Elettronika TXUP3500 User Manual
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
Section 4 - Diagram
Contents:
- Cable diagram
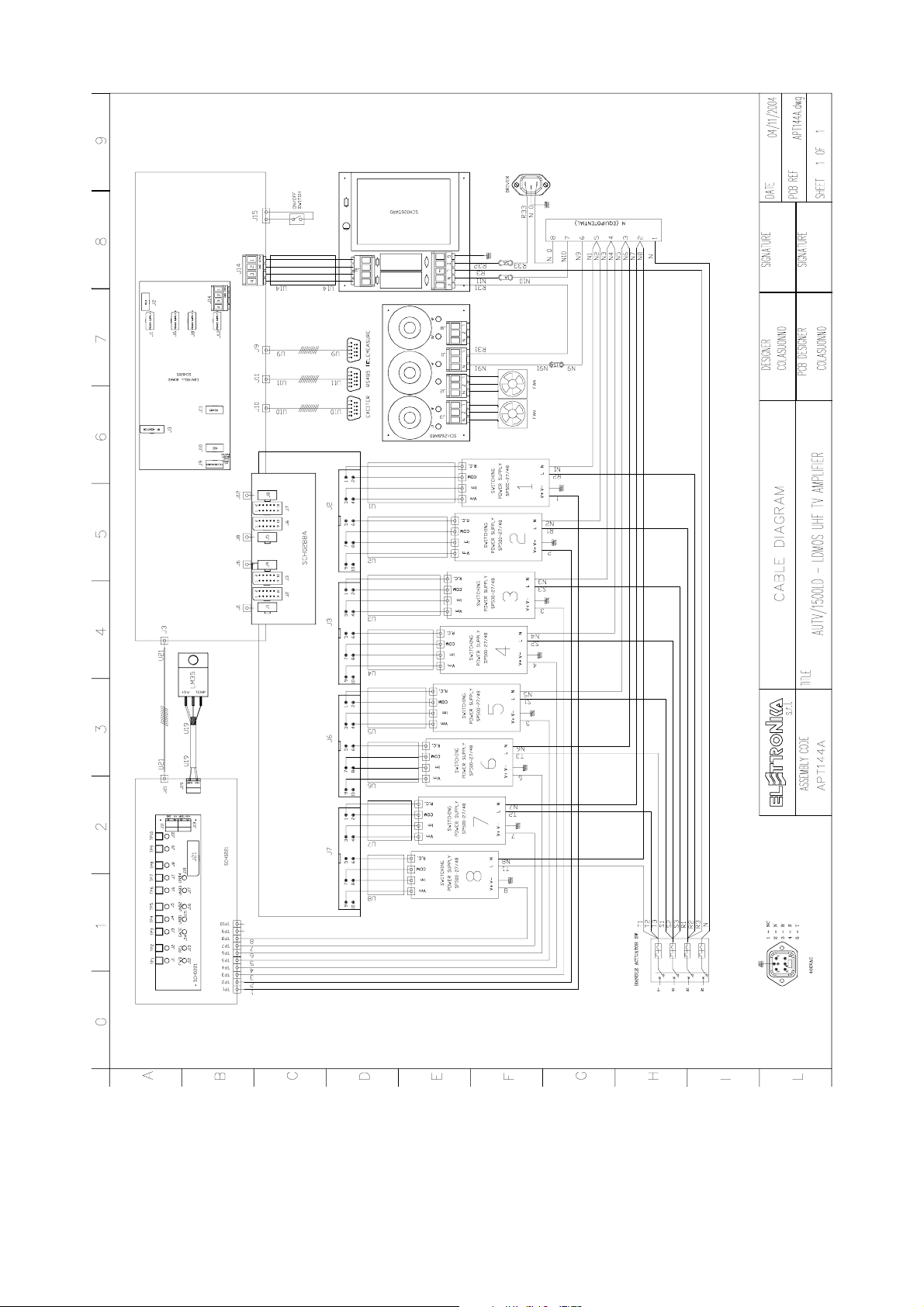
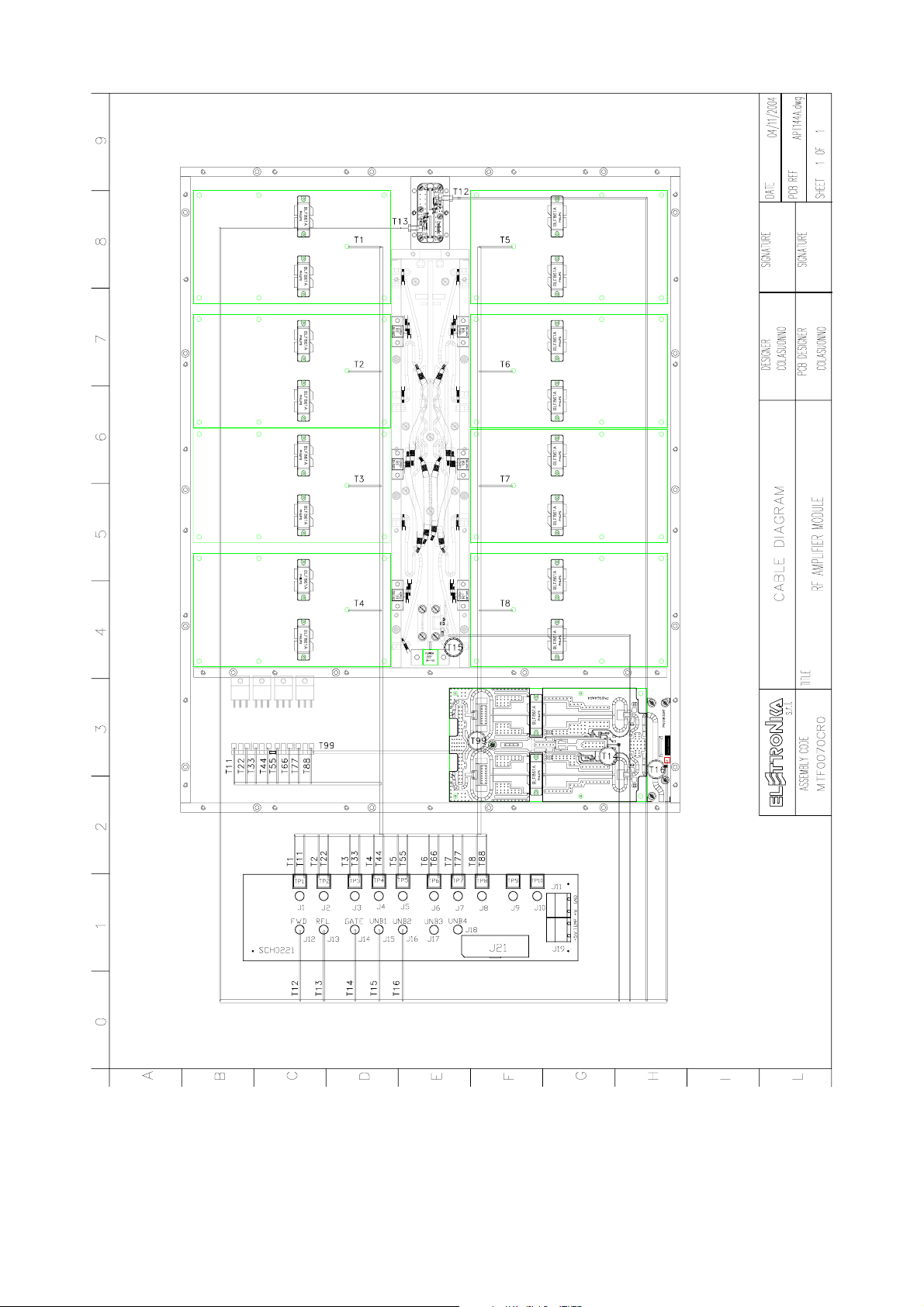
- MTF0070CR0 RF Amplifier module Cable Diagram
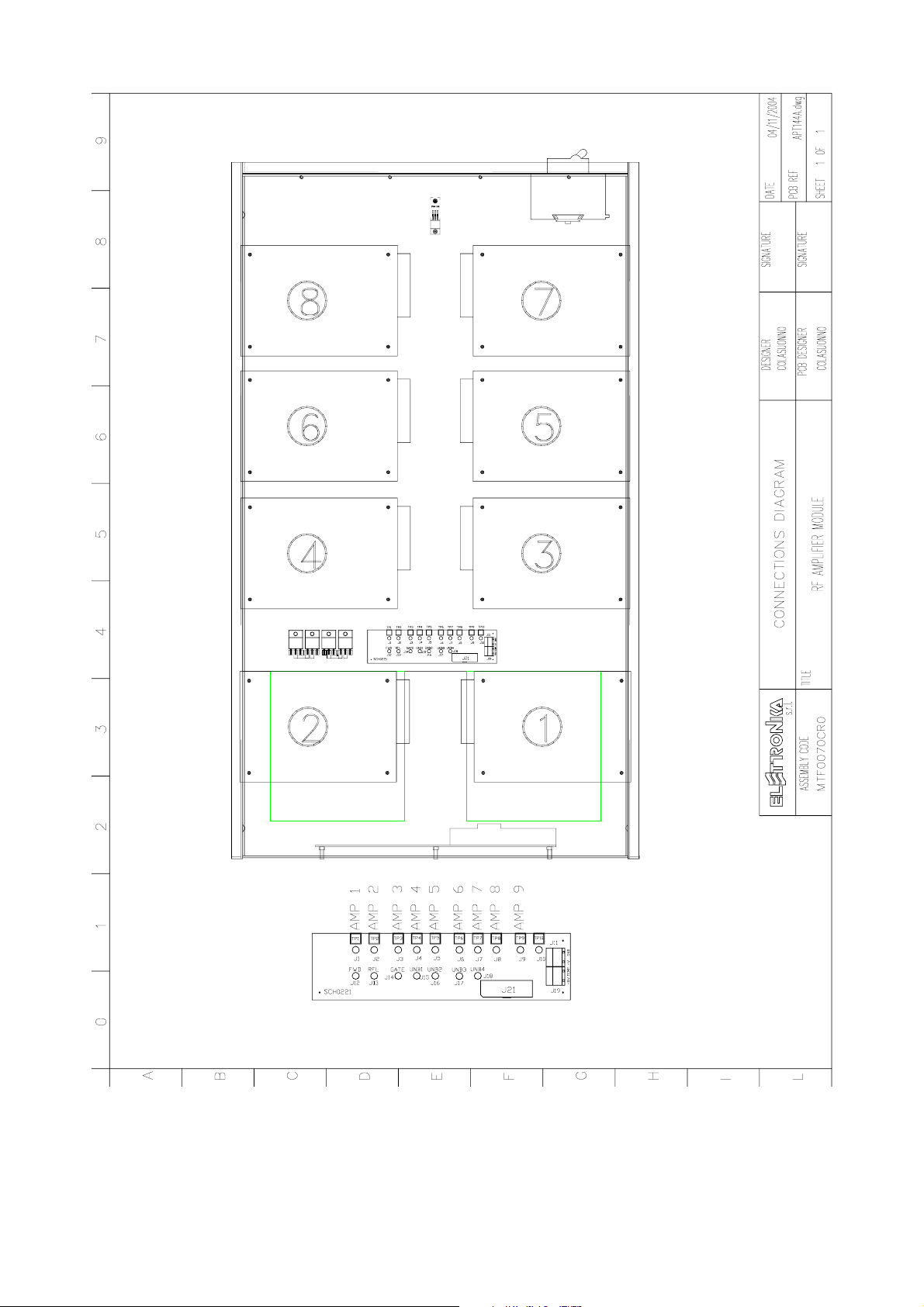
- MTF0070CR0 RF Amplifier module Connections Diagram
- MTF0070CR0 Amplifier module - Component list
- SCH0192AR0 (200W UHF LDMOS Amplifier module)
- SCH0223AR1 (Control board and display)
- SCH0221AR1 (Amplifier interface)
- SCH0265AR0 (Mains distribution board)
- SCH0288AR1 (Interface board)
- E0012 (SP500-27-DI Switching power supply)
73
747576

Component list MTF0070CR0 Amplifier module
Part Name Code Description Qty
00001 0W 1206 SMD RESISTOR 2
01041D 1nF 1206 2% SMD CAPACITOR 2
00221B 75W 1206 1% SMD RESISTOR 2
03207 HSM S-2802*L31 DIODE 2
SCH0192AR0 200W UHF LDMOS AMPLIFIER MODULE 9
SCH0221AR0 AMPLIFIER INTERFACE 1
SCH0248AR0 8 WAY WILKINSON 1
SCH0249AR0 4 WAY WILKINSON Dx 1
SCH0250AR0 4 WAY WILKINSON Sx 1
SCH0251AR0 2 WAY WILKINSON 1
SCH0252AR0 1500W UHF INPUT COUPLER 1
PN1091A C.S. PN1091AR3 OUTPUT DIRECTIONAL COUPLER 1
02402 7/16 FEMALE CONNECTOR cod. 0142 1
02512 J0 1151A0531 SMA SOCKET WITHOUT BAT. 1
01400 2499-003-X5U0-102M FEED-THROUGH CAPACITOR 13
01408 5000PF FEED-THROUGH CAPACITOR 2
DET0726 DET0726R2 SIDE x 1500W UHF AMP. MOD. 2
DET0727 DET0727R1 INTERNAL FRONT SIDE x AMP. MOD. 1
DET0728 DET0728R4 INTERNAL SIDE x AMP. MOD. 2
DET0729 DET0729R2 FRONT SIDE x AMP. MOD. 1
DET0730 DET0730R2 REAR SIDE x AMP. MOD. 1
DET0732 DET0732R1 CONNECTIONS SUPPORT BOARD 1
DET0734 DET0734R0 COVER x AMPLIFIER MODULE P. 2634 1
DET0736 DET0736R6 HEATSINK x AMPLIFIER MODULE 1
DET0807 DET0807R3 SCREEN DIR. COUPLER MODULE 1
DET0810 DET0810R0 PART. x DIRECTIONAL COUPLER 1
DET0811 DET0811R1 COVER x DIRECTIONAL COUPLER 1
DET0812 DET0812R1 TEFLON RING x DIRECTIONAL COUPLER 1
DET0819 DET0819R0 SPESS. x INPUT DIR. COUPLER 1
DET0828 DET0828R0 COVER x AMPLIFIER MODULE P. 2644 1
DET0839 DET0839R2 DIRECTIONAL COUPLER 1
08502 RG316 50W CABLE 3,00
08527 HF- 85 ENDIFORM CABLE 0,20
03017 MBR3045PT DIODE 4
PN0998A PN998AR1 POWER SUPPLY ADDED PCB 2
77

This page is intentionally blank
78
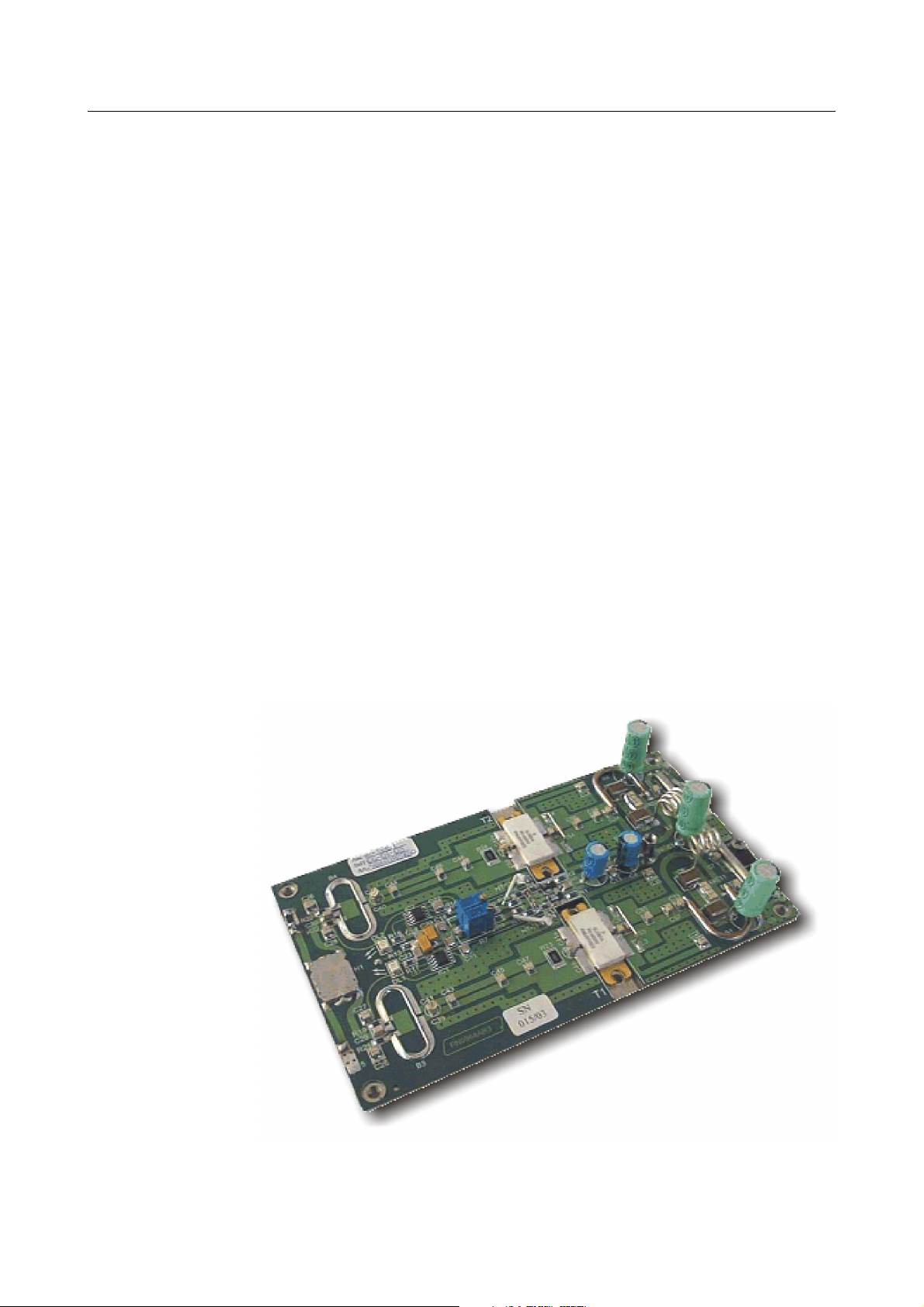
200W UHF LDMOS AMPLIFIER MODULE SCH0192AR0
DESCRIPTION
The RF module is an integrated TV linear amplifier designed for UHF band, this module employs push-pull
LDMOS technology in order to achieve very good efficiency, high linearity and reliability.
LDMOS transistors operate in AB class. It is a wideband amplifier over the full frequency, no adjustment is
required for the channel change. The board includes RF section amplifier, bias circuit, protection circuit and
matching networks. A silver plated copper plate is brazed with PCB in order to obtain low thermal resistance.
Providing a minimum of 200W Pk sync linear power, this module is the perfect amplifier for any broadband
UHF power transmitter.
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Output power 300W max
Input power 15W max
Frequency 470 - 860MHz
Gain > 13dB
LDMOS Power supply 32V ±2%
LDMOS Bias current @+32V Vdc 2A
RF Input impedance 50W
RF Output impedance 50W
Input / Output return loss > = 15dB
Drain efficiency 47% @ 250W
Storage temperature range -50° to +150°C
Dimensions (LxWxH) 165x95x29mm
79
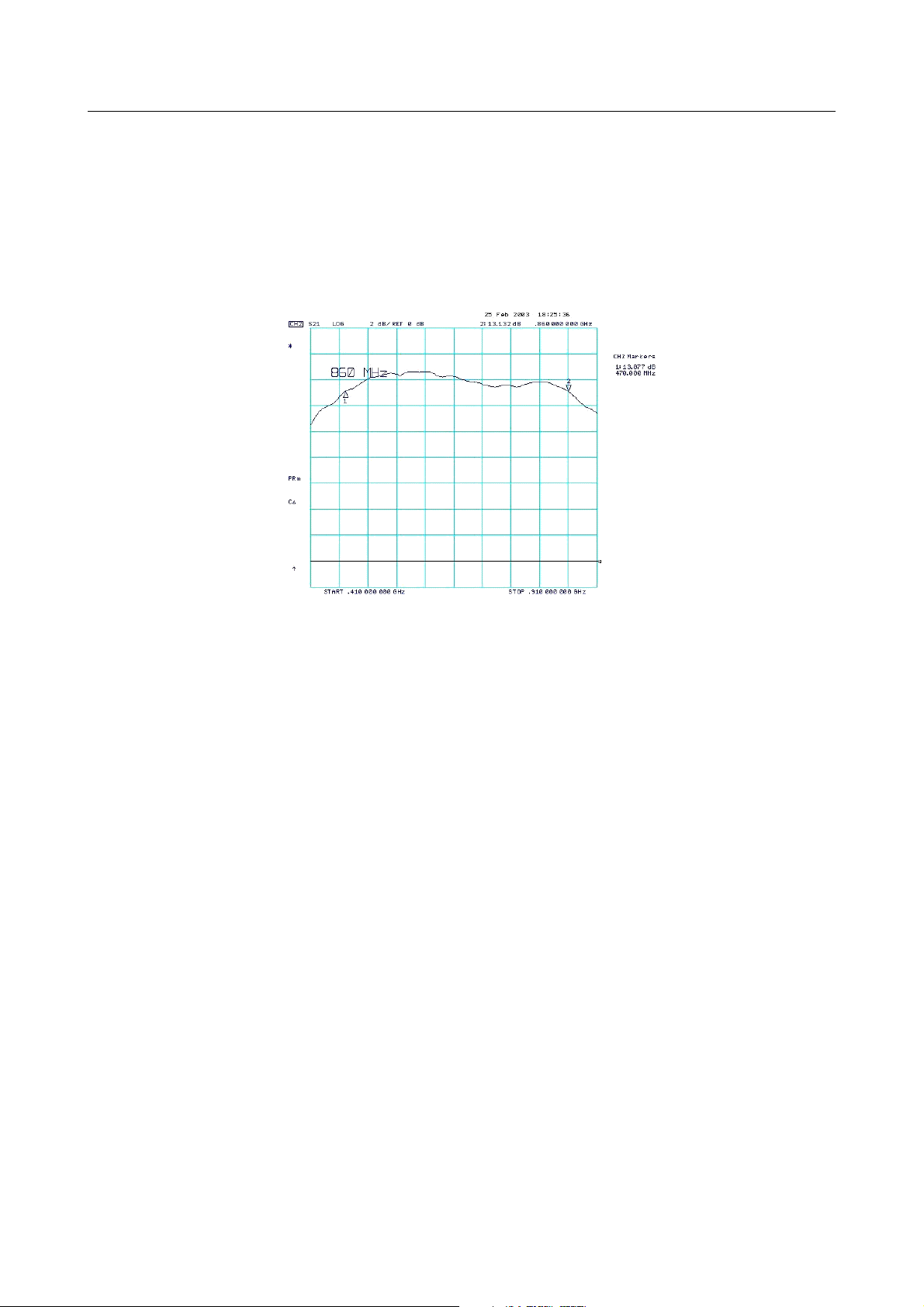
- Curve response graphic
Middle frequency 660MHz, span 500MHz, 2dB/div., reference to the arrow
CALIBRATION PROCEDURE
- Technical characteristics
Power supply voltage 32V (± 2%)
Polarisation current 1.0 cold for each device (2A total), ± 0.1A
Gain for low signal Not less than 13dB in the 470-860MHz band (± 1dB)
Compare to the typical curve eclosed
- Adjustment procedure
Polarisation current calibration 32V stabilised power supply
10A amperometer
Gain curve Network analyser
- Adjustment points description
R7-R8 (Trimmers) Adjust the current absorbed in stand-by (1.0A per device)
80
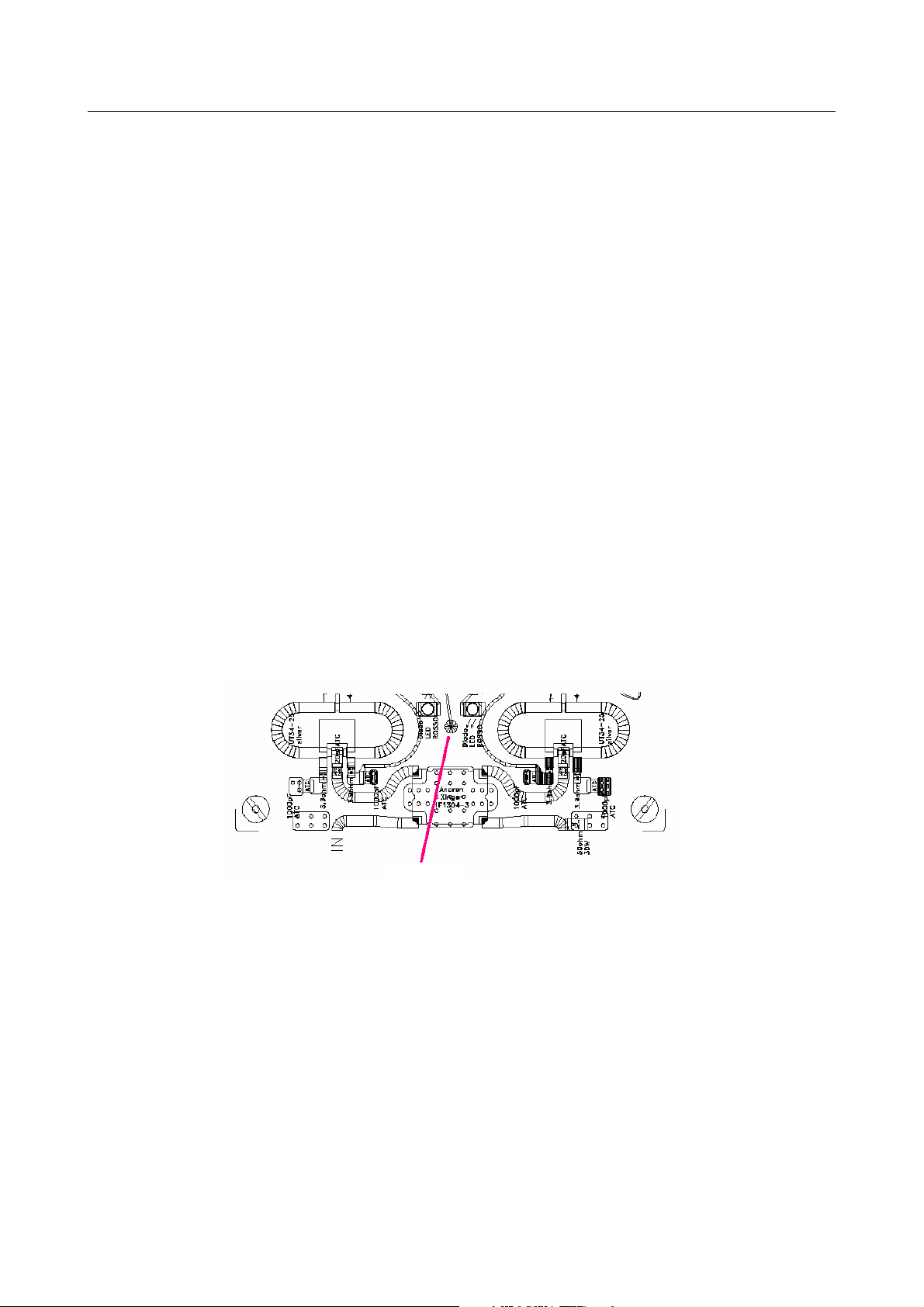
- Calibration steps
STEP 1. Close the input and the output of the module by connecting them to a 50
WW
W dummy load
WW
and connect the spectrum analyser through a directive sample, in order to look for self-oscillation of the
module, if any (anyway the module has been designed so that it would not self-oscillate even if totally decoupled, without any input or output load).
STEP 2. Check the voltages of the polarisation circuits without assembling the transistors first:
connect the 32V power supply to the proper turret by means of a fastening screw, then give power and check
data:
- the stabilised voltage on the zener diodes DZ1 and DZ2 is about 15V compared to the ground;
- the stabilised voltage on the zener diodes DZ3 and DZ4 is about 6.8V compared to the ground;
- the voltage on the pads to which the gates of the LDMOS transistors will be soldered (R23 and R24
resistors side) changes from 0V to a maximum value of about 6V when moving the relevant trimmer (R7-R8).
STEP 3. Check the work of the protections.
- Set both trimmers so that there is a value of about 4.5V on the pads of the gates;
- solder some wire to the pad between the two LEDs, next to the serigraphy of the input hybrid H1;
Solder a wire
- in order to check the work of the protections aboard, a power of about 4V has to be supplied to the wire,
for example by touching with it the reophore of C23 or C24 which is not connected to ground; the two red
LEDs will immediately light up and the two RF transistors will be switched off at the same time: the polarisation
current (2A) will decrease to 0 and of course the gain curve displayed by the spectrum analyser will decrease;
- after this it is important to restore the position of the two trimmers for the minimum voltage! Then
disconnect the 32V power supply.
STEP 4. Fastening of the LDMOS transistors: after properly cleaning the plate surface, smear a thin
layer of silicone fat on the lower side of the flange of the MOSFETs, fasten them to the heat sink and solder
the gate first, then the drain. Solder the two 13pF (ATC) chip capacitors and above them the two 1-5pF
81

capacitive trimmers, between the two pair of gates, as shown by the mounting plan.
STEP 5. Connect serially a c.c. amperometer to the power supply, with scale starting from more than 5A
(i.e. 10A).
STEP 6. Power the module and check the MOSFET is not absorbing current; this means that the device
is integral and working correctly.
STEP 7. Slowly turn the R7 trimmer until the MOSFET absorbs 1A, always checking that there are no
self-oscillation; under this conditions it is possible to check by means of a digital tester that the voltage on the
gate is about 5.2-5.4V.
STEP 8. Repeat the previous step for the other section of the module, this time turnign R8 and checking
that the indication of the current on the amperometer increases to 2A total (which includes the current of the
other device left on).
STEP 9. Check the response curve of the module by means of the network analyser.
STEP 10. Check the response curve for low signal with centre 660MHz and span 500MHz, 2dB/div.
STEP 11. The curve should be similar to the one enclosed, with a tolerance of ± 0.5dB. To obtain this, act
on the four trimmers C41-C41a and C42-C42a with the proper calibrator, inorder to flatten the curve as
much as possible, especially at the edged of the band which represents the minimum values.
STEP 12. Finally, check that the current in stand-by does not increase by more than 15÷20%, reaching at
worst 2.3÷2.4A when the heat sink is hot and not ventilated.
Note: when mounting-removing the PALLET on the heat sink, tightly fasten the screw of each all N input and output
connectors. These are mounted with a single 3mm screw and if it is not properly fastened it may be detached from the PCB
by a movement of the connector once it has already been soldered to the path.
82
 Loading...
Loading...