
SR-200D
Professional HD
Integrated Receiver Decoder
User Manual
EMCEE COMMUNICATIONS
2546 West Birchwood Avenue, Mesa, Arizona 85281 USA

V1.02-N

Preface
About This Manual
This manual provides introduction to users about how to operate the device correctly. The
content includes introduction to product installation, product characteristics and product
settings, etc. It is highly suggested that users should read this document before actually
operating the device.
Intended Readers
This manual is suggested to be studied by the following readers:
l Technical Service Engineer
l Maintenance Engineer
l Test Engineer
l Sales Engineer
Symbols Definition
For the symbols that might appear in this document, the meanings they represent are as the
following:
Symbol Meaning
There is highly potential danger. If it cannot be avoided, it will lead to the deaths or
serious injury.
There is medium or low potential danger. If it cannot be avoided, it will lead to medium
or slight injury.
There are potential risks. If ignore these texts, it may cause damage to the device,
data loss, equipment performance reduce or unpredictable results.
Tips that help you to solve problems or save your time.
Remarks. Additional information to the text, in order to emphasize something.
1

Contents
1 About This Product ...........................................................................................................4
1.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................4
1.2 Safety .........................................................................................................................4
1.3 Architecture ................................................................................................................5
1.4 Methods of Operation.................................................................................................6
1.4.1 Operation through WEB UI .............................................................................6
1.4.2 Operation through Front Panel Operation ......................................................7
1.5 Technical Specifications .............................................................................................7
1.5.1 Physical Specifications ....................................................................................7
1.5.2 Performance and Capacity ..............................................................................8
1.5.3 Interfaces and Protocols ..................................................................................8
2 Installation ..................................................................................................................... 10
2.1 Installation Procedure ............................................................................................. 10
2.2 Preparation before Installation ................................................................................ 10
2.3 Check Package and Accessories............................................................................. 11
2.4 Equipment Wiring and Connection .......................................................................... 11
2.4.1 Connection Setup for RF Signal Input .......................................................... 12
2.4.2 Connection Setup for ASI signal input .......................................................... 12
2.4.3 Connection Setup for IP signal input ............................................................ 12
3 Operation Guide ............................................................................................................ 13
3.1 Operation Overview ................................................................................................. 13
3.2 Powering Up and Initialization ................................................................................. 13
3.3 Front Panel Operation ............................................................................................. 13
3.3.1 Front Panel Menu Structure .......................................................................... 14
3.3.2 Front Panel Operation Guide ........................................................................ 16
3.4 WEB UI Operation (Recommended) ....................................................................... 17
3.4.1 WEB Management Connecting .................................................................... 17
3.4.2 Parameters Configuration ............................................................................. 19
2

3.5 Preparation before Officially Operation ................................................................... 36
3.5.1 Clear all useless data.................................................................................... 37
3.5.2 Configure the equipment with working data ................................................. 37
3.5.3 Full checking before implementation ............................................................ 37
4 FAQ ............................................................................................................................... 38
5 Terminology ................................................................................................................... 40
3

1
About This Product
1.1 Introduction
This product is a new generation integrated receiver decoder to support the growing
demands for multi-format, multi-standard video delivery and distribution. It can receive
digital signals from several inputs (DVB-S/S2, DVB-C (optional), DVB-T/T2/ISDB-T (optional)
and ASI), decrypt and process/select programs to various outputs including CVBS, HDMI,
SD/HD SDI and ASI. It supports multi-channel descrambling, multiplexing, external
table/data insertion, transcoding and transmodulating. It also supports video decoding with
two audio channels. With remote web-based management interface, it is ideal to support
advanced application such as content distribution, real-time signal conversion and
transmission.
1.2 Safety
l To avoid electric-shock hazards, do not open the receiver; refer service to qualified
personnel only.
l Do not expose the device in the sunlight, and keep it away from the heat source.
l Do not block ventilation holes of the device so that air can circulate freely.
l Switch the device off whenever it remains out of service for an extended period.
l Be sure to turn the device off and disconnect the AC power cord before cleaning the
receiver surface.
l The apparatus shall be connected the mains socket outlet with a protective earthing
connection
l The appliance coupler used as the disconnect device shall remain readily operable.
l This product has gone through regulated EMC test and meets with EMC safety
requirement.
( Such tests are conducted in a controlled EMC environment. A controlled
EMC environment exists in a building where the installation has been designed
4

having special regards to EMC, and where technical personnel are present with
experience of EMC technology.)
1.3 Architecture
The equipment of this section is shown in schematic diagram. It is subject
to change for improvement on the real product without advanced notice.
Front Panel
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
PIC-1.3-1
1. Power status indicator: This LED light is turned on when the IRD is power on.
2. (Signal) Lock status indicator: This LED light is turned on when a channel is locked.
Otherwise there is no channel locked.
3. Alarm status indicator: This LED flickers when there is something abnormal. For
example, the strength of the input signal is too weak.
4. Display screen: This LCD screen can show the program and configuration information.
5. CI SLOTS: There are two CI slots for various CAS CAM (PCMCIA) modules.
6. KEY PADS:
l Up/Down/Left/Right arrow keys: To change channels, to adjust volumes and
configure the IRD.
l Menu: To enter the menu and the quit function of the sub menus.
l OK: To confirm the operation in the setup.
5
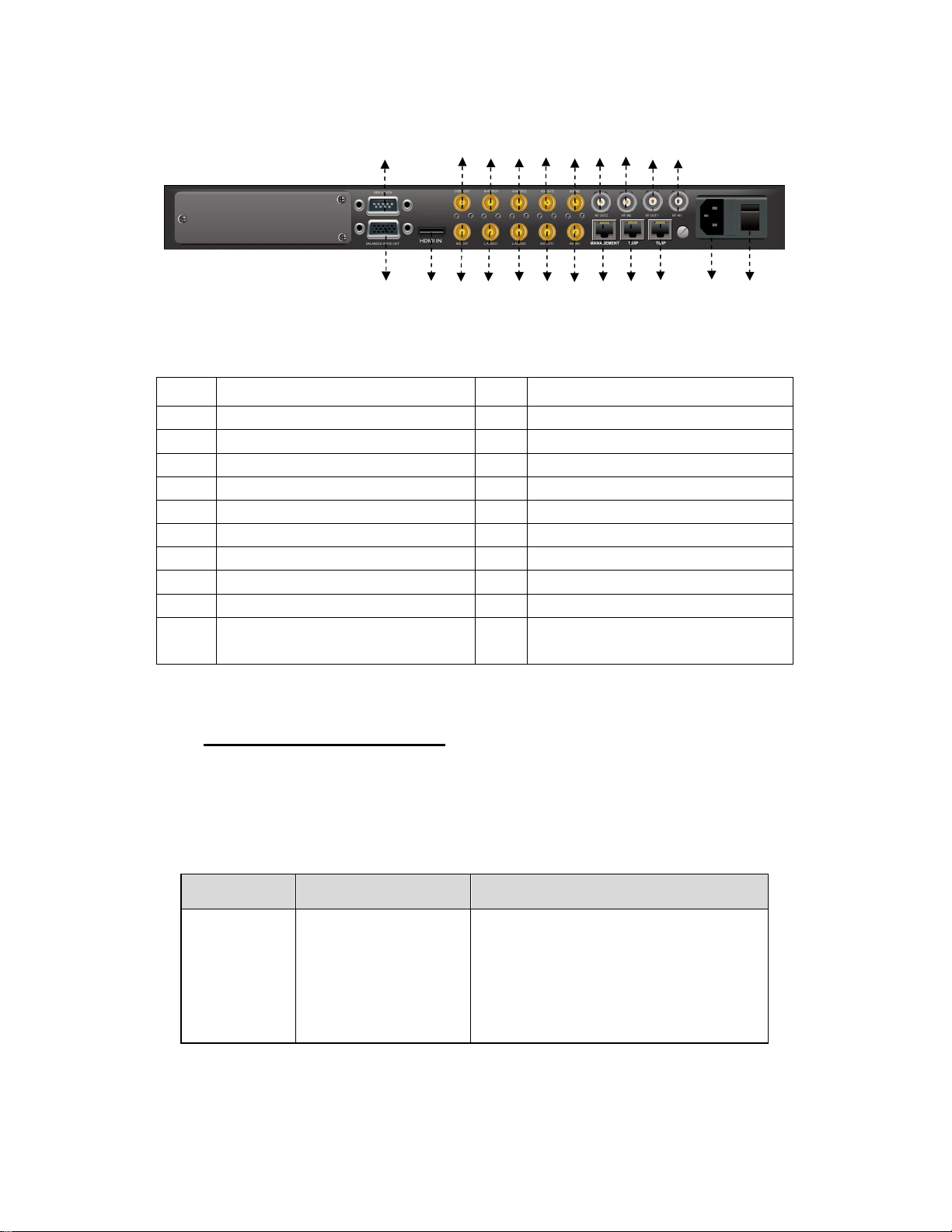
Rear Panel
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
PIC-1.3-2
1
GPI/LS DATA Out
2
CVBS Out
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
21
R-AUDIO1
ASI OUT2
RF OUT2
RF Out1
BALANCED AUDIO OUT
SDI OUT
L-AUDIO2
ASI IN1
TS/IP
POWER CORD IN
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
R-AUDIO2
ASI IN2
RF IN2
RF IN1
HDMI
L-AUDIO1
ASI OUT1
MANAGEMENT
TS/IP (Redundant)
POWER SWITCH
Redundant POWER (Optional)
1.4 Methods of Operation
1.4.1 Operation through WEB UI
Operate the IRD remotely through WEB UI. The WEB UI operation supports:
Functions Description Related Items
WEB UI allows users to
conduct operations of
Signal receive setup
Parameters
parameters
CI setup
Setting
configuration,
Decoder setup
modification and setup.
6
Functions Description Related Items
Support unit upgrade
Size 1RU Dimension
480
mm (
W
) × 44mm (
H) × 440mm (
D)
Status
Monitoring
Upgrade
Support real-time
monitoring on running
status of input signal,
CI descrambling, etc.
through WEB UI
RF signal strength indication
CI slot/CAM information
HW/SW version information
1.4.2 Operation through Front Panel Operation
Operation through front panel control buttons; users can configure all the parameters as the
followings:
Functions Description Related Items
Allows users to
Parameters
conduct operations of
parameters
Setting
configuration,
Signal receive setup
CI setup
Decoder setup
modification and setup.
Support real-time
Status
Monitoring
monitoring on running
status of input signal,
CI descrambling, etc.
1.5 Technical Specifications
1.5.1 Physical Specifications
Items Index
Power AC100~240VAC
Max. Power Consumption Approx 40W
RF signal strength indication
CI slot/CAM information
HW/SW version information
Net Weight Approx 3.8Kg
Gross Weight Approx 5Kg
7
CI Max. Output Bitrate
100Mbps
1.5.2 Performance and Capacity
Items Index
ASI Max. Input Bitrate 100Mbps
ASI Max. Output Bitrate 100Mbps
Decoder Max. Resolution 1920 X 1080i
1.5.3 Interfaces and Protocols
IP input ASI input
Interface: 1 x 1000 Mbps Interface: 2 ASI inputs, 75Ω
IP Encapsulation: UDP/RTP
MPEG TS: MPTS and SPTS Max bit rate: 100 Mbps
Input processing: Up to 2
channels, max at 72 Mbps per
channel.
DVB-T2 (Optional) DVB-T (Optional)
Constellation: 16/32/64/128/256
QAM
Bandwidth: 1.7Mhz, 5Mhz,
6Mhz, 7Mhz, 8Mhz, 10Mhz
Input frequency: 48~862MHz Input frequency: 48~862MHz
Inputs
Max. bitrate: 50Mbps Max. bitrate: 31.67Mbps
Transmission mode: 1K, 2K, 4K,
8K, 16K, 32K
DVB-S/S2 DVB-C (Optional)
Input Frequency: 950~2150 MHz Frequency: 48~862 MHz
Constellation: QPSK, 8 PSK
ISDB-T/Tb (Optional) ATSC (Optional)
Constellation: QPSK/16/64QAM
DQPSK
Bandwidth: 1.7Mhz, 5Mhz,
6Mhz, 7Mhz, 8Mhz, 10Mhz
Input frequency: 48~862MHz
Transmission mode: 1K, 2K, 4K, Max bitrate: 19.39Mbps
MPEG Format: 188/204 Bytes per
TS
Support input redundancy.
Constellation: QPSK/16/64QAM
Bandwidth: 6/7/8Mhz
Transmission mode: 2K, 8K
Constellation: 16/32/64/128/256
QAM
Constellation: 8VSB
Bandwidth: 6Mhz
Input frequency: 57~803MHz
(fixed)
8

8K, 16K, 32K
IP output ASI output
Interface: RJ45 Interface: 2 ASI outputs, 75Ω
MPEG Format: 188/204 Bytes per
TS
Outputs
IP Encapsulation: UDP/RTP
MPEG TS: MPTS and SPTS Max bit rate: 100 Mbps
Output processing: Up to 2
channels, max at 72 Mbps per
channel, support TS/IP
redundancy.
The physical connector design is subject to change without advanced notice
(either the connector type or specific connector location) according to user’s specific
order, performance improvement, or for better user experience.
9

2 Installation
Installation
and Accessories
2.1 Installation Procedure
Preparation before
Check Package
Setup Connection
(signals, wiring)
Parameters
Configuration
System Debug
Finish
2.2 Preparation before Installation
Before installation, the installation personnel should read through and confirm the
followings:
· Go through this user manual.
· Has the knowledge of digital television system.
· Has defined the sources, racks allocation, and set-up plan system wiring.
· Knows how to operate this unit and parameters configuration.
· Go through related engineering design documents about the system.
10
2.3 Check Package and Accessories
The IRD package includes the following accessories:
l Base Unit x1
l Power cord x1
l Earth cord x1
l BNC cord x1
l BNC-RCA cord x2
l User Guide Disc x1
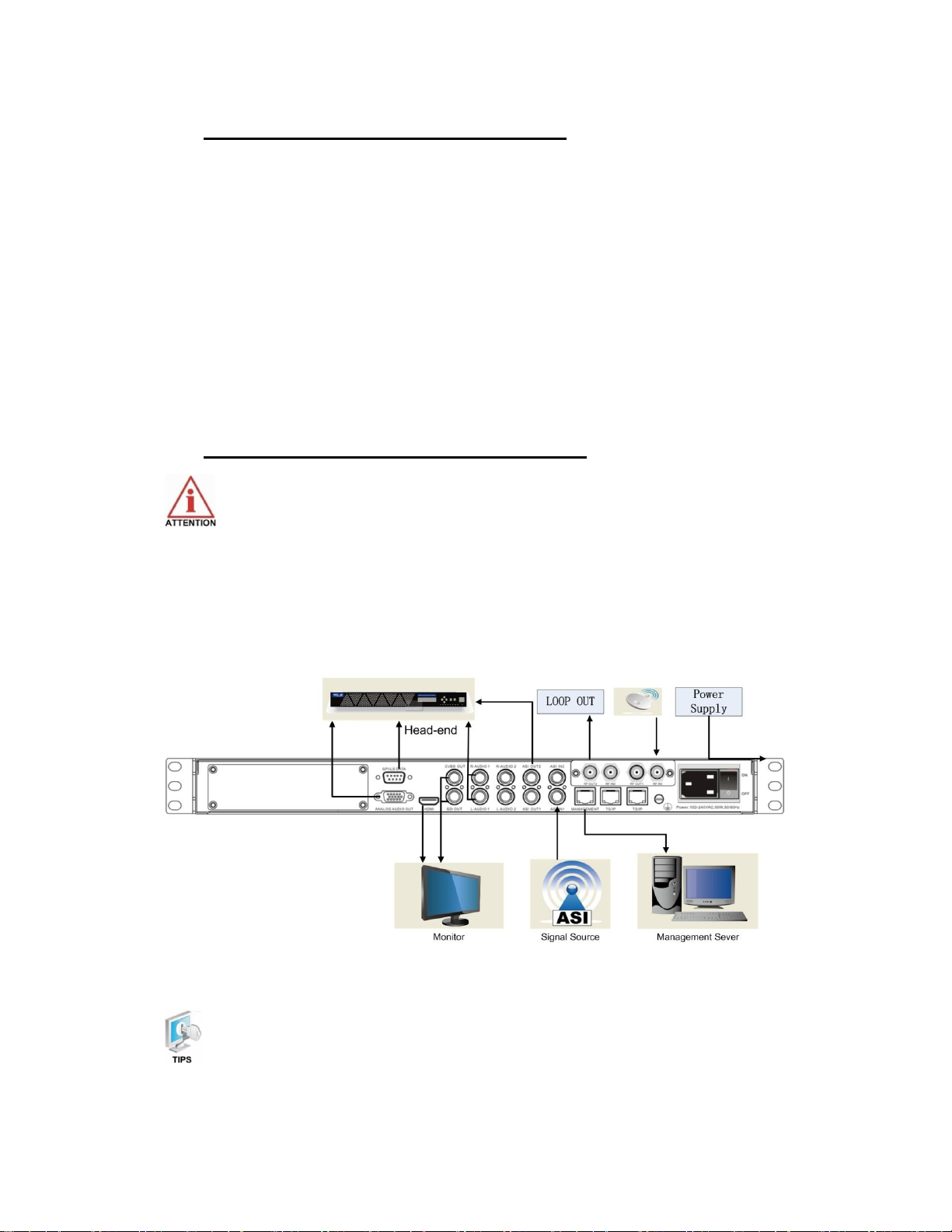
2.4 Equipment Wiring and Connection
To avoid electric shock and damage to the equipment, before setting up the
wiring connection, please power off the equipment and all other connected external
devices. The equipment and external devices must be grounded. Powering on the
equipment only after all the wiring connection is completed.
Connection Diagram
PIC-2.4-1
In actual application, not all connection interfaces need to be connected with
signal/external devices. Please connect according to actual application purpose.
11

To ensure a smooth communication between the management PC and the
IRD, please try to connect the IRD management port to a switch without large data
processing.
2.4.1 Connection Setup for RF Signal Input
l Connect signal to tuner input (either RF1 or RF2 input) with a RF cable.
l Connect the IRD “Management” port to a switch, set up a management network with
the management PC.
l Connect the IRD with the monitor via HDMI, SDI or CVBS ports.
2.4.2 Connection Setup for ASI signal input
l Connect ASI signal to IRD “ASI IN” port with a BNC cable.
l Connect the IRD “Management” port to a switch, set up a management network with
the management PC.
l Connect the IRD with the monitor via HDMI, SDI or CVBS ports.
2.4.3 Connection Setup for IP signal input
l Connect IP signal to IRD “TS/IP” port with a twisted cable.
l Connect the IRD “Management” port to a switch, set up a management network with
the management PC.
l Connect the IRD with the monitor via HDMI, SDI or CVBS ports.
12

3 Operation Guide
3.1. Operation Overview
This chapter provides information on how to operate the IRD through front panel and WEB
UI. User can select the most proper operation method to set up the unit.
3.2. Powering Up and Initialization
Switch on the equipment through the rear power switch, and the unit is powered up and
starts the initialization.
The LCD screen is lighted up, and display information as following:
H.264 SD/HD IRD
Setting System…
The initialization takes about 20 seconds to complete, and then the IRD shows the IP
address information as following:
H.264 SD/HD IRD
IP: 192.168.001.098
Before powering-up the device, make sure that all cabling is correctly
connected (refer to chapter 3.4 of this manual). The device is correctly connected to
the power inlet and grounded.
If the unit fails to initialize and hangs at the “booting” stage, switching off the
device and then powering up again may help. If the device still fails to initialize,
please contact your service representative for help.
3.3. Front Panel Operation
Ways of operation: use the 6 navigation keys on front panel: Up / Down / Left / Right / Menu /
Ok to configure the IRD parameters. The configuration and settings are displayed through
front panel LCD.
13

3.3.1 Front Panel Menu Structure
Front Panel Menu Structure
1st Layer 2nd Layer 3rd Layer
Lock Status
FEC
PER
Frequency Offset
Status
Input Tuner 1/2
Input ASI 1/2
Input IP 1/2
Decoder
Frequency Tune
TS Rate
RF Level
C/N
BER
Lock Status
TS Rate
Lock Status
TS Rate
TS Rate
PCR PID
Audio PID
Video PID
PMT PID
Program No.
CI CI Slot 1/2
ASI 1 TS Rate
Output ASI
ASI 2 TS Rate
IP 1 TS Rate
Output IP
IP 2 TS Rate
14

Enable
TS Standard
LNB Frequency
Satellite Frequency
Tuner 1/2 Tuner 1/2 Params
Symbol Rate
LNB Power Supply
Inputs
ASI 1/2
IP
Decoder
LNB 22KHz
Scan TS
Enable
TS Standard
Scan TS
Local Setting
TSIP Channel 1/2
TS Source
Playing Program
Program List
Video Standard
Video
Aspect Ratio
Video Format
Audio Volume
Outputs
Audio
Subtitle Subtitle Standard
Teletext Teletext Standard
ASI ASI 1/2 TS Source
IP TSIP Channel 1/2
15
Audio Mixer
Audio 1/2 Language
Tuner 1/2
Mux 1/2
ASI 1/2
Enable
TS Source

CA
Common Interface
Dest IP Address
Dest Port
Protocol
Time to Live
TS Packet Number
Enable Dest MAC
Dest MAC
TS Source
CI 1/2
Descrambling
CAM Max Bitrate
BISS Mode
BISS Setting BISS Setup
Local IP Address
Local Network Mask
Local Gateway
System Local Setup
MAC Address
Factory Setting
3.3.2 Front Panel Operation Guide
· Enter “Menu”:
o Press “MENU” button to enter main menu.
BISS-1 Setup
BISS-E Setup
Version
Reboot
· Exit Menu/Back to parent Menu
o Upon completion of configuration settings, press “MENU” button until you
go back to the Parent Menu.
16

· Enter Sub-Menu
o Press MENU button to enter main menu.
o Select a sub-menu by pressing arrow UP and arrow DOWN button.
o Press OK button on the selected sub-menu.
· To change parameter
o Step 1: Enter main menu by pressing MENU button.
o Step 2: Scroll sub-menu by pressing arrow UP and arrow DOWN button,
and press OK button to change the selected sub-menu.
o Step 3: To change parameter settings, press arrow RIGHT and arrow LEFT
button to move the cursor in which change must be made.
o Press arrow UP button and arrow DOWN to input / select an appropriate
setting, then press OK button to save.
3.4. WEB UI Operation (Recommended)
Accessing the equipment via Web can be very convenient for remote configuration of the
equipment. Relative to the front panel settings WEB operation can provide a friendlier
man-machine interface, and with less limits in space. WEB Management is recommended.
3.4.1 WEB Management Connecting
Connection Instruction:
PIC-3.4-1
1. Connect the “MANAGEMENT” port of the IRD to a network switch and connect the
management PC/server to the same network switch.
2. The IRD default IP address is 192.168.1.98. It is important to set the IP address of
17

the IRD and the monitoring severs in the same section to ensure a smoothly
connection between them.
3. Open a web browser (e.g. Mozilla, internet explorer, safari and etc.), enter the
equipment’s IP address in format: http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx refers to
IRD’s IP address) and press ENTER button to confirm. The browser will attempt to
connect to the device. If succeed, a login page will appear. (see PIC-3.4.2)
Note: Through WEB browser, you can manage several pieces of HD IRD at the
same time, as long as those equipments are connected to the server via Network
Switch. Make sure that the equipment and server’s IP address should be in the
same section. Nevertheless, Subnet Mask and Gateway should be the same for
both the server and the equipment.
PIC-3.4-2
l To login, you need to enter the default username “admin” and password “admin”.
Then click “Submit”.
l If the user name and password is correct, it will redirect to the main page.
18

3.4.2
Menu Area
Parameters Area
Parameters Configuration
3.4.2.1
The main page can be divided into two functional areas:
l Menu Area: you can switch between the menus to display the corresponding parameter
Main Page
PIC-3.4-3
setting and monitoring pages.
l Parameters Area: displays the corresponding parameters pages according to the menu
selection.
The WEB management page allows you to monitor and/or configure: Status, Receiver,
Program Setup, CA, Local Setup, Alarms Setup, User Management, Preset, Upgrade, Log
and etc.
Menu Area:
This area shows the main menu items of the machine, you can click the item you want to
configure or monitor, then the detailed information will appear in the right area.
19

PIC-3.4-4
Parameters Area:
This section is the main section for monitoring and configuration of the machine. It shows
the detailed information of the machine of each menu. Its detailed function will be introduced
in to following chapters.
3.4.2.2
This page allows you to monitor the status of input and output signal, and check the
information of CI cards.
Status Page
20

PIC-3.4-5
· Input status (tuner/ ASI/ IP): It shows the main information of input streams, such
as lock status, RF BER, RF Level, Total RF Rate , ASI total rate, ASI effective rate
etc.
· Decoder status: Here you can see the decoder information: video PID, Audio PID
and PMT PID.
· CI status: You are able to monitor the status of CI cards.
· Output status (ASI/ IP): You can check the output TS rate and the TS status.
3.4.2.3
If you want to configure the parameters of multiplexed programs, just click the “programs
Mux Setting” button on the left bar. Then you will turn to the programs information interface,
where you are able to check and modify the parameters of programs.
Programs Mux Setting
1
PIC-3.4-6
3
2
21

① Input Program Configuration: The “Input Program Configuration” is on the left
side of the window. It displays the entire information of the received input streams
② Output Program Configuration: In the “Output Program Configuration” window, it
shows the ports which can be set to transmit output stream. The programs set to be
outputted are shown in the submenu of each port.
③ Operation Buttons: This area contains three functional buttons: Refresh, Apply
and Save.
Apply: to make the programs configuration take effect. Once the device is
powered off, the programs configuration will lose and device will be restored to the last
saved configuration.
Save: to make the programs configuration take effect as well as save the
configuration information.
Refresh: by clicking this button to refresh the programs information.
How to dispose the Inputs:
To get the input programs, you should choose the sub-menu in the Inputs menu on the left.
Then it will turn to the corresponding page where you are able to set the receiving
parameters to lock the signals. (Referring to chapter 3.4.2.4) If the signal is locked then
programs information will be listed on the frame as the following picture shows.
PIC-3.4-7
How to configure the Outputs (Mux1 and Mux2):
22
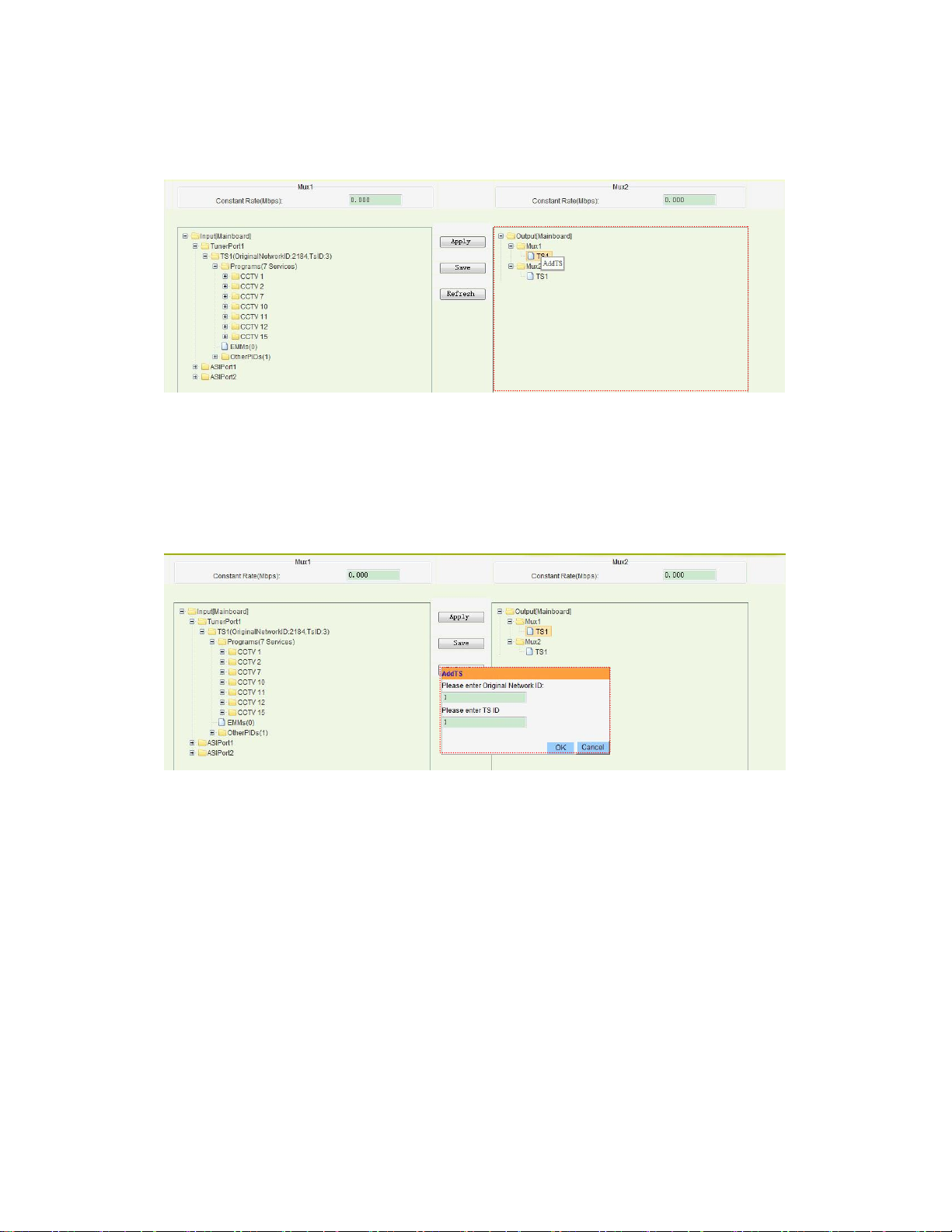
Firstly, select the port which you want to transmit the output stream. Right click the TS in that
port and a pop-up menu will appear. Click “ADD TS” item and you will get the input box.
PIC-3.4-8
Secondly, Input the “Original Network ID” and “TS ID” for the channel, and click the “OK”
button. Then new “Original Network ID” and “TS ID” will be assigned to the selected output
TS (channel).
PIC-3.4-9
Additionally, by clicking the editing icon, you are able to modify the TS name, network ID and
TS ID.
To delete existing TS, you can click the cross icon as follows:
23

PIC-3.4-10
And it is able to delete the TS or programs in the Mux menu by click the cross icon at the behind
of the program or TS. Shown as the following picture:
PIC-3.4-11
After completing the configuration, you should click “Apply” button to enforce it or
“Save” button to enforce and save it.
The outputs ( Mux1 and Mux2) will be available for ASI/ IP inputs after configuration.
24

3.4.2.4
l DVB-S/S2
Inputs
Area 1
Area 2
Area 3
PIC-3.4-12
Area 1/ Area 2: Additionally, in this section, you are able to set the dual RF receiver
parameters including the Satellite Frequency, Symbol Rate, LNB Frequency, and LNB
Voltage (Polarization) with accurate values. Then you can press the “Submit” button to save
your settings or click “Refresh” button to refresh the screen.
Area 3: When the signal is locked, it is able to get the program list in by clicking the ScanTS
(Tuner1/Tuner2).
l Enable: Enable or disable corresponding input channel
l Satellite Frequency (MHz): set the satellite down conversion frequency.
You can get this parameter from the satellite program provider.
l Symbol Rate (KBaud): set the correct symbol rate. You can get this
parameter from the satellite program provider.
l LNB Frequency: this is the LNB’s local oscillation (LO) frequency, every
LNB have one or two oscillation frequencies which can be obtained from the
LNB provider, or you can check on the LNB label. The value is between
5000 and 6000.
25
l LNB Power Supply: LNB voltage is the power that supply to the LNB in
order to receive satellite signal with different polarization. Generally 18V is
for Horizontal while 13V is for Vertical.
l LNB 22 KHz: Generally this is used to control 22KHz switch, typically used
for LNB with double L.O. in Ku band. “ON” is for high L.O and “OFF” is for
low L.O.
l TS Standard: there are two options for TS standards: DVB and ATSC.
Sometimes the parameters may change; it is advisable to check through
www.lyngsat.com for the updated satellite parameters.
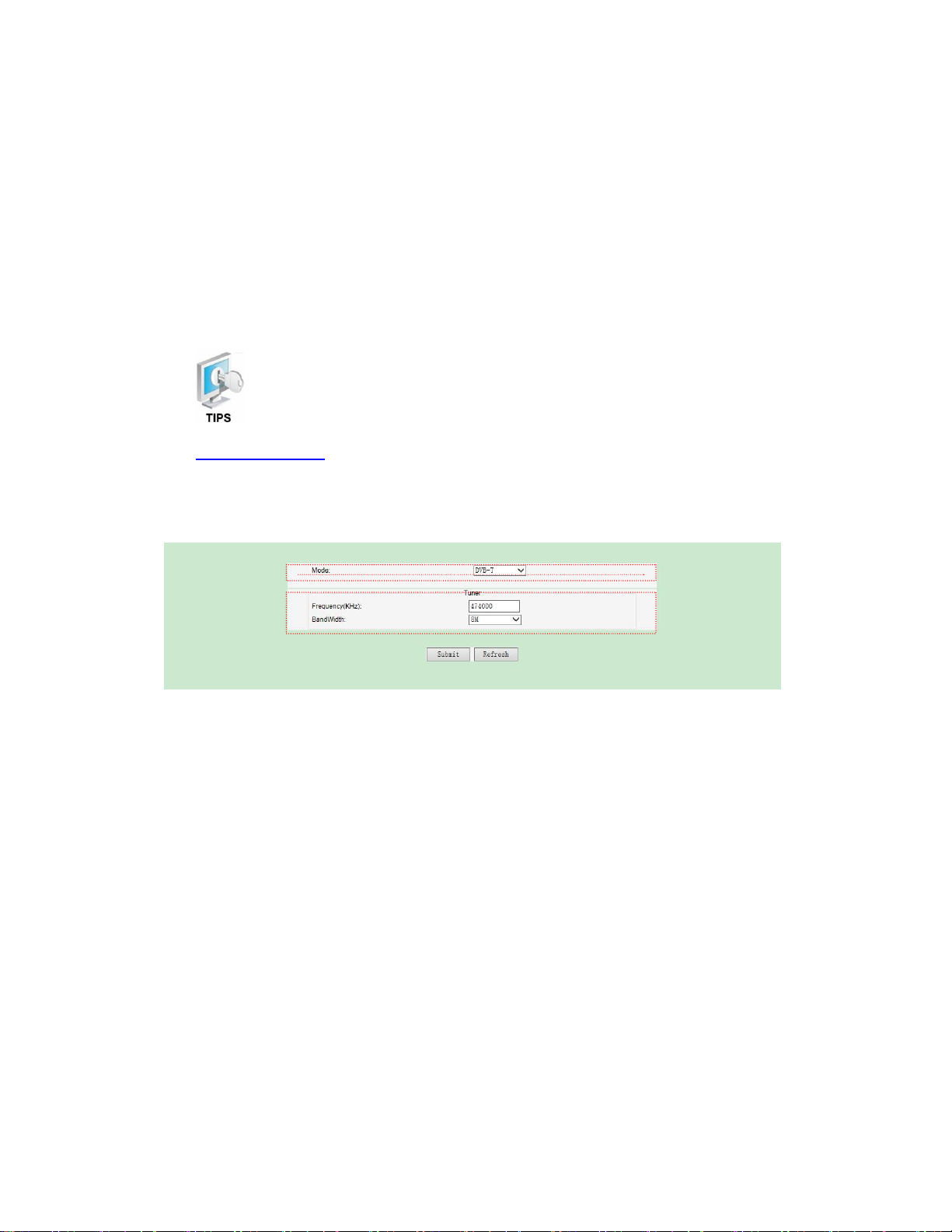
l DVB-T/T2 (Optional)
If the tuner is for DVB-T/T2 receiving, it will turn to the above interface when clicking the
inputs menu. This page is to configure the parameters of DVB-T/T2 receiving. There are
three parameters as following:
l Mode: to set DVB-T or DVB-T2 receiving.
l Frequency: to input the frequency that the receiver is appointed to
receiving..
l Bandwidth: There are three options: 6M/7M/8M. Set the corresponding
parameter according to the operator requirement.
l DVB-C (Optional)
Regarding DVB-C parameters, user only needs to input the frequency, symbol
rate and QAM mode to scan and receive the input signal.
26

l ASI
Area 1
Area 2
PIC-3.4-13
This page shows the Input ASI information. There are two channels available to receive ASI
streams: ASI1 and ASI2.
Area1: set the ASI parameters, include Enable and TS Standard.
Enable: enable / disable the ASI channel to receive input stream.
TS Standard: select the correct TS standard: DVB or ATSC
Area2: displays the programs list of the input stream. You can get the programs list by
clicking the ScanTS (ASI1) and ScanTS (ASI2).
l IP
Area 1
Area 2
Area 3
PIC-3.4-14
From this page, you can setup the device’s local IP parameters (Area1) as well as the TSIP
ports’ output parameters (Area2 and Area3). There are two TSIP channels available for
27

receiving IP streams.
Area1: Set the devices’ local IP parameters to enable it to be connected into the network:
l IP Address: Local IP setting for connecting to the server. This IP and the
management server’s IP should be in the same section.
l SubnetMask: Network Mask setting for connecting to the server. It should be
the same as management server: 255.255.255.0
l GateWay: Gateway setting for connecting to the server. It should be the same
as the management server.
l IGMP Version: The IP transmission supports IGMP V2 and IGMP V3, you can
choose the one you need manually.
Area2: The parameter of channel 1 and channel 2. After finishing the configuration, click
“Submit” to make it into effect.
l Enable: Enable or disable corresponding output channel
l Source IP Address: it is the IP address of the source IP streams.
l Source Port: It is the port of source IP streams.
l Protocol: You can choose UDP or RTP for multicast/unicast.
Area3: To get the program list of IP input by clicking ScanTS (Tuner1) / ScanTS (Tuner2).
l Backup Setting
PIC-3.4-15
In the Backup Setting page, user can set redundant sources for the main input signal. The
main and backup input source can be selected from Tuner, ASI or IP.
In case there is any error for the main input signal, the IRD will automatically switch the input
from main to the backup, to ensure the IRD output non-stop.
28

3.4.2.5
l Decoder
In this page, user can view and configure the decoding output program parameters,
including: Program, CAM, Video, Audio, Subtitle and Teletext.
Outputs
PIC-3.4-16
The device can decode the input streams and output by CVBS or HDMI. For
each time only one program can be decoded and output.
The parameters set in “Program Setup” interface work for all selected
program.
² Playing Programs:
This interface, all the programs received will be listed in “TS Source” region. By changing
the program’s operation, you can determine which program to decode.
PIC-3.4-17
If the input signal is not locked and searched, the “program” section shows empty. User
29

cannot do any setup at the moment.
² Video:
Here, you can configure the video parameter, as follows:
PIC-3.4-18
o Video Standard: in this item, you can select video standard, available options
include: Automatic, SECAM, NTSC, PAL-N, PAL-M and PAL.
o Aspect Ratio Conversion: you can setup the aspect ratio for the decoded
programs, available options include: Pillarbox (Side Bars), 16:9 Pan and
Scan, 4:3 LetterBox, and 4:3 Pan and Scan.
o Video Output Resolution, you can select the video format (resolution) for the
decoded program, available options include:
Auto / 480i / 576i / 720p50 / 720p59 / 720p60 / 1080i50 / 1080i59 / 1080i60.
The decoder output video resolution should meet with the monitor resolution
setting.
² Audio:
In this section, you can configure the information of Audio, as follows:
PIC-3.4-19
o Audio Volume: Set the output audio level from -63 to max. 0 in dB.
o Mixer: set the format of audio, including Stereo, Left, Right, Mono and Dual.
o Audio1/2 Preferred Language: Select audio language if there are multiple
² Subtitle:
audios contained in the signal.
30
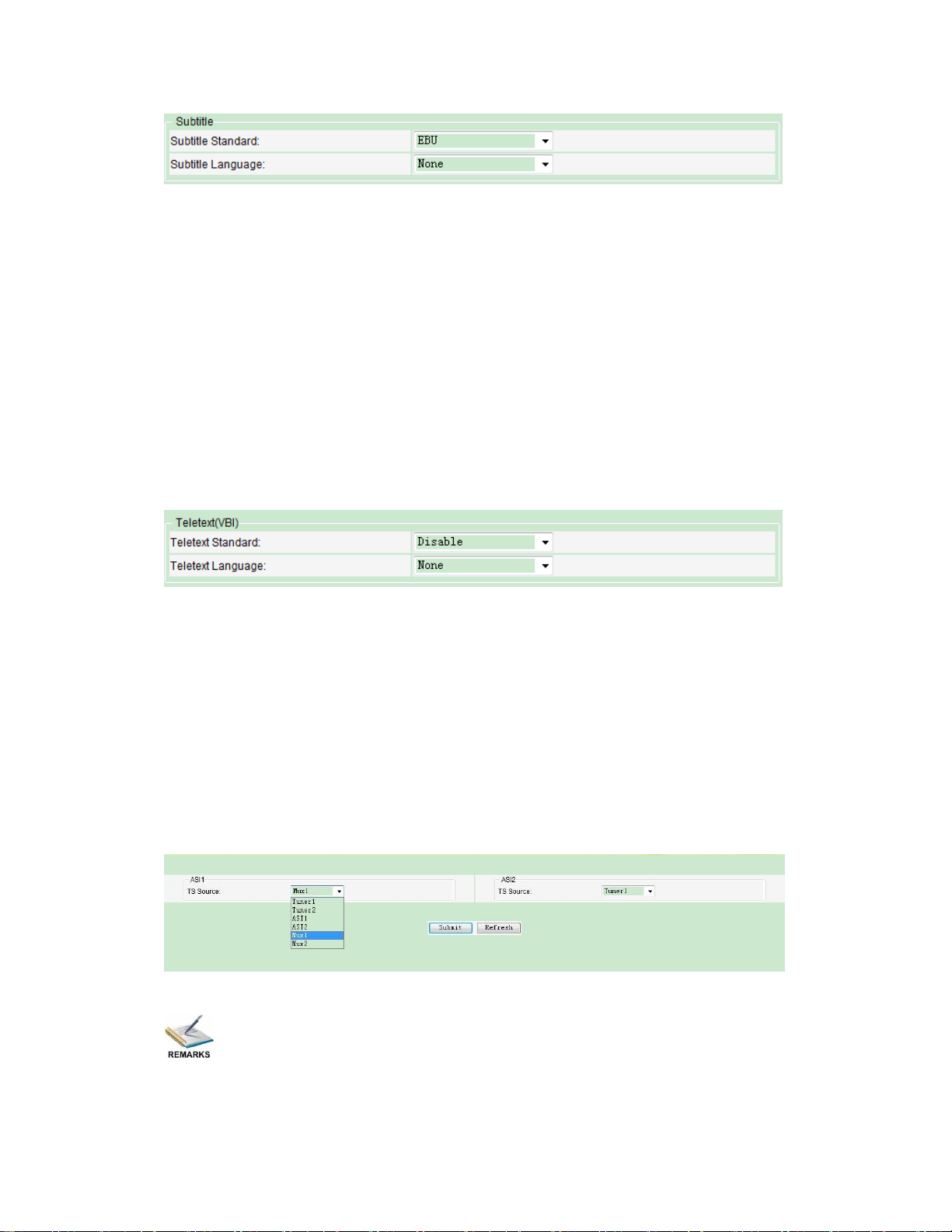
o Subtitle Standard: You can set the subtitle to be EBU or DVB.
o Subtitle Language: Here you can set the language of subtitle from the
² Teletext
PIC-3.4-20
EBU: The European Broadcasting Union is the world's foremost alliance of
public service media entities
DVB: It means Digital Video Broadcasting, a set of standards relating to
digital television
existing selections.
PIC-3.4-21
o Teletext Standard: choose disable to turn off the Teletext or enable to turn on
the Teletext.
o Teletext Language: You can set the teletext language here.
l ASI
In this page you are able to choose the input signal from Tuner, ASI, IP or Mux as singal
source for the ASI output. After configuration you need to click submit button to make it
taking effect immediately.
PIC-3.4-22
Only the Enabled Input will be listed on the TS source list.
l IP
31

In this page, you can set up the parameter of IP output. There are two channels for output
and you can set both of them.
PIC-3.4-23
l Enable: Enable or disable corresponding output channel
l TS Source: to choose the input signal as IP output.
l Dest IP Address: The IP address for the multicast/unicast.
l Dest Port: The port of the multicast/unicast, it must stay same with the value
of the dest device.
l Protocol: You can choose UDP OR RTP for multicast/unicast.
l Time to Live: Range is 1-255. (Num 8 is recommended)
l Enable Dest MAC: You can decide whether to set the MAC of destination
device.
3.4.2.6
In this page, user can manage the configuration setting related to the device decryption and
descrambling capability.
CA
Area 1
Area 2
Area 3
PIC-3.4-24
Area1: this area is for CAM bit-rate setting, where you can set the maximum bit rate
32

according to the CAM inserted.
Area2: This area is for the Biss setting.
l BISS (Basic Interoperable Scrambling System): is a satellite signal scrambling
system developed by the European Broadcasting Union and a consortium of
hardware manufacturers. There are two types:
o BISS-1, transmission are protected by a 12 digit hexadecimal “session key”
that is agreed by the transmitting and receiving parties prior to transmission.
The key is entered into both the encoder and decoder, this key then forms
part of the encryption of the digital TV signal and any receiver with
BISS-support with correct key will decrypt the signal.
o BISS-E (E for encrypted), is a variation where the decoder has stored one
secret BISS-key entered by for example a rights holder. This is unknown to
the user of the decoder. The user is then sent a 16-digit hexadecimal code,
which is entered as a “session key”. This session key is then mathematically
combined internally to calculate a BISS-1 key that can decrypt the signal.
o
BISS-E ID, an identification ID given prior to transmission and reception.
Area3: In this area, it is able to choose the programs that need to be descrambled and set
the CAM info. All the received signals will be listed in the “TS Source” menu. Then you can
choose the programs that you want to descramble on the program list and click the “Submit”
button to make it into effect.
l TS Source: to choose the input signal as IP output.
Usually a standard CAM can support a certain data processing unless it has
instruction for higher bit rate support. Selecting a wrong CAM output bit rate will
cause video mosaic issue because the actual processed data exceeds the CAM Max
handling capability.
3.4.2.7
System
33

l LocalSetup
PIC-3.4-25
In this page, you are able to configure the following parameters:
l IP Address: Local IP setting for connecting to the server. This IP and the
management server’s IP should be in the same section.
l Network Mask: Network Mask setting for connecting to the server. It should be
the same as management server: 255.255.255.0
l Gateway: Gateway setting for connecting to the server. It should be the same
as the management server.
l Trap IP Address: This IP should be the same as the monitoring server’s IP.
After correct setup, the IRD will pass the alarming and running information to
the monitoring server.
l Language: to configure the UI displaying language.
l Import/Export
This menu is for user to import/export the machine configuration file.
34
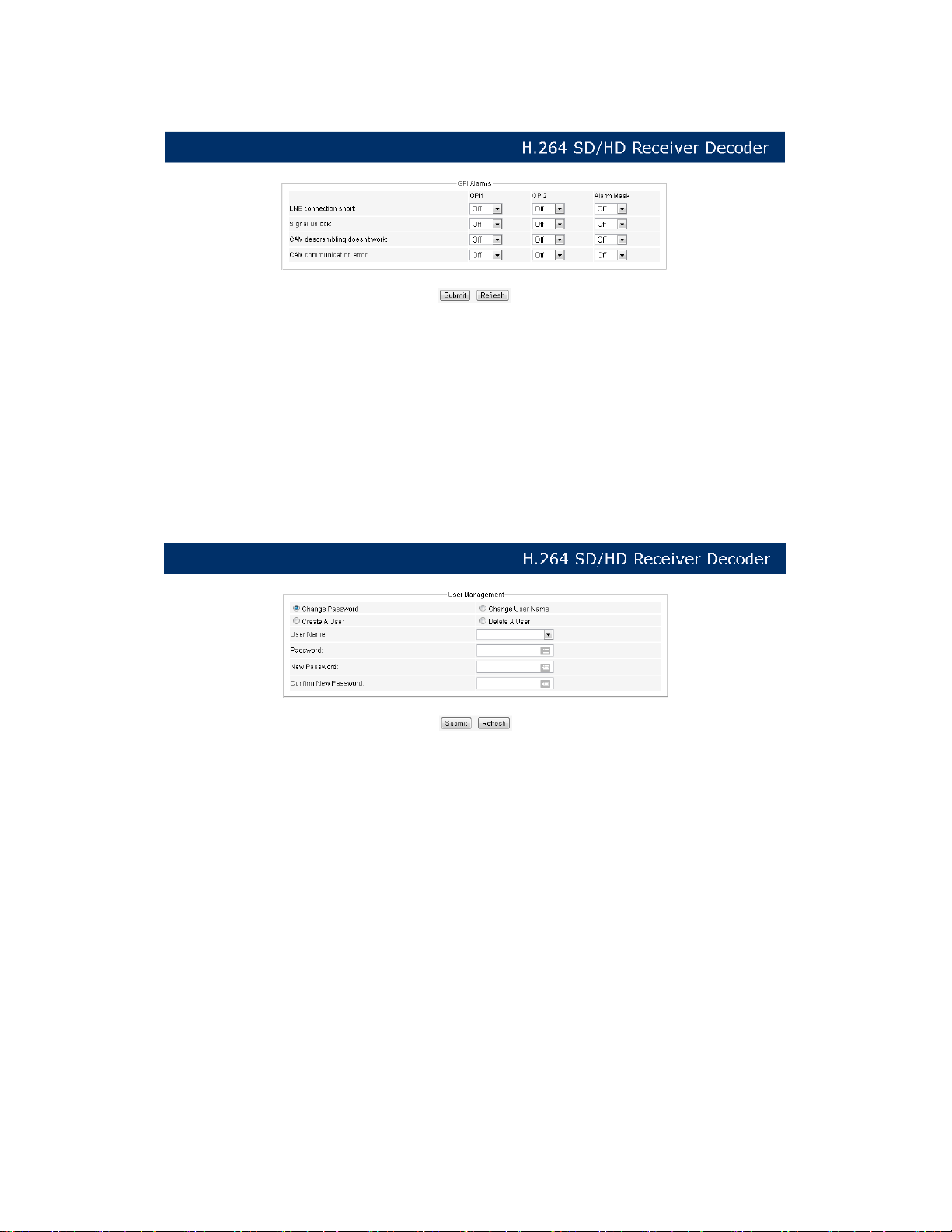
l GPI Alarms
PIC-3.4-26
In this section, user can set the alarm information to monitor the device and signal. After
setting the “Alarm Mask” on, the “GPI” item will be available to be set as On or Off. If the GPI
is set to on, when there are LNB Disconnect, Signal unlocked or CAM error, the alarm
information will be sent out via GPI.
l User Management
PIC-3.4-27
l Change Password:
When user put a check on this button, user can change the password with a new
one.
l Change Username:
Here, you can change the existed username to a new one.
l Create a User:
The device allows you to add up to 10 new users to operate the device. You can
set the new username and password after select “Create a User” button.
l Delete a User:
35

By selecting this section, you are able to delete the user account from the existing
account. If the user account is deleted, the user will have no right to access the
device.
l License
PIC-3.4-28
This menu is for licensing control on the machine. User can purchase upgrade package
from service provider to extend the machine function and capability. User shall check with
service provider first whether the on-hand machine supports license upgrade or not.
l Upgrade
PIC-3.4-29
Click Browse button, then user can select the upgrade file, and click “Upgrade” button to
start the upgrade. If succeed, restart the device and it will load the new version
l Log
In this page user can export and review the log of the machine.
l LogOut
PIC-3.4-30
User can logout the management system by clicking this button.
3.5. Preparation before Officially Operation
This section advises what need to be performed on the IRD before formally starts operation.
It includes but not limited to the following:
36

l Clear test data
l Configure the equipment with working data.
l Routing inspection.
3.5.1 Clear all useless data
To do a factory default setting on the device in order to clean up all test data generated in the
process of debugging and testing.
3.5.2 Configure the equipment with working data
According to the formal system plan to configure the IRD from signal input, descramble and
decoding output.
3.5.3 Full checking before implementation
After completion of the test and configuration, users are recommended to give the
equipment a final full-scale checking to ensure everything is on track for working with
long-term stability. It shall contain (but not limited to) the following items:
l
Check the strength and quality of all input signals.
l
Check if there is any alarm lights up on front panel LED indicator.
l
Check whether the cable connection is in good condition with each external device.
37

other factors that affect the
No cable connection or the
4 FAQ
Problem Possible Reasons What to do
Check whether the power
The LCD display on the front
No power.
panel does not light up.
cord is plugged into the
power socket.
No Video output
No or bad signal.
Parameters are not
properly configured.
No signal
The TV set is not tuned to
the right TV mode.
program does not exist in
current satellite.
Check the parameters
configuration
Check the source and
signal reception.
Set TV in right mode, e.g.
(Set TV to CVBS display
mode for CVBS decoding
input from IRD, and HDMI
mode for IRD HDMI input,
etc.)
Check the cable
connections, LNB and
other equipment
connected between the
LNB and the STB, and /or
Bad picture / Blocking error.
The satellite dish is not
properly oriented to the
satellite.
The satellite dish is not
properly oriented to the
satellite.
38
adjust the dish.
Align the dish. Check the
signal level in the IRD
menu.
Align the dish.

Problem Possible Reasons What to do
Signal is good. But No picture and
good one and connect well
Haven’t selected decrypted
Select decrypted programs
Connect a signal
no audio on decoding output
Cannot have access to the IRD
Signal is too strong.
attenuator to the LNB
input.
Signal is too weak. Change to a larger dish.
LNB noise figure is too
high.
Change a LNB with lower
noise figure.
The LNB is defective Change a LNB.
Insert correct CAM and
The picture and audio are
authorized smart card to
scrambled.
descramble the programs.
Check whether the
management PC IP and
IP setting
the IRD IP have been set
to be in same section.
through WEB UI
Cannot Decrypt Programs.
Make sure the cable is
Network cable problem
to the IRD management
port.
programs or select
to be correctly.
incorrectly.
CAM Modular Error. Change for another CAM.
Smart Card no
authorization
Incorrect insertion of CAM
or Smart card.
Change for an authorized
smart card
Correctly insert CAM and
Smart card.
39
5 Terminology
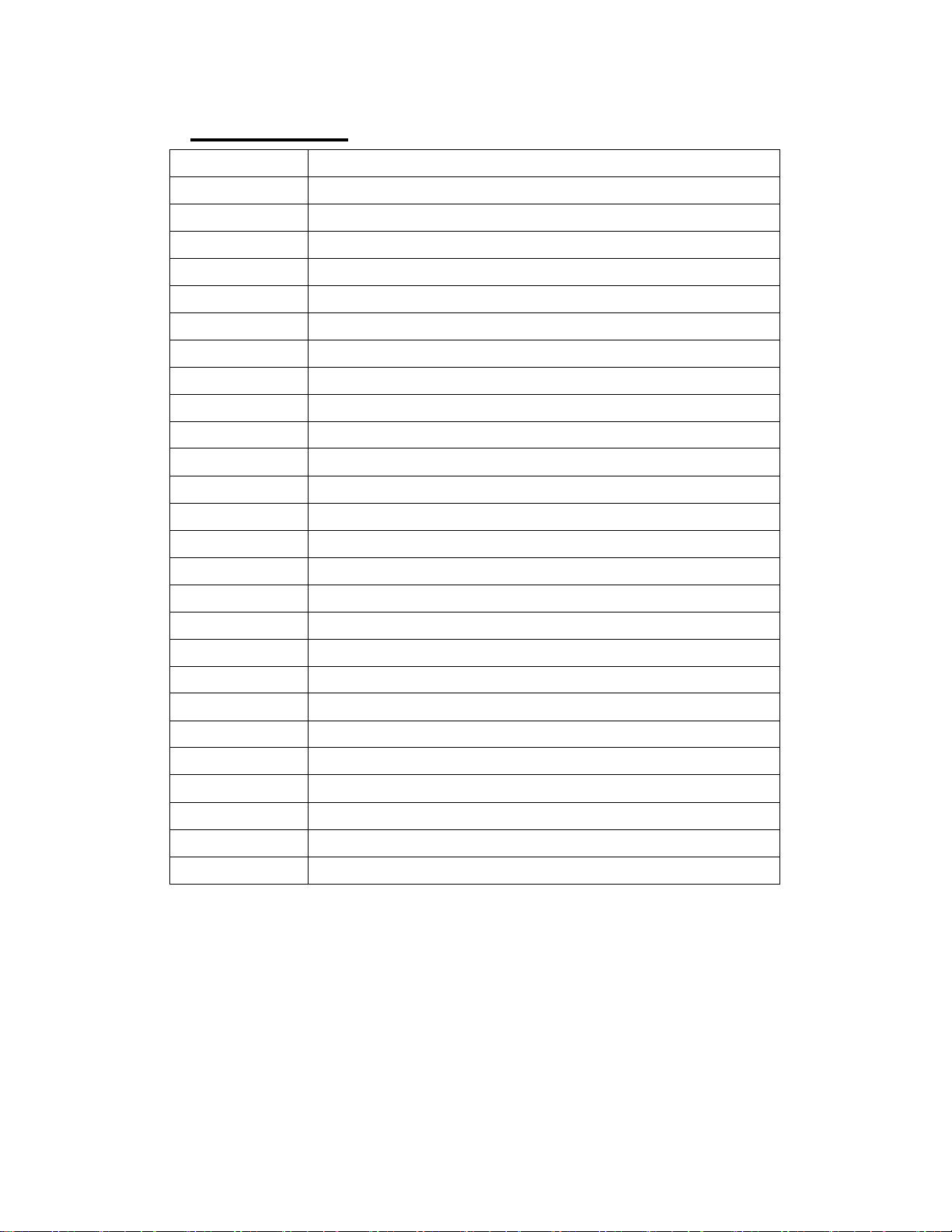
A - Z Abbreviation
Specific Meaning
AES
ASI
BISS
Basic Interoperable Scrambling System
BNC
CI
CVBS
Composite Video Broadcast Signal
DVB
DVB
-C
DVB
-
Cable
DVB
-
S/S2
DVB
-
Sate
llite
DVB
-T
EBU
European Broadcasting Union
ETSI
European Telecommunications Standards Institute
FEC
HD
High Definition
HDMI
ISO
ITU
I
nternational Telecommunications Union
LNB
MPEG
PCMCIA
Personal Computer Memory Card International Association
RTP
SD
SDI
Serial Digital Interface
TS
UDP
Audio Engineering Society
Asynchronous Serial Interface
Bayonet Nut Connector
Common Interface
Digital Video Broadcast
DVB-Terrestrial
Forward Error Correction
High Definition Multimedia Interface
International Standard Organization
Low Noise Block
Moving Pictures Experts Group
Real-time Transport Protocol
Standard Definition
Transport Stream
User Datagram Protocol
40
 Loading...
Loading...