Emerson Copeland 71, Copeland 611, Copeland 121, Copeland 271, Copeland 65 Technical Information
...
Technical Information
Date of last update: Jul-05
Ref: CC7.5.1/0705/E
Application Engineering Europe
F
F
AANNSS FFOORR
C
C
OONNDDEENNSSIINNGG
U
U
NNIITTS
S
1 Introduction
Condensing units manufactured by Copeland are equipped with fan(s).
Various fan models are and were used.
That is to say that today, it is possible to meet various fan(s) on the after-sales market.
2 General information
Condensing units can be equipped with 1, 2 or 4 fans.
The complete fan consists of an external rotor motor with the fan blades permanently fixed to the rotor and the fan
guard. The grid has 4 feet to mount it on the condenser.
Fan motors are protected by a thermostatic switch. A single-pole bimetallic-element switch protects the motor
against damage from:
Motor overload
Over-voltage and under-voltage
Electrical and mechanical blockages
Inadequate cooling.
The fans protection is IP 54 and its insulation class is "F".
Most fans can be equipped with a speed controller connected to the condensing pressure.
3 Fans for Copeland Scroll and DWM Copeland semi-hermetic condensing units
The fan is positioned in order to blow the air from the condenser to the compressor, so the compressor additional
fan is not necessary any more.
NOTE: After connecting the condensing unit electrically, check the rotational direction. The fan must blow from
the condenser to the compressor.
NOTE: All fans presently used on condensing units are single-phase fans.
3.1 Single-phase fans
Single-phase fans are used since January 2003.
3.1.1 Technical data
As described in table 1, various fan models are used.
Blade
diamete
r
Power input Voltage
Motor
current
mm W V (±10%) / Ph / Hz EBM Rotomatika A Main Auxilary
71 300 95 220 - 240 / 1 / 50 3 / 400 2.5 / 400 0.44 115 129
121 350 117 220 - 240 / 1 / 50 0.54 72 108
271 420 300 220 - 240 / 1 / 50 5 / 400 6.3 / 400 1.35 25 88
611 500 570 220 - 240 / 1 / 50 2.4 8.5 20.5
10 / 400
Winding resistance
Ω
(±10%), 25°C
Run capacitor
µF / V
4 / 400
Fan model
Table 1: Technical data – single-phase fans
1/4
CC7.5.1/0705/E
Technical Information
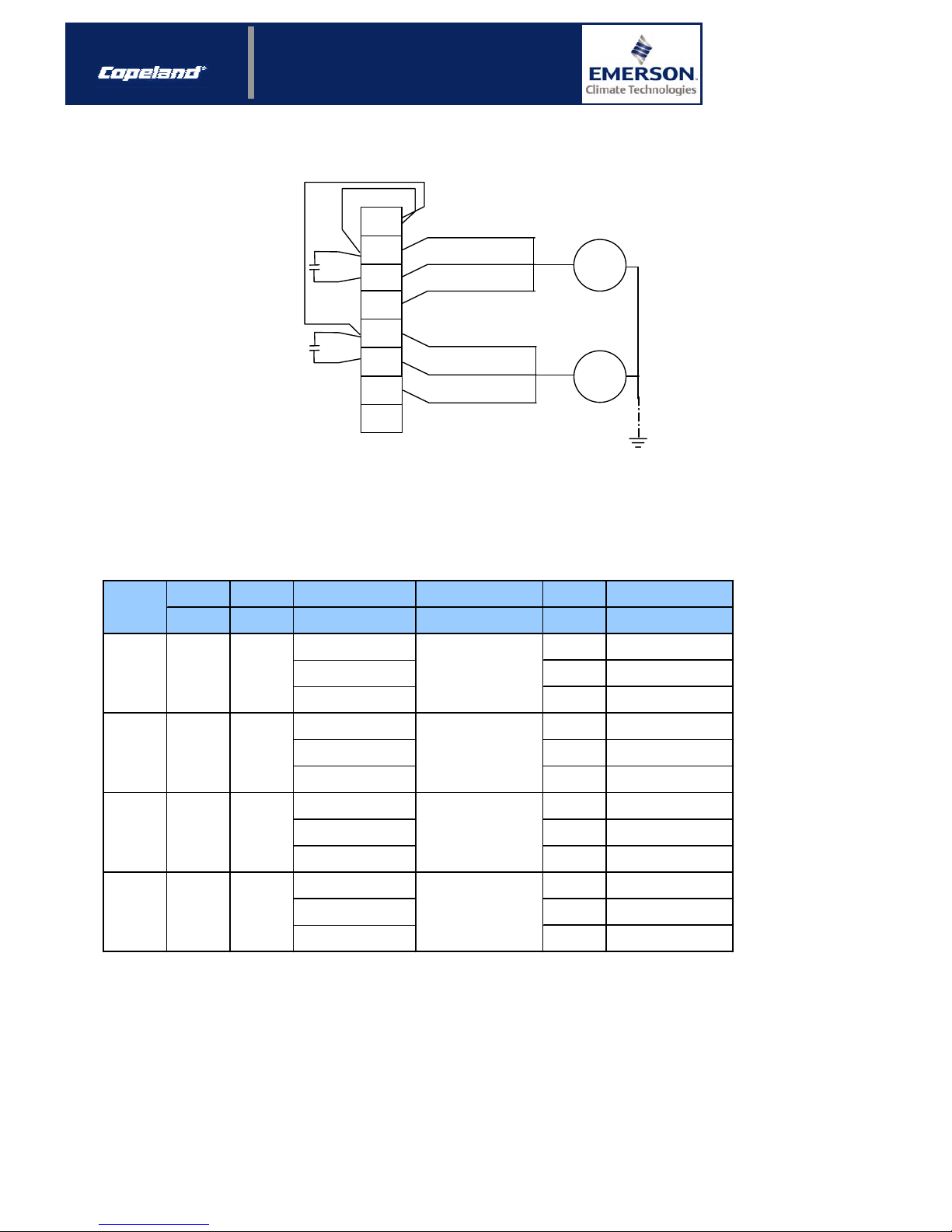
3.1.2 Single-phase fan wiring diagram
Z1 Black
U2 Blue
U1 Brown
M
1 ~
Z1 Black
U2 Blue
U1 Brown
M
1 ~
14
N
16
X1
15
13
L
9
10
11
L
C1
C1
12
Figure 1: Single-phase wiring diagram (230V ±15% / 1 ~ / 50-60 Hz)
3.2 Three-phase fans
Before January 2003, three-phase fans were used.
3.2.1 Technical data
Blade
diamete
r
Power input Voltage
Motor
current
mm W V (±10%) / Ph / Hz A
220 - 240 / 1 / 50 0.36
220-240 ∆ / 380-420 Y /
3 / 50
0.33 / 0.19
500 - 550 / 3 / 50 0.15
220 - 240 / 1 / 50 0.63
220-240 ∆ / 380-420 Y /
3 / 50
0.55 / 0.32
500 - 550 / 3 / 50 0.25
220 - 240 / 1 / 50 1.3
220-240 ∆ / 380-420 Y /
3 / 50
1.10 / 0.65
500 - 550 / 3 / 50 0.52
220 - 240 / 1 / 50 3.6
220-240 ∆ / 380-420 Y /
3 / 50
2.95 / 1.70
500 - 550 / 3 / 50 1.1
9.3
Winding resistance
5 / 400
8 / 400
16 / 400
25 / 400
20 / 60
51
6.2
6.2 / 18.6
54.7
57 ± 3 / 172 ± 10
325 ± 24
20
Ω (±10%), 25°C
102
104 ± 3 / 218 ± 6
574 ± 37
270 420 280
610 500 630
Fan model
75 300 80
Run capacitor
µF / V
120 350 135
Table 2: Technical data – three-phase fans
“Old” units were delivered with three-phase fans as a standard, but it is possible to convert these fans into singlephase motor by the mean of a capacitor. The characteristics of this run capacitor are given in table 2.
“New” single-phase kits can be used for retrofitting on units equipped with three-phase fans.
fan 75 is replaced by 71
fan 120 is replaced by 121
fan 210 is replaced by 211
fan 610 is replaced by 611
2/4
 Loading...
Loading...