Page 1

EAP2316A
Powered by Accton
2.4 GHz
Wireless Access Point
Installatio n Gu id e
www.edge-core.com
Page 2

Page 3

Installation Guide
2.4 GHz Wireless Access Point
IEEE 802.11b/g Access Point
with Integrated Diversity Antennas
Page 4

EAP2316A
E072005-R01
Page 5

Compliances
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipme nt and receiver
• Connect the equipment in to an outlet on a circuit different from th at to w hi ch the
receiver is connected
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technici an for help
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment. This
device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must
accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with a minimum distance
of 20 centimeters (8 inches) between the radiator and your body. This transmitter must
not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
Countries of Operation & Conditions of Use in the European
Community
This device is intended to be operated in all countries of the European Community.
Requirements for indoor vs. outdoor operation, license requirements and allowed
channels of operation apply in some countries as described below:
Note: The user must use the configuration utility provided with this product to ensure the
channels of operation are in conformance with the spectrum usage rules for
European Community countries as described below.
• This device requires that the user or installer properly enter the current country of
operation in the command line interface as described in the user guide, before operating
this device.
i
Page 6

• This device will automatically limit the allowable channels determined by the current
country of operation. Incorrectly entering the country of operation may result in illegal
operation and may cause harmful interference to other system. The user is obligated to
ensure the device is operating according to the channel limitations, indoor/outdoor
restrictions and license requirements for each European Community country as
described in this document.
• The 2.5 GHz Turbo Mode feature is not allowed for operation in any European
Community country. The current setting for this feature is found in the 2.5 GHz 802.11g
Radio Settings Window as described in the user guide.
• This device may be operated indoors or outdoors in all countries of the European
Community using the 2.4 GHz band: Channels 1 - 13, except where noted below.
- In Italy the end-user must apply for a license from the national spectrum authority to
operate this device outdoors.
- In Belgium outdoor operation is only permitted using the 2.46 - 2.4835 GHz band:
Channel 13.
- In France outdoor operation is only permitted using the 2.4 - 2.454 GHz band:
Channels 1 - 7.
Declaration of Conformity in Languages of the European
Community
English Hereby, Edgecore, declares that this Radio LAN device is in com-
Finnish Valmistaja Edgecore vakuuttaa täten että Radio LAN device tyyp-
Dutch Hierbij verklaart Edgecore dat het toestel Radio LAN device in
French Par la présente Edgecore déclare que l'appareil Radio LAN device
Swedish Härmed intygar Edgecore att denna Radio LAN device står I öve-
Danish Undertegnede Edgecore erklærer herved, at følgende udstyr Ra-
pliance with the essential requirements and other relevant provisions of Directive 1999/5/EC.
pinen laite on direktiivin 1999/5/EY oleellisten vaatimusten ja sitä
koskevien direktiivin muiden ehtojen mukainen.
overeenstemming is met de essentiële eisen en de andere relevante bepalingen van richtlijn 1999/5/EG
Bij deze Edgecore dat deze Radio LAN device voldoet aan de essentiële eisen en aan de overige relevante bepalingen van Richtlijn 1999/5/EC.
est conforme aux exigences essentielles et aux autres dispositions
pertinentes de la directive 1999/5/CE
rensstämmelse med de väsentliga egenskapskrav och övriga relevanta bestämmelser som framgår av direktiv 1999/5/EG.
dio LAN device overholder de væsentlige krav og øvrige relevante
krav i direktiv 1999/5/EF
ii
Page 7

German Hiermit erklärt Edgecore, dass sich dieser/diese/dieses Radio LAN
Greek ΜΕ ΤΗΝ ΠΑΡΟΥΣΑ Edgecore ∆ΗΛΩΝΕΙ ΟΤΙ Radio LAN device
Italian Con la presente Edgecore dichiara che questo Radio LAN device
Spanish Por medio de la presente Edgecore declara que el Radio LAN de-
Portuguese Edgecore declara que este Radio LAN device está conforme com
device in Übereinstimmung mit den grundlegenden Anforderungen und den anderen relevanten Vorschriften der Richtlinie 1999/
5/EG befindet". (BMWi)
Hiermit erklärt Edgecore die Übereinstimmung des Gerätes Radio
LAN device mit den grundlegenden Anforderungen und den anderen relevanten Festlegungen der Richtlinie 1999/5/EG. (Wien)
ΣΥΜΜΟΡΦΩΝΕΤΑΙ ΠΡΟΣ ΤΙΣ ΟΥΣΙΩ∆ΕΙΣ ΑΠΑΙΤΗΣΕΙΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΙΣ
ΛΟΙΠΕΣ ΣΧΕΤΙΚΕΣ ∆ΙΑΤΑΞΕΙΣ ΤΗΣ Ο∆ΗΓΙΑΣ 1999/5/ΕΚ
è conforme ai requisiti essenziali ed alle altre disposizioni pertinenti stabilite dalla direttiva 1999/5/CE.
vice cumple con los requisitos esenciales y cualesquiera otras disposiciones aplicables o exigibles de la Directiva 1999/5/CE
os requisitos essenciais e outras disposições da Directiva 1999/5/
CE
iii
Page 8

iv
Page 9

Contents
Chapter 1: Introduct ion 1-1
Package Checklist 1-2
Hardware Description 1-3
Component Description 1-4
Chapter 2: Hardware Installation 2-1
Access Point Configuration 2-4
Chapter 3: Network Configuration 3-1
Network Topologies 3-2
Ad Hoc Wireless LAN (no Access Point) 3-2
Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3-2
Infrastructure Wireless LAN for Roaming Wireless PCs 3-3
Infrastructure Wireless Bridge 3-4
Infrastructure Wireless Repeate r 3-5
Appendix A: Troubleshooting A-1
Diagnosing Access Point Indicators A-1
Appendix B: Cables and Pinouts B-1
Twisted-Pair Cable Assignments B-1
10/100BASE-TX Pin Assignments B-1
Straight-Through Wiring B-2
Crossover Wiring B-3
Appendix C: Specifications C-1
General Specifications C-1
Sensitivity C-3
Transmit Power C-3
Operating Range C-4
v
Page 10

Contents
vi
Page 11

Chapter 1: Introduction
The 2.4 GHz Wireless Access Point is an IEEE 802.11b/g access point that provides
transparent, wireless high-speed data communications between the wired LAN and
fixed or mobile devices equipped with an 802.11b, or 802.11g wireless adapter.
This solution offers fast, re liable wireless c onnectivity with co nsiderable cost savings
over wired LANs (which include long-term maintenance overhead for cabling). Using
802.11b and 802.11g technology, this access point can easily r epl ac e a 10 M b ps
Ethernet connection or se am lessly integrate into a 10/100 M bps Eth er net LAN.
This solution offers fast, re liable wireless c onnectivity with co nsiderable cost savings
over wired LANs (which include long-term maintenance overhead for cabling). Using
802.11b and 802.11g technology, this access point can easily r epl ac e a 10 M b ps
Ethernet connection or se am lessly integrate into a 10/100 M bps Eth er net LAN.
The access point radio interface can operate in one of five modes:
• Access Point – Providing conectivity to wireless clients in the service area.
• AP Client – Act as a wireless clients in th e service area.
• Repeater – Providing an extended link to a remote access point from the wired
LAN. In this mode the access point does not have a connection to a wired Ethernet
LAN.
• Bridge – Providing links to other access points in “Bridge” or “Root Bridge” mode
connecting wired LA N seg ments.
• Root Bridge – Providing links to other access points in “Bridge” mode connecting
wired LAN segments. O nly one unit in the wireless bridge net w or k can be set to
“Root Bridge” mode.
In addition, the access point offers full network management capabilities through an
easy to configure web in te rface, a command line interfa ce for initial configuration
and troubleshooting, and support for Simple Network Management tools , su ch as
HP’s OpenView.
Radio Characteristics – The IEEE 802.11g standard uses a radio modul at io n
technique known as O rthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM), an d a
shared collision domain (CSMA/CA). It operates at the 2.4 GHz Unlicensed National
Information Infrastru ct ur e (UNII) band for connections to 802.1g clients.
IEEE 802.11g includes backward compatibility with the IEEE 802.11b standard.
IEEE 802.11b also operates at 2.4 GHz, but uses Direct Se quence Spread
Spectrum (DSSS) and Complementary Code Keying (CCK) modulation t echnology
to achieve a communication rate of up to 11 Mbps.
The access point suppo rts a 54 M bps hal f-duplex connection to Ether net networks
for each active channel .
1-1
Page 12
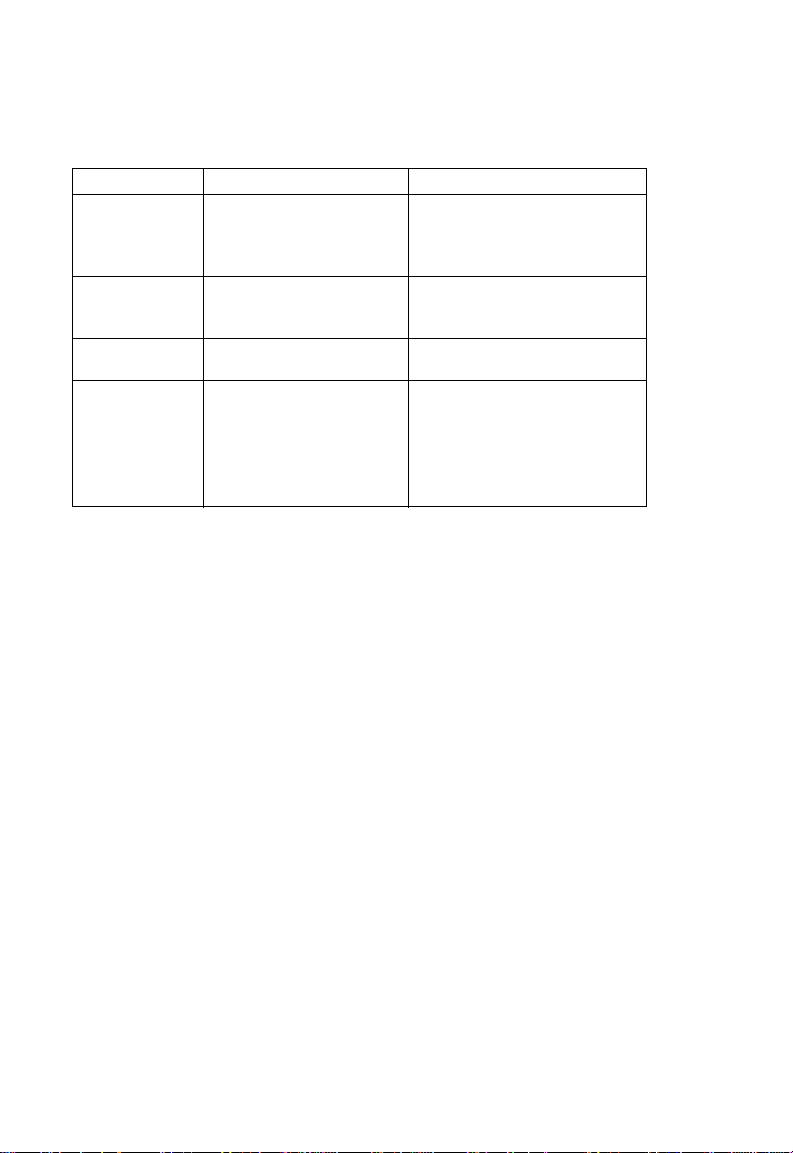
Introduction
Super G– The Atheros proprietary Super G performance en han cements are
supported by the access point. Features and benifits of Super G are described in the
following table:
Feature Characteristics Benifit
Bursting More data frames per given time
Compression Real-time hardware data
Fast Frames Utilizes frame aggregation and
Dynamic Turbo Similar to trunking techniques
period
Standards-based
Relevant to STA
compression
Standards-based (Lempel Ziv)
timing modifications
used in Fast Ethernet networks,
utilizes dual channels to “double”
transmission rates
Analyzes environment and
adjusts bandwidth utilization
accordingly
Increased throughput via overhead
reduction
802.11e subset
Advantage applies to any AP
Increased data throughput using
compressed frames
No impact on host processor
Increases throughput by transmitting
more data per frame
Maximises bandwidth using multiple
channels
Environment-aware
Package Checklist
The 2.4 GHz Wireless Access Point package includ es:
• One 2.4 GHz Wireless Access Point
• One Category 5 network cable
• One AC power adapte r an d power cord
• Two wall-mounting screws
• This Installation Guide
• Documentation CD (inc l udes Installation Guide an d M anagement Guide)
Inform your dealer if there are any incorrect, missing or dam aged parts. If possible,
retain the carton, including the original packing materials. Use them again to repack
the product in case there is a need to return it.
1-2
Page 13

Hardware Description
Top Panel
Hardware Description
Power
WLAN
Power LED
WLAN LED
Side Panels
External Antenna Connector
(not currently implemented)
WAN
WAN LED
Traffic Rate
Traffic Rate LED
Rest Button
ANT
Reset
10/100 Ethernet
Port
WAN
External Antenna Connector
(not currently implemented)
Power Socket
DC5V
ANT
1-3
Page 14

Introduction
Component Description
Antennas
The access point includes integrated internal dive rs ity ant ennas for wireless
comunications. A dive rs ity antenna system uses tw o identical antennas to recei ve
and transmit signals, he lp ing t o avoid multipath fading effects. When receiving, the
access point checks bot h antennas and selects the one wi th the st ro ngest signal.
When transmitting, it will continue to use the antenna previously selected for
receiving. The access point never transmits from both antennas at the same time.
LED Indicators
The access point includes four status LED indicators, as d escribed in the following
figure and table.
Power
LED Status Description
Power On Green Indicates that the system is working normally
WLAN On Green Indicates the 802.11g radio is enabled.
WAN On Green Indicates a valid link on the Ethernet port.
Traffic Rate On or Flashing
802.11g
Wireless
Link/Activity
Flashing Green System running its power-on-self-test
On Amber Indicates system errors
Flashing Green Indicates that the access point is transmitting or receiving
Off Indicates the 802.11g radio is disabled.
Flashing Green Indicates that the access point is transmitting or receiving
Off The Ethernet port has no link or is administratively
Green
Ethernet
Link/Activity
Traffic Rate
data through wireless links. Flashing rate is proportional
to network activity.
data through the Ethernet port. Flashing rate is
proportional to network activity.
disabled.
Indicates the level of wireless activity ranging from 0% to
100% of bandwidth utilization.
1-4
Page 15

Hardware Description
Ethernet Port
The access point has one 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX RJ-45 port that can be attached
directly to 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX LAN segments. These segments must conform
to the IEEE 802.3 or 802.3u spe ci fic at ions.
This port supports automatic MDI/MDI-X operation, so you can use straight-through
cables for all network con nections to PCs, switches, or hu bs.
The access point appea rs as an E th er net no de and performs a bridging function by
moving packets from the wired LAN to remote workstations on t he w ireless
infrastructure.
Note: The RJ-45 port also supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) based on the IEEE
802.3af standard. Refer to the description for the “Power Connector” for
information on supplying power to the access point’s network port from a
network device, such as a switch, that provides Power over Ethernet (PoE).
Reset Button
This button is used to reset the access point or restore the factory default
configuration. If you hold down the button for less than 5 seconds, the access po in t
will perform a hardware res et. If you hold down the button for 5 se conds or more,
any configuration changes you may have made are removed, and the factory default
configuration is restor ed to the access point.
Power Connector
The access point does not have a power switch. It is powered on when connected to
the AC power adapter, and the power adapter is connected to a power source. The
power adapter autom at ically adjusts to any voltage betw een 1 00 -240 volts at 50 or
60 Hz. No voltage range settings are required.
The access point may also r ece iv e Power over Ethernet (PoE) fro m a swi tch or
other network device that supplies power over the network cable based on the IEEE
802.3af standard.
Note that if the access poi nt is connected to a PoE source dev ic e and also
connected to a local power source through the AC power adapter, PoE will be
disabled.
1-5
Page 16

Introduction
1-6
Page 17

Chapter 2: Hardware Installation
1. Select a Site – Choose a proper place for the access point. In general, the best
location is at the center of your wireless coverage area, within line of sight of all
wireless devices. Try to place the access poin t in a posit ion that ca n best cover
its Basic Service Set (refer to “Infrastructure Wireless LAN” on page 3-2). For
optimum performance, consider these points:
• Mount the access point as high as possible above any obstructions in the
coverage area.
• Avoid mounting next to or near building support columns or other obstructions
that may cause reduced signal or null zones in parts of the c o ve rage area.
• Mount away from any signal absorbing or reflecting structures (such as those
containing metal).
2. Mount the Access Point – The access point can be mounted on any
horizontal surface, wall or suspended ceiling.
Mounting on a horizontal surface – The four attached rubber fee t keep the
access point from slidin g on sm ooth surfaces.
Rubber Feet
Bottom of Access Point
A
N
T
R
e
s
e
t
WA
N
D
C
5
V
2-1
Page 18

Hardware Installation
Mounting on a wall – The access point should be mounted only to a wall or
wood surface that is at lea st 1/2 -inch plywood or its equivalen t . M ar k t he
position of the mounting scr ew s o n the w all so they line up with the two
mounting slots on the bott om of th e ac cess point. Set the 5/8-inch num b er 12
wood screws into the wall, leaving about 3 mm (0.12 in.) clearance from the
wall. And then slide the acces s point down onto the screws.
Wall Mounting Slots
T-rail Mounting Tracks
Fastening Clip
Bottom of Access Point
Mounting on a suspended ceiling – To mount the access point to a suspended
ceiling, do the following:
• Choose a location on the ceiling where the access point will be installed on the
suspended ceiling T-ra il .
• Align the mounting track and fastening clip with the T-rail and slide sideways
so that the T-rail engages with the second mounting track. The access point
will snap into place.
2-2
Page 19

T-rail (ceiling mount)
A
N
T
R
e
s
e
t
WA
N
D
C
5
V
3. Connect the Power Cord – Connect the powe r a dapter to the access point,
and the power cord to an AC pow er out let .
Note: If the access point is connected to both a PoE source device and an AC power
source, PoE will be disabled.
Caution: Use ONLY the power adapter supplied with this access point. Otherwise, the
product may be damaged.
4. Observe the Self Test – When you power on the access point, verify that the
Power indicator stops flashing and remains on, and that th e ot her in di cators
start functioning as described under “LED Indicators” on page 1-4. If the Power
LED turns on amber, the self test has not completed correctly. Refer to
“Troubleshooting” on page A-1.
5. Connect the Ethernet Cable – The access point can be wi red to a
10/100 Mbps Ethernet throu gh a network device such as a h ub or a switch.
Connect your network to the RJ-45 port on the back panel with category 3, 4, or
5 UTP Ethernet cable. When the access point and the connected device are
powered on, the WAN LED should tu rn on indi cating a valid network
connection. If the WAN LED fails to turn on refer to
“Troubleshooting” on page A-1.
2-3
Page 20

Hardware Installation
Note: The RJ-45 port on the access point supports automatic MDI/MDI-X operation, so
you can use straight-through cables for all network connections to PCs, switches,
or hubs.
Access Point Configuration
The access point can be c onfi gured by connecting a PC to its Ether net port and
accessing the web interf ace. The default IP address of the access point is
192.168.1.50, with def ault user name and password of ‘adm in ’.
For detailed information on configuring the access poi nt refer to the Management
Guide.
2-4
Page 21

Chapter 3: Network Configuration
Wireless networks su pport a stand-alone configurat i on as w el l as an i nt egrated
configuration with 10/100 Mbps Ethernet LANs. The 2.4 GHz Wireless Access Point
also provides repeate r a nd br i dging services.
Access points can be deployed to support wireless clients and connect wired LANs
in the following configurat i ons:
• Ad hoc for departmental, SOHO or enterprise LANs
• Infrastructure for wirel ess LAN s
• Infrastructure wireless LAN for roaming wireless PCs
• Infrastructure wirele ss bridge to connect wired LA N s
• Infrastructure wirele ss r epeater for extended rang e
The 802.11b and 802.11g frequency band, which operates at 2.4 GHz, can easily
encounter interferen ce f ro m other 2.4 GHz devices, suc h as other 802.11b or g
wireless devices, cordless phones and microwave ovens. If you experience poor
wireless LAN perform ance, try the following meas ur es:
• Limit any possible sources of radio interference within the service area
• Increase the distance bet ween neighboring acces s po in t s
• Decrease the signal strength of neighboring acc es s poi nt s
• Increase the channel se paration of neighboring ac ces s points (e.g. up to 3
channels of seperation f or 80 2 .1 1b, or up t o 5 channels for 802.11g)
3-1
Page 22

Network Configuration
Network Topologies
Ad Hoc Wireless LAN (no Access Point)
An ad hoc wireless LAN cons ists of a gr oup of computers, each equip ped with a
wireless adapter, connected via radio signals as an independent wirel ess LAN.
Computers in a specific ad hoc wireless LAN must ther ef or e be configured to the
same radio channel. An ad hoc wireless LAN can be used for a branch office or
SOHO operation.
Ad Hoc Wireless LAN
Notebook with
Wireless USB Adapter
Notebook with
Wireless PC Card
PC with Wireless
PCI Adapter
Infrastructure Wireless LAN
The access point also provides access to a wir ed LAN for wir eless workstations. An
integrated wired/wireless LAN is called an Infrastructure configuration. A Basic
Service Set (BSS) consists of a gr oup of wi r eless PC users, and an access poi nt
that is directly connected to the wired LAN. Each wireless PC in this BSS can talk to
any computer in its wireless group via a radio link, or access other computers or
network resources in t he wi re d LAN infrastructure via the access point.
The infrastructure configuration not only extends the accessibility of wireless PCs to
the wired LAN, but also increases the effective wireless transmission range for
wireless PCs by passing their signal through one or more access points.
A wireless infrastructur e c an be used for access to a central database, or for
connection between mo bi l e workers, as shown in the follo wi ng f ig ur e.
3-2
Page 23

Server
Network Topologies
Wired LAN Extension
to Wireless Clients
Desktop PC
Switch
Access Point
Notebook PC
Desktop PC
Infrastructure Wireless LAN for Roaming Wireless PCs
The Basic Service Set (BSS) defines the communications domain for each access
point and its associated wirele ss cl ients. The BSS ID is a 48-bit binary number
based on the access po int ’s wirel es s M A C ad dress, and is set automatical l y and
transparently as clients associ ate w i th the access point. The BSS ID is used in
frames sent between the access point and its clients to identify traffic in the service
area.
The BSS ID is only set by the access point, never by its clients. The clients on ly
need to set the Service Set Iden tifi er (SSID ) that ide nti fies the ser vice set provided
by one or more access points. The SSID can be m anually configured by the clients,
can be detected in an access point’s beacon, or can be obtained by querying for the
identity of the nearest access point. For clients that do not need to roam, set the
SSID for the wireless card to that used by the access point to which you want to
connect.
A wireless infrastructure can also support roaming for mobile workers. More than
one access point can be conf igured to create an Extended S er vice Set (ESS). By
placing the access poi nts so tha t a c ont i nuous coverage area is creat ed, wireless
users within this ESS can roam freely. All wireless network cards and adapters and
wireless access points within a specific ESS must be configured with the same
SSID.
3-3
Page 24

Network Configuration
Desktop PC
Server
Seamless Roaming
Between Access Points
Switch
Switch
Notebook PC
Access Point
<BSS 1>
Desktop PC
Access Point
Notebook PC
<BSS 2>
<ESS>
Infrastructure Wireless Bridge
The IEEE 802.11 standard defines a WIreless Distribution System (WDS) for bridge
connections between BSS areas (access points). The access point uses WDS to
forward traffic on links between units.
Up to six WDS bridge links can be specified for each unit in the w i re le ss bridge
network. One unit only must be configured as the “root bridge” in the wireless
network. The root bridge sh oul d be the unit connected to the mai n core of the wired
LAN. Other bridges must configure one “parent” link to the root bridge or to a bridge
connected to the root bridge. The other five available WDS links can be specified as
“child” links to other bridges. This forms a tiered-star topology for the wireless bridge
network.
When using WDS on the access point radio, only wireless bridge units can associate
to each other. Wireless clients can only assoc ia te w ith the access point when the
radio is set to access poin t or re peater mode.
3-4
Page 25

Network Topologies
Network
Core
Bridge
Root Bridge
Wireless Bridge Links
Between Access Points
Bridge
Bridge
Infrastructure Wireless Repeater
The access point can also operate in a bridge “repeater ” mo de t o extend the range
of links to wireless clients. The ac cess point uses WDS to forw ar d t ra ffic between
the repeater bridge and th e ro ot br idge. The access point supports up to si x W D S
repeater links.
In repeater mode, the access point does not support an Ethernet link to a wired LAN.
Note that when the acce ss point operates in this mode o nl y half the normal
throughput is possible . Th is is bec ause the access point has to receive and then
re-transmit all data on the same channel.
3-5
Page 26

Network Configuration
Network
Core
Root Bridge
802.11gRadio
Repeater Link
Wireless Repeater Links
Between Access Points
802.11gRadio
Repeater Link
802.11gRadio
AP Link
Repeater
802.11gRadio
AP Link
Repeater
3-6
Page 27

Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Diagnosing Access Point Indicators
Troubleshooting Chart
Symptom Action
Power LED is Off
Power LED is Amber • The access point has detected a system error. Reboot the access
WAN LED is Off • Verify that the access point and attached device are powered on.
• AC power adapter may be disc onnec ted. Check connec tion s betwe en
the access point, the power adapter, and the wall outlet.
• PoE power to the access point may be disabled at the connected
switch port. Check the switch configuration to be sure that PoE power
is enabled for the switch and specified port. Also check that the switch
has not exceeded its power budget and turned off the port power.
point to try and clear the condition.
• If the condition does not clear, contact your local dealer for assistance.
• Be sure the cable is plugged into both the access point and
corresponding devic e.
• Verify that the proper cable type is used and its length does not exceed
specified limits.
• Check the cable connections for possible defects. Replace the
defective cable if necessary.
Note: For information on troubleshooting wireless connectivity issues, refer to the
Management Guide.
A-1
Page 28

Troubleshooting
A-2
Page 29

Appendix B: Cables and Pinouts
Twisted-Pair Cable Assignments
For 10/100BASE-TX connections, a twisted-pair cable must have two pairs of wires.
Each wire pair is identified by two di fferent co lo rs . Fo r ex am p le , on e w ire might be
green and the other, green with white stripes. Al so, an RJ-45 connector must be
attached to both ends of the cab l e.
Caution: Each wire pair must be attached to the RJ-45 connectors in a specific
orientation. (See “Straight-Through Wiring” on page B-2 and “Crossover
Wiring” on page B-3 for an explanation.)
Caution: DO NOT plug a phone jack connector into the RJ-45 port. Use only twisted-pair
The following figure illustr at es how t he pins on the RJ-45 connector ar e num bered.
Be sure to hold the connectors in the same orientation when attaching the wires to
the pins.
cables with RJ-45 connectors that conform with FCC standards.
8
1
8
10/100BASE-TX Pin Assignments
Use unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) or shielded twisted-pair (STP) cable for RJ-45
connections: 100-oh m Ca te gory 3 or better cable for 10 Mbps connections, or
100-ohm Category 5 or better cable for 100 Mbps connections. Also be sure
length of any twisted-pair connection does not exceed 100 meters (328 feet).
The RJ-45 port on the access point supports automatic M D I/M DI - X operation, so
you can use straight-through or crossover cables for all network connections to PCs,
switches, or hubs. In stra ight-through cable, pins 1, 2, 3, and 6, at one end of the
cable, are connected straight through to pins 1, 2, 3, and 6 at the other end of the
cable.
that the
B-1
Page 30

Cables and Pinouts
Pin MDI Signal Name MDI-X Signal Name
1 Transmit Data plus (TD+) Receive Data plus (RD+)
2 Transmit Data minus (TD-) Receive Data minus (RD-)
3 Receive Data plus (RD+) Transmit Data plus (TD+)
4 GND (Positive Vport) GND (Positive Vport)
5 GND (Positive Vport) GND (Positive Vport)
6 Receive Data minus (RD-) Transmit Data minus (TD-)
7 -48V feeding power
(Negative- Vport)
8 -48V feeding power
(Negative- Vport)
-48V feeding power
(Negative- Vport)
-48V feeding power
(Negative- Vport)
Note: The “+” and “-” signs represent the polarity of the wires that make up each wire pair.
Straight-Through Wiring
If the twisted-pair cable is to join two ports and only one of the ports has an inter nal
crossover (MDI-X), th e two pairs of wires must be straigh t-t hrough.
EIA/TIA 568B RJ-45 WiringStandard
10/100BASE-TX Straight-through Cable
White/Orange Stripe
Orange
End A
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
White/Green Stripe
Blue
White/Blue Stripe
Green
White/Brown Stripe
Brown
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
End B
B-2
Page 31

Twisted-Pair Cable Assignments
Crossover Wiring
If the twisted-pair cable is to join two ports and either both ports are labele d wi th an
“X” (MDI-X) or neither port is labeled with an “X” (MDI), a crossover must be
implemented in the wiring .
EIA/TIA 568B RJ-45 WiringStandard
10/100BASE-TX Crossover Cable
White/Orange Stripe
Orange
End A
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
White/Green Stripe
Blue
White/Blue Stripe
Green
White/Brown Stripe
Brown
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
End B
B-3
Page 32

Cables and Pinouts
B-4
Page 33

Appendix C: Specifications
General Specifications
Maximum Channels
802.11b/g:
FCC/IC: 1-11
ETSI: 1-13
France: 10-13
MKK: 1-14
Taiwan: 1-11
Maximum Clients
64 per VAP interface
Data Rate
802.11g: 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 Mbps per channe l
802.11b: 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbps per channel
Modulation Type
802.11g: CCK, BPSK, QPSK, OFDM
802.11b: CCK, BPSK, QPSK
Network Configuration
Infrastructure
Operating Frequency
802.11b:
2.4 ~ 2.4835 GHz (US, Canada, ETSI)
2.4 ~ 2.497 GHz (Japan)
2.400 ~ 2.4835 GHz (Taiwan)
AC Power Adapter
Input: 100-240 AC, 50-60 Hz
Output: 5 VDC, 2A
Maximum Power: 13.2 Watts
Unit Power Supply
DC Input: 5 VDC, 2 A maximum
PoE input: - 48 VDC, 0.27 A maximum
Power Consumption: 9. 6 W m axi m um
Physical Size
15.6 x 11.7 x 2.8 cm (6.14 x 4.6 x 1.1 in)
C-1
Page 34

Specifications
Weight
0.205 kg (0.44 lbs)
LED Indicators
PWR (Power), WAN (Ethernet Link/Activity), WLAN (802.11b/g Wireless Link/
Activity), Traffic Rate (Wireless LAN band width ut ilization)
Network Management
Web-browser, SNMP
Temperature
Operating: 0 to 55
Storage: 0 to 70
Humidity
15% to 95% (non-con densing)
Compliances
FCC Part 15B Class B
Radio Signal Certification
FCC Part 15C 15.247, 15.207 (2.4 G Hz)
Safety
CSA/C US (CSA60950-1 & UL6 0950-1)
IEC60950-1 (CB)
°C (32 to 131 °F)
°C (32 to 158 °F)
Standards
IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T, IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX,
IEEE 802.11b, g
C-2
Page 35

Sensitivity
IEEE 802.11g
Data Rate Sensitivity (dBm)
6 Mbps -88
9 Mbps -87
12 Mbps -86
17 Mbps -85
24 Mbps -81
36 Mbps -77
48 Mbps -72
54 Mbps -70
IEEE 802.11b
Data Rate Sensitivity (dBm)
1 Mbps -93
2 Mbps -90
5.5 Mbps -90
11 Mbps -87
General Specifications
Transmit Power
IEEE 802.11g Maximum Output Power (GHz - dBm)
Data Rate 2.412 2.417~2.467 2.472
6 Mbps 20 20 18
9 Mbps 20 20 18
12 Mbps 20 20 18
18 Mbps 20 20 18
24 Mbps 20 20 18
36 Mbps 18 19 17
48 Mbps 17 16 15
54 Mbps 15 14 13
C-3
Page 36

Specifications
IEEE 802.11b Maximum Output Power (GHz - dBm)
Data Rate 2.412 2.417~2.467 2.472
1 Mbps 15 16 15
2 Mbps 15 16 15
5.5 Mbps 15 16 15
11 Mbps 15 16 15
Operating Range
Note: The operating range distances listed in the following tables are for typical
environments only. Operating ranges can vary considerably depending on
factors such as local interference and barrier composition. It is recommended
to do a site survey to determine the maximum ranges for specific access point
locations in your environment.
802.11g Wireless Distance Table
Speed and Distance Ranges
54
48
36
24
18
Mbps
Mbps
Mbps
Mbps
1
148 m
235 m
415 m
LoS
Non-LoS
2
485 ft
43 m
141 ft
771 ft
50 m
164 ft
136 ft
57 m
187 ft
500 m
1640 ft
63 m
207 ft
1. A line-of-sight (LoS) environment with no obstructions between the access point and clients.
2. A typical non-LoS environment (office or home) with floor to ceiling obstructions between the access point
and clients.
12
Mbps
Mbps11Mbps9 Mbps6 Mbps5 Mbps2 Mbps1 Mbps
522 m
570 m
620 m
650 m
680 m
1712 ft
67 m
220 ft
1870 ft
71 m
233 ft
2034 ft
75 m
246 ft
2132 ft
77 m
253 ft
2230 ft
81 m
266 ft
780 m
2558 ft
85 m
279 ft
782 m
2565 ft
85 m
279 ft
790 m
2591 ft
85 m
279ft
802.11b Wireless Distance Table
Speed and Distance Range s
11 Mbps 5.5 Mbps 2 Mbps 1 Mbps
1
LoS
Non-LoS
2
578 m
1896 ft
70 m
230 ft
617 m
2024 ft
75 m
246 ft
694 m
2276 ft
85 m
279 ft
875 m
2870 ft
85 m
279 ft
1. A line-of-sight (LoS) environment with no obstructions between the access point and clients.
2. A typical non-LoS environment (office or home) with floor to ceiling obstructions between the access point
and clients.
C-4
Page 37

Page 38

Model Number: EAP2316A
Pub. Number: 150200023800E, E072005-R01
 Loading...
Loading...