates within the constraints specified by the designer.
Figure 4-1 SM-EtherCAT daisy chain network topology
Master / PLC
Commander SK
SM -
EtherCAT
Unidrive SP Digitax ST
SM -
EtherCAT
4.4 Minimum node-to-node cable length
There is no minimum length of cable recommended in the Ethernet standards. To avoid
possible problems it is recommended that you allow sufficient cable length to ensure
good bend radii on cables and avoid unnecessary strain on connectors.
I/ O
SM -
EtherCAT
12 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 13
5 Getting Started
Information
Safety
5.1 Quick start guide
This section is intended to provide a generic guide for setting up SM-EtherCAT with a
master/controller PLC. It will cover the basic steps required to get cyclic data
communicating using the CANopen over EtherCAT (CoE) protocol on the SM-EtherCAT
module.
5.1.1 SM-EtherCAT version compatibility
Table 5.1 SM-EtherCAT version compatibility
Drive Type Drive Firmware SM-EtherCAT firmware
Unidrive SP V01.08.00 or later V01.00.00 or later
Affinity V01.02.00 or later V01.00.00 or later
Digitax ST V01.02.00 or later V01.00.00 or later
Commander SK V01.06.00 or later V01.00.00 or later
Mentor MP V01.00.00 or later V01.02.00 or later
For the purpose of the example this section will follow the steps required to set up cyclic
communications using one RxPDO and two TxPDOs. These PDOs will consist of the
mappings shown in
Table 5.2 PDO test mappings
Mapping 1 0x6040 (controlword)
Mapping 2 0x6042
Mapping 3 Pr 20.21 (32-bits) N/A N/A
NOTE
It is strongly recommended that the latest firmware be used where possible to ensure
that all features are supported.
Due to the large number of different masters that support CoE, details cannot be
provided for a specific master. Generic support is available through your supplier or
local Control Techniques Drive Centre. Before contacting your supplier or local Control
Techniques Drive Centre for support please ensure you have read
9 Diagnostics on page 56 of this manual and have checked that the SDO/PDO
configurations are correct.
5.1.2 SM-EtherCAT XML file
Control Techniques provides an EtherCAT device description file (Control Techniques
SM-EtherCAT.xml). This file provides the master with information about the SMEtherCAT module to aid with its configuration. The file can be downloaded from the
Control Techniques CTSupport.com website or from your local Control Techniques
Drive Centre or supplier. It should be placed in the directory specified by the master e.g.
When using TwinCAT this could be C:\TwinCAT\Io\EtherCAT.
NOTE
The master may have to be re-started for the file to be loaded.
Table 5.2:
RxPDO1 TxPDO1 TxPDO6
(16-bits)
(vl_target_velocity)
(16-bits)
0x6041 (statusword)
(16-bits)
0x6064
(position_actual_value)
(32-bits)
Pr 18.22 (16-bits)
Pr 20.21 (32-bits)
section
Installation
Installation
Started
support
features
Reference
Ter m s
Introduction
Mechanical
Electrical
Getting
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
Advanced
Diagnostics
Quick
Glossary Of
Index
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 13
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Page 14
5.1.3 Configuring the SM-EtherCAT module for cyclic communications
Unlike other Control Techniques fieldbus communication protocols, CoE does not
require that any module parameters be changed in order to achieve communications.
The baud rate of the network is fixed and the module is automatically allocated an
address.
To check that the ethernet cable connected to the SM-EtherCAT module on the drive is
connected correctly, look at the LED on the front of the SM-EtherCAT module relating to
the connector being used, if this light is a solid green color then a link is established with
the master, if this light if off then check the cabling and also check that the master has
started communications.
In the master, scan the network ensuring that the SM-EtherCAT module is connected
correctly to the master. If the network is configured correctly the SM-EtherCAT node(s)
should be visible in the PLC Master.
Decide on the input / output data you wish to send cyclically (objects and/or
parameters).
Cyclic data is implemented on CoE networks by using "Process Data Objects" or PDOs.
Separate data objects are used for receiving (TxPDOs - from the slave to the master)
and transmitting (RxPDOs - from the master to the slave) data.
These PDOs contain the cyclic data (objects and/or parameters), the RxPDOs available
are 1, 2, 6 and 22, the TxPDOs available are 1, 2, 3, 6 and 22 (for more information on
these PDOs including default mappings please see
page 21 and section 6.1.3 TxPDO mappings on page 23).
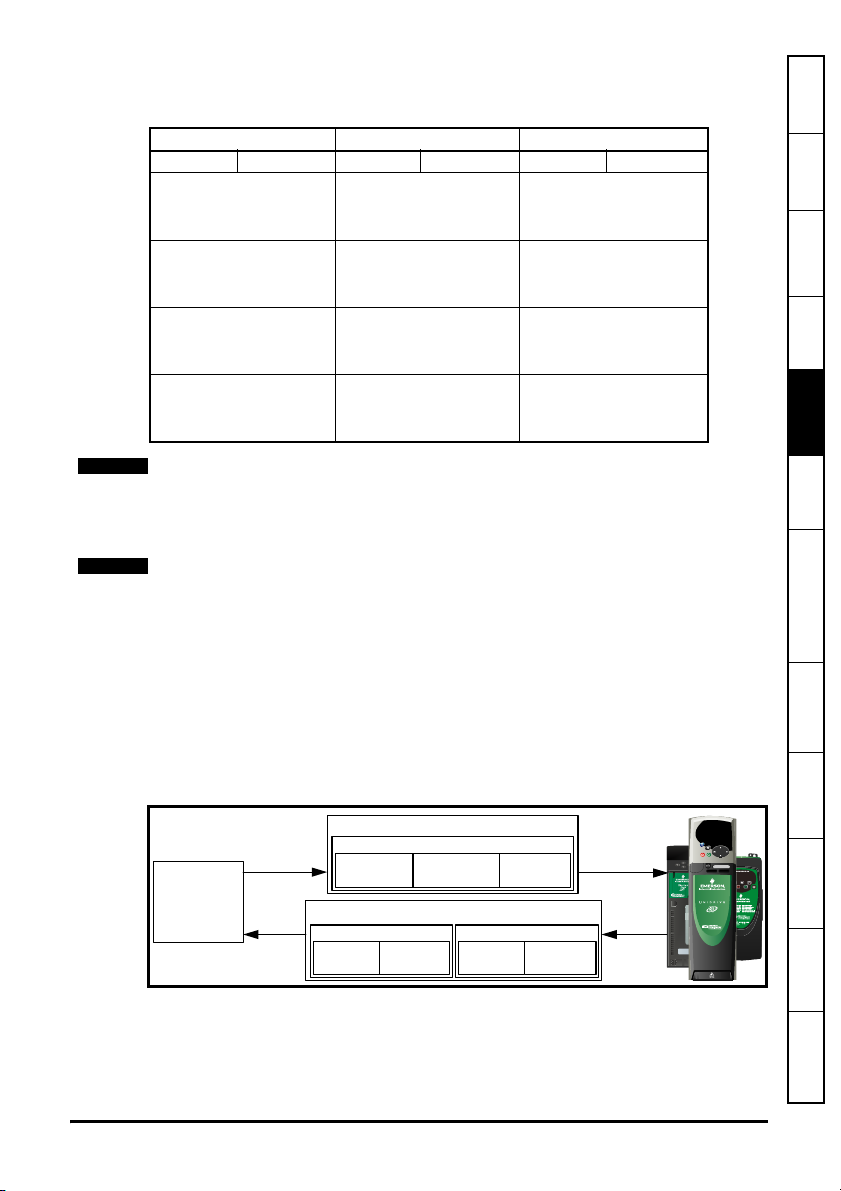
Figure 5-1 SM-EtherCAT PDO configuration
RxPDO1
PLC
TxPDO1
0x6041
Status word
0x6040
Control word
0x6064 position
actual value
0x6042
vl_target_velocity
section 6.1.2 RxPDO mappings on
Pr 20.21
TxPDO6
Pr 18.22 Pr 20.22
RxPDO1, TxPDO1 and TxPDO6 will need to be enabled in the master. Once enabled
you will need to add mappings to the PDOs.
The format used when mapping objects to PDOs is as follows:
• Index: Object index number (0x0000)
• Sub-index: Object sub-index number (0x00)
• Size: Dependant on the size (in bytes) of the object to be mapped (range: 1-4)
The format of mapping drive parameters to PDO is as follows:
• Index: 0x2000 + menu number
• Sub-index: 0x00 + parameter number
• Size: Dependant on the size (in bytes) of the object to be mapped (range: 1-4)
For example Pr 20.21 would be index 0x2014, sub-index 0x15 and the size would be 4
(the parameter is a 32-bit signed value).
NOTE
The values are normally expressed in hexadecimal, so care must be taken to enter the
correct parameter number.
14 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 15
For this example the following objects will need to be set in order to achieve the
mappings of the parameters/objects in the PDOs.
Table 5.3 Cyclic data mapping configuration
RxPDO1: TxPDO1: TxPDO6:
Object: 0x1600 Object: 0x1A00 Object: 0x1A05
Sub-index: 0x00 Sub-index: 0x00 Sub-index: 0x00
Size: 1 Size: 1 Size: 1
Value: 3 Value: 2 Value: 2
Sub-index: 0x01 Sub-index: 0x01 Sub-index: 0x01
Size: 4 Size: 4 Size: 4
Value: 0x60400010 Value: 0x60410010 Value: 0x20121610
Sub-index: 0x02 Sub-index: 0x02 Sub-index: 0x02
Size: 4 Size: 4 Size: 4
Value: 0x60420010 Value: 0x60640020 Value: 0x20141620
Sub-index: 0x03
Not Used Not Used
Size: 4
Value: 0x20141520
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting
Started
NOTE
The format used to define the value of a mapped object is as follows:
Bit 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits (if a gap, bit length of the gap).
Bit 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object (if a gap, zero).
Bit 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object (if a gap, zero).
NOTE
The maximum number of mappings in one PDO is five. There are no restrictions on the
data length of these 5 parameters (i.e. It is possible to map five, 32-bit parameters in
one PDO). It is also possible to use a maximum of 2 x RxPDOs and 2 x TxPDOs.
5.1.4 Configuring the Sync Managers
The Sync manager is used to control the transmission of CANopen PDOs over the
EtherCAT network.
The following objects 0x1C12 - Sync manager 2 PDO assignment (RxPDO) and
0x1C13 - Sync manager 3 PDO assignment (TxPDO) are required to assign PDOs to
the synchronization task. For the purpose of the example assign one RxPDO to sync
manager 2 and two TxPDOs to sync manager 3.
Figure 5-2 SM-EtherCAT sync manager configuration
0x1C12
RxPDO1
0x6040
Control word
PLC
0x1C13
TxPDO1
0x6041
Status word
actual value
vl_target_velocity
0x6064
position
0x6042
TxPDO6
Pr 18.22 Pr 20.22
Pr 20.21
support
features
Reference
Ter m s
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
Advanced
Diagnostics
Quick
Glossary Of
Index
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 15
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Page 16

Assigning RxPDO to the Sync Manager
To assign RxPDO1 to sync manager 2 PDO assignment set the values below to the
following objects:
• Index: 0x1C12
• Sub index: 0x00
•Size: 1
• Value: 1
Setting object 0x1C12, sub-index 0 to a value of 1 (as above) indicates that one RxPDO
will be assigned to the sync manager 2 assignment.
• Index: 0x1C12
• Sub index: 0x01
•Size: 2
• Value: 0x1600
Setting object 0x1C12, sub-index 1 to a value of 0x1600 (as above) maps RxPDO1 to
the process data output sync.
Assigning TxPDO to the Sync Manager
To assign TxPDO1 to sync manager 3 PDO assignment set the values below to the
following objects:
• Index: 0x1C13
• Sub index: 0x00
•Size: 1
• Value: 2
Setting object 0x1C13, sub-index 0 to a value of 2 (as above) indicates that two
TxPDO's will be assigned to the sync manager 3 assignment.
• Index: 0x1C13
• Sub index: 0x01
•Size: 2
• Value: 0x1A00
• Index: 0x1C13
• Sub index: 0x02
•Size: 2
• Value: 0x1A05
Setting object 0x1C13, sub-index 1 to a value of 0x1A00 and sub-index 2 to a value of
0x1A05 (as above) maps TxPDO1 and TxPDO6 to the process data input sync.
Download the configuration to the master.
After downloading the configuration to the master the LED(s) on the front of the SMEtherCAT should flash, depending on the port(s) connected.
Values written to parameters over RxPDOs should now be viewable using the drive’s
keypad so long as the master has put the slave into the Operational state; also,
parameter values changed using the drive keypad will be updated on the master.
16 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 17
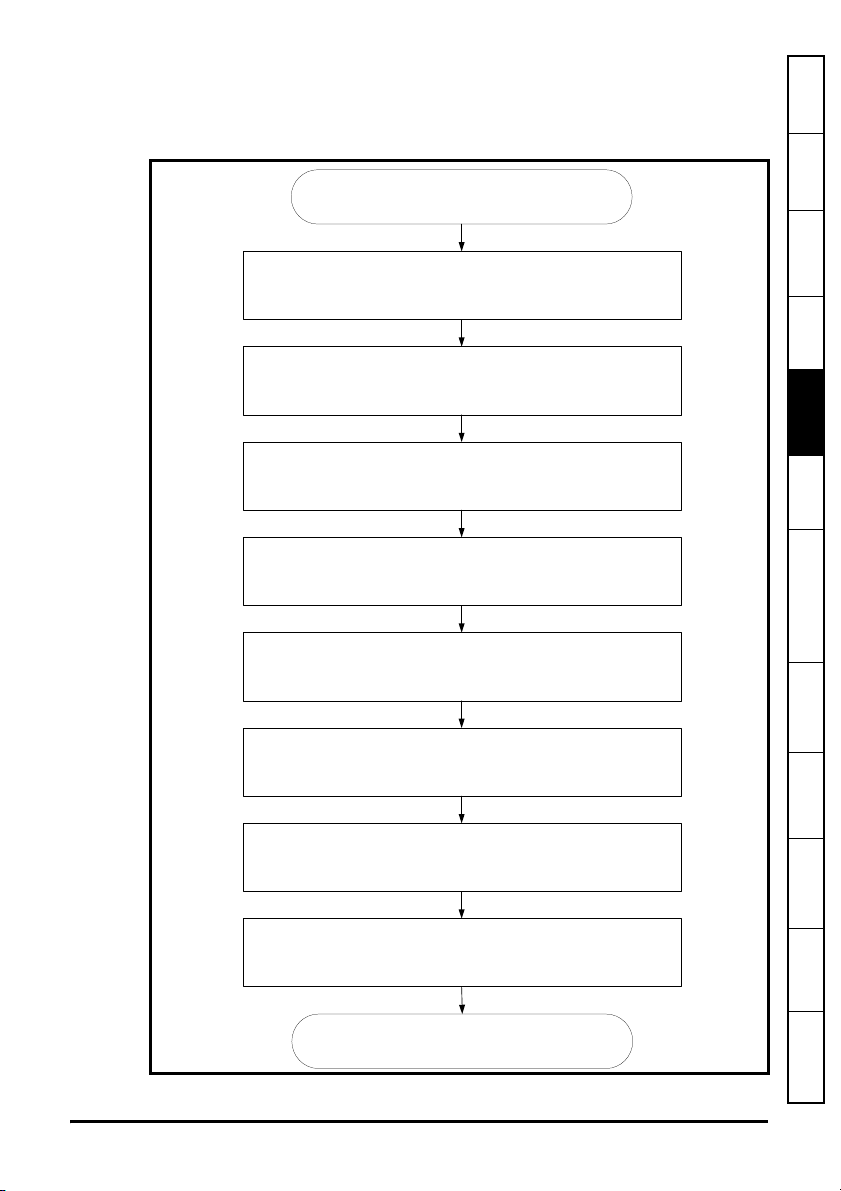
5.2 Quick start flowchart
Figure 5-3 details the steps required to achieve cyclic communications on the EtherCAT
network. This flowchart should be used as the starting point for all configurations.
Figure 5-3 Quick start flowchart
START
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Ensure the Control Techniques .xml file is in the appropriate
folder on the hard drive of the master
Check the LED status of the SM-EtherCAT module
In the master, scan the EtherCAT network
Select required PDOs
Configure the PDOs with the mappings required
Configure the Sync managers using the required PDOs
Download or activate the configuration to the master
Installation
Started
support
features
Reference
Electrical
Getting
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
Advanced
Diagnostics
Quick
Check the front of the SM-EtherCAT module to ensure that the
LED relating to the connection being used is flashing, this
confirms that communications are functioning
END
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 17
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Glossary Of
Ter m s
Index
Page 18
5.3 Saving parameters to the drive
On the Unidrive SP, Affinity, Digitax ST and Commander SK to avoid loss of the
configured settings when the drive is powered down it is necessary to write 1000 to
Pr MM.00 followed by pressing the reset button to perform a drive save. On Mentor MP
Pr MM.00 needs to be set to a value of ‘SAVE’ followed by pressing the reset button.
To store drive parameters:
•Set Pr MM.00 to 1000 (Mentor MP Pr MM.00=SAVE).
• Press the red RESET button.
The drive will store all parameters (except Menu 20) but the operation of the SMEtherCAT will not be affected. Changes made to the SM-EtherCAT configuration
parameters will not take effect until the SM-EtherCAT is reset.
NOTE
Unidrive-SP, Mentor MP, Affinity and Digitax ST: Menu 20 applications parameters may
be saved if an Application Module is fitted, menu 20 is stored in the Application
Module’s memory. See the relevant Application Module documentation for more
information. If the drive is running on backup supply only, Pr MM.00 must be set to 1001
to perform a save.
NOTE
This saves only drive and module parameters and not SM-EtherCAT related objects.
5.4 Re-initialising the SM-EtherCAT
Table 5.4 SM-EtherCAT re-initialise
SM-EtherCAT re-initialise
Default 0 (OFF)
Pr MM.32
Range 0 (OFF) to 1 (ON)
Access RW
Changes to the SM-EtherCAT configuration in menu 15, 16 or 17 parameters (menu 15
and 16 on Affinity, menu 15 on Commander SK) will not take effect until the SMEtherCAT has been re-initialised.
To re-initialise SM-EtherCAT:
1. Set Pr MM.32 to ON.
2. When the sequence has been completed, Pr MM.32 will be reset to OFF.
3. The SM-EtherCAT will re-initialise using the updated configuration.
NOTE
The above sequence does NOT store the SM-EtherCAT configuration parameters in the
drive or the SM-EtherCAT’s internal FLASH memory. This parameter will change back to
off immediately and as such the change may not be visible on the display.
5.5 Re-initialise all Solutions Modules
To re-initialise all Solutions Modules fitted on a Unidrive SP, Affinity or Digitax ST:
1. Set Pr MM.00 to 1070.
2. Press the red RESET button on the drive.
NOTE
This sequence does NOT store the SM-EtherCAT configuration parameters in the drive
or the SM-EtherCAT FLASH memory.
NOTE
On Commander SK drives, Pr 00.00 is not available.
18 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 19
6 Protocols
Information
Safety
6.1 CANopen over EtherCAT (CoE)
The CoE protocol over EtherCAT uses a modified form of the CANopen object
dictionary. This is specified in
Table 6.1 CoE object dictionary
Index Object dictionary area
0x0000 to 0x0FFF Data type area
0x1000 to 0x1FFF CoE communication area
0x2000 to 0x5FFF Manufacturer specific area
0x6000 to 0x9FFF Profile area
0xA000 to 0xFFFF Reserved area
The object description format describes object related information such as size, range
and descriptions and is detailed in
Table 6.2 Object description format
<index> <object name>
Access: <access> Range: <range> Size: <size> Unit: <unit>
Default: <default>
Description: <description>
For entries having sub-indices:
Table 6.3 Object description format with sub-indices
<index> <object name>
Sub-index 0
Access: <access> Range: <range> Size: <size> Unit: <unit>
Default: <default>
Description: <description>
Sub-index 1
Access: <access> Range: <range> Size: <size> Unit: <unit>
Default: <default>
Description: <description>
...
Access: <access> Range: <range> Size: <size> Unit: <unit>
Default: <default>
Description: <description>
Sub-index n-1
Access: <access> Range: <range> Size: <size> Unit: <unit>
Default: <default>
Description: <description>
Sub-index n
Access: <access> Range: <range> Size: <size> Unit: <unit>
Default: <default>
Description: <description>
Table 6.1:
Table 6.2:
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Ter m s
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 19
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Index
Page 20

Definitions:
• <index> : A signed 16-bit number. This is the index of the object dictionary
entry specified in four hexadecimal characters.
• <access> : A value describing how the object may be accessed (RW = read/
write, RO = read-only and WO = write-only).
• <size> : The size of the object/sub-index in bytes.
• <unit> : The physical unit (e.g. ms, counts per second etc.).
6.1.1 CoE communication area
The first set of objects specify general communication settings.
Table 6.4 Device type object
0x1000 Device type
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x00030192
Description: The primary CoE functional profile is DSP-402, the value of the object is defined as follows:
Bits 0 to 15 (Device profile number): 402 (0x192)
Bit 16 (Frequency converter): x
Bit 17 (Servo drive): y
Bit 18 (Stepper motor): 0
Bit 24 (DC drive - manufacturer specific : z
Bits 25 to 31 (Manufacturer specific): 0
This value will depend on the drive operating mode and/or type. On a Unidrive SP in openloop or closed-loop mode or a Mentor MP in closed-loop mode, bit 16 will be set, while bits
17 and 24 will be cleared. On a Unidrive SP in Servo mode or a Digitax ST, bit 17 will be
set, while bits 16 and 24 will be cleared.
Table 6.5 Identity object
0x1018 Identity object
Sub-index 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 4
Description: The nu mber of the last sub-index in this object.
Sub-index 1
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x000000F9
Description: This contains the EtherCAT Technology Group vendor ID for Control Techniques
Sub-index 2
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: See Pr MM.01.
Description: This has the value of the option ID code.
Sub-index 3
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: High word: Pr MM.02. Low word: Pr MM.51.
Description: Contains the option module software version number (the major and minor version
Sub-index 4
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: See Pr MM.35.
Description: Contains the option hardware serial number.
(0x000000F9).
parameter are placed in the high word of this object, and the sub-version parameter is the
low word).
20 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 21
6.1.2 RxPDO mappings
Objects with indices from 0x1600 to 0x17FF specify receive PDO mappings. The
mappings from DSP-402 are included as standard (the PDO mappings will have the
following default values):
Table 6.6 RxPDO mappings
PDO number Mapping object index Mapping object name
1 0x6040 controlword
2 0x6040
6 0x6040
The RxPDO mappings objects are defined below. Each mapping object has the
maximum number of sub-indices (each representing an object mapped to a PDO)
defined in the XML configuration file (specified as “CF” in the descriptions below).
Table 6.7 RxPDO mapping 1
0x1600 Receive PDO mapping 1
Sub-index 0: Number of mapped objects
Access: RW Range: 0 to (CF) Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: The number of mapped objects in thie PDO
Sub-index 1: 1st mapped object
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x60400010 - the DSP-402 control word (0x6040)
Description: A mapping to an object with the following format:
Bits 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits, e.g. a 32-bit parameter would have a length
of 32 or 0x20.
Bits 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object.
Bits 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object.
0x6060
0x6042
controlword
modes of operation
controlword
vl_target _velocity
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 21
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Ter m s
Index
Page 22

Table 6.8 RxPDO mapping 2
0x1601 Receive PDO mapping 2
Sub-index 0: Number of mapped objects
Access: RW Range: 0 to (CF) Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of mapped objects in this PDO.
Sub-index 1: 1st mapped object
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x60400010 - the DSP-402 control word (0x6040)
Description: A mapping to an object with the following format:
Bits 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits, e.g. a 32-bit parameter would have a length
of 32 or 0x20.
Bits 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object.
Bits 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object.
Sub-index 2: 2nd mapped object
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x60600008 - the DSP-402 modes of operation object (0x6060)
Description: A mapping to an object with the following format:
Bits 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits, e.g. a 32-bit parameter would have a length
of 32 or 0x20.
Bits 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object.
Bits 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object.
Table 6.9 RxPDO mapping 6
0x1605 Receive PDO mapping 6
Sub-index 0: Number of mapped objects
Access: RW Range: 0 to (CF) Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of mapped objects in this PDO.
Sub-index 1: 1st mapped object
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x60400010 - the DSP-402 control word (0x6040)
Description: A mapping to an object with the following format:
Bits 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits, e.g. a 32-bit parameter would have a length
of 32 or 0x20.
Bits 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object.
Bits 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object.
Sub-index 2: 2nd mapped object
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x60600008 - the DSP-402 modes of operation object (0x6060)
Description: A mapping to an object with the following format:
Bits 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits, e.g. a 32-bit parameter would have a length
of 32 or 0x20.
Bits 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object.
Bits 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object.
22 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 23

Table 6.10 RxPDO mapping 22
0x1615 Receive PDO mapping 22
Sub-index 0: Number of mapped objects
Access: RW Range: 0 to (CF) Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 0
Description: The number of mapped objects in thie PDO
Sub-indices 1 to 255: 1st to 255th mapped objects in this PDO.
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0
Description: A mapping to an object with the following format:
Bits 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits, e.g. a 32-bit parameter would have a length
of 32 or 0x20.
Bits 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object.
Bits 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object.
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
6.1.3 TxPDO mappings
Objects with the indices from 0x1A00 to 0x1BFF specify transmit PDO mappings. The
following mappings from DSP-402 are included as standard:
Table 6.11 TxPDO mappings
PDO number Mapping object index Mapping object name
1 0x6041 statusword
2 0x6041
3 0x6041
6 0x6041
The PDO mapping objects are defined below. Each mapping object has the maximum
number of sub-indices (each representing an object mapped to a PDO) defined in the
XML configuration file.
Table 6.12 TxPDO mapping 1
0x1A00 Transmit PDO mapping 1
Sub-index 0: Number of mapped objects
Access: RW Range: 0 to (CF) Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: The number of mapped objects in thie PDO
Sub-index 1: 1st mapped object
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x60410010 - the DSP-402 status word (0x6041)
Description: A mapping to an object with the following format:
Bits 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits, e.g. a 32-bit parameter would have a length
of 32 or 0x20.
Bits 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object.
Bits 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object.
0x6061
0x6064
0x6044
statusword
modes_of_operation_display
statusword
position_actual_value
statusword
vl_velocity_actual_value
Getting Started
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Ter m s
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 23
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Index
Page 24

Table 6.13 TxPDO mapping 2
0x1A01 Transmit PDO mapping 2
Sub-index 0: Number of mapped objects
Access: RW Range: 0 to (CF) Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of mapped objects in this PDO.
Sub-index 1: 1st mapped object
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x60410010 - the DSP-402 status word (0x6041)
Description: A mapping to an object with the following format:
Bits 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits, e.g. a 32-bit parameter would have a length
of 32 or 0x20.
Bits 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object.
Bits 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object.
Sub-index 2: 2nd mapped object
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x60610008 - the DSP-402 modes of operation display object (0x6061)
Description: A mapping to an object with the following format:
Bits 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits, e.g. a 32-bit parameter would have a length
of 32 or 0x20.
Bits 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object.
Bits 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object.
Table 6.14 TxPDO mapping 3
0x1A02 Transmit PDO mapping 3
Sub-index 0: Number of mapped objects
Access: RW Range: 0 to (CF) Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of mapped objects in this PDO.
Sub-index 1: 1st mapped object
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x60410010 - the DSP-402 status word (0x6041)
Description: A mapping to an object with the following format:
Bits 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits, e.g. a 32-bit parameter would have a length
of 32 or 0x20.
Bits 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object.
Bits 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object.
Sub-index 2: 2nd mapped object
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x60640020 - the DSP-402 actual position (0x6064)
Description: A mapping to an object with the following format:
Bits 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits, e.g. a 32-bit parameter would have a length
of 32 or 0x20.
Bits 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object.
Bits 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object.
24 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 25

Table 6.15 TxPDO mapping 6
0x1A05 Transmit PDO mapping 6
Sub-index 0: Number of mapped objects
Access: RW Range: 0 to (CF) Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of mapped objects in this PDO.
Sub-index 1: 1st mapped object
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x60410010 - the DSP-402 status word (0x6041)
Description: A mapping to an object with the following format:
Bits 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits, e.g. a 32-bit parameter would have a length
of 32 or 0x20.
Bits 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object.
Bits 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object.
Sub-index 2: 2nd mapped object
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x60440010 - the DSP-402 vl_control_effort (0x6044).
Description: A mapping to an object with the following format:
Bits 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits, e.g. a 32-bit parameter would have a length
of 32 or 0x20.
Bits 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object.
Bits 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object.
Table 6.16 TxPDO mapping 22
0x1A15 Transmit PDO mapping 22
Sub-index 0: Number of mapped objects
Access: RW Range: 0 to (CF) Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 0
Description: The number of mapped objects in thie PDO
Sub-indices 1 to 255: 1st to 255th mapped objects in this PDO.
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: 4 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0
Description: A mapping to an object with the following format:
Bits 0 to 7: Length of the mapped object in bits, e.g. a 32-bit parameter would have a length
of 32 or 0x20.
Bits 8 to 15: Sub-index of the mapped object.
Bits 16 to 31: Index of the mapped object.
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 25
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Ter m s
Index
Page 26

6.1.4 Sync manager configuration
The sync managers are the EtherCAT means for setting access attributes for different
areas of memory and triggering or notifying the application when the memory is
accessed. The following objects specify how the sync managers (and thus
corresponding memory areas) are utilised by the CoE protocol.
Table 6.17 Sync manager communication type object
0x1C00 Sync manager communication type
Sub-index 0 - number of sync manager channels used
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 4
Description: The number of sync manager protocols used by the CoE protocol.
Sub-index 1 - Usage of sync manager 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: Sync manager 0 is used by CoE as the mailbox receive channel (master to slave).
Sub-index 2 - Usage of sync manager 1
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: Sync manager 1 is used by CoE as the mailbox send channel (slave to master).
Sub-index 3 - Usage of sync manager 2
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 3
Description: Sync manager 2 is used by CoE as the process data output (RxPDOx - master to slave).
Sub-index 4 - Usage of sync manager 3
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 4
Description: Sync manager 3 is used by CoE as the process data input (TxPDOs - slave to master).
Table 6.18 Sync manager 0 PDO assignment object
0x1C10 Sync manager 0 PDO assignment
Sub-index 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 0
Description: Number of assigned PDOs. The mailbox received sync manager can never have PDOs
assigned to it.
Table 6.19 Sync manager 1 PDO assignment object
0x1C11 Sync manager 1 PDO assignment
Sub-index 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 0
Description: Number of assigned PDOs. The mailbox send sync manager can never have PDOs
assigned to it.
26 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 27

Table 6.20 Sync manager 2 PDO assignment object
0x1C12 Sync manager 2 PDO assignment
Sub-index 0
Access: RW Range: 0 to 512 Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: The number of RxPDOs assigned to this sync manager (used for process data output).
Sub-indices 1 to (sub-index 0)
Access: RW Range: 0x1600 to 0x17FF Size: 2 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x1605
Description: The object index of an RxPDO to assign to this sync manager. By default this is assigned
to RxPDO mapping 6 (vl_target_velocity and controlword).
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Table 6.21 Sync manager 3 PDO assignment object
0x1C13 Sync manager 3 PDO assignment
Sub-index 0
Access: RW Range: 0 to 512 Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: The number of TxPDOs assigned to this sync manager (used for process data input).
Sub-indices 1 to (sub-index 0)
Access: RW Range: 0x1A00 to 0x1BFF Size: 2 bytes Unit: N/A
Default: 0x1A05
Description: The object index of an TxPDO to assign to this sync manager. By default this is assigned to
TxPDO mapping 6 (vl_velocity_actual_value and statusword).
6.1.5 Feedback encoder source
Table 6.22 Feedback encoder source
0x2802 Feedback encoder source
Sub-index 0
Access: RW Range: 0 to 3 Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 0
Description: This object specifies the source position for position controller feedback.
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 27
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Glossary Of
Ter m s
Index
Page 28

7 Drive profile (DSP-402) support
SM-EtherCAT supports the following modes of the DSP-402 profile:
• Interpolated position mode
• vl velocity mode
• Profile torque mode
7.1 0x6040 Controlword
This provides the primary method of controlling the behavior of the drive e.g. enabling,
disabling, resetting, etc.
individual bits are used in combinations (see Table 7.2) to sequence the drive through
the state machine described in Figure 7-1.
Table 7.1 Controlword
0x6040 Controlword
Access: RW Range: 0 to 65535 Size: Unsigned 16 Unit: N/A
Default: N/A
Description: Provides the primary method of controlling the behavior of the drive.
Table 7.2 Controlword bit functions
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved r oms h fr oms hos eo qs ev so
LEGEND: ms = manufacturer-specific; r = reserved; oms = operation mode specific; h = halt;
fr = fault reset; hos = homing operation start; eo = enable operation; qs = quick stop; ev =
enable voltage; so = switch on
Table 7.3 Command coding
Command
Shutdown 0 X 1 1 0
Switch on 0 0 1 1 1
Switch on + enable
operation
Disable voltage 0 X X 0 X
Quick stop 0 X 0 1 X
Disable operation 0 0 1 1 1
Enable operation 0 1 1 1 1
Table 7.1 describes the format of the control word. The
Bits of the controlword
Bit 7 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 1 1 1 1
Fault reset X X X X
NOTE: Automatic transition to Enable operation state after executing SWITCHED
ON state functionality.
28 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 29

7.2 0x6041 Statusword
This provides feedback about the current operating state of the drive. Table 7.4
describes the format of the status word and illustrates how the individual statusword bits
are combined to represent the current state of the drive.
Table 7.4 Statusword
0x6041 Statusword
Access: RW Range: 0 to 65535 Size: Unsigned 16 Unit: N/A
Default: N/A
Description: This provides feedback about the current operating state of the drive.
Table 7.5 Statusword bit functions
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
ms ha lla tr rm ms w sod qs ve f oe so rtso
LEGEND: ms = manufacturer-specific; ha = homing attained; oms = operation mode specific; ila =
internal limit active; tr = target reached; rm = remote; w = warning; sod = switch on disabled; qs =
quick stop; ve = voltage enabled; f = fault; oe = operation enabled; so = switched on; rtso = ready to
switch on
Table 7.6 State coding
Statusword State
xxxx xxxx x0xx 0000b Not ready to switch on
xxxx xxxx x1xx 0000b Switch on disabled
xxxx xxxx x01x 0001b Ready to switch on
xxxx xxxx x01x 0011b Switched on
xxxx xxxx x01x 0111b Operation enabled
xxxx xxxx x00x 0111b Quick stop active
xxxx xxxx x0xx 1111b Fault reaction active
xxxx xxxx x0xx 1000b Fault
Information
Introduction
Installation
Installation
Getting Started Protocols
support
Safety
Mechanical
Electrical
Drive profile (DSP-402)
7.3 Common profile features
7.3.1 Sequencing control
These are the supported objects used to control the drive:
Table 7.7 Sequencing control supported objects
Index Name
0x6040 controlword
0x6041 statusword
0x605B shutdown_option_code
0x605C disable_operation_option_code
0x605A quick_stop_option_code
0x605D halt_option_code
0x605E fault_reaction_option_code
0x6060 modes_of_operation
0x6061 modes_of_operation_display
0x6085 quick_stop_deceleration
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 29
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
Index
Page 30

The behavior of the sequencing control is shown in Figure 7-1 CoE state machine
diagram . This state machine indicates how the drive will be controlled. For clarity the
Statusword is abbreviated to ‘SW’ in the diagram.
When in the ‘QUICK STOP ACTIVE’ state, the currently selected mode of operation
indicates how a quick stop function should be handled. When the drive is stopped, and
the Quick stop option code doesn’t indicate that the state should remain at ‘QUICK
STOP ACTIVE’, the state will move to ‘SWITCH ON DISABLED’.
When in the ‘OPERATION ENABLED’ or ‘QUICK STOP ACTIVE’ states it is not
possible to change the mode_of_operation object. This is to ensure that the motor is
stopped before changing the operation mode.
The SM-EtherCAT master device must be in the operational state before the state
machine can move from the ‘SWITCH ON DISABLED’ state to the ‘READY TO
SWITCH ON’ state. If the master leaves the operational state while the state machine is
in the ‘SWITCH ON’, ‘OPERATION ENABLE’ , ‘QUICK STOP ACTIVE’ or ‘READY TO
SWITCH ON’ state then the option will transition to the ‘SWITCH ON DISABLED’ state.
This implies that the drive will be inhibited and the motor will coast.
30 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 31

Figure 7-1 CoE state machine diagram
Information
Safety
Shutdown
Disable
voltage
START
Drive not
tripped
NOT READY TO
SWITCH ON
SWITCH ON
DISABLED
2
Shutdown
READY TO
SWITCH ON
3
Switch On
SWITCHED ON
4
Enable
operation
8
OPERATION
ENABLE
9
Any drive
trip
0
Pr 10.01 = 1
1
Pr 10.02 = 0
Quick stop
7
Shutdown
6
Disable
operation
5
10
16
Disable
voltage
Quick stop
Enable
operation
FaultPower disabled
FAULT REACTION
Power enabled
12
QUICK STOP
ACTIVE
11
ACTIVE
FAULT
Disable
voltage
13
Any drive
trip
14
Fault reaction
complete
15
Fault reset
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 31
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Index
Page 32

Table 7.8 CoE state machine transition and events
Transition Event(s) Action(s)
0 Automatic transition after power-on or
1 Automatic transition Communication shall be activated
2 Shutdown command from control
3 Switch on command received from
4 Enable operation command received
5 Disable operation command received
6 Shutdown command received from
7 Quick stop or disable voltage command
8 Shutdown command from control
9 Disable voltage command from control
10 Disable voltage or quick stop command
11 Quick stop command from control
12 Automatic transition when the quick
13 Fault signal The configure fault reaction function
14 Automatic transition The drive function shall be disabled; the
15 Fault reset command from control
16 Enable operation command from control
stop function is completed and quick
stop option code 1, 2, 3 or 4 disable
voltage command received from control
device (dependant on the quick stop
device, if the quick stop option code is
reset application
device or local signal
control device or local signal
from control device or local signal
from control device or local signal
control device or local signal
from control device or local signal
device or local signal
device or local signal
from control device or local signal
device or local signal
option code)
device or local signal
5, 6, 7 or 8
Drive device self-test and/or self
initialisation shall be performed
None
Power section shall be switched on if
not already switched on
Drive function shall be enabled and
clear all internal set-points
Drive function shall be disabled
The high-power shall be switched-off
immediately, and the motor shall be free
to rotate if not braked; additional action
depends on the shutdown option code
None
The high-power shall be switched off
immediately if possible, and the motor
shall be free to rotate if not braked
The high-power shall be switched off
immediately if possible, and the motor
shall be free to rotate if not braked
The high-power shall be switched off
immediately if possible, and the motor
shall be free to rotate if not braked
The quick stop function shall be started
The power section shall be switch off
shall be executed
high-power may be switched off
A reset of the fault condition is carried
out, if no fault exists currently on the
drive device; after leaving the Fault
state, the Fault reset bit in the
controlword shall be cleared by the
The drive function shall be enabled
control device
32 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 33

When the SM-EtherCAT module transitions from the EtherCAT Safe-operational state to
the EtherCAT Operational state, a number of drive parameters are set to allow the CoE
profiles to control the drive and motor (unless object 0x2805 has been set to disable
this). These parameters are set in the following order:
•Pr 6.42 to 0
•Pr 6.43 to On
•Pr 3.22 to 0 (where present)
•Pr 3.23 to On (where present)
•Pr 3.13 to Off (In open-loop operating modes)
•Pr 2.10 to 1
•Pr 2.20 to 1
•Pr 2.02 to On
•Pr 1.04 to 0
•Pr 1.21 to 0
•Pr 1.38 to 0
•Pr 1.08 to Off
•Pr 1.10 to On
•Pr 1.09 to Off
•Pr 1.15 to 1
•Pr 1.14 to 3
These values are set once and not continuously forced. They are not reset when leaving
the Operational state. In addition, the option starts to write parameters implicitly mapped
by the CoE profiles, when moving to the Operational state.
7.3.2 0x605A Quick stop option code
This object indicates what action is perfomed when the quick stop function is executed.
The slow down ramp is the deceleration value of the used mode of operations.
Table 7.9 Quick_stop_option_code
0x605A Quick_stop_option_code
Access: RW Range: 0 to 6 Size: Unsigned 16 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: Specifies what action is performed in the event of a quick stop function. See Table 7.8 CoE
state machine transition and events for more information.
Information
Introduction
Installation
Installation
Getting Started Protocols
support
features
Diagnostics
Safety
Mechanical
Electrical
Drive profile (DSP-402)
Advanced
Table 7.10 Quick stop value definitions
Value Definition
0 Disable drive function
1 Slow down on slow down ramp and transit into Switch on disabled
2 Slow down on quick stop ramp and transit into Switch on disabled
5 Slow down on slow down ramp and stay in Quick stop active
6 Slow down on quick stop ramp and stay in Quick stop active
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 33
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
Index
Page 34

7.3.3 0x605B Shutdown_option_code
This object is used to control what action is performed if there is a transition from the
Operation Enabled state to the Ready To Switch On state.
Table 7.11 Shutdown_option_code
0x605B Shutdown_option_code
Access: RW Range: 0 to 1 Size: Unsigned 16 Unit: N/A
Default: N/A
Description: Used to control what action is performed if there is a transition from the Operation Enabled
state to the Ready To Switch On state.
Table 7.12 Shutdown_option_code values
Value Definition
0 Disable drive function (switch-off the drive power stage)
1 Slow down with slow down ramp; disable the drive function
7.3.4 0x605C Disable_operation_option_code
Disable drive function (switch-off the drive power stage).
This object is used to control what action is performed if there is a transition from the
‘Operation Enabled’ state to the ‘Switched On’ state.
Table 7.13 Disabled_operation_option_code
0x605C Disable_operation_option_code
Access: RW Range: 0 to 1 Size: Unsigned 16 Unit: N/A
Default: N/A
Description: This object is used to control what action is performed if there is a transition from the
Table 7.14 Disable_operation_option_code values
Value Definition
Operation Enabled state to the Switched On state.
0 Disable drive function (switch-off the drive power stage)
1 Slow down with slow down ramp; disable the drive function
7.3.5 0x605E Fault_reaction_option_code
This object is used to control what action is performed when a fault is detected. This
object is ignored if the drive is tripped.
Table 7.15 Fault_reaction_option_code
0x605E Fault_reaction_option_code
Access: RW Range: 0 to 2 Size: Unsigned 16 Unit: N/A
Default: N/A
Description: This object is used to control what action is performed when a fault is detected.
Table 7.16 Fault_reaction_option_code values
Value Definition
0 Disable drive function, motor is free to rotate
1 Slow down on slow down ramp
2 Slow down on quick stop ramp
34 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 35

7.3.6 0x6060 Modes_of_operation
This object is used to request a change in the mode of operation.
Table 7.17 Modes_of_operation
0x6060 Modes_of_operation
Access: RW Range: 0 to 7 Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: This object is used to request a change in the mode of operation.
Table 7.18 Modes_of_operation values
Value Definition
0 No mode change
2 vl velocity mode
4 Profile torque mode
6 Homing mode
7 Interpolated position mode
7.3.7 0x6061 Modes_of_operation_display
This read only object indicates the active mode of operation.
Table 7.19 Modes_of_operation_display
0x6061 Modes_of_operation_display
Access: RO Range: 0 to 7 Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: N/A
Description: Used to provide the active mode of operation.
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
Table 7.20 Modes_of_operation_display values
Value Definition
0 No mode change
2 vl velocity mode
4 Profile torque mode
6 Homing mode
7 Interpolated position mode
7.3.8 0x6085 Quick_stop_deceleration
This object is used to configure the deceleration rate used to stop the motor when the
quick stop function is activated and the quick stop code object (0x605A) is set to 2 or 6.
The quick stop deceleration is also used if the fault reaction code object (0x605E) is 2.
The value is given in user-defined acceleration units.
Table 7.21 Quick_stop_deceleration
0x6085 Quick_stop_deceleration
Sub-index 0
Access: RW Range:0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: Quick stop function for the positioning related modes.
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 35
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
Index
Page 36

7.3.9 Profile units
The implementation provides a means to convert profile units into position controller and
drive units. All scaling values are standard profile objects. The following objects are
supported:
Table 7.22 Supported profile units
Index Name
0x608F position_encoder_resolution
0x6091 gear_ratio
0x6092 feed_constant
For positions, the scaling control includes a feed constant, a gear ratio and an encoder
revolution. These values are combined by the implementation into a simple scaling
numerator and denominator. It is possible to change these values non-cyclically (i.e.
using SDOs), in which case the scaling numerator and denominator and any position
limit values are recalculated in the background. It is not, however, possible to change
these values cyclically (i.e. by mapping PDOs to them).
For velocities, in addition to the position constants described above. These values are
combined into a simple numerator and denominator to scale velocities to internal
velocity units. This scaling also properly handles remainders (i.e. when used on a
reference or feedback, accumulate the remainder and add it to subsequent velocity
values, and when used with a limit, round up or down). It is possible to change these
values non-cyclically (i.e. using SDOs), in which case the scaling numerator and
denominator is recalculated in the background. It is also necessary to re-scale velocity
limit values with the new factor. It is not possible to change these values cyclically (i.e.
by mapping PDOs to them).
7.3.10 0x608F Position_encoder_resolution
This read only object indicates the configured encoder increments per number of motor
revolutions. The information is read from the drive's encoder configuration.
Table 7.23 Position_encoder_resolution
0x608F Position_encoder_resolution
Sub-index 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description:
Sub-index 1
Access: RO Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: Enco der increments
Sub-index 2
Access: RO Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: Motor revolutions
7.3.11 0x6091 Gear_ratio
This object is used to apply scaling. When configured, appropriate user units can be
used to control the position of the shaft beyond a gearbox. The gear ratio is calculated
using the following formula:
gear ratio = motor shaft revolutions / driving shaft revolutions
36 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 37

Table 7.24 Gear_ratio
0x6091 Gear_ratio
Sub-index 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description:
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: Motor revolutions
Sub-index 2
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: Shaft revolutions
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
7.3.12 0x6092 Feed_constant
This is used to configure a feed constant. This is the measurement distance per one
revolution of the output shaft of the gearbox. The feed constant is calculated using the
following formula:
feed constant = feed / driving shaft revolutions
The feed should be provided in user-defined position units
Table 7.25 Feed_constant
0x6092 Feed_constant
Sub-index 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description:
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: Feed
Sub-index 2
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: Shaft revolutions
7.3.13 Basic position control
Basic position control is supported on the Unidrive SP in servo mode, closed-loop
vector mode and RFC mode. It works on the Digitax ST and Mentor MP but is not
supported in open-loop or regen mode on any of the drives. If is also not available on
Commander SK or Affinity. The position control described here is used under the
interpolated position mode of operation.
Getting Started Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 37
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Index
Page 38

Table 7.26 lists the objects that are supported:
Table 7.26 Basic position control supported objects
Index Name
0x6062 position_demand_value
0x6064 position_actual_value
0x6065 following_error_window
0x6067 position_window
0x60F4 following_error_actual_value
0x60FB position_control_parameter_set
7.3.14 0x6062 Position_demand_value
This read only object is used to provide the currently demanded position value. The
value is given in user defined position units.
Table 7.27 Position_demand_value
0x6062 Position_demand_value
Access: RO Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: N/A
Default: N/A
Description: Used to provide the currently demanded position value.
7.3.15 0x6064 Position_actual_value
This read only object provides the actual value of the position feedback device. The
value is given in internal units.
Table 7.28 Position_actual_value
0x6064 Position_actual_value
Access: RO Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: N/A
Default: N/A
Description: This read only object provides the actual value of the position feedback device. The value
is given in internal units.
7.3.16 0x60F4 Following_error_actual_value
This read only object provides the actual value of the following error. The value is given
in user-defined position units.
Table 7.29 Following_error actual_value
0x60F4 Following_error actual_value
Access: RO Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: N/A
Default: N/A
Description:
This read only object provides the actual value of the following error.
38 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 39

7.3.17 0x60FB Position_control_parameter_set object
Table 7.30 Position_control_parameter_set object
0x60FB Position_control_parameter_set
Sub-index 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of control loop parameters.
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: 0 to 65535 Size: Unsigned 16 Unit: 0.01 rad/s/rad
Default: 2500
Description: The po sition controller proportional gain.
Sub-index 2
Access: RW Range: 0 to 65535 Size: Unsigned 16 Unit: 1 / 1000
Default: 1000 (i.e. a gain of 1)
Description: The position controller speed feed forward gain.
The APC position controller kernel is used by the basic internal position control.
The position_demand_value object contains the value supplied by either the
interpolated position mode or the profile position mode (in user units). It is updated
every control loop cycle. This object can be mapped as cyclic data.
7.4 Interpolated position mode
Interpolated position mode operates on the Unidrive SP in servo mode, closed-loop
vector mode and RFC mode. This mode also operates on the Digitax ST and Mentor
MP.
Table 7.31 lists the objects that are supported:
Table 7.31 Supported Interpolated position mode objects
Index Name
0x60C0 interpolation_submode_select
0x60C1 interpolation_data_record
0x60C2 interpolation_time_period
7.4.1 0x60C0 Interpolation_sub-mode_select
Table 7.32 0x60C0 Interpolation_sub-mode_select
0x60C0 Interpolation_sub-mode_select
Access: RW Range: 0 Size: Signed 16 Unit: N/A
Default: 0 (Linear interpolation)
Description: Specifies the interpolation type. The values have the following meanings:0 = Linear
Interpolation.
Information
Introduction
Installation
Installation
Getting Started Protocols
support
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Safety
Mechanical
Electrical
Drive profile (DSP-402)
Advanced
Quick
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 39
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Glossary Of
Te rm s
Index
Page 40

7.4.2 0x60C1 Interpolation_data_record
This object is used to specify the target position. Linear interpolation is used to generate
position demand values every 250µs. The position is specified in user-defined position
units. The value is written into sub-index 1.
Table 7.33 0x60C1 Interpolation_data_record
0x60C1 Interpolation_data_record
Sub-index 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: This object is used to specify the target position.
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: N/A
Default: N/A
Description: The set-point
7.4.3 0x60C2 Interpolation_time_period
Table 7.34 Interpolation_time_period
0x60C2 Interpolation_time_period
Sub-index 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of last sub-indexes in this object.
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: 0 to 255 Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: (sub-index 2)
Default: 250 (units are dependant on the value in sub-index 2)
Description: The number of time units between interpolator re-starts. A time unit is defined by sub-index
Sub-index 2
Access: RW Range: -6 to 0 Size: Signed 8 Unit: N/A
Default: -6 (a time unit of 1µs)
Description: This specifies the time unit for the interpolation time period. Sub-index 2 specifies the unit
The implementation of interpolated position mode allows synchronous operation only,
where a fixed, common interpolation interval is defined. The time specified must always
be an integer multiple of the control loop cycle time. The time period index has a
minimum value of -6 (i.e. the smallest time unit will be microseconds), see
more information.
Table 7.35 Interpolation time period units
2. The interpolator time period value is checked to ensure that it is valid. Valid values are
250µs, 500µs or any multiple of 1ms. An attempt to write other values re sults in an SDO
Abort code.
exponent. The time unit, therefore, is 10(sub-index 2). The range of values allows for the
shortest time unit to be 1µs, and the longest to be 1s.
Value in 0x60C2, sub-index 2 Description
0 1 second
-1 0.1 of a second
-2 0.01 of a second
-3 0.001 of a second
-4 0.0001 of a second
-5 0.00001 of a second
-6 0.000001 of a second
Table 7.35 for
40 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 41

The time period is checked to ensure that it is an integer multiple of the control loop
cycle time. Only linear interpolation is currently supported. This type inserts a delay of
one interpolation time period.
The input buffer has a maximum size of 1 data record, and a data record contains one
position in profile-defined units. The buffer is a FIFO buffer. Every interpolator time
period, a value is read from this buffer. The correct number of data points for a specific
interpolation mode are stored internally. When a new position command is loaded in, the
oldest position command in the data set is discarded.
7.5 vl velocity mode
Velocity mode is supported on Unidrive SP, Digitax ST, Affinity, Mentor MP and
Commander SK. It is not, however, supported in regen modes. This mode uses the
drive’s speed handling and ramps.
When the attached drive is in either of the closed-loop or servo operating modes the
scaled velocity is written to the drive internal speed shortcut. When the attached drive is
in an open-loop operating mode the scaled velocity is written to the user preset
reference parameter (Pr 1.21).
Table 7.36 vl velocity mode supported objects
Index Name
0x6042 vl_target_velocity
0x6043 vl_velocity_demand
0x6044 vl_velocity_actual_value
0x6046 vl_velocity_min_max_amount
0x6047 vl_velocity_min_max
0x6048 vl_velocity_accleration
0x6049 vl_velocity_deceleration
0x604A vl_velocity_quick_stop
0x604B vl_setpoint_factor
0x604C vl_dimension_factor
7.5.1 0x6042 vl_target_velocity
This object is used to set the required velocity of the system. It is multiplied by the
vl_dimension_factor and the vl_setpoint_factor. The value is given in rpm, If the
vl_dimension_factor has the value of 1, otherwise the value is in user units. Positive
values indicate forward direction and negative values indicate reverse direction.
Table 7.37 vl_target_velocity
0x6042 vl_target_velocity
Access: RW Range: -32768 to +32767 Size: Signed 16 Unit: rpm
Default: 0
Description: Used to set the required velocity of the system.
Table 7.36 lists the objects that are supported:
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 41
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Index
Page 42

7.5.2 0x6043 vl_velocity_demand
This read only object provides the instantaneous velocity demand generated by the
drive ramp function. The value is given in rpm if the vl_dimension_factor and the
vl_setpoint_factor have the value 1, otherwise the value is in user units. Positive values
indicate forward direction and negative values indicate reverse direction.
Table 7.38 vl_velocity_demand
0x6043 vl_velocity_demand
Access: RO Range: -32768 to +32767 Size: Signed 16 Unit: rpm
Default: 0
Description: Provides the instantaneous velocity demand generated by the drive ramp function
7.5.3 0x6044 vl_velocity_actual_value
This read only object provides the velocity at the motor spindle or load. In a closed loop
system this is determined from the motor feedback device and in an open loop system it
is a copy of vl_velocity_demand.
The value is given in rpm if the vl_dimension_factor has the value of 1, otherwise the
value is in user units. Positive values indicate forward direction and negative values
indicate reverse direction.
Table 7.39 vl_velocity_actual_value
0x6044 vl_velocity_actual_value
Access: RO Range: -32768 to +32767 Size: Signed 16 Unit: N/A
Default: 0
Description: Provides the velocity at the motor spindle or load.
Only available when in vl_velocity_mode.
7.5.4 0x6046 vl_velocity_min_max_amount
This object is used to configure the minimum and maximum velocity.
The value is given in rpm if the vl_dimension_factor has the value of 1, otherwise the
value is in user units.
Table 7.40 vl_velocity_min_max_amount
0x6046 vl_velocity_min_max_amount
Sub-index 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of last sub-indexes in this object.
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: rpm
Default: 0
Description: Used to configure the minimum velocity (both in the forward and reverse direction) that the
Sub-index 2
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: rpm
Default: 2147483647
Description: Used to configure the maximum velocity (both in the forward and reverse direction) that the
system can operate at. Writing to this sub index will overwrite vl_velocity_min positive and
vl_velocity_min negative.
system can operate at. Writing to this sub index will overwrite vl_velocity_max positive and
vl_velocity_max negative.
42 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 43

7.5.5 0x6047 vl_velocity_min_max
This object is used to configure the minimum and maximum velocity.
The value is given in rpm if the vl_dimension_factor has the value of 1, otherwise the
value is in user units.
Table 7.41 0x6047 vl_velocity_min_max
0x6047 vl_velocity_min_max
Sub-index 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 4
Description: The number of last sub-indexes in this object.
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: rpm
Default: 0
Description: Used to configure the minimum positive velocity at which the system can operate.
Sub-index 2
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: rpm
Default: 2147483647
Description: Used to configure the maximum positive velocity at which the system can operate.
Sub-index 3
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: rpm
Default: 0
Description: Used to configure the minimum negative velocity at which the system can operate.
Sub-index 4
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: rpm
Default: 2147483647
Description: Used to configure the maximum negative velocity at which the system can operate.
7.5.6 0x6048 vl_velocity_acceleration
This object is used to configure the delta speed and delta time of the slope of the
acceleration ramp.
Example: To ramp to 1000 rpm in 5s, possible values for delta speed and delta time
are 10000 and 50 respectively.
vl_velocity_acceleration = delta speed / delta time
Table 7.42 0x6048 vl_velocity_acceleration
0x6048 vl_velocity_acceleration
Sub-index 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of last sub-indexes in this object.
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: rpm
Default: 1000
Description: The value of delta speed is given in rpm if the vl_dimension_factor and the
Sub-index 2
Access: RW Range: 0 to 65535 Size: Unsigned 16 Unit: s
Default: 2
Description: The val ue of delta time is given in seconds.
vl_setpoint_factor have the value 1, otherwise the value is in user units.
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
Index
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 43
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Page 44

7.5.7 0x6049 vl_velocity_deceleration
This object is used to configure the delta speed and delta time of the slope of the
deceleration ramp.
Example: To decelerate by 800 rpm in 10s, possible values for delta speed and delta
time are 8000 and 100 respectively.
vl_velocity_deceleration = delta speed / delta time
Table 7.43 0x6049 vl_velocity_deceleration
0x6049 vl_velocity_deceleration
Sub-index 0
Access: C Range: N/A Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of last sub-indexes in this object.
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: rpm
Default: 1000
Description: The value of delta speed is given in rpm if the vl_dimension_factor and the
Sub-index 2
Access: RW Range: 0 to 65535 Size: Unsigned 16 Unit: s
Default: 2
Description: The val ue of delta time is given in seconds.
vl_setpoint_factor have the value 1, otherwise the value is in user units.
7.5.8 0x604A vl_velocity_quick_stop
This object is used to configure the delta speed and delta time of the slope of the
deceleration ramp for quick stop.
Example: To decelerate by 800 rpm in 10s, possible values for delta speed and delta
time are 8000 and 100 respectively.
vl velocity deceleration = delta speed / delta time
Table 7.44 0x604A vl_velocity_quick_stop
0x604A vl_velocity_quick_stop
Sub-index 0
Access: C Range: N/A Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of last sub-indexes in this object.
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: rpm
Default: 1000
Description: The value of delta speed is given in rpm if the vl_dimension_factor and the
vl_setpoint_factor have the value 1, otherwise the value is in user units.
Sub-index 2
Access: RW Range: 0 to 65535 Size: Unsigned 16 Unit: s
Default: 2
Description: The val ue of delta time is given in seconds.
44 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 45

7.5.9 0x604B vl_setpoint_factor
This object is used to configure the numerator and denominator of the
vl_setpoint_factor. The vl_setpoint_factor modifies the resolution or directing range of
the specified setpoint. It does not influence the velocity limit function and the ramp
function. A value of 0 must not be used.
Table 7.45 0x604B vl_setpoint_factor
0x604B vl_setpoint_factor
Sub-index 0
Access: C Range: N/A Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of last sub-indexes in this object.
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: -32768 to +32767 Size: Signed 16 Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: vl_setpoint_factor numerator (a value of 0 is not valid)
Sub-index 2
Access: RW Range: -32768 to +32767 Size: Signed 16 Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: vl_setpoint_factor denominator (a value of 0 is not valid)
7.5.10 0x604C vl_dimension_factor
This object is used to configure the numerator and denominator of the
vl_dimension_factor. The vl_dimension_factor is used to scale the user units so that
they can be used in a way that relates to the specific application.
Calculating the vl dimension factor:
Every user-specific velocity consists of a specific unit referred to as a specific unit of
time (e.g. 1/s, bottles/min, m/s,...). The purpose of the vl_dimension_factor is to convert
this specific unit to the revolutions/minute unit. A value of 0 must not be used.
Velocity [user-defined unit] / Dimension factor [rpm/user-defined unit] = Velocity [rpm]
Table 7.46 0x604C vl_dimension_factor
0x604C vl_dimension_factor
Sub-index 0
Access: C Range: N/A Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of last sub-indexes in this object.
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: -32768 to +32767 Size: Signed 16 Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: vl_dimension_factor numerator (a value of 0 is not valid)
Sub-index 2
Access: RW Range: -32768 to +32767 Size: Signed 16 Unit: N/A
Default: 1
Description: vl_dimension_factor denominator (a value of 0 is not valid)
The vl_target_velocity object is re-read every new profile cycle. It is scaled to
appropriate units using the vl_dimension_factor and vl_setpoint_factor objects and then
written to the drive preset reference 1 parameter (Pr 1.21).
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
Index
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 45
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Page 46

The object vl_velocity_min_max is handled every profile cycle. The vl_target_velocity is
limited according to the values set in the object vl_velocity_min_max, which is read
every profile cycle. The object vl_velocity_min_max_amount is mapped to
vl_velocity_min_max.
The value of the vl_velocity_demand object is calculated in the background. The option
reads the value of parameter Pr 2.01 (post ramp reference), scaled from RPM to user
units using vl_dimension_factor and vl_setpoint_factor, and writes the value to the
vl_velocity_demand object.
On a closed-loop drive, the speed feedback is read from the drive internally every profile
cycle, scaled to the same units as vl_target_velocity and written to the
vl_velocity_actual_value object. On an open-loop drive, the estimated motor speed is
read from Pr 5.04 (motor RPM) in the background, scaled to the units of
vl_target_velocity and written to the vl_velocity_actual_value object.
The vl_velocity_acceleration and vl_velocity_deceleration objects are handled in the
background. They are read, scaled to drive acceleration units (depending on the drive
operating mode), and written to the drive acceleration rate and deceleration rate
presets. In addition, if the drive acceleration rate preset is changed, the
vl_velocity_acceleration object is updated, and if the drive deceleration rate preset is
changed (Pr 2.21), the vl_velocity_deceleration object is updated.
7.6 Profile Torque mode
The profile torque mode is supported on Unidrive SP, Digitax ST, Affinity, Mentor MP
and Commander SK. It is possible to use this profile in regen mode on the Unidrive SP.
On the Unidrive SP and Digitax ST in closed-loop or servo mode, this mode operates on
the profile cycle time, using the drives internal torque shortcut (which is read by the
drive every 250µs). On the Commander SK, Unidrive SP and Affinity in open-loop
mode, the torque reference is written to the drive user torque parameter, which is
handled every 4ms. When using profile torque mode object 0x604A
vl_velocity_quick_stop will be used in the event of a quick stop (also for quick stop
option codes 2 and 6 the 0x6049 vl_velocity_deceleration object will be used).
Table 7.47 shows the objects that are supported:
Table 7.47 Profile torque mode supported objects
Index Name
0x6071 Target_torque
0x6075 Motor_rated_current
0x6078 Current_actual_value
0x6087 Torque_slope
7.6.1 0x6071 Target_torque
This object indicates the configured input value for the torque controller in profile torque
mode. The value of this object is given per thousand of rated torque.
Table 7.48 0x6071 Target_torque
0x6071 Target_torque
Access: RW Range: -32768 to +32767 Size: Signed 16 Unit: 0.1% of rated torque
Default: 0
Description: Indicates the configured input value for the torque controller in profile torque mode.
46 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 47

7.6.2 0x6075 Motor_rated_current
This object indicates the configured motor rated current. It is taken from the motor’s
name-plate. Depending on the motor and drive technology this current is DC, peak or
rms (root-mean-square) current. All relative current data refers to this value. The value
of this object is given in mA.
Table 7.49 0x6075 Motor_rated_current
0x6075 Motor_rated_current
Access: RO Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: mA
Default: 0
Description: Indicates the configured motor rated current (Pr 5.07).
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
7.6.3 0x6078 Current_actual_value
This object provides the actual value of the current. It shall correspond to the current in
the motor. The value of this object is given per thousand of rated current.
Table 7.50 0x6078 Current_actual_value
0x6078 Current_actual_value
Access: RO Range: -32768 to +32767 Size: Signed 16 Unit: 0.1% of rated current
Default: 0
Description: Provides the actual value of the current.
7.6.4 0x6087 Torque_slope
This object indicates the configured rate of change of torque. The value of this object is
given in units of per thousand of rated torque per second.
Table 7.51 Torque_slope
0x6087 Torque_slope
Access: RW Range: 0 to 0xFFFFFFFF Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: 0.1% of rated torque per second
Default: 0
Description: Indicates the configured rate of change of torque.
7.7 Homing Mode
This section describes the method by which a drive seeks the home position (also
called, the datum, reference point or zero point).
Figure 7-2 Homing mode function on page 47 shows the defined input objects as well
as the output objects. The user may specify the speeds, acceleration and the method of
homing. There is a further object home offset, which allows the user to displace zero in
the user's coordinate system from the home position.
There is no output data except for those bits in the statusword, which return the status or
result of the homing process and the demand to the position control loops.
Figure 7-2 Homing mode function
Controlword (6040 )
Homing method (6098 )
Homing Speeds (6099 )
Homing acceleration (609A )
Home offset (607C )
h
h
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
h
Statusword (6041 )
h
Homing
method
Position demand value (6062 )
h
h
h
Glossary Of
Te rm s
Index
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 47
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Page 48

By choosing a homing method the following behaviour is determined: The homing signal
(positive limit switch, negative limit switch, home switch), the direction of actuation and
where appropriate the position of the index pulse.
An encircled number in Figure 7-3 to Figure 7-10 indicates the code for selection of this
homing position. The direction of movement is also indicated.
There are four sources of homing signal available: These are the negative and positive
limit switches, the home switch and the index pulse from an encoder.
In the diagrams of homing sequences shown below, the encoder count increases as the
axis's position moves to the right, in other words the left is the minimum position and the
right is the maximum position.
7.7.1 General homing definitions
Method 1: Homing on negative limit switch and index pulse
Using this method as shown in Figure 7-3 Homing on negative limit switch and index
pulse on page 48, the initial direction of movement shall be leftward if the negative limit
switch is inactive (here: low). The home position shall be at the first index pulse to the
right of the position where the negative limit switch becomes inactive.
Figure 7-3 Homing on negative limit switch and index pulse
Method 2: Homing on positive limit switch and index pulse
Using this method as shown in Figure 7-4 Homing on positive limit switch and index
pulse on page 48, the initial direction of movement shall be rightward if the positive limit
switch is inactive (here: low). The position of home shall be at the first index pulse to the
left of the position where the positive limit switch becomes inactive.
Figure 7-4 Homing on positive limit switch and index pulse
48 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 49

Method 3 and 4: Homing on positive home switch and index pulse
Using these methods as shown in Figure 7-5 Homing on positive home switch and
index pulse on page 49, the initial direction of movement shall be dependent on the
state of the home switch. The home position shall be at the index pulse either to the left
or the right of the point where the home switch changes state. If the initial position is
sited so that the direction of movement shall reverse during homing, the point at which
the reversal takes place is anywhere after a change of state of the home switch.
Figure 7-5 Homing on positive home switch and index pulse
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started Protocols
Method 5 and 6: Homing on negative home switch and index pulse
Using these methods as shown in Figure 7-6 Homing on negative home switch and
index pulse on page 49, the initial direction of movement shall be dependent on the
state of the home switch. The home position shall be at the index pulse either to the left
or the right of the point where the home switch changes state. If the initial position is
sited so that the direction of movement shall reverse during homing, the point at which
the reversal takes place is anywhere after a change of state of the home switch.
Figure 7-6 Homing on negative home switch and index pulse
Method 7 to 14: Homing on home switch and index pulse
These methods use a home switch, which is active over only a portion of the travel; in
effect the switch has a 'momentary' action as the axis's position sweeps past the switch.
Using the methods 7 to 10, the initial direction of movement shall be to the right, and
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
Index
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 49
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Page 50

using methods 11 to 14 the initial direction of movement shall be to the left except if the
home switch is active at the start of the motion. In this case the initial direction of motion
shall be dependent on the edge being sought. The home position shall be at the index
pulse on either side of the rising or falling edges of the home switch, as shown in
7-7 Homing on home switch and index pulse - positive initial motion on page 50 and
Figure 7-8 Homing on home switch and index pulse - negative initial motion on page
50. If the initial direction of movement leads away from the home switch, the drive shall
reverse on encountering the relevant limit switch.
Figure 7-7 Homing on home switch and index pulse - positive initial motion
Figure
Figure 7-8 Homing on home switch and index pulse - negative initial motion
50 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 51

Method 15 and 16: Reserved
These methods are reserved.
Method 17 to 30: Homing without index pulse
These methods are similar to methods 1 to 14 except that the home position is not
dependent on the index pulse but only dependent on the relevant home or limit switch
transitions. For example methods 19 and 20 are similar to methods 3 and 4 as shown in
Figure 7-9 Homing on positive home switch on page 51.
Figure 7-9 Homing on positive home switch
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started Protocols
Method 31 and 32: Reserved
These methods are reserved.
Method 33 and 34: Homing on index pulse
Using these methods, the direction of homing is negative or positive respectively. The
home position shall be at the index pulse found in the selected direction as shown in
Figure 7-10 Homing on index pulse on page 51.
Figure 7-10 Homing on index pulse
Method 35: Homing on index pulse
In this method, the current position shall be taken to be the home position. This method
does not require the drive device to be in operational enabled state.
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
Index
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 51
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Page 52

Use of controlword and statusword
The homing mode uses some bits of the controlword and the statusword for modespecific purposes.
Table 7.52 Definition of bits 4 and 8 of the controlword on page 52
defines the values for bits 4 and 8 of the controlword.
Table 7.52 Definition of bits 4 and 8 of the controlword
Bit Value Definition
4
8
0 Do not start homing procedure.
1 Start or continue homing procedure.
0 Enable bit 4.
1 Stop axis according to halt option code (0x605D).
Table 7.53 Definition of bits 10 and 12 of the statusword on page 52 defines the values
for bits 10 and 12 of the statusword.
Table 7.53 Definition of bits 10 and 12 of the statusword
Bit 12 Bit 10 Definition
0 0 Homing procedure is in progress.
0 1 Homing procedure is interrupted or not started.
1 0 Homing is attained, but target is not reached.
1 1 Homing procedure was completed successfully.
0 0 Homing error occurred, velocity is not 0.
0 1 Homing error occurred, velocity is 0.
1 X Reserved.
7.7.2 Homing mode object definitions
0x2803 Homing source
This object indicates the configured source of the homing switch used during the
homing procedure.
description.
Table 7.54 Homing source
0x2803 Homing source
Sub-index 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: Unigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of the last sub-index in this object.
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: 1 to 8
Default: 5
Description: The source of the homing switch. This will specify a digital input as follows:
1 to 6 - The number of a Drive digital input
7 to 8 - SM-EtherCAT option module digital input 0 or 1
Sub-index 2
Access: RW
Default: 0
Description: Use the feedback source freeze for homing. This will cause the freeze from the selected
feedback device to be used instead of the index (marker) pulse when it is required during homing.
Table 7.54 Homing source on page 52 specifies the object
Range: 0 to 1 Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
52 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 53

0x2804 Freeze object
This object is used to configure the freeze function that can be used within the Homing
mode profile.
Table 7.55 Freeze object on page 53 specifies the object description.
Table 7.55 Freeze object
0x2804
Sub-index 0
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: Unigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of the last sub-index in this object.
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: 0 to 1
Default: 0
Description: Route the option freeze onto the drive. Setting a value of 1 here will route the option
digital input 0 onto the drive freeze line.
Sub-index 2
Access: RW
Default: 0
Description: Option to drive freeze invert. Setting a value of 1 will invert the freeze signal routed onto
the drive from the option input 0 (if 0x2804, sub-index 1 is set to 1). This value will be read only on a
transition from 0 to 1 in sub-index 1.
Freeze object
Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Range: 0 to 1 Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
0x607C Home offset
This object indicates the configured difference between the zero position for the
application and the machine home position (found during homing). During homing the
machine home position is found and once the homing is completed the zero position is
offset from the home position by adding the home offset to the home position. All
subsequent absolute moves shall be taken relative to this new zero position. This is
illustrated in
Figure 7-11 Home offset definition on page 53. The value of this object
shall be given in user-defined position units. Negative values indicate the opposite
direction.
Figure 7-11 Home offset definition
Information
Introduction
Installation
Installation
Getting Started Protocols
support
features
Safety
Mechanical
Electrical
Drive profile (DSP-402)
Advanced
Table 7.56 Home offset
0x607C Home offset
Access: RW
Default: 0
Description: Homing offset value.
Range: -32768 to
+32767
Size: Signed 32
Unit: User-defined
position units
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 53
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
Index
Page 54

0x6098 Homing method
This object indicates the configured homing method that shall be used. Ta b le
7.57 Homing method on page 54 specifies the object description, and Table
7.58 Homing method values on page 54 specifies the value ranges for this object.
Table 7.57 Homing method
0x6098 Homing Method
Access: RW Range: 0 - 35 Size: Unsigned 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 0
Description: The homing method that shall be used.
Table 7.58 Homing method values
Value Definition
0 No homing method assigned
1 Method 1 shall be used
to
34 Method 34 shall be used
35 Method 35 shall be used
0x6099 Homing speeds
This object indicates the configured speeds used during the homing procedure. The
values shall be given in user-defined velocity units.
Table 7.59 Homing speeds on page
54 specifies the object description.
Table 7.59 Homing speeds
0x6099 Homing speeds
Sub-index 0
Access: C Range: 2 Size: Signed 8 Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of supported sub-indices.
Sub-index 1
Access: RW Range: Unsigned 32
Default: 0
Description: Speed during search for a switch.
Sub-index 2
Access: RW
Default: 0
Description: Speed during search for a zero.
Range: Unsigned 32 Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: N/A
Size: Unsigned 32 Unit: N/A
0x609A Homing acceleration
This object indicates the configured acceleration and deceleration to be used during the
homing operation. The value shall be given in user-defined acceleration units.
Table
7.60 Homing acceleration on page 54 specifies the object description.
Table 7.60 Homing acceleration
0x609A Homing acceleration
Access: RW Range: Unsigned 32 Size: Unsigned 32
Default: 0
Description:
Indicates the configured acceleration and deceleration to be used during homing
operation.
Unit: User-defined
acceleration units
54 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 55

8 Advanced features
Information
Safety
8.1 Distributed clocks
SM-EtherCAT supports Distributed clocks. This is the scheme used by EtherCAT to
accurately time synchronize slave devices. Position, speed and current control loops
can all be synchronized.
When the option module is connected to a drive which can take a time synchronization
signal (e.g. a Unidrive SP or Digitax ST), the EtherCAT distributed clocks facility can be
used to provide this signal so the drive speed and current tasks are synchronized to the
network. The position controller, and appropriate motion features will also be
synchronized to the drive speed task.
NOTE
In CoE interpolated position mode the position command provided by the master every
interpolation cycle time is used to generate a position command for the drive every
250µs.
8.2 SM-EtherCAT protocol support
The following are supported:
• Four Sync Managers. Two are used for the Mailbox Protocol (non-cyclic data)
and two are used for process data (cyclic data)
• Distributed Clocks
• CANopen over EtherCAT (CoE)
• CMP protocol through Modbus RTU (only on the Unidrive SP, Digitax ST,
Mentor MP and Affinity)
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting
Star ted
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 55
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
Index
Page 56

9 Diagnostics
9.1 Module identification parameters
The basic menu parameters can be accessed through the slot menu in the drive,
Pr MM.PP, where MM is the menu for SM-EtherCAT in the host drive. The basic menu
parameters may also be accessed using menu 60, i.e. Pr 60.PP.
9.1.1 SM-EtherCAT module ID code
Table 9.1 SM-EtherCAT module ID code
SM-EtherCAT module ID code
Default 421 (SM-EtherCAT)
Pr MM.01
The module ID code indicates the type of module installed in the slot corresponding to
menu MM. This is useful for checking the module is of the correct type.
9.1.2 SM-EtherCAT firmware version
Table 9.2 SM-EtherCAT firmware - major version
SM-EtherCAT firmware - major version (xx.yy)
Pr MM.02
Table 9.3 SM-EtherCAT firmware - minor version
SM-EtherCAT firmware - minor version (zz)
Pr MM.51
Unidrive SP/ Unidrive SPM/ Mentor MP
The software version of the Solutions Modules can be identified by looking at Pr 15.02 /
Pr 16.02 or Pr
Menu 15,16 or 17 is Solutions Module slot dependent with menu 17 being the lowest
position nearest the control terminal connections.
Range -
Access RO
Default N/A
Range 00.00 to 99.99
Access RO
Default N/A
Range 0 to 99
Access RO
17.02 and Pr 15.51 / Pr 16.51 or Pr 17.51.
The software version takes the form of xx.yy.zz, where Pr 15.02 displays xx.yy and
Pr
15.51 displays zz (e.g. for software version 01.01.00 on a module in the middle Solu-
tions Module slot, Pr 16.02 will display 1.01 and Pr 16.51 will display 0).
Digitax ST / Unidrive ES / Affinity
The software version of the Solutions Modules can be identified by looking at Pr 15.02 or
Pr 16.02 and Pr 15.51 or Pr 16.51.
Menu 15 or 16 is Solutions Module slot dependent with menu 15 being the position
nearest the control terminal connections.
The software version takes the form of xx.yy.zz, where Pr 15.02 displays xx.yy and
Pr
15.51 displays zz (e.g. for software version 01.01.00 on a module in the middle Solu-
tions Module slot, Pr 16.02 will display 1.01 and Pr 16.51 will display 0).
56 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 57

Commander SK / Commander SL
The software version of the Solutions Module can be identified by looking at Pr 15.02 and
Pr 15.51.
The software version takes the form of xx.yy.zz, where Pr 15.02 displays xx.yy and
Pr
15.51 displays zz (e.g. for software version 01.01.00 Pr 15.02 will display 1.01 and
Pr
15.51 will display 0).
Information
Safety
Introduction
9.2 Network configuration objects
9.2.1 SM-EtherCAT network loss trip
Table 9.4 Network loss behavior object
0x2813 Network loss behavior
Sub-index 0:
Access: RO Range: N/A Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 2
Description: The number of last sub-indexes in this object.
Sub-index 1: Maximum time interval
Access: RW Range: 0 to 65535 Size: 2 bytes Unit: ms
Default: 0 (by default the network loss behavior is disabled)
Description: The maximum time, in ms, allowed between accesses to PDOs (read or write). If no PDO
Sub-index 2: Trip type
Access: RW Range: 0 to 2 Size: 1 byte Unit: N/A
Default: 0
Description: Network loss trip type. If this value is set to 0, a network loss trip will never occur; however,
SM-EtherCAT resets an internal timer when a valid message is received from the
EtherCAT network. The network loss trip is triggered when no new messages are
received before the timer times out. The SM-EtherCAT will trip the drive and the SMEtherCAT error code parameter (Pr MM.50) will show 120.
After power-up or reset the network loss trip is not armed until one of the following
events occur:
• SYNC message is received.
• RxPDO is received
Once the trip has been armed, a minimum of one of the above messages must be
received or transmitted in each time period set in sub-index 2 of the Network loss
behavior object (0x2813).
access occurs for this period, the option will start network loss handling. If a value of zero is
set, no network loss handling will occur.
a network loss will still be handled by stopping the drive and indicating a warning as
previously described. If this value is set to 1, the network loss trip will occur only after the
motor has been stopped according to the Fault reaction option code. If the value is set to 2,
the network loss trip will occur immediately on network loss (this implies that the motor will
coast).
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting
Star ted
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 57
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Glossary Of
Ter m s
Index
Page 58

9.3 Diagnostic parameters
Table 9.5 SM-EtherCAT operating status
SM-EtherCAT operating status
Default N/A
Pr MM.06
9.3.1 Running states
Table 9.6 Diagnostic information - running states
Pr MM.06 Meaning Description
0 Link established A link has been established but no frames are being
> 0 Handled messages per
Table 9.7 Diagnostic information - application
Pr MM.06 Meaning Description
-99 Application started The main application has been launched.
-70 Initialising file system The file system is initialising.
-50 Initialising databases The databases are initialising.
-30 Initialising fieldbus The fieldbus is initialising.
-25 Starting fieldbus The fieldbus is starting.
-1 Initialisation complete The option module has initialised correctly but no
Table 9.8 Diagnostic information - bootloader
Pr MM.06 Meaning Description
-199 Boot loader start The bootloader is starting up.
-180 Initialising memory The memory manager is being initialised.
-150 Initialising file system The file system handler is being initialised.
-149 Format file system The file system is being formatted.
-148 Verify file system The file system is being verified.
-130 Check boot mode The required boot mode is being checked.
-110 Loading application The requested application image is being copied from
-101 Launching application The application is being launched.
-100 Default mode The bootloader has finished but no application was
Range -9999 to 9999
Access RO
second
transmitted or received.
The number of cyclic PDO messages that the active
EtherCAT is handling per second.
network communication is taking place. i.e. no
EtherCAT frames have been transmitted or received.
the file system to memory.
launched.
58 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 59

9.4 Drive trip display codes
If the SM-EtherCAT detects an error during operation, it will force a trip on the drive.
However, the trip code displayed on the drive will only indicate which slot initiated the
trip. The exact reason for the trip will be indicated in the SM-EtherCAT error code
parameter, Pr MM.50.
Table 9.9 shows the possible trip codes that will be displayed on the drive when a
problem is detected with SM-EtherCAT or when SM-EtherCAT initiates a trip.
Table 9.9 Drive trip display codes
Trip
Code
SLX.HF/
SL.HF
SLX.Er/
SL.Er
SLX.nF/
SL.nF
SLX.dF/
SL.dF
Fault
Hardware
Error Error trip generated by SM-EtherCAT
Not fitted
Different
module
fault
fitted
Description
The drive has detected that a Solutions Module is present, but is unable
to communicate with it. If this occurs, please contact your supplier or
local Control Techniques Drive Centre.
This trip will occur if a drive slot is configured for an option module, but
no module is fitted in the slot.
The slot configuration parameters stored in the drive are not valid SMEtherCAT configuration parameters. This trip will also occur when an
SM-EtherCAT is fitted to a previously un-used slot.
9.5 SM-EtherCAT module temperature
Table 9.10 SM-EtherCAT module temperature
SM-EtherCAT module temperature
Default N/A
Pr MM.44
This parameter shows the option module temperature reading in degrees celcius.
Range 0 - 255
Access RO
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting
Star ted
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
9.6 SM-EtherCAT serial number
Table 9.11 SM-EtherCAT serial number
SM-EtherCAT serial number
Default N/A
Pr MM.35
The serial number is loaded into the SM-EtherCAT during manufacture and cannot be
changed. It contains the last eight digits of the 10-digit serial number of the label.
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 59
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Range 0 - 16777215
Access RO
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Ter m s
Index
Page 60

9.7 SM-EtherCAT error codes
Table 9.12 SM-EtherCAT error codes
SM-EtherCAT error codes
Default N/A
Pr MM.50
If an error is detected during operation the module will force a trip on the drive and
update the error code parameter (Pr MM.50). Table 9.13 shows the SM-EtherCAT error
codes.
Table 9.13 SM-EtherCAT error codes
Error code Fault
1 No fieldbus mode has been selected.
2 Critical task over-run.
3 Invalid feedback source
4 Unknown drive type
5 Unsupported drive type
10 Invalid or missing application
62 Database initialisation error.
63 File system initialisation error.
64 Error initialising fieldbus stack.
74 The option module has overheated.
75 The drive is not responding.
76 The Modbus connection has timed out.
80 Inter-option communication failure.
81 Inter-option communication to slot 1 timeout.
82 Inter-option communication to slot 2 timeout.
83 Inter-option communication to slot 3 timeout.
84 Memory allocation error.
85 File system error.
86 Configuration file error.
98
99 Software fault.
Range 0 to 255
Access RO
The option module background task has not been
completed.
60 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 61

9.8 Critical task % free
Table 9.14 SM-EtherCAT critical task % free
SM-EtherCAT critical task % free
Default N/A
Pr MM.46
Range 0 to 100
Access RO
9.9 Worst case critical task % free
Table 9.15 Worst case critical task % free
SM-EtherCAT worst case critical task % free
Default N/A
Pr MM.47
Range 0 to 100
Access RO
Parameters Pr MM.46 and Pr MM.47 indicate how much of the cycle time allocated to
the critical task is remaining and available for other module tasks.
9.10 FLASH file system % free
Table 9.16 SM-EtherCAT FLASH file system % free
SM-EtherCAT FLASH file system % free
Default N/A
Pr MM.48
Range 0 to 100
Access RO
Indicates what percentage of the flash based file system is unused and still available.
9.11 Updating SM-EtherCAT firmware
The SM-EtherCAT firmware is available from your local Control Techniques Drive
Centre or supplier and can also be downloaded from CTSupport.com. To upload
firmware to the SM-EtherCAT module the use of Winflasher is required, this application
is also available from your local Control Techniques Drive Centre or supplier.
NOTE
NOTE
It is important that the filename of the SM-EtherCAT firmware application file is not
altered, doing so may result in problems with the firmware upload process.
It is strongly recommended that the latest firmware be used where possible to ensure
that all features are supported.
Information
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting
Star ted
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
Diagnostics
NOTE
The minimum Winflasher firmware version with SM-EtherCAT support is V03.07.00.
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 61
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Ter m s
Index
Page 62

10 Quick Reference
Table 10.1 and Table 10.2 list of all the SM-EtherCAT set-up objects and parameters
that are required to configure the module.
Table 10.1 SM-EtherCAT objects reference
Object Name Description Cross reference
0x10000
0
0x1018
0x1600
0x1601
0x1605
0x1621
0x1A00
0x1A01
0x1A02
0x1A05
0x1A21
0x1C00
0x1C10
0x1C11
0x1C12
0x1C13
0x2813
0x6040
0x6041
0x6042
0x6043
Device type
Identity object
Receive PDO
mapping 1
Receive PDO
mapping 2
Receive PDO
mapping 6
Receive PDO
mapping 22
Transmit PD O
mapping 1
Transmit PD O
mapping 2
Transmit PD O
mapping 3
Transmit PD O
mapping 6
Transmit PD O
mapping 22
Sync manager
communication
type
Sync manager 0
PDO
assignment
Sync manager 1
PDO
assignment
Sync manager 2
PDO
assignment
Sync manager 3
PDO
assignment
Network loss
behavior object
Controlword
Statusword
vl_target_velocity
vl_velocity
demand
Specifies the device profile being used
(DSP-402).
Contains SM-EtherCAT specific identity
information.
Contains the mapping information for
receive PDO mapping 1.
Contains the mapping information for
receive PDO mapping 2.
Contains the mapping information for
receive PDO mapping 6.
Contains the mapping information for
receive PDO mapping 22.
Contains the mapping information for
transmit PDO mapping 1.
Contains the mapping information for
transmit PDO mapping 2.
Contains the mapping information for
transmit PDO mapping 3.
Contains the mapping information for
transmit PDO mapping 6.
Contains the mapping information for
transmit PDO mapping 22.
This read-only object provides sync
manager usage details.
This read-only object contains
information relating to the non-cyclic
receive mailbox.
This read-only object contains
information relating to the non-cyclic
send mailbox.
Contains the currently in use receive
PDOs.
Contains the currently in use transmit
PDOs.
Used to configure the network loss trip
behavior (watchdog).
Provides the primary method of controlling the behavior of the drive.
This provides feedback about the current
operating state of the drive.
Used to set the required velocity of the
system.
Provides the instantaneous velocity
demand generated by the drive ramp
function.
Section 6.1.1 on page 20
Section 6.1.1 on page 20
Section 6.1.2 on page 21
Section 6.1.2 on page 21
Section 6.1.2 on page 21
Section 6.1.2 on page 21
Section 6.1.3 on page 23
Section 6.1.3 on page 23
Section 6.1.3 on page 23
Section 6.1.3 on page 23
Section 6.1.3 on page 23
Section 6.1.4 on page 26
Section 6.1.4 on page 26
Section 6.1.4 on page 26
Section 6.1.4 on page 26
Section 6.1.4 on page 26
Section 9.2.1 on page 57
Section 7.1 on page 28
Section 7.2 on page 29
Section 7.5.1 on page 41
Section 7.5.2 on page 42
62 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 63

Table 10.1 SM-EtherCAT objects reference
Object Name Description Cross reference
0x6044
0x6046
0x6047
0x6048
0x6049
0x604A
0x604B
0x605A
0x605B
0x605C
0x605E
0x6060
0x6061
0x6062
0x6064
0x6085
0x608F
0x6091
0x6092
0x60F4
0x60FB
vl_velocity_actual
value
vl_velocity_min
max_amount
vl_velocity_min
max
vl_velocity
acceleration
vl_velocity
deceleration
vl_velocity_quick
stop
vl_setpoint
factor
Quick_stop
option_code
Shutdown_option
code
Disable
operation_option
code
Fault_reaction
option_code
Modes_of
operation
Modes of opera-
tion display
Position_demand
value
Position_actual
value
Quick_stop
deceleration
Position_encoder
resolution
Gear_ratio This object is used to apply scaling. Section 7.3.11 on page 36
Feed_constant This is used to configure a feed constant. Section 7.3.12 on page 37
Following_error
actual_value
Position_control
parameter_set
object
Provides the velocity at the motor spindle or load.
This object is used to configure the minimum and maximum velocity.
This object is used to configure the minimum and maximum velocity.
This object is used to configure the delta
speed and delta time of the slope of the
acceleration ramp.
This object is used to configure the delta
speed and delta time of the slope of the
deceleration ramp.
This object is used to configure the delta
speed and delta time of the slope of the
deceleration ramp for quick stop.
This object is used to configure the
numerator and denominator of the
vl_setpoint_factor.
Specifies what action is performed in the
event of a quick stop function
Used to control what action is performed
if there is a transition from the Operation
Enabled state to the Ready To Switch On
state.
This object is used to control what action
is performed if there is a transition from
the Operation Enabled state to the
Switched On state.
This object is used to control what action
is performed when a fault is detected.
This object is used to request a change
in the mode of operation.
This read only object is used to provide
the active mode of operation.
Used to provide the currently demanded
position value.
This read only object provides the actual
value of the position feedback device.
This object is used to configure the
deceleration rate used to stop the motor
when the quickstop function is activated
and the quick stop code object (0x605A)
is set to 2 or 6.
This read only object indicates the configured encoder increments per number
of motor revolutions.
This read only object provides the actual
value of the following error.
Used to configure the positional control
gains.
Section 7.5.3 on page 42
Section 7.5.4 on page 42
Section 7.5.5 on page 43
Section 7.5.6 on page 43
Section 7.5.7 on page 44
Section 7.5.8 on page 44
Section 7.5.9 on page 45
Section 7.3.2 on page 33
Section 7.3.3 on page 34
Section 7.3.4 on page 34
Section 7.3.5 on page 34
Section 7.3.6 on page 35
Section 7.3.7 on page 35
Section 7.3.14 on page 38
Section 7.3.15 on page 38
Section 7.3.8 on page 35
Section 7.3.10 on page 36
Section 7.3.16 on page 38
Section 7.3.17 on page 39
Information
Installation
Installation
Star ted
support
features
Reference
Ter m s
Safety
Introduction
Mechanical
Electrical
Getting
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
Advanced
Diagnostics
Quick
Glossary Of
Index
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 63
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Page 64

Table 10.1 SM-EtherCAT objects reference
Object Name Description Cross reference
0x60C0
0x60C1
0x60C2
Interpolation
sub-mode_select
Interpolation
data_record
Interpolation
time_period
Specifies the interpolation type. Section 7.4.1 on page 39
This object is used to specify the target
position.
The number of time units between interpolator re-starts.
Section 7.4.2 on page 40
Section 7.4.3 on page 40
Table 10.2 SM-EtherCAT parameter reference
Object Description Default Range Cross reference
Pr MM.01
Pr MM.02
Pr MM.06
Pr MM.32
Pr MM.35
Pr MM.44
Pr MM.46
Pr MM.47
Pr MM.48
Pr MM.50
Pr MM.51
SM-EtherCAT
module ID code
SM-EtherCAT
firmware - major
version
SM-EtherCAT
operating status
SM-EtherCAT re-
initialise
SM-EtherCAT
serial number
SM-EtherCAT
module
temperature
Critical task %
free
Worst case criti-
cal task % free
Flash file
system % free
SM-EtherCAT
error code
SM-EtherCAT
firmware - minor
version
421 --- Section 9.1.1 on page 56
N/A 00.00 to 99.99 Section 9.1.2 on page 56
N/A -9999 to 9999 Section 9.3 on page 58
0 (OFF) 0 (OFF) to 1 (ON) Section 5.4 on page 18
N/A 0 - 16777215 Section 9.6 on page 59
N/A 0 - 255 Section 9.5 on page 59
N/A 0 to 100 Section 9.8 on page 61
N/A 0 to 100 Section 9.9 on page 61
N/A 0 to 100 Section 9.10 on page 61
N/A 0 to 255 Section 9.7 on page 60
N/A 0 to 99 Section 9.1.2 on page 56
64 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 65

11 Glossary Of Terms
Information
Safety
Address: This is the unique network identification given to a networked device to allow
communication on a network. When a device sends or receives data the address is
used to determine the source and the destination of the message.
Bit: A binary digit, this may have the value of 1 or 0.
Byte: A collection of eight binary digits that collectively store a value. This may be
signed or unsigned.
Control word: A collection of binary digits that are used to control the drive. Features
typically include directional controls, run controls and other similar functions.
Cyclic: Data that is transmitted at regular intervals over the network.
Data rate: Determines the communication speed of the network, the higher the value
the more data can be sent across the network in the same time period.
Device: A piece of equipment connected to a network, this may be any type of
equipment including repeaters, hubs, masters or slaves.
Double word: A 32-bit word, this may be signed or unsigned.
Earthing / Grounding: Describes the electrical safety or shielding connections for the
module.
LED: Light emmiting diode.
Long word: A 32-bit data word that may be signed or unsigned.
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting
Star ted
Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Advanced
features
LSB: Least significant bit/byte.
MSB: Most significant bit/byte.
Node: A device on the network. This may be either a device such as a drive or part of
the network such as a repeater.
Non-cyclic data: Data that is requested or sent as required and not on a regular basis.
Octet: A collection of eight binary digits which form a byte.
PC: Personal computer.
PLC: Programmable logic controller.
Poll rate: The rate at which cyclic data is sent and received on the network.
Polled data: See Cyclic data.
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 65
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Diagnostics
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Ter ms
Index
Page 66

Scan rate: See Poll rate.
Screening: A connection to provide additional immunity to noise used on a network
cable.
Shielding: A connection to provide additional immunity to noise used on a network
cable.
Status word: A value that denotes the status of the drive. Each bit within the word will
have a specific meaning.
Word: A collection of sixteen binary digits.
66 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 67

Index
Information
Safety
A
Address ......................................................................................................65
Adjusting parameters ...................................................................................6
B
Bit ...............................................................................................................65
Byte ............................................................................................................65
C
Control word ...............................................................................................65
Cyclic data ..................................................................................................65
D
Data rate ..................................................................................................... 65
Device ........................................................................................................65
Diagnostics .................................................................................................56
Domain .......................................................................................................65
E
Earthing ......................................................................................................65
Electrical installation ...................................................................................11
Electrical safety ............................................................................................5
F
Functional blocks ........................................................................................19
G
Getting started ............................................................................................13
Glossary of terms .......................................................................................65
H
Homing mode .............................................................................................47
I
Index ...........................................................................................................67
Introduction ...................................................................................................8
L
Long word ................................................................................................... 65
LSB .............................................................................................................65
M
Mechanical installation ...............................................................................10
MSB ............................................................................................................65
N
Node ...........................................................................................................65
Non-cyclic data ...........................................................................................65
O
Octet ...........................................................................................................65
Introduction
Mechanical
Installation
Installation
Electrical
Getting Started Protocols
Drive profile (DSP-402)
support
Diagnostics
Advanced
features
Reference
Quick
Glossary Of
Te rm s
Index
SM-EtherCAT User Guide 67
Issue Number: 2 www.controltechniques.com
Page 68

P
PC ..............................................................................................................65
PLC ............................................................................................................65
Poll rate ......................................................................................................65
Q
Quick Reference ......................................................................................... 62
S
Safety considerations ...................................................................................7
Safety information ........................................................................................5
SECURE DISABLE ......................................................................................5
Status word ................................................................................................66
W
Word ...........................................................................................................66
68 SM-EtherCAT User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 2
Page 69

Page 70

0471-0128-02
 Loading...
Loading...