Page 1
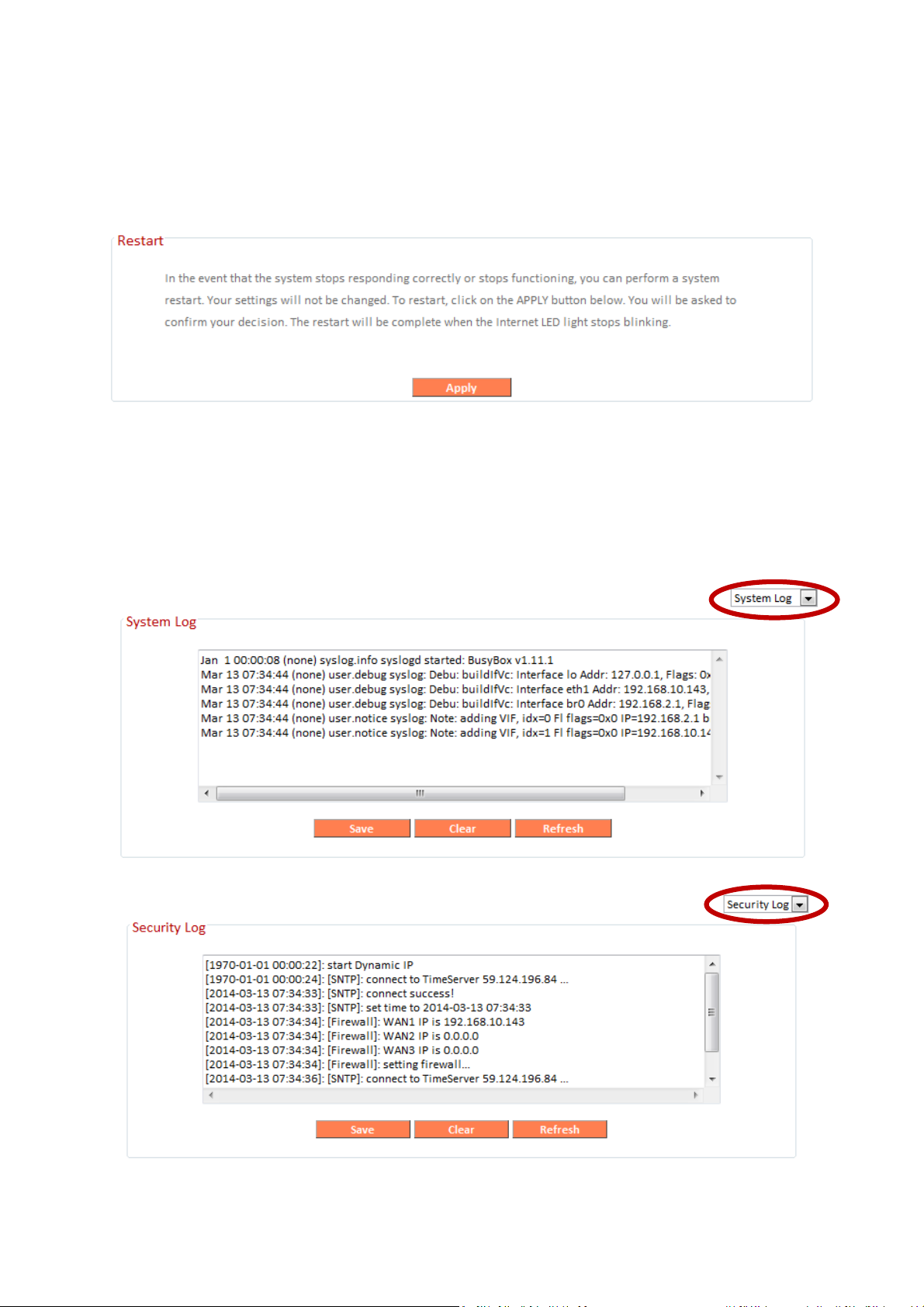
III-3-9-6. Restart
In the event that the router malfunctions or is not responding, then it is
recommended that you restart the device.
III-3-9-7. Logs
You can view the system log and security log here. Use the drop down menu
in the top-right corner to select which log to view.
109
Page 2
Save
Click
“
Save
” to save the
log on your computer
as
.txt
file.
Clear
Click
“Clear” to clear/erase the existing log.
Refresh
Click “Refresh” to refresh the log and update any
activity.
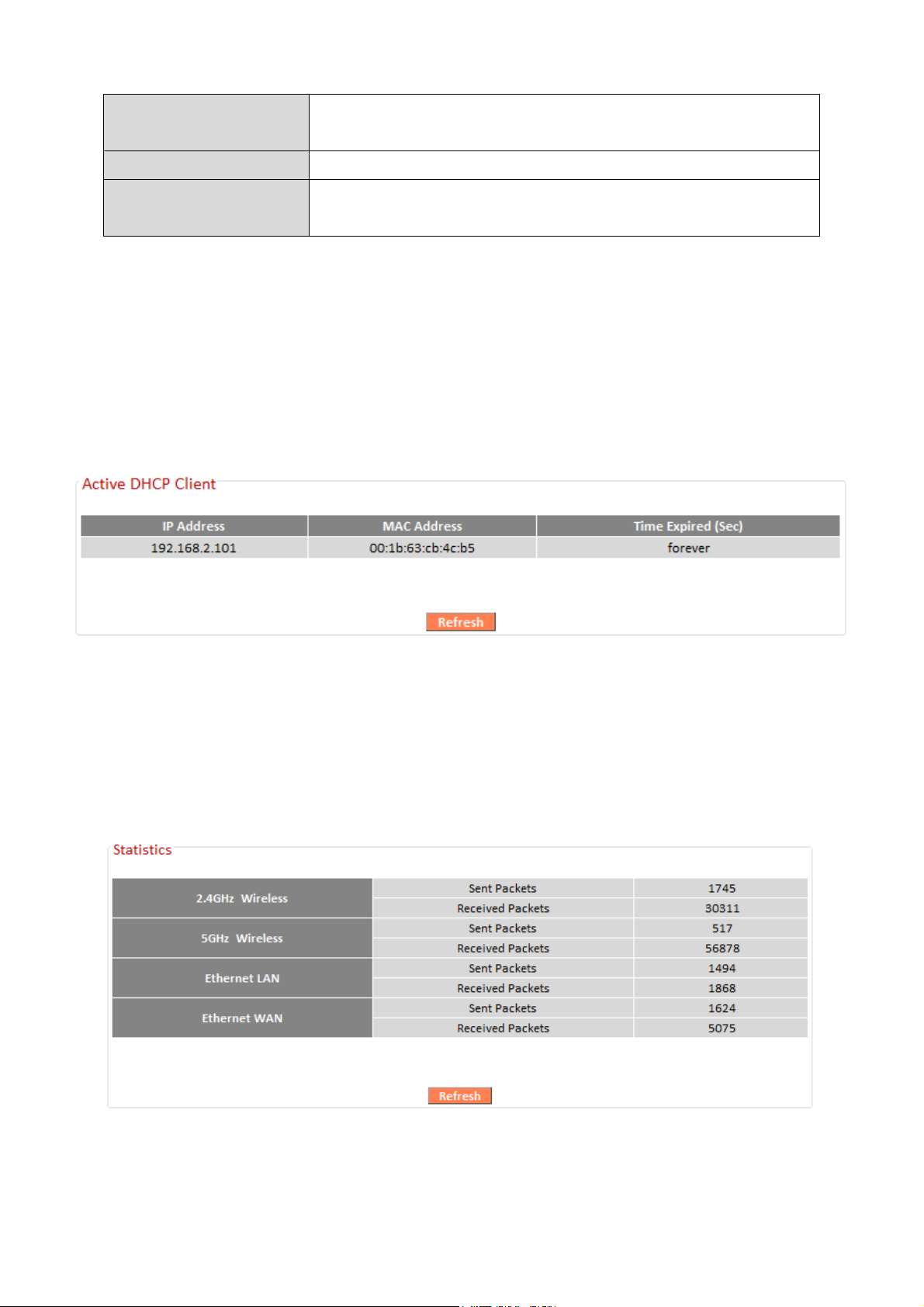
III-3-9-8. Active DHCP Client
Information about active DHCP clients is shown in the table, which displays
the DHCP server assigned IP address, MAC address and time expired for
each computer or device on the local network.
III-3-9-9. Statistics
Displays sent and received packet network statistics.
110
Page 3
IV. Appendix
IV-1. Configuring your IP address
For first time access to the URL http://edimax.setup please ensure your
computer is set to use a dynamic IP address. This means your computer can
obtain an IP address automatically from a DHCP server. You can check if your
computer is set to use a dynamic IP address by following IV-1-1. How to check
that your computer uses a dynamic IP address.
Static IP users can also temporarily modify your computer’s IP address to be
in the same IP address subnet e.g. 192.168.2.x (x = 3 – 254) as the
BR-6288ACL in order to access http://edimax.setup.
The BR-6288ACL’s default IP address is 192.168.2.1.
The procedure for modifying your IP address varies across different operating
systems; please follow the guide appropriate for your operating system in
IV-1-2. How to modify the IP address of your computer.
Static IP users please make a note of your static IP before you
change it.
You can assign a new IP address to the device which is within the subnet of
your network during setup or using the browser based configuration interface
(refer to III-3-4. LAN). Then you can access the URL http://edimax.setup in
future without modifying your IP address.
Please remember to change your IP address back to its original
value after the device is properly configured.
111
Page 4
IV-1-1. How to check that your computer uses a dynamic IP address
Please follow the instructions appropriate for your operating system.
IV-1-1-1. Windows XP
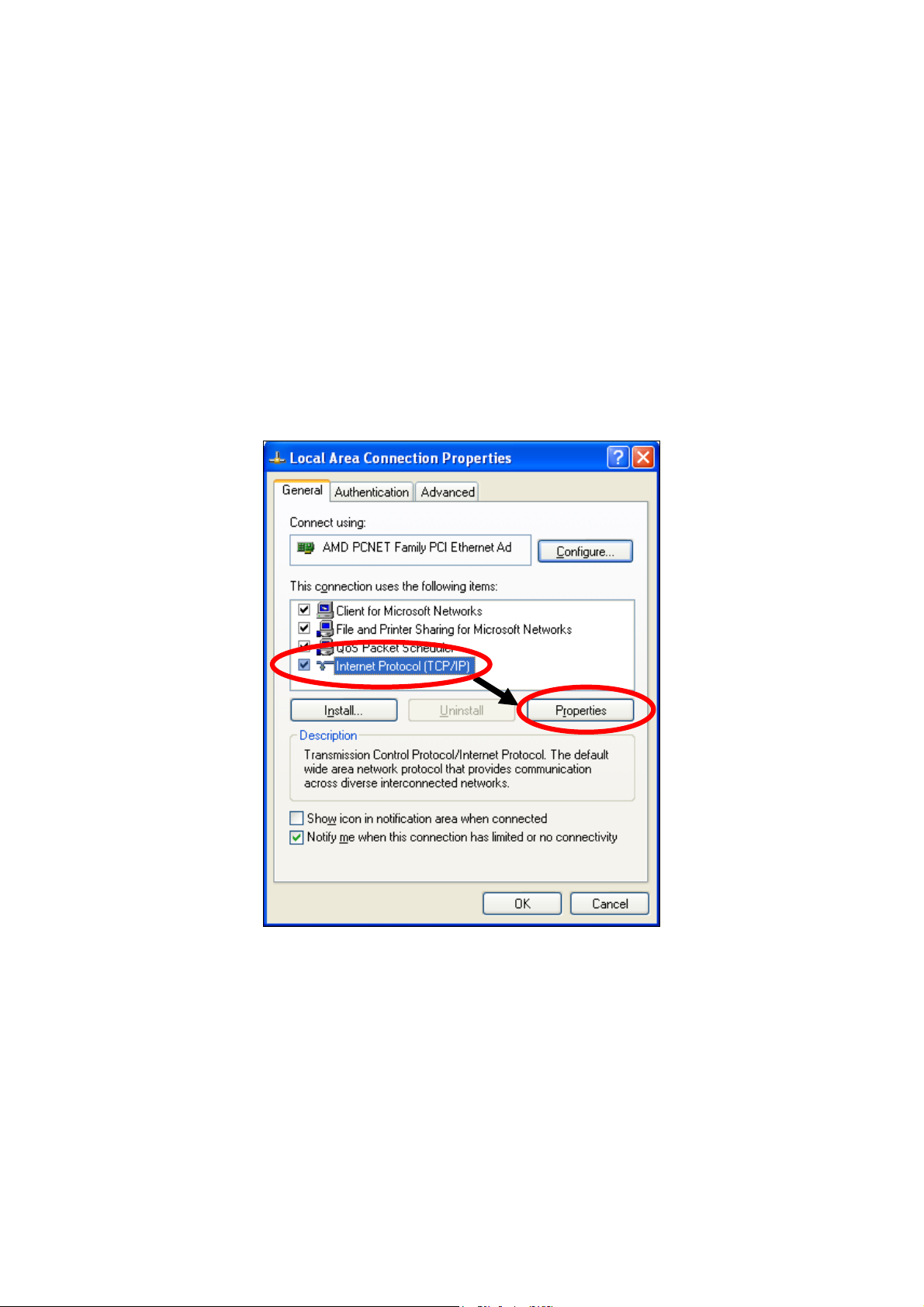
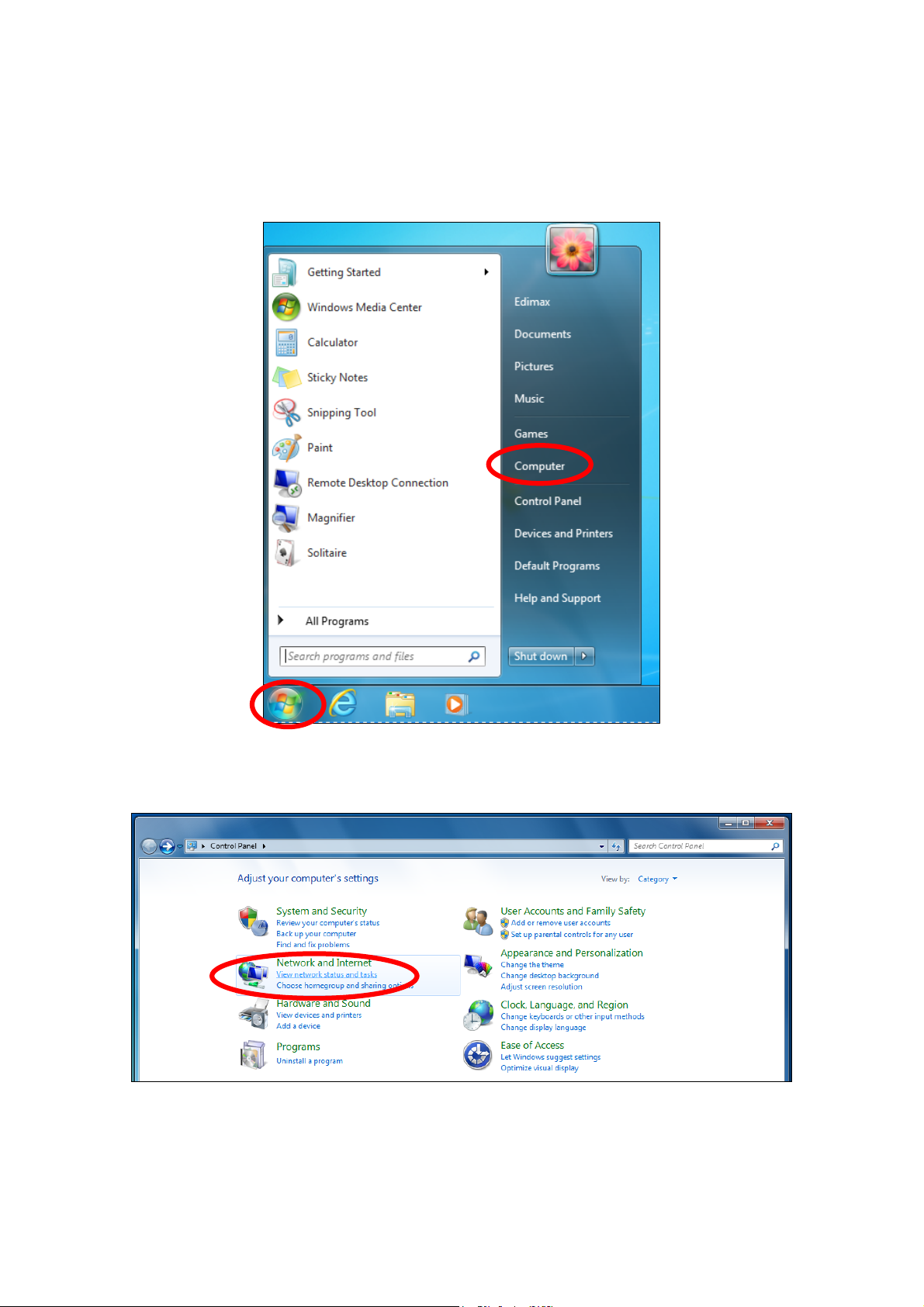
1. Click the “Start” button (it should be located in the lower-left corner of
your computer), then click “Control Panel”. Double-click the “Network and
Internet Connections” icon, click “Network Connections”, and then
double-click “Local Area Connection”. The “Local Area Connection Status”
window will then appear, click “Properties”.
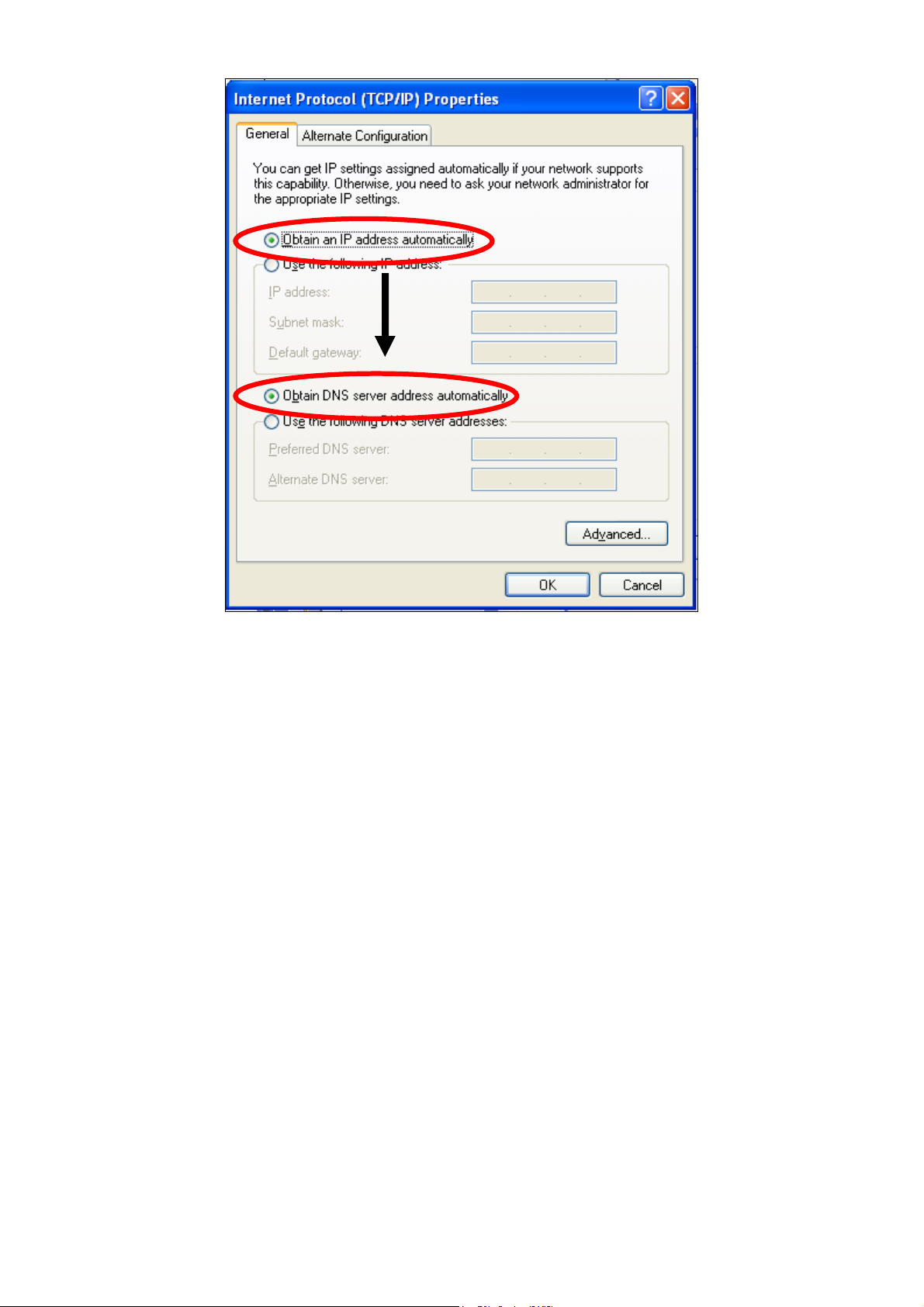
2. “Obtain an IP address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server address
automatically” should be selected.
112
Page 5
113
Page 6
IV-1-1-2. Windows Vista
1. Click the “Start” button (it should be located in the lower-left corner of
your computer), then click “Control Panel”. Click “View Network Status and
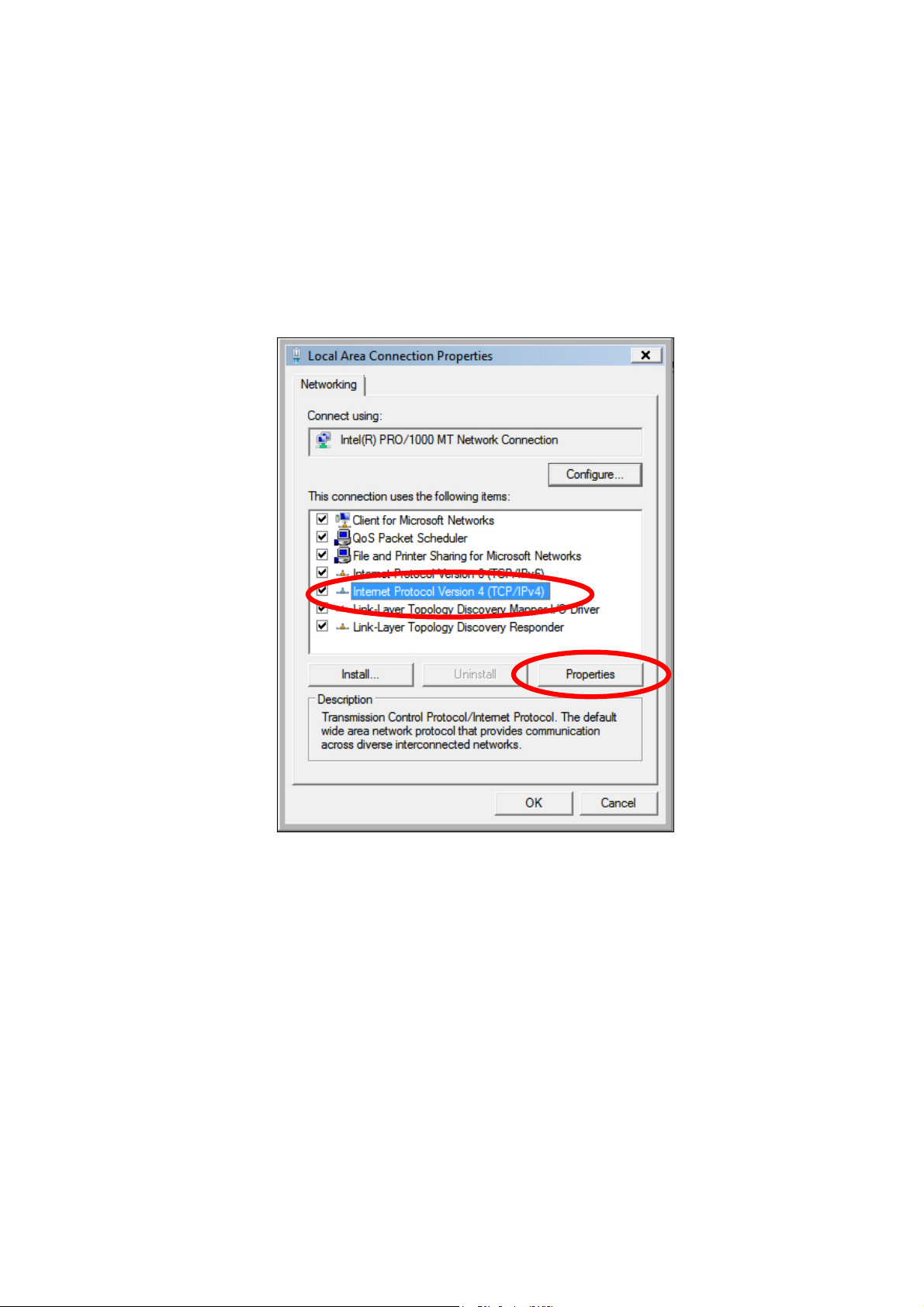
Tasks”, then click “Manage Network Connections”. Right-click “Local Area
Network”, then select “Properties”. The “Local Area Connection Properties”
window will then appear, select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP / IPv4)”,
and then click “Properties”.
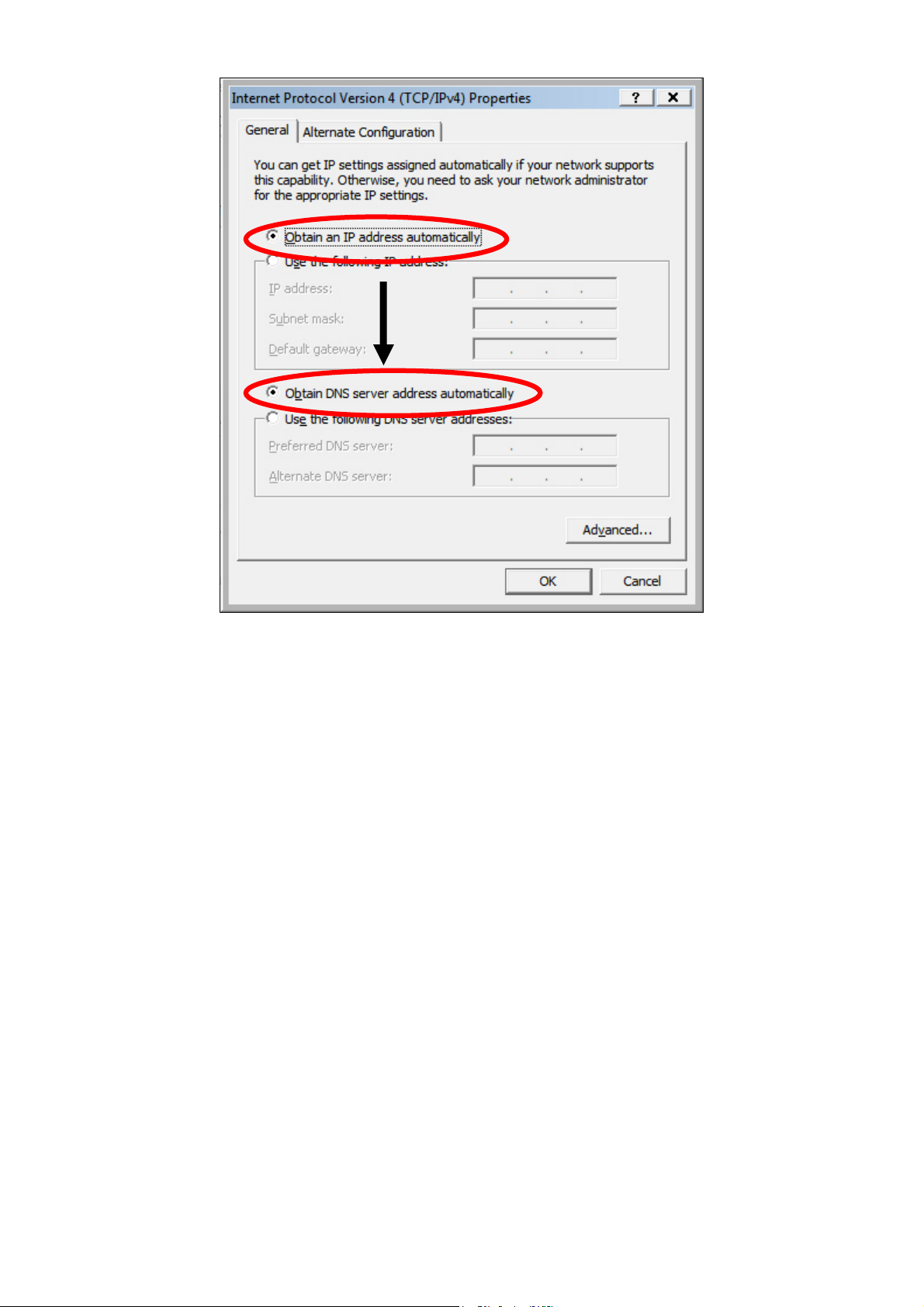
2. Select “Obtain an IP address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server
address automatically” should be selected.
114
Page 7
115
Page 8
IV-1-1-3. Windows 7
1. Click the “Start” button (it should be located in the lower-left corner of
your computer), then click “Control Panel”.
2. Under “Network and Internet” click “View network status and tasks”.
3. Click “Local Area Connection”.
116
Page 9
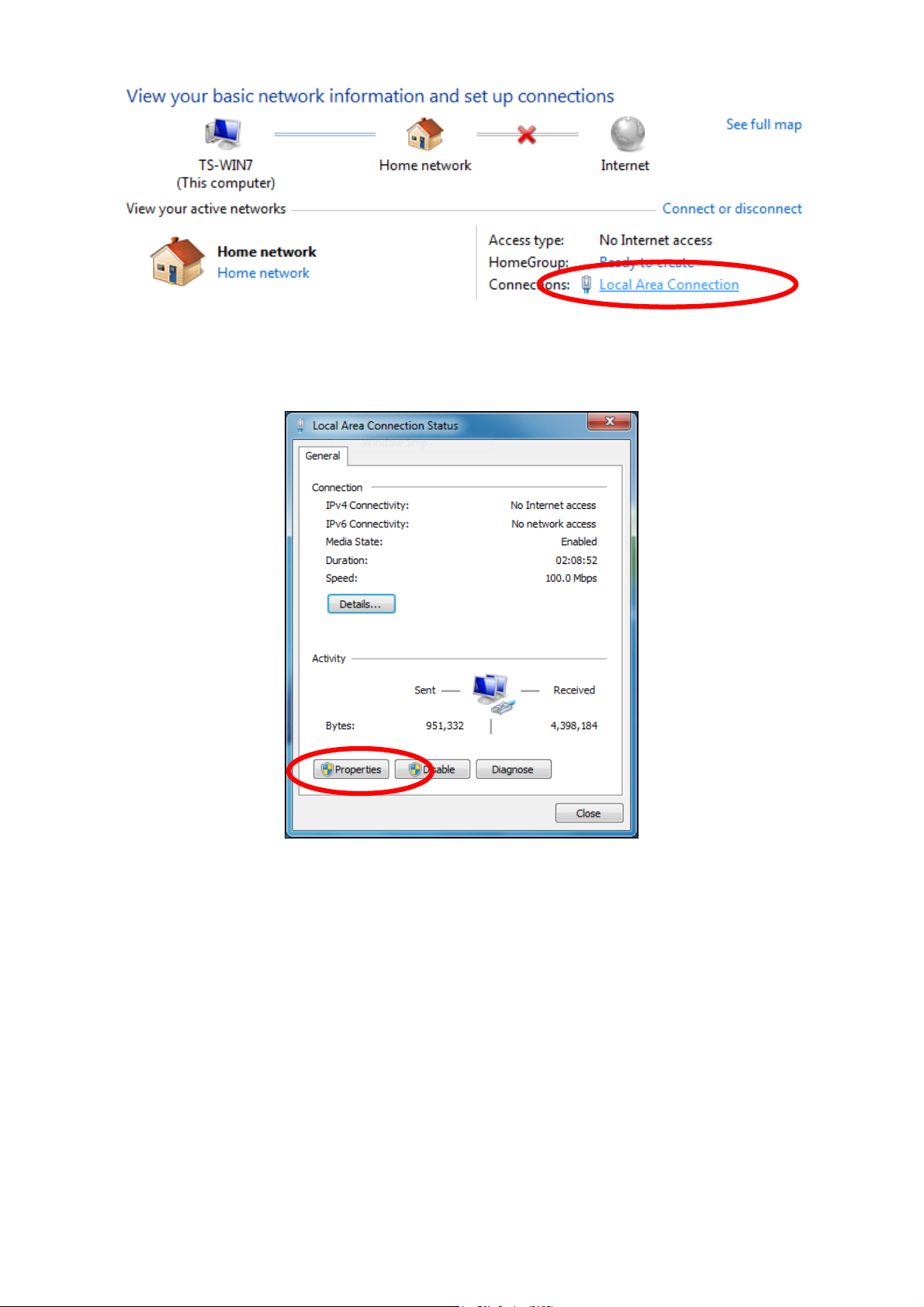
4. Click “Properties”.
5. Select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and then click “Properties”.
117
Page 10
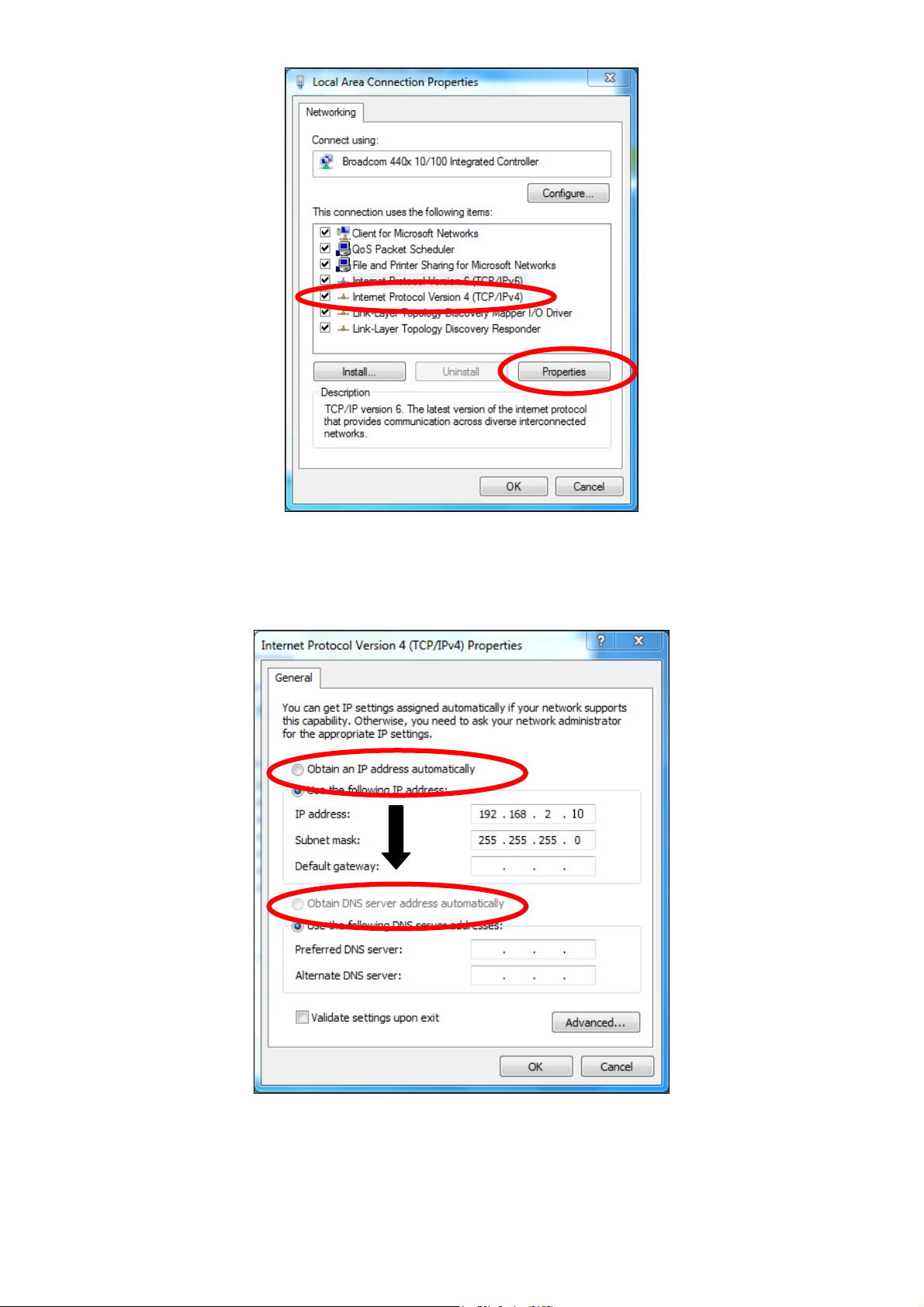
6. Select “Obtain an IP address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server
address automatically” should be selected.
118
Page 11
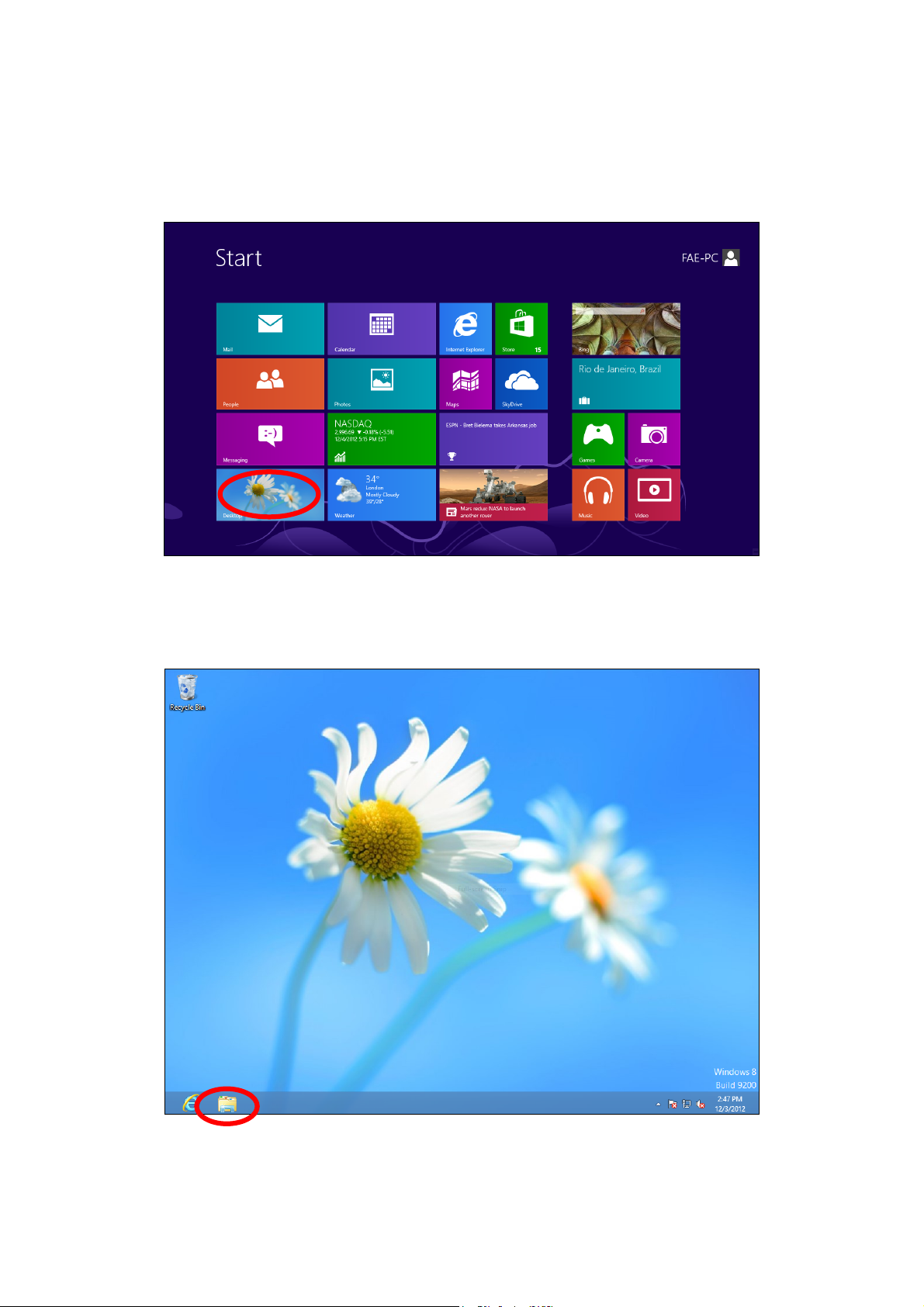
IV-1-1-4. Windows 8
1. From the Windows 8 Start screen, you need to switch to desktop mode.
Move your curser to the bottom left of the screen and click.
2. In desktop mode, click the File Explorer icon in the bottom left of the
screen, as shown below.
3. Right click “Network” and then select “Properties”.
119
Page 12
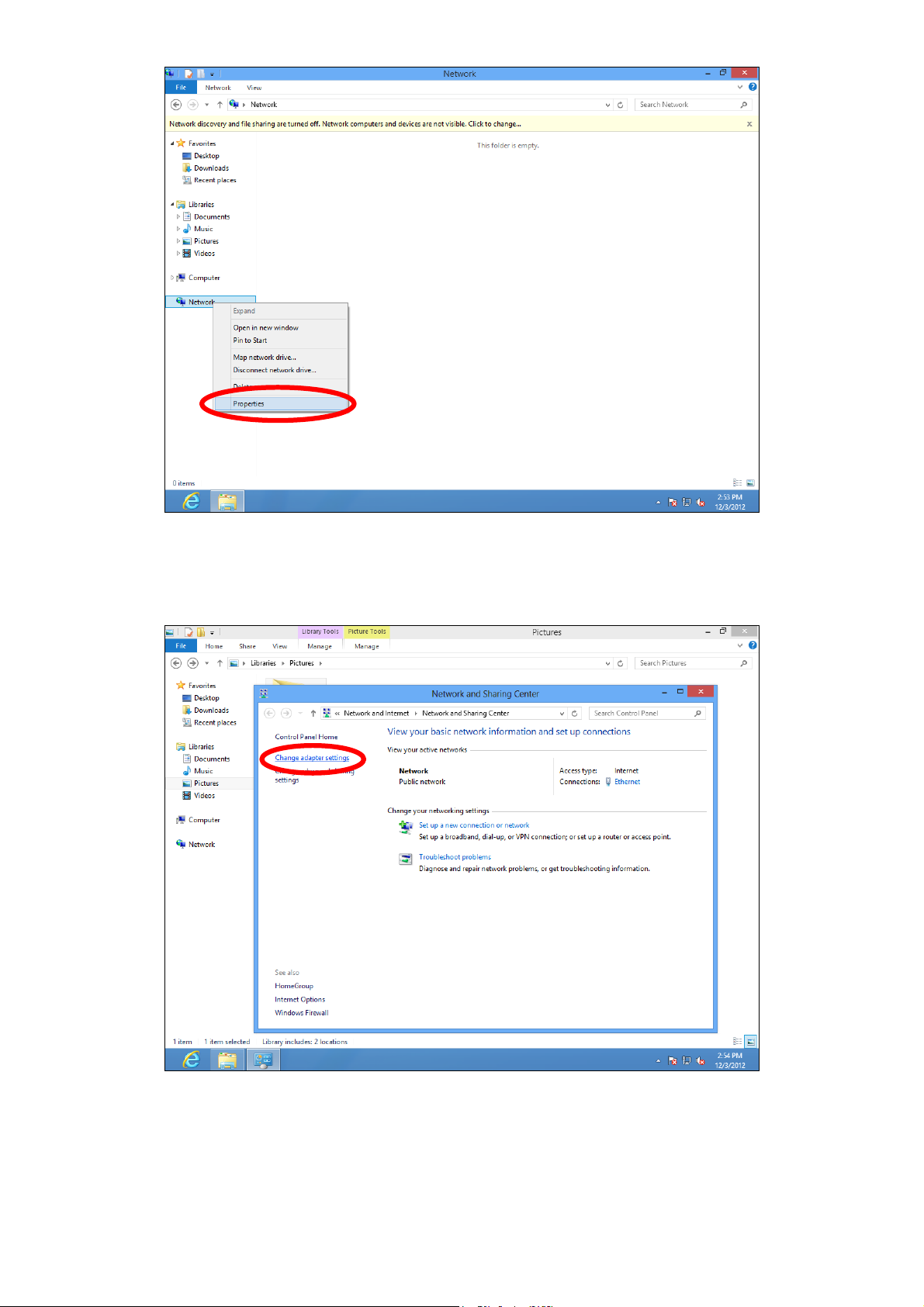
4. In the window that opens, select “Change adapter settings” from the left
side.
5. Choose your connection and right click, then select “Properties”.
120
Page 13
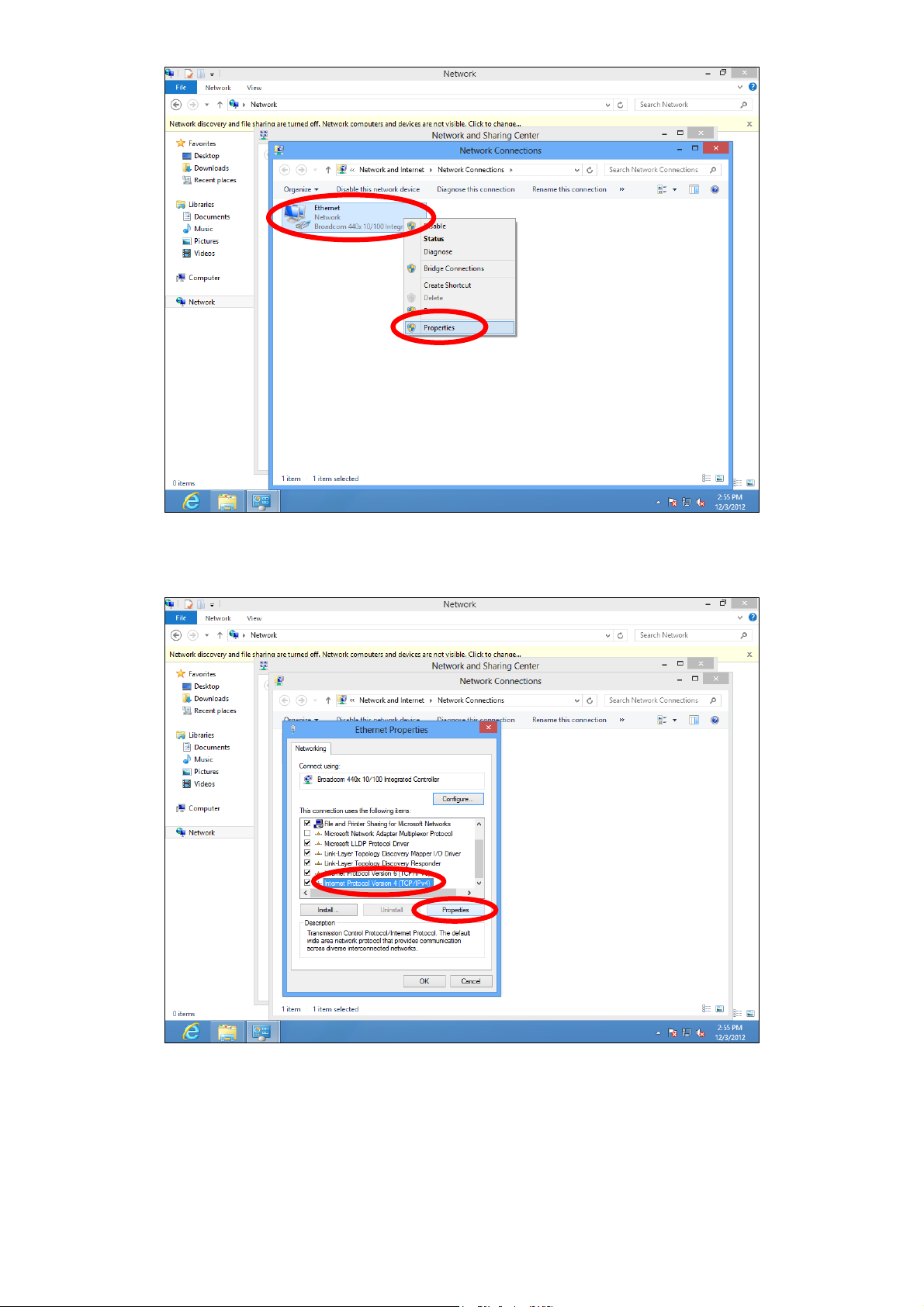
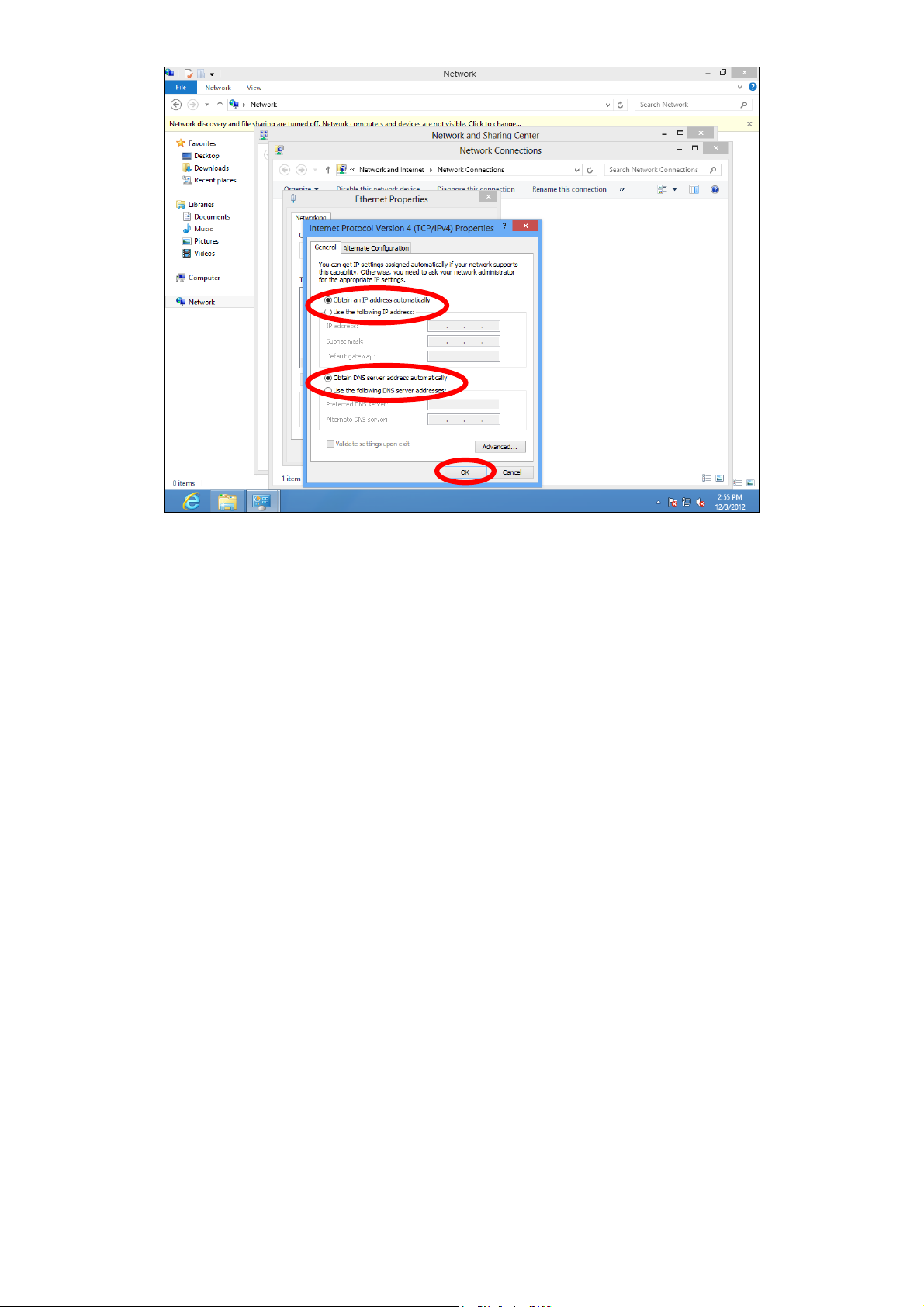
6. Select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and then click “Properties”.
7. Select “Obtain an IP address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server
address automatically” should be selected.
121
Page 14
122
Page 15
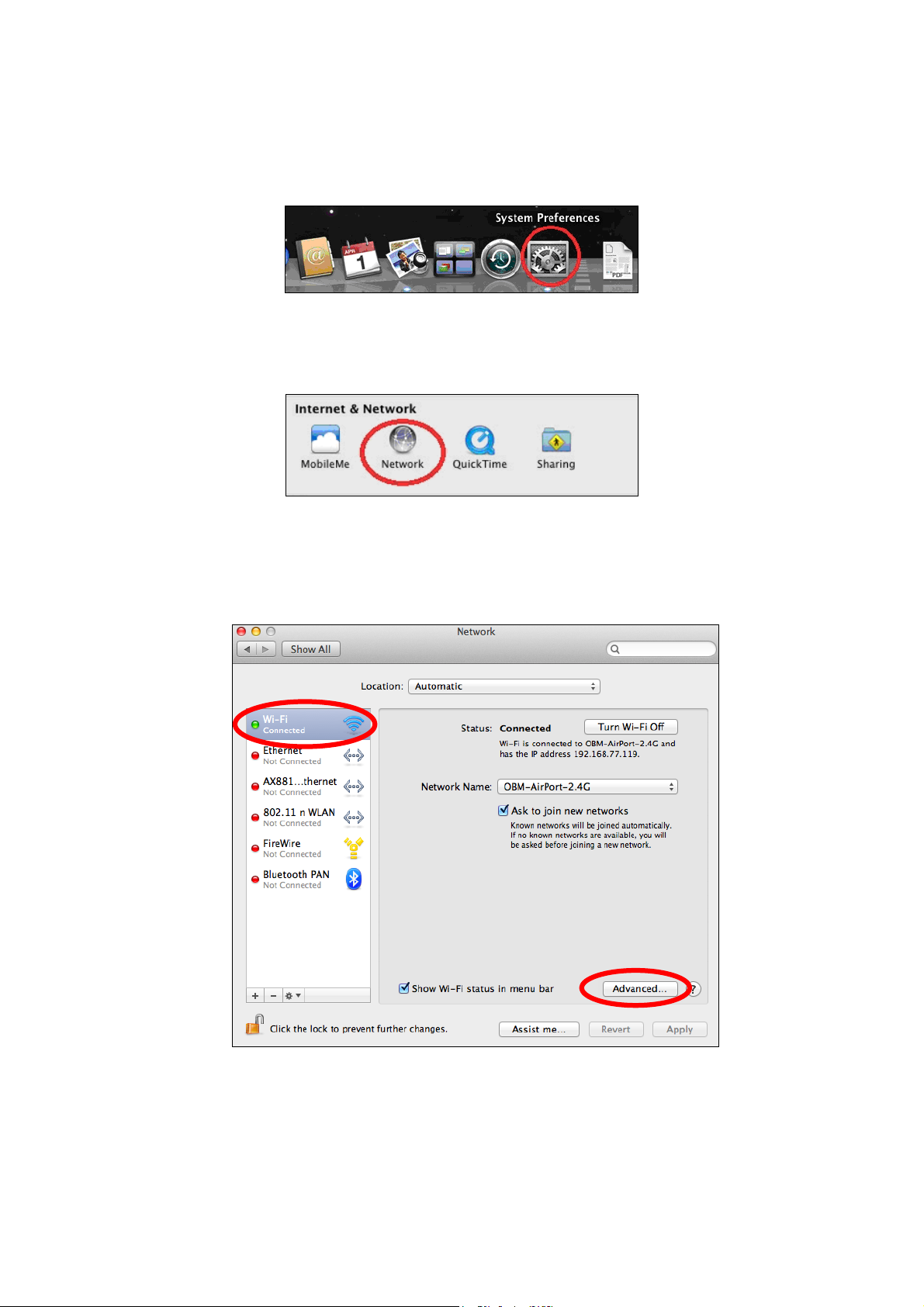
IV-1-1-5. Mac OS
1. Have your Macintosh computer operate as usual, and click on “System
Preferences”.
2. In System Preferences, click on “Network”.
3. Click on “Wi-Fi” in the left panel and then click “Advanced” in the lower
right corner.
4. Select “TCP/IP” from the top menu and “Using DHCP” in the drop down
menu labeled “Configure IPv4” should be selected.
123
Page 16

124
Page 17
IV-1-2. How to modify the IP address of your computer
Please follow the instructions appropriate for your operating system. In the
following examples we use the IP address 192.168.2.10 though you can use
any IP address in the range 192.168.2.x (x = 3 – 254) in order to access iQ
Setup/browser based configuration interface.
Please make a note of your static IP before you change it.
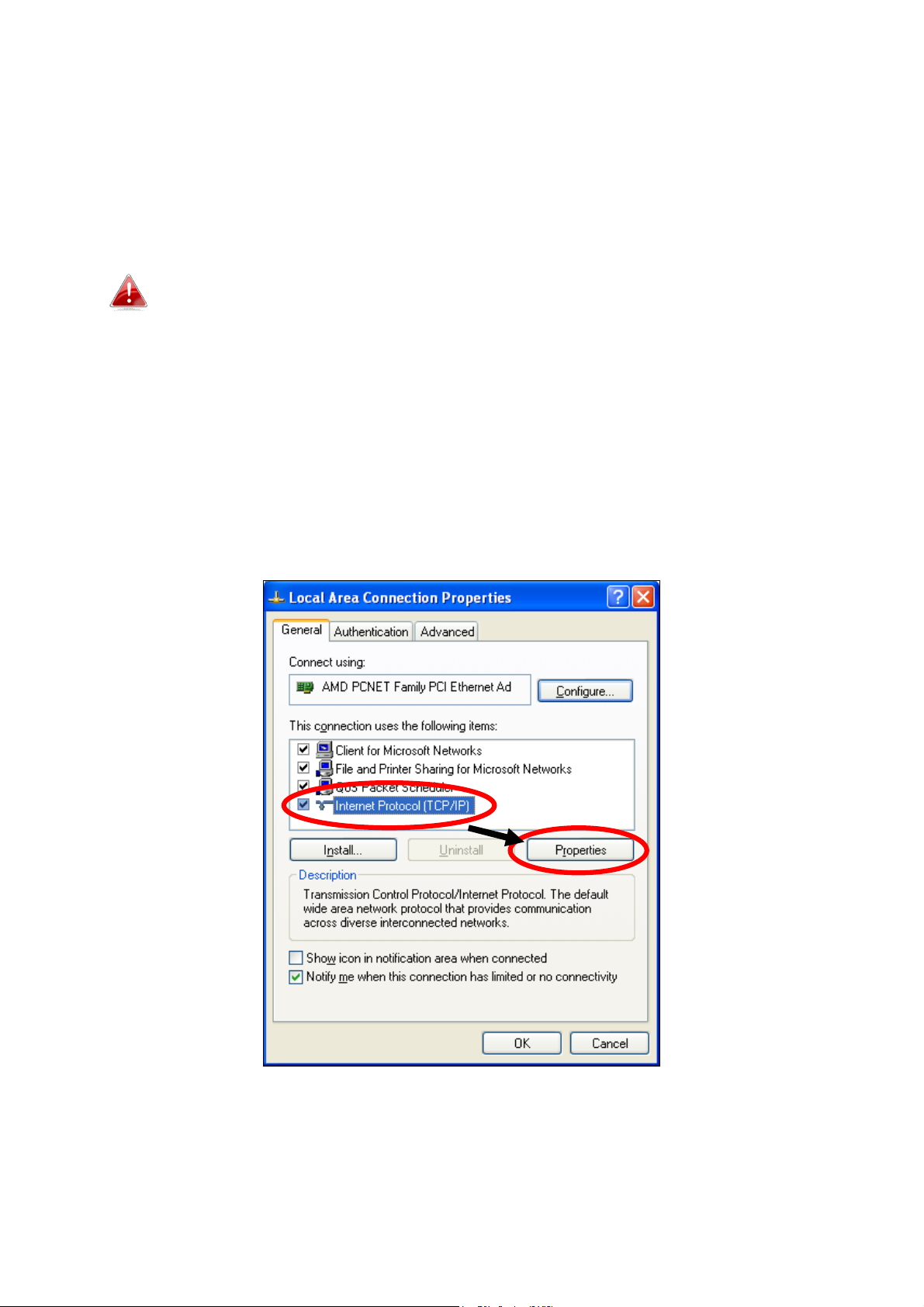
IV-1-2-1. Windows XP
1. Click the “Start” button (it should be located in the lower-left corner of
your computer), then click “Control Panel”. Double-click the “Network and
Internet Connections” icon, click “Network Connections”, and then
double-click “Local Area Connection”. The “Local Area Connection Status”
window will then appear, click “Properties”.
2. Select “Use the following IP address” and “Use the following DNS server
addresses”, then input the following values:
125
Page 18

Your existing static IP address will be displayed in the “IP
address” field before you replace it. Please make a note of this IP
address, subnet mask, default gateway and DNS server
addresses.
IP address: 192.168.2.10
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Preferred DNS Server: 192.168.2.1
Click ‘OK’ when finished.
126
Page 19

IV-1-2-2. Windows Vista
1. Click the “Start” button (it should be located in the lower-left corner of
your computer), then click “Control Panel”. Click “View Network Status and
Tasks”, then click “Manage Network Connections”. Right-click “Local Area
Network”, then select “Properties”. The “Local Area Connection Properties”
window will then appear, select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP / IPv4)”,
and then click “Properties”.
2. Select “Use the following IP address” and “Use the following DNS server
addresses”, then input the following values:
Your existing static IP address will be displayed in the “IP address”
field before you replace it. Please make a note of this IP address,
subnet mask, default gateway and DNS server addresses.
IP address: 192.168.2.10
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Preferred DNS Server: 192.168.2.1
Click ‘OK’ when finished.
127
Page 20

IV-1-2-3. Windows 7
1. Click the “Start” button (it should be located in the lower-left corner of
your computer), then click “Control Panel”.
2. Under “Network and Internet” click “View network status and tasks”.
128
Page 21

3. Click “Local Area Connection”.
4. Click “Properties”.
129
Page 22

5. Select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and then click “Properties”.
6. Select “Use the following IP address” and “Use the following DNS server
addresses”, then input the following values:
Your existing static IP address will be displayed in the “IP
address” field before you replace it. Please make a note of this IP
address, subnet mask, default gateway and DNS server
addresses.
IP address: 192.168.2.10
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Preferred DNS Server: 192.168.2.1
Click ‘OK’ when finished.
130
Page 23

IV-1-2-4. Windows 8
1. From the Windows 8 Start screen, you need to switch to desktop mode.
Move your curser to the bottom left of the screen and click.
2. In desktop mode, click the File Explorer icon in the bottom left of the
screen, as shown below.
131
Page 24

3. Right click “Network” and then select “Properties”.
4. In the window that opens, select “Change adapter settings” from the left
side.
132
Page 25

5. Choose your connection and right click, then select “Properties”.
133
Page 26

6. Select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and then click “Properties”.
7. Select “Use the following IP address” and “Use the following DNS server
addresses”, then input the following values:
Your existing static IP address will be displayed in the “IP
address” field before you replace it. Please make a note of this IP
address, subnet mask, default gateway and DNS server
addresses.
IP address: 192.168.2.10
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Preferred DNS Server: 192.168.2.1
Click ‘OK’ when finished.
134
Page 27

IV-1-2-5. Mac
1. Have your Macintosh computer operate as usual, and click on “System
Preferences”
2. In System Preferences, click on “Network”.
3. Click on “Wi-Fi” in the left panel and then click “Advanced” in the lower
right corner.
4. Select “TCP/IP” from the top menu and select “Manually” from the drop
down menu labeled “Configure IPv4”, then click “OK”.
135
Page 28

Your existing static IP address will be displayed in the “IP
address” field before you replace it. Please make a note of this IP
address, subnet mask, default gateway and DNS server
addresses.
5. In the “IPv4 Address” and “Subnet Mask” field enter IP address
192.168.2.10 and subnet mask 255.255.255.0. Click on “OK”.
136
Page 29

6. Click “Apply” to save the changes.
137
Page 30

IV-1-3. How to Find Your Network Security Key
To find your network security key, please follow the instructions appropriate
for your operating system.
If you are using Windows XP or earlier, please contact your ISP or
router manufacturer to find your network security key.
IV-1-3-1. Windows 7 & Vista
1. Open “Control Panel” and click on “Network and Internet” in the top
menu.
2. Click on “View network status and tasks” which is under the heading
“Network and Sharing Center”.
138
Page 31

3. Click on “Manage wireless networks” in the left menu.
4. You should see the profile of your Wi-Fi network in the list. Right click on
your Wi-Fi network and then click on “Properties”.
5. Click on the “Security” tab, and then check the box labeled “Show
characters”. This will show your network security key. Click the “Cancel”
button to close the window.
139
Page 32

IV-1-3-2. Mac
1. Open a new Finder window, and select “Applications” from the menu on
the left side. Open the folder labeled “Utilities” and then open the
application “Keychain Access”.
2. Select “Passwords” from the sub-menu labeled “Category” on the left side,
as shown below. Then search the list in the main panel for the SSID of your
network. In this example, the SSID is “EdimaxWireless” – though your SSID
will be unique to your network.
140
Page 33

3. Double click the SSID of your network and you will see the following
window.
4. Check the box labeled “Show password” and you will be asked to enter
your administrative password, which you use to log into your Mac. Enter
your password and click “Allow”.
141
Page 34

Your network security password will now be displayed in the field next to
the box labeled “Show password”. In the example below, the network
security password is “edimax1234”. Please make a note of your network
security password.
142
Page 35

IV-1-4. How to Find Your Router’s IP Address
To find your router’s IP address, please follow the instructions appropriate for
your operating system.
IV-1-4-1. Windows XP, Vista & 7
1. Go to “Start”, select “Run” and type “cmd”, then press Enter or click “OK”.
2. A new window will open, type “ipconfig” and press Enter.
143
Page 36

3. Your router’s IP address will be displayed next to “Default Gateway”.
144
Page 37

IV-1-4-2. Windows 8
1. From the Windows 8 Start screen, move your curser to the top right
corner of the screen to display the Charms bar.
2. Click “Search” and enter “cmd” into the search bar. Click the “Command
Prompt” app which be displayed on the left side.
145
Page 38

3. A new window will open, type “ipconfig” and press Enter.
146
Page 39

4. Your router’s IP address will be displayed next to “Default Gateway”.
147
Page 40

IV-1-4-3. Mac
1. Launch “System Preferences” and click on “Network”.
2. If you are using an Ethernet cable to connect to your network, your
router’s IP address will be displayed next to “Router”.
3. If you are using Wi-Fi, click “Wi-Fi” in the left panel, and then “Advanced”
in the bottom right corner.
148
Page 41

4. Click the “TCP/IP” tab and your router’s IP address will be displayed next
to “Router”.
149
Page 42

IV-2. Connecting to a Wi-Fi network
For help connecting to your device’s Edimax.Setup SSID for initial setup, or to
connect to your device’s new Wi-Fi network (SSID) after setup is complete,
follow the guide below:
Below is an example of how to connect using Windows Vista – the
process may vary slightly for other versions of Windows.
1. Click the network icon ( , or ) in the system tray and select “Connect
to a network”.
2. Search for the SSID of your BR-6288ACL and then click “Connect”. If you
set a password for your network, you will then be prompted to enter it.
150
Page 43

3. After correctly entering your password, you will be successfully connected
to the BR-6288ACL’s wireless network.
151
Page 44

IV-3. Troubleshooting
1. In range extender mode, is my BR-6288ACL dual-band?
a. Yes. The BR-6288ACL can extend 2.4GHz & 5GHz Wi-Fi signals concurrently, but
you must connect your BR-6288ACL to each (2.4GHz & 5GHz) network
separately during iQ setup. During iQ Setup, you will be asked to select both a
2.4GHz & 5GHz Wi-Fi network to extend, as well as specify a new SSID (name)
and password for each of the networks that your BR-6288ACL’s will
broadcast/extend.
You can disable either 2.4GHz or 5GHz Wi-Fi during iQ setup if
there is no appropriate source network available, or if you do not
wish to use it. If either the 2.4GHz or 5GHz frequency band is
disabled, wireless clients/devices on the same frequency band will
be unable to connect to your range extender.
2. In range extender mode, if my BR-6288ACL is set up as a
dual-band extender, what happens when I connect a wired
Ethernet client?
a. When you connect a network device to your BR-6288ACL in range extender
mode via Ethernet cable, by default the network device will connect to the 5GHz
network. If there is no 5GHz network available, the network device will connect
to the 2.4GHz network instead.
3. In range extender mode, how do I connect to a network which
has a hidden SSID?
a. During iQ Setup, you can manually enter a SSID in the “Wi-Fi network name”
field as shown below, for either/both 2.4GHz and 5GHz, along with the relevant
encryption information.
152
Page 45

hidden network.
existing router’s SSID (above) +"_2EX".
your existing, hidden network.
Wi-Fi network name Enter the SSID (network name) of your existing,
Range extender SSID Enter an SSID for the BR-6288ACL or leave it
blank to use a default which consists of your
Encryption Select and enter the encryption information for
4. I can’t access the Internet.
a. Ensure that all cables are connected properly. Try a different Ethernet cable.
b. Check if you can access the web based configuration interface. If not, please
ensure your Wi-Fi device is set to use a dynamic IP address. If you are unsure
how to do this, try using a computer and refer to the user manual for guidance.
c. Login to the web based configuration interface and go to Internet > WAN Setup
and check that the connection type is correct. If you are unsure which internet
connection type you have, please contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
d. Connect a computer directly to your modem and check if you can access the
internet. If you can’t, please contact your Internet service provider for
assistance.
5. I can’t open the web based configuration interface.
a. Please ensure your Wi-Fi device is set to use a dynamic IP address. If you are
unsure how to do this, try using a computer and refer to IV-1-1. How to check
that your computer uses a dynamic IP address.
153
Page 46

6. I forgot my password.
a. Reset the router to its factory default settings and use the default username
admin and default password 1234.
7. My BR-6288ACL has a weak wireless signal.
Weak signals are usually caused by interference from other devices or obstacles
blocking the BR-6288ACL’s wireless signal:
a. Keep the device away from other radio devices such as microwaves or cordless
phones.
b. Do not put the device in the corner of a room or under/nearby metal.
c. Ensure there are as few obstacles as possible between the BR-6288ACL and your
wireless network device.
In range extender mode, the BR-6288ACL’s weak wireless signal may be in turn
caused by a weak signal from your existing router. It’s important to choose a good
location for the BR-6288ACL in relation to your existing wireless router. The best
location is roughly in the middle between your existing wireless router and the area
you would like to be covered by the BR-6288ACL. If you are too far away from your
existing router, then it is difficult for the BR-6288ACL to receive a wireless signal.
8. A firmware upgrade failed and the BR-6288ACL isn’t working.
Firmware upgrade failures can happen occasionally due to power cuts or
unstable connections. In this scenario, you need to first connect a computer to
one of your BR-6288ACL’s LAN ports using an Ethernet cable. Then you need to
modify your computer’s IP address to 192.168.2.x where x is any value between
3 and 254. Refer to IV-1-2. How to modify the IP address of your computer if you
need guidance to do so.
From there, you need to go to 192.168.2.1 in a web browser, and you will see
the page below:
154
Page 47

Click “Browse” to locate the firmware file on your computer and then click
“Upload” to upload the new firmware. It may take several minutes to complete,
please wait and follow the instructions on screen.
155
Page 48

V. Glossary
Default Gateway (Wireless bridge): Every non-access point IP device needs to
configure a default gateway’s IP address. When the device sends out an IP
packet, if the destination is not on the same network, the device has to send
the packet to its default gateway, which will then send it out towards the
destination.
DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. This protocol automatically gives
every computer on your home network an IP address.
DNS Server IP Address: DNS stands for Domain Name System, which allows
Internet servers to have a domain name (such as www.Broadbandaccess
point.com) and one or more IP addresses (such as 74.125.128.104). A DNS
server keeps a database of Internet servers and their respective domain
names and IP addresses, so that when a domain name is requested (as in
typing "Broadbandaccess point.com" into your Internet browser), the user is
sent to the proper IP address. The DNS server IP address used by the
computers on your home network is the location of the DNS server your ISP
has assigned to you.
DSL Modem: DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line. A DSL modem uses your
existing phone lines to transmit data at high speeds.
Ethernet: A standard for computer networks. Ethernet networks are
connected by special cables and hubs, and move data around at up to 10/100
million bits per second (Mbps).
IP Address and Network (Subnet) Mask: IP stands for Internet Protocol. An IP
address consists of a series of four numbers separated by periods, that
identifies a single, unique Internet computer host in an IP network. Example:
192.168.2.1. It consists of 2 portions: the IP network address, and the host
identifier.
The IP address is a 32-bit binary pattern, which can be represented as four
cascaded decimal numbers separated by “.”: aaa.aaa.aaa.aaa, where each
“aaa” can be anything from 000 to 255, or as four cascaded binary numbers
separated by “.”: bbbbbbbb.bbbbbbbb.bbbbbbbb.bbbbbbbb, where each “b”
can either be 0 or 1.
156
Page 49

A network mask is also a 32-bit binary pattern, and consists of consecutive
leading 1’s followed by consecutive trailing 0’s, such as
11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000. Therefore sometimes a network
mask can also be described simply as “x” number of leading 1’s.
When both are represented side by side in their binary forms, all bits in the IP
address that correspond to 1’s in the network mask become part of the IP
network address, and the remaining bits correspond to the host ID.
For example, if the IP address for a device is, in its binary form,
11011001.10110000.10010000.00000111, and if its network mask is,
11111111.11111111.11110000.00000000
It means the device’s network address is
11011001.10110000.10010000.00000000, and its host ID is,
00000000.00000000.00000000.00000111. This is a convenient and efficient
method for access points to route IP packets to their destination.
ISP Gateway Address: (see ISP for definition). The ISP Gateway Address is an
IP address for the Internet access point located at the ISP's office.
ISP: Internet Service Provider. An ISP is a business that provides connectivity
to the Internet for individuals and other businesses or organizations.
LAN: Local Area Network. A LAN is a group of computers and devices
connected together in a relatively small area (such as a house or an office).
Your home network is considered a LAN.
MAC Address: MAC stands for Media Access Control. A MAC address is the
hardware address of a device connected to a network. The MAC address is a
unique identifier for a device with an Ethernet interface. It is comprised of
two parts: 3 bytes of data that corresponds to the Manufacturer ID (unique
for each manufacturer), plus 3 bytes that are often used as the product’s
serial number.
NAT: Network Address Translation. This process allows all of the computers
on your home network to use one IP address. Using the broadband access
point’s NAT capability, you can access the Internet from any computer on
your home network without having to purchase more IP addresses from your
ISP.
157
Page 50

Port: Network Clients (LAN PC) uses port numbers to distinguish one network
Application
Protocol
Port Number
Telnet
TCP
23
FTP
TCP
21
SMTP
TCP
25
POP3
TCP
110
H.323
TCP
1720
SNMP
UCP
161
SNMP Trap
UDP
162
HTTP
TCP
80
PPTP
TCP
1723
PC Anywhere
TCP
5631
PC Anywher
e UDP
5632
application/protocol over another. Below is a list of common applications and
protocol/port numbers:
Access point: A access point is an intelligent network device that forwards
packets between different networks based on network layer address
information such as IP addresses.
Subnet Mask: A subnet mask, which may be a part of the TCP/IP information
provided by your ISP, is a set of four numbers (e.g. 255.255.255.0) configured
like an IP address. It is used to create IP address numbers used only within a
particular network (as opposed to valid IP address numbers recognized by the
Internet, which must be assigned by InterNIC).
TCP/IP, UDP: Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and
User Datagram Protocol (UDP). TCP/IP is the standard protocol for data
transmission over the Internet. Both TCP and UDP are transport layer protocol.
TCP performs proper error detection and error recovery, and thus is reliable.
UDP on the other hand is not reliable. They both run on top of the IP (Internet
Protocol), a network layer protocol.
WAN: Wide Area Network. A network that connects computers located in
geographically separate areas (e.g. different buildings, cities, countries). The
Internet is a wide area network.
158
Page 51

Web-based management Graphical User Interface (GUI): Many devices
support a graphical user interface that is based on the web browser. This
means the user can use the familiar Netscape or Microsoft Internet Explorer
to Control/configure or monitor the device being managed.
159
Page 52

COPYRIGHT
Copyright Edimax Technology Co., Ltd. all rights reserved. No part of this publication
may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated
into any language or computer language, in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, manual or otherwise, without the prior written
permission from Edimax Technology Co., Ltd.
Edimax Technology Co., Ltd. makes no representations or warranties, either expressed or
implied, with respect to the contents hereof and specifically disclaims any warranties,
merchantability, or fitness for any particular purpose. Any software described in this
manual is sold or licensed as is. Should the programs prove defective following their
purchase, the buyer (and not this company, its distributor, or its dealer) assumes the
entire cost of all necessary servicing, repair, and any incidental or consequential damages
resulting from any defect in the software. Edimax Technology Co., Ltd. reserves the right
to revise this publication and to make changes from time to time in the contents hereof
without the obligation to notify any person of such revision or changes.
The product you have purchased and the setup screen may appear slightly different from
those shown in this QIG. The software and specifications are subject to change without
notice. Please visit our website www.edimax.com for updates. All brand and product
names mentioned in this manual are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their
respective holders.
160
Page 53

Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part
15 of FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a
residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
1. Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
2. Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
3. Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
4. Consult the dealer or an experienced radio technician for help.
FCC Caution
This device and its antenna must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter. This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation. Any changes or modifications not expressly
approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the authority to operate equipment.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure set forth for an uncontrolled environment. In order to avoid
the possibility of exceeding the FCC radio frequency exposure limits, human proximity to the antenna shall not be
less than 20cm during normal operation.
The equipment version marketed in US is restricted to usage of the channels 1-11 only. This equipment is
restricted to indoor use.
R&TTE Compliance Statement
This equipment complies with all the requirements of DIRECTIVE 1999/5/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND
THE COUNCIL of March 9, 1999 on radio equipment and telecommunication terminal equipment and the mutual
recognition of their conformity (R&TTE). The R&TTE Directive repeals and replaces in the directive 98/13/EEC
(Telecommunications Terminal Equipment and Satellite Earth Station Equipment) As of April 8, 2000.
Safety
This equipment is designed with the utmost care for the safety of those who install and use it. However, special
attention must be paid to the dangers of electric shock and static electricity when working with electrical
equipment. All guidelines of this and of the computer manufacture must therefore be allowed at all times to
ensure the safe use of the equipment.
EU Countries Intended for Use
The ETSI version of this device is intended for home and office use in Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Czech,
Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta,
Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Turkey, and United Kingdom. The ETSI
version of this device is also authorized for use in EFTA member states: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and
Switzerland.
EU Countries Not Intended for Use
None
161
Page 54

EU Declaration of Conformity
English: This equipment is in compliance with the essential requirements and other relevant
provisions of Directive 1999/5/EC, 2009/125/EC.
Français: Cet équipement est conforme aux exigences essentielles et autres dispositions de la
directive 1999/5/CE, 2009/125/CE.
Čeština: Toto zařízení je v souladu se základními požadavky a ostatními příslušnými ustanoveními
směrnic 1999/5/ES, 2009/125/ES.
Polski: Urządzenie jest zgodne z ogólnymi wymaganiami oraz szczególnymi warunkami
określonymi Dyrektywą UE 1999/5/EC, 2009/125/EC.
Română: Acest echipament este în conformitate cu cerinţele esenţiale şi alte prevederi relevante ale
Directivei 1999/5/CE, 2009/125/CE.
Русский: Это оборудование соответствует основным требованиям и положениям Директивы
1999/5/EC, 2009/125/EC.
Magyar: Ez a berendezés megfelel az alapvető követelményeknek és más vonatkozó irányelveknek
(1999/5/EK, 2009/125/EC).
Türkçe: Bu cihaz 1999/5/EC, 2009/125/EC direktifleri zorunlu istekler ve diğer hükümlerle ile
uyumludur.
Українська: Обладнання відповідає вимогам і умовам директиви 1999/5/EC, 2009/125/EC.
Slovenčina: Toto zariadenie spĺňa základné požiadavky a ďalšie príslušné ustanovenia smerníc
1999/5/ES, 2009/125/ES.
Deutsch: Dieses Gerät erfüllt die Voraussetzungen gemäß den Richtlinien 1999/5/EC, 2009/125/EC.
Español: El presente equipo cumple los requisitos esenciales de la Directiva 1999/5/EC,
2009/125/EC.
Italiano: Questo apparecchio è conforme ai requisiti essenziali e alle altre disposizioni applicabili
della Direttiva 1999/5/CE, 2009/125/CE.
Nederlands: Dit apparaat voldoet aan de essentiële eisen en andere van toepassing zijnde bepalingen
van richtlijn 1999/5/EC, 2009/125/EC.
Português: Este equipamento cumpre os requesitos essênciais da Directiva 1999/5/EC, 2009/125/EC.
Norsk: Dette utstyret er i samsvar med de viktigste kravene og andre relevante regler i Direktiv
1999/5/EC, 2009/125/EC.
Svenska: Denna utrustning är i överensstämmelse med de väsentliga kraven och övriga relevanta
bestämmelser i direktiv 1999/5/EG, 2009/125/EG.
Dansk: Dette udstyr er i overensstemmelse med de væsentligste krav og andre relevante
forordninger i direktiv 1999/5/EC, 2009/125/EC.
Suomi: Tämä laite täyttää direktiivien 1999/5/EY, 2009/125/EY oleelliset vaatimukset ja muut
asiaankuuluvat määräykset.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WEEE Directive & Product Disposal
At the end of its serviceable life, this product should not be treated as household or general waste. It
should be handed over to the applicable collection point for the recycling of electrical and electronic
equipment, or returned to the supplier for disposal.
162
Page 55

Declaration of Conformity
We, Edimax Technology Co., Ltd., declare under our sole responsibility, that the
equipment described below complies with the requirements of the European R&TTE
directives.
Equipment: AC600 Multi-Function Dual-Band Wi-Fi Router
Model No.: BR-6288ACL
The following European standards for essential requirements have been followed:
Directives 1999/5/EC
Spectrum : ETSI EN 300 328 V1.8.1 (2012-06);
ETSI EN 301 893 V1.7.1 (2012-06)
EMC : EN 301 489-1 V1.9.2 (2011-09);
EN 301 489-17 V2.2.1 (2012-09);
Safety (LVD) : IEC 60950-1:2005 (2nd Edition);Am 1:2009
EN 60950-1:2006+A11:2009+A1:2010+A12:2011
Recommendation19 99/5/EC
EMF : EN 62311:2008
Directives 2006/95/EC
Safety (LVD) : IEC 60950-1:2005 (2nd Edition);Am 1:2009
EN 60950-1:2006+A11:2009+A1:2010+A12:2011
Edimax Technology Co., Ltd.
No. 3, Wu Chuan 3rd Road,
Wu-Ku Industrial Park,
New Taipei City, Taiwan
Date of Signature: Sep, 2014
Signature:
Printed Name:
Albert Chang
Title: Director
Edimax Technology Co., Ltd.
163
Page 56

164
 Loading...
Loading...