Page 1

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
EL-O-Matic F-Series
Rack and Pinion Pneumatic Actuators
EL Matic
TM
EL Matic
TM
Page 2

Page 3

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Table of Contents
September 2017
I
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Section 1: Before You Start
1.1 Installation, Operation and Maintenance Reference Documents .................... 1
1.2 Warehouse Storage ....................................................................................... 1
1.3 On-Site Storage ............................................................................................. 2
Section 2: Introduction
2.1 Identication ................................................................................................. 3
2.2 Intended Use .................................................................................................5
2.3 Specications ................................................................................................ 5
Section 3: Configuration Code
Section 4: Installation
4.1 Before You Start ............................................................................................ 9
4.2 Actuator Rotation Direction .......................................................................... 9
4.2.1 Valve Rotation .................................................................................... 9
4.2.2 Position After Failure ........................................................................ 10
4.3 Principles of Operation ................................................................................ 10
4.3.1 Solenoid Valve .................................................................................. 10
4.3.2 Ingress Protection (IP) rating ............................................................ 11
4.3.3 Double-Acting Actuators .................................................................. 12
4.3.4 Spring-Return Actuators ................................................................... 13
4.4 Actuator Assembly Codes ........................................................................... 14
4.5 Actuator to Valve Installation ...................................................................... 15
4.6 Mounting of control and feedback accessories ............................................ 18
4.7 Recommended Tubing Sizes ........................................................................ 18
Section 5: Mechanical Stroke Adjustment
5.1 Travel Stop Adjustment ............................................................................... 20
5.1.1 Double-Acting Actuators .................................................................. 20
5.1.2 Spring-Return Actuators ................................................................... 20
5.1.3 Angular Displacement ...................................................................... 21
Section 6: Maintenance
6.1 Normal Maintenance ................................................................................... 22
6.2 Inspection and Repair .................................................................................. 23
6.2.1 Service Kits ....................................................................................... 23
6.2.2 Spring-Return Actuator .................................................................... 23
Section 7: Decommission (Out of Service)
7.1 Before You Start .......................................................................................... 24
7.2 Removing the actuator from the valve ........................................................ 25
Page 4

II
Table of Contents
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Table of Contents
Section 8: Disassembly
8.1 Removing End Caps (Sizes 25 to 600) .......................................................... 27
8.2 Removing End Caps (Sizes 950 to 4000) ...................................................... 29
8.3 Removing Spring Cartridges or Springs ....................................................... 30
8.4 Removing of Limit Stop screws .................................................................... 31
8.5 Removing Pistons ........................................................................................31
8.6 Removing pinion ......................................................................................... 32
8.7 Cleaning the Components .......................................................................... 33
Section 9: Reassembly
9.1 Grease Instructions ..................................................................................... 35
9.2 Reassembly of the pinion ............................................................................ 36
9.3 Reassembly of the pistons ........................................................................... 37
9.4 Reassembly and settings of the limit stops ..................................................39
9.5 Reassembly of the end caps ......................................................................... 40
9.5.1 Double-Acting actuators .................................................................. 40
9.5.2 Spring-Return actuators (Size 25 to 600) .......................................... 41
9.5.3 Spring-Return actuators - Size 950 to 4000....................................... 43
9.6 Basic function and Air Leak Test ................................................................... 45
Section 10: Troubleshooting
10.1 Mechanical Problems .................................................................................. 46
10.2 Pneumatic Problems ................................................................................... 46
10.3 Electrical Problems ...................................................................................... 48
Section 11: Parts List and Spare Parts Recommendations
11.1 Actuator size F12.........................................................................................49
11.2 Actuator sizes F25 to F600 ..........................................................................50
11.3 Actuator sizes F950 to F2500 ......................................................................51
11.4 Actuator sizes F4000 ................................................................................... 52
Appendix A: Spring load removal
A.1 Spring load relief ......................................................................................... 53
Appendix B: Tool & Torque Table
Appendix C: Full Stroke Adjustment Option
C.1 Full Stroke Adjustment Option .................................................................... 57
C.2 Convert a standard actuator into a Full Stroke Adjustment version .............. 58
C.2.1 Procedure ........................................................................................ 59
C.3 Full Stroke Adjustment Setting .................................................................... 60
C.3.1 Factory Setting Procedure ................................................................ 60
C.3.2 Setting the Full Stroke Adjustment screw to the required angle. ....... 61
Page 5

Before You Start
Section: 1 Before You Start
This section explains:
• Base safety procedures.
• Where to nd detailed information relating safety.
• Storage guidelines.
Installation, adjustment, putting into service, use, assembly, disassembly and maintenance
of the pneumatic actuator must be performed by qualied personnel.
NOTICE
Failure to follow the above guidelines will void warranty.
WARNING
Actuator must be isolated both pneumatically and electrically before any (dis)assembly
starts. Before mounting or (dis)assembly, the actuator consult the relevant sections of this
manual.
1.1 Installation, Operation and Maintenance
Reference Documents
Before you start, read the following documents:
• All chapters in this manual.
• Safety Guide (Document No. DOC.SG.EF.EN).
For Safety Instrumented Systems application, read the following document:
• SIL Safety Manual EL-O-Matic F-Series (Document No. DOC.SILM.EF.EN).
NOTICE
Failure to read the Safety Guide will void the warranty.
Not following the instructions of the Safety Guide can lead to failure of the product and
harm to personnel or equipment.
1.2 Warehouse Storage
• All actuators should be stored in a clean, dry warehouse, free from excessive vibra-
tion and rapid temperature changes.
• All actuators should not be stored directly to the oor surface - it must be placed in
racks/shelves or use a pallet.
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
1
Section 1: Before You Start
Page 6
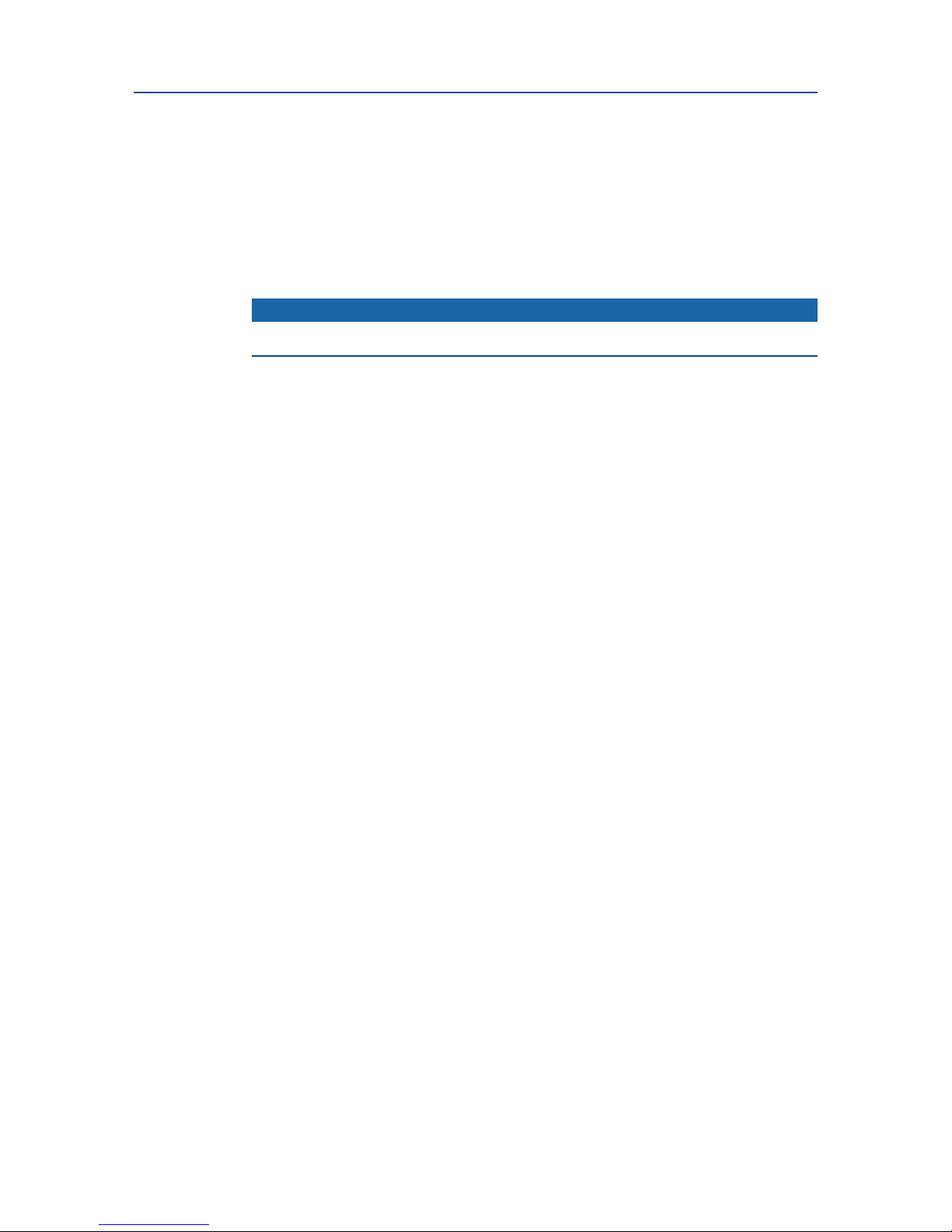
Before You Start
2
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 1: Before You Start
1.3 On-Site Storage
• All actuators should be stored in a clean, dry warehouse, free from excessive vibra-
tion and rapid temperature changes.
• Prevent moisture or dirt from entering the actuator. Plug or seal both air connec-
tion ports.
NOTICE
Failure to follow the above guidelines (Warehouse and On Site Storages) will void warranty.
Page 7

Introduction
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
3
Section 2: Introduction
Section: 2 Introduction
This section explains:
• How to identify the received product.
• The intended use of the product.
• Construction details.
• Actuator specications.
2.1 Identification
The EL-O-Matic F-Series Rack and Pinion actuators are available as double-acting or springreturn versions. 13 models are available, ranging from 12 Nm to 4000 Nm (106 to 35000
lbf.in) nominal torque output.
The EL-O-Matic F-Series uses standardized interfaces for solenoid, switchbox or positioner
mounting (VDI/VDE3845; NAMUR). The valve interface is equipped with an insert in the
pinion bottom that allows both ISO5211 or DIN3337 mounting.
The springs in the spring-return version allow a fail action in case of loss of air supply
pressure (Fail-to-Close or Fail-to-Open).
As from size FD150 double-acting versions have at end caps to reduce actuator length
and internal air volume.
Page 8
Introduction
12
25 100
150 -
600
4000
Size End cap design
5
Spring design
6
Pinion bottom /
Insert design
2
950 -
2500
SR
Maximum 2
loose springs
Maximum 12
spring cartridges
Maximum 6
loose springs
Left
Right
Left Right
Left Right
Left Right
DA
SR DA
SR DA
SR DA
SR DA
Maximum 12
spring cartridges
Maximum 6
loose springs
or
Left Right
Notes
1. Top auxilliaries and Solenoid interface (VDI/VDE 3845; NAMUR) for size 25 to 4000.
Size 12 has propriatary interface for top auxilliaries and solenoid mounting.
2. Valve interface availalable according ISO5211 or DIN 3337. Actuator size 12 is fitted with a parallel or
diagonal square. Actuator sizes 25 to 2500 can be fitted with drive inserts with various inner shapes.
Actuator size 4000 is fitted with a double square; parallel and diagonal.
3. Spring-Return actuators: - with springs
4. Double-Acting actuators: - no springs
5. Actuator sizes 25 to 100 have high end caps for double -acting and spring-return models. Actuator sizes
12 and 150 to 4000 have low end caps for double-acting models and high end caps for spring-return
models.
6. Actuator size 12 is fitted with a maximum of 2 loose springs. Actuator sizes 25 to 600 are fitted with a
maximum of 12 spring cartridges. Actuator sizes 950 to 4000 are fitted with a maximum of 6 loose
springs.
2
1
3
4
4
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 2: Introduction
Figure 1 Identification
Page 9

Introduction
2.2 Intended Use
The EL-O-Matic F Rack and Pinion actuators are intended for the automation and operation
of quarter-turn valves like Buttery, Ball and Plug valves.
Rack and Pinion actuators can also be used to operate dampers or any other quarter-turn
applications.
2.3 Specifications
Table 1. Pressure Range
Actuator Type Pressure
Double-Acting 0.2 to 8.3 barg (2.9 to 120 psig)
Spring-Return
6 to 8.3 barg (87 to 120 psig), with maximum spring set
3 to 8.3 barg (43.5 to 120 psig), reduced spring quantity
Table 2. Operating Media
Actuator Type Operating Media
Double-Acting and Single-Acting
Air, dry or lubricated and inert gases
Dew point at least 10K below ambient temperature
For sub-zero applications, take appropriate measures
Mentioned pressure levels are "gauge pressures".
Gauge pressure is equal to absolute pressure minus
atmospheric pressure.
1. Recommended air quality according ISO 8573-1 for normal operation: 7-5-4.
NOTE:
Use of lters, pressure regulators, lubricator and an oil/water separator mounted in the air
supply line, will allow a smooth and durable operation of the actuator.
For lubricated supply air, it is recommended to use a non-detergent oil without aggressive
additives, VG32, group 2 (ISO 3448).
Table 3. Temperature Range
Actuator Type Temperature
Standard -20°C to +80°C (-4°F to +176°F)
Option: Low Temperature -40°C to +80°C (-40°F to +176°F)
Option: High Temperature -10°C to +120°C (14°F to +248°F)
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
5
Section 2: Introduction
Page 10

Introduction
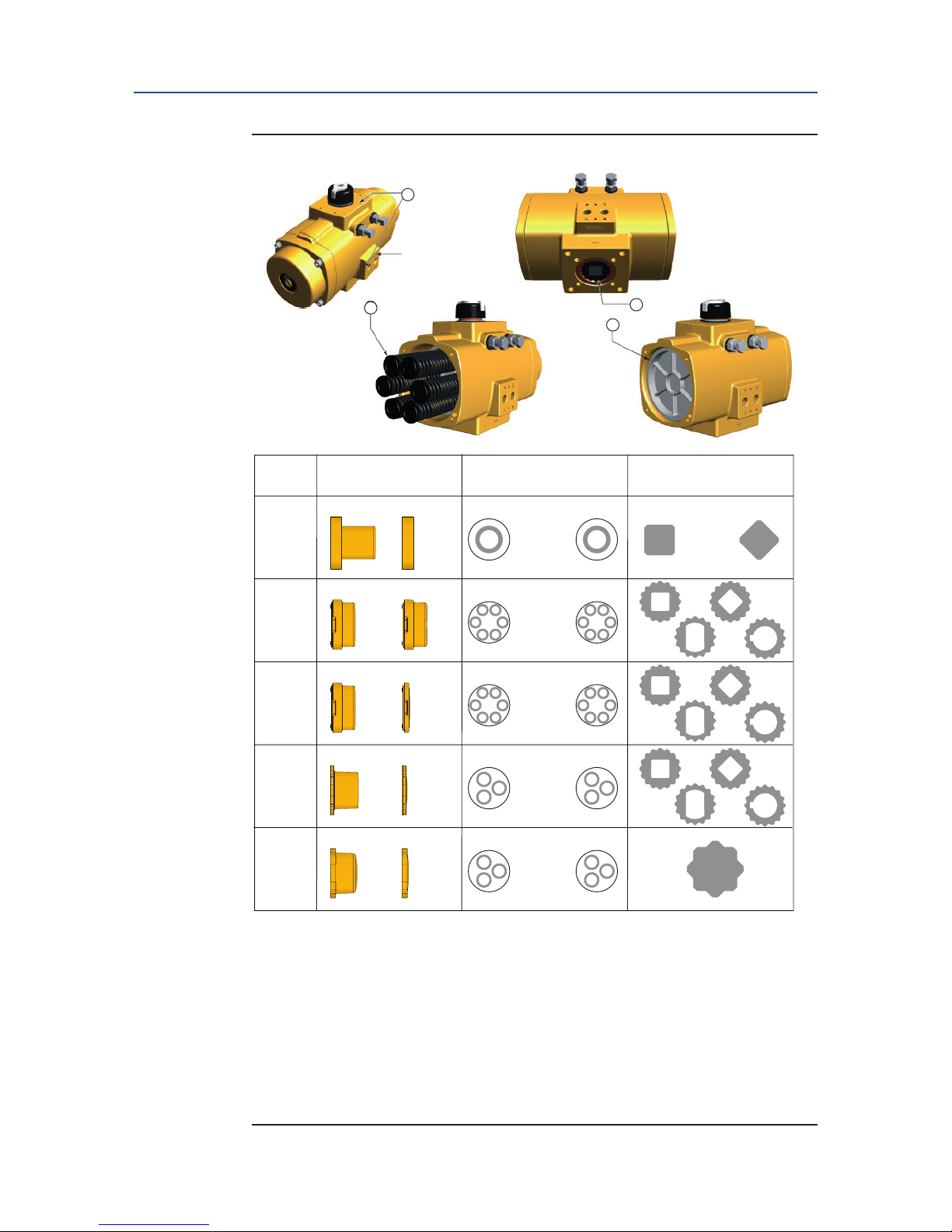
Table 4. Air Volumes and Consumption
Actuator volumes:
Consumption per stoke
(in liters, pressure in barg)
Actuator
size
Maximum volume (in liters) Outward Stroke Inward Stroke
Central
1
chamber
End cap
2
chamber
Displaced
3
volume
Double-Acting
and Spring-Return
Double-Acting only
2.0 barg 4.0 barg 8.0 barg 2.0 barg 4.0 barg 8.0 barg
12
0.05 0.06 0.04 0.14 0.24 0.44 0.16 0.28 0.52
25 0.11 0.19 0.08 0.36 0.64 1.2 0.48 0.88 1.7
40
0.16 0.36 0.15 0.67 1.2 2.2 0.89 1.6 3.1
65 0.36 0.55 0.22 1.02 1.8 3.4 1.3 2.4 4.7
100 0.4 0.8 0.3 1.5 2.7 5.0 2.0 3.8 7.2
150
0.8 0.7 0.5 2.4 4.3 8.1 2.1 3.6 6.7
200
0.8 1.0 0.7 3.2 5.7 11 2.8 4.9 9.1
350 1.9 1.7 1.2 5.5 9.8 18 5.0 8.8 16
600 3.6 3.3 2.1 9.4 17 31 8.7 15 28
950 5.1 4.3 3.2 13 24 44 12 20 37
1600 7.8 7.0 5.2 21 37 68 19 33 62
2500
10.4 11.1 8.2 29 50 92 30 53 97
4000 18.4 18.9 14.0 51 88 161 52 89 165
Actuator volumes:
Consumption per stoke
(in Cu.in., pressure in psig)
Actuator
size
Maximum volume (Cu.in.) Outward Stroke Inward Stroke
Central
1
chamber
End cap
2
chamber
Displaced
3
volume
Double-Acting
and Spring-Return
Double-Acting only
40 psig 80 psig 120 psig 40 psig 80 psig 120 psig
12 3.1 3.7 2.5 11 19 28 13 23 33
25 6.4 11.8 4.7 28 52 75 38 72 106
40 10.0 22 8.9 53 96 140 71 133 196
65 22 34 13.5 81 148 215 107 200 294
100 22 50 19.9 118 216 314 165 310 455
150 48 43 32 192 352 512 163 293 424
200 50 59 44 255 466 676 220 397 573
350 118 103 76 436 796 1157 392 709 1025
600 222 201 129 742 1354 1967 683 1237 1790
950 310 260 193 1049 1905 2760 910 1628 2346
1600 477 430 319 1635 2951 4267 1505 2691 3877
2500 638 676 501 2259 4018 5776 2367 4232 6097
4000 1122 1151 853 3946 7040 10134 4027 7202 10377
1. For Double-Acting and Spring-Return. Pistons at 90° outward position.
2. Only for Double-Acting. Pistons at 0° inward position.
3. Stroke is 90°.
Figure 2 Actuator air volumes
A
B
Central air chamber volume
Double-Acting and Spring-Return
End cap air chamber volume
Double-Acting only
6
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 2: Introduction
Page 11

Configuration Code
Section: 3 Conguration Code
This section explains:
• How to create or read the conguration code for a actuator.
Typ e
FD Double Acting
FS Spring Return
Size
0012 Size 0012 0350 Size 0350
0025 Size 0025 0600 Size 0600
0040 Size 0040 0950 Size 0950
0065 Size 0065 1600 Size 1600
0100 Size 0100 2500 Size 2500
0150 Size 0150 4000 Size 4000
0200 Size 0200
Rotation angle
N 90° rotation angle
Threads
M Metric ISO 5211
U UNC/NPT/Imperial
Spring Set
00 Double Acting (no springs)
10 Spring Set 10 40 Spring Set 40
20 Spring Set 20 50 Spring Set 50
30 Spring Set 30 60 Spring Set 60
Rotation direction
CW Spring to Close/Clock Wise
CC Spring to Open/Counter Clock Wise
Pinion Material
AL High Grade Aluminium, Hard anodized
SS Stainless steel ASI 316 (+ A4-70 SS fasteners)
Valve Interface
(2
TN Standard ISO 5211 interface
SY Small interface with center plate (DIN3337)
LY Large interface with center plate (DIN3337)
Valve Stem Connection
Actuator
size
Square
Aluminum
Stainless
Steel
(4
Parallel
drive
Diagonal
drive
Star drive
No insert 000 Not applicable
0012 (39mm / 0.354" L09 D09 Q09
0025 11mm / 0.433" L11 D11 Q11
0040 &
0065
14mm / 0.551" L17 D14 Q14
0100
17mm / 0.669" D17 Q19
19mm / 0.748" L19
0150
17mm / 0.669" D17 Q22
19mm / 0.748" L19
0200 22mm / 0.866" L22 D22 Q22
0350
22mm / 0.866" D22 Q27
27mm / 1.063" L27
0600 27mm / 1.063" L27 D27 Q27
0950 36mm / 1.417" L36 D36 Q36
1600 &
2500
46mm / 1.811" L46 D46 Q46
4000 (355mm / 2.165" Q55 Q55 Q55
Temperature Range
S Standard: -20°C to +80°C (-4°F to +176°F)
H High: -10°C to +120°C (14°F to +248°F)
L Low: -40°C to +80°C (-40°F to +176°F)
G (6Standard: -20°C to +80°C (-4°F to +176°F) PED Group 1 Label
Visual Indication Code
K Standard (Knob)
N No Visual Indication
Finish
A Standard coating (EL-O-Matic Yellow)
G CSR Coating
Internal code 1
00 Standard
Miscellaneous options
XX Standard
H1 1/2" High Flow plate
P1 1/2" Porting according EN 15714-3 (only sizes 950-4000)
FS Full stroke adjustement
Notes:
See next page.
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
7
Section 3: Configuration Code
FS 0150 - N U 40 CW AL TN - NL19 S K A - 00 XX
Typ e
Size
Rotation angle
Threads
Spring set
Rotation
Pinion material
Valve interface
Miscellaneous options
Internal code 1
Color / nish
Visual indicator
Temperature
Valve stem connection
Page 12

Configuration Code
Notes:
1. The options, listed here, are all options available. Not all options apply to all con-
gurations.
2. Valve Interface: Size 0012 has no center plate option. Option "S"; Small Interface
with Center Plate (DIN3337) is not available for size 0025.
3. Size 0012 does not have inserts but has the inner square directly in the bottom of
the pinion.
Size 4000 does not have inserts but has two inner squares (diagonally and parallel
oriented) directly in the bottom of the pinion.
4. Actuators with stainless steel pinions do not have inserts but have two inner
squares (diagonally and parallel oriented aka "Star Drive") directly in the bottom of
the pinion.
5. Contact you local EL-O-Matic representative for additional insert options.
6. PED Group 1 Label only available up to size 950.
8
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 3: Configuration Code
Page 13

Installation
The valve is closed after
a clockwise rotation.
The valve is open after
a counterclockwise rotation.
Section: 4 Installation
This section explains:
• The actuator rotation direction.
• In which position the actuator will end after a failure.
• Principles of operation:
— Solenoid operation.
— Double acting and Spring return operation.
• Assembly codes.
• Actuator to valve assembly.
4.1 Before You Start
SAFETY
In case of an air or electrical failure, it is important to know the behavior of the actuator.
Before mounting the actuator on a valve, consult the following sections below.
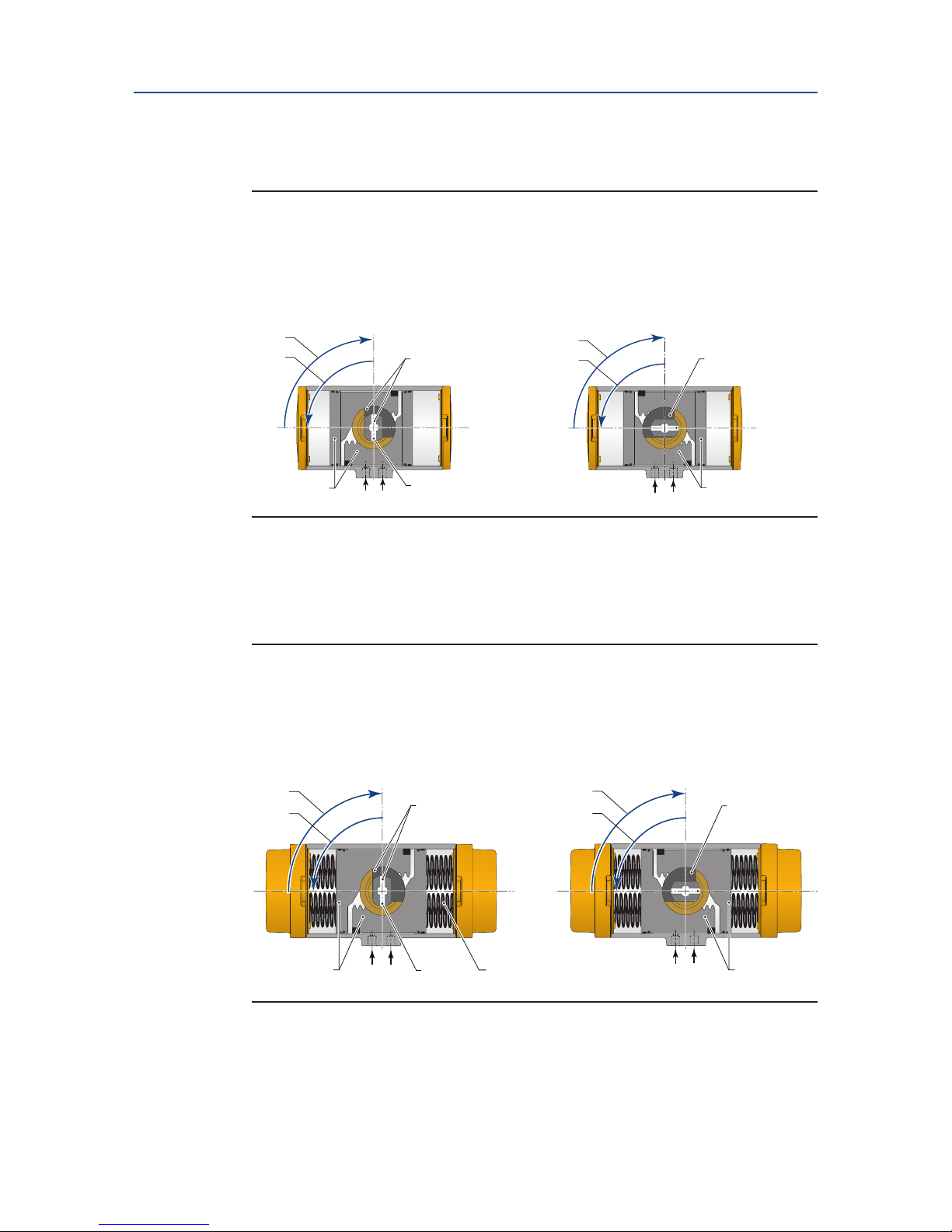
4.2 Actuator Rotation Direction
4.2.1 Valve Rotation
For the following paragraphs we assume that valves rotate as indicated in gure 3.
Figure 3 Normal valve rotation
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
9
Section 4: Installation
Page 14

Installation
4.2.2 Position After Failure
The position of the actuator after a failure depends on the:
1. Principle of operation (see paragraph 4.3)
2. Assembly codes (see paragraph 4.4)
3. Kind of failure. Refer to the table below.
Table 5. Position After Failure
Principle of
Operation
Assembly Code Kind of Failure Position
Double-Acting
Actuator
Pressure Not dened
Signal Closed
Supply Voltage Closed
Pressure Not dened
Signal Open
Supply Voltage Open
Single-Acting
(Spring-Return)
Actuator
Pressure Closed
Signal Closed
Supply Voltage Closed
Pressure Open
Signal Open
Supply Voltage Open
4.3 Principles of Operation
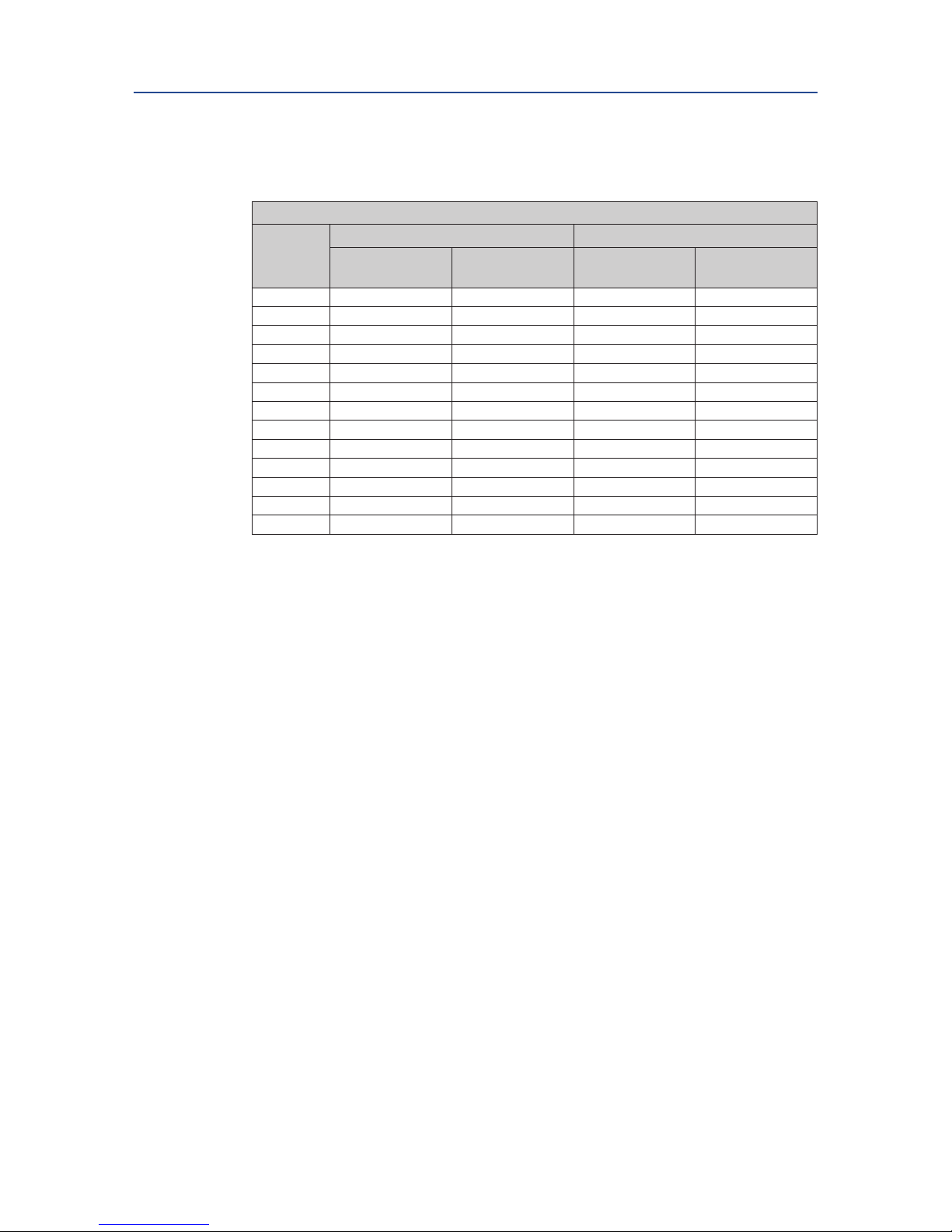
4.3.1 Solenoid Valve
All actuators can be either piped with solid or exible tubing with the solenoid valve
mounted remotely from the actuator or by mounting a VDI/VDE 3845 (NAMUR) designed
solenoid valve DIRECTLY onto the NAMUR mounting pad on the side of the actuator.
Figure 4 Typical solenoid operation
A
BA
Spring-Return Operation Double-Acting Operation
CW
CW
10
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 4: Installation
Page 15
Installation
The table below represents the cycle time (operating time) per different Actuator sizes:
Table 6. Operating Speed
Cycle time in seconds
Actuator
size
Spring-Return Double-Acting
A-port
pressurized
Spring
stroke
A-port
pressurized
B-port
pressurized
F 12 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4
F 25 0.5 0.4 0.5 0.4
F 40 0.6 0.5 0.6 0.5
F 65 0.7 0.5 0.6 0.6
F 100 0.8 0.6 0.8 0.7
F 150 1.0 0.8 0.9 0.8
F 200 1.3 0.9 1.0 1.0
F 350 1.9 1.3 1.4 1.5
F 600 3.2 1.9 2.2 2.2
F 950 6.6 2.2 2.4 2.0
F 1600 10.6 3.5 3.6 3.3
F 2500
16.9 5.7 5.8 5.2
F 4000 29.1 9.2 9.2 9.0
Operating time is average with actuator under load and solenoid valve tted.
Test conditions:
1. Solenoid with ow capacity: 0.6 m3/hr
2. Pipe diameter: 6mm
3. Medium: clean air
4. Supply pressure: 5.5 bar (80psi)
5. Load: with average load
6. Stroke: 90°
7. Temperature: Room temperature
4.3.2 Ingress Protection (IP) rating
EL-O-Matic F actuators are IP66/IP67 rated. In case of IP66 or IP67 requirements, take
precautions that comply with the IP66/IP67 requirements to prevent moisture or dust from
entering the actuator through the open air exhaust port(s), either directly on the actuator
or at the exhaust ports of the connected solenoid valve.
We recommend to connect tubing to the exhaust(s) and lead this into a dry and dust free
area, or to use check valves in the exhaust.
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
11
Section 4: Installation
Page 16
Installation
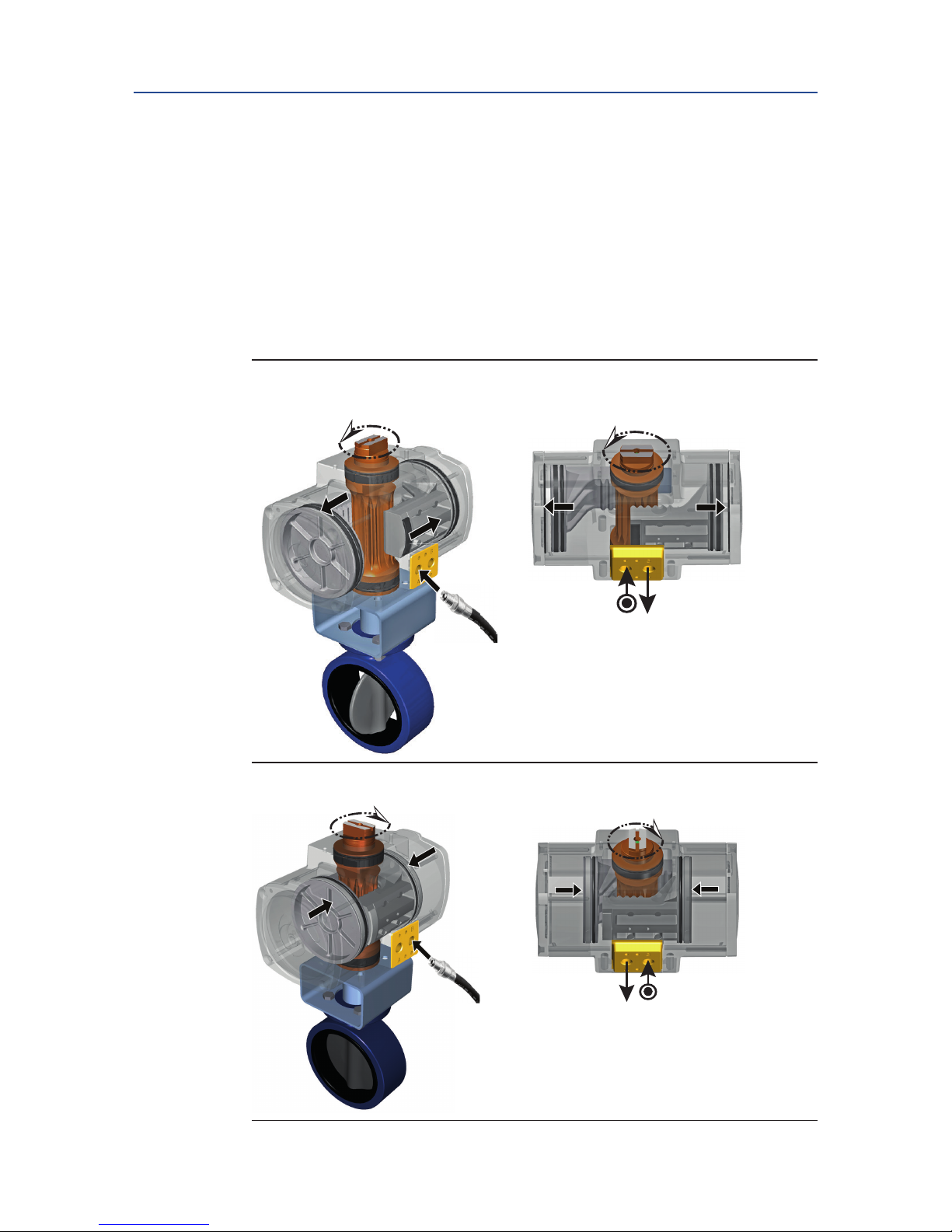
4.3.3 Double-Acting Actuators
The operating principle, as explained here, is applicable for actuators with assembly code
CW (direct acting).
• Applying supply pressure to port A will move the pistons outward to the "Open"
position of the valve.
• Applying supply pressure to port B will move the pistons inward to the "Close" posi-
tion of the valve.
• For assembly codes CC, the operating principle is reversed (reverse acting).
Figure 5 Double-Acting Operation
Outward Stroke
A
BA
Inward Stroke
A
B
B
12
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 4: Installation
Page 17

Installation
4.3.4 Spring-Return Actuators
The operating principle, as explained here, is applicable for actuators with assembly code
CW (direct acting).
• Applying supply pressure to port A will move the pistons outwards to the "Open"
position of the valve.
• Venting the supply pressure from port A will cause the springs to move the pistons
inwards to the "Close" position of the valve.
• For assembly codes CC, the operating principle is reversed (reverse acting).
Figure 6 Stroke Movements
Outward Stoke
A
A
B
Inward Stroke
B
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
13
Section 4: Installation
Page 18
Installation
4.4 Actuator Assembly Codes
Figure 7 Assembly Code - Double-Acting
Assembly code: CW Assembly code: CC
= Standard, Clockwise-to-Close rotation = Reverse, Counterclockwise-to-Open
= Fail-to-Close = Fail-to-Open
AB
A
B
A
B
A
B
Pinion and
cam position
Dot in
pinion slot
Default
pistons position
Reversed
pistons position
Pinion 90°
rotated
A = Rotation when central air chamber is pressurized.
B = Rotation when end cap air chambers are pressurized.
All views are from above. Pistons are shown in inward position.
Figure 8 Assembly Code - Spring-Return
Assembly code: CW Assembly code: CC
= Standard, Clockwise-to-Close rotation = Reverse, Counterclockwise-to-Open
= Fail-to-Close = Fail-to-Open
AB
A
B
A
BA
B
Pinion and
cam position
Dot in
pinion slot
Default
pistons position
Reversed
pistons position
Springs
Pinion 90°
rotated
14
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 4: Installation
Page 19

Installation
4.5 Actuator to Valve Installation
WARNING: MOVING PARTS
Actuator must be isolated pneumatically and electrically before any (dis)assembly starts.
Stay away from moving parts to prevent serious injuries. When test cycling the actuator
and valve assembly by applying pressure to the A or B port, be aware that there are moving
parts like pinion top, actuator to valve coupling and the valve- blade, ball, plug, etc.
NOTICE
The actuator is designed to be installed, commissioned and maintained using generic tools
like wrenches, Allen keys and screwdrivers. For the removal of inserts, a special extractor
tool can be supplied on request.
During assembly to the valve, do not hit with hammer on pinion top. This can damage the
pinion top washer and cause premature failure.
Before mounting the actuator on the valve or valve bracket, be sure that both the
actuator and the valve are in the same closed or open position.
Refer to appendix B, Tool and Torque tables, for using the right size tool.
Table 7. Tool Table
Symbol Tool Symbol Too l
Wrench – All types and sizes.
Metric and Imperial
Allen key
Circlip Pliers
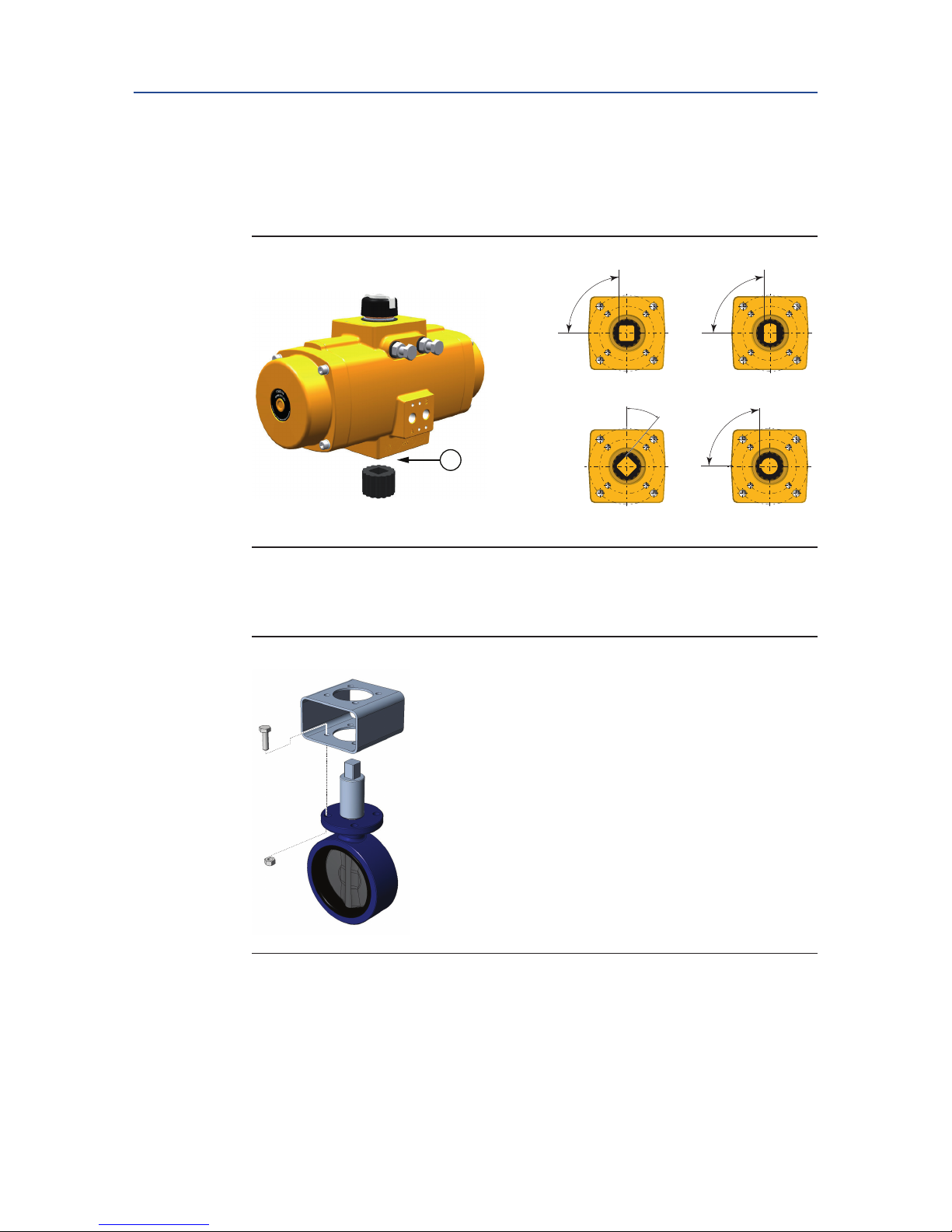
1. Remove handle nut, handle, lock washer, and etc. from the valve if required.
2. Visually check to make sure the valve is CLOSED.
Figure 9 Valve handle removal
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
15
Section 4: Installation
Page 20
Installation
3. When required, check if the insert drive (23) is mounted. If not, use a plastic mallet
and tap slightly until the reducer square is in the required position.
Be sure that the insert is mounted at 90° or 45°. It is possible to mount the insert
turned 22.5°. This way the valve will not open or close the right way.
Figure 10 Insert drive Installation
23
90°
45°
90°
90°
Parallel
square
Diagonal
square
Flat head
Round with
key way
4. Install the bracket to the valve ange. Tighten all bolts and nuts and apply the cor-
rect torque.
Figure 11 Bracket Installation
16
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 4: Installation
Page 21
Installation
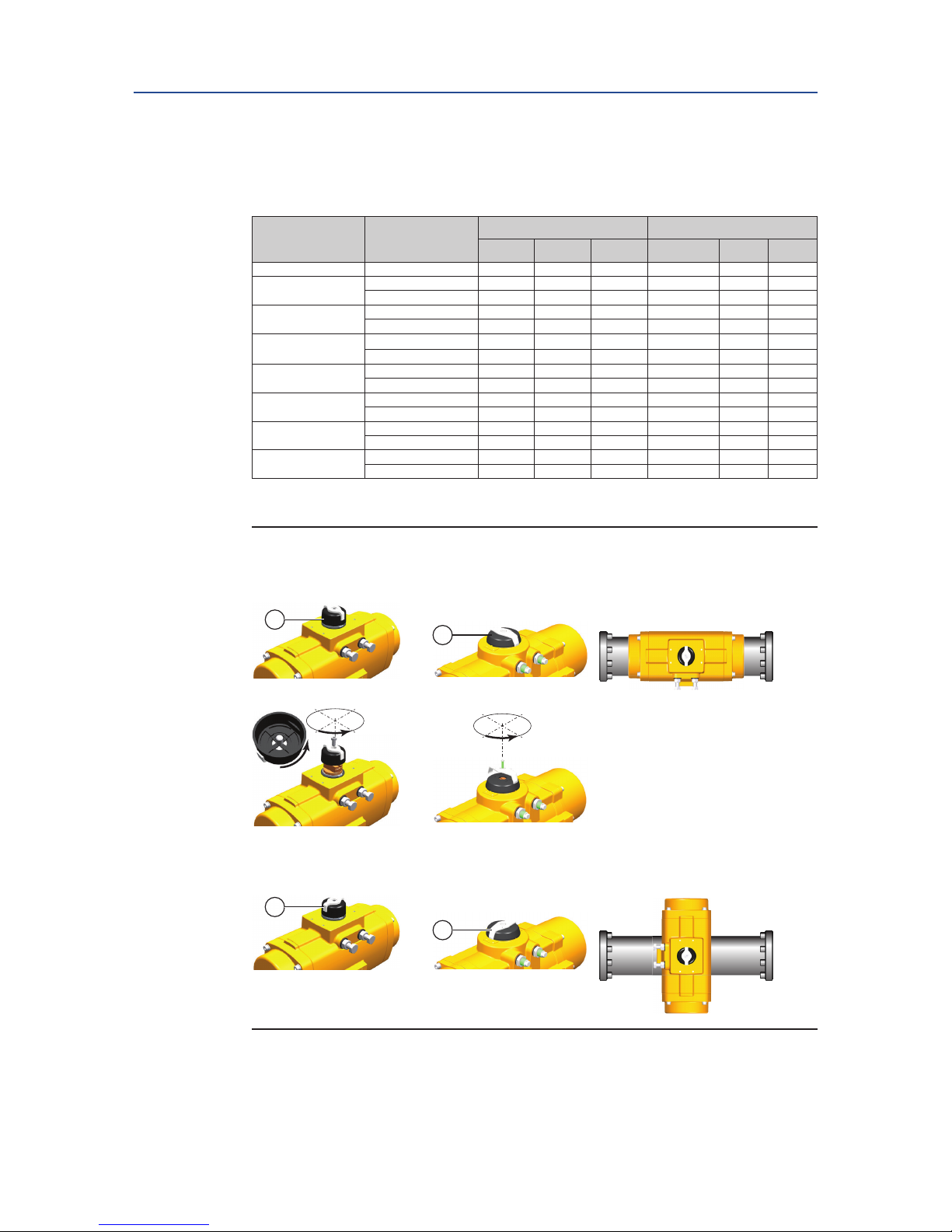
5. Install the actuator to the bracket. Tighten all bolts and apply the correct torque
(refer to Table 8).
Table 8. Bottom flange torque values
Actuator Size ISO Pattern
Torque (Nm) Torque (lbf.ft)
Thread Min. Max. Thread Min. Max.
12 F04 M6 4.5 5 10-24UNC 3.3 3.7
25
F03 inner pattern M5 2.0 3.0 10-24UNC 1.5 2.2
F05 outer pattern M6 4.5 5.0 1/4"-20 3.3 3.7
40, 65, 100
F05 inner pattern M6 4.5 5.0 1/4"-20 3.3 3.7
F07 outer pattern M8 10.5 12.5 5/16"-18 7.7 9.2
150, 200, 350
F07 inner pattern M8 10.5 12.5 5/16"-18 7.7 9.2
F10 outer pattern M10 21.0 24.5 3/8"-16 15.5 18.1
600
F10 inner pattern M10 21.0 24.5 3/8"-16 15.5 18.1
F12 outer pattern M12 34.5 43.0 1/2"-13 25.4 31.7
950
F10 inner pattern M10 21.0 24.5 3/8"-16 15.5 18.1
F14 outer pattern M16 90.0 104.0 5/8"-11 66.4 76.7
1600, 2500
F16 inner pattern M20 170.0 204.0 3/4"-10 125.4 150.5
F25* outer pattern 4x M16 90.0 104.0 4x 5/8"-11 66.4 76.7
4000
F16 inner pattern M20 170.0 204.0 3/4"-10 125.4 150.5
F25 outer pattern 8x M16 90.0 104.0 8x 5/8"-11 66.4 76.7
6. When required, mount or adjust the visual indicator (22).
Figure 12 Indicator mounting
Indicator mounting “In-line”
Indicator mounting “Across Line”
Size 12 - 350 Size 600 - 4000
21
21
90°
90°
90°
21
21
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
17
Section 4: Installation
Page 22

Installation
4.6 Mounting of control and feedback accessories
Solenoid valve and or switch boxes can now be mounted to the actuator. Check the
instructions as shipped with these components for installation, operating and maintenance
instructions.
We recommend to test-cycle the complete assembly to check correct operation.
4.7 Recommended Tubing Sizes
In case the solenoid valve is mounted remotely (i.e. in a central solenoid cabinet) and in
order to supply sufcient ow of air supply to the actuator, the following tubing sizes are
recommended.
Table 9. Tubing Sizes
Actuator size
Runs up to Runs over to
1.2 meters 4 feet 1.2 meters 4 feet
25, 40, 65 6 mm 1/4 inch 6 mm 1/4 inch
100, 150, 200,
350, 600
6 mm 1/4 inch 8 mm 5/16 inch
950, 1600, 2500,
4000
6 mm 1/4 inch 10 mm 3/8 inch
18
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 4: Installation
Page 23

Mechanical Stroke Adjustment
Section: 5 Mechanical Stroke Adjustment
This section explains:
• What mechanical stroke adjustment is.
• What the factory settings are.
• How to adjust the travel stops.
EL-O-Matic F actuator sizes 25 to 4000 have two stroke adjustment stops for adjusting
accurately the stroke of the actuator/valve assembly in open and closed position.
The smallest actuator, size F12, does not have limit stops.
The factory setting of the stroke is 90°. Most quarter-turn valve applications will not require
readjustment of these settings.
If required the stroke can be adjusted by means of two-stroke adjustment bolts.
Figure 13 Factory Setting
Closed
-3°10°
Open
80°
93°
Size 950 - 4000Size 25 - 600
90°
Limit Stop 2Limit Stop 1
Closed
-5°10°
Open
80°
95°
90°
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
19
Section 5: Mechanical Stroke Adjustment
Page 24

Mechanical Stroke Adjustment
5.1 Travel Stop Adjustment
CAUTION: PRESSURIZED ACTUATOR
Do not turn out the travel stops completely when the actuator is pressurized.
When adjusting the travel stops and the actuator is still pressurized, the travel stops can be
“shot” away when completely turned out.
5.1.1 Double-Acting Actuators
1. Operate valve/actuator assembly to the required "Closed" position.
2. Remove air supply.
3. Slacken locknut on the “closed” stop (2).
Figure 14
Stop 1
Stop 2
4. Turn the “closed” stop clockwise to reduce or counterclockwise to increase the
travel. Consult chapter 5.1.3 (angular displacement of the pinion), to dene how
far the limit stop must be turned in or out.
5. Tighten the lock nut.
6. Connect air and cycle the actuator to check that the position is correct.
If not repeat from 2.
7. Remove air supply.
8. For adjusting the open position repeat steps 1 to 7, but now for the open position
and “open” stop (1).
5.1.2 Spring-Return Actuators
1. Connect air supply to the A port. Actuator will move to the open position.
2. Slacken locknut (24) on the “closed” stop (2).
Figure 15
Stop 1
Stop 2
20
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 5: Mechanical Stroke Adjustment
Page 25

Mechanical Stroke Adjustment
3. Turn the “closed” stop clockwise to reduce or counterclockwise to increase the
travel. Consult chapter 5.1.3 (angular displacement of the pinion), to dene how
far the limit stop must be turned in or out.
4. Remove air supply. Actuator will move to the closed position.
5. Check whether the actuator valve assembly is in the required position.
If not repeat steps 1 to 5.
6. Remove air supply.
7. For adjusting the open position repeat steps 1 to 6, but now for the open position
and "open" stop (1).
Table 10. Limit stop dimensions
Actuator size Thread
Bolt Wrench Nut wrench
size (mm) size (mm)
25 M 6 10 10
40 M 8 13 13
65 M 10 17 (16)* 17 (16)*
100 M 10 17 (16)* 17 (16)*
150 M 10 17 (16)* 17 (16)*
200 M 12 19 (18)* 19 (18)*
350 M 16 24 24
600 M 20 30 30
950 M 22 12 32
1600 M 24 14 36
2500 M 27 17 41
4000 M 22 12 32
1. Default dimension according DIN933 standard.
2. Dimensions in brackets according ISO4017 standard.
3. Actuator size 12 is not available with limit stops.
5.1.3 Angular Displacement
Below table identies, per actuator size, what the angular displacement of the pinions is,
when using the limit stop screws.
— Turn the limit stop clockwise reduces the stroke.
— Turn the limit stop counterclockwise to increase the stroke.
Table 11. Angular Displacement limit stops
Actuator size
Turns for 5° adjustment of the pinion: 360° revolution of limit stop screw will adjust
F 12 Actuator size 12 is not available with limit stops
F 25 0.7 7.1°
F 40 0.8 6.3°
F 65 0.6 8.3°
F 100 0.7 7.1°
F 150 1.2 4.2°
F 200 1.0 5.0°
F 350 0.8 6.3°
F 600 0.8 6.3°
F 950 1.1 4.7°
F 1600 1.3 4.1°
F 2500 1.5 3.4°
F 4000 3.2 1.6°
NOTICE
In case of air leakage over the limit stop bolts, turn the lock nut of the limit stop bolts
tighter, until leakage stops.
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
21
Section 5: Mechanical Stroke Adjustment
Page 26

Maintenance
Section: 6 Maintenance
This section explains:
• When and how to do maintenance.
— Normal maintenance.
— Extraordinary maintenance.
• What to do when replacing springs.
• What the availability is of spare parts, action conversion kits and temperature
conversion kits.
WARNING
Actuator must be isolated pneumatically and electrically before any (dis)assembly starts.
Before mounting or (dis)assembling the actuator, consult the relevant sections of this manual.
6.1 Normal Maintenance
EL-O-Matic F actuators are designed to operate without maintenance for their normal
working life. Normal working life is 500,000 cycles* for sizes up to F1600 and 250,000 for
sizes F2500 and F4000.
For actuators with the optional low temperature silicon seals, we advise to replace these
seals after 250.000 cycles*.
NOTE:
*Cycles = one open stroke and one close stroke.
We recommend regular inspections to make certain that the actuator / valve assembly
operates smoothly and to check that there are no visible or audible defects. We advise to
perform the following checks upon each proof test interval complying with the rules and
regulations of the country of nal installation:
• Visually check the entire actuator as well as the control system (where foreseen).
• Ensure there are no leaks on the actuator parts under pressure.
• Check pneumatic connections for leaks. Tighten tube ttings as required.
• Check if manual override (where foreseen) is regular.
• Check if pneumatic lter cartridge (where foreseen) is sound and lter bowl
(where foreseen) has been cleaned properly.
• Check the setting of the relief valves (where foreseen).
• Verify that the power uid supply pressure value is within the required range.
• Remove built-up dust and dirt from all actuator surfaces.
22
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 6: Maintenance
Page 27

Maintenance
• Inspect actuator paint work for damages to ensure continued corrosion protection.
Touch-up as required in accordance with the applicable paint specication.
• Operate the Actuator/Valve assembly for 2 complete open/close cycles with com-
plete closing of the valve.
• Verify the correct performing of open – close operations (e.g. check locally,
or automatically via Logic solver, the correct movement of the actuator).
All actuators are supplied with sufcient lubrication for their normal working life.
If required, see Section 9.1 (Grease instructions) for the recommended grease.
For mounting the parts of the repair kit follow the instruction of the Decommission,
Disassembly and Reassembly chapters of this manual.
6.2 Inspection and Repair
Replacement of internal seals and bearings allows to you extend the normal working
life. Service kits, containing all necessary spare parts (like seals, bearings, grease and
instructions) can be obtained through authorized Emerson – Actuation Technologies
distributors.
6.2.1 Service Kits
All soft seals, bearings, and nonreusable parts are included in the recommended service
kit. The service kit is identical for both the double-acting and the spring-return models.
6.2.2 Spring-Return Actuator
For the spring-return models, we recommend a set of spare springs for each different
model in addition to the recommended spare parts kit.
On spring-return actuators, the spring cartridges can be replaced. SPRING CARTRIDGES
SHOULD ALWAYS BE REPLACED IN COMPLETE SETS. Spring kits are available through
authorized Emerson – Actuation Technologies distributors.
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
23
Section 6: Maintenance
Page 28

Decommission (Out of Service)
Section: 7 Decommission (Out of Service)
This section explains:
• How to decommission an actuator in a safe way.
7.1 Before You Start
WARNING: MOVING PARTS
Actuator must be isolated pneumatically and electrically before any (dis)assembly starts.
Before mounting or (dis)assembling the actuator consult the relevant sections of this manual.
Actuator can move when removing supply pressure and/or electrical control signal of
actuators. If not already there, a spring-return actuator will cycle to its fail position.
When removing any ball valve or plug valve assemblies from a pipe system, isolate the
piping system on which the Actuator is installed and relieve any media pressure that may
be trapped in the valve cavities before removing the actuator for maintenance.
A spring-return actuator mounted on a valve, which is stuck in mid stroke, contains a
high spring load which will cause a sudden rotation of the actuator versus the valve or
valve bracket during disassembly. This can cause serious injury to personnel or damage
to property.
Refer to Appendix A for instructions to safely remove the spring load before disassembling
the spring-return actuator from valve or bracket.
Important
Refer to the Safety Guide for Lifting Instructions.
24
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 7: Decommission (Out of Service)
Page 29

Decommission (Out of Service)
7.2 Removing the actuator from the valve
1. Disconnect all air supply hoses (Ports A and B or solenoid).
2. Disconnect all electrical wirings of the switch box.
3. Disconnect the electrical wiring of the solenoid valve.
4. Remove the bolts and nuts from the valve ange.
5. Remove the bracket from the actuator.
6. Remove the switch box and solenoid valve. Refer to the documentation of the
switch box and solenoid valve for safe disassembly.
Figure 16 Removing actuator from valve
1
3
2
4
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
25
Section 7: Decommission (Out of Service)
Page 30

Disassembly
Section: 8 Disassembly
This section explains:
• How to disassemble an actuator safely.
Tip
The instructions of this section can be used for maintenance or reconguration like spring
set change or maintenance.
Reference numbers for components refer to the exploded view in section 11.
In case of maintenance, discard all the used soft parts like O-ring seals, guide bands,
wear strips and circlip.
WARNING
Actuator must be isolated pneumatically and electrically before any (dis)assembly starts.
Before mounting or (dis)assembling the actuator consult the relevant sections of this manual.
CAUTION: SPRING FORCE
Spring-return actuators contain springs in a compressed state. Follow these instructions to
release the spring force safely.
The end caps of spring-return actuators sizes 25 to 600 should be free of the spring load
after 10 full turns (crosswise relaxing) of the end cap screws. If there is still spring load on
the end cap, this might indicate a broken spring cartridge. Stop this disassembly procedure
immediately. Continuing might cause the end cap to be “shot” away causing serious injury.
Spring return actuator size 950 to 4000 have long end cap screws to release the spring load
safely.
Refer to Appendix A for instructions to safely remove the spring load before disassembling
the end cap of a spring-return actuator with a broken spring cartridge.
NOTICE
The actuator is designed to be installed, commissioned and maintained using generic tools
like wrenches, Allen keys and screwdrivers.
Refer to the tables in this section or refer to appendix B Tool and Torque tables.
26
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 8: Disassembly
Page 31

Disassembly
8.1 Removing End Caps (Sizes 25 to 600)
1. For Double-acting actuators, do the following:
a. Remove the screws (8) and washers (10) of the end caps (6).
b. Remove the o-ring (11) and "B" port seal (2). Discard these parts.
Figure 17 Double-Acting End Caps Removal
2
6
8
6
11
6
5
10
8
10
11
2
Double acting end caps (6) are fitted with a white warning sticker. Spring return end
caps (5) are fitted with a black warning sticker.
The above end caps (5) are for actuator sizes 25, 40, 65 and 100.
End caps (6) for double acting actuator sizes 150 and larger will have flat end caps.
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
27
Section 8: Disassembly
Page 32

Disassembly
2. For Spring-return actuators, do the following:
a. Tip: For actuators with assembly code CW, turn back the right hand limit
stop screw (30) 2 full turns.
For actuators with assembly code CC, turn back the left hand limit stop
screw (30) 2 full turns.
This will lower the spring force on the end cap and reduces the screw out
length of the end cap screws.
b. Uniformly loosen the screws (9) of the end caps (5) 1/4-1/2 turns at a
time, in sequence, as per gure 18, to relieve the pre-load of the springs.
c. Remove the o-rings (11) and "B" port seals (2). Discard these parts.
Figure 18 Spring-Return End Caps Removal
3
1
4
5
11
2
30
5
9
11
10
2
9
10
2
28
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 8: Disassembly
Page 33

Disassembly
8.2 Removing End Caps (Sizes 950 to 4000)
1. For Double-acting actuators, do the following:
a. Remove the screws (8) and washers (10) of the end caps (6).
b. Remove the o-ring (11) and "B" port seal (2). Discard these parts.
Figure 19 Double-Acting End Caps Removal sizes 950 to 4000
6
2
11
6
8
10
8
10
2
11
2. For Spring-return actuators, do the following:
a. Tip: For actuators with assembly code CW, turn back the right hand limit
stop screw (30) 2 full turns.
For actuators with assembly code CC, turn back the left hand limit stop
screw (30) 2 full turns.
This will lower the spring force on the end cap and reduces the screw out
length of the end cap screws.
b. Uniformly loosen the screws (9) of the end caps (5) 1/4-1/2 turns at a
time, in sequence, as per gure 18, to relieve the pre-load of the springs.
c. Remove the o-rings (11) and "B" port seals (2). Discard these parts.
Figure 20 Spring-Return End Caps Removal sizes 950 to 4000
5
30
5
1
2
3
4
5
6
9
10
9
10
11
2
2
11
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
29
Section 8: Disassembly
Page 34

Disassembly
8.3 Removing Spring Cartridges or Springs
1. Remove the spring cartridges or springs (7).
Figure 21 Removing Spring Cartridges size 25 to 600
7
7
Figure 22 Removing Springs size 950 to 4000
7
7
30
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 8: Disassembly
Page 35

Disassembly
8.4 Removing of Limit Stop screws
1. Remove the limit stop screws (30), limit stop nuts (31), limit stop washers (32) and
limit stop o-rings (33). Discard the o-rings.
Figure 23 Limit Stop Removal
33 30
31
32
8.5 Removing Pistons
1. Use a wrench and turn the pinion counterclockwise until the pistons (14) come out
of the body.
2. Remove the piston bearings (15), piston rack bearing strips (17) and piston o-ring
seals (16). Discard these parts.
Figure 24 Removing Pistons
17
14
16
15
15
16
17
14
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
31
Section 8: Disassembly
Page 36

Disassembly
8.6 Removing pinion
1. Remove the circlip (27) and thrust bearing (23) on top of the pinion assembly.
For sizes 950 to 4000 remove also the top pinion bearing (19).
2. Remove the pinion (18) by pushing it downwards. For Size 4000, remove the
backup ring (29), O-ring pinion top (21) the cam (24) and cam thrust washer (25)
through the main bore of the housing.
3. Remove the pinion O-ring seals (21/22) and the pinion bearings (19/20).
For Size 950 to 2500, remove also the backup ring (29).
4. Discard all of these parts.
Figure 25 Pinion Removal
27
23
27
23
Sizes 950, 1600, and 2500
Sizes 25 to 600
Size 4000
19
21
19
21
18
18
27
23
19
29 19
18
19
22
22
29 25
24
21
20
20
21
Table 12. Recommended circlip pliers according DIN 5254 (or equal) for shaft circlips.
Actuator
size
Pinion top
diameter
Pliers according
DIN 5254
Actuator
size
Pinion top
diameter
Pliers according
DIN 5254
12 16 mm 0.630" A1 950 65 mm 2.559 A3
25 - 100 22 mm 0.866" A2 1600 75 mm 2.953 A3
150 - 350 36 mm 1.417" A3 2500 95 mm 3.74 A4
600 55 mm 2.165" A3 4000 96 mm 3.78 A4
32
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 8: Disassembly
Page 37

Disassembly
8.7 Cleaning the Components
In case of maintenance, use a clean dry cloth and thoroughly wipe clean and remove old
grease from:
• The inside and outside of the body including thread holes and crevices/grooves
• The pinion gears.
• The pistons.
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
33
Section 8: Disassembly
Page 38

Reassembly
Section: 9 Reassembly
This section explains:
• Which parts and how to grease them.
• How to reassemble a complete actuator.
• How to set the stroke adjustment bolts after reassembly.
• How to do a basic function and air leak test.
Tip
The instructions of this section can be used for maintenance or reconguration like spring
set change or maintenance.
Reference numbers for components refer to the exploded view in section 11.
In case of maintenance, discard all used soft parts like O-ring seals, guide bands and wear
strips and circlip and replace them with the parts as supplied in the repair kit.
In case of reconguration replace the parts as supplied in the conversion kit
(see also chapter 6).
Refer to the Safety Guide for Lifting Instructions.
NOTICE
The actuator is designed to be installed, commissioned and maintained using generic tools
like wrenches, Allen keys and screwdrivers.
Refer to the tables in this section or refer to Appendix B Tool and Torque tables.
34
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 9: Reassembly
Page 39

Reassembly
9.1 Grease Instructions
Check the product coding on the product labels and chapter 3 of this manual, to dene
which type of grease to use.
- For standard actuators (-20°C to +80°C / -4°F to +176°F):
Castrol High Temperature grease (or equivalent).
- For low temperature operation (-40°C to +80°C / -40°F to +176°F):
Castrol Optitemp TT1 or LG2 grease (or equivalent).
- For high temperature operation (-10°C to +120°C / 14°F to +248°F):
Castrol High Temperature grease (or equivalent).
We recommend using a suitable sized paint brush to apply the required amount of grease
on the parts as per Table 12 and Figure 23.
Table 13. Grease Instructions
Part Section of part Amount of grease
O-rings: A Completely Light lm
Housing Parts:
B Piston bore Light lm
C Top pinion bore Light lm
D Bottom pinion bore Light lm
Piston Parts:
E O-ring & bearing groove Light lm
F Rack teeth Half the teeth depth full with grease
G Piston bearing Light lm on outside
H Piston rack bearing strip Light lm
Piston Parts:
J Pinion bottom & O-ring groove Light lm
K Pinion top & O-ring groove Light lm
L Gear teeth Half the teeth depth
M Pinion top bearing Light lm (inside and out)
N Pinion bottom bearing Light lm (inside and out)
Figure 26 Grease Instructions
A
E
F
G
H
C
A
K
J
M
L
A
A
A
A
B
N
D
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
35
Section 9: Reassembly
Page 40

Reassembly
9.2 Reassembly of the pinion
1. Grease the pinion parts according to chapter 9.1.
2. Install the pinion bearings (19/20) and the O-ring seals (21/22) on the pinion (18).
For Size 950 to 2500, install also the the backup ring (29).
3. Insert the pinion (18) in the housing. For size 4000: mount rst the cam (24), cam
thrust washer (25), pinion top O-ring (21) and backup ring (29) through the mainbore onto the pinion (18).
4. For sizes 950 to 4000 install rst the top pinion bearing (19). For all sizes, install
the thrust washer (23) and mount the circlip (27) on the pinion top.
— Install the new circlip onto its mating groove on the top shaft extension
and with the non-sharp edge (2) towards the housing and the sharp edge
(1) towards the top of the shaft.
Figure 27 Reassemble the pinion
27
23
23
27
Sizes 950, 1600, and 2500
Sizes 25 to 600
Size 4000
19
21
19
21
18
18
27
23
19
29 19
18
19
2221
22
29 25
24
21
20
20
1
2
1
2
1
2
Table 14. Recommended circlip pliers according DIN 5254 (or equal) for shaft circlips.
Actuator
size
Pinion top
diameter
Pliers according
DIN 5254
Actuator
size
Pinion top
diameter
Pliers according
DIN 5254
12 16 mm 0.630" A1 950 65 mm 2.559 A3
25 - 100 22 mm 0.866" A2 1600 75 mm 2.953 A3
150 - 350 36 mm 1.417" A3 2500 95 mm 3.74 A4
600 55 mm 2.165" A3 4000 96 mm 3.78 A4
36
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 9: Reassembly
Page 41

Reassembly
9.3 Reassembly of the pistons
NOTICE
Before reassembling the pistons, check the required assembly code (see section 4.2).
1. Grease the piston parts according to step 9.1.
2. Install the piston rack bearing strips (17) and piston O-ring seals (16) on the pistons (14). Ensure all these parts are kept in place during assembly.
Figure 28 Reassemble the pistons
17
14
16
16
17
14
15
15
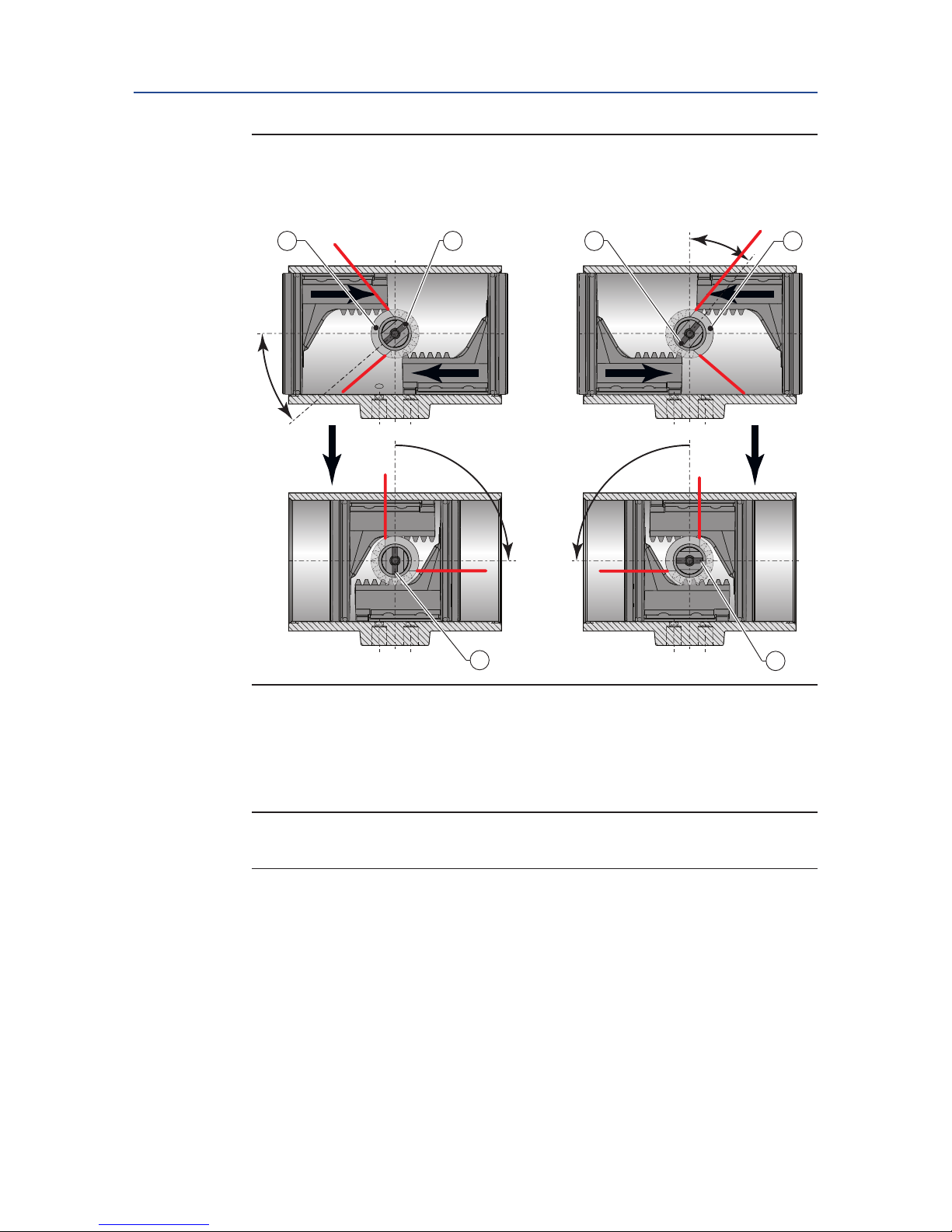
3. Align the pinion (see Figure 26) so that the teeth on the pinion will pick up the
pistons rack teeth when turning the pinion. The position of the pinion top slot and
the cam on the pinion top:
— For standard or Spring-to-Close: Assembly Code CW.
— For reverse or Spring-to-Open: Assembly Code CC.
4. Slightly push the pinion inward to engage with the pinion.
— Ensure that smooth movement and 90-degree operation can occur with-
out moving the pistons out of the actuator body.
— For larger pistons, use a rubber mallet and slightly hitting the pistons
inward to engage with the pinion.
5. When the pistons are moved 90° inwards (see gure 26), check that the pinion slot
on the pinion top is:
— Perpendicular to the length centre line of the house for assembly code CW.
— In line to the length centre line of the house for assembly code CC.
6. If not, turn pinion to move the pistons outward until they disengage from the
pinion. Shift one tooth of the pinion, reassemble and check again.
7. Move the pistons outward so that just the bearing groove sticks out of the housing. Fold the piston bearings (15) around the piston and hold the bearing ends in
place while moving the pistons inwards.
— For larger pistons, use a rubber mallet and slightly hitting the pistons
inward to engage with the pinion.
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
37
Section 9: Reassembly
Page 42
Reassembly
Figure 29 Position of the slot and the cam on the pinion top
90°
90°
Assembly code CW Assembly code CC
(Standard; Spring-to-Close) (Reverse; Spring-to-Open)
A
B
A
B
C
C
A = Position of cam
B = Position of slot and dot in pinion
C = Final position of pinion dot
NOTE:
When the pistons are completely moved inwards, the pinion top will show a 5° over travel.
38
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 9: Reassembly
Page 43

Reassembly
9.4 Reassembly and settings of the limit stops
1. Install the limit stop screws (30), limit stop nuts (31), limit stop washers (32) and
limit stop O-rings (33).
Figure 30 Install Limit Stop Bolts
33 30
31
32
2. Move the pistons inward until the slot in the top of the pinion is perpendicular to
centerline of the housing.
3. Double check if the position of the slot and the cam on the pinion top is in the cor-
rect position (see gure 26). Screw in the right hand travel stop until it comes into
contact with the pinion stop face.
4. Move the pistons outward until the slot in the top of the pinion is in line with the
centerline of the housing.
5. Screw in the left hand travel stop until it comes into contact with the pinion stop
face.
— For accurate travel stop adjustment of the actuator on the valve,
see section 5.
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
39
Section 9: Reassembly
Page 44

Reassembly
9.5 Reassembly of the end caps
9.5.1 Double-Acting actuators
1. Grease the O-ring seals (11) and B port seals (2) according to step 9.1.
2. Ensure that O-ring seals (11) and B port seals (2) are kept in place during assembly.
3. Install the end caps (6) and tighten the end cap screws (8).
Refer to Table 15 for the correct torque.
Figure 31 Double-acting end cap assembly
2
6
8
6
11
6
5
10
8
10
11
2
Double acting end caps (6) are fitted with a white warning sticker. Spring return end
caps (5) are fitted with a black warning sticker.
The above end caps (5) are for actuator sizes 25, 40, 65 and 100.
End caps (6) for double acting actuator sizes 150 and larger will have flat end caps.
Table 15. End cap Screw Torque
Actuator
size
Thread To ol Size
Torque (Nm) Torque (lbf.ft)
Target Min. Max. Target Min. Max.
12 M4
Allen key
SW 3 1.1 0.8 1.3 0.8 0.6 1.0
25 M5 SW 4 2.0 1.6 3.0 1.5 1.2 2.2
40 M5 SW 4 2.0 1.6 3.0 1.5 1.2 2.2
65 M5 SW 4 2.0 1.6 3.0 1.5 1.2 2.2
100 M5 SW 4 2.0 1.6 3.0 1.5 1.2 2.2
150 M6 SW 5 3.3 2.6 5.1 2.4 1.9 3.8
200 M6 SW 5 3.3 2.6 5.1 2.4 1.9 3.8
350 M8 SW 6 8.4 6.7 12.2 6.2 4.9 9.0
600 M10 SW 8 15.3 12.2 24.8 11.3 9.0 18.3
950 M12 SW10 24.3 19.4 41.6 17.9 14.3 30.7
1600 M12 SW10 24.3 19.4 41.6 17.9 14.3 30.7
2500 M12 SW10 24.3 19.4 41.6 17.9 14.3 30.7
4000 M14 SW12 43.5 34.8 66.4 32.1 25.7 49.0
40
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 9: Reassembly
Page 45

Reassembly
9.5.2 Spring-Return actuators (Size 25 to 600)
Important
EL-O-Matic F-Series Spring return actuators are supplied with springs on each side of the
actuator. Throughout the F-Series size range, there are three different spring designs:
— Size F12 has only 1 spring on each side.
— Sizes F25 to F600 have 6 springs on each side (see gure below).
— Sizes F950 to F4000 have 3 springs on each side (see chapter 9.5.3 ).
Check below gures to see where to place the spring cartridges in case of spring set
conversion.
When replacing spring cartridges in a spring-return actuator, ensure that the cartridges are
replaced in their identical position from where they were removed.
Before assembling the spring cartridges and end caps, make sure that the pistons are
completely inwards.
Figure 32 Spring placement size 25 to 600
1
2 3
4
56
A
B
1
2
3
4
56
1
23
4
56
N = 10 N = 20
N = 30
1
2 3456
1
23
4
5
6
1
23
4
5
6
N = 40
N = 50
N = 60
A = Piston top view
B = Position of gear rack
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
41
Section 9: Reassembly
Page 46

Reassembly
1. Grease the O-ring seals (11) and B port seals (2) according to step 9.1.
2. Ensure that O-ring seals (11) and B port seals (2) are kept in place during assembly.
3. Place the spring cartridges in actuator as per required spring set (see Figure 32).
4. Put the end cap screw washer (10) on the end cap screw (9) and tighten each end
cap screw in small equal turns and in the sequence as per Figure 33. Refer to Table
15 for the correct torque. We recommend to use some grease on the screws for
easier fastening.
Figure 33 Spring Return End cap assembly size 25 to 600
3
1
4
5
11
2
30
5
9
11
10
2
9
10
2
42
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 9: Reassembly
Page 47

Reassembly
9.5.3 Spring-Return actuators - Size 950 to 4000
Important
EL-O-Matic F-Series Spring return actuators are supplied with springs on each side of the
actuator. Throughout the F-Series size range, there are three different spring designs:
— Size F12 has only 1 spring on each side.
— Sizes F25 to F600 have 6 springs on each side (Chapter 9.5.2).
— Sizes F950 to F4000 have 3 springs on each side (see gure below).
Check below gures to see where to place the springs in case of spring set conversion.
When replacing springs in a spring-return actuator, ensure that the springs are replaced in
their identical position from where they were removed.
Before assembling the springs and end caps, make sure that the pistons are completely
inwards.
Figure 34 Spring cartridge placement
A
B
1 spring 0 spring 1 spring 1 spring 2 springs1 spring
2 springs
2 springs 3 springs2 springs3 springs3 springs
Left RightLeftRight Left Right
Left
Right Left RightLeft Right
N = 10 N = 20 N = 30
N = 40 N = 50 N = 60
A = Piston top view
B = Position of gear rack
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
43
Section 9: Reassembly
Page 48

Reassembly
1. Grease the O-ring seals (11) and B port seals (2) according to step 9.1.
2. Ensure that O-ring seals (11) and B port seals (2) are kept in place during assembly.
3. Place the spring in actuator as per required spring set (see Figure 29).
4. Put the end cap screw washer (10) on the end cap screw (9) and tighten each end
cap screw in small equal turns and in the sequence as per Figure 35.
Refer to Table 15 for the correct torque. We recommend to use some grease on
the screws for easier fastening.
Figure 35 Spring Return end cap assembly size 950 to 4000
5
30
5
1
2
3
4
5
6
9
10
9
10
11
2
2
11
44
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 9: Reassembly
Page 49

Reassembly
9.6 Basic function and Air Leak Test
CAUTION: MOVING PARTS
Applying pressure to the actuator will cause the actuator/valve assembly to operate.
1. Apply pressure (max. 8 bar/120 psi) to ports A and B. Use some soap suds at the
indicated points: around pinion top (1), pinion bottom (2), the end caps (3) and
limit stops (4).
2. In case of leakage around:
a. The limit stop bolts: Turn the lock nut of the bolts tighter, until the leakage
stops.
b. The end caps: Disassemble the end caps, replace o-rings and reassemble.
c. The pinion top or bottom and A- or B- port: Disassemble the complete
actuator, replace o-rings and reassemble.
Figure 36 Basic function and air leak test
A
B
AB
2
3
3
1
4
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
45
Section 9: Reassembly
Page 50

Troubleshooting
Section: 10 Troubleshooting
10.1 Mechanical Problems
Problem Possible error Solution Where to find
Feedback position and
actual position are not
the same.
Actuator and valve are
mounted 90° rotated in
relation to each other.
Remove actuator from
valve. Check assembly code
of actuator. Put both valve
and actuator in “Closed”
position. Mount actuator on
valve.
Section 4
Valve is in “Closed”
position, actuator is in
“Open” position and will
not move anymore.
Valve does not reach the
completely “Closed” or
“Open” position.
Limit stop screws are not
set correctly.
Readjust the limit stop
screws.
Section 5
Insert is not mounted
properly.
Mount the insert in the right
position. Remark: Rotate
insert to one cam = 22.5°.
Section 4.5
Pressure to low. Apply pressure as per sizing.
Sizing is wrong.
Check valve torque data
with actuator torque data.
Pinion is mounted in the
wrong position.
Re assemble actuator. Section 9
Actuator rotates, valve
does not.
No coupling between
actuator shaft and valve
spindle.
Install a coupling between
actuator shaft and valve
spindle.
Section 4.5
Actuator does not
rotate or does not rotate
smoothly.
Broken gearing on
pistons or pinion.
Contact nearest EL-O-Matic
representative to replace
actuator.
Spring or Spring
cartridge is broken.
Contact nearest EL-O-Matic
representative to replace
actuator.
Appendix A.
Limit stop screws cannot
be turned out anymore.
Limit stop screws is
bend.
Contact nearest EL-O-Matic
representative to replace
actuator.
46
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 10: Troubleshooting
Page 51
Troubleshooting
10.2 Pneumatic Problems
Problem Possible error Solution Where to find
Actuator does not react
to electrical control
signal.
There is no supply
pressure at the
actuator.
Supply the right
pressure to the
actuator.
Section 2.3
Check that the actual
supply pressure is
higher than the sizing
pressure.
Actuator does not
react good to electrical
control signal.
There is sufcient
supply air pressure but
insufcient supply air
capacity.
Take care the supply
air tubing has the right
dimensions.
Section 4.6
Supply pressure too
low, causing pilot
operated solenoid valve
to fail.
Check that supply
pressure at the
actuator and solenoid
is sufcient to operate
the actuator.
Section 2.3
Check that the actual
supply pressure is
higher than the sizing
pressure.
Solenoid valve is not
mounted properly.
Check the solenoid
valve mounting.
Instructions shipped
with the solenoid valve.
Speed control throttle
(if present) blocks air
ow.
Turn the speed control
more open.
Instructions shipped
with the speed control
valve.
Manual override
(if present) on the
Solenoid Valve is
locked.
Unlock manual override
on the solenoid valve.
Instructions shipped
with the manual
override.
Air leakage between
actuator and solenoid
valve.
Sealing between
solenoid valve and
actuator is not
mounted air tight.
Reassemble solenoid
valve taking care, that
all seals are in place.
Instructions shipped
with the solenoid valve.
Double-acting actuator
will only move to
“open” position.
Actuator has wrong
solenoid valve
conguration.
Mount a solenoid valve
suitable for doubleacting actuators
(4/2 or 5/2 function).
Instructions shipped
with the solenoid valve.
Check that conversion
plate on solenoids, that
have both 3/2 and 5/2
functions, is in the right
position.
Instructions shipped
with the solenoid valve.
Leakage notice on the
actuator.
Seals on the limit stops
screws are not air tight.
Turn the lock nut of the
bolts tighter; until the
leakage stops.
Section 9.6
Seals on the end caps
are not air tight.
Disassemble the end
caps, replace O-rings
and reassemble.
Consider to replace
all O-ring seals and
bearings.
Section 9.6 or Section 6
Seals on the pinion top
and bottom are not air
tight.
Disassemble the
complete actuator,
replace O-rings and
reassemble. Consider
to replace all O-ring
seals and bearings.
Section 9.6 or Section 6
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
47
Section 10: Troubleshooting
Page 52

Troubleshooting
10.3 Electrical Problems
Problem Possible error Solution Where to find
Actuator does not react
to control signals.
Control wiring. Power
supply wiring or
feedback wiring are not
right connected.
Connect all wiring in
the right way.
Instructions of the
control or feedback
accessories.
The power supply
voltage is not is not the
same as the voltage of
the applicable solenoid
valve.
Connect the right
power supply voltage.
Instructions of the
solenoid valve.
There are problems
with position feedback
after sending the
actuator to either the
“Open” or “Closed”
position.
The wiring of the
feedback signals may
be switched.
Connect the feedback
wiring in the right way.
Instructions of the
feedback device.
48
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 10: Troubleshooting
Page 53
Parts List and Spare Parts
Section: 11 Parts List and Spare Parts
Recommendations
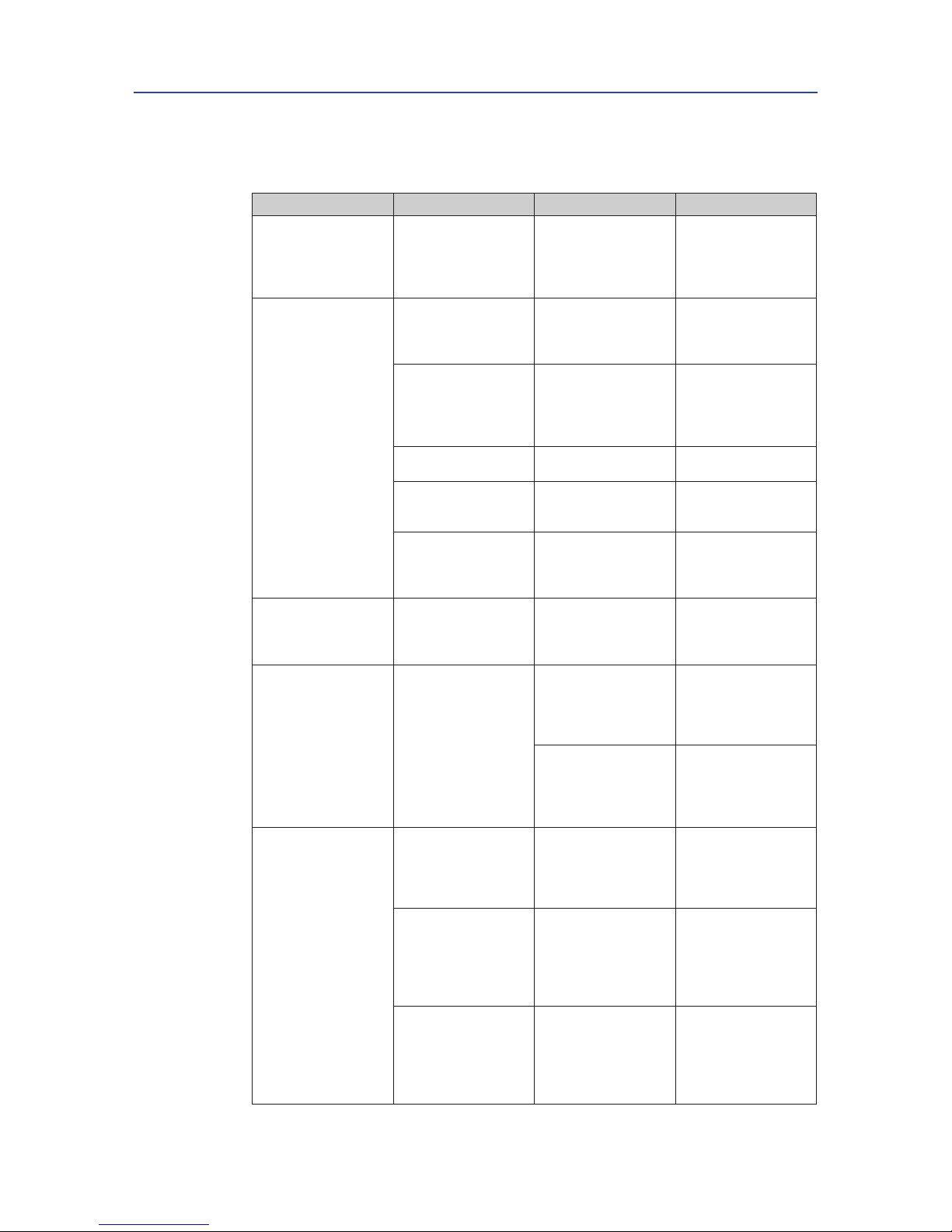
11.1 Actuator size F12
1
14
15
16
17
18
19
21
22
20
5
6
8
9
13
12
26
27
23
2
711
Table 16. Parts List
Pos. Qty Notes Description Material
1 1 House Extruded aluminium alloy
2 2 1 B-port ball Steel
5 2 End cap SR (DA) Cast Aluminium alloy
6 2 End cap DA Cast Aluminium alloy
7 Max. 2 Springs Spring steel
8 8 End cap screw DA Stainless Steel
9 8 End cap screw SR Stainless Steel
11 2 1 O-ring end cap Nitrile rubber
12 2 Warning sticker DA Polyester
13 2 Warning sticker SR Polyester
14 2 Piston Cast Aluminium alloy
15 2 1 Bearing piston PTFE 25% carbon-lled
16 2 1 O-ring piston Nitrile rubber
17 1 1 Guide band Nylatron
18 2 Pinion High grade aluminium
19 1 1 Bearing pinion top POM
20 1 1 Bearing pinion bottom POM
21 1 1 O-ring pinion top Nitrile rubber
22 1 1 O-ring pinion bottom Nitrile rubber
23 1 1 Thrust bearing pinion POM, black UV stabilized
26 1 Indicator assembly ABS + stainless steel screw
27 1 1 Circlip Spring steel
Notes:
1 Included in Service Kit.
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
49
Section 11: Parts List and Spare Parts
Page 54

Parts List and Spare Parts
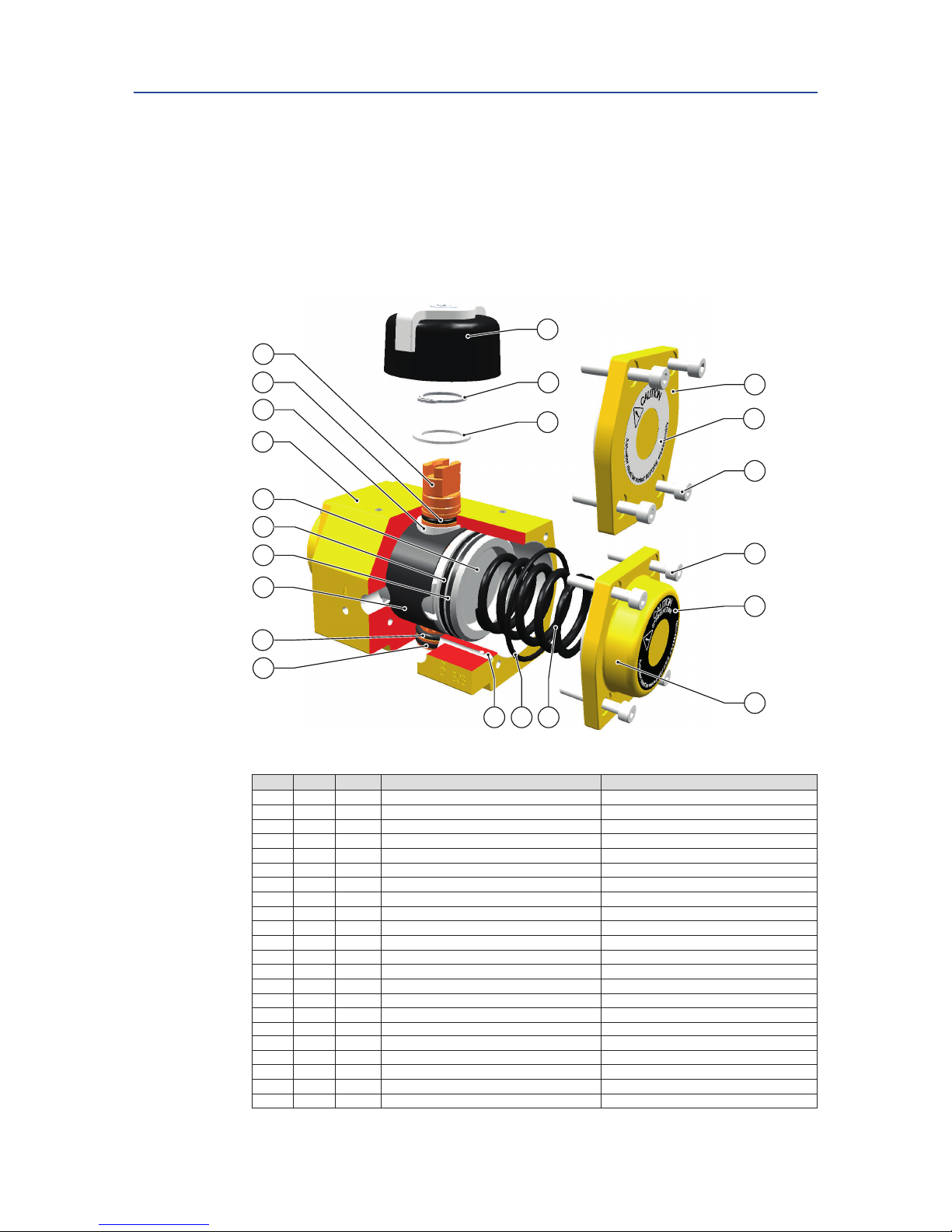
11.2 Actuator sizes F25 to F600
1
33
7
12
19
21
3
17
2
8
6
32
16
30
15
28
31
13
5
10
14
9
10
11
19
2118
27
26
23
Table 17. Parts List
Pos. Qty Notes Description Material
1 1 House Cast Aluminium alloy
2 2 1 B-port seal Silicon rubber
3 1 Center plate (option) Nylon PA6, Black
5 2 2 End cap SR (DA) Cast Aluminium alloy
6 2 2 End cap DA Cast Aluminium alloy
7 Max. 12 Spring cartridge Spring steel
8 8 End cap screw DA Stainless Steel
9 8 End cap screw SR Stainless Steel
10 8 End cap screw washer Stainless Steel
11 2 1 O -ring end cap Nitrile rubber
12 2 Warning sticker DA Polyester
13 2 Warning sticker SR Polyester
14 2 Piston Cast Aluminium alloy
15 2 1 Bearing piston PTFE 25% carbon-lled
16 2 1 O -ring piston Nitrile rubber
17 2 1 Bearing strip piston rack POM
18 2 Pinion High grade aluminium
19 2 1 Bearing pinion POM
21 2 1 O -ring pinion Nitrile rubber
23 1 1 Thrust bearing pinion POM, black UV stabilized
26 1 Indicator assembly ABS + stainless steel screw
27 1 1 Circlip Spring steel
28 1 Drive insert Aluminium
30 2 Limit stop screw Stainless steel
31 2 Limit stop nut Stainless steel
32 2 1 Limit stop washer PA66
33 2 1 O -ring limit stop Nitrile rubber
Notes:
1 Included in Service Kit.
2 Actuator sizes 25 to 100 have high end caps for double-acting and spring-return models. Actuator sizes
150 to 4000 have low end caps for double-acting models and high end caps for spring-return models.
50
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 11: Parts List and Spare Parts
Page 55

Parts List and Spare Parts
11.3 Actuator sizes F950 to F2500
1
33
7
12
23
27
20
26
22
3
17
2
8
6
32
16
30
18
15
28
31
13
5
10
14
9
10
11
4
19
21
29
Table 18. Parts List
Pos. Qty. Description Material
1 1 House Cast Aluminium alloy
2 2 1 B-port seal Silicon rubber
3 1 Center plate (option) Nylon PA6, Black
4 12 Thread insert Steel
5 2 End cap SR Cast Aluminium alloy
6 2 End cap DA Cast Aluminium alloy
7 Max. 6 Springs Spring steel
8 12 End cap screw DA Stainless Steel
9 12 End cap screw SR Stainless Steel
10 12 End cap screw washer Stainless Steel
11 2 1 O-ring end cap Nitrile rubber
12 2 Warning sticker DA Polyester
13 2 Warning sticker SR Polyester
14 2 Piston Cast Aluminium alloy
15 2 1 Bearing piston PTFE 25% carbon-lled
16 2 1 O-ring piston Nitrile rubber
17 2 1 Bearing strip piston rack POM
18 1 Pinion High grade aluminium
19 2 1 Bearing pinion top POM
20 1 1 Bearing pinion bottom POM
21 1 1 O-ring pinion top Nitrile rubber
22 1 1 O-ring pinion bottom Nitrile rubber
23 1 1 Thrust bearing pinion POM, black UV stabilized
26 1 Indicator assembly ABS + stainless steel screw
27 1 1 Circlip Spring steel
28 1 Drive insert Aluminium
29 1 1 Backup ring POM
30 2 Limit stop screw Stainless steel
31 2 Limit stop nut Stainless steel
32 2 1 Limit stop washer PA66
33 2 1 O-ring limit stop Nitrile rubber
Notes:
1 Included in Service Kit.
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
51
Section 11: Parts List and Spare Parts
Page 56
Parts List and Spare Parts
11.4 Actuator sizes F4000
133
7
12
23
27
29
26
22
3
17
2
8
6
32
16
30
18
15
21
31
13
5
10
14
9
10
11
4
20
25
24
19
Table 19. Parts List
Pos. Qt y. Notes Description Material
1 1 House Cast Aluminium alloy
2 2 1 B-port seal Silicon rubber
3 1 Center ring Stainless Steel AISI 304
4 12 Thread insert Steel
5 2 End cap SR Cast Aluminium alloy
6 2 End cap DA Cast Aluminium alloy
7 Max. 6 Springs Spring steel
8 12 End cap screw DA Stainless Steel
9 12 End cap screw SR Stainless Steel
10 12 End cap screw washer Stainless Steel
11 2 1 O-ring end cap Nitrile rubber
12 2 Warning sticker DA Polyester
13 2 Warning sticker SR Polyester
14 2 Piston assembly Cast Aluminium alloy
15 2 1 Bearing piston PTFE 25% carbon-lled
16 2 1 O-ring piston Nitrile rubber
17 2 1 Bearing strip piston rack POM
18 1 Pinion High grade aluminium
19 2 1 Bearing pinion top POM
20 1 1 Bearing pinion bottom POM
21 1 1 O-ring pinion top Nitrile rubber
22 1 1 O-ring pinion bottom Nitrile rubber
23 1 1 Thrust washer pinion POM, black UV stabilized
24 1 Cam stroke adjustment Steel
25 1 1 Cam thrust washer POM, black UV stabilized
26 1 Indicator assembly ABS + stainless steel screw
27 1 1 Circlip Spring steel
29 1 1 Backup ring POM
30 2 Limit stop screw Stainless steel
31 2 Limit stop nut Stainless steel
32 2 1 Limit stop washer PA66
33 2 1 O-ring limit stop Nitrile rubber
Notes:
1 Included in Service Kit.
52
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Section 11: Parts List and Spare Parts
Page 57

Appendix
Appendix: A Spring load removal
This section explains:
• How to remove the spring load safely of spring-return actuators in case:
— The valve gets “stuck” in mid position.
— One of the spring cartridges is broken.
WARNING: MOVING PARTS
A spring-return actuator mounted on a valve, which is stuck in mid stroke, contains a high
spring load which will cause a sudden rotation of the actuator versus the valve during
disassembly. This can cause serious injury to personnel or damage to material.
On spring-return actuators with a broken spring cartridge, the end cap can be “shot” away
during disassembly of the actuator. This can cause serious injury to personnel or damage to
material.
A.1 Spring load relief
CAUTION: ROTATING ACTUATOR
In case of an actuator/valve assembly “stuck” in mid position, leave the actuator on the
valve and/or mounting bracket during this procedure.
Figure A-1 Spring load removal
Crush / Amputaion Hazard
Failure to follow instructions
for removal of spring loaded
actuator may result in
surious personal injury
WARNING
1
2
3
4
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
53
Appendix
Page 58

Appendix
1. Depressurize the actuator completely.
2. Based on the actuator size, choose the correct threaded rod kit from Table A-1.
3. Replace one by one each end cap screw for the threaded rod kit and turn down the
adjusting nut until it touches the end cap.
4. Once all for end cap screws have been replaced, gradually turn the adjustment nuts
on threaded rod in CCW direction by turning the nuts half turn at a time. Make sure
the rod itself does not turn. Continue this until the load of springs are relieved.
5. Repeat the same procedure for the end cap screws on the other size of the actua-
tor as shown in gure A-1.
6. In case of an actuator/valve assembly “stuck” in mid position: The actuator now
can be disassembled from Valve, by removing the mounting studs/bolts.
Table A-1. Threaded rod dimensions in mm
Actuator Size Thread
Threaded rod length
(mm) (inch)
12 M4 132 5.2
25 M5 140 5.5
40 M5 140 5.5
65 M5 140 5.5
100 M5 140 5.5
150 M6 145 5.7
200 M6 145 5.7
350 M8 185 7.3
600 M10 185 7.3
950 M12 498 19.6
1600 M12 498 19.6
2500 M12 498 19.6
4000 M14 600 23.6
Figure A-1 Spring load removal rod dimensions
Threaded Rod
Washer
Adjusting nut
Holding nuts
Length
Thread
54
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Appendix
Page 59

Appendix
Appendix: B Tool & Torque Table
This section explains:
• Which tools to use for the indicated fasteners.
• The recommended amount of torque to apply on the indicated fasteners.
Table B-1. End cap bolts
Actuator
size
Thread To ol Size
Torque (Nm) Torque (lbf.ft)
Target Min. Max. Target Min. Max.
12 M4
Allen key
SW 3 1.1 0.8 1.3 0.8 0.6 1.0
25 M5 SW 4 2.0 1.6 3.0 1.5 1.2 2.2
40 M5 SW 4 2.0 1.6 3.0 1.5 1.2 2.2
65 M5 SW 4 2.0 1.6 3.0 1.5 1.2 2.2
100 M5 SW 4 2.0 1.6 3.0 1.5 1.2 2.2
150 M6 SW 5 3.3 2.6 5.1 2.4 1.9 3.8
200 M6 SW 5 3.3 2.6 5.1 2.4 1.9 3.8
350 M8 SW 6 8.4 6.7 12.2 6.2 4.9 9.0
600 M10 SW 8 15.3 12.2 24.8 11.3 9.0 18.3
950 M12 SW10 24.3 19.4 41.6 17.9 14.3 30.7
1600 M12 SW10 24.3 19.4 41.6 17.9 14.3 30.7
2500 M12 SW10 24.3 19.4 41.6 17.9 14.3 30.7
4000 M14 SW12 43.5 34.8 66.4 32.1 25.7 49.0
Table B-2. Bottom flange, Metric units
Actuator
size
ISO Pattern
Metric Torque (Nm) Imperial Torque (lbf.ft)
Thread Min. Max. Thread Min. Max.
12 F04 M6 4.5 5.0 10-24UNC 3.3 3.7
25
F03 inner pattern M5 2.0 3.0 10-24UNC 1.5 2.2
F05 outer pattern M6 4.5 5.0 1/4"-20 3.3 3.7
40, 65, 100
F05 inner pattern M6 4.5 5.0 1/4"-20 3.3 3.7
F07 outer pattern M8 10.5 12.5 5/16"-18 7.7 9.2
150, 200, 350
F07 inner pattern M8 10.5 12.5 5/16"-18 7.7 9.2
F10 outer pattern M10 21.0 24.5 3/8"-16 15.5 18.1
600
F10 inner pattern M10 21.0 24.5 3/8"-16 15.5 18.1
F12 outer pattern M12 34.5 43.0 1/2"-13 25.4 31.7
950
F10 inner pattern M10 21.0 24.5 3/8"-16 15.5 18.1
F14 outer pattern M16 90.0 104.0 5/8"-11 66.4 76.7
1600, 2500
F16 inner pattern M20 170.0 204.0 3/4"-10 125.4 150.5
F25* outer pattern 4x M16 90.0 104.0 4x 5/8"-11 66.4 76.7
4000
F16 inner pattern M20 170.0 204.0 3/4"-10 125.4 150.5
F25 outer pattern 8x M16 90.0 104.0 8x 5/8"-11 66.4 76.7
1. For actuator sizes 1600 and 2500 only 4 holes of the ISO5211 F25 drilling pattern are available.
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
55
Appendix
Page 60
Appendix
Table B-3. NAMUR (VDE/VDI 3845) flanges
Flange
Metric Torque (Nm) Imperial Torque (lbf.ft)
Thread Min. Max. Thread Min. Max.
Solenoid ange screw threads M5 2.0 3.0 10-24UNC 1.5 2.2
Top ange screw threads M5 2.0 3.0 10-24UNC 1.5 2.2
Table B-4. Limit stop screws
Actuator size Thread
Bolt Wrench Nut wrench
size (mm) size (mm)
25 M 6 10 10
40 M 8 13 13
65 M 10 17 (16)
1
17 (16)
1
100 M 10 17 (16)
1
17 (16)
1
150 M 10 17 (16)
1
17 (16)
1
200 M 12 19 (18)
1
19 (18)
1
350 M 16 24 24
600 M 20 30 30
950 M 22 12 32
1600 M 24 14 36
2500 M 27 17 41
4000 M 22 12 32
1. Default dimension according DIN933 standard
2. Dimensions in brackets according ISO4017 standard
3. Actuator size 12 is not available with limit stops
Table B-5. Recommended circlip pliers according DIN 5254 (or equal)
for shaft circlips
Actuator
size
Pinion top
diameter
Pliers
according DIN
Actuator
size
Pinion top
diameter
Pliers
according DIN
F12 16 mm 0.630" A1
950 65 mm 2.559" A3
F25 - F100 22 mm 0.866" A2
1600 75 mm 2.953" A3
F150 - F350 36 mm 1.417" A3
2500 95 mm 3.74" A4
F600 55 mm 2.165" A3
4000 96 mm 3.78" A4
Table B-6. Angular Displacement Limit Stops
Actuator size
Turns for 5°
adjustment of the pinion:
360° revolution of
limit stop screw will adjust
F 12 Actuator size 12 is not available with limit stops
F 25 0.7 7.1°
F 40 0.8 6.3°
F 65 0.6 8.3°
F 100 0.7 7.1°
F 150 1.2 4.2°
F 200 1 5.0°
F 350 0.8 6.3°
F 600 0.8 6.3°
F 950 1.1 4.7°
F 1600 1.3 4.1°
F 2500 1.5 3.4°
F 4000 3.2 1.6°
56
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Appendix
Page 61
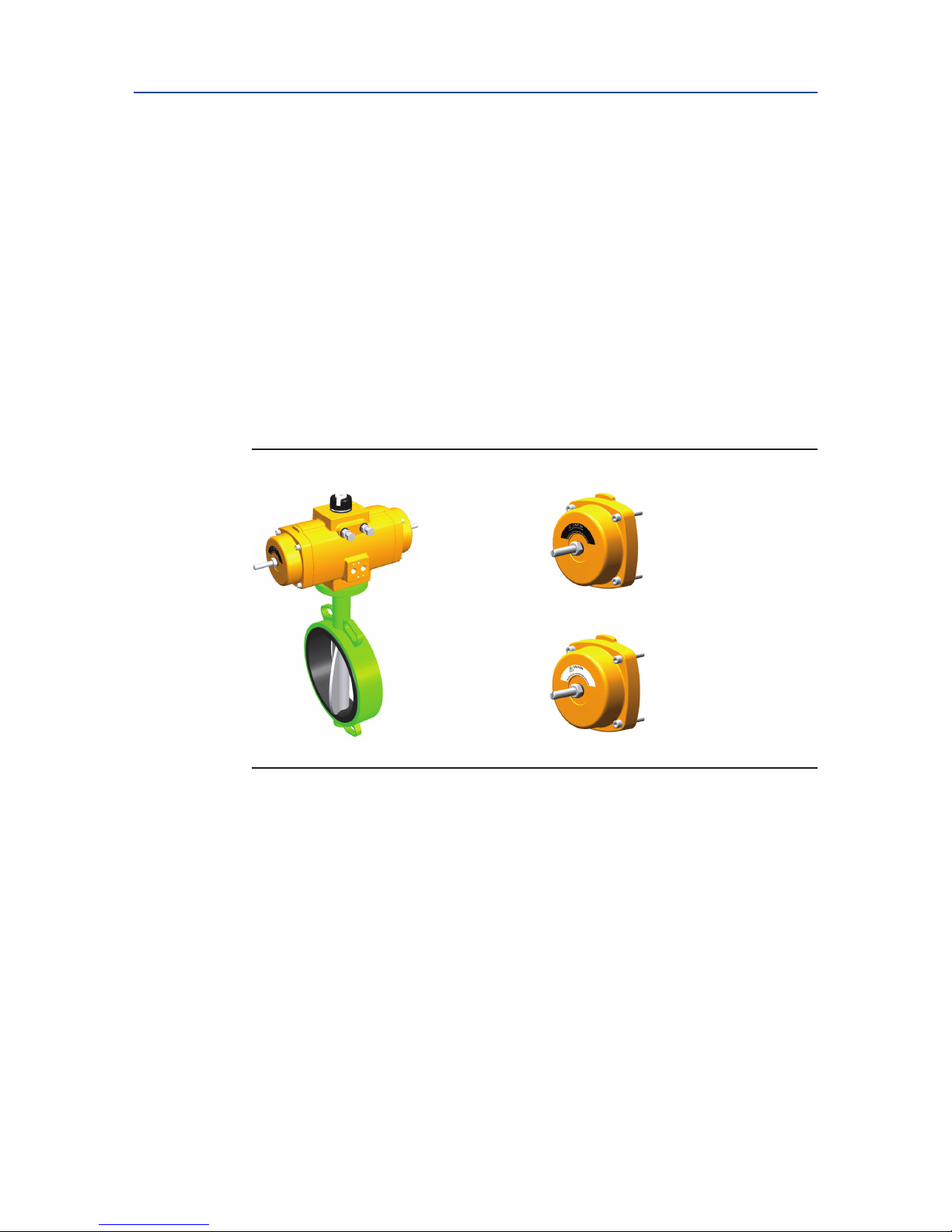
Appendix
Appendix: C Full Stroke Adjustment Option
This section explains:
• How to mount the Full Stroke Adjustment option to an actuator
• How to adjust the Full Stroke Adjustment option to a required rotation angle.
C.1 Full Stroke Adjustment Option
The Full Stroke Adjustment option is available as a complete actuator or as an end cap
conversion kit in order to upgrade a standard actuator into a Full Stroke Ajdustment
version.
The option is available for sizes 25 to 600 and both the double acting kit and spring return
kit use the spring return end cap.
Figure C-1 Availability formats of the full Stroke Adjustment option
Spring Return Full
Stroke Adjustment kit
Double Acting Full
Stroke Adjustment Kit
Complete Spring Return
or Double Acting
actuator
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
57
Appendix
Page 62

Appendix
C.2 Convert a standard actuator into a Full Stroke
Adjustment version
Before starting to assemble the Full Stroke adjustment kit, please check the kit for com-
pleteness. See gure C-2.
Figure C-2 Full Stroke adjustment kit content
41 42 43 44
45 46 11
40 9 10
12
13
Table C-1 Content Full Stroke Adjustment kit
Pos. Description Material Qty. Notes
40 End cap - Full stroke adjustment Cast Aluminium alloy 2 1
41 Full Stroke adjustment screw Stainless steel 2
42 Full Stroke adjustment Nut Stainless steel 2
43 Full Stroke adjustment washer PA66 2
44 O-Ring - Full Stroke adjustment screw Nitrile rubber 2
45 O-Ring - Thread bush Nitrile rubber 2
46 Thread bush Aluminium 2
9 End cap screw Stainless steel 8
10 Washer end cap screw Stainless steel 8
11 O-ring end cap Nitrile rubber 2
12 Warning sticker DA Full Stroke adjustment Polyester 2
13 Warning sticker SR Full Stroke adjustment Polyester 2
2. The same Full Stroke adjustment end cap is used for both double acting and spring return actuators
(at double acting actuator end caps with Full Stroke Adjustoment options are not available).
58
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Appendix
Page 63
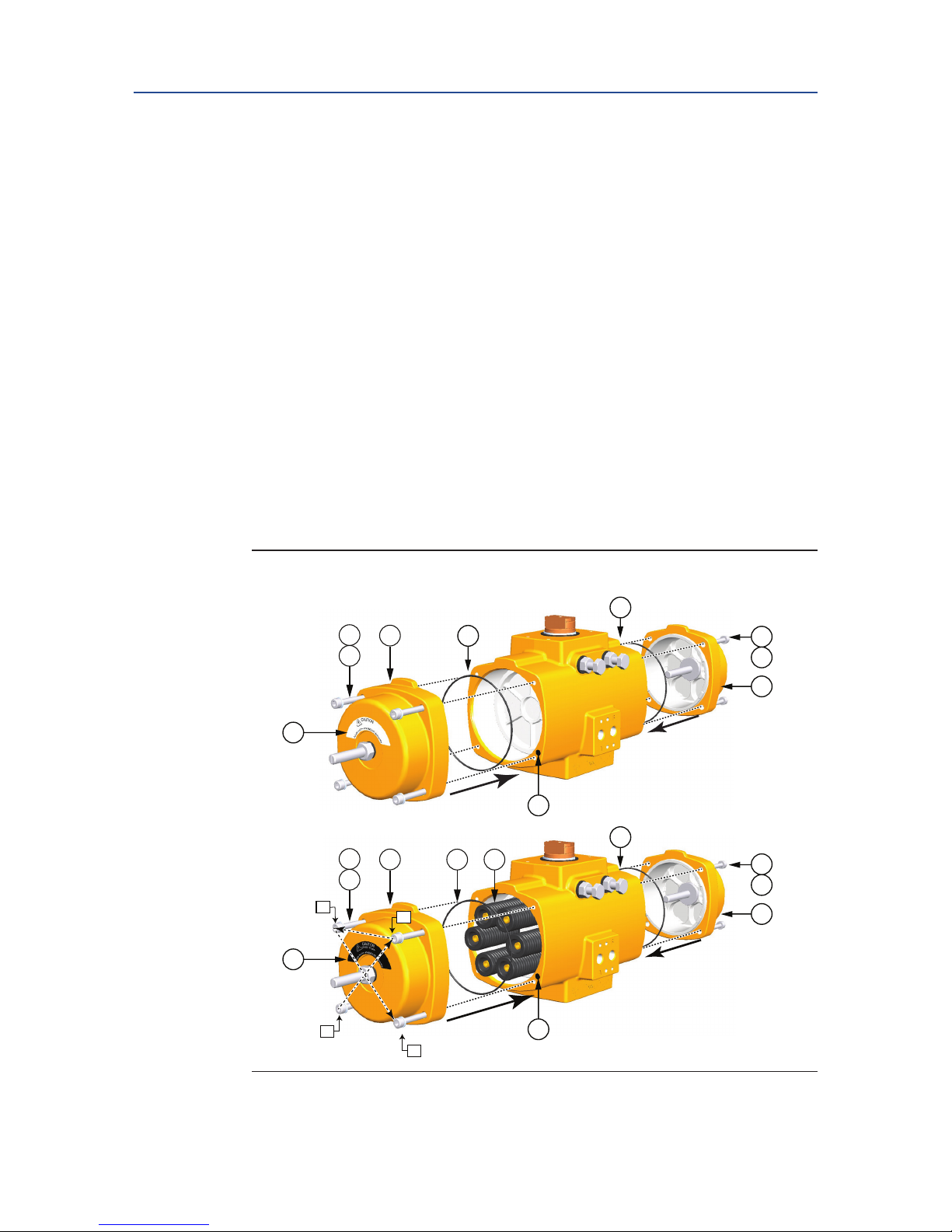
Appendix
C.2.1 Procedure
1. Remove the existing end caps of a standard actuator.
— Follow the instructions of Section 8 to remove both the end caps of the
actuator.
— For spring return actuators; note the original positions of the spring car-
tridges.
2. Mount the Full Stroke Adjustment End cap kit to the actuator.
— The stroke adjustment screw (41) is factory set at the 90° position.
3. Grease the O-ring seals (11) and B port seals (2) according to section 9.1.
4. Ensure that O-ring seals (11) and B port seals (2) are kept in place during assembly.
5. For spring return actuators; place the spring cartridges (7) back in their original
positions.
6. Install the Full Stroke end cap kits and tighten the end cap screws (9,10). For spring
return units; tighten each endap screw (9,10) in small equal turns and in the sequence as per Figure C-3. Refer to Appendix B, Table B-1 for the correct torque.
7. For Spring Return units, place the black warning sticker (13) on the end cap. For
Double Acting units, place the white warning sticker (12) on the end cap.
Figure C-3 Assembly of Full Stroke adjustment end cap kit
7
40
10
9
3
1
4
2
11
11
2
2
11
11
10
9
10
9
10
9
40
40
40
13
12
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
59
Appendix
Page 64

Appendix
C.3 Full Stroke Adjustment Setting
Note:
Standard actuators or actuators with the Full Stroke Adjustment option are shipped by
default with a rotation setting of 90° +/-0.5°.
The stroke adjustment setting procedure can be two steps:
1. Setting the Full Stroke Adjustment screw to the 90° (factory) poisiton.
— This step can be applicable if a standard actuator needs to be converted
with a Full Stroke Adjustment end cap kit or if the position of the Full
Stroke Adjustment screw is somehow lost.
2. Setting the Full Stroke Adjustment screw to the required angle.
C.3.1 Factory Setting Procedure
1. In order to set the Full Stroke Adjustment Screws accurately to the outward position:
— Do not change the setting of the DSA limit stop screws (A and B) located
above the air connection interface.
— Move the pistons of the actuator outwards by applying pressure to the
A-port.
2. Screw in both the Full Stroke Adjustment Screws (41) until the screws touch the
pistons. You will feel an obstruction.
Important: Do not overtighten the screws.
Figure C-4 DSA limit stop screw setting
A
B
A-port
41
41
You have now set the adjustment screw to the factory setting
Notes:
1. Only the outward stroke can be adjusted with the Full Stroke Adjustment screws.
— In case of assembly code CW, the left side limit stop (A) is redundant.
— In case of assembly code CC, the right side limit stop (B) is redundant.
2. For the inward stroke the standard limit stops can be used:
— The right side limit stop (B) for assembly code CW
— The left side limit stop (A) for assembly code CC
60
September 2017
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
Appendix
Page 65

Appendix
C.3.2 Setting the Full Stroke Adjustment screw to the required
angle.
1. Move the pistons of the actuator inwards.
— For Spring Return actuators this happens automatically when the actuator
is vented.
— For double acting actuators vent the A-port and apply pressure to the
B-port.
2. In order to set the actuator to the required angle, use next table to dene the
number of revolutions which you have to turn in the Full Stroke Adjustment
Screws.
3. Turn in both the adjustment screws (41) as dened in step 2. Both the adjustment
screws should be turned in with the same length or number of revolutions.
CAUTION: DO NOT SET SCREWS UN-EQUAL
Screwing in only one adjustment screw or un-equal setting of both the screws will lead to
high point loads on the pistons and can cause premature failure of the actuator.
4. Test cycle the actuator to check if the correct rotation angle is set. If required,
repeat steps 1 to 3 to adjust the rotation angle to the required angle.
Table C-2 Actuator angle rotation per full revolution of Full Stroke adjustment screw
Actuator
size
Stroke
Flathead
screw driver
Screw
Actuator angle rotation per
full revolution of screw
mm inch Thread Pitch (mm)
25 15.7 0.62 1.0 x 5.5 M6 1 5.7°
40 18.8 0.74 1.2 x 6.5 M8 1.25 6.0°
65 22.0 0.87 1.2 x 6.5 M8 1.25 5.1°
100 25.1 0.99 1.2 x 6.5 M10 1.5 5.4°
150 31.4 1.24 1.2 x 6.5 M10 1.5 4.3°
200 37.7 1.48 1.2 x 6.5 M10 1.5 3.6°
350 37.7 1.48 1.2 x 6.5 M12 1.75 4.2°
600 44.0 1.73 1.2 x 6.5 M16 2 4.1°
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
DOC.IOM.EF.EN Rev. 7
September 2017
61
Appendix
Page 66

Page 67

For complete list of sales and manufacturing sites, please visit
www.emerson.com/actuationtechnologieslocations or contact us at
info.actuationtechnologies@emerson.com
World Area Configuration Centers (WACC) offer sales support, service,
inventory and commissioning to our global customers.
Choose the WACC or sales office nearest you:
NORTH & SOUTH AMERICA
19200 Northwest Freeway
Houston TX 77065
USA
T +1 281 477 4100
F +1 281 477 2809
Av. Hollingsworth
325 Iporanga Sorocaba
SP 18087-105
Brazil
T +55 15 3238 3788
F +55 15 3228 3300
ASIA PACIFIC
No. 9 Gul Road
#01-02 Singapore 629361
T +65 6777 8211
F +65 6268 0028
No. 1 Lai Yuan Road
Wuqing Development Area
Tianjin 301700
P. R. China
T +86 22 8212 3300
F +86 22 8212 3308
MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA
P. O. Box 17033
Dubai
United Arab Emirates
T +971 4 811 8100
F +971 4 886 5465
P. O. Box 10305
Jubail 31961
Saudi Arabia
T +966 3 340 8650
F +966 3 340 8790
24 Angus Crescent
Longmeadow Business Estate East
P.O. Box 6908 Greenstone
1616 Modderfontein Extension 5
South Africa
T +27 11 451 3700
F +27 11 451 3800
EUROPE
Berenyi u. 72- 100
Videoton Industry Park
Building #230
Székesfehérvár 8000
Hungary
T +36 22 53 0950
F +36 22 54 3700
www.emerson.com/el-o-matic
©2017 Emerson. All rights reserved.
The Emerson logo is a trademark and service mark of Emerson Electric Co.
EL-O-Matic
TM
is a mark of one of the Emerson family of companies.
All other marks are property of their respective owners.
The contents of this publication are presented for information purposes
only, and while every effort has been made to ensure their accuracy,
they are not to be construed as warranties or guarantees, express or
implied, regarding the products or services described herein or their use
or applicability. All sales are governed by our terms and conditions, which
are available on request. We reserve the right to modify or improve the
designs or specifications of our products at any time without notice.
EL Matic
TM
EL Matic
TM
 Loading...
Loading...