Page 1
1
Read Carefully !
ENGLISH Version
R36-01-18
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS FO R
“ MAX5” INSTRUMENT
This manual contains safety information that if ignored
can endanger life or result in serious injury. They are
indicated by this icon.
Keep the instrument protected from sun and water.
Avoid water splashes.
Configuration and screenshots may be different and not including
some functions. A maximum of 5 channels can be set.
DOWNLOAD ERMES COMMUNICATION SOFTWARE
www.ermes-server.com
Page 2

2
Danger!
GENERAL SAFETY GUIDELINES
In emergencies the instrument should be switched off immediately! Disconnect the power cable
from the power supply!
When installing always observe local regulations!
Manufacturer is not liable for any unauthorized use or misuse of this product that may cause injury,
damage to persons and / or materials.
Caution!
Instrument must be accessible at all times for both operating and servicing. Access must not be
obstructed in any way!
Feeder should be interlocked with a no-flow protection device to automatically shut-off the pumps
when there is no flow!
Pumps and accessories must be serviced and repaired by qualified and authorized personnel only!
Always discharge the liquid end before servicing the instrument!
Empty and rinse the liquid end before work on a pump which has been used with hazardous or
unknown chemicals!
Always read chemical safety datasheet!
Always wear protective clothing when handling hazardous or unknown chemicals!
Instrument must be operated / serviced by trained technicians only!
All connection operations must be performed while the instrument is not connected to main
supply!
NORME CE
EC RULES(STANDARD EC)
NORMAS DE LA CE
Direttiva Bassa Tensione
Low Voltage Directive
Directiva de baja tensión
Direttiva EMC Compatibilità Elettromagnetica
EMC electromagnetic compatibility directive
EMC directiva de compatibilidad electromagnética
2014/35/UE
2014/30/UE
⎬
⎬
Page 3

3
Introduction.
The MAX5 is a multiple digital controller system. It reads and controls up to 5 channels that can be programmed to
control* pH - ORP - Chlorine - Turbidity - Temperature - Combined Chlorine (see Chlorine function for main options) Total Chlorine control (see Chlorine function for main options) - Conductivity - Dissolved Oxygen. It features 6 setpoint
outputs, 6 proportional pump outputs, 6 mA outputs,1 cleaning probe output and 5 level tank inputs. Three way setpoint
outputs program mode: on/off - PID - PWM. MAX5 can be connected to a PC for remote controlling / programming using
a standard USB port, RS485 connection, GSM or GPRS modem, ETHERNET.
Working ranges are:
pH : from 0 to 14pH
ORP: from 0 to 1000mv
Chlorine: from 0 to 10 mg/l
Turbidity: from 0 to 9999 NTU
Temperature: from 0 to 200 °C
Conductivity: from 0 to 300.0 mS
Dissolved Oxygen: from 0 to 20 mg/l
All information are provided through a widescreen LCD display (240x64). Using a revolutionary wheel control the instrument can be easily programmed. MAX5 is housed into an IP65 plastic box. Measures are: L325 x H235 x D125 (including
wheel and connectors).
The wheel.
Located in the upper right side of MAX5 there is a wheel that must be used to control the instrument. Wheel can be
rotated in both directions to scroll over the menus and / or pressed to conrm highlighted selection / value.
NOTE: Once changes are made press “OK” to save and exit from submenu. Press “ESC” to exit without saving.
Into main menu rotate the wheel to cycle-loop through all options.
Clockwise: setpoint --> Calibration --> Option --> Manual -->Exit
or Counterclockwise.
Press wheel to move on submenu for selected option.
*conguration and screenshots may be different and not including some functions. A maximum of 5 channels can be set.
Page 4

4
Mainboard Connections.
Unplug instrument from main power supply then perform connections to probes and / or selected outputs by following the
above picture. For easy understanding board as been divided into two parts: Power connections and I/O connections.
For EClx series probes, NTU connections and ETHERNET version, see APPENDIX A at page 30.
Power Connections:
F1: Main fuse (6.3AT)
F2: Circuit fuse (3.15AT)
LA - LB: Relay Output Disable Jumper (remove wire to disable outputs)
Main power supply (from 90VAC to 265VAC): L (live), E (earth), N(neutral)
Setpoint Outputs (VAC same on main power supply):
(free contact versione are NOT fuse protected with a max insulation of 250V)
1 - E - N (F2 fuse protected)
2 - E - N (F2 fuse protected)
3 - E - N (F2 fuse protected)
4 - E - N (F2 fuse protected)
5 - E - N (F2 fuse protected)
6 - E - N (F2 fuse protected)
Probe Cleaning output: 7(N.C.), 8(C), 9(N.O.) Voltage free contact
General Alarm output: 10(N.C.), 11(C), 12(N.O.) Voltage free contact
Warning: Connections must be perfomed by qualied and trained personnel only.
Block numbers are related only to its own part of the board.
]
Power Connections
]
I/O Connections
L 1 2 3 4 5 6
E E E E E E E
7 8 9 10 11 12
F1
F2
A B
29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
N N N N N N N
Page 5

5
I/O Connections:
Proportional pump (mod. “IS” driven by pulses) outputs:
1(-) ; 2(+): Output P1
3(-) ; 4(+): Output P2
5(-) ; 6(+): Output P3
7(-) ; 8(+): Output P4
9(-) ; 10(+): Output P5
11(-) ; 12(+): Output P6
mA outputs (max resistive load: 500 Ohm):
13: Common
14: mA output 1
15: mA output 2
16: mA output 3
17: mA output 4
18: mA output 5
19: mA output 6 (temperature*)
*0°C / 4mA - 100°C / 20mA
RS485:
26: + Signal RS485 (A)
27: - Signal RS485 (B)
Tank Level inputs:
29 (-) ; 30 (+) Level 1
31 (-) ; 32 (+) Level 2
33 (-) ; 34 (+) Level 3
35 (-) ; 36 (+) Level 4
37 (-) ; 38 (+) Level 5
Proximity Sensor (mod. “SEPR”) input:
39(+ Brown) ; 40(Black) ; 41(- Blue)
41 shortcut with block n.37
Contact input*: 39(White) ; 40(Black)
41 shortcut with block n.37
set ow option from setup menu
(Hall effect) pulse sender water meter: 42(+12VDC) ; 43(INPUT) ; 44(GND)
(Contact) Pulse sender water meter: 43(INPUT) ; 44(GND)
Temperature Probe input for mod. “PT100”** only: 50(green) ; 51(brown) ; 52(white) ; 53(yellow)
(remove resistance before to install probe)
Temperature Probe input for “PT100” with 50(green) ; 51(orange or pink) ; 52(white) ; 53(yellow)
ECDIND probe: (Ref. A Appendix - Inductive Conductivity module)
Standby signal input: 54(+) ; 55(GND)
*This is “FLOW1” for “MAX5 PH CL PH CL double ow” model only
**This is “TEMP2” for “MAX5 PH CL PH CL double ow” model only
OPTO COUPLED
SIGNALS
(-) is NOT a shared
signal !
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS
on demand
GND is a shared ground
(-) is a shared (GND)
ground signal !
OPTIONS
OPTIONS
OPTIONS
Page 6

6
Main screen.
From main screen all instrument fucntions can be reached by rotating the wheel and highlighting the selected option.
Options available are located in the low right corner of the screen.
Status control. Press here to scroll through:
main menu alternate view
status of inputs - outputs - alarms - timers
log entries
service (it shows also ID DEVICE and ID USB DEVICE)
Use Code Number when register
for ERMES WEB services
Setup menu. (passcode protected area)
Off menu. Press here to turn off instrument
Alarm menu. Press here to stop alarms
Connection Status
LAN CONNECTION OK - ERMES CONNECTION OK
LAN CABLE DISCONNECTED
LAN CABLE CONNECTED - ERMES NOT AVAILABLE
g. 1
Page 7

7
Passcode.
From main screen rotate wheel until to highlight then press wheel.
Note: This is a passcode protected area. For this reason every time this menu is reached, the instrument will ask for a
passcode as shown.
If this is a “rst time visit” the default passcode is “0000” (both Administrator and User).
Just press four times the wheel. Otherwise rotate wheel to move through digits and press wheel to choose.
Rotate wheel to ESC and press wheel to go back to main screen without accessing setup menu.
Setup.
From main screen rotate wheel until to highlight then press wheel. Enter passcode as described in previous paragraph.
Rotate wheel to scroll through all options and press wheel to enter into menu of selected option.
Setpoint option. Use this menu to dene instrument operating mode, output conguration, alarm condition, mA outputs.
Calibration option. Use this menu to calibrate main instrument readings (pH, ORP Chlorine, Turbidity and, Temperature ).
Option. Use this menu for TAU setup, delay output, ow detect, clock setup, probe clean, reset, RS485 setup, alarm setup,
log setup, passcode setup.
Manual. Use this menu for manual outputs activation (Relay, pulse, mA, level).
Exit. Use this option to go back to main screen.
g. 2
g. 3
Page 8
8
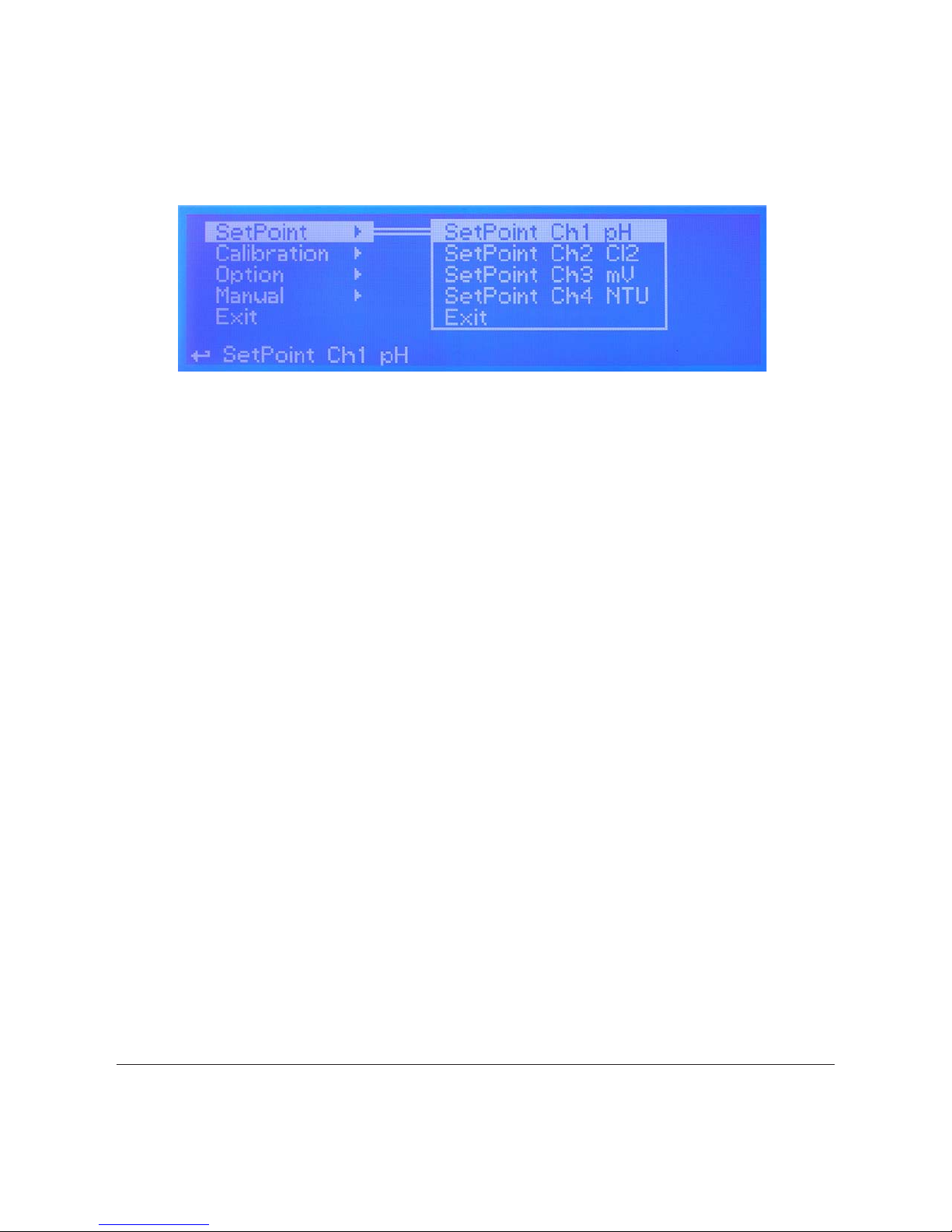
Setpoint.
From setup menu (g.3) rotate wheel to highlight “Setpoint” then press wheel. Again rotate wheel until to reach desired
measure between pH - Cl
2
- mV - NTU - Temperature. Customized version includes: potentiostat (mg/l Cl2) and Fluorine (F)
Once into “measure submenu”*, is possible to edit (all or some) the following setpoint parameters:
[Da] “setpoint output A” that can be congured as on/off, PWM or PID and settable as 1 to 6 channel
[Db] “setpoint output B” that can be congured as on/off, PWM or PID and settable as 1 to 6 channel
[Pa] “proportional pump output A” and settable as 1 to 6 channel
[Pb] “proportional pump output B” and settable as 1 to 6 channel
[mA] “mA output” settable as 1 to 6 channel
[Aa] “general alarm A” for “out of limits” reading parameters
[Ab] “general alarm B” for “out of limits” reading parameters
[Ad] “general alarm” for maximum dosing time
[Ar] “general alarm” for damaged probe (same reading after a set time)
Total amount of output-channels available is 6. This number decreases every time a channel is assigned to a specic
function during setup. Once there are no more channels available the instrument will read only probe’s value. For
temperature channel is available ON/OFF mode only during setpoint setup.
Da and Db.
Using Da and / or Db is possible to control the status of “setpoint outputs” and “level outputs” based on some rules.
Refer to “power connections” and “I/O connections” blocks at page 4 and 5 to locate these outputs on mainboard.
Once that Da or Db function is enabled (move wheel over “disable” , press, rotate to “enable”, press again to exit) the
main parameters are
MODE (ON/OFF - PWM - PID), RL, LEV and STOP.
g. 4
“Channel” is the related output of mainboard connections.
*Setpoint pH or Cl2 or mV or NTU
Page 9
9
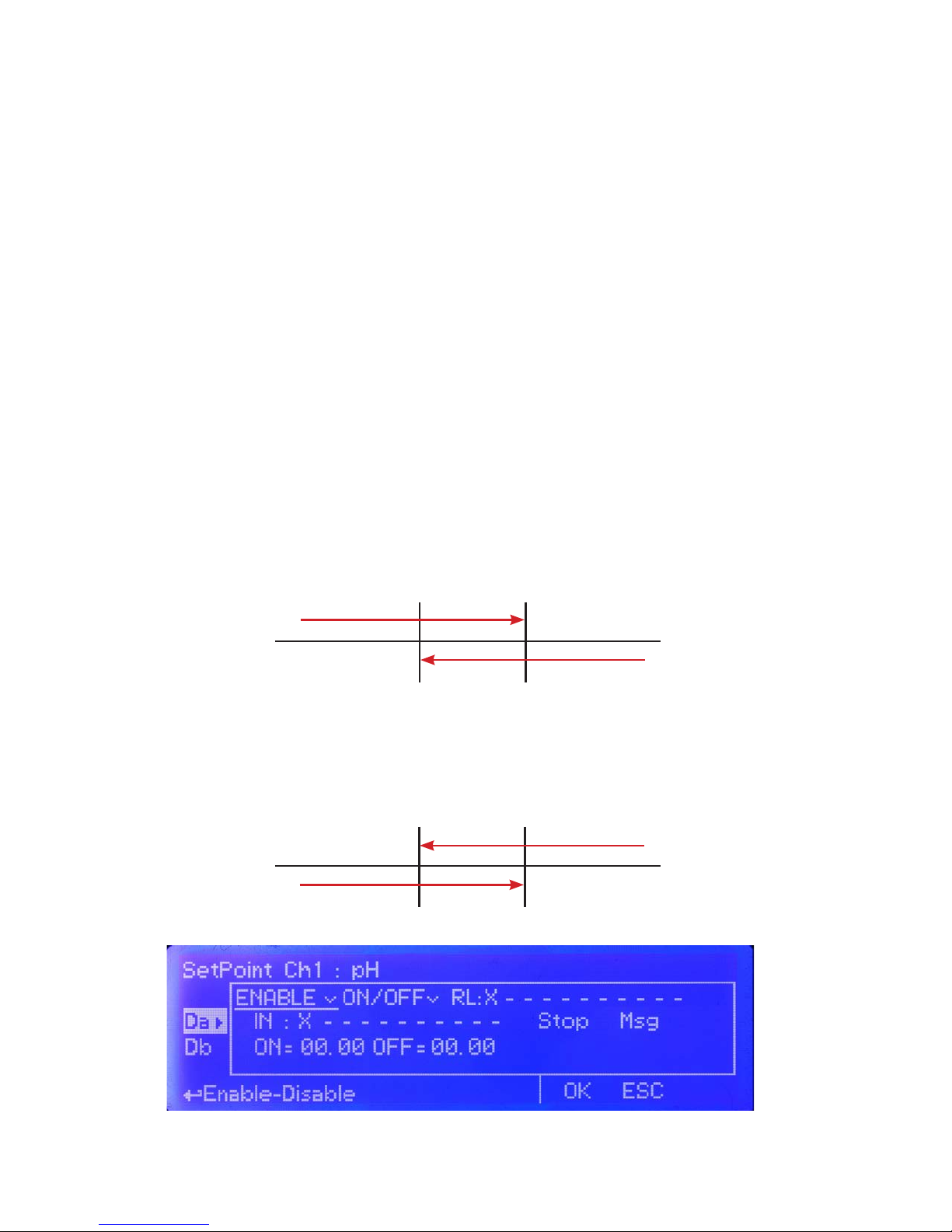
Da and Db WORKING MODES.
ON/OFF Mode.
On/Off mode set the instrument to operate using two set values that enable or disable the related setpoint output.
Parameters to set for this mode are:
ON: Activate RL and LEV on moving towards the unit value (for example: pH)
OFF: Disable RL and LEV on moving towards the unit value (for example: pH)
IN: assign “input” number then edit the name by moving wheel. If the “input” number is already used then it will not be
shown. Choose “X” instead of a number to disable input.
RL: assign “relay” number then edit the name by moving wheel. If the “relay” number is already used then it will not be
shown. Choose “X” instead of a number to disable relay.
STOP: (“ON”: when product into tank is ending, then the related output will be off and an alarm condition will pop-up.
“OFF”: when product into tank is ending, then the related output will continue to stay on and an alarm condition will pop-up.)
MSG: when agged an SMS or EMAIL alarm message will be sent to destination edited in GSM menu.
ON/OFF mode while dosing ALKALI
Set pH value at 6.90 ON and 7.00 OFF.
Instrument will leave related output active until reading value will increase up to 7.00pH.
At 7.00pH the related output will be disabled until reading value will decrease under 6.90pH.
ON/OFF mode while dosing ACID
Set pH value at 7.00 OFF and 7.10 ON.
Instrument will leave related output active until reading value will decrease up to 7.00pH
At 7.00pH the related output will be disabled until reading value will increase up to 7.10pH.
6.90 7.00
ON
OFF
7.00 7.10
ON
OFF
g. 5
Page 10

10
PWM Mode.
Pulse-width modulation (PWM) of a signal or power source involves the modulation of its duty cycle, to either convey
information over a communications channel or control the amount of power sent to a load.
This mode works over a settable (0 to 100 seconds) time to switch on or off selected output.
Time resolution is 5 seconds, 5 steps. During this time if reading value will move towards a set value (on or off) the PWM
will operate the output on timered basis. Reaching the set value the PWM will permanently leave on or off the output.
Parameters to set for this mode are:
Unit Value + %: (time activity towards set value. 0% means 0 seconds. 100% means 100 seconds.)
IN: assign “input” number then edit the name by moving wheel. If the “input” number is already used then it will not be
shown. Choose “X” instead of a number to disable input.
RL: assign “relay” number then edit the name by moving wheel. If the “relay” number is already used then it will not be
shown. Choose “X” instead of a number to disable relay.
STOP: (“ON”: when product into tank is ending, then the related output will be off and an alarm condition will pop-up.
“OFF”: when product into tank is ending, then the related output will continue to stay on and an alarm condition will pop-up.)
MSG: when agged an SMS or EMAIL alarm message will be sent to destination edited in GSM menu.
For example: set rst pH value at 10.00 = 100% and second pH value at 5.0 = 0%.
For reading values ≥ to 10.00 the output will be permanently ON.
For reading values ≤ 5.0 the output will be permanently OFF.
For reading value of 9.50 the output will be OFF for 10 seconds, ON for 90 seconds.
If reading value decreases to 8.00 then the output will be OFF for 20 seconds, ON for 80 seconds.
Notes: for values within 1% and 5% MAX5 will assume 5% as usable value.
for values within 95% and 99% MAX5 will assume 95% as usable value.
g. 5
Page 11
11
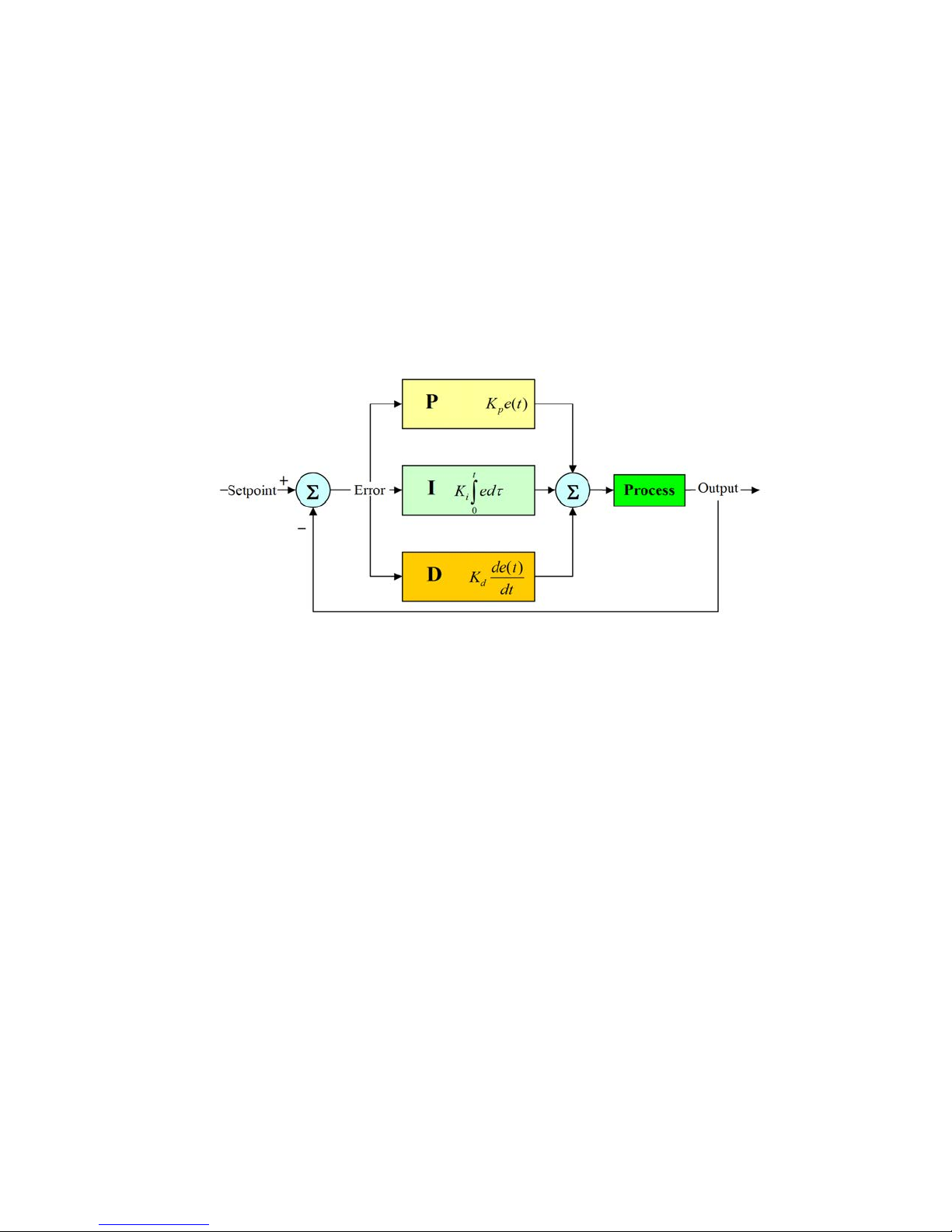
PID Mode.
A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller) is a generic control loop feedback mechanism.
PID controller attempts to correct the error between a measured process variable and a desired setpoint by calculating
and then outputting a corrective action that can adjust the process accordingly.
The PID controller calculation (algorithm) involves three separate parameters; the Proportional, the Integral and
Derivative values. The Proportional value determines the reaction to the current error, the Integral determines the
reaction based on the sum of recent errors and the Derivative determines the reaction to the rate at which the error has
been changing. The weighted sum of these three actions is used to adjust the process. By “tuning” the three constants
in the PID controller algorithm the PID can provide control action designed for specic process requirements. The
response of the controller can be described in terms of the responsiveness of the controller to an error, the degree to
which the controller overshoots the setpoint and the degree of system oscillation. Note that the use of the PID algorithm
for control does not guarantee optimal control of the system or system stability.
(K
p
) is the constant proportional gain
(K
i
) is the constant integral gain
(K
d
) is the constant derivative gain
(e): error
(t): Time in the past contributing to the integral response
Parameters to set for this mode are:
IN: assign “input” number then edit the name by moving wheel. If the “input” number is already used then it will not be
shown. Choose “X” instead of a number to disable input.
RL: assign “relay” number then edit the name by moving wheel. If the “relay” number is already used then it will not be
shown. Choose “X” instead of a number to disable relay.
STOP: (“ON”: when product into tank is ending, then the related output will be off and an alarm condition will pop-up.
“OFF”: when product into tank is ending, then the related output will continue to stay on and an alarm condition will pop-up.)
ON: Activate RL and LEV on moving proportionally towards the unit value (for example: pH)
OFF: Disable RL and LEV on moving proportionally towards the unit value (for example: pH)
I: integral time (from 0s to 59m:59s)
D: derivative time (from 0s to 59m:59s)
g. 6
Page 12

12
Pa and Pb.
Using PxA and / or PxB is possible to control the status of “Proportional pump outputs” based on some parameters.
Refer to “I/O connections” blocks at page 5 to locate these outputs over the mainboard. Once that PxA or PxB function
is enabled (move wheel over “disable” , press, rotate to “enable”, press again to exit) then main parameters are
OUTOPTO, LEV, STOP and pH - PM.
OUT: is referred to “Porportional pump outputs” from “I/O Connections” of mainboard. Set this value between available
outputs. If an output is already used then it’ll be hided from list.
IN: assign “input” number then edit the name by moving wheel. If the “input” number is already used then it will not be
shown. Choose “X” instead of a number to disable input.
STOP: (“ON”: when product into tank is ending, then the related output will be off and an alarm condition will pop-up.
“OFF”: when product into tank is ending, then the related output will continue to stay on and an alarm condition will pop-up.)
MSG: when agged an SMS or EMAIL alarm message will be sent to destination edited in GSM menu.
pH - PM
These elds require to set two pH values with pulses for a proportional working mode. This mode let the instrument to
modulate output pulses proportionally to reaching value.
For example: Set rst pH to 10.00 with 250PM. Set second pH to 7.00 with 0PM.
If reading value is 10.00 then 250pulses per minute will be forwarded to related output.
If reading value is 7.00 then no pulses will be forwarded to related output.
If reading values are 8.5 then 125pulses per minute will be forwarded to related output.
g. 6
Page 13

13
mA.
Using mA is possible to control the status of “mA outputs” based on some parameters. Refer to “I/O connections”
blocks at page 5 to locate these outputs over the mainboard. Once that mA1 function is enabled (move wheel over
“disable” , press, rotate to “enable”, press again to exit) then main parameters are
OUTmA, LEV, STOP and pH - mA.
Out: is referred to “mA outputs” from “I/O Connections” of mainboard. Set this value between available outputs. If an
output is already used then it’ll be hided from list.
IN: assign “input” number then edit the name by moving wheel. If the “input” number is already used then it will not be
shown. Choose “X” instead of a number to disable input.
STOP: (“ON”: when product into tank is ending, then the related output will be off and an alarm condition will pop-up.
“OFF”: when product into tank is ending, then the related output will continue to stay on and an alarm condition will pop-up.)
MSG: when agged an SMS or EMAIL alarm message will be sent to destination edited in GSM menu.
pH - mA
These elds require to set two pH values with mA for a proportional working mode. This mode let the instrument to
modulate mA proportionally to reaching value. mA range is from 0 to 20mA.
For example: Set rst pH to 10.00 with 15mA. Set second pH to 7.00 with 0mA.
If reading value is 10.00 then 15mA will be forwarded to related output.
If reading value is 7.00 then no mA will be forwarded to related output.
If reading values are 8.5 then 7.5mA will be forwarded to related output.
Note: for 2 CD channels and 5 4/20mA outputs version the setpoint on Ch. 2 operates for all mA outputs
g. 7
Page 14

14
Aa and Ab
Using Aa and / or Ab is possible to set a visual alarm with delay for values ≥ or ≤ than set value. Once that Aa or Ab
function is enabled (move wheel over “disable” , press, rotate to “enable”, press again to exit) then main parameters are
ALARM and DELAY.
ALARM.
Alarm condition can be set “ON” or “OFF” and for pH values ≥ or ≤ than set value. Reaching that value an alarm
message will pop-up.
DELAY.
A delay from 0 to 99 minutes can be set before the instrument generates the alarm.
MSG.
when agged an SMS or EMAIL alarm message will be sent to destination edited in GSM menu.
AD
Using AD is possible to set a maximum dosing time. This alarm prevents connected pump to dose if set time is
reached. Time can be set between 1minute and 9hours and 59minutes. Related setpoint output will be disabled when
AD alarm condition is reached.
MSG.
when agged an SMS or EMAIL alarm message will be sent to destination edited in GSM menu.
g. 8
g. 9
Page 15

15
AR
Using AR is possible to set a visual alarm if probe’s reading value continues to be the same for a set time. Time can be
set between 1minute and 9hours and 59minutes.
MSG.
when agged an SMS or EMAIL alarm message will be sent to destination edited in GSM menu.
g. 10
Page 16

16
Calibration.
From setup menu (g.3) rotate wheel to highlight “Calibration” then press wheel. Again rotate wheel until to reach desired
calibration measure pH - Cl2 - mV - NTU and Temperature.
pH Calibration.
pH calibration procedure involves two calibration points and it requires two buffer solutions. Default buffer solutions are
pH 4.00 and pH 7.00. pH reading value can be also automatically temperature compensated.
In the following example instrument will calibrate pH using default buffer solutions value.
This procedure assumes that instrument is correctly congured and a working pH probe connected.
Otherwise unattended results may occurr.
Calib 1st Point.
Once into “Calibration pH” menu move wheel on “Calib 1st Pt” then press wheel to enter into rst point calibration
submenu. Prepare 7.00pH buffer solution and dip probe’s sensor on it. Wait until reading value is stable and according
to buffer solution value move wheel until it is the same on display (“pH default” eld). Default value is 7.00pH. To end
procedure move cursor on “OK” and press wheel to proceed to next step.
Note: buffer solution value may change if environment temperature it’s different than 20°C. Read solution’s label for more
information. According to this occurrence “pH Default” must be changed.
Calib 2nd Point.
Move wheel on “Calib 2nd Pt” then press wheel to enter into second point calibration submenu. Prepare 4.00pH buffer
solution and dip probe’s sensor on it. Wait until reading value is stable and according to buffer solution value move
wheel until it is the same on display (“pH default” eld). Default value is 4.00pH. To end procedure move cursor on “OK”
g. 11
g. 12
Page 17
17
and press wheel to proceed to next step.
Note: buffer solution value may change if environment temperature it’s different than 20°C. Read solution’s label for more
information. According to this occurrence “pH Default” must be changed.
Comp Auto / Select Temp.
Once into submenu, to enable automatic temperature compensation, move wheel on “DISABLE” , press it and change
option to “ENABLE”. This procedure will automatically set temperature compensation.
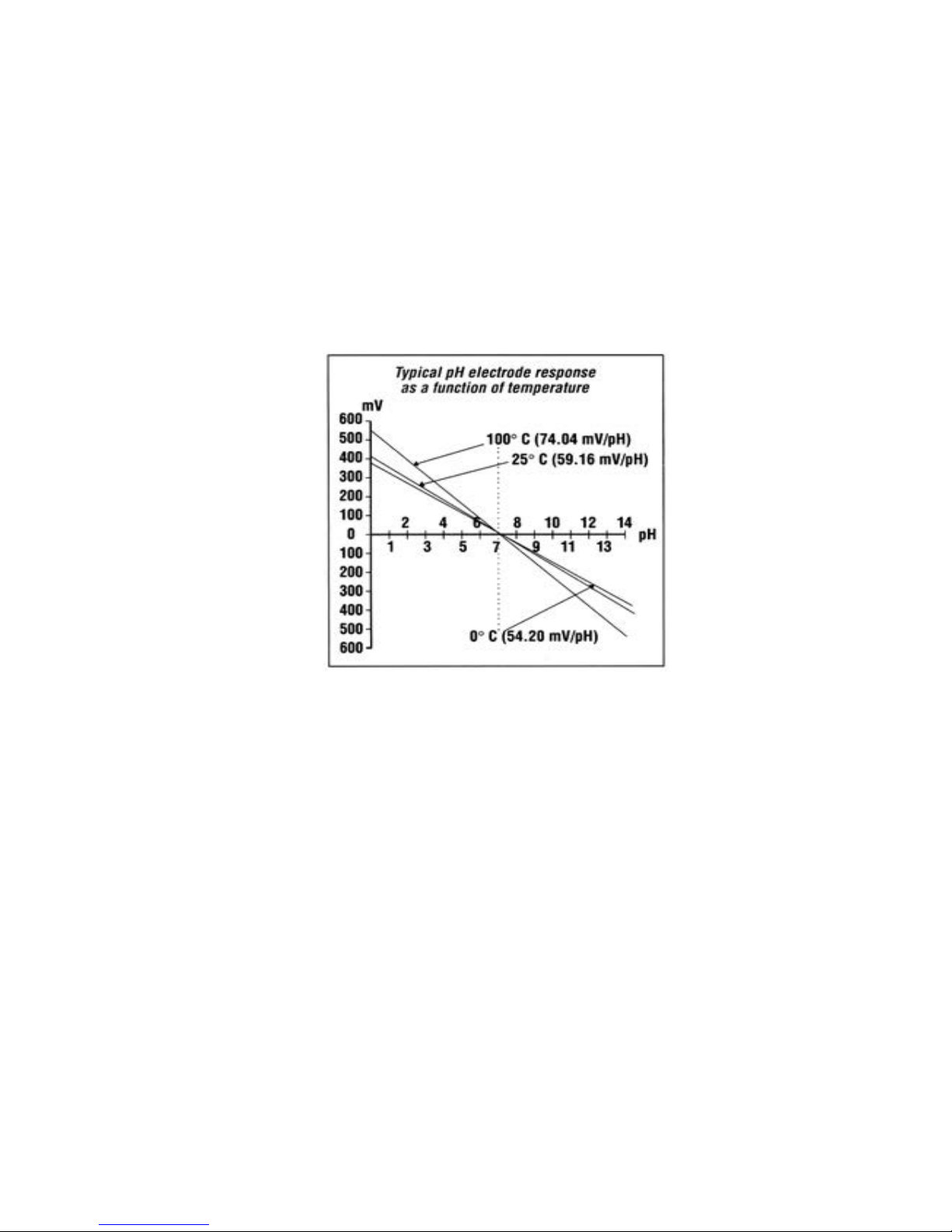
Otherwise exit from this menu, move wheel on “Select Temp” and according to the following table enter required tempe-
rature. This procedure will manually set temperature compensation.
End procedure by moving cursor on “Exit” from “Calibration pH” main menu and press it. If an error occurred during calibration procedure then the instrument will show an error message and will ask to proceed to a new calibration, cancel
current operation or restore default settings.
g. 13
Page 18

18
Cl Calibration.
Cl calibration procedure involves probe’s selection, Zero and 2nd Point calibration.
This procedure assumes that instrument is correctly congured and a working Chlorine probe connected and installed
on system. Measurement must be performed using plant water.
Otherwise unattended results may occurr.
Select Probe.
Once into “Calibration Cl” menu move on “Select Probe” then press wheel to enter into probe list. According to system
choose most suitable probe by moving the wheel. Then press to conrm. Note: SCLxx probes series don’t require
ZERO calibration and select probe.
g. 14
Probe Scale (mg/l)
ECL 1/2 2.000mg/l Cl2
ECL 1/5 5.00mg/l Cl2
ECL 1/20 20.00mg/l Cl2
ECL 1/200 200.0mg/l Cl2
ECL 2/2 2.000mg/l Cl2O2
ECL 2/20 20.00mg/l Cl2O2
ECL 3/2 2.000mg/l Cl2
ECL 3/10 10.00mg/l Cl2
ECL4,5,6,7 10.00mg/l Cl2 or Br
ECL 8/2 2.000 mg/l Cl2Tot
ECL 8/20 20.00 mg/l Cl2Tot
ECL 9/200 200.0mg/l H2O2
ECL9/2000 2000mg/l H2O2
ECL10/1 0.5mg/l O3
ECL 10/10 10.00mg/l O3
ECL11/200 200.0mg/l peracetic acid
ECL11/2000 2000mg/l peracetic acid
ECL 13 60.00mg/l O2
ECL 17/10 10.00mg/l Cl2O2
ECL 18/10 10.00 mg/l Cl2
Page 19

19
Calib Zero.
Once into “Calibration Cl” menu move on “Calib Zero” then press wheel to enter into calibration mode. For a correct
system calibration proceed as follows.
- install an “activated carbon lter” prior to probe’s holder.
- let system water ow into probe holder for about 30 minutes.
- press wheel (cursor must be on “OK”).
- remove “activated carbon lter”.
Calib 2nd point.
Once into “Calibration Cl” menu move on “Calib 2nd Pt” then press wheel to enter into calibration mode. For a correct
system calibration use a Photometer or a DPD device to read chlorine on system. Enter value using the wheel the move
cursor on “OK” then press wheel.
End procedure by moving cursor on “Exit” from “Calibration Cl” main menu and press it. If an error occurred during ca-
libration procedure then the instrument will show an error message and will ask to proceed to a new calibration, cancel
current operation or restore default settings.
Carbon Filter System
Photometer
Page 20

20
mV Calibration.
ORP calibration procedure involves one calibration point and it requires one buffer solution. Default buffer solution is
650mV.
This procedure assumes that instrument is correctly congured and a working ORP probe connected.
Otherwise unattended results may occurr.
Once into “Calibration mV” menu move wheel on “Calibration” then press wheel to enter into calibration submenu.
Prepare 650mV buffer solution and dip probe’s sensor on it. Wait until reading value is stable and according to buffer
solution value move wheel until it is the same on display (“mV default” eld). Default value is 650mV. To end procedure
move cursor on “OK” and press wheel to proceed to next step.
Note: buffer solution value may change if environment temperature it’s different than 20°C. Read solution’s label for more
information. According to this occurrence “mV Default” must be changed.
End procedure by moving cursor on “Exit” from “Calibration mV” main menu and press it. If an error occurred during calibration procedure then the instrument will show an error message and will ask to proceed to a new calibration, cancel
current operation or restore default settings.
g. 15
Page 21

21
Range (NTU).
Once into “Calibration NTU” menu move wheel on “Range” to see probe’s scale.
“ETORBH” probe’s reading range can be set within: 9,999NTU - 99,99NTU - 999,9NTU - 9999NTU.
For reset calibration procedure select “Redo calibration”.
SONDA “ETORBH”
Page 22

22
Temp Calibration.
Temperature calibration needs an external thermometer to match probe’s reading value.
This procedure assumes that instrument is correctly congured and a working temperature probe connected.
Otherwise unattended results may occurr.
Once into “Calibration Temp” menu move wheel on “Calibration” then press wheel to enter system temperature obtained
from a thermometer. Press wheel to conrm then move cursor on “OK” and press wheel to proceed “Calibration Temp”
main menu. End procedure by moving cursor on “Exit” from “Calibration Temp” main menu and press it.
If an error occurred during calibration procedure then the instrument will show an error message and will ask to proceed
to a new calibration, cancel current operation or restore default settings.
g. 17
Page 23

23
Conductivity (uS) Calibration.
Conductivity calibration involves the following steps:
1) Working scale setup
Move cursor on “Range” then press wheel. Acording to probe reading capacity select proper scale by rotating wheel.
Once satised press wheel, move cursor on “OK” and press wheel again. See page 35 for proper scale settings. Also
available TDS conductivity with 0-9999 scale.
2) Turn off MAX5. Remove cover and locate CD module jumper settings as shown on page 35. Set jumpers as required.
Put cover back to MAX5.
3) Turn on MAX5. Once into conductivity menu choose Calib 1st Pt.Calibration.
Conductivity calibration procedure involves a zero calibration (1st point calib) and a 2nd calibration point that requires
a buffer solution with value near working range. During this procedure probe must be dry and clean and not installed in
plant. Once into “Calibration uS” menu move wheel on “Calib 1st Pt” then press wheel, move cursor on “OK” and press
wheel again.
Move wheel on “Calib 2nd Pt” then press wheel to enter into second point calibration submenu. Prepare buffer solution
and dip probe’s sensor on it. Wait until reading value is stable and according to buffer solution value move wheel until it
is the same on display (“uS default” eld). End procedure moving cursor on “OK”
This procedure assumes that instrument is correctly congured. Otherwise unattended results may occurr.
g. 38
g. 39
g. 40
Page 24

24
4) Move cursor on “Comp Auto” then press wheel. Rotate wheel to Enable or disable automatic temperature compensation.
Enabling this option will override “Select Temp” setup then move cursor on “ESC” or “OK” and press wheel to conrm.
5) Move cursor on “Temp Coeff” then press wheel. This option set conductivity % variation based on temperature. To
disable it enter 0.0 % as value. Move cursor on “ESC” or “OK” and press wheel to conrm.
6) Move cursor on “Select Temp” then press wheel. If a temperature probe is not connected, pool temperature must be
set manually. Rotate wheel to set it and conrm by pressing wheel. Move cursor on “ESC” or “OK” and press wheel to
conrm.
Measurement temperature has a signicant inuence on conductivity readings; but appropriate temperature compensation is a powerful tool to allow meaningful comparison of
readings taken at different temperatures. The analyst must ensure that the type of temperature compensation utilized is appropriate for both the type of sample being analyzed
and the required test accuracy. This is an essential factor for determining the suitability of a conductivity instrument for measurement applications. A conductivity measurement
taken with the sample at the reference temperature will always be more accurate than a temperature compensated reading taken away from the reference temperature – this
point is essential for critical applications requiring high accuracy of measurements.
g. 41
g. 42
g. 43
Page 25

25
TIMER
Timers are usually used for activities such as a “shock chlorination”. Once the function is enabled (move wheel on
disable, click and then rotate) there are ve main parameters to set. T
imer available may be up to 5.
Timer will start at a specied time of a set day (multiple days can be selected).
Out
Choose one or both two related outputs (not previously assigned , chlorine output exception) that will be enabled during
set time. Out1, Out2, ect. are referred to MAX5 channel.
Ton
This is the activity starting time.
Toff
This is the activity ending time.
Mo (Monday), Tu (Tuesday), We (Wednesday), Th (Thursday), Fr (Friday), Sa (Saturday), Su (Sunday).
These are the days in which activity will be enabled. Multiple days can be selected.
Shock chlorination is a process used in many swimming pools, water wells, springs, and other water sources to reduce the bacterial and algal residue in the water. Shock
chlorination is performed by mixing a large amount of sodium hypochlorite, which can be in the form of a powder or a liquid such as chlorine bleach, into the water. Water that
is being shock chlorinated should not be swum in or drunk until the sodium hypochlorite count in the water goes down to three ppm or less.
g. 31
main menu
Page 26

26
TIMER 2 (to 5)
Timer2 is usually used for activities such as a “anti algae treatment”. Once the function is enabled (move wheel on
disable, click and then rotate) there are 6 main parameters to set.
Timer starts at a specied time of the year and can be repeated every xx days.
Out1 and Out2.
Choose one or both two related outputs (not previously assigned , chlorine output exception) that will be enabled during
set time.
Ton
This is the activity starting date and time.
Toff
This is the activity ending time.
LOOP
These are the day-countdown in which activity will be repeated.
E.g.: LOOP 03 means that every three days activity will be repeated at specied time.
Anti algae treatment is a process used in many swimming pools, water wells, springs, and other water sources for killing and preventing all pool algae types.
g. 32
Page 27

27
Options.
From setup menu (g.3) rotate wheel to highlight “Options” then press wheel. Main options are:
TAU : It determines how quickly reading on display follows the reading of the probe. It can be changed between 0 and
30. The more close to 0 this value is set and the more quickly the reading on the display will change, take in consideration
that quickly changes on the display will result in unstable readings.
DELAY : it’s the pump output activation delay. Can be set between 0 and 99 minutes and it takes effect on start up of
the instrument, quitting from stand-by condition and after a “Flow Alarm”. “Delay SMS”: sends warning message if alarm
condition persists after set time. Delay Init: countdown after instrument’s initialization (booting) before to return operative.
g. 18
g. 19
g. A
g. B g. C
FM Counter
Use this function to enable ow monitoring for connected pulse sender water meter (blocks 37 and 38). Set metering
control unit to Liters (LIT) or gallons (GAL). Move on Imp/LIt to choose between Pulses per liter or Liters per pulses and
counter value. Move on OK and press wheel to save parameters. To see counter status press twice from main menu.
g. 20
Page 28

28
FLOW DETECT
Choose the ow sensor input, set to “Direct” activates the standard ow sensor (“SEPR” proxy
sensor). Set to “Reverse” the digital logic of the sensor is inverted. Set to “Disable” the ow sensor is not enabled.
MSG.
If agged an SMS / EMAIL alarm message will be sent to recipients added in communication menu.
OUT mA.
If agged and the mA module is properly installed, all current outputs will be disabled during a ow alarm.
CLOCK SETUP
Change date and time according to local zone and international format. Move wheel to change between different congurations.
g. 21
g. 22
Page 29

29
PROBE CLEAN
Once into submenu, to enable probe clean, move wheel on “DISABLE” , press it and change option to “ENABLE”.
CYCLE: time until next probe clean. HH (hours) and MM (minutes).
CYCLE T: probe cleaning duration. MM (minutes) and SS (seconds).
RESTORE T: idle time after probe clenaing procedure. MM (minutes).
CLEAN A: Set “ON” to activate clenaing procedure when a setpoint alarm occurs.
Note: during cleaning and restoring procedure all setpoint outputs are disabled.
EEPROM RESET
To restore instrument to its original settings press “LOAD” and wait until “busy” message disappears.
RS485 SETUP
Prior to install the instrument into an RS485 local system a unique ID NUMBER and ID NAME (station name) must be
congured. Rotate wheel and edit elds. If ID number has already assigned an error message will follow. In this event try
using another number.
g. 24
g. 25
g. 23
Page 30
30
GSM MODEM
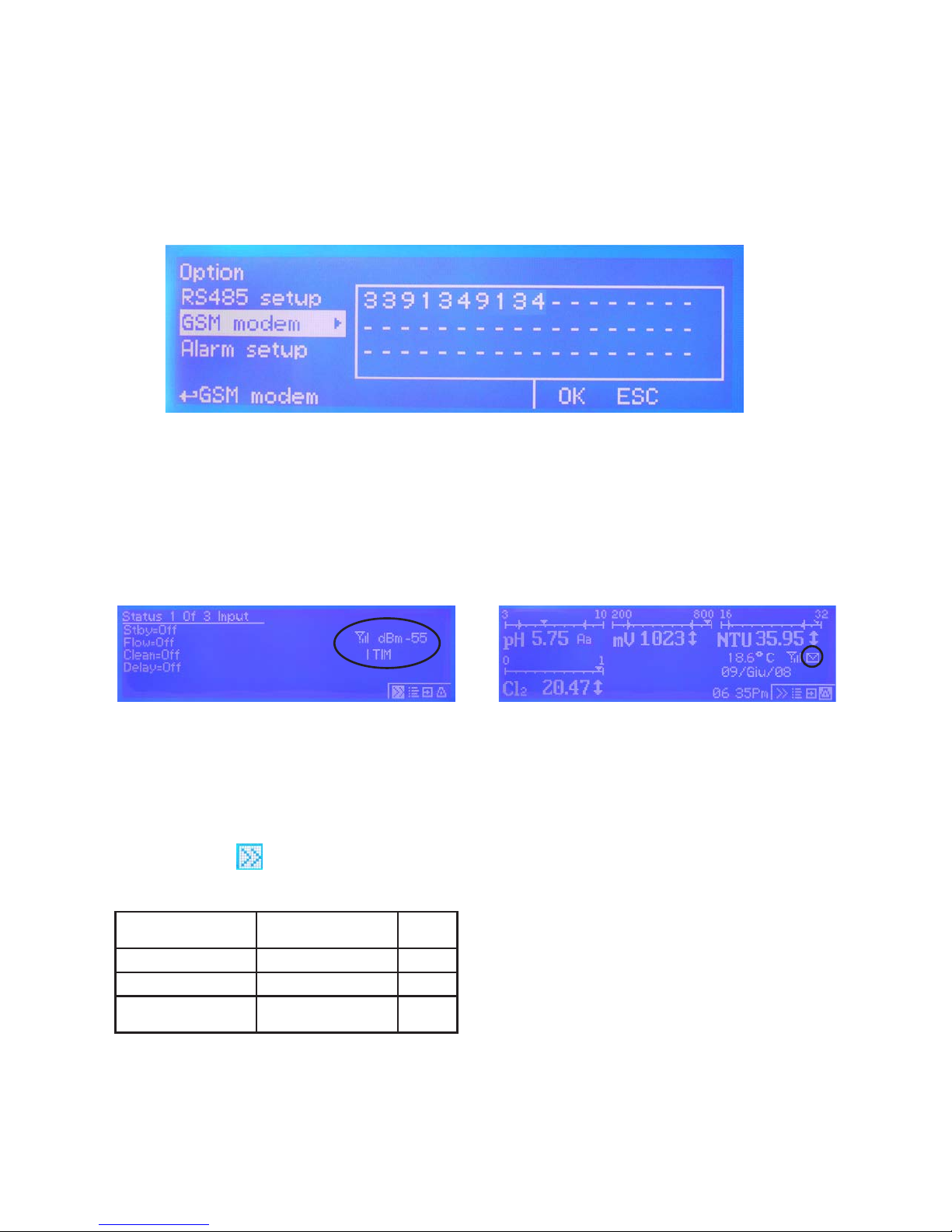
MAX5 may remotely send SMS alarm messages using its own modem (where available). Options can be congured as
follows:
SMS1 / SMS2 /SMS3: Using the wheel enter a mobile phone that will receive alert SMS messages if something wrong
occurrs. Log level (and SMS frequency alert) may be set using options in “Log setup” menu. SMS number must be set
using local number format. For example : 3391349134 will send an SMS message to mobile phone.
- TO AVOID UNDESIRED MESSAGES USE CAREFULLY LOG SETUP -
- WARNING: THIS FUNCTION COULD NOT BE FREE OF CHARGE. DEPENDING ON YOUR OPERATOR CONTRACT IT
COULD GENERATE PAYING SMS TRAFFIC !
g. 26
GSM SIGNAL STATUS
Before to congure SMS phone number ensure that
internal gsm modem has enough signal to operate
correctly.
To check this press twice from main menu and
verify signal strength as following:
0 or 1 bar (-113dBm to -103dBm) no signal or very low signal re-orient
antenna
1 or 2 bars (-103dBm to -95dBm) low signal slow conn.
2 or 3 bars (-95dBm to -85dBm) good signal ok
3 or 4 bars (-85dBm to -51dBm
or more)
optimum signal ok
MAX GSM MODEM VERSION
Antenna icon on MAX5 display means that modem is
correctly installed.
Blinking envelope means that MAX5 is trying to
send an alert message to preferred numbers (SMS1
and/or SMS2 and/or SMS3). If this condition stays for
more that 1 minute it could be an error while sending
message. Check modem status or instrument condition.
Fixed envelope means that MAX5 has successfully
sent an alert message to preferred numbers.
Page 31

31
TCP/IP
MAX5 may be remotely operated using a standard ethernet connection (on demand). A static or dynamic IP address
and a CAT5 ethernet cable is required. According to your network capacity connection speed is 10/100Mbps.To obtain
a valid IP address and subnet mask contact your net administrator. Enter parameters and move cursor on “SEND” to
store parameters then move on “OK” and press wheel to save and activate conguration.
From RS485 menu assign
a unique ID number to the MAX5 (page 29 - g. 25). Congure “ERMES Software” to use TCP/IP protocol and check
connection by clicking on “TEST” (pc software). Furthermore, using router IP and port 2020 forwarding option, MAX5
can be controlled through the internet (see scheme).
See “ERMES Software” manual for proper PC software conguration.
Based on your network conguration choose “Dynamic” (automatically MAX5 will receive network parameters) or
“Static” (enter manually data) conguration type.
Move wheel on “OK” to save and move on “ESC” to go back to main menu.
g. 27
What is a static IP address/dynamic IP address?
A static IP address is a number (in the form of a dotted quad) that is assigned to a computer by an Internet service provider (ISP)
to be its permanent address on the Internet. Computers use IP addresses to locate and talk to each other on the Internet, much the
same way people use phone numbers to locate and talk to one another on the telephone. When you want to visit whatis.com, your
computer asks a domain name system (DNS) server (think telephone information operator) for the correct dotted quad number
(think phone number) for whatis.com and your computer uses the answer it receives to connect to the whatis.com server.
It would be simple if every computer that connects to the Internet could have its own static IP number, but when the Internet was
rst conceived, the architects didn’t foresee the need for an unlimited number of IP addresses. Consequently, there are not enough
IP numbers to go around. To get around that problem, many Internet service providers limit the number of static IP addresses
they allocate, and economize on the remaining number of IP addresses they possess by temporarily assigning an IP address to
a requesting Dynamic Host Conguration Protocol (DHCP) computer from a pool of IP addresses. The temporary IP address is
called a dynamic IP address.
Requesting DHCP computers receive a dynamic IP address (think temporary phone number) for the duration of that Internet ses-
sion or for some other specied amount of time. Once the user disconnects from the Internet, their dynamic IP address goes back
into the IP address pool so it can be assigned to another user. Even if the user reconnects immediately, odds are they will not be
assigned the same IP address from the pool. To keep our telephone telephone analogy going, using a dynamic IP address is simi-
lar to using a pay phone. Unless there is a reason to receive a call, the user does not care what number he or she is calling from.
There are times, however, when users who connect to the Internet using dynamic IP wish to allow other computers to locate them.
Perhaps they want to use CU-SeeMe or use a VoIP application to make long distance phone calls using their IP connection. In that
case, they would need a static IP address. The user has two choices; they can contact their ISP and request a static IP address, or
they can use a dynamic DNS service. Either choice will probably involve an additional monthly fee.
Using a dynamic DNS service works as if there was an old-fashioned telephone message service at your computer’s disposal.
When a user registers with a DNS service and connects to the Internet with a dynamic IP address, the user’s computer contacts
the DNS service and lets them know what IP address it has been assigned from the pool; the service works with the DNS server
to forward the correct address to the requesting DHCP computer. (Think of calling the message service and saying “Hi. I can be
reached at 435.44.32.111 right now. Please tell anyone who tries to reach me to call that number.) Using a dynamic DNS service to
arrange for computers to nd you even though you are using a dynamic IP address is the next-best thing to having a static IP.
MAX5 ASSIGNED IP ADDRESS
SUBNET MASK ADDRESS
ROUTER GATEWAY ADDRESS
PRIMARY DNS ADDRESS
Page 32

32
GPRS
MAX5 may be remotely operated using an embedded standard GPRS modem. In order to activate this service please
ensure that the following steps are correctly completed:
- Make certain the antenna location is not shielded by metal objects or near sources of electrical ‘noise’.
- Make certain the distance from the antenna and the “MAX5” or its accessories is of a minimum of 1meter (3.28ft).
- Do not route the cable where it could be pinched in doors, windows etc.
- Ensure that SIM into “MAX5” modem is correctly inserted, activated and within operator range.
IF REQUIRED ENTER APN MANUALLY
SIM PIN CODE (4 DIGITS): enter pin code if “error pin” message appears on main screen. PIN can’t be edited.
ERMES-SERVER: enable or disable ERMES communication through SIM CARD*
APN SIM SERVICE PROVIDER: enter SIM INTERNET PROVIDER ACCESS manually if required.
USERNAME / PASSWORD FOR SIM INTERNET ACCESS: enter these information only if required.
Please locate CODE NUMBER in SERVICE MENU for using to gain acess to ERMES WEB SERVICES
*WARNING: THIS FUNCTION COULD NOT BE FREE OF CHARGE. DEPENDING ON YOUR OPERATOR CONTRACT IT
COULD GENERATE PAYING DATA TRAFFIC !
EMAIL
MAX5 may send alarm email messages if properly congured through ETHERNET connection. In order to activate this
option enter the following information:
g. 28
Access point name (APN) identies an IP packet data network (PDN), that a mobile data user wants to communicate with. In addition to identifying a PDN, an
APN may also be used to dene the type of service, (eg connection to wireless application protocol (WAP) server, multimedia messaging service (MMS)), that
is provided by the PDN. APN is used in 3GPP data access networks, eg general packet radio service (GPRS), evolved packet core (EPC).
g. 29
1st email address (to destination)
2nd email address (to destination)
Page 33

33
LOG SETUP
Log setup stores instrument activities when an alarm (ow, level, general) occurs or after a set
time.
ENABLE: enable or disable log function
TIME: log starting time (format 23h 59min)
EVERY: frequency of recording (format 23h 59min)
OUTPUT ON: Enable / disable Log For Outputs
DATA FILTER: lter that allows you to avoid repeating for the same alarm (max 59 minutes). If the
same alarm is repeated during set time the instrument won’t send any SMS.
SET DATE & TIME BEFORE TO ENABLE LOG. IF NOT POWERED FOR ABOUT 30 DAYS THE INSTRUMENT WILL
LOOSE DATE/TIME
PASSCODE
Change default passcode (“00 00”) by rotating wheel on each of two-digits groups. Press “OK” to conrm or “ESC”
to exit without saving. Administrator can also set passcode for “User” with limited access (no instrument reset / mA
setpoint unavailable).
g. 31
g. 32
ALARM SETUP
When an alarm condition is displayed and general alarm output is possible to choose between two working modes.
Continuos: alarm condition never stops until “ESC” is pressed.
Timered: alarm condition ends after set time.
g. 30
Page 34

34
Manual.
Outputs may be activated manually for testing purposes.
“Manual Relay” will activate “setpoints outputs” (see page 4). Exiting from manual mode will revert selected output to its
original condition.
“Manual Pulse” will activate “Proportional pump outputs” (see page 5) with selectable pulses from 0 to 150 for each
ouptut. Exiting from manual mode will revert selected output to its original condition.
g. 33
g. 34
g. 35
Page 35

35
“Manual mA” will activate “mA outputs” (see page 5) with selectable pulses from 0 to 20mA for each ouptut. Exiting from
manual mode will revert selected output to its original condition.
“Manual Level” will show “Tank level inputs” (see page 5).
g. 36
g. 37
Page 36

36
Appendix A - Probes Connections.
Located in upperside of mainboard there are four connectors that can be used to install probe modules. Modules
come pre-installed upon request and may appear different as shown (different congurations). Identify installed modules
to correctly connect probes. For Ethernet version a standard ethernet cable (RJ45) is required.
MDCL-6
1 2
MDCL-1
1 2 3 4
Module suitable for:
ECL1
ECL2
ECL3
ECL8
ECL9
ECL10
ECL11
ECL17
ECL18
Connect probe as follows:
Block n.1 : Brown(+) wire
Block n.2 : White(-) wire
Block n.3 : Green(IN) wire
Block n.4 : Yellow(GND) wire
Module suitable for:
ECL4
ECL5
ECL6
ECL7
Connect probe as follows:
Block n.1 : Black(-) wire
Block n.2 : Red (+) wire
ETHERNET
CONNECTOR
CH1 CH2 CH3 CH4 CH5
CHLORINE module
Probes conguration
for “MAX5 PH CL PH CL double
FLOW”
model only
Ch1: PH1
Ch2: CL1
Ch3: PH2
Ch4: CL2
Ch5: Temp1
Temp1 is related to PH1 / CL1
Temp2 is related to PH2 / CL2
1 2 3
Module suitable for:
Temperature probe
Temp1 ( “MAX5 PH CL PH CL double ow” model only)
Connect as follows:
Block n.1 : Red wire
Block n.2 : White wire
Block n.3 : Black wire
TEMP1
MDSCL
Module suitable for:
SCLxx probes
Connect probe
as follows:
1 (-485) green wire
2 (+485) white wire
3 (GND) black wire
4 (+5VDC) red wire
1 2 3 4
Page 37

37
J5
J4
J3
MDCD
1 2 3
Connect probe as follows:
Block n.1 :Shield
Block n.2 : Black (probe)
Block n.3 : Red (probe)
MAX5
Probe
Scale
PROBE TYPE JUMPERS SETTINGS
K Platinum Graphite Inox J3 J4 J5
0 - 300.0 uS 0.1 ECDHL/01 x ECDI/01 OPEN CLOSED CLOSED
0 - 3000 uS 1 ECDHL/1 ECDC/1 ECDI/1 OPEN CLOSED OPEN
0 - 30.00 mS 1 ECDHL/1 ECDC/1 x CLOSED OPEN OPEN
0 - 30.00 mS 10 ECDHL/10 ECDC/10 x OPEN OPEN OPEN
0 - 300.0 mS 10 ECDHL/10 ECDC/10 x CLOSED OPEN OPEN
CONDUCTIVITY modules
MDCDT
Connect probe as follows:
Block n.1 : Conductivity Probe (red)
Block n.2 : Conductivity Probe (hot-black)
Block n.3 : GND (Shield-blue)
Block n.4 : NTC 10Kohm 25°C Temperature Probe (white)
Block n.5 : NTC 10Kohm 25°C Temperature Probe (green)
MAX5
Probe
Scale
PROBE TYPE JUMPERS SETTINGS
K Platinum Graphite Inox J3 J4 J5
0 - 300.0 uS 0.1 ECDHL/01 x ECDI/01 OPEN CLOSED CLOSED
0 - 3000 uS 1 ECDHL/1 ECDC/1 ECDI/1 OPEN CLOSED OPEN
0 - 30.00 mS 1 ECDHL/1 ECDC/1 x CLOSED OPEN OPEN
0 - 30.00 mS 10 ECDHL/10 ECDC/10 x OPEN OPEN OPEN
0 - 300.0 mS 10 ECDHL/10 ECDC/10 x CLOSED OPEN OPEN
J5
J4
J3
12345
Page 38

38
Connect turbidity probe as follow:
mod. ETORBH mod. ETORB40*
1 Green 1 Blue
2 Yellow 2 Brown
3 Black 3 Black
4 White 4 White
5 Brown 5 Green
If ETORBH pobe is supplied with extra cable connect wires as follows:
1 Green
2 Yellow
3 Black+ White
4 Blu
5 Brown+Red
Note: If probe has been purchased with the instrument then is already
congured to work properly on its own channel. Otherwise, you must
assign an ID / CHANNEL to the probe using the OPTIONS menu and
choosing Turbidity INDEX.
*terminals for the ETORB40 are horizontal
MDETORBH
Note: If probe has been purchased with the instrument then is already con-
gured to work properly on its own channel. Otherwise, you must assign
an ID / CHANNEL to the probe using the OPTIONS menu and choosing
EOLUM INDEX.
MDEOLUM
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
TURBIDITY module (ETORBH / ETORB40 probe)
DISSOLVED OXYGEN module (EOLUM probe)
Connect “EOLUM” probe as follow:
1 Pink
2 Blue
3 Brown
4 Grey
5 Y ellow
Note: probe has a built in temperature sensor.
If pobe is supplied with extra cable connect wires as follows:
1 Pink
2 White
3 Brown
4 Grey and Black
5 Yellow
Not connected blu wire (shield)
1
2 3 4
5
Page 39

39
MDPS potentiostat probe series module
Located under mainboard cover there are two connectors that can be used to install probe modules. Modules come
pre-installed upon request and may appear different as shown (different configurations). Identify installed modules
to correctly connect probes.
To ensure reliable results probe’s head must be cleaned
on regular basis. This menu enable the embedded
wiper to clean probe’s head.
Cycle Time: time until next cleaning procedure (from
6hours up to 10 days)
Clean Time: overall time required to perform cleaning
procedure (from 0 to 999 secdonds)
Restore Time: time that probe needs to return reliable after
cleaning procedure (from 0 to 999 minutes)
Self Clean Menu
Within calibration menu enable or disable pH &
temperarure compensation. For proper probe’s
calibration please refer to Cl channel
pH & Temperature compensation
Block n. 1 Probe Wire Green
Block n. 2 Probe Wire White
Block n. 3 Probe Wire Brown
Block n. 4 Probe Wire Blue + Wire Yellow
Block n. 5 Probe Black on Block n.8 mainboard (N)
Block n. 6 Probe Red on Block n.9 mainboard (N.O.)
1 2 3 4 5 6
Page 40

40
8 WIRES CABLE:
4 PROBE WIRES
4 PT100 WIRES
Connect 4 probe wires to MDIND module as follows:
Block n.1 : blue
Block n.2 : black
Block n.3 : grey
Block n.4 : red
Connect 4 PT100 wires to mainboard (ref. p. 5) as follows:
Block n. 40 : green
Block n.41 : orange
Block n. 42 : white
Block n.43 : yellow
INDUCTIVE CONDUCTIVITY module (ECDIND probe)
ECDS IND PT PROBE
Connect 4 probe wires to MDIND module as follow:
Block n.1 : blue
Block n.2 : green
Block n.3 : red
Connect 4 PT100 wires to mainboard (ref. p. 5)
as follow:
Block n. 40 + 41: white
Block n. 42 + 43 : black
MDECDSIND
1 2 3
MDIND
1 2 3 4
MDECDSIND
When using two probes the scale settings
must be the same for both!
Page 41

41
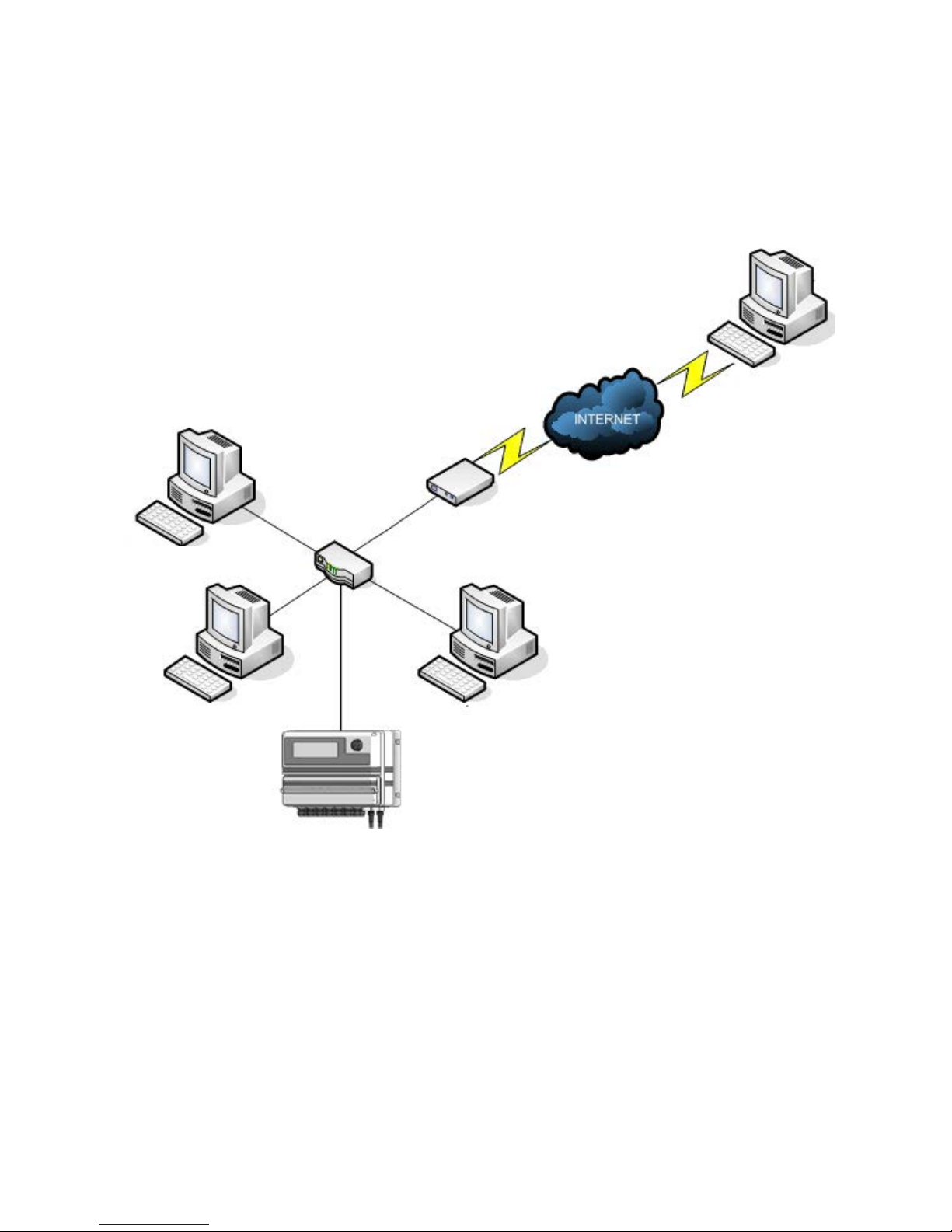
Appendix B - Installation draw
Page 42
42
ROUTER WITH
DSL MODEM
SWITCH
PC with
“ERMES Software”
PC with
“ERMES Software”
MAX5 with
ETHERNET
CONNECTION
Appendix C - Network logical installation scheme
Page 43

43
Appendix D - “LOG USB” Module
Located under mainboard cover there is a four pins connector that can be used to install “USB data log module”
or “SMS module”. Modules come pre-installed upon request and may appear different as shown (different
configurations).
“USB data log module” records instrument activities. These information can be permanently stored into a standard
USB pendrive. Pendrive can be connected to a PC using “ERMES” web www.ermes-server.com to review and print
instrument’s activities. To obtain reliable results with this feature please set instrument ID and NAME from
“RS485 Setup” menu and activate log recording from “LOG SETUP” menu.
HOW TO RECORD INSTRUMENT’S ACTIVITIES INTO USB PENDRIVE ?
Insert USB pendrive into USB connector (located on the right side of instrument). Instrument will save data log on
USB pendrive.
HOW TO REVIEW INSTRUMENT’S ACTIVITIES RECORDED INTO USB PENDRIVE ?
It’s necessary to connect to web “ERMES” www.ermes-server.com to review USB pendrive info on a PC.
Activity LED
Power LED
Standard USB pendrive
(not included)
Insert USB pendrive here
(right side of instrument)
After usage put back USB cap
Page 44

44
Appendix E - EOLUM Probe Setup and calibration
To correctly use the dissolved oxygen (fluorescence membrane) probe perform calibration as described.
At first start-up, sensor calibration is required in order to the measuring system to be able to generate accurate
measuring values. The slope calibration of the oxygen sensor can be performed in air, saturated water or using a
reference solution.
Calibration in AIR.
Calibration in air is only possible if air temperature is ≥-5 °C (≥23 °F). From calibration menu choose “Calib Chxx
LDO”. Choose “RANGE” to setup reading scale. Choose “AIR” as calibration method. Remove sensor from the
medium and dry completely. Leave it in air. Start calibration by clicking on “START”. Reading value is real time
displayed on upper screen side. 600s means how many seconds are left until the end of procedure. Move cursor on
“OK” when “CALIBRATION OK” message appears. If an error message appears repeat procedure.
Calibration in air saturated WATER.
From calibration menu choose “Calib Chxx LDO”. Choose “RANGE” to setup visulization scale. Choose “WATER” as
calibration method. Dip head’s probe into water. Start calibration by clicking on “START”. Reading value is real time
displayed on upper screen side. Time shown is how many seconds are left to the end of procedure. Move cursor on
“OK” when “CALIBRATION OK” message appears. If an error message appears repeat procedure.
Calibration using a REFERENCE solution.
From calibration menu choose “Calib Chxx LDO”. Choose “RANGE” to setup visulization scale. Choose “REF” as
calibration method. Dip sensor’s probe into reference solution. Start calibration by clicking on “START”. Reading
value is real time displayed on upper screen side. Time shown is how many seconds are left to the end of procedure.
Move cursor on “OK” when “CALIBRATION OK” message appears. If an error message appears repeat procedure.
Probe’s temperature sensor calibration.
Temperature calibration needs an external thermometer to match probe’s reading value.
From “Calib CHxx LDO menu, move wheel on “Temp”, press wheel to enter system temperature obtained from a ther-
mometer. Press wheel to conrm then move cursor on “OK” and press wheel. End procedure by moving cursor on “Exit”
from “Temp” main menu and press it. If an error occurred during calibration procedure then the instrument will show an
error message and will ask to proceed to a new calibration, cancel current operation or restore default settings.
To restore probe’s calibration parameters to factory values select “FACTORY DEFAULT” within “Default” menu.
Power cycling off then on the instrument to properly save probe new calibration values.
Page 45

45
Appendix F - MODBUS Setup
Modbus is a serial communications protocol originally published by Modicon (now Schneider Electric) in 1979 for
use with its programmable logic controllers (PLCs). Simple and robust, it has since become a de facto standard
communication protocol, and it is now a commonly available means of connecting industrial electronic devices.
From main menu select COMMUNICATION then MODBUS to access the options. Set the communication speed
according to the PLC system available. Set the ID assigning an UNIQUE address to avoid conflicts.
1 2 3
1: GND
2: A-RS485 (+)
3: B-RS485 (-)
Page 46

46
Appendix G - SETPOINT Temperature
Set values to enable (ON) or disable (OFF) the temperature realy output. The instrument will proceed to the ON/
OFF working mode.
Example: set ON at 30 °C and OFF at 25 ° C
The output will be active for values lower than 30 ° C and it will switch off for values greater than 30 ° C , then
it’ll reactivate for values lower than 25 ° C. The difference between these two values (30 ° C and 25 ° C) is called
hysteresis. In order to avoid that the relay is switched on and off repeatedly avoid setting hysteresis values below 2 ° C.
Page 47

47
Appendix H - Water salinity for CD module
For “%” version this is NaCl based on conductivity. See graphic below for comparison and relationship
between concentration of Solutions and Conductivity (at 18°C).
Page 48

48
Appendix I - Fluorine probe module & calibration
Carbon Filter System
Photometer
In the upper part of the motherboard there are two connectors for the installation of the probe modules. On request,
these modules are installed by the manufacturer. For the form of fluoride probe simply connect the probe’s BNC
connector. The probe must be calibrated for properly operate. Chosoe FULL calibration for two points calibration
involing zero point (P1) and the second point (P2).
The FAST Calibration is performed by a single point from the value closest to work
Warning: This procedure assumes that instrument is correctly configured, it is connected to the probe running and
installed on your system. The measurement must be performed using the system water.
Otherwise, the results may not be reliable.
Zero point calibration (P1).
In the probe’s calibration menu move the cursor to “P1” and select it to enter
in the calibration procedure. For a correct calibration, proceed as follows:
- Install an “activated carbon filter” in the filter holder.
- Flow water inside the filter-holder for about 30 minutes.
- Press the knob with the cursor positioned on “Cal.at”. Remove the filter.
2nd calibration point (P2).
Move the cursor on “P2” and select to enter the calibration procedure.
For a correct calibration using a photometer or a DPD system to read the mg / l (F)
in the plant. Enter the value read in the “Cal. at “.
To complete the procedure, move the cursor to “OK” and press the wheel for saving.
If during calibration an error occurs, the instrument will signal with a message and
ask for a new calibration. Clear current settings or restore the default values.
Page 49

49
Appendix L - Chlorine Index / Chlorine S/N
For proper SCLxx probe installation channel assignment is required. Within “OPTIONS” menu, select “Chlorine
Index” and assign a free channel to the probe. To check probe’s serial number see “Chlorine S/N”. This index is
related to phisical slot installation on mainboard. By default slot 3 is assigned to the chlorine probe. Please remove
chlorine probe prior to assign it to the controller.
Chlorine Index Menu
Chlorine S/N Menu
Page 50

50
Appendix - WIFI Connection
Within Communication Menu choose “WIFI” to bring wireless sub-menu.To manually enter the WiFi Network highlight
and click on first line to the right side of the menu and choose cryptography type (WPA, WEP or OPEN). Otherwise
move cursor below to choose within an existing network. If network doesn’t apper move cursor on SCAN and click
on it. Wait until desired wireless network appears, then move wheel on it then click. Enter WEP / WPA / WPA2
password (if required) and wait until connection has been estabilished and WiFi signal strength appears. To obtain
a reliable connection be sure to install the controller within WiFi range. See your router features and installation
procedure for best results.
Note: if an existing network doesn’t appear at first scan please repeat scanning procedure after a while.
WiFi signal strength
Page 51

51
Index.
Introduction......................................... page 3
The wheel................................ page 3
Mainboard connections..................... page 4
Power Connections................. page 4
I/O Connections...................... page 5
Main Screen........................................ page 6
Passcode................................ page 7
Setup...................................... page 7
Setpoint............................................... page 8
Da & Db.................................... page 8
Da & Db Working Modes...... page 9
PWM Mode............................... page 10
PID Mode................................... page 11
Pa & Pb................................... page 12
mA............................................ page 13
Aa & Ab................................... page 14
Ad............................................ page 14
Ar.............................................. page 15
Calibration........................................... page 16
pH Calibration......................... page 16
Cl Calibration.......................... page 18
mV Calibration......................... page 20
Range (NTU) ....................... page 21
Temp Calibration.................... page 22
uS Calibration......................... page 23
Timer.................................................... page 25
Page 52

52
Index.
Options................................................ page 27
TAU......................................... page 27
Delay (outputs & sms)............. page 27
FM Counter................................. page 27
Flow Detect............................. page 28
Clock Setup............................. page 28
Probe Clean............................. page 29
EEprom Reset.......................... page 29
RS485...................................... page 29
GSM MODEM........................... page 30
TCP/IP.......................................... page 31
GPRS........................................... page 32
EMAIL.......................................... page 32
Alarm Setup............................. page 33
Log Setup................................ page 33
Passcode Setup....................... page 33
Manual................................................. page 34
Manual Relay........................... page 34
Manual Pulse........................... page 34
Manual mA............................... page 35
Manual Level........................... page 35
Appendix A Probes connection............. page 36
Appendix Potentiostat probe............... page 39
Appendix B Installation Draw.................. page 41
Appendix C Network Draw............... page 42
Appendix D EOLUM Probe Setup.... page 44
Appendix E USB Module................... page 44
Appendix F MODBUS........................ page 45
Appendix G Setpoint TEMP............... page 46
Appendix H Water Salinity............... page 47
Appendix I Fluorine probe............. page 48
Appendix L Chlorine Index / SN............. page 49
Appendix WIFI.......................................... page 50
Page 53

53
Page 54

54
Page 55

55
Page 56

56
When dismantling this instrument please separate material types and send them according to local recycling disposal requirements.
We appreciate your efforts in supporting your local Recycle Environmental Program.
Working together we’ll form an active union to assure the world’s invaluable resources are conserved.
 Loading...
Loading...