Page 1

802.11g Wireless
Converter
IEEE 802.11g
54Mbps
Page 2

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction............................................................................. 1
1.1 Package Contents.......................................................................................... 2
1.2 Features.........................................................................................................2
1.3 Specifications................................................................................................2
1.4 Physical Description .....................................................................................3
Chapter 2 Wireless Converter Connection............................................. 5
Chapter 3 Wireless Converter Configuration........................................ 6
3.1 Getting Started ..............................................................................................6
3.2 Configuring the Wireless Converter...........................................................10
3.2.1 Status and Information.......................................................................................10
3.2.2 Basic Setting ......................................................................................................10
3.2.3 Advanced Setting...............................................................................................21
3.2.4 Security ..............................................................................................................24
3.2.5 MAC Address Filtering......................................................................................44
3.2.6 System Utility ....................................................................................................46
3.2.7 Configuration Tool.............................................................................................48
3.2.8 Firmware Upgrade .............................................................................................49
3.2.9 Reset...................................................................................................................50
4. Troubleshooting.............................................................................. 51
Page 3

Introduction
Chapter 1 Introduction
This product is a wireless converter for IEEE 802.11g/b 2.4GHz wireless network. It
converts not only a computer but also several computers into wireless station and
easily connects to the wireless network without installing any software. Plug and play
is not hard to reach anymore.
This product can also setup to be a wireless Converter or a bridge among wired LANs.
With the valuable function, you can simply build up a wireless LAN network.
To secure the wireless communication, the product supports WEP, WPA, ESSID and
MAC address filter functions. With ESSID authentication, 64/128-bit WEP
encryption, WPA and MAC address filtering you can prevent unauthorized wireless
stations from accessing your wireless network.
The product’s dipole antenna is detachable by connecting to a RP-SMA connector.
Users can install a high gain antenna to the connector for better network link quality,
so that you can build wireless network with more flexibility.
This product provides easy to use user interface and allows users to configuring from
web browser. Also it integrates DHCP server to provide multiple wireless and wired
users to get their IP address automatically.
With the versatile of features, this product is the best choice for you to integrate your
wireless and wired networks seamlessly.
1
Page 4

1.1 Package Contents
The Wireless Converter includes the following items:
One Wireless Converter
One Power Adapter
One User’s Manual
1.2 Features
Comply with the IEEE 802.11g/b 2.4GHz specification.
High data rate – up to 54Mbps network speed.
Supports Plug-and-play, no software program needs to be installed.
Saving wireless device cost by converting several computers into wireless
Introduction
stations.
Auto rate fallback in case of obstacles or interferences.
Provide 64/128-bit WEP, WPA function to protect the wireless data
transmissions.
Built-in DHCP server supports auto IP addresses assignment.
Supports Web-based configuration.
1.3 Specifications
Standards: IEEE 802.11g/b (Wireless), IEEE 802.3 (Wired)
Data Rate: 54/48/36/24/18/12/11/9/6/5.5/2/1Mbps auto fallback
Security: 64/128-bit WEP, WPA
Frequency Band: 2.4000~2.4835GHz (Industrial Scientific Medical Band)
Antenna: External detachable dipole antenna (with RP-SMA connector)
Connectors: 10/100Mbps RJ-45 x 1
Power: 5VDC, 2A
Transmit Power: 16dBm~18dBm
LEDs: LAN, Ready, WLAN
Dimension: 20(H) x 58(W) x 82(D) mm
Temperature:
Operating: 32~131°F (0~55°C)
Storage: -4~158°F (-20~70°C)
2
Page 5
Introduction
Humidity: 10-90% (Noncondensing)
Certification: FCC, CE
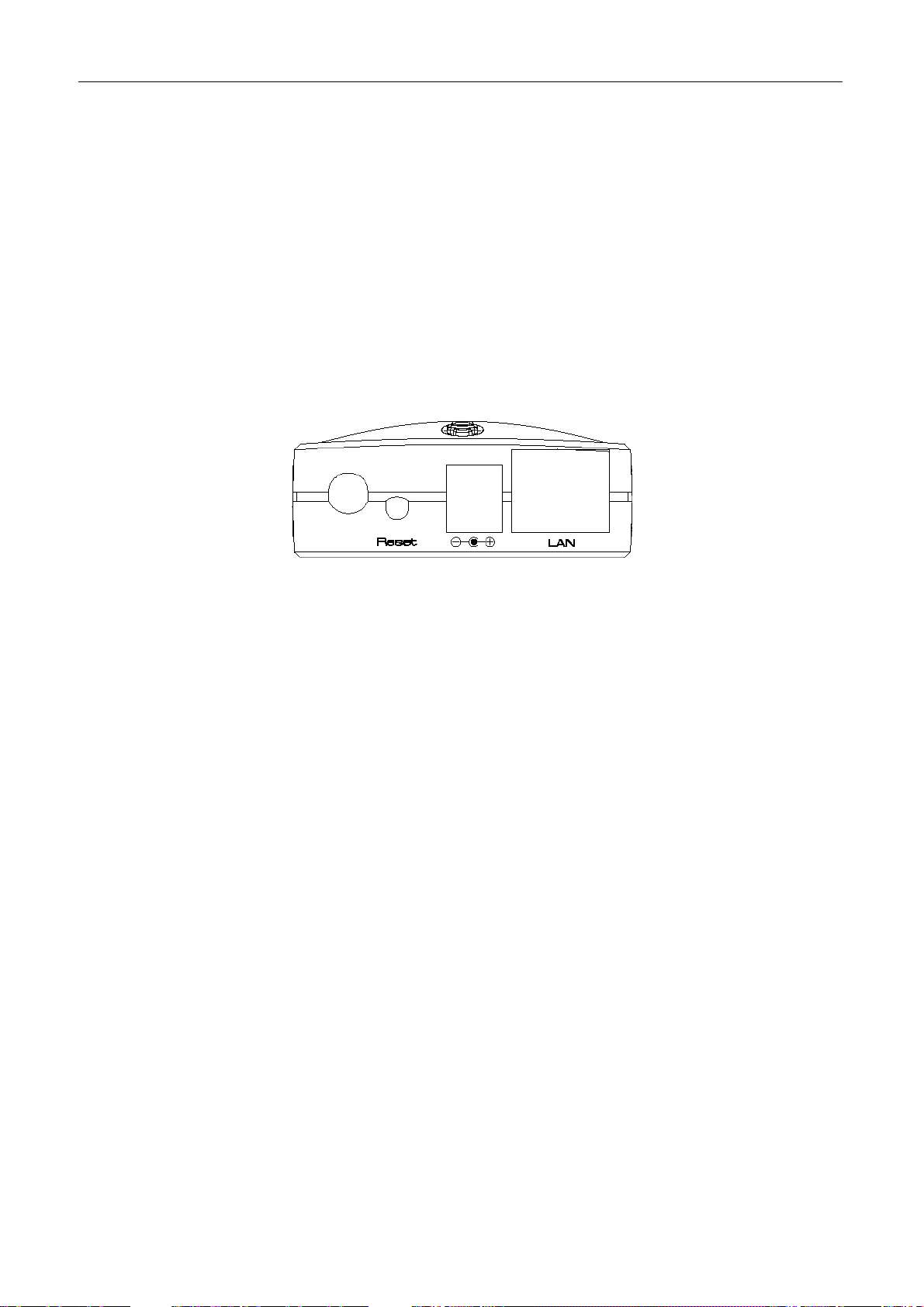
1.4 Physical Description
Connector Explanation
Please refer to the following explanation for the usage of the connectors in the
Wireless Converter.
Antenna Connector
This round connection is standard Reverse SMA connector where any antennas
with Reverse SMA connector can connect to the Wireless Converter.
Reset
The Reset button allows you to do one of two things.
1) If problems occur with your Wireless Converter, press the reset button with
a pencil tip (for less than 2 seconds) and the Wireless Converter will re-boot
itself, keeping your original configurations.
2) If problems persist or you experience extreme problems or you forgot your
password, press the reset button for longer than 5 seconds and the Wireless
Converter will reset itself to the factory default settings (warning: your
original configurations will be replaced with the factory default settings).
DC Adapter Port
Insert the power jack of the power adapter into this port.
LAN Port
3
Page 6

Introduction
The Wireless Converter’s LAN port is where you connect to your LAN’s network
devices.
LED Explanation
LED Color Status Description
Lit Wireless function is enabled.
WLAN
Green
Flash Wireless data is transmitted or received.
Off Wireless function is not enabled.
When the Wireless Converter is in “StationAd Hoc mode” or “Station-Infrastructure
mode” and is connecting to a wireless
device, “Ready” LED lit.
When the Wireless Converter is in “AP
Lit
Ready Green
mode”, “AP Bridge-Point to Point mode”,
“AP Bridge-Point to Multi-Point mode” or
“AP Bridge-WDS mode”, the “Ready” LED
lit meaning the Wireless Converter is stand
by to accept connection.
Off This Wireless Converter is not ready yet.
LAN Green
On A valid link is established.
Flash It is transmitting or receiving data.
Off No link is established.
4
Page 7

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Connection
Chapter 2 Wireless Converter
Connection
1. Locate an optimum location for the Wireless Converter.
The best location for your Wireless Converter is usually at the center of your
wireless network, with line of sight to all of your mobile stations.
2. Connect the Wireless Converter to your router, hub, switch or computer.
Connect one end of standard UTP cable to the Wireless Converter’s LAN Port
and connect the other end of the cable to a switch, a router, a hub, or a computer.
The Wireless Converter Wireless Converter will then be connected to your
existed wired LAN Network.
3. Connect the DC Power Adapter to the Wireless Converter’s Power Socket.
Only use the power adapter supplied with the Wireless Converter. Using a
different adapter may damage the product.
The Hardware Installation is complete.
5
Page 8

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Chapter 3 Wireless Converter
Configuration
3.1 Getting Started
This Wireless Converter provides web-based configuration tool allowing you to
configure from wired or wireless stations. Follow the instructions below to get started
configuration.
From Wired Station
1. Make sure your wired station is in the same subnet with the Wireless Converter.
The default IP Address and Sub Mask of the Wireless Converter is:
Default IP Address: 192.168.2.1
Default Subnet: 255.255.255.0
Configure your PC to be in the same subnet with the Wireless Converter.
1a) Windows 95/98/Me
1. Click the Start button and select Settings, then click Control Panel. The Control Panel
window will appear.
2. Double-click Network icon. The Network windo w will appear.
3. Check your list of Network Components. If TCP/IP is not installed, click the Add button to
install it now. If TCP/IP is installed, go to step 6.
4. In the Network Component Type dialog box, select Protocol and cli ck Add button.
5. In the Select Network Protocol dialog box, select Microsoft and TCP/IP and then click the
OK button to start installing the TCP/IP protocol. You may need your Windows CD to
complete the installation.
6. After installing TCP/IP, go back to the Network dialog box. Select TCP/IP from the list of
Network Components and then click the Properties button.
7. Check each of the tabs and verify the following settings:
• Bindings: Check Client for Microsoft Networks and File and printer sharing for
Microsoft Networks.
• Gateway: All fields are blank.
• DNS Configuration: Select Disable DNS.
• WINS Configuration: Select Disable WINS Resolution.
6
Page 9

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
• IP Address: Select Specify an IP Address. Specify the IP Address and Subnet Mask
as following example.
IP Address: 192.168.2.3 (any IP address within 192.168.2.2~192.168.2.254 is
available, do not setup 192.168.2.1)
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
8. Reboot the PC. Your PC will now have the IP Address you specified.
1b) Windows 2000
1. Click the Start button and select Settings, then click Control Panel. The Control Panel
window will appear.
2. Double-click Network and Dial-up Connections icon. In the Network and Dial-up
Connection window, double-click Local Area Connection icon. The Local Area Connection
window will appear.
3. In the Local Area Connection window, click the Properties button.
4. Check your list of Network Components. You should see Internet Protocol [TCP/IP] on
your list. Select it and click the Properties button.
5. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window, select Use the following IP address
and specify the IP Address and Subnet mask as following.
IP Address: 192.168.2.3 (any IP address within 192.168.2.2~192.168.2.254 is
available, do not setup 192.168.2.1)
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
6. Click OK to confirm the setting. Your PC will now have the IP Address you specified.
1c) Windows NT
1. Click the Start button and select Settings, then click Control Panel. The Control Panel
window will appear.
2. Double-click Network icon. The Network window will appea r. Select the Protocol tab from
the Network window.
3. Check if the TCP/IP Protocol is on your list of Network Protocols. If TCP/IP is not installed,
click the Add button to install it now. If TCP/IP is installed, go to step 5.
4. In the Select Network Protocol window, select the TCP/IP Protocol and click the Ok
button to start installing the TCP/IP protocol. You may need your Windows CD to
complete the installation.
5. After you install TCP/IP, go back to the Network window. Select TCP/IP from the list of
Network Protocols and then click the Properties button.
6. Check each of the tabs and verify the following settings:
7
Page 10
Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
• IP Address: Select Specify an IP address. Specify the IP Address and Subnet Mask
as following example.
IP Address: 192.168.2.3 (any IP address within 192.168.2.2~192.168.2.254 is
available, do not setup 192.168.2.1)
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
• DNS: Let all fields are blank.
• WINS: Let all fields are blank.
• Routing: Let all fields are blank.
7. Click OK to confirm the setting. Your PC will now have the IP Address you specified.
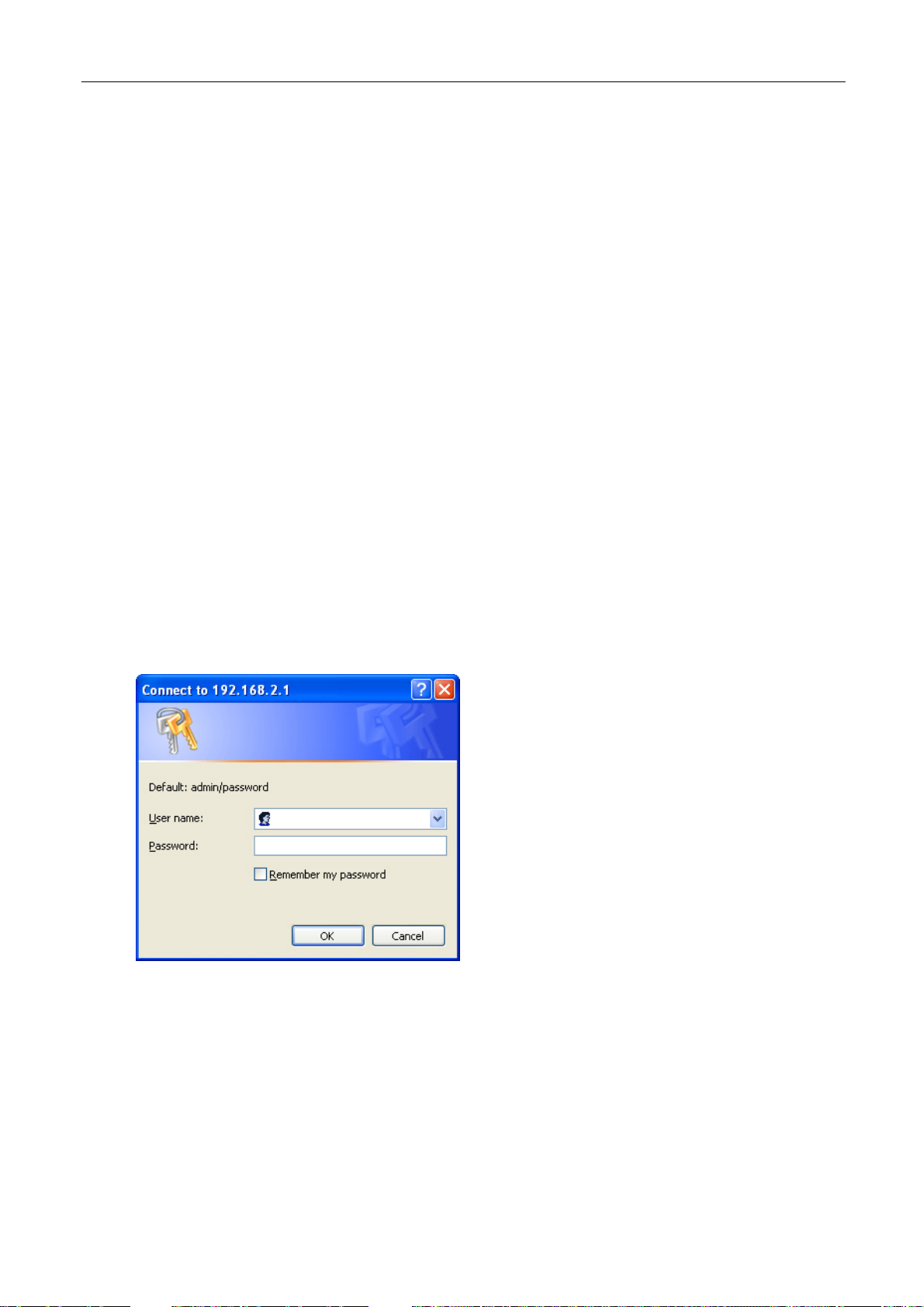
2. Enter 192.168.2.1 from Web Browser to get into the Wireless Converter’s
configuration tool.
3. A screen will be popped up and request you to enter user name and password.
The default user name and password is as follows.
User Name: Admin
Password: 1234
Enter the default user name and password, then press OK button directly.
4. You can start configuring the Wireless Converter.
From Wireless Station
1. Connect your wireless station to the same AP which the Wireless Converter is
connecting to.
8
Page 11

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
2. Make sure your wireless station is in the same subnet with the Wireless
Converter. Please refer to the step 1 above for configuring the IP Address and
Sub Mask of the wireless station.
3. Enter 192.168.2.1 from Web Browser to get into the Wireless Converter’s
configuration tool.
4. Enter the user name and password and then press OK button and you are
available to configure the Wireless Converter now.
9
Page 12
Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
3.2 Configuring the Wireless Converter
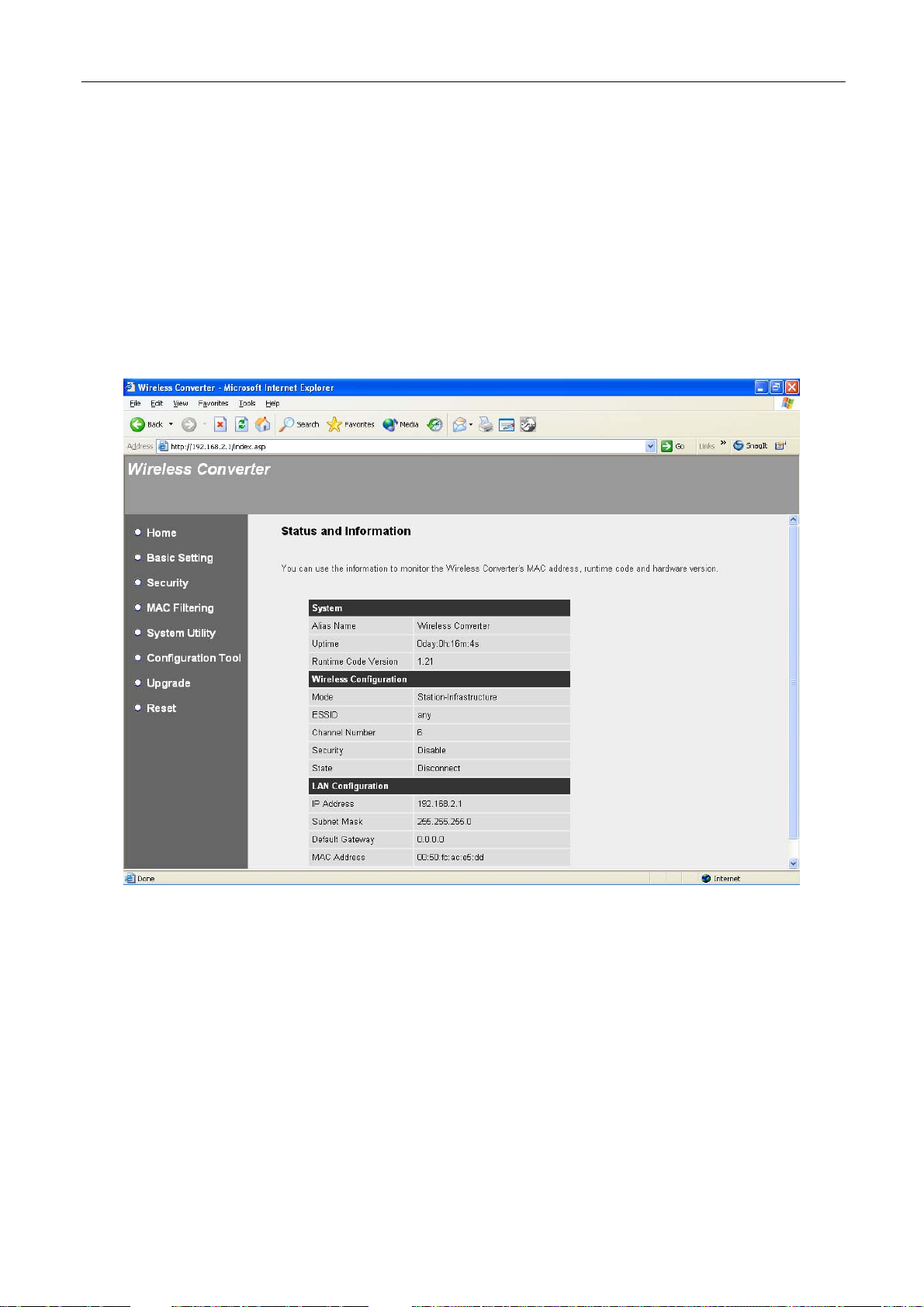
3.2.1 Status and Information
On this screen, you can see the general information of the Wireless Converter
including Alias Name, Firmware Version, ESSID, Channel Number, Status, IP
Address, MAC Address, etc.
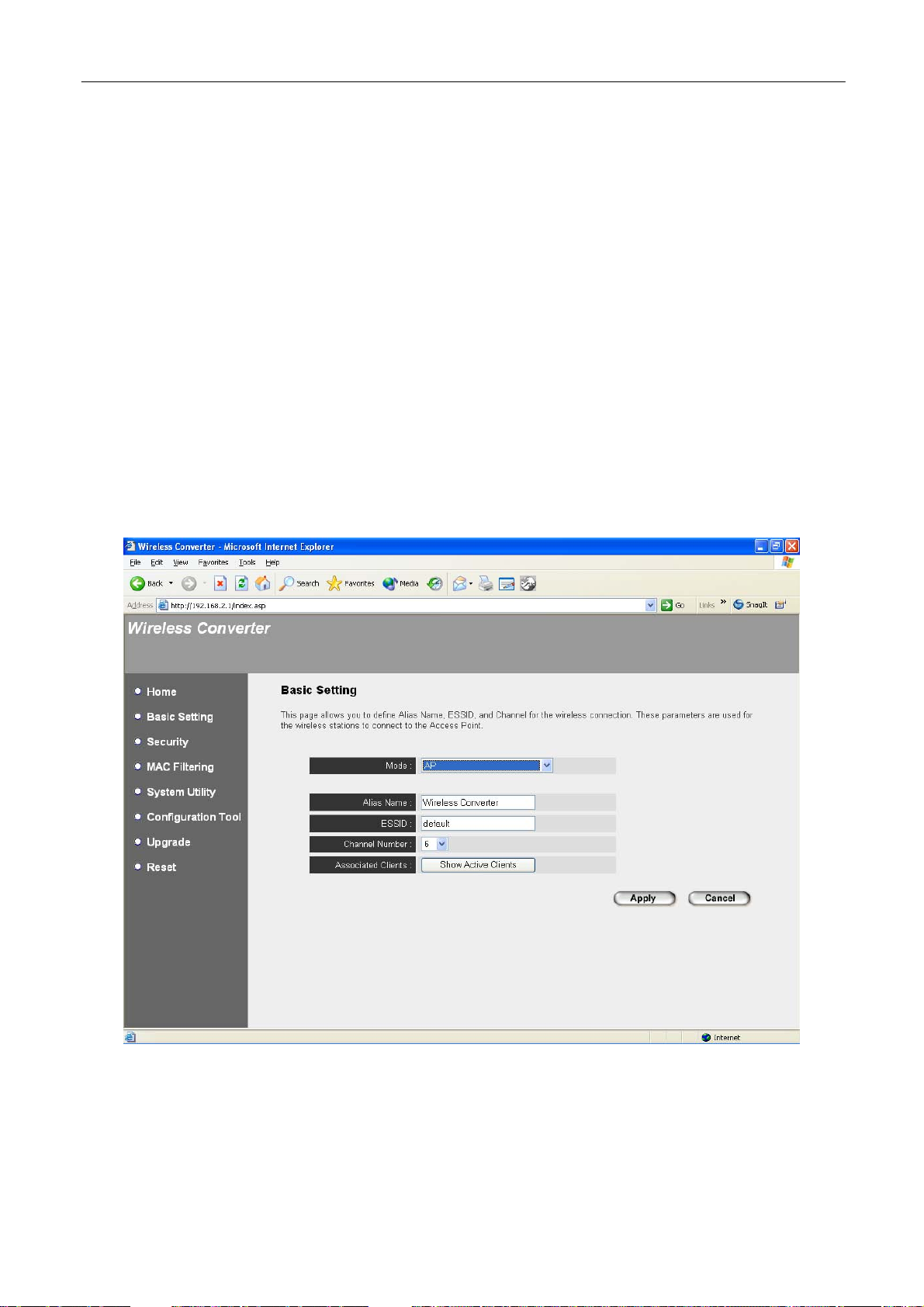
3.2.2 Basic Setting
This Wireless Converter supports AP, Station, Bridge and WDS modes. “AP Mode”
provides pure Access Point function. The simplest way to build up a wireless LAN is
to use “AP Mode”. “Station Mode” enables the computers become wireless stations.
“AP Bridge Mode” provides the function to bridge more than 2 wired Ethernet
networks together by wireless LAN. You can use two Access Points with “AP
Bridge-Point to Point mode” to bridge two wired Ethernet networks together. If you
10
Page 13
Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
want to bridge more than two wired Ethernet networks together, you have to use
enough Access Points with “AP Bridge-Point to Multi-Point mode”. An Access Point
with “AP Bridge-Point to Point mode” or “AP Bridge-Point to Multi-Point mode”
can only be used to bridge wired Ethernet networks together. It can’t accept
connection from other wireless station at the same time. If you want an Access Point
to bridge wired Ethernet network and provide connection service for other wireless
station at the same time, you have to set the Access Point to “AP Bridge-WDS mode”.
Simply speaking, “AP Bridge-WDS mode” function is the combination of “AP
mode” and “AP Bridge-Point to Multi-Point mode”.
3.2.2.1 AP, Bridge and WDS Mode
AP Mode Setting Page:
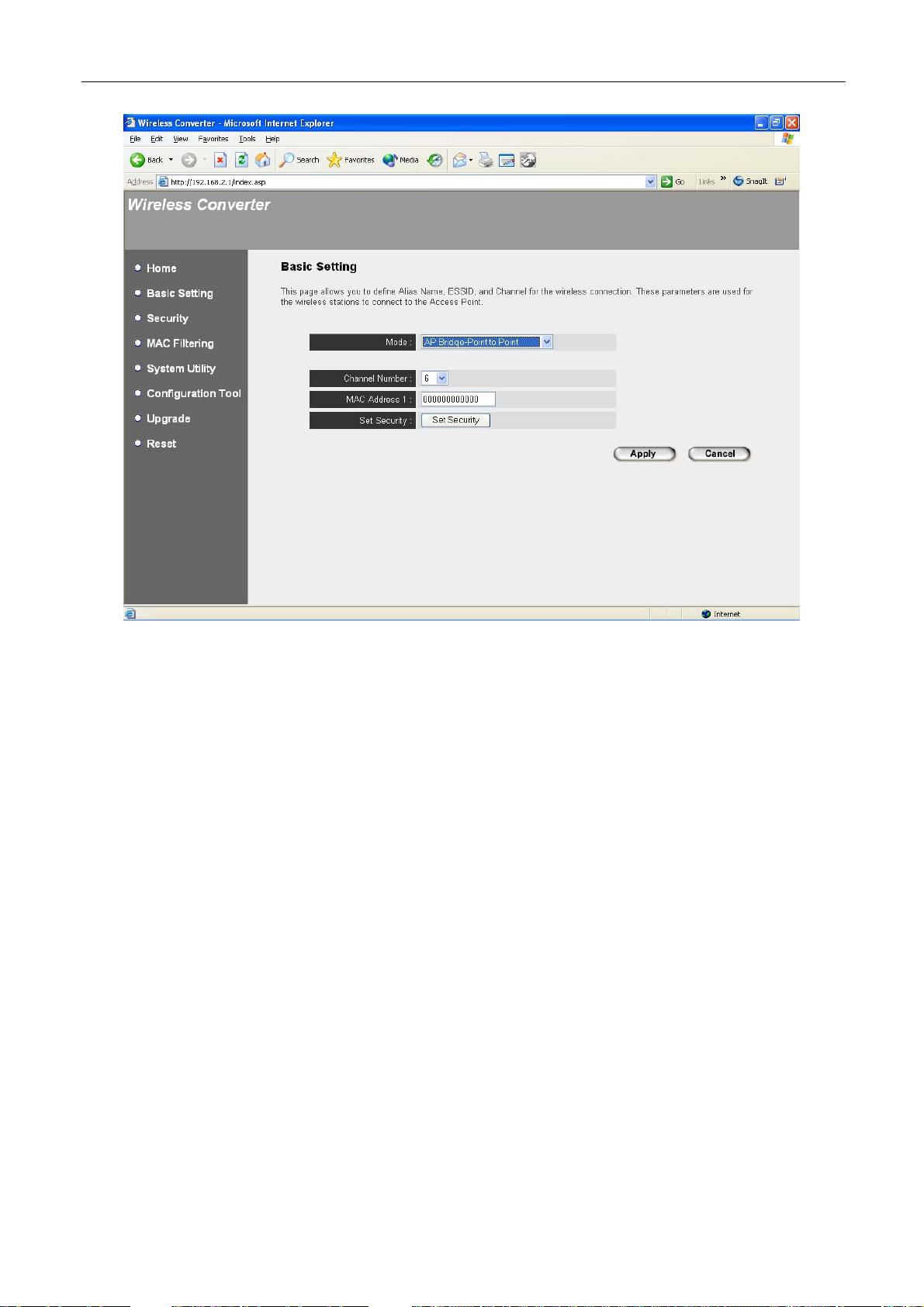
AP Bridge-Point to Point Mode Setting Page:
11
Page 14
Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
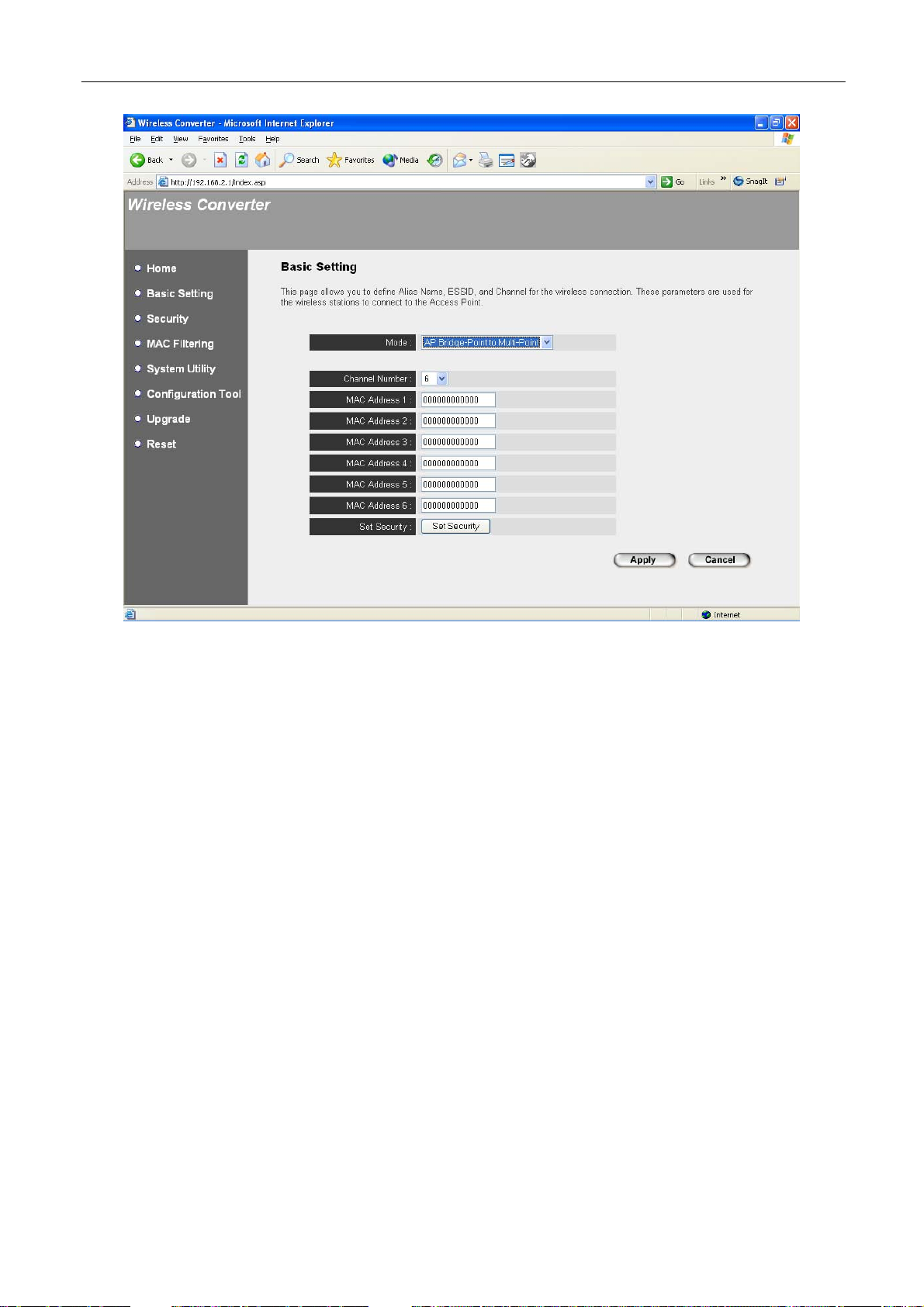
AP Bridge-Point to Multi-Point Mode Setting Page:
12
Page 15
Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
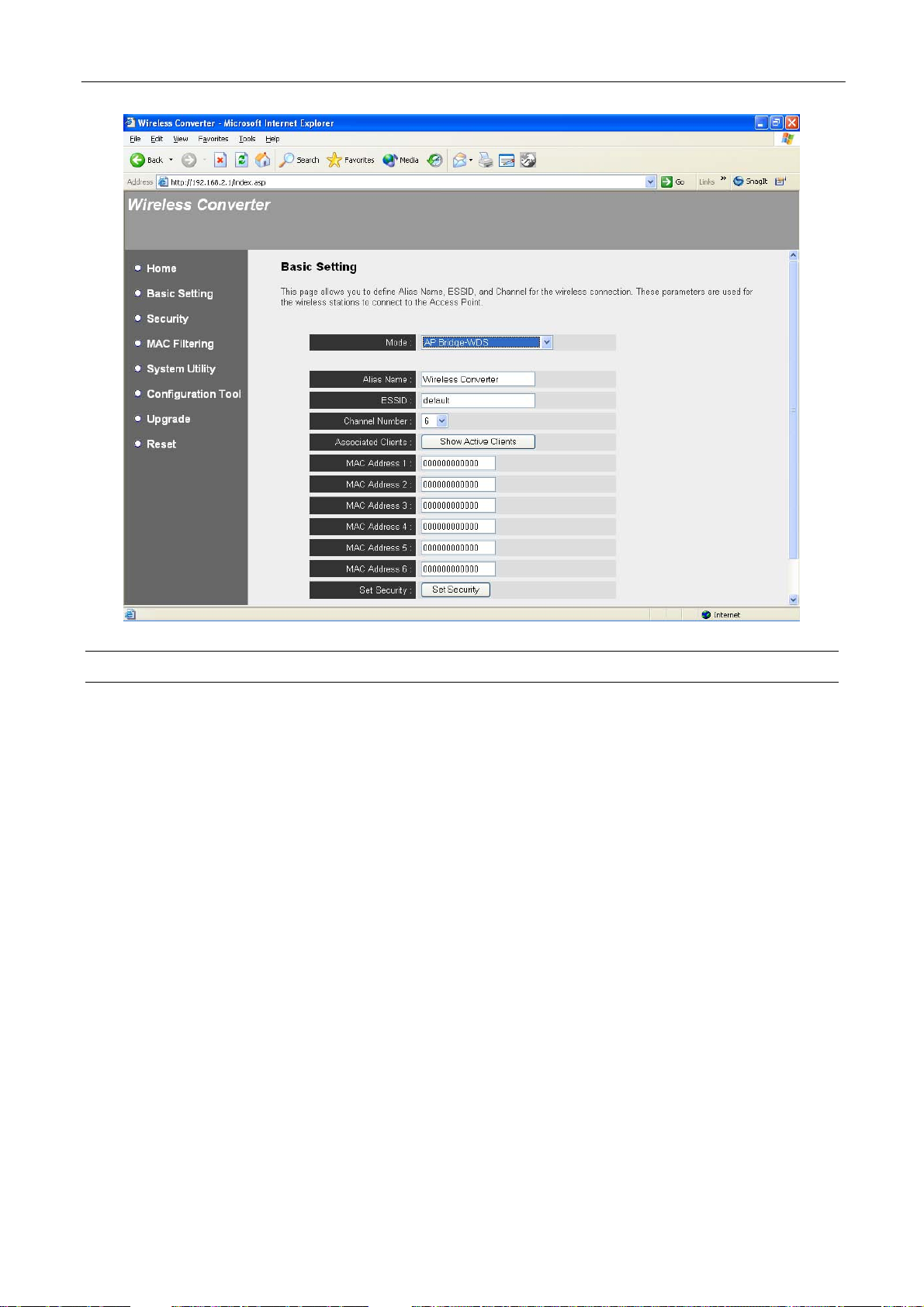
AP Bridge-WDS Mode Setting Page:
13
Page 16
Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Parameter Description
Alias Name
ESSID
Channel Number
Define a recognizable name to be the alias name for this Wireless
Converter.
The ESSID (up to 32 printable ASCII characters) is the unique name
identified in a WLAN. The ID prevents the unintentional merging of two
co-located WLANs. Please make sure that the ESSID of all stations in
the same WLAN network are the same. The default ESSID is “default”.
Select the appropriate channel from the list provided to correspond with
your network settings. Channels differ from country to country.
Channel 1-11 (North America)
Channel 1-14 (Japan)
Channel 1-13 (Europe)
Associated Clients
There are 14 channels available.
Click “Show Active Clients” button, then an “Active Wireless Client Table”
will pop up. You can see the status of all active wireless stations that are
14
Page 17

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
connecting to the Wireless Converter.
MAC Address
Set Security
Click Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now configure
other advance sections or start using the Wireless Converter.
If you want to bridge more than one wired Ethernet network together with
wireless LAN, you have to set this Wireless Converter to “AP BridgePoint to Point mode”, “AP Bridge-Point to Multi-Point mode” or “AP
Bridge-WDS mode”. You have to enter the MAC addresses of other
Wireless Converters that join the bridging network.
Click “Set Security” to set up security. From here, you can only enable
WEP setting, for more setting, please enter into “Security” option in the
left side of the screen.
Active Wireless Client Table
“Active Wireless Client Table” records the status of all active wireless stations that
are connecting to the Wireless Converter in “AP mode”, “AP Bridge-Point to Point
mode”, “AP Bridge-Point to Multi-Point mode” and “AP Bridge-WDS mode”. You
can lookup the MAC Address and Power Saving Status of each active wireless client
in this table.
15
Page 18

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Parameter Description
MAC Address
Power Saving
MAC address of this active wireless station.
Shows if the wireless client is in Power Saving mode.
Set Security
Please refer to section 3.2.4 for the detail description of WEP setting.
16
Page 19

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
3.2.2.2 Station-Ad-Hoc/Infrastructure Mode
Station-Ad Hoc Mode Setting Page:
17
Page 20

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Station-Infrastructure Mode Setting Page:
18
Page 21

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Parameter Description
Alias Name
ESSID
Wireless Site Survey
Define a recognizable name to be the alias name for this Wireless
Converter.
The ESSID (up to 32 printable ASCII characters) is the unique name
identified in a WLAN. The ID prevents the unintentional merging of two
co-located WLANs. Please make sure that the ESSID of all stations in
the same WLAN network are the same. The default ESSID is “default”.
When you use this wireless converter as a wireless station for wired
network device to have wireless capability, you have to associate it will a
working access point. Click “Select Site Survey” button, then a “Wireless
Site Survey Table” will pop up. It will list all available access points near
by. You can select one access point in the table and it will join wireless
WLAN MAC
LAN through this access point.
If you wan to change the MAC Address of the converter to the PC’s MAC
Address that the Converter is connecting to, please select “Clone MAC”.
19
Page 22

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
When the MAC address filtering function of AP is enabled, the AP can
filter the PC, but not the converter.
Instruction:
1. Enter “000000000000” in WLAN MAC and click “Clone MAC” the
2. Enter “xxxxxxxxxxxx” in WLAN MAC and click “Clone MAC” the MAC
3. Let the text box blank and click “Clone MAC”, the MAC Address is
Click Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now configure
other advance sections or start using the Wireless Converter.
AP
MAC Filtering
0050FC123456
MAC Address is based on Converter’s.
Address is based on the MAC Address you entered.
based on the PC’s MAC Address.
0050FC1234
0050FC0000 0050FC1234
Convert
Clone
PC
Select Site Survey
When this wireless converter is in “Station-Ad Hoc mode” or “Station-Infrastructure
mode”, it should associate with a wireless station or an access point. “Wireless Site
Survey” searches for all available access points and wireless stations nearby. You can
select one of wireless devices listed in this table.
20
Page 23

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
3.2.3 Advanced Setting
You can set advanced parameters of this Wireless Converter. The parameters include
Authentication Type, Fragment Threshold, RTS Threshold, Beacon Interval, DTIM
Period, Transmit Rate, Broadcast ESSID, Operating Rates Mode, CTS Protection,
Transmit Bust Mode. You should not change these parameters unless you know what
effect the changes will have on this Wireless Converter.
21
Page 24

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Parameter Description
Authentication Type
Fragment Threshold
There are two authentication types: “Open System” and “Shared Key”.
When you select “Open System”, wireless stations can associate with
this Wireless Converter without WEP encryption. When you select
“Shared Key”, you should also setup WEP key in the “Encryption” page
and wireless stations should use WEP encryption in the authentication
phase to associate with this Wireless Converter. If you select “Both”, the
wireless client can associate with this Wireless Converter by using any
one of these two authentication types.
“Fragment Threshold” specifies the maximum size of packet during the
fragmentation of data to be transmitted. If you set this value too low, it will
result in bad performance.
RTS Threshold
When the packet size is smaller the RTS threshold, the Wireless
Converter will not use the RTS/CTS mechanism to send this packet.
22
Page 25

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Beacon Interval
DTIM Period
Transmit Rate
Preamble Type
The interval of time that this Wireless Converter broadcast a beacon.
Beacon is used to synchronize the wireless network.
Determines the interval the Wireless Converter will send its broadcast
traffic.
The “Transmit Rate” is the rate this Wireless Converter uses to transmit
data packets. The Wireless Converter will use the highest possible
selected transmission rate to transmit the data packets.
Preamble type defines the length of preamble block in the frames during
the wireless communication. “Short Preamble” is suitable for high traffic
wireless network. “Long Preamble” can provide more reliable
Broadcast ESSID
Operating Rates Mode
CTS Protection
communication.
If you enable “Broadcast ESSID”, every wireless station located within
the coverage of this Wireless Converter can discover this Wireless
Converter easily. If you are building a public wireless network, enabling
this feature is recommended. Disabling “Broadcast ESSID” can provide
better security.
It allows to select the “Mixed Mode(11g/b)” or “11g only mode”.
It is recommended to enable the protection mechanism. This mechanism
can decrease the rate of data collision between 802.11b and 802.11g
wireless stations. When the protection mode is enabled, the throughput
of the AP will be a little lower due to many of frame traffic should be
transmitted.
Auto – Based on the status of the network and automatically
disable/enable protection mode.
Always – Always enable the protection mode.
None – Always disable the protection mode.
23
Page 26

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Transmit Burst Mode
IAPP
Click Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now configure
other advance sections or start using the Wireless Converter.
Transmit Burst enables the AP to deliver the better throughput in the
same period and environment.
If you enable “IAPP”, the wireless converter will automatically broadcast
information of associated wireless stations to its neighbors. This will help
wireless station roaming smoothly between access points. If you have
more than one wireless converters in your wireless LAN and wirel ess
stations have roaming requirements, enabling this feature is
recommended. Disabling “IAPP” can provide better security.
3.2.4 Security
This Wireless Converter provides complete wireless LAN security functions, the
authentication methods including Open System, Shared Key, WPA-PSK, WPARADIUS and full function of IEEE 802.1x; the encryption functions including WEP,
TKIP and AES. With these security functions, you can prevent your wireless LAN
from illegal access. Please make sure your wireless stations use the same security
function.
The security setting for Station Mode and AP mode are different. For the security
setting in Station Mode including “Station-Ad Hoc Mode” and “Station-Infrastructure
Mode”, please refer to section 3.2.4.1. For the security setting in AP mode including
“AP Mode”, “AP Bridge-Point to Point Mode”, “AP Bridge-Point to Multi-Point
Mode” and “AP Bridge-WDS Mode, please refer to section 3.2.4.2.
3.2.4.1 Security Setting in Station Mode
Authentication Type
24
Page 27

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
The authentication type defines the way that the access point recognizes the identity
of wireless clients.
Parameter Description
Open System
Shared Key
WPA-PSK
No authentication is needed among the wireless network. Open System
mode only supports WEP encryption way.
Only wireless devices using a shared key (WEP Key identified) are
allowed to connect each other. Shared Key mode only supports WEP
encryption way.
It is a special mode designed for home and small business users who do
not have access to network authentication servers. In this mode, known
as Pre-Shared Key, the user manually enters the starting password in
their access point or router, as well as in each station on the wireless
network. WPA takes over automatically from that point, keeping
unauthorized users that don't have the matching password from joining
the network, while encrypting the data traveling between authorized
25
Page 28

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
devices. WPA-PSK mode only supports encryption ways including TKIP
and AES.
WPA-RADIUS
Enable 802.1x
Authentication
Click Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now configure
other advance sections or start using the Wireless Converter.
This mode is for enterprise with an Authentication Server (Radius
Server), a Certificate Server, WPA-enabled access point/router, and a
WPA-enabled wireless station. Once WPA is enabled, all stations and
access points on the network must be WPA-enabled in order to access
the network. WPA mode only supports encryption ways including TKIP
and AES.
IEEE 802.1x is an authentication protocol. This Wireless Converter
supports multiple 802.1x authentication type including PEAP, TLS, TTLS
and MD5-Challenge. The authentication conditionally needs an
Authentication Server and a Certificate.
WEP
WEP is an encryption algorithm, which protects authorized Wireless LAN users
against eavesdropping. The WEP key of wireless stations must be the same with the
Wireless Converter. This Wireless Converter supports 64/128-bit WEP Encryption
function. With this function, your data will be transmitted over the wireless network
securely.
26
Page 29

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Parameter Description
Key Length
Key Format
Default Key
You can select the 64-bit or 128-bit key to encrypt transmitted data.
Larger WEP key length will provide higher level of security, but the
throughput will be lower. You can also select Disable to transmit data
without encryption.
You may select to select ASCII Characters (alphanumeric format) or
Hexadecimal Digits (in the “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9” range) to be the WEP
Key. For example:
ASCII Characters: guest
Hexadecimal Digits: 12345abcde
Select one of the four keys to encrypt your data. Only the key you select
it in the “Default key” will take effect.
Key 1 - Key 4
The WEP keys are used to encrypt data transmitted in the wireless
network. Fill the text box by following the rules below.
64-bit WEP: input 10-digit Hex values (in the “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9” range)
27
Page 30

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
or 5-digit ASCII character as the encryption keys.
128-bit WEP: input 26-digit Hex values (in the “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9”
range) or 13-digit ASCII characters as the encryption keys.
Click Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now configure
other advance sections or start using the Wireless Converter.
WPA-PSK
Parameter Description
Encryption Type
There are two ways for data encryption including TKIP and AES.
TKIP – TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) changes the temporal key
every 10,000 packets. This insures much greater security than the
standard WEP security.
AES – AES has been developed to ensure the highest degree of security
and authenticity for digital information and it is the most advanced
solution defined by IEEE 802.11i for the security in the wireless network.
28
Page 31

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Pre-shared Key
Click Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now configure
other advance sections or start using the Wireless Converter.
It is the setting for WPA-PSK mode. Enter 8 to 63 digits of ASCII format
to be the password for the authentication within the network.
WPA-RAIUS
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is an advanced security standard. You can use an
external RADIUS server to authenticate wireless stations and provide the session key
to encrypt data during communication. It uses TKIP and AES to change the
encryption key frequently. This can improve security very much.
Get the Client Certificate
Before using EAP-TLS to login the RADIUS server, you have to get the Client
Certificate first. In general, there are three steps.
29
Page 32

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
1. Use Microsoft Internet Explore to import or install a Client Certificate issued from
the Certificate Server.
2. Export the Client Certificate from the Microsoft Internet Explore into a PFX file.
3. Use the tool transfer.exe to transform the PFX Client Certificate into a
CLTCER.TGZ file that you have to upload to the Wireless Converter.
Note: If you already have Client Certificate files in DER/PEM or PFX format. You
can just skip step 1 and 2 and directly jump to step 3.
Note: Your Internet Explore version should 5.0 or above.
Below are the detail descriptions about the three steps.
Step 1
Use Microsoft Internet Explore to import or install a Client Certificate issued from
the Certificate Server. The Client Certificate installation method depends on the
Certificate Server. Please refer to the user’s manual of the Certificate Server.
Step 2
Export the Client Certificate from the Microsoft Internet Explore into a PFX file. In
the Microsoft Internet Explore, go to the “Tools Internet Options”. In the “Internet
Options” window, go to tab “Content”.
30
Page 33

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Click “Certificates” button, then pop-up the “Certificates” window. In the
“Certificates” window, you can find the Client Certificate that you just import or
install.
31
Page 34

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Select the Client Certificate that you want to export and then click “Export”, then the
“Certificate Export Wizard” will pop-up. The “Certificate Export Wizard” will guide
you through all the procedures to export the Client Certificate.
32
Page 35

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Click “Next”.
Select “Yes, export the private key” and click “Next”.
33
Page 36

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Check “Enable strong protection” and click “Next”.
34
Page 37

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Enter the password used to protect the private key and then click “Next”.
Assign the path and file name to save the exported Client Certificate and then click
“Next”. A window will pop-up to display the conclusion information about the Client
Certificate export procedure.
35
Page 38

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Click “Finish” to confirm, then pop-up a window to hint the success.
You have successfully export the Client Certificate from the Microsoft Internet
Explore.
Step 3
Before uploading the Client Certificate into the Wireless Converter, you have to
transform the Client Certificate to the format used by the Wireless Converter. You
can use the transformation utility, shipped with this Wireless Converter, to do this
transformation.
To install the transformation utility, just unzip transfer.zip into a folder. You can see
a executable file transfer.exe in the folder. The transfer.exe is the main program of
the transformation utility.
36
Page 39

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
transfer.exe can transform DER/PEM or PFX format Client Certificate into the
format used by this Wireless Converter. If your Client Certificate is not one of these
two formats, please transform it into one of these two formats first. (Microsoft
Internet Explore is a good option to do this kind of transformation.)
Before the transformation, you have to copy the Client Certificate to be transformed
into the same folder as the transfer.exe. Then execute transfer.exe.
1. Select the Client Certificate format according the format of your Client Certificate.
2. If your Client Certificate is PFX format, there is only one .PFX file. If your Client
Certificate is CER/PEM format, there are two files – .DER file and .PEM file.
Click “Browse” button to assign the path of you Client Certificate files.
3. Enter the password used to protect the private key of Client Certificate.
4. Click “Apply”.
5. After a few seconds, there exists a file CLTCER.TGZ in the installation folder of
transfer.exe. You have finished the Client Certificate transformation. You have to
upload CLTCER.TGZ file into the Wireless Converter.
6. Click “Close” to close the transformation utility.
37
Page 40

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
802.1x
IEEE 802.1x is an authentication protocol. Every user must use a valid account to
login to this Wireless Converter before accessing the wireless LAN. The
authentication is executed by a RADIUS server. You have to build up an external
RADIUS server within the network.
Parameter Description
RADIUS Server IP address
RADIUS Server Port
RADIUS Server Password
Click Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now configure
other advance sections or start using the Wireless Converter.
Enter the IP address of external RADIUS server.
The service port of the external RADIUS server.
The password used by external RADIUS server.
802.1x WEP static key
38
Page 41

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
IEEE 802.1x is an authentication protocol, while WEP is a data encryption protocol.
Using IEEE 802.1x to authenticate a valid account and also protect the data
communication within the wireless network by WEP encryption.
Parameter Description
Key Length
Key Format
Default Key
You can select the 64-bit or 128-bit key to encrypt transmitted data.
Larger WEP key length will provide higher level of security, but the
throughput will be lower. You also can select Disable to transmit data
without encryption.
You may select to select ASCII Characters (alphanumeric format) or
Hexadecimal Digits (in the “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9” range) to be the WEP
Key. For example:
ASCII Characters: guest
Hexadecimal Digits: 12345abcde
Select one of the four keys to encrypt your data. Only the key you select
it in the “Default key” will take effect.
39
Page 42

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Key 1 - Key 4
RADIUS Server IP address
RADIUS Server Port
RADIUS Server Password
Click Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now configure
other advance sections or start using the Wireless Converter.
The WEP keys are used to encrypt data transmitted in the wireless
network. Fill the text box by following the rules below.
64-bit WEP: input 10-digit Hex values (in the “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9” range)
or 5-digit ASCII character as the encryption keys.
128-bit WEP: input 26-digit Hex values (in the “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9”
range) or 13-digit ASCII characters as the encryption keys.
The IP address of external RADIUS server.
The service port of the external RADIUS server.
The password used by external RADIUS server.
WPA pre-shared key
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is an advanced security standard. You can use a preshared key to authenticate wireless stations and encrypt data during communication.
It uses TKIP to change the encryption key dynamically, so it can improve security
significantly.
Note: This Wireless Converter does not provide AES encryption method.
40
Page 43

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Parameter Description
WPA Unicast Cipher Suite
Pre-shared Key Format
Pre-shared Key
There are two ways for data encryption including TKIP and AES. AES will
be supported in the near future.
TKIP can change the encryption key frequently to enhance the wireless
LAN security.
You may select to select ASCII Characters (alphanumeric format) or
Hexadecimal Digits (in the “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9” range) to be the Pre-
shared Key. For example:
ASCII Characters: iamguest
Hexadecimal Digits: 12345abcde
The Pre-shared key is used to authenticate and encrypt data transmitted
in the wireless network. Fill the text box by following the rules below.
Hex WEP: input 64-digit Hex values (in the “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9” range) or
at least 8 characters pass phrase as the pre-shared keys.
Click Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now configure
other advance sections or start using the Wireless Converter.
41
Page 44

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
WPA RAIUS
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is an advanced security standard. You can use an
external RADIUS server to authenticate wireless stations and provide the session key
to encrypt data during communication. It uses TKIP to change the encryption key
frequently. This can improve security very much.
Note: This Wireless Converter does not provide AES encryption method.
Parameter Description
WPA Unicast Cipher Suite
RADIUS Server IP address
There are two ways for data encryption including TKIP and AES. AES will
be supported in the near future.
TKIP can change the encryption key frequently to enhance the wireless
LAN security.
The IP address of external RADIUS server.
42
Page 45

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
RADIUS Server Port
RADIUS Server Password
Click Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now configure
other advance sections or start using the Wireless Converter.
The service port of the external RADIUS server.
The password used by external RADIUS server.
43
Page 46

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
3.2.5 MAC Address Filtering
This Wireless Converter provides MAC Address Filtering, which prevents the
unauthorized MAC Addresses from accessing your wireless network.
Parameter Description
Filtering
MAC Address Filtering Table
Add MAC address into the
table
Enable or disable the MAC Address Filtering function.
This table records the MAC addresses of wireless stations you want to
allow to access your network. The “Comment” field is the description of
the wireless station associated with the “MAC Address” and is helpful for
you to recognize the wireless station.
In the bottom “New” area, fill in the “MAC Address” and “Comment” of the
wireless station to be added and then click “Add”. Then this wireless
station will be added into the “MAC Address Filtering Table” above. If you
find any typo before adding it and want to retype again. Just click “Clear”
44
Page 47

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
and both “MAC Address” and “Comment” fields will be cleared.
Remove MAC address from
the table
Reset
Click Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now configure
other advance sections or start using the Wireless Converter.
If you want to remove some MAC address from the “MAC Address
Filtering Table”, select the MAC addresses you want to remove in the
table and then click “Delete Selected”. If you want remove all MAC
addresses from the table, just click “Delete All” button.
Click “Reset” will clear your current selections.
45
Page 48

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
3.2.6 System Utility
From here, you can define the Wireless Converter’s IP Address and Login Password
and enable the Wireless Converter to be a DHCP Server.
Parameter Description
Current Password
New Password
Re-Enter Password
IP Address
Enter the current password (up to 15-digit alphanumeric string) of the
Wireless Converter. The default password for the Wireless Converter is
1234. Note that the password is case-sensitive.
Enter the password (up to 15-digit alphanumeric string) you want to login
to the Wireless Converter. Note that the password is case-sensitive.
Reconfirm the password (up to 15-digit alphanumeric string) you want to
login to the Wireless Converter. Note that the password is case-sensitive.
Designate the Wireless Converter’s IP Address. This IP Address should
be unique in your network. The default IP Address is 192.168.2.1.
46
Page 49

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
Subnet Mask
DHCP Server
Click Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now configure
other advance sections or start using the Wireless Converter.
Specify a Subnet Mask for your LAN segment. The Subnet Mask of the
Wireless Converter is fixed and the value is 255.255.255.0.
Enable or disable the DHCP Server.
3.2.6.1 DHCP Server Setting
DHCP Server will automatically give your LAN client an IP address. If the DHCP is
not enabled then you’ll have to manually set your LAN client’s IP address.
Parameter Description
Default Gateway IP
Specify the gateway IP in your network. This IP address should be
Domain Name Server IP
Start IP/End IP
Domain Name
Lease Time
different from the Management IP.
This is the ISP’s DNS server IP address that they gave you; or you can
specify your own preferred DNS server IP address.
You can designate a particular IP address range for your DHCP server to
issue IP addresses to your LAN Clients. By default the IP range is from: Start
IP 192.168.2.100 to End IP 192.168.2.200.
You can specify the Domain Name for your Wireless Converter.
The DHCP Server when enabled will temporarily give your LAN client an IP
address. In the Lease Time setting you can specify the time period that the
DHCP Server lends an IP address to your LAN clients. The DHCP Server will
change your LAN client’s IP address when this time threshold period is
reached.
Click Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now configure
other advance sections or start using the Wireless Converter.
47
Page 50

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
3.2.7 Configuration Tool
The Configuration Tools screen allows you to save (Backup) the Wireless
Converter’s current configuration setting. Saving the configuration settings provides
an added protection and convenience should problems occur with the Wireless
Converter and you have to reset to factory default. When you save the configuration
setting (Backup) you can re-load the saved configuration into the Wireless Converter
through the Restore selection. If extreme problems occur you can use the Restore to
Factory Default selection, this will set all configurations to its original default
settings (e.g. when you first purchased the Wireless Converter).
Parameter Description
Configuration Tools
Use the "Backup" tool to save the Wireless Converter’s current
configuration to a file named "config.bin" on your PC. You can then use
the "Restore" tool to upload and restore the saved configuration to the
Wireless Converter. Alternatively, you can use the "Restore to Factory
Default" tool to force the Wireless Converter to perform a power re set
and restore the original factory settings.
48
Page 51

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
3.2.8 Firmware Upgrade
This page allows you to upgrade the Wireless Converter’s firmware.
Parameter Description
Firmware Upgrade
Once you’ve selected the new firmware file, click Apply button at the bottom of the screen to start the upgrade
process. (You may have to wait a few minutes for the upgrade to complete). Once the upgrade is complete you
can start using the Wireless Converter.
This tool allows you to upgrade the Wireless Converter’s system
firmware. To upgrade the firmware of your Wireless Converter, you need
to download the firmware file to your local hard disk, and enter that file
name and path in the appropriate field on this page. You can also use the
Browse button to find the firmware file on your PC. Please reset the
Wireless Converter when the upgrade process is complete.
49
Page 52

Wireless LAN Wireless Converter Configuration
3.2.9 Reset
You can reset the Wireless Converter’s system should any problem exist. The reset
function essentially Re-boots your Wireless Converter’s system.
Parameter Description
Reset
In the event that the system stops responding correctly or in some way stops
functioning, you can perform a reset. Your settings will not be changed. To
perform the reset, click on the Apply button. You will be asked to confirm
your decision. Once the reset process is complete you may start using the
Wireless Converter again.
50
Page 53

Troubleshooting
4. Troubleshooting
This chapter provides solutions to problems usually encountered during the
installation and operation of the Wireless Converter.
1. How to manually find your PC’s IP and MAC Address?
1) In Windows, open the Command Prompt program
2) Type Ipconfig /all and Enter
Your PC’s IP address is the one entitled IP address
Your PC’s MAC Address is the one entitled Physical Address
2. What is BSS ID?
A group of wireless stations and an Wireless Converter compose a Basic Service
Set (BSS). Computers in a BSS must be configured with the same BSSID.
3. What is ESSID?
An Infrastructure configuration could also support roaming capability for mobile
workers. More than one BSS can be configured as an Extended Service Set (ESS).
Users within an ESS could roam freely between BSSs while maintaining a
continuous connection to the wireless network stations and the Wireless LAN
Wireless Converters.
4. Can data be intercepted while transmitting through the air?
WLAN features two-fold protection in security. On the hardware side, as with
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum technology, it has the inherent scrambling
security feature. On the software side, the WLAN series offers the encryption
function (WEP) to enhance security and access control.
5. What is WEP?
WEP stands for Wired Equivalent Privacy, a data privacy mechanism based on a
64(40)-bit shared key algorithm.
6. What is a MAC Address?
51
Page 54

Troubleshooting
The Media Access Control (MAC) address is a unique number assigned by the
manufacturer to any Ethernet networking device, such as a network adapter, that
allows the network to identify it at the hardware level. For all practical purposes,
this number is usually permanent. Unlike IP addresses, which can change every
time a computer logs on to the network, the MAC address of a device stays the
same, making it a valuable identifier for the network.
52
Page 55

Troubleshooting
FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:(1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2)
this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user‘s authority to operate the equipment.
NOTE
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiated radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
-Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
-Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
-Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
-Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Note:
This device and its antenna(s) used for this transmitter must not be co-located or
operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. In order to avoid the possibility of exceeding the FCC
radio frequency exposure limits, human proximity to the antenna shall not be less
than 20cm (8 inches) during normal operation.
53
 Loading...
Loading...