
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
VDSL2 Router
User’s Manual
1

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
Table of Contents
1 Introduction .......................................................... 7
Features ................................................................................ 7
Device Requirements ........................................................... 7
Using this Document ............................................................. 8
Notational conventions .................................................. 8
Typographical conventions ............................................ 8
Special messages .......................................................... 8
Getting Support ..................................................................... 8
2 Getting to know the device .................................. 9
Computer / System requirements ........................................ 9
Package Contents ................................................................ 9
For Annex-B VDSL2 Router .......................................... 9
For Annex-A VDSL2 Router .......................................... 9
Installation & Setup ............................................................. 10
LED meanings & activations .............................................. 12
Back Panel Connectors ............................................... 13
3 Computer configurations under
different OS, to obtain IP address
automatically ................................................... 14
4 Utility CD execution ........................................... 27
Connecting the Hardware ................................................... 27
VDSL WAN Configuration (VDSL Line User) .................... 28
DSL WAN Configuration (ADSL Line User) ....................... 37
5 Getting Started with the Web pages ................. 47
Accessing the Web pages .................................................. 47
Testing your Setup .............................................................. 49
Default device settings ........................................................ 50
6 Overview ........................................................... 53
Internet access settings ...................................................... 54
About VDSL2 Router .......................................................... 54
7 Status ................................................................ 55
Device Info .......................................................................... 55
IPv6 ..................................................................................... 56
8 Local Network Configuration ............................. 57
Changing the LAN IP address and subnet
mask ................................................................................ 57
2

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
Adding the Secondary LAN IP address and
subnet mask .................................................................... 59
Change IP Pool Range and Subnet mask ......................... 60
9 PTM WAN ......................................................... 62
Configuring PTM WAN IPoE Static IP
connection ....................................................................... 65
Configuring PTM WAN IPoE DHCP Client
connection ....................................................................... 69
Configuring PTM WAN PPPoE connection ....................... 70
Configuring PTM WAN DS-Lite connection ....................... 72
Configuring PTM WAN 6rd connection .............................. 73
10 ATM WAN ......................................................... 74
Types of DSL WAN Internet Access .................................. 75
Configuring your PPPoE DSL connection ......................... 7 6
Configuring your PPPoA DSL connection ......................... 7 8
Configuring your Bridged DSL connection ......................... 80
Configuring your 1483 MER by DHCP .............................. 81
Configuring your 1483 MER by Fixed IP ........................... 81
ATM Settings ....................................................................... 83
DSL Settings ....................................................................... 86
11 DHCP Settings .................................................. 88
DHCP Server Configuration ............................................... 88
DHCP Relay Configuration ................................................. 90
DHCP None Configuration ................................................. 91
12 DHCPv6 Settings .............................................. 92
DHCP Server (Manual) Configuration ................................ 92
DHCP Server (Auto) Configuration .................................... 95
DHCP Relay Configuration ................................................. 96
DHCP None Configuration ................................................. 97
13 DNS Configuration ............................................ 98
DHCP Server Configuration - Attain DNS
Automatically ................................................................... 98
DHCP Server Configuration - Set DNS
Manually ........................................................................... 99
14 Dynamic DNS Configuration ...........................101
Overview of Dynamic DNS ............................................... 101
Dynamic DNS Configuration – DynDNS.org ................... 103
Dynamic DNS Configuration – TZO ................................. 104
15 IP/Port Filtering ................................................106
IP/Port Filtering .................................................................. 106
3

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
16 MAC Filtering ...................................................108
Configuring MAC filtering to Deny for
outgoing access ............................................................. 108
17 Port Forwarding ...............................................110
Port Forwarding for TCP with specified IP ....................... 112
Port Forwarding for UDP with specified IP ....................... 114
18 URL Blocking ...................................................116
Configuring URL Blocking of FQDN ................................. 116
Configuring URL Blocking of Keyword ............................. 118
19 Domain Blocking .............................................120
Configuring Domain Blocking ........................................... 120
20 DMZ .................................................................122
Configuring DMZ ............................................................... 122
21 UPnP ...............................................................124
Configuring UPnP ............................................................. 125
UPnP Control Point Software on Windows
ME .................................................................................. 126
UPnP Control Point Software on Windows
XP with Firewall ............................................................. 126
SSDP requirements ................................................... 127
22 RIP ...................................................................130
23 ARP Table .......................................................132
ARP Table ......................................................................... 132
24 Bridging ...........................................................133
Bridging ............................................................................. 133
25 Routing ............................................................134
Static Route ....................................................................... 134
26 SNMP ..............................................................136
SNMP ................................................................................ 136
27 Remote Access ...............................................138
Remote Access ................................................................. 138
28 Others ..............................................................139
Others ................................................................................ 139
29 IPv6 .................................................................140
IPv6 ................................................................................... 140
RADVD .............................................................................. 140
DHCPv6 ............................................................................ 141
MLD Proxy ........................................................................ 141
MLD Snooping .................................................................. 142
4

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
IPv6 Routing ...................................................................... 143
IP/Port Filtering .................................................................. 144
30 Diagnostic ........................................................145
Ping ................................................................................... 145
ATM Loopback .................................................................. 146
ADSL Tone Diagnostics ................................................... 147
ADSL Connection Diagnostics ......................................... 148
31 Commit/Reboot ...............................................149
Commit and Reboot .......................................................... 149
32 Backup/Restore ...............................................150
Backup settings ................................................................. 150
Restore settings ................................................................ 151
Resetting to Defaults ......................................................... 151
33 System Log .....................................................153
System Log ....................................................................... 153
34 Password .........................................................155
Setting your username and password ............................. 155
35 Firmware Update .............................................157
About firmware versions ................................................... 157
Manually updating firmware .............................................. 157
36 ACL Configuration ...........................................161
ACL Config ........................................................................ 161
37 Time Zone .......................................................162
SNTP Server and SNTP Client
Configuration settings .................................................... 162
38 TR-069 ............................................................167
TR-069 Configuration ....................................................... 167
39 Statistics ..........................................................169
Statistics - Interface ........................................................... 169
Statistics - ADSL ............................................................... 170
A Configuring your Computers ...........................171
Configuring Ethernet PCs ................................................. 171
Before you begin ........................................................ 171
Windows® XP PCs .................................................... 171
Windows 2000 PCs ................................................... 171
Windows Me PCs ...................................................... 173
Windows 95, 98 PCs ................................................. 173
Windows NT 4.0 workstations ................................... 174
5

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
Assigning static Internet information to
your PCs ................................................................. 175
B IP Addresses, Network Masks, and
Subnets ........................................................176
IP Addresses ..................................................................... 176
Structure of an IP address ......................................... 176
Network classes ......................................................... 176
Subnet masks ................................................................... 177
C Troubleshooting ...............................................179
Troubleshooting Suggestions ........................................... 179
Diagnosing Problem using IP Utilities .............................. 181
ping ............................................................................. 181
nslookup ..................................................................... 181
D Glossary ..........................................................183
6
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
1 Introduction
Congratulations on becoming the owner of the VDSL2
Router. You will now be able to access the Internet using
your high-speed DSL connection.
This User Guide will show you how to connect your VDSL2
Router, and how to customize its configuration to get the
most out of your new product.
Features
The list below contains the main features of the device and
may be useful to users with knowledge of networking
protocols. If you are not an experienced user, the chapters
throughout this guide will provide you with enough
information to get the most out of your device.
Features include:
Internal DSL modem for high-speed Internet access
10/100Base-T Ethernet Router to provide Internet
connectivity to all computers on your LAN
Network address translation (NAT) functions to provide
security for your LAN
Network configuration through DHCP Server and DHCP
Client
Services including IP route and DNS configuration, RIP, and
IP and DSL performance monitoring
User-friendly configuration program accessed via a web
browser
User-friendly configuration program accessed via EasySetup
program
Device Requirements
In order to use the VDSL2 Router, you must have the
following:
DSL service up and running on your telephone line
Instructions from your ISP on what type of Internet
access you will be using, and the addresses needed to set
up access
One or more computers each containing an Ethernet
card (10Base-T/100Base-T network interface card (NIC))
For system configuration using the supplied
a. web-based program: a web browser such as Internet
Explorer v4 or later, or Netscape v4 or later. Note that version
4 of each browser is the minimum version requirement – for
optimum display quality, use Internet Explorer v5, or
Netscape v6.1
b. EasySetup program: Graphical User Interface
7

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
You do not need to use a hub or switch in order to connect more
Note
than one Ethernet PC to your device. Instead, you can connect
up to four Ethernet PCs dire ctly to you r devi ce using t he po rts
labeled Ethernet on the rear panel.
Using this Document
Notational conventions
Acronyms are defined the first time they appear in the
text and also in the glossary.
For brevity, the VDSL2 Router is referred to as “the
device”.
The term LAN refers to a group of Ethernet-connected
computers at one site.
Typographical conventions
Italic text is used for items you select from menus and
drop-down lists and the names of displayed web pages.
Bold text is used for text strings that you type when
prompted by the program, and to emphasize important
points.
Special messages
This document uses the following icons to draw your
attention to specific instructions or explanations.
Note
Provides clarifying or non-essential information on the current
topic.
Definition
Explains terms or acronyms that may be unfamiliar to many
readers. These terms are also included in the Glossary.
Provides messages of high importance, including messages
relating to personal safety or system integrity.
WARNING
Getting Support
Supplied by:
Helpdesk Number:
Website:
8
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
2 Getting to know the device
Computer / System requirements
1. Pentium 200MHZ processor or above
2. Windows 98SE, Windows Me, Windows 2000, Windows
XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8
3. 64MB of RAM or above
4. 25MB free disk space
Package Contents
For Annex-B VDSL2 Router
1. VDSL2 Router
2. CD-ROM (Software & Manual)
3. Quick Installation Guide
4. 1 x Telephone Cable (RJ-11)
5. Ethernet Cable (RJ-45)
6. Power Adaptor
7. Annex-B Splitter (Optional, with an extra RJ-11
Telephone cable)
For Annex-A VDSL2 Router
1. VDSL2 Router
2. CD-ROM (Software & Manual)
3. Quick Installation Guide
4. 1 x Telephone Cable (RJ-11)
5. Ethernet Cable (RJ-45)
6. Power Adaptor
7. Annex-A Splitter (Optional, with an extra RJ-11
Telephone cable)
9
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
Installation & Setup
Follow each STEP carefully and only go to the next step once you have complete the
previous STEP.
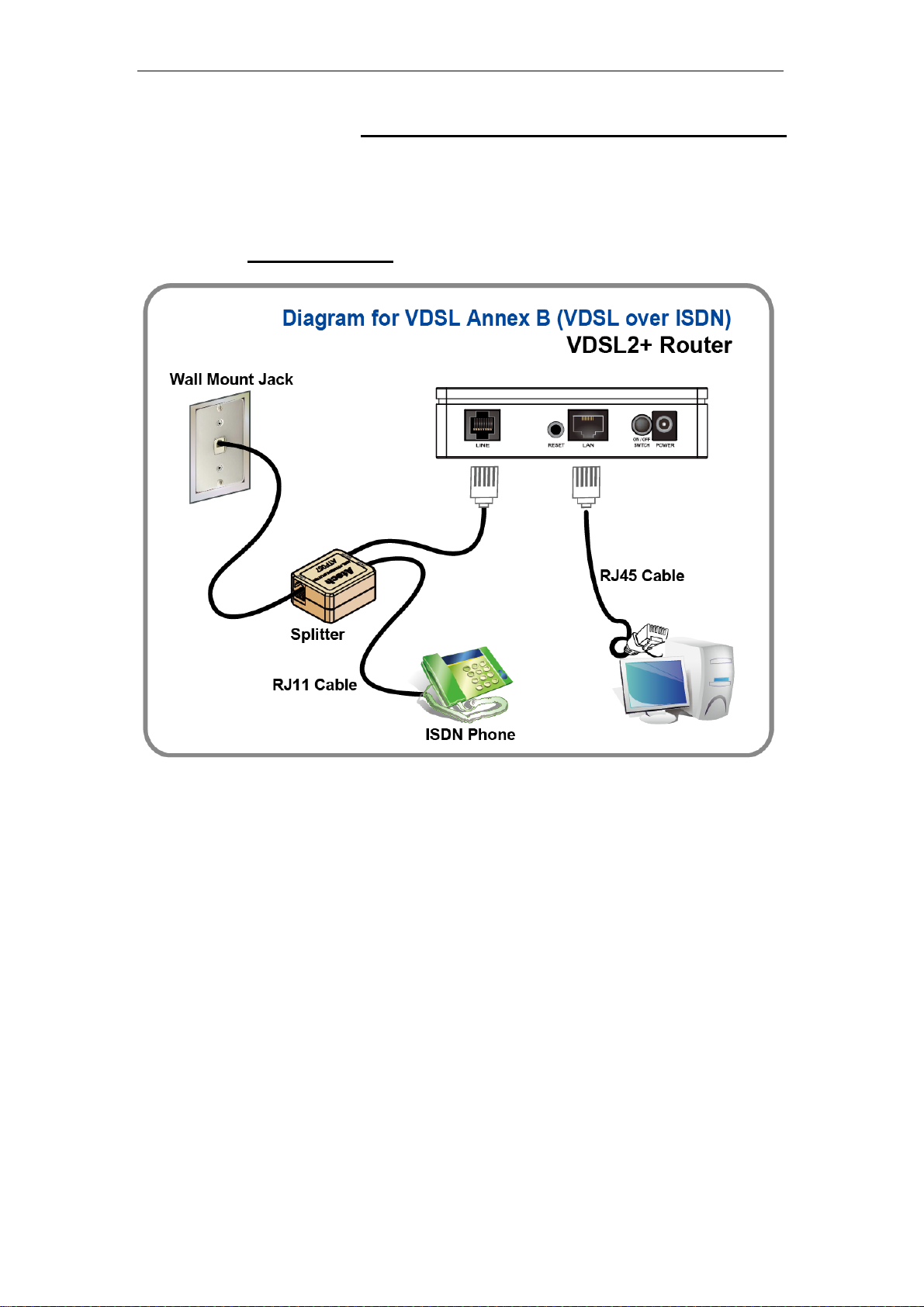
Connection of VDSL2 Router
If you have an ISDN telephone line
connect the modem router as shown below:
1. Connect the supplied RJ45 Ethernet cable from your PC's Ethernet port to VDSL2
Router's LAN Port.
2. Connect the supplied RJ11 telephone cable from your home's telephone jack to the
“LINE” port of the supplied splitter. Connect another RJ11 telephone cable to the
“MODEM” port of the splitter and connect the other end of this cable to the LINE port of
your VDSL2 Router.
telephone cable from your home's telephone jack to the “LINE” port of your VDSL2
Router.)
3. Connect a RJ11 telephone cable to the “PHONE” port of the splitter and connect the other
end to your telephone.
4. Connect the power adapter to the power inlet “POWER” of the VDSL2 Router and turn
the “ON/OFF SWITCH” switch of your VDSL2 Router on.
(If there is no option Splitter, please connect the supplied RJ11
10
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
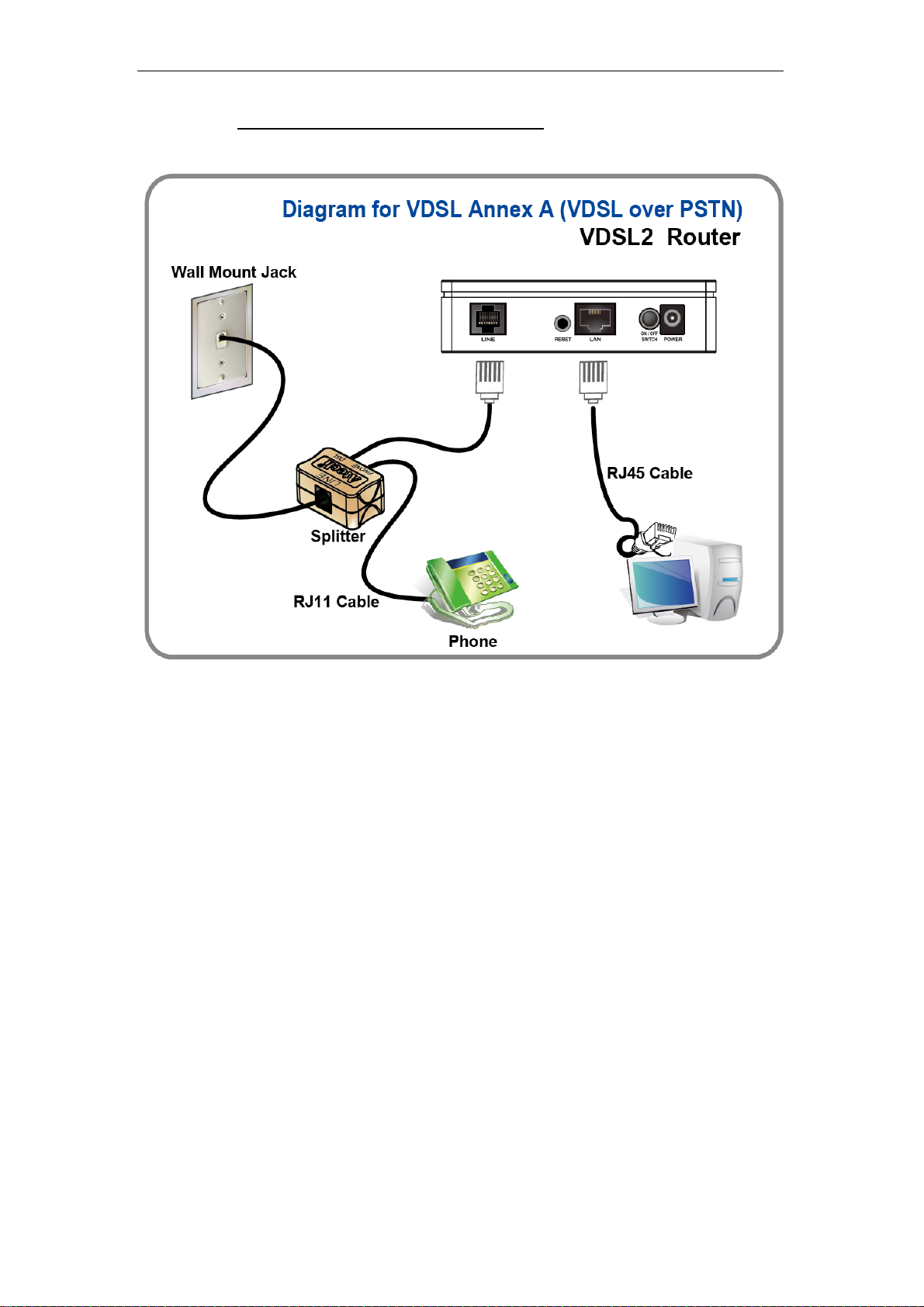
If you have a PSTN telephone line (normal analog line) connect the router as shown
below:
1. Connect the supplied RJ45 Ethernet cable from your PC's Ethernet port to VDSL2
Router's LAN Port.
2. Connect the supplied RJ11 telephone cable from your home's telephone jack to the
“LINE” port of the supplied splitter. Connect the other supplied RJ11 telephone cable to
the “DSL” port of the splitter and connect the other end of this cable to the “LINE” port of
your VDSL2 Router. (If there is no option Splitter, please connect the supplied RJ11
telephone cable from your home's telephone jack to the “LINE” port of your VDSL2
Router.)
3. Connect a RJ11 telephone cable to the “PHONE” port of the splitter and connect the other
end to your telephone.
4. Connect the power adapter to the power inlet “POWER” of the VDSL2 Router and turn
the “ON/OFF SWITCH” switch of your VDSL2 Router on.
11
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
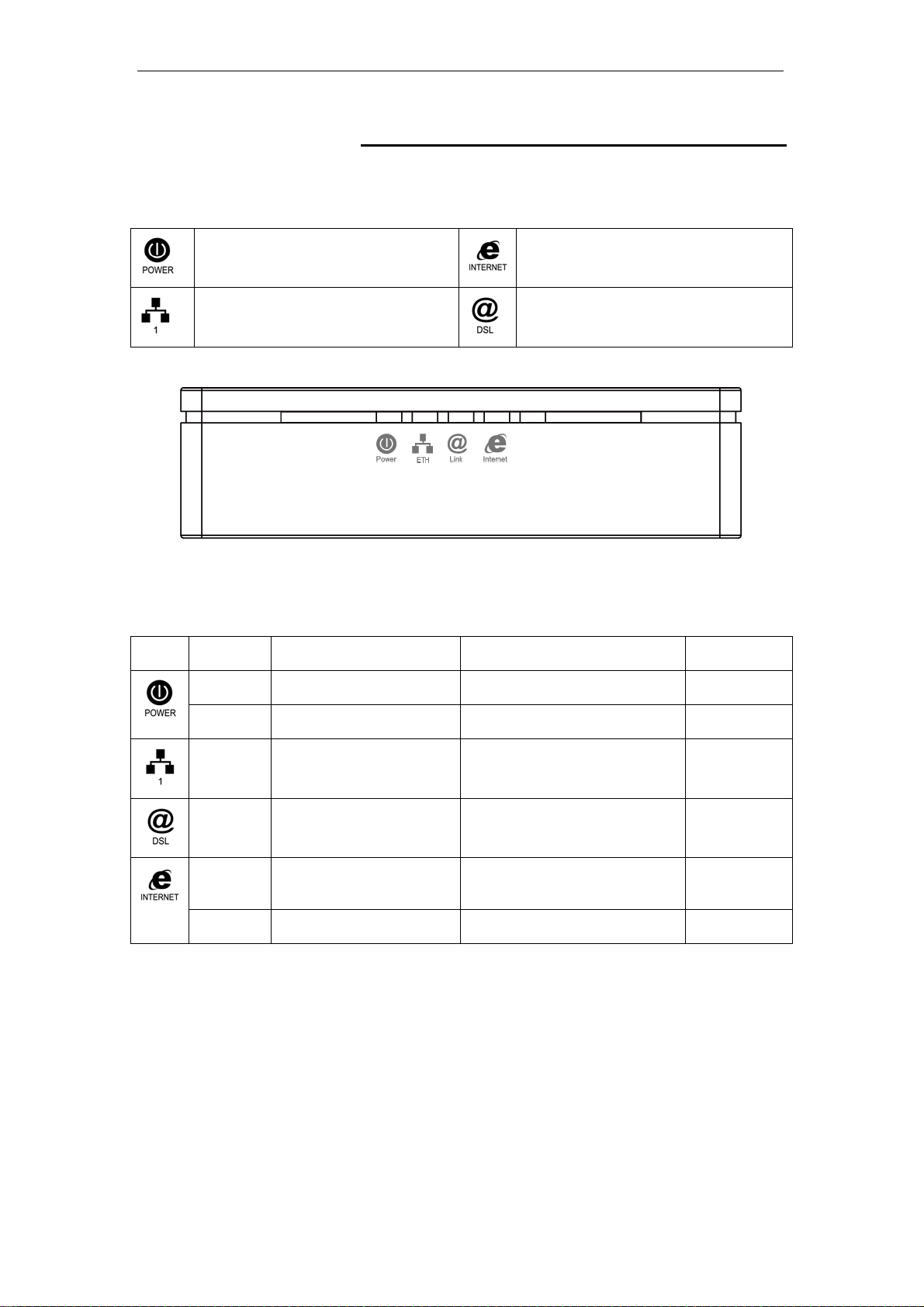
LED meanings & activations
Your VDSL2 Router has indicator lights on the front side.
Please see below for an explanation of the function of each
indicator light.
Power indicator
Ethernet Active indicator
Table1. LED function
Label Color On Flash Off
Red N/A N/A N/A
Internet Active indicator
ADSL Link indicator
Green Ready Waiting for device ready Power Off
Green Ethernet Connected Transmit / Receive Data Ethernet
Green Connect to DSLAM Disconnect to DSLAM N/A
Green The device has a WAN IP
Red N/A N/A N/A
address from ISP
The icons appear on the products are for application indication
only.
The trademark or intellectual property is belonging to their
respective owners.
Transmit / Receive Data N/A
Disconnected
12
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
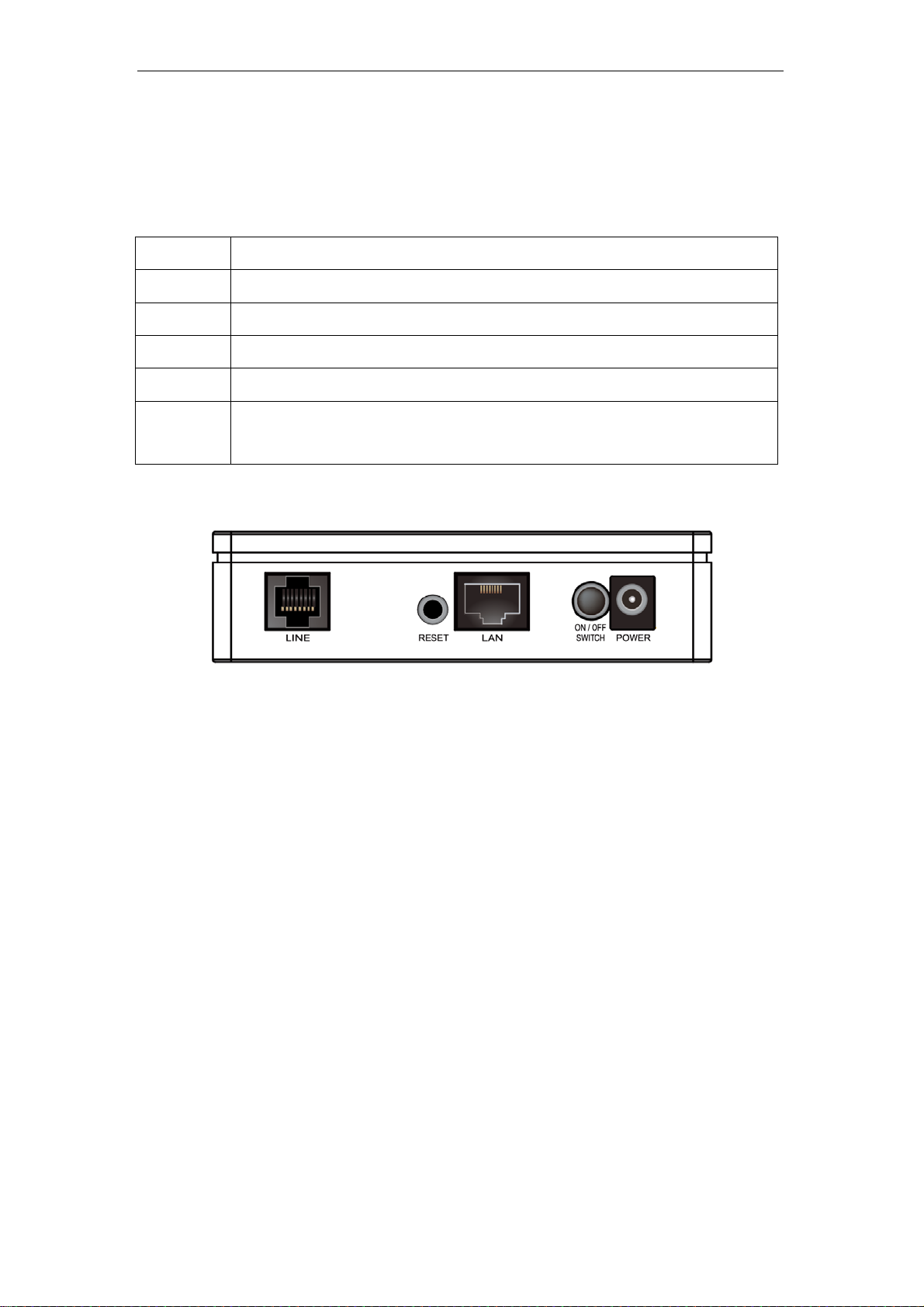
Back Panel Connectors
Table 2 shows the function of each connector and switch of the device.
Table 2. Function / Description of Connectors
Connector Description
POWER
SWITCH
LAN1~4
LINE
RESET
Connects to your VDSL2 Router 12Vdc power adaptor
Power Switch
RJ-45 Jack (Ethernet Cable) connection to your PC, or HUB
Connects to your VDSL2 line – for VDSL2 Line input
Reset button. RESET the VDSL2 Router to its default settings.
Press this button for at least 5 full seconds to start to reset it to its default
settings.
Figure1. Rear View of the VDSL2 Router
13
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
3 Computer configurations under different OS,
to obtain IP address automatically
Before starting the VDSL2 Router configuration, please kindly
configure the PC computer as below, to have automatic IP
address / DNS Server.
For Windows 98SE / ME / 2000 / XP
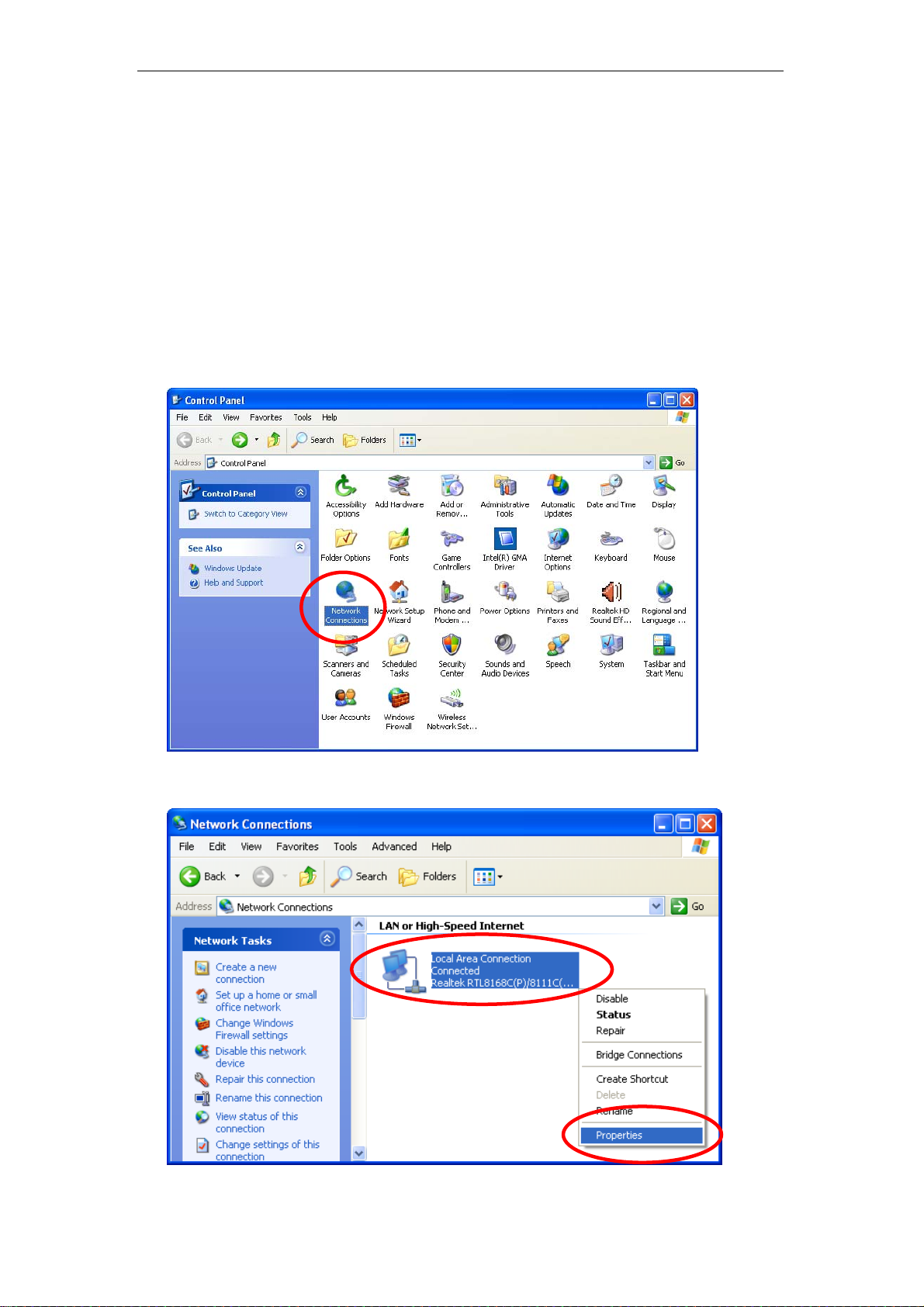
1. Click on “Start” -> “Control Panel” (in Classic View). In the Control Panel,
double click on “Network Connections” to continue.
2. Single RIGHT click on “Local Area connection”, then click “Properties”.
14
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
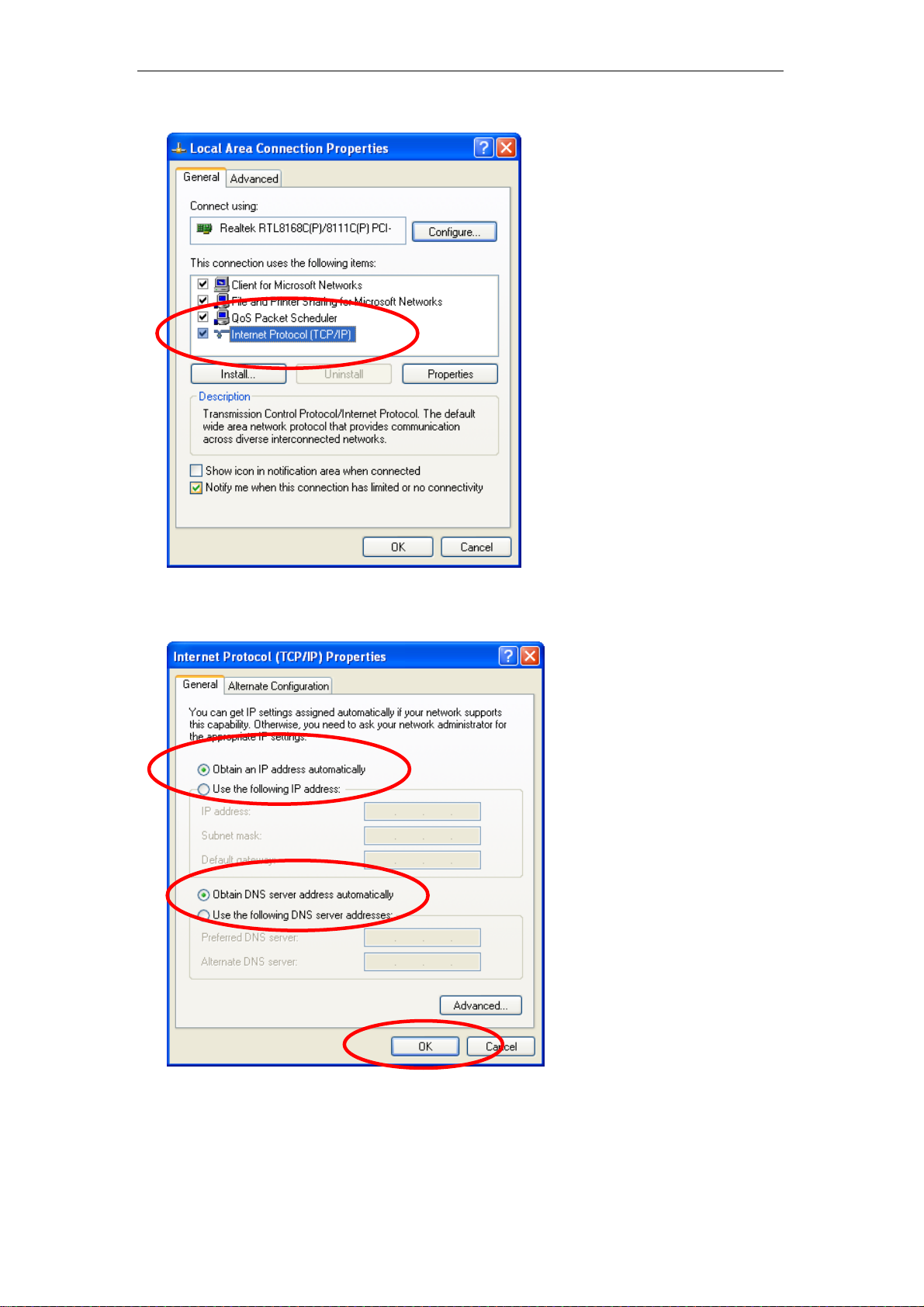
3. Double click on "Internet Protocol (TCP/ IP)".
4. Check "Obtain an IP address automatically" and “Obtain DNS server
address automatically” then click on "OK" to continue.
5. Click "Show icon in notification area when connected" (see screen
image in 3. above) then Click on "OK" to complete the setup procedures.
15
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
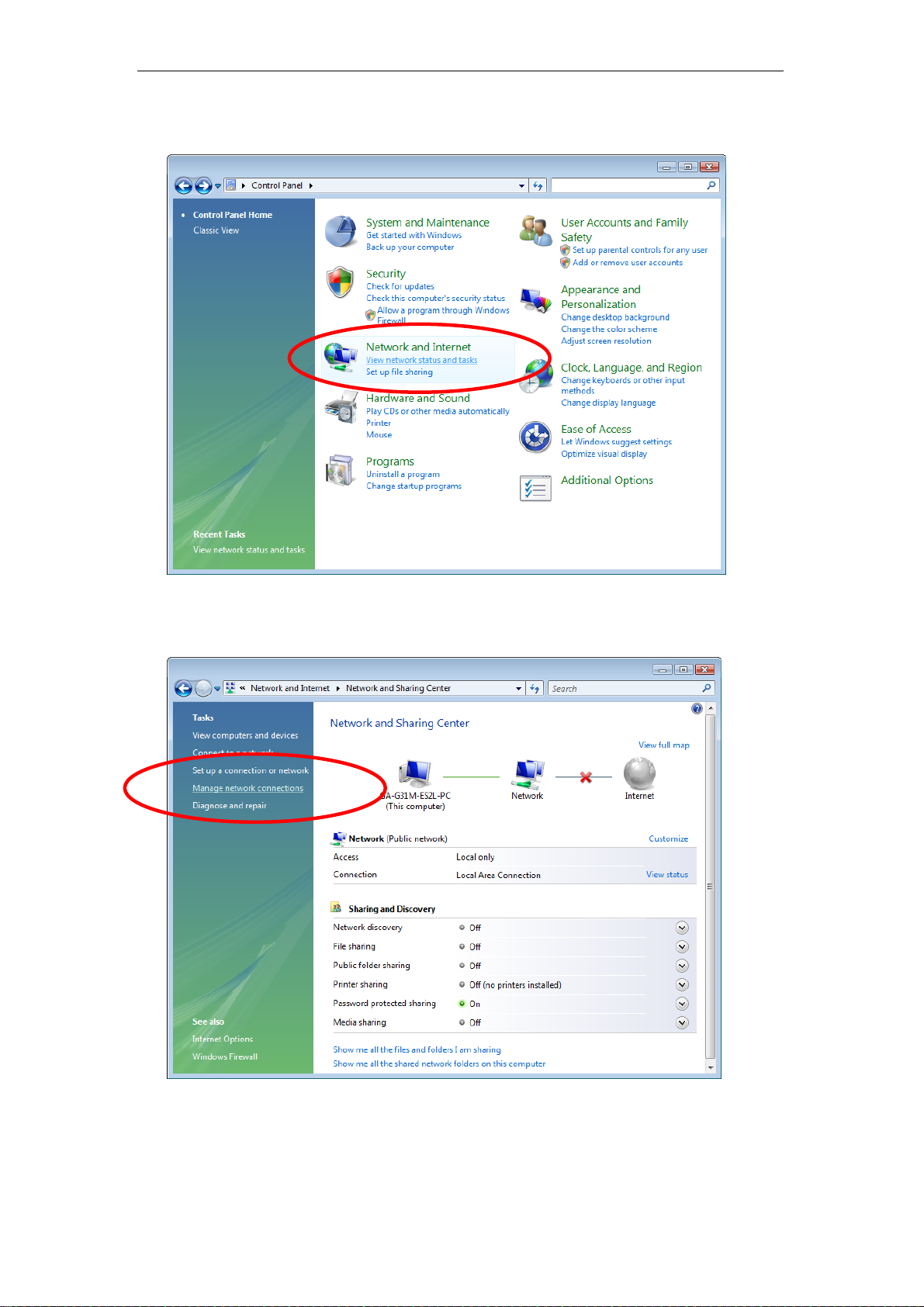
For Windows Vista-32/64
1. Click on “Start” -> “Control Panel” -> “View network status and tasks”.
2. In the Manage network connections, click on “Manage network
connections” to continue.
16
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
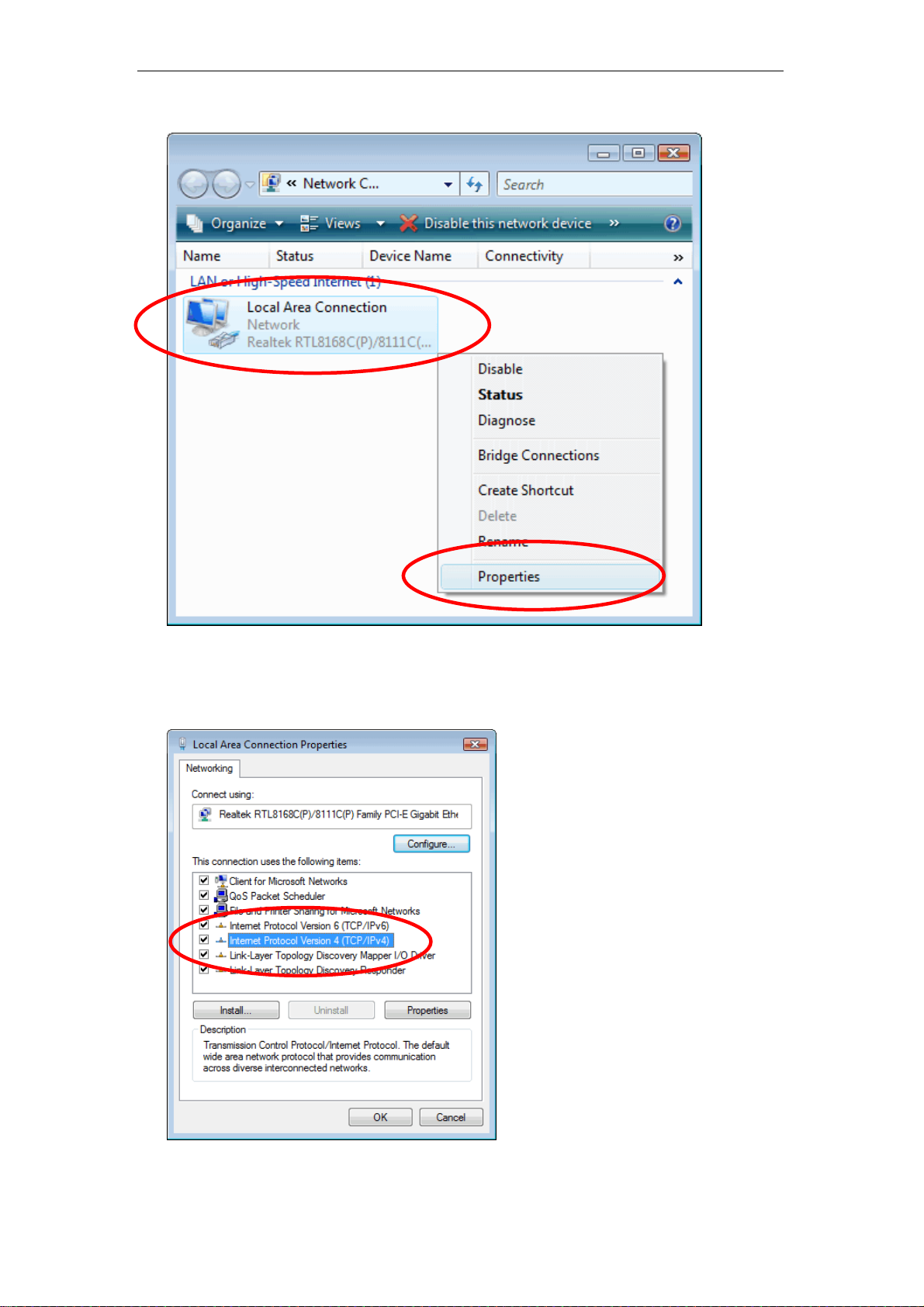
3. Single RIGHT click on “Local Area connection", then click "Properties".
4. The screen will display the information “User Account Control” and click
“Continue” to continue.
5. Double click on "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)".
17
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
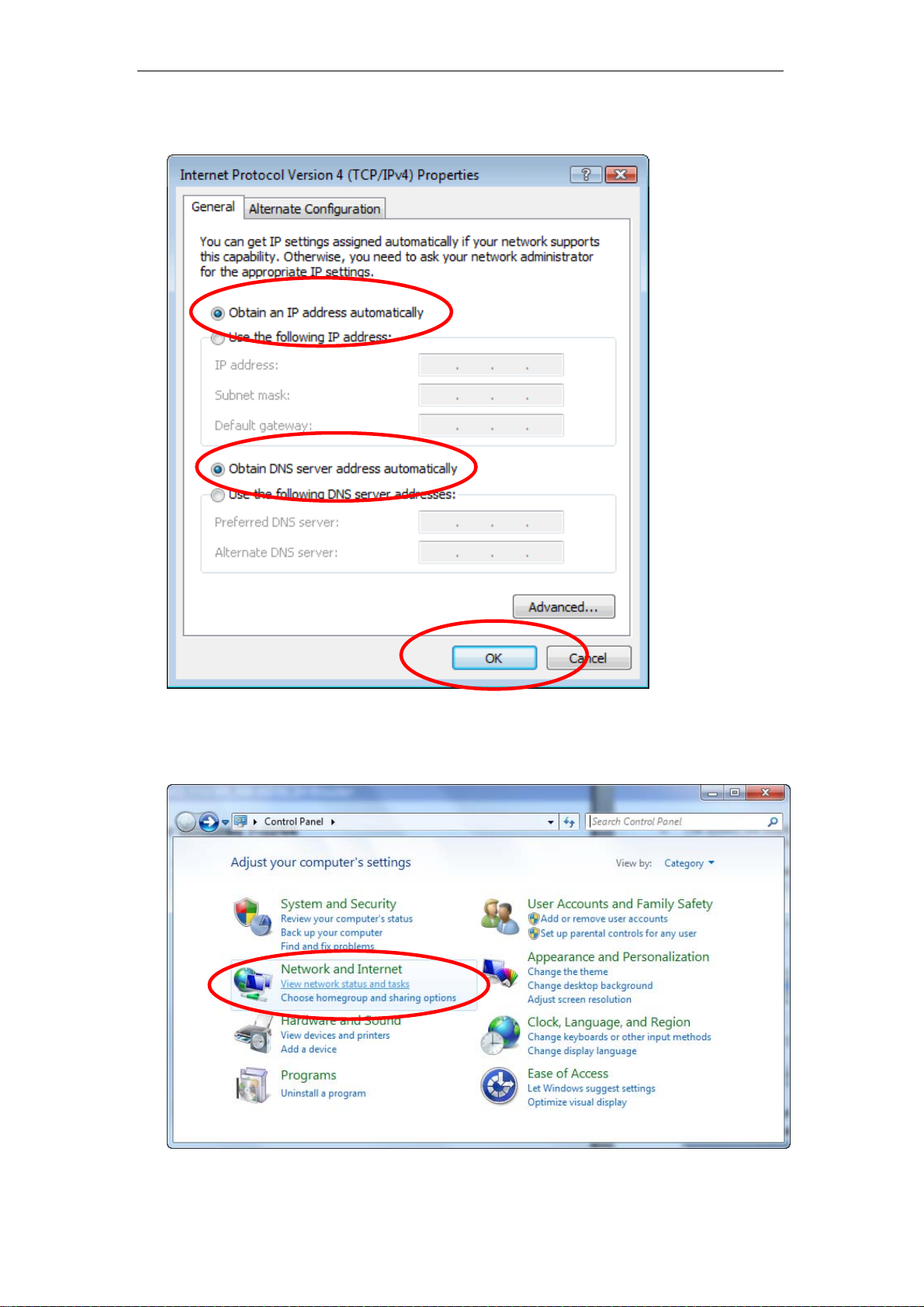
6. Check "Obtain an IP address automatically" and “Obtain DNS server
address automatically” then click on "OK" to continue.
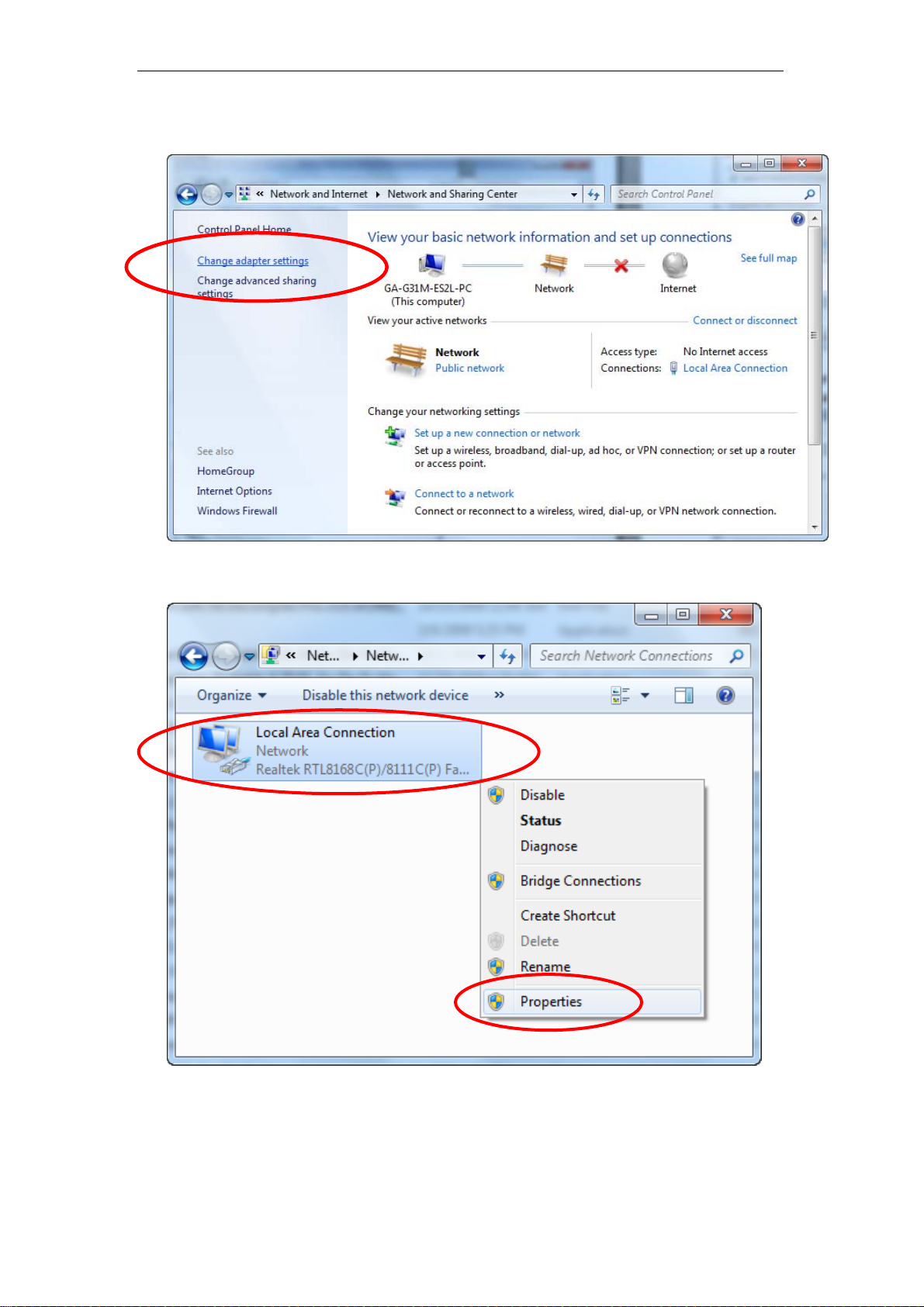
For Windows 7-32/64
1. Click on “Start” -> “Control Panel” (in Category View) -> “View network
status and tasks”.
18
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
2. In the Control Panel Home, click on “Change adapter settings” to
continue.
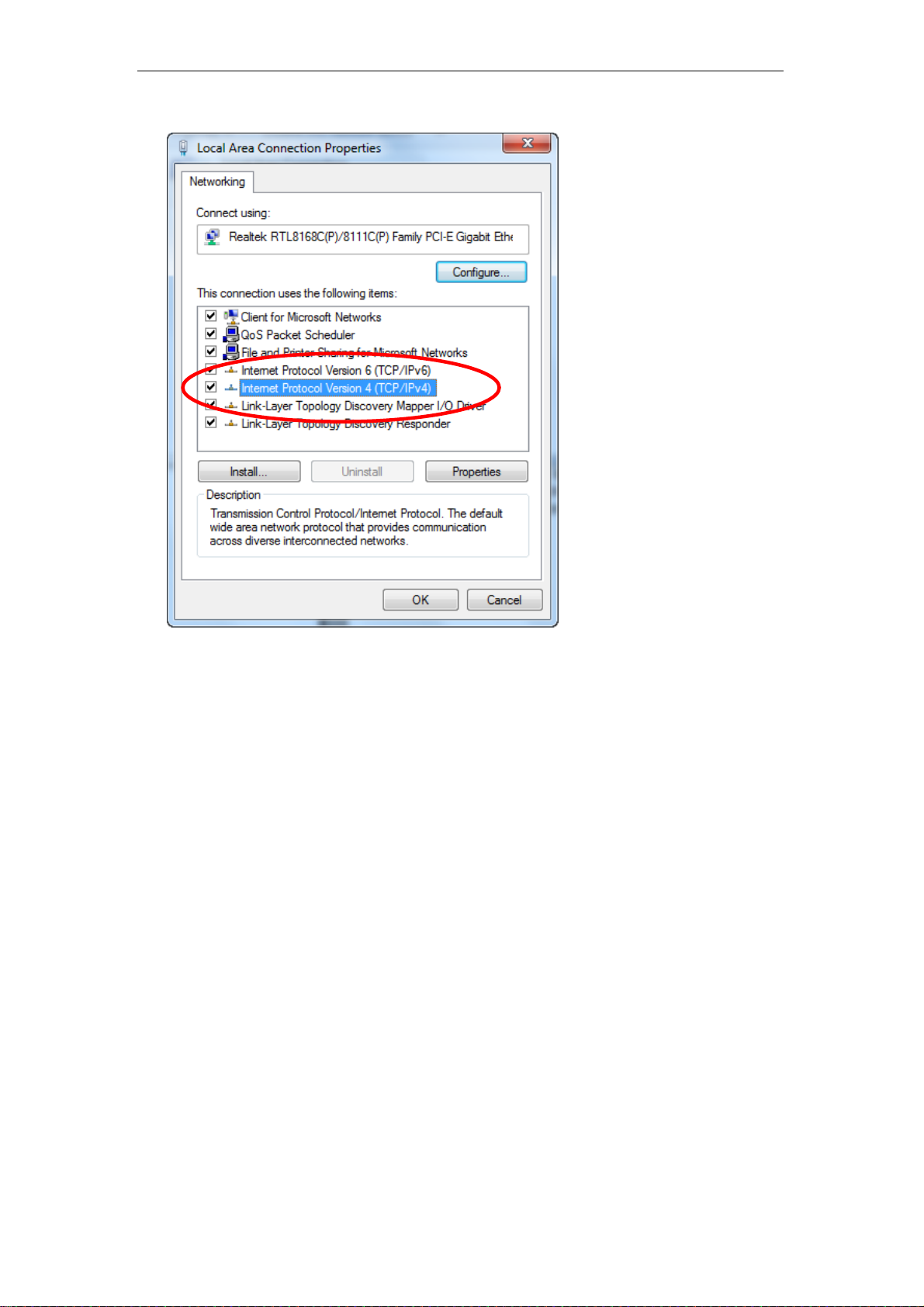
3. Single RIGHT click on “Local Area connection", then click "Properties".
19
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
4. Double click on "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)".
20
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
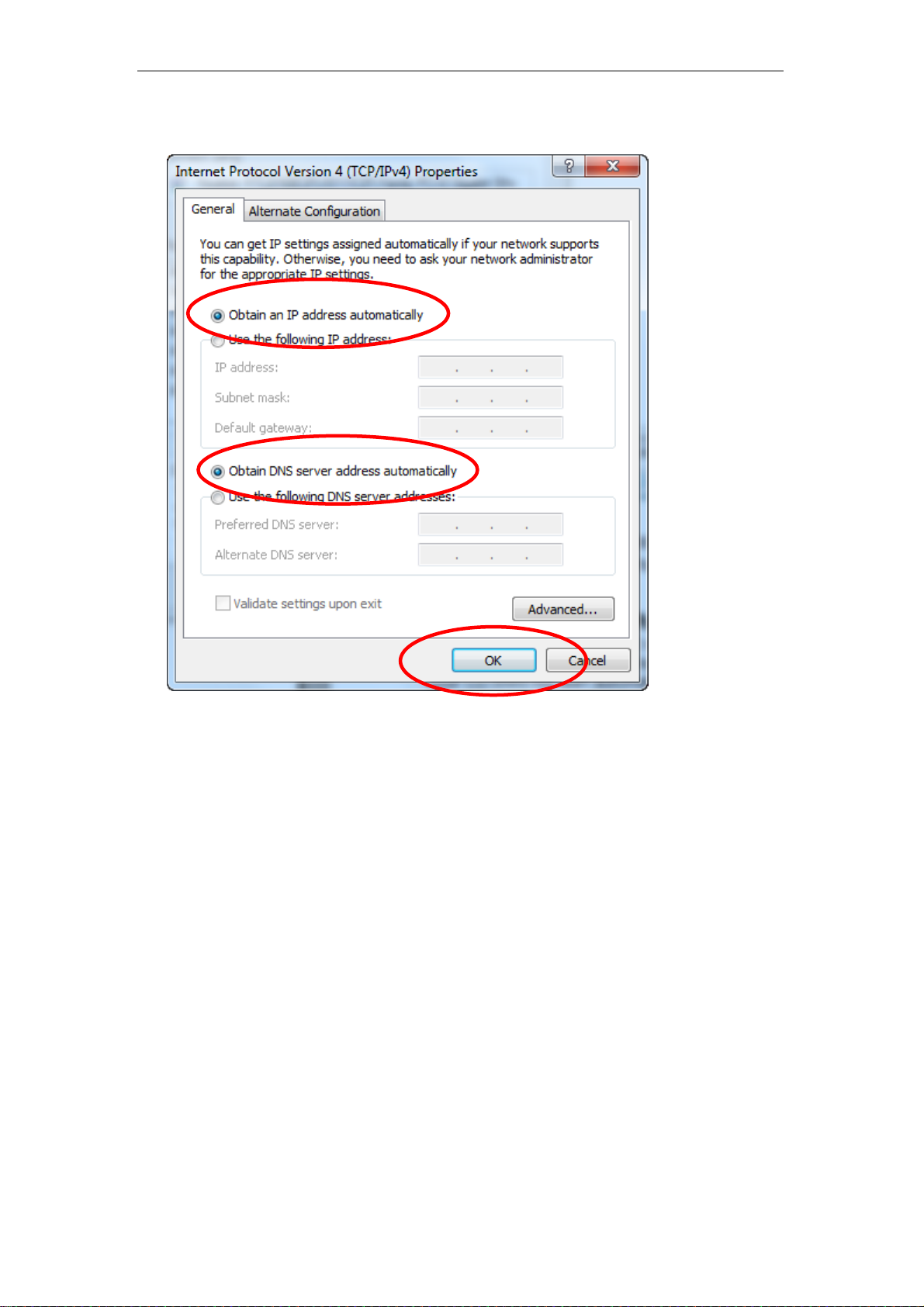
5. Check "Obtain an IP address automatically" and “Obtain DNS server
address automatically” then click on "OK" to continue.
21

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
For Windows 8-32/64
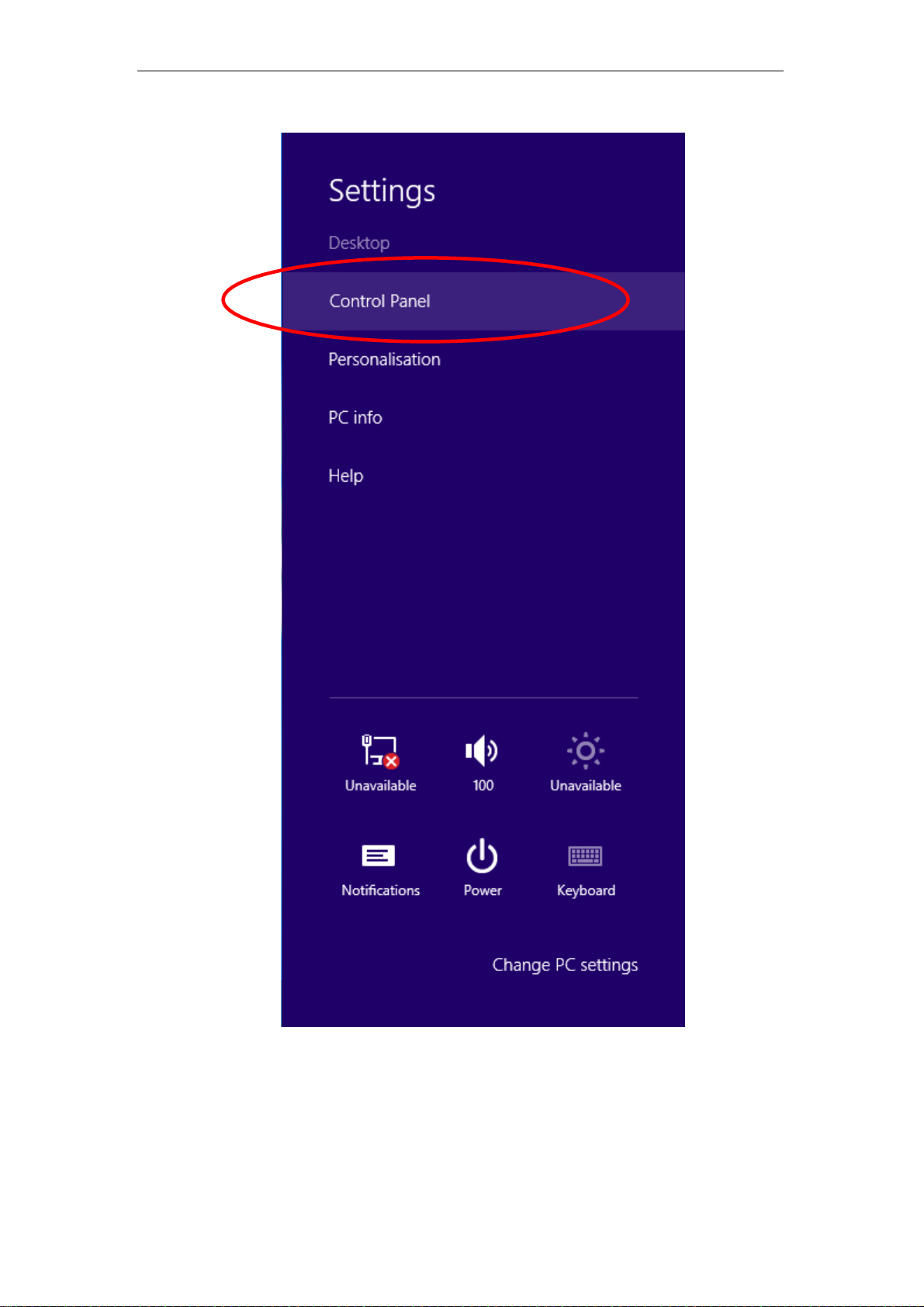
1. Move the mouse or tap to the upper right corner and click on “Settings”.
22
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
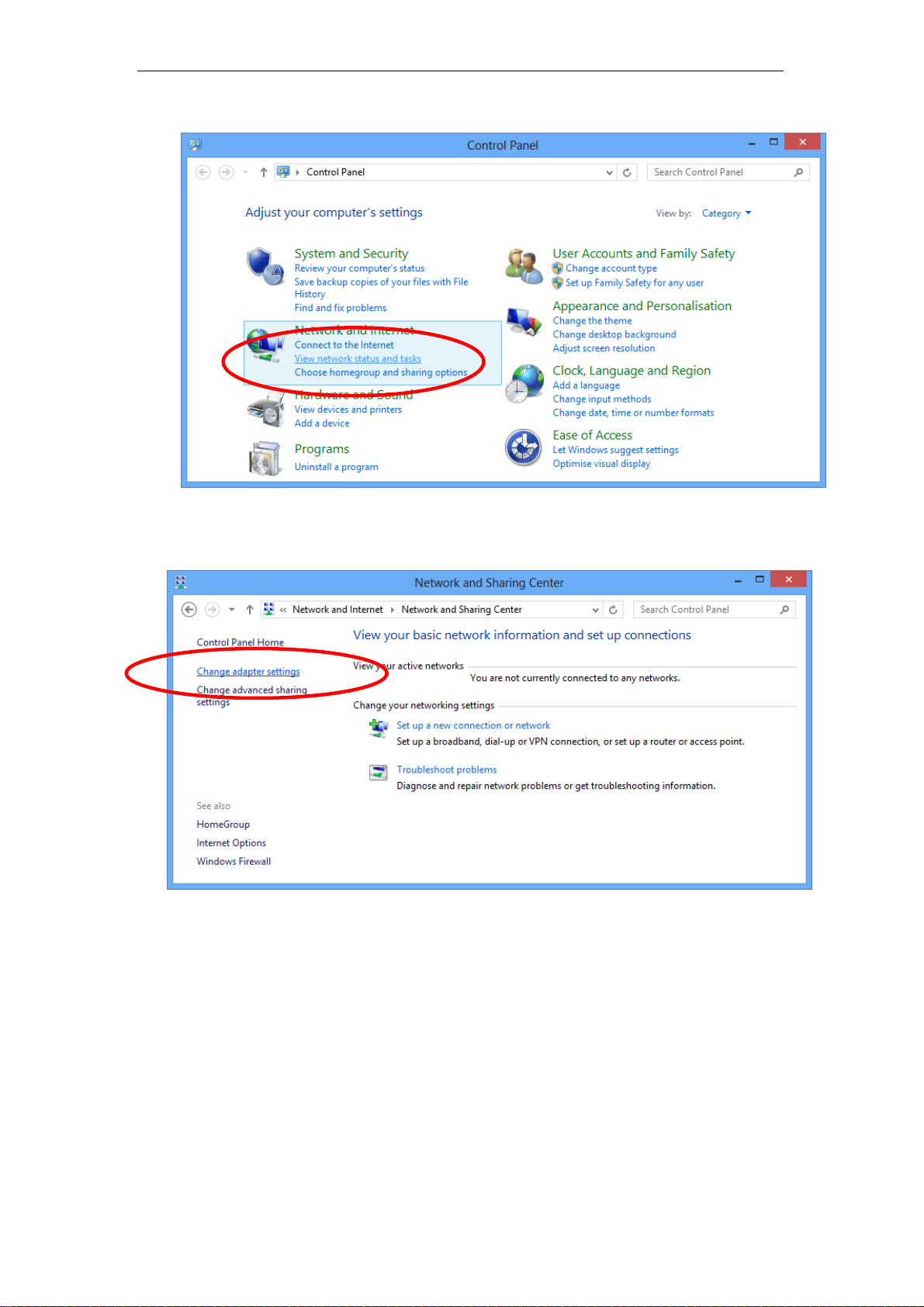
2. Click on “Control Panel”.
23
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
3. Click on “View network status and tasks”.
4. In the Control Panel Home, click on “Change adapter settings” to
continue.
24
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
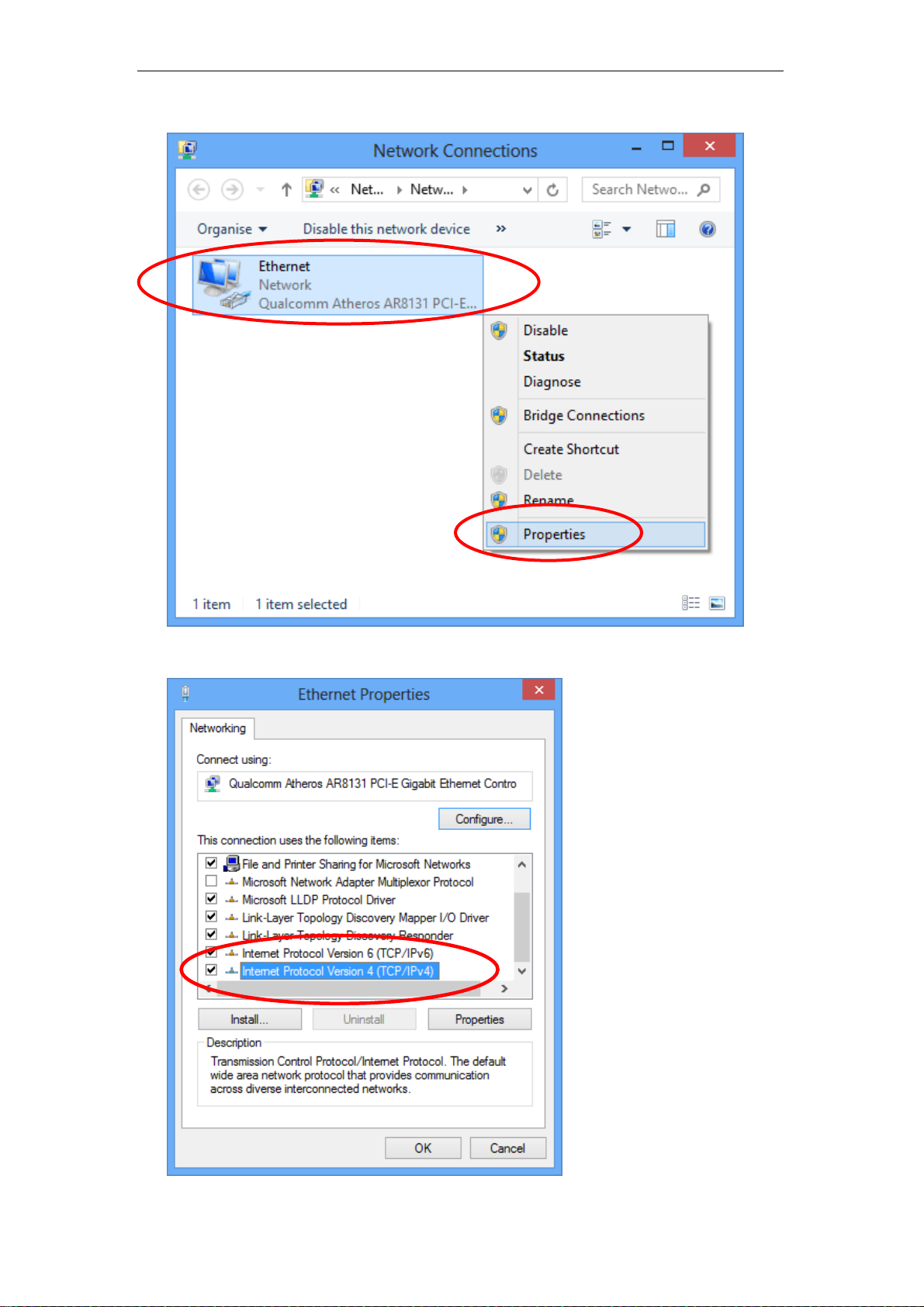
5. Single RIGHT click on “Ethernet", then click "Properties".
6. Double click on "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)".
25
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
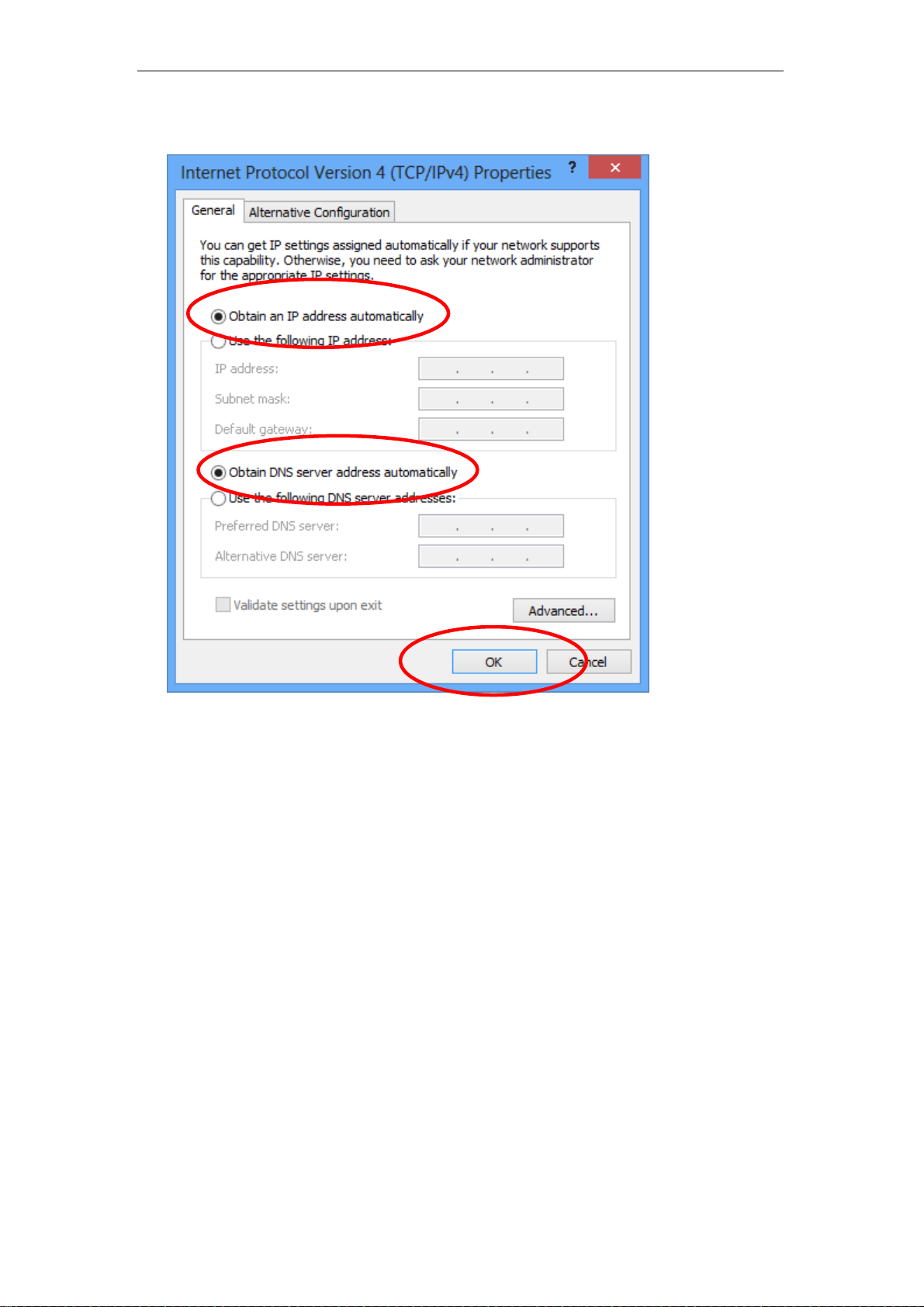
7. Check "Obtain an IP address automatically" and “Obtain DNS server
address automatically” then click on "OK" to continue.
26

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
4 Utility CD execution
Connecting the Hardware
This section describes how to connect the device to the wall
phone port, the power outlet and your computer(s) or network.
1. Before you begin to execute utility CD Installations, please
ensure the VDSL2 Router has been powered on.
2. Please insert the supplied CD into your CD-ROM drive.
3. The CD should auto-start, displaying the window shown in 4.
below. If your CD does not start automatically, go to
Windows Explorer, Select your CD drive and double click
"Autorun.exe".
4. To configure the Internet configuration, please click the "
Advanced Configuration ".
27
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
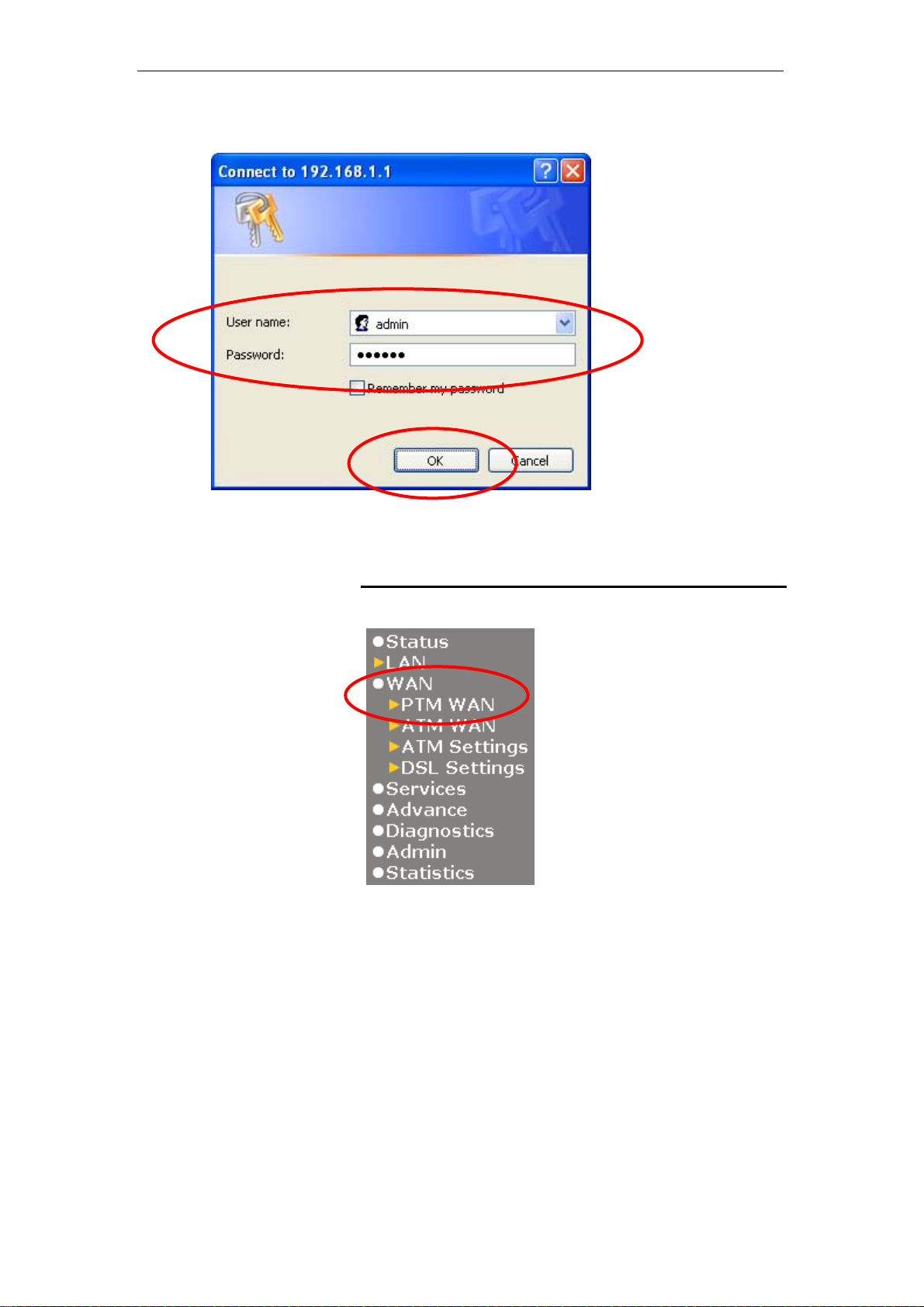
5. Please enter the User Name: admin and Password: admin
and then click on OK button.
VDSL WAN Configuration (VDSL Line User)
1. From the left-hand menu, click on WAN -> PTM WAN.
28

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
Examples
8-1. PPPoE
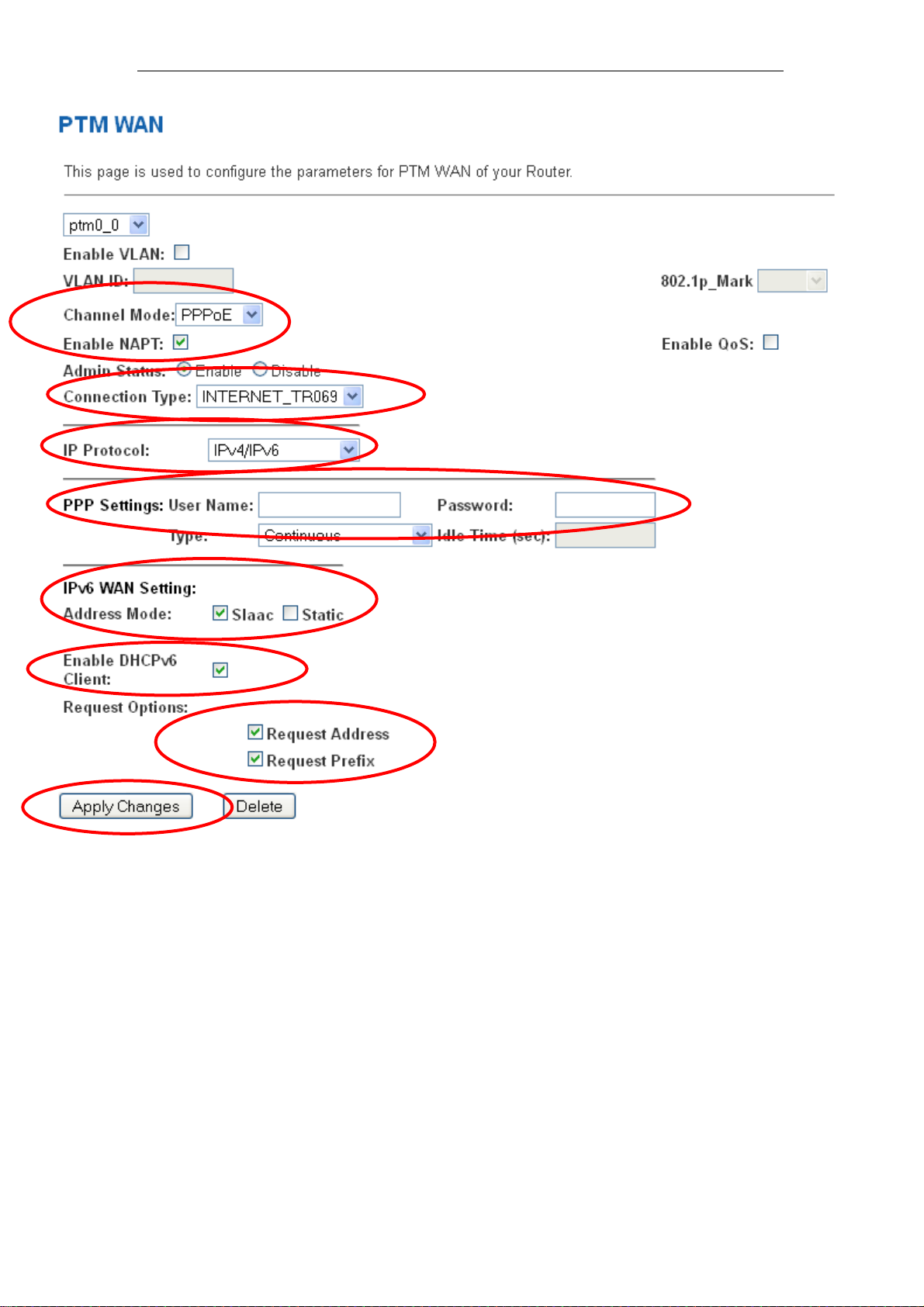
From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select PPPoE setting.
Enable Enable NAPT
From the Connection Type drop-down list, select
INTERNET_TR069 setting.
From the IP Protocol drop-down list, select the IP Protocol, IPv4,
IPv6 or dual stacks IPv4/IPv6 determined by your ISP.
Enter User Name/Password provided by your ISP. Type them in
the relevant boxes.
Configure IPv6 WAN setting determined by your ISP if any.
If you are happy with your settings, click Apply Changes
29
VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
30

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
8-2. Bridged
From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select Bridged setting.
From the Connection Type drop-down list, select
INTERNET_TR069 setting.
If you are happy with your settings, click Apply Changes
Now you can load your PPPoE Client Software onto your PC.
Now you can load your PPPoE Client Software with user name
and password which determined by your ISP onto your PC.
31

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
8-3. IPoE by DHCP
From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select IPoE
Enable Enable NAPT
From the Connection Type drop-down list, select
INTERNET_TR069 setting.
From the IP Protocol drop-down list, select the IP Protocol, IPv4,
IPv6 or dual stacks IPv4/IPv6 determined by your ISP.
From the Type ratio, click DHCP.
Configure IPv6 WAN setting determined by your ISP if any.
If you are happy with your settings, click Apply Changes
32

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
8-4. IPoE by Fixed IP
From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select IPoE setting.
Enable Enable NAPT
From the Connection Type drop-down list, select
INTERNET_TR069 setting.
From the IP Protocol drop-down list, select the IP Protocol, IPv4,
IPv6 or dual stacks IPv4/IPv6 determined by your ISP.
From the Type ratio, click Fixed IP.
Enter Local IP Address, Subnet Mask and Remote IP Address
which was given by Telecom or by your Internet Service
Provider (ISP).
Configure IPv6 WAN setting determined by your ISP if any.
If you are happy with your settings, click Apply Changes
33

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
34

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
From the left-hand Service menu, click on Services -> DHCP.
From the Type ratio, click Set Manually.
Enter DNS setting determined by your ISP.
If you are happy with your settings, click Apply Changes
35

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
Click OK
2. From the left-hand menu, click on Admin -> Commit/Reboot.
3. Click on Commit and Reboot.
4. Click on OK.
36

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
5. System rebooting, Please wait ...
DSL WAN Configuration (ADSL Line User)
1. From the left-hand menu, click on WAN -> ATM WAN.
Examples
8-1. PPPoE
Enter VCI and VPI setting determined by your ISP.
Select the Encapsulation determined by your ISP.
From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select PPPoE setting.
Enable Enable NAPT
From the Connection Type drop-down list, select
INTERNET_TR069 setting.
From the IP Protocol drop-down list, select the IP Protocol, IPv4,
IPv6 or dual stacks IPv4/IPv6 determined by your ISP.
Enter User Name/Password provided by your ISP. Type them in
the relevant boxes.
Configure IPv6 WAN setting determined by your ISP if any.
If you are happy with your settings, click Add
37

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
38

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
8-2. PPPoA
Enter VCI and VPI setting determined by your ISP.
Select the Encapsulation determined by your ISP.
From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select PPPoA setting.
Enable Enable NAPT
From the Connection Type drop-down list, select
INTERNET_TR069 setting.
From the IP Protocol drop-down list, select the IP Protocol, IPv4,
IPv6 or dual stacks IPv4/IPv6 determined by your ISP.
Enter User Name/Password provided by your ISP. Type them in
the relevant boxes.
Configure IPv6 WAN setting determined by your ISP if any.
If you are happy with your settings, click Add
39

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
8-3. Bridged
Enter VCI and VPI setting determined by your ISP.
Select the Encapsulation determined by your ISP.
From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select 1483 Bridged
setting.
From the Connection Type drop-down list, select
INTERNET_TR069 setting.
If you are happy with your settings, click Add
Now you can load your PPPoE Client Software onto your PC.
Now you can load your PPPoE Client Software with user name
and password which determined by your ISP onto your PC.
40

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
8-4. 1483 MER by DHCP
Enter VCI and VPI setting determined by your ISP.
Select the Encapsulation determined by your ISP.
From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select 1483 MER
Enable Enable NAPT
From the Connection Type drop-down list, select
INTERNET_TR069 setting.
From the IP Protocol drop-down list, select the IP Protocol, IPv4,
IPv6 or dual stacks IPv4/IPv6 determined by your ISP.
From the Type ratio, click DHCP.
Configure IPv6 WAN setting determined by your ISP if any.
If you are happy with your settings, click Add
41

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
8-5. 1483 MER by Fixed IP
Enter VCI and VPI setting determined by your ISP.
Select the Encapsulation determined by your ISP.
Enable Enable NAPT
From the Connection Type drop-down list, select
INTERNET_TR069 setting.
From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select 1483 MER
setting.
From the IP Protocol drop-down list, select the IP Protocol, IPv4,
IPv6 or dual stacks IPv4/IPv6 determined by your ISP.
From the Type ratio, click Fixed IP.
Enter Local IP Address, Subnet Mask and Remote IP Address
which was given by Telecom or by your Internet Service
Provider (ISP).
Configure IPv6 WAN setting determined by your ISP.
If you are happy with your settings, click Add
42

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
43

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
From the left-hand Service menu, click on Services -> DHCP.
From the Type ratio, click Set Manually.
Enter DNS setting determined by your ISP.
If you are happy with your settings, click Apply Changes
44

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
Click OK
2. From the left-hand menu, click on Admin -> Commit/Reboot.
3. Click on Commit and Reboot.
4. Click on OK.
45

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
5. System rebooting, Please wait ...
6. Click on " Exit " to exit this program.
7. Now, the VDSL2 Router has been configured completely,
and suitable for Internet Connections.
46

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
5 Getting Started with the Web pages
The VDSL2 Router includes a series of Web pages that provide
an interface to the software installed on the device. It enables
you to configure the device settings to meet the needs of your
network. You can access it through your web browser from any
PC connected to the device via
Accessing the Web pages
To access the Web pages, you need the following:
A PC or laptop connected to the LAN port on the device.
A web browser installed on the PC. The minimum browser
version requirement is Internet Explorer v4 or Netscape v4.
For the best display quality, use latest version of Internet
Explorer, Netscape or Mozilla Firefox.From any of the LAN
computers, launch your web browser, type the following
URL in the web address (or location) box, and press [Enter]
on your keyboard:
http://192.168.1.1
the LAN ports.
The Status homepage for the web pages is displayed:
47

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
Figure 1: Homepage
The first time that you click on an entry from the lefthand menu, a login box is displayed. You must enter
your username and password to access the pages.
A login screen is displayed:
48

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
Figure 2: Login screen
1. Enter your user name and password. The first time you log
into the program, use these defaults:
User Name:
Password:
admin
admin
You can change the password at any time or you can configure your
Note
Note
device so that you do not need to enter a password. See Password.
2. Click on OK. You are now ready to configure your device.
This is the first page displayed each time you log in to the Web
pages. This page contains links to the following pages:
Addressing; links to the Addressing page that controls your
device’s network address. See Addressing.
Internet Access; links to the Internet Access page that
controls how your device connects to the Internet. See
Internet Access.
If you receive an error message or the Welcome page is not
displayed, see Troubleshooting Suggestions.
Testing your Setup
Once you have connected your hardware and configured your
PCs, any computer on your LAN should be able to use the
device’s DSL connection to access the Internet.
To test the connection, turn on the device, wait for 30 seconds
and then verify that the LEDs are illuminated as follows:
49

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
Table 1. LED Indicators
LED Behavior
POWER
ETH
Link
INTERNET
Solid green to indicate that the device is turned on. If this
light is not on, check the power cable attachment.
Flashing on/off while the device is booting. After about 1015 seconds, solid green to indicate that the device can
communicate with your LAN.
Flashing on/off while data is being transmitted. Solid green
to indicate that the device has successfully established a
connection with your ISP.
Flashing on/off while data is being transferred. Solid green
when a valid IP address has been assigned to the device
by the ISP.
If the LEDs illuminate as expected, test your Internet connection
from a LAN computer. To do this, open your web browser, and
type the URL of any external website (such as
http://www.yahoo.com
). The LED labeled INTERNET should
blink rapidly and then appear solid as the device connects to the
site.
WARNING
If the LEDs do not illuminate as expected, you may need to
configure your Internet access settings using the information
provided by your ISP. For details, see Internet Access. If the
LEDs still do not illuminate as expected or the web page is not
displayed, see Troubleshooting Suggestions or contact your
ISP for assistance.
Default device settings
In addition to handling the DSL connection to your ISP, the DSL
Modem can provide a variety of services to your network. The
device is preconfigured with default settings for use with a
typical home or small office network.
The table below lists some of the most important default settings;
these and other features are described fully in the subsequent
chapters. If you are familiar with network configuration, review
these settings to verify that they meet the needs of your network.
Follow the instructions to change them if necessary. If you are
unfamiliar with these settings, try using the device without
modification, or contact your ISP for assistance.
We strongly recommend that you conta ct your ISP prior to
changing the default configuration.
Option Default Setting Explanation/Instructions
LINE Port IP
Address
50
Unnumbered interface:
192.168.1.1
Subnet mask:
255.255.255.255
This is the temporary public IP address of the WAN
port on the device. It is an unnumbered interface that
is replaced as soon as your ISP assigns a ‘real’ IP
address. See Internet Access.

VDSL2 Router User’s Guide
Option Default Setting Explanation/Instructions
LAN Port
IP Address
Assigned static IP address:
192.168.1.1
Subnet mask:
This is the IP address of the LAN port on the device.
The LAN port connects the device to your Ethernet
network. Typically, you will not need to change this
address. See LAN.
255.255.255.0
DHCP (Dynamic
Host Configuration
Protocol)
NAT (Network
Address Translation)
DHCP server enabled with the
following pool of addresses:
192.168.1.33
through
192.168.1.254
NAT enabled
The VDSL2 Router maintains a pool of private IP
addresses for dynamic assignment to your LAN
computers. To use this service, you must have set up
your computers to accept IP information dynamically,
as described in Services -> DHCP Settings.
Your computers’ private IP addresses (see DHCP
above) will be translated to your public IP address
whenever the PCs access the Internet. See Services
-> Firewall.
51


User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
6 Overview
The Overview page displays useful information about the setup
of your device, including:
details of the device’s Internet access settings
version information about your device
To display this page:
From the left menu, click on Status - Devic e. The following page
is displayed:
Figure 3: Overview page
The information displayed on this page is explained in detail in
the following sections.
53

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Internet access settings
This section displays details of the settings that allow your
device to access the Internet. These details include:
IP address and
subnet mask:
Default gateway: The address of the ISP server through
DNS servers: The Domain Name System (DNS)
Your ISP assigns all of these settings. In most cases, you will
not need to make changes to these settings in order for your
Internet connection to work. If your ISP does ask you to change
any of these settings, follow the instructions for manually
configuring your device in Internet Access.
The IP address and subnet mask
assigned to your WAN interface. This
address is used temporarily until your
ISP assigns a real IP address (via DHCP
or PPP – see Internet Access.
which your Internet connection will be
routed.
servers used by your ISP to map domain
names to IP addresses.
About VDSL2 Router
This section displays details of your device’s hardware and
firmware versions. If you need to contact your ISP’s support
team, they may need to know which hardware/firmware
versions you are using in order to answer your query.
Your hardware version details contain information about the
make and model of your device and its exact hardware
components.
Your firmware version details contain information about the
software program running on your device. They then make the
latest updated version available to you via the Internet. For
details of how to update your firmware, see Admin -> Upgrade
Firmware.
54

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
7 Status
You can view statistics on the processing of IP packets on the
networking interfaces. You will not typically need to view this
data, but you may find it helpful when working with your ISP to
diagnose network and Internet data transmission problems.
Device Info
This page shows the current status and some basic settings of
the device.
1. From the left Status menu, click on Device. The following
page is displayed:
2. To display updated statistics showing any new data since
you opened this page, click Refresh.
55

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
IPv6
This page shows the ADSL line statistic information.
1. From the left Status menu, click on IPv6 The following page
is displayed:
2. To display updated statistics showing any new data since
you opened this page, click Refresh.
56

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
8 Local Network Configuration
The Addressing page displays information about your LAN IP
address and allows you to change the address and subnet
mask assigned to your device.
You should only change the addressing details if your ISP asks
Note
you to, or if you are familiar with network configuration. In mo st
cases, you will not need to make any changes to this
configuration.
Changing the LAN IP address and subnet mask
1. From the left menu, click on LAN. The following page is
displayed:
57

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
2. From the left-hand LAN menu, click on LAN.
3. Type a new IP Address and Subnet Mask.
4. Click Apply Changes.
5. The primary IP address is being changed to 10.0.0.2
netmask 255.255.255.0. Then please go to http://10.0.0.2 to
continue. Your browser communicates with the web server
via the LAN connection, and changing the IP address may
disrupt this.
You may also need to renew your DHCP lease:
Windows 95/98
a. Select Run... from the Start menu.
b. Enter winipcfg and click OK.
c. Select your ethernet adaptor from the pull-down menu
d. Click Release All and then Renew All.
e. Exit the winipcfg dialog.
Windows NT/Windows 2000/Windows XP
a. Bring up a command window.
b. Type ipconfig /release in the command window.
c. Type ipconfig /renew.
d. Type exit to close the command window.
Linux
a. Bring up a shell.
b. Type pump -r to release the lease.
c. Type pump to renew the lease.
58

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Note
If you change the LAN IP address of the device while conne cted
through your Web browser, you will be disconnected. You must
open a new connection by entering your new LAN IP address as
the URL.
Adding the Secondary LAN IP address and subnet
mask
1. From the left-hand LAN menu, click on LAN.
2. Check on Secondary IP.
3. Type the Secondary IP Address and Subnet Mask.
4. Click Apply Changes.
5. Change setting successfully!
6. Click OK.
59

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Change IP Pool Range and Subnet mask
1. From the left-hand Services menu, click on DHCP.
60

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
2. Change the IP Pool Range/Subnet Mask and then click
Apply Changes button.
3. Change setting successfully!
4. Click OK.
61

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
9 PTM WAN
This chapter describes how to configure the way that your
device connects to the Internet. Your ISP determines what type
of Internet access you should use and provides you with any
information that you need in order to configure the Internet
access to your device.
The device supports four methods of obtaining the WAN IP
address:
Option Description
Bridged Choose this option to have the device to be a AP
IPoE Fixed
IP
IpoE DHCP
Client
PPPoE Choose this option if you are connected to the Internet through a DSL line
DS-Lite Choose this option if you are connected to the DS-Lite Server
6rd Choose this option if you are connected to the 6rd Server
Choose this option if you are a leased line user with a fixed IP address.
Choose this option if you are connected to the Internet through a Cable
modem line.
62

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
5. From the left-hand Network Settings -> PTM WAN menu.
The following page is displayed:
Option Description
Enable VLAN Enable or disable VLAN
VLAN ID Enter the VLAN ID
63

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
802.1p_Mark Choose the 802.1p_Mark
Channel
Bridged Choose this option to have the device to be a AP
Mode
IPoE Fixed IP Choose this option if you are a leased line user with a
fixed IP address.
IPoE DHCP Client Choose this option if you are connected to the Internet
through a Cable modem line.
PPPoE Choose this option if you are connected to the Internet
through a DSL modem line
DS-Lite Choose this option if you are connected to the DS-Lite
Server
6rd Choose this option if you are connected to the 6rd
Server
Enable NAPT Enable or disable NAPT
Enable IGMP Enable or disable IGMP
Enable Default Route Enable or disable Default Route
Enable Admin Status Enable or disable Admin Status
IP Protocol IPv4/IPv6, IPv4 or IPv6
Local IP Address Check with your ISP provider
Subnet Mask Check with your ISP provider
Remote IP Address Check with your ISP provider
User Name User name for PPPoE registration recognized by the
Internet service provider
Password Password for PPPoE registration recognized by the
Internet service provider
Connection
Type
Continuous The connection is always on
Connect on
Demand
Enter the minutes after which the session must be
disconnected, if no activity takes place
Manual Manually connect
Idle Time Enter the minutes after which the session must be
disconnected
IPv6 WAN Address Mode Check with your ISP provider
Enable DHCPv6 Client Check with your ISP provider
Port Mapping Port Mapping configuration
64

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Configuring PTM WAN IPoE Static IP connection
If you are a leased line user with a fixed IP address, enter in the
IP address, subnet mask, gateway address, and DNS (domain
name server) address(es) provided to you by your ISP.
If your ISP wants you to connect to the Internet using Static IP,
follow the instructions below.
6. From the left-hand WAN Settings -> PTM WAN menu. The
following page is displayed:
7. From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select IPoE setting.
8. Enable Enable NAPT
9. Select proper Connection Type
10. Enable Fixed IP
11. Enter Local IP Address, WAN Subnet Mask and Remote IP
Address which was given by Telecom or by your Internet
Service Provider (ISP).
12. Click Apply Changes.
65

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
66

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
13. From the left-hand menu, click on Services -> DHCP.
67

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
14. From the Type ratio, click Set Manually.
15. Enter DNS setting determined by your ISP.
16. If you are happy with your settings, click Apply Changes
17. Click OK.
68

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Configuring PTM WAN IPoE DHCP Client
connection
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), Dynamic IP (Get
WAN IP Address automatically). If you are connected to the
Internet through a Cable modem line, then a dynamic IP will be
assigned.
If your ISP wants you to connect to the Internet using DHCP
Client, follow the instructions below.
1. From the left-hand WAN Settings -> PTM WAN menu. The
following page is displayed:
2. From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select IPoE setting.
3. Enable Enable NAPT
4. Select proper Connection Type
5. Enable DHCP
6. Click Apply Changes.
69

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Configuring PTM WAN PPPoE connection
If your ISP’s Internet service uses PPPoE you need to set up a
PPP login account. The first time that you login to the Internet,
your ISP will ask you to enter a username and password so
they can check that you are a legitimate, registered Internet
service user. Your device stores these authentication details, so
you will not have to enter this username and password every
time you login.
If your ISP wants you to connect to the Internet using PPP,
follow the instructions below.
1. From the left-hand WAN Settings -> PTM WAN menu. The
following page is displayed:
2. From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select PPPoE
setting.
3. Enable Enable NAPT
4. Select proper Connection Type
5. Enter User Name/Password provided by your ISP. Type
them in the relevant boxes.
6. Click Apply Changes.
70

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
71

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Configuring PTM WAN DS-Lite connection
If you are a leased line with DS-Lite user with a fixed IP address,
enter in the IP address, subnet mask, gateway address, and
DNS (domain name server) address(es) provided to you by
your ISP.
If your ISP wants you to connect to the Internet using DS-Lite,
follow the instructions below.
1. From the left-hand WAN Settings -> PTM WAN menu. The
following page is displayed:
2. From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select DS-Lite
setting.
3. Enable Enable NAPT
4. Select proper Connection Type
5. Enter Local IPv6 Address, Remote IPv6 End point Address
and Gateway IPv6 Address which was given by Telecom or
by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
6. Click Apply Changes.
72

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Configuring PTM WAN 6rd connection
If you are a leased line with 6rd user with a fixed IP address,
enter in the IP address, subnet mask, gateway address, and
DNS (domain name server) address(es) provided to you by
your ISP.
If your ISP wants you to connect to the Internet using 6rd, follow
the instructions below.
1. From the left-hand WAN Settings -> PTM WAN menu. The
following page is displayed:
2. From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select 6rd setting.
3. Enable Enable NAPT
4. Select proper Connection Type
5. Enter Board Router v4 Address, 6rd IPv4 Mask Len, 6rd
Prefix (EX:"2001:db8::") and 6rd Prefix length which was
given by Telecom or by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
6. Click Apply Changes.
73

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
10 ATM WAN
This chapter describes how to configure the way that your
device connects to the Internet. Your ISP determines what type
of Internet access you should use and provides you with any
information that you need in order to configure the Internet
access to your device.
Your device needs the following address information in order to
access the Internet:
ATM PVC To configure ATM PVC, enter the VPI
and VCI provided by ISP. Select the
Service Type Index, Service Category
and enter the following information:
Peak Cell Rate
Sustainable Cell Rate
Maximum Burst Size
Channel Mode To configure the connection type, select
the protocol and encapsulation type as
indicated by ISP. Supported Protocol
types are:
RFC1483 Bridged
RFC1483 MER
PPPoE
PPPoA
RFC1483 Routed
Supported Encapsulation types are:
VCMUX
LLC/SNAP
WAN IP Settings To configure WAN IP settings, enter the
information as indicated by ISP.
Enable/Disable the Access Concentrator
option. Either enter the WAN IP or select
the option to automatically obtain IP
address.
Check as applicable the following two
options:
Enable NAT
Add default Route
Broadband
Username and
Password
74
To configure Broadband Username and
Password, enter the user name and
password details. Also set the session
establishment condition as one of the
following:
Continuous

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Connect on demand. Enter the
minutes after which the session
must be disconnected, if no
activity takes place.
Manual. Enter the minutes after
which the session must be
disconnected, if no activity takes
place.
In most cases, you will not need to configure your device with
these addresses because your ISP is likely to use an Internet
access type which automatically assigns addresses to your
device. For more information, see Types of Internet Access.
Types of DSL WAN Internet Access
The types of DSL WAN Internet access available are as follows:
PPP Internet access – your device uses a Point to Point
Protocol (PPP) to carry data between your ISP and your
computer. To use PPP Internet access, you must enter a
PPP login username and password the first time to log
on. The IP addresses required to access your ISP’s Internet
service are automatically configured.
Your device supports PPPoE (over Ethernet).
PPP Internet access – your device uses a Point to Point
Protocol (PPP) to carry data between your ISP and your
computer. To use PPP Internet access, you must enter a
PPP login username and password the first time to log
on. The IP addresses required to access your ISP’s Internet
service are automatically configured.
Your device supports PPPoA (over ATM).
Bridged Internet access – your device uses a Bridge mode
with your PPPoE Client Software to carry data between
your ISP and your computer. To use Bridged Internet
access with your PPPoE Client Software, you must enter a
PPP login username and password the first time to log
on. The IP addresses required to access your ISP’s Internet
service are automatically configured.
Your device supports RFC 1483 Bridged Mode).
75

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Configuring your PPPoE DSL connection
If your ISP’s Internet service uses PPPoE you need to set up a
PPP login account. The first time that you login to the Internet,
your ISP will ask you to enter a username and password so
they can check that you are a legitimate, registered Internet
service user. Your device stores these authentication details, so
you will not have to enter this username and password every
time you login.
Your ISP may also tell you to set unique path and circuit
numbers (called VPI and VCI) in order to connect your device to
the ISP’s Internet service. In most cases, your device will use
default settings, so you may not need to enter these values.
Note
Your ISP will provide you with the login details and VPI/VCI
values necessary to set up a PPP login account.
If your ISP wants you to connect to the Internet using PPP,
follow the instructions below.
76

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
7. From the left WAN menu, click on ATM WAN. The following
page is displayed:
8. Enter VCI and VPI setting determined by your ISP.
9. Select the Encapsulation determined by your ISP.
10. From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select PPPoE
setting.
11. Enable Enable NAPT
12. Select proper Connection Type
13. From the IP Protocol drop-down list, select the IP Protocol,
IPv4, IPv6 or dual stacks IPv4/IPv6 determined by your ISP.
14. Enter User Name/Password provided by your ISP. Type
them in the relevant boxes.
15. Configure IPv6 WAN setting determined by your ISP.
16. If you are happy with your settings, click Add
17. Your configuration is complete.
18. Now you are ready to Surf the Internet !!!
77

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Configuring your PPPoA DSL connection
If your ISP’s Internet service uses PPPoA you need to set up a
PPP login account. The first time that you login to the Internet,
your ISP will ask you to enter a username and password so
they can check that you are a legitimate, registered Internet
service user. Your device stores these authentication details, so
you will not have to enter this username and password every
time you login.
Your ISP may also tell you to set unique path and circuit
numbers (called VPI and VCI) in order to connect your device to
the ISP’s Internet service. In most cases, your device will use
default settings, so you may not need to enter these values.
Note
Your ISP will provide you with the login details and VPI/VCI
values necessary to set up a PPP login account.
If your ISP wants you to connect to the Internet using PPP,
follow the instructions below.
1. From the left WAN menu, click on ATM WAN. The following
page is displayed:
78

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
2. Enter VCI and VPI setting determined by your ISP.
3. Select the Encapsulation determined by your ISP.
4. From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select PPPoA
setting.
5. Enable Enable NAPT
6. Select proper Connection Type
7. From the IP Protocol drop-down list, select the IP Protocol,
IPv4, IPv6 or dual stacks IPv4/IPv6 determined by your ISP.
8. Enter User Name/Password provided by your ISP. Type
them in the relevant boxes.
9. Configure IPv6 WAN setting determined by your ISP.
10. If you are happy with your settings, click Add
11. Your configuration is complete.
12. Now you are ready to Surf the Internet !!!
79

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Configuring your Bridged DSL connection
1. From the left WAN menu, click on ATM WAN. The following
page is displayed:
2. Enter VCI and VPI setting determined by your ISP.
3. Select the Encapsulation determined by your ISP.
4. From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select 1483
Bridged setting.
5. Select proper Connection Type
6. If you are happy with your settings, click Add
7. Now you can load your PPPoE Client Software onto your
PC.
8. Now you can load your PPPoE Client Software with user
name and password which determined by your ISP onto
your PC.
80

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Configuring your 1483 MER by DHCP
1. From the left WAN menu, click on ATM WAN. The following
page is displayed:
2. Enter VCI and VPI setting determined by your ISP.
3. Select the Encapsulation determined by your ISP.
4. From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select 1483 MER
setting.
5. Enable Enable NAPT
6. Select proper Connection Type
7. From the IP Protocol drop-down list, select the IP Protocol,
IPv4, IPv6 or dual stacks IPv4/IPv6 determined by your ISP.
8. From the Type ratio, click DHCP.
9. IPv6 WAN setting determined by your ISP.
10. If you are happy with your settings, click Add
11. Your configuration is complete.
12. Now you are ready to Surf the Internet !!!
Configuring your 1483 MER by Fixed IP
1. From the left WAN menu, click on ATM WAN. The following
page is displayed:
81

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
2. Enter VCI and VPI setting determined by your ISP.
3. Select the Encapsulation determined by your ISP.
4. From the Channel Mode drop-down list, select 1483 MER
setting.
5. Enable Enable NAPT
6. Select proper Connection Type
7. From the IP Protocol drop-down list, select the IP Protocol,
IPv4, IPv6 or dual stacks IPv4/IPv6 determined by your ISP.
8. From the Type ratio, click Fixed IP.
9. Enter Local IP Address, Subnet Mask and Remote IP
Address which was given by Telecom or by your Internet
Service Provider (ISP).
10. IPv6 WAN setting determined by your ISP.
11. If you are happy with your settings, click Add
1. From the left Service menu, click on DHCP.
2. Check on Set Manually ratio.
3. Enter DNS setting determined by your ISP.
4. Click Apply Changes button.
82

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
5. Click OK button.
6. Your configuration is complete.
7. Now you are ready to Surf the Internet !!!
ATM Settings
The page is for ATM PVC QoS parameters setting. The DSL
device support 4 QoS mode —CBR/rt-VBR/nrt-VBR/UBR.
1. From the left-hand WAN menu, click on ATM. The following
page is displayed:
83

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Field Description
84

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
VPI
VCI
QoS
PCR
SCR
MBS
Virtual Path Identifier. This is read-only field and is
selected on the Select column in the Current ATM VC
Table.
Virtual Channel Identifier. This is read-only field and is
selected on the Select column in the Current ATM VC
Table. The VCI, together with VPI, is used to identify
the next destination of a cell as it passes through to the
ATM switch.
Quality of Server, a characteristic of data transmission
that measures how accurately and how quickly a
message or data is transferred from a source host to a
destination host over a network. The four QoS options
are:
−UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate): When UBR is selected,
the SCR and MBS fields are disabled.
−CBR (Constant Bit Rate): When CBR is selected, the
SCR and MBS fields are disabled.
−nrt-VBR (non-real-time Variable Bit Rate): When nrtVBR is selected, the SCR and MBS fields are enabled.
−rt-VBR (real-time Variable Bit Rate): When rt-VBR is
selected, the SCR and MBS fields are enabled.
Peak Cell Rate, measured in cells/sec., is the cell rate
which the source may never exceed.
Sustained Cell Rate, measured in cells/sec., is the
average cell rate over the duration of the connection.
Maximum Burst Size, a traffic parameter that specifies
the maximum number of cells that can be transmitted
at the peak cell rate.
Function Button Description
Apply Changes
Undo Discard your settings.
Set new PVC OoS mode for the selected PVC. New
parameters will take effect after save into flash
memory and reboot the system. See section “Admin”
for save details.
85

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
DSL Settings
The DSL setting page allows you to select any combination of
DSL training modes.
1. From the left-hand WAN menu, click on DSL Settings. The
following page is displayed:
86

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Field Description
ADSL modulation Choose prefered xdsl standard protocols.
AnnexL Option Enable/Disable ADSL2/ADSL2+ Annex L capability.
AnnexM Option Enable/Disable ADSL2/ADSL2+ Annex M capability.
VDSL2
G.lite : G.992.2 Annex A
G.dmt : G.992.1 Annex A
T1.413 : T1.413 issue #2
ADSL2 : G.992.3 Annex A
ADSL2+ : G.992.5 Annex A
Choose prefered xdsl standard protocols:
8a/8b/8c/8d/12a/12b/17a/30a
ADSL Capability “Bitswap Enable” : Enable/Disable bitswap capability.
Function Button Description
Tone Mask
Apply Changes
“SRA Enable” : Enable/Disable SRA (seamless rate
adaptation) capability.
Choose tones to be masked. Mased tones will not
carry any data.
Click to save the setting to the configuration and the
modem will be retrained.
87

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
11 DHCP Settings
You can configure your network and DSL device to use the
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). This page
provides DHCP instructions for implementing it on your network
by selecting the role of DHCP protocol that this device wants to
play. There are two different DHCP roles that this device can act
as: DHCP Serve and DHCP Relay. When acting as DHCP
server, you can setup the server parameters at the DHCP
Server page; while acting as DHCP Relay, you can setup the
relay at the DHCP Relay page.
DHCP Server Configuration
1. From the left-hand Services menu, click on DHCP.
2. From DHCP Mode check ratio, click on DHCP Server.
3. Type a new IP Pool Range, Subnet Mask, Max Lease Time,
Domain Name and Gateway Address.
4. Click on Apply Changes.
88

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Field Description
IP Pool Range Specify the lowest and highest addresses in the pool.
Max Lease Time
The Lease Time is the amount of time that a network
user is allowed to maintain a network connection to the
device using the current dynamic IP address. At the
end of the Lease Time, the lease is either renewed or
a new IP is issued by the DHCP server. The amount of
time is in units of seconds. The default value is 86400
seconds (1 day). The value –1 stands for the infinite
lease.
Domain Name
A user-friendly name that refers to the group of hosts
(subnet) that will be assigned addresses from this pool.
Function Button Description
Apply Changes
MAC-Based
Assignment
Set new DHCP server configuration. New parameters
will take effect after save into flash memory and reboot
the system. See section “Admin” for save details.
Configure the static IP base on MAC Address. You can
assign/delete the static IP.
5. Click OK button.
89

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
DHCP Relay Configuration
1. From the left-hand Services menu, click on DHCP.
2. From DHCP Mode check ratio, click on DHCP Relay.
3. Type DHCP server IP Addresses.
4. Click on Apply Changes.
Field Description
DHCP Server
Address
Function Button Description
Apply Changes
5. Click OK button.
6. You need to renew your DHCP lease:
Windows 95/98
Specify the IP address of your ISP’s DHCP server.
Requests for IP information from your LAN will be
passed to the default gateway, which should route the
request appropriately.
Set new DHCP server configuration. New parameters
will take effect after save into flash memory and reboot
the system. See section “Admin” for save details.
a. Select Run... from the Start menu.
b. Enter winipcfg and click OK.
c. Select your ethernet adaptor from the pull-down menu
d. Click Release All and then Renew All.
e. Exit the winipcfg dialog.
Windows NT/Windows 2000/Windows XP
90

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
a. Bring up a command window.
b. Type ipconfig /release in the command window.
c. Type ipconfig /renew.
d. Type exit to close the command window.
Linux
a. Bring up a shell.
b. Type pump -r to release the lease.
c. Type pump to renew the lease.
DHCP None Configuration
1. From the left-hand Services menu, click on DHCP.
2. From DHCP Mode check ratio, click on None.
3. Click on Apply Changes.
Function Button Description
Apply Changes
Set new DHCP server configuration. New parameters
will take effect after save into flash memory and reboot
the system. See section “Admin” for save details.
4. Click OK button.
91

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
12 DHCPv6 Settings
You can configure your network and DSL device to use the
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). This page
provides DHCP instructions for implementing it on your network
by selecting the role of DHCP protocol that this device wants to
play. There are two different DHCP roles that this device can act
as: DHCP Serve and DHCP Relay. When acting as DHCP
server, you can setup the server parameters at the DHCP
Server page; while acting as DHCP Relay, you can setup the
relay at the DHCP Relay page.
DHCP Server (Manual) Configuration
1. From the left-hand Advance menu, click on IPv6 - DHCPv6.
2. From DHCPv6 Mode check ratio, click on DHCP Server
(Manual).
3. Type a new IP Pool Range and Prefix Length.
4. Click on Apply Changes.
92

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
93

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
Field Description
IP Pool Range Specify the lowest and highest addresses in the pool.
Prefix Length Configure Prefix Length
Valid Lifetime Configure Valid Lifetime
Preferred
Lifetime
Renew Time Configure Renew Time
Configure Preferred Lifetime
Rebind Time Configure Rebind Time
Client DUID Configure Client DUID
Domain Name
A user-friendly name that refers to the group of hosts
(subnet) that will be assigned addresses from this pool.
Function Button Description
Apply Changes
Set new DHCP server configuration. New parameters
will take effect after save into flash memory and reboot
the system. See section “Admin” for save details.
5. Click OK button.
94

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
DHCP Server (Auto) Configuration
1. From the left-hand Services menu, click on DHCPv6.
2. From DHCPv6 Mode check ratio, click on DHCP Server
(Auto).
3. Click on Apply Changes.
Function Button Description
Apply Changes
Set new DHCP server configuration. New parameters
will take effect after save into flash memory and reboot
the system. See section “Admin” for save details.
4. Click OK button.
95

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
DHCP Relay Configuration
1. From the left-hand Services menu, click on DHCP.
2. From DHCPv6 Mode check ratio, click on DHCP Relay.
3. Configure the Upper Interface (server link).
4. Click on Apply Changes.
Field Description
Upper Interface Configure the upper interface (server link)
Function Button Description
Apply Changes
Set new DHCP server configuration. New parameters
will take effect after save into flash memory and reboot
the system. See section “Admin” for save details.
5. Click OK button.
6. You need to renew your DHCP lease:
Windows 95/98
a. Select Run... from the Start menu.
b. Enter winipcfg and click OK.
c. Select your ethernet adaptor from the pull-down menu
d. Click Release All and then Renew All.
e. Exit the winipcfg dialog.
Windows NT/Windows 2000/Windows XP
96

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
a. Bring up a command window.
b. Type ipconfig /release in the command window.
c. Type ipconfig /renew.
d. Type exit to close the command window.
Linux
a. Bring up a shell.
b. Type pump -r to release the lease.
c. Type pump to renew the lease.
DHCP None Configuration
1. From the left-hand Services menu, click on DHCP.
2. From DHCPv6 Mode check ratio, click on None.
3. Click on Apply Changes.
Function Button Description
Apply Changes
Set new DHCP server configuration. New parameters
will take effect after save into flash memory and reboot
the system. See section “Admin” for save details.
4. Click OK button.
97

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
13 DNS Configuration
This page is used to configure the DNS server ip addresses for
DNS Relay.
DHCP Server Configuration - Attain DNS
Automatically
1. From the left Services menu, click on DNS -> DNS Server.
2. From check ratio, click on Attain DNS Automatically.
3. Click on Apply Changes.
Field Description
Attain DNS
Automatically
Set DNS
Manually
Function Button Description
Apply Changes
4. Click OK button.
Select this item if you want to use the DNS servers
obtained by the WAN interface via the autoconfiguration mechanism.
Select this item to configure up to three DNS IP
addresses.
Set new DNS relay configuration. New parameters will
take effect after save into flash memory and reboot the
system. See section “Admin” for save details.
98

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
DHCP Server Configuration - Set DNS Manually
1. From the left Services menu, click on DNS -> DNS Server.
2. From check ratio, click on Set DNS Manually.
3. Enter the IP Address of DNS.
4. Click on Apply Changes.
Field Description
IPv4 WAN
Interface Binding
DNSv4 1/2/3
IPv6 WAN
Interface Binding
DNSv6 1/2/3
Enable or disable IPv4 WAN Interface Binding
Select this item to configure up to three DNSv4 IP
addresses.
Enable or disable IPv6 WAN Interface Binding
Select this item to configure up to three DNSv6 IP
addresses.
Function Button Description
Apply Changes
Set new DNS relay configuration. New parameters will
take effect after save into flash memory and reboot the
system. See section “Admin” for save details.
99

User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
5. Click OK button.
100
 Loading...
Loading...