Page 1

Elecraft Transverter Models XV50, XV144, XV222, XV432
Owner’s Manual
Rev F1, April 16, 2013
Copyright © 2013, Elecraft; All Rights Reserved
Page 2

Page 3

Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION .................................................................................................................................................................... 1
Features
Using an Elecraft K2 or K3 as the I.F. Transceiver ...................................................................................................................................................... 1
Customer Service and Support
Technical Assistance .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 2
Repair / Alignment Service ........................................................................................................................................................................................... 2
........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 1
..................................................................................................................................................................................... 1
SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................................................................................................................. 3
General
Transmitter
Receiver
......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 3
.................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 3
........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 3
INSTALLATION ..................................................................................................................................................................... 4
Quick-Start Installation .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 4
Installation Options ....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 4
Elecraft K3 Setup Instructions ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 4
Elecraft K2 Setup Instructions ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 6
Non-Elecraft 28 MHz Rig – Separate Transmit and Receive RF Connections ............................................................................................................ 9
Non-Elecraft 28 MHz Rig – Single Transmit and Receive RF Connection ................................................................................................................. 10
Transverter Control Cable........................................................................................................................................................................................... 11
Daisy-Chaining Multiple Transverters ......................................................................................................................................................................... 14
Using an External Receive Preamplifier ..................................................................................................................................................................... 15
Using an External Power Amplifier ............................................................................................................................................................................. 15
OPERATION ........................................................................................................................................................................ 16
Cautions to Avoid Spurious Emissions From Your Station ......................................................................................................................................... 16
Turning the Transverter On......................................................................................................................................................................................... 16
Power Output Control ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 16
Page 4

Local Oscillator Power Control ................................................................................................................................................................................... 16
I.F. Overload Condition ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 17
Transmit-Receive Switching Delay ............................................................................................................................................................................. 17
Front Panel Display Control ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 17
OPTIONS AND MODIFICATIONS ....................................................................................................................................... 18
Tools Required ............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 18
Optional Crystal Oven ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 19
Changing Between Split and Common Antennas ...................................................................................................................................................... 20
Reducing Receive Gain to Preserve System Dynamic Range ................................................................................................................................... 21
Optional Feet and Bail Attachment ............................................................................................................................................................................. 21
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION ..................................................................................................................................................... 22
Signal Flow ................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 22
Circuit Details .............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 24
ALIGNMENT AND TEST ..................................................................................................................................................... 27
Part I - Initial Setup ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 27
Part II – Power Control ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 28
Part III - Local Oscillator Level .................................................................................................................................................................................... 28
Part IV – Receiver RF Amplifier Bias Adjustment ....................................................................................................................................................... 29
Part V – RF Power Amplifier Quiescent Current Adjustment. .................................................................................................................................... 29
Part VI – Filter Alignment. ........................................................................................................................................................................................... 29
Part VII – Power Display LED Calibration. .................................................................................................................................................................. 30
Part VIII – Receiver Input Alignment. .......................................................................................................................................................................... 30
Part IX - Overload Protection Circuit Test ................................................................................................................................................................... 31
Local Oscillator Frequency Calibration (Optional) ...................................................................................................................................................... 32
SCHEMATICS AND PARTS PLACEMENT DIAGRAMS.....................................................................................Appendix A
TROUBLESHOOTING..........................................................................................................................................Appendix B
JUMPER AND DIP SWITCH SETTINGS..............................................................................................................Appendix C
Page 5

Introduction
The Elecraft XV Series high-performance transverters may be used with
any transceiver or transmitter/receiver pair that covers the 10 meter band.
Separate transverters are offered for the following bands:
Model XV50: 50 to 52 MHz
Model XV144: 144 to 146 MHz
Model XV222: 222 to 224 MHz
Model XV432: 432 to 436 MHz
Features
I.F. connections to the transceiver can be either single-port, using a single
RF cable, or dual port, using separate receive and transmit cables.
The transverters include an adjustable input level control that will provide
full output from the transverter with I.F. power levels as low as 0.01
milliwatts up to 8 watts. Full protection against accidental high-power
transmit of up to 100 watts into the I.F. port is also included.
The receiver features a very low noise figure with a PHEMT RF stage for
weak-signal work. Relays are used for transmit/receive switching to
avoid receive performance degradation by diode switches in the signal
path.
Using an Elecraft K2 or K3 as the I.F. Transceiver
While the transverters will work with nearly any HF transceiver, using
them with our Elecraft K2 or K3 offers additional benefits. These highperformance transceivers provide:
Low noise, single-conversion, wide dynamic range receiver.
Single conversion to a low I.F. with roofing filters as narrow as
200 Hz
K2, 6 transverter bands. K3, 9 transverter bands
Direct display of the transverter operating frequency to 10 Hz (1
Hz for the k3), including per-band adjustable offsets of +/- 9.99
kHz.
Low current drain, ideal for Field Day or rover use.
We recommend that K2’s with serial numbers 3445 and below be
equipped with Elecraft-approved modifications that reduce spurious
responses and enhance frequency stability. See Special Notes for Elecraft
K2 Owners on page 4.
Customer Service and Support
The transverters are housed in attractive, low-profile enclosures that may
be stacked for multi-band operation. An illuminated band label identifies
the transverter in use. Several transverters may be connected to a single
transceiver. Internal relays select only the transverter for the band in use,
avoiding the need to switch I.F. cables.
Whether you build the kit or buy a factory-built transverter, you’ll find a
wealth of information on our web site at
materials there you’ll find the latest application notes, photographs, any
updates to this manual, and information on new products. We also have a
popular e-mail forum. You can sign up for it from the web site. It's a
great way to interact with other Elecraft owners, exchange ideas and find
answers to many questions.
- 1 -
www.elecraft.com. Among the
Page 6

Technical Assistance
You can send e-mail to support@elecraft.com and we will respond
quickly - typically the same day Monday through Friday. Telephone
assistance is available from 9 A.M. to 5 P.M. Pacific time (weekdays
only) at 831-763-4211. Please use e-mail rather than calling when
possible since this gives us a written record of the details of your problem
and allows us to handle a larger number of requests each day.
Repair / Alignment Service (We want to make sure everyone
succeeds!)
If necessary, you may return your Elecraft product to us for repair or
alignment. (Note: We offer unlimited email and phone support to get
your kit running, so please try that route first as we can usually help you
find the problem quickly.)
IMPORTANT: You must contact Elecraft before mailing your
product to obtain authorization for the return, what address to ship it to
and current information on repair fees and turnaround times. (Frequently
we can determine the cause of your problem and save you the trouble of
shipping it back to us.) Our repair location is different from our factory
location in Aptos. We will give you the address to ship your kit to at the
time of repair authorization. Packages shipped to Aptos without
authorization will incur an additional shipping charge for reshipment
from Aptos to our repair depot
To ship the unit, first seal it in a plastic bag to protect the finish. Use a
sturdy packing carton with at least 3-in (8 cm) of foam or shredded paper
on all sides. Seal the package with reinforced tape. (Neither Elecraft or
the carrier will accept liability for damage due to improper packaging.)
.
Elecraft 1-Year Limited Warranty
This warranty is effective as of the date of first consumer purchase (or if
shipped from the factory, the date the product is shipped to the customer). It
covers both our kits and fully assembled products. For kits, before requesting
warranty service, you should fully complete the assembly, carefully following
all instructions in the manual.
Who is covered: This warranty covers the original owner of the Elecraft
product as disclosed to Elecraft at the time of order. Elecraft products
transferred by the purchaser to a third party, either by sale, gift, or other
method, who is not disclosed to Elecraft at the time of original order, are not
covered by this warranty. If the Elecraft product is being bought indirectly for
a third party, the third party’s name and address must be provided at time of
order to ensure warranty coverage.
What is covered: During the first year after date of purchase, Elecraft will
replace defective or missing parts free of charge (post-paid). We will also
correct any malfunction to kits or assembled units caused by defective par ts
and materials. Purchaser pays inbound shipping to us for warranty repair; we
pay shipping to return the repaired equipment to you by UPS ground service or
equivalent to the continental USA and Canada. For Alaska, Hawaii, and other
destinations outside the U.S. and Canada, actual return shipping cost is paid by
the owner.
What is not covered: This warranty does not cover correction of kit assembly
errors. It also does not cover misalignment; repair of damage caused by
misuse, negligence, battery leakage or corrosion, or builder modifications; or
any performance malfunctions involving non-Elecraft accessory equipment.
The use of acid-core solder, water-soluble flux solder, or any corrosive or
conductive flux or solvent will void this warranty in its entirety. Also not
covered is reimbursement for loss of use, inconvenience, customer assembly or
alignment time, or cost of unauthorized service.
Limitation of incidental or consequential damages: This warranty does not
extend to non-Elecraft equipment or components used in conjunction with our
products. Any such repair or replacement is the responsibility of the customer.
Elecraft will not be liable for any special, indirect, incidental or consequential
damages, including but not limited to any loss of business or profits.
- 2 -
Page 7

Specifications
Numeric values are typical; your results may be somewhat different.
Specifications may be affected by the options or accessories chosen. See
www.elecraft.com for details about options and accessories currently
available. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
General
Size
Cabinet: 1.3” H x 7.8” W x 8.3” D
(3.3 x 19.8 x 21 cm)
Overall: 1.5 H x 7.8 W x 9.5 D incl. feet and connectors
(3.8 x 19.8 x 21 cm)
Weight: 2.5 lbs (1.1 kg)
Supply Voltage: 13.8 VDC
Current Drain:
Receive: 250 mA (typical)
Transmit
Frequency Ranges:
XV50: 50 – 52 MHz
XV144: 144 – 146 MHz
XV222: 222 – 224 MHz
XV432: 432 – 436 MHz
T/R Switching Time: 3 ms (typical)
T/R Key Input: Ground for transmit: must pull 5 volt
I.F. Overload Protection: Survives 100 watts RF input at the I.F.
1
: 6 A typical for XV432, 4 A typical for XV50,
XV144, XV222
logic level to within 0.5 volts of ground
at < 1 ma
Port without damage with transverter
un-keyed (in receive mode)
Amplifier Key Output: Ground on transmit: 200 VDC at 1 A
maximum
Connectors:
K2 or K3 Interface: DB9
Keying Line Input: RCA
Keying Line Output: RCA
I.F. In/Out: BNC
Aux (Rx-Only Ant): BNC
Antenna: SO-239 (UHF) on XV50
Type N on XV144, XV222 & XV432
Transmitter
Power Out (50-ohm load): 20 watts SSB/CW
10 watts continuous carrier modes
Minimum Supply
Voltage Recommended: 12 VDC
Operating Modes: CW, SSB, AM, FM, Digital Modes
I.F. Input Frequency Range: 28 – 30 MHz (XV50, 144 & 222)
28 – 32 MHz (XV432)
I.F. Input Power Range: 0.01 mW (-20 dBm) to
8 watts (+ 39 dBm)
Harmonic Content: < - 60 dBc at 20 watts output
Receiver
Noise Figure: < 1 dB
Conversion Gain: 25 dB typical for XV50, XV144,
XV222, 20 dB typical for XV432
Image Rejection: > 60 dB
1
Current varies with supply voltage, load impedance and power output.
3rd-Order Intercept: +20 dBm (typical)
- 3 -
Page 8
Installation
Your transverter is designed to integrate closely with the Elecraft K2 and
K3 transceivers. Also it will perform well with a variety of 28 MHz rigs
and connection setups. Start with the Quick-Start Installation that matches
your setup. Once you have the transverter working as desired, refer to the
Installation Options below for ways you might better integrate the
transverter into your station.
Quick-Start Installation
Choose the setup you wish to use from the list below and go to that
procedure for your initial setup. If you aren’t sure which to choose, check
the drawings associated with each of the following procedures to see
which matches the 28 MHz rig you are using with your transverter.
1. Elecraft K3: go to Elecraft K3 Setup Instructions on page 4.
2. Elecraft K2: go to Elecraft K2 Setup Instructions on page 6
3. Non-Elecraft 28 MHz Rig – Separate Transmit and Receive RF
Connections. Go to page 9.
4. Non-Elecraft 28 MHz Rig – Single Transmit and Receive RF
Connection. Go to page 10.
Installation Options
Elecraft K3 Setup Instructions
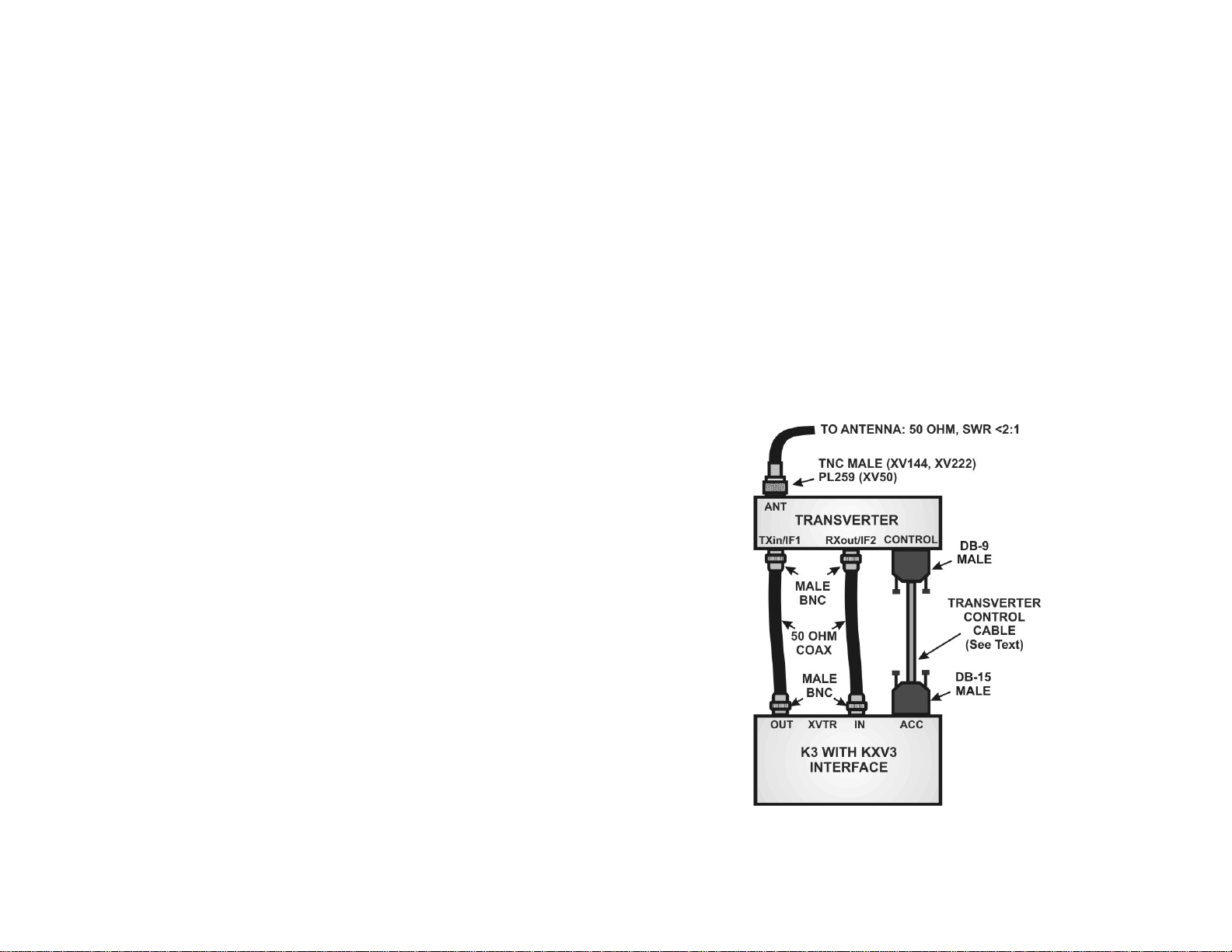
All K3s are equipped with a KIO3 interface that provides the control
signals needed through the rear-panel ACC connector.
While not required, the Elecraft KXV3 RX Ant. I/O, IF Output and
Transverter Interface is highly recommended for use with the transverters.
The KXV3 interface provides separate (split) receive transmit connections
to the transverter and a low-level (1 milliwatt) transmit drive independent
of the K3 power amplifier stages that eliminates the need to switch
between the transverter and an external H.F. antenna.
Elecraft K3 with KXV3 Adapter
This setup uses the low-level transmit and separate receiver connections
provided by the KXV3 Adapter.
We recommend that you first use the appropriate Quick-Start Installation
and verify that your transverter is operating as expected. Once that has
been done, the following optional setup configurations may help you
better integrate the transverter into your station:
1. Daisy-Chaining Multiple Transverters. Using multiple
transverters without swapping cables. See page 14.
2. Using an External Receive Preamplifier. Using the transverter
with an antenna-mounted preamplifier to optimize noise figure
with long feed lines. See page 15.
3. Using an External Power Amplifier. Controlling an external
power amplifier from the transverter. See page 15.
Figure 1. Connecting the Transverter to an Elecraft K3 With a
KXV3 Interface.
- 4 -
Page 9
Refer to the Using Transverters in your K3 Owner’s Manual to
configure the K3 for operation with the transverter:
Connect a 13.8 VDC, 6 ampere power supply to the transverter using
a cable equipped with an Anderson Powerpole® connector.
_ Note the XVn ADR number you have set up for the transverter.
_ Set the maximum output to: L1.00 (1.00 milliwatts).
Refer to the following table and set the DIP switches on the RF PCB
for the XVn address you assigned.
XVn
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1 2 3 4
ON
OFF
OFF OFF
OFF OFF OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF OFF
OFF
DIP SWITCH POSITIONS
OFF OFF OFF
ON
OFF OFF
ON
ON
ON ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON ON
ON ON ON
Place 2-pin shorting blocks on the transverter RF PCB jumpers
shown below:
_ JP1: 1-2 _ JP2: 2-3 _ JP3: 1-2
_ JP4: 1-2 _ JP5: 2-3 _ JP6: 2-3
_ JP9: 1-2
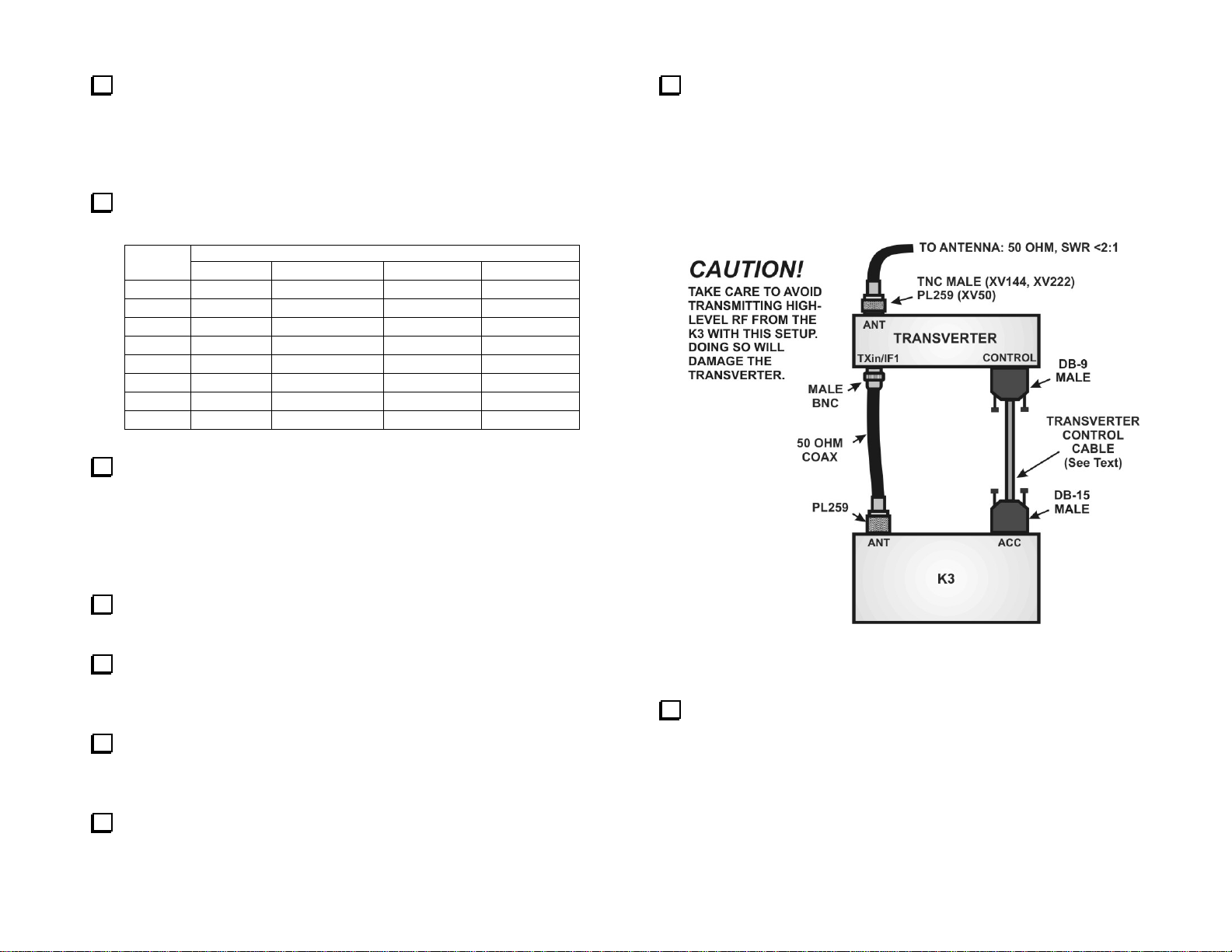
Elecraft K3 with No KXV3 Adapter
This setup uses the K3’s antenna port for both the transmit and receive
signal path to the transverter.
OFF
OFF
Place a shorting block on 2-pin jumper JP8 (near the ON/OFF switch
on the RF PCB) and verify that there is no shorting block on JP7.
Locate front panel PCB 2-pin jumper, JP1, at the end of the socketmounted controller IC. Verify that there is no shorting block on this
jumper. (Do not confuse this JP1 with JP1 on the RF PCB.)
Refer to Transverter Control Cable on page 11 to make up a new
transverter control cable or to add connections for the transverter to your
existing cable.
Connect the cables as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 2. Connecting the transverter to an Elecraft K3 Without a
KXV3 Interface.
.
Refer to the Using Transverters in your K3 Owner’s Manual to
configure the K3 for operation with the transverter:
_ Note the XVn ADR number you have set up for the transverter.
_ Set the maximum output to: H5.0 (5 watts).
- 5 -
Page 10

Refer to the following table and set the DIP switches on the RF PCB
for the XVn number you assigned.
XVn
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1 2 3 4
ON
OFF
OFF OFF
OFF OFF OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF OFF
OFF
DIP SWITCH POSITIONS
OFF OFF OFF
ON
ON ON
ON
ON ON ON
OFF OFF
ON
OFF
ON ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
Elecraft K2 Setup Instructions
Your K2 must be equipped with:
KIO2 Interface. Either the stand-alone KIO2 interface for the
QRP version of the K2, or the KIO2 interface built into the
KPA100 amplifier is suitable.
Revision 2 (or later) Firmware. To see your firmware version,
hold any front-panel button while turning on the power to your
K2. Upgraded firmware is available from Elecraft.
K2’s with serial numbers 3445 and earlier should be equipped with the
following Elecraft-approved modifications.
Place 2-pin shorting blocks on transverter RF PCB jumpers shown
below:
_ JP1: 2-3 _ JP4: 2-3
_ JP2: 1-2 _ JP5: 1-2
_ JP3: 2-3 _ JP6: 1-2
_ JP9: 1-2
Place a shorting block on 2-pin jumper JP8 (near the ON/OFF switch
on the RF PCB) and verify that there is no shorting block on JP7.
Locate front panel PCB 2-pin jumper, JP1, at the end of the socketmounted controller IC. Verify that there is no shorting block on this
jumper. (Do not confuse this JP1 with JP1 on the RF PCB.)
Refer to Transverter Control Cable on page 11 to make up a new
transverter control cable or to add connections for the transverter to your
existing Aux I/O cable.
Connect the cables as shown in Figure 2
Connect a 13.8 VDC, 6 ampere power supply to the transverter using
a cable equipped with an Anderson connector
10 Meter Bandpass Filter and VFO/ALC modification, applicable
to all K2’s S/N 2999 and down. This modification reduces
spurious signals. It is very strongly recommended.
K2 BFO Toroid & PLL Ref Osc Xtal Upgrade, applicable to
K2’s S/N 2999 and down. This modification substantially
reduces frequency drift in the K2’s reference oscillator and BFO.
Temperature-Compensated PLL Reference Upgrade, applicable
to K2’s S/N 3445 and down. This modification further reduces
the K2’s reference oscillator frequency drift.
While not required, the Elecraft K60XV 60-M and Transverter Adapter is
highly recommended for use with the transverters. The adapter provides
separate (split) receive transmit connections to the transverter. It provides
a low-level (1 milliwatt) transmit drive that is independent of the K2
power amplifier stages eliminating the need to switch between the
transverter and an external antenna when using the K2 as both the
transverter I.F. and as an H.F. rig.
If your K2 has a K60XV adapter, go to page 7.
If your K2 does not have a K60XV adapter, go to page 8.
- 6 -
Page 11
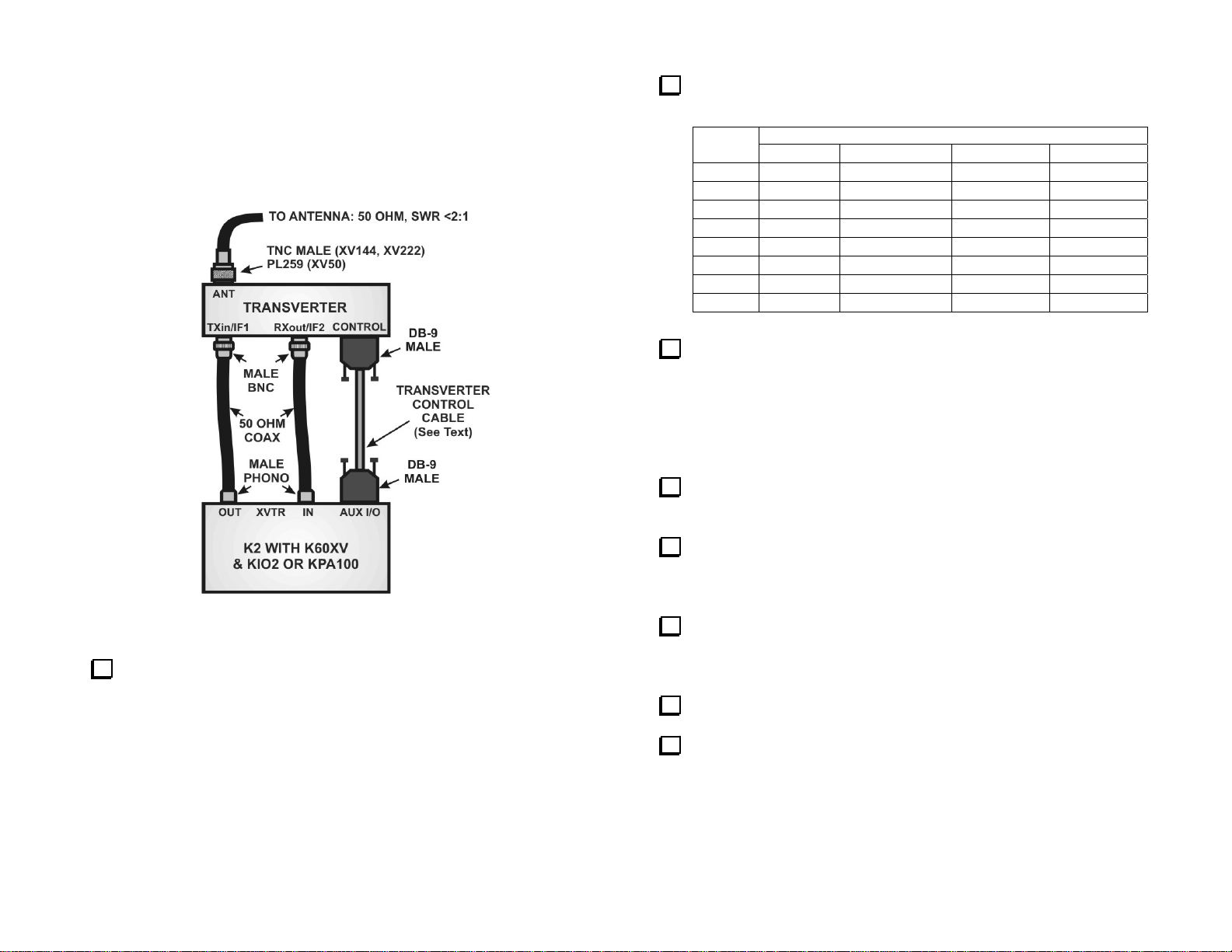
Elecraft K2 with K60XV Adapter
This setup uses the low-level transmit and separate receiver connections
provided by the K60XV Adapter. The K2 must be equipped with an
auxiliary input/output either through a KIO2 interface or the one built into
the KPA100 amplifier.
Refer to the following table and set the DIP switches on the RF PCB
for the TRN number you assigned.
TRN
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1 2 3 4
ON
OFF
OFF OFF
OFF OFF OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF OFF
OFF
DIP SWITCH POSITIONS
OFF OFF OFF
ON
OFF OFF
ON
OFF
ON
ON ON
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
ON ON
ON ON ON
Place 2-pin shorting blocks on the transverter RF PCB jumpers
shown below:
_ JP1: 1-2 _ JP2: 2-3 _ JP3: 1-2
_ JP4: 1-2 _ JP5: 2-3 _ JP6: 2-3
_ JP9: 1-2
Place a shorting block on 2-pin jumper JP8 (near the ON/OFF switch
on the RF PCB) and verify that there is no shorting block on JP7.
Figure 3. Connecting the Transverter to an Elecraft K2 with a K60XV
Interface.
Refer to the Transverter Operation section of the Elecraft K60XV
60-M and Transverter Adapter Assembly and Operating Instructions and
use the K2’s MENU commands to configure the K60XV for operation
with the transverter:
_ Note the TRN number you have set up for the transverter.
_ Set the maximum output to: Out L 1.00 (1.00 milliwatts).
Locate front panel PCB 2-pin jumper, JP1, at the end of the socketmounted controller IC. Verify that there is no shorting block on this
jumper. (Do not confuse this JP1 with JP1 on the RF PCB.)
Refer to Transverter Control Cable on page 11 to make up a new
transverter control cable or to add connections for the transverter to your
existing Aux I/O cable.
Connect the cables as shown in Figure 3.
Connect a 13.8 VDC, 6 ampere power supply to the transverter using
a cable equipped with an Anderson Powerpole® connector.
- 7 -
Page 12
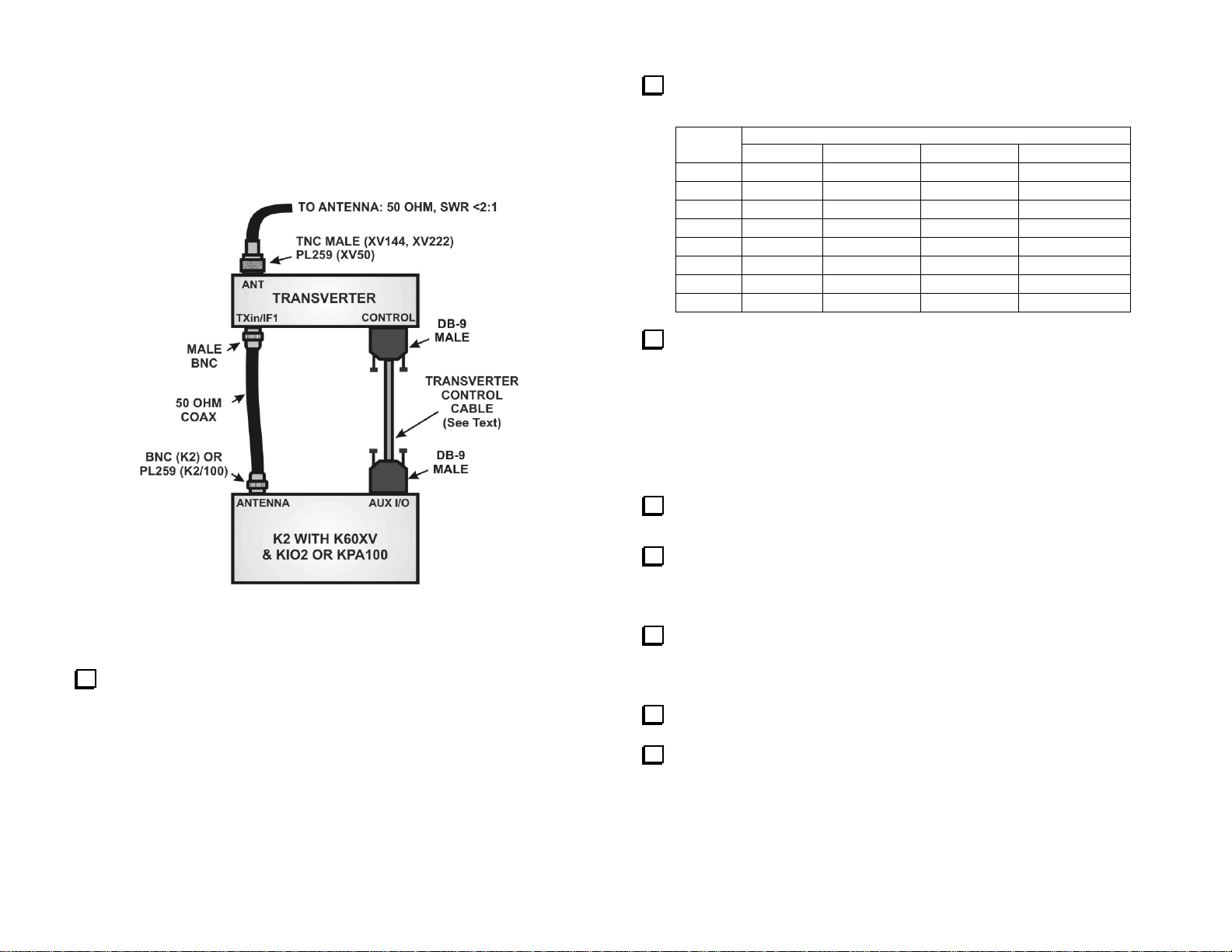
Elecraft K2 with No K60XV
This setup uses the K2’s antenna port for both the transmit and receive
signal path to the transverter. The K2 must be equipped with an auxiliary
input/output either through a KIO2 interface or the one built into the
KPA100 amplifier.
Refer to the following table and set the DIP switches on the RF PCB
for the TRN number you assigned.
TRN
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1 2 3 4
ON
OFF
OFF OFF
OFF OFF OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF OFF
OFF
DIP SWITCH POSITIONS
OFF OFF OFF
ON
OFF OFF
ON
OFF
ON
ON ON
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
ON ON
ON ON ON
Place 2-pin shorting blocks on transverter RF PCB jumpers shown
below:
_ JP1: 2-3 _ JP4: 2-3
_ JP2: 1-2 _ JP5: 1-2
_ JP3: 2-3 _ JP6: 1-2
_ JP9: 1-2
Place a shorting block on 2-pin jumper JP8 (near the ON/OFF switch
on the RF PCB) and verify that there is no shorting block on JP7.
Figure 4. Connecting the transverter to an Elecraft K2 without a
K60XV interface
.
Refer to your K2 Operating Manual and the instructions that came
with your current firmware and use the K2’s MENU commands to do the
following.
_ Note the TRN number you have set up for the transverter.
_ If using a K2/100, set the MENU command for PA OFF.
Locate front panel PCB 2-pin jumper, JP1, at the end of the socketmounted controller IC. Verify that there is no shorting block on this
jumper. (Do not confuse this JP1 with JP1 on the RF PCB.)
Refer to Transverter Control Cable on page 11 to make up a new
transverter control cable or to add connections for the transverter to your
existing Aux I/O cable.
Connect the cables as shown in Figure 4.
Connect a 13.8 VDC, 6 ampere power supply to the transverter using
a cable equipped with an Anderson connector
- 8 -
Page 13
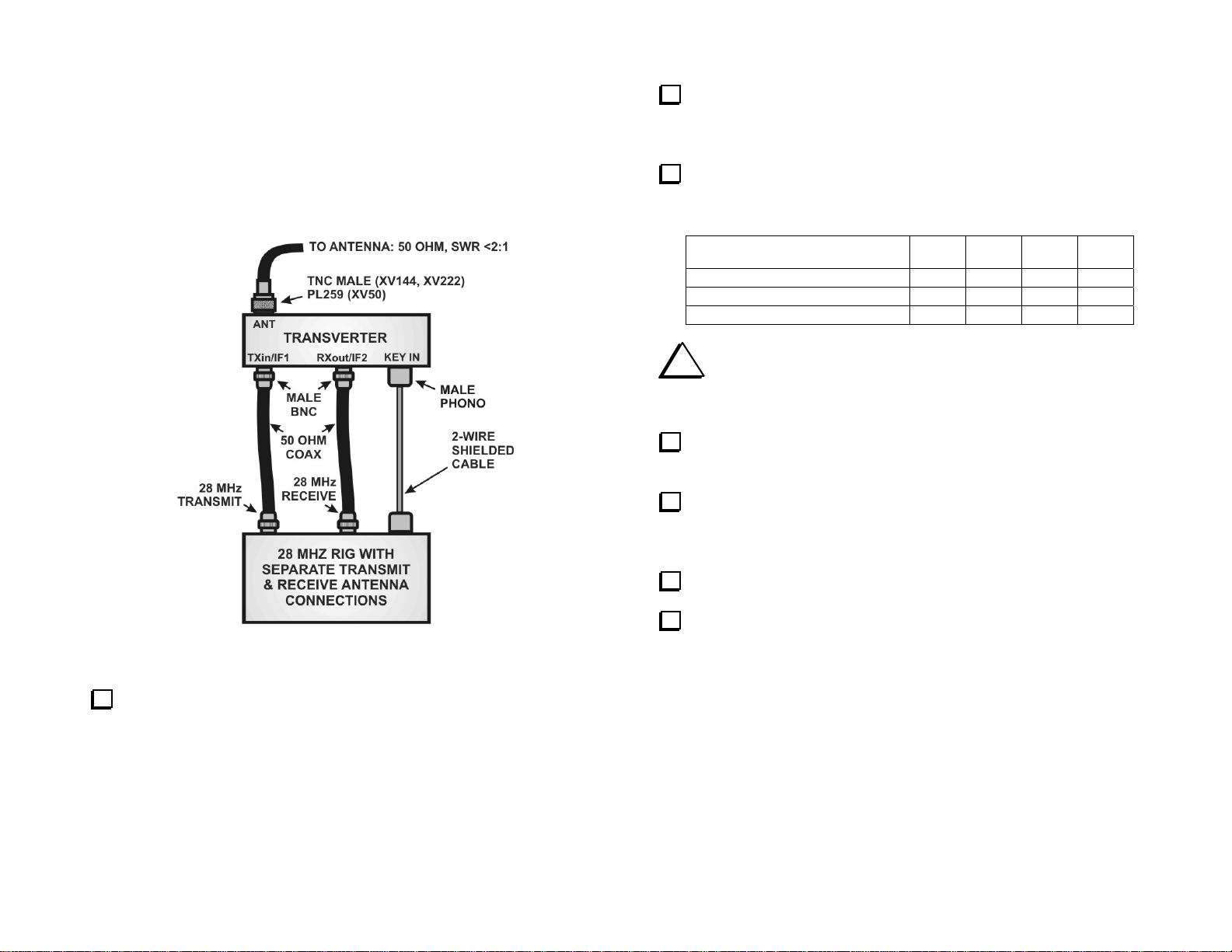
Non-Elecraft 28 MHz Rig – Separate Transmit and
Receive RF Connections
This setup is for any 28 MHz rig capable of providing separate transmit
and receive connections. The transmitter must be capable of providing a
variable RF output of up to 1 milliwatt, 251 milliwatts or 5 watts, and
provide a key line that will ground a 5 volt logic level on transmit.
Place 2-pin shorting blocks on the transverter RF PCB jumpers
shown below:
_ JP1: 1-2 _ JP2: 2-3 _ JP9: 1-2
From the options below, choose the power output from your 28 MHz
rig that will drive the transverter to full output. Place 2-pin shorting blocks
on the corresponding RF PCB jumpers as shown:
Figure 5. Connecting the Transverter to a Non-Elecraft 28-MHz Rig
with Separate Transmit and Receive RF Paths.
28 MHZ DRIVE LEVEL FOR
FULL TRANSVERTER OUTPUT
1 milliwatt 1-2 1-2 2-3 2-3
251 milliwatts 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2
5 watts 2-3 2-3 1-2 1-2
i
Take care not to exceed the maximum power level you set up
the transverter for in the previous step. Doing so may result in
damage to the transverter.
Place a shorting block on 2-pin jumper JP7 (near the ON/OFF switch
on the RF PCB) and verify that there is no shorting block no JP8.
Place a shorting block on front panel PCB 2-pin jumper JP1 at the
end of the socket-mounted controller IC. (Do not confuse this JP1 with
three-pin jumper JP1 on the RF PCB.)
Connect the cables as shown in Figure 5.
Connect a 13.8 VDC, 6 ampere power supply to the transverter using
the cable equipped with an Anderson connector
JP3 JP4 JP5 JP6
On the transverter RF PCB, set all four DIP switches to OFF.
- 9 -
Page 14
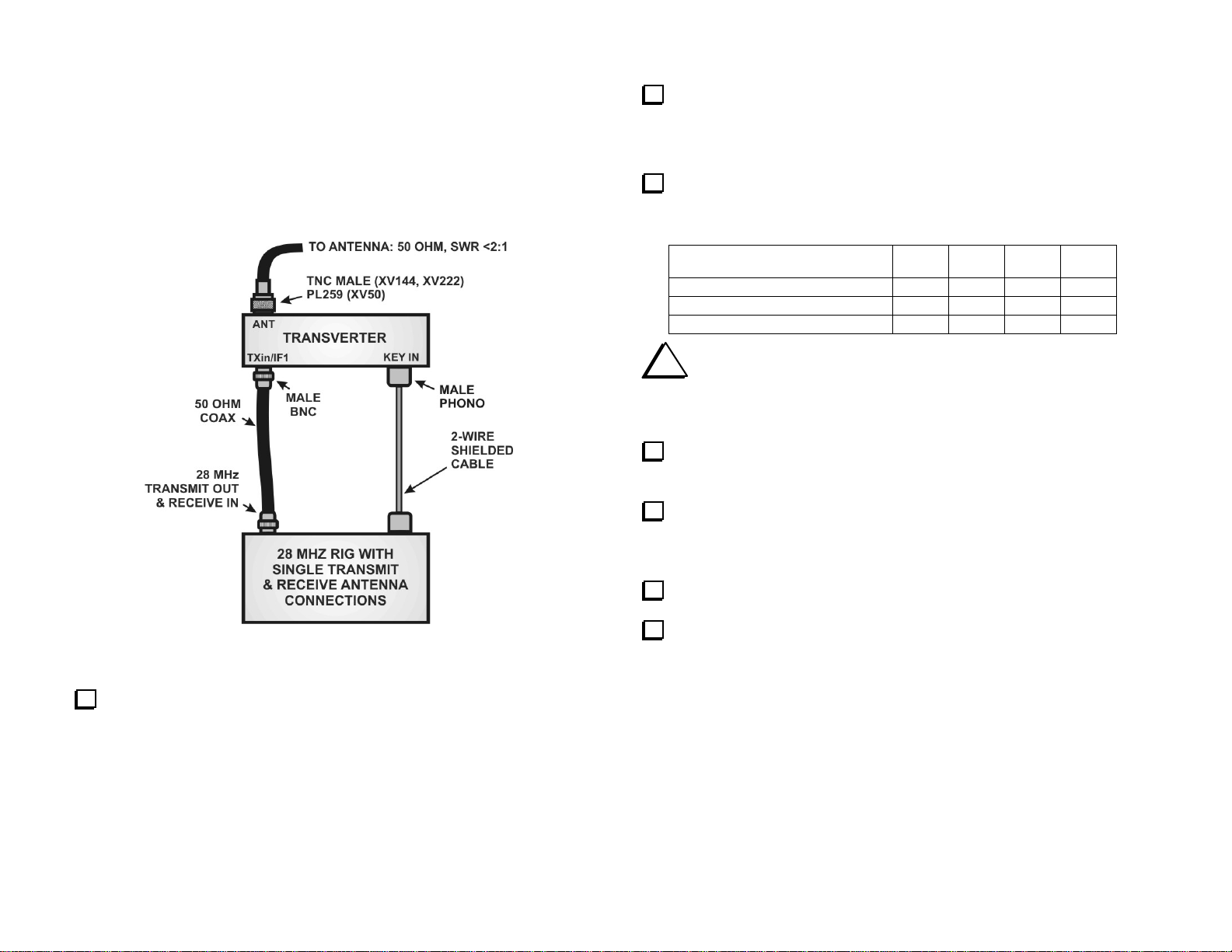
Non-Elecraft 28 MHz Rig – Single Transmit and Receive
RF Connection
This setup is for any 28 MHz rig with a single RF port for transmit and
receive. The transmitter must be capable of providing a variable RF power
output of up to 1 milliwatt, 251 milliwatts or 5 watts, and provide a key
line that will ground a 5 volt logic level on transmit.
Place 2-pin shorting blocks on transverter RF PCB jumpers shown
below:
_ JP1: 2-3 _ JP2: 1-2 _ JP9: 1-2
From the options below, choose the power output from your 28 MHz
rig that will drive the transverter to full output. Place 2-pin shorting blocks
on the corresponding RF PCB jumpers as shown:
Figure 6. Connecting the Transverter to a Non-Elecraft 28-MHz Rig
with a Single Transmit and Receive RF Path.
On the transverter RF PCB, set all four DIP switches to OFF.
28 MHZ DRIVE LEVEL FOR
FULL TRANSVERTER OUTPUT
1 milliwatt 1-2 1-2 2-3 2-3
251 milliwatts 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2
5 watts 2-3 2-3 1-2 1-2
i
Take care not to exceed the maximum power level you set up
the transverter for in the previous step. Doing so may result in
damage to the transverter.
Place a shorting block on 2-pin jumper JP7 (near the ON/OFF switch
on the RF PCB) and verify that there is no shorting block on JP8.
Place a shorting block on front panel PCB 2-pin jumper JP1 at the
end of the socket-mounted controller IC. (Do not confuse this JP1 with
three-pin jumper JP1 on the RF PCB.)
Connect the cables as shown in Figure 6.
Connect a 13.8 VDC, 6 ampere power supply to the transverter using
the cable equipped with an Anderson connector.
JP3 JP4 JP5 JP6
- 10 -
Page 15
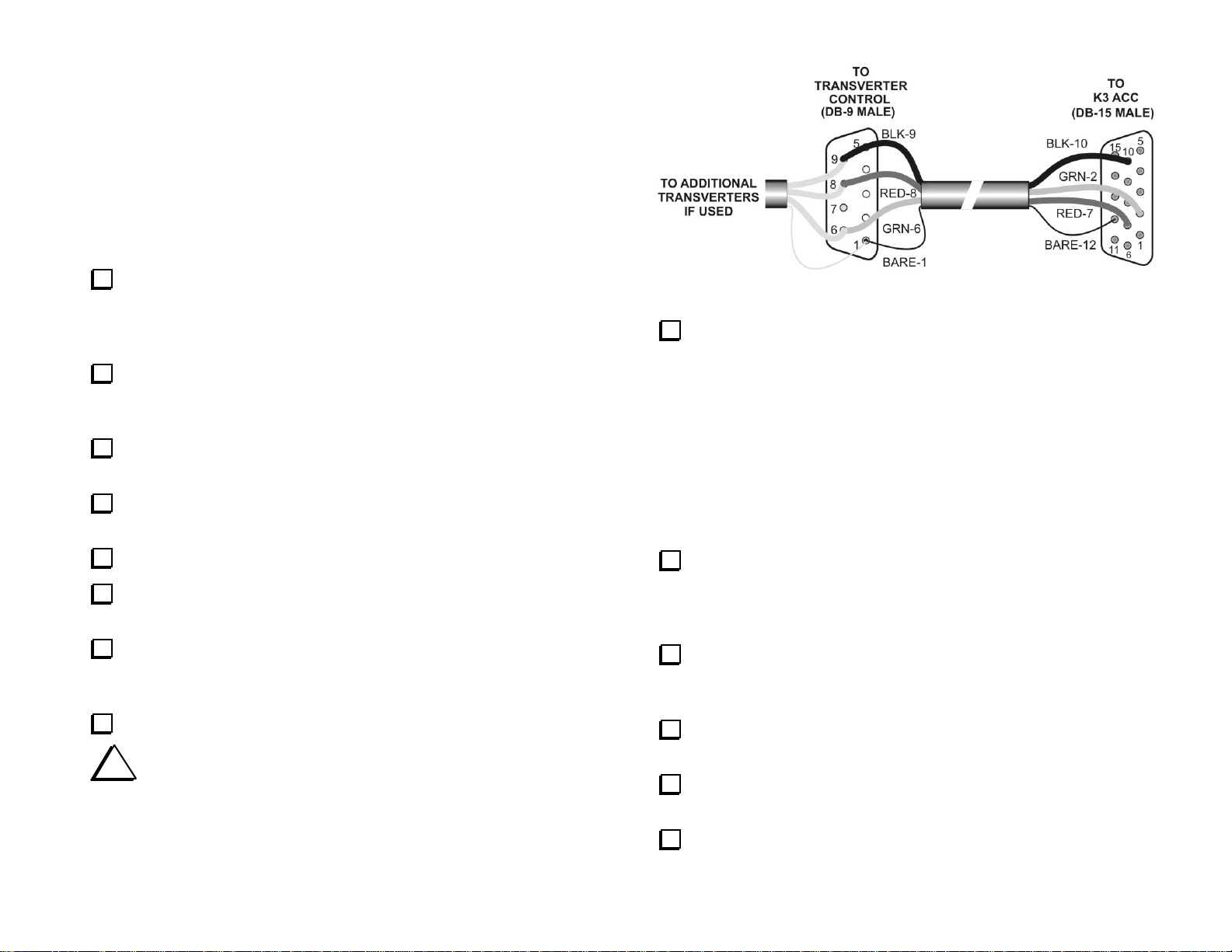
Transverter Control Cable
Your transverter was supplied with a DB-9 cable connector and a length
of multi-conductor wire for making up the transverter control cable for use
with an Elecraft K3, K2 or K2/100.
Elecraft K3
A male DB-15 connector is provided with your kit to mate with the ACC
connector on the back of your K3. Wire your control cable as follows:
Cut a length of the 4-conductor cable to suit the needs of your station
layout. Keep the cable length as short as practical. A length of 2’ (60 cm)
is recommended. Longer lengths may be used, but you may need to supply
a more heavily-shielded cable to avoid RF interference.
Figure 7. K3 Control Cable Wiring.
Attach the connector housings (see Figure 9).
If you are integrating two or more transverters into the station at this
time, cut a length of cable to reach from the first transverter to the next
transverter in a daisy-chain arrangement (see Figure 7).
Remove 1/2” (12 mm) of the jacket from the cable at each end. Be
very careful not to nick the individual wires.
Peel back and cut away the foil shield. Do not cut the bare ground
wire.
Cut the white wire where it exits the jacket. It will not be used.
Strip of 3/16” (5 mm) of insulation from the black, red and green
wires.
Twist the strands of each wire together. If you are daisy-chaining
cables, twist the ends of leads with like colors together. Tin lightly with
solder.
Solder the wires to the connectors as shown in Figure 7.
i
Follow the color codes shown below when wiring the
connector. The same color code is used in the control interface cables
for other Elecraft equipment. Keeping a consistent color code will
help avoid mistakes and make troubleshooting easier.
Elecraft K2 or K2/100
You will need the DB-9 connector that came with your KIO2 or KPA100
to complete the cable. Follow the procedure below to make up your
control cable.
If you are already using the K2 Aux I/O port to control a KPA100 ATU or
to communicate with your personal computer, you may add the transverter
control cable to the existing cable at the DB-9 connector so you won’t
need to switch connectors when using the transverter (see Figure 10).
Cut a length of the 4-conductor cable to suit the needs of your station
layout. Keep the cable length as short as practical. A length of 2’ (60 cm)
is recommended. Longer lengths may be used, but you may need to supply
a more heavily-shielded cable to avoid RF interference.
If you are integrating two or more transverters into the station at this
time, cut a length of cable to reach from the first transverter to the next
transverter in a daisy-chain arrangement (see Figure 10).
Remove 1/2” (12 mm) of the jacket from the cable at each end. Be
very careful not to nick the individual wires.
Peel back and cut away the foil shield. Do not cut the bare ground
wire.
Cut the white wire where it exits the jacket. It will not be used.
- 11 -
Page 16
Strip of 3/16” (5 mm) of insulation from the black, red and green
wires.
Twist the strands of each wire together. If you are daisy-chaining
cables, twist the ends of leads with like colors together. Tin lightly with
solder.
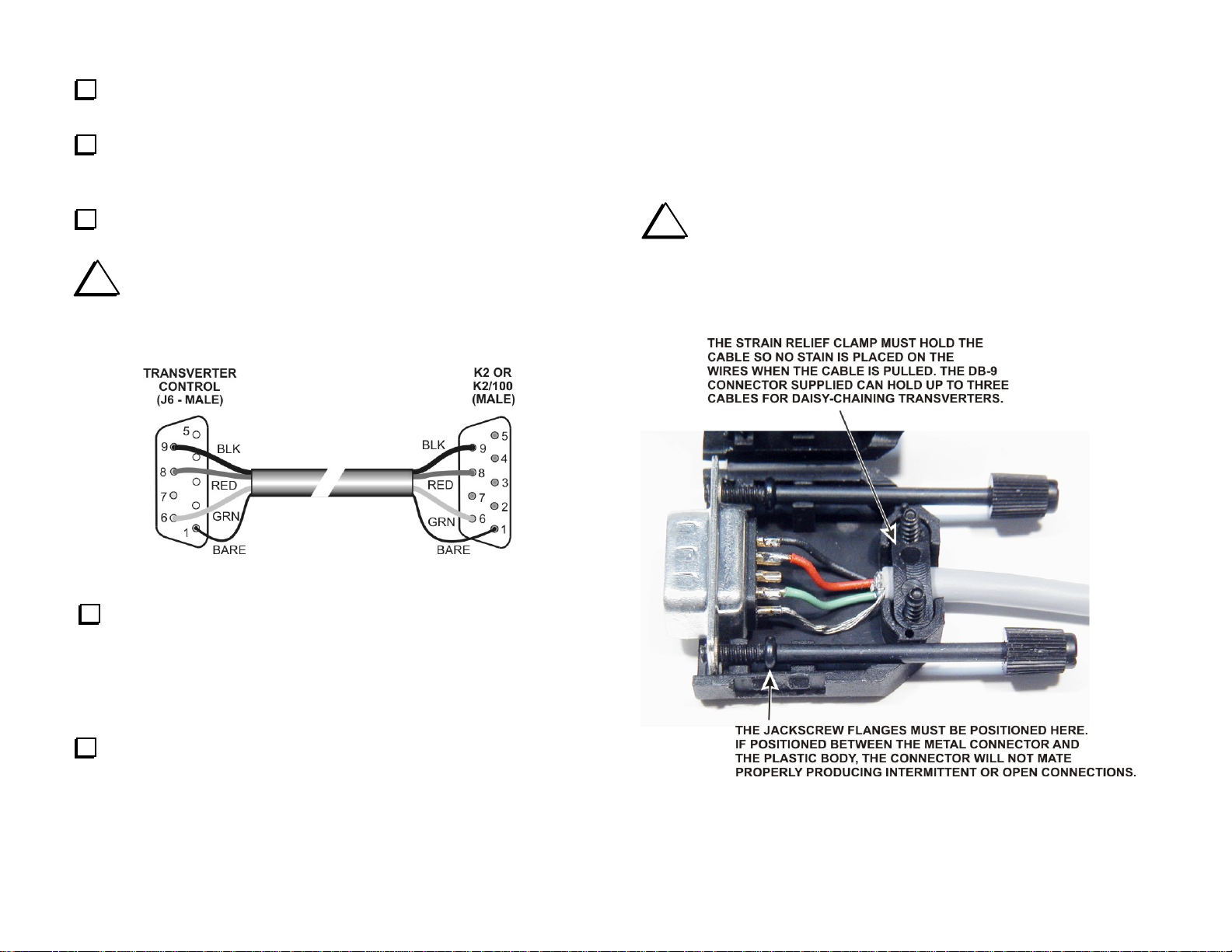
Installing the Connector Housing
The connector housing is essential for a reliable, secure cable connection.
A typical DB-9 housing is shown in Figure 9. Attach it to the cable as
shown. Other makes of housings may be somewhat different, but should
provide jack screws to secure it and an effective strain relief to prevent
broken wires.
Solder the wires to the male DB-9 connector supplied with your
transverter as shown in Figure 8.
i
Follow the color codes shown below when wiring the
connector. The same color code is used in the control interface cables
for other Elecraft equipment. A consistent color code will help avoid
mistakes and make troubleshooting easier.
Figure 8. K2 Control Cable Wiring.
If you have not built an RS-232 or control cable to connect other
equipment to your K2, you should have an unused DB-9 male connector
that was supplied with the KI02 or KPA100 kit. In that case, wire the
connector as shown in Figure 8. If you have wired the cable for the K2
and other accessories already, add the transverter extension(s) to it as
shown in Figure 10.
i
Be especially careful to position the jack screws as shown so
the connectors fully mate when they are tightened. Otherwise you
may find that the connections are intermittent or open even though
the connector is securely mounted to the transverter or rig.
Attach the connector housings (see Figure 9).
This completes your transverter control cable. If, in the future, you
chose to add more transverters, add a KAT100 ATU interface to your
H.F. station, or connect your K2 to a personal computer, you can add
the connections to your existing cable as shown in Figure 10.
Figure 9. Installing the Connector Housing.
- 12 -
Page 17

TRANSVERTER
(MALE) (MALE)
K2 OR K2/100
PC
(FEMALE)
TO ADDITIONAL
TRANSVERTERS
DB-9
MALE
CONTROL
TRANSVERTER
DB-9
MALE
KAT100
ATU
(MALE)
TRANSVERTER CONTROL
CABLE
OPTIONAL KAT100 CONTROL CABLE
(SEE KAT100 MANUAL)
5
9
4
8
3
7
2
6
1
OPTIONAL RS232 CABLE TO PC
(SEE K2/100 OR KI02 MANUAL)
CONTROL
TRANSVERTER
CONTROL
TRANSVERTER
DB-9
MALE
DB-9
MALE
DB-9
MALE
K2/100 OR
KAT100 ATU
K2 WITH KIO2
Figure 10. K2 Extended Control Cabling Hookup Diagram.
- 13 -
DB-9
FEMALE
PERSONAL
COMPUTER
Page 18

Daisy-Chaining Multiple Transverters
&
S
You can “daisy chain” several transverters together as shown in Figure 11
to avoid swapping cables when switching between them.
Relays inside the transverters disconnect the transverters not in use so
they do not load the RF lines.
When using an Elecraft K3 or K2 for the 28 MHz I.F. rig, a multi-wire
control cable is required. See Transverter Control Cable on page 11 for
instructions to prepare the cable. The control cable connects between the
AUX I/O DB-9 connector on the K2 or the ACC DB-15 connector in a
K3 and the CONTROL DB-9 connector on each transverter.
When using a non-Elecraft rig, the two-wire key line is connected in
parallel to the KEY IN RCA connector on each transverter.
The transverter in use is selected as follows:
When using an Elecraft K2 or K3, the desired transverter is
enabled when the transverter band is selected.
When using a non-Elecraft rig for the 28 MHz I.F., the desired
transverter is selected by its front panel ON/OFF switch.
RX I.F.
TX
28 MHZ
RIG
CONTROL OR
KEY LINE
(SEE TEXT)
COMBINED RECEIVE AND TRANSMIT RF CONNECTIONS
TX I.F.
RX I.F.
28 MHz
RIG
TRANSVERTER
TRANSVERTER
TO ADDITIONAL
TRANSVERTERS
BNC
“T” CONNECTORS
TRANSVERTER
CONTROL OR
KEY LINE
(SEE TEXT)
SEP A RATE RECEIVE AND TRANSMIT RF CONNECTION
TRANSVERTER
TO ADDITIONAL
TRANSVERTERS
Figure 11. Daisy-Chaining Transverters.
- 14 -
Page 19

Using an External Receive Preamplifier
A
A
A
Using an External Power Amplifier
An external receiver preamplifier is sometimes mounted at the antenna to
offset transmission line losses and provide the best possible system noise
figure.
When using an external receive preamplifier, you may want to reduce the
transverter receive gain to maintain the best possible system dynamic
range. A procedure for reducing the transverter receive gain without
adversely affecting the noise figure is described in Reducing Receive Gain
to Preserve System Dynamic Range on page 21.
If the external preamplifier does not provide a bypass switch when
transmitting, separate transmit and receive antennas and transmission
lines are required as shown in Figure 12. In this case, the transverter
needs to be wired for separate transmit and receive antenna connections.
See Changing Between Split and Common Antennas on page 20.
PREAMP
The transverter may be used to drive an external power amplifier as
shown in Figure 13.
The external power amplifier must present an SWR of less than
2:1 to the transverter output.
The external power amplifier must key with a closure to ground
and present less than +200 volts to the transverter KEY OUT
connector during receive.
See Changing Between Split and Common Antennas on page 20 for
instructions on rewiring the transverter RF outputs as needed.
SINGLE RF PATH TRANSMIT AND RECEIVE:
TX & RX RF
TX KEY
EXTERNAL
ANT
TRANSVERTER
POWER
MPLIFIER
w/TR switching
ANT
TX
SPLIT RF PATH TRANSMIT AND RECEIVE:
TX RF
RX
AUX
TRANSVERTER
Figure 12. Using an External Receive Preamplifier Without Transmit
Bypass Capability.
RX RF
TX KEY
AUX
NT
TRANSVERTER
EXTERNAL
POWER
MPLIFIER
Figure 13. Using an External Power Amplifier.
- 15 -
Page 20

Operation
Once your transverter is hooked up to your antenna system and other
equipment as described under Installation (page 4), operation consists of
turning on the transverter and setting the output power.
Cautions to Avoid Spurious Emissions From Your Station
Do not use an antenna relay to switch the 28 MHz rig output between an
HF antenna and the transverter unless it has adequate isolation to ensure
that no RF energy leaks to the antenna when it is not selected. Most
normal coaxial relays do not provide adequate attenuation
When using a K2, do not use the 2nd antenna position. The K60XV
Adapter provides a well isolated transverter interface allows you to have
an HF antenna connected to the K2 without concern for spurious radiation
when using the transverter.
Turning the Transverter On
If an Elecraft K3 or K2 is being used for the I.F., the transverter power is
turned on automatically when the band assigned to the transverter is
selected. The front-panel band label on the transverter will light indicating
that power is applied and the transverter is operating.
When a rig other than an Elecraft K2 or K3 is used for the I.F., the
transverter is made active by pressing the front panel switch to turn the
transverter on. The front-panel band label on the transverter will light.
Local Oscillator Power Control
To minimize frequency drift you may want to have the local oscillator
running at all times, even when the transverter is inactive. However, in
some installations it is possible that a harmonic of the local oscillator
may produce unwanted birdies when operating on other bands.
In the Installation section you set up the local oscillator to switch on and
off with the transverter power.
The behavior of the local oscillator may be selected by a 2-terminal
shorting block at JP9 as follows:
JP9, 1-2: Default: The local oscillator power goes off whenever
the power is turned off or, when used with an Elecraft K2 or
K3, the transverter is deselected by changing bands.
JP9, 2-3: The local oscillator power is on whenever the
transverter power is on or, when used with an Elecraft K2 or
K3, whenever the K2 or K3’s power is on even though the
transverter band may not be selected.
JP9, 4-5: The local oscillator power is on whenever 12 volts is
applied at J7 on the back panel regardless of the state of the
power or band switches. This is the recommended jumper
setting if you have installed the optional crystal oven so the
oven will remain at operating temperature.
Power Output Control
Set the output power on your 28 MHz rig for the transverter power output
desired. Do not exceed 20 watts output from the transverter in CW or
SSB. Limit the output to 10 watts in FM or data modes that require a
steady carrier. On the transverter front panel, a yellow LED indicates 20
watts. Green LEDs indicate levels below 20 watts and red LEDs indicate
levels above 20 watts.
Regardless of the jumper setting you choose, power to the receive
circuits (other than the local oscillator) is turned off except during
receive mode. This avoids the possibility of strong signals leaking into
the I.F system when several transverters are used with the same H.F. rig.
- 16 -
Page 21

I.F. Overload Condition
Front Panel Display Control
The transverter switches to transmit mode when the transmit enable signal
is received from the 28 MHz rig. When used with an Elecraft K2 or K3,
this signal is supplied through the CONTROL connector. When used with
other 28 MHz rigs, this signal is supplied to the transverter KEY IN RCA
jack.
If the transverter fails to switch to transmit mode before a high-level
transmit I.F. signal is applied, a protective circuit will disable the
transverter. All of the front panel power display LEDs will flash in unison
to alert you that an overload condition has occurred.
An I.F. overload condition will occur if the transmit enable signal is not
present whenever high-level transmit I.F. is applied to the transverter.
This is normally the result of an unplugged cable or circuit failure, but it
may also be caused by a timing problem with the 28 MHz rig being used.
See Transmit-Receive Switching Delay below.
To clear the overload condition, turn the transverter power off, then on
again. (If you’re using the transverter with an Elecraft K2 or K3, turn the
K2 or K3’s power off then on again since the transverter power is
controlled by the K2 or K3’s power switch).
Transmit-Receive Switching Delay
When used with an Elecraft K2, the front panel LEDs are controlled by
the K2 through the Menu commands. The Menu LCD DAY command
provides full brightness and the LCD NIGHT command dims the LEDs.
The GRPH Menu command controls the behavior of the K2 bargraph
and the Power Output LEDs on the transverter as follows:
DOT: Just one LED representing the power output will illuminate.
BAR: All LEDs to the left of the current LED will illuminate,
resulting in a more visible display.
OFF: The LEDs operate in DOT mode.
When used with the K3 or other 28 MHz rigs, the brightness of all the
front panel LEDs is fixed.
When the transverter is used with rigs other than an Elecraft K2 or K3,
the transmit-receive switching is controlled by the signal furnished by the
28-MHz rig to the transverter TX KEY input. If the 28 MHz rig switches
the TX KEY line to receive before it stops transmitting, it will trigger in
I.F. overload condition in the transverter when using a high-level RF
drive from the 28 MHz rig (see I.F. Overload Condition above for
details). In the Installation section, you set up the transverter for a 200
millisecond delay to avoid timing problems. If your 28 MHz rig can
provide the switching speed needed, you can reduce the delay time to 50
ms by removing the shorting block on jumper JP1. JP1 is located on the
back of the front panel PCB between the left side panel and socketmounted processor U1.
JP1 Open – 50 ms delay.
JP1 Shorted – 200 ms delay (Default)
- 17 -
Page 22

Options and Modifications
The transverter is designed for the greatest possible flexibility when
integrating it with other equipment in a high-performance station.
It is Elecraft’s policy to encourage owners to experiment with their own
(careful) modifications. You can build-in accessories and make changes
to the circuitry if desired. However, this policy has one firm limitation: If
you make a modification other than those described below that damages
or alters normal operation, it may not be repairable by Elecraft.
Any personal modifications that you create should be installed in such a
way that they can be easily disabled (turned off, unplugged, etc.). This
will allow us to test and repair your kit if it becomes necessary. Repair
charges will be higher if our technician has to un-modify your
modification for any reason. Of course, any Elecraft-approved
modification, such as those described below, may be left in place should
you need to send in your transverter for repair. There will be no additional
charges caused by the transverter having any of these modifications. They
will not be removed by the Elecraft technician.
In addition to the options and modifications described here, check the
Elecraft web site at www.elecraft.com for the latest information about
using your transverter with the latest systems and station equipment.
Optional Crystal Oven. Improves the stability of the local
oscillator by maintaining the crystal at a constant temperature.
Changing Between Split and Common Antennas. Allows you
to configure your transverter for use with a common transmit and
receive antenna or with separate transmit and receive antennas.
Reducing Receive Gain to Preserve System Dynamic Range.
Reduces the gain of the transverter receive circuitry to help
preserve the system dynamic range when an external preamplifier
is used.
Tools Required
Some of these options and modifications require soldering. We
recommend you use the following:
Fine-tip temperature-controlled soldering station with 700 or
800F tip (370-430C). Do not use a high-wattage iron or gun to
avoid damaging printed circuit board (PCB) pads, traces, or the
parts themselves.
IC-grade, small-diameter (.031”) solder (Kester #44 or
equivalent).
A good vacuum desoldering tool such as the Soldapullt® model
DS017LS.
i
DO NOT use acid-core solder, water-soluble flux solder,
additional flux or solvents of any kind. Use of any of these will void
your warranty.
In addition, you will need small hand tools including the following:
Screwdrivers: a small, #2 Phillips and a small flat-blade for
slotted screws.
Needle-nose pliers.
Small-point diagonal cutters, preferably flush-cutting.
Digital Multimeter (DMM) for voltage checks and confirming
resistance values.
Refer to
www.elecraft.com for tool sources and other information.
Optional Feet and Bail. Elevates the front of the transverter to a
convenient viewing angle.
- 18 -
Page 23

Optional Crystal Oven
The crystal oven elevates the temperature of the local oscillator crystal
and keeps it constant so long as power is applied. The oven greatly
reduces frequency drift due to changes in the ambient temperature that
affect the crystal. Contact Elecraft or visit the web site at
www.electraft.com to order the crystal oven.
Install the oven as follows:
i
The oven fits over the existing crystal. Be sure the crystal is
installed before installing the oven.
Remove the four screws and the top cover to gain access to the top
of the RF PCB.
i
In the following step, you will remove the 4-40 nuts holding
the long screws at each end of the RF power module. Do not allow the
screws to fall out of the bottom of the transverter.
Remove the 4-40 nut and lock washer on each end of the RF power
module.
Invert the transverter so the bottom side is up. Place it on a clean
surface to avoid scratching the paint.
Remove the four corner screws holding the bottom cover.
Carefully lift the bottom cover off of the transverter. The two long
screws that secure the RF power module should come out with the bottom
cover. Be careful not to disturb the flat washers between the RF amplifier
module and the PCB. If one does slip out of place, reposition it. The
correct hardware placement is shown in Figure 14.
Remove the two long screws from the bottom cover and replace
them through the holes at each end of the RF power module. Replace the
nuts finger-tight to keep the washers and module in place while you work
on the RF PCB.
Position the oven over the circle marked OV1 on the top of the RF
PCB. The crystal will fit into a space on the bottom of the oven. The
three leads on the oven fit into the +, - and NC pads on the PCB.
Bend the leads over on the bottom of the RF PCB to hold the oven in
place, then tack-solder one lead.
Check to be sure the oven is fully seated down over the crystal and
against the PCB. If necessary, re-heat the soldered lead and adjust the
oven’s position.
Solder and trim all three leads.
Remove the two screws you replaced at each end of the RF amplifier
module. Be sure the flat washers are in place between the module and the
PCB. If necessary adjust their position so the screws will drop through
them when the bottom cover is replaced.
Set the bottom cover in place and drop the two long screws back
through their holes. Replace the lock washers and nuts on the top of the
PCB to hold the screws and hardware in place. Do not tighten the nuts
yet.
Replace the four black screws at the corners of the bottom cover and
tighten them.
Tighten the nuts at each end of the RF module. Inspect the RF
module to ensure that both flat washers are between the module and
bottom of the PCB (see Figure 14). Remove the cabinet side panel, if
necessary, to get a clear view of the RF module mounting hardware.
- 19 -
Page 24

N
O
WER
RF P
AMPLIFIER
MODULE
NUT
LOCK WASHER
FLAT WASHER
PCB
i
In the following step, you will remove the 4-40 nuts holding
the long screws at each end of the RF power module. Do not allow
the screws to fall out of the bottom of the transverter.
THERMAL
CONDUCTIO
PADS
HEAT SPREADER
BOTTOM COVER
1/2” SCREW
Figure 14. RF Module Mounting Hardware.
Configure the local oscillator power jumper, JP9, as desired (see page
16 for details). Normally you will want to place the jumper on JP9, pins
4-5. This will supply power to the oven whenever there is +12 volts at the
rear panel connector, even if the transverter power is off. This will keep
the oven and crystal warm and ready for operation at any time.
Replace the top cover and tighten the four corner screws to secure it.
Changing Between Split and Common Antennas
Your transverter may be configured to work with either a common
transmit and receive antenna or with separate transmit and receive
antennas. The procedure requires removing or installing a relay and two
jumpers. The relay and jumpers are located in the upper left corner of the
RF PCB, near ANT connector J1. Make the change as follows:
Remove the four screws and the top cover to gain access to the top of
the RF PCB.
Remove the 4-40 nut and lock washer on either end of the RF power
module.
Invert the transverter so the bottom side is up. Place it on a clean
surface to avoid scratching the paint.
Remove the four corner screws holding the bottom cover.
Carefully lift the bottom cover off of the transverter. The two long
screws that secure the RF power module should come out with the
bottom cover. Be careful not to disturb the flat washers between the RF
amplifier module and the PCB. If one does slip out of place, reposition it
(See Figure 14).
Remove the two long screws from the bottom cover and replace
them through the holes at each end of the RF power module. Replace the
nuts finger-tight to keep the washers and module in place while you work
on the RF PCB.
If you are switching from a common antenna to split transmit and
receive antennas, do the following. Otherwise skip this step.
Desolder and remove relay K1.
Install jumper W2. It is shown on the silkscreen on the top of the
RF PCB next to the outline for K2 directly behind J8 (AUX).
Install jumper W3 between the solder pads shown in the space
where relay K1 was sitting. Be sure to elevate W3 off of the PCB
enough to avoid shorting to the solder pad underneath it.
Trim the excess wire for both jumpers on the bottom of the PCB.
Store the relay in a safe place in case you want to reinstall it at
some future time.
- 20 -
Page 25

If you are switching from split transmit and receive antennas to a
common antenna, do the following:
Remove jumper W2. W2 is next to the outline for K2 directly
behind connector J8 (AUX) in the upper left corner of the RF
PCB.
Remove jumper W3. W3 is also near relay K1.
Install relay K1. Be sure it is sitting solidly against the PCB
when you solder it. Solder all five pins. Do NOT trim the relay
pins on the bottom side of the PCB.
Remove the two screws you replaced at each end of the RF amplifier
module. Be sure the flat washers are in place between the module and the
PCB. If necessary adjust their position so the screws will drop through
them when the bottom cover is replaced.
Set the bottom cover in place and drop the two long screws back
through their holes. Replace the lock washers and nuts on the top of the
PCB to hold the screws and hardware in place. Do not tighten the nuts
yet.
Reducing Receive Gain to Preserve System Dynamic
Range
Although your Elecraft transverter has a very low noise figure, it can be
improved by using an external pre-amplifier at the antenna to overcome
the losses in your transmission line. If you use an external preamplifier,
you may want to reduce the overall gain to preserve the dynamic range
of the receive system. You can reduce the receive gain about 12 dB by
removing an amplifier stage in the transverter.
i
The following procedure will destroy MMIC U1 in the
transverter. If you decide to restore the transverter to its original
configuration, order a replacement MMIC from Elecraft.
Remove the four screws at the corners of the top cover and remove
the cover to gain access to the top of the RF PCB.
Locate MMIC U1 on the RF PCB. It is in the upper left quadrant to
the right of the Power Cal potentiometer.
Use sharp diagonal cutters to clip off the leads to U1 and remove it.
Replace the four black screws at the corners of the bottom cover and
tighten them.
Tighten the nuts at each end of the RF module. Inspect the RF
module to ensure that both flat washers are between the module and
bottom of the PCB (See Figure 14). Remove the cabinet side panel, if
necessary, to get a clear view of the RF module hardware.
Replace the top cover and tighten all four corner screws.
If you have configured your transverter for a common transmit and
receive antenna, connect it to the ANT connector (J1). If you have
configured your transverter for separate transmit and receive antennas:
Connect the transmit antenna to the ANT connector (J1).
Connect the receive antenna to the AUX connector (J8).
Inspect the PCB to be sure the solder pads for U1 are not shorted. If
necessary use a desoldering tool to remove the remnants of the leads and
excess solder to be sure there are no solder bridges between the pads.
Use your DMM to identify the two pads for U1 that are not
grounded. They are the pads closest to the back panel and the pad
opposite, closest to the front panel.
Install a short jumper across the pads that are not grounded. Be sure
the jumper is not shorted to any other pads.
Replace the top cover and tighten the screws.
Optional Feet and Bail Attachment
A bail and feet that elevates the front of the transverter to a convenient
viewing angle is available as an optional accessory from Elecraft.
Contact Elecraft or visit
- 21 -
www.elecraft.com to order the feet and bail.
Page 26

Circuit Description
The circuits of the transverter for each band are similar. The signal flow is
described below at a block diagram level. This is followed by details of
the circuits based on the schematic diagrams.
Signal Flow
Refer to the block diagram on the following page. Many of the circuits in
the signal path are used for both receive and transmit. Switching between
receive and transmit is done by relays to preserve the low noise figure of
the receiver. The relays are shown in their de-energized state which puts
them in receive mode position.
In receive mode, signals from the antenna are routed by relay K1 to the
RF amplifiers and then through a band-pass filter to the mixer.
The local oscillator input to the mixer is 28 MHz below the signal
frequency, producing an intermediate frequency (I.F.) output from the
mixer in the 28 MHz range. Mixer responses outside of the 28 MHz I.F.
range are attenuated by the filter at the mixer output.
Relays K6 and K7 route the 28 MHz I.F. signal to the port selector circuit.
This circuit may be configured to work with an external rig that uses
either a single connection for both transmit and receive or separate
transmit and receive connections.
In transmit mode, the 28 MHz I.F. signal from the external rig is applied
to the TXin/IF1 connector. Relay K7 routes the 28 MHz I.F. signal
through the I.F. level control. The I.F. level control is adjustable to
provide the correct drive to the mixer from a wide range of I.F. transmit
levels from the 28 MHz rig.
Relay K6 routes the 28 MHz I.F. signal from the attenuator to the I,F,
filter and limiter. The limiter is part of a protective circuit described
below.
The mixer uses the local oscillator signal to convert the 28 MHz I.F.
signal to the transmit frequency. The RF band-pass filter selects this
frequency and attenuates the other mixing products.
Relay K2 routes the RF signal to the transmit driver. The transmit driver
raises the signal level as required to drive the RF power module. The RF
power module produces up to 20 watts output.
The output of the RF power module is routed through a low-pass filter
and relay K1 to the antenna connector.
The power monitor samples the output of the RF power module and
returns an analog signal to the controller. The controller illuminates the
power level LEDs on the front panel to indicate the RF output power.
A DB-9 connector is provided for connection to an Elecraft K2 or K3
transceivers. This connection includes the control signals needed by the
transverter.
When used with rigs other than an Elecraft K2 or K3, the KEY IN line
must be grounded by the external transmitter to switch the transverter
from receive mode to transmit mode. When the transverter is used with
an Elecraft K2 or K3, this command is furnished via the DB-9
CONTROL connector and the KEY IN line is not used.
When the controller switches the transverter from receive mode to
transmit mode, a transistor switch grounds the KEY OUT line to enable
an external power amplifier, if used.
The overload detector protects the transverter in the event a high-level
28-MHz I.F. signal is applied while the transverter is in receive mode.
The overload detector commands controller U1 to open relays in the I.F.
port selector to disconnect the transverter from the I.F. rig and blink the
front panel LEDs in unison to alert the operator. To reset the detector, the
transverter must be turned off, then on again. When used with an Elecraft
K2 or K3, the K2 or K3 must be turned off, then on again to reset the
detector.
Since the attenuator is switched out of the signal path in receive mode,
the mixer is vulnerable to damage from a high-level 28 MHz I.F. signal.
The limiter keeps the signal at a safe level while the controller reacts to
an overload condition.
- 22 -
Page 27

RF AMP
I.F.
LEVEL
CONTROL
ANT
(J1)
K1
RF
LOW-PASS
FILTER
K2
RF XMIT
DRIVER
RF POWER
AMPLIFIER
RF
BAND-PASS
FILTER
MIXER
LOCAL OSC.
BAND
SELECT
SWITCH
I.F FILTER
&
LIMITER
OVERLOAD
DETECTOR
K6
K7
RXout/IF2
(J2)
I.F. PORT
SELECTOR
TXin/IF1
(J3)
EXT PA KEY
KEY OUT
(J5)
RF POWER
MONITOR
SIGNAL FLOW KEY
RECEIVE ONLY
TRANSMIT ONLY
TRANSMIT AND RECEIVE
CONTROL SIGNAL
Figure 15. Transverter Block Diagram.
- 23 -
CONTROLLER
FRONT
PANEL
DISPLAY
KEY IN
(J4)
DC POWER
CONTROL
CONTROL
( J6 )
Page 28

Circuit Details
Separate schematic diagrams are provided in Appendix A for each of the
transverter RF PCBs. The location of the circuits on the schematic
diagrams is similar to the block diagram except for the control logic. The
Controller, display LEDs and associated drivers are on the front panel
PCB shown on a separate schematic diagram. The same front panel PCB
is used on all of the transverters.
Receive Circuits
The first active device in the receiver is Q3, a low noise PHEMT that
provides an exceptionally low noise figure. The current through Q3 is set
for optimum performance by potentiometer R13.
U1 further amplifies the incoming signal which is then passed on to mixer
Z1 through relay K2 and an RF band-pass filter.
The local oscillator signal is generated by crystal oscillator, Q1. In the
XV50, XV144 and XV222, the local oscillator signal is amplified by Q2,
and in the XV432 by U9. The local oscillator signal is 28 MHz below the
RF signal frequency on all bands.
In the XV50 the second harmonic of the local oscillator at 44 MHz is very
close to the 50 MHz pass band, so a low-pass filter is used between
amplifier Q2 and mixer Z1 to attenuate the 44 MHz signal.
The intermediate frequency (I.F.) output of mixer Z1 passes through
another band-pass filter that includes a diplexer formed by C57, L17 and
R25. C57 and L17 are series resonant at 28 MHz, so the I.F. signal passes
through to the band-pass filter section. C57 and L17 present a high
impedance to frequencies removed from the 28 MHz I.F. These signals
are terminated by R25.
LEDs D10 and D11 are used as limiters to protect the mixer during
transmit as described below. Inductor L9 resonates with the capacitance of
the LEDs at 28 MHz to avoid attenuating the I.F. signal.
The 28 MHz I.F. signal is routed around the transmit signal attenuator to
the I.F. port selector circuits by relays K6 and K7. Relays K8 and K9
disconnect the I.F. RX and TX/RX ports whenever the transverter is not in
use as described below. This permits several transverters to be connected
to the same external rig without loading the signal lines.
If separate transmit and receive connections are used for the 28 MHz I.F.,
the receive line is connected to J2. A jumper is placed across JP1 pins 1
and 2 and across JP2 pins 2 and 3. JP1 routes the receiver signal through
relay K9 to K6. JP2 routes the transmit signal through the attenuator.
If the external rig uses a single connection for both transmit and receive,
jumpers are placed across JP1 pins 1 and 2 and across JP2 pins 1 and 2. In
receive mode, relay K7 routes the I.F. signal to the RXout/IF2 output at
J3. In transmit mode relay K7 routes the 28 MHz I.F. signal coming in at
J3 to the attenuator.
When the external rig uses a common I.F. connection for both transmit
and receive, a cable connected to J2 will carry the transmit and receive I.F.
signals to another transverter.
Transmit Circuits
In transmit mode, the 28 MHz I.F. signal at J3 is routed through the I.F.
port selector circuits to the I.F. level control. The I.F. level control either
amplifies or attenuates the I.F. signal to the proper level for the mixer. The
I.F. level control can handle signal levels of from -20 dBm to +39 dBm
from the external rig. For low-level I.F. input levels amplifier Q6 may be
switched into the circuit by jumpers JP5 and JP6. For higher level I.F.
input levels, jumpers JP3 and JP4 permit adding or bypassing a fixed 30
dB attenuator as needed. Potentiometer R22 permits continuous
adjustment of the attenuation.
Mixer Z1 uses the local oscillator signal to produce an RF output at the
desired transmit frequency. Unwanted mixer products are attenuated by
the RF band-pass filter.
Relay K2 routes the transmit RF signal to RF driver U6, which amplifies
the signal to drive RF power module U7. A different RF power module is
required for each band. The RF power modules for the 144 MHz and 220
MHz bands require a bias adjustment to set the amplifier current at the
proper level. The bias is adjusted by R39, which is set for the proper total
current drain on the 12 volt line. The current drain is measured by
connecting a DMM to TP3 and TP4
RF from power module U7 passes through a low-pass filter and relay K1
to the antenna connector. In the XV432, an additional relay, K10, grounds
the input to the receive RF amplifier during transmit.
- 24 -
Page 29

Control Circuits
transverter ID corresponding to the setting of SW1 is received.
Power Control: The DC power control circuit is configured with jumpers
to allow it to work with an Elecraft K2, K3 or any other suitable rig.
When used with a rig other than an Elecraft K2 or K3, a jumper is placed
at JP5 to bypass Q5 and D16. The transverter power is then controlled by
front panel power switch S2. Closing S2 enables relay K3, applying +12
volts to the transverter circuits.
When the transverter is used with an Elecraft K2 or K3, the control circuit
automatically turns the transverter power off whenever the K2 or K3 is
turned off. No jumper is used at JP7. As long as the K2 or K3 power is on,
+12 volts is supplied via pin 8 of the DB-9 connector to Q5, which
grounds the return side of power switch S2 through D19. When the K2 or
K3 power is turned off, Q5 will turn the transverter off automatically.
Of course, power switch S2 on the transverter must be on. If desired, a
jumper may be placed at JP8 to disable the transverter power switch. The
transverter power then is controlled only by the K2 or K3 transceiver.
Controller U1 on the front panel PCB enables the three-diode light bar
D11 through Q6 whenever the transverter is active. If the transverter is
used with an Elecraft K2 or K3, it is active whenever DC power is applied
at J2 and it is selected by the K2 or K3 as described below. If the
transverter is not used with a K2 or K3, light bar D11 is enabled whenever
DC power is applied at J2 and power switch S2 is on.
Fan Control: The XV432 has an internal cooling fan that operates
whenever +12 vdc is present at the transverter power connector.
Transmit-Receive Switching: Switching between receive mode and
transmit mode is by a ground at the KEY IN connector or, if an Elecraft
K2 or K3 is used, when the 8R signal at pin 9 of the DB-9 interface goes
to a logic low.
When used with an Elecraft K2 or K3, the transverter is enabled
automatically by the BAND switch on the K2 or K3. A K2 identifies the
transverters as TRN1, TRN2 or TRN3. A K3 identifies the transverter as
XV1, XV2 or XV3. Switch SW1 associates the transverter with the
corresponding number at the K2 or K3. SW1 selects an analog voltage
level depending upon the position of the switches. This voltage is sent as
the ID signal to controller U1. Controller U1 monitors the AuxBus signal
from the K2 or K3 and enables transmit/receive switching when the
When the transverter is used with rigs other than an Elecraft K2 or K3, all
the switches are off. The transverter is enabled whenever the transverter
power switch is on.
When a transmit mode command is received via the KEY IN connector or
by the 8R line from a K2 or K3, controller U1 provides a ground return to
close relay K5. Relay K5 provides +12 volts to relays K1, K2, K6 and K7
and supplies bias voltage to RF power module U7.
I.F. Port Enable: Relays K8 and K9 must be energized to connect the
external rig to the transverter circuits. These relays are energized by
controller U1 by providing a ground return on the IF EN command line.
When the transverter is used with an Elecraft K2 or K3, the controller
enables the I.F. port only when the transverter is selected by the K2 or K3
band switch as described above. This feature allows several transverters to
be “daisy-chained” together through the 28 MHz TX/RX and 28 MHz RX
connectors.
When the transverter is used with other rigs, the I.F. port is enabled
whenever power switch S2 is on. If several transverters are “daisychained” together, the desired transverter selected by turning its power
switch on and leaving any other transverters off.
I.F. Overload Protection: If the transverter is not switched to transmit
mode before a high-level I.F. signal is applied to the 28 MHz TX/RX
input, mixer Z1 might be damaged. This will happen if the external rig
does not supply a ground the KEY IN connector or, if a K2 or K3 is used,
the 8R signal at the DB-9 connector does not go low to change the
transverter into transmit mode. To prevent damage to the mixer, a
protection system will automatically disconnect the external rig from the
transverter circuits and limit the signal level at the mixer I.F. port.
Diodes D6 and D12 in the overload detector circuit rectify a sample of the
transmit RF and produce a DC level that will cause the control circuits to
open relays K8 and K9. This voltage is supplied as the ODET (overload
detect) signal to controller U1 on the front panel PCB. Also, when an
overload is detected controller U1 flashes the front panel LEDs at about a
1 Hz rate to alert the operator. The transverter will remain disconnected
with the LEDs flashing until the controller is reset by turning the power
switch off, then on again.
- 25 -
Page 30

The control circuits may not release relays K8 and K9 fast enough to
prevent damage to mixer Z1 from a high-level 28 MHz I.F. signal, so
LEDs D10 and D11 are used to protect the mixer. LEDs D10 and D11 will
conduct and limit the I.F. signal to a safe level. LEDs are used because
their greater forward-conduction voltage avoids the need to use diodes in
series.
External PA Keying: When the transverter switches to transmit mode,
controller U1 sends a signal to Q4 that turns it on, providing a path to
ground at EXT PA KEY jack J5 to key an external power amplifier.
Power Monitor: D1 produces a DC voltage proportional to the RF power
output of U7. The voltage, Po, is sent to controller U1 on the front panel.
The controller drives D1 through D10 to indicate the RF power level from
1 through 30 watts. The LEDs below 20 watts are green. The 20-watt LED
is yellow, and the 25 and 30 watt LEDs are red to indicate that the
specified maximum power output is being exceeded.
The metering circuit is calibrated by potentiometer R10.
Display Mode: When the transverter is used with an Elecraft K2, the
behavior of the LEDs on the front panel follows the display mode selected
by the operator at the K2. These selections determine the LED brightness
and whether the power output LEDs illuminate in a line extending from
the left (bar mode) or if only one LED corresponding to the power output
illuminates (dot mode). The display mode information is reported to
controller U1 via the AuxBus. The controller changes the brightness by
varying the bias on Q2 and Q5 on the front panel PCB.
- 26 -
Page 31

Alignment and Test
A complete alignment and test using the following procedures is essential
after assembling your kit. These procedures can be repeated whenever
desired to confirm that the transverter is working correctly and adjusted
for optimal performance.
Perform the first seven parts of the procedure in the order given. Each part
assumes you have completed the adjustments and set up your transverter
as described in the earlier parts.
The following test equipment will be needed:
28 MHz transceiver or transmitter and receiver to use as the I.F.
system, with interconnecting cables.
Power supply capable of providing 13.8 VDC at 6 A, minimum.
Digital Multimeter (DMM).
Noise Generator (Elecraft N-Gen or equivalent) or signal
generator with output in the RF frequency range of the
transverter.
RF Wattmeter capable of measuring 20 watts with good
accuracy.
RF dummy load, 20 watts minimum
Adjustment tool for the inductors in the transverter (supplied
with transverter).
RCA plug with the center pin wired to the shell.
Part I - Initial Setup
Pre-set the potentiometers on the RF PCB as follows:
R10 (Power Cal) at mid-range.
R13 (LNA Bias) XV50, XV144 or XV222: full CCW (counter
clockwise). XV432: full CW (clockwise).
R22 (Input Atten. Adjust) full CCW.
R39 (PA Bias) full CCW.
Skip this step if you are aligning an XV432. On an XV50, XV144 or
XV222, verify that the tuning slugs have been removed from the
following inductors. If not, remove the cores and discard them. These
slugs will not be used:
L1
L10 (In the XV50 this inductor is a toroid and has no slug.)
L11
i
In the next step you will use the alignment tool supplied with
your transverter to preset inductor slugs a certain number of turns
down from the top of the coil. You may find it easier to count the
turns if you place a readily-visible mark on the alignment tool.
If you are aligning an XV50 or XV432 transverter and wish to perform the
optional local oscillator frequency calibration, you will need one of the
following:
A frequency counter capable of measuring signals in the 22 or 50
MHz range for the XV50, or 404 MHz for the XV432.
A calibrated signal generator capable of producing output with
good frequency accuracy at 432 MHz (for the XV432) or at 50
MHz (for the XV50). An H.F. transmitter with a well-calibrated
VFO that covers the 12 meter Amateur band may be used for the
XV50.
- 27 -
Page 32

Pre-set the inductors in the transverter as follows. Turns are measured
down from the point where the slug is flush with the top of the coil.
Part III - Local Oscillator Level
Verify the proper local oscillator level as follows:
COIL XV50 XV 144 XV222 XV432
L3 N/A* N/A* N/A* 5.5
L4 N/A* N/A* N/A* 3.5
L5 N/A* N/A* N/A* 2.5
L12 0 6 6 N/A*
L13 3 6 6 N/A*
L14 1.5 6 6 N/A*
L15 2 2 2 1
L16 2 2 2 2
L17 2 2 2 0
* Inductor not used on this model.
If you are aligning an XV222, set the slug in inductor L4A even with
the top of the form. This slug will not be adjusted in the following
procedure. L4A is used only in the XV222 transverter.
Connect an RF power meter and dummy load to the transverter ANT
connector.
Verify that the transverter Power switch is off (button out).
If you haven’t already done so, turn to the Installation section
(Page 4) and hook up your transverter to your 28 MHz rig,
Connect your DMM between a ground test point and TP1 in the
lower right quadrant of the RF PCB.
If you are aligning an XV222, preset the slug in L19 (near the
crystal in the lower right quadrant) so it is about half-way out of the top
of the core.
Apply power to your 28 MHz rig and verify that the transverter
power control operates as follows:
If you are using a non-Elecraft 28 MHz rig, press the transverter
Power pushbutton in. Verify that the band label lights.
If you are using an Elecraft K2 or K3, confirm that the
transverter band label lights when you select the band assigned
to the transverter on the K2 or K3, and that the band label goes
off when you select any other band. The transverter Power
pushbutton should be inoperative.
Verify that the local oscillator voltage levels are as follows. If you
find no reading, make sure you have a 2-pin shorting block on JP9. The
local oscillator is disabled if this shorting block in not installed. See
Local Oscillator Power Control on page 16 to choose the correct
position for the shorting block on JP9.
XV50: 0.8 to 1.2 VDC (No adjustments).
Part II – Power Control
Apply power to your 28 MHz rig and verify that the transverter power
control operates as follows:
If you are using a non-Elecraft 28 MHz rig, press the transverter
Power pushbutton in. Verify that the band label lights.
If you are using an Elecraft K2 or K3, confirm that the
transverter band label lights when you select the band assigned to
the transverter on the K2 or K3, and that the band label goes off
when you select any other band. The transverter Power
pushbutton should be inoperative.
XV144: 1.2 to 1.8 VDC (No adjustments).
XV222: If the voltage is between 1.0 and 1.5 VDC, remove the
slug from the L19. It will not be used. If there is no voltage, or if
it is below 1.0 VDC, screw in the slug while watching for the
point where the voltage stops rising and stop (do not adjust for a
“peak”).
XV432: Adjust L3, L4 and L5 for maximum: The peak voltage
should be between 1.5 and 3.0 VDC (nominally 2.5 VDC).
- 28 -
Page 33

If aligning an XV222 or XV432, turn the power off, then on again
(either using the front panel switch or, if using an Elecraft K2 or K3 for
the I.F., use the K2 or K3 BAND switch to deselect and select the
transverter). Make sure the local oscillator voltage returns when power is
turned off then on again. If not, adjust L19 (XV222) or L4 (XV432) for
reliable starting each time power is turned on.
Adjust R39 for a reading of 20 mV on your DMM. If R39 has no
effect when aligning an XV40, XV144 or XV222, ensure W1 is installed
on RF board between C60 and R28.
Reconnect the 28 MHz rig KEY IN line to the transverter, if used.
Reset the Band Select DIP switches to their former positions.
Part IV – Receiver RF Amplifier Bias Adjustment
Adjust the receiver low-noise amplifier (LNA) bias current as follows:
Connect your DMM to measure DC voltage between TP2 in the
upper left quadrant and ground.
Adjust R13 as follows:
XV50, XV144 or XV222: between 175 and 275 millivolts.
XV432: 5 volts.
Part V – RF Power Amplifier Quiescent Current
Adjustment.
Attach a 50 ohm dummy load to the transverter ANT connector.
Connect your DMM between TP3 (-) and TP4 (+) near J7 in the
upper right corner of the RF PCB.
If you are using an Elecraft K2 or K3 for the 28 MHz I.F., note the
settings on the Band Select DIP switches. You’ll need them later.
Set all four Band Select DIP switches to Off (toggles toward the front
panel). If you are using a non-Elecraft rig for the I.F., they will already be
in the Off position.
Disconnect the 28 MHz rig KEY IN line to the transverter, if used.
Part VI – Filter Alignment.
Align the tunable filters in the I.F. and R.F. path as follows:
Adjust your 28 MHz rig output for the level chosen to drive your
transverter to full output (normally 1 milliwatt, 251 milliwatts or 5 watts)
Attach your DMM ground probe to one of the ground test points on
the RF PCB.
i
If you drive the transverter with 5 watts from your 28 MHz
rig, you may notice that some of the 1-watt resistors are quite warm to
the touch. This is normal. They are operating well within their design
ratings. These resistors were mounted above the PCB to promote
good cooling air circulation around them.
Connect your DMM to measure DC voltage between a ground test
point and TP5 in the upper left quadrant near potentiometer R10.
Set the 28 MHz rig frequency to transmit at 50.5 MHz, 144.5 MHz,
222.5 MHz or 432.5 MHz. If you are using an Elecraft K2 or K3 in
transverter mode, the frequency display will show the actual transmit
frequency. Other rigs must be set to 28.5 MHz.
Key the 28 MHz rig to provide transmit RF to the transverter and
advance R22 (Input Atten. Adjust) until the DMM reads anywhere
between 0.1 and 10 volts. Key the 28 MHz rig only as long as needed for
each adjustment.
Insert the shorted RCA plug into the KEY IN jack on the back of the
transverter. This will put the transverter in transmit mode. The 28 MHz rig
must not be keyed to provide RF drive to the transverter for this
adjustment.
i
While performing the alignment, take care not to overheat
your 28 MHz I.F. rig by holding the key down too long.
- 29 -
Page 34

Key the 28 MHz rig to provide transmit I.F to the transverter and
adjust the following inductors for maximum voltage at TP5. If the voltage
exceeds 10 volts, turn R22 (Input Atten Adjust) counter clockwise (CCW)
to reduce the voltage. The front panel Power Output LEDs may begin
lighting up as you peak the inductors:
XV50, XV144 or XV222:
L12, L13, L14, L15, L16 and L17. The adjustment of L17 is
very broad. Maximum output may occur with the slug removed.
If so, leave the slug out.
Key the 28 MHz rig to provide a transmit signal and adjust R22
(Input Atten. Adjust) for 20 watts indicated on your external wattmeter.
When finished, do NOT change the output power from your 28 MHz rig
before performing the next step.
Key the 28 MHz rig to provide a transmit signal. With the external
wattmeter indicating 20 watts, adjust pot R10 (Power Cal) in the upper left
quadrant of the RF Board so that the yellow (20 watt) LED on the
transverter front panel just lights.
XV432:
L15, L16, L17, the three adjustments in FL1 and the three
adjustments in FL2. The adjustment of L17 is extremely broad
because of the wide bandwidth of this filter. Maximum output
may occur with the slug removed. If so, leave the slug out.
Repeat the above adjustments several times for maximum voltage at
TP5. Some of the adjustments interact. Adjust R22 (Input Atten. Adjust)
CCW as needed to keep the voltage below 10 VDC.
Part VII – Power Display LED Calibration.
Calibrate the front panel Power Output display as follows:
Set your 28 MHz rig transmit frequency to 28.0 MHz. If you are
using an Elecraft K2 or K3 in transverter mode, the frequency displayed
will be 50, 144, 222 or 432 MHz. (Normally you’d not use an XV50 with
an Elecraft K3 since the basic K3 covers the 50 MHz band.)
Set your 28 MHz rig to the transmit level that corresponds with 20
watts output from this transverter (1 milliwatt, 251 milliwatts or 5 watts).
This depends upon how you configured the I.F. power level jumpers in the
Installation procedure.
Part VIII – Receiver Input Alignment.
i
Accidentally transmitting while performing the following steps
could destroy your noise generator.
On your 28 MHz rig:
If possible, turn the AGC off.
Set the receive frequency to 29.0 MHz. If you are using an
Elecraft K2 or K3 in transverter mode, the frequency display will
be 51 (K2 only), 145, 223 or 433 MHz.
Place your DMM in AC volts mode and connect it across the phone
or speaker output of your 28 MHz rig to measure the audio level.
Connect a noise generator to the transverter antenna input. Normally
this will be the ANT connector unless you wired your transverter for
separate transmit and receive connections (see page 20). In that case,
connect your noise generator to the AUX connector.
Turn your noise generator on. You should see an increase in the AC
voltage reading on your DMM.
i
from your 28 MHz rig, depending upon how you configured the
transverter jumpers. Exceeding the maximum level may damage the
transverter.
Do not exceed the recommended maximum transmit power
Adjust trimmer capacitor C1 in the upper left quadrant of the PCB for
maximum voltage shown on the DMM. You may need to reduce the input
from the noise generator to see the peak clearly.
- 30 -
Page 35

i
Adjusting C1 for maximum conversion gain (noise) will
normally result in a receive noise figure of less than 1 dB. However,
the adjustment for maximum gain and minimum noise figure do not
coincide exactly because the optimum impedance for lowest noise
figure differs from an exact conjugate match. With the filter design
used in the transverter, adjusting C1 for maximum gain 1 MHz above
the lower band limit as described above produces very nearly the
optimum noise figure at the bottom of the band. It may be possible to
achieve an 0.1 to 0.2 dB improvement in noise figure by adjusting C1
with a calibrated Noise Figure Meter.
Disconnect the transmit/receive control from the I.F rig as follows:
If you are using a non-Elecraft rig for the I.F., disconnect the
Key In connector
If you are using an Elecraft K2 or K3, disconnect the interface
cable at the Control connector.
Momentarily key the transmitter. Verify that all of the Power LEDs
begin flashing and keep flashing even after the transmit signal is removed.
This is the Overload warning indicating that a transmit signal was applied
to the transverter while the transverter was still in receive mode.
Part IX - Overload Protection Circuit Test
This test verifies that the transverter will protect itself in the event a highlevel transmit signal is applied while the transverter is still in receive
mode. This is an optional test that only checks the protective circuit. It is
not required to properly align your transverter.
i
Do not perform this test if you are using a low-level
(1 milliwatt) output from your 28 MHz rig. The overload circuit will
not respond to a low-level transmit signal.
Disconnect the noise generator from the transverter Antenna output
and reconnect the dummy load.
If you are using an Elecraft K2 or K3, temporarily change the XV
configuration as follows, otherwise skip this step:
Remove the jumper header from JP8 on the RF Board (near the
front corner on the right side).
Write down the settings of the Band Select DIP switch positions.
Switch all four DIP switches off.
Turn the transverter Power off, then on again to clear the overload
display.
If you are using an Elecraft K2 or K3:
Replace the jumper shorting block on JP8.
Switch all four DIP switches off, then reset the switches as they
were before performing this test.
Reconnect the Key In or Control line to the transverter.
- 31 -
Page 36

Local Oscillator Frequency Calibration (Optional)
The local oscillator frequency in the XV50 and XV432 transverters is
adjustable over a narrow range to provide the best frequency calibration
for both transmit and receive on the 28 MHz I.F. rig. Although the local
oscillator in XV222 is not adjustable, the firmware in an Elecraft K2 or
K3 transceiver allows you to compensate for frequency errors using the
menu commands. Once the proper compensation is entered, the K2 or K3
frequency display will show the actual transmit and receive frequencies
accurately. The same menu commands may be used to correct for small
errors in the XV50 and XV432 frequency as well. See the Revision 2 and
up K2 firmware instructions or the K3 Owner’s Manual for details. See
the next page for adjusting the XV144 Local Oscillator frequency.
The frequency adjustment range is limited and you may not be able to put
the local oscillator exactly on the desired frequency. In most cases the
local oscillator will stop oscillating when the frequency is adjusted too far.
This is most likely to happen with the XV432. If the stock crystal supplied
with your kit does not have adequate adjustment range, an optional highaccuracy local oscillator crystal is available for the XV432 transverter.
This should not be a concern when using an Elecraft K2 or K3 for the I.F.
because any remaining frequency error can be compensated for in the K2
or K3 using the menu commands as described above.
The following procedures allow you to calibrate the local oscillator in
several ways:
Use a counter to measure the local oscillator frequency at 22 MHz
(XV50) or 404 MHz (XV432).
Use a counter to measure the output frequency of the transverter.
Use a received signal produced by a calibrated signal generator,
transmitter or other known source.
Using a Counter to Measure the Local Oscillator Frequency
Turn the transverter power on and allow the transverter to stabilize
for at least 5 minutes at room temperature (approx. 20 – 25º C).
Connect a DMM set to measure DC volts between a ground point and
TP1 in the lower left quadrant of the RF PCB.
i
In the next step you will connect the frequency counter to a
circuit that has a DC voltage. If your counter does not provide
protection against DC voltages, or if you aren’t sure, place a capacitor
in series with the counter input. Any value from 100 pF to .01 µF is
suitable.
(near T1 on the RF PCB).
and off several times to be sure the local oscillator starts reliably.
Using a Counter to Measure the Transverter Output Frequency
for at least 5 minutes at room temperature (approx. 20 – 25º C).
transverter. Do NOT connect your counter directly to the antenna
output without a suitable attenuator to protect the counter input. If
you do not have a suitable attenuator, connect an insulated wire to the
counter input and position the wire near antenna relay K1 on the RF PCB.
You may need to experiment with the position of the wire to pick up
enough RF to operate the counter. Do not wrap the wire around L10 or
L11. That would detune the output filter and could damage the RF power
module.
Elecraft K2 or K3 for the I.F. and have the transverter menu enabled, set
Attach the frequency counter to either end of molded inductor L3
Adjust the local oscillator frequency as follows:
XV50: Adjust trimmer capacitor C33 for a reading of 22.00000
MHz on the frequency counter. Make sure the voltage at TP1
remains between 0.8 and 1.2 VDC.
XV432: Adjust L4 for a reading as close as possible to 404.000
MHz on the frequency counter. Make sure the voltage at TP1
remains between 2 and 3.5 VDC.
Monitor the voltage at TP1 while switching the transverter power on
Turn on power to the transverter and allow the transverter to stabilize
Attach a dummy load to the transverter output.
Connect the frequency counter to sample the RF output from the
Set the 28-MHz rig to transmit at 28.0000 MHz. If you are using an
- 32 -
Page 37

the K2 or K3 to display a frequency of either 50000.00 kHz or 432000.0
kHz and ensure that the Menu OFS (Frequency Offset) command is set to
0.00. (Refer to your Rev. 2 and up Firmware instructions for the
procedure). Be sure that SPLIT and RIT are turned off.
Key the rig to produce a steady carrier and adjust the local oscillator
frequency as follows:
XV50: Adjust trimmer capacitor Z6 for a reading of 22.00000
MHz on the frequency counter. Make sure the voltage at TP1
remains between 0.8 and 1.2 VDC.
XV432: Adjust L4 for a reading as close as possible to 404.000
MHz n the frequency counter. Make sure the voltage at TP1
remains between 2 and 3.5 VDC.
Monitor the voltage at TP1 while switching the transverter power on
and off several times to be sure the local oscillator starts reliably.
Adjust the local oscillator frequency to bring the received signal into
the center of the I.F. receiver band pass. If you are comfortable zero
beating CW signals, you can listen in CW mode and zero beat the signal
against the sidetone.
XV50: Adjust trimmer capacitor Z6. Make sure the voltage at
TP1 remains between 0.8 and 1.2 VDC.
XV432: Adjust L4. Make sure the voltage at TP1 remains
between 2 and 3.5 VDC.
Monitor the voltage at TP1 while switching the transverter power on
and off several times to be sure the local oscillator starts reliably.
XV144 Local Oscillator Adjustment
If you cannot compensate for frequency error using the K2 or K3 Offset
menu command, do the following:
Using a Received Signal
Turn on power to the transverter and allow the transverter to stabilize
for at least 5 minutes at room temperature (approx. 20 – 25º C).
Set up your external signal source to produce an audible signal as
follows:
XV432: 432.000 MHz.
XV50: 50.000 MHz. If you use an HF rig transmitting into a
dummy load for the signal source, set it at 25.000 MHz to
produce a second harmonic at 50.000 MHz. If it won’t transmit
outside the 12 meter Amateur band, set it for 24.990 MHz to
produce a second harmonic at 49.980 MHz.
Adjust the slug in L19 so it is flush with the top of the inductor
frame.
Use the K2 or K3 offset (OFS) menu command to correct any
frequency error. If the correction required is more than the 9.99 kHz range
turn the slug into L19 and retry the offset command. Turning the slug
into L19 too far may cause the local oscillator to stop. It may take
several iterations to move the local oscillator frequency within range of
the offset command.
Measure the voltage between TP1 LO LEVEL and ground while
switching the XV144 on and off repeatedly. This voltage is normally
between 1.2 and 1.8 VDC. Verify that the voltage returns to the same level
each time power is switched on, indicating that the local oscillator is
starting reliably
This completes the alignment and testing of your transverter.
- 33 -
Page 38

Appendix A - Schematics and Parts Placement Diagrams
Front Panel Board Parts Placement Drawing (all models)...................................................A-2
Front panel Board Schematic Diagram (all models).............................................................A-3
XV50, XV144 and XV 222 Models Only:
RF Board Parts Placement Drawing..........................................................................A-4
RF Board I.F. and Control Circuits Schematic...........................................................A-5
RF Board XV50 Circuits Schematic...........................................................................A-6
RF Board XV144 Circuits Schematic.........................................................................A-7
RF Board XV222 Circuits Schematic.........................................................................A-8
XV432 Model Only:
RF Board Parts Placement Drawing..........................................................................A-9
RF Board I.F. and Control Circuits Schematic...........................................................A-10
RF Board XV432 Circuits Schematic.........................................................................A-11
Elecraft XV Series Transverters
Page A-1
Page 39

Front Panel Board Parts Placement Drawing (All Models)
Elecraft XV Series Transverters
Page A-2
Page 40

Front Panel Board Schematic Diagram (All Models)
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10
LED 10
5V
220
R1
Q1
PN2222
Q5
P N 2222
RB7 AUXBUS
RB6 8R/KEY
RB5 COR
RB4 LED 2
RB3 LED 3
RB2 LED 4
RB1 LED 5
RB0 LED 6
RC7 LED 7
RC6 LED 8
RC5 LED 9
RC4 LED 10
AN0 PW R OUT
RA1 LED 1
RA2 ID
RA3 PILOT LITE, HIGH ON
RA4 S TRAP FOR DIM LEDS
RA5 DIM LEDS
RC0 PWR T-R,HIGH TOTX
RC1 PWR ENABLE
RC2 IF ENABLE
RC3 KEY OUT
470
R2
120
R22
LED 1
D11 3 Diode Light Bar
120
R21
P N 2222
Q6
2.2K
R24
PN2222
Q7
120
R16
.047uF
R4
100K
C1
R10
R11
R12
R14
27
2
RB6
AN0
.001uF
C4
26
3
R15
R6
R8
R7
R9
22
23
24
25
RB5
RB4
RB3
RB2
RA1
RA2
RA3
RA4
4
5
6
JP 1
2.2K
R20
20
21
RB1
RB0
Vdd
RA5
Vss
OS C1
7
8
9
Z1
100K
2.2K
R19
R17
17
18
19
Vss
RC7
RC6
OS C2
RC0
RC1
1011121314
16
2.2K
R18
120X 10
15
RC5
RC4
RC2
P I C16F 872
RC3
U4
120
R13
.01uF
C2
28
.01uF
C3
120
R23
RB7
MCLR
1
R51 M
R310K
R25
270K
Elecraft XV Series Transverters
5V
ID
Po
12V
COR
IF E N
8R /K ey
AuxBus
PWR En
PWR T R
Key Out
Q4
P N 2222
Q3
P N 2222
Q2
P N 2222
Page A-3
Page 41

RF Board Parts Placement Drawing
XV50
XV144
XV222
May be shown as
C58 on some
boards.
Elecraft XV Series Transverters
Page A-4
Page 42

XV50
XV144
XV222
I.F. and Control Schematic
(RF Board)
150pF
Mixer IF Port
R25
C57100pF
L17
270pF
56
C56
C52
18pF
L15 L16
C53
150pF
C54
.047uF
12V
270pF
C55
C84
12T
.047uF
180
R19
C85
L9
0.47uH
C9
.01uF
K6
D10 D11
10 pF
.01uF
C34
100K
R23
C35
K9
D12
1N4148
1N4148
K8
IRF620
Q4
12V
To 28 MHz RX
JP1
J2
1
D9
2
3
To 28 MHz TX/RX
J3
EXT PA KEY
J5
.01uF
C38
U5
MAR-3
C70
27pF
C10
.01uF
12T
R18 620
1
C67
.01uF
3
2
C68
.047uF
R40
PN2222
22K
160
R27
K7
12T
1N4148
JP2
1
2
3
D6
Q6
C64
.01uF
3
2
1
JP5JP6
100
R22
JP4
1
2
820
3
R21
160
R20
160
R26
JP3
1
2
3
R32 3.9K
23
1
SW1
BAND SELECT
R30 7.5K
4
R31 15K
R33 10K
R35 5.1K
Elecraft XV Series Transverters
12PRI
JP9
8R/KEY
Po
AUXBUS
1N4148
1N4148
D16
D15
12V
JP8
.01uF
C71
2N7000
Q5
12R
12T
100K
R34
15 uH
L8
.001uF
C39
D7
1N5711
D8
1N5711
.01uF
C36
KEY IN
J4
.01uF
C37
16
J6
9
5
8R
45
12LO
12V
123
TP3
TP4
D5
SG530
J7
12PRI
F1
5A
12V INPUT
K3
1N4148
D14
D13
S2
.02
R17
P1
5V
GND
PWR TR
1N4148
U4
ID
PWR EN
LM7805
OD
IF EN
K4 K5
JP7
Po
KEY OUT
Page A-5
Page 43

XV50 R.F. Circuits Schematic
(R.F. Board)
Elecraft XV Series Transverters
Page A-6
Page 44

XV144 R.F. Circuits Schematic
(R.F. Board)
.047uF
C29
180
R12
C4
D36.8V
C42
C44
C43
Ant
J1
10K
12T
.01uF
C61
27pF
47pF
27pF
2.2 pF
C5
R1
.01uF
C6
K1L13-12 pF
C1
L10
L11
22uF
C26
D1
1N4148
1K
R11
.01uF
C22
100K
R10
4.7pF
C28
.047 uF
POWER CAL
.047uF
.047uF
C66
LNABIAS ADJ
200nH
L7
C25
TP5
56
R15
Q3
AT F 34143
C31
TP2
C41
.047 uF
1K
R39
.047 uF
R A30H 1317M
C63
.01uF
C21
C2
100 pF
4.7pF
.047uF
R13
100
12V
.047 uF
Po
.047uF
C65
56
R29
BIAS ADJ
R281K
C24
C72
4.7
ERA6
R14
U7
U1
C27
.01uF
U3
LM78L05
22uF
100 nH
C60
.001uF
C7
120
R16
L2
100nH
Z3
12R
.01uF
C23
C3
.001uF
.01uF
120
R24
C40
C48
4.7pF
12pF
C45
.01uF
ERA-5
.01uF
C62
U6
12T
D4
1N4148
12T
K2
C8
C491pF C501pF C5 14.7pF
15pF
C46
L12 L13
10K
12pF
C47
R9
C19
.01uF
1N4148
D2
TP1
L14
2.2pF
C18
R
.001uF
C17
ADEX-10H
L
IF Port
Z1
12L O
120
.01uF
R8
C16
1
2
T1 C15
Q2
3
4
BFR96
10K
R7
.001uF
0.15uH
470
R6
.01uF
Z4
L4
C20
56
MP S 918
Q1
10 pF
.047uF
C13
C12
33pF
C14
5.6K
R4
5.6K
R5
LM78L09
U2
116 MH z
.22uF
C30
Y1
Elecraft XV Series Transverters
Page A-7
Page 45

XV222 R.F. Circuits Schematic
(R.F. Board)
.047uF
C29
180
R12
C4
D36.8V
C42
10pF
C44
10pF
C43
10pF
Ant
J1
10K
R1
12T
.01uF
C61
2.2 pF
.01uF
K1L13-12 pF
C5
C6
.01uF
C22
4.7pF
C1
L10
C44A
10pF
L11
22uF
C26
D1
1N4148
1K
R11
100K
R10
C28
.047 uF
POWER CAL
.047uF
LNA BIAS ADJ
200nH
L7
C25
TP5
.047uF
56
R15
Q3
C66
C41
.047 uF
.047 uF
R A 30H 2125M
.01uF
C2
100 pF
4.7pF
AT F 34143
.047uF
C31
R13
100
TP2
1K
R39
C21
C63
12V
.047uF
C65
R281K
.047 uF
C24
Po
C72
R14
4.7
56
R29
BIAS ADJ
U7
ERA6
U1
C27
.01uF
U3
LM78L05
22uF
C60
120
R16
100 nH
.001uF
C7
L2
100nH
Z3
12R
.01uF
C23
C3
.001uF
.01uF
56
R24
C40
C46
C45
12T
D4
1N4148
12T
L12
C49
1pF
C46A
1pF
C48
3.3pF
10pF
1pF
C45A
K2
.01uF
C62
C8
.01uF
SGA
7489
U6
12pF
L13
C50
1pF
10K
R9
C47A
1pF
.01uF
C19
C47
12pF
1N4148
D2
TP1
L14
2.2pF
C18
C51
3.3pF
.001uF
C17
AD E X -10H
IF Port
Z1
12L O
120
.01uF
R8
C16
1
2
T1 C15
Q2
3
4
BFR96
10K
R7
.001uF
220
R6
L4A
.01uF
56
Z4
C20
MP S 918
Q1
15 pF
.047uF
C13
C12
22pF
C14
5.6K
R4
5.6K
R5
L M78L 09
U2
194 MH z
.22uF
C30
Y1
L19
11 April 2007
Elecraft XV Series Transverters
Page A-8
Page 46

RF Board Parts Placement Drawing XV432
Elecraft XV Series Transverters
Page A-9
Page 47

XV432 I.F. and Control Circuits Schematic
(RF Board)
Mixer IF Port
R25
C57100pF
56
150pF
L17
180pF
C56
23
1
SW1
BAND SELECT
4
22pF
C52
L15 L16
150pF
C53
R32 3.9K
R30 7.5K
R31 15K
R33 10K
R35 5.1K
C54
.047uF
12V
180pF
C55
12PRI
C84
12T
.047uF
180
R19
C85
L9
0.47uH
C9
.01uF
K6
D10 D11
45
123
JP9
U5
12LO
12V
MAR-3
27pF
C70
TP3
TP4
C10
.01uF
12PRI
10 pF
.01uF
C34
100K
R23
C35
D7
1N5711
D8
1N5711
.01uF
C36
K9
K8
D12
1N4148
D9
1N4148
12V
IRF620
Q4
8R
9
JP1
1
2
3
.01uF
C38
.01uF
C37
16
CONTROL
J6
5
RXout/IF2
TXin/IF1
J3
KEY OUT
J5
KEY IN
J4
J2
12T
R18 620
1N4007
D5
D13
1N4148
F1
8A
.02
R17
C68
.047uF
22K
R40
12T
K7
1
2
1N4148
15 uH
L8
.001uF
C39
JP2
3
D6
PN2222
Q6
FAN
1N4148
3
2
JP5JP6
1
PCB SOLDER PAD B
U4
C64
.01uF
K4 K5
1N4148
LM7805
JP7
C67
.01uF
3
2
1
R42
4.7
K3
D14
S2
D15
1N4148
Po
D16
100
R22
JP4
1
2
820
3
R21
160
R20
12V
JP8
2N7000
.01uF
C71
JP3
1
2
3
160
R26
Q5
12R
12T
100K
R34
160
R27
Elecraft XV Series Transverters
J7
12V INPUT
P1
ID
5V
GND
PWR TR
Po
OD
IF EN
PWR EN
8R/KEY
AUXBUS
KEY OUT
Page A-10
Page 48

XV432 RF Circuits Schematic
(RF Board)
C29
.047uF
C4
C44
3.3pF
J1Ant
K1
12TPo12T
.047uF
C61
6.8pF
C42
6.8pF
C43
L23
C5
1 pF
10K
R1
.047uF
C6
.047uF
C22
L10
22uF
C26
D1
1N4148
1K
R11
100K
R10
2-6 pF
K10
.047 uF
POWER CAL
C1
TP5
C25
200nH
TP2
.047uF
5.6pF
R15
C81
Q3
L1
.047uF
C66
LNA BIAS ADJ
C41
.047 uF
BIAS ADJ
.047 uF
L7
C3
C21
.047 uF
SAU82L
C63
.047uF
56
12V
.22uF
C65
R39 1K
R29
56
R28 1K
.047 uF
C24
180
R12
D36.8V
R36
15
ATF 34143
.047uF
C31
R13
25
C87
10 pF
U7
C2
100 pF
U3
LM78L05
C27
100 pF
MAV11
U1
22uF
C60
DIGIKEY TK3411-ND
120
R16
100 nH
.047uF
C84
FL2
R41 100K
12R
.047uF
C23
L2
100pF
C48
DIGIKEY TK3411-ND
FL1
100pF
C59
ADEX-10H
R
IF Port
L
Z1
XV432 RF Section
100nH
Z3
C7
.047 uF
D17
1N4148
.047 uF
C86
.047uF
C62
12T
C8
68
R24
.047uF
C40
.047uF
SGA
7489
12T
D4
1N4148
U6
D18
1N5711
.01uF
C19
1N5711
D2
TP1
4.7pF
C18
100pF
C17
SGA
U9 4586
0.1uH
C58
1pF
L22
C33
1.5pF
C16 .047uF
C80
1pF
L5
R8 180
1pF
240
R6
12LO
U2
5.6K
R4
5.6K
R5
LM78L09
134.6667 MHz
14 SEPTEMBER 2006
.047uF
C20
L3C82
MPS918
15pF
C14
.047uF
C13
18pF
C12
15pF
C14A
Q1
L4
Y1
0.07uH
L19
.047uF
C30
K2
TP5
Elecraft XV Series Transverters
Page A-11
Page 49

Appendix B – Troubleshooting
RF Power Module U7 voltages:
Typical voltages active devices (VDC unless otherwise noted):
Transverters U7 Pin (from rear) RX Mode TX Mode
do not
XV50,
XV144,
XV222, &
XV432
1 0
2 13.6
3 0 3.5 – 4.5
4 0
measure
do not
measure
Typical Voltages at test points (VDC unless otherwise noted):
Location Rx Mode Tx Mode
TP1 XV50 0.8 – 1.2 0.8 – 1.2
XV144 1.2 – 1.8 1.2 – 1.8
XV222 1.0 – 1.5 1.0 – 1.5
XV432 2.2 nom. 2.2 nom.
TP2 XV50, 144, 222 200-275 mV N/A
XV432 5.0 VDC N/A
TP5 XV50 N/A XV144 N/A XV222 N/A XV432 N/A 9*
TP6 XV432 Only N/A 1.5*
* at 20 watts output.
Location Rx Mode Tx Mode
U6 Output Pin 0 5
U4 1 13.6 13.6
2 0 0
3 5 5
Q2 B 0.25 – 0.8 0.25 – 0.8
E 0 0
C 6.5 6.5
Q1 B 4,1 4.1
E 3.6 3.6
C 8.5 8.5
U5 Output Pin 0 4.7
U1 Output Pin 3.0 – 6.0 0
U3 Input 0 13.6
Output 0 5
Page 50

Appendix C – Jumper and DIP Switch Settings
Jumpers
The following is a summary of all the jumpers and their functions. The
recommended jumper settings are provided in the Installation instructions
for most station configurations. This summary is provided for general
information and to aid troubleshooting in case your transverter does not
behave as expected.
POWER SWITCH OPTIONS
These are two-pin jumpers. X indicates a shorting block in place. O
indicates no shorting block.
Function JP7 JP8 Notes
If the transverter is connected
If 28 MHz Rig is not an
Elecraft K2 or K3
Disables the transverter
On/Off pushbutton
when an Elecraft K2 or
K3 is used with the
transverter.
Enables the transverter
On/Off pushbutton
when an Elecraft K2 or
K3 is used with the
transverter.
X O
O X
O O
to an Elecraft K2 or K3, be
sure there is no jumper on J7.
Possible damage to the
transverter may result.
Transverter power is turned On
when the transverter is selected
by the K2 or K3 BAND
switches.
NOT RECOMMENDED.
This configuration will not
damage the equipment, but
may result in unexpected
behavior of the transverter
power switch.
I.F. POWER CONTROL
The following jumpers are set according to the approximate driving
power from the 28 MHz rig. Fine adjustment is done using Input Atten
Adjust, R22, on the transverter RF board. If you find R22 is difficult to
adjust because it is set too close to one limit of its range, adjust the
jumpers accordingly.
i
Do not exceed the maximum input power from the 28 MHz
rig shown for each jumper configuration. Excessive power may
damage the transverter.
Transmit I.F.
Power from
28 MHz Rig
-20 dBm (0.01 mw)
to
0 dBm (1 mw) max.
Up to +24 dBm
(251 mw) max.
Up to +39 dBm
(8 watts) max.
JP3 JP4 JP5 JP6 Notes
JP3 and JP4 bypasses
1-2 1-2 2-3 2-3
1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2
2-3 2-3 1-2 1-2
the fixed attenuator.
JP5 and JP6 enables
amplifier Q6.
JP3 and JP4 bypasses
the fixed attenuator.
JP5 and JP6 bypasses
amplifier Q6.
JP3 and JP4 enables
the fixed attenuator.
JP5 and JP6 bypasses
amplifier Q6.
Elecraft XV Series Transverters Page C-1
Page 51

I.F. PORT CONFIGURATION
TRANSMIT DELAY OPTION
These jumpers configure the I.F. ports for either separate transmit and
receive RF connections to the 28 MHz rig or common transmit and
receive RF connection to the 28 MHz rig.
Function JP1 JP2 Notes
Single I.F. Port Sharing
Transmit and Receive
2-3 1-2
When single coaxial cable
connects transverter to 28
MHz rig antenna connector.
When separate coaxial
Separate Transmit and
Receive I.F. Ports
1-2 2-3
cables are used for transmit
and receive (e.g. K2 with
K60XV module or K3 with
KXV3 interface).
LOCAL OSCILLATOR POWER CONTROL OPTIONS
These jumpers allow the local oscillator to be left operating at all times
power is applied to the transverter for maximum stability, or to turn it off
to avoid possible interference from the local oscillator on other bands.
Power Option JP-9
Local oscillator power turns Off when transverter is deselected
at the Elecraft K2 or K3, or when the transverter Power switch
1-2
is Off (if the transverter Power switch is enabled).
Local oscillator power is On whenever transverter power
switch is On (if the transverter Power switch is enabled) even
2-3
when the transverter is not selected by the Elecraft K2 or K3.
Local oscillator power is On whenever +12 volts is applied to
the transverter, regardless of the Power Switch setting or
4-5
whether the transverter is selected by the Elecraft K2 or K3.
This option allows holding the transverter in transmit mode for up to 200
milliseconds after the 28 MHz rig has switched the KEY line to receive
to avoid timing problems with some rigs. It is not available when using
an Elecraft K2 or K3. The K2 or K3 has the proper timing to work with
the transverter as the fastest-possible speeds.
i
This jumper is located on the front panel board, between the
end of the socket-mounted processor and the side of the transverter.
Do not confuse it with JP1 on the transverter RF board.
These are two-pin jumpers. X indicates a shorting block in place. O
indicates no shorting block.
Function JP1
50 ms T/R delay O
200 ms T/R delay X
DIP Switch
The DIP switch on the transverter RF board is used to identify whether
the 28-MHz rig used with the transverter is an Elecraft K2 or K3 and, if
the rig is a K2 or K3, which TRN number (K2) or XVn number (K3) has
been assigned to the transverter.
TRN or
XVN
No K2
or K3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1 2 3 4
ON
OFF
OFF OFF
OFF OFF OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF OFF
OFF
DIP SWITCH POSITIONS
ALL SWITCHES OFF
OFF OFF OFF
ON
ON ON
ON
ON ON ON
OFF OFF
ON
OFF
ON ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
Elecraft XV Series Transverters Page C-2
 Loading...
Loading...