eMachines EL1200 User Manual

Desktop PC
User Guide


Contents
Chapter 1: Getting Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Thank you for purchasing our computer! . . . . . . . . .2
Using the eMachines Web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Using your Reference Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Using Help and Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Searching for a topic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Using online help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Getting technical support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Finding your model and serial number . . . . . . . . .4
Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Chapter 2: Using Windows XP . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Using the Windows desktop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Using the Start menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Adding icons to the desktop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Identifying window items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Working with files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Viewing drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Creating folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Copying and moving files and folders . . . . . . . . 10
Deleting files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Searching for files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Using the Windows Search utility . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Browsing for files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Working with documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Creating a new document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Saving a document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Opening a document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Printing a document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Shortcuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Chapter 3: Using the Internet and Faxing . 19
Learning about the Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Setting up an Internet account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Accessing your Internet account . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Using the World Wide Web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Connecting to a Web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Downloading files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Using e-mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Sending e-mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Checking your e-mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Installing and configuring Microsoft Fax . . . . . . . . . 24
Installing Fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Configuring Microsoft Fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Setting up your cover page template . . . . . . . . . 26
Sending a fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Sending a quick fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
i

Contents
Faxing from programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Faxing a scanned document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Automatically retry sending a fax . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Canceling a fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Automatically canceling a fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Receiving and viewing a fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Chapter 4: Playing and Creating Media Files31
Playing music and movies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Playing WAV audio files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Playing audio and video files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Playing optical discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Creating audio files and music libraries . . . . . . . . . . 35
Creating music files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Building a music library . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Editing track information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Creating and editing videos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Editing videos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Transferring your video to your computer . . . . . 38
Editing your video . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Saving your video . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Creating music CDs and video DVDs . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Creating a music CD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Creating data CDs and DVDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Using Windows Media Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Manually updating the Media Center Program Guide 43
Chapter 5: Networking Your Computer . . . 45
Introduction to Networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Using a router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Creating an Ethernet network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Installing Ethernet cards and drivers . . . . . . . . . 48
Making sure your broadband connection works 48
Naming the computers and the workgroup . . . 48
Configuring the TCP/IP protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Setting up an Ethernet network . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Testing your network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Sharing resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Sharing drives and printers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Using the network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Viewing shared drives and folders . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Mapping a network drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Opening files across the network . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Copying files across the network . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Printing files across the network . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Adding a printer to your network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
ii

www.emachines.com
Chapter 6: Customizing Windows . . . . . . . . 57
Adjusting the screen and desktop settings . . . . . . .58
Adjusting the color depth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Adjusting the screen resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Changing the colors on your Windows desktop 60
Changing the desktop background . . . . . . . . . . .61
Selecting a screen saver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Using an extended desktop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Using a second monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Viewing the display on a television . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Modifying television settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Changing the mouse settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Adding and modifying user accounts . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Changing power-saving settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Changing the power scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Changing advanced power settings . . . . . . . . . . .69
Activating and using Hibernate mode . . . . . . . .70
Installing an uninterruptible power supply . . . .71
Chapter 7: Protecting Your Computer . . . . 73
Hardware security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Kensington lock slot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Data security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
About startup and hard drive passwords . . . . . . 74
About Windows XP user accounts . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Protecting your computer from viruses . . . . . . . . 75
Using McAfee SecurityCenter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Using Windows XP Security Center . . . . . . . . . . .80
Security updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .81
Windows Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
BigFix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
iii

Contents
iv

Chapter 1
Getting Help
Getting Help
•
Using the eMachines Web site
•
Using your Reference Guide
•
Using Help and Support
•
Getting technical support
•
Using online help
•
Getting technical support
1

Chapter 1: Getting Help
Thank you for purchasing our computer!
You have made an excellent decision choosing eMachines. We are sure that you will
be pleased with the outstanding quality, reliability, and performance of your new
computer. Each and every eMachines computer uses the latest technology and passes
through the most stringent quality control tests to ensure that you are provided with
the best product possible.
Please read this manual carefully to familiarize yourself with our range of services
and support. We have highlighted some basic care and safety information to help
you keep your computer in good operating condition.
eMachines stands behind our value proposition to our customers—to provide
best-of-class service and support in addition to high-quality, brand-name components
at affordable prices. If you ever have a problem, our knowledgeable, dedicated
customer service department will provide you with fast, considerate service.
We sincerely hope that you will receive the utmost satisfaction and enjoyment from
your new eMachines computer for years to come.
Thanks again, from all of us at eMachines.
Using the eMachines Web site
eMachines’ online support is available 24 hours per day, 7 days per week and provides
the most current drivers, product specifications, tutorials, and personalized
information about your computer. Visit the eMachines Web support site at
www.emachines.com
.
Using your Reference Guide
The
Reference Guide
and troubleshooting information. Your reference guide is a file stored on your
computer.
To access your online
for your computer contains setting up, hardware, configuration,
Reference Guide
:
• Click Start, All Programs, then then click Gateway Documentation.
Using Help and Support
Your computer includes
information, troubleshooters, and automated support. Use Help and Support to
answer questions about Windows and to help you quickly discover and use the many
features of your eMachines computer.
To start Help and Support:
• Click Start, then click Help and Support. Help and Support opens. You can find
help information by clicking a link, performing a search, or browsing the index.
Help and Support
, an easily accessible collection of help
2
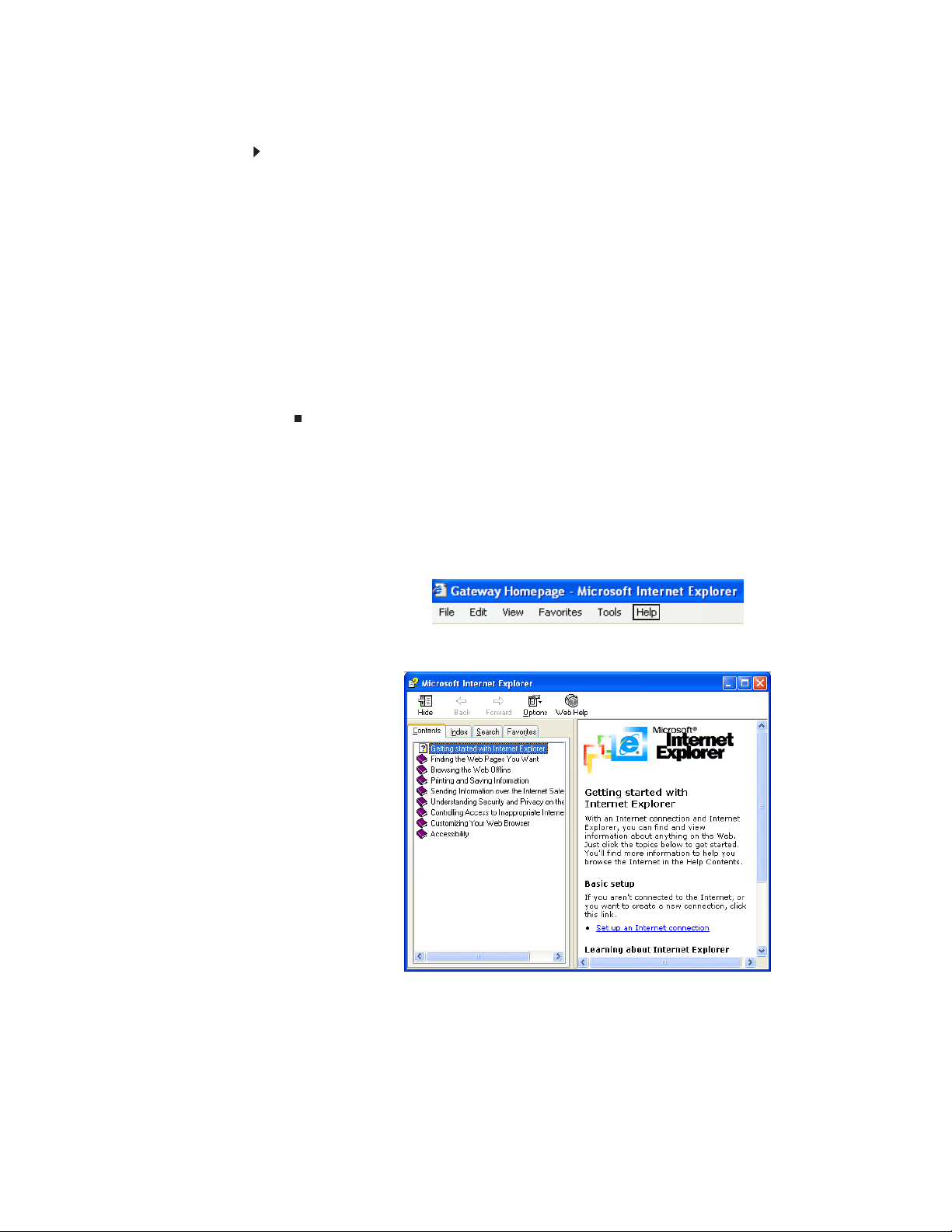
Searching for a topic
To search for a topic in Help and Support:
1 Type a word or phrase (keyword) in the
Help and Support screen, then press ENTER.
For each search, you receive the following search result types:
• Suggested Topics—These topics are located in Help and Support and are relevant
to your search topic.
• Full-text Search Matches—These topics are located in Help and Support and
contain the words you entered in the Search box.
• Microsoft Knowledge Base—These topics are located on the Microsoft Web site
and contain the words you entered in the Search box. You must be connected
to the Internet to search for and access these topics.
2 To view a list of your search results, click the results header for the type of results
you want to view.
3 To view a topic, click the topic name in the Search Results list.
Using online help
www.emachines.com
Search box located at the top of any
Many programs provide information online so you can research a topic or learn how
to perform a task while you are using the program. You can access most online help
information by selecting a topic from a Help menu or by clicking a Help button.
You can search for information by viewing the help contents, checking the index,
searching for a topic or keyword, or browsing through the online help.
3

Chapter 1: Getting Help
Getting technical support
For more information on contacting Customer Care (technical support), see the
“Troubleshooting” chapter in your
on your computer.
Reference Guide
or see the Customer Care label
Finding your model and serial number
The label on the top, side, or bottom of your computer case includes your computer
serial number. eMachines Customer Care will need this information if you call for
assistance.
Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity
The Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity label found on your computer includes the
product key code for your operating system. If you ever reinstall Windows from the
installation CD or DVD, you will need to enter these numbers to activate Windows.
4

Chapter 2
Using Windows XP
•
Using the Windows desktop
•
Working with files and folders
•
Searching for files
•
Working with documents
•
Shortcuts
5
Chapter 2: Using Windows XP
Using the Windows desktop
After your computer starts, the first screen you see is the Windows
desktop
. The
desktop is like the top of a real desk. Think of the desktop as your personalized work
space where you open programs and perform other tasks.
Help
For more information about the Windows desktop, click Start, then click
Help and Support. Type Windows desktop in the Search box, then press E
NTER.
Your desktop may be different from this example, depending on how your computer
is set up.
The desktop contains the taskbar, the Start button, and the Recycle Bin icon.
Desktop elements Description
The
taskbar
Start button on the left and a clock on the right. Other buttons on the taskbar
represent programs that are running.
Click a program’s
The
Start button
other programs, and computer tools and utilities.
Click the Start button, then open a file or program by clicking an item on the
menu that opens.
Recycle Bin
The
stored. You must empty the Recycle Bin to permanently delete them from your
computer. For instructions on how to use the Recycle Bin, see “Deleting files
and folders” on page 11.
The Windows Security Center icon may appear on the taskbar near the clock.
The icon changes appearance to notify you when the security settings on your
computer are set below the recommended value or when updates are
available. Double-click this icon to open the Windows Security Center. For
more information, see “Modifying security settings” on page 80.
is the bar at the bottom of the computer display containing the
button
on the taskbar to open the program’s window.
provides access to programs, files, help for Windows and
is where files, folders, and programs that you discarded are
6
Using the Start menu
Help
For more information about the Windows Start menu, click Start, then
click Help and Support. Type Windows Start menu in the Search box, then
press E
NTER.
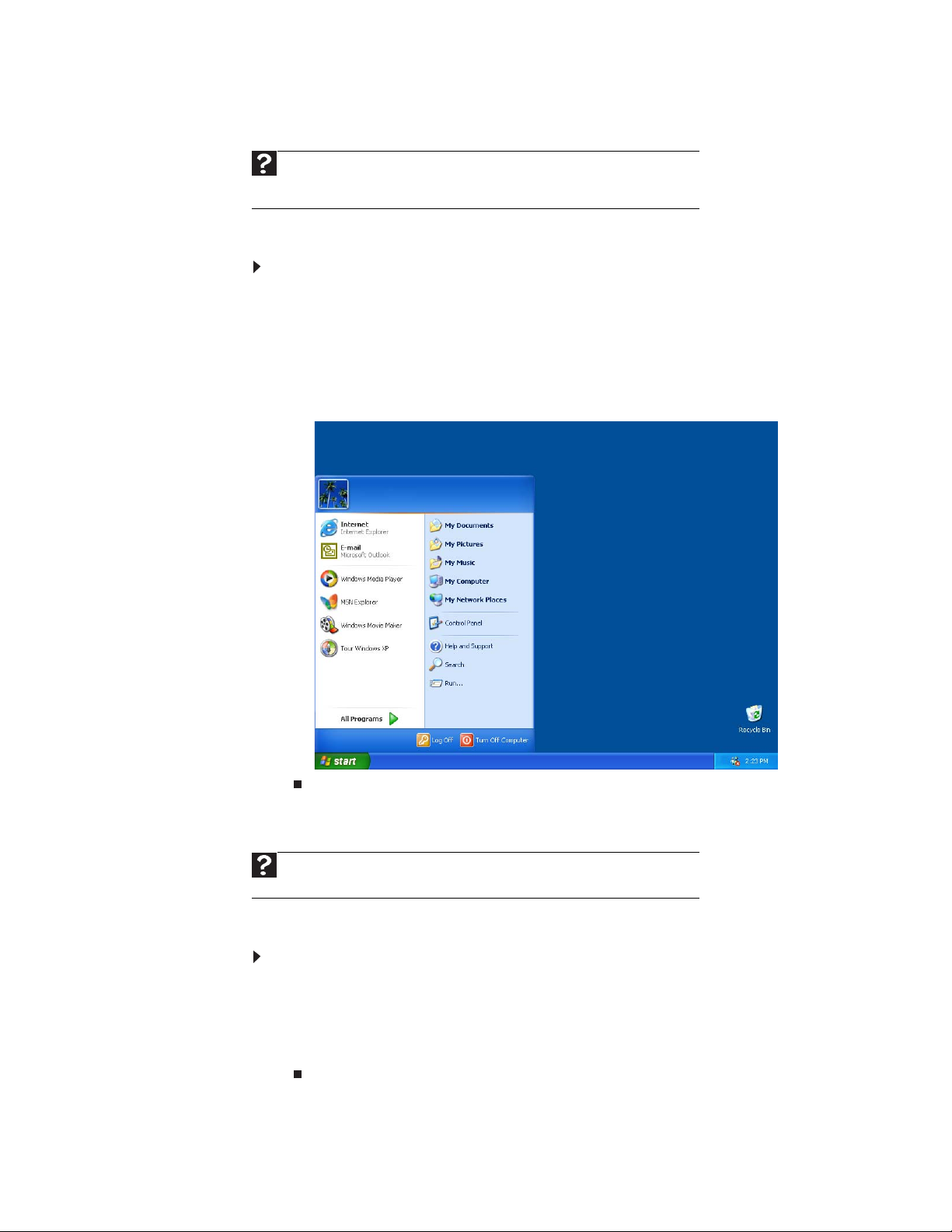
You can start programs, open files, customize your system, get help, search for files
and folders, and more using the Start menu.
To use the Start menu:
1 Click the Start button on the lower left of the Windows desktop. The Start menu
opens showing you the first level of menu items.
2 Click All Programs to see all programs and files in the Start menu. When you
move the mouse pointer over any menu item that has an arrow next to it,
another menu, called a
commands.
3 Click a file or program to open it.
www.emachines.com
submenu
, opens and reveals related files, programs, or
Adding icons to the desktop
Help
For more information about desktop icons, click Start, then click Help
and Support. Type desktop icons in the Search box, then press E
You may want to add an icon (shortcut) to the desktop for a program that you use
frequently.
To add icons to the desktop:
1 Click Start, then click All Programs.
2 Right-click (press the right mouse button) the program that you want to add
to the desktop.
3 Click Send To, then click Desktop (create shortcut). A shortcut icon for that
program appears on the desktop.
NTER.
7
Chapter 2: Using Windows XP
Identifying window items
Help
For more information about windows, click Start, then click Help and
Support. Type window in the Search box, then press E
NTER.
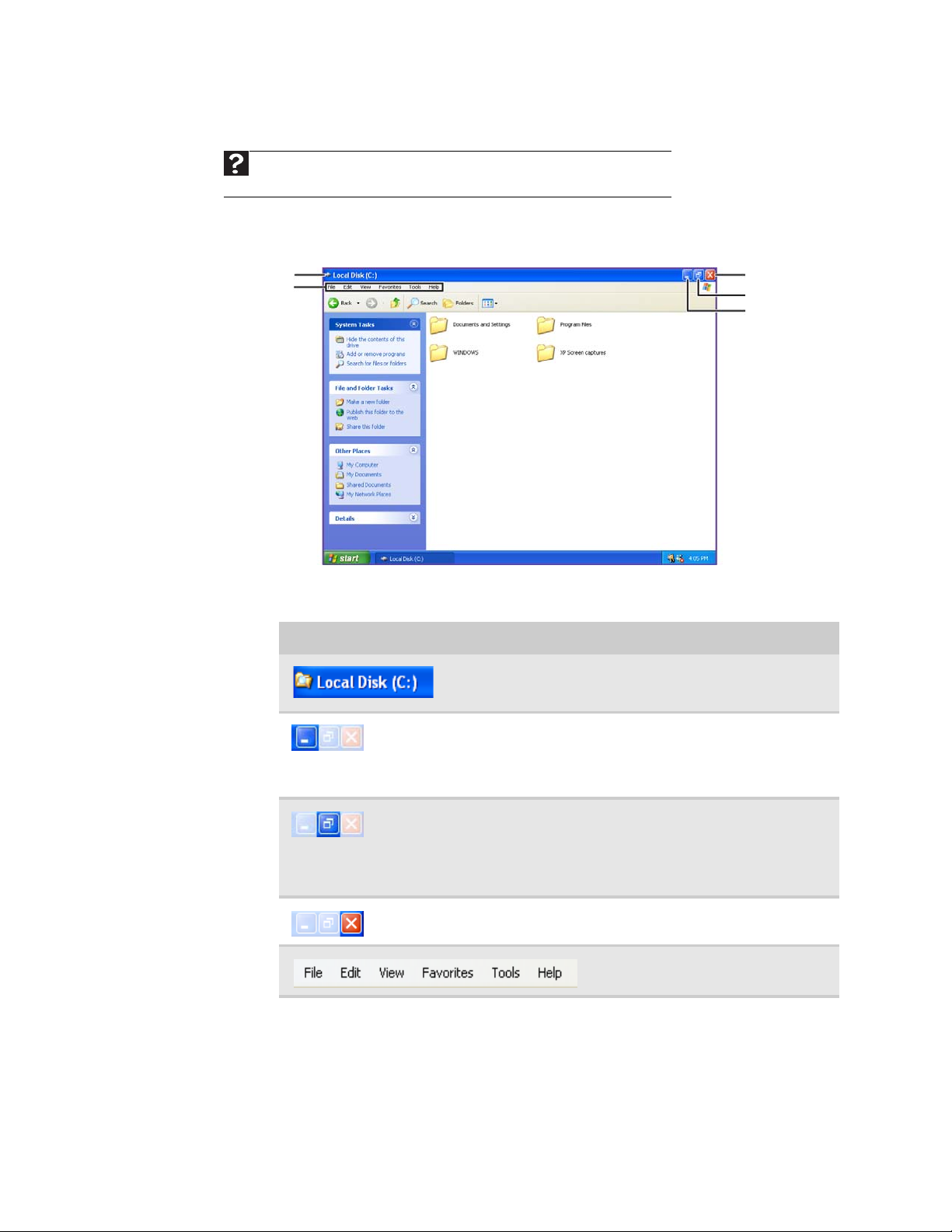
When you double-click the icon for a drive, folder, file, or program, a
window
opens
on the desktop. This example shows the Local Disk (C:) window, which opens after
you double-click the Local Disk (C:) icon in the
Title bar
Menu bar
My Computer
window.
Close
Maximize
Minimize
Every program window looks a little different because each has its own menus, icons,
and controls. Most windows include these items:
Window item Description
The
title bar
the top of a window that shows the
window title.
Clicking the
reduces the active window to a
button on the taskbar. Clicking the
program button in the taskbar
opens the window again.
Clicking the
expands the active window to fit
the entire computer display.
Clicking the maximize button again
restores the window to its former
size.
Clicking the
active window or program.
Clicking an item on the
starts an action such as Print or Save.
is the horizontal bar at
minimize button
maximize button
close button
closes the
menu bar
8
www.emachines.com
Working with files and folders
You can organize your files and programs to suit your preferences much like you
would store information in a file cabinet. You can store these files in folders and copy,
move, and delete the information just as you would reorganize and throw away
information in a file cabinet.
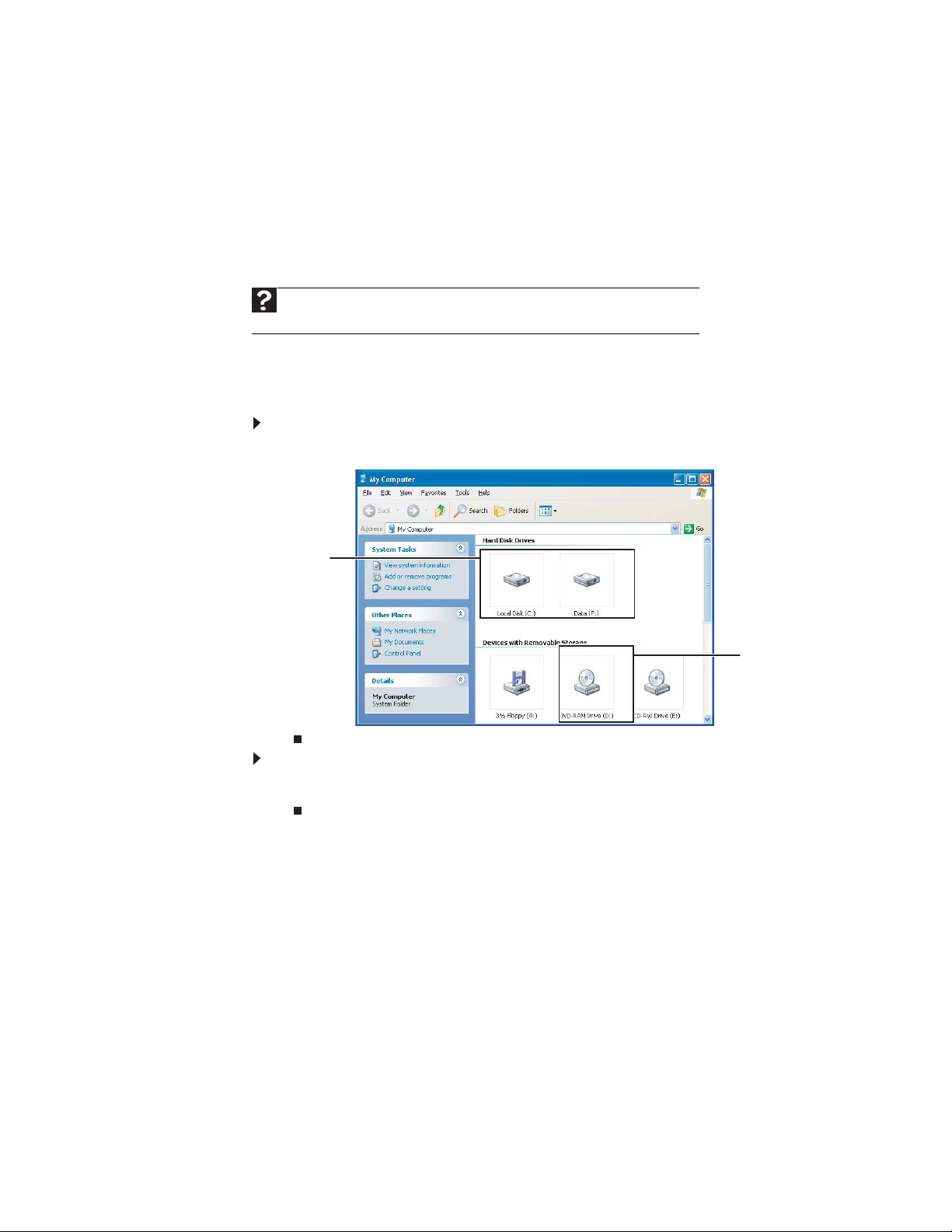
Viewing drives
Help
For more information about files and folders, click Start, then click Help
and Support. Type files and folders in the Search box, then press E
Drives
are like file cabinets because they hold files and folders. A computer almost
always has more than one drive. Each drive has a letter, usually Local Disk (C:) for
the hard drive and 3½ Floppy (A:) for the diskette drive. You may also have more
drives such as a CD or DVD drive.
To view the drives on your computer:
• Click Start, then click My Computer.
NTER.
Hard drives
Disc drive
To see the files and folders on a drive:
• Double-click the drive icon. If you do not see the contents of a drive after you
double-click its icon, click Show the contents of this drive.
9
Creating folders
Chapter 2: Using Windows XP
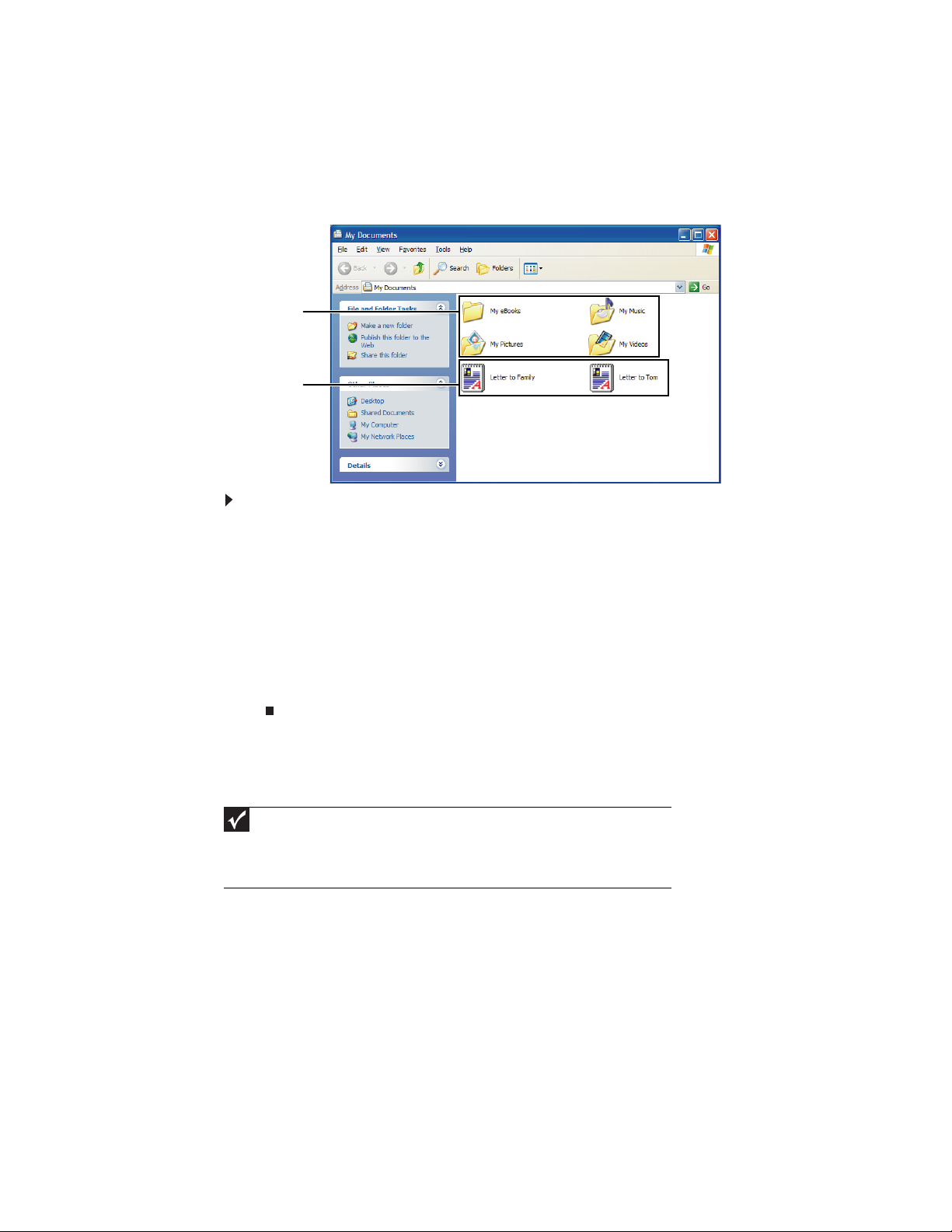
Folders
folders.
Files
keep on your computer. In fact, all information on a computer is stored in files.
are much like the folders in a file cabinet. They can contain files and other
are much like paper documents—letters, spreadsheets, and pictures—that you
Folders
Files
To create a folder:
1 Click Start, then click My Computer on the Start menu.
2 Double-click the drive where you want to put the new folder. Typically, Local
Disk (C:) is your hard drive and 3½ Floppy (A:) is your diskette drive. If you do
not see the contents of the drive, click Show the contents of this drive.
3 If you want to create a new folder inside an existing folder, double-click the
existing folder. If you do not see the contents of the drive or folder, click Show
the contents of this drive or Show the contents of this folder.
4 Click File, New, then click Folder. The new folder is created.
5 Type a name for the folder, then press E
the folder icon.
NTER. The new folder name appears by
For information about renaming folders, see “Shortcuts” on page 18.
Copying and moving files and folders
Important
The clipboard stores whatever you cut or copy until you cut or copy
again. Then the clipboard contains the new information only. Therefore, you
can paste copies of a file or folder into more than one place, but as soon as
you copy or cut a different file or folder, the original file or folder is deleted
from the clipboard.
The skills you need to copy and move files are called
When you
the Windows
folder you want the copy to go in (the
When you
location and place the file or folder on the Windows clipboard. When you decide
where you want the file or folder to go, you paste it there.
copy and paste
clipboard
cut and paste
, which temporarily stores it. Then, when you decide what
a file or folder, you remove the file or folder from its original
a file or folder, you place a
10
destination
copying, cutting
copy
of the file or folder on
folder), you
paste
, and
pasting
it there.
.
www.emachines.com
To copy a file or folder to another folder:
Help
For more information about copying or moving files and folders,
click Start, then click Help and Support. Type copying files and folders
or moving files and folders in the Search box, then press E
NTER.
1 Locate the file or folder you want to copy. For more information, see “Viewing
drives” on page 9 and “Searching for files” on page 12.
2 Right-click (press the right mouse button) the file or folder that you want to
copy. A pop-up menu opens on the desktop.
3 Click Copy on the pop-up menu.
4 Open the destination folder.
5 With the pointer inside the destination folder, right-click.
6 Click Paste. A copy of the file or folder appears in the new location.
To move a file or folder to another folder:
1 Locate the file or folder you want to move. For more information, see “Viewing
drives” on page 9 and “Searching for files” on page 12.
2 Right-click (press the right mouse button) the file or folder that you want to
move. A pop-up menu opens on the desktop.
3 Click Cut on the pop-up menu.
4 Open the destination folder.
5 With the pointer inside the destination folder, right-click.
6 Click Paste. The file or folder you moved appears in its new location and is
removed from its old location.
Deleting files and folders
When you throw away paper files and folders, you take them from the file cabinet
and put them in a trash can. Eventually the trash can is emptied.
In Windows, you throw away files and folders by first moving them to the Windows
trash can, called the
You can recover any file in the Recycle Bin as long as the bin has not been emptied.
To delete files or folders:
Help
For more information about deleting files and folders, click Start,
then click Help and Support. Type deleting files and folders in the
Search Help box, then press E
1 In My Computer or Windows Explorer, click the files or folders that you want
to delete. For instructions on how to select multiple files and folders, see
“Shortcuts” on page 18.
If you cannot find the file you want to delete, see “Searching for files” on
page 12.
2 Click File, then click Delete. Windows moves the files and folders to the Recycle
Bin.
To recover files or folders from the Recycle Bin:
1 Double-click the Recycle
files and folders you have thrown away since you last emptied it.
2 Click the files or folders that you want to restore. For instructions on how to
select multiple files and folders, see “Shortcuts” on page 18.
Recycle Bin
NTER.
Bin icon. The
, where they remain until you decide to empty the bin.
Recycle Bin
window opens and lists the
11

Chapter 2: Using Windows XP
3 Click File, then click Restore. Windows returns the deleted files or folders to their
original locations.
To empty the Recycle Bin:
Caution
Emptying the Recycle Bin permanently erases any files or folders
in the bin. These files cannot be restored.
Help
For more information about emptying the Recycle Bin, click Start,
then click Help and Support. Type emptying the Recycle Bin in the
Search box, then press E
NTER.
1 Double-click the Recycle Bin icon on the desktop. The
2 Click File, then click Empty Recycle Bin. Windows asks you if you are sure that
you want to empty the bin.
3 Click Yes. Windows permanently deletes all files in the Recycle Bin.
Searching for files
If you are looking for a particular file or folder or a set of files or folders that have
characteristics in common, but you do not remember where they are stored on your
hard drive, you can use the Search utility to search by:
• Name or part of a name
• Creation date
• Modification date
• File type
• Text contained in the file
• Time period in which it was created or modified
You can also combine search criteria to refine searches.
Files and folders found using this utility can be opened, copied, cut, renamed, or
deleted directly from the list in the results window.
Recycle Bin
window opens.
12
www.emachines.com
Using the Windows Search utility
Help
For more information about searching for files and folders, click Start,
then click Help and Support. Type searching in the Search box, then press
E
NTER.
To find files and folders using the Search utility:
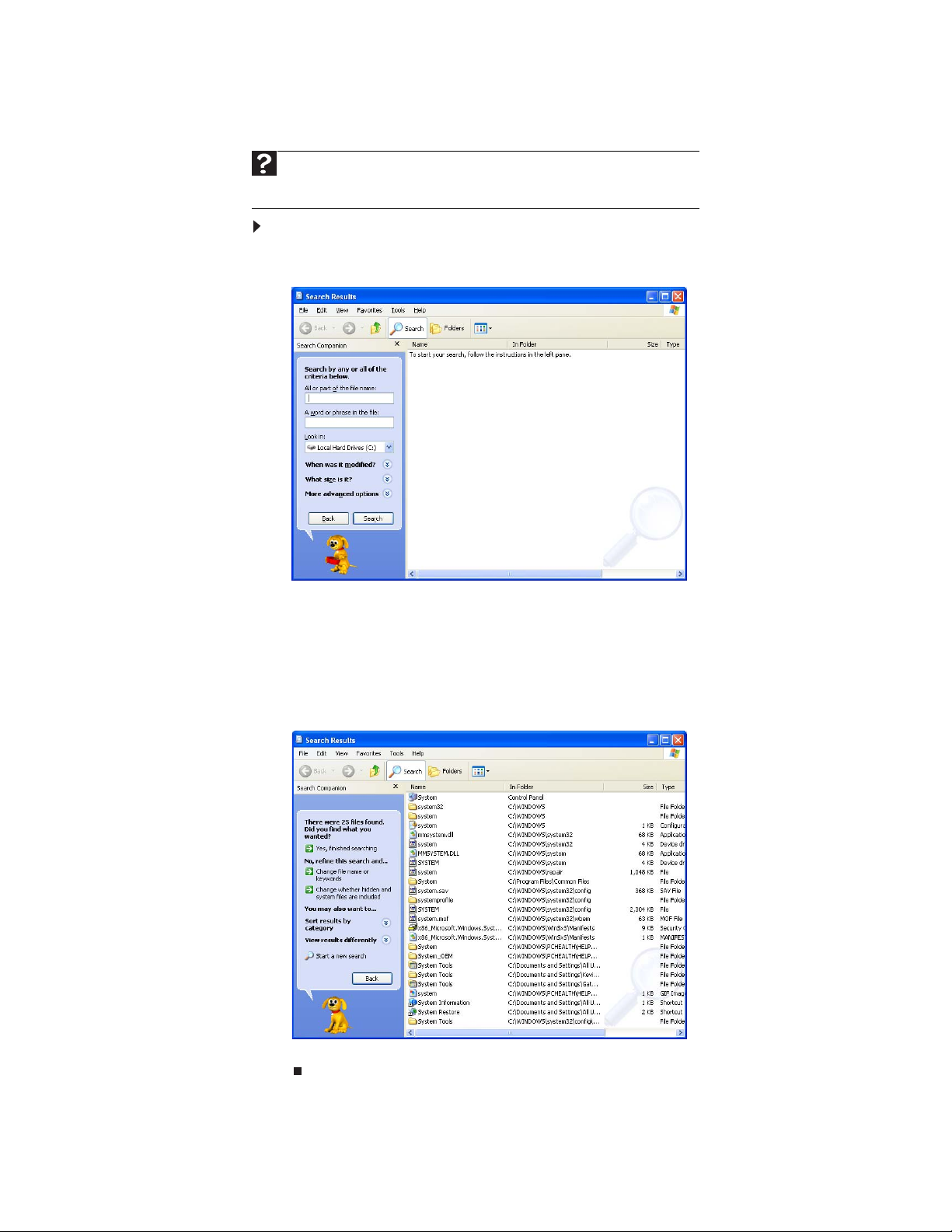
1 Click Start, then click Search. The
and folders.
Search Results
window opens. Click All files
2 If you want to search by file or folder name, type in all or part of the file or
folder name in the name box in the left pane of the window.
• If you type all of the name, Search will list all files and folders of that name.
• If you type part of the name, Search will list all of the file and folder names
containing the letters you typed.
3 Click Search. When the search is completed, Windows lists the files and folders
whose names contain the text that you searched for.
4 Open a file, folder, or program by double-clicking the name in the list.
13

Chapter 2: Using Windows XP
Using advanced search options
Search can find files meeting more criteria than file name. You can narrow your search
by selecting the search options that you want. You can search by the:
• Date the file was created or modified.
• Size of the file.
• Type of file, such as a program or a text document.
Browsing for files and folders
A file or folder that you need is rarely right on top of your Windows desktop. It is
usually on a drive inside a folder that may be inside yet another folder, and so on.
Windows drives, folders, and files are organized in the same way as a real file cabinet
in that they may have many levels (usually many more levels than a file cabinet, in
fact). So you usually will have to search through levels of folders to find the file or
folder that you need. This is called
To browse for a file:
Help
For more information about browsing for files and folders, click
Start, then click Help and Support. Type files and folders in the Search
box, then press E
NTER.
browsing
.
1 Click Start, then click My Computer. The
2 Double-click the drive or folder that you think contains the file or folder that
you want to find. If you do not see the contents of a folder, click Show the
contents of this drive or Show the contents of this folder.
3 Continue double-clicking folders and their subfolders until you find the file or
folder you want.
My Computer
window opens.
14
www.emachines.com
Working with documents
Computer documents include word processing files, spreadsheet files, or other similar
files. The basic methods of creating, saving, opening, and printing a document apply
to most of these types of files.
The following examples show how to create, save, open, and print a document using
Microsoft
WordPerfect, Microsoft Word, and Microsoft Excel.
For more information about using a program, click Help on its menu bar.
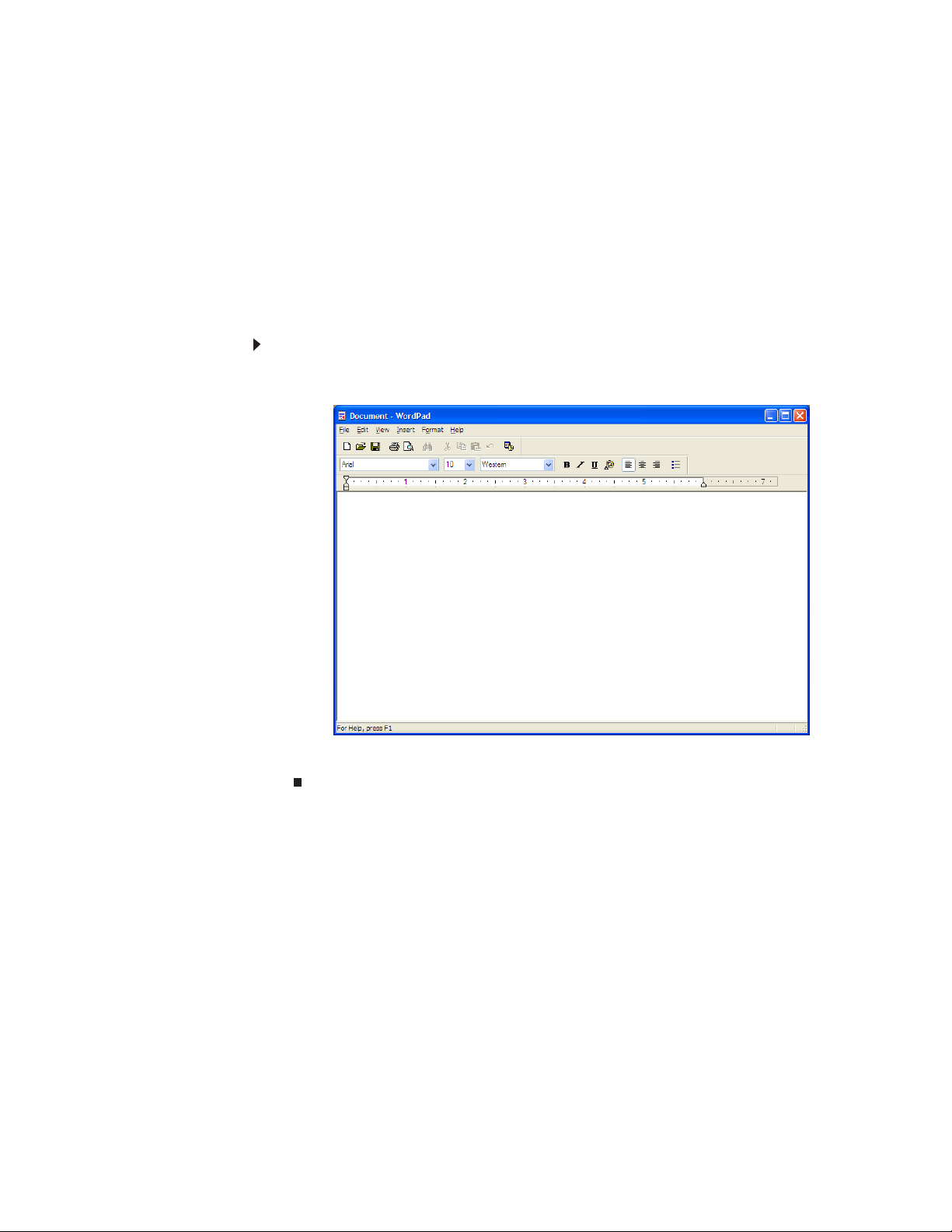
Creating a new document
To create a new document:
1 Click Start, All Programs, Accessories, then click WordPad. Microsoft WordPad
®
WordPad. Similar procedures apply to other programs such as
starts and a blank document opens.
2 Begin composing your document. Use the menus and toolbar buttons at the top
of the window to format the document.
15
Saving a document
Help
For more information about saving documents, click Start, then click
Help and Support. Type saving in the Search box, then press E
After you create a document, you need to save it if you want to use it later.
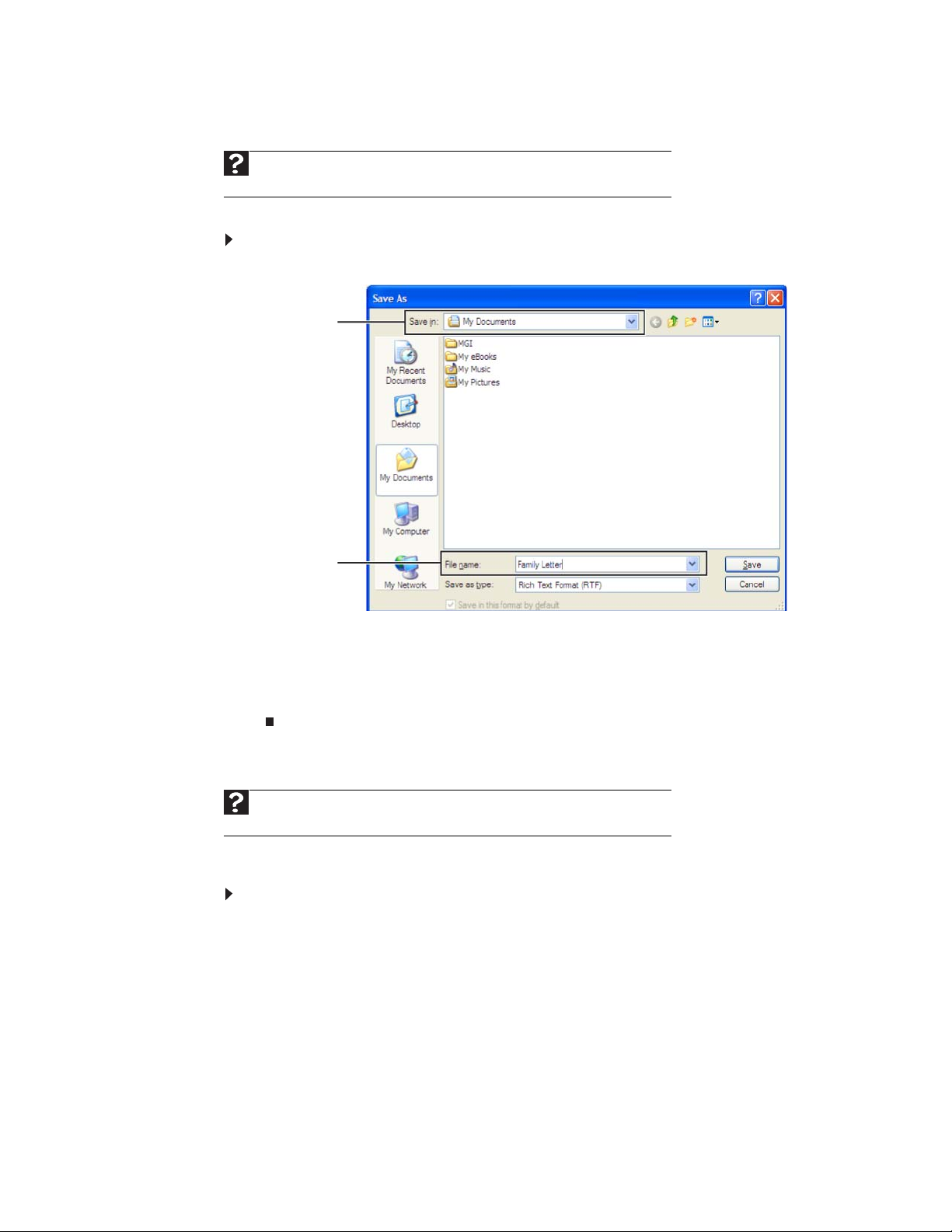
To save a document:
1 Click File, then click Save. The
Save in list
Chapter 2: Using Windows XP
Save As
dialog box opens.
NTER.
name
2 Click the arrow button to open the Save in list, then click the folder where you
want to save the file. If you do not see the folder you want, browse through
the folders listed below the
3 Type a new file name in the File name box.
4 Click Save.
Opening a document
Help
For more information about opening documents, click Start, then click
Help and Support. Type opening files in the Search box, then press E
To view, revise, or print an existing document, first you need to open it. Open the
document in the program that it was created in.
To open a document:
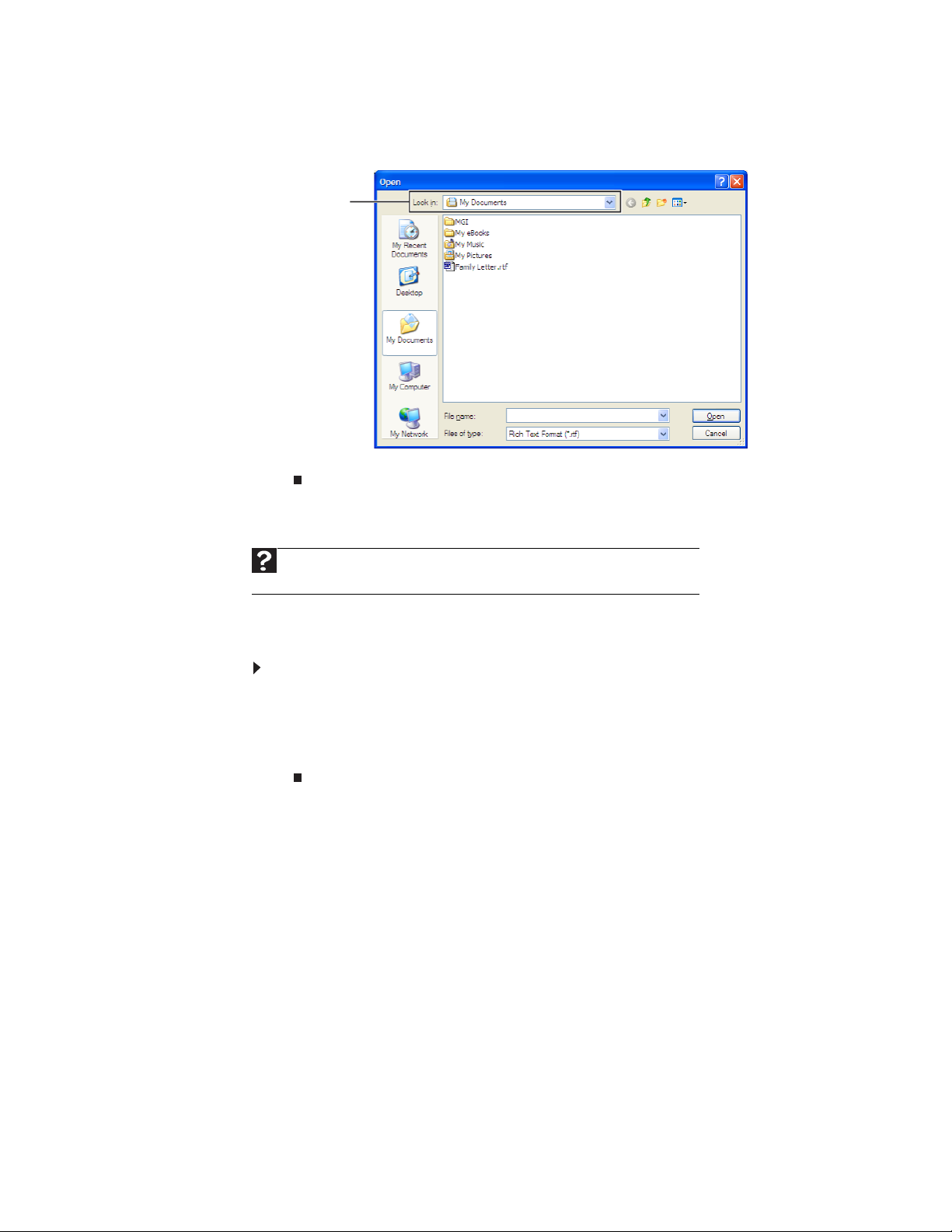
1 Start the program.
2 Click File, then click Open.
File
Save in
list.
NTER.
16
www.emachines.com
3 Click the arrow button to open the Look in list, then click the folder you want
to open. If you do not see the folder you want, browse through the folders listed
below the
Look in list
4 Double-click the document file name. The document opens.
Look in
list.
Printing a document
Help
For more information about printing documents, click Start, then click
Help and Support. Type printing in the Search box, then press E
To print a document, you must have a printer connected to your computer or have
access to a network printer. For more information about installing or using your
printer, see the printer documentation.
To print a document:
1 Make sure that the printer is turned on and loaded with paper.
2 Start the program and open the document.
3 Click File, then click Print. The
4 Set the print options, then click OK. The document prints.
Print
dialog box opens.
NTER.
17
Shortcuts
Help and Support. Type Windows keyboard shortcuts in the Search box, then
press E
The following table shows a few shortcuts that you can use in Windows and almost
all programs that run in Windows. For more information about shortcuts, see your
Windows or program documentation.
Chapter 2: Using Windows XP
Help
For more information about keyboard shortcuts, click Start, then click
NTER.
To... Do this...
Copy a file, folder, text, or
graphic
Cut a file, folder, text, or
graphic
Paste a file, folder, text, or
graphic
Select multiple items in a list
or window
Select multiple adjacent items
in a list or window
Permanently delete a file or
folder
Rename a file or folder Click the file or folder, press F2, type the new name,
Close the active window or
program
Switch to a different file,
folder, or running program
Click the item, then press CTRL + C.
Click the item, then press C
Click inside the folder or window where you want
to paste the object, then press CTRL + V.
Click the first item, press and hold down the C
key, then click each of the remaining items.
Click the first item in the list, press and hold down
the SHIFT key, then click the last item in the list.
Click the file or folder, then press S
The file or folder is permanently deleted. The file
or folder is not stored in the Recycle Bin.
then press ENTER.
Press A
Press ALT +TAB.
LT + F4.
TRL + X.
TRL
HIFT + DELETE.
18

Chapter 3
Using the
Internet and
•
Learning about the Internet
•
Setting up an Internet account
•
Using the World Wide Web
•
Using e-mail
•
Installing and configuring Microsoft Fax
•
Sending a fax
•
Receiving and viewing a fax
Faxing
19
Chapter 3: Using the Internet and Faxing
Learning about the Internet
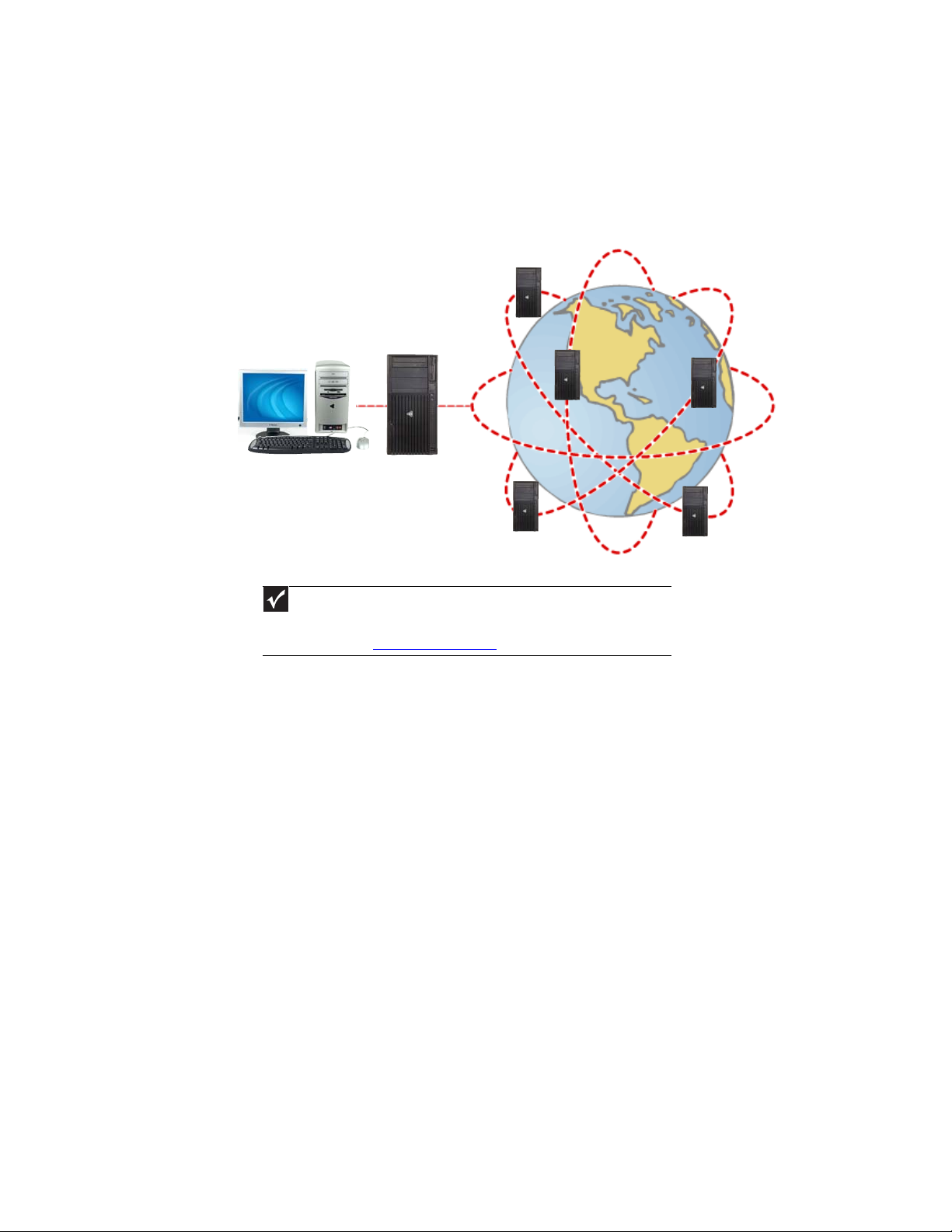
The
Internet
information to people everywhere. The two most popular services on the Internet
are e-mail and the World Wide Web. You can access this network by connecting your
computer to a telephone, DSL (Digital Subscriber Line), or cable television line and
signing up with an Internet service provider (ISP).
is a worldwide network of computers linked together to provide
Internet Servers
store information so other computers
can access it from the Internet.
Your computer
connects to the
Internet through an
ISP.
ISP Servers
let you connect to the
Internet and access your
e-mail messages.
If you want to access the Internet you need:
Important
To determine if you have an Ethernet jack on your computer, see
your
Hardware Reference
computer and would like to purchase an Ethernet card, visit the
Accessory Store at www.emachines.com
. If you do not have an Ethernet jack on your
.
• A modem—a device that connects your computer to other computers or servers
using a telephone, DSL, or cable television line. Your computer may have a
built-in dial-up telephone modem. Cable and DSL modems connect to your
computer through an Ethernet jack and provide a faster connection speed than
a standard telephone modem.
• An Internet service provider—a company that provides access to the Internet
through an ISP server. When you connect to an ISP, the ISP server lets you access
the Internet and your e-mail messages. Check your telephone book for a list of
Internet service providers available locally.
• A Web browser—a program that displays information from the World Wide
Web. Microsoft Internet Explorer was included with your computer. For more
information, see “Using the World Wide Web” on page 21.
• An e-mail program—a program that lets you create, send, and receive e-mail
messages over the Internet. Microsoft Outlook or Outlook Express was included
with your computer. For more information, see “Using e-mail” on page 23.
20
www.emachines.com
Setting up an Internet account
Before you can view the information on the World Wide Web, you need to set up
an Internet account with an Internet service provider (ISP). To set up an ISP service
or to transfer an existing account to this computer, contact the ISP directly.
Dial-up Internet connections are those using a telephone system to connect to the
Internet. This may include ordinary analog telephone lines, ISDN connections, and in
some cases ADSL over PPP, or other technologies. Because dial-up connections are
designed to be temporary connections to the Internet, dial-up charges (with both your
telephone company and Internet service provider) often increase the longer you
connect to the Internet. To minimize the cost for dial-up Internet users, we suggest
that you only connect to the Internet during your e-mail and Web browsing session,
then disconnect when you are finished. Your Internet service provider can provide
instructions on how to connect to and disconnect from the Internet.
Cable and DSL modems, a connection known as broadband, use your cable television
or special telephone lines to connect to your ISP and access the Internet. In many
instances, broadband is considered an always-connected service. With this type of
service, your cost is the same regardless of the amount of time you use your Internet
connection.
Accessing your Internet account
Help
For general information about using Internet accounts, click Start, then
click Help and Support. Type the keyword ISP in the Search box, then click
the arrow.
The method you use to access your Internet account varies from ISP to ISP. Contact
your ISP for the correct procedure.
Using the World Wide Web
The World Wide Web is a multimedia window to the Internet that gives you access
to millions of information sources.
Information on the Web comes to you on
that you view using a Web page display program called a
of the commercially available Web browsers, like Microsoft Internet Explorer or
Mozilla Firefox.
Web pages can contain text, animations, music, and other multimedia features. A
group of related Web pages is called a
track investments, read the news, download programs, and much more.
You can explore a Web site or visit other Web sites by clicking areas on a Web page
called
animated image. You can identify a link by moving the mouse pointer over it. If the
pointer changes to a hand, the item is a link.
To learn more about using the Web browser features, click Help in the menu bar.
links
or
hyperlinks
Connecting to a Web site
After you set up an account with an Internet service provider (ISP), you can access
the many information sources on the World Wide Web.
To connect to a Web site:
1 Connect to your Internet account.
2 Depending on the method you use to connect to your Internet account, you
may need to start your Web browser. Click Start, then click Internet. Your default
Web browser opens showing an opening page or welcome screen.
. A link may be colored or underlined text, a picture, or an
Web pages
Web site
, which are electronic documents
browser
. You can access Web sites to shop,
. You can use any
21

Chapter 3: Using the Internet and Faxing
3 To go to a different Web site, type the
Resource Locator”) in the browser address bar (for example
www.emachines.com), then click GO
- OR On the current Web page, click a link to a Web site.
then click Help and Support. Type connecting to Web site in the Search
box, then press E
The Web browser locates the server computer on the Internet,
(transfers) data to your computer, and displays the page on the site that you
requested.
Sometimes Web pages display slowly. The speed that a Web page displays on your
screen depends on the complexity of the Web page and other Internet conditions.
Additionally, the speed of your connection will determine how fast Web pages
display.
Downloading files
Caution
To protect your computer against viruses, make sure that you scan the
files you download. For more information, see “Protecting your computer
from viruses” on page 75.
Downloading
your computer.
To download files or programs from a Web site:
1 Connect to your Internet account.
2 In the address bar, type the address of the Web site that contains the file or
program you want to download, then click GO
- OR Click a link on a Web page to navigate to the Web site containing the file that
you want to download.
3 Create or locate the folder where you want to store the file on your computer.
For more information, see “Working with files and folders” on page 9.
4 Click the link on the Web page for the file that you want to download.
5 Follow the on-screen instructions for saving the file in the folder that you want.
A copy of the file is downloaded to your computer. The time that it takes to
transfer the file to your computer depends on file size and Internet conditions.
6 Open the folder that you created.
address
on the browser address bar.
(called a
URL
for “Universal
Help
For more information about connecting to a Web site, click Start,
NTER.
downloads
is the process of transferring files from a computer on the Internet to
on the browser address bar.
22
Help
For more information about downloading files, click Start, then
click Help and Support. Type downloading files in the Search box, then
press E
NTER.
7 Install or view the downloaded file by double-clicking it. If applicable, follow
the instructions provided on the Web site to run or install the program.
Using e-mail
E-mail
(electronic mail) lets you send messages to anyone who has an Internet
connection and e-mail address. E-mail is usually a free service of your Internet account.
The Internet never closes, so you can send e-mail messages at any time. Your e-mail
messages arrive at most e-mail addresses in minutes.
An
e-mail address
name
of the Internet service provider (ISP) or company that “hosts” that user. Your
e-mail address is assigned when you sign up for an account with an ISP. For example,
a person with an account with Hotmail might have an e-mail address that is similar
to this one:
Sending e-mail
To send e-mail using Outlook or Outlook Express:
1 Connect to your Internet service provider.
2 Click Start, then click E-Mail. Your default e-mail program opens.
3 Click New.
4 Type the e-mail address of the recipient you want to send e-mail to in the
5 Type the subject of your e-mail in the Subject box.
6 Type the e-mail message.
www.emachines.com
consists of a user name, the @ symbol, and the Internet
jdoe@hotmail.com
User name Internet domain name
domain
To box.
Tip
Most e-mail programs let you attach files, such as photographs,
to your e-mail. For more information, see the help for your e-mail
program.
7 When finished, click Send. Your e-mail is sent over the Internet to the e-mail
address you specified.
Checking your e-mail
Help
For more information about using e-mail, click Start, then click Help and
Support. Type e-mail in the Search box, then press E
To check your e-mail using Outlook Express:
1 Connect to your Internet service provider.
2 Click Start, then click E-Mail. Your default e-mail program opens.
3 Click Send/Recv.
4 Double-click the message you want to read.
Tip
To protect your computer from viruses, check any e-mail attachments
using Norton Antivirus. For more information, see “Protecting your computer
from viruses” on page 75.
For more information about managing and organizing your e-mail messages, see the
online help in your e-mail program.
NTER.
23
 Loading...
Loading...