Page 1

Elecraft Transverter Models XV50, XV144, XV222
Assembly Manual
Rev E, January 31, 2012
Copyright © 2012, Elecraft; All Rights Reserved
Page 2

Page 3

Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION ......................................................................................................................................................................... 1
CUSTOMER SERVICE AND SUPPORT .................................................................................................................................... 1
Technical Assistance ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 1
Repair / Alignment Service (We want to make sure everyone succeeds!) .......................................................................................................................... 1
PREPARING FOR ASSEMBLY .................................................................................................................................................. 2
Overview of the Kit ............................................................................................................................................................................................................... 2
Tools Required ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 2
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage ....................................................................................................................................................................... 3
Unpacking and Inventory ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 3
Identifying Parts ................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 3
Assembly Process ................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 5
Forming Component Leads .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 5
Step-By-Step Procedures .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 5
Soldering, Desoldering and Plated-Through Holes ............................................................................................................................................................. 6
PARTS INVENTORY .................................................................................................................................................................. 7
FRONT PANEL PCB ASSEMBLY ............................................................................................................................................ 21
Uninstalled Components .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 25
RF PCB ASSEMBLY – PART I ................................................................................................................................................. 26
RF PCB ASSEMBLY – PART II ................................................................................................................................................ 39
XV50 – 50 MHz Transverter............................................................................................................................................................................................... 39
XV144 –144 MHz Transverter ........................................................................................................................................................................................... 41
XV222 – 222 MHz Transverter .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 44
RF PCB ASSEMBLY – PART III ............................................................................................................................................... 47
FINAL ASSEMBLY ................................................................................................................................................................... 50
FINAL TEST AND ALIGNMENT ............................................................................................................................................... 54
Page 4

- 1 -
Introduction
This is the assembly manual for the Elecraft XV50, XV144 or XV222
transverter kits. A separate manual covers the assembly of the Elecraft
XV432 transverter.
Full details of the Elecraft transverters including specifications,
installation, operation, circuit descriptions, options and modifications
available, troubleshooting and maintenance instructions are included in
the Owner’s Manual which accompanies this kit.
This is an intermediate to advanced kit, yet you'll be surprised at how
uncomplicated it is to build. All of the radio frequency (RF) circuits are on
one printed circuit board (PCB). A second smaller PCB holds the
microcontroller and front-panel LEDs. High-quality, double-sided PCBs
are used, with plated-through holes for optimal RF performance. Point-topoint wiring is minimal. All components to be installed have wire leads;
the few surface-mount devices required are pre-installed on the PCB.
This kit uses just one toroidal inductor, which is easy to wind. However, if
you prefer not to wind this inductor yourself, you can order one prewound with the leads tinned and ready to install from an Elecraft-qualified
source. Ordering information is on our web site at
www.elecraft.com.
Customer Service and Support
Technical Assistance
You can send e-mail to support@elecraft.com and we will respond
quickly - typically the same day Monday through Friday. Telephone
assistance is available from 9 A.M. to 5 P.M. Pacific time (weekdays
only) at 831-763-4211. Please use e-mail rather than calling when possible
since this gives us a written record of the details of your problem and
allows us to handle a larger number of requests each day.
Repair / Alignment Service (We want to make sure
everyone succeeds!)
If necessary, you may return your Elecraft product to us for repair or
alignment. (Note: We offer unlimited email and phone support to get your
kit running, so please try that route first as we can usually help you find
the problem quickly.)
Important: You must contact Elecraft before mailing your product to
obtain authorization for the return, what address to ship it to and current
information on repair fees and turnaround times. (Frequently we can
determine the cause of your problem and save you the trouble of shipping
it back to us.) Our repair location is different from our factory location in
Aptos. We will give you the address to ship your kit to at the time of
repair authorization. Packages shipped to Aptos without authorization will
incur an additional shipping charge for reshipment from Aptos to our
repair depot.
Elecraft's 1-Year Limited Warranty
This warranty is effective as of the date of first consumer purchase (or if shipped from
factory, date product is shipped to customer). It covers both our kits and fully assembled
products. For kits, before requesting warranty service, you should fully complete the
assembly, carefully following all instructions in the manual.
Who is covered: This warranty covers the original owner of the Elecraft product as
disclosed to Elecraft at the time of order. Elecraft products transferred by the purchaser
to a third party, either by sale, gift or other method, who is not disclosed to Elecraft at the
time of original order, are not covered by this warranty. If the Elecraft product is being
bought indirectly for a third party, the third party's name and address must be provided to
Elecraft at time of order to insure warranty coverage.
What is covered:
During the first year after date of purchase, Elecraft will replace
defective or missing parts free of charge (post-paid). We will also correct any
malfunction to kits or assembled units caused by defective parts and materials. Purchaser
pays inbound shipping to Elecraft for warranty repair, Elecraft will pay shipping to return
the repaired equipment to you by UPS ground service or equivalent to the continental
USA and Canada. Alaska, Hawaii and outside U.S. and Canada actual return shipping
cost paid by owner
.
What is not covered:
This warranty does not cover correction of kit assembly errors.
It also does not cover misalignment; repair of damage caused by misuse, negligence, or
builder modifications; or any performance malfunctions involving non-Elecraft accessory
equipment. The use of acid-core solder, water-soluble flux solder, or any corrosive or
conductive flux or solvent will void this warranty in its entirety. Also not covered is
reimbursement for loss of use, inconvenience, customer assembly or alignment time, or
cost of unauthorized service.
Limitation of incidental or consequential damages:
This warranty does not
extend to non-Elecraft equipment or components used in conjunction with our products.
Any such repair or replacement is the responsibility of the customer. Elecraft will not be
liable for any special, indirect, incidental or consequential damages, including but not
limited to any loss of business or profits
.
Page 5
- 2 -
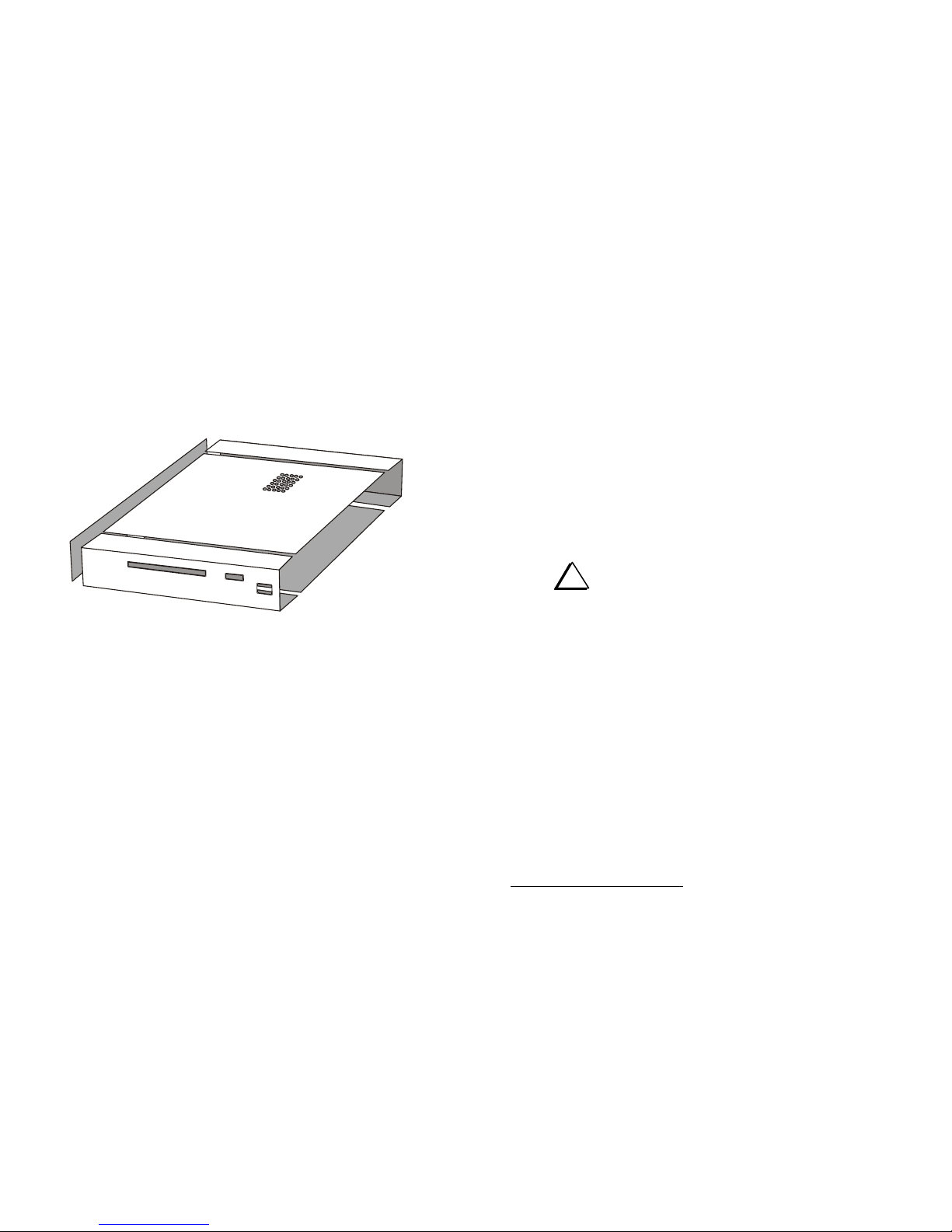
Preparing for Assembly
Overview of the Kit
The Elecraft XV transverters use modular construction, both physically
and electrically. This concept extends to the chassis (Figure 1). Any
chassis element can be removed to provide access.
Figure 1. XV Transverter Modular Cabinet Parts.
There are two printed circuit boards (PCBs) in the transverter: the front
panel PCB, which sits vertically behind the front panel, and the large RF
PCB visible in the cover photograph.
The PCBs are interconnected using board-to-board connectors which
eliminates the need for a wiring harness. Gold-plated contacts are used on
these connectors for reliability.
Tools Required
You will need the following tools to build this kit1:
Fine-tip temperature-controlled soldering station with 700 or
800F tip (370-430C). Do not use a high-wattage iron or gun
since this can damage pads, traces, or the parts themselves.
IC grade, small-diameter (.031”) solder (Kester #44 or equivalent).
Desoldering tools and supplies are invaluable if you make any
modifications or need to do any repairs. Narrow solder wick or a
good vacuum desoldering tool such as the Soldapullt® model
DS017LS are recommended. See Soldering, Desoldering and
Plated-Through Holes, on page 6 for more information.
i
DO NOT use acid-core solder, water-soluble flux
solder, additional flux or solvents of any kind. Use of any of
these will void your warranty.
Screwdrivers: a small, #2 Phillips and a small flat-blade for slotted
screws.
Needle-nose pliers.
Small-point diagonal cutters, preferably flush-cutting.
Digital Multimeter (DMM) for voltage checks and confirming
resistor values. A DMM with capacitance measurement capability
is desirable, but not required.
Noise generator (Elecraft N-Gen or equivalent) or signal generator
with output in the RF frequency range of the transverter.
RF power meter capable of measuring RF power levels up to 25
watts at the frequency used by the transverter.
50-ohm dummy load capable of handling 25 watts, minimum.
1
Refer to www.elecraft.com for tool sources and solder recommendations.
BACK PANEL
LEFT
SIDE PANEL
TOP
COVER
FRONT
PANEL
BOTTOM
COVER
(RIGHT SIDE
PANEL NOT
SHOWN)
Page 6

- 3 -
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Your XV transverter uses integrated circuits and transistors that can be
damaged by electrostatic discharge (ESD). Problems caused by ESD can
be difficult to troubleshoot because components may be degraded but still
operating, rather than fail completely.
To avoid such problems, touch an unpainted, grounded metal surface
before handling any such components and occasionally as you build,
especially after moving about.
For maximum protection, we recommend you take the following antistatic
precautions (listed in order of importance):
1. Leave ESD-sensitive parts in their antistatic packaging until you
install them. The packaging may be a special bag, other container
or the leads may be inserted in conductive foam (Figure 2). Parts
which are especially ESD-sensitive are identified in the parts list.
2. Wear a conductive wrist strap with a series 1 megohm resistor.
DO NOT ground yourself directly as this poses a serious
shock hazard.
3. Make sure your soldering iron has a grounded tip.
4. Use an antistatic mat on your work bench.
Figure 2. A common antistatic packaging is conductive foam which
keeps all of the terminals of a device at the same potential.
Unpacking and Inventory
We strongly recommend that you do an inventory of the parts before
beginning to assemble the kit. Even if you don’t count all the parts, an
inventory is helpful to familiarize yourself with them. A complete parts list
is included in the next section.
Identifying Parts
The parts list contains illustrations of the parts to help you identify them.
Identifying marks on the individual parts are shown in the text in
parenthesis. For example, “Transistor Q4 (PN2222)…” indicates a
transistor, Q4, which may be located in the parts list that has the characters
shown in parenthesis printed on it. Sometimes these letters are not
obvious. For example, they may be printed in light gray on a black body.
Also, there may be other marks on the device in addition to the letters
listed.
Identifying Resistors
Resistors are identified by their power capacity and their resistance value.
The power rating in watts determines the physical size of a resistor. The
most common resistors are 1/4 watt. Higher wattage resistors are
proportionately larger. The resistance value and wattage of each resistor is
shown in the Parts Lists and in the individual steps of the assembly
procedures. The silk-screened outlines on the PCBs indicate the relative
physical size of the resistors as well.
Most resistors use a color code. The color bands are listed in the text along
with the values of each resistor. For example, “R4, 100k (brn-blk-yel)…”
indicates a 100k ohm resistor and the colors to look for are brown, black
and yellow, starting with the band nearest the end of the resistor.
Some resistors use numbers instead of color bands. For example, an 820
ohm resistor might be stamped with the digits 821 instead of having gray,
red and brown color bands. Some larger resistors have their value in ohms
stamped on the body using numbers. For, example the 820 ohm resistor
would be stamped with 820 instead of 821 as described above. Normally,
when the value is shown in ohms it will be followed with the word “ohms”
or the Greek letter omega: Ω
Page 7

- 4 -
Reading Resistor Color Codes
It is very helpful if you learn to read the color codes. A color-code chart
showing how to read the four-color bands on resistors with a 5% or 10%
tolerance is shown in Figure 3. 1% resistors are similar except that they
use a fifth band to provide a way of showing another significant digit. For
example, a 1,500 ohm (1.5 k-ohm) 5% resistor has the color bands brown,
green and red signifying one, five and two zeros. A 1,500 ohm (1.5 k-ohm)
1% tolerance resistor has the color bands brown, green, black and brown
signifying one, five, zero, and one zero.
The optional band shown in Figure 3 indicates other performance
specifications for the resistor. When used, it is separated from the other
color bands by a wider space.
i
If in doubt of a resistor’s value, use a DMM. It may be difficult
to see the colors on some resistors, particularly 1% tolerance resistors with
a dark blue body. Do not be concerned with minor deviations of your
DMM reading from the expected value. Typical errors in most DMMs and
the tolerances of the resistors normally produce readings that are slightly
different from the value indicated by the color bands
.
Identifying Molded Inductors
Small molded inductors have color bands that use the same numeric values
as resistors but they start near the center of the inductor and work toward
the end. These colors are listed in the text after the value of the inductor,
for example: 27H (red-vio-blk). The red stripe would be near the center
of the inductor and the black stripe would be closer to the end. On very
small chokes, the first color will be only slightly farther from one end than
the last color. There may be a variety of other stripes on inductors as well,
indicating their tolerance, conformance to certain specifications and other
data.
FIRST DIGIT
TOLERANCE:
OPTIONAL
SECOND DIGIT
MULTIPLIER
Black
Brown
Red
Orange
Yellow
Green
Blue
Violet
Gray
White
Silver
Gold
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
-
-
X 1
X 10
X 100
X 10K
X 10K
X 100K
X 1M
-
-
X 0.01
X 0.1
COLOR
DIGIT
MULTIPLIER
GOLD = 5%
SILVER = 10%
Figure 3. Resistor Color Code.
Identifying Capacitors
Capacitors are identified by their value and the spacing of their leads.
Small-value fixed capacitors usually are marked with one, two or three
digits and no decimal point. The significant digits are shown in parenthesis
in the text. For example: “C2, .01 (103)”.
If one or two digits are used, that is always the value in picofarads (pF). If
there are three digits, the third digit is the multiplier. For example, a
capacitor marked “151” would be 150 pF (15 multiplied by 10
1
).
Similarly, “330” is 33 pF and “102” is 1000 pF (or .001 F). You may
think of the multiplier value as the number of zeros you need to add on to
the end of the value.
Page 8

- 5 -
Note: In rare cases, a capacitor manufacturer may use “0” as a
decimal placeholder. For example, “820” might mean 820 pF rather
than 82 pF. Such exceptions are usually covered in the parts list. If
possible, measure the values of all capacitors below .001 F. Most DMMs
include capacitance measurement capability.
Fixed capacitors with values of 1000 pF or higher generally use a decimal
point in the value, such as .001 or .002. This is the value in microfarads
(F). Capacitors also may have a suffix after the value, such as “.001J”.
The lead spacing is noted in the Parts Lists for most capacitors. If two
different types of capacitors have the same value, the lead spacing will
indicate which one to use. When the lead spacing is important, both the
value and the lead spacing is shown in the assembly procedure. For
example, “LS 0.1” means that the Lead Spacing is 0.1 in.
Hard-to-Identify Capacitor Values
2.2 pF: These are “disc ceramic” capacitors with round, pillow-shaped
bodies about 1/8” (3 mm) in diameter and a black mark on the top. The
capacitor should be labeled “2.2” but the marking sometimes requires a
magnifying glass to see clearly.
150 pF: These capacitors are marked “151” on one side, but the other side
may be marked #21ASD. The “#21” may look like “821”.
Assembly Process
There are seven steps in the transverter assembly process:
1. Front panel PCB assembly.
2. RF PCB assembly, part I: Parts common to all models.
3. RF PCB assembly, part II: Band-specific parts.
4. RF PCB assembly, part III: Installing the RF power module.
5. Final assembly.
6. Interconnect cabling.
7. Test and alignment.
Follow the assembly process in the order given. Each part builds on what
has been completed before it. For example, the front panel assembly
procedure contains details about installing certain parts that are not
repeated when similar parts are installed later.
Forming Component Leads
Sometimes the space provided for a component on the PCB is larger than
the distance between the leads on the part itself. In such cases, you’ll need
to carefully bend the leads out and then down to fit the given space.
Always use long-nose pliers to accomplish this task, and bend the leads –
don’t tug on them. This is especially important with capacitor leads, which
are fragile.
Step-By-Step Procedures
Perform the assembly steps in each procedure in the order given, and
do not skip any steps. Otherwise you may find that you’ve installed
one component that hinders the installation of another. When groups
of components are installed, they are listed in a logical order as you work
around the PCB to reduce the time needed to find where each part goes.
Each step in the assembly procedures has a check box.
Some steps have more than one task. For example, you may be installing a
number of components listed. When a step has a number of tasks, each
task is indented with space for a check mark:
Check off each task as you complete it.
Page 9

- 6 -
Soldering, Desoldering and Plated-Through Holes
CAUTION: Solder contains lead, and its residue can be toxic. Always
wash your hands after handling solder.
The printed circuit boards have circuitry on both sides (“double sided”).
PCBs of this type require plated-through holes to complete the electrical
connections between the two sides.
When you solder components on these PCBs the solder fills the plated
holes making excellent contact. This means that you do not need to leave a
large “fillet” or buildup of solder on top of the pads themselves. A small
amount of solder will do for all connections.
Unfortunately, removing components from double-sided PCBs can be
difficult. To remove a multi-pin component you’ll need to get all of the
solder out of every hole to free the leads. You will need to use solder wick
or a vacuum desoldering tool (see Techniques below).
The best strategy for avoiding desoldering is to place all components
properly the first time. Double-check values, component placement and
orientation. Take care to avoid ESD damage to components.
Techniques to Avoid Damaging the PCB when Desoldering
Don’t pull a lead or pin out of a hole unless the solder has been
removed completely, or you are applying sufficient heat melt the
solder. Otherwise you can pull the entire plating out of the hole.
Limit soldering iron contact to a few seconds at a time.
Use small-size solder wick, about 0.1” (2.5 mm) wide. Use wick
on both the top and bottom solder pads when possible. This helps
get all of the solder out of the hole.
Buy and learn to use a large hand-operated vacuum desoldering
tool such as the Soldapullt® model DS017LS. Small solder
suckers are not effective.
When removing ICs and connectors, clip all of the pins at the body
first, then remove each pin one at a time, working slowly. You
may damage pads and traces by trying to remove a component
intact, possibly leaving a PCB very difficult to repair.
Invest in a PCB vise with a heavy base if possible. This makes
removing parts easier because it frees up both hands.
If in doubt about a particular repair, ask for advice from Elecraft
or someone with PCB repair experience. Our e-mail reflector is an
excellent source of help.
Page 10

- 7 -
Parts Inventory
You should do a complete inventory. Contact Elecraft if you find anything missing.
i
Leave painted panels wrapped until they are needed during assembly. This will protect the finish.
Cabinet and RF PCB components used in all transverters.
Picture Ref. Designator(s) QTY Description Part #
1
Printed Circuit Board, XV, 50,144,222
i
Handle with care – ESD Sensitive. This PCB is supplied with a
number of surface-mount devices (smd) pre-mounted. Some of these
components are static-sensitive and vulnerable until other parts are installed
on the PCB. There is a temporary jumper across the solder pads for L1 on
the PCB to prevent static damage to Q3. Do not remove this jumper until
instructed to do so.
E100169
1 Front Panel E100153
1 Rear Panel E100154
See Figure 1.
2 Side Panel E100140
1 Top Cover E100267
1 Bottom Cover E100268
1 Heat Spreader E100156
8 2-D Fastener E100078
2 Right Angle Bracket E700073
40 Pan Head Black Machine Screw, 3/16 inch. 4-40. E700015
5 Pan Head Zinc or Stainless Steel Machine Screw, 5/16 inch, 4-40 E700077
2 Pan Head Black Machine Screw, 1/2 inch, 4-40 E700030
Page 11

- 8 -
Picture Ref. Designator(s) QTY Description Part #
10 Machine Screw Nut, 4--40 E700011
14 Split Lock washer, #4 (Includes two spares) E700004
8 Internal Tooth Lock washer, #4 E700010
2 Flat Washer, #4 E700044
1 Ground Lug E700062
2 M-F Standoff for DB9 Connector E700078
4
Rubber Foot, Self Adhesive
i
A Bail kit is available as an optional accessory if desired. The
Bail will hold the front of the transverter up at a convenient viewing angle.
See www.elecraft.com for details
E980067
J4, J5 2 Jack, RCA E620057
1 Connector, RCA, Male (Mates with J4) E620108
J2, J3, J8
3 BNC Connector, PC Mount E620020
3 Nut for BNC Connector E700059
3 Lock washer for BNC Connector E700058
J6 1 DB9 Female Connector, PC Mount E620058
(Typical)
1 DB9 (9 pin) Male Cable Connector (Mates with J6) E620049
1 DB15 (15 pin) Male Cable Connector (mates with ACC Connector on K3) E620161
2
DB9 Back Shell (Shell components are normally packaged together in a
transparent bag).
E620050
Page 12

- 9 -
Picture Ref. Designator(s) QTY Description Part #
4 Anderson Powerpole® Connector Crimp Contact E620062
1 Anderson Powerpole® Connector Roll Pin E700071
J6
2 Anderson Powerpole® Housing , Red E620059
2 Anderson Powerpole® Housing, Black E620060
P1 1 Header Connector, 12 Pin , Right Angle E620065
JP5,JP6, JP9 3 Header Connector, 2 Pin E620054
JP1,JP2,JP3,JP4, JP5,
JP6, JP9
2
7 Header Connector, 3 Pin E620007
9 Header Shorting Block, 2 Pin E620055
S2 1 DPDT Power switch E640006
SW1 1 4 Pole DIP switch E640014
1 Key Cap, Black E980023
F1 1 Resettable Fuse, 8 Ampere, 16 Volt E980113
K1, K2, K4, K5, K6, K7,
K8, K9
8
Relay, Small
(G6E-134P)
E640011
K3 1 Relay, SPDT, 12 A, 12 VDC, Large (KLT1C12DC12). E640012
D3 1 Diode, Zener, 6.8 volt, 1N5235B E560011
D5 1 Diode, SB530 E560003
2
JP9 comprises a three pin and a two pin header connector.
Page 13

- 10 -
Picture Ref. Designator(s) QTY Description Part #
D10, D11 2 Diode, LED, Red E570007
Pre-mounted on the
PCB
Z1 1 Frequency Mixer, ADEX-10H E600050
U1 1 MMIC Amplifier, ERA-6 E600051
U5 1 MMIC Amplifier, MAR-3 E600073
U2 1 Voltage Regulator, 9 volt, LM78L09 E600054
Q6 1 Transistor, NPN, PN2222A E580001
U4 1 Voltage Regulator, 5 volt, LM7805 E600024
Q5 1
Transistor, MOSFET, 2N7000
i
Handle with care – ESD Sensitive. May be shipped loose in an
ESD-safe bag with other parts.
E580002
Q4 1
Transistor, HEXFET, IRL620
E580018
Pre-mounted on
the PCB
Q3 1 Transistor, PHEMT, ATF 34143 E580020
Q2 1 Transistor, NPN , BFR96 E580021
R21 1 Resistor, metal oxide, 1 watt, 5%, 820 ohm (821) E500094
R20, R26, R27 3 Resistor, metal oxide, 3 watt, 5%,160 ohm (160) E500095
R10 1 Trimmer Potentiometer, PC mount, 100K ohm (104) E520001
R13, R22 2 Trimmer Potentiometer, PC mount, 100 ohm (101) E520008
D1, D2, D4, D13, D6,
D12, D9, D14, D15, D16
10 Diode, 1N4148 E560002
D7, D8 2 Diode, 1N5711 E560004
Page 14

- 11 -
Picture Ref. Designator(s) QTY Description Part #
R25 1 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 5%, 56 ohm (grn-blu-blk) E500096
R14 1 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 5%, 4.7 ohm (yel-vio-gld) E500062
R1, R7, R9, R33 4 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 5% , 10K ohm (brn-blk-org) E500015
R11 1 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 5%, 1K ohm (brn-blk-red) E500013
R18 1 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 5%, 620 ohm (blu-red-brn) E500097
R4, R5 2 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 5%, 5.6K ohm (grn-blu-red) E500007
R23, R34 2 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 5%, 100K ohm (brn-blk-yel) E500006
R40 1 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 5%, 22k ohm (red-red-org) E500090
R31 1 Resistor, Metal Film, 1/4 watt, 1%, 15.0K ohm (brn-grn-blk-red) E500112
R32 1 Resistor, Metal Film, 1/4 watt, 1%, 3.92K ohm (org-wht-red-brn) E500110
R30 1 Resistor, Metal Film, 1/4 watt, 1%, 7.50K ohm (vio-grn-blk-brn) E500111
R35 1 Resistor, Metal Film, 1/4 watt, 1%, 5.11K ohm (grn-brn-brn-brn) E500109
R16, R8 2 Resistor, 1 watt , 5%,120 ohm (brn-red-brn) E500105
R12, R19 2 Resistor, 1 watt, 5%, 180 ohm (brn-gry-brn) E500113
Pre-mounted on the
PCB
R15 1 Resistor 56 ohm SMD, 1206 size E500099
R17 1 Resistor, .02 ohm SMD, 2512 size E500100
Capacitors shown
are typical. Different
styles may be
supplied.
C2,C57 2 Monolithic Ceramic Capacitor, 100 pF (101) E530117
C35 1 Monolithic Ceramic Capacitor, 10 pF (100) E530118
C55,C56 2 Monolithic Capacitor, 270 pF (271) E530050
C52,C54 2 Monolithic Capacitor , 150 pF (151) E530049
C53 1 Monolithic Capacitor, 18 pF (180) or (18), LS 0.2 E530088
C3, C17, C15, C7, C39 5
Monolithic Capacitor, .001
F (102), LS 0.1
E530129
C8, C9, C10, C27, C16,
C19, C23, C20, C34,
C38, C37, C36, C63,
C22, C40, C6, C61, C62,
C64, C67, C71
21
Monolithic Capacitor, .01F (103), LS 0.1
E530130
C65, C68, C29 3
Monolithic Capacitor, .047
F (473), LS 0.1
E530131
C30 1
Monolithic Capacitor, .22
F (224), LS 0.1
E530132
None 2
Monolithic Ceramic Capacitor. 0.1
F (104), 50V, LS 0.1”
E530020
C18 1 Disc Ceramic Capacitor, 2.2 pF (2.2), LS 0.1 E530047
Pre-mounted on the
PCB
C70 1 Ceramic SMD Capacitor, 27 pF E530121
C72 1 Ceramic SMD Capacitor, 4.7 pF E530125
C25, C21, C24, C41,
C66, C31, C4, C84, C85
9
Ceramic SMD Capacitor, .047 F, 50 V
E530120
Page 15
- 12 -
Picture Ref. Designator(s) QTY Description Part #
C26, C60 2
Electrolytic Capacitor, 22 F, 25 V
E530012
None 1
Electrolytic Capacitor, 10 F, 16V
E530142
L9 1
Molded Inductor, .47 H (yel-vio-silver)
E690020
L8 1
Molded Inductor, 15 H (brn-grn-blk)*
E690012
L15,L16,L17 3 Variable Inductor, .243-.297 µH, shielded, grey plastic insert. E690025
L7 2 Ferrite Bead E980029
T1 1 Toroid Core, FT37-43 E680003
1 5” Hex Tuning Tool E980068
12 in.
(30 cm)
Solid Insulated Wire, #24 E760008
12 in.
(30 cm)
Red magnet wire, , #26 E760002
12 in.
(30 cm)
Green magnet wire, #26 E760004
3 in.
(7.5 cm)
Bare copper wire, , #14 E760023
5 ft.
(1.5 m)
Red/Black 2-conductor wire, #12 stranded (for DC power wiring) E760017
3 ft.
(91 cm)
4-conductor shielded cable (serial I/O cable) E760009
1 Heat sink gasket, large E100170
1 Heat sink gasket, small E100171
* The color codes on these inductors are different than those used on resistors. See Identifying Molded Inductors on page 4.
Page 16

- 13 -
Front panel circuit PCB components.
Picture Ref. Designator(s) QTY Description Part #
1 Printed Circuit Board E100168
2 Screw, Fillister Head, 1/8 inch, 2-56 E700023
U1 1
Microcontroller PIC16F872, Programmed (packaged in foam)
i
Handle with care – ESD Sensitive. Do not remove it from its
conductive foam until you are instructed to install it.
E610014
1 IC Socket, 28 pin (packaged in foam) E620011
J1 1 Header Socket, 12 Pin E620008
D1, D2 2 Rectangular LED, Red E570007
D3 1 Rectangular LED, Yellow E570009
D4, D5, D6, D7, D8,
D9, D10,
7 Rectangular LED, Green E570008
R6, R7, R8, R9, R10,
R11, R12, R13,R14,
R15, R16, R21, R22,
R23
14 Resistor, Metal Film, 1/4 watt 120 ohm (brn-red-brn) E500022
R1 1 Resistor, Metal Film 1/4 watt, 5%, 220 ohm (red-red-brn) E500002
R2 1 Resistor, Metal Film 1/4 watt, 5%, 470 ohm (yel-vio-brn) E500003
R3 1 Resistor, Metal Film 1/4 watt, 5%, 10K ohm (brn-blk-orn) E500015
R4, R17 2 Resistor, Metal Film 1/4 watt, 5%, 100K ohm (brn-blk-yel) E500006
R25 1 Resistor, Metal Film 1/4 watt, 5%, 270K ohm (red-vio-yel) E500101
R18, R19, R20,R24 4 Resistor, Metal Film 1/4 watt, 5%, 2.2K ohm (red-red-red) E500104
R5 1 Resistor, Metal Film 1/4 watt, 5%, 1 megohm (brn-blk-grn) E500024
C4 1
Capacitor, Monolithic, .001
F, (102), LS 0.1
E530129
C2, C3 2
Capacitor, Monolithic, .01
F, (103), LS 0.1
E530130
C1 1
Capacitor, Monolithic, .047 F (473), LS 0.1
E530131
D11 1 LED Light Bar, Yellow (packaged in foam) E570011
Page 17

- 14 -
Picture Ref. Designator(s) QTY Description Part #
Q1,Q2,Q3,Q4,Q5,Q6,
Q7
7 Transistor, NPN, PN2222 E580001
Z1 1 Ceramic Resonator, 4 MHz E660001
JP1 1 Header Connector, 2 pin E620054
1 Header Shorting block, 2 pin E620055
Page 18

- 15 -
i
The remainder of the parts in your kit depend upon the band of operation. Check only the list that corresponds to your transverter.
XV50: The following parts are included only in the XV50 transverter.
Picture Ref. Designator(s) QTY Description Part #
1 Front Panel Label, XV50 E980059
Pre-mounted on the
PCB
U6 1
SGA7489, Sirenza Gain Block Amplifier (Three-lead device with tab. Two leads
and tab are soldered to the PCB. Center lead is not connected)
E600055
U3 1 Voltage Regulator, 5-volt, LM78L05 E600029
Q1 1 Transistor, NPN, NTE108 E580022
U7 1 RF Power Module, RA30H0608M E600056
J1 1 SO-239 Chassis Mount Connector E620064
R24 1 Resistor, Metal Oxide, 2 watt, 5%, 68 ohm (68J) E500078
Z4 1 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 5%, 56 ohm (grn-blu-blk) E500096
R6 1 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 5%, 330 ohm (org-org-brn) E500103
R29 1 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 56 ohm (grn-blu-blk) E500096
R28 1 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 1K ohm (brn-blk-red) E500013
R39 1 Pot, PC mount, 1K ohm (102) E520010
C69 1 Ceramic Capacitor, LS 0.1 , 10 pF (100) E530118
C14, C58, C59 3 Ceramic Capacitor, LS 0.1, 390 pF (391) E530051
C12 1 Ceramic Capacitor LS 0.1, 100 pF (101) E530117
Pre-Mounted on the
PCB.
C42,C43 2 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V, 82 pF E530133
C44 1 Ceramic Capacitor, SM D, 50 V, 150 pF E530134
C5,C49,C50 3 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V, 2.2 pF E530123
C48,C51 2 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V, 10 pF E530135
C28 1 Ceramic Capacitor, SM D, 50 V, 15 pF E520127
C45,C47 2 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V, 22 pF E530136
C46 1 Ceramic Capacitor, SM D, 50 V, 27 pF E530121
C32 1
Ceramic SMD Capacitor, .047
F, 50 V
E530120
Page 19

- 16 -
Picture Ref. Designator(s) QTY Description Part #
C1, C33 2 Ceramic Trimmer Cap, 1-40 pF E540002
Z3 1
Molded Inductor, .15
H (brn-grn-silver)*
E690022
L2, L3 2
Molded Inductor, .22 H (red-red-silver)*
E690028
L11 1
Variable Inductor,
.198-.240 µH, Blue
E690032
L1 1
Variable Inductor,
.333-.407 µH, Grey
E690033
L12,L13,L14 3 Variable Inductor, .243-.297 µH, Shielded, Grey Plastic Insert. E690025
L10 1 Toroid Core, T44-6 E680007
L10 12” Magnet Wire, #22 E760018
Y1 1 Crystal, 22 MHz Fundamental (22.00) E660004
* The color codes on these inductors are different than those used on resistors. Identifying Molded Inductors on page 4.
Page 20

- 17 -
XV144: The following parts are included only in the XV144 transverter.
Picture Ref. Designator(s) QTY Description Part #
1 Front Panel Label, XV144 E980060
Pre-mounted on the
PCB
U6 1
Amplifier, MMIC, ERA-5 (Four-lead device with no tab. All four leads soldered to
PCB)
E600052
U3 1 Voltage Regulator, 5-volt, LM78L05 E600029
Q1 1 Transistor, NPN, NTE108 E580022
U7 1 RF Power Module, RA30H1317M E600058
R39 1 Pot, PC mount, 1K ohm (102) E520010
Z4, R29 2 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 56 ohm (grn-blu-blk) E500096
R24 1 Resistor, 1 watt, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn) E500105
R28 1 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 1K ohm (brn-blk-red) E500013
R6 1 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 470 ohm (yel-vio-brn) E500003
C14 1 Ceramic Capacitor, 0.1 LS, 33 pF (330) E530116
C12 1 Ceramic Capacitor, 0.1 LS, 10 pF (100) E530118
C13 1
Ceramic Capacitor, 0.1 LS, .047
F (473)
E530131
Pre-mounted on the
PCB
C42,C43 2 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V , 27 pF E530121
C44 1 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V , 47 pF E530122
C5 1 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V, 2.2 pF E530123
C48,C51, C28 3 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V, 4.7 pF E530125
C45,C47 2 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V, 12 pF E530126
C46 1 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V, 15 pF E530127
C49,C50 2 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V, 1 pF E530128
C1 1 Ceramic Trimmer Capacitor, 4-15 pF (Has a blue dot for identification) E540003
L19 1 198 nH,7MM,RF Inductor, red E690226
Page 21

- 18 -
Picture Ref. Designator(s) QTY Description Part #
L2, Z3 2
Molded Inductor, .1 H (brn-blk-silver)*
E690021
L4 1
Molded Inductor, .15 H (brn-grn-silver)
E690022
L10,L11 2 Variable Inductor,
.085-0.1µH, Orange E690023
L1 1
Variable Inductor,
.108-.132 µH, Orange
E690024
L12,L13,L14 3
Variable Inductor, .059-070 µH, Red Plastic Insert.
E690027
Y1 1 Crystal, 116 MHz, 5th Overtone Series Resonant (116.000) E660016
J1 1 Type “N” Chassis Mount Female Connector E620069
Teflon Tubing E980075
* The color codes on these inductors are different than those used on resistors. Identifying Molded Inductors on page 4.
Page 22

- 19 -
XV222: The following parts are included only in the XV222 transverter.
Picture Ref. Designator(s) QTY Description Part #
1 Front Panel Label, XV222 E980061
Pre-Mounted on the
PCB
U6 1
SGA7489, Sirenza Gain Block Amplifier (Three-lead device with tab. Two leads
and tab are soldered to the PCB. Center lead is not connected)
E600055
U3 1 Voltage Regulator, 5-volt, LM78L05 E600029
Q1 1 Transistor, NPN, NTE108 E580022
U7 1 RF Power Module, RA30H2125M or RA30H2127M E600057
R28 1 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 5%, 1K ohm (brn-blk-red) E500013
R6 1 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 5%, 220 ohm (red-red-brn) E500002
R24 1 Resistor, 2 watt, 5%, 56 ohm (grn-blu-blk) E500102
R29, Z4 2 Resistor, 1/4 watt, 5%, 56 ohm (grn-blu-blk) E500096
C14 1 Ceramic Capacitor, LS 0.1, 22 pF (220) E530139
C12 1 Ceramic Capacitor, LS 0.1, 15 pF (15) E530140
C13 1
Ceramic Capacitor LS 0.1, .047 F (473)
E530131
R39 1 Trimmer Potentiometer, PC mount, 1K ohm (102) E520010
Pre-mounted on the
PCB
C42, C43, C44, C44A,
C45, C47
6 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V, 10 pF E530135
C5, 1 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V, 2.2 pF E530123
C48,C51 2 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V, 3.3 pF E530124
C46 1 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V 12 pF E530126
C49, C50, C45A,
C46A, C47A
5 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V, 1 pF E530128
C28 1 Ceramic Capacitor, SMD, 50 V, 4.7 pF E530125
C1 1 Ceramic Trimmer Capacitor, 4-15 pF (Has a blue dot for identification) E540003
L2, Z3 2
Molded Inductor, .1 H (brn-blk-silver)*
E690021
* The color codes on these inductors are different than those used on resistors. Identifying Molded Inductors on page 4.
Page 23

- 20 -
Picture Ref. Designator(s) QTY Description Part #
L10, L11, L4A, L19 4
Variable Inductor,
.064-.080 µH, Red
E690029
L1 1
Variable Inductor,
.041-.044 µH, Brown
E690034
L12, L13, L14 3
Variable Inductor, Shielded,
.038-.040 µH, Brown Plastic Insert
E690031
Y1 1 Crystal, 194 MHz 7th Overtone Series Resonant (194.000) E660017
J1 1 Type “N” Chassis Mount Female Connector E620069
1 in Teflon Tubing E980075
Page 24

- 21 -
Front Panel PCB Assembly
Place the front panel PCB on top of the heat spreader with the silkscreened side down as shown in Figure 4. Temporarily attach the PCB to
the heat spreader with a single 3/16” (4.8 mm) pan-head screw.
FRONT-PANEL PCB
SILK-SCREENED SIDE DOWN
Figure 4. Preparing Front Panel PCB to Install Light Bar.
Prepare the leads of the yellow light bar for mounting on the PCB by
bending them as shown in Figure 5. Press the leads against a smooth, hard
surface and roll the roll the light bar until they are at about a 45 degree
angle to the side of the light bar.
1
23
.
Figure 5. Preparing Light Bar Leads.
Position the light bar in the cutout of the PCB as shown in Figure 6.
Adjust the leads as necessary so they line up with the six solder pads at
the edge of the cutout. The leads will not pass through the solder pads.
The tips of the leads will rest just inside the top of each solder pad.
Figure 6. Installing Light Bar.
Solder the six terminals to the PCB pads.
Remove the front panel PCB from the heat spreader.
Page 25

- 22 -
i
The front panel PCB has parts on both sides of the PCB.
Follow the instructions carefully. If parts are placed on the wrong
side of the PCB, it will not mate with the RF PCB properly or it will
not fit inside the enclosure when construction is finished. Parts that
go on the back (not silk-screened) side of the PCB are identified by
asterisks on the silk screening.
Place the 28 pin IC socket in the holes provided on the front panel
PCB at the end opposite the light bar you just installed. The socket goes
on the back of the PCB (the side opposite the silk-screened outline).
Orient the socket so the notch in the end is facing away from the end of
the PCB, as shown on the outline.
While holding the IC socket against the PCB, wet the tip of your
soldering iron with a very small amount of solder and then touch it to a
pin and solder pad at one end of the socket to tack-solder it in place.
Tack-solder a second pin at the opposite end of the socket.
Check the IC socket carefully to ensure:
The socket is on the side of the PCB that is not silk-screened.
The notched end of the socket is on the end farthest from the end
of the PCB (as shown on the silk-screened outline).
The socket is against the PCB at both ends. If necessary, heat the
tack-soldered joints and adjust the socket so it is flush.
Solder all 28 pins of the IC socket and trim the leads. Be sure to
solder properly the two pins you tack-soldered above.
i
If your solder joints are not clean and shiny, your iron may
not be hot enough, or you may be using the wrong type of solder.
These "cold" solder joints will likely result in poor performance,
reliability problems, or component failure. You may wish to consult
our web site for additional soldering instructions and tool
recommendations.
Locate the silk-screened outline for Q5 near the yellow light bar.
Install a PN2222 transistor on the back side of the PCB (the side that is
not silk-screened). The transistor’s leads should protrude through the
PCB on the silk-screened side.
Note: The wide, flat side of the transistor must line up with the flat
side of the silk-screened outline on the PCB (See Figure 8). The part
number may be on either side of the transistor.
O
R
FLATTENED
BACK
ROUNDED
BACK
PCB OUTLINE
Figure 7. Transistor Orientation Guide.
Position the transistor on the PCB as shown in Figure 8 and bend the
leads to hold it in place. Solder and trim the leads as short as possible.
A
PPROX.
3/16” (3 mm)
SPACE
SOLDER & TRIM LEAD
S
Figure 8. Installing Transistors.
Page 26

- 23 -
i
In the steps that follow, you'll be installing groups of
components. When working from a long list, install all of the items on
one line before moving on to the next. Arrows () appear in the list
to remind you of this order. Components may be soldered one at a
time or in groups. Leads can be trimmed either before or after
soldering. After trimming, leads should be 1/16" (1.5 mm) or less in
length.
Install six additional PN2222 transistors on the back side of the PCB
(the side that is not silk-screened) just as you did Q5. Align the flat side of
each transistor with the outline shown on the silk screening.
__ Q6
__ Q1 __ Q7
__ Q2
__ Q3
__ Q4
Install capacitor C1, .047 F (473) on the back side of the PCB (the
side that is not silk-screened). Position the capacitor as shown in Figure 9
.
INSERT LEADS U
P
TO THE PLASTIC
COATING
473
BE SURE NUMBERS SHOWN IN PARENTHESIS
IN TEXT APPEAR ON BODY. THERE MAY BE
ADDITIONAL MARKINGS AS WELL.
SOLDER & TRIM LEADS
Figure 9. Installing Capacitors.
Install capacitor C4, .001 F (102) on the back side of the PCB (the
side that is not silk-screened).
Install ceramic resonator Z1 (4.0 MG) or (4.00 MG) on the back side
of the PCB (the side that is not silk-screened). This part may be inserted
in either direction. Like the capacitors, insert the resonator as far as the
plastic coating on the leads will allow.
Install JP1, a two-pin header connector on the back side of the PCB
(the side that is not silk-screened) as shown in Figure 10 . Temporarily
place a shorting block on the pins to provide a finger rest while
soldering. Do not hold the solder iron on the pins more than 1 or 2
seconds. Excessive heat will melt the plastic part of the header.
SILK SCREENED SIDE
SHORT PINS GO
THROUGH
B
O
ARD
Figure 10. Installing Header Connectors.
Check to ensure that:
_ All of the above parts were installed in the back of the PCB (the
side that is not silk-screened).
_ All parts are soldered.
_ All leads are trimmed to 1/16” (1.5 mm) or less.
Page 27

- 24 -
i
The remaining parts will be installed on the front of the
circuit PCB
Follow the LED installation instructions carefully to preserve the
appearance of your transverter’s front panel. When finished, the
LEDs should be perpendicular to the PCB and in a straight line (See
Figure 11).
Figure 11. Power LEDs Installed on Front Panel PCB.
Sort the rectangular LEDs into groups according to color.
Note that one lead of each LED is longer than the other. This is the
anode lead. It must be inserted in the right hand hole for each LED as
shown on the front panel PCB. The right hand holes have square
PCB pads to help identify them. The LEDs will not illuminate if the
leads are reversed.
Insert the leads of a green LED through the holes provided for D10
on the silk-screened side of the front panel PCB. Be sure the long lead is
in the right-hand hole (with the square pad). Do not solder yet.
Hold the LED with the back of the plastic housing flat against the
PCB (not tilted). Bend the leads outward on the bottom side to hold it in
place.
Solder one lead of the LED, keeping soldering time to 1 to 2 sec.
If the LED is tilted or is not flat against the PCB, reheat the lead
while pressing the LED down.
Once the LED is correctly positioned, solder the other lead, again
keeping soldering time to 1 or 2 seconds. Then trim both leads.
Install a green LED at D9. Make sure the long lead is to the right
as shown on the PCB. Before soldering, adjust the LED's position as
with D10.
Install green LEDs at D8, D7, D6, D5, and D4. Make sure the long
lead is to the right for these and all remaining LEDs.
Install a yellow LED at D3.
Install red LEDs at D2 and D1.
Page 28

- 25 -
Sort all of the resistors by value. If the color bands are difficult to
read, use a DMM (digital multimeter) to verify their values. Tape them to
a piece of paper with the values labeled.
Install the resistors below on the front (silk-screened) side of the
PCB. Align each resistor to rest against the PCB inside the silk-screened
outline (See Figure 12). Start with R1 near the light bar end of the PCB.
__R1, 220 ohm (red-red-brn)
__R16, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn)
__R22, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn)
__R21, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn)
__R24, 2.2k (red-red-red)
__R2, 470 ohm (yel-vio-brn)
__R25, 270k (red-vio-yel)
__R23, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn)
__R14, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn)
__R15, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn)
__R13, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn)
__R5, 1 meg (brn-blk-grn)
__R3, 10k (brn-blk-org)
__R18, 2.2k (red-red-red)
__R20, 2.2k (red-red-red)
__R4, 100k (brn-blk-yel)
__R17, 100k (brn-blk-yel)
__R19, 2.2k (red-red-red)
__R12, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn)
__R11, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn)
__R10, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn)
__R9, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn)
__R8, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn)
__R7, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn)
__R6, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn)
BODY OF PART
AGAINST THE BOAR
D
ENSURE MARKINGS AGREE WITH
INSTRUCTIONS IN TEXT
SOLDER & TRIM LEADS
Figure 12. Installing Resistors.
Install the two capacitors listed below on the front (silk-screened)
side of the PCB, near the outline of the 28-pin IC socket. Check each
capacitor's labeling carefully (shown in parentheses).
__C2, .01
F (103) __C3, .01 F (103)
Inspect the PCB carefully for the following:
All connections soldered.
No solder bridges between pads (use a magnifier as needed).
All leads clipped to no more than 1/16” (2 mm) long.
Uninstalled Components
Verify that all component locations on the front panel PCB are
filled, except the following:
U1 (controller 16F872) should not be installed in its socket yet.
J1 at the bottom center of the PCB. This will be installed in the
next section.
You’ve finished the front panel PCB assembly procedure. Go to the RF
PCB Assembly – Part I on the next page to continue.
Page 29

- 26 -
RF PCB Assembly – Part I
RF circuit assembly is divided into three parts:
Part 1: DC, control circuits and RF components common to all of the
transverters.
Part 2: Additional RF components unique to the specific band transverter
you are building.
Part 3: Installation of the RF power module.
To help you locate the component positions on the large RF PCB, the
following steps refer to the five general areas of the PCB shown in Figure
13 . Orient the PCB as shown with the component side up.
TOP LEFT
QUADRANT
TOP RIGHT
QUADRANT
LOWER LEFT
QUADRANT
LOWER RIGHT
QUADRANT
CENTER
Figure 13. RF PCB Orientation.
i
Take ESD precautions (see page 3) when handling the RF
PCB. Some surface-mounted components are used in the RF circuits
for optimal transverter performance. The PCB is supplied with these
components pre-mounted. Take care not to damage them.
i
Do NOT remove the temporary wire jumper across the solder
pads for L1 until instructed to do so. This jumper protects U1 from
static damage until the circuits are completed.
Locate the two small L-brackets. Identify the shorter side of the
"L", which will be attached to the RF PCB.
On the RF PCB, locate the hole at either end of the silk-screened
lettering:
P1 MOUNTS ON OTHER SIDE OF BOARD. These are the holes
where “L” brackets will be installed.
Secure the shorter leg of an L-bracket loosely to the RF PCB in
each hole using a 4-40 x 3/16” (4.8 mm) black screw. A lock washer is
not required at this time.
Locate the 12-pin female connector (J1) and the 12-pin male
connector (P1). Normally J1 is included with the front panel PCB parts
and P1 is with the RF PCB parts.
Slide the 12-pin female connector (J1) onto the pins of the 12-pin
male connector (P1). There should be no gap between them.
Insert P1's right-angle pins into the holes on the bottom of the RF
PCB near the letters:
P1 MOUNTS ON THIS SIDE OF BOARD. Do not
solder yet.
Position the front panel PCB as shown in Figure 14. The pins of J1
should be inserted into the holes in the front panel PCB, and the two Lbrackets should be aligned with their outlines on the back of the front
panel PCB. The edge of the RF PCB fits between the socket for U1 and
Q2, Q3, Q4 and Z1 on the front panel PCB.
Secure the L-brackets loosely to the front panel using two 4-40 x
3/16" (4.8 mm) screws (black). It is not necessary to use lock washers at
this time.
Page 30

- 27 -
Adjust the L-bracket positions so the front panel PCB is aligned
with the RF PCB. If the gap between the front panel PCB and the RF PCB
is wider at one end than the other, you probably have one of the brackets
installed backward. Be certain the shorter legs are attached to the RF
PCB.
P1
Top of RF board
J1
Figure 14. Installing J1 and P1.
Tighten all four L-bracket screws.
Solder all pins of J1 and P1.
Remove the two screws holding the front panel PCB to the brackets.
Unplug the front panel PCB and set it aside in a safe place.
Remove the brackets and screws from the RF PCB and set them
aside.
Sort the fixed resistors by wattage and value as follows:
Divide the resistors by wattage: 3-watt (physically largest), 1-watt
and 1/4 watt (smallest).
Among the 1/4 watt resistors, separate the four 1% tolerance
resistors. These resistors have five color bands: four color bands
show the value plus a brown color band at one end that is wider
than the others. The wide band indicates that it is a 1% tolerance
resistor.
Sort the remaining 1/4 watt resistors by value. If the color bands
are difficult to read, use a DMM (digital multimeter) to verify
their values. Tape them to a piece of paper with the values
labeled.
Place the PCB with the silk-screened side up and the cutout to your
left. The lettering in the center of the PCB will read right side up. All of
the remaining parts will be installed on the top, silk-screened side of the
PCB.
i
Save the longer clipped leads from the following resistors.
You will use several of them to make jumpers and test points later.
Install the 1-watt resistors listed below. Space each resistor about
1/16” (1.5 mm) above the PCB by placing the long end of one of the
right-angle brackets between the resistor and PCB until the resistor is
soldered in place (See Figure 15). The objective is to leave space for air
to flow around the resistor. The resistors that should be spaced above the
PCB are shown by a double silk screen outline.
R12, 180 ohm (brn-gry-brn), near U1 in the upper left quadrant
of the PCB.
R16, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn) next to R12.
R21, 820 ohms (821), 1 watt next to Q6.
R19, 180 ohm (brn-gry-brn), near U5 at the center of the PCB.
R8, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn) near Z1 in the lower right quadrant
of the PCB.
PLACE RIGHT-ANGLE BRACKET
UNDER EACH RESISTOR UNTIL
IT IS SOLDERED IN PLACE
SOLDER & TRIM LEADS
Figure 15. Spacing the 1-watt and 3-watt Resistors above the PCB.
Page 31

- 28 -
Install the following 3-watt resistors above R21 near the center of
the PCB. Space each resistor about 1/16” (1.5 mm) above the PCB just
like you did for the 1-watt resistors.
__R20, 160 ohm (160)
__R26, 160 ohm (160)
__R27, 160 ohm (160)
Install the 1/4-watt 1% tolerance resistors listed below in the lower
left quadrant of the PCB. Place these and all of the rest of the resistors
directly against the PCB.
R35, 5.11k (grn-brn-brn-brn)
R31, 15.0k (brn-grn-blk-red)
R30, 7.5k (vio-grn-blk-brn)
R32, 3.92k (or-wht-red-brn)
Install the 1/4 watt resistors listed below. Start with R1, which is in
the upper left quadrant just above the cutout in PCB. The locations follow
the perimeter of the PCB going clockwise.
__R1, 10k (brn-blk-org)
__R11, 1k (brn-blk-red)
__R14, 4.7 ohm (yel-vio-gld)
__R23, 100k (brn-blk-yel)
Install the 1/4 watt resistors listed below. Start with R4, which is in
the lower right quadrant above Z4. The locations follow the perimeter of
the PCB going clockwise.
__R4, 5.6k (grn-blu-red)
__R25, 56 ohm (grn-blu-blk)
__R5, 5.6K (grn-blu-red)
__R7, 10k (brn-blk-org)
__R34 (on the right edge of the PCB), 100k (brn-blk-yel)
__R9, 10k (brn-blk-org)
__R33, 10k (brn-blk-org)
Install the following 1/4 watt resistors next to Q6 at the center of the
PCB:
R18, 620 ohm (blu-red-brn)
R40, 22k (red-red-org)
Locate the silk-screened space for D5 on the PCB near R23 in the
upper right quadrant of the PCB.
i
Diodes must be oriented correctly. A black band around the
diode indicates the cathode end. Install each diode so the cathode end
goes to the square solder pad and the band is oriented to match the silkscreened outline (see Figure 16 below). If a diode has more than one
band, the widest band indicates the cathode end.
Figure 16. PCB Diode Orientation Guides. The cathode always goes
to the square solder pad on the PCB.
Install D5 (SB530) so it is against the PCB and the banded end of
the diode is aligned with the banded end of the PCB outline. Save the
excess leads when you clip them.
Put the clipped leads from D5 in a safe place. Keep them separate
from the other clipped leads you are saving for test points and jumpers.
You will use the leads from D5 when you install antenna connector J1
later.
Sort the small glass diodes by type. If necessary use a strong
magnifier to read the tiny numbers printed on the glass body. Tape each
group to a piece of paper marked by the type number.
1 ea. 1N5235
2 ea. 1N5711
10 ea. 1N4148
Page 32

- 29 -
Install zener diode D3 (1N5235) in the upper left quadrant of the
PCB near R12. Position it against the PCB with the banded end aligned
with the banded end of the PCB outline.
Install the two 1N5711 diodes in the lower right quadrant of the PCB.
Place each diode against the PCB with the cathode band oriented as you
did in the previous steps.
__D7 __D8
Install the 1N4148 diodes listed below. Start with D1, which is near
resistor R1 in the upper left quadrant of the PCB and work clockwise
around the PCB.
__D1
__D12 __D6 __D9 __D13
__D14
__D15 __D16 (In lower right quadrant),
__D2
__D4
i
In the following steps you will install molded inductors. These
inductors look much like 1-watt resistors but the color codes read
differently. The color codes on the inductors read from the center to
the end instead of from the end towards the center like resistors.
Install molded inductor L8, 15H (brn-grn-blk) in the upper right
quadrant of the PCB.
Install molded inductor L9, 0.47 H (yel-vio-silver) about half way
up the PCB about 2 inches (5 cm) from the right-hand edge.
Install transistor Q6 (PN2222) next to R21 near the center of the
PCB. Orient the transistor as shown by the silk-screened outline on the
PCB.
Prepare transistor Q2 (BFR96) for installation as follows:
Place the transistor over the outline on the PCB with the lettered
side up and note the lead lengths required to match the three
solder pad areas on the PCB. Trim the leads to match these pads.
Gently bend the leads down so they make solid contact with the
PCB starting close to the body of the transistor. This is easily
done by pressing down on the lead with a small flat-blade
screwdriver (see Figure 17).
Figure 17. Installing Transistor Q2. Use gentle pressure with a small
screwdriver blade to form the leads.
Page 33

- 30 -
Solder Q2 in place as follows:
_ Wet your soldering iron with a small amount of solder and touch
it to one lead of Q2 tack-solder it in place.
_ Check alignment of the other two leads to be sure they are over
the solder pads. If necessary reheat the tack-soldered lead and
adjust the position of the transistor.
_ Solder all three leads properly, soldering the tack-soldered lead
last. Keep your soldering time as short as possible to avoid overheating the transistor. Do not hold the iron on the leads more
than two seconds.
i
Check each capacitor's labeling carefully to ensure the values
agree with the numbers shown in parenthesis.
Install the monolithic capacitors listed below near U3 and Q6 at the
center of the PCB.
__C68, .047 F(473) __C67, .01 F (103) __C64, .01
F (103)
__C65, .047F (473)
__C10, .01 F(103) __C9, .01
F (103)
Install the monolithic capacitors listed below. With the PCB oriented
with the cutout to the left, start with C62 near the lower left and work
around the PCB clockwise to the upper right quadrant.
_
_C62, .01 F (103)
_
_C40, .01 F (103) __C7, .001 F (102)
_
_C8, .01 F (103)
_
_C3, .001 F (102) __C63, .01F (103)
_
_C6, .01 F (103)
_
_C22, .01 F (103) __C61, .01 F (103)
_
_C2, 100 pF (101)
_
_C23, .01 F (103) __C38, .01 F (103)
_
_C27, .01 F (103)
_
_C29, .047 F(473) __C37, .01 F (103)
_
_C35, 10 pF (100)
_
_C36, F .01 (103) __C34, .01 F (103)
_
_C39, .001 F (102)
Install the monolithic capacitors listed below. Start with C71 on the
edge of the PCB in the lower right quadrant and work from right to left
across the lower part of the PCB.
__C71,.01 F (103)
__C15, .001
F(102) __C16, .01 F (103)
__C20, .01 F (103)
__C30, 0.22
F(224) __C17, .001 F(102)
__C19, .01 F (103)
__C57, 100 pF (101)
Install disc ceramic capacitor C18 (2.2) next to C17 in the lower
right quadrant of the PCB.
Install the capacitors listed below in the area near the center of the
PCB marked
28 MHZ IF BANDPASS FILTER. The lead spacing of these
capacitors may be narrower than the hole spacing on the PCB. If
necessary, form the leads to avoid stress on the capacitor when they are
inserted in the PCB. Do not force the capacitors down against the
PCB. The capacitors may sit about 1/16” (1.5 mm) above the PCB as
shown in Figure 18 .
__C55, 270 (271)
__C54, 150 (151) __C53, 18 (180) or (18)
__C52, 150 (151)
__C56, 270 (271)
The capacitors shown are typical.
Other styles may be supplied.
Figure 18. Installing I.F. Filter Capacitors.
Page 34

- 31 -
Use a discarded lead to create test point TP3. Two holes for TP3 are
directly below R17 in the upper right quadrant of the PCB. Bend the lead
in a “U” shape and insert it in the holes indicated by a line between them
on the PCB. The loop formed should rise about 1/4” (4 mm) above the
PCB. Solder the leads.
Use a discarded lead to create TP4 next to TP3, following the
procedure described above. Solder the leads.
Make two ground test points just like you did for TP3 and TP4. The
places on the PCB are indicated by ground symbols. One is directly
below the “Elecraft” label and the other is in the lower left quadrant
below U6. Solder the leads.
Remove the eight small relays (G6E-134P) from the carrier tube. If
any of the pins are bent, straighten them carefully using long-nose pliers.
i
Most likely you’ll want to use a single antenna for both
transmitting and receiving with your transverter. However, some
operators use separate transmitting and receiving antennas and
separate feed lines. The following step provides special instructions to
follow only if you are building your transverter for use with separate
transmit and receive antennas.
If you are building your transverter for separate (split-path) transmit
and receive antenna connections, do the following:
_ In the next step, cross out relay “K1”. It will not be installed.
Remove K1 from your parts and set it aside in a safe place. You
may want it later if you decide to re-wire your transverter for
single antenna operation.
_ Use discarded leads to form jumpers across W2 and W3 near the
outline for K1 as shown in Figure 19. Solder them in place.
Figure 19. Installing W2 and W3 for split path (separate transmit
and receive antenna) operation. Do NOT Install Relay K1
Working around the PCB clockwise from the upper left quadrant,
place the relays at the following locations. They can only be installed one
way. Do not solder the relays yet and do not clip or bend the relay
leads.
__K1
__K8 __K9 __K7
__K4
__K5 __K6 __K2
Using a thin, hardcover book to hold the relays in place, flip the
PCB and book over together.
Solder just two diagonally opposite corner pins on each relay.
Turn the book back over and check each relay. If any relay is not flat
against the PCB, reheat its corner pins while pressing it down against the
PCB.
Once all the relays are properly seated, solder the remaining pins.
Take care to locate and solder all five pins on every relay. Do not trim
the relay pins. Trimming the pins can cause mechanical stress which
may reduce the life of the relay.
Page 35

- 32 -
Install resettable fuse F1 in the space provided next to relay K9 in
the upper right quadrant. F1 may be oriented either way. Solder and trim
the leads.
Check the pins on the large relay (KLT1C12DC12). If any pins are
bent, straighten them carefully using long-nose pliers.
Install the main power relay K3 (KLT1C12DC12) next to F1 and
solder two diagonally opposite corner pins. Check the relay to ensure it is
flush against the circuit PCB. If necessary, reheat the solder while
pressing down on the relay.
Solder all five pins on relay K3. Do not trim the relay pins.
Trimming the pins can cause mechanical stress which may reduce the life
of the relay.
Install a 3-terminal header at JP1 adjacent to relay K8. Put a shorting
block over two pins of the header to provide a surface where you can
place your finger to keep it straight and against the PCB. While holding
the assembly, touch one of the pins on the bottom of the PCB with a
soldering iron to tack-solder it in place. Check to ensure that the header is
sitting vertically on the PCB (see Figure 10 on page 23). Reheat and
adjust as necessary, then solder all three pins. Do not hold the solder
iron on the pins more than 1 or 2 seconds. Excessive heat will melt the
plastic part of the header.
Remove the shorting block from JP1.
Install the following 3-terminal headers:
JP2 next to relay K8.
JP3 next to relay K8.
JP4 near resistor R21.
JP5 near relay K6.
JP6 near relay K6.
Install JP9 next to K4 and K5. JP9 requires one 2-terminal header
and one 3-terminal header.
Install the 100 k-ohm (104) potentiometer R10 (Power Cal) in the
upper left quadrant of the PCB. The center lead goes toward the beveled
end of the silk screen outline (see Figure 20). The shoulders on the leads
should touch the top of the PCB. This pot also may be marked 15K. That
is a manufacturer’s mark, not the value.
Figure 20. Installing PC Board Pots. Orient the center pin toward
the beveled end of the silk-screened outline.
Spread the leads on R10, if necessary, to hold it in place, then solder
and trim the leads.
Install the two 100 ohm PC board potentiometers just as you did
R10:
R13 (101) in the upper left quadrant of the PCB near D3.
R22 (101) below the three 160-ohm 3-watt resistors near the
center of the PCB.
Verify that all three terminals on each pot are soldered.
Page 36

- 33 -
Install 4-pole DIP switch SW1 in the space provided in the lower
left quadrant of the PCB. The DIP switch may not have a notch at one end
to line up with the silk-screened outline. Orient the switch so that the ON
positions are on the side with the silk-screened numbers. If you aren’t
sure, use your DMM to check the orientation of the switch assembly so
there is continuity through each switch when the toggle is toward the silkscreened number on the PCB.
Bend the leads of voltage regulator U4 (UA78M05C) to fit on the
PCB as shown in Figure 21. Bend the leads around the shaft of a small
screwdriver to create smooth rather than sharp bends.
USE SMOOTH BEND
Figure 21. Installing Voltage Regulator U4.
Insert U4’s leads into the holes. Secure it with a zinc or stainless steel
4-40 x 5/16” (8 mm) screw, #4 inside-tooth lock washer and 4-40 nut as
shown. The metal tab on the transistor sits directly against the metal foil
on the circuit PCB.
Solder all three leads to U4 on the bottom side of the PCB and trim
them short.
Locate the two 0.1 F (104), 50V, LS 0.1” Monolithic Ceramic
capacitors. These are the capacitors that do not have reference designators
in the parts list.
Install the two 0.1 μF (104) capacitors between U4’s center and outer
pins as shown in Figure 22. Solder the capacitors directly to U4’s pins
with very short leads. Hint: Bend the capacitor leads and hold them with
your pliers while tacking one lead onto U4 with your soldering iron
carrying a small drop of solder. Then solder the other lead, clean up the
first connection if needed, and trim off the excess leads.
Figure 22. Installing the U4 Bypass Capacitors.
Check the resistance between the center pin and each outside pin
using your DMM. It must be greater than 500 ohms to confirm no shorts
between U4’s pins.
Locate the 10 F, (10) 16V electrolytic capacitor. This is the
electrolytic that does not have a reference designator shown on the parts
list.
Solder the 10 μF (10) electrolytic capacitor directly to P1 pins 1
(negative) and 2 as shown below using short leads. Be sure to connect
the negative (-) lead to pin 1 as shown.
Figure 23. Installing the 10 μF Electrolytic Capacitor on P1.
Check the resistance between P1 pins 1 and 2. It must be greater
than 500 ohms to confirm no short between the pins.
Page 37

- 34 -
Install two 22 F, 25 VDC electrolytic capacitors near the notch on
the left side of the PCB. Be sure to observe polarity. The longer
positive lead goes in the square solder pad with a
+ silk-screened
next to it.
__C26 __C60
Locate diodes D10 and D11. They are square, red LEDs identical to
the ones you installed on the front panel PCB.
Locate the positions for D10 and D11 on the PCB, near the center on
the right hand side. Note that the square solder pad for D10 is to the left
and the square solder pad for D11 is to the right. The diodes must be
installed turned 180 degrees with respect to each other.
Position diode D10 on the PCB with the long lead through the square
pad on the left and the short lead through the round pad. Position the body
of the LED directly against the PCB within the silk screen outline and
spread the leads under the PCB to hold the diode in place.
Solder one lead on the bottom of the PCB. Check to be sure the LED
is still positioned directly against the PCB. Reheat and adjust the LED as
necessary, then solder and trim both leads.
Position diode D11 on the PCB with the long lead through the square
pad on the right, opposite the orientation of D10. Solder and trim the
leads as you did for D10.
Locate the inductors provided for L15, L16 and L17 in the I.F.
Bandpass filter. They have grey plastic forms visible inside the shields.
Prepare the inductors for installation as follows:
Use the inductor alignment tool to exercise the core in each
inductor. If the alignment tool fits tightly, insert it from the
bottom to avoid pushing the inductor out of the shield. Run the
core up and down through the coil to ensure it runs smoothly
(some inductors are very stiff at first) then position the core near
the top of the coil.
Check the two leads and the two tabs on the case of each
inductor. If they are bent, straighten them carefully using long
nose pliers.
Position each inductor on the PCB so that its tabs and pins protrude
through on the bottom. The inductors can be positioned either way.
Ensure that the shoulders of the tabs are against the top of the PCB, and
then bend the tabs toward each other until they are flat on the PCB to
hold the inductor in place.
__L16
__L15 __L17
Solder the two tabs and the two pins on all three inductors.
Install voltage regulator U2 (78L09) in the space provided near L17.
Be sure to align the body with the silk screen outline on the PCB.
Install transistor Q4 (620) in the space provided near diodes D7 and
D8 as shown in Figure 24. Be sure the leads are inserted until their
shoulders are against the top of the PCB. If the leads are not inserted
far enough, the tab on the top of the transistor may short against the
top cover when the cabinet is assembled. Trim the leads as short as
possible on the bottom of the PCB.
Figure 24. Installing Transistor Q4.
Page 38

- 35 -
i
The following transistor is particularly sensitive to
electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage. If you are not wearing a
grounded antistatic wrist strap, touch an unpainted, grounded object
before handling Q5.
Install transistor Q5 (2N7000) in the space provided in the lower
right quadrant at the edge of the PCB.
Install two 2-pin header connectors next to Q5.
__JP8 __JP7
Wind toroidal transformer T1 on the FT37-43 (gray) toroid core as
follows
3
. T1 uses a bi-filar winding, which means that two wires are
wound on the core together. The wires will be twisted together loosely
before they’re wound onto the core.
Twist the red and green enameled wires together over their entire
length. The wires should cross over each other 2 to 4 times per
inch (1 to 2 times per cm).
Wind 4 turns of the twisted pair on the FT37-43 toroid core as
shown in Figure 25 on the next page. Each time the wire passes
through the center of the core counts as one turn, so verify that
the wires pass through the toroid four times. Spread the turns
around the core as shown.
Separate the leads and trim them to a length of about
1” (2.5 cm).
3
A pre-wound toroid is available from an Elecraft-approved source. See page 2.
i
In the next step the toroid leads will be stripped and tinned.
The leads must be prepared correctly to provide good electrical
contact when installed
.
Strip the insulation and tin the leads using one of the following
techniques:
1. Heat Stripping:
a. Place a small amount of solder (a.k.a. a “blob” of solder) on
your soldering iron.
b. Insert the clipped end of the wire into the hot solder. If the
iron is hot enough, you should see the insulation bubble and
vaporize after 4 to 6 seconds.
c. Add more solder and feed more wire into the solder as the
enamel melts. Continue tinning the wire up to the edge of the
core, and then slowly pull the wire out of the solder.
d. If any enamel remains on the lead, scrape it away using your
thumbnail or sharp tool.
2. Burning: The insulation can be burned off by heating it with a
butane lighter for a few seconds. Use sandpaper to remove the
residue, then tin the bare wires.
3. Scraping: Use a sharp tool to scrape the insulation away. Work
carefully and gently: do not nick the wire. Work around the
entire circumference of the wire to remove all of the enamel and
tin the bare wires.
Page 39

- 36 -
Insert the tinned leads in the holes on the PCB and position the
toroid as shown in Figure 25. Be sure the correct lead goes to each hole.
Use a magnifier to check the following:
Bare, tinned wire should be visible where the wire enters the
hole at the top of the PCB. If necessary remove the toroid and
strip the wire further to ensure the wire going through the hole is
free of enamel and tinned.
Check carefully for shorts between the wires. The toroid core is
not a conductor. Bare wire may touch the core. Be sure that the
tinned wires do not touch each other.
Figure 25. Installing T1.
Solder the wires on the bottom of the PCB and trim the leads as short
as possible.
Locate the solder pads for choke L7 on the left side of the PCB next
to the notch.
Choke L7 consists of a bare wire passing through two ferrite beads
as shown in Figure 26. Prepare and install L7 as follows:
Strip the insulation from 3” (7.5 cm) of the #24 solid insulated
wire provided.
Bend the wire into a U shape to match the spacing of the holes
on the PCB. Place a bead on either side of the bend.
Thread the ends of the wires through the solder pads for L7.
Make sure the beads are sitting vertically on the PCB over each
hole and bend the leads on the bottom of the PCB to hold the
assembly in place.
Solder both leads and trim them as short as possible.
Figure 26. Installing Choke L7.
Install the DPDT power switch at SW2 in the lower right corner of
the PCB. Orient the switch so the pushbutton shaft extends out over the
edge of the PCB. Be sure the two feet on the bottom of the switch are
resting against the PCB before soldering.
Page 40

- 37 -
Locate the two RCA Jacks, J4 and J5. Use your flush cutters to trim
off the two small plastic feet on each jack (see Figure 27). Be sure they
are cut flush so the jacks will sit squarely against the PCB when installed
in the next step.
TRIM OFF THE TWO PLASTIC
FEET FLUSH WITH THE
BOTTOM OF THE JACK.
Figure 27. Preparing the RCA Jacks for Installation.
Install two RCA jacks at the top of the PCB. Solder one pin first
then check to be sure the jack is sitting flat against the PCB. If necessary,
reheat the solder while pressing down on the jack. Solder the second pin
then trim the leads.
__J5 __J4
i
J8, installed in the next step, is not required if you are
building your transverter to use a common transmit and receive
antenna. J8 is needed only if you plan to use separate (split-path)
transmit and receive antennas. It won’t hurt to install it in any case.
Install three BNC jacks at the top of the PCB. Line up the two
supports and the two small conductor pins with the holes and gently press
the connectors down until the four plastic pins on the jack rest directly
against the PCB. Solder one of the large pins, then check the position. If
necessary, reheat the solder while pressing down on the jack. After
soldering all four pins, trim off the excess length of the small pins.
__J8 __J2 __J3
Install the DB-9 connector at J6 and solder the pins including the two
larger mounting pins.
The Anderson power connector is held in place by two heavy copper
wires soldered to the PCB (See Figure 28). Prepare and install the
connector as described in the following steps.
Figure 28. Installing J7.
Cut the length of #14 copper wire provided in half.
Solder each length of the #14 copper wire into the crimp terminal
end of an Powerpole® contact. Solder, do not rely on a crimp
connection. Take care to keep solder off of the terminal.
Orient each contact as shown in Figure 29 and slide it into a
housing until it “clicks” in place. Tug on the wire to be sure it is locked
in place. If the contact comes out, you probably have it in upside down.
SPRING
#14 WIRE
S
OLDERED
TERMINAL L
OCKS
OVER END OF SPRING
Figure 29. Inserting Contact into Anderson Connector Housing.
Page 41

- 38 -
Inspect the end of each connector. You should see the contact
pressing up against the end as shown in Figure 30. If necessary, press the
contact in from the back until it reaches the end. If you don’t get the
contact pushed all the way in so it locks over the end of the spring, it
will not make reliable contact with the mating connector.
WRONG RIGHT
Terminal
reaches end of
the shell.
Figure 30. Verify Contact is Fully Inserted.
Orient the housings with dimpled side up so that the red and black
housings are over the colors marked on the PCB exactly as shown in
Figure 31. Be sure the housings are oriented as shown. If they are
upside down they will not mate to the connectors on the power cord.
Figure 31. Orienting J7 on the RF PCB.
Look closely at the sides of the housings. Each has a small tongue
on one side and a groove on the other. Slide the two housings together
engaging the tongue in the groove. Be sure they are fully meshed. No roll
pin is needed to lock the shells together.
Bend the copper wire at right angles to the housings so that when it
is placed in the holes on the PCB, the housings lie against the PCB
within their outline as shown in Figure 31. Be sure the red housing is
on the
+ side and the housings are oriented as shown.
Solder the wires in place and cut them as close to the PCB as
possible.
You’ve finished Part I of the RF PCB Assembly Procedure. Go to the RF
PCB Assembly – Part II to continue the RF PCB assembly.
Page 42

- 39 -
RF PCB Assembly – Part II
In the following steps you will install components unique to each band on the
RF PCB. These components are provided in the XV50, XV144 or XV222
band completion kit package. Perform only the assembly procedure for the
transverter you are building.
XV50 – 50 MHz Transverter
Perform the following steps on the RF PCB only if you are building the
XV50 transverter.
Install resistor R24, 68 ohm (68J), 2 watt, in the lower left quadrant
near U6. Space this resistor about 1/16” (1.5 mm) above the PCB like you did
the 1-watt and 3-watt resistors earlier (See Figure 15).
Install resistor R6, 330 ohm (org-org-brn), 1/4 watt, above Q2 and U2.
Place this resistor directly against the circuit PCB.
Install Z4, a 56 ohm (grn-blu-blk), 1/4 watt resistor near U2.
Install transistor Q1 (NTE108) near U2.
Install the molded inductors listed below:
L2, .22 H (red-red-silver) near U1 in the upper left quadrant of the
PCB.
Z3, .15 H (brn-grn-silver) near U6 in the lower left quadrant of the
PCB.
L3, .22 H (red-red-silver) near frequency mixer Z1 in the lower
right quadrant of the PCB.
Install the following capacitors near transistor Q1:
__C12, 100 pF (101) __C14, 390 pF (391)
Install the following capacitors near frequency mixer Z1:
__C58, 390 pF (391) __C59, 390 pF (391)
Install capacitor C69, 10 pF (100) near L15 and L16.
Install the two 1-40 pF trimmer capacitors as follows. Align the flat
end of each trimmer with the flat end on the silk-screened outline
C33, near L17 on the right lower quadrant of the PCB. (On
some PCBs C33 may be marked C64).
C1, to the right relay K1 in the upper left part of the PCB.
Install crystal Y1 where indicated by the silk-screened outline inside
circle OV1. The crystal may be oriented either way. Be sure the crystal
case is sitting directly on the PCB. Do not hold your soldering iron on
the leads more than 2 or 3 seconds maximum. Excessive heat may
damage the crystal.
If you purchased the optional crystal oven with your transverter
(Elecraft part number E980076) install it now as follows:
Position the oven down over the crystal so the three leads on the
oven pass through the +, - , and NC holes in the PCB. The oven
will only go on the crystal one way.
Bend the leads over on the bottom of the RF PCB to hold the
oven in place, then tack-solder one lead.
Check to be sure the oven fully seated down over the crystal and
against the PCB. If necessary, reheat the soldered lead and adjust
its position.
Solder and trim all three leads.
Install a jumper across the solder pads for L4A near C13 on the right
side of the PCB. Use a discarded lead to make the jumper.
Install voltage regulator U3 (LM78L05) to the left of relay K6 at the
center of the PCB.
Install R29, 56 ohm (grn-blu-blk), 1/4 watt, near the center of the
PCB.
Install PC trimmer potentiometer R39, 1K ohm (102) near R29.
Page 43

- 40 -
Install R28, 1k (brn-blk-red), 1/4 watt, near L7 on the left center of the
PCB.
Install a jumper across the solder pads at W1 near the notch and
electrolytic capacitor C60 on the left side of the PCB.
Wind L10 with 6 turns of #22 enameled wire on the T44-6 (yellow) core
as shown in Figure 30. Strip and tin the wires like you did for T1.
REMOVE INSULATION
UP TO THE CORE
THIS LEAD PASSES
OVER FRONT OF
CORE
Figure 30. Winding Inductor L10.
Install L10 within the square outline near the upper left corner of the
PCB with the leads through the solder pads at the corners of the outline and
the toroid sitting upright against the PCB diagonally across the square
outline.
Unscrew and remove the tuning slug from L1, the larger gray variable
inductor. The tuning slug will not be used.
i
If you are not wearing a grounded antistatic wrist strap, touch an
unpainted, grounded object before performing the next step. Once the
temporary jumper across L1 is removed, Q3 is particularly sensitive to
electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage until inductor L1 is soldered in
place.
Remove the temporary jumper and install L1 next to trimmer capacitor
C1 in the upper left quadrant. Be sure the plastic frame of the inductor is
resting against the PCB
.
Unscrew and remove the tuning slug from L11, the blue variable
inductor. The tuning slug will not be used.
Install L11 near the upper left corner of the PCB. Be sure the plastic
frame of the inductor is resting against the PCB.
Locate the shielded inductors with gray inserts provided for L12,
L13 and L14. Prepare the inductors for installation as follows:
Use the inductor alignment tool to exercise the core in each
inductor. If the alignment tool fits tightly, insert it from the
bottom to avoid pushing the inductor out of the shield. Run the
core up and down through the coil to ensure it runs smoothly
(some inductors are very stiff at first) then position the core near
the top of the coil.
Check the two leads and the two tabs on the case of each
inductor. If they are bent, straighten them using long nose pliers.
Install the RF Bandpass Filter inductors in the lower right quadrant
of the PCB:
__L12 __L13 __L14
Locate the male RCA plug. Solder a jumper between the center pin
and the shield. This plug will be used during the alignment procedures.
Carefully inspect the bottom of the PCB for the following:
All component leads are soldered. Be especially careful when
checking relays and other components with several leads to
ensure that all the leads are soldered. There will be some
component locations on the PCB that are not filled. This is
normal. The same RF PCB is used for the XV50, XV144 and
XV222 transverters, and some components are specific to each
band.
All component leads are clipped at least as short as the relay
pins. Do not cut the relay pins.
This finishes Part II of the RF PCB Assembly. Proceed directly to RF
PCB Assembly Part III.
Page 44

- 41 -
XV144 –144 MHz Transverter
Perform the following steps on the RF PCB only if you are building the
XV144 transverter.
Install the resistors listed below.
R24, 120 ohm (brn-red-brn), 1 watt in the lower left quadrant near
U6. Space this resistor about 1/16” (1.5 mm) above the PCB like
you did the 1-watt and 3-watt resistors earlier (See Figure 15).
R28, 1k (brn-blk-red), 1/4 watt, near L7 on the middle left. Place this
resistor directly against the PCB.
R29, 56 ohm (grn-blu-blk), 1/4 watt, in center of PCB.
R6, 470 ohm (yel-vio-brn), 1/4 watt, near the circle for OV1 in the
lower right quadrant of the PCB.
Install Z4, a 56 ohm (grn-blu-blk) 1/4 watt resistor near U2 in the lower
right quadrant.
Install the following capacitors near the circular outline for OV1 in the
lower right quadrant:
__C13, .047 F (473)
__C12, 10 pF (100)
__C14, 33 pF (330)
Install a jumper made from a discarded lead across the solder pads for
L3 near toroidal transformer T1 in the lower right quadrant.
Install the molded inductors listed below:
L2, .1 H (brn-blk-silver) near U1 in the upper left quadrant of
the PCB.
Z3, .1 H (brn-blk-silver) near U6 in the lower left quadrant of
the PCB.
L4, .15 H (brn-grn-silver) near R6 on the right side of the PCB.
Cut the Teflon tubing to a length of 3/8” (8 mm).
Slide the 3/8” (8mm) length of Teflon tubing over the center lead of
transistor Q1 (NTE108).
Install transistor Q1 (NTE108) near the circular outline in the lower
right quadrant so that the Teflon tubing acts as a spacer to hold the
transistor above the PCB. One end of the tubing should contact the
bottom of Q1’s case and the other end should rest against the top of the
PCB (see Figure 32).
Figure 32. Installing Q1 with Teflon Spacer.
Page 45

- 42 -
Install crystal Y1 where indicated by the silk-screened outline inside
the circular outline for OV1. The crystal may be oriented either way. Be sure
the crystal case is sitting directly on the PCB. Do not hold your soldering
iron on the leads more than 2 or 3 seconds maximum. Excessive heat
may damage the crystal.
If you purchased the optional crystal oven with your transverter
(Elecraft part number E980076) install it now as follows:
Position the oven down over the crystal so the three leads on the
oven pass through the +, - , and NC holes in the PCB. The oven
will only go on the crystal one way.
Bend the leads over on the bottom of the RF PCB to hold the oven in
place, then tack-solder one lead.
Check to be sure the oven fully seated down over the crystal and
against the PCB. If necessary, reheat the soldered lead and adjust its
position.
Solder and trim all three leads.
Install voltage regulator U3 (78L05) to the left of relay K6 at the center
of the PCB.
Install PC trimmer potentiometer R39, 1K ohm (102) near the center of
the PCB.
Install trimmer capacitor C1, 4-15 pF, to the right of relay K1 in the
upper left quadrant of the PCB. This capacitor has a blue dot to identify it.
Remove the tuning slug from L1, the larger variable inductor with an
orange plastic frame. The tuning slug will not be used.
i
If you are not wearing a grounded antistatic wrist strap, touch an
unpainted, grounded object before performing the next step. Once the
temporary jumper across L1 is removed, Q3 is particularly sensitive to
electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage until inductor L1 is soldered in
place.
Remove the temporary jumper across the space for L1 in the upper
left quadrant of the PCB and install the orange variable inductor. Be sure
the plastic frame of the inductor is resting against the PCB.
Unscrew and remove the tuning slugs from L10 and L11, the smaller
orange variable inductors. The tuning slugs will not be used.
Install L10 and L11 near the upper left corner of the PCB. Be sure
the plastic frames of the inductors are resting against the PCB.
__L10 __L11
Install L19 (red) near crystal Y1 on the right side of the PCB. Be
sure the plastic frame of the inductor is against the PCB.
Adjust the slug in L19 so it is flush with the top of the inductor
frame.
Connect the XV144 to your K2 or K3 and apply power prepare to
measure the local oscillator frequency tune into a signal of known
frequency as described in your XV Owner’s manual under Local
Oscillator Frequency Calibration.
Use the K2 or K3 offset (OFS) menu command to correct any
frequency error. If the correction required is more than the 9.99 kHz
range turn the slug into L19 and retry the offset command. Turning the
slug into L19 too far may cause the local oscillator to stop. It may take
several iterations to move the local oscillator frequency within range of
the offset command.
Measure the voltage between TP1 LO LEVEL and ground while
switching the XV144 on and off repeatedly. This voltage is normally
between 1.2 and 1.8 VDC. Verify that the voltage returns to the same
level each time power is switched on, indicating that the local oscillator is
starting reliably.
Page 46

- 43 -
Locate the shielded inductors with red inserts provided for L12, L13
and L14 in the R.F. Bandpass filter. Prepare the inductors for installation as
follows:
Use the inductor alignment tool to exercise the core in each inductor.
If the alignment tool fits tightly, insert it from the bottom to avoid
pushing the inductor out of the shield. Run the core up and down
through the coil to ensure it runs smoothly (some inductors are very
stiff at first) then position the core near the top of the coil.
Check the two leads and the two tabs on the case of each inductor. If
they are bent, straighten them carefully using long nose pliers.
Install the RF Bandpass Filter inductors in the lower right quadrant:
__L12 __L13 __L14
Install a jumper across the solder pads at W1 near the notch and
electrolytic capacitor C60 on the left side of the PCB.
Carefully inspect the bottom of the PCB for the following:
All component leads are soldered. Be especially careful when
checking relays and other components with several leads to
ensure that all the leads are soldered. There will be some
component locations on the PCB that are not filled. This is
normal. The same RF PCB is used for the XV50, XV144 and
XV222 transverters, and some components are specific to each
band.
All component leads are clipped at least as short as the relay
leads. Do not cut the relay pins.
Locate the male RCA plug. Solder a jumper between the center pin
and the shield. This plug will be used during the Alignment procedures.
This finishes Part II of the RF PCB Assembly. Proceed directly to RF
PCB Assembly Part III.
Page 47

- 44 -
XV222 – 222 MHz Transverter
Perform the following steps on the RF PCB only if you are building the
XV222 transverter.
Install the resistors listed below.
R24, 56 ohm (grn-blu-blk), 2 watt, in the lower left quadrant near
U6. Space this resistor about 1/16” (1.5 mm) above the PCB like
you did the 1-watt and 3-watt resistors earlier (See Figure 15).
R28, 1k (brn-blk-red), 1/4 watt, near L7 on the middle left. Place this
resistor directly against the PCB.
R29, 56 ohm (grn-blu-blk), 1/4 watt, in center of PCB.
R6, 220 ohm (red-red-brn), 1/4 watt, above Q2 and U2.
Install Z4, a 56 ohm (grn-blu-blk) 1/4 watt resistor in the lower right
quadrant of the PCB.
Install a jumper wire across the solder pads for L3 to the left of toroidal
transformer T1 in the lower right quadrant.
Install two .1 H (brn-blk-silver) molded inductors:
L2 near U1 in the upper left quadrant of the PCB.
Z3 near U6 in the lower left quadrant of the PCB.
Install the following capacitors near the circular outline for OV1 in the
lower right quadrant:
__C13, .047 F (473)
__C12, 15 pF (15)
__C14, 22 pF (220)
Cut the Teflon tubing to a length of 3/8” (8mm).
Slide the 3/8” (8mm) length of Teflon tubing over the center lead of
transistor Q1 (NTE108).
Install transistor Q1 (NTE108) near U2 so that the Teflon tubing acts
as a spacer to hold the transistor above the PCB. One end of the tubing
should contact the bottom of Q1’s case and the other end should rest
against the top of the circuit PCB (see Figure 33).
Figure 33. Installing Q1 with Teflon Spacer.
Install voltage regulator U3 (78L05) to the left of relay K6 at the
center of the PCB.
Install crystal Y1 where indicated by the silk-screened outline inside
circle OV1. The crystal may be oriented either way. Be sure the crystal
case is sitting directly on the PCB. Do not hold your soldering iron on
the leads more than 2 or 3 seconds maximum. Excessive heat may
damage the crystal.
Page 48

- 45 -
If you purchased the optional crystal oven with your transverter
(Elecraft part number E980076) install it now as follows:
Position the oven down over the crystal so the three leads on the
oven pass through the +, - , and NC holes in the PCB. The oven will
only go on the crystal one way.
Bend the leads over on the bottom of the RF PCB to hold the oven in
place, then tack-solder one lead.
Check to be sure the oven fully seated down over the crystal and
against the PCB. If necessary, reheat the soldered lead and adjust its
position.
Solder and trim all three leads.
Install pc pot R39, 1K ohm (102) near the center of the PCB.
Install trimmer capacitor C1, 4-15 pF, to the right of relay K1 at the
upper left part of the PCB. This capacitor has a blue dot to identify it.
Adjust the slug in L4A (red plastic frame) so it is flush with the top of
the coil form.
Install L4A near crystal Y1 on the right side of the PCB. Be sure its
plastic frame is resting against the PCB.
Install L19 near crystal Y1 on the right side of the PCB. Be sure the
plastic frame of the inductor is against the PCB.
Unscrew and remove the tuning slug from L1, the larger variable
inductor with a brown plastic frame. The tuning slug will not be used.
i
If you are not wearing a grounded antistatic wrist strap,
touch an unpainted, grounded object before performing the next
step. Once the temporary jumper across L1 is removed, Q3 is
particularly sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage until
inductor L1 is soldered in place.
Remove the jumper and install L1 next to trimmer capacitor C1 in
the upper left quadrant.
Unscrew and remove the tuning slugs from the two remaining red
inductors L10 and L11. The tuning slugs will not be used.
Install the inductors near the upper left corner of the PCB. Be sure
the plastic frames of the inductors are resting against the PCB.
__L10 __L11
Locate the shielded inductors with brown inserts provided for L12,
L13 and L14 in the R.F. Bandpass filter. Prepare the inductors for
installation as follows:
Use the inductor alignment tool to exercise the core in each
inductor. If the alignment tool fits tightly, insert it from the
bottom to avoid pushing the inductor out of the shield. Run the
core up and down through the coil to ensure it runs smoothly
(some inductors are very stiff at first) then position the core near
the top of the coil.
Check the two leads and the two tabs on the case of each
inductor. If they are bent, straighten them carefully using long
nose pliers.
Page 49

- 46 -
Install the RF Bandpass Filter inductors in the spaces provided
between relay K2 and frequency mixer Z1:
__L12 __L13 __L14
Install a jumper across the solder pads at W1 on the left side of the PCB
near the notch and electrolytic capacitor C60.
Carefully inspect the bottom of the PCB for the following:
All component leads are soldered. Be especially careful when
checking relays and other components with several leads to ensure
that all the leads are soldered. There will be some component
locations on the PCB that are not filled. This is normal. The same
RF PCB is used for the XV50, XV144 and XV222 transverters, and
some components are specific to each band.
All component leads are clipped at least as short as the relay leads.
Do not cut the relay pins.
Locate the male RCA plug. Solder a jumper between the center pin and
the shield. This plug will be used during the Alignment procedures.
This finishes Part II of the RF PCB Assembly. Proceed directly to RF PCB
Assembly Part III
Page 50

- 47 -
RF PCB Assembly – Part III
In the following steps you will install the RF power module. The procedure is
the same for all three transverter models.
If you purchased the optional feet and bail for your transverter, install
them on the bottom cover now.
You will use the following small hardware:
14 pan head black screws, 3/16” (4.8 mm) 4-40 thread.
2 pan head black screws, 1/2” (12.7 mm) 4-40 thread.
2 nuts, 4-40 thread.
4 2-D fasteners.
2 flat washers, #4.
2 inside tooth lock washers, #4.
8 split lock washers, #4.
Install four 2-D fasteners on the bottom corners of the RF PCB. Line up
the offset holes of each 2-D fastener so the side of the connector is flush with
the edge of the PCB (see Figure 34). Secure each connector to the PCB with
two black 3/16” (4.8 mm) pan head screws and split lock washers.
HOLES OFFSET
FROM CENTER
T
OP O
F
BOARD
LINES UP FLUSH
WITH EDGE OF
BOARD
C
L
Figure 34. 2-D Fasteners.
i
In the following steps you will install the hardware that
attaches the RF power module to the bottom cover. Follow the steps
carefully to ensure the module makes good thermal contact with the
bottom cover and the leads line up properly with the RF PCB. The
completed hardware assembly is shown in Figure 38 .
Locate the bottom cover. The bottom cover has two sets of cooling
holes.
On the inside surface of the bottom cover, locate the four holes that
match the holes in the heat spreader. They are between the two sets of
cooling holes. Test-fit the larger of the two thermal conduction pads so
that the holes in the pad line up with the holes in the cover. Orient the pad
so it does not hang over the edge of the bottom cover.
Lift the thermal conduction pad and clean the surface of the bottom
cover under the pad using sandpaper, a sharp knife or other tool. The pad
must rest against clean, bare metal.
Clean the paint off of the inside surface of the bottom cover around
the screw holes in the four corners where the 2-D fasteners will attach it
to the RF PCB (See Figure 37).
Inspect the edges of the heat spreader and remove any burrs with the
edge of a flat-blade screwdriver, knife or small file.
Replace the larger of the two thermal conduction pads over the clean
metal area on the inside of the bottom cover so that the holes line in the
pad line up with the holes in the cover. Be sure the pad does not hang
over the edge of the bottom cover.
Place the heat spreader on the thermal conduction pad on so the
screw holes line up. Put a 1/2” (12.7 mm) pan head screw through each
unthreaded hole with the head on the bottom cover. Place a nut on each
screw and finger tighten.
Insert two black 3/16” (4.8 mm) pan head screws through the bottom
cover into the threaded holes in the head spreader. Tighten the screws.
Page 51

- 48 -
Lay the bottom cover on a clean, smooth surface with the heat spreader
facing up.
Remove the nuts from the long screws but do not remove the screws. If
you have installed feet on the bottom cover, place a small book that fits
between the feet under the cover so the long screws do not fall out.
Place the smaller thermal conduction pad over the screws. Orient the pad
so it does not hang over the edge of the heat spreader.
Position the RF power module on the two screws as shown in Figure 35.
Be sure the thermal conduction pad on the heat spreader is resting directly
against the bottom of the RF power module.
Place a flat washer on each screw as shown in Figure 35.
Figure 35. RF Power Module and Flat Washers in Place on the Heat
Spreader.
Slide the PCB under the leads on the RF power module and over the
screws until they pass through the holes in the PCB (see Figure 36). You
can rock the RF Power Module slightly on the screws and bend the leads
up as needed to slip the PCB under them and over the tops of the
mounting screws.
Place an internal tooth lock washer and nut on each screw and
tighten them finger tight.
Figure 36. RF PCB attached to the RF Power Module Screws.
Pick up the entire assembly and secure the four 2-D fasteners to the
bottom cover. Each corner is attached with one 3/16” (4.8 mm) black
screw (see Figure 37). The other two screw holes in each 2-D fastener
will secure the front, rear and side covers in later steps.
Figure 37. Bottom Cover Attached to 2-D Fastener.
Page 52

- 49 -
Inspect the RF Power module to be sure you have the module and
hardware installed exactly as shown in Figure 38.
Figure 38. RF Amplifier Module Mounting Hardware.
Adjust the position of the RF Power module to provide the best
alignment of the leads with the solder pads on the PCB. If necessary, loosen
the nuts slightly to allow the module to move within the limits of its screw
holes.
Hold the RF Power module in place and tighten both screws and nuts to
secure it.
i
Be sure the four screws holding the RF Power module and heat
spreader are tightened securely to ensure good heat transfer. Otherwise
the RF Power module may overheat and fail.
Solder the RF power module leads to their corresponding pads on the
PCB. Before soldering, trim the leads as needed so they do not extend
beyond the solder pads.
This finishes Part III of the RF PCB Assembly. Proceed directly to
Final Assembly.
Page 53

- 50 -
Final Assembly
In the following steps you’ll finish assembling the transverter.
Remove paint overspray from around the screw holes on the inside
surface of the cabinet back panel where the 2-D fasteners will be attached
(see Figure 44). The 2-D fasteners should make good electrical contact with
the back panel
i
Good electrical contact between all of the chassis parts is essential
for optimum shielding and system noise figure.
Mount antenna connector J1 on the cabinet back panel using four 5/16”
4-40 pan head zinc or stainless steel screws, lock washers, nuts and one
ground lug as shown in Figure 39. Be sure the ground lug is on the lower
screw nearest the end of the back panel and faces upward as shown. The
antenna connector is an S0-239 (UHF) connector on the XV50 transverter,
and a type “N” connector on the XV144 and XV222 transverters.
INSIDE TOOTH
LOCK WASHER
ON EACH SCREW
GROUND LUG ON
BOTTOM SCREW
NEAREST THE EN
D
Figure 39. Mounting the Antenna Connector J1 on the Back Panel.
Solder the two clipped leads you saved when you installed D5 (Page
28) to the J1 solder pads on the RF PCB. The J1 pads are near K1 (see
Figure 40).
Figure 40. J1 Solder Pads on RF PCB.
Position the cabinet back panel on the rear of the RF PCB so the 12
VDC, Control, TXn/IF1, RXout/IF2, Key In and Key Out jacks project
through the holes in the cover. Attach the cover to the 2-D fasteners at the
rear of the RF PCB using two 3/16” (4.8 mm) black pan head screws.
Attach the two DB-9 male-female standoffs to the Control
connector. Use a #4 inside tooth lock washer between each standoff and
the rear cover. Note: Do not force the threads. When assembling the
modular chassis, screw holes will sometimes not align perfectly. Loosen
the other screws holding the panel so it can move as needed to align the
holes so all the screws can start easily, then tighten all hardware.
Slip the finish lock washers and nuts over the BNC connectors and
tighten them.
Page 54

- 51 -
Connect J1 to the leads already soldered to the RF PCB as follows (See
Figure 41):
_ Solder the lead that is farthest from the edge to the center pin on the
antenna connector. This is the lead that goes to the circuit trace on
the PCB. Keep the lead as short as possible.
_ Solder the lead attached to the RF PCB at J1 that is closest to the
corner to the ground lug on the antenna connector. This is the lead
that goes to the ground plane on the PCB. Bend the ground lug as
shown to reach it. Keep the lead as short as possible.
Figure 41. Installing J1.
Mount the two right-angle brackets on the edge of the RF PCB (see
Figure 14 on page 27). Place the shorter side of each bracket against the top
of the RF PCB and secure it with a 3/16” (4.8 mm) screw and split lock
washer.
i
Either wear a grounded antistatic wrist strap or touch an
unpainted, grounded object before handling the processor (U1) in
the next steps, or at any time you handle the front panel PCB
unplugged from the RF PCB with processor U1 installed.
Remove processor U1 from its conductive foam packing and inspect
the pins. The two rows of pins must be straight and parallel to each other
to establish the proper pin spacing for insertion into the socket. To
straighten the pins, rest one entire row of pins against a hard, flat surface.
Press down gently and rock the IC forward to bend the pins into position
as shown in Figure 42.
FLARED
STRAIGHT
PRESS AND
ROCK TO
STRAIGHTEN
Figure 42. Straightening IC Pins.
Identify the end of the IC where Pin 1 is located. It will have a notch,
a dimple or both at this end (see Figure 43).
DIMPLE AT
PIN 1
NOTCH
Figure 43. IC Orientation.
Page 55

- 52 -
i
When U1 is pressed into its socket, you must be careful to avoid
jamming its pins. Make sure all the pins are lined up with the associated holes
before pressing down on the IC. Watch the pins on both rows as you press down
to be sure each pin goes straight down into its socket hole and does not bend in
under the IC or outward alongside the socket. Realign each pin individually
with its socket hole, if necessary.
Insert processor U1 in its socket with pin 1 or the notched end lined up
with the notched end of the socket (the end farthest from the edge of the front
panel PCB). Be careful while pressing U6 into its socket not to bend or
damage the power indicator LEDs on the front side of the PCB.
Insert plug P1 on the front panel PCB into J1 on the bottom of the RF
PCB, and then secure the front panel PCB to the two right angle brackets
with 3/16” (4.8 mm) screws and split lock washers.
Place the cabinet front panel face up on your work surface and attach the
label with two 2-56 screws. Orient the label with the lighter side upward so
that the band identification reads correctly when viewed from the front.
Fit the front panel over the power pushbutton and power LEDs. Attach
the front panel to the 2-D fasteners on the bottom of the RF PCB with two
3/16” (4.8 mm) screws.
Press the key cap onto the On/Off switch shaft until it clicks in place.
Attach a 2-D fastener to the each screw hole at the top corners of the
front and rear chassis end panels with 3/16” (4.8 mm) screws. Be sure
the widest side of each 2-D fastener is facing toward the end of the panel
so the edge lines up flush with the edge of the panel as shown in Figure
44.
Figure 44. Attaching 2-D Fasteners to Cabinet End Covers.
Inspect the inside surface of the side covers and remove any paint
overspray around the screw holes to ensure good electrical contact with
the 2D fasteners.
Attach the side panels using four 3/16” (4.8 mm) screws in each
panel. You many need to loosen the other screws holding the end covers
temporarily to line up the screw holes properly.
Page 56

- 53 -
i
In the following step be sure to orient the Anderson power
connector shells exactly as shown. Otherwise, the connector will not mate
with the connector on the transverter.
Locate the two Anderson power connector shells. Orient them as shown
in Figure 45 and slide them together so the tongue on one side fully engages
the groove on the other half.
BLACK
RED
SOLDER
Figure 45. Power Cable Connector Assembly.
i
Use only the supplied 12 AWG, 2-conductor stranded wire
(red/black) for the DC power cable.
Separate the two conductors at one end of the 12 AWG, 2-conductor
cable. Remove 5/16” (8 mm) of insulation from the red and black wires at
one end. Do not nick or cut off any of the strands.
Insert the wires into the terminals as shown above. Solder the wires to
the crimp terminals, using enough solder to completely surround the wire and
fill the interior of the terminal. (This may take as long as 10 seconds if you’re
using a small iron.) Be careful not to get solder on the tongue that extends
from the front of the terminal.
Insert the terminals into the housings exactly as shown in Figure 45. The
terminals should snap securely in place. Pull on the wires individually and
make sure they cannot be pulled out (if so, the terminals are probably inserted
upside down).
Optional: The supplied spring pin may be inserted as shown in the
figure above to keep the red and black housing from slipping apart. The
manufacturer of the connectors recommends securing the pin with a drop
of super-glue.
Prepare the opposite end of the 2-conductor stranded wire and attach
the red wire to your power supply positive (+) terminal and the black
wire to the power supply negative (-) terminal.
Locate the top cover and the four 3/16” (4.8 mm) screws provided to
attach it to the 2-D fasteners on the top of the transverter.
Clean any paint from the areas where the inside surface of the top
cover will contact the 2-D fasteners when it is installed. You may leave
the top cover off at this time if desired. You will need the top open to
complete the installation and alignment procedures.
Locate and set aside the nine, 2-pin header shorting blocks. They
will be used in the Installation section to configure your transverter to
work with your station equipment.
i
Skip the next step if you have installed the optional feet and
bail assembly.
Attach the self-stick rubber feet to the bottom of your transverter.
Use the pre-drilled holes for the optional feet as a guide.
Place the rear feet over the screw holes.
There are two screw holes provided for each front foot. Position
each front foot between the holes.
This completes the assembly of your transverter. Go to the next section
to test and align your transverter.
Page 57

- 54 -
Final Test and Alignment
In the following steps you will connect your transverter to your station
equipment and perform a complete alignment and test procedure.
Turn to the Installation Procedures in your Transverter Owner’s
Manual and follow those instructions to connect your transverter to your
other station equipment including the rig you will us for a 28 MHz I.F.
Perform the complete Alignment and Test Procedures in your
Owner’s Manual to properly adjust and calibrate your transverter and
verify that it is operating normally.
If you encounter any difficulties in the alignment and test procedures:
_ Carefully check your setup to ensure all cables are properly
connected.
_ Inspect again your parts placement and soldering on the PC
PCBs. Most initial difficulties are eventually traced to an
incorrectly placed component or a bad solder connection. The
circuit description and schematic diagrams in your Owner’s
manual can help you decide which circuits to check, based on
where in the alignment and test procedures you experience
difficulty.
_ Refer to the Troubleshooting information in your Owner’s
Manual for nominal voltages at key points in normal operation.
Congratulations
You have completed the assembly, test and alignment of your
transverter. Turn to your Owner’s Manual for complete installation and
operating instructions.
Your Owner’s Manual also describes modifications and optional
accessories for your transverter that you may choose to best integrate it
with your station equipment.
 Loading...
Loading...