Page 1

ELENCO
®
Copyright © 2012 by ELENCO®All rights reserved. 753014
No part of this book shall be reproduced by any means; electronic, photocopying, or otherwise without written permission from the publisher.
DIGITAL MULTIMETER KIT
MODEL M-1008K
Assembly and Instruction Manual
Page 2

PARTS LIST
If you are a student, and any parts are missing or damaged, please see instructor or bookstore. If you purchased this meter
kit from a distributor, catalog, etc., please contact ELENCO®(address/phone/e-mail is at the back of this manual) for
additional assistance, if needed.
RESISTORS (Parts mounted on card)
Qty. Symbol Value Color Code Part #
r 1R7 0.99Ω 0.5% 1/4W black-white-white silver-green 109950
r 1R8 9Ω 0.5% 1/4W white-black-black-silver-green 119050
r 1 R19 10Ω 1% 1/4W brown-black-black-gold-brown 121030
r 1 R18 100Ω 1% 1/4W brown-black-black-black-brown 131030
r 1 R1 100Ω 0.5% 1/4W brown-black-black-black-green 131050
r 1 R23 470Ω 1% 1/4W yellow-violet-black-black-brown 134730
r 1 R12 900Ω 1% 1/4W white-black-black-black-brown 139030
r 1 R2 900Ω 0.5% 1/4W white-black-black-black-green 139050
r 1R9 1.5kΩ PTC Resistor 141569
r 3 R22,26,27 47kΩ 1% 1/4W yellow-violet-black-red-brown 144730
r 1 R10 9kΩ 1% 1/4W white-black-black-brown-brown 149030
r 1R3 9kΩ 0.5% 1/4W white-black-black-brown-green 149050
r 1 R11 20.5kΩ 1% 1/4W red-black-green-red-brown 152130
r 1 R4 90kΩ 0.5% 1/4W white-black-black-red-green 159050
r 2 R14,17 100kΩ 1% 1/4W brown-black-black-orange-brown 160030
r 6 R16,20,21,25,28,29 220kΩ 1% 1/4W red-red-black-orange-brown 162230
r 1 R5 352kΩ 0.5% 1/4W orange-green-red-orange-green 163550
r 1 R6 548kΩ 0.5% 1/4W green-yellow-gray-orange-green 165450
r 1 R15,24,30,31,32 1MΩ 1% 1/4W brown-black-black-yellow-brown 171030
Resistors tolerance may be lower than listed
These parts are not mounted on card:
r 1 R13 0.01Ω Shunt wire 100165
r 1 VR1 200Ω (201) Potentiometer 191300
CAPACITORS
Qty. Symbol Value Description Part #
r 1 C6 100pF (101) Disc 221017
r 1 C7 220pF (221) Disc 222210
r 3 C3, C4, C5 0.1μF (104) Mylar (small) 251017S
r 1C2 0.22μF (224) Mylar (large) 251017L
r 1C1 2.2μF 50V Electrolytic 262247
SEMICONDUCTORS
Qty. Symbol Value Description Part #
r 1 D1,D2,D3 1N4007 Diode (mounted on resistor card) 314007
r 1 Q1 2SA9013 Transistor 329013
r 1 Q2 2SA9015 Transistor 329015
MISCELLANEOUS
Qty. Description Part #
r 1 Liquid crystal display (LCD) 351117
r 1 Zebra 7.5 x 40mm 500008
r 1 PC board, ICs installed 516110
r 1 Fuse 200mA, 250V 5 x 20mm 530020
r 1 Battery 9V 590009
r 1 Battery snap 590098
r 1 Buzzer with wires 595208
r 1 Selector knob 622107
r 1 Case top 623080
r 1 Case bottom 623080
r 1 Zebra frame 629018
r 5 Screw 2.0mm x 6mm (PC Board) 643439
r 2 Screw 2.0mm x 10mm (Case) 643447
Qty. Description Part #
r 2 Fuse holder clips 663100
r 1 Transistor socket 664007
r 3 Input socket 664105
r 2 Ball bearing 666400
r 6 Slide contact 680013
r 2 Spring 2.7 x 4mm (selector knob) 680014
r 1 Spring 3.2 x11mm 680015
r 1 Label shield 750010
r 1 Label meter 724010
r 1 Grease 790004
r 1 Lead-free solder 9LF99
r 1 Test lead set 9TL1008
-1-
Page 3
-2-
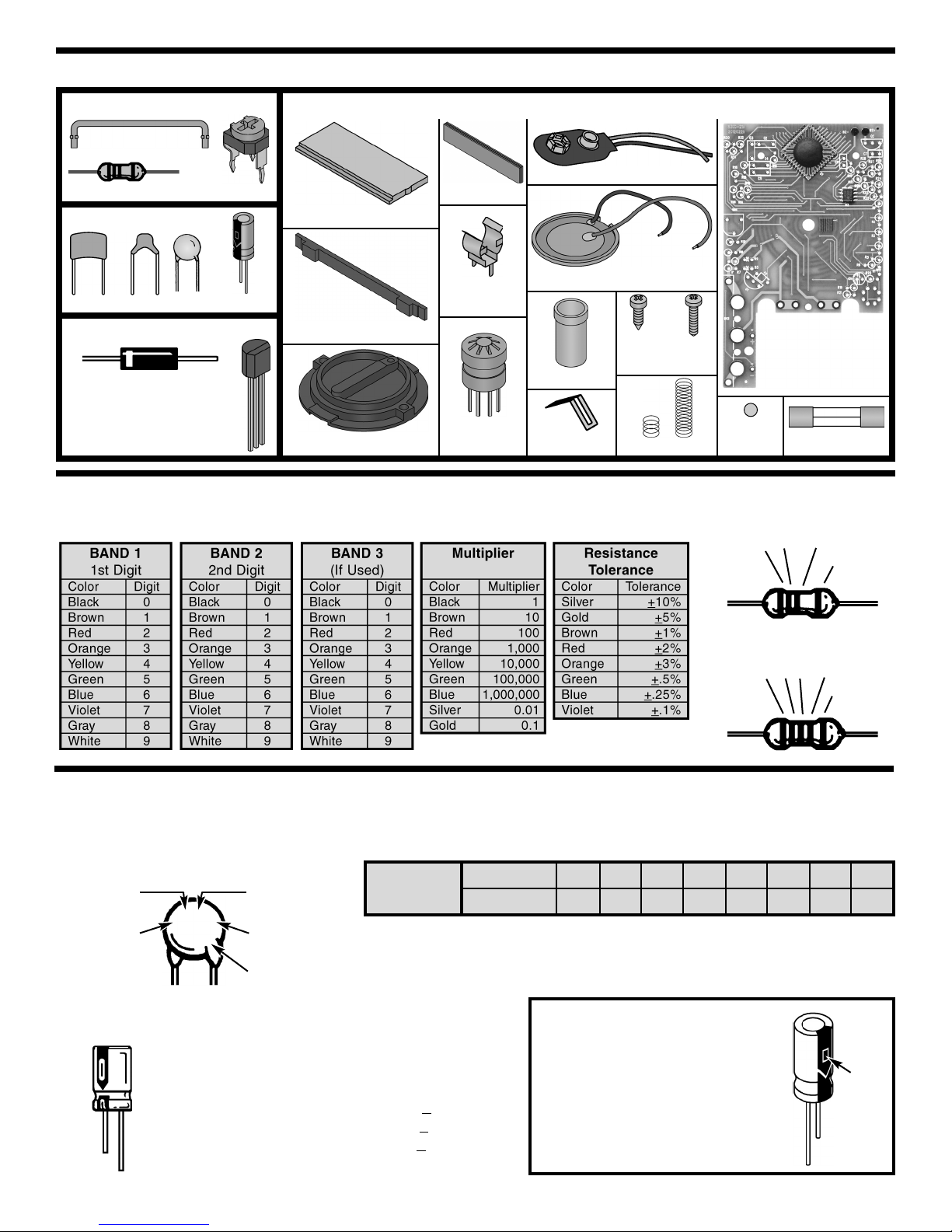
IDENTIFYING RESISTOR VALUES
Use the following information as a guide in properly identifying the value of resistors.
5 Bands
1 2
Multiplier
Tolerance
PARTS IDENTIFICATION
Battery snap
3
4 Bands
1
2
Multiplier
Tolerance
IDENTIFYING CAPACITOR VALUES
Capacitors will be identified by their capacitance value in pF (picofarads), nF (nanofarads), or μF (microfarads). Most
capacitors will have their actual value printed on them. Some capacitors may have their value printed in the following
manner. The maximum operating voltage may also be printed on the capacitor.
Second digit
First digit
Multiplier
Tolerance*
For the No.01234589
Multiply By 1 10 100 1k 10k 100k .01 0.1
Multiplier
Note: The letter “R” may be used at times to
signify a decimal point; as in 3R3 = 3.3
10μF 16V
103K
100V
The letter M indicates a tolerance of +20%
The letter K indicates a tolerance of +10%
The letter J indicates a tolerance of +
5%
Maximum working voltage
The value is 10 x 1,000 = 10,000pF or .01μF 100V
*
Electrolytic capacitors have a positive and a negative
electrode. The negative lead is indicated on the
packaging by a stripe with minus signs and possibly
arrowheads.
Warning:
If the capacitor is connected
with incorrect polarity, it may
heat up and either leak, or cause
the capacitor to explode.
Polarity
marking
(+)
(–)
RESISTORS
CAPACITORS
Shunt wire
Disc
Mylar
C2
Diode
Carbon film
Transistor
MISCELLANEOUS
Electrolytic
SEMICONDUCTORS
PC board
with ICs installed
Liquid crystal display (LCD)
Zebra
Zebra frame
Buzzer with wires
Selector knob
Fuse holder
clip
Transistor
socket
Input socket
Ball
bearing
Slide contact
Potentiometer
Fuse
Springs
Screws
2.0mm x
6mm
2.0mm x
10mm
Page 4
-3-
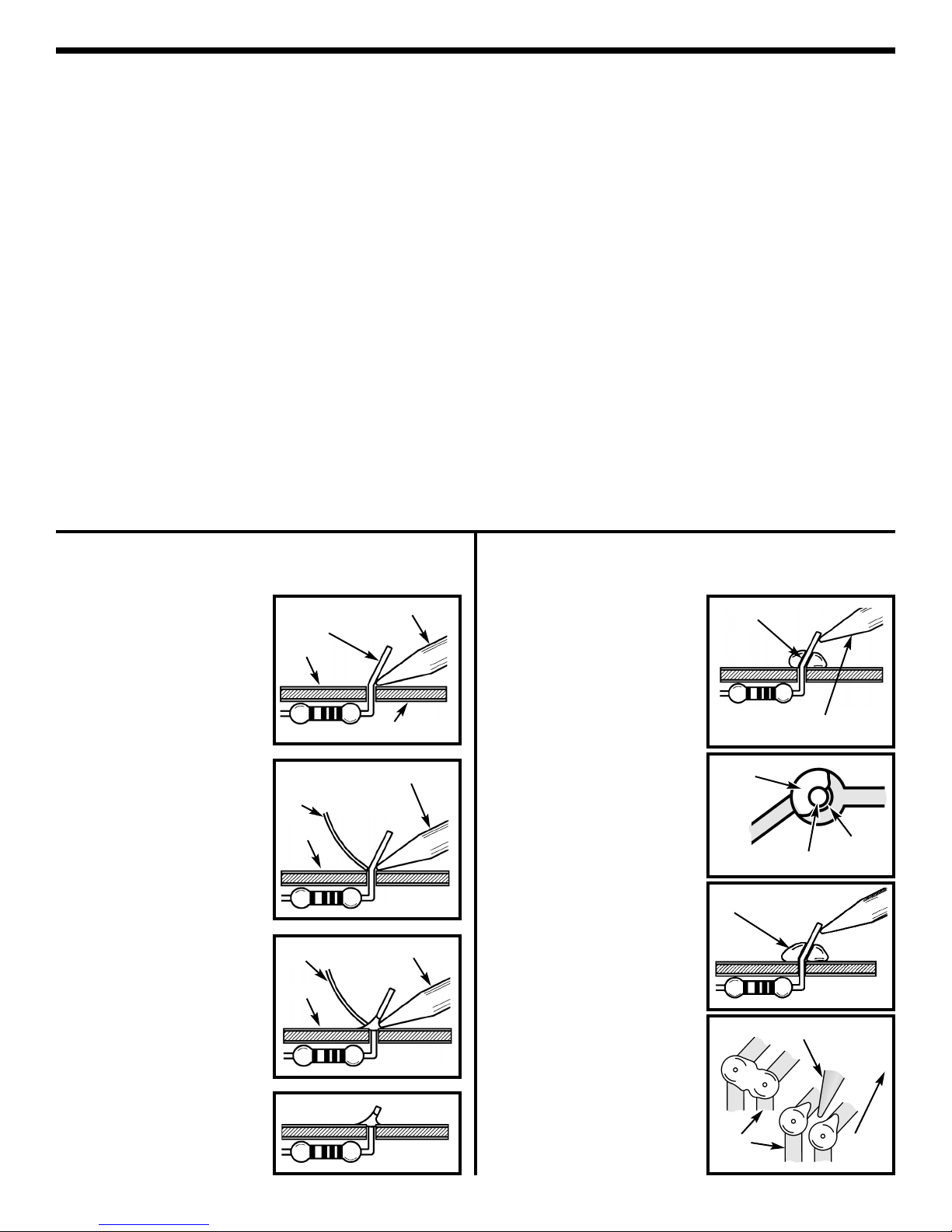
CONSTRUCTION
Solder
Soldering Iron
Foil
Solder
Soldering Iron
Foil
Component Lead
Soldering Iron
Circuit Board
Foil
Rosin
Soldering iron positioned
incorrectly.
Solder
Gap
Component Lead
Solder
Soldering Iron
Drag
Foil
1. Solder all components from the
copper foil side only. Push the
soldering iron tip against both the
lead and the circuit board foil.
2. Apply a small amount of solder to
the iron tip. This allows the heat to
leave the iron and onto the foil.
Immediately apply solder to the
opposite side of the connection,
away from the iron. Allow the
heated component and the circuit
foil to melt the solder.
1. Insufficient heat - the solder will
not flow onto the lead as shown.
3. Allow the solder to flow around
the connection. Then, remove
the solder and the iron and let the
connection cool. The solder
should have flowed smoothly and
not lump around the wire lead.
4.
Here is what a good solder
connection looks like.
2. Insufficient solder - let the
solder flow over the connection
until it is covered.
Use just enough solder to cover
the connection.
3. Excessive solder - could make
connections that you did not
intend to between adjacent foil
areas or terminals.
4. Solder bridges - occur when
solder runs between circuit paths
and creates a short circuit. This is
usually caused by using too much
solder.
To correct this, simply drag your
soldering iron across the solder
bridge as shown.
What Good Soldering Looks Like
A good solder connection should be bright, shiny, smooth, and uniformly
flowed over all surfaces.
Types of Poor Soldering Connections
Introduction
The most important factor in assembling your M-1008K Digital Multimeter Kit is
good soldering techniques. Using the proper soldering iron is of prime
importance. A small pencil type soldering iron of 25 - 40 watts is recommended.
The tip of the iron must be kept clean at all times and well tinned.
Solder
For many years leaded solder was the most common type of solder used
by the electronics industry, but it is now being replaced by lead-free solder
for health reasons. This kit contains lead-free solder, which contains
99.3% tin, 0.7% copper, and has a rosin-flux core.
Lead-free solder is different from lead solder: It has a higher melting point
(about 440
O
F, compared to about 360OF for lead solder), so you need
higher temperature for the solder to flow properly. Recommended tip
temperature is 700OF-800OF; higher temperatures improve solder flow but
accelerate tip decay. An increase in soldering time may be required to
achieve good results. Soldering iron tips wear out faster since lead-free
solders are more corrosive and the higher soldering temperatures
accelerate corrosion, so proper tip care is important. The solder joint finish
will look slightly duller with lead-free solders.
Use these procedures to increase the life of your soldering iron tip when
using lead-free solder:
• Keep the iron tinned at all times.
• Use the largest tip possible for best heat transfer.
• Turn off iron when not in use or reduce temperature setting when
using a soldering station.
•
Tips should be cleaned frequently to remove oxidation before it becomes
impossible to remove. Use Dry Tip Cleaner (Elenco®#SH-1025) or Tip
Cleaner (Elenco®#TTC1).
• DO NOT use a sponge, this worsens tip life because the temperature
shocks accelerate corroding of the tip. If you insist on using a sponge,
use distilled water (tap water has impurities that accelerate corroding).
Safety Procedures
• Always wear safety glasses or safety goggles to protect
your eyes when working with tools or soldering iron,
and during all phases of testing.
• Be sure there is adequate ventilation when soldering.
• Locate soldering iron in an area where you do not have to go around
it or reach over it. Keep it in a safe area away from the reach of
children.
• Do not hold solder in your mouth. Solder is a toxic substance. Wash
hands thoroughly after handling solder.
Assemble Components
In all of the following assembly steps, the components must be installed
on the top side of the PC board unless otherwise indicated. The top legend
shows where each component goes. The leads pass through the
corresponding holes in the board and are soldered on the foil side.
Use only rosin core solder.
DO NOT USE ACID CORE SOLDER!
'
Page 5

ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
Identify and install the following parts as shown. After soldering each part, mark a check þ in the box provided.
Be sure that solder has not bridged to an adjacent pad.
Figure B
Figure A
Stand resistor on
end as shown.
Solder and cut off
the excess leads.
R14 - 100kΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
(brown-black-black-orange-brown)
(see Figure A)
C2 - 0.22μF (224) Mylar cap.
C3 - 0.1μF (104) Mylar cap.
R32 - 1MΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
R30 - 1MΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
R31 - 1MΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
R15 - 1MΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
(brown-black-black-yellow-brown)
(see Figure A)
R16 - 220kΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
(red-red-black-orange-brown)
(see Figure A)
R18 - 100Ω 1% 1/4W Resistor
(brown-black-black-black-brown)
(see Figure A)
VR1 - 200Ω (201) Potentiometer
(see Figure B)
R11 - 20.5kΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
(red-black-green-red-brown)
(see Figure A)
R10 - 9kΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
(white-black-black-brown-brown)
(see Figure A)
C4 - 0.1μF (104) Mylar cap.
C5 - 0.1μF (104) Mylar cap.
Mount the potentiometer to the PC board
as shown.
C6 - 100pF (101) Discap
R17 - 100kΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
(brown-black-black-orange-brown)
(see Figure A)
R23 - 470Ω 1% 1/4W Resistor
(yellow-violet-black-black-brown)
(see Figure A)
R28 - 220kΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
(red-red-black-orange-brown)
(see Figure A)
Q2 - 2SA9015 Transistor
(see Figure C)
C7 - 220pF (221) Discap
R29 - 220kΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
(red-red-black-orange-brown)
(see Figure A)
R24 - 1MΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
(brown-black-black-yellow-brown)
(see Figure A)
R22 - 47kΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
(yellow-violet-black-red-brown)
(see Figure A)
C1 - 2.2
μF
50V Electrolytic cap.
(see Figure D)
R19 - 10Ω 1% 1/4W Resistor
(brown-black-black-gold-brown)
(see Figure A)
NOTE: The 7106 IC1 is already installed
on the PC board. This type of installation
is called C.O.B. (chip on board). The
LM358 U2 IC is also mounted and uses
a surface mount package.
Figure D
Be sure that the negative (short) lead is
in the correct hole on the PC board.
Warning:
If the capacitor is connected with incorrect
polarity, it may heat up and either leak, or
cause the capacitor to explode.
Polarity
mark
(–)
(+)
Figure C
Flat
Top legend marking
on PC board
Mount the transistor with
the flat side in the same
direction as the marking on
the PC board as shown.
-4-
Page 6

Install the following parts. Then, mark a check þ in the box provided.
-5-
ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
Identify and install the following parts as shown. After soldering each part, mark a check þ in the box provided.
Be sure that solder has not bridged to an adjacent pad.
R26 - 47kΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
R27 - 47kΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
(yellow-violet-black-red-brown)
(see Figure A)
R25 - 220kΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
(red-red-black-orange-brown)
(see Figure A)
R1 - 100Ω 0.5% 1/4W Resistor
(brown-black-black-black-green)
(see Figure A)
R2 - 900Ω 0.5% 1/4W Resistor
(white-black-black-black-green)
(see Figure A)
R3 - 9kΩ 0.5% 1/4W Resistor
(white-black-black-brown-green)
(see Figure A)
R4 - 90kΩ 0.5% 1/4W Resistor
(white-black-black-red-green)
(see Figure A)
R5 - 352kΩ 0.5% 1/4W Resistor
(orange-green-red-orange-green)
(see Figure A)
D1 - 1N4007 Diode
(see Figure E)
R20 - 220kΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
(red-red-black-orange-brown)
(see Figure A)
D3 - 1N4007 Diode
D2 - 1N4007 Diode
(see Figure E)
R12 - 900Ω 1% 1/4W Resistor
(white-black-black-black-brown)
(see Figure A)
R8 - 9Ω 0.5% 1/4W Resistor
(white-black-black-silver-green)
(see Figure A)
R7 - 0.99Ω 0.5% 1/4W Resistor
(black-white-white-silver-green)
(see Figure A)
Q1 - 2SA9013 Transistor
(see Figure C)
R9 - 1.5kΩ PTC Resistor
R6 - 548kΩ 0.5% 1/4W Resistor
(green-yellow-gray-orange-green)
(see Figure A)
R21 - 220kΩ 1% 1/4W Resistor
(red-red-black-orange-brown)
(see Figure A)
r Insert the narrow end of the three input sockets
into the PC board from the top legend, as shown
in Figure F. Solder the sockets to the PC board on
the top legend only. The solder should extend
completely around the socket (see Figure F).
r
Insert the shunt wire (R13) into the PC board
holes from the component side as shown in
Figure F. Solder the wire to the PC board on the
component side only.
r Insert the 8-pin transistor socket into the PC board
holes from the solder side as shown in Figure F.
Be sure that the tab lines up with the hole as
shown in the figure. Solder the socket to the PC
board on the component side of the PC board as
shown in the figure and cut off excess leads.
r Insert the two fuse clips into the PC board holes
on the component side as shown in Figure F.
Solder the clips to the PC board.
r Solder the 11mm spring to the solder pad on the
top legend side of the PC board as shown in
Figure G.
Figure E
Stand diode on end. Mount with band as shown
on the top legend.
Band
Top legend marking on PC board
D2
D3
D1
Page 7

-6-
Figure F
Ta b
Input sockets
Shunt wire
Red wire
Black wire
Solder
Battery snap
Transistor socket
Fuse clips
Clear protective film
Figure L
Spring holes
4mm Springs
Figure I
LCD
Zebra
Zebra frame
Figure K
Mounting
tabs
Ta b
Figure J
Mounting tabs
LCD
Mounting tab
Figure G
Input socket
Ta b
r Feed the battery snap wires up through the holes
in the PC board from the solder side as shown in
Figure F. Insert the red wire into the hole marked
(+) and black wire into hole marked (–) as shown.
Solder the wires to the PC board.
r
Peel the backing off the foam tape on the buzzer
and attach it to the PC board as shown in Figure H.
r Solder the red wire to the BZ+ pad and black wire
to the BZ– pad as shown in Figure H.
r Remove the clear protective film from the front of
the LCD as shown in Figure I.
(Note: DO
NOT remove the white backing on the
other side of the LCD).
r Insert the LCD into the frame (the tab on the LCD
must be in the same direction shown in Figure J).
r Insert the zebra frame as shown in Figure K.
r Place the zebra onto the grooved surface of the
LCD as shown in Figure K.
r Cut open the plastic envelope containing the
grease and put a small amount of grease in each
spring hole of the selector knob as shown in
Figure L. Then, insert a 4mm spring into each hole
as shown in the figure.
Figure H
Buzzer
Red wire (BZ+)
Black wire (BZ–)
11mm Spring
Solder pad
on PC board
Page 8

r Put the ball bearings into two opposite indents in
the case top as shown in Figure M.
r Place the six slide contacts on the selector knobs
as shown.
r Place the selector knob into the case top so that
the springs fit over the ball bearings as shown.
r Place the PC board over the selector knob. Be
sure that the 8-pin socket slides into its hole. Then
fasten the PC board with five 6mm screws as
shown.
r Insert the 200mA, 250V fuse into the fuse clips.
r Peel the backing off of the front label and place it
on the case top.
r Connect a 9V battery to the battery snap.
-7-
Figure M
PC board
6mm Screws
Slide
contacts
Rib
Close-up view
Ball bearings
Battery compartment
Case top
Selector knob
Page 9

1) ACV Range: 600 HV 0 0 0
200 0 0.0
2) DCA,10A Ranges: 200μ 0 0.0
2,000μ 0 0 0
20m 0.0 0
200m 0 0.0
10A 0.0 0
3) Ohms, Diode and hFE Ranges: B indicates blank.
hFE 0 0 0
Diode “ ” “ ” 1 B B B
200 1 B B.B
200 1 B B.B
2,000 1 B B B
20k 1 B.B B
200k 1 B B.B
2,000k 1 B B B
4) DCV Range: 200m 0 0.0
2,000m 0 0 0
20 0.0 0
200 0 0.0
600 HV 0 0 0
-8-
TESTING, CALIBRATION, AND TROUBLESHOOTING
TESTING OF LCD
With no test leads connected to the meter, move the selector switch around the dial. You should obtain the following
readings. A (–) sign may also be present or blinking.
If any of these tests fail:
a) Check that the battery is good.
b) Check the values of resistors R14 - R17, R30 - R32.
c) Check the values of capacitors C1 - C6.
d) Check the PC board for solder bridges and bad solder connections.
e) Check that the slide contacts are seated correctly.
f ) Check that the LCD and zebras are seated correctly.
CALIBRATION
Refer to the METER OPERATION section for test
lead connections and measurement procedure.
A/D CONVERTER CALIBRATION
Turn the range selector switch to the 20V position
and connect the test leads to the VΩmA and COM
sockets. Using another meter of known accuracy,
measure a DC voltage of less than 20 volts (such as
a 9V battery). Calibrate the kit meter by measuring
the same voltage and adjusting VR1 until the kit
meter reads the same as the accurate meter (do not
use the kit meter to measure its own battery). When
the two meters agree, the kit meter is calibrated. Turn
the knob to the OFF position and remove the voltage
source.
SHUNT WIRE CALIBRATION
To calibrate the shunt wire, you will need a 1A current
source such as a 5V power supply and a 5Ω, 5W
resistor. If no supply is available, it is not important to
do this test. Set the range switch to the 10A position
and connect the test leads as shown in Figure N. If
the meter reads higher than 1A, resolder the shunt
wire so that there is less wire between the 10A DC
and COM sockets.
If the meter reads low, resolder the shunt wire so that
there is more wire between the sockets.
If the calibration fails:
a) Check the PC board for solder bridges and bad
solder connections.
b) Check the value of resistors R10 - R12 and VR1.
Attach the bottom case without screws.
10A DC
VΩmA
COM
Figure N
5Ω
5 Watts
Power Supply
5VDC
–
+
123
Page 10

DC AMPS TEST
1) Set the range switch to 200μA and connect the
meter as in Figure Q. With R
A equal to 100kΩ the
current should be about 90μA. Compare the
reading to a known accurate meter.
2) Set the range switch and R
A as in the following
table. Read the currents shown and compare to a
known accurate meter.
If any of the above tests fail:
a) Check the fuse.
b) Check the value and soldering of resistors R7,
R8,R13,D2 and D3.
-9-
Figure Q
VΩmA
COM
10A DC
123
Accurate
Meter
R
A
9V
AC VOLTS TEST
To test the ACV ranges, we will need a source of AC
voltage. The AC power line is the most convenient.
CAUTION: Be very careful when working with
120VAC. Be sure that the range switch is in the 200
or 600VAC position before connecting the test leads
to 120VAC.
1) Set the range to 200VAC and measure the AC
power line. The voltage should be about 120VAC.
Compare the reading to a meter of known
accuracy.
2) Set the range to 600VAC and measure the AC
power line. The voltage should be about 120VAC.
Compare the reading to a meter of known
accuracy.
If either if the above tests fail:
a) Check the values and the soldering of resistors
D1,R1-6 and R19.
b) Check that diode D1 is mounted as shown in the
assembly instructions.
Range Switch R
A
Current (approx.)
2mA 10kΩ 900μA
20mA 1kΩ 9mA
200mA 470Ω 19mA
DC VOLTS TEST
Figure O
1kΩ
10A DC
VΩmA
COM
100Ω
9V
123
Figure P
10kΩ
10A DC
VΩmA
COM
100Ω
9V
123
1) If you have a variable power supply, set the supply to about the
midpoint of each of the DCV ranges and compare the kit meter
reading to a meter known accuracy.
2) If you do not have a variable power supply, make the following two
tests:
a) Set the range switch to 2V and measure the voltage across
the 100Ω resistor of Figure O. You should get about 820mV.
Compare the reading to a meter of known accuracy.
b) Set the range switch to 200mV and measure the voltage
across the 100Ω resistor of Figure P. You should get about
90mV. Compare the reading to a meter of known accuracy.
If any of these tests fail:
a) Recheck the meter calibration.
b) Check the value and the soldering of resistors R1 - R6, R10 - R12,
R14 - R17, VR1, and capacitor C4.
Page 11

-10-
FINAL ASSEMBLY
r Peel the backing off of the shield label and stick it onto the case bottom in the location shown in Figure Ra.
r Snap the case bottom onto the case top and fasten with the two 10mm screws as shown in Figure R.
Case
bottom
10mm Screws
Case top
Figure R
Battery
Case bottom
Shield label
Figure Ra
RESISTANCE / DIODE TEST
1) Measure a resistor of about half of the full scale
value of each resistance range. Compare the kit
meter readings to those from a meter of known
accuracy.
2) Measure the voltage drop of a good silicon diode.
You should read about 700mV. Power diodes and
the base to emitter junction of power transistors
may read less.
If any of these tests fail:
a) Check the values and the soldering of
resistors PTC, R1-6, R9, and R16.
h
FE
TEST
1) Set the range switch to hFEand insert a small
transistor into the appropriate NPN or PNP holes
in the transistor socket.
2) Read the h
FE
of the transistor. The hFEof
transistors varies over a wide range, but you will
probably get a reading between 100 and 300.
If this check fails:
a) Check the value and soldering of resistors
R19-21.
CONTINUITY TEST
1) Set the range switch to the “ ” position.
2) Touch the tips together and all zeros displays as
the buzzer sounds.
If this check fails:
a) Check the value and soldering of resistors
R22-29, Q2, C7, and buzzer.
Page 12

-11-
THEORY OF OPERATION
Figure 1
Input
Selector
Switches
AC
Converter
Ohms
Converter
Current
Shunt
V
V
Ω
I
Voltage
Divider
Selector
Switches
V
A/D
Converter
& Display
Driver
Display
Decimal
Point
DC
Analog
Data
For resistance measurements, an internal voltage
source drives the test resistor in series with a known
resistor. The ratio of the test resistor voltage to the
known resistor voltage is used to determine the value
of the test resistor.
The input of the 7106 IC is fed to an A/D converter.
Here the DC voltage is changed to a digital format.
The resulting signals are processed in the decoders
to light the appropriate LCD segments.
Timing for the overall operation of the A/D converter
is derived from an external oscillator whose
frequency is selected to be 25kHz. In the IC, this
frequency is divided by four before it clocks the
decade counters. It is then further divided to form the
three convert-cycles phases. The final readout is
clocked at about two readings per second.
The digitized measurements are presented to the
display as four decoded digits (seven segments) plus
polarity. The decimal point position on the display is
determined by the selector switch setting.
A/D CONVERTER
A simplified circuit diagram of the analog portion of
the A/D converter is shown in Figure 3. Each of the
switches shown represent analog gates which are
operated by the digital section of the A/D converter.
The basic timing for switch operation is keyed by the
external oscillator. The conversion process is
continuously repeated. A complete cycle is shown in
Figure 3.
Any given measurement cycle performed by the A/D
converter can be divided into three consecutive time
periods, autozero (AZ), integrate (INTEG) and read.
A counter determines the length of the time periods.
The integrate period is fixed at 1,000 clock pulses.
The read period is a variable time that is proportional
to the unknown input voltage. It can vary from zero
counts for zero input voltage to 2,000 counts for a full
scale input voltage. The autozero period varies from
1,000 to 3,000 counts. For an input voltage less than
full scale autozero gets the unused portion of the
read period. The value of the voltage is determined
by counting the number of clock pulses that occur
during the read period.
During autozero a ground reference is applied as an
input to the A/D converter. Under ideal conditions,
the output of the comparator would also go to zero.
However, input-offset-voltage errors accumulate in
the amplifier loop and appear at the comparator
output as an error voltage. This error is impressed
across the AZ capacitor where it is stored for the
remainder of the measurement cycle. The stored
level is used to provide offset voltage correction
during the integrate and read periods.
A block diagram of the M-1008K is shown in Figure 1.
Operation centers around a custom LSI chip. This
chip contains a dual slope A/D (analog to digital)
converter, display latches, seven segment decoder
and display drivers. A block diagram of the IC
functions is shown in Figure 1. The input voltage or
current signals are conditioned by the selector
switches to produce an output DC voltage with a
magnitude between 0 and 199mV. If the input signal
is 100VDC, it is reduced to 100mVDC by selecting a
1000:1 divider. Should the input be 100VAC, it is first
rectified and then divided down to 100mVDC. If
current is to be read, it is converted to a DC voltage
by internal shunt resistors.
Page 13

-12-
The integrate period begins at the end of the
autozero period. As the period begins, the AZ switch
opens and the INTEG switch closes. This applies the
unknown input voltage to the input of the A/D
converter. The voltage is buffered and passed on to
the integrator to determine the charge rate (slope) on
the INTEG capacitor. At the end of the fixed integrate
period, the capacitor is charged to a level
proportional to the unknown input voltage. During
the read period, this voltage is translated to a digital
indication by discharging the capacitor at a fixed rate
and counting the number of clock pulses that occur
before it returns to the original autozero level.
As the read period begins, the INTEG switch opens
and the read switch closes. This applies a known
reference voltage to the input to the A/D converter.
The polarity of this voltage is automatically selected
to be opposite that of the unknown input voltage,
thus causing the INTEG capacitor to discharge at a
fixed rate (slope). This rate is determined by the
known reference voltage. When the charge is equal
to the initial starting point (autozero level), the read
period is ended. Since the discharge slope is fixed
during the read period, the time required for
discharge is proportional to the unknown input
voltage. Specifically, the digital reading displayed is
1000 (V
IN / VREF).
The autozero period and thus a new measurement
cycle begins at the end of the read period. At the
same time the counter is released for operation by
transferring its contents (the previous measurement
value) to a series of latches. This stored data is then
decoded and buffered before being used to drive the
LCD display.
Page 14

-13-
Figure 2
7106 IC Functions
Figure 3
a
b
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
TYPICAL SEGMENT OUTPUT
0.5mA
2mA
V+
Segment
Output
Internal Digital Ground
LCD PHASE DRIVER
LATCH
7 Segment
Decode
7 Segment
Decode
7 Segment
Decode
Thousand
Hundreds
Tens Units
*
CLOCK
To Switch Drivers
From Comparator Output
–4
LOGIC CONTROL
Internal Digital Ground
200
BACKPLANE
28
V+
TEST
V
500Ω
3
8
6.2V
1V
* Three inverters.
One inverter shown for clarity.
7
6
4
OSC 1
OSC 2
OSC 3
DIGITAL SECTION
ANALOG SECTION of 7106
C
REF
R
INT
C
AZ
C
INT
INT
C
REF
+
REF HI
REF LO
C
REF
BUFFER
V+
35
42 44 43
41
36
37
1
AUTO
ZERO
+
A-Z &
Z1
A-Z &
Z1
A-Z
DE (+)
DE (+)
DE (–)
DE (–)
IN HI
COMMON
IN LO
40
39
INT
10μA
V+
38
INT
+
+
+
2.8V
A-Z & DE(+)
& Z1
34
V
Z1
6.2V
A-Z
COMPARATOR
ZERO
CROSSING
DETECTOR
POLARITY
FLIP/FLOP
TO
DIGITAL
SECTION
INTEGRATOR
+ REF
(Flying
Capacitor)
Unknown
Input
Voltage +
Read
Integ.
AZ
AZ
Integ.
To
Digital
Control
Logic
AZ Integ. Read
AZ
+
.20
.15
.10
.05
0
10000
160ms
Counter Output
0
500 1000 1500 2000
DUAL SLOPE A/D CONVERTER
Page 15

-14-
DC VOLTAGE MEASUREMENT
Figure 4 shows a simplified diagram of the DC voltage
measurement function. The input voltage divider resistors
add up to 1 megaohm. Each step down divides the voltage
by a factor of ten. The divider output must be within the
range –0.199 to +0.199 volts or the overload indicator will
function. The overload indication consists of a 1 in the most
significant digit and blanks in the remaining digits.
AC VOLTAGE MEASUREMENT
Figure 5 shows a simplified diagram of the AC voltage
measurement function. The AC voltage is first rectified and
passed through a low pass filter to smooth out the
waveform. A scaler reduces the voltage to the DC value
required to give the correct RMS reading.
CURRENT MEASUREMENT
Figure 6 shows a simplified diagram of the current
measurement function. Internal shunt resistors convert the
current to between –0.199 to +0.199 volts which is then
processed in the 7106 IC to light the appropriate LCD
segments. When current in the range of 10A is to be read,
it is fed to the 10A input and does not pass through the
selector switch.
Figure 4 Simplified DC Voltage Measurement Diagram
7106
100mV
REF
Low Pass
Filter
200mV
2V
600V
200V
20V
900kΩ
90kΩ
100Ω
900Ω
9kΩ
Volts
Common
Figure 5 Simplified AC Voltage Measurement Diagram
Volts
Common
7106
100mV
REF
Low Pass
Filter
Rectifier
Low Pass
Filter - Scaler
600V
200V
100Ω
900Ω
Figure 6 Simplified DC Amps Measurement Diagram
Common
10A
A
9Ω
.99Ω
.01Ω
20mA
2mA
200μA
200mA
10A
900Ω
100Ω
2mA
200μA
20mA
200mA
10A
7106
100mV
REF
Low Pass
Filter
Figure 7
Simplified Resistance Measurement Diagram
Ω
900kΩ
Tes t
Resistor
100Ω
900Ω
2MΩ/Dio
200Ω
7106
Reference
Voltage
Low Pass
Filter
Voltage
Source
Common
90kΩ
9kΩ
2mΩ
20kΩ
200kΩ
Fuse
RESISTANCE MEASUREMENT
Figure 7 shows a simplified diagram of the resistance measurement
function. A simple series circuit is formed by the voltage source, a
reference resistor from the voltage divider (selected by the selector
switches), and the test (unknown) resistor. The ratio of the two resistors
is equal to the ratio of their respective voltage drops. Therefore, since
the value of one resistor is known, the value of the second can be
determined by using the voltage drop across the known resistor as a
reference. This determination is made directly by the A/D converter.
Overall operation of the A/D converter during a resistance
measurement is basically as described earlier with one exception. The
reference voltage present during a voltage measurement is replaced by
the voltage drop across the reference resistor. This allows the voltage
across the unknown resistor to be read during the read period.
Page 16

DIODE CHECK
RANGE RESOLUTION MAX TEST CURRENT MAX OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE
DIODE 1mV 1.4mA 2.8V
TRANSISTOR hFETEST
RANGE TEST RANGE TEST CURRENT TEST VOLTAGE
NPN/PNP 0 - 1000 Ib = 10μA Vce 3V
CONTINUITY TEST
Audible Indication: Less than 20Ω approx.
-15-
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL
DISPLAY 3 1/2 digit LCD, with polarity
OVERRANGE INDICATION 3 least significant digits blanked.
MAXIMUM VOLTAGE BETWEEN
TERMINALS AND EARTH GROUND CAT II 600V
STORAGE ENVIRONMENT –10OC to 50OC.
TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENT (0
O
C to 18OC and 28OC to 50OC)
less than 0.1 x applicable accuracy
specification per OC.
POWER 9V alkaline or carbon zinc battery.
FUSE 200mA/250V
DIMENSIONS 126 x 70 x 24mm.
DC VOLTAGE
RANGE RESOLUTION ACCURACY
200mV 0.1mV +
0.5% rdg + 2d
2000mV 1mV +
0.5% rdg + 2d
20V 10mV +
0.5% rdg + 2d
200V 100mV +0.5% rdg + 2d
600V 1V +
0.5% rdg + 2d
MAXIMUM ALLOWABLE INPUT 250V rms for 200mV, 600VDC
or rms AC for other ranges.
INPUT IMPEDANCE 1MΩ.
DC CURRENT
RANGE RESOLUTION ACCURACY
200μA0.1μA+
1.8% rdg + 2d
2000μA1μA+
1.8% rdg + 2d
20mA 10μA+
1.8% rdg + 2d
200mA 100μA+
2.5% rdg + 2d
10A 10mA +
3% rdg + 3d
OVERLOAD PROTECTION 200mA/250V fuse (μA,mA input only).
10A not fused (15 seconds only)
AC VOLTAG E
RANGE RESOLUTION ACCURACY
200V 100mV +
2% rdg + 10d
600V 1V +
2% rdg + 10d
MAXIMUM ALLOWABLE INPUT 600VDC or rms AC.
FREQUENCY 45 - 450Hz.
RESISTANCE
RANGE RESOLUTION ACCURACY
200Ω 0.1Ω +1% rdg + 10d
2000Ω 1Ω +
1% rdg + 10d
20kΩ 10Ω +1% rdg + 10d
200kΩ 100Ω +
1% rdg + 10d
2000kΩ 1kΩ +
1% rdg + 4d
MAXIMUM OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE 3.2V.
MAXIMUM ALLOWABLE INPUT 250V rms AC
hFEMEASUREMENT
Figure 9 shows a simplified diagram of the h
FE
measurement function. Internal circuits in the
7106 IC maintain the COMMON line at 2.8 volts
below V+. When a PNP transistor is plugged into
the transistor socket, base to emitter current
flows through resistor R1. The voltage drop in
resistor R1 due to the collector current is fed to
the 7106 and indicates the h
FE
of the transistor.
For an NPN transistor, the emitter current
through R2 indicates the hFEof the transistor.
Figure 9
R1
Common
R3
R2
PNP
NPN
7106
100mV
Ref.
Low Pass
Filter
V+
EC
CE
B
B
CONTINUITY MEASUREMENT
Figure 8 shows a diagram of the continuity
measurement function. The circuit uses two opamps and a piezoelectric buzzer. When the
leads are connected across a circuit and the
resistance less than 20Ω the circuit oscillates
and the buzzer sounds.
Figure 8
Page 17

-16-
METER OPERATION
PRECAUTIONS AND PREPARATIONS FOR MEASUREMENT
1) Be sure the battery is connected to the battery
snap and correctly placed in the battery
compartment.
2) Before connecting the test leads to the circuit, be
sure the range switch is set to the correct
position.
3) Be sure that the test leads are connected to the
correct meter terminals before connecting them
to the circuit.
4) Before changing the range switch, remove one of
the test leads from the circuit.
5) Operate the instrument only in temperatures
between 0 and 50°C and in less than 80% RH.
6) Pay careful attention to the maximum rated
voltage of each range and terminal.
7) When finished making measurements, set the
switch to OFF. Remove the battery when the
instrument will not be used for a long period of
time.
8) Do not use or store the instrument in direct
sunlight or at high temperature or humidity.
1) Connect the black test lead to the “COM”
terminal.
2) Connect the red test lead to the “VΩmA” terminal.
3) Set the range switch to the desired “DCV” or
“ACV” position. If the magnitude of the voltage is
not known, set the switch to the highest range.
4) Connect the leads across the points to be
measured and read the display. If the range
switch is too high, reduce it until a satisfactory
reading is obtained.
VOLTAGE MEASUREMENTS
HIGH CURRENTS (200mA to 10A)
1) Connect the black test lead to the “COM”
terminal.
2) Connect the red test lead to the “10ADC”
terminal.
3) Set the range switch to the 10A position.
4) Open the circuit to be measured and connect the
leads in series with the load to be measured.
5) Read the display. If the display read less than
200mA, follow the low current procedure below.
6) Turn off all of the power to the circuit being tested
and discharge all of the capacitors before
disconnecting the test leads.
LOW CURRENTS (less than 200mA)
7) Connect the black test lead to the “COM”
terminal.
8) Connect the red test lead to the VΩmA terminal.
9) Set the range switch to the desired DCA position.
If the magnitude of the current is not known, set
the switch to the highest position.
10) Open the circuit to be measured and connect
the leads in series with the load to be measured.
11) Read the display. If the range switch is too high,
reduce it until a satisfactory reading is obtained.
12) Turn off all power to the circuit being tested and
discharge all capacitors before disconnecting
the test leads.
DCA MEASUREMENTS
1) Connect the black test lead to the “COM”
terminal.
2) Connect the red test lead to the “VΩmA” terminal.
3) Set the range switch to the desired “Ω” position.
4) If the resistance being measured is connected to
a circuit, turn off the power to the circuit being
tested and discharge all of the capacitors.
5) Connect the leads across the resistor to be
measured and read the display. When measuring
high resistance, be sure not to contact adjacent
points even if insulated. Some insulators have
relatively low resistance and will cause the
measured resistance to be lower than the actual
resistance.
RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS
Page 18

-17-
DIODE CHECK
1) Connect the black test lead to the “COM”
terminal.
2) Connect the red test lead to the “VΩmA” terminal.
3) If the diode being measured is connected to a
circuit, turn off all power to the circuit and
discharge all capacitors.
4) Set the range switch to “ ”.
Forward Voltage Check
5) Connect the red lead to the anode and the black
lead to the cathode of the diode. Normally the
forward voltage drop of a good silicon diode
reads between 450 and 900mV.
Reverse Voltage Check
6) Reverse the leads to the diode. If the diode is
good, an overrange indication is given (a 1 in the
most significant digit and blanks in the remaining
digits). If the diode is bad, “000” or some other
value is displayed.
hFEMEASUREMENTS
1) Set the range switch to hFEand
insert the test transistor into the
appropriate NPN or PNP holes in
the transistor socket.
2) Read the h
FE
of the transistor.
CONTINUITY CHECK
1) Set the range switch to the “ ” position.
2) Touch the tips across two points and if the
resistance is less than 20Ω the buzzer will sound.
BATTERY & FUSE REPLACEMENT
If “ ” appears on the display, it indicates that the
battery should be replaced.
To replace battery and fuse (200mA/250V), remove
the 2 screws in the bottom of the case. Simply
remove the old fuse/battery and replace with a new
fuse/battery. Fuse 200mA # 530020.
QUIZ
1. The function of the A/D converter is to . . .
r A) convert digital to analog.
r B) divide the analog signal by 2.
r C) convert analog to digital.
r D) convert AC to DC.
2.
The divider used for DC voltage measurements is a . . .
r A) divide by 20.
r B) capacitance divider.
r C) divide by 5.
r D) resistor divider.
3. When the AC voltage is measured, it is first . . .
r A) divided by 2.
r B) rectified.
r C) divided by 100.
r D) sent to a high pass filter.
4. When measuring current, the shunt resistors convert
the current to . . .
r A) –0.199 to +0.199 volts.
r B) –1.199 to +1.199 volts.
r C) –0.099 to +0.099 volts.
r D) –199 to +199 volts.
5. The DC voltage divider resistors add up to . . .
r A) 100Ω.
r B) 1000Ω.
r C) 100kΩ.
r D) 1MΩ.
6. Resistance measurements are made by . . .
r A) comparing voltage drops in the unknown
resistor and a reference resistor.
r B) measuring the current in the unknown resistor.
r C) measuring the current in the reference resistor.
r D) equalizing the voltage drops in the unknown
and the reference resistors.
7. The measurement cycle performed by the A/D converter can be divided into time periods known as . . .
r A) long and short.
r B) autozero, integrate and read.
r C) zero, read and interphase.
r D) convert, integrate and display.
8. A resistor with the band colors green-black-greenbrown-green is . . .
r A) 50.5kΩ +
5%.
r B) 5.15kΩ +
10%.
r C) 5.05kΩ +
.5%.
r D) 5.05kΩ +
1%.
9. The M-1008K has . . .
r A) a 3 digit display.
r B) a 3½ digit display.
r C) a 4½ digit display.
r D) none of the above.
10. When measuring 450mA, the meter leads should be
connected to . . .
r A) COM and VΩmA.
r B) COM and 10A.
r C) 10A and VΩmA.
r D) COM and Building GND.
+
Page 19

-18-
Answers to Quiz: 1. C, 2. D, 3. B,
4. A, 5. D, 6. A, 7. B, 8. C, 9. B, 10. B
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
Page 20

ELENCO
®
150 Carpenter Avenue
Wheeling, IL 60090
(847) 541-3800
Website: www.elenco.com
e-mail: elenco@elenco.com
050712
 Loading...
Loading...