Page 1

GS-5654PLX & GS-5654LX
User Manual
05-2021 / v1.0
Page 2

Contents
I. Product Information ................................................. 1
I-1. Package Content ........................................................................ 2
I-2. Hardware Overview ................................................................... 3
I-3. LED Status .................................................................................. 5
II. Installation .............................................................. 7
II-1. Mounting the Switch ................................................................. 7
II-1-1. Placement Tips .................................................................................... 7
II-1-2. Rack Mounting .................................................................................... 8
II-1-3. Connecting to Power ........................................................................ 10
II-1-4. Connecting to Network ..................................................................... 10
II-1-5. Starting the Web-based Configuration Utility ................................... 11
III. Web-based Switch Configuration ........................... 13
III-1. Status ....................................................................................... 13
III-1-1. System Information .......................................................................... 13
III-1-2. Logging Message ............................................................................... 15
III-1-3. Port ................................................................................................... 16
III-1-3-1. Statistics ............................................................................................ 16
III-1-3-2. Error Disabled ................................................................................... 19
III-1-3-3. Bandwidth Utilization ........................................................................ 20
III-1-4. Link Aggregation ............................................................................... 20
III-1-5. MAC Address Table ........................................................................... 21
III-2. Network ................................................................................... 22
III-2-1. IP Address ......................................................................................... 22
III-2-2. System Time ..................................................................................... 24
III-3. Port .......................................................................................... 27
III-3-1. Port Setting ....................................................................................... 27
III-3-2. Error Disable ..................................................................................... 29
III-3-3. Link Aggregation ............................................................................... 30
III-3-3-1. Group ................................................................................................ 30
III-3-3-2. Port Setting ....................................................................................... 33
III-3-3-3. LACP .................................................................................................. 35
III-3-3-4. EEE .................................................................................................... 36
III-3-4. Jumbo Frame .................................................................................... 37
III-4. PoE ........................................................................................... 38
III-4-1. Global Setting ................................................................................... 38
III-4-2. Priority Setting .................................................................................. 41
Page 3

III-4-3. Power Limit ....................................................................................... 41
III-4-4. PoE Status ......................................................................................... 42
III-5. VLAN ........................................................................................ 43
III-5-1. VLAN ................................................................................................. 43
III-5-1-1. Create VLAN ...................................................................................... 43
III-5-1-2. VLAN Configuration ........................................................................... 45
III-5-1-3. Membership ...................................................................................... 46
III-5-1-4. Port Setting ....................................................................................... 47
III-5-2. Voice VLAN ....................................................................................... 49
III-5-2-1. Property ............................................................................................ 50
III-5-2-2. Voice OUI .......................................................................................... 51
III-5-3. Protocal VLAN ................................................................................... 53
III-5-3-1. Protocol Group .................................................................................. 53
III-5-3-2. Group Binding ................................................................................... 54
III-5-4. MAC VLAN ........................................................................................ 55
III-5-4-1. MAC Group ....................................................................................... 55
III-5-4-2. Group Binding ................................................................................... 57
III-5-5. Surveillance VLAN ............................................................................. 58
III-5-5-1. Property ............................................................................................ 59
III-5-5-2. Surveillance OUI ................................................................................ 60
III-6. MAC Address Table .................................................................. 61
III-6-1. Dynamic Address .............................................................................. 61
III-6-2. Static Address ................................................................................... 62
III-6-3. Filtering Address ............................................................................... 62
III-7. Spanning Tree .......................................................................... 63
III-7-1. Property ............................................................................................ 63
III-7-2. Port Setting ....................................................................................... 65
III-7-3. MST Instance .................................................................................... 67
III-7-4. MST Port Setting ............................................................................... 69
III-7-5. Statistics ........................................................................................... 71
III-8. Discovery ................................................................................. 72
III-8-1. LLDP .................................................................................................. 72
III-8-1-1. Property ............................................................................................ 73
III-8-1-2. MED Network Policy ......................................................................... 76
III-8-1-3. MED Port Setting ............................................................................... 77
III-8-1-4. Packet View ....................................................................................... 79
III-8-1-5. Local Information .............................................................................. 82
Page 4

III-8-1-6. Neighbor ........................................................................................... 84
III-8-1-7. Statistics ............................................................................................ 88
III-9. Multicast .................................................................................. 89
III-9-1. General ............................................................................................. 89
III-9-1-1. Property ............................................................................................ 89
III-9-1-2. Group Address .................................................................................. 90
III-9-1-3. Router Port ....................................................................................... 92
III-9-1-4. Forward All ........................................................................................ 94
III-9-1-5. Throttling .......................................................................................... 96
III-9-1-6. Filtering Profile .................................................................................. 98
III-9-1-7. Filtering Binding ................................................................................ 99
III-9-2. IGMP Snooping ............................................................................... 101
III-9-2-1. Property .......................................................................................... 101
III-9-2-2. Querier ............................................................................................ 104
III-9-2-3. Statistics .......................................................................................... 106
III-9-3. AV Over IP ....................................................................................... 107
III-9-3-1. General Property ............................................................................. 107
III-9-3-2. IGMP Property ................................................................................ 108
III-9-3-3. Querier ............................................................................................ 111
III-9-3-4. Statistics .......................................................................................... 112
III-9-4. MLD Snooping ................................................................................. 112
III-9-4-1. Property .......................................................................................... 113
III-9-4-2. Statistics .......................................................................................... 116
III-9-5. MVR ................................................................................................ 117
III-9-5-1. Property .......................................................................................... 117
III-9-5-2. Port Setting ..................................................................................... 118
III-9-5-3. Group Address ................................................................................ 119
III-10. Security .................................................................................. 120
III-10-1. RADIUS ........................................................................................... 120
III-10-2. TACACS+ ......................................................................................... 123
III-10-3. Method List ..................................................................................... 125
III-10-4. Login Authentication ....................................................................... 126
III-10-5. Management Access ....................................................................... 127
III-10-5-1. Management VLAN ......................................................................... 127
III-10-5-2. Management Service ...................................................................... 127
III-10-5-3. Management ACL ............................................................................ 129
III-10-5-4. Management ACE ........................................................................... 130
Page 5

III-10-6. Authentication Manager ................................................................. 133
III-10-6-1. Property .......................................................................................... 133
III-10-6-2. Port Setting ..................................................................................... 138
III-10-6-3. MAC-Base Local Account ................................................................ 141
III-10-6-4. WEB-Base Local Account ................................................................. 143
III-10-6-5. Sessions .......................................................................................... 144
III-10-7. Port Security ................................................................................... 145
III-10-8. Traffic Segmentation....................................................................... 146
III-10-9. Storm Control ................................................................................. 148
III-10-10. DoS ................................................................................................. 150
III-10-10-1. Property .......................................................................................... 150
III-10-10-2. Port Setting ..................................................................................... 152
III-10-11. DHCP Snooping ............................................................................... 153
III-10-11-1. Property .......................................................................................... 154
III-10-11-2. Statistics .......................................................................................... 156
III-10-11-3. Option82 Property .......................................................................... 157
III-10-11-4. Option82 Circuit ID .......................................................................... 159
III-10-12. IP Source Guard .............................................................................. 160
III-10-12-1. Port Setting ..................................................................................... 160
III-10-12-2. IMPV Binding................................................................................... 161
III-10-12-3. Save Database ................................................................................. 163
III-11. ACL ......................................................................................... 164
III-11-1. MAC ACL ......................................................................................... 164
III-11-2. MAC ACE ......................................................................................... 165
III-11-3. IPv4 ACL .......................................................................................... 167
III-11-4. IPv4 ACE .......................................................................................... 168
III-11-5. ACL Binding ..................................................................................... 171
III-12. QoS ........................................................................................ 172
III-12-1. General ........................................................................................... 172
III-12-1-1. Property .......................................................................................... 173
III-12-1-2. Queue Scheduling ........................................................................... 175
III-12-1-3. CoS Mapping ................................................................................... 176
III-12-1-4. DSCP Mapping ................................................................................. 177
III-12-1-5. IP Precedence Mapping................................................................... 178
III-12-2. Rate Limit ........................................................................................ 179
III-12-2-1. Ingress/Egress Port ......................................................................... 179
III-13. Diagnostics ............................................................................ 180
Page 6

III-13-1. Logging ........................................................................................... 180
III-13-1-1. Property .......................................................................................... 180
III-13-1-2. Remote Server ................................................................................ 181
III-13-2. Mirroring ........................................................................................ 183
III-13-3. Ping ................................................................................................. 185
III-13-4. Traceroute ...................................................................................... 186
III-13-5. Copper Test .................................................................................... 187
III-13-6. Fiber Module .................................................................................. 188
III-13-7. UDLD ............................................................................................... 189
III-13-7-1. Property .......................................................................................... 189
III-13-7-2. Neighbor ......................................................................................... 191
III-14. Management ......................................................................... 191
III-14-1. User Account .................................................................................. 192
III-14-2. Fireware .......................................................................................... 194
III-14-2-1. Upgrade / Backup ........................................................................... 194
III-14-2-2. Active Image ................................................................................... 198
III-14-3. Configuration .................................................................................. 199
III-14-3-1. Upgrade / Backup ........................................................................... 199
III-14-3-2. Save Configuration .......................................................................... 203
III-14-4. SNMP .............................................................................................. 203
III-14-4-1. View ................................................................................................ 203
III-14-4-2. Group .............................................................................................. 204
III-14-4-3. Community ..................................................................................... 206
III-14-4-4. User ................................................................................................ 208
III-14-4-5. Engine ID ......................................................................................... 211
III-14-4-6. Trap Event ....................................................................................... 213
III-14-4-7. Notification ..................................................................................... 213
III-14-5. Time Range ..................................................................................... 217
Page 7

I. Product Information
The EDIMAX Pro GS-5654LX and GS-5654PLX fully utilizes the power of your office
networking for demanding tasks, such as data backup, video conferencing, high volume
transaction processing, large file transferring, and more.
With smart features such as SNMP v1/v2/v3, PoE PD Alive Check (GS-5654PLX only),
DHCP Snooping, QoS, CoS, STP, 802.1Q VLAN, IPv4/IPv6, Port Trunking, IGMP v1/v2/v3
Snooping and Port Mirroring, the EDIMAX Pro GS- 5654LX web smart switch and
GS-5654PLX PoE web smart switch provide a cost-effective, reliable, scalable and
secure switch solution for SMB networks.
You can find all supporting documents from the link below or via QR Code:
https://www.edimax.com/download
(Once you’ve visited the Edimax official website, please enter the model no. “GS-5654PLX
or GS-5654LX” into the search box to search for your product.)
1
Page 8

I-1. Package Content
Power Cord
GS-5654LX or
GS-5654PLX
QIG
Rack-Mount Kit & Screws
Before start using this product, please check if there is anything missing in the package,
and contact your dealer to claim the missing item(s):
2
Page 9

I-2. Hardware Overview
No.
Descriptions
1
Reset Button
2
LED (PWR)
3
LED (SYS)
4
LED (SYS ALM)
5
PoE Ports (1~48)
6
SFP+ Port (49~54)
7
Fan
8
Console Port
9
Power Jack
1
2
5
4 3 6
7 8 9
GS-5654LX:
3
Page 10

GS-5654PLX:
No.
Descriptions
1
Reset Button
2
LED (PWR)
3
LED (SYS)
4
LED (PoE MAX)
5
LED (SYS ALM)
6
PoE Ports (1~48)
7
SFP+ Port (49~52)
8
LED (Link/Act)
9
LED Slide Switch
(Link or PoE Powered)
10
Console Port
11
Power Jack
1 2 4 3 5 6 7
8 9 10
11
4
Page 11
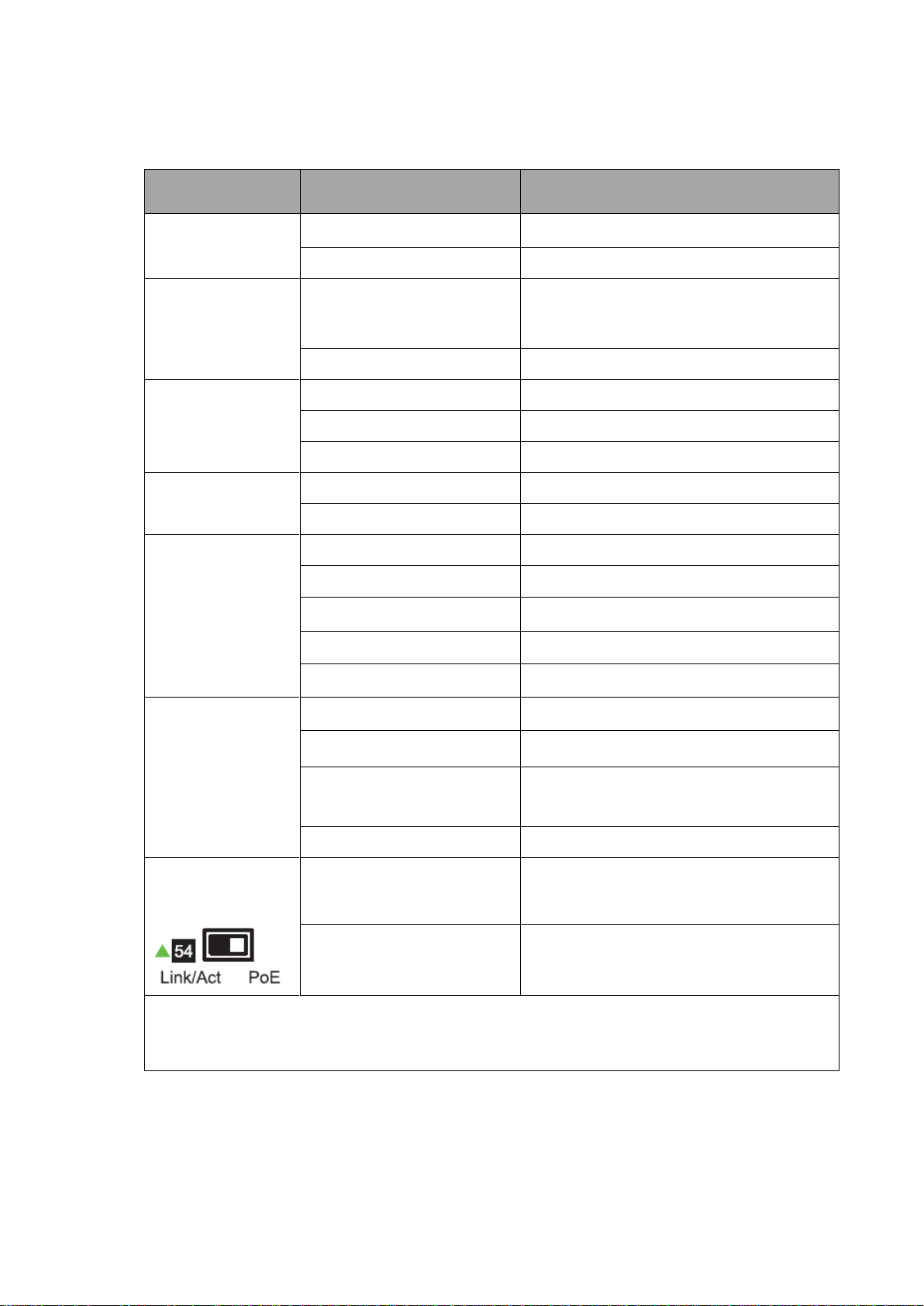
I-3. LED Status
Function
Status
Description
PWR
On (Green)
Power on
Off
Power off
SYS ALM
On (RED)
System failure (Overheat, wrong
voltage)
Off
Device in good condition
SYS
On (Green)
Power on
Off
Power off
Blinking (Green)
System boot up
PoE Max
On (Green)
Over PoE max power
Off
Not over PoE max power
Link/ACT
(1-48 port)
On (Green)
Link at 1000M
Blinking (Green)
Sending or receiving data
On (Amber)
Link at 10/100M
Blinking (Amber)
Sending or receiving data
Off
Port disconnected or link fail
SPF+
(49-54 port)
On (Green)
Link at 1000Mbps
On(Blue)
Link at 10Gbps
Blinking
(Green or Blue)
Sending data
Off
Port disconnected or link fail
LED Slide
Switch
Left (Link/Act)
LAN port connection status
Right (PoE)
PoE connection status
NOTE: LED Slide Switch: LAN Port status ( Left side) or PoE status( Right side)
GS-5654PLX:
5
Page 12

Left (Link/Act)
1-48 Port
On (Green)
Link at 1000M
Blinking (Green)
Sending or receiving data
On (Amber)
Link at 10/100M
Blinking (Amber)
Sending or receiving data
Right(PoE)
1-48 Port
On (Green)
Feeding power to PoE Devices
Off
PoE function is not active
Blinking(Green)
PoE Device required power supply
over 30W
Function
Status
Description
PWR
On (Green)
Power on
Off
Power off
SYS ALM
On (RED)
System failure (Overheat,
wrong voltage)
Off
Device in good condition
SYS
On (Green)
Power on
Off
Power off
Blinking (Green)
System boot up
Link/ACT
(1-48 port)
On (Green)
Link at 1000M
Blinking (Green)
Sending or receiving data
On (Amber)
Link at 10/100M
Blinking (Amber)
Sending or receiving data
Off
Port disconnected or link fail
SPF+
(49-54 port)
On (Green)
Link at 1000Mbps
On(Blue)
Link at 10Gbps
Blinking
(Green or Blue)
Sending data
Off
Port disconnected or link fail
GS-5654LX:
6
Page 13

II. Installation
This chapter describes how to install and connect your Edimax Switch. Read the following
topics and perform the procedures in the correct order. Incorrect installation may cause
damage to the product.
II-1. Mounting the Switch
There are two ways to physically set up the switch.
Place the switch on a flat surface. To place the switch on a desktop, install the four
rubber feet (included) on the bottom of the switch.
Mount the switch in a standard rack (1 rack unit high).
II-1-1. Placement Tips
Ambient Temperature — To prevent the switch from overheating, do not operate it
in an area that exceeds an ambient temperature of 122°F (50°C).
Air Flow — Be sure that there is adequate air flow around the switch.
Mechanical Loading — Be sure that the switch is level and stable to avoid any
hazardous conditions.
Circuit Overloading — Adding the switch to the power outlet must not overload that
circuit.
Follow these guidelines to install the switch securely.
Put the switch in a stable place such as a desktop, to avoid it falling.
Ensure the switch works in the proper AC input range and matches the voltage
labeled.
Ensure there is proper heat dissipation from and adequate ventilation around the
switch.
Ensure the switch’s location can support the weight of the switch and its accessories.
7
Page 14

Figure 4 - Desktop Installation
II-1-2. Rack Mounting
You can mount the switch in any standard size, 19-inch (about 48 cm) wide rack. The
switch requires 1 rack unit (RU) of space, which is 1.75 inches (44.45 mm) high.
For stability, load the rack from the bottom to the top, with the heaviest devices on the
bottom. A top-heavy rack is likely to be unstable and may tip over.
When mounting smaller switch products into a standard 19-inch rack, a pair of extension
brackets (sometimes referred to as ears) are needed to adapt the switch to the rack size.
These extension brackets are mounted on the switch using the screws provided in the kit,
and have two holes that are used to then screw the switch into the rack.
An example of one type of these extension brackets is shown in the following figure.
A common problem that occurs during rack mounting is the distance between the screw
holes on the rack. Some racks are made with a uniform distance between all of the holes,
and others have the holes organized into groups (see photo on the next page for an
example).
When organized into groups, the switch must be placed in the rack so that the holes in
the extension brackets line up correctly.
8
Page 15
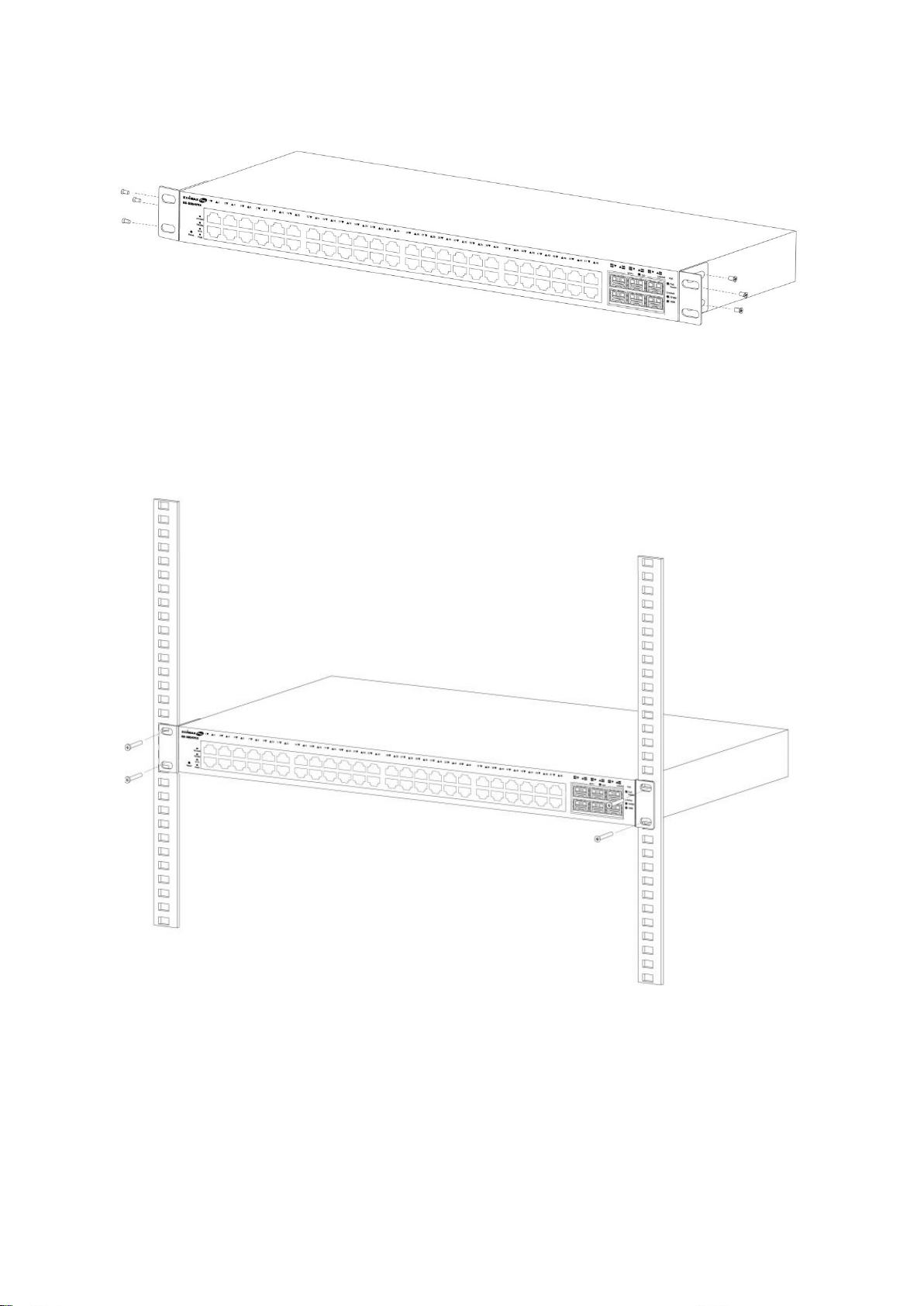
1. Align the mounting brackets with the mounting holes on the switch’s side panels and
secure the brackets with the screws provided.
Figure 5 - Bracket Installation
2. Secure the switch on the equipment rack with the screws provided.
Figure 6 - Rack Installation
9
Page 16

II-1-3. Connecting to Power
Power down and disconnect the power cord before servicing or wiring a switch.
Do not disconnect modules or cabling unless the power is first switched off. The device
only supports the voltage outlined in the type plate. Do not use any other power
components except those specifically designated for the switch.
Disconnect the power cord before installation or cable wiring.
The switch is powered by the AC 100-240 V 50/60Hz internal high-performance power
supply. It is recommended to connect the switch with a single-phase three-wire power
source with a neutral outlet, or a multifunctional computer professional source.
Connect the AC power connector on the back panel of the switch to the external power
source with the included power cord, and check the power LED is on.
Figure 7 - Rear View AC Power Socket
II-1-4. Connecting to Network
To connect the switch to the network:
1. Connect an Ethernet cable to the Ethernet port of a computer.
2. Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to LAN Port of the switch. The LED of
the port lights if the device connected is active.
3. Connect an Ethernet cable to the IP Cameras
Connect the switch to end nodes using a standard Cat5e Ethernet cable to connect the
switch to end nodes as shown in the illustration below.
Switch ports will automatically adjust to the characteristics (MDI/MDI-X, speed, duplex)
of the device to which the switch is connected.
10
Page 17
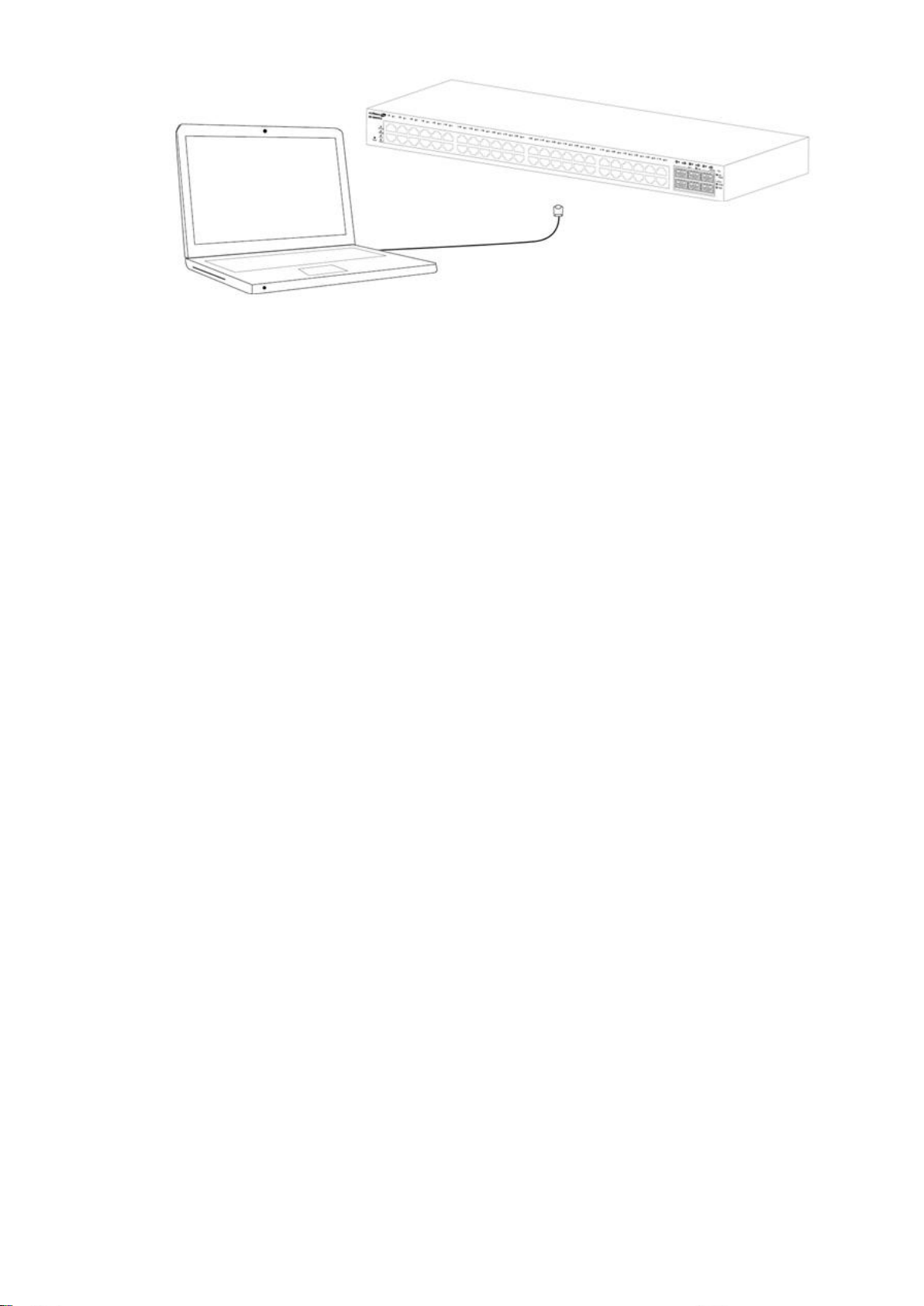
Figure 8 - PC Connect
II-1-5. Starting the Web-based Configuration Utility
This section describes how to navigate the web-based switch configuration utility.
Be sure to disable any pop-up blocker.
Browser Restrictions
If you are using older versions of Internet Explorer, you cannot directly use an IPv6
address to access the device. You can, however, use the DNS (Domain Name System)
server to create a domain name that contains the IPv6 address, and then use that
domain name in the address bar in place of the IPv6 address.
If you have multiple IPv6 interfaces on your management station, use the IPv6 global
address instead of the IPv6 link local address to access the device from your browser.
11
Page 18
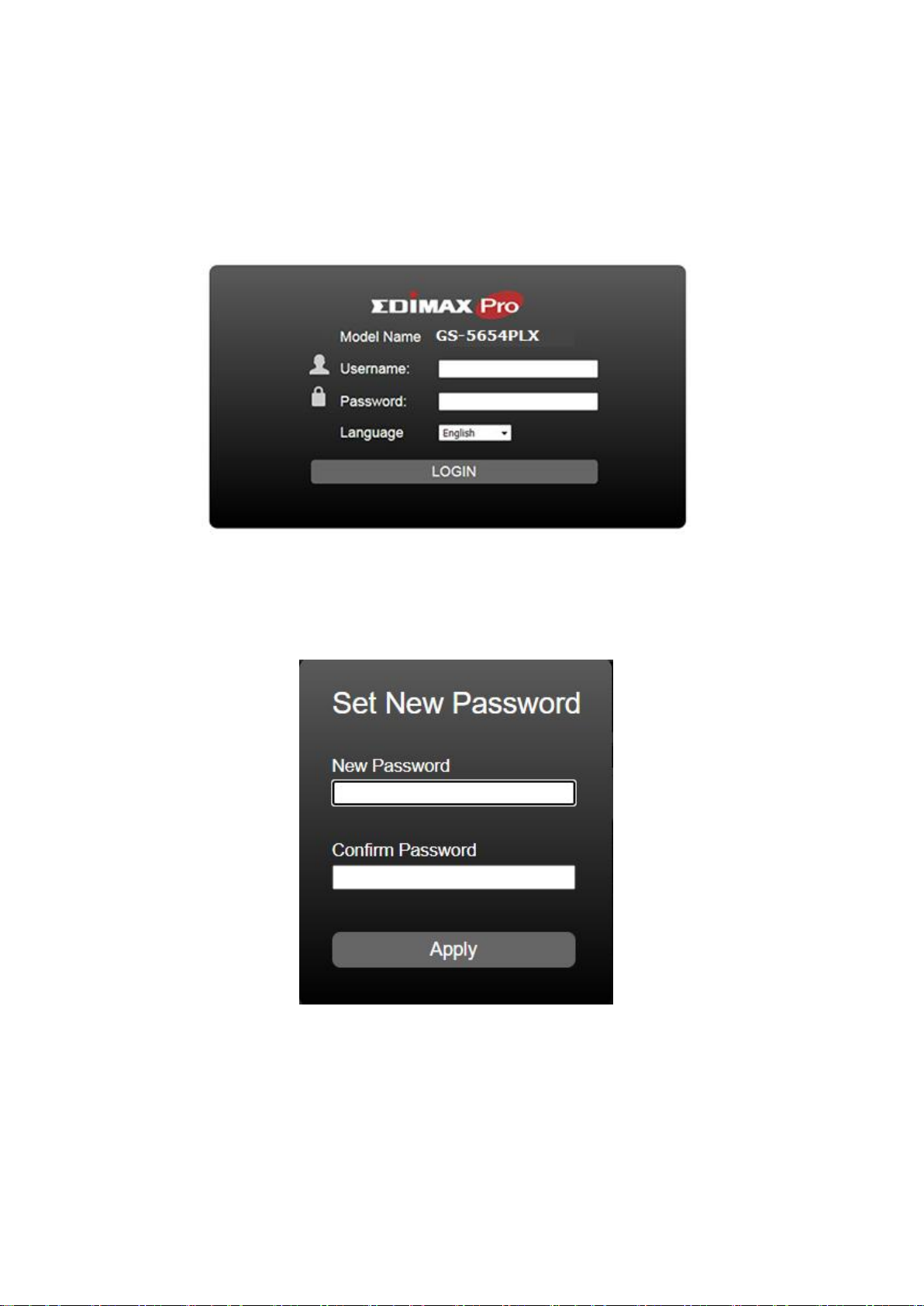
Launching the Configuration Utility
Open the web-based configuration utility:
1. Open a Web browser.
2. Enter the IP address of the device you are configuring in the address bar on the
browser (factory default IP address is 192.168.2.1) and then press Enter.
3. The default username is “admin” and the default password is “1234”.
4. The first time that you log in with the default username and password, you are
required to enter a new password.
12
Page 19

III. Web-based Switch Configuration
The Surveillance VLAN PoE+ Web Smart switches provide rich functionalities.
This chapter describes how to use the web-based management interface (Web UI) to
configure the switch’s features.
For the purposes of this manual of GS-5654PLX and GS-5654LX, the user interface is
separated into five sections, as shown in the following figure:
III-1. Status
Use the Status pages to view system information and status.
III-1-1. System Information
This page shows switch panel, CPU utilization, Memory utilization and other system
current information. It also allows user to edit some system information.
To display the Device Information web page, click Status > System Information.
13
Page 20

Item
Description
Model
Model name of the switch.
System Name
System name of the switch. This name will also use as CLI
prefix of each line. (“Switch>” or “Switch#”).
System Location
Location information of the switch.
System Contact
Contact information of the switch.
MAC Address
Base MAC address of the switch.
IPv4 Address
Current system IPv4 address.
IPv6 Address
Current system IPv6 address.
System Uptime
Total elapsed time from booting.
Current Time
Current system time.
Loader Version
Boot loader image version.
Loader Date
Boot loader image build date.
Firmware Version
Current running firmware image version.
Firmware Date
Current running firmware image build date.
Telnet
Current Telnet service enable/disable state.
SSH
Current SSH service enable/disable state.
HTTP
Current HTTP service enable/disable state.
HTTPS
Current HTTPS service enable/disable state.
SNMP
Current SNMP service enable/disable state.
Figure 12 - Status > System Information
Click “Edit” button on the table title to edit following system information.
14
Page 21

Figure 13 - Status > System Information > Edit System Information
Item
Description
System Name
System name of the switch. This name will also use as CLI prefix
of each line. (“Switch>” or “Switch#”).
System Location
Location information of the switch.
System Contact
Contact information of the switch.
Item
Description
Log ID
The log identifier.
Time
The time stamp for the logging message.
Severity
The severity for the logging message.
Description
The description of logging message.
Viewing
RAM: Show the logging messages stored on the RAM.
III-1-2. Logging Message
To view the logging messages stored on the RAM and Flash, click Status > Logging
Message.
Figure 14 - Status > Logging Message
15
Page 22

Flash: Show the logging messages stored on the Flash.
Clear
Clear the logging messages.
Refresh
Refresh the logging messages.
III-1-3. Port
III-1-3-1. Statistics
This page displays standard counters on network traffic form the Interfaces, Ethernet
-like and RMONMIB. Interfaces and Ethernet-like counters display errors on the traffic
passing through each port. RMON counters provide a total count of different frame types
and sizes passing through each port. The “Clear” button will clear MIB counter of current
selected port.
To display the Port Flow Chart web page, click Status > Port > Statistics.
16
Page 23

17 18
Page 24

Figure 15 - Status > Port > Statistics
Item
Description
Port
Select one port to show counter statistics.
MIB Counter
Select the MIB counter to show different counter type
All: All counters.
Interface: Interface related MIB counters.
Etherlike: Ethernet-like related MIB counters.
RMON: RMON related MIB counters.
Refresh Rate
Refresh the web page every period of seconds to get new
counter of specified port.
Page 25

III-1-3-2. Error Disabled
Item
Description
□
Select one or more port to operate.
Port
Interface or port number.
Reason
Port will be disabled by one of the following error reason:
BPDU Guard
UDLD
Self Loop
Broadcast Flood
Unknown Multicast Flood
Unicast Flood
ACL
Port Security Violation
DHCP rate limit
ARP rate limit
Time Left (sec)
The time left in second for the error recovery.
Refresh
Refresh the current page.
Recover
Recover the selected port status.
To display the Error Disabled web page, click Status > Port > Error Disabled.
Figure 16 - Status > Port > Error Disabled
19
Page 26

III-1-3-3. Bandwidth Utilization
Item
Description
Refresh Rate
Refresh the web page every period of seconds to get new
bandwidth utilization data.
This page allow user to browse ports’ bandwidth utilization in real time. This page will
refresh automatically in every refresh period.
To display Bandwidth Utilization web page, click Status > Port > Bandwidth Utilization.
Figure 17 - Status > Port > Bandwidth Utilization
III-1-4. Link Aggregation
To display the Link Aggregation web page, click Status > Link Aggregation.
20
Page 27
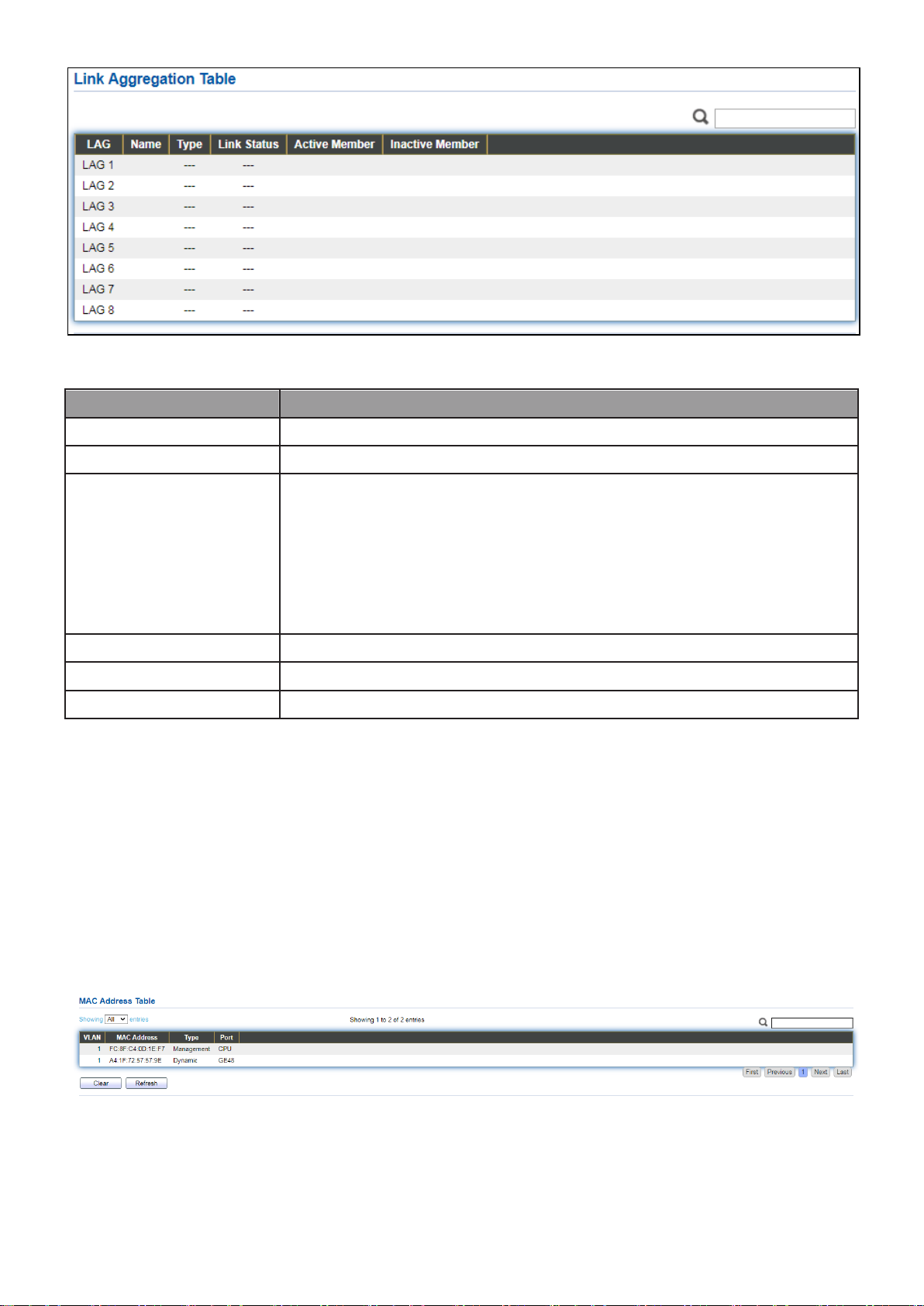
Item
Description
LAG
LAG Name.
Name
LAG port description.
Type
The type of the LAG.
Static: The group of ports assigned to a static LAG are always
active members.
LACP: The group of ports assigned to dynamic LAG are
candidate ports. LACP determines which candidate ports
are active member ports.
Link Status
LAG port link status.
Active Member
Active member ports of the LAG.
Inactive Member
Inactive member ports of the LAG.
Figure 18 - Status > Link Aggregation
III-1-5. MAC Address Table
The MAC address table page displays all MAC address entries on the switch including
static MAC address created by administrator or auto learned from hardware. The “Clear”
button will clear all dynamic entries and “Refresh” button will retrieve latest MAC
address entries and show them on page.
To display the MAC Address Table web page, click Status > MAC Address Table.
Figure 19 - Status > MAC Address Table
21
Page 28

Item
Description
VLAN
VLAN ID of the mac address.
MAC Address
MAC address.
Type
The type of MAC address
Management: DUT’s base mac address for management
Purpose.
Static: Manually configured by administrator
Dynamic: Auto learned by hardware.
Port
The type of Port
CPU: DUT’s CPU port for management purpose.
Other: Normal switch port.
III-2. Network
Use the Network pages to configure settings for the switch network interface and how
the switch connects to a remote server to get services.
III-2-1. IP Address
This section allows you to edit the IP address, Netmask, Gateway and DNS server of the
switch.
To view the IP Address menu, navigate to Network > IP Address.
22
Page 29
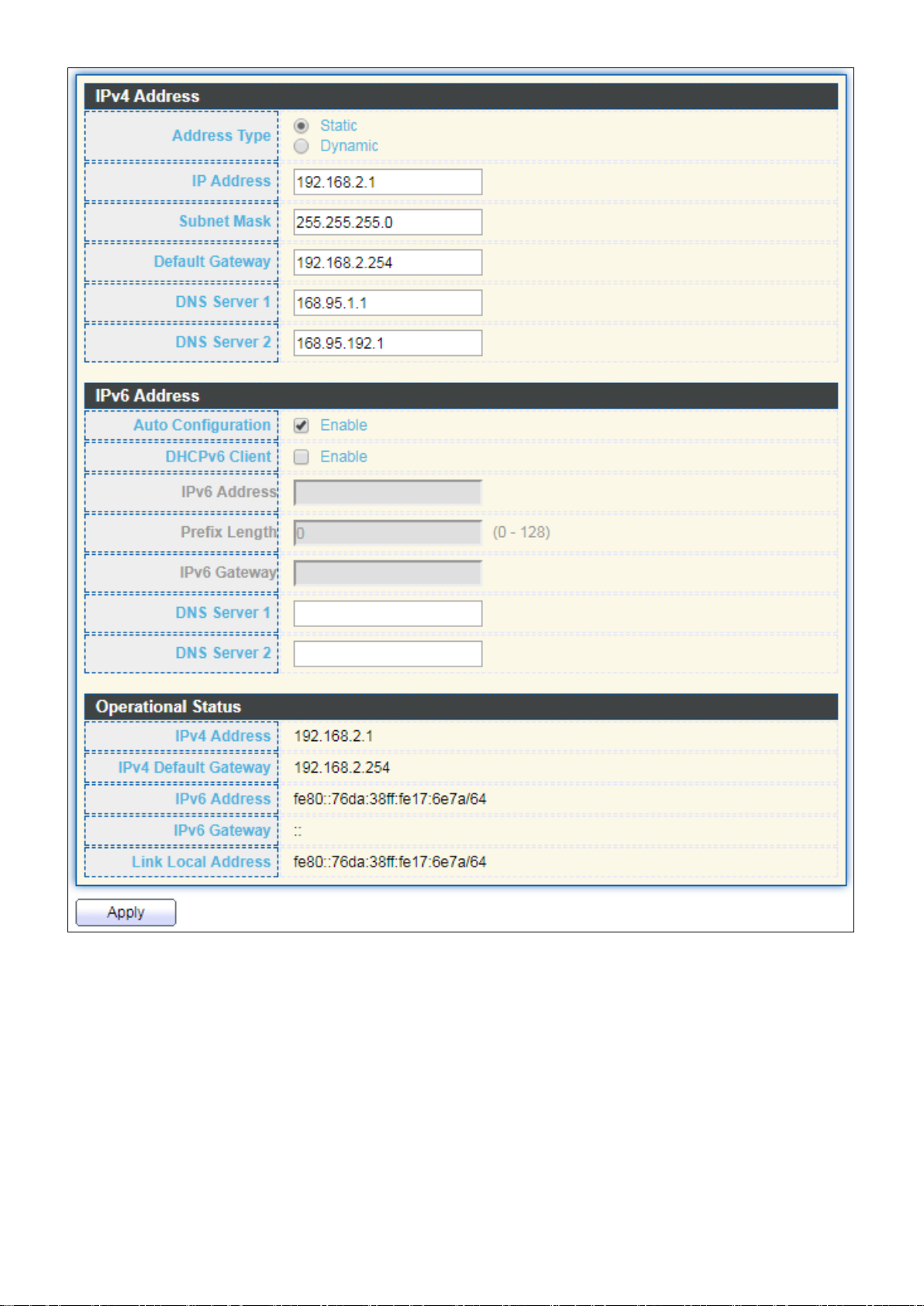
Figure 20 - Network > IP Address
23
Page 30
Item
Description
Address Type
The address type of switch IP configuration including
Static: Static IP configured by users will be used.
Dynamic: Enable the DHCP to obtain the IP address from a
DHCP server.
IP Address
Specify the switch static IP address on the static configuration.
Subnet Mask
Specify the switch subnet mask on the static configuration.
Default Gateway
Specify the default gateway on the static configuration. The
default gateway must be in the same subnet with switch IP
address configuration.
DNS Server 1
Specify the primary user-defined IPv4 DNS server configuration.
DNS Server 2
Specify the secondary user-defined IPv4 DNS server
configuration.
Table 3-2: IPv6 Address fields
IPv4 Address
The operational IPv4 address of the switch.
IPv4 Gateway
The operational IPv4 gateway of the switch.
IPv6 Address v6
The operational IPv6 address of the switch.
IPv6 Gateway
The operational IPv6 gateway of the switch.
Link Local Address
The IPv6 link local address for the switch.
III-2-2. System Time
This page allow user to set time source, static time, time zone and daylight saving
settings. Time zone and daylight saving takes effect both static time or time from SNTP
server.
To display System Time page, click Network > System Time.
24
Page 31

Figure 21 - Network > System Time
25
Page 32

Item
Description
Source
Select the time source.
SNTP: Time sync from NTP server.
From Computer: Time set from browser host.
Manual Time: Time set by manually configure.
Time Zone
Select a time zone difference from listing district.
SNTP
Address Type
Select the address type of NTP server. This is enabled when time
source is SNTP.
Server Address
Input IPv4 address or hostname for NTP server. This is enabled
when time source is SNTP.
Server Port
Input NTP port for NTP server. Default is 123. This is enabled
when time source is SNTP.
Manual Time
Date
Input manual date. This is enabled when time source is manual.
Time
Input manual time. This is enabled when time source is manual.
Daylight Saving Time
Type
Select the mode of daylight saving time.
Disable: Disable daylight saving time.
Recurring: Using recurring mode of daylight saving time.
Non-Recurring: Using non-recurring mode of daylight saving
time.
USA: Using daylight saving time in the United States that
starts on the second Sunday of March and ends on the first
Sunday of November.
European: Using daylight saving time in the Europe that
starts on the last Sunday in March and ending on the last
Sunday in October.
Offset
Specify the adjust offset of daylight saving time.
Recurring From
Specify the starting time of recurring daylight saving time. This
field available when selecting “Recurring” mode.
Recurring To
Specify the ending time of recurring daylight saving time. This
field available when selecting “Recurring” mode.
Non-recurring From
Specify the starting time of non-recurring daylight saving time.
This field available when selecting “Non-Recurring” mode.
Non-recurring To
Specify the ending time of recurring daylight saving time. This
field available when selecting “Non-Recurring” mode.
Non-recurring From
Specify the starting time of non-recurring daylight saving time.
This field available when selecting “Non-Recurring” mode.
Non recurring To
Specify the ending time of recurring daylight saving time. This
field available when selecting “Non-Recurring” mode.
26
Page 33

III-3. Port
Item
Description
Port
Port Name.
Type
Port media type.
Description
Port Description.
Use the Port pages to configure settings for switch port related features.
III-3-1. Port Setting
This page shows port current status and allow user to edit port configurations. Select port
entry and click “Edit” button to edit port configurations.
To display Port Setting web page, click Port > Port Setting.
Figure 22 - Port > Port Setting
27
Page 34

State
Port admin state
Enabled: Enable the port.
Disabled: Disable the port.
Link Status
Current port link status
Up: Port is link up.
Down: Port is link down.
Speed
Current port speed configuration and link speed status.
Duplex
Current port duplex configuration and link duplex status.
Flow Control
Current port flow control configuration and link flow control
status.
Item
Description
Port
Selected Port list.
Description
Port media type.
State
Port admin state.
Enabled: Enable the port.
Disabled: Disable the port.
Speed
Port speed capabilities.
Auto: Auto speed with all capabilities.
Auto-10M: Auto speed with 10M ability only.
Click “Edit” button to edit Port Setting menu
Figure 23 - Port > Port Setting > Port Setting
28
Page 35

Auto-100M: Auto speed with 100M ability only.
Auto-1000M: Auto speed with 1000M ability only.
Auto-10M/100M: Auto speed with 10M/100M abilities.
10M: Force speed with 10M ability.
100M: Force speed with 100M ability.
1000M: Force speed with 1000M ability.
Duplex
Port duplex capabilities.
Auto: Auto duplex with all capabilities.
Half: Auto speed with 10M and 100M ability only.
Full: Auto speed with 10M/100M/1000M ability only.
Flow Control
Port flow control.
Auto: Auto flow control by negotiation.
Enabled: Enable flow control ability.
Disabled: Disable flow control ability.
Item
Description
Recover Interval
Auto recovery after this interval for error disabled port.
BPDU Guard
Enabled to auto shutdown port when BPDU Guard reason occur. This
reason caused by STP BPDU Guard mechanism.
UDLD
Enabled to auto shutdown port when UDLD violation occur.
III-3-2. Error Disable
To display Error Disabled web page, click Port > Error Disabled
Figure 25 - Port > Error disable
29
Page 36

Self Loop
Enabled to auto shutdown port when Self Loop reason occur.
Broadcast Flood
Enabled to auto shutdown port when Broadcast Flood reason occur.
This reason caused by broadcast rate exceed broadcast storm control
rate.
Unknown Multicast
Flood
Enabled to auto shutdown port when Unknown Multicast Flood
reason occur. This reason caused by unknown multicast rate exceed
unknown multicast storm control rate.
Unicast Flood
Enabled to auto shutdown port when Unicast Flood reason occur.
This reason caused by unicast rate exceed unicast storm control rate.
ACL
Enabled to auto shutdown port when ACL shutdown port reason
occur. This reason caused packet match the ACL shutdown port
action.
Port Security
Enabled to auto shutdown port when Port Security Violation reason
occur. This reason caused by violation port security rules.
DHCP rate limit
Enabled to auto shutdown port when DHCP rate limit reason occur.
This reason caused by DHCP packet rate exceed DHCP rate limit.
ARP rate limit
Enabled to auto shutdown port when ARP rate limit reason occur.
This reason caused by DHCP packet rate exceed ARP rate limit.
III-3-3. Link Aggregation
III-3-3-1. Group
This page allow user to configure link aggregation group load balance algorithm and
group member.
To view the Group menu, navigate to Port > Link Aggregation > Group.
30
Page 37

Figure 26 - Port > Link Aggregation > Group
Item
Description
Load Balance
Algorithm
LAG load balance distribution algorithm
src-dst-mac: Based on MAC address.
src-dst-mac-ip: Based on MAC address and IP address.
LAG
LAG Name.
Name
LAG port description.
Type
The type of the LAG
Static: The group of ports assigned to a static LAG are always
active members.
LACP: The group of ports assigned to dynamic LAG are
candidate ports. LACP determines which candidate ports are
active member ports.
Link Status
LAG port link status
Active Member
Active member ports of the LAG.
Inactive Member
Inactive member ports of the LAG.
Click “Edit” to edit Link Aggregation Group menu.
31
Page 38

Figure 27 - Port > Link Aggregation > Group > Edit Link Aggregation Group
Item
Description
LAG
Selected LAG group ID.
Name
LAG port description.
Type
The type of the LAG
Static: The group of ports assigned to a static LAG are always
active members.
LACP: The group of ports assigned to dynamic LAG are
candidate ports. LACP determines which candidate ports are
active member ports.
Member
Select available port to be LAG group member port.
32
Page 39

III-3-3-2. Port Setting
Item
Description
LAG
LAG Port Name.
Type
LAG Port media type.
Description
LAG Port description.
State
LAG Port admin state
Enabled: Enable the port.
Disabled: Disable the port.
Link Status
Current LAG port link status
Up: Port is link up.
Down: Port is link down.
Speed
Current LAG port speed configuration and link speed status.
Duplex
Current LAG port duplex configuration and link duplex status.
Flow Control
Current LAG port flow control configuration and link flow control
status.
This page shows LAG port current status and allow user to edit LAG port configurations.
Select LAG entry and click “Edit” button to edit LAG port configurations.
To display LAG Port Setting web page, click Port > Link Aggregation > Port Setting.
Figure 28 - Port > Link Aggregation > Port Setting
33
Page 40

Click “Edit” to view Edit Port Setting menu.
Item
Description
Port
Selected Port list.
Description
Port description.
State
Port admin state
Enabled: Enable the port.
Disabled: Disable the port.
Speed
Port speed capabilities
Auto: Auto speed with all capabilities.
Auto-10M: Auto speed with 10M ability only.
Auto-100M: Auto speed with 100M ability only.
Auto-1000M: Auto speed with 1000M ability only.
Auto-10M/100M: Auto speed with 10M/100M abilities.
10M: Force speed with 10M ability.
100M: Force speed with 100M ability.
1000M: Force speed with 1000M ability.
Flow Control
Port flow control
Auto: Auto flow control by negotiation.
Enabled: Enable flow control ability.
Disabled: Disable flow control ability.
Figure 29 - Port > Link Aggregation > Port Setting > Edit Port Setting
34
Page 41

III-3-3-3. LACP
Item
Description
System Priority
Configure the system priority of LACP. This decides the system
priority field in LACP PDU.
Port
Port Name.
Port Priority
LACP priority value of the port.
Timeout
The periodic transmissions type of LACP PDUs.
Long: Transmit LACP PDU with slow periodic (30s).
Short: Transmit LACPP DU with fast periodic (1s).
This page allow user to configure LACP global and port configurations. Select ports and
click “Edit” button to edit port configuration.
To display the LACP Setting web page , click Port > Link Aggregation > LACP.
Figure 30 - Port > Link Aggregation > LACP
Click "Edit" button to view Edit LACP Port Setting menu.
35
Page 42

Figure 31 - Port > Link Aggregation > LACP > Edit LACP Port Setting
Item
Description
Port
Selected port list.
Port Priority
Enter the LACP priority value of the port
Timeout
The periodic transmissions type of LACP PDUs.
Long: Transmit LACP PDU with slow periodic (30s).
Short: Transmit LACPP DU with fast periodic (1s).
III-3-3-4. EEE
This page allow user to configure Energy Efficient Ethernet settings.
To display the EEE web page, click Port > EEE.
36
Page 43

Item
Description
Port
Port Name.
State
Port EEE admin state
Enabled: EEE is enabled.
Disabled: EEE is disabled.
Operational Status
Port EEE operational status
Enabled: EEE is operating.
Disabled: EEE is no operating.
Item
Description
Port
Port Name
State
Port EEE admin state
Enabled: EEE is enabled.
Disabled: EEE is disabled.
Click “Edit” to edit the EEE menu.
Figure 32 - Port > EEE
Figure 33 - Port > EEE > Edit EEE Setting
III-3-4. Jumbo Frame
This page allow user to configure switch jumbo frame size.
To display Jumbo Frame web page, click Port > Jumbo Frame.
37
Page 44

Figure 34 - Port > Jumbo Frame
Item
Description
Jumbo Frame
Enable or disable jumbo frame. When jumbo frame is enabled,
switch max frame size is allowed to configure. When jumbo frame is
disabled, default frame size 1522 will be used.
III-4. PoE
Port security can set port isolation and specific behavior.
NOTE: This section is only for GS-5654PLX.
III-4-1. Global Setting
To display the Global web page, click PoE > Global Setting.
38
Page 45

Figure 35 - PoE > Global Setting
Item
Description
Nominal Power
Maximum supply power.
Consuming Power
Current consumed power.
Remaining Power
Remaining available power.
Schedule Status
Schedule status global switch.
Name
PoE Schedule Name.
39
Page 46

Port List
The ports provide power in designated schedule index.
Schedule Status
The current schedule status.
Item
Description
Index
The serial number of schedule list.
Schedule Status
Schedule Status
Checked: Schedule status is enabled.
Unchecked: Schedule status is disabled.
Name
Enter the PoE schedule name.
Date
Select a valid time for this schedule.
Port List
Select the port provide power.
Click “Edit” to view PoE Schedule List menu.
Figure 36 - PoE > Priority Setting > Edit PoE Schedule Edit
40
Page 47

III-4-2. Priority Setting
There are 3 levels of priority you can choose for each port which are critical, high and low.
Total power budget of the switch is 400W, if one of the ports selected Critical Priority
then this port will get the power from the switch first if the total power exceeds 400W.
III-4-3. Power Limit
This page shows the information of each ports, including power limit.
To display port setting page, please click the “Edit” button.
41
Page 48

Item
Description
Port list
Display the interface of port entry.
Power Limit
Specify the power limit (0-30000, default 30000)
III-4-4. PoE Status
42
Page 49

Per Port PoE Status
Checked: Port PoE status is enabled.
Unchecked: Port PoE status is disabled.
III-5. VLAN
A virtual local area network, virtual LAN or VLAN, is a group of hosts with a common set
of requirements that communicate as if they were attached to the same broadcast
domain, regardless of their physical location. A VLAN has the same attributes as a
physical local area network (LAN), but it allows for end stations to be grouped togeth-er
even if they are not located on the same network switch. VLAN membership can be
configured through software instead of physically relocating devices or connections.
III-5-1. VLAN
Use the VLAN pages to configure settings of VLAN.
III-5-1-1. Create VLAN
This page allows user to add or delete VLAN ID entries and browser all VLAN entries that
add statically or dynamic learned by GVRP. Each VLAN entry has a unique name, user can
edit VLAN name in edit page.
To display Create VLAN page, click VLAN > VLAN > Create VLAN.
43
Page 50

Item
Description
Available VLAN
VLAN has not created yet.
Select available VLANs from left box then move to right box to
add.
Created VLAN
VLAN had been created.
Select created VLANs from right box then move to left box to
delete
VLAN
The VLAN ID.
Name
The VLAN Name.
Type
The VLAN Type.
Static: Port base VLAN.
Dynamic: 802.1q VLAN.
Item
Description
Name
Input VLAN name.
Figure 41 - VLAN > VLAN > Create VLAN
Click “Edit” button to view Edit VLAN Name menu.
Figure 42 - VLAN > VLAN > Create VLAN > Edit VLAN Name
44
Page 51

Item
Description
VLAN
Select specified VLAN ID to configure VLAN configuration.
Port
Display the interface of port entry.
Mode
Display the interface VLAN mode of port.
Membership
Select the membership for this port of the specified VLAN ID.
Forbidden: Specify the port is forbidden in the VLAN.
Excluded: Specify the port is excluded in the VLAN.
Tagged: Specify the port is tagged member in the VLAN.
Untagged: Specify the port is untagged member in the VLAN.
PVID
Display if it is PVID of interface.
III-5-1-2. VLAN Configuration
This page allow user to configure the membership for each port of selected VLAN.
To display VLAN Configuration page, click VLAN > VLAN > VLAN Configuration.
Figure 43 - VLAN > VLAN > VLAN Configuration
45
Page 52

Item
Description
Port
Display the interface of port entry.
Mode
Display the interface VLAN mode of port.
Administrative
VLAN
Display the administrative VLAN list of this port.
Operational
VLAN
Display the operational VLAN list of this port. Operational VLAN means
the VLAN status that really runs in device. It may different to
administrative VLAN.
III-5-1-3. Membership
This page allow user to view membership information for each port and edit membership
for specified interface.
To display Membership page, click VLAN > VLAN > Membership.
Figure 44 - VLAN > VLAN > Membership
Click "Edit" button to view the Edit Port Setting menu
46
Page 53

Item
Description
Port
Display the interface.
Mode
Display the VLAN mode of interface.
Membership
Select VLANs of left box and select one of following membership then move
to right box to add membership. Select VLANs of right box then move to left
box to remove membership. Tagging membership may not choose in differ
VLAN port mode. Select the time source.
Forbidden: Set VLAN as forbidden VLAN.
Excluded: This option is always disabled.
Tagged: Set VLAN as tagged VLAN.
Untagged: Set VLAN as untagged VLAN.
PVID: Check this checkbox to select the VLAN ID to be the port-based
VLAN ID for this port. PVID may auto select or can’t select in differ
settings.
Figure 45 - VLAN > VLAN > Membership > Edit Port Setting
III-5-1-4. Port Setting
This page allow user to configure ports VLAN settings such as VLAN port mode, PVID
etc…The attributes depend on different VLAN port mode.
To display Port Setting page, click VLAN > VLAN > Port Setting.
47
Page 54

Item
Description
Port
Display the interface.
Mode
Display the VLAN mode of interface.
PVID
Display the Port-based VLAN ID of port.
Accept Frame Type
Display accept frame type of port.
Ingress Filtering
Display ingress filter status of port.
Uplink
Display uplink status.
TPID
Display TPID used of interface.
Figure 46 - VLAN > VLAN > Port Setting
Click “Edit” button to Edit Port Setting menu.
48
Page 55

Item
Description
Port
Display selected port to be edited.
Mode
Select the VLAN mode of the interface.
Forbidden: Set VLAN as forbidden VLAN.
Hybrid: Support all functions as defined in IEEE 802.1Q specification.
Access: Accepts only untagged frames and join an untagged VLAN.
Trunk: An untagged member of one VLAN at most, and is a tagged
member of zero or more VLANs.
PVID
Specify the port-based VLAN ID (1-4094). It’s only available with Hybrid and
Trunk mode.
Accepted
Type
Specify the acceptable-frame-type of the specified interfaces. It’s only
available with Hybrid mode.
Ingress
Filtering
Set checkbox to enable/disable ingress filtering. It’s only available with
Hybrid mode.
Uplink
Set checkbox to enable/disable uplink mode. It’s only available with trunk
mode.
TPID
Select TPID used of interface. It’s only available with trunk mode.
Figure 47 - VLAN > VLAN > Port Setting > Edit Port Setting
III-5-2. Voice VLAN
Use the Voice VLAN pages to configure settings of Voice VLAN.
49
Page 56

Item
Description
State
Set checkbox to enable or disable voice VLAN function.
VLAN
Select Voice VLAN ID. Voice VLAN ID cannot be default VLAN.
Cos/802.1p
Select a value of VPT. Qualified packets will use this VPT value as inner
priority.
Remarking
Set checkbox to enable or disable 1p remarking. If enabled, qualified
packets will be remark by this value.
Aging Time
Input value of aging time. Default is 1440 minutes. A voice VLAN entry will
be age out after this time if without any packet pass through.
Port Setting Table
Port
Display port entry.
State
Display enable/disabled status of interface.
Mode
Display voice VLAN mode.
QoS Policy
Display voice VLAN remark will effect which kind of packet.
III-5-2-1. Property
This page allow user to configure global and per interface settings of voice VLAN.
To display Property Web page, click VLAN> Voice VLAN> Property.
Figure 48 - VLAN > Voice VLAN > Property
Click “Edit” button to view Edit Port Setting menu.
50
Page 57

Item
Description
Port
Display selected port to be edited.
State
Set checkbox to enable/disabled voice VLAN function of interface.
Mode
Select port voice VLAN mode
Auto: Voice VLAN auto detect packets that match OUI table and add
received port into voice VLAN ID tagged member.
Manual: User need add interface to VLAN ID tagged member
manually.
QoS Policy
Select port QoS Policy mode
Voice Packet: QoS attributes are applied to packets with OUIs in the
source MAC address.
All: QoS attributes are applied to packets that are classified to Voice
VLAN.
Figure 49 - VLAN > Voice VLAN > Property > Edit Port Setting
III-5-2-2. Voice OUI
This page allow user to add, edit or delete OUI MAC addresses. Default has 8 pre-defined
OUI MAC.
To display the Voice OUI Web page, click VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice OUI.
51
Page 58

Item
Description
OUI
Display OUI MAC address.
Description
Display description of OUI entry.
Item
Description
OUI
Input OUI MAC address. Can’t be edited in edit dialog.
Description
Input description of the specified MAC address to the voice VLAN
OUI table.
Figure 50 - VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice OUI
Click “Add” or “Edit” button to Add/Edit Voice OUI menu.
Figure 51 - VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice OUI > Add/Edit Voice OUI
52
Page 59

Item
Description
Group ID
Display group ID of entry.
Frame Type
This function maps packets to protocol‐defined VLAN by
examining the type octet within the packet header to
discover the type of protocol associated with it.
Protocol Value
Display the Ether type of the target protocol.
III-5-3. Protocal VLAN
Use the Protocol VLAN pages to configure settings of Protocal VLAN.
III-5-3-1. Protocol Group
This page allow user to add or edit groups settings of Protocol VLAN.
To display the Protocol page, click VLAN > Protocol VLAN > Protocol Group.
Click “Add” button or "Edit" button to view Add/Edit MAC menu.
53
Page 60

Item
Description
Group ID
Input group ID that is a unique ID of group entry. The range from
1 to8. Only available on Add Dialog.
Frame Type
Select a frame type (Ethernet_II, IEEE802.3_LLC_Other,
RFC_1042) for Group ID.
- Ethernet_II: Packet type is Ethernet version 2.
- IEEE802.3_LLC_Other: packet type is 802.3 packet with LLC
other header.
- RFC_1042: This RFC specifies a standard method of
encapsulating the Internet Protocol (IP) datagrams and Address
Resolution Protocol (ARP) requests and replies on IEEE 802
Networks to allow compatible and interoperable
implementations. This RFC specifies a protocol standard for the
Internet community.
Protocol Value
Input the Ether type of the target protocol.
Item
Description
Port
Display port ID that binding with group entry.
Group ID
Display group ID that port binding with.
VLAN
Display VLAN ID that assign to packets which match group.
III-5-3-2. Group Binding
This page allow user to bind VLAN group to each port with Group ID.
To display Group Binding page, click VLAN> Protocol VLAN > Group Binding.
Click “Add” or “Edit” button to view the Add/Edit Group Binding menu.
54
Page 61

Item
Description
Port
Select ports in left box then move to right to binding with group. Or select
ports in right box then move to left to unbind with group. Only interface
has hybrid VLAN mode can be selected and bound with protocol group.
Only available on Add dialog.
Group ID
Select a Group ID to associate with port. Only available on Add dialog.
VLAN
Input VLAN ID that will assign to packets which match group.
III-5-4. MAC VLAN
Use the MAC VLAN pages to configure settings of MAC VLAN.
III-5-4-1. MAC Group
This page allow user to add or edit groups settings of MAC VLAN.
To display the MAC page, click VLAN > MAC VLAN > MAC Group.
55
Page 62

Item
Description
Group ID
Display group ID of entry.
MAC Address
Display mac address of entry.
Mask
Display mask of mac address for classified packet.
Item
Description
Group ID
Input group ID that is a unique ID of mac group entry. The range
from 1 to 2147483647. Only available on Add Dialog.
MAC Address
Input mac address for classifying packets.
Mask
Input mask of mac address.
Figure 52 - VLAN > MAC VLAN > MAC Group
Click “Add” button or "Edit" button to view Add/Edit MAC menu.
Figure 53 - VLAN > MAC VLAN > MAC Group > Add/Edit MAC
56
Page 63

Item
Description
Port
Display port ID that binding with MAC group entry.
Group ID
Display group ID that port binding with.
VLAN
Display VLAN ID that assign to packets which match MAC group.
III-5-4-2. Group Binding
This page allow user to bind MAC VLAN group to each port with VLAN ID.
To display Group Binding page, click VLAN> MAC VLAN > Group Binding.
Figure 54 - VLAN > MAC VLAN > Group Binding
Click “Add” or “Edit” button to view the Add/Edit Group Binding menu.
57
Page 64

Item
Description
Port
Select ports in left box then move to right to binding with MAC group. Or
select ports in right box then move to left to unbind with MAC group. Only
interface has hybrid VLAN mode can be selected and bound with protocol
group. Only available on Add dialog.
Group ID
Select a Group ID to associate with port. Only available on Add dialog.
VLAN
Input VLAN ID that will assign to packets which match MAC group.
Figure 55 - VLAN > MAC VLAN > Add/Edit Group Binding
III-5-5. Surveillance VLAN
Use the Surveillance VLAN pages to configure settings of Surveillance VLAN.
58
Page 65

III-5-5-1. Property
59
Page 66

Item
Description
State
Enable/Disable
VLAN
Choose none or indicate VLAN
CoS/802.1P Remarking
The 802.1p standard defines seven levels of CoS from 0 through
to 7 (highest priority). 802.1p is a sub-set of the 802.1q standard
which added additional fields into the header of a standard
Ethernet frame allowing it to contain VLAN identifiers as well as
the priority values.
Port Aging Time
When aging is configured on an interface that's using port
security, all the dynamically learned secure addresses age out
when the aging time expire
Item
Description
Port
Display port entry.
State
Display enable/disabled status of interface.
Mode
Display voice VLAN mode.
QoS Policy
Display voice VLAN remark will effect which kind of packet.
To display Port Setting page, click the “Edit” button.
III-5-5-2. Surveillance OUI
60
Page 67

Item
Description
OUI
An organizationally unique identifier (OUI) is a 24-bit number
that uniquely identifies a vendor, manufacturer, or other
organization. ... In MAC addresses, the OUI is combined with a
24-bit number (assigned by the assignee of the OUI) to form the
address.
OUI Mask
Specifies a set of MAC addresses using a bit mask to indicate the
bits of the MAC addresses that must fit to the specified MAC
address attribute.
To change the description of your IP camera, click the “Edit” button.
III-6. MAC Address Table
Use the MAC Address Table pages to show dynamic MAC table and configure settings for
static MAC entries.
III-6-1. Dynamic Address
To display the Dynamic Address web page, click MAC Address Table > Dynamic Address.
Figure 56 - MAC Address Table > Dynamic Address
61
Page 68

Item
Description
Aging Time
The time in seconds that an entry remains in the MAC address
table. Its valid range is from 10 to 630 seconds, and the default
value is 300 seconds.
Item
Description
MAC Address
The MAC address to which packets will be statically forwarded.
VLAN
Specify the VLAN to show or clear MAC entries.
Port
Interface or port number.
Item
Description
MAC Address
Specify unicast MAC address in the packets to be dropped.
VLAN
Specify the VLAN to show or clear MAC entries.
III-6-2. Static Address
To display the Static Address web page, click MAC Address Table > Static Address.
Figure 57 - MAC Address Table > Static Address.
III-6-3. Filtering Address
To display the Filtering Address web page, click MAC Address Table > Filtering Address.
Figure 58 - MAC Address Table > Filtering Address.
62
Page 69

III-7. Spanning Tree
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that ensures a loop-free topology
for any bridged Ethernet local area network.
III-7-1. Property
To display the Property web page, click Spanning Tree > Property.
Figure 59 - Spanning Tree > Property
63
Page 70

Item
Description
State
Enable/disable the STP on the switch.
Operation Mode
Specify the STP operation mode.
STP: Enable the Spanning Tree (STP) operation.
RSTP: Enable the Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP) operation.
MSTP: Enable the Multiple Spanning Tree (MSTP) operation.
Path Cost
Specify the path cost method.
Long: Specifies that the default port path costs are within the range:
1-200,000,000.
Short: Specifies that the default port path costs are within the range:
1-65,535.
BPDU Handling
Specify the BPDU forward method when the STP is disabled.
Filtering: Filter the BPDU when STP is disabled.
Flooding: Flood the BPDU when STP is disabled.
Priority
Specify the bridge priority. The valid range is from 0 to 61440, and the
value should be the multiple of 4096. It ensures the probability that the
switch is selected as the root bridge, and the lower value has the higher
priority for the switch to be selected as the root bridge of the topology.
Hello Time
Specify the STP hello time in second to broadcast its hello message to
other bridges by Designated Ports. Its valid range is from 1 to 10 seconds.
Max Age
Specify the time interval in seconds for a switch to wait the configuration
messages, without attempting to redefine its own configuration.
Forward Delay
Specify the STP forward delay time, which is the amount of time that a
port remains in the Listening and Learning states before it enters the
Forwarding state. Its valid range is from 4 to 10 seconds.
TX Hold Count
Specify the tx-hold-count used to limit the maximum numbers of packets
transmission per second. The valid range is from 1 to 10.
Region Name
The MSTP instance name. Its maximum length is 32 characters. The
default value is the MAC address of the switch.
Revision
The MSTP revision number. Its valid rage is from 0 to 65535.
Max Hop
Specify the number of hops in an MSTP region before the BPDU is
discarded. The valid range is 1 to 40.
Operational Status
Bridge Identifier
Bridge identifier of the switch.
Designated Root
Identifier
Bridge identifier of the designated root bridge.
Root Port
Operational root port of the switch.
Root Path Cost
Operational root path cost.
Topology Change
Count
Numbers of the topology changes.
Last Topology
Change
The last time for the topology change.
64
Page 71

Item
Description
Port
Specify the interface ID or the list of interface IDs.
State
The operational state on the specified port.
Path Cost
STP path cost on the specified port.
Priority
STP priority on the specified port.
BPDU Filter
The states of BPDU filter on the specified port.
BPDU Guard
The states of BPDU guard on the specified port.
Operational Edge
The operational edge port status on the specified port.
Operational
Point-to-Point
The operational point-to-point status on the specified port.
Port Role
The current port role on the specified port. The possible values are:
“Disabled”, “Master”, “Root”, “Designated”, “Alternative”, and
“Backup”.
Port State
The current port state on the specified port. The possible values are:
“Disabled”, “Discarding”, “Learning”, and “Forwarding”.
Designated Bridge
The bridge ID of the designated bridge.
Designated Port
ID
The designated port ID on the switch.
Designated Cost
The path cost of the designated port on the switch.
Protocol
Migration Check
Restart the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) migration process
(re-negotiate with its neighborhood) on the specific interface.
III-7-2. Port Setting
To configure and display the STP port settings, click STP > Port Setting.
Figure 60 - Spanning Tree > Port Setting
Click "Edit" button to view Edit Port Setting menu.
65
Page 72

Item
Description
Port
Selected port ID.
State
Enable/Disable the STP on the specified port.
Path Cost
Specify the STP path cost on the specified port.
Priority
Specify the STP path cost on the specified port.
Edge Port
Specify the edge mode.
Enable: Force to true state (as link to a host).
Disable: Force to false state (as link to a bridge).
In the edge mode, the interface would be put into the
Forwarding state immediately upon link up. If the edge mode is
enabled for the interface and there are BPDUs received on the
interface, the loop might be occurred in the short time before
the STP state change.
BPDU Filter
The BPDU Filter configuration avoids receiving / transmitting
BPDU from the specified ports.
Enable: Enable BPDU filter function.
Figure 61 - Spanning Tree > Port Setting > Edit Port Setting
66
Page 73

Disable: Disable BPDU filter function.
BPDU Guard
The BPDU Guard configuration to drop the received BPDU
directly.
Enable: Enable BPDU guard function.
Disable: Disable BPDU guard function.
Point-to-Point
Specify the Point-to-Point port configuration:
Auto: The state is depended on the duplex setting of the port
Enable: Force to true state.
Disable: Force to false state
Item
Description
MSTI
Designated port number.
Priority
The bridge priority on the specified MSTI.
Bridge Identifier
The bridge identifier on the specified MSTI.
Designated Root Bridge
The designated root bridge identifier on the specified MSTI.
Root Port
The designated root port on the specified MSTI.
Root Path Cost
The designated root path cost on the specified MSTI.
Remaining Hop
The configuration of remaining hop on the specified MSTI.
VLAN
The VLAN configuration on the specified MSTI.
III-7-3. MST Instance
To configure MST instance setting, click STP > MST Instance.
Figure 62 - Spanning Tree > MST Instance
67
Page 74

Item
Description
VLAN
Select the VLAN list for the specified MSTI.
Priority
Specify the bridge priority on the specified MSTI. The valid range
is from 0 to 61440, and the value must be the multiple of 4096. It
ensures the probability that the switch is selected as the root
bridge, and the lower values has the higher priority for the
switch to be selected as the root bridge of the STP topology.
Click "Edit" button to view Edit MST Instance menu.
Figure 63 - Spanning Tree > MST Instance > Edit MST Instance Setting
68
Page 75

Item
Description
MSTI
Specify the port setting on the specified MSTI.
Port
Specify the interface ID or the list of interface IDs.
Path Cost
The port path cost on the specified MSTI.
Priority
The port priority on the specified MSTI.
Port Role
The current port role on the specified port. The possible values are:
“Disabled”, “Master”, “Root”, “Designated”, “Alternative”, and
“Backup”.
Port State
The current port state on the specified port. The possible values are:
“Disabled”, “Discarding”, “Learning”, and “Forwarding”.
Mode
The operational STP mode on the specified port.
Type
The possible value for the port type are:
Boundary: The port attaching an MST Bridge to a LAN that is not in
the same region.
Internal: The port attaching an MST Bridge to a LAN that is not in
the same region.
Designated
Bridge
The bridge ID of the designated bridge.
Designated Port
ID
The designated port ID on the switch.
Designated Cost
The path cost of the designated port on the switch.
Remaining Hop
The remaining hops count on the specified port.
III-7-4. MST Port Setting
To configure and display MST port setting, click STP > MST Port Setting.
Figure 64 - Spanning Tree > MST Port Setting
69
Page 76

Item
Description
Path Cost
Specify the STP port path cost on the specified MSTI.
Priority
Specify the STP port priority on the specified MSTI.
Click "Edit" button to view Edit MST Port Setting menu.
Figure 65 - Spanning Tree > MST Port Setting > Edit MST Port Setting
70
Page 77

Item
Description
Refresh Rate
The option to refresh the statistics automatically.
Receive BPDU (Config)
The counts of the received CONFIG BPDU.
Receive BPDU (TCN)
The counts of the received TCN BPDU.
Receive BPDU (MSTP)
The counts of the received MSTP BPDU.
Transmit BPDU (Config)
The counts of the transmitted CONFIG BPDU.
Transmit BPDU (TCN)
The counts of the transmitted TCN BPDU.
Transmit BPDU (MSTP)
The counts of the transmitted MSTP BPDU.
Clear
Clear the statistics for the selected interfaces
View
View the statistics for the interface.
III-7-5. Statistics
To display the STP statistics, click STP > Statistics.
Figure 66 - Spanning Tree > Statistics
Click "View" button to view the STP Port Statistic menu.
71
Page 78

Item
Description
Refresh Rate
The option to refresh the statistics automatically.
Clear
Clear the statistics for the selected interfaces.
Figure 67 - Spanning Tree > Statistics > STP Port Statistic
III-8. Discovery
Use this section to configure LLDP.
III-8-1. LLDP
LLDP ( Link Layer Discovery Protocol)is a one-way protocol; there are no
request/response sequences. Information is advertised by stations implementing the
transmit function, and is received and processed by stations implementing the receive
function. The LLDP category contains LLDP and LLDP-MED ( Link Layer Discovery
Protocol-Media Endpoint Discovery )pages.
72
Page 79

Item
Description
State
Enable/ Disable LLDP protocol on this switch.
LLDP Handling
Select LLDP PDU handling action to be filtered, bridging or flooded
when LLDP is globally disabled.
Filtering: Deletes the packet.
Bridging: (VLAN-aware flooding) Forwards the packet to all VLAN
members.
Flooding: Forwards the packet to all ports
TLV Advertise
Interval
Select the interval at which frames are transmitted. The default is 30
seconds, and the valid range is 5–32767 seconds.
Holdtime
Multiplier
Select the multiplier on the transmit interval to assign to TTL (range
2–10, default = 4).
Reinitialization
Delay
Select the delay before a re-initialization (range 1–10 seconds, default
= 2).
Transmit Delay
Select the delay after an LLDP frame is sent (range 1–8191 seconds,
default = 3).
Fast Start Repeat
Count
Select fast start repeat count when port link up (range 1–10, default =
3).
III-8-1-1. Property
To display LLDP Property Setting web page, click Discovery > LLDP > Property.
Figure 68 - Discovery > LLDP > Property
73
Page 80

Item
Description
Port
Port Name.
Mode
The port LLDP mode.
Selectde TLV
The Selected LLDP TLV.
Port Setting
To display LLDP Port Setting, click Discovery > LLDP > Port Setting.
Figure 69 - Discovery > LLDP > Port Setting
Click "Edit" button to view Edit Port Setting menu.
74
Page 81

Item
Description
Port
Select specified port or all ports to configure LLDP state.
Mode
Select the transmission state of LLDP port interface.
Disable: Disable the transmission of LLDP PDUs.
RX Only: Receive LLDP PDUs only.
TX Only: Transmit LLDP PDUs only.
TX And RX: Transmit and receive LLDP PDUs both.
Optional TLV
Select the LLDP optional TLVs to be carried (multiple selection is
allowed).
System Name
Port Description
System Description
System Capability
802.3 MAC-PHY
802.3 Link Aggregation
802.3 Maximum Frame Size
Management Address
802.1 PVID.
802.1 VLAN
Name
Select the VLAN Name ID to be carried (multiple selection is
allowed).
Figure 70 - Discovery > LLDP > Port Setting > Edit Port Setting
75
Page 82

Item
Description
Policy ID
Showing the MED Network is defined or undefined.
Application
Define an application for LLDP.
Voice
Voice Signaling
Guest Voice
Guest Voice Signaling
Softphone Voice
Video Conferencing
Streaming Video
Video Signaling
VLAN
Configure VLAN (Valid values are from 1 to 4094)
VLAN Tag
Define VLAN Tag (Tagged/Untagged).
VLAN tagging is used to tell which packet belongs to which VLAN on
the other side. To make recognition easier, a packet is tagged with a
VLAN tag in the Ethernet frame.
Priority
Define the priority
DSCP
Enter a Differentiated Serves Code Point (DSCP)
III-8-1-2. MED Network Policy
To display MED Network Policy Setting web page, click Discovery > LLDP > MED Network
Policy.
76
Page 83

Item
Description
Entry
Entry of number.
Port
Port Name.
State
Status of LLDP (Enabled or Disabled).
Network Policy
Display LLDP whether active.
Location
MED location.
Inventory
MED Inventory.
III-8-1-3. MED Port Setting
To display MED Network Policy Setting web page, click Discovery > LLDP > MED Port
Setting.
77
Page 84

Item
Description
Port
Port Name.
State
Enable/ Disable MED Port on this switch.
Optional TLV
Select the LLDP optional TLVs to be carried (multiple selection is
allowed).
Location
Extended Power-via-MDI
Inventory
Network Policy
Network Policy
Select the Network Policy to be carried
Coordinate
Configures a coordinate-based location for an endpoint device.
Civic
Configures a civic-address-based location for Link Layer Discovery
Protocol-Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED)
ECS ELIN
Configures an Emergency Call Service (ECS) based location for Link
Layer Discovery Protocol Media Endpoint Device (LLDP-MED)
Click "Edit" button to view MED Port Setting menu.
78
Page 85

Item
Description
Port
Port Name.
In-Use (Bytes)
Total number of bytes of LLDP information in each packet.
Available (Bytes)
Total number of available bytes left for additional LLDP information
in each packet.
Operational Status
Overloading or not.
III-8-1-4. Packet View
To display LLDP Overloading, click Discovery > LLDP > Packet View.
Figure 71 - Discovery > LLDP > Packet View
Click "Detail" button to view Packet View Detail menu.
79
Page 86

80
Page 87

Item
Description
Port
Port Name.
Mandatory TLVs
Total mandatory TLV byte size. Status is sent or overloading.
MED Capabilities
Total MED Capabilities TLV byte size. Status is sent or
overloading.
MED Location
Total MED Location byte size. Status is sent or overloading.
MED Network Policy
Total MED Network Policy byte size. Status is sent or
overloading.
MED Inventory
Total MED Inventory byte size. Status is sent or overloading
MED Extended Power via
MDI
Total MED Extended Power via MDI byte size. Status is sent or
overloading.
802.3 TLVs
Total 802.3 TLVs byte size. Status is sent or overloading.
Optional TLVs
Total Optional TLV byte size. Status is sent or overloading.
802.1 TLVs
Total 802.1 TLVs byte size. Status is sent or overloading.
Total
Total number of bytes of LLDP information in each packet.
Figure 72 - Discovery > LLDP > Packet View > Packet View Detail
81
Page 88

Item
Description
Chassis ID Subtype
Type of chassis ID, such as the MAC address.
Chassis ID
Identifier of chassis. Where the chassis ID subtype is a MAC address,
the MAC address of the switch is displayed.
System Name
Name of switch.
System
Description
Description of the switch.
Capabilities
Supported
Primary functions of the device, such as Bridge, WLAN AP, or Router.
Capabilities
Enabled
Primary enabled functions of the device.
Port ID Subtype
Type of the port identifier that is shown.
LLDP Status
LLDP Tx and Rx abilities.
LLDP Med Status
LLDP MED enable state.
III-8-1-5. Local Information
Use the LLDP Local Information to view LLDP local device information.
To display LLDP Local Device, click Discovery > LLDP > Local Information.
Figure 73 - Discovery > LLDP > Local Information
82
Page 89

Click “Detail” button on the page to view detail information of the selected port.
83
Page 90

Figure 74 - Discovery > LLDP > Local Information > Detail
III-8-1-6. Neighbor
Use the LLDP Neighbor page to view LLDP neighbors information.
To display LLDP Remote Device, click Discovery > LLDP > Neighbor.
Figure 75 - Discovery > LLDP > Neighbor
84
Page 91

Item
Description
Local Port
Number of the local port to which the neighbor is connected.
Chassis ID Subtype
Type of chassis ID (for example, MAC address).
Port ID Subtype
Type of the port identifier that is shown.
Port ID
Identifier of port.
System Name
Published name of the switch.
Time to Live
Time interval in seconds after which the information for this
neighbor is deleted.
Click “detail” to view selected neighbor detail information
85
Page 92

86
Page 93

Figure 76 LLDP Neighbor Detail Page
87
Page 94

Item
Description
Insertions
The number of times the complete set of information advertised by a
particular MAC Service Access Point (MSAP) has been inserted into
tables associated with the remote systems.
Deletions
The number of times the complete set of information advertised by
MSAP has been deleted from tables associated with the remote
systems.
Drops
The number of times the complete set of information advertised by
MSAP could not be entered into tables associated with the remote
systems because of insufficient resources.
Age Outs
The number of times the complete set of information advertised by
III-8-1-7. Statistics
The Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) Statistics page displays summary and per-port
information for LLDP frames transmitted and received on the switch.
To display LLDP Statistics status, click Discovery > LLDP > Statistics.
Figure 77 - Discovery > LLDP > Statistics
88
Page 95

MSAP has been deleted from tables associated with the remote
systems because the information timeliness interval has expired.
Statistics Table
Port
Interface or port number.
Transmit Frame
Total
Number of LLDP frames transmitted on the corresponding port.
Receive Frame
Total
Number of LLDP frames received by this LLDP agent on the
corresponding port, while the LLDP agent is enabled.
Receive Frame
Discard
Number of LLDP frames discarded for any reason by the LLDP agent on
the corresponding port.
Receive Frame
Error
Number of invalid LLDP frames received by the LLDP agent on the
corresponding port, while the LLDP agent is enabled.
Receive TLV
Discard
Number of TLVs of LLDP frames discarded for any reason by the LLDP
agent on the corresponding port.
Receive TLV
Unrecognized
Number of TLVs of LLDP frames that are unrecognied while the LLDP
agent is enabled.
Neighbor Timeout
Number of age out LLDP frames.
III-9. Multicast
Use this section to configure Multicast.
III-9-1. General
Use the General pages to configure settings of IGMP and MLD common function.
III-9-1-1. Property
To display multicast general property Setting web page, click Multicast> General>
Property.
89
Page 96

Item
Description
Unknown Multicast
Action
Set the unknown multicast action
Flood: flood the unknown multicast data.
Drop: drop the unknown multicast data.
Router port: forward the unknown multicast data to router port.
IPv4
Set the ipv4 multicast forward method.
MAC-VID: forward method dmac+vid.
DIP-VID: forward method dip+vid.
IPv6
MAC-
DIP-VID: forward method dip+vid(dip is ipv6 low 32 bit).
Figure 78 - Multicast > General > Property
III-9-1-2. Group Address
This page allow user to browse all multicast groups that dynamic learned or statically
added.
To display Multicast General Group web page, click Multicast> General > Group Address.
Figure 79 - Multicast > General > Group Address
90
Page 97

Item
Description
IP Version
IP Version
IPv4: ipv4 multicast group
IPv6: ipv6 multicast group
VLAN
The VLAN ID of group.
Group Address
The group IP address.
Member
The member ports of group.
Type
The type of group. Static or Dynamic.
Life(Sec)
The life time of this dynamic group.
Click “Add” or “Edit” button to view Add or Edit Group Address menu.
Figure 80 - Multicast > General > Group Address > Add/Edit Group Address
91
Page 98

Item
Description
VLAN
The VLAN ID of group.
IP Version
IP Version
IPv4: ipv4 multicast group
IPv6: ipv6 multicast group
Group Address
The group IP address.
Member
The member ports of group.
Available Port: Optional port member
Selected Port: Selected port member
Item
Description
IP Version
IP Version
IPv4: ipv4 multicast router
IPv6: ipv6 multicast router
VLAN
The VLAN ID router entry.
Member
Router Port member (include static and learned port member).
Static Port
Static router port member.
Forbidden Port
Forbidden router port member.
Life (Sec)
The expiry time of the router entry.
III-9-1-3. Router Port
This page allow user to browse all router port information. The static and forbidden
router port can set by user.
To display multicast router port table web page, click Multicast > General > Router Port.
Figure 81 - Multicast > General > Router Port
Click "Add" or “Edit” button to view Add/Edit Router Port menu.
92
Page 99

Figure 82 - Multicast > General > Router Port > Add/Edit Router Port
93
Page 100

Item
Description
VLAN
The VLAN ID for router entry
Available VLAN: Optional VLAN member
Selected VLAN: Selected VLAN member.
IP Version
IP Version
IPv4: ipv4 multicast router
IPv6: ipv6 multicast router
Type
The router port type
Static: static router port
Forbidden: forbidden router port, can’t learn dynamic router
port member
Port
The member ports of router entry.
Available Port: Optional router port member
Selected Port: Selected router port member
Item
Description
IP Version
IP Version
IPv4
IPv6
VLAN
The VLAN ID entry.
Static Port
Static port member.
Forbidden Port
Forbidden port member.
III-9-1-4. Forward All
This page allow user to browse all forward port information.
94
 Loading...
Loading...