Page 1

ADSL Wir eless Router
AR-6024WG
User’s Manual
Page 2

Table of Contents
Specification----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3
Package Contents --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
General Setting----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------12
OnePage Setup --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 16
Wireless ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 22
Status ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 24
Network Statistics ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 24
Connection Status ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 26
System Log---------------------------------------------------------------------------------27
Advanced Setting ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 28
LAN Setup ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 28
DHCP Configuration---------------------------------------------------------------------- 28
Management IP---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 29
Firewall/NAT Services-------------------------------------------------------------------- 30
WAN Setup --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 31
Add New Connection--------------------------------------------------------------------- 31
Advanced ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 37
UPnP-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------37
Multicast-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------38
LAN Clients---------------------------------------------------------------------------------39
Web Filters---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 40
Bridge Filters------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 41
Modem Setup------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 42
Static Routing ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 43
Access Control----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 44
Port Forwarding --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 47
Dynamic Routing--------------------------------------------------------------------------50
Wireless Security-------------------------------------------------------------------------- 51
Advanced Security------------------------------------------------------------------------ 53
Wireless Management------------------------------------------------------------------- 54
Tools------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 55
Ping Test ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 55
Remote Log -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 56
Modem Test -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 57
1
Page 3

UI Preferences----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 58
Update Gateway -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 59
User Management------------------------------------------------------------------------ 60
System Commands----------------------------------------------------------------------- 61
Status ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 62
System Log---------------------------------------------------------------------------------62
DHCP Clients ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 63
Modem Status------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 64
Network Statistics ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 65
Connection Status ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 67
Product Information----------------------------------------------------------------------- 68
Appendix ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------69
2
Page 4

Specification
ADSL Wireless-g Broadband Router
Features
ADSL Standards
DMT modulation and demodulation
Tone detection for low power mode
ITU 992.1 (G.dmt) Annex A, B, C
ITU 992.2 (G.lite)
ITU 992.3 ADSL2 (G.dmt.bis)
ITU 992.4 ADSL2 (G.lite.bis)
ITU 992.5 AD SL2+
ANSI T1.413 Issue 2
Dying Gasp (Optional)
Full-rate adaptive modem
Maximum downstream rate of 24 Mbps (ADSL2+)
Maximum upstream rate of 1 Mbps
G.lite adaptive modem
Maximum downstream rate of 1.5 Mbps
Maximum upstream rate of 512 Kbps
WAN Mode Support
PPP over ATM (RFC 2364)
PPP over Ethernet (RFC 2516)
LAN Mode Support
Bridged/routed Ethernet over ATM (RFC 2684/1483)
Classical IP over ATM (RFC 1577) and PPP over Ethernet (RF C 2 516)
Bridge Mode Support
Ethernet to ADSL self-learning Transparent Bridging (IEEE 802.1D)
Supports up to 128 MAC learning addresses
Router Mode Support
IP routing-RIPv2 (backward compatible with RIPv1)
3
Page 5

Static routing
DHCP Server and Client
NAPT (Network Address and Port Translation)
NAT (Network Address Translation)
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
Simultaneous USB and Ethernet operation
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)
802.11g Wireless Access Point
54Mbps Access Point for wireless connectivity
Interoperable with IEEE 802.11g (PBCC & OFDM Modulation
Technology supports) 2.4GHz compliant equipment
Supports full mobility and seamless roaming from cell to cell
Support Ad hoc and Infrastructure mode
Support AP client architecture
Support WEP (64/128 bit)
Provides up to 30 users wireless connection
Work range: per node indoors approximately 30m~100m,
Outdoor (line of sight) 200m~300m dependin g on data rates
External antenna: one 2dbi detachable antennas with diversity support (Reverse SMA connector)
RF Specification
Frequency band 2400-24835 MHZ (ISM), DSSS spreading, CCK, OFDM modulation
Max Power T ransmission 100mW
1 internal antenna, 1 external antenna
Ethernet Features
Four RJ-45 connectors for 10/100 Mbps Ethernet LAN connection,
DMZ function can be set up between them
Complies with IEEE 802.3u specification
Supports Auto-Negotiation
Supports Auto-MDIX, Auto-MDI
Supports IEEE 802.3x Flow control in Full Duplex mode
Security & Firewall Functions
WEP/Firewall + MAC filter
Specification
Hardware
Line Connection: RJ-11, RJ-45 Connection
4
Page 6

Power: Input: 90~120V or 200~240V, 50/60Hz
Output: 7.5VDC/1.5A
OS: Windows 98SE/ 2000/ ME/ XP
System Requirement: PII-266 + 32M RAM
LED Indication: PWR, ADSL LINK, WLAN, LAN
Software Upgrade: Upgrade by Ethernet Port
Certification
FCC Part 15, CE,
5
Page 7

ADSL Wireless Router
Features
ADSL Standards
DMT modulation and demodulation
Tone detection for low power mode
ITU 992.1 (G.dmt) Annex A, B, C
ITU 992.2 (G.lite)
ITU 992.3 ADSL2 (G.dmt.bis)
ITU 992.4 ADSL2 (G.lite.bis)
ITU 992.5 AD SL2+
ANSI T1.413 Issue 2
Dying Gasp (Optional)
4 Ports LAN
Full-rate adaptive modem
Maximum downstream rate of 24 Mbps (ADSL2+)
Maximum upstream rate of 1 Mbps
G.lite adaptive modem
Maximum downstream rate of 1.5 Mbps
Maximum upstream rate of 512 Kbps
WAN Mode Support
PPP over ATM (RFC 2364)
PPP over Ethernet (RFC 2516)
LAN Mode Support
Bridged/routed Ethernet over ATM (RFC 2684/1483)
Classical IP over ATM (RFC 1577) and PPP over Ethernet (RF C 2 516)
Bridge Mode Support
Ethernet to ADSL self-learning Transparent Bridging (IEEE 802.1D)
Supports up to 128 MAC learning addresses
Router Mode Support
IP routing-RIPv2 (backward compatible with RIPv1)
Static routing
DHCP Server and Client
6
Page 8

NAPT (Network Address and Port Translation)
NAT (Network Address Translation)
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
Simultaneous USB and Ethernet operation
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)
802.11g Wireless Access Point
54Mbps Access Point for wireless connectivity
Interoperable with IEEE 802.11g (PBCC & OFDM Modulation
Technology supports) 2.4GHz compliant equipment
Supports full mobility and seamless roaming from cell to cell
Support Ad hoc and Infrastructure mode
Support AP client architecture
Support WEP (64/128 bit)
Provides up to 30 users wireless connection
Work range: per node indoors approximately 30m~100m,
Outdoor (line of sight) 200m~300m dependin g on data rates
External antenna: one 2dbi detachable antennas with diversity support (Reverse SMA connector)
RF Specification
Frequency band 2400-24835 MHZ (ISM), DSSS spreading, CCK, OFDM modulation
Max Power T ransmission 100mW
1 internal antenna, 1 external antenna
Ethernet Features
Four RJ-45 connectors for 10/100 Mbps Ethernet LAN connection,
DMZ function can be set up between them
Complies with IEEE 802.3u specification
Supports Auto-Negotiation
Supports Auto-MDIX, Auto-MDI
Supports IEEE 802.3x Flow control in Full Duplex mode
Security & Firewall Functions
WEP/Firewall + MAC filter
7
Page 9
Specification
Hardware
Line Connection: RJ-11 (2 wires) RJ-45 (4 port) Connection
Power: Input: 90~120V or 200~240V, 50/60Hz
Output: 7.5VDC/1.5A
OS: WIN 98SE ; WIN 2000;WIN ME;WIN XP
System Requirement: PII-266 + 32M RAM
LED Indication: PWR, ADSL LINK, WLAN, LAN 1~4
Software Upgrade: Upgrade by Ethernet Port
Certification
FCC Part 15, CE,
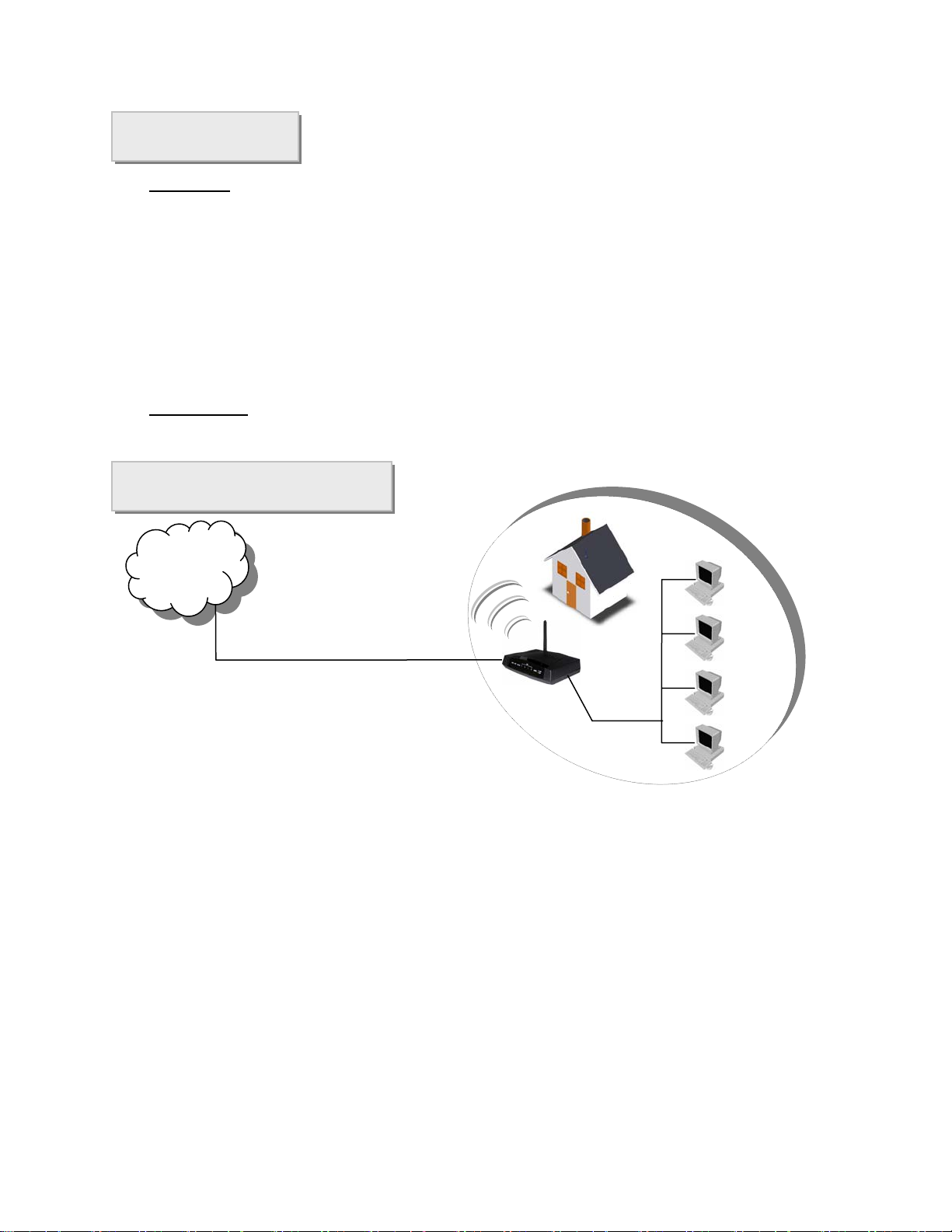
Application Diagram
Internet
XDSL
8
Page 10

Package Contents
ADSL Wireless Router
CD-ROM containing Manual
Ethernet Cable (CAT.5 UTP Straight-Through)
ADSL Cable (Standard telephone cable)
Power Adapter
Quick Installation Guide
9
Page 11
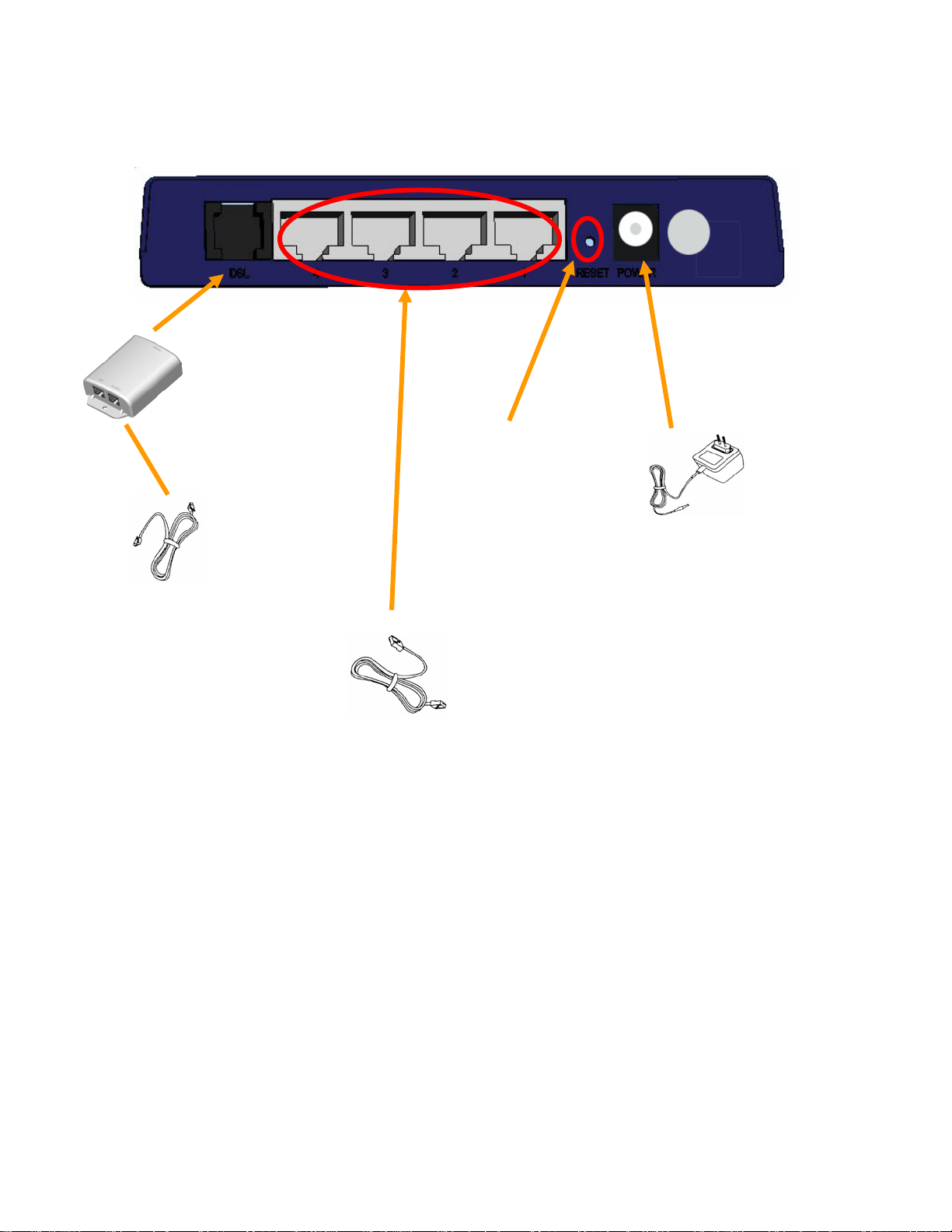
r
4 Port ADSL Wireless Route
RJ-11 ADSL port connect
ADSL cable here
Splitter (optional and
changes depending on
country specification)
Factory Reset button
RJ-45 Ethernet port connect
Ethernet cable here
Power Adapter
Power cord connect here
10
Page 12

4 Port
ADSL Wireless Router
Label Meaning Status Indicates
Power Power On Power is on
Off Power is off
WLAN Wireless LAN Flashing Check wireless device.
LAN 1/ LAN 2/
LAN 3/ LAN 4
On
Off
ADSL Link Link
Active Act
LAN Link Flashing
Flashes when data is being sent or
received on the LAN connection.
Indicates a link to your LAN or Network
card is active.
Indicates no link to LAN
A valid ADSL connection.
An active WAN session.
11
Page 13
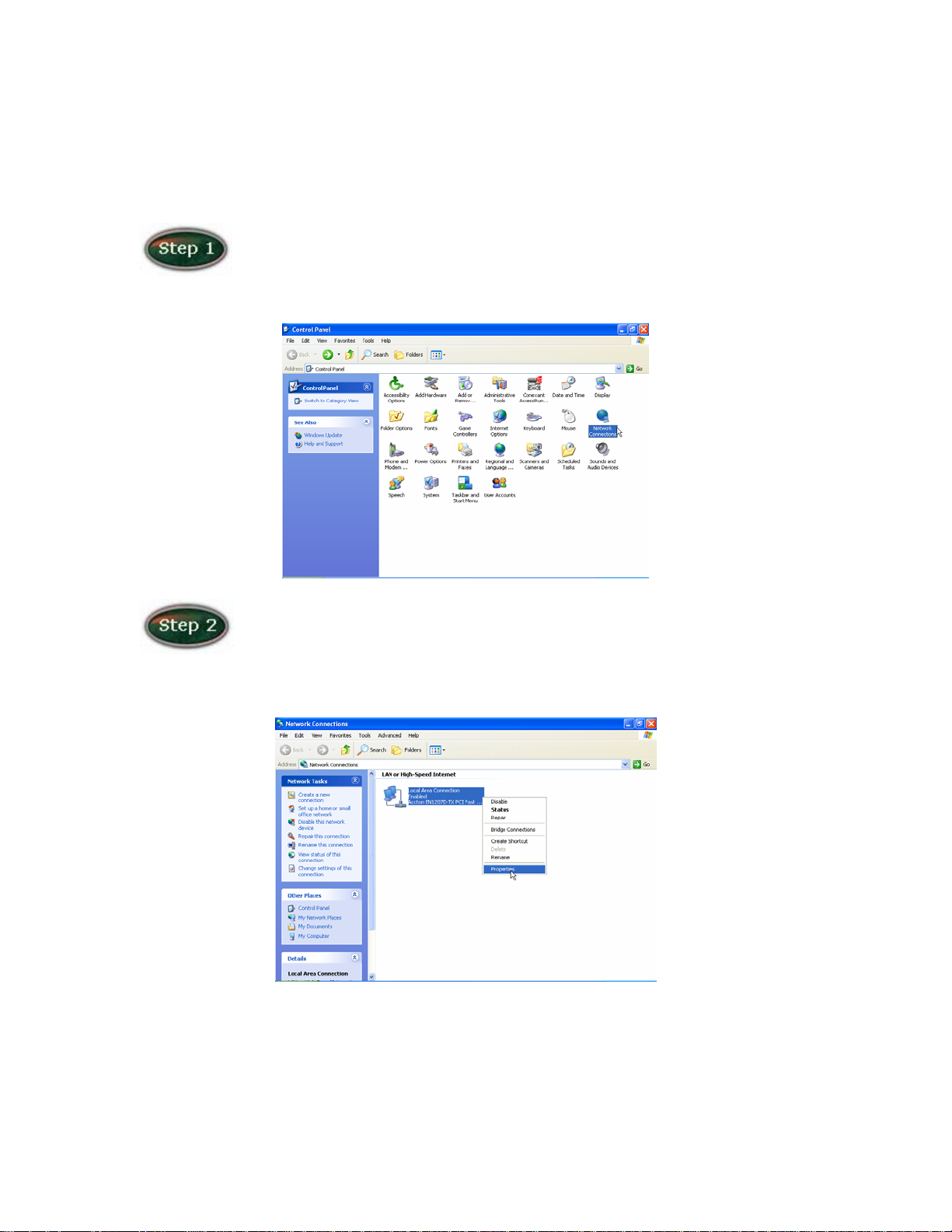
General Setting
Move your cursor as following sequence Start \ Settings \ Control
Panel and click Control Panel. Then double-click on the Network Connections
In the LAN or High-Speed Internet window, right-click on icon
corresponding to your network interface card (NIC) and select Properties.(This
icon may be labeled Local Area Connection).
12
Page 14
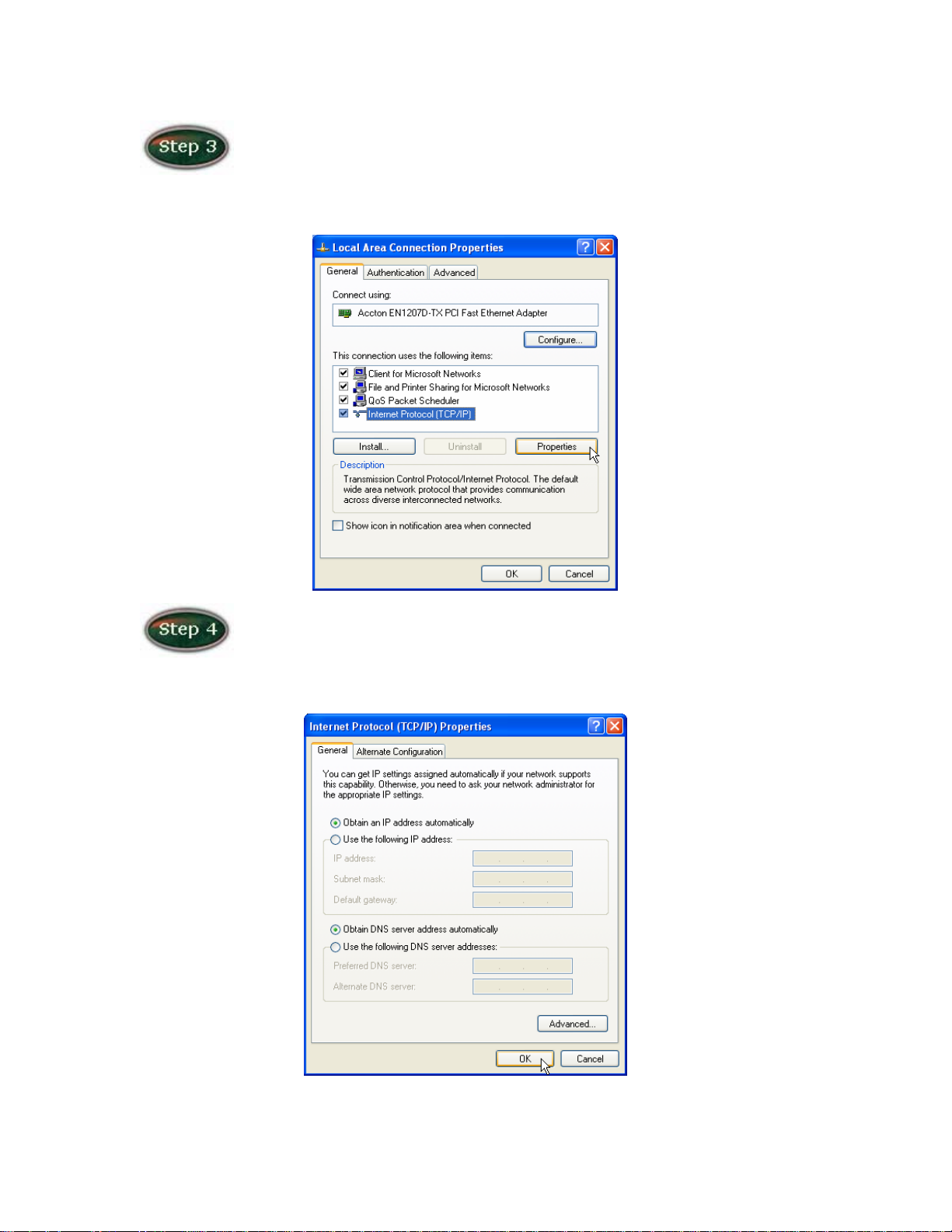
In the General Tab of the Local Area Connection Properties menu.
Highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) under “This connection uses the following
items.” by click on it once. Click on the Properties button.
Select Obtain an IP Address automatically: by clicking once in the
circle. Click OK button to confirm and save your changes, and the close the
Control Panel.
13
Page 15
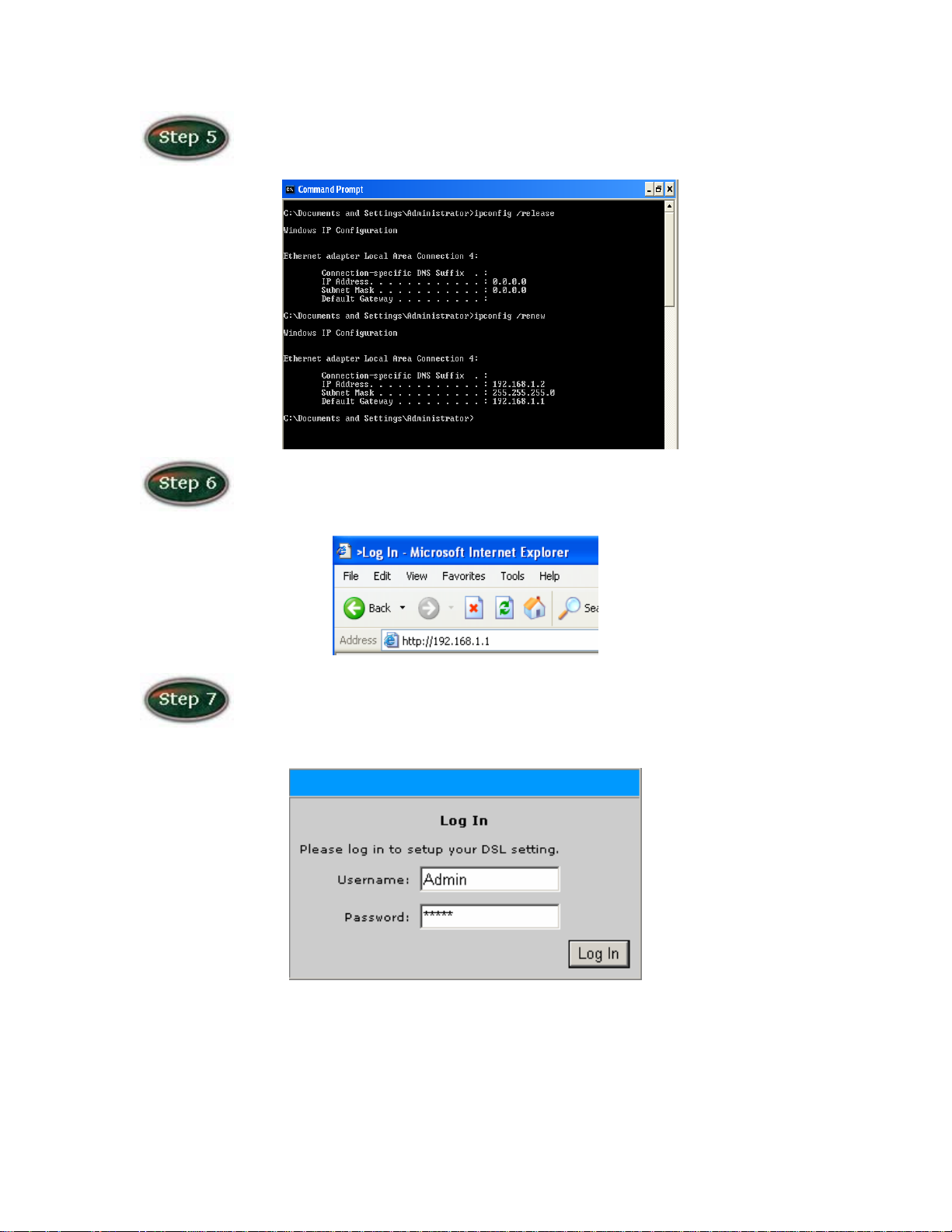
Release IP & Renew IP, then Check Default Gateway: 192.168.1.1.
Launch your PC web browser and enter the URL: http://192.168.1.1
default.
In the User name/Password prompt, please type in Admin/Admin as
14
Page 16

Please wait for the Home page to appear.
15
Page 17

OnePage Setup
When working with wide area connections, the first thing you must do is to have the
handle of the connection. Once you have the handle for a Connection you must define
the PVC and protocol settings for it.
Name: Enter the name of your ISP. This information is for identification purposes only.
Type: There six kinds of method (PPPoE/ PPPoA/ Static/ DHCP/ Bridge/ CLIP).
PPP Settings
Encapsulation: Select you encapsulation type. (Supplied by your ISP).
Username: Enter the username provided by your ISP.
Password: Enter the password provided by your ISP.
Idle Timeout: Idle timeout means the router will disconnect after being idle for a
16
Page 18

preset amount of time. The default is 60 seconds. If you set the time to 0, the
ISDN connection will remain always connected to the ISP.
Keep Alive: If mode is LCP, This is the Keep Alive timer. If a reply to the LCP echo is
not received in this amount if time, the connection is dropped. The Default is 10.
Authentication: Set the required authentication protocol. (Auto/ CHAP/ PAP)
MRU: Maximum Receive Unit indicates the peer of PPP connection the maximum size
of the PPP information field this device can be received. The default value is 1492
and is used in the beginning of the PPP negotiation. In the normal negotiation, the
peer will accept this MRU and will not send packet with information field larger
than this value.
PVC Settings
VPI: If instructed to change this, type in the VPI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
VCI: If instructed to change this, type in the VCI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
QoS: Quality of Service type. Select CBR (Continuous Bit Rate) to specify fixed
(always-on) bandwidth for voice or data traffic. Select UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate)
for applications that are non-time sensitive, such as e-mail. Select VBR (Variable
Bit Rate) for burst traffic and bandwidth sharing with other applications.
PCR: Divide the DSL line rate (bps) by 424 (the size of an ATM cell) to find the Peak
Cell Rate (PCR). This is the maximum rate at which the sender can send cells.
SCR: The Sustain Cell Rate (SCR) sets the average cell rate (long-term) that can be
transmitted.
Name: Enter the name of your ISP. This information is for identification purposes only.
17
Page 19

Type: There six kinds of method (PPPoE/ PPPoA/ Static/ DHCP/ Bridge/ CLIP).
Static Settings
Encapsulation: Select you encapsulation type. (Supplied by your ISP).
IP Address: Private IP address for connecting to a local private network (Default:
192.168.1.1).
Netmask: Netmask for the local private network (Default: 255.255.255.0).
Default Gateway: This field is optional. Enter in the IP address of the router on your
network.
DNS: Sets the IP address of the DNS server.
Mode: Bridged and Routed
PVC Settings
VPI: If instructed to change this, type in the VPI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
VCI: If instructed to change this, type in the VCI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
QoS: Quality of Service type. Select CBR (Continuous Bit Rate) to specify fixed
(always-on) bandwidth for voice or data traffic. Select UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate)
for applications that are non-time sensitive, such as e-mail. Select VBR (Variable
Bit Rate) for burst traffic and bandwidth sharing with other applications.
PCR: Divide the DSL line rate (bps) by 424 (the size of an ATM cell) to find the Peak
Cell Rate (PCR). This is the maximum rate at which the sender can send cells.
SCR: The Sustain Cell Rate (SCR) sets the average cell rate (long-term) that can be
transmitted.
Name: Enter the name of your ISP. This information is for identification purposes only.
18
Page 20
Type: There six kinds of method (PPPoE/ PPPoA/ Static/ DHCP/ Bridge/ CLIP).
DHCP Settings
Encapsulation: Select you encapsulation type. (Supplied by your ISP).
IP Address: Private IP address for connecting to a local private network (Default:
192.168.1.1).
PVC Settings
VPI: If instructed to change this, type in the VPI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
VCI: If instructed to change this, type in the VCI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
QoS: Quality of Service type. Select CBR (Continuous Bit Rate) to specify fixed
(always-on) bandwidth for voice or data traffic. Select UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate)
for applications that are non-time sensitive, such as e-mail. Select VBR (Variable
Bit Rate) for burst traffic and bandwidth sharing with other applications.
PCR: Divide the DSL line rate (bps) by 424 (the size of an ATM cell) to find the Peak
Cell Rate (PCR). This is the maximum rate at which the sender can send cells.
SCR: The Sustain Cell Rate (SCR) sets the average cell rate (long-term) that can be
transmitted.
Name: Enter the name of your ISP. This information is for identification purposes only.
Type: There six kinds of method (PPPoE/ PPPoA/ Static/ DHCP/ Bridge/ CLIP).
Bridge Settings
Encapsulation: Select you encapsulation type. (Supplied by your ISP).
PVC Settings
19
Page 21

VPI: If instructed to change this, type in the VPI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
VCI: If instructed to change this, type in the VCI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
QoS: Quality of Service type. Select CBR (Continuous Bit Rate) to specify fixed
(always-on) bandwidth for voice or data traffic. Select UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate)
for applications that are non-time sensitive, such as e-mail. Select VBR (Variable
Bit Rate) for burst traffic and bandwidth sharing with other applications.
PCR: Divide the DSL line rate (bps) by 424 (the size of an ATM cell) to find the Peak
Cell Rate (PCR). This is the maximum rate at which the sender can send cells.
SCR: The Sustain Cell Rate (SCR) sets the average cell rate (long-term) that can be
transmitted.
Name: Enter the name of your ISP. This information is for identification purposes only.
Type: There six kinds of method (PPPoE/ PPPoA/ Static/ DHCP/ Bridge/ CLIP).
CLIP Settings
IP Address: Private IP address for connecting to a local private network (Default:
192.168.1.1).
Netmask: Netmask for the local private network (Default: 255.255.255.0).
ARP Server: Translating an IP address to an ATM address.
Default Gateway: This field is optional. Enter in the IP address of the router on your
network.
20
Page 22

PVC Settings
VPI: If instructed to change this, type in the VPI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
VCI: If instructed to change this, type in the VCI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
QoS: Quality of Service type. Select CBR (Continuous Bit Rate) to specify fixed
(always-on) bandwidth for voice or data traffic. Select UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate)
for applications that are non-time sensitive, such as e-mail. Select VBR (Variable
Bit Rate) for burst traffic and bandwidth sharing with other applications.
PCR: Divide the DSL line rate (bps) by 424 (the size of an ATM cell) to find the Peak
Cell Rate (PCR). This is the maximum rate at which the sender can send cells.
SCR: The Sustain Cell Rate (SCR) sets the average cell rate (long-term) that can be
transmitted.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
21
Page 23

Wireless
This page allow you to enable and disable the wireless LAN function, create a SSID,
and select the channel for wireless communications..
Channel: Select a transmission channel for wireless communications. The channel of
any wireless device must match the channel selected here in order for the
wireless device to access the LAN and WAN via the router.
SSID: Type an SSID in the text box. The SSID of any wireless device must match the
SSID typed here in order for the wireless device to access the LAN and WAN via
the router.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
22
Page 24

Advanced
Beacon Period: Type the Beacon Period in the text box. You can specify a value from
0 to 65535. The default Beacon Period is 200.
DTIM Period: Type a DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) Period in the text
box. You can specify a value between 1 and 255. The default value is 2.
RTS Threshold: Type the RTS (Request-To-Send) threshold in the text box. You can
specify a value from 0 to 4096. The default value is 2347.
Frag Threshold: Type the fragmentation in the text box. You can specify a value from
0 to 4096. The default value is 2346.
Power Level: Adjust the power of the antenna transmission by selecting from the
dropping list.
b/g Mode: Select mode from the dropping list. (Mixed/ b/ b+/ 11g only)
Hidden SSID: Select it to hidden your SSID.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
23
Page 25

Status
Network Statistics
The Ethernet Network Statistics page shows the statistics for the Ethernet connection.
The DSL Network Statistics page shows the statistics for the DSL connection.
24
Page 26

The Wireless Network Statistics page shows the statistics for the Wireless connection.
25
Page 27

Connection Status
The Connection Status page shows the status of PPP for each PPP interface.
26
Page 28

System Log
The System Log page shows the events triggered by the system.
27
Page 29

Advanced Setting
LAN Setup
The following is displayed LAN Setup.
DHCP Configuration
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. It can automatically dispatch
related IP settings to any local user configured as a DHCP client.
Server On: Enables the DHCP server.
Start IP: Sets the start IP address of the IP address pool.
End IP: Sets the end IP address of the IP address pool.
Lease time: The lease time is the amount of time of a network user will be allowed to
connect with DHCP server. If all fields are 0, the allocated IP address will be
effective forever.
Relay On: Allow PCs on LAN to request IP from other DHCP server.
Relay IP: Sets the other DHCP server IP address.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
28
Page 30

Management IP
The Management IP page shows the ADSL physical layer status.
IP Address: Private IP address for connecting to a local private network (Default:
192.168.1.1).
Netmask: Netmask for the local private network (Default: 255.255.255.0).
Default Gateway: This field is optional. Enter in the IP address of the router on your
network.
Host Name: Required by some ISPs. If the ISP does not provide the Host name,
please leave it blank.
Domain Name:
www.dynsns.org will provid e you with a Domain Name. Enter this
name in the “Domain Name” field.
Physical Port: There are five kinds of mode for data transfer (Auto)(10/Half
Duplex)(10/Full Duplex)(100/Half Duplex)(100/Full Duplex).
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
29
Page 31

Firewall/NAT Services
Network Address Translation (NA T): Is a method of mapping one or more IP
addresses and/or IP service ports into different specified values.
Firewall: In addition to the built-in NAT mechanism.
Firewall/NAT Services: Select Enable to turn on the Firewall/NAT Service.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
30
Page 32

WAN Setup
The following is displayed WAN Setup.
Add New Connection
When working with wide area connections, the first thing you must do is to have the
handle of the connection. Once you have the handle for a Connection you must define
the PVC and protocol settings for it.
Name: Enter the name of your ISP. This information is for identification purposes only.
Type: There six kinds of method (PPPoE/ PPPoA/ Static/ DHCP/ Bridge/ CLIP).
PPP Settings
Encapsulation: Select you encapsulation type. (Supplied by your ISP).
Username: Enter the username provided by your ISP.
31
Page 33

Password: Enter the password provided by your ISP.
Idle Timeout: Idle timeout means the router will disconnect after being idle for a
preset amount of time. The default is 60 seconds. If you set the time to 0, the
ISDN connection will remain always connected to the ISP.
Keep Alive: If mode is LCP, This is the Keep Alive timer. If a reply to the LCP echo is
not received in this amount if time, the connection is dropped. The Default is 10.
Authentication: Set the required authentication protocol. (Auto/ CHAP/ PAP)
MRU: Maximum Receive Unit indicates the peer of PPP connection the maximum size
of the PPP information field this device can be received. The default value is 1492
and is used in the beginning of the PPP negotiation. In the normal negotiation, the
peer will accept this MRU and will not send packet with information field larger
than this value.
PVC Settings
VPI: If instructed to change this, type in the VPI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
VCI: If instructed to change this, type in the VCI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
QoS: Quality of Service type. Select CBR (Continuous Bit Rate) to specify fixed
(always-on) bandwidth for voice or data traffic. Select UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate)
for applications that are non-time sensitive, such as e-mail. Select VBR (Variable
Bit Rate) for burst traffic and bandwidth sharing with other applications.
PCR: Divide the DSL line rate (bps) by 424 (the size of an ATM cell) to find the Peak
Cell Rate (PCR). This is the maximum rate at which the sender can send cells.
SCR: The Sustain Cell Rate (SCR) sets the average cell rate (long-term) that can be
transmitted.
32
Page 34

Name: Enter the name of your ISP. This information is for identification purposes only.
Type: There six kinds of method (PPPoE/ PPPoA/ Static/ DHCP/ Bridge/ CLIP).
Static Settings
Encapsulation: Select you encapsulation type. (Supplied by your ISP).
IP Address: Private IP address for connecting to a local private network (Default:
192.168.1.1).
Netmask: Netmask for the local private network (Default: 255.255.255.0).
Default Gateway: This field is optional. Enter in the IP address of the router on your
network.
DNS: Sets the IP address of the DNS server.
Mode: Bridged and Routed
PVC Settings
VPI: If instructed to change this, type in the VPI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
VCI: If instructed to change this, type in the VCI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
QoS: Quality of Service type. Select CBR (Continuous Bit Rate) to specify fixed
(always-on) bandwidth for voice or data traffic. Select UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate)
for applications that are non-time sensitive, such as e-mail. Select VBR (Variable
Bit Rate) for burst traffic and bandwidth sharing with other applications.
PCR: Divide the DSL line rate (bps) by 424 (the size of an ATM cell) to find the Peak
Cell Rate (PCR). This is the maximum rate at which the sender can send cells.
SCR: The Sustain Cell Rate (SCR) sets the average cell rate (long-term) that can be
transmitted.
33
Page 35

Name: Enter the name of your ISP. This information is for identification purposes only.
Type: There six kinds of method (PPPoE/ PPPoA/ Static/ DHCP/ Bridge/ CLIP).
DHCP Settings
Encapsulation: Select you encapsulation type. (Supplied by your ISP).
IP Address: Private IP address for connecting to a local private network (Default:
192.168.1.1).
PVC Settings
VPI: If instructed to change this, type in the VPI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
VCI: If instructed to change this, type in the VCI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
QoS: Quality of Service type. Select CBR (Continuous Bit Rate) to specify fixed
(always-on) bandwidth for voice or data traffic. Select UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate)
for applications that are non-time sensitive, such as e-mail. Select VBR (Variable
Bit Rate) for burst traffic and bandwidth sharing with other applications.
PCR: Divide the DSL line rate (bps) by 424 (the size of an ATM cell) to find the Peak
Cell Rate (PCR). This is the maximum rate at which the sender can send cells.
SCR: The Sustain Cell Rate (SCR) sets the average cell rate (long-term) that can be
transmitted.
34
Page 36

Name: Enter the name of your ISP. This information is for identification purposes only.
Type: There six kinds of method (PPPoE/ PPPoA/ Static/ DHCP/ Bridge/ CLIP).
Bridge Settings
Encapsulation: Select you encapsulation type. (Supplied by your ISP).
PVC Settings
VPI: If instructed to change this, type in the VPI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
VCI: If instructed to change this, type in the VCI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
QoS: Quality of Service type. Select CBR (Continuous Bit Rate) to specify fixed
(always-on) bandwidth for voice or data traffic. Select UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate)
for applications that are non-time sensitive, such as e-mail. Select VBR (Variable
Bit Rate) for burst traffic and bandwidth sharing with other applications.
PCR: Divide the DSL line rate (bps) by 424 (the size of an ATM cell) to find the Peak
Cell Rate (PCR). This is the maximum rate at which the sender can send cells.
SCR: The Sustain Cell Rate (SCR) sets the average cell rate (long-term) that can be
transmitted.
35
Page 37

Name: Enter the name of your ISP. This information is for identification purposes only.
Type: There six kinds of method (PPPoE/ PPPoA/ Static/ DHCP/ Bridge/ CLIP).
CLIP Settings
IP Address: Private IP address for connecting to a local private network (Default:
192.168.1.1).
Netmask: Netmask for the local private network (Default: 255.255.255.0).
ARP Server: Translating an IP address to an ATM address.
Default Gateway: This field is optional. Enter in the IP address of the router on your
network.
PVC Settings
VPI: If instructed to change this, type in the VPI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
VCI: If instructed to change this, type in the VCI value for the initial connection (using
PVC 0). Default = 0.
QoS: Quality of Service type. Select CBR (Continuous Bit Rate) to specify fixed
(always-on) bandwidth for voice or data traffic. Select UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate)
for applications that are non-time sensitive, such as e-mail. Select VBR (Variable
Bit Rate) for burst traffic and bandwidth sharing with other applications.
PCR: Divide the DSL line rate (bps) by 424 (the size of an ATM cell) to find the Peak
Cell Rate (PCR). This is the maximum rate at which the sender can send cells.
SCR: The Sustain Cell Rate (SCR) sets the average cell rate (long-term) that can be
transmitted.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
36
Page 38

Advanced
UPnP
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) is a distributed, open networking standard that uses
TCP/IP for simple peer-to –peer network connectivity between devices a UPnP device
can dynamically join a network, obtain and IP address, convey is capabilities and learn
about other devices on the network. In turn, a device can leave a network smoothly
and automatically when it is no longer in use.
Enable UPNP: Enable the UPnP.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
37
Page 39

Multicast
The NSP is capable of proxying for applications that are using multicast IP for
accessing Video content. This application needs to be run when NAT is enabled.
Enable IGMP Multicast: Enable or Disable IGMP Multicast.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
38
Page 40

LAN Clients
The LAN Clients page allows you to set the configuration for the LAN port.
New IP Address: Enter the IP Address.
Hostname: Enter the Hostname.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
39
Page 41

Web Filters
The following queries manage the Content Filtering capabilities of the NSP.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
40
Page 42

Bridge Filters
The bridge filtering page allows users to set the configuration of IP filtering.
Source MAC: When the bridge filtering is enabled, enter the Source MAC address,
select Block and click Add. Then all incoming WAN and LAN Ethernet packets
matched with this source MAC address will be filtered out. If the Forward is
selected, then the packets will be forwarded to the destination PC.
Destination MAC: When the bridge filtering is enabled, enter the Destination MAC
address, select Block and click Add. Then all incoming WAN and LAN Ethernet
packets matched with this destination MAC address will be filtered out. If the
Forward is selected, then the packets will be forwarded to the destination PC.
Type: Enter the hexadecimal number for the Ethernet type field in Ethernet_II packets.
For example, 0800 is for IP protocol.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
41
Page 43

Modem Setup
Select ADSL Transmission Rate.
T1413: Full-Rate (ANSI T1.413 Issue 2) with line rate support of up to 8 Mbps
downstream and 832 Kbps upstream.
GDMT: Full-Rate (G.dmt, G992.1) with line rate support of up to 8 Mbps downstream
and 832 Kbps upstream.
GLITE: G.lite (G.992.2) with line rate support of up to 1.5 Mbps downstream and 512
Kbps upstream.
MMODE: Support Multi-Mode standard (ANSI T1.413 Issue 2; G.dmt(G.992.1);
G.lite(G.992.2)).
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
42
Page 44

Static Routing
The following queries manage the RIP routing application and static routing entries for
the NSP. The RIP application su pports both version 1 and 2.
New Destination IP: Enter the New Destination IP.
Gateway: Enter the IP Address of the Gateway.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
43
Page 45

Access Control
Access Control allows users to define the outgoing traffic permitted or denied access
through the WAN interface. The default is to permit all outgoing traffic.
44
Page 46

45
Page 47

Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
46
Page 48

Port Forwarding
The Port Forwarding page allows the user define a port forwarding rule without using
the firewall policy database definitions and apply it to the connection.
47
Page 49

48
Page 50

Choose a connection: You can choose a connection to do this.
LAN IP: type your LAN IP. For example 192.168.1.2.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
49
Page 51

Dynamic Routing
The following queries manage the RIP routing application and static routing entries for
the NSP. The RIP application su pports both version 1 and 2.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
50
Page 52

Wireless Security
Select a Wireless Security level
None: Disable Wireless encryption.
WEP: WEP encryption scrambles the data transmitted between the wireless stations
and the access points to keep network communications private. It encrypts
unicast and multicast communications in a network. Both the wireless stations
and the access points must use the same WEP key for data encryption and
decryption.
51
Page 53

802.1x: The IEEE 802.1x standards outline enhanced security methods for both the
authentication of wireless stations and encryption key management.
WPA: Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a subset of the IEEE 802.11i security
specification draft. Key differences between WPA and WEP are user
authentication and improved data encryption.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
52
Page 54

Advanced Security
The Advanced Security page provides advanced rules that can be applied to a
particular Connection.
Enable DMZ: Enable or Disable DMZ.
Enable Remote Web: Allow or deny incoming access to the modems Web pages
remotely.
Enable Remote Telnet: Allow or deny incoming access to the modems Telnet
Interface remotely.
Enable Incoming ICMP Ping: Allow or deny incoming Pings to the Modem.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
53
Page 55

Wireless Management
The Wireless Management page allows your prestige can check the MAC addresses
of Wireless stations against a list of allowed or denied MAC addresses.
Enable Access List: Enable the Wireless Management by Access List.
MAC Address: Enter the MAC Address.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
54
Page 56

Tools
The Tools section allows you to save the configuration, restart the gateway , update the
gateway firmware, setup user and remote log information and run Ping and Modem
tests.
Ping Test
Packet INternet Groper is protocol that sends out ICMP echo requests to test whether
or not a remote host is reachable.
55
Page 57

Remote Log
The Router Table page displays routing table and allows the user to manually enter
the routing entry. The routing table will display the routing status of Destination,
Netmask, Gateway and Interface. The interface br0 means the USB interface; Io0
means the loopback interface and ppp1 means the PPP interface. The Gateway is the
learned Gateway.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
56
Page 58

Modem Test
This test can be used to check whether your Modem is properly connected to the
Network. This test may take a few seconds to complete. To perform the test, select
your connection from the list and press the Test button.
57
Page 59

UI Preferences
The UI preferences page allows user to set screen size.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
58
Page 60

Update Gateway
To update your gateway firmware, choose an update image (Kernel/ File system) or
configuration file In Select a File, and then click the Update Gateway button.
Additionally, you may download your configuration file from the system by clicking Get
Configuration.
59
Page 61

User Management
User Management is used to change your User Name or Password.
User Name: Default is ‘Admin’.
Password: Default is ‘Admin’.
Apply: Click Apply to save the changes.
60
Page 62

System Commands
System commands allow you to carry out basic system actions. Press the button to
execute a command.
61
Page 63

Status
The Status section allows you to view the Status/Statistics of different connections and
interfaces.
System Log
The System Log page shows the events triggered by the system.
62
Page 64

DHCP Clients
The DHCP Clients page shows the MAC Address, IP Address, Host Name and Lease
Time.
63
Page 65

Modem Status
The Modem Status page shows the modem status and DSL statistics.
64
Page 66

Network Statistics
The Ethernet Network Statistics page shows the statistics for the Ethernet connection.
The DSL Network Statistics page shows the statistics for the DSL connection.
65
Page 67

The Wireless Network Statistics page shows the statistics for the Wireless connection.
66
Page 68

Connection Status
The Connection Status page shows the status of PPP for each PPP interface.
67
Page 69

Product Information
The Product Information page shows the product information and software versions.
68
Page 70

Appendix
Country ISP PVC
Australia All Internet providers
Belgium
Canada Telus
Cybercity
Danmark
Tiscali
1 & 1 Internet DSL
AOL DSL
Arcor DSL
VPI:8
VCI:35
VPI:0
VCI:33
VPI:0
VCI:35
VPI:8
VCI:35
VPI:8
VCI:35
VPI:1
VCI:32
VPI:1
VCI:32
VPI:8
VCI:35
Freenet DSL
Fireline networks
Deutschland
GMX Internet
Hansenet
Netcologne
Schlund
Snafu ADSL
69
VPI:1
VCI:32
VPI:1
VCI:32
VPI:1
VCI:32
VPI:8
VCI:35
VPI:8
VCI:35
VPI:1
VCI:35
VPI:1
VCI:32
Page 71

Country ISP PVC
Tiscali
T-online
Anderer Anbieter
Wannadoo
France
Tiscali
ISRAEL KPN PPPoE LLC
Telecom Italia
Italian
Rest oil presente
VPI:1
VCI:32
VPI:1
VCI:32
VPI:1
VCI:32
VPI:8
VCI:35
VPI:8
VCI:35
VPI:8
VCI:48
VPI:8
VCI:35
VPI:8
VCI:35
KPN PPPoA VC-MuX
Netherlands
BBeyond Bridge LLC
BBeyond PPPoA VC-MuX
New Zealand New Zealand Telecom
Portugal Todos os apresentador
Albura
Spanish
Colt Teeccom
Earth
VPI:8
VCI:48
VPI:0
VCI:33
VPI:0
VCI:35
VPI:0
VCI:100
VPI:0
VCI:35
VPI:1
VCI:32
VPI:0
VCI:35
VPI:8
VCI:32
70
Page 72

Country ISP PVC
Spanish
Eresmas
Jazztel
Ola Internet
Retevision
Terra
Tiscali
Telefornica
Telepac
VPI:8
VCI:35
VPI:8
VCI:35
VPI:8
VCI:35
VPI:0
VCI:35
VPI:8
VCI:32
VPI:1
VCI:32
VPI:8
VCI:32
VPI:8
VCI:35
Uni2
Ya.com
Wanadoo
Island ssimi
Suomi
Landssimi
Vortex
Switserland Alle anbieter
Sverige Skanova
VPI:1
VCI:33
VPI:8
VCI:32
VPI:8
VCI:32
VPI:0
VCI:35
VPI:8
VCI:48
VPI:8
VCI:48
VPI:1
VCI:32
VPI:8
VCI:35
71
Page 73

Country ISP PVC
Hinet
Taiwan
Seednet
User
United Arab Emirates
Etisalat Classical IP for
Business
United Kingdom British Telecom
VPI:0
VCI:33
VPI:0
VCI:33
VPI:8 Etisalat Classical IP Single
VCI:35
VPI:8
VCI:35
VPI:0
VCI:38
72
 Loading...
Loading...