Page 1

IGS-5208
User Manual
01-2019 / v1.0
Page 2

FCC Warning
This Equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class-A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy. It may cause harmful interference to radio communications if the equipment is not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Intended Readers .................................................................................................................... 1
Icons for Note, Caution, and Warning .................................................................................... 1
I. Product Overview ........................................................................................... 2
I-1 Product Brief Description............................................................................... 2
I-2 Product Specification ........................................................................................................ 2
I-3. Hardware Description ..................................................................................................... 5
I-4. DIN-Rail Mounting ........................................................................................................... 9
I-5. Console Connection ..................................................................................................... 10
I-6. Connecting Cable ......................................................................................................... 10
II.
Preparing for Management ........................................................................... 11
II-1. Preparation for Web Interface ..................................................................................... 11
III. Web Management ......................................................................................... 12
III-1. Web Management - Overview .................................................................................... 12
III-2. Web Management - System ........................................................................................ 14
III-3. Web Management – IPv4 Settings ............................................................................. 15
III-4. Web Management – IPv6 Settings ............................................................................. 17
III-5. Web Management – System Time .............................................................................. 19
III-6. Web Management – RSTP Configuration .................................................................. 21
III-7. Web Management – ERPS .......................................................................................... 27
III-8. Web Management – SNMP ......................................................................................... 30
III-9. Web Management – DHCP ......................................................................................... 35
III-10. Web Management – ModBUS/TCP ........................................................................... 41
III-11. Web Management – UPnP ........................................................................................ 47
III-12. Web Management – Port Management .................................................................... 48
III-13. Web Management – IGMP Snooping ....................................................................... 51
III-14. Web Management – 802.1Q VLAN ........................................................................... 53
III-15. Web Management – Quality of Service (QoS) ......................................................... 59
III-16. Web Management – Port Trunk ................................................................................ 65
III-17. Web Management – Storm Control .......................................................................... 67
III-18. Web Management – 802.1X ......................................................................................... 69
III-19. Web Management – Port Mirroring .......................................................................... 73
III-20. Web Management – Ping .......................................................................................... 74
III-21. Web Management – LLDP ........................................................................................ 75
III-22. Web Management – System Warning ...................................................................... 77
III-23. Web Management – MAC Table ............................................................................... 83
III-24. Web Management – Authorization ........................................................................... 85
III-25. Web Management – Firmware Upgrade .................................................................. 86
III-26. Web Management – Config Backup......................................................................... 91
III-27. Web Management – Config Restore ........................................................................ 92
III-28. Web Management – USB Auto-Load &Auto-Backup .............................................. 93
Appendix A: IP Configuration for Your PC .......................................................................... 94
Appendix B: CLI Command Reference ................................................................................ 97
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement ....................................................... 118
R&TTE Compliance Statement ................................................................................................... 11 8
Page 4
icon indicates important information which will guide you to use this
icon indicates either a potential for hardware damage or data loss,
Intended Readers
This manual provides information regarding to all the aspects and functions needed to install, configure,
use, and maintain the product you’ve purchased.
This manual is intended for technicians who are familiar with in-depth concepts of networking
management and terminologies.
Icons for Note, Caution, and Warning
To install, configure, use, and maintain this product properly, please pay attention when you see these
icons in this manual:
A Note
product properly.
A Caution
including information that will guide you to avoid these situations.
A Warning icon indicates potentials for property damage and personal injury.
If you have any questions, please contact our technical support via email:
service@edimax.com.tw.
1
Page 5

Interface
10/100/1000 Base RJ45 Ports
8
1000Base-X SFP Slot
2
Console Port for CLI Management
1
1x USB 2.0 storage for firmware update,
I. Product Overview
This section will give you an overview of this product, including its feature functions and hardware/software
specifications.
Product Brief Description
Product Specification
Hardware Description
Hardware Installation
I-1 Product Brief Description
Introduction
This switch is a DIN Rail type industrial Gigabit managed Switch is designed with eight 10/100/1000M RJ45
ports and two Gigabit SFP slots for highly critical applications such as real time IP video surveillance, WiMAX
systems and Wireless APs.
Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPSv2)
Ring network topology ensures the reliability of the connections among all the switches in the network. This
switch supports ERPSv2 with easy to set up user interface, which allows it to recover from network
disconnection in less than 20ms with 250 switches connected in a ring network topology while
transmitting/receiving data at full network speed. Also, this switch supports multiple ERPS instances, allowing
different VLANs have their own ERPS instances.
USB Port for Save/Restore Configuration & System Log/Firmware Storage
This switch comes with a USB port for connecting a USB storage device to the industrial switch. Configuration
files, switch system log and firmware can be stored in the USB storage device for the switch to access. When a
USB storage device is connected to the switch, it will load the configuration file in the storage device and apply
all the settings, saving on-site installation time and effort.
Redundant Power Inputs & Embedded Protecting Circuit
This switch provides two power inputs that can be connected simultaneously to live DC power source. If one of
the power input fails, the other live source acts as a backup to automatically support the switch’s power needs
without compromising network service qualities. Also, it supports automatic protection switching and load
balance, while its embedded protecting circuit can protect your system from over input/output voltages and
rectifier malfunctions.
Outstanding Management and Enhanced Security
This switch provides various network control and security features to ensure the reliable and secure network
connection. To optimize the industrial network environment the switch supports advanced network features,
such as Tag VLAN, IGMP Snooping, Quality of Service (QoS), Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP), Rate
Control, etc. The switch can be smartly configured through Web Browser, SNMP Telnet and RS-232 local console
with its command like interface. The failure notifications are sent through e-mail, SNMP trap, Local/Remote
system log, multiple event alarm relay.
I-2 Product Specification
USB Port
configuration backup, restore, boot up and
system log
2
Page 6
System Performance
Packet Buffer
12Mbits
MAC Address Table Size
16K
Switching Capacity
20Gbps
Forwarding Rate
14.88Mpps
L2 Features
Auto-negotiation
Auto MDI/MDIX
Flow Control
802.3x (Full)
Back-Pressure
IEEE 802.1D
IEEE 802.1w
IEEE 802.1s
VLAN Group
4K
Tagged Based
Port-based
Voice VLAN
Link
IEEE 802.3ad
IGMP Snooping
IGMP Static
Querier,
Storm Control
G.8032 - Ethernet Ring Protection
Jumbo Frame Support
9.6KB
QoS Features
CoS DSCP
WRR/SPQ Queuing
Security
Management System User
IEEE 802.1x Port-based Access Control
RADIUS (Authentication, Authorization,
HTTP & SSL (Secure Web)
SSH v2.0 (Secured Telnet Session)
Management
Command Line Interface (CLI)
Web Based Management
Telnet
Firmware Upgrade via HTTP
(duplex)
Spanning Tree
VLAN
Aggregation
IGMP Snooping
(Half)
(STP)
(RSTP)
(MSTP)
with LACP
v1/v2/v3
Multicast
Addresses
Immediate
Leave
Supports 1023 IGMP groups
Switching (ERPS)
Name/Password Protection
Accounting)
3
Page 7
Configuration Download/Upload
SNMP (v1/v2c/v3)
RMON (1,2,3,&9 groups)
DHCP (Client/Relay/Option82)
System Event/Error Log
NTP/LLDP
Port Mirroring
Industrial Profiles
Ethernet/IP, Modbus TCP
Mechanical
Input Power
DC12~48V, Dual Redundant
Power Connection
1 removable 4-contact terminal block
Max. Power Consumption
17W
Dimension (H*W*D)
72.2 x 145 x 113 mm
Weight
0.85KG
Per unit: PWR1, PWR2, Fault, Ring Master,
Link/Active with highest speed
Button
1 mulltiple function reset button
Operating Temperature
-40 to 75°C
Storage Temperature
-40 ~ 85°C
Operating Humidity
5~95% (non-condensing)
MTBF
>100,000 Hours
Industrial Standard
1 relay output with current carrying capacity
Reverse Polarity Protection
Overload Current Protection
Casing
IP30 protection, aluminum alloy case
FCC Part 15 Subpart B Class A, CE EN 55022
IEC61000-4-2 (ESD Level 4), IEC61000-4-3 (RS
Shock
IEC60068-2-27
Free Fall
IEC60068-2-32
Vibration
IEC60068-2-6
Green
RoHS Compliant
Installation
DIN-Rail mounting or optional wall mounting
Standard
IEEE 802.3 – 10BaseT
IEEE 802.3u – 100BaseTX
IEEE 802.3ab – 1000BaseT
IEEE 802.3z 1000BaseSX/LX
IEEE 802.3x – Flow Control
IEEE 802.1Q – VLAN
IEEE 802.1p – Class of Service
IEEE 802.1D – Spanning Tree
IEEE 802.1w – Rapid Spanning Tree
LED
Alarm Contact
EMI
EMS
Ring State
Ports:
(Green), low speed (Amber)
of 1A @ 24 VDC
Class A
Level 3)
IEC61000-4-4 (EFT Level 4), IEC61000-4-5
(Surge Level 4)
IEC61000-4-6 (CS Level 3), IEC61000-4-8
(Magnetic Field Level 4)
4
Page 8
IEEE 802.1s – Multiple Spanning Tree
IEEE 802.3ad – Link Aggregation Control
IEEE 802.1AB – LLDP (Link Layer Discovery
IEEE 802.1X – Access Control
ITU-T G.8032/Y.1344 - Ethernet Ring
Protocol (LACP)
Protocol)
Protection Switching (ERPS)
I-3. Hardware Description
This section mainly describes the hardware of this switch and gives a physical and functional overview on the
certain switch.
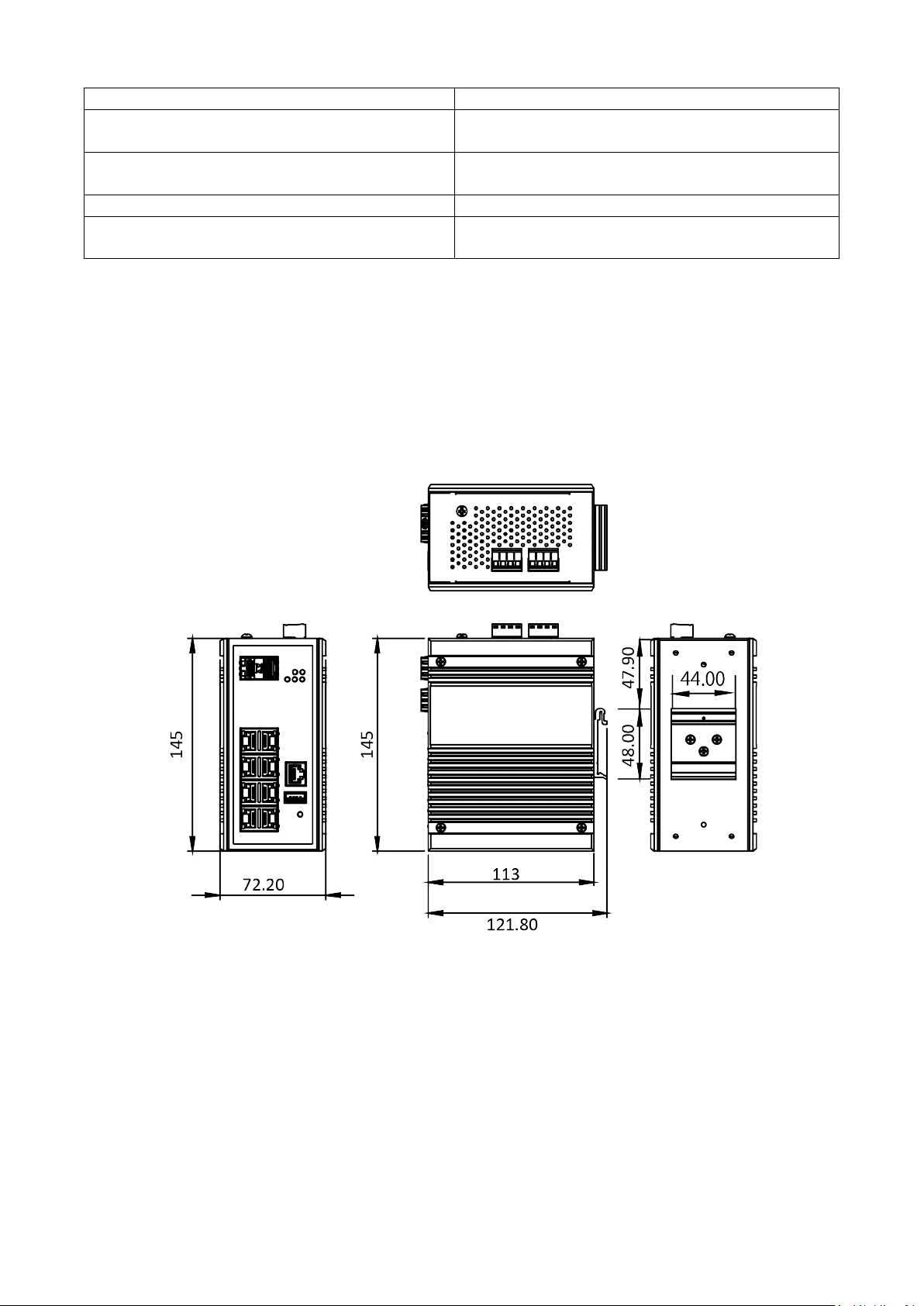
Dimension
The dimension of this Switch is 145 mm (H) x 72.20 mm (W) x 113 mm (D). The figure down below is the
drawing of detail mechanical design:
5
Page 9

Wiring Power Inputs
1. Insert the positive and negative wires into the PWR1 (+,-) and PWR2 (+,-) on the 4-contact
terminal block connector.
2. 2. Tighten the screws to prevent the wires from loosening.
Wiring Fault Alarm
1. Insert the wires into the left two contacts of the 4-contact terminal block (Fault Alarm
Relay).
2. Tighten the screws to prevent the wires from loosening.
3. The relay will detect the power and link failure.
4. Users can connect the relay to an alarm and buzzer so that when the relay forms an open
circuit, the users will be notified.
Wiring Digital Inputs
1. Insert the positive and negative wires into the right two contacts (+,-) of the 4-contact
terminal block (DI).
2. Tighten the screws to prevent the wires from loosening.
3. The system will detect the voltage go through the DI.
• +13 to +30V for state "1"
• -30 to +3V for state "0"
• Max. input current: 8mA
6
Page 10

Double-Secure Power Input Fault Alarm
The power inputs are designed as a "common negative", which implies that the negative input is connected, but
"double-secure" is supported to prevent the un-notified failure of power from one of the negative inputs. If one
of the negative power input fails, the system will detect it and the system will trigger the event if the users set
the fault alarm or event log for powers.
7
Page 11
LED
Color
Status
Description
On
Power is supplied on the power input 1.
Off
Power is not supplied on the power input 1.
On
Power is supplied on the power input 2.
Off
Power is not supplied on the power input 2.
On
The system boots up and in normal operation.
Off
The system is powered off or during booting.
Red
On
The configured event of failure is triggered.
On
This device has the Ring Master.
Off
The Ring Master is not on the device.
On
The Ring protocol is enabled and works normally.
Flickering
The Ring protocol is enabled, but works abnormally.
Off
The Ring protocol is disabled.
On
The 1000Mbps link of the fiber port is active.
Flickering
Data is transmitted on the fiber port at 1000Mbps.
Off
The 1000Mbps link of the fiber port is inactive.
LAN Port
On
The 1000Mbps link of the port is active.
Flickering
Data is transmitted on the port at 1000Mbps.
Off
The 1000Mbps link of the port is inactive.
On
The 10/100Mbps link of the port is active.
Flickering
Data is transmitted on the port at 10/100Mbps.
Off
The 10/100Mbps link of the port is inactive.
Press Time (Sec)
Action
Save the running configuration to the USB device named
4
Reboot the system.
More than 7
Reset the system to factory default and reboot it.
LED Status
PWR1 Green
PWR2 Green
Fault
RM Green
Ring Green
SFP Slot
P9 to P10
Green
Green
(1000M)
P1 to P8
Green
(1000M)
LAN Port
P1 to P8
Green
(10/100M)
Reset Button
A multifunctional reset button is provided. Use a pointed object such as toothpick or paper clip
(straightened) to press the reset button.
1
"running-config".
8
Page 12
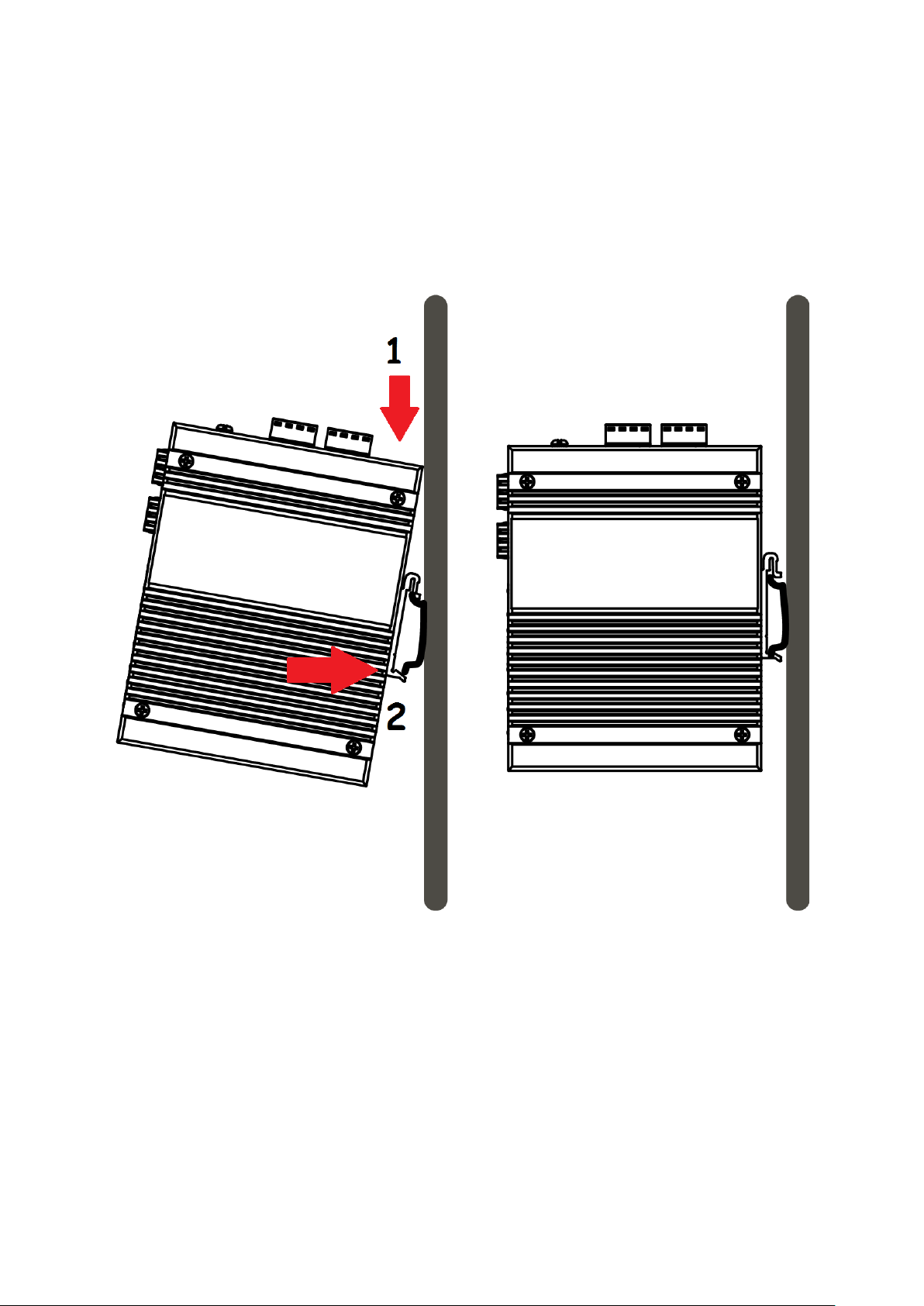
I-4. DIN-Rail Mounting
The DIN-Rail clip is already attached on the rear side of the switch supports EN 50022 standard DIN Rail, in the
following diagram includes the dimension of EN 50022 DIN Rail.
Follow the steps below to mount the switch on the DIN-Rail track.
1. Insert the upper end of the DIN-Rail clip into the back of the DIN-Rail track from its upper side
2. Lightly push the bottom of the DIN-Rail clip into the track.
3. Check if the DIN-Rail clip is tightly attached to the track.
4. To remove the switch from the track, reverse the steps above.
9
Page 13

I-5. Console Connection
The Console port is for local management by using a terminal emulator or a computer with terminal emulation
software.
DB9 connector connect to computer COM port
Baud rate: 115200bps
8 data bits, 1 stop bit
None Priority
None flow control
I-6. Connecting Cable
The port 1~4 is the copper ports, it requests UTP/STP cable.
The port 5 ~ 6 are the SFP slots, purchase the suitable fiber transceiver from your supplier and connect the fiber
cable for the link.
Ethernet cable Request
The wiring cable types for data transmission are as below.
10 Base-T: 2 -pair UTP/STP Cat. 3, 4, 5 cable, EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm (Max. 100m)
100 Base-TX: 2-pair UTP/STP Cat. 5 cable, EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm (Max. 100m)
1000 Base-T: 4 -pair UTP/STP Cat. 5 cable, EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm (Max. 100m)
The wiring cable types for data transmission and power delivery in any speed are Cat. 5 or above.
SFP Installation
While install the SFP transceiver, make sure the SFP type of the 2 ends is the same and the transmission
distance, wavelength, fiber cable can meet your request. It is suggested to purchase the SFP transceiver with
the switch provider to avoid any incompatible issue.
The way to connect the SFP transceiver is to Plug in SFP fiber transceiver fist. The SFP transceiver has 2 plug for
fiber cable, one is TX (transmit), the other is RX (receive). Cross-connect the transmit channel at each end to
the receive channel at the opposite end.
The switch is equipped with one dry relay output for port link fails or power fails. This session introduces how to
enable the event alarm DIP switch to alert field technician once the failure event is occurred. The new
configuration is activated immediately without system reset when DIP SWITCH is changed.
On the bottom side of the switch, there is one 9-Pin DIP SWITCH for alarm control. By inserting the port and
power wiring to set up the alarm, the DIP SWITCH of the intended Alarm is switched to “ON”. The relay output
will form a short circuit if the alarm occurred.
10
Page 14
II. Preparing for Management
This section will guide your how to manage this product via serial console, management web page, and
Telnet/SSH interface.
The switch provides in-band managements.
In-Band Management: In-band management allows you to manage your switch with a web browser (such as
Microsoft IE, Mozilla Firefox, or Google Chrome) as long as your PC and the switch are connected to the same
network.
Preparation for Web Interface
II-1. Preparation for Web Interface
The management web page allows you to use a web browser (such as Microsoft IE, Google Chrome, or Mozilla
Firefox) to configure and monitor the switch from anywhere on the network.
Before using the web interface to manage your switch, please verify that your switch and your PC are on the
same network. Please follow the steps down below to configure your PC properly:
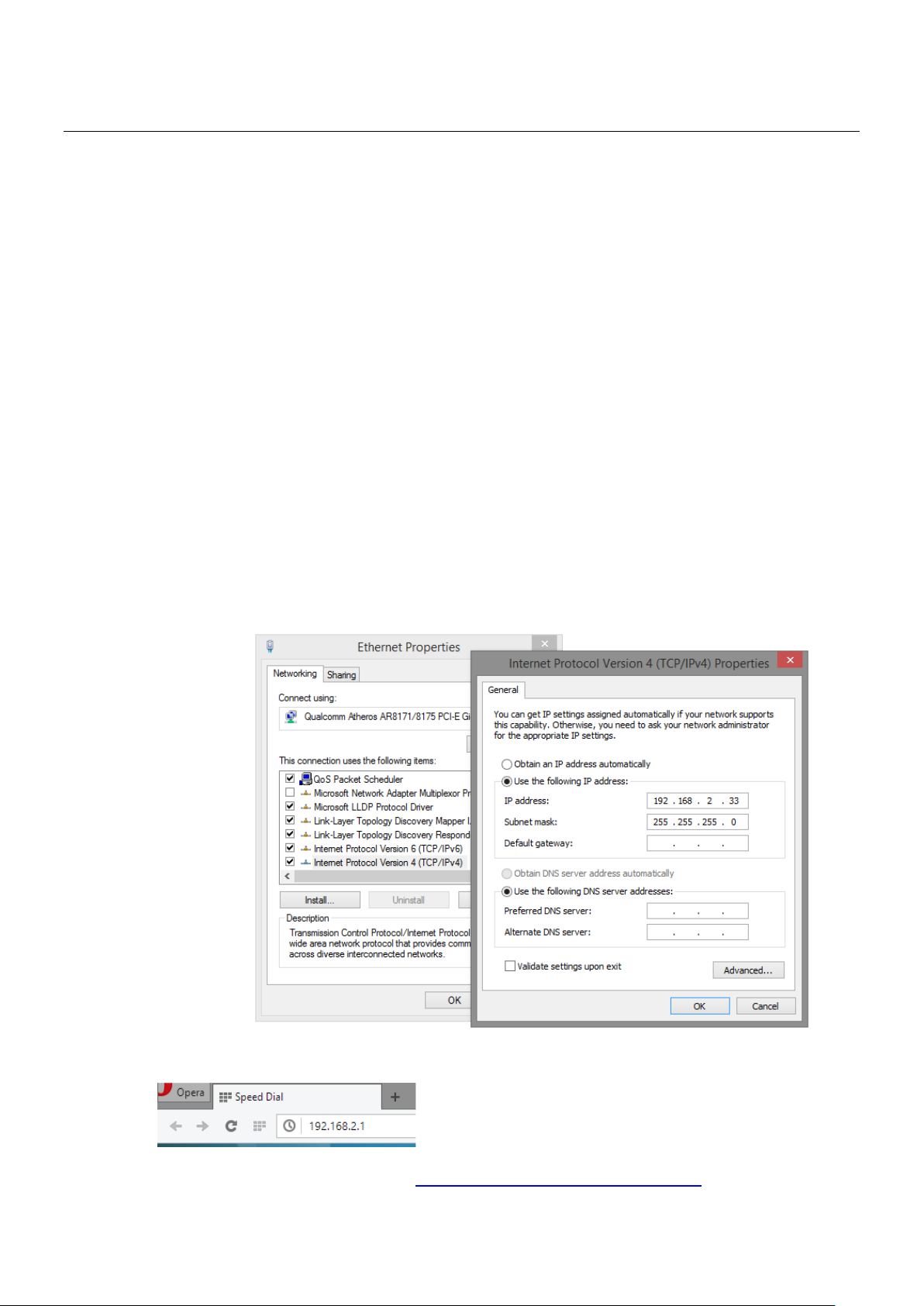
1. Verify that the network interface card (NIC) of your PC is operational and properly installed, and
that your operating system supports TCP/IP protocol.
2. Connect your PC with the switch via an RJ45 cable.
3. The default IP address of the switch is 192.168.2.1. The switch and your PC should locate within
the same IP Subnet. Change your PC's IP address to 192.168.2.X, where X can be any number from
2 to 254. Please make sure that the IP address you’ve assigned to your PC cannot be the same with
the switch.
4. Launch the web browser (IE, Firefox, or Chrome) on your PC.
5. Type 192.168.2.1 (or the IP address of the switch) in the web browser’s URL field, and press Enter.
6. The web browser will prompt you to sign in. The default username/password is admin/admin.
For more information, please refer to
Appendix A: IP Configuration for Your PC.
11
Page 15

III. Web Management
As mentioned in II-1. Preparation for Web Interface, This switch provides a web-based management interface.
You can make all settings and monitor system status with this management web page.
III-1. Web Management - Overview
When you log in, the configuration web page will display current system status.
1. Hide/Show Model Information
When a low-resolution environment is used to configure the system via the web console, the "Model
Information" field can be hidden to have a better view.
Show Model Information:
Hide Model Information:
12
Page 16
2. Save Configuration
After configuring, click the icon to save the configurations to the "startup-config" file. The configurations
are retained in the system until a factory reset default is done.
3. Restore Factory Default
Removes the configurations saved in the system. After restoring factory default, all the settings will be
set to default values.
4. Reboot System
Reboots the device and restarts the system.
5. System Logout
This option enables you to sign out from the system. Users have to login again if they want to configure
the settings.
The system will auto-logout after the "timeout" timer expires. The "timeout" timer is configured in the
CLI mode by using the "exec-timeout" command.
The maximum value of the timer in the web console is 30 mins.
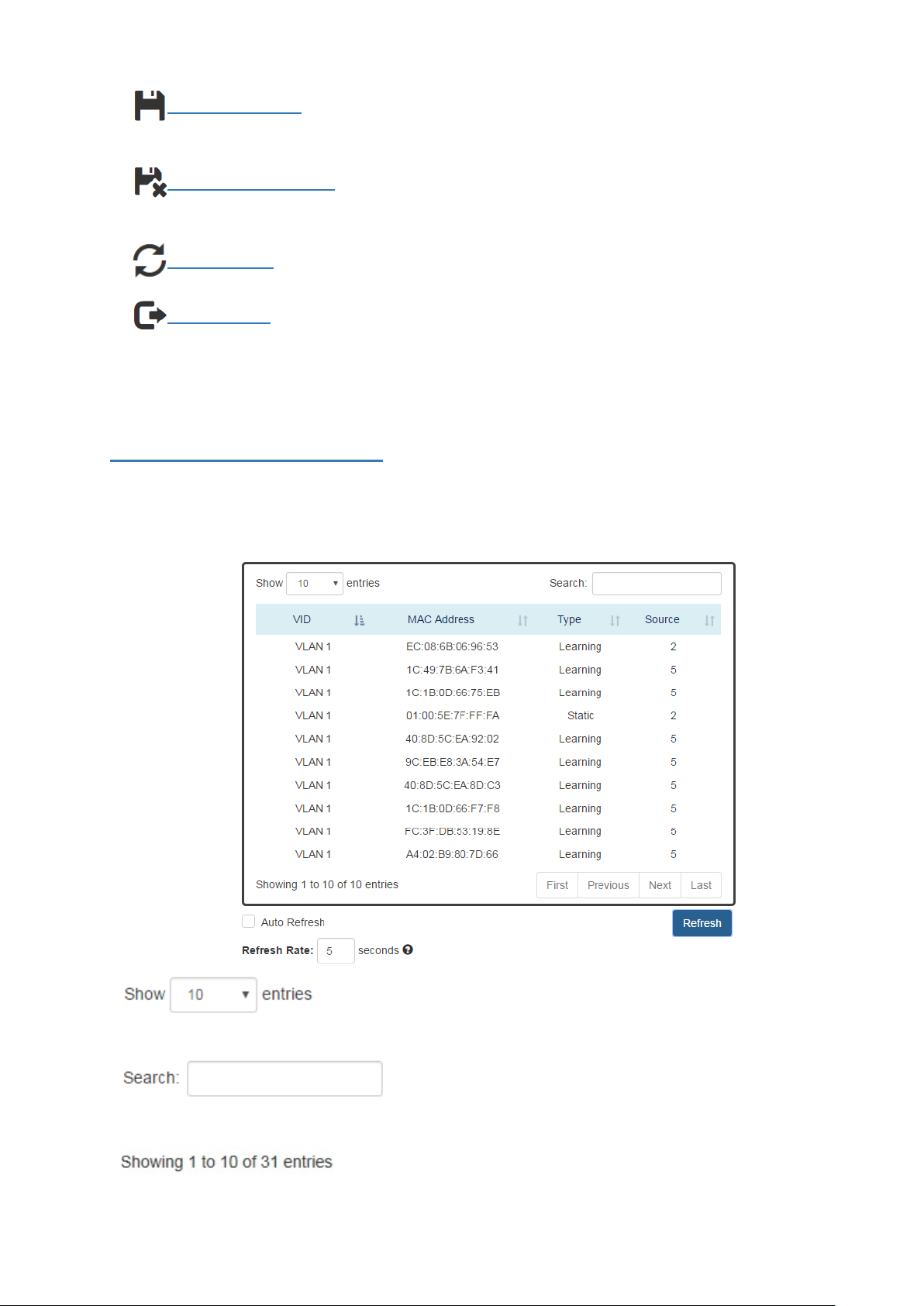
A USER-FRIENDLY DATA TABLE
A user-friendly data table is provided on the“IPv6 Neighbor Table”, “IGMP Snooping Table”, “ VLAN
Table”, “ LLDP Neighbor Table”, and “MAC Address Table”. The following section details how to use the
data table functions to help the users to observe the information easily.
The following example is “MAC Address Table”.
•
Users will be able to select a value to display the numberof entries in one page. The following values can
be selected - “10”, “25”, “ 50”, and “100” selections. By default, “10” is selected.
•
The search option enables you to search a key word in the data. It will search all the columns and
identify the data rows that match the search criteria.
•
It displays the total number of entries and the current entry number.
13
Page 17
•
and
This option orders the field from smaller to larger or from larger to smaller.
•
Changes to “First”, “Previous”, “Next”, or “Last” page.
In addition to the above functions, “Refresh” and “Auto Refresh” function are available for all status
page including “IPv6 Neighbor Table”, “RSTP Port Status”, “ Port Status”, “ IGMP Snooping Table”, “ VLAN
Table”, “ Trunking Status”, “LLDP Neighbor Table”, and “MAC Address Table”.
•
Selecting this checkbox enablesthe “Auto Refresh” function and deselecting the checkbox disables
the“Auto Refresh” function.
•
The Refresh Rate option is a global configurable variable. When the Auto Refresh option is enabled, the
status will refresh automatically based on the Refresh Rate interval.
The range of theRefresh Rate is from 5 to 300 second(s).
The default Refresh Rate is 5 seconds.
•
(Refresh Button)
You can click the “Refresh” button to manually refresh the status.
III-2. Web Management - System
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
• Host Name
It is useful to identify the difference between the switches, for example: CoreSwitch01.
The max. length for the Host Name is 32 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
• Device Description
The Device Description is fixed and defined by the system.
It contains the copper port number, fiber port number, and PoE information (if supported).
14
Page 18
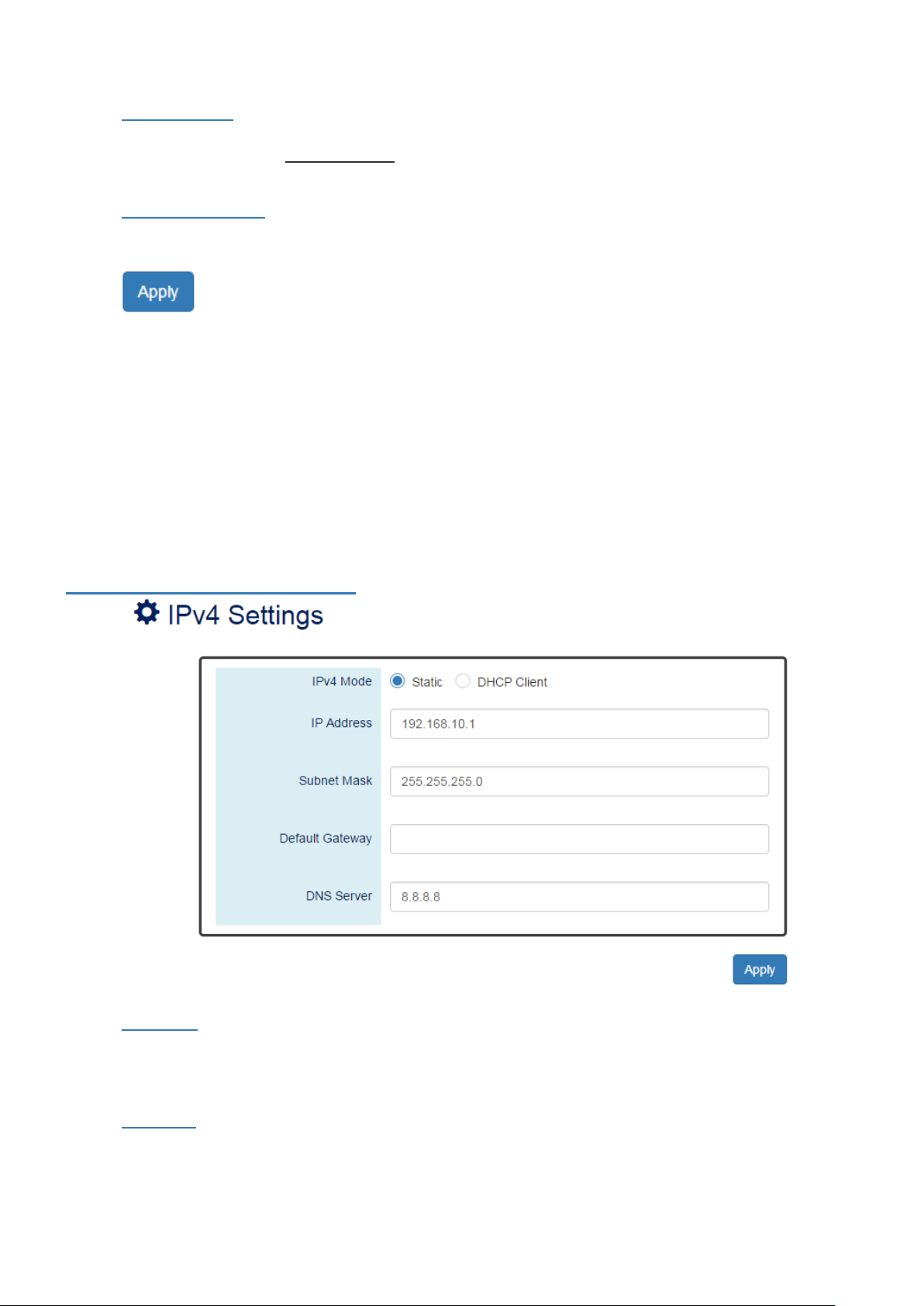
• Switch Location
It is useful to find the location of the switches, for example: Area01.
The max. length for the Switch Location is 32 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
• Contact Information
Records the information of the person responsible for this device and also the contact details.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
•
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
(Apply Button)
III-3. Web Management – IPv4 Settings
Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol. It is used on the
packet-switched networks and with connectionless communication. IPv4 has four bytes (32 bits) address and
the address space is limited to 4,294,967,296 (232) unique addresses. On the local area network (LAN), the
“Private Network” is used. It starts from 192.168.0.0 and the address space contains 65,025 (216) IP addresses.
The frames can only be sent to the host in the same subnet. For example, the default IP Address of the switch is
“192.168.10.1”.When the users want to connect to the web console of the switch, an IP address from
“192.168.10.2” to “192.168.10.254” must be assigned to the host.
CONFIGURE IPV4 INFORMATION
• IPv4 Mode
There are 2 ways to configure IPv4 address - one is to configure a static IP address manually and
another one is to get an IP address by DHCP.
If the IPv4 mode is "DHCP Client", IPv4 information fields will be set to "Disabled".
• IP Address
Assigns an unique static IP Address in the subnet to access the system.
The default IP Address is "192.168.2.1".
15
Page 19
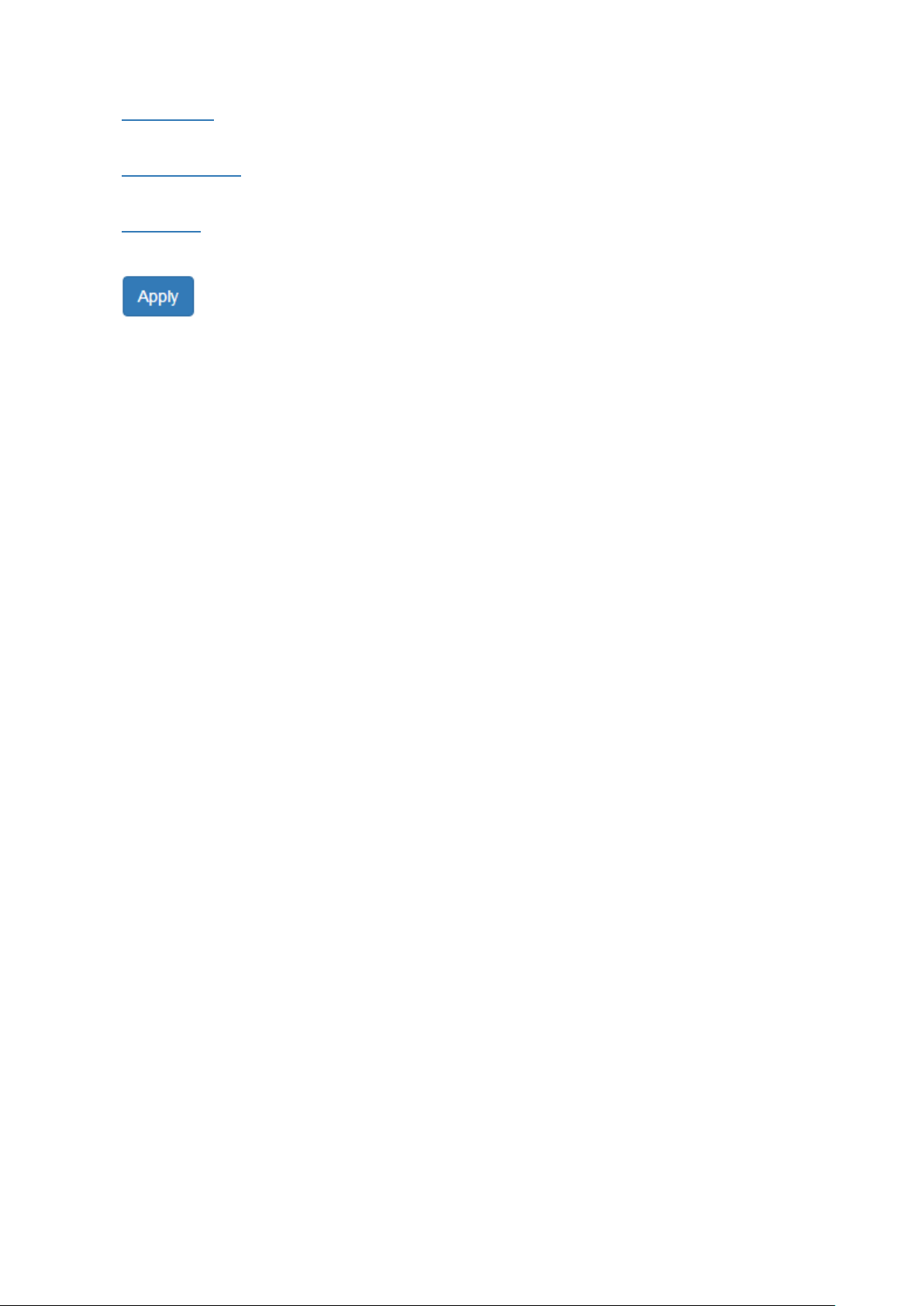
• Subnet Mask
Defines the type of network, to which this device is connected to.
• Default Gateway
The IP address of the router used to connect a LAN to a WAN.
• DNS Server
Specifies the IP address of the DNS Server so that the users can connect to another device based on the
URL instead of the IP address.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
16
Page 20
III-4. Web Management – IPv6 Settings
Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) is a solution to deal with the address space limitation of IPv4 and it is the
most recent version of Internet Protocol. It is intended to replace IPv4. IPv6 is a Layer 3 (Internet Layer) protocol,
which is used on the packet-switched networks and with connectionless communication. There are 16 bytes
(128 bits) for an IPv6 address and the address space is up to 2
represented in hexadecimal digits, 8 groups of 4 digits, and each group is separated by a “:” (colon). For
example, the DNS server address in IPv6 is “2001:4860:4860:0000:0000:0000:0000:8888”.
CONFIGURE IPV6 INFORMATION
128
unique addresses. The IPv6 address is usually
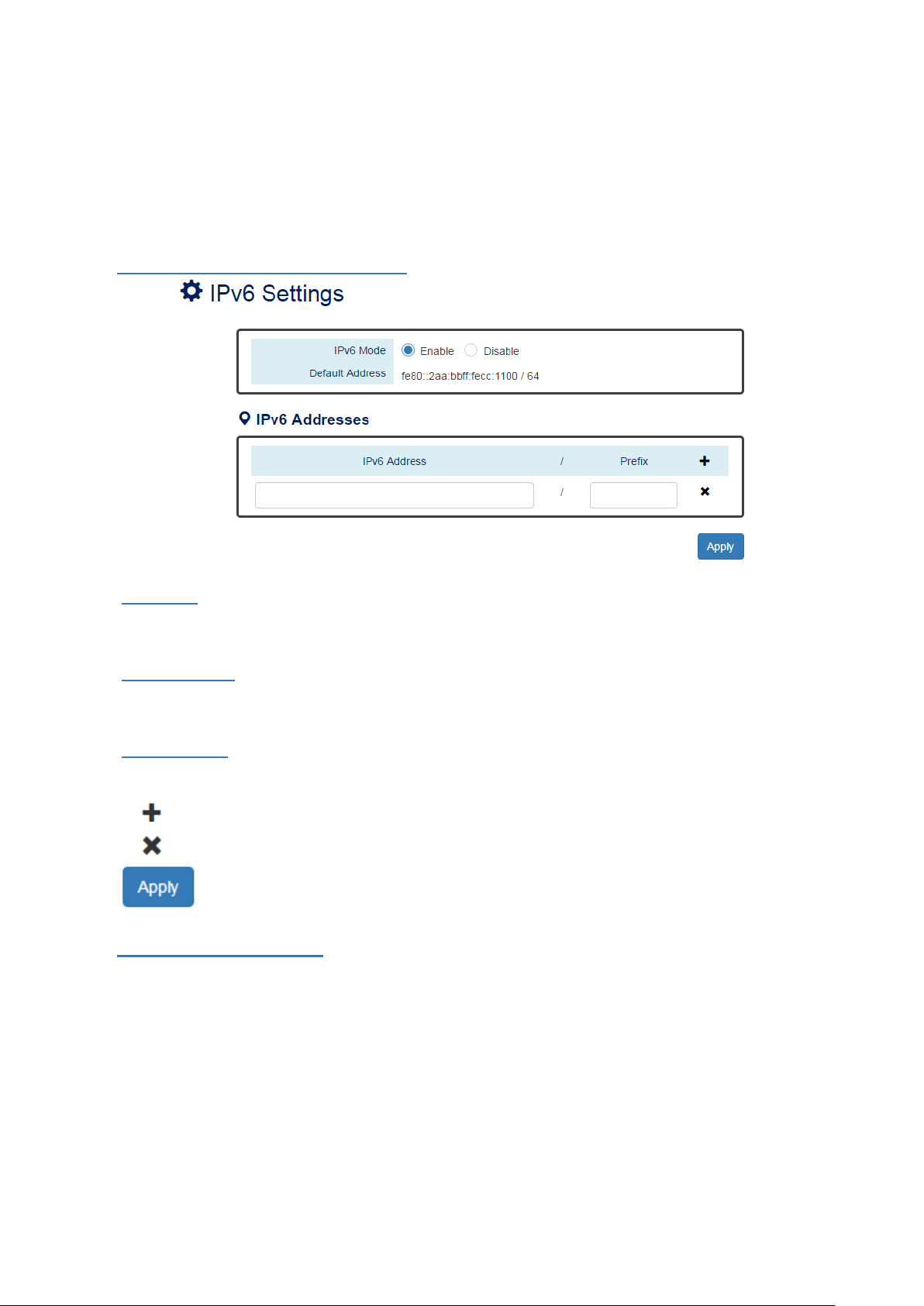
• IPv6 Mode
"Enable" or "Disable" IPv6. When the IPv6 Mode is enabled, other devices can connect to this unit.
The default IPv6 Mode is "Enable".
• Default Address
This is the Default IPv6 Address for this device. It is a Link-Local address and is automatically generated
from the MAC Address of the device.
• IPv6 Addresses
Enables the users to define other IPv6 addresses for this device.
The IPv6 address contains 2 section - IPv6 address and prefix. The default Prefix is 64-bit.
: Click the plus icon to add a IPv6 Address row.
: Click the remove icon to delete the IPv6 Address row.
•
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
(Apply Button)
IPV6 NEIGHBOR TABLE
17
Page 21
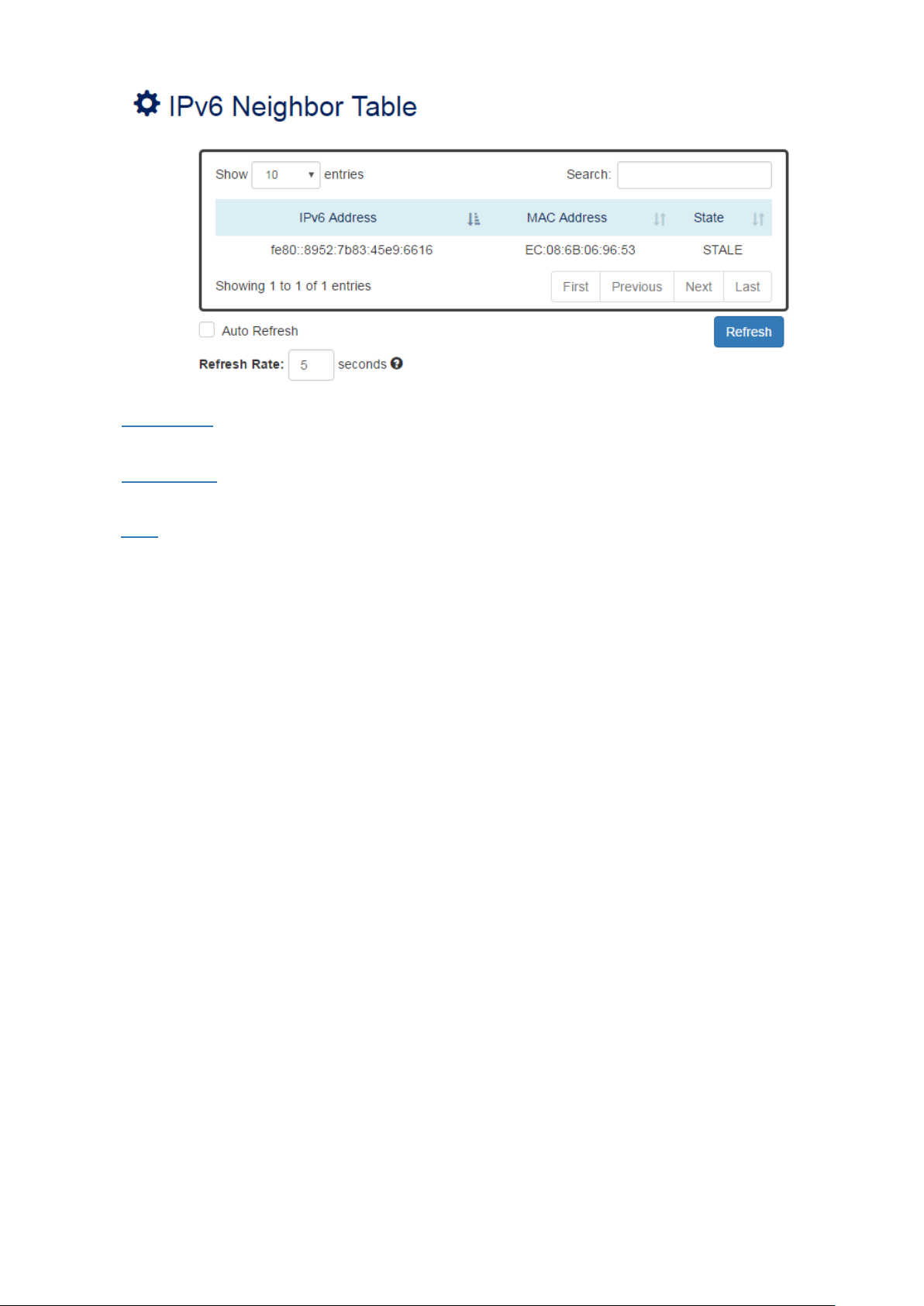
• IPv6 Address
This filed displays the IPv6 address of the neighbor.
• MAC Address
This filed displays the MAC address of the neighbor.
• State
The connection state can be “DELAY”, “REACHABLE”, “STALE”, “FAILED”, or “PROBE”.
18
Page 22
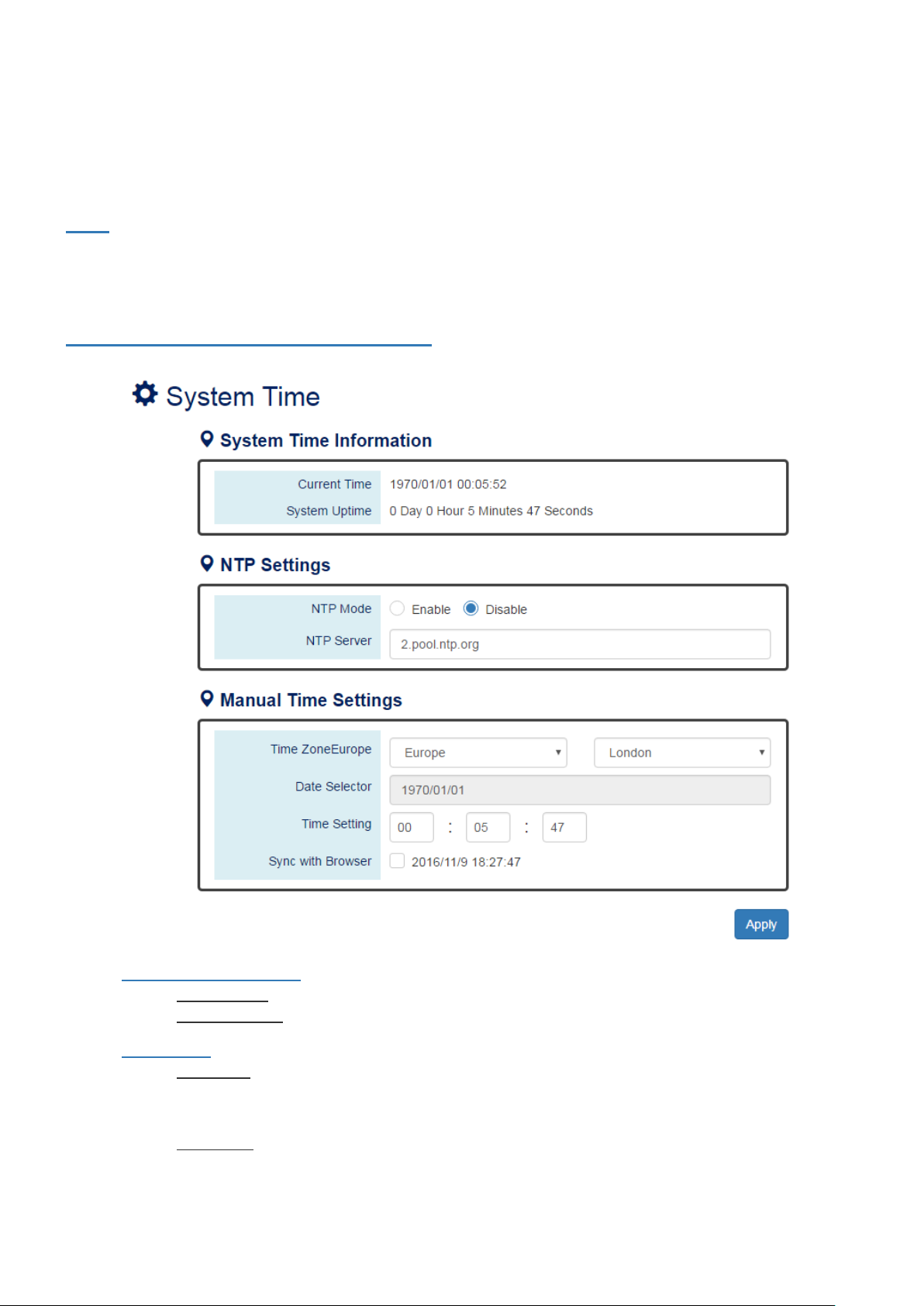
III-5. Web Management – System Time
The System Time represents the date and time. The system uptime defines the passing time after the system
boots up. There is no battery on the switch and hence the system time cannot be saved in the system. Users can
configure the time zone and system time manually by synchronizing the time with the browser or by enabling
the “NTP” service to get the time from a NTP Server.
NTP
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a clock synchronization protocol, which is used to synchronize the system time
with the NTP server. NTP is one of the oldest Internet Protocols in use from 1985 until now. It works based on a
client-server model, but it can also be used in peer-to-peer relationships. The NTP application on the switch is
follows the client-server model and the switch plays a role in the NTP Client.
CONFIGURE SYSTEM TIME INFORMATION
• System Time Information
。 Current Time: The current date time of the system.
。 System Uptime: The system boot up duration.
• NTP Settings
。 NTP Mode
"Enable" or "Disable" NTP Service. If NTP Mode is enabled, the system will sync time with NTP
Server on an hourly basis.
。 NTP Server
This field displays the URL or the IP address of the host that provides the NTP Service.
19
Page 23
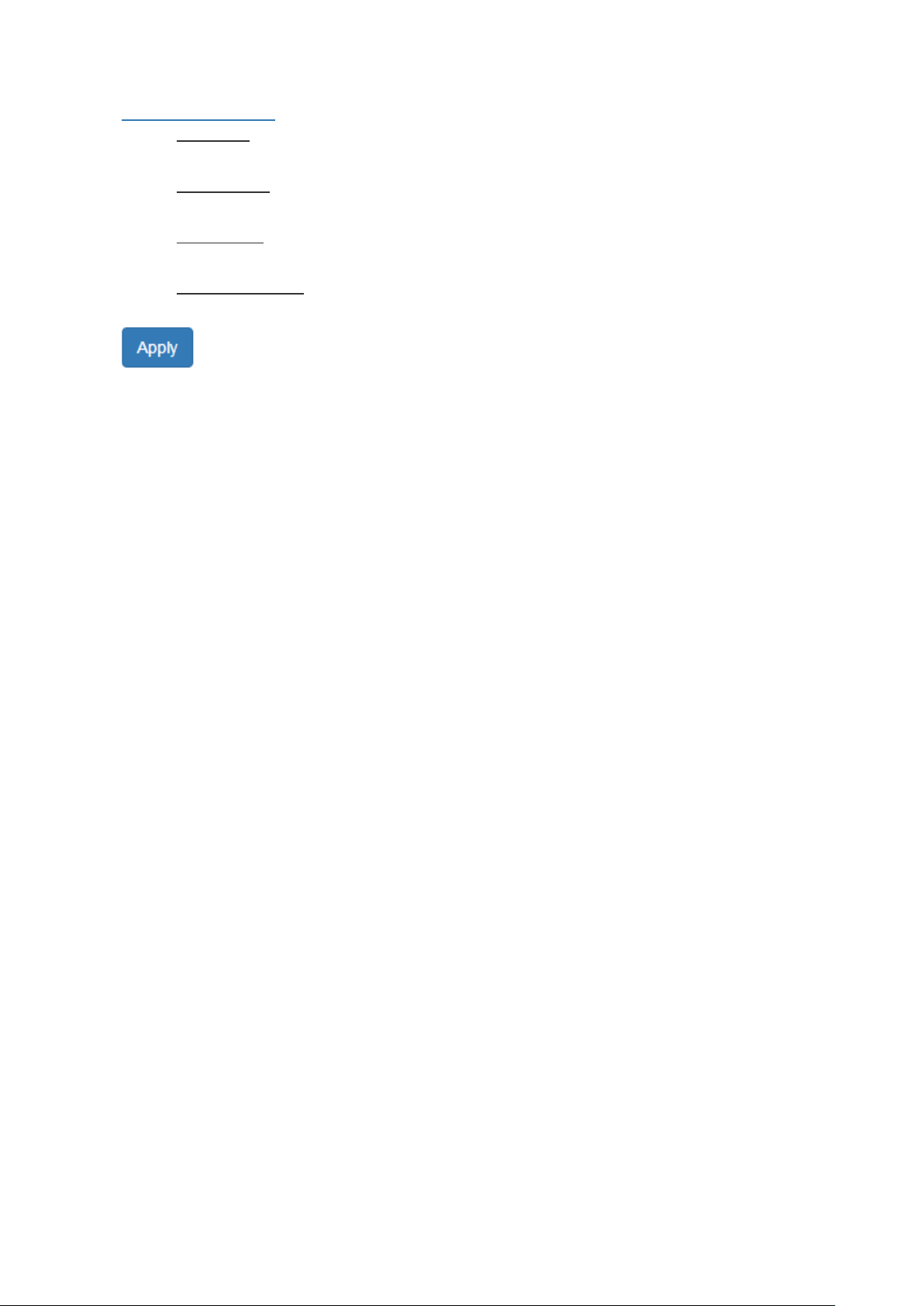
• Manual Time Settings
。 Time Zone
Select the Time Zone to define the local time offset from GMT.
。 Date Selector
Select the system date manually. The format is "year/month/day".
。 Time Setting
Define the system time manually. The format is "hour:minute:second".
。 Sync with Browser
Select the checkbox to synchronize the system time with the browser time.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
20
Page 24

III-6. Web Management – RSTP Configuration
The Spanning-Tree Protocol is a standard protocol that is defined in IEEE 802.1D. It is used to build a logical
loop-free topology for layer-2 Networks. The basic function of the protocol is to prevent loops and broadcast
flooding around the switches. STP allows spare links in the network design to provide backup paths when the
active link fails and requires a convergence time of 30-50 seconds to recover the topology when the topology is
changed. This prompted the use of Rapid Spanning-Tree Protocol as it provides a faster convergence when the
topology is changed.
RSTP was introduced by IEEE as 802.1w. It can respond within 3 x "Hello Time" when a topology is changed.
The "Hello Time" is a configurable value and it is very important for RSTP. The default RSTP value is 2 seconds
and typically, the convergence time for RSTP is under 6 seconds. This is much better than STP and makes RSTP
to be the mainstream.
CONFIGURE RSTP BASICINFORMATION
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
• System Time Information
RSTP: Enable STP and run "RSTP" for redundancy.
Disable: Disable STP. Users have to enable another protocol to prevent from loop.
• Root Priority
It is used to define the "Root Bridge". The bridge with the lowest Root Priority is the "Root Bridge". If all
the bridges are set to the same Root Priority value, the system will select the Root Bridge based on
the MAC Addresses.
The range of Root Priority is from 0 to 61440(multiple of 4096).
The default Root Priority is 32768.
• Hello Time
It is very important and used to determine the interval to send BPDU (management frame) to check the
RSTP topology and status.
The range of Hello Time is from 1 to 10 second(s).
The default Hello Time is 2 seconds.
• Forward Delay
A delay/timer is used to determine when to change the Path State from Learning/Listening to
Forwarding.
The range of Forward Delay is from 4 to 30 seconds.
The default Forward Delay is 15 seconds.
21
Page 25

• Maximum Age
A timer that is used to wait for the Hello BPDU from the Root Bridge. If this device receives the BPDU
before the timer expires, the timer will be reset. Else, the device will send the topology changed BPDU
to notify other devices.
The range of Maximum Age is from 6 to 40 seconds.
The default Maximum Age is 20 seconds
The relationship between "Hello Time", "Forward Delay", and "Maximum Age" is:
2 x (Forward Delay - 1 sec) >= Max Age >= 2 x (Hello Time + 1 sec)
22
Page 26
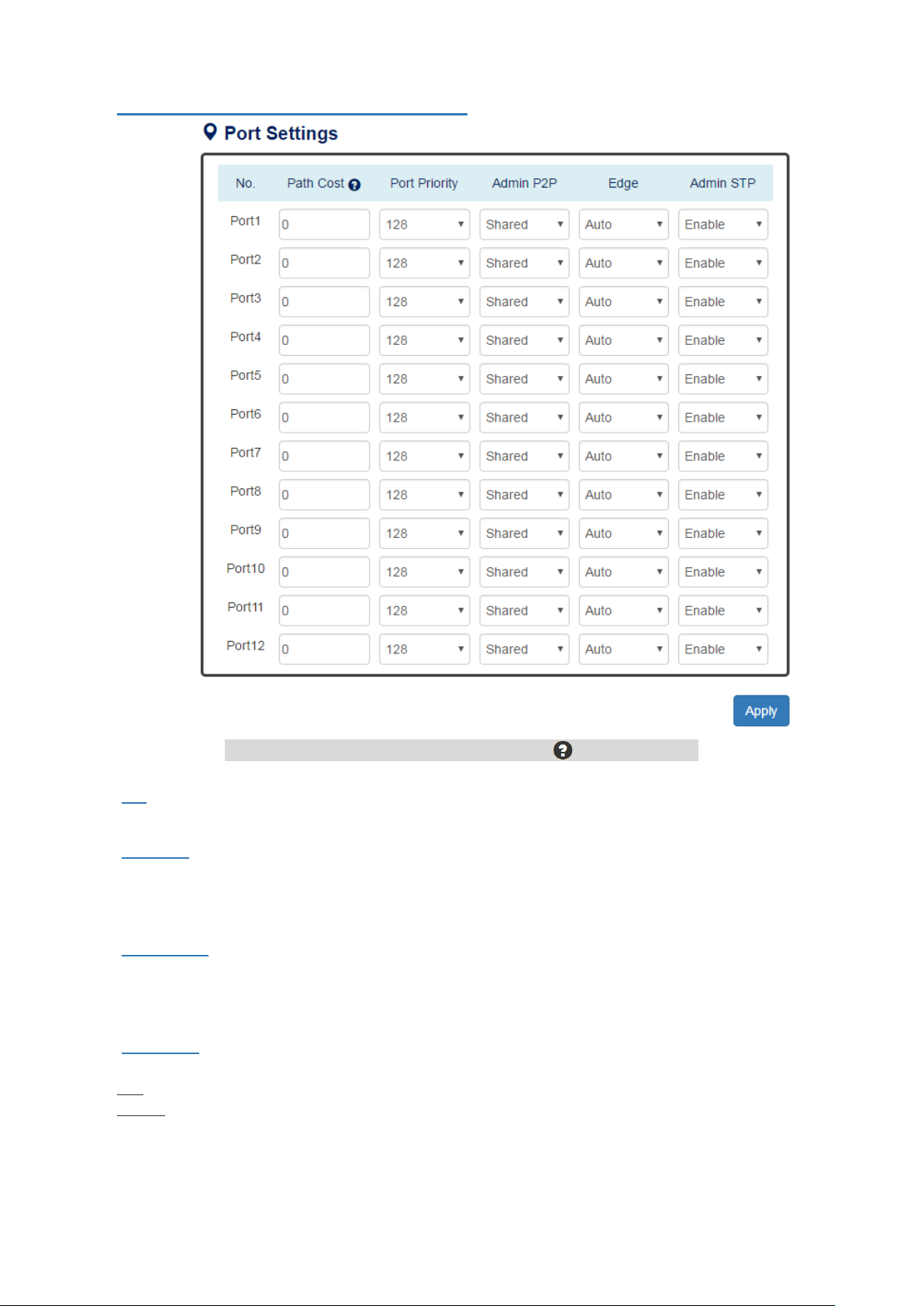
CONFIGURE RSTP PORT INFOR MATION
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
• No.
Port1 to PortN, where N is based on the total port number.
• Path Cost
The costfrom the current node to another device.
The range of Path Cost is from 0 to 200000000.
The default Path Cost is 0. This implies that the Path Cost is decided by the system.
• Port Priority
Used to decide the port to be blocked in the Ring topology.
The range of Root Priority is from 0 to 240 and are in multiple of 16.
The default Root Priority is 128.
• Admin P2P
The Admin P2P is the link-type for each port.
P2P: It is a full-duplex link.
Shared: It is a half-duplex link.
23
Page 27
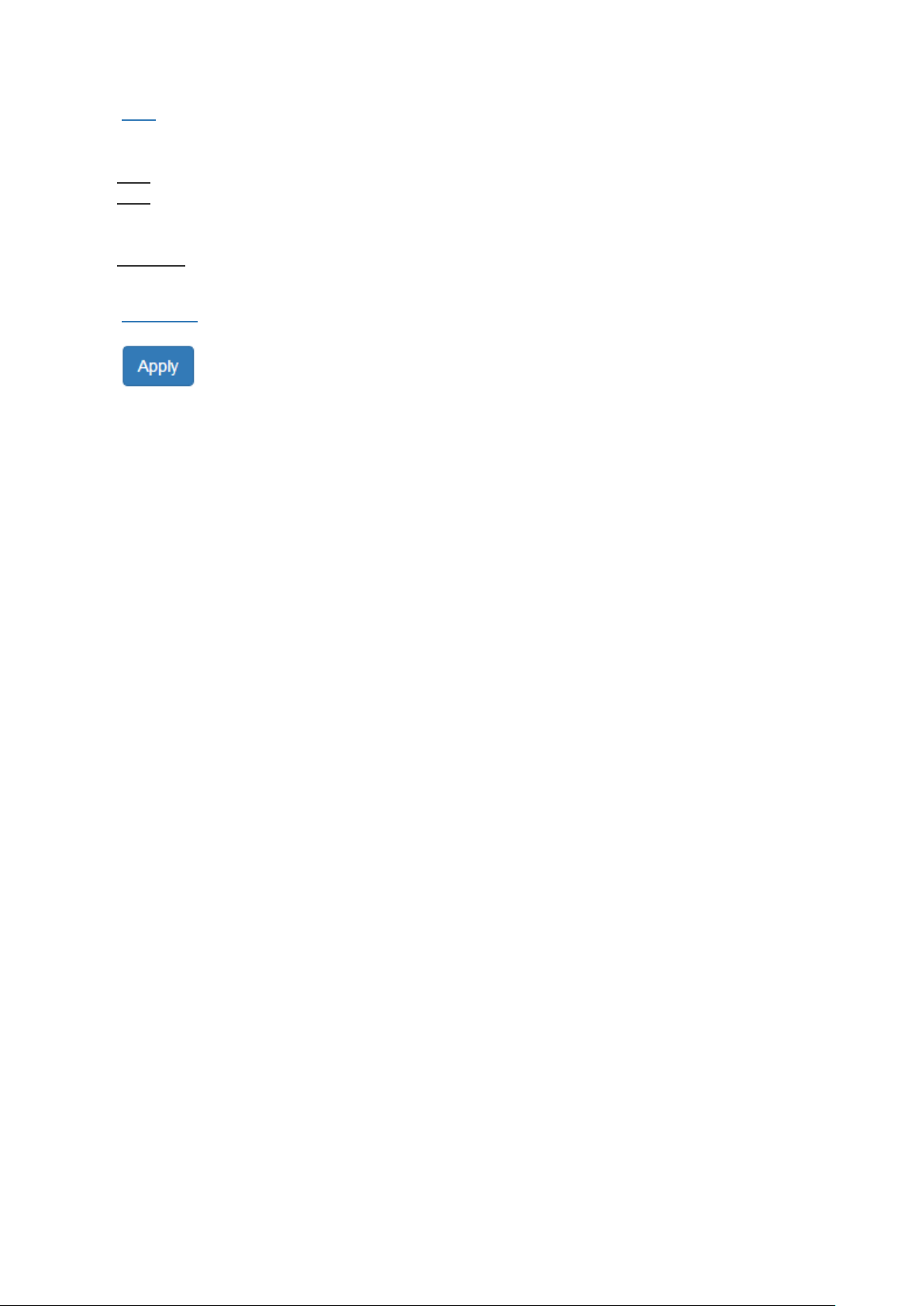
• Edge
A port that can connect to a non-STP device is called an Edge port. Users can manually fix a port to
non-Edge or Edge.
Auto: The system automatically identifies an Edge or Non-Edge.
Edge: The port is forced to be an Edge port. An edge port will directly be transitioned to the
"Forwarding" state and is not required to wait for the "Forward Delay". If a port is directly connected to
a non-STP device, users can manually set it to "Edge" and enable it to transmit faster.
Non-Edge: The port is forced to be a Non-Edge port. This implies that the port will go through
Learning/Listening to Forwarding state even though it is connected to an end device or not.
• Admin STP
"Enable" or "Disable" the Spanning-tree protocol that is running on the specific port.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
24
Page 28

RSTP STAT US
• Bridge ID
This field shows the unique identity of this node when it is part of a network. It contains 8 bytes - the
first 2 bytes are for Bridge Priority (configurable) and the remaining 6 bytes are for the MAC Address
(unique).
• Root Bridge
It is elected from the switches in the STP topology via several STP messages (BPDU). The Root Bridge is
the node with the lowest Root Priority. If all of the nodes are with the same Root Priority, the Root
Bridge will be selected based on their MAC Addresses.
• Root Priority
It is used to define the "Root Bridge". The bridge with the lowest Root Priority is the "Root Bridge". If all
bridges are set to the same Root Priority value, the system will select the Root Bridge based on the MAC
Addresses.
• Root Port
It is the port that is connected to the Root Bridge and with the lowest cost. If the Root Port shows
"none", it implies this node is the Root Bridge.
• Root Path Cost
It is the cost from the current node to the Root Bridge.
• Hello Time
It is used to determine the interval to send BPDU (management frame) to check the RSTP topology and
status.
• Forward Delay
It is used to determine when to change the Path State from Learning/Listening to Forwarding.
• Max Age
It is used during waiting for Hello BPDU from the Root Bridge.
25
Page 29

Speed
RSTP Path Cost
Speed
RSTP Path Cost
4 Mbps
5,000,000
1000 Mbps (1Gbps)
20,000
10 Mbps
2,000,000
2000 Mbps (2 Gbps)
10,000
16 Mbps
1,250,000
10000 Mbps (10 Gbps)
2,000
100 Mbps
200,000
• No.
Port1 to PortN, N is based on the total port number.
• Role
This field shows the role of the STP port.
Root: This is the root port, which is connected to the Root Bridge with the lowest cost.
Designated: This is the designated port, which can send the best BPDU on the segment to other
connected nodes.
Alternate: This is the alternate port, which is blocked. This port can still receive useful BPDU from
another bridge. When it receives a useful BPDU, it will help to forward it on the segment.
Backup: This is the backup port, which is blocked. It corresponds with “Alternate Port” to the blocking
state. This port also receives useful BPDU, but the BPDU is from the same bridge. When it receives a
useful BPDU, it will help to forward it on the segment.
Disabled: The port is not linked up.
• Path State
This field shows the path state of this STP port.
Discarding: The port state can be “Disabled”, “Blocking”, or “Listening”. The incoming frames are
dropped and learning MAC addresses are stopped.
Learning: The port is learning MAC addresses, but the incoming frames are dropped.
Forwarding: The port in the forwarding state forwards the incoming frames based on the learned MAC
address table.
• Port Cost
This is the cost from the port to the Root Bridge. Spanning-tree Protocol assumes the path cost is
determined by the access speeds of the links. The default RSTP path cost is shown in the following
table:
• Port Priority
The Port Priority is used to determine the Root Port on a non-root bridge. The port with the lowest Port
Priority value gets the higher priority.
• Oper. P2P
This field shows the link-type of the STP port. P2P means “point-to-point” and Shared means
“point-to-multiple”.
• Oper. Edge
This field shows the edge state of this STP port.
26
Page 30

III-7. Web Management – ERPS
Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS) applies the protection switching mechanism for Ethernet traffic in a
ring topology. This mechanism is defined in ITU-T G8032. You can avoid the possible loops in a network by
implementing the ERPS function. This is done by blocking the flow of traffic to the Ring Protection Link (RPL)
there by protecting the entire Ethernet ring.
When an ERPS is implemented in a ring topology, only one switch is allocated as the owner. This switch is in
charge of blocking the traffic in the RPL to avoid loops. The switch adjacent to the RPL owner is called the RPL
neighbor node and it is responsible for blocking the end of the RPL during normal condition. The participating
switches that are adjacent to the RPL owner or neighbor in a ring are called the members or RPL next-neighbor
nodes. The primary function of these switches is to forward the received traffic.
To make sure that a ring is up and loop-free, Ring Automatic Protection Switching message is sent regularly as
control messages by nodes on the ring. The RPL owner identifies a signal failure (SF) in a ring when the RPL
owner misses the poll packets or reads from the fault detection packets. When the fault is identified, the RPL
owner unblocks the ring protection link (RPL) and permits the protected VLAN traffic through.
ERPS, similar to STP, provides a loop-free network by using polling packets to detect faults. If a fault occurs,
ERPS restores itself by sending traffic over a protected reverse path rather than making a calculation to identify
the forwarding path. The fault detection mechanism in the ERPS enables the ERPS to join in less than 50
milliseconds and recovers quickly to forward traffic.
27
Page 31

Role
Description
Owner
There is only one “Owner” in the ERPS ring topology. The Owner is
Neighbor
There is only one“Neighbor” in the ERPS ring topology. The Neighbor is the
CONFIGURE ERPSINFORMATION
• Basic Settings
。 ERPS Status
“Enable” or “Disable” ERPS protocol running on the switch. By default, the ERPS protocol is
enabled.
。 ERPS Port 0
The ERPS Port 0 is also called “West Port”. Select one of the switch ports to be the Port 0 of ERPS
and decide the role of the port.
。 ERPS Port 1
The ERPS Port 1 is also called “East Port”. Select one of the switch ports to be the Port 1 of ERPS
and decide the role of the port.
Note: Only One of the switch ports can be configured as ERPS Port 0 or ERPS Port 1.
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
responsible for blocking the traffic in RPL and protects one side of the RPL.
port connected with the Owner port and protects another side of the RPL.
28
Page 32

None
The “None” implies that theport is other than an Owner or aNeighbor.
。 ERPS Ring ID
The ID is the identifier of the ring. The members in the same ring must be set to the same ERPS
Ring ID.
The range of the ERPS Ring ID is from 1 to 239.
The defaultERPS Ring ID is 1.
。 R-APS Channel
The R-APS Channel is used to forward ERPS information and is mapped to the VLAN IDs. These
VLAN IDs cannot be set as traffic VLANID. The members in the same ring must be set to the same
R-APS Channel.
The range of the R-APS Channel is from 1 to 4094.
The defaultR-APS Channel is 1000.
• Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings field is only displayed when the “Advanced Settings” checkbox is selected in the
Basic Settings.
。 Revertive Mode
“Enable” or “Disable”the ERPS Revertive Mode. If the Revertive Mode is enabled, the blocked link
will revert to the RPL link after the failed link is recovered.
By default, the ERPS Revertive Mode is enabled.
。 MEL Value
The MEL implies the MEG Level. The MEL is afield in the R-APS PDU. Alarge MEL value involves
more devices. For example, level 7 contains levels 0 to 6.
The range of the MEL Value is from 0 to 7.
The default MEL Value is 7.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
29
Page 33

v1 &
Read Only Community
Community String
No
String match for authentication
Read-Write Community
Community String
No
String match for authentication
Security Level –
Access by an account (admin or
Access by an account (admin or
III-8. Web Management – SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a standard for collecting and structuring information
on the managed devices of the IP network. It can also modify some of the information to change the
behavior of the devices. SNMP is usually used in monitoring the network. The users can remotely query
the information provided by the devices running SNMP.
The switches support SNMP v1, v2c, and v3. SNMP v1 and v2c authenticates with a community string
for “read-only” or “read-write” permission. The SNMP v3 authentication requires to select an
authentication level (MD5 or SHA) and also supports data encryption to make the data safer.
For the SNMP version and authentication method relationship, refer to the table below:
Version Web Setting Authentication Encryption Method
v2c
v3
No Authentication, No
Privacy
Security Level –
Authentication, No
Privacy
Security Level –
Authentication, Privacy
No No
MD5 / SHA No
MD5 / SHA
Yes
AES / DES
Access by an account (admin or
user)
user) and password with more than
8 characters, which is based on MD5
or SHA
user) and password more than 8
characters, which is based on MD5
or SHA. The data encryption is based
on AES or DES and the key requires 8
to 32 characters.
30
Page 34

CONFIGURE SNMP SERVER INFORMATION
• Basic Settings
。 SNMP Version
The system enables the SNMP “v1, v2c and v3” authentication by default. The users can enable
the SNMP server on only “v1 and v2c” or “v3”. “ None” refers to disabling the SNMP server.
。 Read Only Community
The community used to access the SNMP server with the “read-only” privilege.
The max.length for the Read Only Community is 32 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
。 Read-Write Community
The community used to access the SNMP server with the “read-write” privilege.
The max.length for the Read-Write Community is 32 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
31
Page 35

• SNMPv3 Settings
This section is displayed only when the SNMP Version is set to “v3” or “v1, v2c and v3”. Two accounts are
provided – Admin and User to access the SNMP agent. The users can set different levels for the 2
accounts.
。 Security Level
No Authentication, No Privacy: Access by an account “admin” or “user”.
Authentication, No Privacy: Access by an account “admin” or “user” with password.
Authentication, Privacy: Access by an account “admin” or “user” with password and the data will
be encrypted.
。 Authentication Type
Two algorithms are provided - MD5 and SHA for authentication password.
。 Authentication Password
A string/key is used to authenticate the SNMP Server and obtain the access permission. It will be
hashed by MD5 or SHA before authentication.
The min. length for the Read-Write Community is 8 characters.
The max.length for the Read-Write Community is 32 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
。 Encryption Type
Two algorithms are provided - AES and DES for data encryption.
。 Encryption Password
A string/key is used to encrypt the data that is sent to the SNMP server.
The min. length for theRead-Write Communityis 8 characters.
The max.length for the Read-Write Community is 32 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
32
Page 36

CONFIGURE SNMP TRAP INFORMATION
• Basic Settings
。 Tra p Mode
The system enables the SNMP “v1, v2c and v3” authentication by default. Users can enable the
SNMP server only on “v1 and v2c” or “v3”. “ None” indicates disabling the SNMP server.
。 Inform Retry
The SNMP trap will send “Retry” times when the trap set to “v2 Inform” or “v3 Inform” mode.
The range of the Inform Retry is from 1 to 100.
The default Inform Retry is 5.
。 Inform Timeout
The interval is used to send trap when the trap set to “v2 Inform” or “v3 Inform” mode.
The range of the Inform Retry is from 1 to 300 second(s).
The default Inform Retry is 1 second.
。 Trap Receiver IP
The IP address is the IP address of the trap server to receive the trap information.
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
33
Page 37

。 Community
The string in the SNMP trap is the identity of the device.
The max.length for the Community is 32 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
• SNMPv3 Trap/Inform Settings
This section is displayed only when Trap Mode are set to “v3 Trap” or “v3 Inform”.
。 Username
Specify the username for authentication with the SNMP trap server.
。 Engine ID
The Engine ID is the identifier for the given SNMP application.
。 Security Level
No Authentication, No Privacy: Access using the username assigned to the users.
Authentication, No Privacy: Access using the username assigned to the users with password.
Authentication, Privacy: Access using the username assigned to the users with password and the
data will be encrypted.
。 Authentication Type
Two algorithms are provided - MD5 and SHA for authentication password.
。 Authentication Password
A string/key is used to authenticate the SNMP trap server and obtain the permission. It will be
hashed by MD5 or SHA before authentication.
The min. length for the Read-Write Community is 8 characters.
The max.length for the Read-Write Community is 32 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
。 Encryption Type
Two algorithms are provided - AES and DES for data encryption.
。 Encryption Password
A string/key is used to encrypt the data sent to the SNMP trap server.
The min. length for the Read-Write Community is 8 characters.
The max.length for the Read-Write Community is 32 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
34
Page 38

III-9. Web Management – DHCP
DHCP SERVER/CLIENT
DHCP, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, is a standardized protocol used in the IP networks. The DHCP
Server holds an IP address pool and when a DHCP Client request for an IP address, the DHCP Server picks an IP
address from the pool and assigns it to the client. DHCP Server also manages other IP information such as
Default Gateway and DNS Server. DHCP is very useful to configure the IP information for a number of devices.
Only the administrator can enable the DHCP Client for each device and setup the DHCP Server. The clients will
then obtain a unique IP address and other IP settings to connect to the network.
DHCP SERVER BINDING
Apart from dynamically allocating an IP address to a DHCP Client, the DHCP Server also provides a function to
manually assign a static IP address to the device with a specific MAC Address. This is called as DHCP Server
Binding.
DHCP RE LAY/OPTION82
In a large network, there might be several subnets existed and the DHCP Client is not able to serve by DHCP
Servers directly. In this case, we need a relay agent to help to transmit the request frames to the DHCP Servers.
When a relay agent receives the broadcast request frame from a DHCP Client, the relay agent will transmit the
frame to the DHCP Servers, which are in the same subnet by unicast.
Option 82 is an information option to identify the clients by Circuit ID and Remote ID. The Circuit ID is an
identity containing the interface name and/or VLAN information, and the Remote ID is to identify the remote
host (the relay agent). The DHCP Server can distribute an IP address to the DHCP Client according to Option 82
information and make the IP addresses more controllable.
The frame format for the Circuit ID is as below:
• VLAN
The VLAN field is for the management VLAN ID, which is natively set to 1.
• Module
The stack number for the device sending the DHCP request is on. For industrial switches, this byte is
always filled as 0.
• Port
The port number identifies the incoming DHCP request frame/DHCP Client.
The frame format for the Remote ID is as below:
• MAC Address
By default, the MAC address is set to the MAC address of DHCP relay agent.
35
Page 39

CONFIGURE DHCP CLIENT
• IPv4 Mode
Set the IPv4 Mode to “DHCP Client” to enable the DHCP Client. The system sends a discovery frame to
the network and tires to obtain an IP address from the DHCP Server.
After enabling the DHCP Client, users need to connect to the Console Port to get the IP address by using
“show ip address” on the CLI.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
36
Page 40

CONFIGURE DHCP SERVER INFORMATION
For more information, hover the mouse over the icon in the system.
• Server Status
Shows the status of the DHCP server: Down or Up.
• Server Mode
“Enable” or “Disable” the DHCP Server function.
• Start IP Address
Set the range of the IP pool. The “Start IP Address” is the starting.
“Start IP Address” must be in the same subnet as that of the switch itself.
• End IP Address
Set the range of IP pool. The “End IP Address” is the end.
“End IP Address” must be in the same subnet as that of the switch itself.
• Default Gateway
Set the Default Gateway for the DHCP Clients to make them connect to the WAN.
“Default Gateway” must be in the same subnet as that of the switch itself.
• DNS Server
Set the DNS Server for the DHCP Clients to make them connect to another device based on the URL
instead of IP address.
• Lease Time
DHCP Server leases an IP address to a device for a period of time. When the lease time expires, the DHCP
server may assign a different IP address in the pool to the device.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
37
Page 41

CONFIGURE DHCP SERVER BINDING INFORMATION
• Binding ID
An ID used to identify the binding.
The range of the Binding ID is from 1 to 32.
• MAC Address
The device with the specified MAC Address will be assigned to the static Binding IP Address.
For more information, hover the mouse over the icon in the system.
• Binding IP Address
A static IP Address will be assigned to the specified MAC Address.
•
•
•
: Click the plus icon to add a DHCP Binding row.
: Click the remove icon to delete the DHCP Binding row.
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
38
Page 42

CONFIGURE DHCP RELAY INFORMATION
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
• Relay Basic Settings
。 Relay Mode
“Enable” or “Disable” the DHCP Relay function.
。 Relay Option82
“Enable” or “Disable” the DHCP Relay with Option82 tag.
。 Helper Address 1 - 4
The IP Addresses of the DHCP Servers provide IP addresses to the DHCP Clients. A backup of Four
Helper Addresses are available during breakdown.
39
Page 43

• Relay Untrust
。 No.
。 Untrust Status
Port1 to PortN, where N is based on the total port number.
“Enable” or “Disable” to untrust the specific port. If the untrusted status is enabled on a port, the
system will drop the DHCP management frames on the port.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
40
Page 44

Physical Discrete Inputs
2
Read Discrete Inputs
Internal Bits or Physical Coils
1
Read Coils
Word Access
Physical Input Registers
4
Read Input Registers
Physical Output Registers
3
Read Holding Registers
III-10. Web Management – ModBUS/TCP
Modbus is a popular communication protocol used for the industrial serial devices. It is usually working as
“master-slave” architecture and working with programmable logic controllers which are also called PLCs. The
Modbus/TCP implies to provide Modbus Messaging service on the TCP/IP, so that the devices which are running
Modbus can communicate with each other with Modbus messages. The Modbus messages are encapsulated
with an Ethernet TCP/IP wrapper on the basis of the standard. During the transmission, the switches can only
acquire the encapsulated information when the Modbus/TCP is enabled. If users would like to understand the
real content of Modbus message, users have to install other utilities such as “ModScan”. Our switches
implements the Modbus/TCP registers including system information, firmware information, port information,
and packet information. The details refer to the “Modbus Data Mapping Information” section.
DATA FORMAT AND FUNCTION CODE
The primary four types of Modbus/TCP data format are as following:
Data Access Type Function Code Function Name
Bit Access
(16-bit Access)
41
Page 45

Address Offset
Data Type
Interpretation
Description
System Information
Port 1 to Port 8 Status
0x0000:
Disable
0x0001:
Enable
Port 1 to Port 8 Status Configuration
0x0000:
Disable
0x0001:
Enable
Address Offset
Data Type
Interpretation
Description
System Information
Product Name = “MT-0804G”
Word 0 Hi byte =
‘M’
Word 0 Lo byte =
‘T’
Word 1 Hi byte =
‘-‘
Word 1 Lo byte =
‘0’
Word 2 Hi byte =
‘8’
Word 2 Lo byte =
‘0’
Word 3 Hi byte =
‘4’
Word 3 Lo byte =
‘G’
0x0050
1 word
Product Serial Number
Firmware Version
Word 0 =
0x0103
Word 1 =
0x0200
Firmware version is 1.3.2
MODBUS DATA MAPPING INFORMATION
In the following tables, we assume the total port number is 8.
The following table is for Function Code 3 (Holding Registers) / Function Code 6.
0x0000 to
0x0008
The following table is for Function Code 4 (Input Registers). The data map addresses in the following
table starts from Modbus address 30001. For example, the address offset 0x0000H equals Modbus
address 30001, and the address offset 0x0030H equals Modbus address 30049. All the information read
from our switches is in the HEX mode and users can refer to the ASCII table for the translation (e.g.
0x4B=’K’, 0x74=’t’).
0x0030 20 words ASCII
1 word HEX
0x0051 2 words HEX
For example:
42
Page 46

Address Offset
Data Type
Interpretation
Description
System Information
Firmware Release Date
Word 0 =
0x1719
Word 1 =
0x1506
Firmware was released on 2015-06-17 at 19
Ethernet MAC Address
Word 0 Hi byte =
0x01
Word 0 Lo byte =
0x02
Word 1 Hi byte =
0x03
Word 1 Lo byte =
0x0A
Word 2 Hi byte =
0x0B
Word 2 Lo byte =
0x0C
Power 1
0x0000:
Off
0x0001:
On
Address Offset
Data Type
Interpretation
Description
Power 2
0x0000:
Off
0x0001:
On
Fault LED Status
0x0000:
Boot error
0x0001:
Normal
0x0002:
Fault
DO1
0x0000:
Off
0x0001:
On
0x0053 2 words HEX
0x0055 3 words HEX
For example:
o’clock
Ex: MAC = 01:02:03:0A:0B:0C
0x0058 1 word HEX
0x0059 1 word HEX
0x005A 1 word HEX
0x0082 1 word HEX
43
Page 47

Address Offset
Data Type
Interpretation
Description
Port Information
Port 1 to Port 8 Status
0x0000:
Link down
0x0001:
Link up
0x0002:
Disable
0xFFFF:
No port
Port 1 to Port 8 Speed
0x0000:
10M-Half
0x0001:
10M-Full
0x0002:
100M-Half
0x0003:
100M-Full
0xFFFF:
No port
Port 1 to Port 8 Flow Ctrl
0x0000:
Off
0x0001:
On
0xFFFF:
No port
Port 1 to Port 8 Description
Word 0 Hi byte =
‘1’
Word 0 Lo byte =
‘0’
Word 1 Hi byte =
‘0’
Word 1 Lo byte =
‘T’
…
Word 4 Hi byte =
‘4’
Word 4 Lo byte =
‘5’
Word 5 Hi byte =
‘.’
Word 5 Lo byte =
‘\0’
Packet Information
Address Offset
Data Type
Interpretation
Description
Port 1 to Port 8 Tx Packets
Word 0 =
1324
Word 1 =
8635
0x1000 to
0x1008
0x1100 to
0x1108
0x1200 to
0x1208
0x1300 to
0x1313 (Port 1)
0x1314 to
0x1327 (Port 2)
…
0x138C to
0x139F (Port 8)
1 word HEX
1 word HEX
1 word HEX
Port Description = “100Tx,RJ45.”
20 words ASCII
0x2000 to
0x200F
2 words HEX
Ex: port 1 Tx Packet Amount = 13248635
Received Modbus response:
0x13248635
44
Page 48

Address Offset
Data Type
Interpretation
Description
Port 1 to Port 8 Tx Bytes
Word 0 =
1324
Word 1 =
8635
Port 1 to YY Rx Packets
Word 0 =
1324
Word 1 =
8635
Port 1 to Port 8 Rx Bytes
Word 0 =
1324
Word 1 =
8635
0x2080 to
0x208F
0x2100 to
0x21(YY*2-1)
0x2180 to
0x218F
2 words HEX
2 words HEX
2 words HEX
Ex: port 1 Tx Btyes Amount = 13248635
Received Modbus response:
0x13248635
Ex: port 1 Rx Packet Amount = 13248635
Received Modbus response:
0x13248635
Ex: port 1 Rx Btyes Amount = 13248635
Received Modbus response:
0x13248635
45
Page 49

CONFIGURE MODBUS/TCP IN F ORM ATIO N
• Modbus Mode
“Enable” or “Disable”the Modbus/TCP function.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
46
Page 50

III-11. Web Management – UPnP
UPnP is Universal Plug and Play, a set of networking protocol that permits the network devices to seamlessly
discover each other in the networks. It is promoted by the UPnP Forum, but since 2016, all UPnP efforts are
managed by the Open Connectivity Foundation.
UPnP extends “plug and play” to connect to a network device without configuration. When an UPnP device
such as printer, Wi-Fi AP, or mobile device connects to a network, it will automatically establish the working
configurations with another device.
CONFIGURE UPNP INFORMATION
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
• UPnP Mode
“Enable” or “Disable”the UPnP function.
• Advertisement Interval
A time period used to send the UPnP advertisement frame.
The range of the Advertisement Interval is from 300 to 86400 seconds.
The default Advertisement Interval is 1800seconds.
•
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
(Apply Button)
47
Page 51

III-12. Web Management – Port Management
Port Management contains a “Description” field that is used to describe the port, “Enable” or “Disable” option
to turn on or turn off a specific port, configure the speed-duplex for the port, and Flow Control on the port. In
the Port Status page, the users can obtain information such as Link Status, Speed, Duplex, Flow Control, Tx and
Rx in Bytes, and PoE status. These are very helpful for the administrator to manage the interfaces on the switch.
CONFIGURE PORT INFORMATION
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
• No.
Port1 to PortN, where N is based on the total port number.
• Description
The description for the port is helpful for the administrator to identify the difference between the ports.
The max.length for the Description is 32 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
• Link Status
Link Status shows “Up”, “Down”, or “Disable” to reflect the link status of the port.
• Admin Status
“Enable” or “Disable” the Admin Status of the port to restrict the transmission on the port.
Note:Administrator can turn off the un-used port to secure the network with unexpected device.
48
Page 52

• Speed
The users are able to manually fix the speed and duplex or automatically run auto-negotiation to
determine the speed and duplex.
• Flow Control
“Enable” or “Disable”the Flow Control when the speed is set to “Auto”. Enabling the Flow Control helps to
prevent the traffic from losing when the network is in congestion.
。 Auto: The port follows IEEE 802.3u protocol to auto-negotiate with connected device.
。 100M-Full: The port transmits frames with 100Mbits per second speed and full duplex.
。 100M-Half:The port transmits frames with 100Mbits per second speed and half duplex.
。 10M-Full:The port transmits frames with 10Mbits per second speed and full duplex.
。 10M-Half:The port transmits frames with 10Mbits per second speed and half duplex.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
49
Page 53

PORT STATU S
• Port
Port 1 to N, where N is based on the total port number.
• Link Status
Link Status displays the link state (“Up” or “Down”) of the port. If the port is disabled, it displays
“Disabled”.
• Speed
Speed displays the access speed in bit per second of the port. If the port is linked down, it displays“-“.
• Duplex
Duplex displays the link-type (Full or Half) of the port. If the port is linked down, it displays“-“.
• Flow Control
It is the state (On or Off) of the Flow Control.
• Rx Byte
This is the total received frames formatted in byte.
• Tx Byte
This is the total transmitted frames formatted in byte.
• PoE (PoE Model Only)
PoE displaysthe PoE state (Delivery, No PD, Disabled, None) of the port. If the port does not support PoE
function, it displays“None”.
Note: This information is displayed on the system that supports the PoE function.
50
Page 54

III-13. Web Management – IGMP Snooping
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is used in communicating among hosts and establishing a
multicast group membership on the IPv4 networks (Layer 3). IGMP provides the ability to prune multicast
traffic to those who need this kind of traffic and reduce the amount of traffic on the network. However,
switches work on the MAC Layer (Layer 2) and are unable to obtain IGMP information. IGMP Snooping allows
the switch to listen to the IGMP communication between hosts and routers, and maintains a table of multicast
IPs and group members. IGMP Snooping can prevent the hosts on the LAN from receiving traffic from a
non-joined multicast group and save bandwidth of the network.
CONFIGURE IGMP SNOOPING INFORMATION
For more information, hover the mouse over the icon in the system.
• Basic Setting
。 Mode
“Enable” or “Disable” the IGMP Snooping function.
• Querier Settings
。 Querier Mode
“Enable” or “Disable” the IGMP Snooping Querier function. If it is enabled, the system sends IGMP
snooping version 1 and 2 queries.
。 Querier Period
This period is the interval to send the IGMP snooping queries.
The range of theQuerier Period is from 1 to 3600 seconds.
The default Querier Period Interval is 125 seconds.
。 Query Max Response Time
This is a timer to wait for the member response of the IGMP groups. It is used in removing the
information of the IGMP groups if no member responds to the query.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
51
Page 55

IGMP SNOOPING TABLE
• Multicast IP
The Multicast IP is the IP address of the multicast group.
• Group
The group shows the port number, which joined the group.
52
Page 56

III-14. Web Management – 802.1Q VLAN
802.1Q VLAN
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a structure that can ease Network planning. The devices in a VLAN can be
located anywhere without the restriction of physical connections, but work like they are on the same physical
segment.
IEEE 802.1Q defines VLAN tagging conception for the Ethernet frames. VLAN tagging supports frames in the
different VLAN groups transmitting on a link (called VLAN trunk). The maximum number of VLANs on the
Ethernet network is 4096. TheVLAN 0 and VLAN 4095are for specific use and hence the usable VLAN number is
4094.
VLAN Q-IN-Q
VLAN Q-in-Q, also called Stacked VLAN, is an extension for 802.1Q VLAN. It supports a maximum of 4096*4096
VLAN groups. VLAN Q-in-Q can apply a port to a provider, customer, or tunnel for different applications. The
header of the stacked VLAN frame contains two 802.1Q Headers with different Ethertype (TPID). The TPID
“0x88A8” is the outer tag by default and the TPID “0x8100” is the inner tag for 802.1Q VLAN. Customized
ethertype called Specific Provider Ethertype are supported if one or more ports are set to “Specific Provider”.
53
Page 57

CONFIGURE 802.1Q VLAN INFOR MATION
Management VLAN
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
。 VLAN ID
The VLAN ID is for the native VLAN. Only the ports in the same VLAN as Management VLAN can
access the switch configuration console via Ethernet.
The range of theVLAN ID is from 1 to 4094.
The default Management VLAN ID is 1.
• VLAN Member Settings
。 VLAN ID
Assigns a unique VLAN ID to this VLAN group.
The range of the VLAN ID is from 1 to 4094.
。 Name
Assigns a name to this VLAN group to identify the different VLANs.
The max.length for the Name is 32 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
。 Untagged Ports
Sets the untagged ports for this VLAN group. The system removes the VLAN tag before
transmitting from the port that is set to “untagged”. Usually, this port is connected to the end
device that belongs to this VLAN.
。 Tagged Ports
Sets the tagged ports for this VLAN group. The system keeps the VLAN tag when transmitting
from the port that is set to “tagged”. Usually this port is connected to another switch and uses the
VLAN tag to transfer the VLAN information.
。
。
: Click the plus icon to add a VLAN Member row.
: Click the remove icon to delete the VLAN Member row.
54
Page 58

• VLAN ID
802.1Q VLAN TABLE
This is the assigned unique VLAN ID for this VLAN group.
• VLAN Name
This is the assigned VLAN Name for this VLAN group.
• Untag Member
These ports are assigned as VLAN untagged ports.
• Tag Member
These ports are assigned as VLAN tagged ports.
55
Page 59

CONFIGURE 802.1Q VLAN PVID & ACCEPT TYPE
• VLAN PVID
。 No.
Port1 to PortN, where N is based on the total port number.
。 PVID
Assign a VLAN ID to the frames without a VLAN tag that come into the specific port.
• Accept Type
。 No.
Port1 to PortN, where N is based on the total port number.
。 Filter
Three types of filters are provided: All, Tagged Only, Untagged Only.
All: Accept both tagged and untagged frames that come into the port.
Tagged Only: Accept only tagged frames that come into the port.
UNTAGGED ON LY: ACCEPT ONLY UNTAGGED FRAMES THAT COME INTO THE PORT.
•
(Apply Button)
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
After configuring the above fields, click "Apply" button to make it effective.
56
Page 60

CONFIGURE VLAN Q-IN-Q
For more information, hover the mouse over the icon in the system.
• Specific Provider Ethertype
This is a global configuration and an Ethertype is assigned for all ports, which are configured as “Specific
Provider”. This field is locked (disabled) until at least one port is configured to the “Specific Provider” in
the “Q-in-Q Port Settings” section.
The range of theProvider Ethertype is from 0x0000 to 0xFFFF,but 0x8100 is invalid.
The defaultProvider Ethertype is 0x88A8.
• Q-in-Q Port Settings
。 No.
Port1 to PortN, where N is based on the total port number.
。 Mode
Set the port to one of the Q-in-Q mode.
The Egress is dependent on the connected device and hence the egress action is skipped.
Mode Ingress
57
Page 61

Q-in-Q Tunnel
Untagged Frames: Add TPID:0x88A8 tag and forward.
Mode
Ingress
Customer
A port set to “Customer” runs typically 802.1Q VLAN.
Provider
Untagged Frames: Add TPID:0x88A8 tag and forward.
Specific Provider
Users define the Ethertype for the Provider service.
Tagged Frames:
1. TPID:0x8100: Add TPID:0x88A8 tag and forward.
2. TPID:0x88A8: Forward the frames.
Untagged Frames: Add TPID:0x8100 tag and forward.
Tagged Frames:
1. TPID:0x8100:
a. Same VLAN ID: Forward the frames.
b. Different VLAN ID: Discard the frames.
2. TPID:0x88A8: Discard the frames.
Tagged Frames:
1. TPID:0x8100: Discard the frames.
2. TPID:0x88A8:
a. Same VLAN ID: Forward the frames.
b. Different VLAN ID: Discard the frames.
Untagged Frames: Add the user-defined TPID tag and
forward.
Tagged Frames:
1. TPID:0x8100: Discard the frames.
2. TPID:0x88A8: Discard the frames.
3. TPID:[user-defined]:
a. Same VLAN ID: Forward the frames.
b. Different VLAN ID: Discard the frames.
•
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
(Apply Button)
58
Page 62

III-15. Web Management – Quality of Service (QoS)
Quality of Service which known as QoS provides a stable and predictable transmitting service. It is useful to
manage the bandwidth more efficiently based on the requirement of applications. Users are able to set
different priorities for different traffics to satisfy the services which need a fixed bandwidth and have more
sensitive of delay. Quality of Service can also optimize the restrict bandwidth resource and control the network
traffic of the switches.
CONFIGURE QOS INFORMATION
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
• Queue Scheduling
。 Scheduling Mode
Select the scheduling mode for the Quality of Service.
WRR: Weighted Round Robin. WRR ensures that every queue takes turns to transmit the traffic by
its weight.
Strict: Strict Priority Queue. The traffic is transmitted based on the priority, which is from highest
to lowest.
59
Page 63

Queue
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Weight
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
8
• Queue Weight
。 Queue
。 Weight
Eight queues from queue 0 to queue 7 are supported.
Enables you to configure a specific weight for the port.
The range of the Weight is from 1 to 100. There is no need to sum all queues to 100.
The default Weight for each queue is displayed in the table:
60
Page 64

CONFIGURE QOS TRUST MODE AND DEFAULT COS
• Trust Mode
• Default CoS
Class
•
。 No.
Port1 to PortN, where N is based on the total port number.
。 Mode
CoS: Class of Service. Use the 3-bit “PRI” field in the VLAN tag. It enables you to assign traffic to 8
different classes from 0 to 7.
DSCP: Use 6-bit field “DSCP” in the Type of Service (ToS) tag. It enables you to assign traffic to 64
different types from 0 to 63.
。 No.
Port1 to PortN, where N is based on the total port number.
You can assign a default class to the port. The system follows the assigned CoS classes to transmit
frames if there is no VLAN tag in the frame header.
The default Class for each port is 0.
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
61
Page 65

Class
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
7
Queue
1 0 2 3 4 5 6
7
CONFIGURE COS MAPPING
• Class / Priority
There are 3 bits for the “Class of Service” field called “PRI” in the VLAN tag and there are 8 classes from 0
to 7.
• Queue
The chipset supports 8 queues from queue 0 to queue 7. The queue 0 is the lowest priority queue and
the queue 7 is the highest priority queue.
The default Queue for each class is displayed in the table:
62
Page 66

CONFIGURE TOS MAPPING
• DSCP
There are 6 bits for the “DSCP” in ToS tag and hence there are 64 classes from 0 to 63.
• Queue
The chipset supports 8 queues from queue 0 to queue 7. The queue 0 is the least priority queue and the
queue 7 is the highest priority queue.
The default Queue for each type is displayed in the table:
63
Page 67

Type
0-7
8-15
16-23
24-31
32-39
40-47
48-55
56-63
Queue
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
7
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
64
Page 68

III-16. Web Management – Port Trunk
Port Trunk is also known as Link Aggregation, and it is a protocol to group links to a trunk. A total of 8 trunk
groups are provided. It is a good method to reach load balance and link backup. For example, when port 1 to
port 4 are combined to trunk 1 and all ports support 100Tx and set to full-duplex, the bandwidth of the trunk
will be 800Mbps. The traffic transmitting on the trunk is distributed to one of the link by the source MAC
address to reach the load balance. When the trunk mode is set to LACP and when one of the link is broken, the
traffic will transmit on another link on the group.
CONFIGURE PORT TRUNK INFORMATION
• Group
Eight trunk groups from Trunk 1 to Trunk 8 are supported.
• Trunking Mode
Two trunking modes are available: “LACP” and “Static”.
Static: The traffic is transmitted on one of the links in the group. The link is determined by the MAC
Address in the frame header. If the link is broken, the traffic cannot transmit on the other links in the
group.
LACP: It is also known as “Dynamic” trunking. If the current transmitting link is broken, the traffic can be
transmitted on another link in the group.
• Member Ports
The selected ports are joined in the Trunk group. A port can only be in one of the trunk group.
•
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
(Apply Button)
65
Page 69

PORT TRUNK STATU S
• Group
The supported trunk groups are from Trunk 1 to Trunk 8.
• Type
The trunk mode set for this group maybe “LACP” or “Static”. This field displays“-“ if no members are in
the group.
• Ports
The selected member ports in the group will be displayed in this column.
• Link Status
This field displays the link state (Up or Down) for the specific port.
66
Page 70

III-17. Web Management – Storm Control
A traffic storm happens when there is excessive packets flood to the LAN and decreases the performance. The
Storm Control function is used to prevent the system from breaking down by the broadcast, multicast, or
unknown unicast traffic storm. When the Storm Control is enabled on the specific traffic type, the system will
monitor the incoming traffic. If the traffic is more than the configured level, the traffic will be dropped to avoid
the storm.
CONFIGURE STORM CONTROL INFORMATION
• Traffic Type
Three types of traffics are supported in the Storm Control: Broadcast, Multicast, and Unknown Unicast.
• Mode
“Enable” or “Disable” Storm Control function in the specific traffic type.
67
Page 71

• Level
Three frame levels are available: High, Middle, and Low. If the frames of specific traffic type are more
than the set level, the system will drop the type of frames to prevent the system from breaking down.
HIGH: MORE THAN 2500 FRAME PER SECOND.
MID: MORE THAN 1000 FRAME PER SECOND.
LOW: MORE THAN 500 FRAME PER SECOND.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
68
Page 72

III-18. Web Management – 802.1X
802.1X is an IEEE standard defined Port-based Network Access Control. It provides a more secured
authentication mechanism for the devices, which would like to connect to a LAN or a WAN. The Port-based
Network Access Control protocol is a convenient method for the users because the authentication is per-port
and once the port passes the authentication, it is not required to authenticate again when changing to another
device, i.e., without security. Therefore, MAC-based access control is provided. It is a more secure, but less
convenient method for authentication. Only the device with the MAC Address that has passed the
authentication can be added to the networks. These two methods are optional on each port and the users can
select one of them on different ports.
CONFIGURE 802.1X BASIC INFO R MATION
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
• Basic Settings
。 802.1X Mode
“Enable” or “Disable” 802.1X function on the switch.
。 Server Type
Select the 802.1X server type to “Local Database” or “RADIUS Server”.
Local Database: The database is maintained in a table stored in the switch. The client has to send
the username and password to authenticate with the switch’s database.
RADIUS Server: The database is maintained in other devices running RADIUS service. The
authentication follows the RADIUS protocol including communication and encryption.
69
Page 73

CONFIGURE 802.1X PORT IN F O RMATION
• Port Settings
。 No.
Port1 to PortN, where N is based on the total port number.
。 Enable
“Enable” or “Disable” 802.1X function on the port. “Yes” means 802.1X is enabled on the port and
the port is locked until it passes the authentication.
。 Mode
Select the 802.1X mode to “Mac-based” or “Port-based”.
Mac-based: Only the MAC Address, which passed the authentication, can connect to the
networks.
Port-based: If the port had passed the authentication, every device connected to the port can
connect to the networks.
Re-Auth
“Enable” or “Disable” re-authentication on the port. “Yes” means re-authentication is enabled on
the port and the port has to re-authenticate with the server every re-auth period.
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
。 Re-Auth Period
70
Page 74

This is a time interval, which is used in re-authenticating the server.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
CONFIGURE LOCAL DATABA SE INFORMATION
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
• User Name
The User Name is used in authentication.
The max.length for the User Name is 32 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
• Password
The Password is used in authentication.
The max.length for the Password is 20 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
• Confirm Password
The Confirm Password field must be the same as Password field.
•
•
•
: Click the plus icon to add a Username/Password row.
: Click the remove icon to delete the Username/Password row.
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
71
Page 75

CONFIGURE RADIUS SERVER INFORMATION
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
• Server IP
The Server IP is the IP address of the server.
• Service Port
The Service Port is the listening port on the RADIUS server.
• Shared Key
The key is used in establishing the connection between the server and the authenticator before
authentication.
•
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
(Apply Button)
72
Page 76

III-19. Web Management – Port Mirroring
Port Mirroring is a feature that copies the incoming or outgoing packets on one or more ports to another
destination port. It is very useful to monitor the network traffic and analyze the copied traffic. Port Mirroring
helps network management to keep a close eye on the network and debug when some issues arise.
CONFIGURE PORT MIRRORING INFORMATION
• Mirroring Mode
“Enable” or “Disable” the Port Mirroring function. If the user enables Port Mirroring function, the system
will transmit the traffic of the specific “Sniffer Mode” from “Source Port” to “Destination Port”.
• Source Port
The traffic on the Source Ports will be sniffed to the Destination Port.
• Sniffer Mode
Both Tx and Rx: Sniffs both transmitting and receiving traffics.
Tx Only: Sniffs only the transmitting traffic.
Rx Only: Sniffs only the receiving traffic.
• Destination Port
The traffic will sniff to the Destination Port. This port is usually connected to a host running the software
to observe the packets.
•
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
(Apply Button)
73
Page 77

III-20. Web Management – Ping
Ping is a tool used to test the reachability of a device on the IP network. Ping is enabled by sending Internet
Control Message Protocol (ICMP) request to the target device and waits for the response packet from the
target device to check the connection.
PING ANOTHER DEVICE WITH IPV4/IPV6
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
• Type
Ping a connected device with “IPv4” or “IPv6” protocol.
• IP Address
The IP address of the connected device is verified based on the type.
• Count
Sets the count times. The system will send “Count” number ICMP packets to the specific IP address and
wait for the response.
The range of the Count is from 3 to 50.
The default Count is 3.
• Result
The result of the ping shows the response from the specific IP address. If the specific IP address does
notrespond, it dispalys No Response.
• “Start” Button
Click the “Start” Button to start the ping to the IP address.
• “Stop” Button
Click the “Stop” Button to stop the ping to the IP address before the count is completed.
• “Clear” Button
Click the “Clear” Button to clear the “Result”.
• “Reset” Button
Click the “Reset” Button to clear the “Result” and reset the “IP Address” and “Count” number.
74
Page 78

III-21. Web Management – LLDP
LLDP is Link Layer Discovery Protocol and it is a vendor-neutral layer 2 protocol that is defined by IEEE 802.1AB.
LLDP is used in advertising identity of the devices, capabilities and neighbors on the LAN. The information from
the neighbors enables the switch to quickly identify the devices and interoperate with each other more
smoothly and efficiently. The neighbor table shows the information about the device that is next to the port.
The LLDP can only get information from the device that is close to it. If the users want to know the topology of
the LAN, they can collect all information from the device and analysis the neighbor table.
CONFIGURE LLDP INFORMATION
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
• LLDP Mode
“Enable” or “Disable” the LLDP function.
• LLDP Timer
The LLDP Timer is a time interval to send LLDP messages.
The range of the LLDP Timer is from 5 to 32767 seconds.
The default LLDP Timer is 30 seconds.
•
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
(Apply Button)
75
Page 79

LLDP NEIGHBOR TABLE
• Local Port
The port connected to the LLDP neighbor on the local switch.
• Remote System Name
This is the system name of the LLDP neighbor. This value is set and provided by the remote device.
• Chassis ID
The Chassis ID defines the MAC Address of the LLDP neighbor.
• Remote Port
This field displays the port information received from the LLDP neighbor.
• Port ID
The Port ID displays the port identity of the connected port on the LLDP neighbor.
• Address
The Address displays the IP address of the LLDP neighbor.
76
Page 80

III-22. Web Management – System Warning
System Warning contains “System Event Log”, “SMTP Settings”, and “Event Selection” for different types of
services such as “Fault Alarm”, “System Log”, “SMTP”, and “SNMP Trap”. These logs are very useful for the
administrator to manage and debug the system. When the system is powered off or when someone tries to
login the system or the system reboots abnormally, or when some of the interfaces are linked down, the system
sends log messages to notify specific users and record the events on the server or assigned platform. Users can
also connect an alarm buzzer to the relay alarm pins. When the configured “Fault Alarm” events are triggered,
the alarm buzzer will ring to notify the users.
CONFIGURE SYSTEM WARNING INFORMATION
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
• System Log Mode
The port connected to the LLDP neighbor on the local switch.
• Remote Server IP Address
The field contains the IP Address of the remote server. If the “Remote” mode is enabled, users have to
assign this IP Address to receive the system logs.
• Service Port
The port is used to listen to the system log packets on the remote server.
The range of the Service Port is from 1 to 65535.
The default Service Port is 514.
•
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
(Apply Button)
77
Page 81

SYSTEM EVENT LOG
• Log Text Area
The system event information displays if the “Local” system log mode is enabled and the configured
events are triggered.
•
Click the “Clear” button to clear the system event log in the text area.
•
Click the “Refresh” button to refresh the system event log in the text area.
(Clear Button)
(Refresh Button)
78
Page 82

CONFIGURE SMTP INFORMATION
• Server Settings
。 SMTP Status
“Enable” or “Disable” the SMTP function.
。 Server Address
This is the IP address or URL of the SMTP Server. For example, the SMTP server address provided
by Google is “smtp.gmail.com”.
。 Server Port
This field is the port listening on the server for the SMTP request. For security, we suggest users
configure the server port to 465 for SSL or 587 for TLS.
The range of the Service Port is from 1 to 65535.
The default Service Port is 25. Port 25 is the default port for e-mail server.
。 Sender E-mail
The Sender E-mail is the e-mail address used to send the notifications to Recipients.
。 Mail Subject
The Mail Subject is a string that is displayed in the E-mail title.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
。 SMTP Authentication
79
Page 83

“Enable” or “Disable” to authenticate the SMTP server with the configured username and
password.
。 User Name
The username is used in authentication with the SMTP server.
The max.length for the User Name is 32 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
。 Password
The password is used in authentication with the SMTP server.
The max.length for the Password is 32 characters.
Note: #, \, ', ", ? are invalid characters.
• Recipient Settings
。 E-mail Address 1-4
The configured e-mail address will receive the notifications if the SMTP is enabled and the events
set on “Event Selection” are triggered.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
80
Page 84

CONFIGURE EVENT SELECTIONS
• Event
There are 5 events on the System Events.
Authentication Failure: Login failed on the web console or CLI. It maybe caused due to incorrect username
or password.
ERPS Change: The ERPS function is working and the topology is changed.
Power 1 or 2:The power 1 or 2 is powered off.
Cold Start: The system reboots due to interruption of power supply.
Warm Start: The system reboots by issuing “reboot” command on CLI or clicking the “reboot icon” on the
web console.
Digital Input: The signal from the digital input is changed from high to low or low to high.
81
Page 85

• Event
The events on the “Interface Events” display the link status for each port. Fault Alarm is triggered only
during link down and other system log types support both link up and link down.
• Fault Alarm
The Fault LED will turn on red and relay will turn ON, if the configured events are triggered. By default,
the Fault LED is green and relay is turned OFF in the normal situation,.
• System Log
When the configured events are triggered, the logs will be displayed in the “System Event Log” page,
remote server, or saved to a USB file named “message”. This is based on the settings of the “System Log
Mode” in the “System Log Settings” page.
• SMTP
If the SMTP is enabled and the configured events are triggered, the system will send an e-mail notification
to the e-mail addresses of the assigned recipient set in the “SNMP Settings” page.
• SNMP Trap
If the SNMP Trap is enabled and the configured events are triggered, the system will send event
information to the assigned “Trap Receiver IP”, which is set in the “SNMP Trap” page.
•
(Apply Button)
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
82
Page 86

III-23. Web Management – MAC Table
MAC address is Media Access Control address, which is used in layer 2 switching. A MAC Address table is
maintained by the switch to transmit frames more efficiently. When the switch receives a frame, the system will
check the MAC table and forward the frame to the corresponding port. The MAC Address table is built
dynamically by the received frames and when the system receives a frame with an unknown MAC address, it
floods the frame to all LAN ports in the same VLAN. When the destination device replies the system identifies
the MAC Address and the target port.
CONFIGURE STATI C MAC ADDRESS INFORMATION
For more information, hover the mouse over the icon in the system.
• VID
The VID is the VLAN group ID, which contains the configured MAC Address.
The range of the VID is from 1 to 4094.
• MAC Address
This field is the static MAC Address of the configured member ports in the VLAN group.
• Group Member
The Group Member is the port(s) in the VLAN group, to which the configured MAC Address belongs.
•
•
•
: Click the plus icon to add a static MAC Address row.
: Click the remove icon to delete the static MAC Address row.
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
(Apply Button)
83
Page 87

MAC ADDRESS TABLE
• VID
The VID is the VLAN group ID, which contains the configured MAC Address.
• MAC Address
The MAC Address column displays the learnt or configured MAC Addresses.
• Type
The Type column displays the type (Learning or Static) of the MAC Address.
Learning: The MAC address is learnt from the transmitting frames.
Static: The MAC Address is configured by the users or the system.
• Source
The Source column displays the port(s) to which the MAC Address belong.
84
Page 88

III-24. Web Management – Authorization
The "Username" and "Password" are very important information both in the "Command Line Interface" or
"Web Console". Users have to login into the system before doing any configuration. We strongly suggest the
users to change at least the password for security when they are going to use this device.
CONFIGURE LOGIN INFORMATION
For more information, move the mouse over the icon in the system.
• Username
The account used to login to the system.
The maximum length of the Username is 20 characters
Only alphabet (A-Z, a-z) and numbers (0-9) are allowed.
The default Username is admin.
• Password
The password used to login to the system.
The maximum length of the Password is 20 characters.
Only alphabet (A-Z, a-z) and numbers (0-9) are allowed.
The default Password is admin.
• Confirm Password
It is used to confirm the value specified by the users in the "Password" field. The value of the field must be
the same as "Password".
•
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
(Apply Button)
85
Page 89

III-25. Web Management – Firmware Upgrade
For a better performance and wider industrial applications, we constantly develop new features and revise the
issues from the users. We suggest the users to upgrade the system to the newest firmware version to have a
better user experience.
We provide 2 ways to upgrade the firmware from the Web Console, - one is saving the firmware file in the USB
stick and another one is save the firmware file on the PC. If the firmware file is on the PC, the users will have to
only select the file and click Apply button, for the system to upgrade it automatically.
UPGRADE FIRMWARE VERSION - UPLOAD FIRMWARE FILE
• Firmware Image
Click the "Select File" button to select the firmware image provided by the sales or support.
The Firmware Version displayed on the system can be customized by the file name. For example, if you
want the version to be called as 1.2.3, you only need to modify the file name to XXX-v1.2.3 (XXX is the
original file name).
• Selected File
After selecting a firmware image to be uploaded, the selected file name will be displayed in this field.
•
After selecting the firmware image, click "Upload" button to upload it.
(Upload Button)
86
Page 90

UPGRADE FIRMWARE PROCESS - UPLOADING FIRMWARE FILE
The following steps are performed when the system starts to upgrade after the "Apply" button is clicked:
1. Uploading the firmware image
The progress bar displays the uploading percentage.
2. Verifying the uploaded file
When the file is 100% uploaded, the system starts to verify the uploaded file to make sure it is valid. By
default, the firmware image is encrypted to prevent the attack on man-in-the-middle. Optionally, higher
encryption methodology is also provided.
3. Installing the uploaded firmware image
The new firmware will install after the system validates it.
87
Page 91

4. Rebooting the system
The system will reboot automatically if the firmware is upgraded without any issue.
The progress bar displays the rebooting progress.
88
Page 92

UPGRADE FIRMWARE VERSION - COPY FIRMWARE FILE FROM USB
• Image File Name
Enter the name of the firmware image in the USB. The system will try to identify the file with specified file
name to upload it to the system.
•
After entering the firmware image name, click "Upload" button to copy it from the USB to the system.
(Upload Button)
UPGRADE FIRMWARE PROCESS - COPY FIRMWARE FILE FROM USB
1. Copying the firmware image from USB to switch
The system will also check if the USB is inserted and file exists.
89
Page 93

2. Verifying the uploaded file
After copying the firmware file to switch, the system starts to verify the uploaded file to make sure it
is valid. By default, the firmware image is encrypted to prevent the attack on man-in-the-middle.
Optionally, higher encryption methodology is also provided.
3. Installing the uploaded firmware image
The new firmware will install after the system makes sure it is valid.
4. Rebooting the system
The system will reboot automatically if the firmware is upgraded without any issue.
The progress bar displays the rebooting progress.
90
Page 94

III-26. Web Management – Config Backup
In the normal application, there are several switches in the Network and they might be configured to the same
features. To facilitate this, the users can configure one of the switches and save the configuration file to local
host (for example: users' PC) or USB sticks and then restore the configurations on another switch via "Config
Restore" function. Configuration file in the USB can also have a way to fast replace the device when it is
damage.
BACKUP CONFIGURATION FILE
• Backup to Localhost
。 File Name
Specify the File Name for the Startup-config file, which will be saved to the localhost.
• Backup to USB
Ensure there is a USB stick inserted into the USB port.
。 Backup Running-config File
Specify the File Name for the saved Running-config file, which will be saved to the USB.
。 Backup Startup-config File
Specify the File Name for the saved Startup-config file, which will be saved to the USB.
•
Click the "Save" button to save the configuration file to the Localhost or USB.
NOTE:If the File Name filed is empty, the system assigns the default name: config-[datetime].cfg
(Save Button)
91
Page 95

III-27. Web Management – Config Restore
We suggest users to save/backup the configurations after a series of settings. If another device needs the same
configurations, users can use the Config Restore function to restore it.
RESTORE CONFIGURATION FILE
• Restore from Localhost
。 File Name
Select the configuration file, which is saved in the Localhost.
• Restore from USB
Please ensure there is a USB stick inserted into the USB port.
。 File Name in USB
The File Name of the saved configuration file, which is saved to the USB. If the configuration file is
saved in the directory, please specify the full path.
•
Click the "Restore" button to restore the configurations from the Localhost or USB.
(Restore Button)
92
Page 96

III-28. Web Management – USB Auto-Load &Auto-Backup
CONFIGURE USB AUTO-LOAD AND AUTO-BACKUP
• USB Auto-Load
“Enable” or “Disable” the USB Auto-Load function. If “USB Auto-Load” is enabled, the system will search
the configuration file named “startup-config” in the USB and load it when rebooting.
• USB Auto-Backup
“Enable” or “Disable” USB Auto-Backup function. If “USB-Auto-Backup” is enabled, the system will save
the configurations to a file named “running-config” in the USB when users modify the configurations.
•
After configuring above fields, click "Apply" button to make the changes effective.
(Apply Button)
93
Page 97

Appendix A: IP Configuration for Your PC
This appendix describes how to set the IP address of your PC so you can connect to product
configuration webpage. The configuration webpage allows you to set system variables or monitor
system status.
The following section will guide you to set the IP address properly in a Microsoft Windows 8
environment. Setting IP address in other Microsoft operating system (such as Windows 7) is quite the
same and can be related.
1. Open Network and Sharing Center in Control Panel, and click on Change adapter settings as
shown in the figure down below.
2. A Network Connections window will pop up, showing all the network connections available on
your PC. Please double-click on the network connection you are using to connect the device.
94
Page 98

3. An Ethernet Status window will pop up. Please click on the Properties button as shown in the
figure down below.
4. An Ethernet Properties window will pop up. Please double click on the Internet Protocol
Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
5. An Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties window will pop up. Please set your PC’s
IP address and subnet mask as shown in the figure down below.
By default, your product’s IP address should be 192.168.2.1.You can set any IP address as long
as it’s not the same with your product’s IP address and is in the same network segment with
your product’s IP address.
Press OK to apply the TCP/IPv4 settings you just made. Now you can connect to your product
using a web browser (i.e. Internet Explorer, Chrome, or Firefox).
95
Page 99

96
Page 100

Appendix B: CLI Command Reference
The following are the commands that the users can use in the CLI mode. Please check if the mode is
correct before issuing the command.
SYSTEM GROUP
Command Explanation Mode
erase startup-config Reset to factory default and reboot
exec-timeout [MINUTE] [SECOND] Set idle timeout [MINUTE] [SECOND]
hostname [HOSTNAME] Set Switch Host Name
reboot Reboot the switch
system contact [CONTACT] Set system contact
system location [LOCATION] Set device location
username [USER_ID] [PASSWORD] Configure username and password
show exec-timeout Display idle timeout
show hostname Display Switch Host Name
show environment power [1|2] Display power 1/2 status
show event status relay Display relay status
show system contact Display system contact
show system description Display system description
show system location Display system location
show system mac Display system MAC address
show system uptime Display system uptime
show system version firmware Display system version
show username Display admin ID
no exec-timeout Default idle timeout
no hostname Default Switch Host Name
no system contact Clear system contact
no system location Clear device location
no username Default username and password
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
Configure
97
 Loading...
Loading...