Page 1

EMC Fibre Channel with
Qlogic Host Bus Adapters in the
Windows Environment
P/N 300-000-164
REV A01
AUGUST 2003
EMC Corporation
Corporate Headquarters
Hopkinton, MA 01748 -9103
1
-508 -435 -1000
www.EMC.com
:
Page 2

Copyright © 2001–2003 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved.
EMC believes the information in this publication is accurate as of its publication date. The
information is subject to change without notice.
THE INFORMATION IN THIS PUBLICATION IS PROVIDED "AS IS." EMC CORPORATION
MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND WITH RESPECT TO THE
INFORMATION IN THIS PUBLICATION, AND SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Use, copying, and distribution of any EMC software described in this publication requires an
applicable software license.
Trademark Information
ii
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 3

Contents
Preface........................................................................................................................... vii
Chapter 1 Introduction
Understanding Persistent Binding in a Fabric Environment .... 1-2
Chapter 2 Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
Introduction ...................................................................................... 2-2
Downloading QLogic Drivers and Firmware ...................... 2-2
Verifying and Downloading the Documentation ................ 2-2
Installing an HBA ............................................................................ 2-3
Special Installation Sequence for Stratus ftServers and
EMC CLARiiON Arrays .......................................................... 2-4
Special Instructions for CLARiiON CX200-Series
Direct-Connect Dual-Host Clustering Configurations ....... 2-4
EMC HBA Settings .......................................................................... 2-8
Pre-Configured Settings........................................................... 2-8
Configuring NVRAM for Stratus ftServers .......................... 2-9
Fibre-Down Servers with Embedded QLogic HBAs......... 2-10
Updating Firmware/BIOS and Applying NVRAM
Settings ..................................................................................... 2-10
Manually Setting the HBA Data Rate.................................. 2-12
Setting the Topology for QLA22xx/23xx and Windows .. 2-13
Installing the HBA Driver............................................................. 2-14
Driver Revision History......................................................... 2-14
Where to Find the Driver....................................................... 2-14
Windows 2003 STORPort Updates....................................... 2-14
Installation Procedure for Windows NT Hosts.................. 2-15
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
iii
Page 4

Contents
Installation Procedure for Windows 2000 and Windows
2003 Hosts................................................................................ 2-15
Updating the HBA Driver in a Windows 2000 or Windows
2003 Host......................................................................................... 2-17
Upgrading to Windows 2003 from Windows 2000 or
Windows NT 4.0 ............................................................................ 2-19
Chapter 3 Configuring an EMC Boot Device
Introduction...................................................................................... 3-2
How to Determine I/O Latency and Load on the Boot
LUN ............................................................................................ 3-3
Boot Crashdump Save to Disk Behavior............................... 3-4
Configuring a Symmetrix Boot Device......................................... 3-5
Configuring the Boot BIOS ..................................................... 3-5
Installing the Windows OS onto the Boot Device................ 3-7
Configuring a CLARiiON Boot Device ...................................... 3-10
Procedure Flowchart.............................................................. 3-10
Requirements .......................................................................... 3-12
Preparing the Storage System............................................... 3-13
Setting Up the HBA BIOS...................................................... 3-14
Preparing the Fabric............................................................... 3-15
Preparing the Server............................................................... 3-18
Configuring the HBA Boot BIOS.......................................... 3-20
Installing Windows ................................................................ 3-22
Verifying HBA Driver and Digital Signature Installation 3-25
Assigning a Permanent Boot Drive Letter for
Windows NT ........................................................................... 3-26
Installing Multipath and Failover Software ....................... 3-26
Installing Additional Navisphere Host Agent Software .. 3-27
Configuring Additional Boot Port Name Entries in the
Boot BIOS................................................................................. 3-27
Starting a Fresh Installation .................................................. 3-31
Boot Time and LUN Availability................................................. 3-32
Replacing a Boot HBA................................................................... 3-33
EMC Symmetrix ..................................................................... 3-33
EMC CLARiiON ..................................................................... 3-33
How a Server Responds to Failure in the Boot LUN Path....... 3-34
Known Issues ................................................................................. 3-35
iv
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 5

Appendix A Third-Party Software
QLogic SANSurfer SANBlade Manager v2.0.21 ....................... A-2
Veritas Volume Manager 3.x for Windows 2000 ....................... A-3
Appendix B Troubleshooting
Problems and Solutions ................................................................. B-2
Problem...................................................................................... B-2
Problem...................................................................................... B-2
Problem...................................................................................... B-2
Problem...................................................................................... B-3
Index ............................................................................................................................... i-1
Contents
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
v
Page 6

Contents
vi
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 7
Preface
Conventions Used in
This Guide
!
EMC uses the following conventions for notes, cautions, and
warnings.
A note presents information that is important, but not hazard-related.
CAUTION
A caution contains information essential to avoid data loss or
damage to the system or equipment. The caution may apply to
hardware or software.
WARNING
A warning contains information essential to avoid a hazard that can
cause severe personal injury, death, or substantial property damage
if you ignore the warning.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
vii
Page 8

Preface
Typographical Conventions
EMC uses the following type style conventions in this guide:
Related
Documentation
AVANT GARDE
Palatino,
bold
Keystrokes
◆ Dialog box, button, icon, and menu items in text
◆ Selections you can make from the user interface,
including buttons, icons, options, and field
names
Palatino,
italic
Courier,
italic
Courier
◆ New terms or unique word usage in text
◆ Command line arguments when used in text
◆ Book titles
Arguments used in examples of command line
syntax.
System prompts and displays and specific
filenames or complete paths. For example:
working root directory [/user/emc]:
c:\Program Files\EMC\Symapi\db
Courier,
bold
◆ EMC Host Connectivity Guide for Windows 2000 and Windows NT,
◆ User entry. For example:
symmpoll -p
◆ Options in command line syntax
P/N 300-000-603
viii
◆ EMC Navisphere Manager 5.X Administrator’s Guide, P/N
069001143
◆ EMC Navisphere Manager 6.X Administrator’s Guide, P/N
069001125
◆ EMC ControlCenter Navisphere Host Agent and CLI for Windows
2000 and NT Version 6.X Installation Guide , P/N 069001151
◆ EMC Navisphere Application Transparent Failover (ATF) for Windows
2000 and NT Administrator's Guide, P/N 069001164
◆ Storage-System Host Utilities for Windows 2000 and NT
Administrator's Guide, P/N 069001141
◆ PowerPath Installation And Administration Guide for Windows, P/N
300-000-512
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 9
Invisible Body Tag
1
Introduction
This document describes the procedures for installing an
EMC-approved QLogic host bus adapter (HBA) into a Windows NT,
Windows 2000, or Windows 2003 host environment and configuring
the Windows host for connection to an EMC storage array over Fibre
Channel.
Review the EMC Support Matrix for the latest information on
approved HBAs and drivers.
◆ Understanding Persistent Binding in a Fabric Environment ......1-2
Introduction
1-1
Page 10

Introduction
1
Understanding Persistent Binding in a Fabric Environment
Persistent binding is the mechanism to create a continuous logical
route from a storage device object in the Windows host to a volume in
the EMC
Without a persistent binding mechanism, the host cannot maintain
persistent logical routing of the communication from a storage device
object across the fabric to an EMC storage array volume. If the
physical configuration of the switch is changed (for example, the
cable is swapped or the host is rebooted), the logical route becomes
inconsistent, causing possible data corruption if the user application
is modifying data through inconsistent logical routing of the
communication from the driver entry point to a volume in an EMC
storage array across the fabric.
The Windows NT/Windows 2000/Windows 2003 operating system
(OS) does not provide a satisfactory means to allow persistent
binding. Most software applications access storage using file systems
that are managed by the Windows OS. (File systems are represented
by drive letters: colons: C:, D:, etc.) For storage devices containing file
systems, Windows NT/Windows 2000 writes a Disk Signature to the
disk device. The operating system can then identify, and associate
with, a particular drive letter and file system.
®
storage array across the fabric.
1-2
Since the signature resides on the disk device, changes can occur on
the storage end (a cable swap, for example) that can cause a disk
device to be visible to the host server in a new location. However, the
OS looks for the disk signature and, providing that nothing on the
disk changed, associate the signature with the correct drive letter and
file system. This mechanism is strictly an operating system feature
and is not influenced by the Fibre Channel device driver.
Some software applications, however, do not use the Windows file
systems or drive letters for their storage requirements. Instead they
access storage drives directly, using their own built-in “file systems.”
Devices that are accessed in this way are referred to as raw devices and
are known as physical drives in Windows terminology.
The naming convention for physical drives is simple and is always
the same for software applications using them. A raw device under
Windows NT/Windows 2000/Windows 2003 is accessed by the name
\\PHYSICALDRIVEXXX, where XXX is the drive number. For
example, a system with three hard disks attached using a QLogic
Fibre Channel controller assigns the disks the names
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 11

Introduction
\\PHYSICALDRIVE0, \\PHYSICALDRIVE1, and
\\PHYSICALDRIVE2. The number is assigned during the disk
discovery part of the Windows boot process.
During boot-up, the Windows OS loads the driver for the storage
HBAs. Once loaded, the OS performs a SCSI Inquiry command to get
information about all of the attached storage devices. Each disk drive
that it discovers is assigned a number in a semi-biased first come, first
serve fashion based on HBA. (Semi-biased means that the Windows
system always begins with the controller in the lowest-numbered PCI
slot where a storage controller resides. Once the driver for the storage
controller is loaded, the OS selects the adapter in the
lowest-numbered PCI slot to begin the drive discovery process.)
It is this naming convention and the process by which drives are
discovered that makes persistent binding (by definition) impossible
for Windows NT/Windows 2000/Windows 2003. Persistent binding
requires a continuous logical route from a storage device object in the
Windows host to a volume in an EMC storage array across the fabric.
As mentioned above, each disk drive is assigned a number in a first
come, first serve basis. This is where faults can occur.
Example Imagine this scenario—A host system contains controllers in slots 0,
1, and 2. Someone removes a cable from the QLogic controller in host
PCI slot 0, then reboots the host.
1
During reboot, the Windows OS loads the QLogic driver during
reboot and begins disk discovery. Under the scenario presented
above, there are no devices discovered on controller 0, so the OS
moves to the controller in slot 1 and begins naming the disks it finds,
starting with \\PHYSICALDRIVE0. Any software applications that
were accessing \\PHSYICALDRIVE0 before the reboot will be
unable to locate their data on the device, because it has changed.
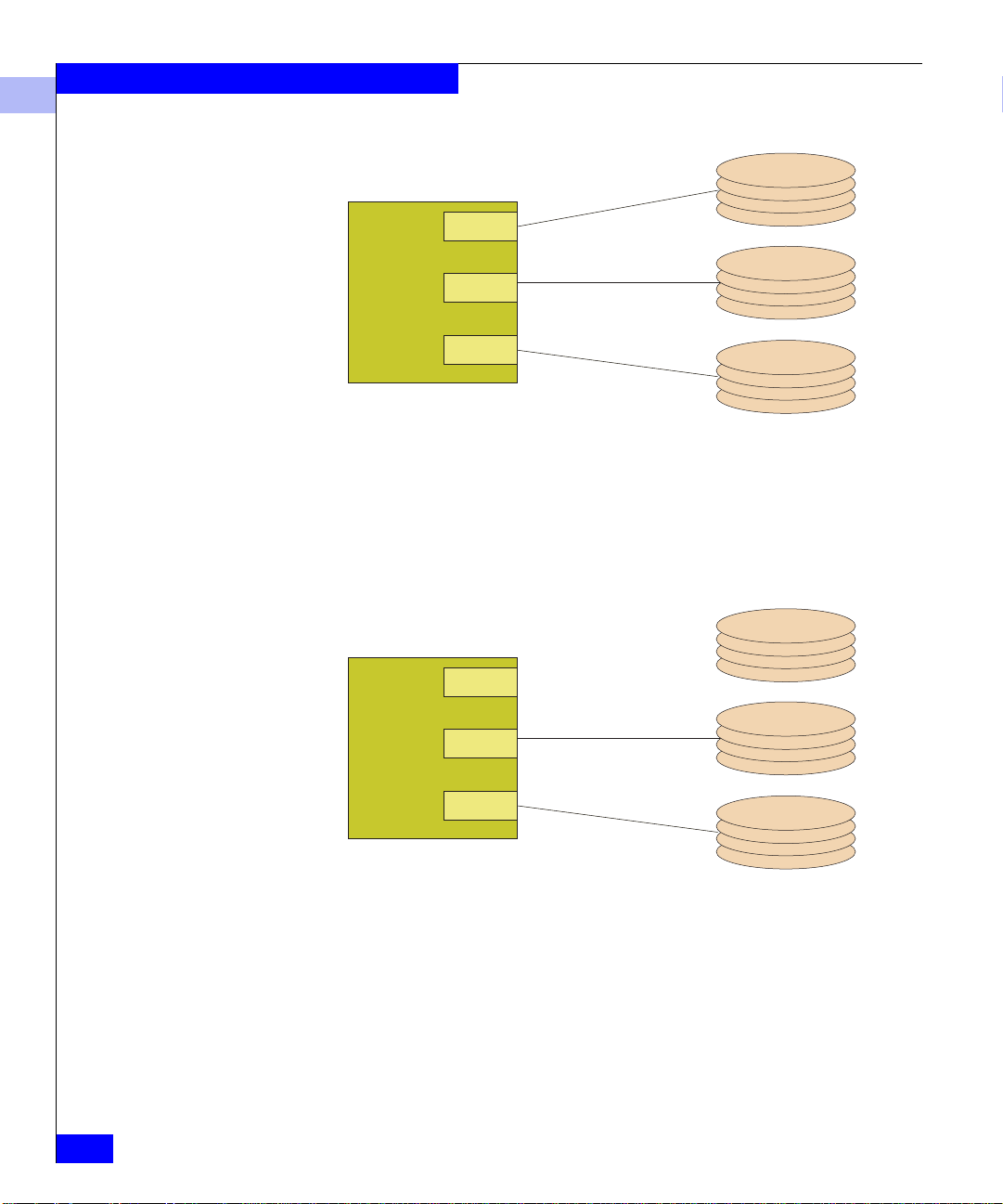
The following figure shows the original configuration before the
reboot. HBA0 is in PCI slot 0 of the Windows host. Each HBA has
four disk devices connected to it, so Windows has assigned the name
\\PHYSICALDRIVE0 to the first disk on HBA0. Each disk after that
is assigned a number in sequence as shown in the figure.
Understanding Persistent Binding in a Fabric Environment
1-3
Page 12
Introduction
1
PHYSICALDRIVE0
HBA 0
Windows
Host
HBA 1
PHYSICALDRIVE4
HBA 2
PHYSICALDRIVE8
The next figure shows the same host after the cable attached to HBA0
has been removed and the host rebooted. Since Windows was not
able to do a discovery on HBA0, it assigned \\PHYSICALDRIVE0
to the first device it discovered. In this case, that first device is
connected to HBA1. Due to the shift, any software application
accessing \\PHYSICALDRIVE0 will not find data previously
written on the original \\PHYSICALDRIVE0.
HBA 0
Windows
Host
HBA 1
HBA 2
PHYSICALDRIVE0
PHYSICALDRIVE4
1-4
The default driver behavior does not store target bindings between
host reboots. The bindings are dynamically generated by the HBA
when new target devices are detected.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 13
Invisible Body Tag
2
Installing and
Configuring the HBA
Driver
This chapter describes the procedures for installing an
EMC-approved QLogic host bus adapter (HBA) into a Windows NT,
Windows 2000, or Windows 2003 host environment and configuring
the Windows host for connection to an EMC storage array over Fibre
Channel.
◆ Introduction ........................................................................................2-2
◆ Installing an HBA...............................................................................2-3
◆ EMC HBA Settings.............................................................................2-8
◆ Installing the HBA Driver...............................................................2-14
◆ Updating the HBA Driver in a Windows 2000 or Windows 2003
Host....................................................................................................2-17
Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2-1
Page 14

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
Introduction
The procedure described here was written specifically for the
QLA22xx and QLA23xx families of Fibre Channel HBAs; however,
the procedures for installing the adapter BIOS and Windows drivers
are identical for QLA21xx, QLA22xx, and QLA23xx.
When installing or upgrading the BIOS and drivers, be sure to use the
latest versions supported by EMC. Review the EMC Support Matrix
for the latest information on approved HBAs and drivers.
Also refer to the EMC Host Connectivity Guide for Windows 2000 and
Windows NT, available on Powerlink, for related information.
Downloading QLogic Drivers and Firmware
Verifying and Downloading the Documentation
If you need to download the latest HBA driver or firmware:
1. Access
2. Click Downloads at the left side of the screen.
3. Click the EMC link to the right of OEM-approved
Drivers/Firmware.
4. Find the description of your HBA driver in the Name column of
the table for your HBA model. Then click the Download link in
the associated Download column.
To check for the latest revision of this document (and download it if
necessary):
1. Access
2. Click Downloads at the left side of the screen.
3. Click the EMC link to the right of OEM-approved
Drivers/Firmware.
4. Find the description of your HBA driver in the Name column of
the table for your HBA model. Then click the Readme link in the
associated Description column.
www.qlogic.com.
www.qlogic.com.
2-2
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 15
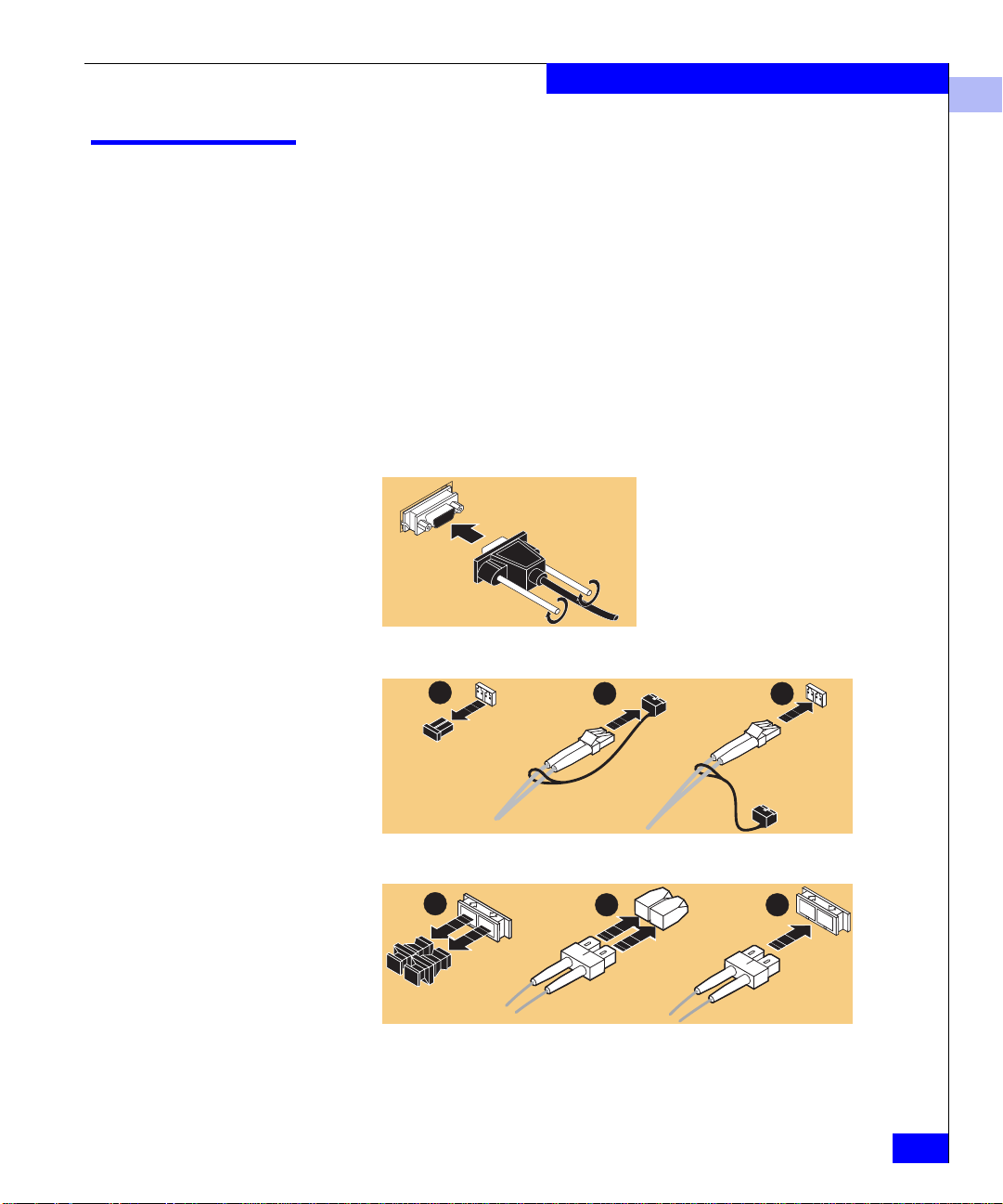
Installing an HBA
Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
Follow the instructions included with your adapter. The adapter
installs into a single slot, and has no user-configurable jumpers or
switches.
Follow these steps to connect the cable to the HBA:
1. (Optical cable only) Remove the protective covers on each
fiber-optic cable.
2. Plug one end of the cable into the connector on the HBA as shown
in the appropriate figure. (The hardware might be rotated 90
degrees clockwise from the orientation shown.)
• Copper Cable:
• LC Optical Cable:
1
• SC Optical Cable:
1
3. Plug the other end of the cable into a connector on the storage
system or a hub/switch port.
2
2
3
3
Installing an HBA
2-3
Page 16

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
4. Label each cable to identify the HBA and the storage/switch/hub
port to which it connects.
5. After connecting all HBAs in the server, power up the server.
Special Installation Sequence for Stratus ftServers and EMC CLARiiON Arrays
A specific installation sequence is required when installing QLogic
HBAs with the Stratus ftServers and EMC CLARiiON
Failure to follow this sequence may result in a
STOP: 0X0000007B
®
storage.
bugcheck error when booting the Stratus server for the first time
when connected to EMC CLARiiON storage.
With the Stratus ftServer, if the HBA detects EMC CLARiiON array
targets but no accessible LUNS, it prevents the Stratus server from
booting. In this configuration, the Stratus ftServer attempts to boot
from the array, instead of booting from the internal boot drive.
To avoid this issue before storage is correctly assigned, either boot the
Stratus ftServer before connecting the fibre cables to the HBAs or, if
connected to a fabric, disable the HBA ports on the switch before
booting the ftServer.
After the system has booted, connect the cables or reenable the switch
ports. Verify that the HBAs are logged in to the EMC CLARiiON
array; then stop and restart the Navisphere agent on the ftServer host.
This will register the HBAs with the CLARiiON array and allow the
HBA to properly detect the available LUNS.
Special Instructions for CLARiiON CX200-Series Direct-Connect Dual-Host Clustering Configurations
For CLARiiON CX200-Series direct-connect dual-host cluster
configurations only with QLA234x HBAs, you must follow all
procedures described in this section.
Check for an Updated
2-4
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
HBA Driver
For CLARiiON CX200-Series direct-connect dual-host cluster
configurations with only QLA234x HBAs, you may need a separate
driver and firmware download. The EMC Support Matrix notes
whether separate driver and firmware files are required.
For each HBA that is determined to require updated firmware and
drivers, follow the instructions under Downloading QLogic Drivers and
Firmware on page 2-2. Be sure to reference the Name and Description
Page 17
Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
fields to select the correct CX200-Series direct-connect dual-host
cluster-compatible files.
2
Reconfigure the HBA
Jumper
!
For CLARiiON CX200-Series direct-connect dual-host cluster
configurations with only QLA234x HBAs, you must change the
default HBA optic jumper position:
CAUTION
Modifying the jumper setting without using the recommended
firmware/drivers can cause the HBA to lose connectivity.
1. Remove the HBA from the server as instructed by your server
guide.
2. Locate jumper(s) J3 (QLA2340) or J3 and J4 (QLA2342), shown in
the following figure:
LED
J3
31
J1
QLA2340
LED1
J3
31
LED2
J4
J1
J2
31
QLA2342
3. Move the jumper(s), onto pins 1–2 (if not already there).
Installing an HBA
2-5
Page 18

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
If later you wish to return the jumper(s) to the default factory position, repeat
step 2, returning the jumper to pins 2–3.
Set the HBA FC-AL
Loop ID
While configuring a QLA234x HBA for Windows NT or Windows
2000 and connection to EMC CLARiiON CX200-Series for
direct-connect cluster configurations, you must manually set the
HBA FC-AL Loop ID. Follow these steps to enable loop hard
addressing and set the loop ID on each HBA:
Perform this procedure on all nodes in the cluster connected to the
CX200-Series array.
1. Boot the Windows host; press CTRL-Q when prompted to Press
<CTRL-Q> for Fast!UTIL
. (This prompt appears with the
QLogic startup banner.)
2. After the Fast!UTIL program loads, the initial display depends on
whether there are multiple QLogic HBAs installed in the server:
• If there is only one QLogic HBA, the Fast!UTIL Options menu
appears.
• If there are multiple QLogic HBAs, a list of memory addresses
occupied by those HBAs appears.
Using the arrow keys, select the desired HBA and press
ENTER.
The Fast!UTIL Options menu appears.
3. Select Configuration Settings from the Fast!UTIL Options menu,
and press
ENTER.
2-6
4. Select Host Adapter Settings from the Configuration Settings
menu.
5. Select Adapter Hard Loop ID from the Host Adapter Settings
menu and press
ENTER until the value is Enabled.
6. Select Hard Loop ID and press
The loop ID value entered here is the decimal representation of
the FC-AL loop ID. You do not need to perform any FC-AL
AL_PA hexadecimal translation.
HBAs connected to the same SP should all have unique hard loop IDs.
Select 0 for all HBAs on one node, select 1 for all HBAs on the next node,
and so on.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
ENTER.
Page 19

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
7. Enter a value for the loop ID and press ENTER.
2
8. Press
9. Press
ESC to return to the Configuration Settings menu.
ESC to return to the Fast!UTIL Options menu.
10. When prompted to save changes made to the current adapter,
select Save Changes and press
ENTER.
11. If there are more adapters to configure, choose Select Host
Adapter, and repeat steps 3 through 11 for each adapter.
12. Press
ESC to exit Fast!UTIL.
13. Reboot the host.
14. Repeat this procedure on all nodes in the cluster connected to the
CX200-Series array.
15. While you are in the BIOS, you can verify that the topology is set
correctly for direct connect (FC-AL). Follow the instructions
under Setting the Topology for QLA22xx/23xx and Windows on
page 2-13.
!
CAUTION
Future use of the firmware NVRAM file to apply settings will
overwrite and possibly invalidate the changes made above. If you
will later update using a firmware NVRAM file, be sure it is listed
and supports this CX200-Series direct-connect cluster
configuration.
To restore EMC default HBA settings, either reload the approved EMC
NVRAM file, or return to step 5 and ensure that Adapter Hard Loop ID is set
to Disabled.
Installing an HBA
2-7
Page 20

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
EMC HBA Settings
EMC requires configuring the QLogic BIOS settings with the
EMC-approved NVRAM settings file. This file contains all of the
BIOS settings for the QLogic adapters that have been tested and
approved for connection to the EMC storage array.
The QLogic CD-ROM contains the latest EMC-approved BIOS and
NVRAM settings files at the time of creation of the CD-ROM. If more
recent files exist, you can find them on the QLogic website. Refer to
Downloading QLogic Drivers and Firmware on page 2-2.
Pre-Configured Settings
The following parameters have been preconfigured in the EMC
NVRAM. They are also configurable in the Host Adapter Settings,
Advanced Adapter Settings, and Extended Firmware Settings
menus.
These settings apply to PowerPath/ATF and non-HA connections.
Parameter QLogic Default Settin g
Data Rate 0 (1 Gb/s) 2 (Auto Select)
Execution Throttle 16 256
Connection options (topology) 2 (Loop preferred,
otherwise point-to-point)
Enable LIP Full Login Yes Yes
Enable Target Reset No Yes
Port Down Retry Count 8 45
Luns Per Target 8 256
Adapter Hard Loop ID Enabled Disabled
Hard Loop ID 125 0
Pre-configured EMC
Setting
1 (point to point only)
2-8
Descending Search LoopID 0 1
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 21

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
Configuring NVRAM for Stratus ftServers
If you have not received QLogic HBAs with the EMC configurations
pre-loaded, you may have to perform the following procedure. If your HBAs
have been pre-configured, proceed to Installing the HBA Driver on page 2-14.
During POST, Stratus ftServers present only one HBA for
configuration in a multiple-HBA system. This is the way the ftServer
manages HBA failover. In order to successfully configure multiple
HBAs, each HBA must be part of an enabled Core PCI chassis at some
point. The following procedure explains how this can be done for
each chassis.
On Stratus ftServer 5200 systems, the HBA must be in a Core Chassis. Cards
in an Expansion Chassis must be moved to a Core Chassis to be available for
configuration.
1. To set the first HBA, follow these procedures:
• Updating Firmware/BIOS and Applying NVRAM Settings on
page 2-10
• Manually Setting the HBA Data Rate on page 2-12
• Setting the Topology for QLA22xx/23xx and Windows on
page 2-13
Ignore any steps that pertain to multiple adapters.
Note the Core PCI Chassis that is powered up while changing the
settings. After completing the changes, power down the system
and prepare to configure the alternate chassis.
2. Noting the PCI Chassis that was powered up in the previous step:
• For Stratus ftServer 3200 systems, loosen the Phillips-head
screw on the top right of the chassis, effectively removing
power from that chassis.
• For Stratus ftServer 5200 systems, leave the chassis powered
down.
3. Power up the system using the alternate PCI Chassis and set the
second HBA by following these procedures:
• Updating Firmware/BIOS and Applying NVRAM Settings on
page 2-10
• Manually Setting the HBA Data Rate on page 2-12
• Setting the Topology for QLA22xx/23xx and Windows on
page 2-13
EMC HBA Settings
2-9
Page 22

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
Ignore any steps that pertain to multiple adapters.
4. Shut down the server.
5. Before powering up the server, restore power to the PCI Chassis:
• For Stratus ftServer 3200 systems, tighten the Phillips-head
screw that you loosened on the top right of the chassis.
• For Stratus ftServer 5200 systems, power up the chassis.
6. Power up the server and proceed to Installing the HBA Driver on
page 2-14.
Fibre-Down Servers with Embedded QLogic HBAs
Updating Firmware/BIOS and Applying NVRAM Settings
!
Updating While
Running Windows
Fibre-Down servers have a vendor-specific firmware utility and
package that is posted on the QLogic website, in the EMC section. Be
sure to use the firmware utility and package that matches your
server model. You can check for updated firmware on the QLogic
website. Follow the steps under Downloading QLogic Drivers and
Firmware on page 2-2.
You can update the HBA firmware/BIOS and NVRAM either from
within a running Windows installation or by booting the server to a
DOS command prompt and running the procedure described in this
section.
Current 64-bit systems can be updated only from within Windows 2003 using
the SANSurfer SANBlade Manager. Refer to QLogic SANSurfer SANBlade
Manager v2.0.21 on page A-2 for instructions.
CAUTION
Do not flash embedded HBAs using the HBA utilities noted in this
section. (Refer to Fibre-Down Servers with Embedded QLogic
HBAs).
To update while running Windows, refer to QLogic SANSurfer
SANBlade Manager v2.0.21 on page A-2.
2-10
Stratus ftServers are not supported using the qLogic SANSurfer SANBlade
Manager Software or Agents, and should only be updated using the DOS
boot diskette. Refer to Updating Using a DOS Boot Diskette.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 23

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
Updating Using a DOS
Boot Diskette
!
To update using a DOS boot diskette, follow these steps:
The QLogic CD-ROM contains the latest EMC-approved BIOS and NVRAM
settings files at the time of creation of the CD-ROM. If more recent files exist,
you can find them on the QLogic website. Refer to Downloading QLogic
Drivers and Firmware on page 2-2.
1. Format a 3.5-inch diskette and extract the BIOS and NVRAM files
from the archive file (
.zip or self-extracting .exe) onto the
diskette.
2. Reboot your Windows host system using a DOS diskette.
3. At the
A:\> prompt, insert the diskette that contains the QLogic
BIOS files (created in step 1).
CAUTION
Do not attempt to run this procedure from a command prompt
window.
• To load firmware/BIOS and NVRAM settings, type
FLASUTIL.EXE /L /F and press ENTER:
• To load NVRAM settings only, type
FLASUTIL.EXE /L
and press ENTER:
Some BIOS archives will have QL2XUTIL.EXE instead of
FLASUTIL.EXE. Run QL2XUTIL.EXE as you would FLASUTIL.EXE.
Also, some BIOS versions might require the /N parameter (which allows
an alternate NVRAM filename to be specified) to load the NVRAM file
correctly.
Example: FLASUTIL /L /F /N NVRAM23o.DAT
Refer to the readme.txt file in the firmware package for complete
instructions on the use of the FLASUTIL.EXE utility
4. When the procedure has finished, remove the diskette and reboot
the host.
EMC HBA Settings
2-11
Page 24

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
Manually Setting the HBA Data Rate
The HBA driver for a QLA2310 has a data rate setting that lets you
specify 1 Gb, 2 Gb, or Auto Select mode. (The EMC default setting is
Auto Select mode.)
For any device connected to the HBA, set the device data rate (if applicable)
before setting the HBA data rate.
Current 64-bit systems can be updated only from within Windows 2003 using
the SANSurfer SANBlade Manager. Refer to QLogic SANSurfer SANBlade
Manager v2.0.21 on page A-2 for instructions.
For every HBA on which you want to manually set the HBA data
rate, follow these steps.
1. Reboot the system.
2. At startup, watch for the QLogic BIOS screen and when
prompted to enter Fast!Util, press
CTRL-Q.
3. Select host adapter.
4. Select Configuration Settings.
5. Select Extended Firmware Settings.
6. Press the Down Arrow until you select Data Rate; then press
ENTER.
2-12
7. Select the appropriate speed for the device to which the HBA
connects. EMC recommends using the default setting of option 2,
Auto Select.
8. Press
ESC repeatedly until you reach the Save Changes prompt,
and save the changes for this adapter.
9. Repeat steps 3 through 8 for each adapter.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 25

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
Setting the Topology for QLA22xx/23xx and Windows
While using a QLA22xx or QLA23xx HBA for Windows NT,
Windows 2000, or Windows 2003, the default EMC configured
topology is set for fabric. If you wish to change this value to FC-AL
(for direct-connect), you can manually set the adapter topology.
Follow these steps to set the topology:
Current 64-bit systems can be updated only from within Windows 2003 using
the SANSurfer SANBlade Manager. Refer to QLogic SANSurfer SANBlade
Manager v2.0.21 on page A-2 for further instructions.
1. Boot the Windows host and press CTRL-Q when prompted to
Press <CTRL-Q> for Fast!UTIL. (This prompt appears with the
QLogic startup banner.)
2. After the Fast!UTIL program loads, the initial display will depend
on whether there are multiple QLogic HBAs installed in the
server:
• If there is only one QLogic HBA, the Fast!UTIL Options menu
appears.
• If there are multiple QLogic HBAs, a list of memory addresses
occupied by those HBAs appears. Using the arrow keys, select
the desired HBA and press
ENTER. The Fast!UTIL Options
menu appears.
3. Select Configuration Settings from the Fast!UTIL Options menu
and press
ENTER.
4. Select Extended Firmware Settings from the Configuration
Settings menu and press
5. Select Connection Options and press
6. Select 0 (Loop Only) or 1 (Fabric) and press
7. Press
8. Press
ESC to return to the Configuration Settings menu.
ESC to return to the Fast!UTIL Options menu.
ENTER.
ENTER.
ENTER.
9. When prompted to save changes made to the current adapter,
select Save Changes and press
ENTER.
10. If there are more adapters to configure, choose Select Host
Adapter and repeat steps 3 through 9 for each adapter.
11. Press
ESC to exit Fast!UTIL.
12. Reboot the host.
EMC HBA Settings
2-13
Page 26

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
Installing the HBA Driver
To use EMC storage array disks with a Windows host, you need an
EMC-qualified Fibre Channel HBA driver. The HBA kit includes an
EMC-approved driver, which must be installed and configured prior
to partitioning the storage array disks. You should also check the
QLogic website for the latest EMC-approved version. (Refer to
Downloading QLogic Drivers and Firmware on page 2-2.)
Driver Revision History
Where to Find the Driver
Windows 2003 STORPort Updates
Driver support is as follows:
◆ Version 8.1.5.20 — QLA22xx, QLA23xx (no CX200-Series
direct-connect dual host cluster), Windows NT, Windows 2000
◆ Version 8.1.5.21 — QLA23xx, Windows NT, Windows 2000
◆ Version 8.2.1.20 — QLA23xx, Windows 2000
◆ Version 8.2.2.20 — QLA23xx STORPort, Windows 2003 only
◆ Version 8.2.2.25 — QLA23xx, Windows 2000 and Windows 2003
You can find the driver:
◆ on the QLogic CD-ROM that accompanied the HBA. Copy the
driver from the OS-specific directory:\WindowsNT4 or
\Windows2000.
◆ on the QLogic website. Refer to Downloading QLogic Drivers and
Firmware on page 2-2.
To ease installation of the driver, unzip the driver file onto a blank
diskette.
Currently the shipping version of Windows 2003 requires post-RTM
hotfixes to resolve some known issues. For all Windows 2003
STORPort installations, you should obtain the hotfix listed in
Microsoft Knowledge Base Article Q820362.
2-14
Install this patch before installing the HBA driver.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 27

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
Installation Procedure for Windows NT Hosts
To install the driver, follow these steps:
1. Boot the host with Windows NT 4.0.
2. Open the Control Panel and double-click the SCSI Adapter icon.
3. Select the Drivers tab.
4. Click the Add button to display the SCSI Adapter Drivers
database.
5. Select HAVE DISK.
6. Locate the disk with the OEMSETUP.INF file for the QLogic
driver and click OK.
7. Select QLogic QLA2300 (or QLA2200) PCI Fibre Channel
Adapter and click OK to install it.
8. Reboot the host. It should recognize all new host adapter cards.
9. After rebooting, verify that the driver is installed and has started
by checking the Control Panel, SCSI Adapter, Drivers window
for a statement similar to the following:
QLogic QLA2300 PCI-Fibre Channel Adapter (Started)
The driver is now loaded and the adapter is available to the
system.
Installation Procedure for Windows 2000 and Windows 2003 Hosts
To install the driver into a Windows 2000 or Windows 2003 host,
follow these steps:
1. Boot the host with Windows 2000 or Windows 2003.
2. From the Windows taskbar, select Start, Programs,
Administrative Tools, Computer Management
3. In the left pane of the Computer Management window, click the
Device Manager icon.
4. If Windows Plug-n-Play does not detect your QLA23xx HBA
model, it will be listed as
Controller
under the Other Devices icon in the right pane.
Unknown or as a Fibre Channel
Installing the HBA Driver
2-15
Page 28

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
Windows 2000 configurations with Service Pack 1 or higher and
Windows 2003 configurations may be able to detect QLA23xx HBAs. If
this occurs, the HBA will already be listed under SCSI Devices; instead
of proceeding with these installation steps, follow the instructions under
Updating the HBA Driver in a Windows 2000 or Windows 2003 Host on
page 2-17.
5. Double-click the first instance of SCSI Controller under Other
Devices.
6. In the next window, click ReInstall Driver, then Next.
7. Select Display a list of the known drivers for this device so that
I can choose a specific driver, then click Next.
8. Select SCSI and RAID Controllers, then click Next.
9. Click Have Disk.
10. Enter the path to the diskette containing the driver (for example,
A:\), then click OK.
11. Select the appropriate QLogic HBA from the list of drivers that
appears; then click Next.
2-16
12. Click Next in the next window.
13. Click YES to continue the installation.
14. Click Finish to complete the driver installation.
15. The system requests that you reboot the system. Select NO and
click Close.
16. The system again requests that you reboot the system. Select NO
again.
17. If there are other QLogic HBAs installed, repeat steps 5 through
16 until all adapters have been installed.
18. Reboot the host.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 29

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
Updating the HBA Driver in a Windows 2000 or Windows 2003 Host
On Windows 2000 and Windows 2003 systems where the QLogic
HBA has been detected automatically or a driver is already installed,
it might be necessary to upgrade the current driver to the latest
EMC-qualified driver, as described in this section.
The following procedure assumes that you have already copied the
latest driver from the QLogic CD-ROM or downloaded it from the
QLogic website and put it onto a diskette.
Refer to the release notes provided with the driver for information that might
be unique to new driver revisions.
To install the driver into a Windows 2000 or Windows 2003 host:
1. Boot the host (if necessary) with Windows 2000 or Windows 2003.
2. From the Windows taskbar, click Start, Programs, Administrative
Tools, Computer Management.
3. In the left pane of the Computer Management window, click the
Device Manager icon.
2
4. Double-click the SCSI & RAID Controllers icon.
5. Under SCSI & RAID Controllers, double-click the adapter you
wish to upgrade.
6. In the next window, click the Driver tab; then click Update
Driver.
7. Follow the update wizard until you are given the choice to
Display a list of the unknown drivers for this device so that I
can choose a specific driver.
Click the button next to this choice; then click Next.
8. In the Select a Driver window, click Have Disk.
9. Enter the path to the diskette containing the driver (A:\, for
example), or use the browse function to locate the driver; then
click OK.
10. Select the driver that is discovered and click Next.
11. In the next window, click Next.
Updating the HBA Driver in a Windows 2000 or Windows 2003 Host
2-17
Page 30

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
12. If prompted, click Yes to continue the installation.
13. Click Finish to complete the installation.
14. If the system requests that you reboot the system and you have
other adapters to update, select NO; then click Close.
15. If the system again requests that you reboot the system and you
have other adapters to update, select NO; then click Close.
16. If you have other adapters to update, select the next adapter
under SCSI & RAID Controllers and repeat steps 6 through 15.
When all adapters have had their drivers updated, select Yes to
the
reboot prompt.
2-18
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 31

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
Upgrading to Windows 2003 from Windows 2000 or
Windows NT 4.0
Note the following if upgrading to Windows 2003:
◆ Upgrading from Windows NT 4.0 — The Windows NT4 drivers
will not be preserved while upgrading to Windows 2003. You
should obtain the correct Windows 2003 drivers (refer to
Downloading QLogic Drivers and Firmware on page 2-2) and
reinstall the drivers after the upgrade is complete.
◆ Upgrading from Windows 2000 — The Windows 2000 drivers
may be preserved while upgrading to Windows 2003. These
SCSIPort drivers (including the native Windows 2003 SCSIPort
drivers) are not supported by EMC for Windows 2003. You
should obtain the correct Windows 2003 drivers (refer to
Downloading QLogic Drivers and Firmware on page 2-2) and
reinstall the drivers after the upgrade is complete.
You may wish to disconnect your storage during the Windows upgrade, and
reconnect it after the approved Windows 2003 drivers have been installed.
2
Upgrading to Windows 2003 from Windows 2000 or Windows NT 4.0
2-19
Page 32

Installing and Configuring the HBA Driver
2
2-20
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 33

Invisible Body Tag
3
Configuring an EMC
Boot Device
Windows hosts have been qualified for booting from EMC storage
array devices interfaced through Fibre Channel as described in the
EMC Support Matrix. This chapter describes the process to configure a
storage array device as a boot device.
◆ Introduction ........................................................................................3-2
◆ Configuring a Symmetrix Boot Device ...........................................3-5
◆ Configuring a CLARiiON Boot Device.........................................3-10
◆ Boot Time and LUN Availability ...................................................3-32
◆ Replacing a Boot HBA.....................................................................3-33
◆ How a Server Responds to Failure in the Boot LUN Path.........3-34
◆ Known Issues....................................................................................3-35
Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3-1
Page 34

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Introduction
Windows hosts have been qualified for booting from EMC array
devices interfaced through Fibre Channel as described under Boot
Device Support in the EMC Support Matrix.
!
CAUTION
Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 use virtual memory
paging files that reside on the boot disk. If the paging file becomes
unavailable to the memory management system when it is needed,
the operating system will crash with a blue screen.
For this reason, EMC recommends that you do not boot a Windows
host from the storage array. However, if it is necessary to use the
storage array as a boot disk, EMC recommends shutting down the
host server during any maintenance procedures that could make the
boot disk unavailable to the host.
Any of these events could crash a system booting from the storage
array:
◆ Lost connection to array (pulled or damaged cable connection)
◆ Array service/upgrade procedures, such as on-line microcode
upgrades and/or configuration changes
◆ Array failures, including failed lasers on Fibre Channel ports
◆ Array power failure
◆ Storage Area Network failures, such as Fibre Channel switches,
switch components, or switch power failures
◆ Storage Area Network service/upgrade procedures, such as
firmware upgrades or hardware replacements
3-2
EMC recommends moving the Windows virtual memory paging file to a
local disk when booting from the storage array. Consult your Windows
NT/Windows 2000 manual for instructions on how to move the paging file.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 35

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
How to Determine I/O Latency and Load on the Boot LUN
The current restrictions for boot-from-array configurations (listed in
the EMC Support Matrix) represent the maximum configuration that
is allowed using typical configurations. There are cases where your
applications, host, array, or SAN may already be utilized to a point
when these maximum values may not be achieved. Under these
conditions, you may wish to reduce the configuration from the
maximums listed in the EMC Support Matri, for improved
performance and functionality.
Here are some general measurements than can be used to determine
if your environment may not support the maximum allowed
boot-from-array configurations:
◆ Using the Windows Performance Monitor, capture and analyze
the Physical Disk and Paging File counters for your boot LUN. (For
Windows NT 4.0, you might have to enable disk performance
counters manually; refer to Microsoft support for the description
and use of the Windows Performance Monitor.) If response time
(sec/operation), or disk queue depth seem to be increasing over
time, you should review any additional loading that may be
affecting the boot LUN performance (HBA/SAN saturation,
failovers, ISL usage, etc.).
◆ Use available Array Performance Management tools to determine
that the array configuration, LUN configuration and access is
configured optimally for each host.
Possible ways to reduce the load on the boot LUN include:
◆ Move application data away from the boot LUN.
◆ Reduce the number of LUNs bound to the same physical disks.
◆ Select an improved performance RAID type.
◆ Contact your EMC support representative for additional
information.
Introduction
3-3
Page 36

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Boot Crashdump Save to Disk Behavior
If you system is configured to write crashdumps after system failures,
and the host is configured to boot from the array, you will be able to
successfully save the crashdump only on the original available boot
device path on which the system started. This is a Windows
limitation, and installing PowerPath will not affect this behavior. At
the time a system crash is to be written to disk, Windows has already
saved the original boot path, and PowerPath cannot redirect the
crashdump file (
MEMORY.DMP) to an alternative available device. If
you have a configuration for which you want to capture a
crashdump, you should ensure that the original primary boot path is
available at the time of the crash.
3-4
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 37

Configuring a Symmetrix Boot Device
Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Configuring the Boot BIOS
This section describes how to install the Windows NT or
Windows 2000 operating system onto an EMC Symmetrix
®
storage
system connected to an Intel-based x86 class server. You can then
boot Windows from the storage system.
The procedure below describes how to configure the boot BIOS. The
procedure assumes that the boot BIOS has been installed to the
adapters already.
1. Connect the EMC storage array boot port to the adapter in the
lowest-numbered PCI slot in the server. For example, if you have
three adapters in the system in slots 2, 4, and 5, connect the cable
to the adapter in slot 2. Do not connect cables to the other
adapters at this time.
2. Boot the server, and press
CTRL-Q when you see the QLogic
banner:
Different HBA models may display different banners. Be sure to select
CTRL-Q for the HBA you wish to configure.
QLogic Corporation
QLA2300 PCI Fibre Channel ROM BIOS Version 1.17
Copyright © Qlogic Corporation 1993-1999 All rights reserved
Press <CTRL - Q> for Fast!UTIL
www.qlogic.com
3. After Fast!UTIL loads, the display depends on whether there are
multiple QLogic HBAs installed:
• If there is only one QLogic HBA, the
Fast!UTIL Options
menu appears.
• If there are multiple QLogic HBAs, a list of addresses occupied
by those HBAs appears. Since the EMC storage array is
attached to the lowest-numbered PCI slot, select the first
adapter from the list; then press
ENTER. The Fast!UTIL
Options menu appears.
4. From the FastUTIL Options menu, select Configuration Settings
and press
ENTER.
Configuring a Symmetrix Boot Device
3-5
Page 38

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
5. From the Configuration Settings menu, select Host Adapter
Settings and press
6. From the Host Adapter Settings menu, select Host Adapter
BIOS and press
Refer to EMC HBA Settings on page 2-8 for a table of EMC-configured
NVRAM settings.
7. Press ESC to exit the Configuration Settings menu.
8. From the Configuration Settings menu, select Selectable Boot
Settings and press
9. From the Selectable Boot Settings menu, select Selectable Boot
Device and press
ENTER.
ENTER to enable it if it is not already enabled.
ENTER.
ENTER to enable it if it is not already enabled.
10. Select Current Boot Node Name and press
ENTER.
The adapter scans for attached storage devices, and displays them
on the screen.
11. Choose the storage array port from which you wish to boot. Its
entry will be similar to the following:
ID VENDOR PRODUCT REV NODE NAME Port ID
12 EMC SYMMETRIX 5566 50060482BFD06C02 0000E4
Select your boot device and press
ENTER.
A list of LUNs will appear in a new window. Select the LUN from
which you wish to boot and press
12. Press
ESC at the Selectable Boot Settings menu to return to the
ENTER.
Configuration Settings menu.
13. Press
14. Press
ESC at the Configuration Settings menu to return to the
Fast!UTIL Options menu.
Select Save Changes and press
ESC to exit Fast!UTIL.
ENTER.
15. Reboot the host.
3-6
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 39

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Installing the Windows OS onto the Boot Device
Windows NT
Follow the appropriate steps below to install the Windows operating
system onto the EMC boot device.
Microsoft does not provide a driver for the QLogic controllers on the
Windows NT installation CD-ROM. In order to properly install Windows NT
on a the EMC storage array boot device connected to a QLogic controller, the
Windows installation diskettes must be used with the CD-ROM.
1. Boot the server with Windows NT installation diskette 1. The
server displays the following message, followed by a blank blue
screen. Press
Setup is inspecting your computer's hardware configuration ---
Pressing F6 tells the Windows installer that you want to load a
third-party driver before proceeding with the installation.
F6 as soon as the blue screen appears:
2. Follow the prompts to insert the necessary diskettes until the
setup stops to allow you to add additional devices.
A screen message will tell you that the setup program cannot
determine the type of one or more mass storage devices.
From this point, press S to specify additional devices. You will need to select
Other and press ENTER.
3. Insert the QLogic driver disk into the diskette drive and press
ENTER.
4. You are prompted to select one of four driver choices. Select
QLogic QLA2300 (or QLA2200) PCI Fibre Channel Adapter and
press
ENTER.
The driver loads and you are brought back to the Additional
Devices screen.
5. You must now load the driver for your CD-ROM drive. The
Windows NT installer assumes that you want to specify all
storage drivers now. If the CD-ROM is not selected, installation
will fail later in the process.
Press
S to specify an additional device.
6. From the list, scroll up to select IDE CD-ROM (ATAPI 1.2)/PCI
IDE Controller and press
ENTER.
Configuring a Symmetrix Boot Device
3-7
Page 40

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
7. Some servers use SCSI CD-ROM drives. If your server has a SCSI
CD-ROM, repeat steps 5 and 6 to select the driver for the SCSI
controller. If your controller is not on the list, obtain the driver on
diskette from the vendor.
8. If you want to specify drivers for other devices installed in your
system, do so; otherwise press
screen to continue with Windows installation.
9. After completing Windows installation, reinstall the QLogic
driver using the steps under Installation Procedure for Windows NT
Hosts on page 2-15.
ENTER at the Additional Devices
Windows 2000
The HP ProLiant BL20p G2 Windows 2000 Installation procedure is described
under HP ProLiant BL20p G2 Windows 2000 Installation on page 3-9.
1. Boot the installation CD-ROM. (On some servers, it might be
necessary to use the Windows 2000 installation diskettes to start
the installation procedure.)
When the installer starts, a message appears at the bottom of the
screen, prompting you to press
F6 to load any other third-party
drivers.
Press
F6.
2. After a few moments, the installer stops to let you add additional
devices. A screen message will tell you that the setup program
cannot determine the type of one or more mass storage devices.
From this point, press S to specify additional devices.
3. Insert the QLogic driver diskette into the drive and press ENTER.
4. Select the model adapter that you have installed from the list that
appears. Be sure to choose the correct model series for the HBA
you have installed (QLA2300, for example) and press
ENTER.
The driver loads and you are brought back to the Additional
Devices screen.
3-8
5. If you want to specify drivers for other devices installed in your
system, do so; otherwise press
screen to continue with Windows installation.
6. After completing Windows installation, reinstall the QLogic
driver using the steps under Installation Procedure for Windows
2000 and Windows 2003 Hosts on page 2-15.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
ENTER at the Additional Devices
Page 41

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
HP ProLiant BL20p G2
Windows 2000
Installation
1. Note these prerequisites:
• RDP server with release 1.30
• BfS Installation script, see HP ProLiant BL20p G2
documentation for creation and installation of this script.
2. Configure BL20p G2. Then reboot the BL20p G2 and select F9 to
RBSU (F10 to save all changes before exit).
a. Select Set Boot Controller Order
i. Ctrl:1 PCI Dual Port Fibre..Port 1
ii. Ctrl:2 PCI Dual Port Fibre..Port 2
iii. Ctrl:3 HP Smart Array 5i Ctrl
b. Set IPL order as follows:
i. PCI Embedded HP NC7781 Gig Server Adapter Port 1
ii. CD-ROM
iii. Floppy Drive
iv. Hard Drive C:
3. Install the Windows 2000 OS:
a. If there is a local hard drive installed, remove it. This drive can
be reinserted after the installation is completed.
b. Open an interface window using the RDP console by
Right-clicking the target server and selecting Power Control/
RILOE Interface.
c. Delete the target server (BfS Server) from the RDP database if
it exists.
d. Reboot the BfS server. (At boot time, the newly created LUN
should be detected.)
The BfS server should now be seen in the RDP New Computer
pane.
e. Start the BfS deployment by dragging and dropping the
FROM SAN BL20p
script task to the BfS server new computer
BOOT
Installation time is approximately 50 minutes.
Configuring a Symmetrix Boot Device
3-9
Page 42

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Configuring a CLARiiON Boot Device
Procedure Flowchart
This section describes how to install a boot device onto an EMC
CLARiiON
server. You can then boot Windows from the storage system.
This section assumes that EMC did not prepare the server or the
storage system to boot Windows from the storage system.
SCSI hard disks are allowed in configurations that boot over Fibre
Channel. However, the BIOS for a SCSI disk’s SCSI adapters must be
disabled. You should also disconnect any SCSI disks before installing
Windows.
The installation procedure includes steps you must follow in a
specific order. The following flowchart outlines the major steps.
®
storage system connected to an Intel-based x86 class
3-10
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 43

Start
Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Boot LUN and
Storage Group
exist
By WWPN
Soft Zoning
Requirements
Satisfied
Prepare Storage
System
Create HBA
Driver Diskettes
Gather Data
and Set Up
HBA BIOS
Prepare Switch
Fabric
Unsatisfied
Complete
Requirements
Need boot LUN and Storage Group
Create boot LUN and
Storage Group
Need to update
firmware and NVRAM
Update firmware
Need to update
NVRAM only
Update NVRAM
By Port Number
Hard Zoning
Prepare Server
Configure HBA Boot BIOS
Install Windows
Verify Driver Installation
A
Install Additional Software
A
Multiple HBA
PowerPath/ATF PowerPath/CDE
Failover Software
Navisphere Agent
Single HBA
Configuring a CLARiiON Boot Device
3-11
Page 44

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Requirements
Topologies,
Configurations, and
Revisions
Hardware and
Software
Requirements
This section lists supported configurations, hardware and software
requirements, and related documentation.
Refer to the EMC Support Matrix.
Refer to the EMC Support Matrix for specific support information.
Some general requirements are:
◆ Boot server with a CD-ROM and diskette drives, and support for
the Windows version you will install. Refer to the EMC Support
Matrix for supported servers.
◆ Latest HBA firmware and drivers for your operating system.
Refer to Downloading QLogic Drivers and Firmware on page 2-2.
◆ One or more PCI Fibre Channel host bus adapters, installed in the
lowest numbered PCI slot(s), which are the slots first scanned at
startup, in the boot server.
◆ If installing in a fabric environment, Fibre Channel switch
configured for IP, and with an available zone configuration utility
(Telnet-based or Web-based).
◆ If required by the EMC Support Matrix, CLARiiON storage system
with Access Logix™ and Access Control enabled (using EMC
ControlCenter Navisphere Management software).
3-12
Until Windows is fully installed, you must connect only the
storage system onto which the operating system will be loaded.
Later, you can connect other storage systems.
◆ Cable connections as appropriate for server between server Fibre
Channel HBA, switch (FC-SW only), and storage system SPs.
◆ Navisphere Management station with EMC ControlCenter
Navisphere Management software or CLI. The station must be
separate from the boot server but networked to the storage
system (FC4700 and later array models) or connected to the
storage system (models earlier than FC4700).
◆ The host system for Windows NT 4 must have less than 4.0 GB of
physical RAM. (MSKB Q160392).
◆ HP ProLiant BL20p G2 requires RDP server with release 1.30 and
a BfS installation script. Refer to HP ProLiant BL20p G2
documentation for creation and installation of this script.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 45

Media Requirements Required media includes the following:
Refer to Downloading QLogic Drivers and Firmware on page 2-2.
◆ Latest EMC-approved Fibre Channel PCI HBA Driver Kit for
Windows
◆ Latest EMC-approved Fibre Channel PCI HBA firmware
◆ MS-DOS boot diskette.
Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Preparing the Storage System
Boot device support requires a Navisphere Management station with
Navisphere Manager or CLI. The station must be separate from the boot
server but networked to the storage system (FC4700 and later model arrays)
or connected to the storage system (models earlier than FC4700).
Before you can install Windows onto a storage system, the storage
system must have at least one bound LUN in a Storage Group for the
boot server. The LUN must be owned by the SP connected to the boot
HBA.
For Windows NT 4.0, the host system boot LUN must be assigned Host LUN
ID 0 by the EMC storage array. (MSKB Q218974)
During this installation procedure, you should have only one LUN in
the boot Storage Group, so that you can easily identify the boot LUN.
Later, you can add other LUNs to this Storage Group.
If you need to create a LUN, refer to the EMC ControlCenter Navisphere
Management software documentation for your array type.
Configuring a CLARiiON Boot Device
3-13
Page 46

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Setting Up the HBA BIOS
Once the HBA is installed in the host and the EMC array is connected
to the fabric (FC-SW) or directly connected to the HBA (FC-AL), you
can configure an EMC-qualified QLogic HBA for boot support using
Fast!UTIL, as described below:
1. Boot the server, and press
CTRL-Q when you see the QLogic
banner:
Different HBA models may display different banners. Be sure to select
CTRL-Q for the HBA you wish to configure.
QLogic Corporation
QLA2300 PCI Fibre Channel ROM BIOS Version 1.17
Copyright © Qlogic Corporation 1993-1999 All rights reserved
Press <CTRL - Q> for Fast!UTIL
www.qlogic.com
2. After Fast!UTIL loads, the display depends on whether there are
multiple QLogic HBAs installed:
• If there is only one QLogic HBA, the
Fast!UTIL Options
menu appears.
• If there are multiple QLogic HBAs, a list of addresses occupies
by those HBAs appears. Use the arrow keys to select the
desired HBA; then press
ENTER. The Fast!UTIL Options menu
appears.
3. Select Configuration Settings from the menu.
3-14
4. Select Host Adapter Settings and enable Host Adapter BIOS.
Refer to EMC HBA Settings on page 2-8 for a table of EMC-configured
NVRAM settings.
5. Press ESC to return to the previous menu.
6. Select Selectable Boot Settings and enable Selectable Boot
Device.
7. For any entry that is not blank (all zeros), highlight the entry and
press
C to clear any previous values.
8. When all parameters are set correctly, press
Fast!UTIL Options menu; then select Save Changes to save the
changes you made to the current adapter.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
ESC to return to the
Page 47

9. Press ESC to exit the Fast!UTIL Options menu.
10. Reboot the host.
What Next? The next step depends on the topology:
◆ FC-AL: Proceed to Preparing the Server on page 3-18.
◆ FC-SW: Proceed to Preparing the Fabric on page 3-15.
Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Preparing the Fabric
You can configure a switched fabric to support multiple hosts and
multiple storage systems. For this setup, we will describe only the
minimum configuration required for the boot LUN and server.
EMC recommends that you use switch zoning in all configurations to
ensure consistency if your fabric grows.
The configuration below requires an existing knowledge of zoning and
switch fabric concepts. The procedure explains the necessary steps to enable
boot functionality for the storage system. This configuration does not cover
the impact of zoning changes to other devices that will use the same
connections. You should confirm your overall topology requirements and
configuration before implementing any zoning changes.
Other devices on the fabric may introduce load and demand on the interlink
components and storage system that can affect boot LUN performance and
correct functionality.
The switch fabric must be configured initially so that the boot HBA is
visible only to a single port on the storage system. That is, there must
be only one zone containing the boot HBA and one SP port until
installation is complete, even if you will install failover software later.
This can be accomplished in one of three ways (described following
this list):
◆ Switch fabric soft zoning (by WWPN)
◆ Switch fabric hard zoning (by switch port)
◆ Physical connection of only one SP port to the fabric
Configuring a CLARiiON Boot Device
3-15
Page 48

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Soft Zoning These instructions let you configure the soft zoning as this setup
requires. They are not a complete explanation of zoning. Refer to the
documentation that is available for your switches for a complete
guide.
1. Ensure that the server and storage system are cabled properly
and powered on.
For the HBA’s WWPN to appear in the Name Server database, the
server must be in the boot BIOS menu. If the server is not in the
boot BIOS menu:
a. Reboot the server. When the QLogic BIOS banner (shown
below) appears, press
Different HBA models may display different banners. Be sure to
select CTRL-Q for the HBA you wish to configure.
QLogic Corporation
QLA2300 PCI Fibre Channel ROM BIOS Version 1.17
Copyright © Qlogic Corporation 1993-1999 All rights reserved
Press <CTRL - Q> for Fast!UTIL
www.qlogic.com
CTRL–Q:
3-16
b. After Fast!UTIL loads, the display depends on whether there
are multiple QLogic HBAs installed:
• If there is only one QLogic HBA, the
Options menu appears.
• If there are multiple QLogic HBAs, a list of
addresses occupies by those HBAs appears. Use the
arrow keys to select the desired HBA; then press
ENTER. The Fast!UTIL Options menu appears.
c. Select Configuration Settings from the menu.
d. Select Selectable Boot Settings from the Host Adapter
Settings menu; then select the first Boot Port Name entry.
The HBA will scan for available target ports. The HBA might
not find any target ports, but this step allows the HBA to
register with the switch database.
e. Leave the server, and continue to step 2.
2. Start a switch web-based or Telnet-based configuration session.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Fast!UTIL
Page 49

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3. Create a member alias for the boot HBA WWPN. Make sure it is a
member alias and that you use the 21... Port Name, not the 20...
Node Name.
4. Create a member alias for one storage system SP port that you
connected earlier and to which you bound the boot LUN. You can
choose either Port 0 or Port 1 of the SP if both ports are connected
to the switch. EMC recommends using Port 0 for consistency.
5. Create a zone and include the HBA alias and SP port alias created
in steps 3 and 4.
6. Create a new zone configuration or select an existing zone
configuration, and add the zone created in step 5.
7. Enable the zone configuration chosen in the previous step, and
click Apply.
8. Ensure that any ports, aliases or zones composed of the HBA
connection referenced above do not appear in any other zones or
configurations that are enabled.
Important: If you have previously soft-zoned servers, they will not adhere
to the new configuration unless they are restarted. Refer to the switch
zoning manual for further information.
3
What Next?
Continue to Preparing the Server on page 3-18.
Hard Zoning To use hard zoning:
1. Start a switch web-based or Telnet-based configuration session.
2. Create a zone and include the boot HBA port and one SP port.
You can choose either Port 0 or Port 1 of the SP if both are
connected to the switch. EMC recommends using Port 0 for
consistency.
3. Create a new zone configuration or select an existing zone
configuration, and add this zone.
4. Enable the zone configuration chosen in the previous step.
5. Ensure that any ports, aliases or zones composed of the HBA
connection referenced above do not appear in any other zones or
configurations that are enabled.
What Next?
Continue to Preparing the Server on page 3-18.
Configuring a CLARiiON Boot Device
3-17
Page 50

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Physical Connection
of Only One SP Port to
the Fabric
Preparing the Server
If the SP that owns the boot LUN has only one port connected to the
switch, and no other target devices are on the fabric, then zoning for
the boot configuration is not necessary. You should make sure any
existing zones still allow the HBA-to-SP connection.
Refer to the switch documentation for possible restrictions.
What Next?
Continue to Preparing the Server.
You must adhere to the configuration rules for your server when you
install and set up the PCI cards. See the server installation and
operation manual. All servers must meet the following requirements:
◆ The PCI Fibre Channel HBA must be the first HBA adapter
scanned for boot.
◆ SCSI hard disks are allowed in configurations that boot from
Fibre Channel. However, the BIOS for the disk’s SCSI adapters
must be disabled. You should also disconnect any SCSI disks before
installing Windows. Reconnect or add SCSI hard disks when the
installation is complete.
◆ You must have at least one EMC-qualified QLogic Fibre Channel
HBA. Depending on your configuration, you can install
additional Fibre Channel HBAs according to the topology rules in
the EMC Support Matrix.
Perform the following steps:
3-18
1. Press
ESC to exit the Fast!UTIL Options menu; then reboot the
system.
You may receive a non-system disk error message; this is normal
at this stage.
2. If any SCSI hard disk drives are connected, continue with step 3.
You might not be able to install Windows on the storage system if the
server has a SCSI hard disk connected. The Windows Setup program
may automatically assign the SCSI disk as drive C and install the
operating system on that disk.
If no SCSI hard disk drives are connected to the server, go to
step 4.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 51

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3. To disconnect all SCSI hard disk drives, unplug the power and
SCSI bus cables connected to a SCSI adapter or controller. For
details, see the installation and operation manual for your server.
4. To prepare your system to boot Windows over a Fibre Channel
connection, you must do the following:
For detailed instructions on the HP ProLiant BL20p G2, refer to
Configuring the HP ProLiant BL20p G2. For other detailed instructions,
refer to the manufacturer’s documentation available for each adapter.
• For any server with IDE CD-ROM drives, you should disable
BIOS on any of the server’s integrated SCSI adapter(s) because
SCSI BIOS is not required to boot from CD-ROM.
• Disable or remove any IDE HDD drives.
• For servers with SCSI CD-ROM drives, enable BIOS on the
SCSI channel that includes the CD-ROM; disable BIOS on any
other integrated SCSI channels. Remove any SCSI hard disks
on the same bus as the CD-ROM drive.
If the CD-ROM is on a SCSI controller and the BIOS is disabled for
that controller, then you will not be able to boot from the CD-ROM.
To boot from CD-ROM in the future, you will need to re-enable the
BIOS for the CD-ROM controller.
3
Configuring the HP
ProLiant BL20p G2
• Disable BIOS on any other HBA BIOS in your system other
than the QLogic HBA(s) designated for booting. See the
documentation that accompanied the HBA for instructions.
Reboot the BL20p G2 and select F9 to RBSU (F10 to save all changes
before exit):
1. Select Set Boot Controller Order:
a. Ctrl:1 PCI Dual Port Fibre..Port 1
b. Ctrl:2 PCI Dual Port Fibre..Port 2
c. Ctrl:3 HP Smart Array 5i Ctrl
2. Set the IPL order as follows:
a. PCI Embedded HP NC7781 Gig Server Adapter Port 1
b. CD-ROM
c. Floppy Drive
d. Hard Drive C:
Configuring a CLARiiON Boot Device
3-19
Page 52

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
What Next? Configure the HBA Boot BIOS as described in the next section.
Configuring the HBA Boot BIOS
Follow these steps to configure the storage system LUN for the HBA
Boot BIOS:
1. Reboot the server.
When the QLogic BIOS banner (shown below) appears, press
CTRL–Q.
Different HBA models may display different banners. Be sure to select
CTRL-Q for the HBA you wish to configure.
QLogic Corporation
QLA2300 PCI Fibre Channel ROM BIOS Version 1.17
Copyright © Qlogic Corporation 1993-1999 All rights reserved
Press <CTRL - Q> for Fast!UTIL
www.qlogic.com
2. After Fast!UTIL loads, the display depends on whether there are
multiple QLogic HBAs installed:
• If there is only one QLogic HBA, the
Fast!UTIL Options
menu appears.
• If there are multiple QLogic HBAs, a list of addresses occupies
by those HBAs appears. Use the arrow keys to select the
desired HBA; then press
ENTER. The Fast!UTIL Options menu
appears.
3. Select Configuration Settings from the menu.
3-20
4. Select Selectable Boot Settings from the Configuration Settings
menu.
Select the first Boot Port Name entry, and in the Device window
scroll to select the CLARiiON port WWN from which you want to
boot.
Depending on the array model, the HBA may not yet detect any LUNs,
or it may detect a LUNZ labeled disk. This is normal behavior.
Leave the server here so the HBA will remain active while you
configure the storage array groups.
5. Using EMC ControlCenter Navisphere Management software,
you must add the HBA to the storage group you created earlier.
Depending on the array model, you may have to first manually
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 53

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
register the HBA connection. If you will later install PowerPath or
ATF, be sure to select the corresponding parameters during the
registration procedure. Refer to your EMC ControlCenter
Navisphere Management software, ATF, or PowerPath
documentation for detailed instructions.
3
6. Press
ESC until you exit the Fast!UTIL Options menu. You do not
need to save any changes if prompted.
7. Reboot the server.
When the QLogic BIOS banner (shown in step 1) appears, press
CTRL–Q.
Different HBA models may display different banners. Be sure to select
CTRL-Q for the HBA you wish to configure.
8. After Fast!UTIL loads, the display depends on whether there are
multiple QLogic HBAs installed:
• If there is only one QLogic HBA, the
Fast!UTIL Options
menu appears.
• If there are multiple QLogic HBAs, a list of addresses occupies
by those HBAs appears. Use the arrow keys to select the
desired HBA; then press
ENTER. The Fast!UTIL Options menu
appears.
9. Select Configuration Settings from the menu.
10. Select Selectable Boot Settings from the Configuration Settings
menu.
Select the first Boot Port Name entry, and in the Device window
select the CLARiiON port WWN from which you want to boot.
After you select the WWN, if there is more than one LUN
detected, select the boot LUN number from the next window.
11. When all parameters are set correctly, press
Fast!UTIL Options menu; then select Save Changes to save the
changes you made to the current adapter.
12. Press
ESC to exit the Fast!UTIL Options menu.
13. Reboot the server.
What Next? Install Windows as described in the next section.
Configuring a CLARiiON Boot Device
ESC to return to the
3-21
Page 54

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Installing Windows
You are ready to install the Windows operating system files.
For HP ProLiant BL20p G2 servers, follow the steps under HP ProLiant BL20p
G2 Windows 2000 OS Installation on page 3-24.
You need the following materials to install Windows:
◆ Windows CD-ROM for the Windows version you wish to install.
◆ EMC-approved QLogic HBA driver diskette for Windows
If you bound a new LUN to serve as your boot disk, ensure that the
bind procedure is complete (EMC ControlCenter Navisphere
Management software, LUN Properties tab Percent Bound).
1. Insert a bootable Windows CD-ROM in the drive and reboot the
system.
If your system has a bootable disk already configured from a
previous installation, the software will prompt you to press any
key to boot from CD-ROM. If the bootable disk is not the storage
array disk on which you want to install Windows, then you
should disable that disk’s SCSI BIOS as described under Preparing
the Server on page 3-18.
2. Immediately after the Windows installation begins, press
F6 when
directed or when the blue screen appears following this banner:
3-22
Setup is inspecting your computer's hardware configuration ---
Pressing F6 tells the Windows installer that you want to load a
third-party driver before proceeding with the installation.
If you do not press F6 in time to add the drivers, restart the server to try
again.
3. When prompted for additional drivers, select S.
4. Insert the EMC HBA Drivers diskette for your OS. Then press
ENTER to continue.
5. Select the appropriate QLogic boot HBA from the next menu.
6. Press
ENTER to continue.
Setup continues to load files. The Welcome to Setup screen
appears.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 55

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
7. Press ENTER to begin the setup procedure.
If you are installing Windows on a newly created LUN, you may
receive a message that your boot disk is new or erased. You can
press
C to continue.
The Windows Licensing Agreement appears.
3
8. Press
PG DN to scroll through and read the license agreement; to
accept it, press
F8.
The Windows Server Setup screen displays disk partition
information (if your system already contains partitions), or lets
you create a new hard disk partition.
The Windows 2000 boot LUN can be larger than 8 GB (Refer to Microsoft
Knowledge Base article Q240672.) Windows NT 4.0 is bound by a Boot
BIOS 8 GB limit. (Refer to Microsoft Knowledge Base article Q224526.)
9. If you are installing an operating system for the first time,
highlight Unpartitioned Space on the qL2xxx adapter; then:
•press
•press
ENTER to use the entire disk as one partition, or
C to create a custom partition, and then specify the
partition size.
If the new disk is displayed as Unformatted or Damaged you
must delete the partition before continuing. To do this, press
then follow the on-screen delete instructions. After you delete the
partition, the space will then appear as Unpartitioned Space
mentioned above.
If you are reinstalling Windows, the Setup software prompts you
to overwrite or upgrade:
D,
• To overwrite, press
• To upgrade, press
ESC and follow instructions.
ENTER.
• If you want to create a new hard disk partition, you must first
delete the existing partition, and then create a new one. To do
so, select the partition you want to delete, press
D, and then
follow the on-screen instructions to complete the deletion of
the partition. Once the system deletes the partition, you can
press
C to create a new one.)
10. The setup software prompts you to specify the file system format
for the partition.
Configuring a CLARiiON Boot Device
3-23
Page 56

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Select NTFS file system format, which is suitable for most sites
unless you have other specific requirements. Then press
(For background information on the choice of the NTFS file
system, refer to Microsoft Knowledge Base Article 0184006.)
Setup now formats the partition, copies the Windows system files
to the partition, and starts rebooting the server.
11. When prompted, remove the diskette and CD-ROM.
If your system prompts you to press any key to boot from CD-ROM,
do not press a key; allow the system to boot from the HBA adapter.
After booting, the system continues installation, displays the
Windows banner, and begins autodetection of mass-storage
devices and adapters.
12. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
When the Completing the Windows Setup Wizard screen
appears, click Finish.
13. If you plan to add SCSI disks in the future, you should disable the
BIOS for the managing SCSI controller so that the system does not
attempt to boot from those disks. For information, refer to
Preparing the Server on page 3-18.
ENTER.
3-24
14. Install the latest EMC-approved Windows Service Pack as
explained in the Microsoft documentation.
HP ProLiant BL20p G2
Windows 2000 OS
Installation
For HP ProLiant BL20p G2 servers:
1. If there is a local hard drive installed, remove it. This drive can be
reinserted after the installation is completed.
2. Open an interface window using the RDP console by
right-clicking the target server and selecting Power Control/
RILOE Interface.
3. Delete the target server (BfS Server) from the RDP database if it
exists.
4. Reboot the BfS server. (At boot time, the newly created LUN
should be detected.)
The BfS server should now be seen in the RDP New Computer
pane.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 57

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
5. Start the BfS deployment by dragging and dropping the BOOT
FROM SAN BL20p
script task to the BfS server new computer.
Installation time is approximately 50 minutes.
What Next? Verify that the Fibre Channel HBA drivers and (Windows 2000 only)
digital signatures are installed and started, as described in the next
section.
3
Verifying HBA Driver and Digital Signature Installation
You should install the HBA driver again here to ensure that the
EMC-required settings are implemented. From the desktop, perform
the appropriate steps:
◆ Windows NT: Follow the procedure under Installation Procedure
for Windows NT Hosts on page 2-15.
◆ Windows 2000: Follow the procedure under Updating the HBA
Driver in a Windows 2000 or Windows 2003 Host on page 2-17.
If duplicate devices appear in the Disk Drives section or Disk
Administrator display, you have made errors in the switch fabric
zoning configuration. Refer to refer to Preparing the Fabric on
page 3-15 for the correct configuration procedure.
If you do not have a driver for Windows 2000 that is digitally signed, check
the EMC section of the QLogic website for an updated driver. (Refer to Where
to Find the Driver on page 2-14.)
What Next?
From here:
◆ If you need to install multipath and failover software, refer to
Installing Multipath and Failover Software.
◆ If you need to start the installation again, refer to Starting a Fresh
Installation.
◆ Otherwise, installation and setup are complete.
Configuring a CLARiiON Boot Device
3-25
Page 58

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Assigning a Permanent Boot Drive Letter for Windows NT
Installing Multipath and Failover Software
If you have installed failover software into a Windows NT 4.0 server,
it is good practice to hard-code the boot volume letter so that it does
not change when rebooting after a LUN trespass. This can be done by
using the following procedure (from MSKB Q153619):
1. Reassign all drive letters (including C: and the CD-ROM drive) to
higher available letters. (You must do this or C: will be taken once
it becomes available. After reassigning C:, you should receive a
message requiring you to reboot for the new assignment to take
effect.
2. Reboot the server.
On system restart you may receive virtual memory errors; this is normal.
3. Rename all drives to their original letters.
4. Reboot and make an ERD of the new configuration.
Multipath and failover software on the host can transfer control of
storage system LUNs on a hardware failure in a LUN path.
Important: If the Navisphere Host Agent is installed, you must
remove it before installing multipath and failover software. (Refer to
the documentation that came with your failover software.) Reinstall
the host agent after installing the multipath and failover software.
3-26
Follow these steps to set up the multipath and failover software:
1. Install the software as described in the your EMC ControlCenter
Navisphere Management software, ATF, or PowerPath
documentation.
2. Create and enable a zone for each additional HBA and SP port
that will be supported by the multipath and failover software.
Refer to Known Issues on page 3-35 for any additional information.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 59

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Installing Additional Navisphere Host Agent Software
Configuring Additional Boot Port Name Entries in the Boot BIOS
The EMC ControlCenter Navisphere Host Agent should be used to
automatically register host connections with the array. PowerPath
and ATF require different registration types and the Navisphere Host
Agent is the preferred method over manual registrations.
You should install the Navisphere Host Agent software to ensure the
HBA connections are all registered correctly. For instructions on how
to perform this operation refer to the EMC ControlCenter Navisphere
Host Agent software documentation for your array type.
After the host agent has started and registered the new HBA paths,
you should refresh the host connections in the storage group to
ensure all available paths are assigned. To do this:
1. Shut down the host.
2. Remove the host from the storage group.
3. Apply the change.
4. Add the host back into the storage group.
5. Restart the host.
6. Check the array connectivity status to ensure all connections you
require are active.
To take advantage of the high-availability features of the HBA boot
BIOS, you must configure additional Boot Port Name entries in the
BIOS for any additional SP ports from which you want the BIOS to
attempt to boot during system startup. Depending on the failover
software installed, follow the appropriate steps:
1. Reboot the host
When the QLogic BIOS banner (shown below) appears, press
CTRL–Q.
Different HBA models may display different banners. Be sure to select
CTRL-Q for the HBA you wish to configure.
QLogic Corporation
QLA2300 PCI Fibre Channel ROM BIOS Version 1.17
Copyright © Qlogic Corporation 1993-1999 All rights reserved
Press <CTRL - Q> for Fast!UTIL
www.qlogic.com
Configuring a CLARiiON Boot Device
3-27
Page 60

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
2. After Fast!UTIL loads, the display depends on whether there are
multiple QLogic HBAs installed:
• If there is only one QLogic HBA, the
Fast!UTIL Options
menu appears.
• If there are multiple QLogic HBAs, a list of addresses occupies
by those HBAs appears. Use the arrow keys to select the
desired HBA; then press
ENTER. The Fast!UTIL Options menu
appears.
3. Select Configuration Settings from the menu.
4. Select Selectable Boot Settings from the Configuration Settings
menu.
The first Boot Port Name entry should already be configured (as
described under Configuring the HBA Boot BIOS on page 3-20).
If you want another SP port to be accessible as a potential boot
path to the current owner SP, select the next Boot Port Name
entry, and in the Device window select the CLARiiON port
WWN from which you want to boot.
5. If you have other HBAs for which you want to assign Boot Port
Name entries, you can press
ESC to go back to the main menu,
save changes, and select another HBA as shown in step 2. If the
other HBA you wish to configure has its own
CTRL-Q BIOS
prompt, reboot the server and configure that HBA's Boot Port
Name entries as you have done here.
3-28
6. Trespass the LUN and repeat steps 1 through 5 to configure any
paths over which you want to be able to boot the LUN from the
other SP.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 61

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
To trespass the LUN, follow the instructions in the EMC
ControlCenter Navisphere Management software documentation
for your array type. The process depends on the failover software
installed:
• With PowerPath configurations, this can usually be done from
the EMC ControlCenter Navisphere Management software
GUI by right-clicking the desired LUN and selecting trespass.
Confirm in the LUN properties that the LUN has trespassed
before you return to configure the remaining Boot Port Name
entries.
• With ATF configurations:
– With FC-series array core code 8.45.x, this can usually be
done from the EMC ControlCenter Navisphere
Management software GUI by right-clicking on the desired
LUN and selecting trespass. Confirm in the LUN
properties that the LUN has trespassed before you return
to configure the remaining Boot Port Name entries.
– With FC-series array core code 8.44.x and earlier, you will
use the
atf_trespass command to trespass the boot LUN.
To do this, follow the steps under Trespassing the Boot LUN
Using atf_trespass on page 3-30.
3
Each HBA can support multiple entries; you should configure Boot Port
Name entries connecting to multiple ports on both SPs for maximum
redundancy in booting after a boot LUN trespass or other link failures.
Refer to Table 3-1 on page 3-34 to determine your high-availability
requirements.
7. When all parameters are set correctly and you have added Boot
Port Name entries for all the SP ports from which you would like
to attempt to boot, press
ESC to return to the Fast!UTIL Options
menu; then select Save Changes to save the changes you made to
the current adapter.
8. Press
ESC to exit the Fast!UTIL Options menu.
9. Reboot the server.
Configuring a CLARiiON Boot Device
3-29
Page 62

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Trespassing the Boot
LUN Using atf_trespass
Follow these steps to use the atf_trespass command to trespass the
boot LUN:
1. Boot the host and log in to Windows.
2. Windows NT 4.0 will have the boot LUN configured for ID 0 as
described under Preparing the Storage System on page 3-13.
For Windows 2000, follow these steps to determine the LUN ID of
the boot LUN as seen by the host:
a. From the Windows task bar, select Start, Programs,
Administrative Tools, Computer Management.
b. On the Computer Management window, click Disk
Management.
c. Locate the System disk in the list. This is typically Drive
C:\
and will be noted with (System).
d. Select the Disk X description area, and from the Action menu,
select Properties.
A display appears with a line similar to the following:
Device Type: SCSI (Port: 3, Target ID: 1, LUN:0)
e. Find this Device Type line and note the LUN value. In this
example, the LUN value is 0. This is the Host LUN ID you will
need in the next step.
3-30
3. Open a command window and direct the multipath and failover
software to trespass the LUN. If you are using ATF, open a
command prompt and change to the multipath and failover
software directory; then enter the
• If the boot LUN is owned by SP A, enter commands in the
following form to transfer it to SP B:
cd Program Files\emc\atf
atf_trespass atf_sp0 1:1:
where
n
is the Host LUN ID you discovered in step 2.
• If the boot LUN is owned by SP B, enter commands in the
following form to transfer it to SP A:
cd Program Files\emc\atf
atf_trespass atf_sp0 0:1:
These commands transfer the boot LUN to the other SP so you
can configure it for failover in the HBA BIOS.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
atf_trespass command:
n
n
Page 63

4. Reboot the server.
Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Starting a Fresh Installation
To start a fresh installation:
◆ Using EMC ControlCenter Navisphere Management software,
remove the old boot Storage Group.
◆ Using Manager, unbind the old boot LUN.
◆ Remove any old boot zoning from the previous installation.
◆ Repeat the installation instructions.
Configuring a CLARiiON Boot Device
3-31
Page 64

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Boot Time and LUN Availability
Boot time is the amount of time a storage system requires to boot.
This time is a function of the number and types of LUNs in the
storage system, and is typically less than five minutes.
If you power up a server and storage system at the same time (cold
start), the server’s extended BIOS might scan the Fibre Channel bus
before the storage system is ready to respond. If this occurs, the
server will not be able to find the boot LUN or Windows operating
system. To avoid this problem, either power up the storage system
and fabric before the server, or if the server is so equipped, set it to
delay the scan until the storage system is ready.
3-32
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 65

Replacing a Boot HBA
If a boot HBA fails, you can replace it with a new one as described in
this section.
Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
EMC Symmetrix
EMC CLARiiON
Follow the procedure under Configuring a Symmetrix Boot Device.
◆ Shut down and power off the server.
◆ Replace the HBA in the identical location and reconnect cabling.
◆ (Fabric configuration only) Repeat the procedure under Preparing
the Fabric on page 3-15, and replace the old HBA’s WWPN with
the new HBA’s WWPN.
◆ Repeat the procedure under Verifying HBA Driver and Digital
Signature Installation on page 3-25.
Replacing a Boot HBA
3-33
Page 66

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
How a Server Responds to Failure in the Boot LUN Path
Failure in the path to a SAN-based boot LUN can halt Windows in a
fatal error condition. Depending on the failure, Windows may be able
to transfer control to another path and continue.
Table 3-1 shows server reactions to failures in different components.
Tab le 3- 1 Server Response to Failure in the Boot LUN Path (Single Fault)
Configuration Server State HBA Failure Switch Failure
2 or more HBAs,
Windows running Multipath STOP error
a
Boot
SP/Director
Port Failure
Multipath Trespass
Boot
SP/Director
Failure
b
Catastrophic
Storage
System Failure
STOP error
failo ver software
Windows booting Halt Halt Halt Halt Halt
a
Multipath Manual No Boot
b
STOP error
1 HBA, failover
Power up Multipath No Boot
Windows running STOP error STOP error Trespass Trespass
software
Windows booting Halt Halt Halt Halt Halt
Power up No boot No boot Manual Manual No boot
1 HBA, no
Windows running STOP error STOP error STOP error STOP error STOP error
failo ver software
Windows booting Halt Halt Halt Halt Halt
Power up No boot No boot No boot No boot No boot
a. Depending on the fabric configuration, if multiple switches are used, then this behavior would
qualify under the Multipath category.
b. CLARiiON only.
Explanations of Entries ◆ STOP Error (fatal blue screen) — Indicates host failure and
chance of data corruption.
◆ No boot — Cannot boot Windows.
◆ Halt — Windows cannot recover before system has completed
startup. (You must reboot and follow the power-up scenario.)
◆ Manual — Manual intervention is required to continue.
(Typically, initiate a LUN trespass using CLI or Manager. With
Manager, enable LUN Auto-Assignment in LUN properties.)
◆ Multipath or Tre s pa ss — This automatic operation allows no
disruption of service. (The delay caused by this operation may
affect Windows stability.)
3-34
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 67

Known Issues
Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
Be aware of these issues:
◆ QLogic BIOS 1.26 and later for QLA23xx and BIOS 1.79 and later
for QLA22xx HBAs allow for multiple Boot Port Name entries to
be configured for high-availability booting after path failures.
Previous BIOS versions do not support this functionality, will
boot only from a single storage array port, and cannot provide
boot capability with path failures.
◆ NTOSKNL BSOD (blue screen) during a link down event can
cause filesystem corruption to mounted filesystems.
◆ HBA boot BIOS does not support high availability while the OS is
booting. It can handle path failures at boot initialization time, and
after the OS has loaded. Path failures while the OS is loading will
require the host to reboot before successfully completing the boot
process. Refer to How a Server Responds to Failure in the Boot LUN
Path on page 3-34 for additional information.
◆ Degraded response time as the I/O load approaches storage
system capacity can make the OS appear hung or result in a
NTOSKNL BSOD.
◆ Boot files, Windows system files, and swap space should all be on
the boot LUN. With certain server models, you can use an internal
disk for the page file for stability; however, this might not
increase fault tolerance and might reduce system recovery
options.
◆ Swap space must be available on %SYSTEMROOT% or core dump
will fail.
Known Issues
3-35
Page 68

Configuring an EMC Boot Device
3
3-36
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 69

Invisible Body Tag
A
Third-Party Software
This appendix contains additional information about third-party
software used with Windows hosts.
◆ QLogic SANSurfer SANBlade Manager v2.0.21...........................A-2
◆ Veritas Volume Manager 3.x for Windows 2000...........................A-3
Third-Party Software
A-1
Page 70

A
Third-Party Software
QLogic SANSurfer SANBlade Manager v2.0.21
Stratus ftServers are not supported using the qLogic SANSurfer SANBlade
Manager Software or Agents.
EMC has approved the use of a specialized version of the QLogic
SANSurfer SANBlade Manager for use with attached EMC
Symmetrix and CLARiiON storage arrays. Only version 2.0.21 should
be used; this version is posted in the EMC section on the QLogic
website.
This Windows utility provides information on the installed QLogic
HBAs, driver versions, mapped targets, statistics, and configuration
settings. It also has a feature to update the HBA firmware/BIOS and
NVRAM. (You should obtain the latest EMC-approved
firmware/BIOS and NVRAM files from the QLogic website. Refer to
Downloading QLogic Drivers and Firmware on page 2-2 for
instructions.)
For information on the use and features of the QLogic SANSurfer
SANBlade Manager utility, refer to the documentation posted with
this utility.
A-2
The SANSurfer software is not multipath-aware, and as such may misreport
HBA targets that are configured in multipath. This does not affect the use of
the tool; however, it will accurately report targets only on ports that own an
active LUN0.
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 71

Veritas Volume Manager 3.x for Windows 2000
Refer to the latest EMC Support Matrix to determine which Veritas Volume
Manager 3.x configurations are supported, and what service packs may be
required.
Third-Party Software
A
!
CAUTION
Configuring large numbers of device paths with Veritas Volume
Manager can cause a Windows system to boot very slowly, and in
some cases overrun the NTLDR boot-time registry size and halt.
Systems that are configured with more than 512 device paths (total
paths to all LUNs) should check with EMC Customer Service
before installing Veritas Volume Manager 3.x.
If using PowerPath with Veritas Volume Manager 3.0 with Service
Pack 1, you must also make the following registry modifications
before PowerPath devices will be available to the Veritas Enterprise
Manager:
Use regedt32.exe to set the registry as follows:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\VERITAS\VxSvc\CurrentVersion\VolumeManager
value name = ShowGateKeeperDevices
data type = REG_DWORD
value = 0x1
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\VERITAS\VxSvc\CurrentVersion\VolumeManager
value name = ShowEmcHiddenDevices
data type = REG_DWORD
value = 0x1
After completing these changes, reboot the host system.
Ver i ta s Vol u m e Ma n a ge r 3 . x f o r W in dows 2 0 00
A-3
Page 72

A
Third-Party Software
A-4
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 73

Invisible Body Tag
B
Troubleshooting
This appendix contains information on troubleshooting problems.
◆ Problems and Solutions.................................................................... B-2
Troubleshooting
B-1
Page 74

Troubleshooting
B
Problems and Solutions
Problem
Problem
Problem
Error Message ID: 51 in event viewer when attempting to install
multiple host access (for clustering) to the same EMC CLARiiON
array storage group. The text of the message is:
An Error was detected on device \Device\Harddisk
during a paging operation
<x>
\DR
Solution Until host cluster software is installed, only a single host should
access a storage group at a time. Refer to the EMC Support Matrix for
supported host configurations.
EMC Primus case emc29097 — If using HBAs connected to both
CLARiiON SPs, without PowerPath installed, duplicate LUNs will be
visible in the Device Manager and Disk Manager. Only one instance
of the LUN will be accessible, and all other matching mappings will
be listed as Unknown, Unreadable and Unallocated.
Solution This is normal behavior when multiple paths are available,
PowerPath is not installed, and the initiator type is registered in
PowerPath mode (array default depending on core code revision).
EMC Primus case emc69307 — When using QLogic HBAs in a
Brocade fabric environment, after upgrading Brocade 3900-series
switch firmware to 3.0.2m, the HBAs report repeated link errors, and
intermittently lose fabric connectivity.
<x>
B-2
PowerPath may report paths lost and then found in quick succession,
and repeated Windows 2000 event log error entries for Link
Down/Link Up events similar to the following:
Event ID: 11
Source: ql2300
Description: The driver detected a controller error on \Device\Scsi\ql2300x.
Data (words): offset 34 = 80120000 [ErrorCode: Link down error]
Event ID: 11
Source: ql2300
Description: The driver detected a controller error on \Device\Scsi\ql2300x.
Data (words): offset 34 = 80110000 [ErrorCode: Link up]
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 75

Troubleshooting
Solution Upgrade to the latest HBA driver. This was corrected for Windows
2000 in 8.2.2.25 and later drivers. The 8.2.2.25 driver is available from
EMC Support. Windows 2003 driver 8.2.2.20 and later already
contain this correction.
B
Problem
Event ID: 11
Source: ql2300
Description: The driver detected a controller error on \Device\Scsi\ql2300x.
Data (words): offset 34 = F003001C [ErrorCode: Target device queue full].
EMC Primus case emc69308 — Direct-connect to EMC CLARiiON
CX200 reports incorrect queue full error messages. Even under light
I/O, a host may log a message noting that disk has reached a
queue-full state similar to the following in the Windows event
viewer:
Problems and Solutions
B-3
Page 76

Troubleshooting
B
B-4
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
Page 77

Index
B
BIOS, updating 2-10
boot device, configuring
CLARiiON 3-10
overview 3-2
Symmetrix 3-5
boot time and LUN availability 3-32
C
configurations, valid 3-12
D
data rate, HBA, setting manually 2-12
driver, HBA
downloading 2-2
installing
in Windows 2000 host 2-15
in Windows 2003 host 2-15
in Windows NT host 2-15
overview 2-14
revision history 2-14
updating
in Windows 2000 host 2-17
in Windows 2003 host 2-17
F
failure in boot LUN path, server response to 3-34
Fibre-Down servers 2-10
firmware, HBA
downloading 2-2
updating 2-10
H
hard zoning (switch) 3-17
HBA, boot, replacing 3-33
HBA, installing 2-3
I
issues with boot support 3-35
L
LUN availability and boot time 3-32
N
NVRAM settings 2-8
P
persistent binding 1-2
S
SANSurfer SANBlade Manager A-2
server response to failure in boot LUN path 3-34
soft zoning (switch) 3-16
T
topology requirements 3-12
topology, HBA, setting 2-13
troubleshooting B-1
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
i-1
Page 78

Index
V
Veritas Volume Manager 3.0 A-3
W
Windows OS, installing onto a CLARiiON boot
device 3-22
Z
zoning, hard 3-17
zoning, soft 3-16
i-2
EMC Fibre Channel with QLogic HBAs in Windows Hosts
 Loading...
Loading...