ELANT EL2276CS, EL2276CN, EL2176CS, EL2176CN Datasheet
EL2176C/EL2276C
70 MHz/1 mA Current Mode Feedback Amp w/Disable
EL2176C/EL2276C December 1995, Rev B
Features
# Single (EL2176C) and dual
(EL2276C) topologies
# 1 mA supply current (per
amplifier)
# 70 MHz
b
3 dB bandwidth
# Low cost
# Fast disable
# Powers down to 0 mA
# Single- and dual-supply
operation down to
# 0.15%/0.15
§
g
1.5V
diff. gain/diff. phase
into 150X
# 800V/ms slew rate
# Large output drive current:
100 mA (EL2176C)
55 mA (EL2276C)
# Also available without disable in
single (EL2170C), dual
(EL2270C) and quad (EL2470C)
# Higher speed EL2180C/EL2186C
family also available (3 mA/
250 MHz) in single, dual and
quad
Applications
# Low power/battery applications
# HDSL amplifiers
# Video amplifiers
# Cable drivers
# RGB amplifiers
# Test equipment amplifiers
# Current to voltage converters
General Description
The EL2176C/EL2276C are single/dual current-feedback operational amplifiers which achieve a
at a gain of
a
1 while consuming only 1 mA of supply current
per amplifier. They will operate with dual supplies ranging
g
from
to
1.5V tog6V, or from single supplies ranging froma3V
a
12V. The EL2176C/EL2276C also include a disable/powerdown feature which reduces current consumption to 0 mA while
placing the amplifier output in a high impedance state. In spite
of its low supply current, the EL2276C can output 55 mA while
swinging to
g
4V ong5V supplies. The EL2176C can output
100 mA with similar output swings. These attributes make the
EL2176C/EL2276C excellent choices for low power and/or low
voltage cable-driver, HDSL, or RGB applications.
For Single, Dual and Quad applications without disable, consider the EL2170C (8-Pin Single), EL2270C (8-Pin Dual) or
EL2470C (14-Pin Quad). For higher bandwidth applications
where low power is still a concern, consider the EL2180C/
El2186C family which also comes in similar Single, Dual and
Quad configurations. The EL2180C/EL2186C family provides a
b
3 dB bandwidth of 250 MHz while consuming 3 mA of supply
current per amplifier.
b
3 dB bandwidth of 70 MHz
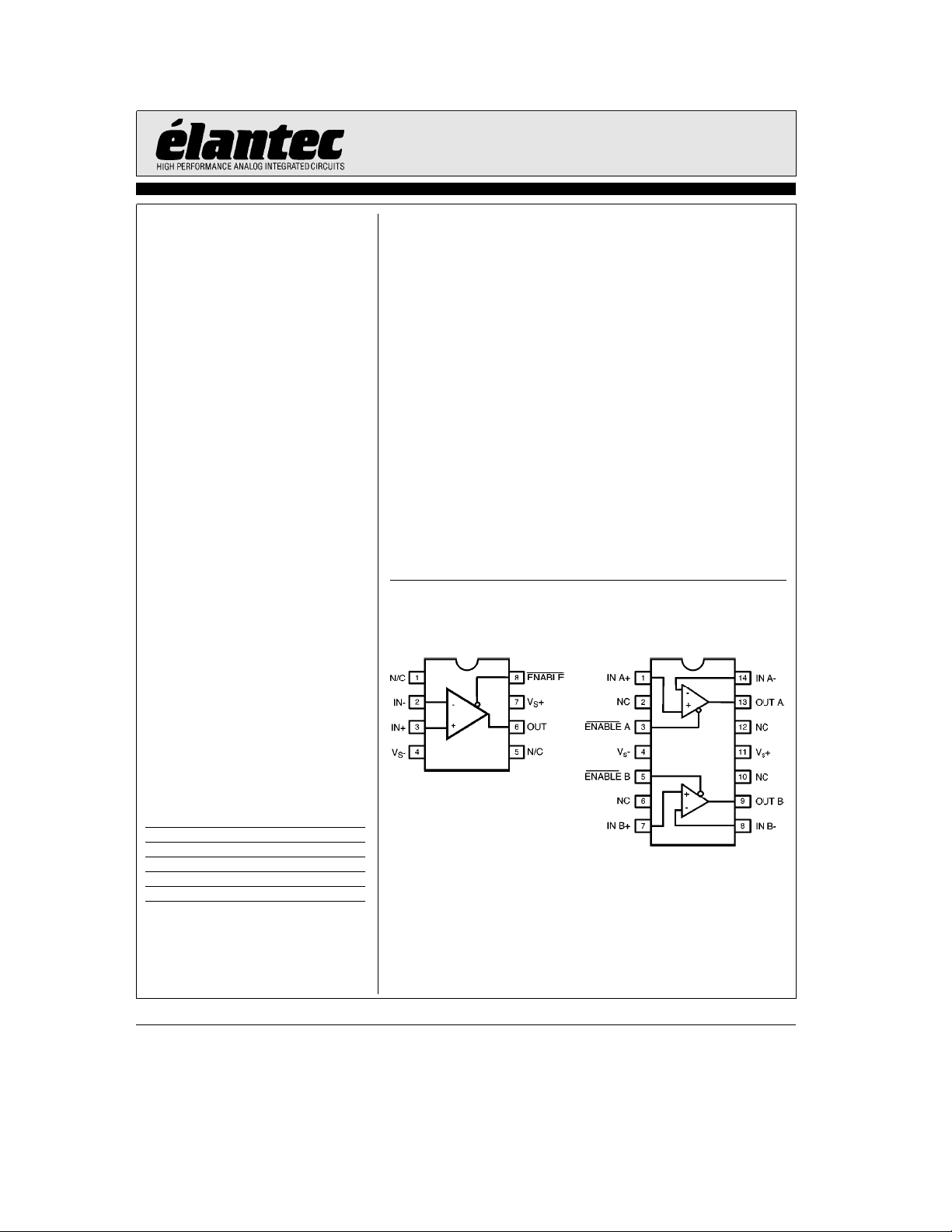
Connection Diagrams
EL2176C SO, P-DIP EL2276C SO, P-DIP
2176– 1
Ordering Information
Part No. Temp. Range Package Outline
EL2176CNb40§Ctoa85§C 8-Pin PDIP MDP0031
EL2176CSb40§Ctoa85§C 8-Pin SOIC MDP0027
EL2276CNb40§Ctoa85§C 14-Pin PDIP MDP0031
EL2276CSb40§Ctoa85§C 14-Pin SOIC MDP0027
Note: All information contained in this data sheet has been carefully checked and is believed to be accurate as of the date of publication; however, this data sheet cannot be a ‘‘controlled document’’. Current revisions, if any, to these
specifications are maintained at the factory and are available upon your request. We recommend checking the revision level before finalization of your design documentation.
©
1995 Elantec, Inc.
Ý
2176– 2
Manufactured under U.S. Patent No. 5,352,989, 5,351,012, 5,418,495

EL2176C/EL2276C
70 MHz/1 mA Current Mode Feedback Amp w/Disable
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Voltage between V
Common-Mode Input Voltage V
Differential Input Voltage
Current into
Internal Power Dissipation See Curves
Operating Ambient Temperature Range
Important Note:
All parameters having Min/Max specifications are guaranteed. The Test Level column indicates the specific device testing actually
performed during production and Quality inspection. Elantec performs most electrical tests using modern high-speed automatic test
equipment, specifically the LTX77 Series system. Unless otherwise noted, all tests are pulsed tests, therefore T
Test Level Test Procedure
I 100% production tested and QA sample tested per QA test plan QCX0002.
II 100% production tested at T
III QA sample tested per QA test plan QCX0002.
IV Parameter is guaranteed (but not tested) by Design and Characterization Data.
V Parameter is typical value at T
S
a
IN orbIN
a
and V
T
MAX
b
S
and T
b
A
per QA test plan QCX0002.
MIN
e
(T
25§C)
A
S
b
g
a
12.6V
to V
g
7.5 mA
Operating Junction Temperature
a
S
6V
Plastic Packages 150
Output Current (EL2176C)
Output Current (EL2276C)
Storage Temperature Range
40§Ctoa85§C
e
25§C and QA sample tested at T
e
25§C for information purposes only.
A
§
g
120 mA
g
b
e
T
J
C
e
25§C,
A
60 mA
65§Ctoa150§C
e
TA.
DC Electrical Characteristics
e
g
V
S
Parameter Description Conditions Min Typ Max
V
OS
TCV
OS
dV
OS
a
I
IN
daI
IN
b
I
IN
dbI
IN
CMRR Common Mode Rejection Ratio V
b
ICMR
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio VSis moved fromg4V tog6V 60 70 I dB
b
IPSR
R
OL
a
R
IN
a
C
IN
CMIR Common Mode Input Range
5V, R
e
150X, ENABLEe0V, T
L
e
25§C unless otherwise specified
A
Input Offset Voltage 2.5 15 I mV
Average Input Offset Voltage Drift Measured from T
MIN
to T
MAX
5VmV/§C
VOSMatching EL2276C only 0.5 V mV
a
Input Current 0.5 5 I mA
a
IINMatching EL2276C only 20 V nA
b
Input Current 4 15 I mA
b
IINMatching EL2276C only 1.5 V mA
e
g
3.5 V 45 50 I dB
CM
b
Input Current Common Mode Rejection V
b
Input Current Power Supply Rejection VSis moved fromg4V tog6V 0.5 5 I mA/V
Transimpedance V
a
Input Resistance V
a
Input Capacitance 1.2 V pF
e
g
3.5V 4 10 I mA/V
CM
e
g
OUT
CM
2.5V 150 400 I kX
e
g
3.5V 1 4 I MX
g
3.5g4.0 I V
Test
Level
Units
C
TDis3.1in
2
EL2176C/EL2276C
70 MHz/1 mA Current Mode Feedback Amp w/Disable
DC Electrical Characteristics
e
g
V
S
Parameter Description Conditions Min Typ Max
V
O
I
O
e
5V, R
150X, ENABLEe0V, T
L
Output Voltage Swing V
Output Current EL2176C only 80 100 I mA
Ð Contd.
e
25§C unless otherwise specified
A
e
g
5
S
ea
V
5 Single-Supply, High 4.0 V V
S
ea
V
5 Single-Supply, Low 0.3 V V
S
Test
Level
g
3.5g4.0 I V
Units
EL2276C only, per Amplifier 50 55 I mA
I
S
I
S(DIS)
C
OUT(DIS)
R
EN
I
IH
I
IL
V
DIS
V
EN
Supply Current ENABLEe2.0V, per Amplifier 1 2 I mA
Supply Current (Disabled) ENABLEe4.5V 0 20 I mA
Output Capacitance (Disabled) ENABLEe4.5V 4.4 V pF
Enable Pin Input Resistance Measured at ENABLEe2.0V, 4.5V 45 85 I kX
Logic ‘‘1’’ Input Current Measured at ENABLE, ENABLEe4.5V
Logic ‘‘0’’ Input Current Measured at ENABLE, ENABLEe0V
b
0.04 V mA
b
53 V mA
Minimum Voltage at ENABLE to Disable 4.5 I V
Maximum Voltage at ENABLE to Enable 2.0 I V
AC Electrical Characteristics
e
g
V
S
Parameter Description Conditions Min Typ Max Test Level Units
b
3dBBWb3 dB Bandwidth A
b
3dBBWb3 dB Bandwidth A
SR Slew Rate V
tr,t
f
t
pd
OS Overshoot V
ts 0.1% Settling V
dG Differential Gain A
dP Differential Phase A
dG Differential Gain A
dP Differential Phase A
t
ON
t
OFF
CS Channel Separation EL2276C only, fe5 MHz 85 V dB
Note 1: DC offset from 0V to 0.714V, AC amplitude 286 mV
Note 2: Measured from the application of the logic signal until the output voltage is at the 50% point between initial and final
e
5V, R
R
F
Rise and Fall Time V
Propagation Delay V
Turn-On Time A
Turn-Off Time A
values.
e
G
1.0 kX,R
e
150X, ENABLEe0V, T
L
ea
1 70 V MHz
V
ea
2 60 V MHz
V
e
g
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
V
V
V
V
V
V
2.5V, A
e
g
500 mV 4.5 V ns
e
g
500 mV 4.5 V ns
e
g
500 mV 3.0 V %
e
g
2.5V, A
ea
ea
ea
ea
ea
ea
2, R
2, R
1, R
1, R
2, V
2, V
e
L
e
L
e
L
e
L
IN
IN
e
25§C unless otherwise specified
A
ea
2 400 800 IV V/ms
V
eb
140Vns
V
150X (Note 1) 0.15 V %
150X (Note 1) 0.15 V
500X (Note 1) 0.02 V %
500X (Note 1) 0.01 V
ea
ea
e
1V, R
L
e
1V, R
L
,fe3.58 MHz.
P-P
150X (Note 2) 40 100 I ns
150X (Note 2) 1500 2000 I ns
§
§
TDis2.8in TDis2.8in
3
EL2176C/EL2276C
70 MHz/1 mA Current Mode Feedback Amp w/Disable
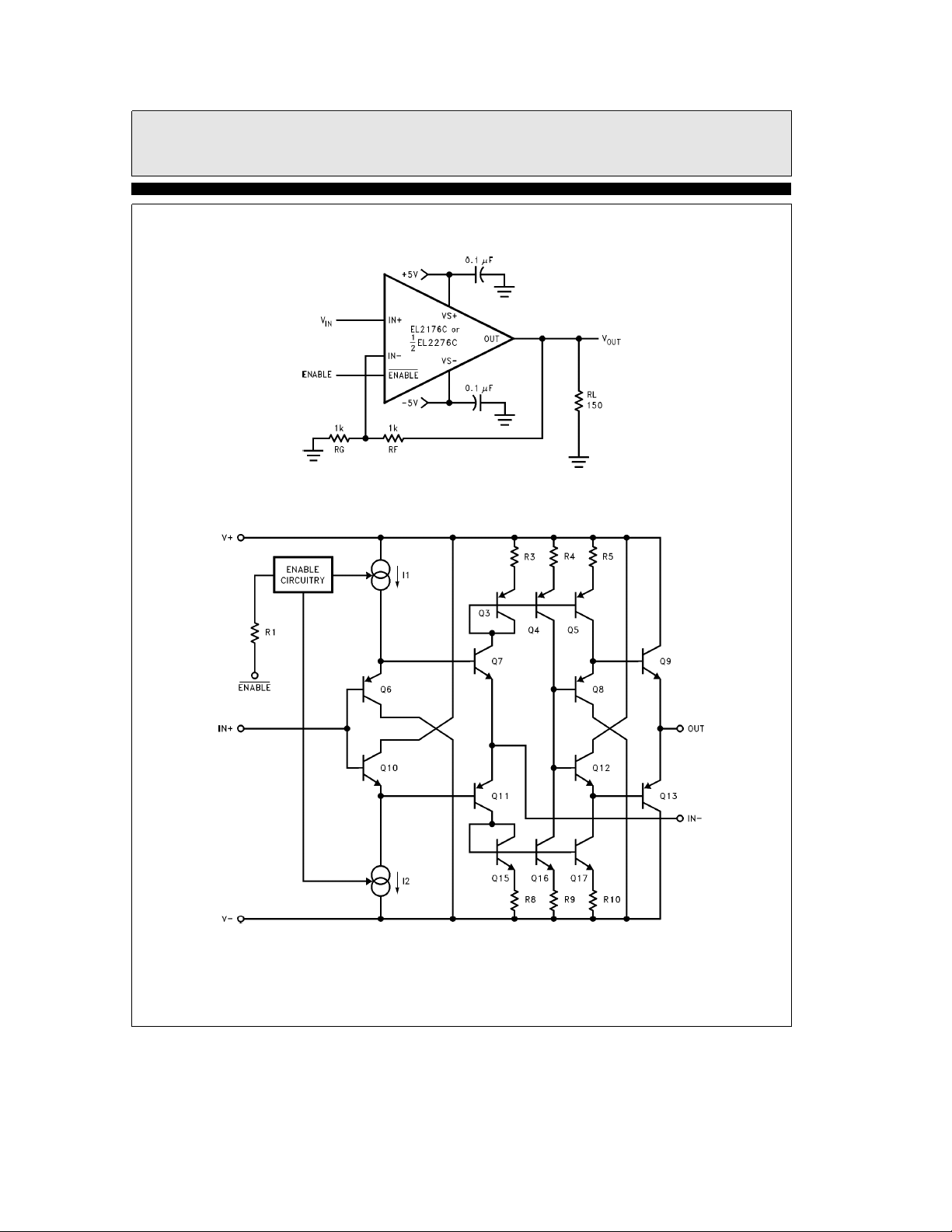
Test Circuit
(per Amplifier)
Simplified Schematic
2176– 3
(per Amplifer)
2176– 4
4
70 MHz/1 mA Current Mode Feedback Amp w/Disable
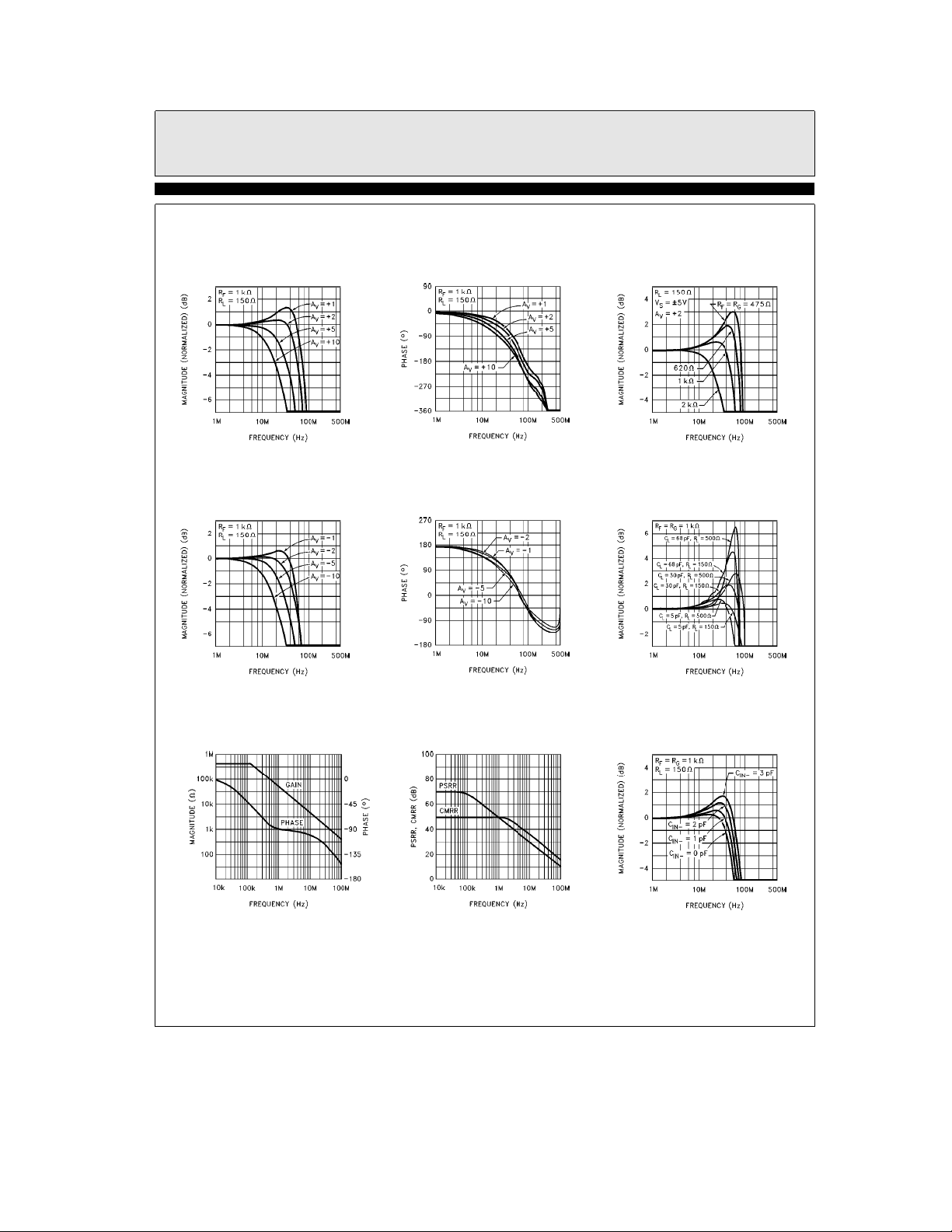
Typical Performance Curves
EL2176C/EL2276C
Non-Inverting
Frequency Response (Gain)
Inverting Frequency
Response (Gain)
2176– 5
2176– 8
Non-Inverting
Frequency Response (Phase)
2176– 6
Inverting Frequency
Response (Phase)
2176– 9
Frequency Response for
Various RFand R
Frequency Response for
Various RLand C
G
L
2176– 7
2176– 10
Transimpedance (ROL)
2176– 11
PSRR and CMRR
5
2176– 12
Frequency Response
for Various C
b
IN
2176– 13
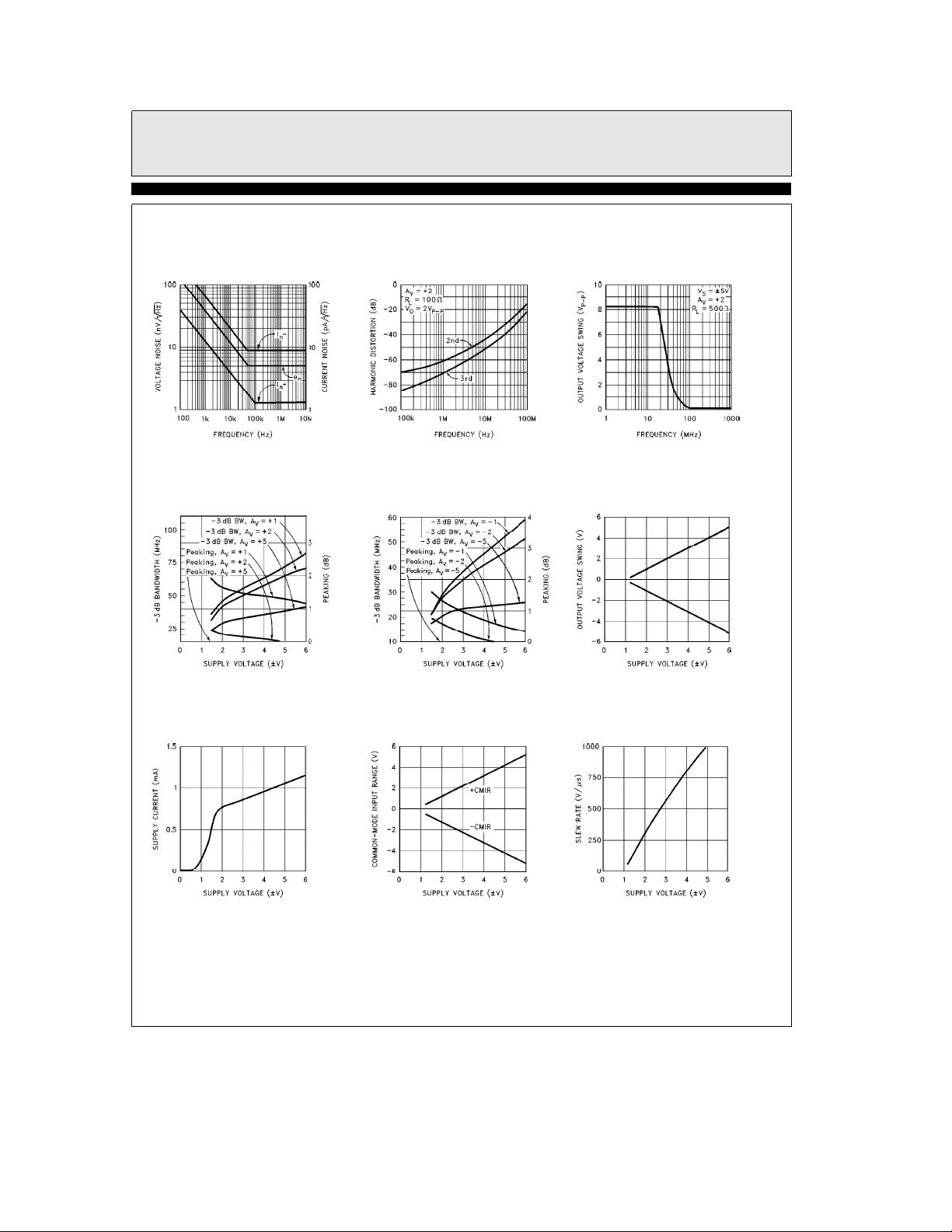
EL2176C/EL2276C
70 MHz/1 mA Current Mode Feedback Amp w/Disable
Typical Performance Curves
Voltage and Current
Noise vs Frequency
2176– 14
b
3 dB Bandwith and Peaking
vs Supply Voltage for
Various Non-Inverting Gains
Ð Contd.
2nd and 3rd Harmonic
Distortion vs Frequency
b
3 dB Bandwith and Peaking
vs Supply Voltage for
Various Inverting Gains
2176– 15
Output Voltage
vs Frequency
Output Voltage Swing
vs Supply Voltage
2176– 16
Supply Current vs Supply
Voltage
2176– 17
2176– 20
Common-Mode Input Range
vs Supply Voltage
6
2176– 18
2176– 21
Slew Rate vs
Supply Voltage
2176– 19
2176– 22
 Loading...
Loading...