Page 1

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
EM78P458 and EM78P459 are 8-bit microprocessors designed and developed with low-power and
high-speed CMOS technology. It is equipped with a 4K*13-bit Electrical One Time Programmable Read
Only Memory (OTP-ROM). With its OTP-ROM feature, it is able to offer a convenient way of developing
and verifying user’s programs. Moreover, user can take advantage of EMC Writer to easily program his
development code.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
1
Page 2

2. FEATURES
• Operating voltage range: 2.3V~5.5V
• Operating temperature range: 0°C~70°C(commercial)
-40°C~85°C(industrial)
• Operating frequency range(base on 2 clocks):
* Crystal mode: DC ~ 20MHz/2clks,5V; DC ~ 8MHz/2clks,3V
* RC mode: DC ~ 4MHz/2clks,5V; DC ~ 4MHz/2clks,3V
• Low power consumption:
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
* Less than 1.5 mA at 5V/4MHz
* Typically 15 µA, at 3V/32KHz
* Typically 1 µA, during sleep mode
• 4K × 13 bits on chip ROM
• 84 × 8 bits on chip registers (SRAM)
• 2 bi-directional I/O ports
• 8 level stacks for subroutine nesting
• 8-bit real time clock/counter (TCC) with selective signal sources, trigger edges, and overflow interrupt
• 8-bit multichannel Analog-to-Digital Converter with 8-bit resolution
• Dual Pulse Width Modulation (PWM ) with 10-bit resolution
• One pair of comparators
• Power-down (SLEEP) mode
• Six available interruptions
* TCC overflow interrupt
* Input-port status changed interrupt (wake up from the sleep mode)
* External interrupt
* ADC completion interrupt
* PWM period match completion
* Comparator high interrupt
• Programmable free running watchdog timer
• 8 Programmable pull-down I/O pins
• 7 programmable pull-high I/O pins
• 8 programmable open-drain I/O pins
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
2
Page 3

• Two clocks per instruction cycle
• Package types:
* 20 pin DIP 300mil : EM78P458AP
* 20 pin SOP 300mil : EM78P458AM
* 24 pin skinny DIP 300mil : EM78P459AK
* 24 pin SOP 300mil : EM78P459AM
• Power on voltage detector available (2.0V± 0.15V)
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
3
Page 4

3. PIN ASSIGNMENT
PWM1,
20
P56/CIN+
P57/CO
P60/ADC1
P61/ADC2
VSS
P62/ADC3
P63/ADC4
P64/ADC5
P65/ADC6
P66/ADC7
1
2
3
4
EM78P458
5
6
7
8
9
10 11
P55/CIN-
19
P54/TCC
18
OSCI
17
OSCO
16
VDD
15
P53/VREF
14
P52/PWM2
13
P51/PWM1
12
P50/INT
P67/ADC8
P56/CIN+
P57/CO
P60/ADC1
P61/ADC2
ENTCC
VSS
VSS
P62/ADC3
P63/ADC4
P64/ADC5
P65/ADC6
P66/ADC7
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
1
24
P55/CIN-
2
23
P54/TCC
3
22
OSCI
4
21
OSCO
5
20
EM78P459
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 13
RESET
19
VDD
18
VDD
17
P53/VREF
16
P52/PWM2
15
P51/PWM1
14
P50/INT
P67/ADC8
Fig. 1 Pin Assignment
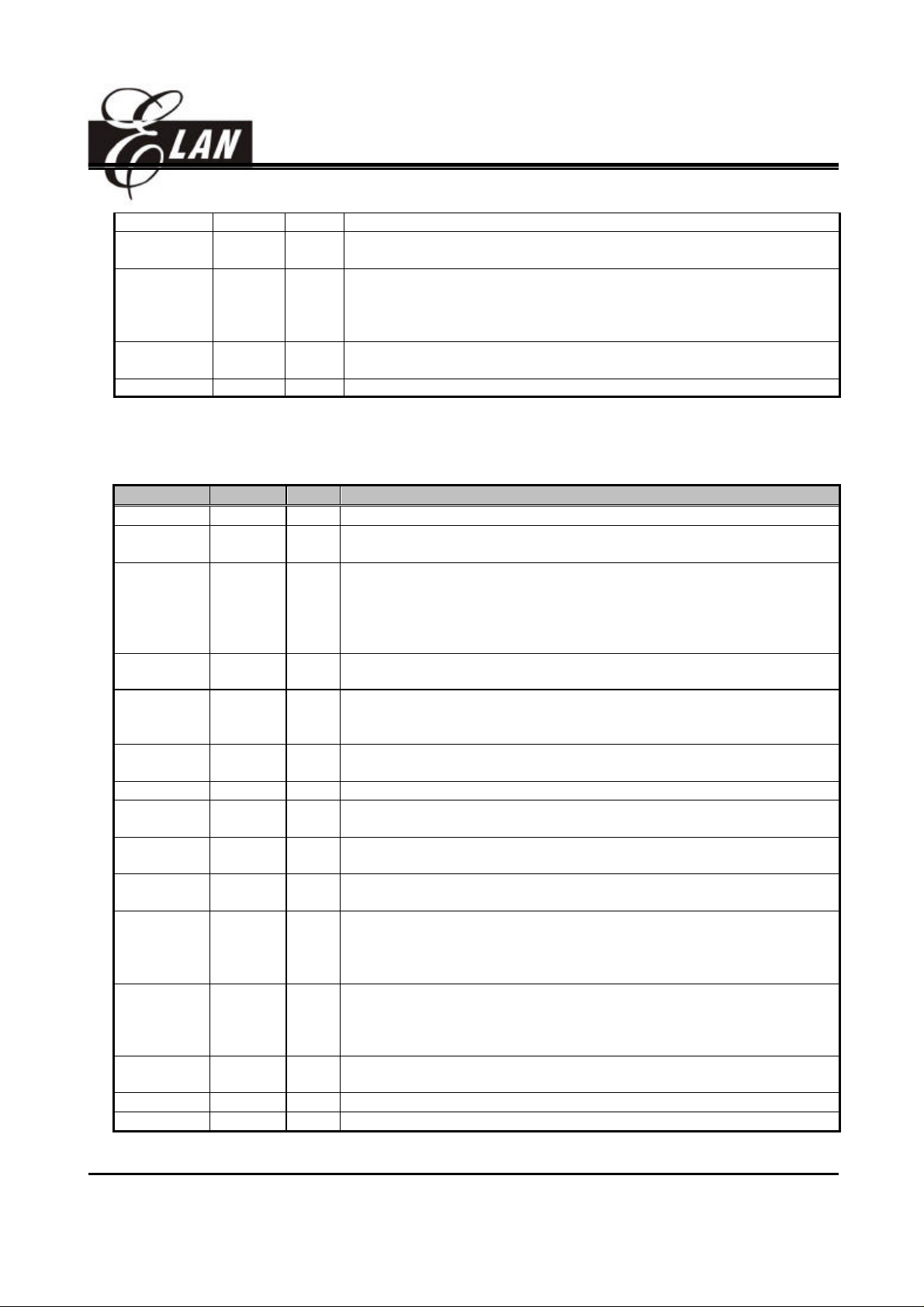
Table 1 EM78P458 Pin Description
Symbol Pin No. Type Function
VDD 16 - Power supply.
OSCI 18 I
* XTAL type: Crystal input terminal or external clock input pin.
* RC type: RC oscillator input pin.
*XTAL type: Output terminal for crystal oscillator or external clock input
pin.
OSCO 17 O
*RC type: Clock output with a period of one instruction cycle time, the
prescaler is determined by the CONT register.
* External clock signal input.
P50 12 I
13~15
P51 ~ P57
19, 20,
1, 2
P60 ~ P67
3, 4,
6~11
* General-purpose Input only.
* Default value while power-on reset.
* General-purpose I/O pin.
I/O
* Default value while power-on reset.
* General-purpose I/O pin.
I/O
* Default value while power-on reset.
INT 12 I * External interrupt pin triggered by falling edge.
ADC1~ADC8
3, 4,
6 ~ 11
* Analog to Digital Converter.
I
* Defined by AD-CMPCON (IOCA0)<2:4>.
13, 14 O * Pulse width modulation outputs.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
4
Page 5
PWM2 * Defined by PWMCON (IOC51)<6, 7>
* Real time clock/counter with Schmitt trigger input pin; it must be tied to
VREF 15 I
CIN-, CIN+,
CO
20, 1,2
* External reference voltage for ADC
* Defined by AD-CMPCON (IOCA0)<7>.
* “-“ -> the input pin of Vin- of the comparator.
I
* “+”-> the input pin of Vin+ of the comparator.
O
* Pin CO is the output of the comparator.
* Defined by AD-CMPCON (IOCA0) <5, 6>
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
TCC 19 I
VSS 5 - Ground.
Table 2 EM78P459 Pin Description
Symbol Pin No. Type Function
VDD 19, 18 - Power supply.
OSCI 22 I
OSCO 21 O
P50 14 I
15~17
P51 ~ P57
P60 ~ P67
INT 14 I * External interrupt pin triggered by falling edge.
ADC1~ADC8
PWM1,
PWM2
VREF 17 I
CIN-, CIN+,
CO
/RESET 20 I
TCC 23 I
ENTCC 5 I 1: Enable TCC; 0: Disable TCC.
VSS 6, 7 - Ground.
23, 24
1, 2
3, 4,
8~13
3, 4,
8~13
15, 16 O
24, 1, 2 I
VDD or VSS if it is not in use.
* XTAL type: Crystal input terminal or external clock input pin.
* RC type: RC oscillator input pin.
* XTAL type: Output terminal for crystal oscillator or external clock input
pin.
* RC type: Clock output with a period of one instruction cycle time, the
prescaler is determined by the CONT register.
* External clock signal input.
* General-purpose Input only.
* Default value while power-on reset.
* General-purpose I/O pin.
I/O
* Default value while power-on reset.
* General-purpose I/O pin.
I/O
* Default value while power-on reset.
* Analog to Digital Converter.
I
* Defined by AD-CMPCON (IOCA0)<2:4>.
* Pulse width modulation outputs.
* Defined by PWMCON (IOC51)<6, 7>
* External reference voltage for ADC
* Defined by AD-CMPCON (IOCA0)<7>.
* ‘-’ -> the Vin- input pins of the comparators.
* ‘+’ -> the Vin+ input pins of the comparators.
* Pin CO is the output of the comparator.
* Defined by AD-CMPCON (IOCA0) <5, 6>
* If it remains at logic low, the device will be reset.
* Wake up from sleep mode when pins status changes.
* Voltage on /RESET/Vpp must not be over Vdd during normal mode.
* Pull-high is on if /RESET is asserted.
* Real time clock/counter with Schmitt trigger input pin; it must be tied to
VDD or VSS if it is not in use.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
5
Page 6

4. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
ENTCC
Oscillator/
Timming
Control
Sleep
&
Wake Up
Control
WDT
Time-out
Prescaler
R1(TCC)
Comparators 8 ADC2 PWMs
P
5
0
Fig. 2 The Functional Block Diagram of EM78P458/459
4.1 Operational Registers
IOC5
P
P
5
5
1
2
RAM
R5
P
P
P
5
5
5
3
4
5
/INT
Interrupt
Control
R4
P
P
5
5
6
7
WDT Timer
DATA & CONTROL BUS
ROM
Instruction
Register
Instruction
Decoder
P C
STACK 0
STACK 1
STACK 2
STACK 3
STACK 4
STACK 5
STACK 6
STACK 7
ALU
ACCR3
IOC6
R6
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1. R0 (Indirect Addressing Register)
R0 is not a physically implemented register. Its major function is to perform as an indirect addressing
pointer. Any instruction using R0 as a pointer, actually accesses data pointed by the RAM Select
Register (R4).
2. R1 (Time Clock /Counter)
• Increased by an external signal edge through the TCC pin, or by the instruction cycle clock.
• The signals to increase the counter are decided by Bit 4 and Bit 5 of the CONT register.
• Writable and readable as any other registers.
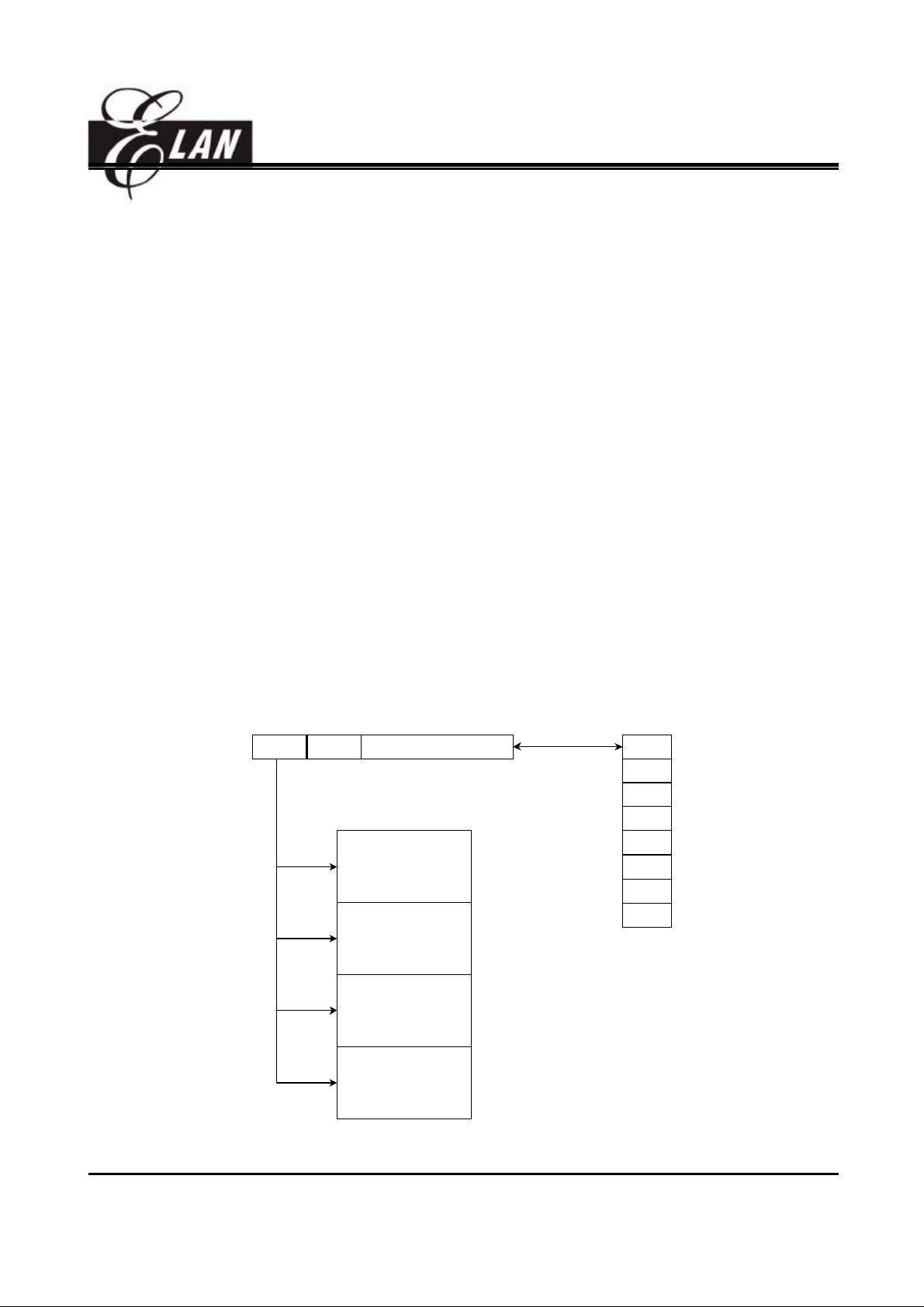
3. R2 (Program Counter) & Stack
• R2 and hardware stacks are 12-bit wide. The structure is depicted in Fig. 4.
• Generates 4K×13 bits on-chip ROM addresses to the relative programming instruction codes. One
program page is 1024 words long.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
6
Page 7
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
• The contents of R2 are set to all "0"s upon a RESET condition.
• "JMP" instruction allows the direct loading of the lower 10 program counter bits. Thus, "JMP" allows
PC to jump to any location within a page.
• "CALL" instruction loads the lower 10 bits of the PC, and then PC+1 is pushed into the stack. Thus,
the subroutine entry address can be located anywhere within a page.
• "RET" ("RETL k", "RETI") instruction loads the program counter with the contents of the top of stack.
• "ADD R2, A" allows a relative address to be added to the current PC, and the ninth and tenth bits of
the PC are cleared.
• "MOV R2, A" allows to load an address from the "A" register to the lower 8 bits of the PC, and the
ninth and tenth bits of the PC are cleared.
• Any instruction that is written to R2 (e.g. "ADD R2, A", "MOV R2, A", "BC R2, 6",⋅⋅⋅⋅⋅) will cause the
ninth bit and the tenth bit (A8~A9) of the PC to be cleared. Thus, the computed jump is limited to the
first 256 locations of a page.
• In the case of EM78P458/459, the most two significant bits (A11 and A10) will be loaded with the
content of PS1 and PS0 in the status register (R3) upon the execution of a "JMP", "CALL", or any
other instructions set which write to R2.
• All instructions are single instruction cycle (fclk/2 or fclk/4) except for the instructions which write to
R2, need one more instruction cycle.
A9 ~ A8A11~A10 A7 ~ A0
000
00
01
10
3 FF
400
7FF
800
Page 0
Page 1
Page 2
CALL K
RET
RETI
RETL K
Stack 0
Stack 1
Stack 2
Stack 3
Stack 4
Stack 5
Stack 6
Stack 7
BFF
C00
11
FFF
Page 3
Fig. 3 Program Counter Organization
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
7
Page 8

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
4. R3 (Status Register)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CMPOUT PS1 PS0 T P Z DC C
• Bit 7 (CMPOUT) the result of the comparator output.
• Bit 6 (PS1) ~ 5 (PS0) Page select bits. PS0~PS1 are used to select a program memory page. When
executing a "JMP", "CALL", or other instructions which cause the program counter to be changed
(e.g. MOV R2, A), PS0~PS1 are loaded into the 11th and 12th bits of the program counter where it
selects one of the available program memory pages. Note that RET (RETL, RETI) instruction does
not change the PS0~PS1 bits. That is, the return will always be to the page from the place where the
subroutine was called, regardless of the current setting of PS0~PS1 bits.
PS1 PS0 Program memory page [Address]
0 0 Page 0 [000-3FF]
0 1 Page 1 [400-7FF]
1 0 Page 2 [800-BFF]
1 1 Page 3 [C00-FFF]
• Bit 4 (T) Time-out bit. Set to 1 by the "SLEP" and "WDTC" commands, or during Power on and reset
to 0 by WDT time-out.
• Bit 3 (P) Power-down bit. Set to 1 during power-on or by a "WDTC" command and reset to 0 by a
"SLEP" command.
• Bit 2 (Z) Zero flag. Set to "1" if the result of an arithmetic or logic operation is zero.
• Bit 1 (DC) Auxiliary carry flag
• Bit 0 (C) Carry flag
5. R4 (RAM Select Register)
• Bits 0~5 are used to select registers (address: 00~3F) in the indirect address mode.
• Bit 6 is used to select bank 0 or bank 1.
• Bit 7 is a general-purpose read/write bit.
• See the configuration of the data memory in Fig. 4.
6. R5 ~ R6 (Port 5 ~ Port 6)
• R5 and R6 are I/O registers.
7. R7 ~ R8
• All of these are 8-bit general-purpose registers.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
8
Page 9

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
00
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
0A
0B
0C
0D
0E
0F
10
11
R0
R1 (TCC)
R2 (PC)
R3 (Status)
R4 (RSR)
R5 (Port 5)
R6 (Port 6)
R7
R8
R9 (ADCON)
RA (ADDATA)
RB (TMR1L)
RC (TMR1H)
RD (TMR2L)
RE (TMR2H)
RF
16x8
Common
Register
STACK 0
STACK 1
STACK 2
STACK 3
STACK 4
STACK 5
STACK 6
STACK 7
R9<5> (IOCS)
0
IOC50
IOC60
IOC90 (GCON)
IOCA0 (AD-CMPCON)
IOCB0
IOCC0
IOCD0
IOCE0
IOCF0
1
IOC51 (PWMCON)
IOC61 (DT1L)
IOC71 (DT1H)
IOC81 (PRD1)
IOC91 (DT2L)
IOCA1 (DT2H)
IOCB1 (PRD2)
IOCC1 (DL1L)
IOCD1 (DL1H)
IOCE1 (DL2L)
IOCF1 (DL2H)
1E
1F
PSR7, PSR6
20
21
3F
00
20
32x8
Bank
Register
(Bank 0)
3F
20
3F
01
32x8
Bank
Register
(Bank 1)
Fig. 4 Data Memory Configuration
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
9
Page 10

EM78P458/459
8. R9 (ADCON: Analog to Digital Control)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - IOCS ADRUN ADPD ADIS2 ADIS1 ADIS0
• Bit 7:Bit 6 Unemployed, read as ‘0’;
• Bit 5(IOCS): Select the Segment of IO control register.
1 = Segment 1 ( IOC51~IOCF1 ) selected;
0 = Segment 0 ( IOC50~IOCF0 ) selected;
• Bit 4 (ADRUN): ADC starts to RUN.
1 = an A/D conversion is started. This bit can be set by software;
0 = reset on completion of the conversion. This bit can not be reset though software;
• Bit 3 (ADPD): ADC Power-down mode.
1 = ADC is operating;
OTP ROM
0 = switch off the resistor reference to save power even while the CPU is operating.
• Bit2:Bit0 (ADIS2:ADIS0): Analog Input Select.
000 = AN0;
001 = AN1;
010 = AN2;
011 = AN3;
100 = AN4;
101 = AN5;
110 = AN6;
111 = AN7;
They can only be changed when the ADIF bit and the ADRUN bit are both LOW.
9. RA (ADDATA: the converted value of ADC)
When the A/D conversion is complete, the result is loaded into the ADDATA. The START//END bit is
cleared, and the ADIF is set.
10. RB
An 8-bit general-purpose register.
11. RC
A 2-bit, Bit 0and Bit 1 register.
12. RD
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
10
Page 11

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
An 8-bit general-purpose register.
13. RE
A 2-bit, Bit 0 and Bit 1 register.
14. RF (Interrupt Status Register)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- CMPIF PWM2IF PWM1IF ADIF EXIF ICIF TCIF
“1” means interrupt request, and “0” means no interrupt occurs.
• Bit 0 (TCIF) TCC overflow interrupt flag. Set when TCC overflows, reset by software.
• Bit 1 (ICIF) Port 6 input status change interrupt flag. Set when Port 6 input changes, reset by
software.
• Bit 2 (EXIF) External interrupt flag. Set by falling edge on /INT pin, reset by software.
• Bit 3 (ADIF) Interrupt flag for analog to digital conversion. Set when AD conversion is completed,
reset by software.
• Bit 4 (PWM1IF) PWM1 (Pulse Width Modulation) interrupt flag. Set when a selected period is
reached, reset by software.
• Bit 5 (PWM2IF) PWM2 (Pulse Width Modulation) interrupt flag. Set when a selected period is
reached, reset by software.
• Bit 6 (CMPIF) High-compared interrupt flag. Set when a change occurs in the output of Comparator,
reset by software.
• Bit 7 Unemployed, read as ‘0’;
• RF can be cleared by instruction but cannot be set.
• IOCF0 is the interrupt mask register.
• Note that to read RF will result to "logic AND" of RF and IOCF0.
15. R10 ~ R3F
• All of these are 8-bit general-purpose registers.
4.2 Special Purpose Registers
1. A (Accumulator)
• Internal data transfer, or instruction operand holding
• It can not be addressed.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
11
Page 12

EM78P458/459
2. CONT (Control Register)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
INTE INT TS TE PAB PSR2 PSR1 PSR0
• Bit 0 (PSR0) ~ Bit 2 (PSR2) TCC/WDT prescaler bits.
PSR2 PSR1 PSR0 TCC Rate WDT Rate
0 0 0 1:2 1:1
0 0 1 1:4 1:2
0 1 0 1:8 1:4
0 1 1 1:16 1:8
1 0 0 1:32 1:16
1 0 1 1:64 1:32
1 1 0 1:128 1:64
1 1 1 1:256 1:128
• Bit 3 (PAB) Prescaler assignment bit.
OTP ROM
0: TCC;
1: WDT.
• Bit 4 (TE) TCC signal edge
0: increment if the transition from low to high takes place on the TCC pin;
1: increment if the transition from high to low takes place on the TCC pin.
• Bit 5 (TS) TCC signal source
0: internal instruction cycle clock. If P54 is used as I/O pin, TS must be 0.
1: transition on the TCC pin
• Bit 6 (INT) Interrupt enable flag
0: masked by DISI or hardware interrupt
1: enabled by the ENI/RETI instructions
• Bit 7 (INTE) INT signal edge
0: interrupt occurs at the rising edge on the INT pin
1: interrupt occurs at the falling edge on the INT pin
• CONT register is both readable and writable.
3. IOC50 ~ IOC60 (I/O Port Control Register)
• "1" puts the relative I/O pin into high impedance, while "0" defines the relative I/O pin as output.
• IOC50 and IOC60 registers are both readable and writable.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
12
Page 13

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
4. IOC90 (GCON: I/O Configuration & Control of ADC )
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
OP2E OP1E G22 G21 G20 G12 G11 G10
• Bit 7 ( OP2E ) Enable the gain amplifier which input is connected to P64 and output is connected to
the 8-1 analog switch.
0 = OP2 is off ( default value ), and bypasses the input signal to the ADC;
1 = OP2 is on.
• Bit 6 ( OP1E ) Enable the gain amplifier whose input is connected to P60 and output is connected to
the 8-1 analog switch.
0 = OP1 is off (default value), and bypasses the input signal to the ADC;
1 = OP1 is on.
• Bit 5:Bit 3 (G22 and G20): Select the gain of OP2.
000 = IS x 1 (default value);
001 = IS x 2;
010 = IS x 4;
011 = IS x 8;
100 = IS x 16;
101 = IS x 32;
Legend: IS = the input signal
• Bit 2:Bit 0 (G12 and G10 ): Select the gain of OP1.
000 = IS x 1 (default value);
001 = IS x 2;
010 = IS x 4;
011 = IS x 8;
100 = IS x 16;
101 = IS x 32;
Legend: S = the input signal
5. IOCA0 ( AD-CMPCON ):
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
VREFS CE COE IMS2 IMS1 IMS0 CKR1 CKR0
• Bit 7: The input source of the Vref of the ADC.
0 = The Vref of the ADC is connected to Vdd (default value), and the P53/VREF pin carries out the
function of P53;
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
13
Page 14

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
1 = The Vref of the ADC is connected to P53/VREF.
• Bit 6 (CE): Comparator enable bit
0 = Comparator is off (default value);
1 = Comparator is on.
• Bit 5 ( COE ): Set P57 as the output of the comparator
0 = the comparator acts as an OP if CE=1.
1 = act as a comparator if CE=1.
• Bit4:Bit2 (IMS2:IMS0):
Input Mode Select. ADC configuration definition bit. The following Table describes how to define the
characteristic of each pin of R6.
Table 3 Description of AD Configuration Control Bits
IMS2:IMS0 P60 P61 P62 P63 P64 P65 P66 P67
000 A D D D D D D D
001 A A D D D D D D
010 A A A D D D D D
011 A A A A D D D D
100 A A A A A D D D
101 A A A A A A D D
110 A A A A A A A D
111 A A A A A A A A
• Bit 1: Bit 0 (CKR1: CKR0): The prescaler of oscillator clock rate of ADC
00 = 1: 4 (default value);
01 = 1: 16;
10 = 1: 64;
11 = 1: WDT ring oscillator frequency.
6. IOCB0 (Pull-down Control Register)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
/PD7 /PD6 /PD5 /PD4 /PD3 /PD2 /PD1 /PD0
• Bit 0 (/PD0) Control bit is used to enable the pull-down of the P60 pin.
0: Enable internal pull-down;
1: Disable internal pull-down.
• Bit 1 (/PD1) Control bit is used to enable the pull-down of the P61 pin.
• Bit 2 (/PD2) Control bit is used to enable the pull-down of the P62 pin.
• Bit 3 (/PD3) Control bit is used to enable the pull-down of the P63 pin.
• Bit 4 (/PD4) Control bit is used to enable the pull-down of the P64 pin.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
14
Page 15

EM78P458/459
• Bit 5 (/PD5) Control bit is used to enable the pull-down of the P65 pin.
• Bit 6 (/PD6) Control bit is used to enable the pull-down of the P66 pin.
• Bit 7 (/PD7) Control bit is used to enable the pull-down of the P67 pin.
• IOCB0 register is both readable and writable.
7. IOCC0 (Open-Drain Control Register)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
/OD7 /OD6 /OD5 /OD4 /OD3 /OD2 /OD1 /OD0
• Bit 0 (OD0) Control bit used to enable the open-drain of the P64 pin.
0: Enable open-drain output
1: Disable open-drain output
• Bit 1 (OD1) Control bit is used to enable the open-drain of the P65 pin.
OTP ROM
• Bit 2 (OD2) Control bit is used to enable the open-drain of the P66 pin.
• Bit 3 (OD3) Control bit is used to enable the open-drain of the P67 pin.
• Bit 4 (OD4) Control bit is used to enable the open-drain of the P51 pin.
• Bit 5 (OD5) Control bit is used to enable the open-drain of the P52 pin.
• Bit 6 (OD6) Control bit is used to enable the open-drain of the P54 pin.
• Bit 7 (OD7) Control bit is used to enable the open-drain of the P57 pin.
• IOCC0 register is both readable and writable.
8. IOCD0 (Pull-high Control Register)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
/PH7 /PH6 /PH5 - /PH3 /PH2 /PH1 /PH0
• Bit 0 (/PH0) Control bit is used to enable the pull-high of the P60 pin.
0: Enable internal pull-high;
1: Disable internal pull-high.
• Bit 1 (/PH1) Control bit is used to enable the pull-high of the P61 pin.
• Bit 2 (/PH2) Control bit is used to enable the pull-high of the P62 pin.
• Bit 3 (/PH3) Control bit is used to enable the pull-high of the P63 pin.
• Bit 4 Not used.
• Bit 5 (/PH5) Control bit is used to enable the pull-high of the P53 pin.
• Bit 6 (/PH6) Control bit is used to enable the pull-high of the P55 pin.
• Bit 7 (/PH7) Control bit is used to enable the pull-high of the P56 pin.
• IOCD0 register is both readable and writable.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
15
Page 16

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
9. IOCE0 (WDT Control Register)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
WDTE EIS - - - - - -
• Bit 7 (WDTE) Control bit is used to enable Watchdog Timer.
0: Disable WDT;
1: Enable WDT.
WDTE is both readable and writable
• Bit 6 (EIS) Control bit is used to define the function of the P50 (/INT) pin.
0: P50, input pin only;
1: /INT, external interrupt pin. In this case, the I/O control bit of P50 (bit 0 of IOC50) must be set to
"1".
When EIS is "0", the path of /INT is masked. When EIS is "1", the status of /INT pin can also be read
by way of reading Port 5 (R5). Refer to Fig. 7.
EIS is both readable and writable.
• Bits 0~5 Not used.
10. IOCF0 (Interrupt Mask Register)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- CMPIE PWM2IE PWM1IE ADIE EXIE ICIE TCIE
• Bit 0 (TCIE) TCIF interrupt enable bit.
0: disable TCIF interrupt
1: enable TCIF interrupt
• Bit 1 (ICIE) ICIF interrupt enable bit.
0: disable ICIF interrupt
1: enable ICIF interrupt
• Bit 2 (EXIE) EXIF interrupt enable bit.
0: disable EXIF interrupt
1: enable EXIF interrupt
• Bit 3 (ADIE) ADIF interrupt enable bit.
0: disable ADIF interrupt
1: enable ADIF interrupt
• Bit 4 (PWM1IE) PWM1IF interrupt enable bit.
0: disable PWM1 interrupt
1: enable PWM1 interrupt
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
16
Page 17

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
• Bit 5 (PWM2IE) PWM2IF interrupt enable bit.
0: disable PWM2 interrupt
1: enable PWM2 interrupt
• Bit 6 (CMPIE) CMPIF interrupt enable bit.
0: disable CMPIF interrupt
1: enable CMPIF interrupt
• Bit 7: Unimplemented, read as ‘0’.
Individual interrupt is enabled by setting its associated control bit in the IOCF0 to "1".
Global interrupt is enabled by the ENI instruction and is disabled by the DISI instruction. Refer to Fig.
11.
IOCF0 register is both readable and writable.
11. IOC51 ( PWMCON ):
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
PWM2E PWM1E T2EN T1EN T2P1 T2P0 T1P1 T1P0
• Bit 7 (PWM2E): PWM2 enable bit
0 = PWM2 is off (default value), and its related pin carries out the P52 function.
1 = PWM2 is on, and its related pin will be set to output automatically.
• Bit 6 (PWM1E): PWM1 enable bit
0 = PWM1 is off (default value), and its related pin carries out the P51 function;
1 = PWM1 is on, and its related pin will be set to output automatically.
• Bit 5 (T2EN): TMR2 enable bit
0 = TMR2 is off (default value).
1 = TMR2 is on.
• Bit 4 (T1EN): TMR1 enable bit
0 = TMR1 is off (default value).
1 = TMR1 is on.
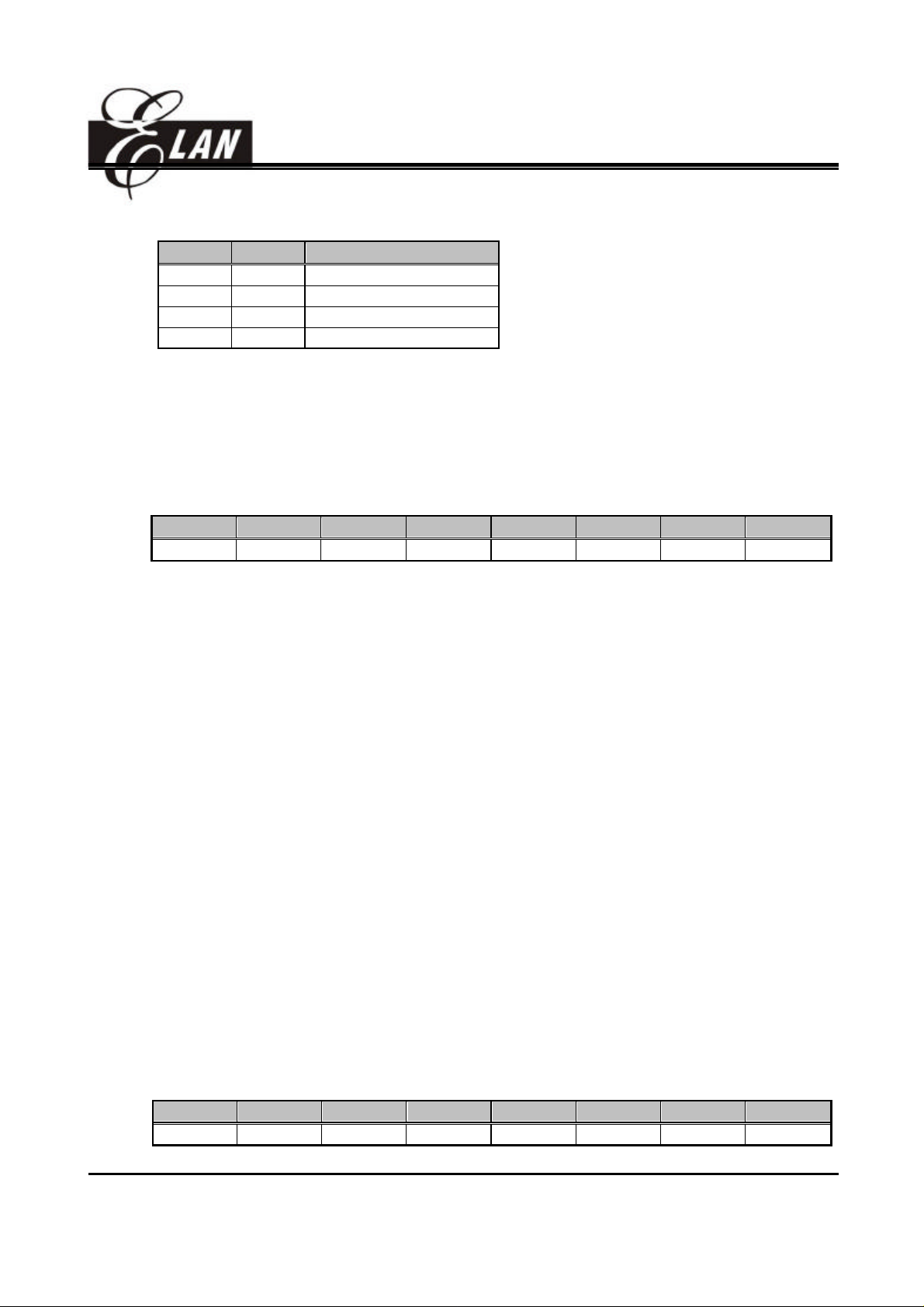
• Bit 3: Bit 2 ( T2P1:T2P0 ): TMR2 clock prescale option bits.
T2P1 T2P0 Prescale
0 0 1:2(Default)
0 1 1:8
1 0 1:32
1 1 1:64
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
17
Page 18
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
• Bit 1 : Bit 0 ( T1P1:T1P0 ): TMR1 clock prescale option bits.
T1P1 T1P0 Prescale
0 0 1:2(Default)
0 1 1:8
1 0 1:32
1 1 1:64
12. IOC61 ( DT1L: the Least Significant Byte ( Bit 7 ~ Bit 0) of Duty Cycle of
PWM1 )
A specified value keeps the output of PWM1 to stay at high until the value matches with TMR1.
13. IOC71 ( DT1H: the Most Significant Byte ( Bit 1 ~ Bit 0 ) of Duty Cycle of
PWM1 )
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CALI1 SIGN1 VOF1[2] VOF1[1] VOF1[0] - PWM1[9] PWM1[8]
• Bit 7 (CALI1): Calibration enable bit
0 = Calibration disable;
1 = Calibration enable.
• Bit 6 (SIGN1): Polarity bit of offset voltage
0 = Negative voltage;
1 = Positive voltage.
• Bit 5:Bit 3 (VOF1[2]:VOF1[0]): Offset voltage bits.
• Bit 1:Bit 0 (PWM1[9]:PWM1[8]): The Most Significant Byte of PWM1 Duty Cycle
A specified value keeps the PWM1 output to stay at high until the value matches with TMR1.
14. IOC81 ( PRD1: Period of PWM1 ):
The content of IOC81 is a period (time base) of PWM1. The frequency of PWM1 is the reverse of the
period.
15. IOC91 ( DT2L: the Least Significant Byte ( Bit 7 ~ Bit 0 ) of Duty Cycle of
PWM2 )
A specified value keeps the of PWM1 output to stay at high until the value matches with TMR2.
16. IOCA1 ( DT2H: the Most Significant Byte ( Bit 1 ~ Bit 0 ) of Duty Cycle of
PWM2 )
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CALI2 SIGN2 VOF2[2] VOF2[1] VOF2[0] - PWM2[9] PWM2[8]
• Bit 7 (CALI2): Calibration enable bit
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
18
Page 19

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
0 = Calibration disable;
1 = Calibration enable.
• Bit 6 (SIGN2): Polarity bit of offset voltage
0 = Negative voltage;
1 = Positive voltage.
• Bit 5:Bit 3 (VOF2[2]:VOF2[0]): Offset voltage bits
• Bit 1:Bit 0 (PWM2[9]:PWM2[8]): The Most Significant Byte of PWM1 Duty Cycle
A specified value keeps the PWM2 output to stay at high until the value matches with TMR2.
17. IOCB1 ( PRD2: Period of PWM2 )
The content of IOCB1 is a period (time base) of PWM2. The frequency of PWM2 is the reverse of the
period.
18. IOCC1 ( DL1L: the Least Significant Byte ( Bit 7 ~ Bit 0 ) of Duty Cycle Latch of
PWM1 )
The content of IOCC1 is read-only.
19. IOCD1 ( DL1H: the Most Significant Byte ( Bit 1 ~ Bit 0 ) of Duty Cycle Latch of
PWM1 )
The content of IOCD1 is read-only.
20. IOCE1 ( DL2L: the Least Significant Byte ( Bit 7 ~ Bit 0) of Duty Cycle Latch of
PWM2 )
The content of IOCE1 is read-only.
21. IOCF1 ( DL2H: the Most Significant Byte ( Bit 1 ~ Bit 0 ) of Duty Cycle Latch of
PWM2 )
The content of IOCF1 is read-only.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
19
Page 20

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
4.3 TCC/WDT & Prescaler
An 8-bit counter is available as prescaler for the TCC or WDT. The prescaler is available for either the
TCC or WDT only at any given time, and the PAB bit of CONT register is used to determine the
prescaler assignment. The PSR0~PSR2 bi ts determine the prescale ratio. The prescaler is cleared
each time the instruction is written to TCC under TCC mode. The WDT and prescaler, when assigned to
WDT mode, are cleared by the WDTC or SLEP instructions. Fig. 5 depicts the circuit diagram of
TCC/WDT.
• R1(TCC) is an 8-bit timer/counter. The TCC clock source can be internal or external clock input (edge
selectable from TCC pin). If TCC signal source is from internal clock, TCC will increase by 1 at every
instruction cycle (without prescaler). Referring to Fig. 5, selection of CLK=Fosc/2 or CLK=Fosc/4
depends on the CODE Option bit CLKS. CLK=Fosc/2 if CLKS bit is "0", and CLK=Fosc/4 if CLKS bit is
"1".
• If TCC signal source is from external clock input, TCC will increase by 1 at every falling edge or rising
edge of TCC pin.
• The watchdog timer is a free running on-chip RC oscillator. The WDT will keep on running even after
the oscillator driver has been turned off (i.e. in sleep mode). During normal operation or sleep mode, a
WDT time-out (if enabled) will cause the device to reset. The WDT can be enabled or disabled at any
time during the normal mode by software programming. Refer to WDTE bit of IOCE0 register. Without
presacler, the WDT time-out period is approximately 18 ms1.
1
NOTE: VDD=5V,Setup time period = 16ms ± 5%.
VDD=3V,Setup time period = 19ms ± 5%.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
20
Page 21

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
CLK (Fosc/2 or Fosc/4)
TCC
Pin
WDT
WDTE
(in IOCE)
0
M
U
X
1
TSTE
1
M
U
X
0
PAB
M
0
U
X
1
PAB
WDT timeout
SYNC
2 cycles
8-bit Counter
8-to-1 MUX
0
1
MUX
DATA BUS
TCC (R1)
TCC overflow
interrupt
PSR0 ~ PSR2
PAB
Fig. 5 Block Diagram of TCC and WDT
4.4 I/O Ports
Port 5, Port 6, and the I/O registers are bi-directional tri-state I/O ports. The function of Pull-high,
Pull-down, and Open-drain can be set internally by IOCB0, IOCC0, and IOCD0, respectively. Port 6
features an input status changed interrupt (or wake-up) function. Each I/O pin can be defined as
"input" or "output" pin by the I/O control register (IOC50 ~ IOC60). The I/O registers and I/O control
registers are both readable and writable. The I/O interface circuits for Port 5 and Port 6 are shown in
the following Fig. 6, Fig. 7, and Fig. 8 respectively.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
21
Page 22

PCRD
Q
_
Q
CLK
C
L
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
D
PCWR
PORT
P
D
Q
R
CLK
_
Q
PDWR
C
L
IOD
PDRD
M
0
U
X
1
NOTE: Pull-down is not shown in the figure.
Fig. 6 The Ccircuit of I/O Port and I/O Control Register for Port 5
PCRD
P
DQ
R
CLK
PCWR
C
L
P
DQ
R
CLK
PDWR
C
L
PDRD
IOD
TI 0
P50, /INT
PORT
P
D Q
R
CLK
C
L
Bit 6 of IOCE0
_
Q
_
Q
_
Q
M
0
U
X
1
P
D Q
R
CLK
_
C
Q
L
INT
NOTE: Pull-high (down) and Open-drain are not shown in the figure.
Fig. 7 The Circuit of I/O Port and I/O Control Register for P50(/INT)
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
22
Page 23

PCRD
_
Q
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
P
DQ
R
CLK
PCWR
C
L
P60 ~ P67
PORT
M
0
U
X
1
_
Q
P
D Q
R
CLK
C
L
P
R
DQ
CLK
PDWR
C
L
PDRD
_
Q
IOD
NOTE: Pull-high (down) and Open-drain are not shown in the figure.
Fig. 8 The Circuit of I/O Port and I/O Control Register for P60~P67
IOCE.1
P
Q
D
R
CLK
_
C
Q
T10
T11
T17
L
D
CLK
RE.1
P
R
Q
_
C
Q
L
P
Q
R
CLK
_
C
Q
L
TI n
Interrupt
ENI Instruction
D
DISI Instruction
Interrupt
/SLEP
(Wake-up from SLEEP)
Next Instruction
(Wake-up from SLEEP)
Fig. 9 Block Diagram of Port 6 with Input Changed Interrupt/Wake-up
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
23
Page 24

Table 4 Usage of Port 6 Input Changed Wake-up/Interrupt Function
Usage of Port 6 Input Status Changed Wake-up/Interrupt
(I) Wake-up from Port 6 Input Status Change (II) Port 6 Input Status Change Interrupt
(a) Before SLEEP 1. Read I/O Port 6 (MOV R6,R6)
1. Disable WDT 2. Execute "ENI"
2. Read I/O Port 6 (MOV R6,R6) 3. Enable interrupt (Set IOCF0.1)
3. Execute "ENI" or "DISI" 4. IF Port 6 changed (interrupt)
4. Enable interrupt (Set IOCF0.1)
5. Execute "SLEP" instruction
(b) After wake-up
1. IF "ENI" → Interrupt vector (008H)
2. IF "DISI" → Next instruction
4.5 RESET and Wake-up
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
→ Interrupt vector (008H)
1. The function of RESET and Wake-up
A RESET is initiated by one of the following events-
(1) Power-on reset
(2) /RESET pin input "low", or
(3) WDT time-out (if enabled).
The device is kept in a RESET condition for a period of approximately 18ms (one oscillator start-up
timer period) after the reset is detected. Once the RESET occurs, the following functions are
performed.
• The oscillator is running, or will be started.
• The Program Counter (R2) is set to all "0".
• All I/O port pins are configured as input mode (high-impedance state).
• The Watchdog Timer and prescaler are cleared.
• When power is switched on, the upper 3 bits of R3 are cleared.
• The bits of the CONT register are set to all "1" except for the Bit 6 (INT flag).
• The bits of the IOCB0 register are set to all "1".
• The IOCC0 register is cleared.
• The bits of the IOCD0 register are set to all "1".
• Bit 7 of the IOCE0 register is set to "1", and Bit 6 is cleared.
• Bits 0~6 of RF register and bits 0~6 of IOCF0 register are cleared.
Executing the “SLEP” instruction will assert the sleep (power down) mode. While entering sleep mode,
the WDT (if enabled) is cleared but keeps on running. The controller can be awakened by-
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
24
Page 25

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
(1) External reset input on /RESET pin.
(2) WDT time-out (if enabled).
(3) Port 6 input status change (if enabled).
(4) Comparator high.
The first two cases will cause the EM78P458/459 to reset. The T and P flags of R3 can be used to
determine the source of the reset (wake-up). Case 3 is considered the continuation of program
execution and the global interrupt ("ENI" or "DISI" being executed) decides whether or not the
controller branches to the interrupt vector following wake-up. If ENI is executed before SLEP, the
instruction will begin to execute from the address 0x8 after wake-up. If DISI is executed before SLEP,
the execution will restart from the instruction right next to SLEP after wake-up.
Only one of the Cases 2, to 4 can be enabled before entering into sleep mode. That is,
[a] if Port 6 Input Status Change Interrupt is enabled before SLEP , WDT must be disabled by
software. However, the WDT bit in the option register remains enabled. Hence, the
EM78P458/459 can be awakened only by Case 1 or 3.
[b] if WDT is enabled before SLEP, Port 6 Input Status Changed Interrupt must be disabled. Hence,
the EM78P458/459 can be awakened only by Case 1 or 2. Refer to the section on Interrupt for
further details.
[c] if Comparator High Interrupt is enabled before SLEP, WDT must be disabled by software.
However, the WDT bit in the option register remains enabled. Hence, the EM78P458/459 can
be awakened only by Case 1 or 4.
If Port 6 Input Status Change Interrupt is used to wake up the EM78P458/459 (as in Case [a] above),
the following instructions must be executed before SLEP:
MOV A, @0Bxx000110 ; Select internal TCC clock
CONTW
CLR R1 ; Clear TCC and prescaler
MOV A, @0Bxxxx1110 ; Select WDT prescaler
CONTW
WDTC ; Clear WDT and prescaler
MOV A, @0B0xxxxxxx ; Disable WDT
IOW RE
MOV R6, R6 ; Read Port 6
MOV A, @0B00000x1x ; Enable Port 6 input change interrupt
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
25
Page 26

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
IOW RF
ENI (or DISI) ; Enable (or disable) global interrupt
SLEP ; Sleep
NOP
Similarly, if the Comparator High Interrupt is used to wake up the EM78P458/459 (as in Case [c]
above), the following instructions must be executed before SLEP:
MOV A, @0Bxx000110 ; Select internal TCC clock
CONTW
CLR R1 ; Clear TCC and prescaler
MOV A, @0Bxxxx1110 ; Select WDT prescaler
CONTW
WDTC ; Clear WDT and prescaler
MOV A, @0B0xxxxxxx ; Disable WDT
IOW RE
MOV A, @0B01xxxxxx ; Enable comparator high interrupt
IOW RF
ENI (or DISI) ; Enable (or disable) global interrupt
SLEP ; Sleep
NOP
One problem user must be aware of, is that after waking up from the sleep mode, the WDT function
will enable automatically. The WDT operation (being enabled or disabled) should be handled
appropriately by software after waking up from the sleep mode.
2. The Status of T, and P of STATUS Register
A RESET condition is initiated by one of the following events:
(1) A power-on condition,
(2) A high-low-high pulse on /RESET pin, or
(3) Watchdog Timer time-out.
The values of T and P, as listed in Table 5 below, are used to check how the processor wakes up.
Table 6 shows the events, which may affect the status of T and P.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
26
Page 27

Table 5 The Values of RST, T, and P after RESET
Reset Type T P
Power-on 1 1
/RESET during Operating mode *P *P
/RESET wake-up during SLEEP mode 1 0
WDT during Operating mode 0 *P
WDT wake-up during SLEEP mode 0 0
Wake-up on pin change during SLEEP mode 1 0
*P: Previous status before reset
Table 6 The Status of RST, T and P being Affected by Events
Event T P
Power-on 1 1
WDTC instruction 1 1
WDT time-out 0 *P
SLEP instruction 1 0
Wake-up on pin changed during SLEEP mode 1 0
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
*P: Previous value before reset
Oscillator
Power-On Reset
Voltage Detector
WDT Timeout
WDT
/RESET
Fig. 10 Block Diagram of Reset of Controller
VDD
D Q
CLK
CLR
Setup time
CLK
Reset
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
27
Page 28

4.6 Interrupt
The EM78P458/459 has six interrupts as listed below:
(1) TCC overflow interrupt
(2) Port 6 Input Status Change Interrupt
(3) External interrupt [(P50, /INT) pin].
(4) Analog to Digital conversion completed.
(5) When TMR1/TMR2 matches with PRD1/PRD2 respectively in PWM.
(6) When the comparators output change.
Before the Port 6 Input Status Change Interrupt is enabled, reading Port 6 (e.g. "MOV R6,R6") is
necessary. Each Port 6 pin will have this feature if its status changes. Any pin configured as output or
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
P50 pin configured as /INT, is excluded from this function. Port 6 Input Status Change Interrupt will
wake up the EM78P458/459 from the sleep mode if it is enabled prior to going into the sleep mode by
executing SLEP. When the controller is wake-up, it will continue to execute the succeeding program if
the global interrupt is disabled, or branches out to the interrupt vector 008H if the global interrupt is
enabled.
RF, the interrupt status register that records the interrupt requests in the relative flags/bits. IOCF0 is
an interrupt mask register. The global interrupt is enabled by the ENI instruction and is disabled by the
DISI instruction. When one of the interrupts (when enabled) occurs, the next instruction will be
fetched from address 008H. Once in the interrupt service routine, the source of an interrupt can be
determined by polling the flag bits in RF. The interrupt flag bit must be cleared by instructions before
leaving the interrupt service routine to avoid recursive interrupts.
The flag (exc ept ICIF bit) in the Interrupt Status Register (RF) is set regardless of the status of its
mask bit or the execution of ENI. Note that the outcome of RF will be the logic AND of RF and IOCF0
(refer to Fig. 11). The RETI instruction ends the interrupt routine and enables the global interrupt (the
execution of ENI).
When an interrupt is generated by the INT instruction (when enabled), the next instruction will be
fetched from address 001H.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
28
Page 29

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
Fig. 11 Interrupt Input Circuit
4.7 Analog-To-Digital Converter (ADC)
The analog-to-digital circuitry consists of an 8-bit analog multiplexer, three control registers
(ADCON/R9, AD-CMP-CON/IOCA0, GCON/IOC90), one data register (ADDATA/RA) and an ADC
with 8-bit resolution. The functional block diagram of the ADC is shown in Fig. 12. The analog
reference voltage (Vref) and analog ground are connected via separate input pins.
The ADC module utilizes successive approximation to convert the unknown analog signal into a
digital value. The result is fed to the ADDATA. Input channels are selected by the analog input
multiplexer via the ADCON register Bits ADIS0, ADIS1, and ADIS2.
ADC8 Vref
ADC7
ADC6
ADC5
ADC4
ADC3
ADC2
ADC1
234 34
+
OP2
-
+
OP1
-
5 4 3 2 1 0
GCON
8-1 Analog Switch
( successive approximation )
Fsco
4-1
MUX
Internal
RC
AD-CMPCON RFAD-CMPCON ADCON ADCON
01012
DATA BUS
ADC
3
ADDATA
01234567
Power-Down
Start to Convert
Fig. 12 The Functional Block Diagram of Analog-to-Digital Conversion
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
29
Page 30

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
1. ADC Control Register (ADCON/R9, AD-CMP-CON/IOCA0, GCON/IOC90)
1.1 ADCON/R9
The ADCON register controls the operation of the A/D conversion and decides which pin should
be currently active.
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SYMBOL - - IOCS ADRUN ADPD ADIS2 ADIS1 ADIS0
*Init_Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
*Init_Value: Initial value at power on reset
• ADRUN (bit 4): ADC starts to RUN.
1 = an A/D conversion is started. This bit can be set by software.
0 = reset on completion of the conversion. This bit can not be reset in software.
• ADPD (bit 3): ADC Power-down Mode.
1 = ADC is operating;
0 = switch off the resistor reference to save power even when the CPU is operating.
• ADIS2~ADIS0 (bit 2~0): Analog Input Select.
000 = AN0;
001 = AN1;
010 = AN2;
011 = AN3;
100 = AN4;
101 = AN5;
110 = AN6;
111 = AN7;
Change occurs only when the ADIF bit and the ADRUN bit are both LOW.
1.2 AD-CMP-CON/IOCA0
The AD-CMP-CON register defines the pins of Port 6 as analog inputs or as digital I/O,
individually.
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SYMBOL VREFS CE COE IMS2 IMS1 IMS0 CKR1 CKR0
*Init_Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
*Init_Value: Initial value at power on reset
• VREFS (Bit 7): The input source of the Vref of the ADC.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
30
Page 31

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
0 = The Vref of the ADC is connected to Vdd (default value), and the P53/VREF pin carries out
the function of P53;
1 = The Vref of the ADC is connected to P53/VREF.
• CE (Bit 6): Control bit used to enable comparator.
0 = Disable comparator
1 = Enable comparator
• COE (Bit 5): Set P57 as the output of the comparator
0 = the comparator acts as an OP if CE=1.
1 = act as a comparator if CE=1.
• IMS2~IMS0 (Bit 4 ~ Bit 2): ADC configuration definition bit.
• CKR1 and CKR0 (Bit 1 and Bit 0): The conversion time select.
00 = Fosc/4;
01 = Fosc/16;
10 = Fsco/64;
11 = Frc (Internal RC clock osc);
1.3 GCON/IOC90
As shown in Fig. 12, OP1 and OP2, the gain amplifiers, are located in the middle of the analog
input pins (ADC1 and ADC5) and the 8-1analog switch. The GCON register controls the gains.
Table 7 Table 7 Shows the Gains and the Operating Range of ADC.
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SYMBOL OP2E OP1E G22 G21 G20 G12 G11 G10
*Init_Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 8 The Gains and the Operating Range of ADC
G10:G12/G20:G22 Gain Range of Operating Voltage
000 1 0 ~ Vref
001 2 0 ~ (1/2)Vref
010 4 0 ~ (1/4)Vref
011 8 0 ~ (1/8)Vref
100 16 0 ~ (1/16)Vref
101 32 0 ~ (1/32)Vref
<Note> Vref can not be less than 3 volts.
2. ADC Data Register (ADDATA/RA)
When the A/D conversion is complete, the result is loaded to the ADDATA. The START/END bit is
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
31
Page 32

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
clear, and the ADIF is set.
3. A/D Sampling Time
The accuracy, linearity, and speed of the successive approximation A/D converter are dependent on
the properties of the ADC and the comparator. The source impedance and the internal sampling
impedance directly affect the time required to charge the sample holding capacitor. The application
program controls the length of the sample time to meet the specified accuracy. Generally speaking,
the program should wait for 1 μs for each KΩ of the analog source impedance and at least 1 μs for
the low-impedance source. After the analog input channel is selected, this acquisition time must be
done before the conversion can be started.
4. A/D Conversion Time
CKR0 and CKR1 select the conversion time (Tct), in terms of instruction cycles. This allows the MCU
to run at the maximum frequency without sacrificing the accuracy of A/D conversion. For the
EM78P458/459, the conversion time per bit is about 4μs. Table 8 shows the relationship between
Tct and the maximum operating frequencies.
Table 9 Tct vs. the Maximum Operation Frequency
CKR0:CKR1 Operation Mode Max. operation frequency
00 Fsco/4 1 MHz
01 Fsco/16 4 MHz
10 Fsco/64 16MHz
11 Internal RC 1 MHz
5. A/D Operation During Sleep Mode
In order to reduce power consumption, the A/D conversion remains operational during sleep mode,
and is obligated to implement the internal RC clock source mode. As the SLEP instruction is executed,
all the operations of the MCU will stop except for the A/D conversion. The RUN bit will be cleared and
the result will be fed to the ADDATA when the conversion is completed. If the ADIE is enabled, the
device will wake up. Otherwise, the A/D conversion will be shut off, no matter what the status of ADPD
bit is.
6. Programming Steps/Considerations
1. Programming steps
Follow these steps to obtain data from the ADC:
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
32
Page 33

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
(1) Write to the three bits (IMS2:IMS0) on the AD-CMP-CON1 register to define the characteristics
of R6: Digital I/O, analog channels, and voltage reference pin;
(2) Write to the ADCON register to configure AD module:
(a) Select A/D input channel ( ADAS2:ADAS0 );
(b) Select the proper gains by writing to the GCON register ( optional );
(c) Define A/D conversion clock rate ( CKR1:CKR0 );
(d) Set the ADPD bit to 1 to begin sampling.
(3) Put “ENI” instruction, if the interrupt function is employed.
(4) Set the ADRUN bit to 1.
(5) Wait for either the interrupt flag to be set or the ADC interrupt to occur.
(6) Read ADDATA, the conversion data register.
(7) Clear the interrupt flag bit (ADIF).
(8) For next conversion, go to Step 1 or Step 2 as required. At least 2 Tct is required before next
acquisition starts.
<Note>: To obtain an accurate value, it is necessary to avoid any data transition on I/O pins during
AD conversion.
2. The Demonstration Programs
; To define the general registers
R_0 == 0 ; Indirect addressing register
PSW == 3 ; Status register
PORT5 == 5
PORT6 == 6
R_F== 0XF ; Interrupt status register
; To define the control register
IOC50 == 0X5 ; Control Register of Port 5
IOC60 == 0X6 ; Control Register of Port 6
C_INT== 0XF ; Interrupt Control Register
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
33
Page 34

EM78P458/459
;ADC Control Registers
ADDATA == 0xA ; The contents are the results of ADC
ADCON R== 0x9 ; 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
; - - IOCS ADRUN ADPD ADIS2 ADIS1 ADIS0
ADCONC== 0xA ; 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
; VREFS X X IMS2 IMS1 IMS0 CKR1 CKR0
GCON == 0x9 ; 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
; OPE2 OPE1 G22 G21 G20 G12 G11 G10
;To define bits
OTP ROM
;In ADCONR
ADRUN == 0x4 ; ADC is executed as the bit is set
ADPD == 0x3 ; Power Mode of ADC
ORG 0 ; Initial address
JMP INITIAL ;
ORG 0x08 ; Interrupt vector
(User program)
CLR R_F ; To clear the ADCIF bit
BS ADCONR, ADRUN ; To start to execute the next AD conversion if necessary
RETI
INITIAL:
MOV A, @0BXXXX1XXX ; Enable the interrupt function of ADC, “X” by application
IOW C_INT
MOV A, @0xXX ; Interrupt disabled:<6>
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
34
Page 35

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
CONTW
MOV A, @0B00000000 ; To employ Vdd as the reference voltage, to define P60 as
IOW ADCONC ; an analog input and set clock rate at fosc/4
En_ADC:
MOV A, @0BXXXXXXX1 ; To define P60 as an input pin, and the others are dependent
IOW PORT6 ; on applications
MOV A, @0B01000101 ; To enable the OP1, and set the gain as 32
IOW GCON
BS ADCONR, ADPD ; To disable the power-down mode of ADC
ENI ; Enable the interrupt function
BS ADCONR, ADRUN ; Start to run the ADC
; If the interrupt function is employed, the following three lines may be ignored
POLLING:
JBC ADCONR, ADRUN ; To check the ADRUN bit continuously;
JMP POLLING ; ADRUN bit will be reset as the AD conversion is completed
(User program)
:
:
:
4.8 Dual Sets of PWM ( Pulse Width Modulation )
1. Overview
In PWM mode, both PWM1 and PWM2 pins produce up to a 10-bit resolution PWM output (see. Fig.
13 for the functional block diagram). A PWM output has a period and a duty cycle, and it keeps the
output in high. The baud rate of the PWM is the inverse of the period. Fig. 14 depicts the relationships
between a period and a duty cycle.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
35
Page 36

EM78P458/459
PWM1
OTP ROM
Fosc
1:2
1:8
1:32
1:64
Fosc
1:2
1:8
1:32
1:64
MUX
T1P0 T1P1 T1EN
T2P0 T2P1 T2EN
MUX
DT2H
+
DT2L
TMR1H + TMR1L
PRD1
DT2H
+
DT2L
TMR2H + TMR2L
PRD2
DL2H + DL2L
Comparator
Comparator
DL2H + DL2L
Comparator
Comparator
reset
reset
latch
latch
To PWM1IF
Duty Cycle
Match
R Q
S
IOC6
Period
Match
Data BusData Bus
To PWM2IF
Duty Cycle
Match
PWM2
R Q
S
IOC6
Period
Match
Fig. 13 The Functional Block Diagram of the Dual PWMs
Period
Duty Cycle
DT1 = TMR1
PRD1 = TMR1
Fig. 14 The Output Timing of the PWM
2. Increment Timer Counter ( TMRX: TMR1H/TWR1L or TMR2H/TWR2L )
TMRX are ten-bit clock counters with programmable prescalers. They are designed for the PWM
module as baud rate clock generators. TMRX can be read, written, and cleared at any reset
conditions. If employed, they can be turned down for power saving by setting T1EN bit
[PWMCON<4>] or T2EN bit [PWMCON<5>] to 0.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
36
Page 37

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
3. PWM Period ( PRDX : PRD1 or PRD2 )
The PWM period is defined by writing to the PRDX register. When TMRX is equal to PRDX, the
following events occur on the next increment cycle:
• TMRX is cleared.
• The PWMX pin is set to 1.
• The PWM duty cycle is latched from DT1/DT2 to DTL1/DTL2.
< Note > The PWM output will not be set, if the duty cycle is 0;
• The PWMXIF pin is set to 1.
The following formula describes how to calculate the PWM period:
PERIOD = (PRDX + 1) * 4 * (1/Fosc) * (TMRX prescale value )
4. PWM Duty Cycle ( DTX: DT1H/ DT1L and DT2H/ DT2L; DTL: DL1H/DL1L and
DL2H/DL2L )
The PWM duty cycle is defined by writing to the DTX register, and is latched from DTX to DLX while
TMRX is cleared. When DLX is equal to TMRX, the PWMX pin is cleared. DTX can be loaded at any
time. However, it cannot be latched into DTL until the current value of DLX is equal to TMRX.
The following formula describes how to calculate the PWM duty cycle:
Duty Cycle = (DTX) * (1/Fosc) * (TMRX prescale value )
5. Comparator X
To change the output status while the match occurs, the TMRXIF flag will be set at the same time.
6. PWM Programming Procedures/Steps
Load PRDX with the PWM period.
(1) Load DTX with the PWM Duty Cycle.
(2) Enable interrupt function by writing IOCF0, if required.
(3) Set PWMX pin to be output by writing a desired value to IOC60.
(4) Load a desired value to IOC51 with TMRX prescaler value and enable both PWMX and TMRX.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
37
Page 38

4.9 Timer
1. Overview
Timer1 (TMR1) and Timer2 (TMR2) (TMRX) are 10-bit clock counters with programmable prescalers,
respectively. They are designed for the PWM module as baud rate clock generators. TMRX can be
read, written, and cleared at any reset conditions.
2. Function description
Fig. 15 shows TMRX block diagram. Each signal and block are described as follows:
Fosc
1:2
1:8
1:32
1:64
MUX
TMR1X
reset
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
To PWM1IF
Period
Match
Comparator
Comparator
reset
Data BusData Bus
Period
Match
To PWM2IF
Fosc
1:2
1:8
1:32
1:64
T1P0 T1P1
T2P0 T2P1 T2EN
T1EN
MUX
TMR2X
*TMR1X = TMR1H + TMR1L;
*TMR2X = TMR2H +TMR2L
PRD1
PRD2
Fig. 15 TMRX Block Diagram
Fosc: Input clock.
Prescaler ( T1P0 and T1P1/T2P1 and T2P0 ): Options of 1:2, 1:8, 1:32, and 1:64 are defined by
TMRX. It is cleared when any type of reset occurs.
TMR1X and TMR2X (TMR1H/TWR1L and TMR2H/TMR2L ): Timer X register; TMRX is
increased until it matches with PRDX, and then is reset to 0. TMRX cannot be read.
PRDX ( PRD1 and PRD2 ): PWM period register.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
38
Page 39

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
ComparatorX ( Comparator 1 and Comparator 2 ): To reset TMRX while a match occurs and the
TMRXIF flag is set at the same time.
3. Programming the Related Registers
When defining TMRX, refer to the related registers of its operation as shown in Table 9.It must be
noted that the PWMX bits must be disabled if their related TMRXs are employed. That is, bit 7 and bit
6 of the PWMCON register must be set to ‘0’.
Table 10 Related Control Registers of TMR1 and TMR2
Address Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
IOC51 PWMCON/IOC51 PWM2E PWM1E T2EN T1EN T2P1 T2P0 T1P1 T1P0
4. Timer programming procedures/steps
(1) Load PRDX with the TIMER period.
(2) Enable interrupt function by writing IOCF0, if required
(3) Load a desired value to PWMCON with the TMRX prescaler value and enable both TMRX and
disable PWMX.
4.10 Comparator
EM78P458/459 has one comparator, which has two analog inputs and one output. The comparator
can be employed to wake up from the sleep mode. Fig. 16 shows the circuit of the comparator.
Cin-
Cin+
Fig. 16 Comparator Operating Mode
1. External Reference Signal
CMP
+
CO
The analog signal that is presented at Cin- compares to the signal at Cin+, and the digital output (CO)
of the comparator is adjusted accordingly.
• The reference signal must be between Vss and Vdd.
• The reference voltage can be applied to either pi of comparator.
• Threshold detector applications may be of the same reference.
• The comparator can operate from the same or different reference source.
2. Comparator Outputs
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
39
Page 40

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
• The compared result is stored in the CMPOUT of R3.
• The comparator outputs is output to P57 by programming bit5<COE> of the AD-CMPCON register
to 1.
• P57 must be defined as an output if implemented as the comparator output.
• Fig. 17 shows the comparator output block diagram.
To C0
From OP I/O
CMRD
ENEN
To CMPOUT
Fig. 17 The Output Configuration of a Comparator
CMRD
Q
RESET
D
Q
From other
comparator
D
To CPIF
3. Using as An Operation Amplifier
The comparator can be used as an operation amplifier if a feedback resistor is connected from the
input to the output externally. In this case, the Schmitt trigger can be disabled for power saving by
setting CE to 1 and COE to 0.
4. Interrupt
• CMPIE (IOCF0.6) must be enabled.
• Interrupt occurs at the rising edge of the comparator output pin.
• The actual change on the pin can be determined by reading the Bit CMPOUT, R3<7>.
• CMPIF (RF.6), the comparator interrupt flag, can only be cleared by software.
5. Wake-up from SLEEP Mode
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
40
Page 41

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
• If enabled, the comparator remains active and the interrupt remains functional, even under SLEEP
mode.
• If a mismatch occurs, the interrupt will wake up the device from SLEEP mode.
• The power consumption should be taken into consideration for the benefit of energy conservation.
• If the function is unemployed during SLEEP mode, turn off comparator before entering into sleep
mode.
4.11 The Initialized Values after Reset
Table 11 The Summary of the Initialized Values for Registers
Address Name Reset Type Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Bit Name C57 C56 C55 C54 C53 C52 C51 C50
N/A IOC50
N/A IOC60
N/A IOCB0
N/A IOCC0
N/A IOCD0
N/A IOCE0
N/A IOCF0
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
IOC90
(GCON)
IOCA0
(AD-CMP
CON)
IOC51
(PWMCON)
IOC61
(DT1L)
Power-on 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
/RESET and WDT 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name C67 C66 C65 C64 C63 C62 C61 C60
Power-on 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
/RESET and WDT 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name /PD7 /PD6 */PD5 */PD4 /PD3 /PD2 /PD1 /PD0
Power-on 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
/RESET and WDT 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name OD7 OD6 OD5 OD4 OD3 OD2 OD1 OD0
Power-on 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
/RESET and WDT 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name /PH7 /PH6 /PH5 /PH4 /PH3 /PH2 /PH1 /PH0
Power-on 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
/RESET and WDT 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name WDTE EIS X X X X X X
Power-on 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
/RESET and WDT 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P 1 1 1 1 1 1
Bit Name X CMPIE PMW2IE PWM1IE ADIE EXIE ICIE TCIE
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed 0 P P P P P P P
Bit Name OP2E OP1E G22 G21 G20 G12 G11 G10
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name VREFS CE COE IMS2 IMS1 IMS0 CKR1 CKR0
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name PWM2E PWM2E T2EN T1EN T2P1 T2P0 T1P1 T1P0
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
41
Page 42

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
Address Name Reset Type Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A CONT
0x00 R0(IAR)
0x01 R1(TCC)
0x02 R2(PC)
0x03 R3(SR)
0x04 R4(RSR)
IOC71
(DT1H)
IOC81
(PRD1)
IOC91
(DT2L)
IOCA1
(DT2H)
IOCB1
(PRD2)
IOCC1
(DL1L)
IOCD1
(DL1H)
IOCE1
(DL2L)
IOCF1
(DL2H)
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
Bit Name CALI1 SIGN1 VOF1[2] VOF1[1] VOF1[0] X Bit1 Bit0
Power-on 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P 0 P P
Bit Name - - - - - - - -
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name CALI2 SIGN2 VOF2[2] VOF2[1] VOF2[0] X Bit1 Bit0
Power-on 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P 0 P P
Bit Name - - - - - - - -
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name X X X X X X Bit1 Bit0
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed 0 0 0 0 0 0 P P
Bit Name Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name X X X X X X Bit1 Bit0
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed 0 0 0 0 0 0 P P
Bit Name INTE INT TS TE PAB PSR2 PSR1 PSR0
Power-on 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
/RESET and WDT 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name - - - - - - - -
Power-on U U U U U U U U
/RESET and WDT P P P P P P P P
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name - - - - - - - -
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name - - - - - - - -
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed Jump to address 0x08 or continue to execute next instruction
Bit Name GP2 PS1 PS0 T P Z DC C
Power-on 0 0 0 1 1 U U U
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 t t P P P
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P t t P P P
Bit Name BS7 BS6 - - - - - -
Power-on 0 0 U U U U U U
/RESET and WDT 0 0 P P P P P P
42
Page 43

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
Address Name Reset Type Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
0x05 P5
0x06 P6
0x7~0x8 R7~R8
0x9
0xA
0xB
0xC
0xD
0xE
0xF
0x10~0x3F R10~R3F
R9
(ADCON)
RA
(ADDDATA)
RB
(TMR1L)
RC
(TMR1H)
RD
(TMR2L)
RE
(TMR2H)
RF
(ISR)
X: not used. U: unknown or don’t care. P: previous value before reset.
Bit Name P57 P56 P55 P54 P53 P52 P51 P50
Power-on 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
/RESET and WDT 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name P67 P66 P65 P64 P63 P62 P61 P60
Power-on 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
/RESET and WDT 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name - - - - - - - -
Power-on U U U U U U U U
/RESET and WDT P P P P P P P P
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name X X IOCS ADRUN ADPD ADAS2 ADAS1 ADAS0
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name - - - - - - - -
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name X X X X X X Bit1 Bit0
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed 0 0 0 0 0 0 P P
Bit Name Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
Bit Name X X X X X X Bit1 Bit0
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed 0 0 0 0 0 0 P P
Bit Name X CMPIF PWM2IF PWM1IF ADIF EXIF ICIF TCIF
Power-on 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
/RESET and WDT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Wake-up from Pin Changed 0 P P P P P P P
Bit Name - - - - - - - -
Power-on U U U U U U U U
/RESET and WDT P P P P P P P P
Wake-up from Pin Changed P P P P P P P P
t: check Table 5
4.12 Oscillator
1. Oscillator Modes
The EM78P458 and EM78P459 can be operated in four different oscillator modes, such as High
XTAL oscillator mode (HXT), Low XTAL oscillator mode (LXT), External RC oscillator mode (ERC),
and RC oscillator mode with Internal capacitor (IC). Users can select one of them by programming the
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
43
Page 44

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
MASK Option. The up-limited operation frequency of crystal/resonator on the different VDDs is listed
in Table 11
Table 12 The Summary of Maximum Operating Speeds
Conditions VDD Fxt max.(MHz)
2.3 4
Two clocks
2. Crystal Oscillator/Ceramic Resonators (XTAL)
EM78P458/459 can be driven by an external clock signal through the OSCI pin as shown in Fig. 18
below.
3.0 8
5.0 20
OSCI
EM78P458
EM78P459
OSCO
Ext.
Clock
Fig. 18 Circuit for External Clock Input
In the most applications, pin OSCI and pin OSCO can be connected with a crystal or ceramic
resonator to generate oscillation. Fig. 19 depicts such circuit. The same applies to the HXT mode and
the LXT mode. Table 12 provided the recommended values of C1 and C2. Since each resonator has
its own attribute, user should refer to their specifications for appropriate values of C1 and C2. RS, a
serial resistor, may be necessary for AT strip cut crystal or low frequency mode.
C1
OSCI
EM78P458
EM78P459
XTAL
OSCO
RS
C2
Fig. 19 Circuit for Crystal/Resonator
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
44
Page 45

EM78P458/459
Table 13 Capacitor Selection Guide for Crystal Oscillator or Ceramic Resonators
Oscillator Type Frequency Mode Frequency C1(pF) C2(pF)
Ceramic
Resonators
Crystal Oscillator
HXT
LXT
HXT
455 kHz 100~150 100~150
2.0 MHz 20~40 20~40
4.0 MHz 10~30 10~30
32.768kHz 25 15
100KHz 25 25
200KHz 25 25
455KHz 20~40 20~150
1.0MHz 15~30 15~30
2.0MHz 15 15
4.0MHz 15 15
330 330
OTP ROM
OSCI
7404
EM78P458
EM78P459
7404 7404
C
XTAL
Fig. 20 Circuit for Crystal/Resonator-Series Mode
7404
OSCI
EM78P458
EM78P459
10K
7404
XTAL
10K4.7K
Vdd
10K
C1 C2
Fig. 21 Circuit for Crystal/Resonator-Parallel Mode
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
45
Page 46

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
3. External RC Oscillator Mode
For some applications that do not require precise timing calculation, the RC oscillator (Fig. 22) could
offer users with an effective cost savings. Nevertheless, it should be noted that the frequency of the
RC oscillator is influenced by the supply voltage, the values of the resistor (Rext), the capacitor(Cext),
and even by the operation temperature. Moreover, the frequency also changes slightly from one chip
to another due to the manufacturing process variation.
In order to maintain a stable system frequency, the values of the Cext should not be less than 20pF,
and that the value of Rext should not be greater than 1M ohm. If they cannot be kept in this range, the
frequency can be affected easily by noise, humidity, and leakage.
The smaller the Rext in the RC oscillator, the faster its frequency will be. On the contrary, for very low
Rext values, for instance, 1 KΩ, the oscillator becomes unstable because the NMOS cannot
discharge the current of the capacitance correctly.
Based on the above reasons, it must be kept in mind that all supply voltage, the operation
temperature, the components of the RC oscillator, the package types, and the way the PCB is layout,
have certain effect on the system frequency.
Vcc
Rext
OSCI
Cext
EM78P458
EM78P459
Fig. 22 Circuit for External RC Oscillator Mode
Table 14 RC Oscillator Frequencies
Cext Rext
Average Fosc 5V,25°C Average Fosc 3V,25°C
3.3k 3.57 MHz 2.94 MHz
20 pF
5.1k 2.63MHz 1.92 MHz
10k 1.30 MHz 1.22 MHz
100k 150 KHz 153 KHz
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
46
Page 47

EM78P458/459
Vcc
OTP ROM
3.3k 1.43 MHz 1.35 MHz
100 pF
300 pF
<Note> 1. Measured on DIP packages.
2. Design reference only
4. RC Oscillator Mode with Internal Capacitor
If both precision and cost are taken into consideration, EM78P257A/B also offers a special oscillation
5.1k 980 KHz 877 KHz
10k 520 KHz 465 KHz
100k 57 KHz 54 KHz
3.3k 820 KHz 600 KHz
5.1k 550 KHz 400 KHz
10k 286 KHz 230 KHz
100k 31 KHz 26 KHz
mode. It is equipped with an internal capacitor and an external resistor (connected to Vcc). The
internal capacitor functions as temperature compensator. In order to obtain more accurate frequency,
a precise resistor is recommended.
Rext
OSCI
EM78P458
EM78P459
Fig. 23 Circuit for Internal C Oscillator Mode
Table 15 R Oscillator Frequencies
Rext
51k 2.22 MHz 2.17 MHz
100k 1.15 MHz 1.14 MHz
300k 375 KHz 370 KHz
Average Fosc 5V,25°C Average Fosc 3V,25°C
<Note> 1. Measured on DIP packages.
2. Design reference only
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
47
Page 48

4.13 Power-on Considerations
Any microcontroller is not warranted to start proper operation before the power supply stabilizes in
steady state.
EM78P458/459 is equipped with Power On Voltage Detector (POVD) with detection level range of 1.4
V to 2.0 V. The circuitry eliminates the extra external reset circuit. It will work well if Vdd rises quickly
enough (50 ms or less). However, under critical applications, extra devices are still required to assist
in solving power on problems.
1. External Power on Reset Circuit
The circuit shown in Fig IV.13.1-1 implements an external RC to produce a reset pulse. The pulse
width (time constant) should be kept long enough to allow Vdd to reach minimum operation voltage.
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
This circuit is used when the power supply has a slow rise time. Because the current leakage from the
/RESET pin is about ±5µA, it is recommended that R should not be great than 40 K. In this way, the
voltage at Pin /RESET is held below 0.2V. The diode (D) acts as a short circuit at power-down. The
capacitor, C, is discharged rapidly and fully. Rin, the current-limited resistor, prevents high current
discharge or ESD (electrostatic discharge) from flowing into Pin /RESET.
VDD
/RESET
EM78P458
EM78P459
Fig. 24 External Power on Reset Circuit
Rin
R
C
D
2. Residue-Voltage Protection
When battery is replaced, device power (Vdd) is taken off but residue-voltage remains. The
residue-voltage may trips below Vdd minimum, but not to zero. This condition may cause a poor
power on reset. Fig. 25 and Fig. 26 show how to build a residue-voltage protection circuit
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
48
Page 49

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
VDD
EM78P458
EM78P459
/RESET
Fig. 25 Circuit 1 for the Residue Voltage Protection
VDD
EM78P458
EM78P459
/RESET
Q1
100K
Q1
R3
33K
10K
1N4684
R1
R2
VDD
VDD
Fig. 26 Circuit 2 for the Residue Voltage Protection
4.14 CODE OPTION
EM78P458/459 has one CODE option word and one Customer ID word that are not a part of the
normal program memory.
Word 0 Word 1
Bit12~Bit0 Bit12~Bit0
Code option12~0 Code option12~0
1. Code Option Register (Word 0)
Bit12 Bit11 Bit10 Bit9 Bit8 Bit7 Bit6 Bit5~Bit0
MS /ENWDT CLKS /PTB HLF RCT HLP ID
• Bit 12 (MS): Oscillator type selection.
0: RC type
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
49
Page 50

1: XTAL type
• Bit 11 (/ENWTD): Watchdog timer enable bit.
0: Enable
1: Disable
• Bit 10 (CLKS): Clocks of each instruction cycle.
0: Two clocks
1: Four clocks
Refer to the section of Instruction Set.
• Bit 9 (/PTB): Protect bit.
0: Enable
1: Disable
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
• Bit 8 (HLF): XTAL frequency selection.
0: Low frequency
1: High frequency
• Bit 7 (RCT): Resistor Capacitor
0: Inter C, External R
1: External RC
• Bit 6 (HLP): Power consumption selection.
0: Low power.
1: High power.
• Bit 5 ~ Bit 0 (ID[5]~ID[0]): Customer’s ID.
2. Code Option Register (Word 1)
Bit12 Bit11 Bit10 Bit9 Bit8 Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4~Bit0
SIGN2 VOF2[2] VOF2[1] VOF2[0] SIGN1 VOF1[2] VOF1[1] VOF1[0] -
• Bit 12 (SIGN2): Polarity bit of offset voltage.
0: Negative voltage
1: Positive voltage
• Bit 11 ~ Bit 9 (VOF2[2]~VOF2[0]): Offset voltage bits
• Bit 8 (SIGN1): Polarity bit of offset voltage.
0: Negative voltage
1: Positive voltage
• Bit 7 ~ Bit 5 (VOF1[2]~VOF210)): Offset voltage bits
• Bit 4 ~ Bit 0 : Not used.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
50
Page 51

4.15 Instruction Set
Each instruction in the instruction set is a 13-bit word divided into an OP code and one or more
operands. Normally, all instructions are executed within one single instruction cycle (one instruction
consists of 2 oscillator periods), unless the program counter is changed by instruction "MOV R2,A",
"ADD R2,A", or by instructions of arithmetic or logic operation on R2 (e.g. "SUB R2,A", "BS(C) R2,6",
"CLR R2", ⋅⋅⋅⋅). In this case, the execution takes two instruction cycles.
In addition, the instruction set has the following features:
(1) Every bit of any register can be set, cleared, or tested directly.
(2) The I/O registers can be regarded as general registers. That is, the same instruction can operate
on I/O registers.
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
The symbol "R" represents a register designator that specifies which one of the registers (including
operational registers and general-purpose registers) is to be utilized by the instruction. The symbol
"b" represents a bit field designator that selects the value for the bit located in the register "R" that is
affected by the operation. The symbol "k" represents an 8 or 10-bit constant or literal value.
Table 16 The list of the instruction set of EM78P458/459
INSTRUCTION BINARY HEX MNEMONIC OPERATION STATUS AFFECTED
0 0000 0000 0000 0000 NOP No Operation None
0 0000 0000 0001 0001 DAA Decimal Adjust A C
0 0000 0000 0010
0 0000 0000 0011
0 0000 0000 0100
0 0000 0000 rrrr
0 0000 0001 0000 0010 ENI Enable Interrupt None
0 0000 0001 0001 0011 DISI Disable Interrupt None
0 0000 0001 0010
0 0000 0001 0011
0 0000 0001 0100
0 0000 0001 rrrr
0 0000 01rr rrrr
0 0000 1000 0000
0 0000 11rr rrrr
0 0001 00rr rrrr
0 0001 01rr rrrr
0 0001 10rr rrrr
0 0001 11rr rrrr
0 0010 00rr rrrr
0 0010 01rr rrrr
0 0010 10rr rrrr
0 0010 11rr rrrr
0 0011 00rr rrrr
0 0011 01rr rrrr
0002 CONTW A → CONT None
0003 SLEP 0 → WDT, Stop oscillator T,P
0004 WDTC 0 → WDT T,P
000r IOW R A → IOCR None <Note1>
0012 RET [Top of Stack] → PC None
0013 RETI [Top of Stack] → PC, Enable Interrupt None
0014 CONTR CONT → A None
001r IOR R IOCR → A None <Note1>
00rr MOV R,A A → R None
0080 CLRA 0 → A Z
00rr CLR R 0 → R Z
01rr SUB A,R R-A → A Z,C,DC
01rr SUB R,A R-A → R Z,C,DC
01rr DECA R R-1 → A Z
01rr DEC R R-1 → R Z
02rr OR A,R A ∨ VR → A Z
02rr OR R,A A ∨ VR → R Z
02rr AND A,R A & R → A Z
02rr AND R,A A & R → R Z
03rr XOR A,R A ⊕ R → A Z
03rr XOR R,A A ⊕ R → R Z
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
51
Page 52

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
INSTRUCTION BINARY HEX MNEMONIC OPERATION STATUS AFFECTED
0 0011 10rr rrrr 03rr ADD A,R A + R → A Z,C,DC
0 0011 11rr rrrr
0 0100 00rr rrrr
0 0100 01rr rrrr
0 0100 10rr rrrr
0 0100 11rr rrrr
0 0101 00rr rrrr
0 0101 01rr rrrr
0 0101 10rr rrrr
0 0101 11rr rrrr
0 0110 00rr rrrr
0 0110 01rr rrrr
0 0110 10rr rrrr
0 0110 11rr rrrr
0 0111 00rr rrrr
0 0111 01rr rrrr
0 0111 10rr rrrr
0 0111 11rr rrrr
0 100b bbrr rrrr
0 101b bbrr rrrr
0 110b bbrr rrrr 0xxx JBC R,b if R(b)=0, skip None
0 111b bbrr rrrr 0xxx JBS R,b if R(b)=1, skip None
1 00kk kkkk kkkk
1 01kk kkkk kkkk
1 1000 kkkk kkkk
1 1001 kkkk kkkk
1 1010 kkkk kkkk
1 1011 kkkk kkkk
1 1100 kkkk kkkk
1 1101 kkkk kkkk
1 1110 0000 0001
1 1111 kkkk kkkk
<Note 1> This instruction is applicable to IOC50~IOC60, IOCB0~IOCF0 only.
03rr ADD R,A A + R → R Z,C,DC
04rr MOV A,R R → A Z
04rr MOV R,R R → R Z
04rr COMA R /R → A Z
04rr COM R /R → R Z
05rr INCA R R+1 → A Z
05rr INC R R+1 → R Z
05rr DJZA R R-1 → A, skip if zero None
05rr DJZ R R-1 → R, skip if zero None
06rr RRCA R R(n) → A(n-1),
R(0) → C, C → A(7)
06rr RRC R R(n) → R(n-1),
R(0) → C, C → R(7)
06rr RLCA R R(n) → A(n+1),
R(7) → C, C → A(0)
06rr RLC R R(n) → R(n+1),
R(7) → C, C → R(0)
07rr SWAPA R R(0-3) → A(4-7),
R(4-7) → A(0-3)
07rr SWAP R R(0-3) ↔ R(4-7) None
07rr JZA R R+1 → A, skip if zero None
07rr JZ R R+1 → R, skip if zero None
0xxx BC R,b 0 → R(b) None <Note2>
0xxx BS R,b 1 → R(b) None <Note3>
1kkk CALL k PC+1 → [SP],
(Page, k) → PC
1kkk JMP k (Page, k) → PC None
18kk MOV A,k k → A None
19kk OR A,k A ∨ k → A Z
1Akk AND A,k A & k → A Z
1Bkk XOR A,k A ⊕ k → A Z
1Ckk RETL k k → A,
[Top of Stack] → PC
1Dkk SUB A,k k-A → A Z,C,DC
1E01 INT PC+1 → [SP],
001H → PC
1Fkk ADD A,k k+A → A Z,C,DC
C
C
C
C
None
None
None
None
<Note 2> This instruction is not recommended for RF operation.
<Note 3> This instruction cannot operate under RF.
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
52
Page 53

4.16 Timing Diagrams
AC Test Input/Output Waveform
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
2.4
0.4
AC Testing : Input is driven at 2.4V for logic "1",and 0.4V for logic "0".Timing measurements are
made at 2.0V for logic "1",and 0.8V for logic "0".
2.0
0.8
TEST POINTS
2.0
0.8
RESET Timing (CLK="0")
NOP
CLK
/RESET
Instruction 1
Executed
Tdrh
TCC Input Timing (CLKS="0")
Tins
CLK
TCC
Ttcc
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
53
Page 54

5. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Items Rating
Temperature under bias
Storage temperature -65°C to 150°C
Input voltage -0.3V to +6.0V
Output voltage -0.3V to +6.0V
0°C
to
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
70°C
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
54
Page 55

6. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
down active, input pin at
All input and I/O pins at VDD,
input and I/O pins at VDD,
Operating supply current (VDD=3V) at two
/RESET='High',Fosc=32KHz
DD=3V) at two
/RESET=‘High',Fosc=32KHz
/RESET='High', Fosc=2MHz
/RESET='High', Fosc=4MHz
6.1 DC Electrical Characteristic(Ta=0°C ~ 70 °C, VDD=5.0V±5%, VSS=0V)
Symbol Parameter Condition Min Typ Max Unit
Fxt
IIL Input Leakage Current for input pins VIN = VDD, VSS
VIH1 Input High Voltage,VDD=5V Ports 5, 6 2.0 V
VIL1 Input Low Voltage,VDD=5V Ports 5, 6 0.8 V
VIHT1 Input High Threshold Voltage,VDD=5V /RESET, TCC 2.0 V
VILT1 Input Low Threshold Voltage,VDD=5V /RESET, TCC 0.8 V
VIHX1 Clock Input High Voltage,VDD=5V OSCI 2.5 V
VILX1 Clock Input Low Voltage,VDD=5V OSCI 1.0 V
VIH2 Input High Voltage,VDD=3V Ports 5, 6 1.5 V
VIL2 Input Low Voltage,VDD=3V Ports 5, 6 0.4 V
VIHT2 Input High Threshold Voltage,VDD=3V /RESET, TCC 1.5 V
VILT2 Input Low Threshold Voltage,VDD=3V /RESET, TCC 0.4 V
VIHX2 Clock Input High Voltage,VDD=3V OSCI 1.5 V
VILX2 Clock Input Low Voltage,VDD=3V OSCI 0.6 V
VOH1
VOL1
VOL2 Output Low Voltage (P64,P65) IOL = 16.0 mA 0.4 V
IPH Pull-high current
IPD Pull-down current
ISB Power down current
ISB Power down current
Output Low Voltage (P51~P57, P60~P63,
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
XTAL: VDD to 3V DC 8 MHz
XTAL: VDD to 5V
RC: VDD to 5V
Output High Voltage
(Ports 5, 6)
P66~P67)
Two cycle with two clocks
R: 5.1KΩ, C: 100pF F±20%
IOH = -12.0 mA 2.4 V
IOL = 12.0 mA 0.4 V
Pull-high active, input pin at
VSS
Pull-
VDD
output pin floating, WDT
enabled
All
output pin floating, WDT
disabled
DC 20 MHz
980
-50 -100 -240
25 50 120
4 µA
0.2 µA
F±20%
±1 µA
KHz
µA
µA
ICC1
ICC2
ICC3
ICC4
Operating supply current (V
Operating supply current (VDD=5.0V) at
Operating supply current (VDD=5.0V) at
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
clocks
clocks
two clocks
two clocks
(Crystal type, two clocks),
output pin floating, WDT
disabled
(Crystal type, two clocks),
output pin floating, WDT
enabled
(Crystal type, two clocks),
output pin floating
(Crystal type, two clocks),
output pin floating
55
1.3 mA
4.0 mA
15 30
19 35
µA
µA
Page 56

EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
6.2 AC Electrical Characteristic(Ta=0°C ~ 70 °C, VDD=5V±5%, VSS=0V)
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Dclk Input CLK duty cycle 45 50 55 %
Tins
Ttcc TCC input period (Tins+20)/N* ns
Tdrh Device reset hold time
Trst /RESET pulse width
Twdt Watchdog timer period
Tset Input pin setup time 0 ms
Thold Input pin hold time 20 ms
Tdelay Output pin delay time Cload=20pF 50 ms
Instruction cycle time
(CLKS="0")
*N= selected prescaler ratio.
Crystal type
RC type
Ta = 25°C
Ta = 25°C
Ta = 25°C
100
500
9 18 30 ms
2000 ns
9 18 30 ms
DC
DC
ns
ns
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
56
Page 57

APPENDIX
Package Types:
OTP MCU Package Type Pin Count Package Size
EM78P458AP DIP 20 pin 300mil
EM78P458AM SOP 20 pin 300mil
EM78P459AK Skinny DIP 24 pin 300mil
EM78P459AM SOP 24 pin 300mil
EM78P458/459
OTP ROM
This specification is subject to change without prior notice. 2002/03/01
57
 Loading...
Loading...