EDATA COMMUNICATIONS DSL2120W User Manual

DSL-2120/2120W Series
ADSL2PLUS 1-port with USB
Router
User Guide
Revision 1.0
Apr/2008
Proprietary & Confidential Page 1 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008

Contents
Chapter 1 - Getting to Know DSL-2120/2120W.....................................................................................6
1.1 Features of the DSL-2120/2120W.....................................................................................................6
1.2 Applications for the DSL-2120/2120W.............................................................................................8
1.2.1 Accessing the Internet...................................................................................................................9
1.2.2 Making LAN to LAN Connections.................................................................................................9
Chapter 2 - Introducing the Web Configurator...................................................................................10
2.1 Accessing the DSL-2120/2120W Web Configurator.....................................................................10
2.2 Navigating the DSL-2120/2120W Web Configurator ....................................................................10
2.3 Resetting the DSL-2120/2120W...................................................................................................... 11
2.3.1 Using The Reset Button .............................................................................................................. 11
Chapter 3 - The Quick Start Wizard.....................................................................................................12
3.1 Setting a New Password ................................................................................................................12
3.2 Choosing the Time Zone................................................................................................................13
3.3 Setting the ISP Connection Type...................................................................................................14
3.3.1 Configuring Dynamic IP Address...............................................................................................14
3.3.2 Configuring Static IP Address.....................................................................................................15
3.3.3 Configuring PPPoE......................................................................................................................16
3.3.4 Configuring PPPoA......................................................................................................................17
3.3.5 Configuring Bridge Mode............................................................................................................18
3.3.6 Multiplexing..................................................................................................................................19
3.3.6.1 VC-based Multiplexing .............................................................................................................19
3.3.6.2 LLC-based Multiplexing............................................................................................................19
3.3.7 VPI and VCI...................................................................................................................................20
3.4 Finishing the Wizard.......................................................................................................................20
Chapter 4 - The Interface Setup Screens............................................................................................21
4.1 Interface Setup Overview...............................................................................................................21
4.2 The Internet Screen ........................................................................................................................21
4.2.1 ATM VC & QoS..............................................................................................................................22
4.2.2 Encapsulation ..............................................................................................................................23
4.2.2.1 Dynamic IP Address .................................................................................................................24
4.2.2.2 Static IP Address.......................................................................................................................24
4.2.2.3 PPPoE/PPPoA...........................................................................................................................25
4.2.2.4 Bridge Mode..............................................................................................................................26
4.3 The LAN Screen ..............................................................................................................................26
4.3.1 Router Local IP.............................................................................................................................27
4.3.1.1 Explaining RIP Setup................................................................................................................27
Proprietary & Confidential Page 2 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008

4.3.2 Introducing DHCP........................................................................................................................28
4.3.3 Enabled DHCP.............................................................................................................................. 28
4.3.4 Relay DHCP..................................................................................................................................29
4.4 The Wireless LAN Screen (for DSL-2120W only) .........................................................................30
4.4.1 Access Point Settings .................................................................................................................31
4.4.2 Multiple SSIDs Settings...............................................................................................................32
4.4.3 Wireless MAC Address Filter......................................................................................................32
4.4.3.1 WEP............................................................................................................................................33
4.4.3.2 WPA-PSK ...................................................................................................................................33
Chapter 5 - The Advanced Setup Screens..........................................................................................35
5.1 The Routing Screen........................................................................................................................35
5.2 The NAT Screen..............................................................................................................................36
5.2.1.1 What NAT Does .........................................................................................................................37
5.2.1.2 How NAT Works ........................................................................................................................37
5.2.1.3 NAT Application ........................................................................................................................38
5.2.1.4 NAT Mapping Types..................................................................................................................39
5.2.2 DMZ...............................................................................................................................................40
5.2.3 Virtual Server................................................................................................................................40
5.3 The QoS Screen..............................................................................................................................41
5.3.1 Rule...............................................................................................................................................42
5.3.2 Action............................................................................................................................................44
5.4 The ADSL Screen............................................................................................................................45
5.5 The Firewall Screen ........................................................................................................................45
Chapter 6 - The Access Management Screens...................................................................................46
6.1 The ACL Screen ..............................................................................................................................46
6.2 The Filter Screen.............................................................................................................................47
6.2.1 Assigning IP/MAC Filter ..............................................................................................................47
6.2.2 Assigning Application Filter........................................................................................................49
6.2.3 Assigning URL Filter....................................................................................................................50
6.3 The SNMP Screen...........................................................................................................................50
6.4 The UPnP Screen............................................................................................................................51
6.4.1.1 NAT Traversal............................................................................................................................51
6.4.1.2 Cautions with UPnP..................................................................................................................52
6.4.1.3 Configuring UpnP..................................................................................................................... 52
6.4.2 Installing UPnP in Windows........................................................................................................52
6.4.2.1 Installing UPnP in Windows Me...............................................................................................53
6.4.2.2 Installing UPnP in Windows XP...............................................................................................54
6.4.2.3 Web Configurator Easy Access...............................................................................................59
Proprietary & Confidential Page 3 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008

6.5 Dynamic DNS ..................................................................................................................................61
6.5.1 DYNDNS Wildcard........................................................................................................................61
6.5.2 Configuring Dynamic DNS..........................................................................................................61
6.6 CWMP ..............................................................................................................................................62
Chapter 7 - The Maintenance Screens ................................................................................................64
7.1 The Administration Screen ............................................................................................................64
7.2 The Time Zone Screen....................................................................................................................64
7.3 The Firmware Screen......................................................................................................................65
7.4 The SysRestart Screen...................................................................................................................66
7.5 The Diagnostics Screen .................................................................................................................66
Chapter 8 - The Status Screen.............................................................................................................67
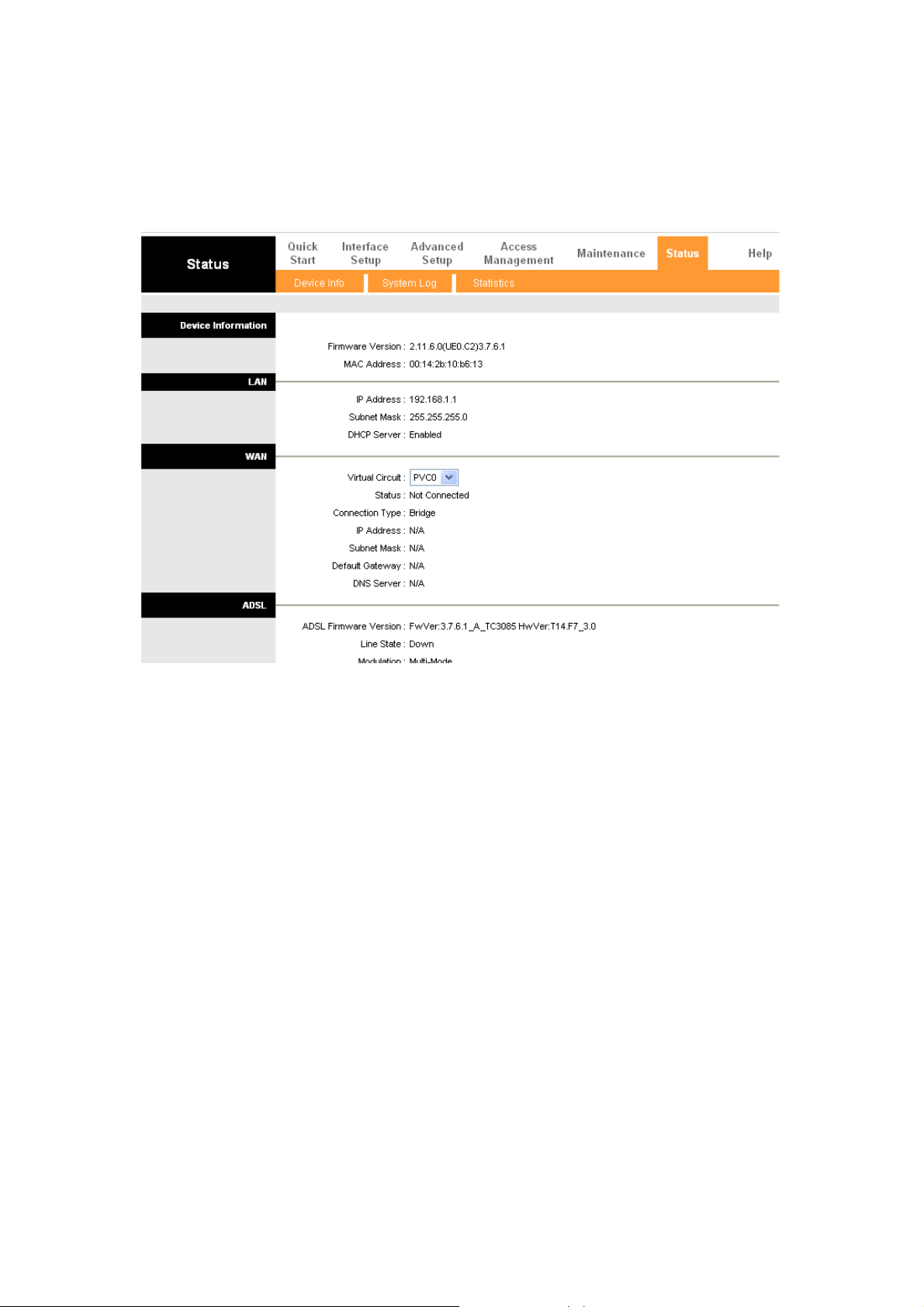
8.1 The Device Info Screen ..................................................................................................................67
8.1.1 Device Information.......................................................................................................................67
8.1.2 LAN ...............................................................................................................................................67
8.1.3 WAN ..............................................................................................................................................67
8.1.4 ADSL.............................................................................................................................................68
8.2 The System Log Screen................................................................................................................. 68
8.3 The Statistics Screen......................................................................................................................69
8.3.1 Ethernet ........................................................................................................................................69
8.3.2 ADSL.............................................................................................................................................70
Appendix A - Troub leshooting.............................................................................................................71
A.1 Using LEDs to Diagnose Problems..............................................................................................71
A.1.1 Problem: POWER LED Doesn’t Light Up...................................................................................71
A.1.2 Problem: ETHERNET LED Doesn’t Light Up.............................................................................71
A.1.3 Problem: DSL LED Doesn’t Light Up.........................................................................................71
A.2 Problem: Can’t Access Through Telnet........................................................................................72
A.3 Problem: Can’t Access Web Configurator ...................................................................................72
A.4 Problem: Forgotten Login Username and Password..................................................................73
A.5 Problem: Can’t Access LAN Interface..........................................................................................73
A.6 Problem: Can’t Access WAN Interface.........................................................................................74
A.7 Problem: Can’t Access the Internet..............................................................................................74
A.9 Problem: Can’t Access Remote Management .............................................................................75
A.9 Problem: Can’t Access Remote Node Connection......................................................................75
Appendix B – USB Driver Installation.................................................................................................76
B.1 Windows2K/XP ...............................................................................................................................76
B.2 Vista32.............................................................................................................................................79
B.3 Vista64.............................................................................................................................................82
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement.........................................................86
Proprietary & Confidential Page 4 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008

FCC Radiation Exposure Statement ....................................................................86
Proprietary & Confidential Page 5 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008

Chapter 1 - Getting to Know DSL-2120/2120W
Your DSL-2120/2120W integrates high-speed 10/100Mbps auto-negotiating LAN
interface(s), USB port and a high-speed ADSL port. The DSL-2120/2120W is perfect for
making LAN-to-LAN connections to remote networks and for high-speed Internet browsing.
The DSL-2120/2120W provides lightning-fast Internet access to multiple users by combining
Direct Subscriber Line (DSL) and Network Address Translation (NAT).
The Web-based Graphical User Interface (GUI) allows easy management and is not
dependent on any single operating system to use.
1.1 Features of the DSL-2120/2120W
¾ High Speed Internet Access
The DSL-2120/2120W ADSL 2/2+ router support downstream transmission rates of up to
24Mbps and upstream transmi ssion rates of 1Mbps.
¾
PPPoE Support (RFC2516)
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) emulates a dial-up connection. It allows
your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to use its existing network configuration with newer
broadband technologies such as ADSL. The PPPoE driver on the DSL-2120/2120W is
transparent to the computers on the LAN. Computers see only Ethernet and are not aware of
PPPoE; you don’t have to manage PPPoE clients on individual computers.
¾
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Network Address Translation (NAT) allows the conversion of an Internet protocol (IP)
address used within one network, such as a private IP address used in a LAN, to a different IP
address known within another network, such as a public IP address used on the Internet.
¾ Universal Plug and Play (UPnP)
Using the standard TCP/IP protocol, the DSL-2120/2120W and other UPnP enabled
devices can dynamically join a network, obtain an IP address and convey its capabilities to
other devices on the network.
¾
10/100M Auto-negotiation Ethernet/Fast Ethernet Interface
Auto-negotiation allows the DSL-2120/2120W to detect incoming transmissions’ speeds
and make necessary adjustments without manual intervention. It also allows data transfer
rates of either 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps, in either half-duplex or full-duplex mode, depending on
your Ethernet network.
¾
Dynamic DNS Support
With Dynamic DNS support, you can have a static hostname alias for a dynamic IP
address, allowing the host to be more easily accessed from other locations on the Internet.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 6 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008

You must register for this service with a Dynamic DNS client.
Multiple PVC (Permanent Virtual Circuit) Support
¾
Your DSL-2120/2120W supports up to 8 PVCs.
¾ ADSL Standards
♦ Compliant to ITU-T G.992.1 (G.dmt), G.992.3 (ADSL2), G.992.4, and G.992.5
(ADSL2+) Annex A, B, I, J, L, and M
♦ Supports Multi-Mode standard (ANSI T1.413, Issue 2; G.dmt (G.992.1); G.994.1
and G.996.1 (for ISDN only); G.991.1; G.lite (G992.2))
♦ Supports OAM F4/F5 loop-back, AIS and RDI OAM cells
♦ ATM Forum UNI 3.1/4.0 PVC
♦ Supports up to 8 PVCs (UBR, CBR, VBR)
♦ Multiple Protocols over AAL5 (RFC 1483)
♦ PPP over AAL5 (RFC 2364)
♦ PPP over Ethernet (RFC 2516)
¾ DHCP Support
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allows individual clients (computers) to get
TCP/IP configuration information at start-up from a DHCP server. The DSL-2120/2120W has
its built-in DHCP server cap ability enabl ed by d efault. It can assign IP addresses, an IP default
gateway and DNS servers to DHCP clients. The DSL-2120/2120 W can also act as a sub stitute
DHCP server (DHCP Relay), relaying IP address assignment from the actual DHCP server to
the clients.
¾ IP Alias
IP Alias allows you to partition a physical network into logical networks over the same
Ethernet interface. The DSL-2120/2120W can support up to 3 logical LAN interfaces through
its physical Ethernet interface with the DSL-2120/2120W acting as the gateway for each
network.
¾ IP Policy Routing (IPPR)
Normally , routing is based o nly on the destination address; the router forwards the packet
along the shortest path. IP Policy Routing (IPPR) is a method to override this routing behavior
and change the forwarding path based on policies defined by the network administrator.
¾ Protocol Support
♦ Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) link layer protocol
- PPP over PAP (RFC 1334)
- PPP over CHAP (RFC 1994)
♦ RIP I/RIP II
♦ IGMP Proxy
♦ ICMP support
♦ MIB II support (RFC 1213)
Proprietary & Confidential Page 7 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008

♦ PPPoE feature
- PPPoE idle time out
- PPPoE dial on demand
¾ Networking Compatibility
The DSL-2120/2120W is compatible with major ADSL Digital Subscriber Line Access
Multiplexer (DSLAM) providers.
¾ Multiplexing
The DSL-2120/2120W supports VC-based and LLC-based multiplexing.
¾ Encapsulation
The DSL-2120/2120W supports PPP over ATM Adaptation Layer 5 (PPPoA, RFC 2364),
RFC 1483 encapsulation over ATM, MAC encapsulated routing (ENET Encapsulation) as well
as PPP over Ethernet (RFC 2516).
¾ Network Management
♦ Embedded Web Configurator
♦ Command Line Interpreter (CLI)
♦ Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) manageable
♦ DHCP Server/Client
♦ Built-in Diagnostic Tools
♦ Syslog
♦ TFTP/FTP server, firmware upgrade and configuration backup/support supported
¾ Diagnostics Capabilities
The DSL-2120/2120W can run self-diagnostic tests. These tests check the status of
the following:
- LAN port
- ADSL circuitry
- RAM
- FLASH memory
¾ Filters
The DSL-2120/2120W's packet filtering abilities gives added network security and
management.
¾ Ease of Installation
The DSL-2120/2120W is designed for fast, simple inst allation.
1.2 Applications for the DSL-2120/2120W
Here are some uses that the DSL-2120/2120W is suitable for:
Proprietary & Confidential Page 8 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008

1.2.1 Accessing the Internet
The DSL-2120/2120W is an ideal high-speed Internet access solution. It supports the
TCP/IP protocol, which the Internet uses exclusively. The DSL-2120/2120W is compatible with
all major ADSL DSLAM providers. A DSLAM is a group of ADSL line cards with data
multiplexed into a network interface/connection, such as T1, OC3, DS3, ATM or Frame Relay.
It is similar to an ADSL modem rack.
An example Internet access application is shown below.
(DSL-2120W Only)
1.2.2 Making LAN to LAN Connections
The DSL-2120/2120W can be used to connect two physically distant networks through
the ADSL line. An example LAN-to-LAN connection is shown below.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 9 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
Chapter 2 - Introducing the Web Configurator
Your DSL-2120/2120W can be managed from anywhere with the embedded Web
configurator using a Web browser, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator.
Internet Explorer 6.0 and later or Netscape Navigator 7.0 and later versions with JavaScript
enabled should be used. A screen resolution of 1024 by 768 pixels is recommended.
2.1 Accessing the DSL-2120/2120W Web Configurator
Step 1. Ensure that the DSL-2120/2120W is properly connected.
Step 2. Prepare your computer/computer network to connect to the DSL-2120/2120W.
Step 3. Launch your Web browser.
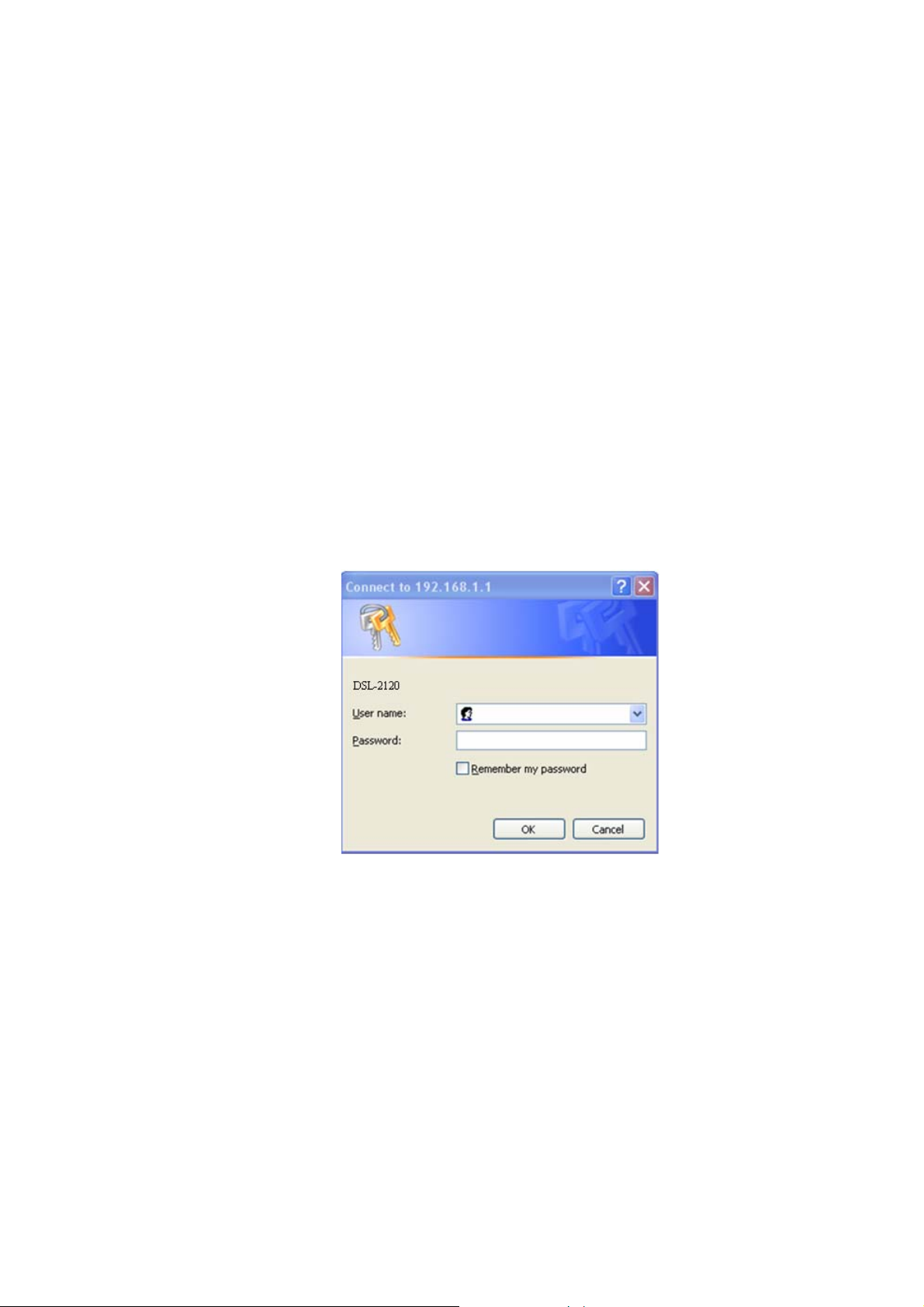
Step 4. Enter "192.168.1.1" as the URL.
Step 5. The Connect to 192.168.1.1 window will open. Enter your User name (“admin” is the
default) and Password (“1234” is the default), and then click on OK.
Step 6. You should now see the Web configurator.
2.2 Navigating the DSL-2120/2120W Web Configurator
Steps to navigate the Web Configurator from the Site Map are summarized below.
¾ Click on Quick Start to begin a wizard that helps to configure your DSL-2120/2120W.
¾ Click on Interface Setup to configure Internet and LAN DSL-2120/2120W functions.
¾ Click on Advanced Setup to configure advanced DSL-2120/2120W features.
¾ Click on Access Management to manage Internet access options.
¾ Click on Maintenance to set a new password, to set the time zone, to upgrade or reload
Proprietary & Confidential Page 10 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
firmware and to run diagnostic tests on the DSL-2120/2120W.
¾ Click on Status to see DSL-2120/2120W device information, system logs and
performance statistics.
¾ Click on Help to see available help topics.
2.3 Resetting the DSL-2120/2120W
If you should forget your password, or if you can’t gain access to the DSL-2120/2120W,
you will have to reload the factory-default configuration file or use the RESET button on the
back of the DSL-2120/2120W device to regain access. Uploading the default configuration file
replaces the current configuration file. You will lose all your previously-saved configurations.
The password will also be reset to “1234”.
2.3.1 Using The Reset Button
Step 1. Make sure the SYS LED is on and not blinking.
Step 2. Press and hold the RESET button for five seconds, and then release it. When the SYS
LED begins to blink, the default configurations have been restored and the
DSL-2120/2120W will then restart.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 11 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
Chapter 3 - The Quick Start Wizard
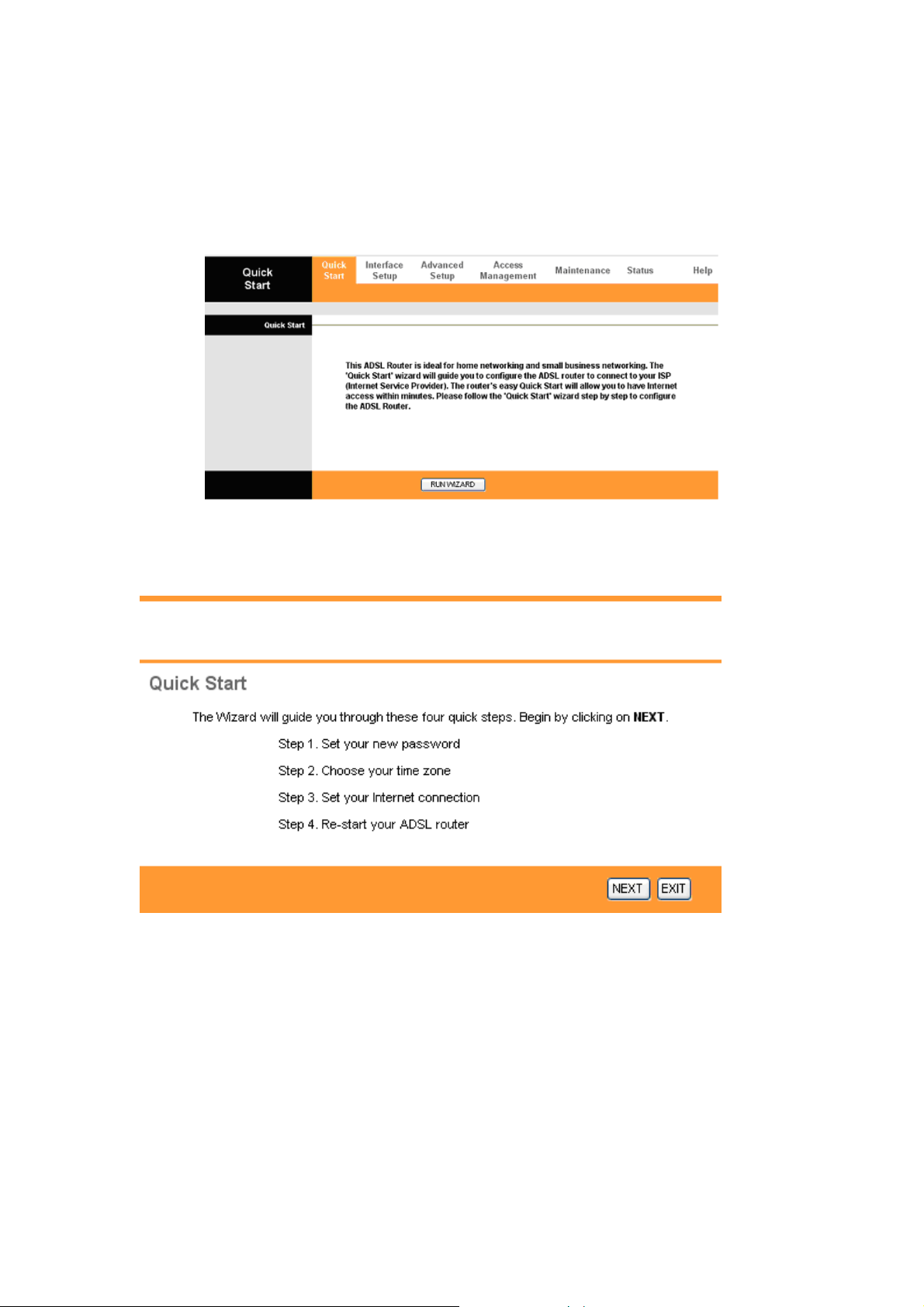
Use the Quick Start wizard to configure your system settings. Your ISP may have
configured some of the fields in the wizard for you.
Click on the RUN WIZARD button to start the Quick Start wizard. The Quick Start wizard
will open a new browser window with the following screen.
Click on NEXT to continue, or on EXIT to exit the wizard without saving.
3.1 Setting a New Password
This screen helps you set a new password, replacing the default password.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 12 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
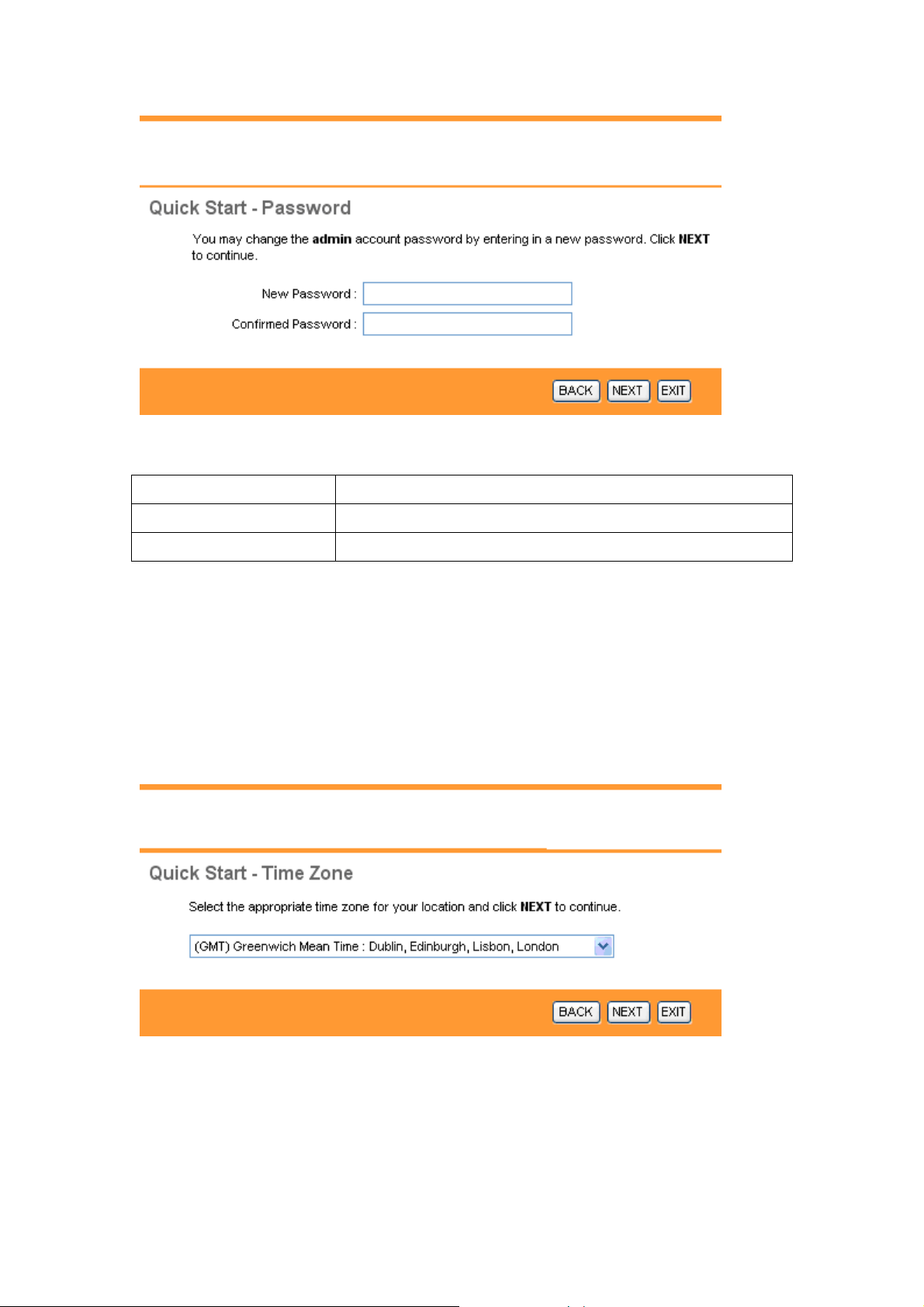
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
New Password Enter the password you wish to use here
Confirmed Password Enter the password again to confirm
Click on BACK to return to the previous screen, on NEXT to continue, or on EXIT to exit
the wizard without saving.
3.2 Choosing the Time Zone
This screen helps you set the time zone for your DSL-2120/2120W.
Select the appropriate time zone for your location from the dropdown list. Click on BACK
to return to the previous screen, on NEXT to continue, or on EXIT to exit the wizard without
saving.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 13 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
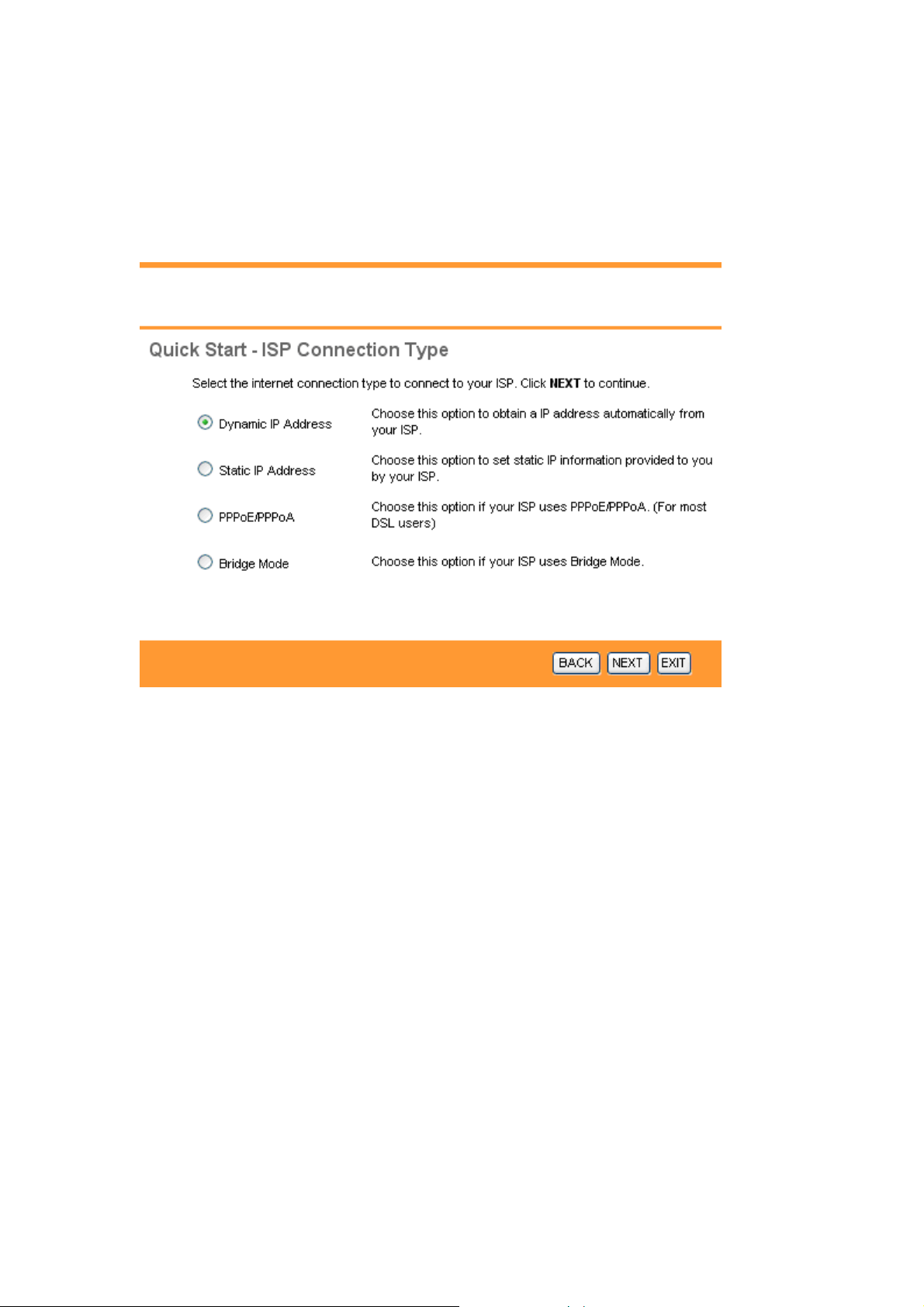
3.3 Setting the ISP Connection Type
This screen helps you select, then configure, your ISP connection type.
Select the Internet connection type you use to connect to your ISP. Click on BACK to
return to the previous screen, on NEXT to continue, or on EXIT to exit the wizard. The
following screen will vary depending on which connection type you chose. Each screen is
explained below.
3.3.1 Configuring Dynamic IP Address
A dynamic IP address connection requests a new IP address from your ISP each time
you connect to it.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 14 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
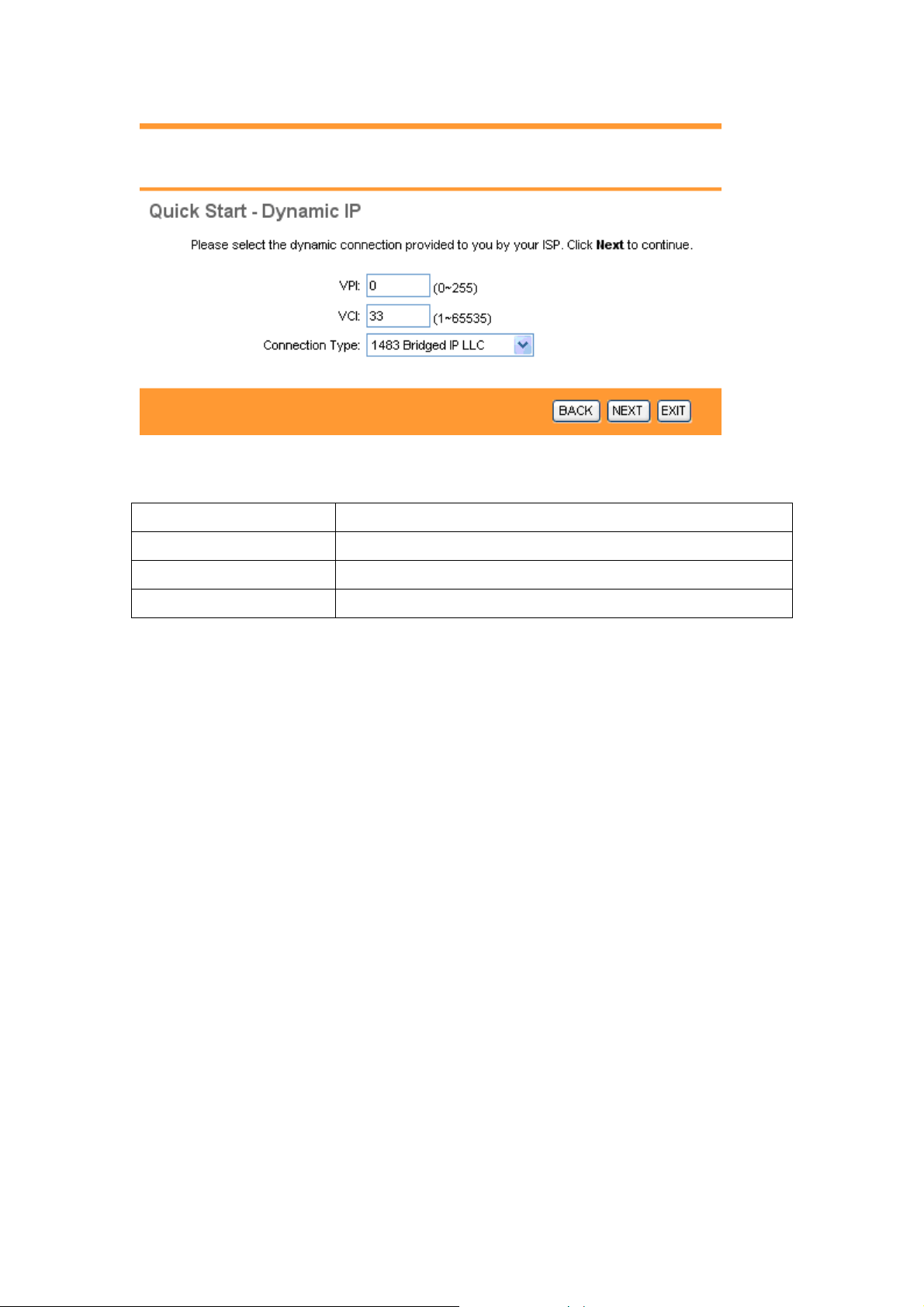
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VPI Enter the VPI here. VPI can range from 0 to 255.
VCI Enter the VCI here. VCI can range from 1 to 65535.
Connection Type Select your connection type from the dropdown list.
Your ISP should provide the above information. Click on BACK to return to the previous
screen, on NEXT to continue, or on EXIT to exit the wizard without saving.
3.3.2 Configuring Static IP Address
A static IP address connection uses the same IP each time you connect to your ISP.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 15 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
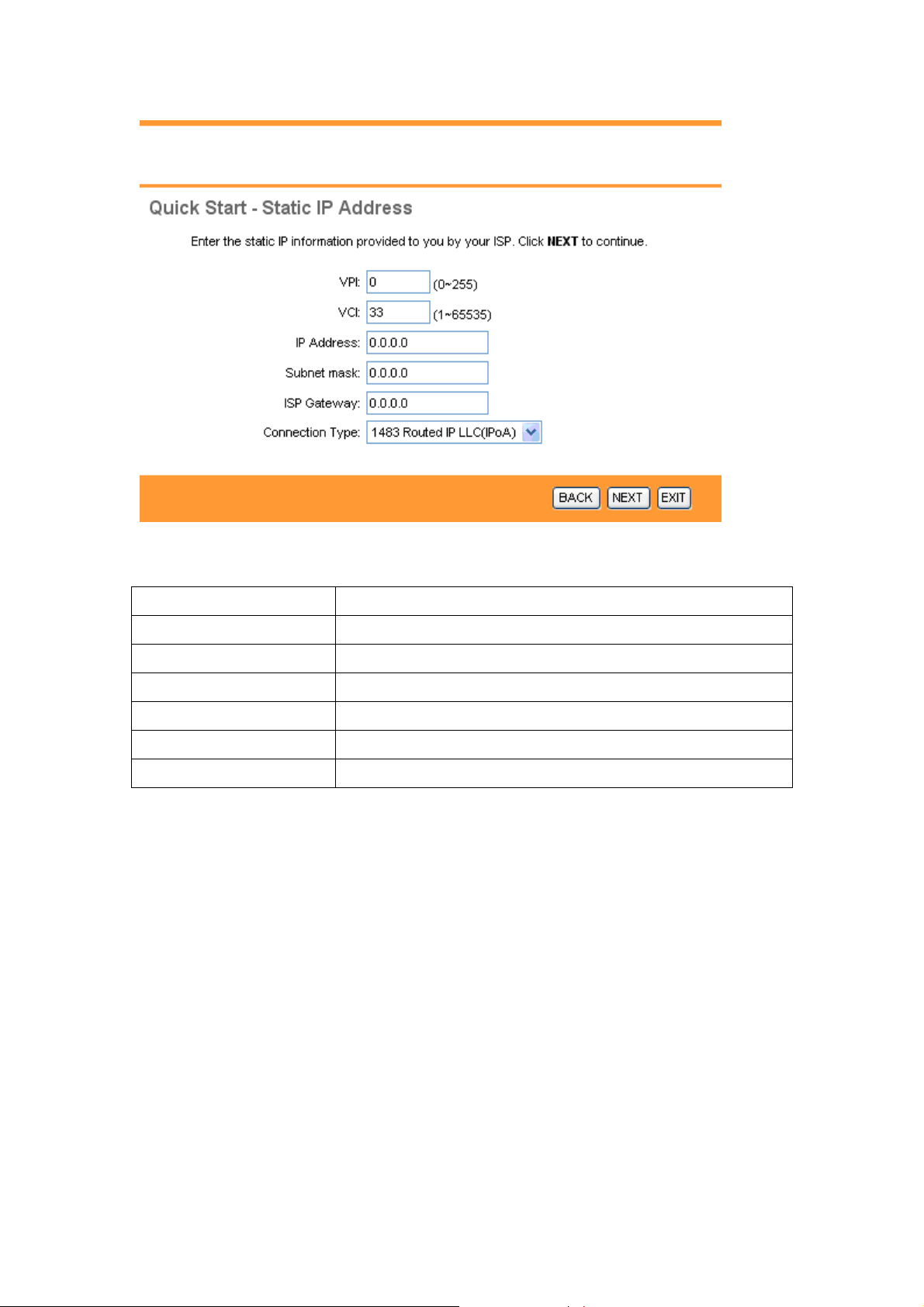
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VPI Enter the VPI here. VPI can range from 0 to 255.
VCI Enter the VCI here. VCI can range from 1 to 65535.
IP Address Enter the IP address here.
Subnet Mask Enter the Subnet Mask here.
ISP Gateway Enter the ISP Gateway here.
Connection Type Select your connection type from the dropdown list.
Your ISP should provide this information. Click on BACK to return t o the p revious screen,
on NEXT to continue, or on EXIT to exit the wizard without saving.
3.3.3 Configuring PPPoE
PPPoE provides access control and billing functionality in a manner similar to dial-up
services using PPP. The DSL-2120/2120W bridges a PPP session over Ethernet (PPP over
Ethernet, RFC 2516) from your computer to an ATM Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC) that
connects to the ADSL Access Concentrator, where the PPP session terminates. A single PVC
can support any number of PPP sessions from your LAN. For more information on PPPoE, see
the appendix.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 16 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
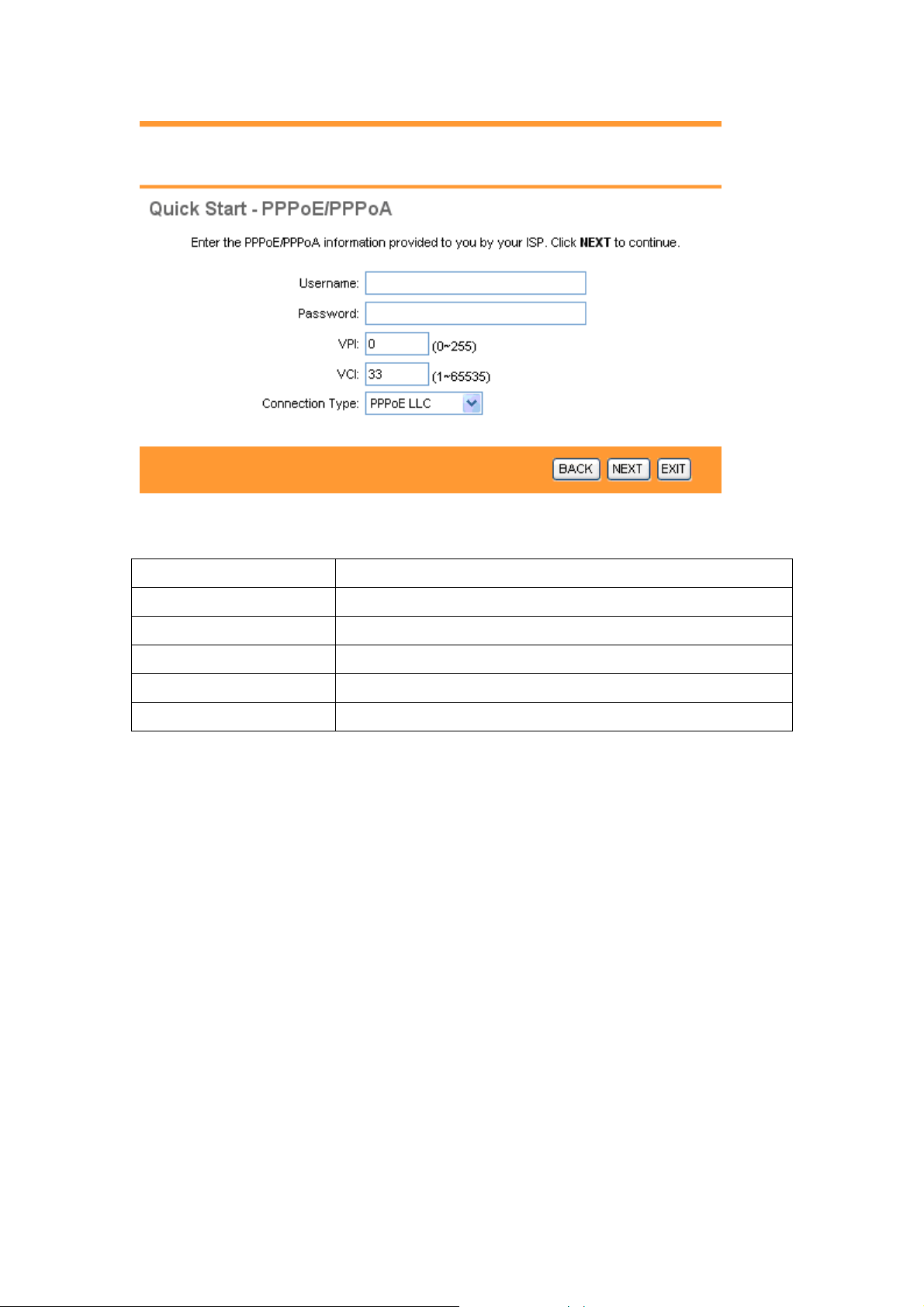
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Username Enter your username here.
Password Enter your password here.
VPI Enter the VPI here. VPI can range from 0 to 255.
VCI Enter the VCI here. VCI can range from 1 to 65535.
Connection Type Select your connection type from the dropdown list.
Your ISP should provide the above information. Note that you must enter the user name
exactly as your ISP assigned it. If the assigned name is in the form of user@domain where
domain identifies a service name, enter it exactly as given. Click on BACK to return to the
previous screen, on NEXT to continue, or on EXIT to exit the wizard without saving.
3.3.4 Configuring PPPoA
Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM Adaptation Layer 5 (AAL5) (PPPoA) provides access
control and billing functionality in a manner similar to dial-up services using PPP. The
DSL-2100 encapsulates the PPP session based on RFC1483 and sends it through an ATM
PVC to the ISP’s DSLAM. Please refer to RFC 2364 for more information on PPPoA. Refer to
RFC 1661 for more information on PPP.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 17 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
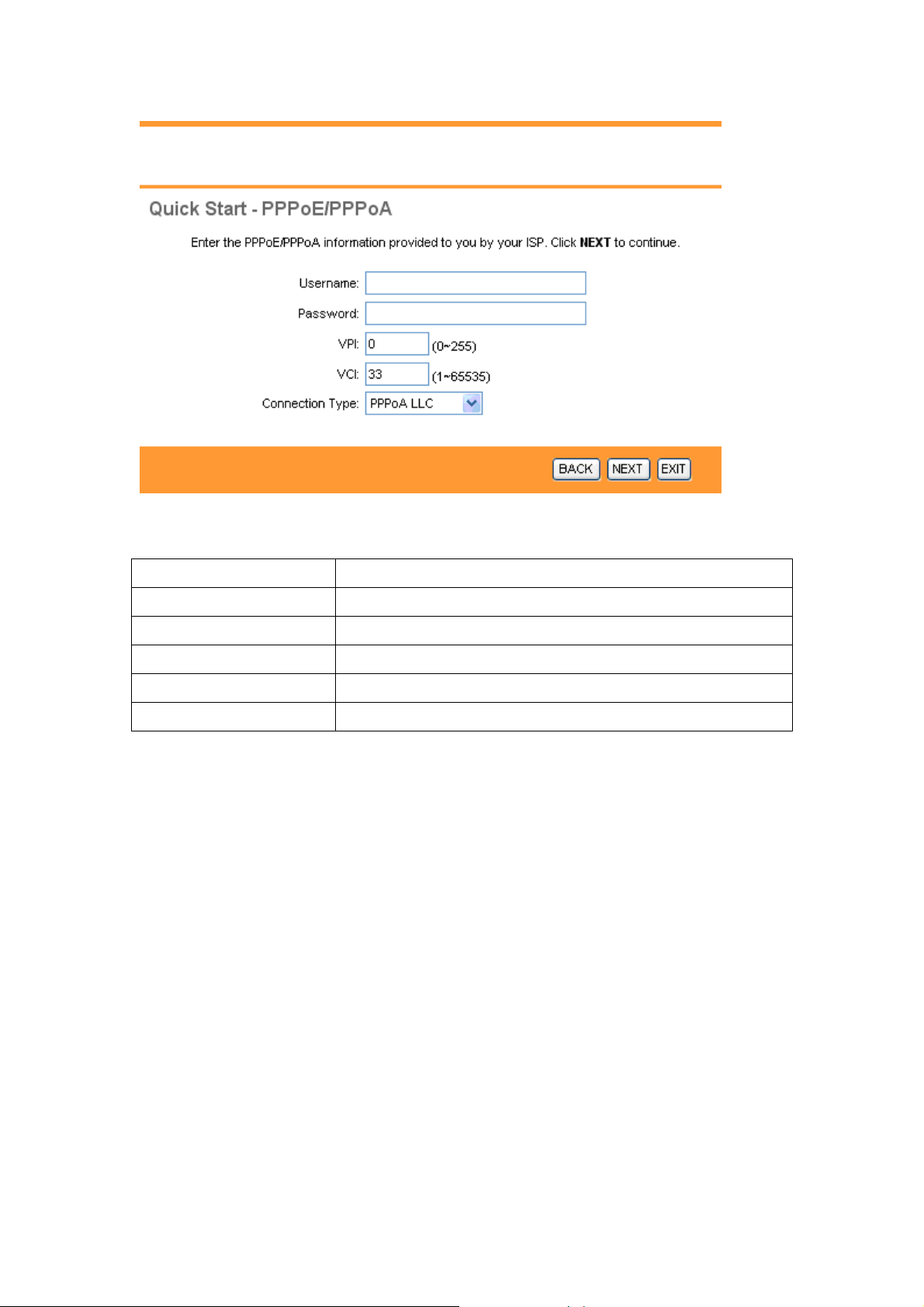
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Username Enter your username here.
Password Enter your password here.
VPI Enter the VPI here. VPI can range from 0 to 255.
VCI Enter the VCI here. VCI can range from 1 to 65535.
Connection Type Select your connection type from the dropdown list.
Your ISP should provide the above information. Note that you must enter the user name
exactly as your ISP assigned it. If the assigned name is in the form of user@domain where
domain identifies a service name, enter it exactly as given. Click on BACK to return to the
previous screen, on NEXT to continue, or on EXIT to exit the wizard without saving.
3.3.5 Configuring Bridge Mode
RFC 1483 explains two methods for Multiprotocol Encapsulation over AAL5. The first
method allows multiplexing of multiple protocols over just one ATM virtual circuit (LLC-based
multiplexing). The second method assumes that each individual protocol is carried over a
separate ATM virtual circuit (VC-based multiplexing). Please refer to RFC 1483 for more
information.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 18 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
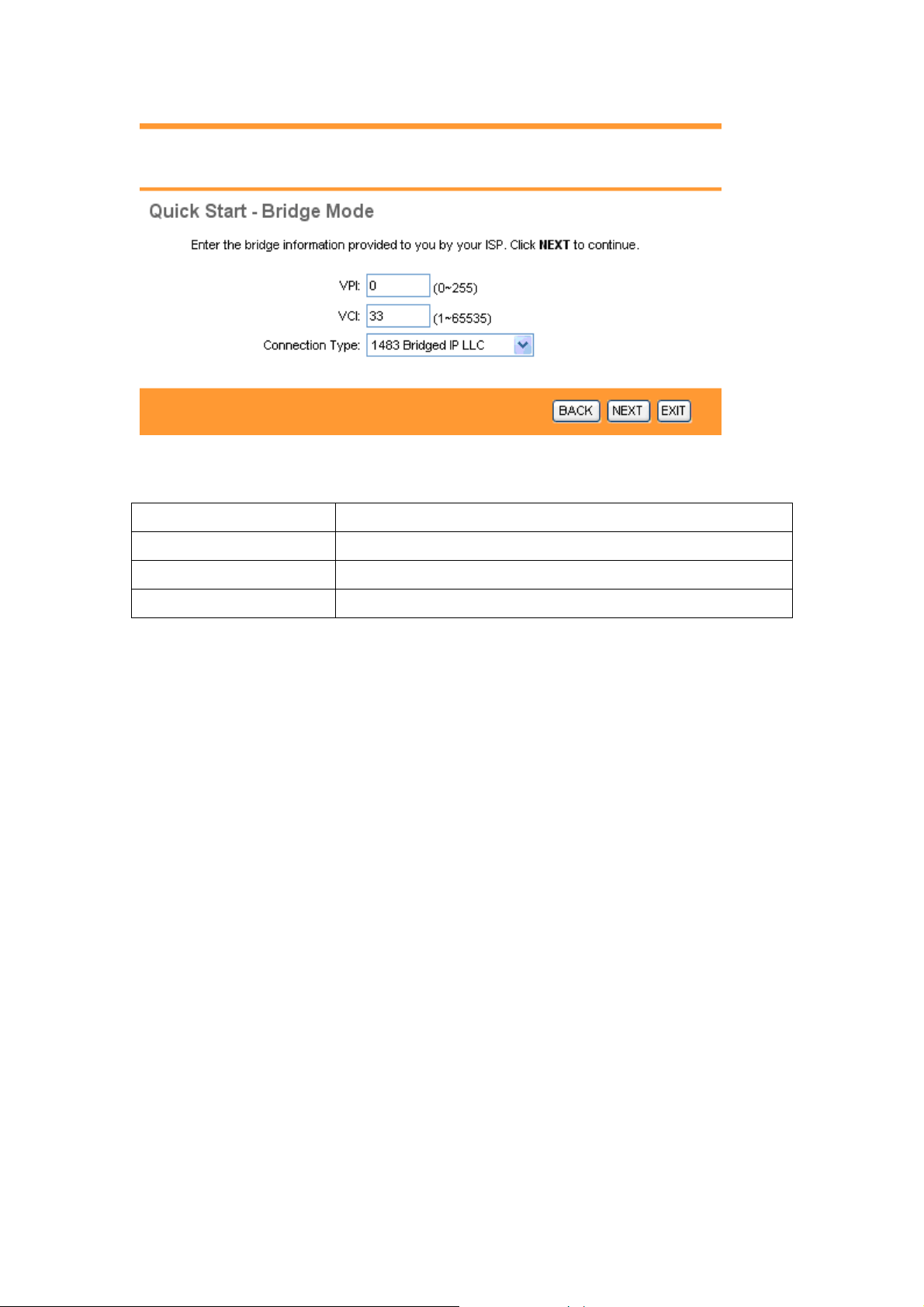
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VPI Enter the VPI here. VPI can range from 0 to 255.
VCI Enter the VCI here. VCI can range from 32 to 65535.
Connection Type Select your connection type from the dropdown list.
Your ISP should provide the above information. Click on BACK to return to the previous
screen, on NEXT to continue, or on EXIT to exit the wizard without saving.
3.3.6 Multiplexing
Two conventions identify what protocols a virtual circuit (VC) is carrying. Be sure to use
the multiplexing method your ISP requires.
3.3.6.1 VC-based Multiplexing
In VC-based multiplexing, by prior mutual agreement, each protocol is assigned to a
specific virtual circuit. For example, VC1 carries IP, etc. VC-based multiplexing may be
dominant in environments where dynamic creation of large numbers of ATM VCs is fast and
economical.
3.3.6.2 LLC-based Multiplexing
In LLC-based multiplexing, one VC carries multiple protocols with protocol-identifying
information contained in each packet header. While this method requires extra bandwidth and
Proprietary & Confidential Page 19 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
processing overhead, this method may be advantageous if it is not pra ctical to have a separate
VC for each carried protocol; for example, if charging heavily depends on the number of
simultaneous VCs.
3.3.7 VPI and VCI
Be sure to use the Virtual Path Identifier (VPI) and Virtual Channel Identifier (VCI)
numbers assigned to you. The valid range for the VPI is 0 to 255. The valid range for the VCI is
32 to 65535. 0 to 31 is reserved for local management of ATM traffic.
3.4 Finishing the Wizard
The Quick Start wizard now has all the information it needs. Click on BACK to make
changes or correct mistakes. Click on NEXT to save the current settings. Click on EXIT to exit
the wizard without saving.
Your changes have been saved. Click on CLOSE. The Quick Start wizard window will
close.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 20 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008

Chapter 4 - The Interface Setup Screens
The Interface Setup screens help you connect your DSL-2120/2120W to the Internet and
to your local network.
4.1 Interface Setup Overview
The physical connections determine whether the DSL-2120/2120W ports are local area
network (LAN) ports or wide area network (WAN) ports. There are two kinds of IP networks.
The local, private kind is the LAN network; the global, public kind is the WAN network. The
following illustration shows the relationship between the DSL-2120/2120W and the two
different networks.
A LAN is a sh ared commun ication system to which m any com puter s are attached. A LAN
is generally limited to the immediate area, usually the same building or floor of a building.
A WAN is an outside connection to another net work or to the Internet.
4.2 The Internet Screen
The Internet screen allows you to set up how your DSL-2120/2120W connects to the
Internet. If you already ran the Quick Start wizard, the information you provided to the wizard
should be entered into the fields already. When you are done making changes, click on the
SAVE button to save your changes.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 21 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008

4.2.1 ATM VC & QoS
Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) is a protocol that arranges data into small,
uniform-sized cells with VCI data, as opposed to varia ble-sized dat a p acket s. ATM settings are
used to connect to your ISP. Your ISP provides your VPI and VCI setting information. You can
configure up to 8 virtual circuits (VC), each using different encapsulations, if you apply for 8
different VCs from your ISP. You must activate each VC for it to take effect. For permanent
virtual circuit (PVC) management, you can use ATM Quality of Service (QoS) to set up each
PVC traffic line's priority.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Virtual Circuit Select the PVC you wish to modify.
Status Each PCV can be toggled Activated or Deactivate.
VPI Enter your VPI number here.
VCI Enter your VCI number here.
ATM QoS Select the QoS type for the PVC in question from the dropdown list.
PCR Enter the PCR here. For all QoS types.
SCR Enter the SCR here. Only for rtVBR and nrtVBR.
MBS Enter the MBS here. Only for rtVBR and nrtVBR.
The PVCs Summary button opens a new window that displays the current PVC settings.
Peak Cell Rate (PCR) is the maximum rate at which the sender can send cells. This
parameter may be lower (but not higher) than the maximum line speed. 1 ATM cell is 53 bytes
(424 bits), so a maximum speed of 832 Kbps gives a maximum PCR of 1962 cells/sec. This
rate is not guaranteed because it is dependent on the line speed.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 22 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
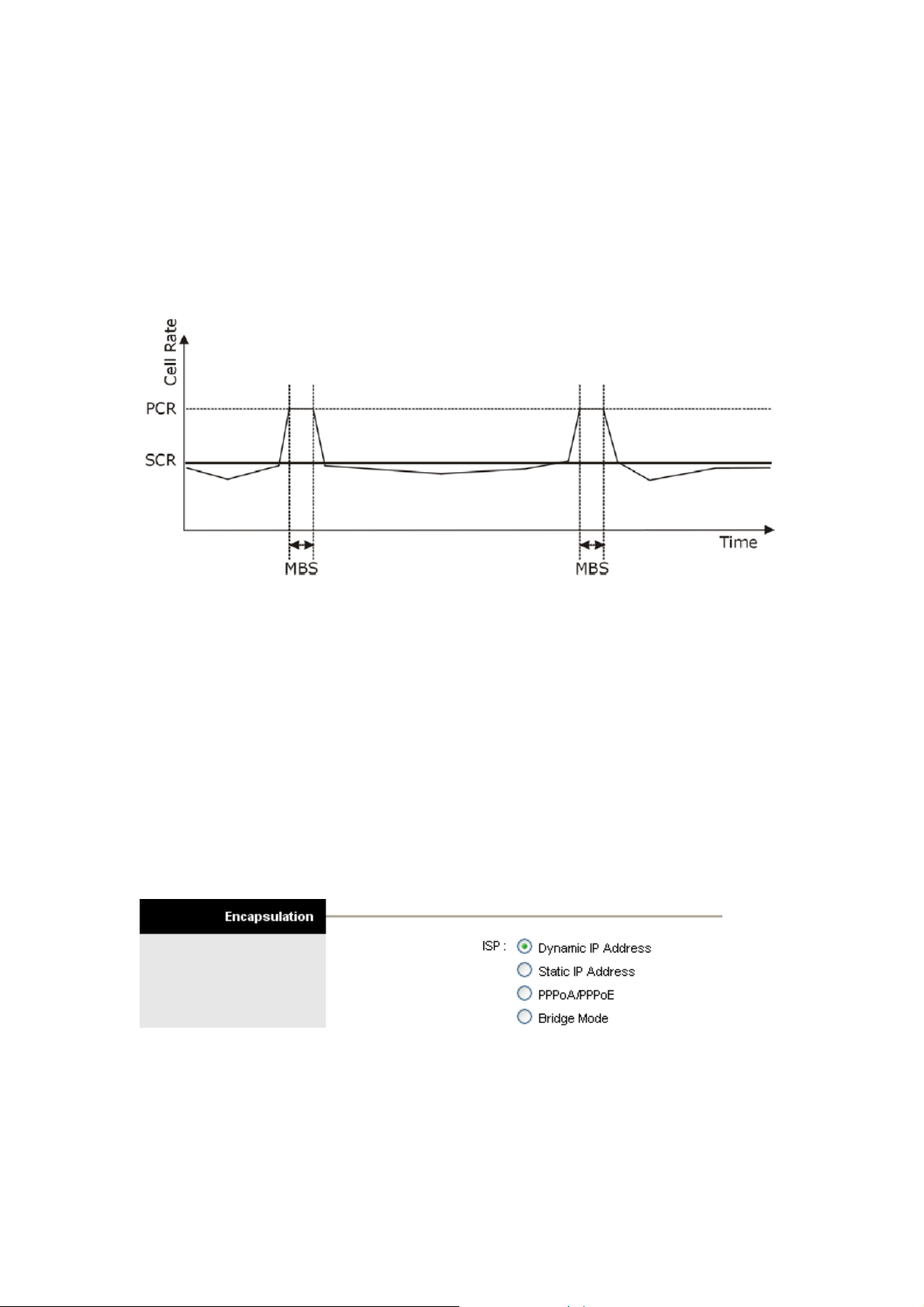
Sustained Cell Rate (SCR) is the mean cell rate of a bursty, on-off traffic source that can
be sent at the peak rate, and a parameter for burst-type traffic. SCR may not be greater than
the PCR; the system default is 0 cells/sec.
Maximum Burst Size (MBS) is the maximum number of cells that can be sent at the PCR.
After MBS is reached, cell rates fall below SCR until cell rate averages to the SCR again. At
this time, more cells (up to the MBS) can be sent at the PCR again.
The following figure illustrates the relationship between PCR, SCR and MBS.
CBR is for connections that support constant rates of data transfer. The only parameter
you need to worry about in CBR is PCR.
UBR is for connections that have variable traffic. The only parameter you need to worry
about in UBR is PCR.
rtVBR is for connections that, while having variable traffic, require precise timing between
traffic source and destination. PCR, SCR and MBS must all be set for rtVBR.
nrtVBR is for connections that have variable traffic, do not require precise timing, but still
require a set bandwidth availability. PCR, SCR and MBS must all be set for nrtVBR.
4.2.2 Encapsulation
Select the encapsulation protocol your ISP uses. The following section will vary
depending on which encapsulation protocol you select.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 23 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
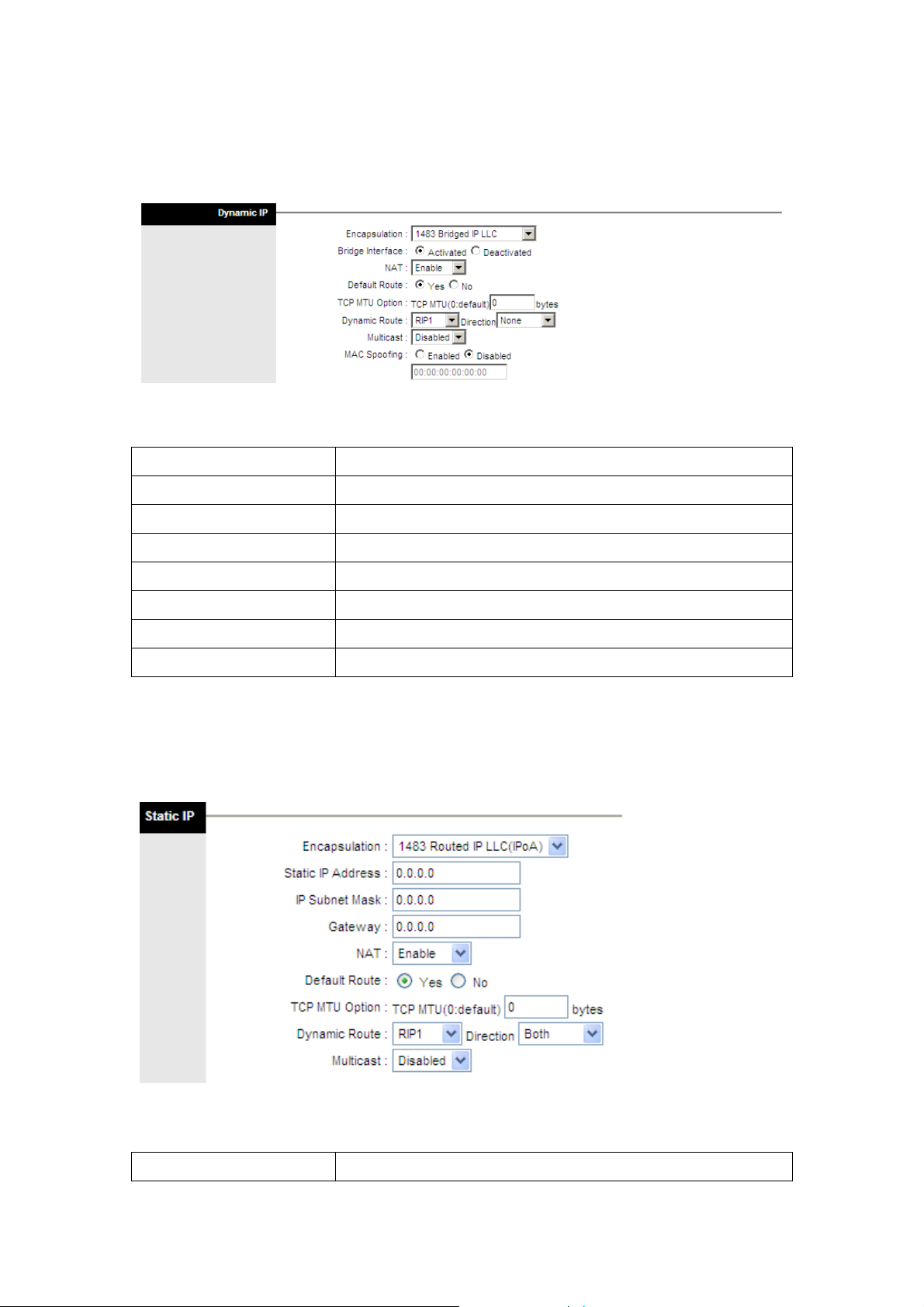
4.2.2.1 Dynamic IP Address
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select your encapsulation type from the dropdown list. Encapsulation
Bridge interface Select whether Bridge interface is activated or deactivated.
NAT Select whether NAT is Enabled or Disabled.
Default Route Select whether this PVC will be the default route for Internet data.
TCP MTU Option Enter you TCP MTU bytes here. (Default is 0 bytes)
Dynamic Route Select the RIP type and direction from the dropdown lists.
Multicast Select the multicast protocol you wish to use from the dropdown list.
4.2.2.2 Static IP Address
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Proprietary & Confidential Page 24 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
Encapsulation Select your encapsulation type from the dropdown list.
Static IP Address Enter the static IP Address here.
IP Subnet Mask Enter the IP Subnet Mask here.
Gateway Enter the Gateway address here.
NAT Select whether NAT is Enabled or Disabled.
Default Route Select whether this PVC will be the default route for Internet data.
TCP MTU Option Enter you TCP MTU bytes here. (Default is 0 bytes)
Dynamic Route Select the RIP type and direction from the dropdown lists.
Multicast Select the multicast protocol you wish to use from the dropdown list.
Your ISP should provide the above information.
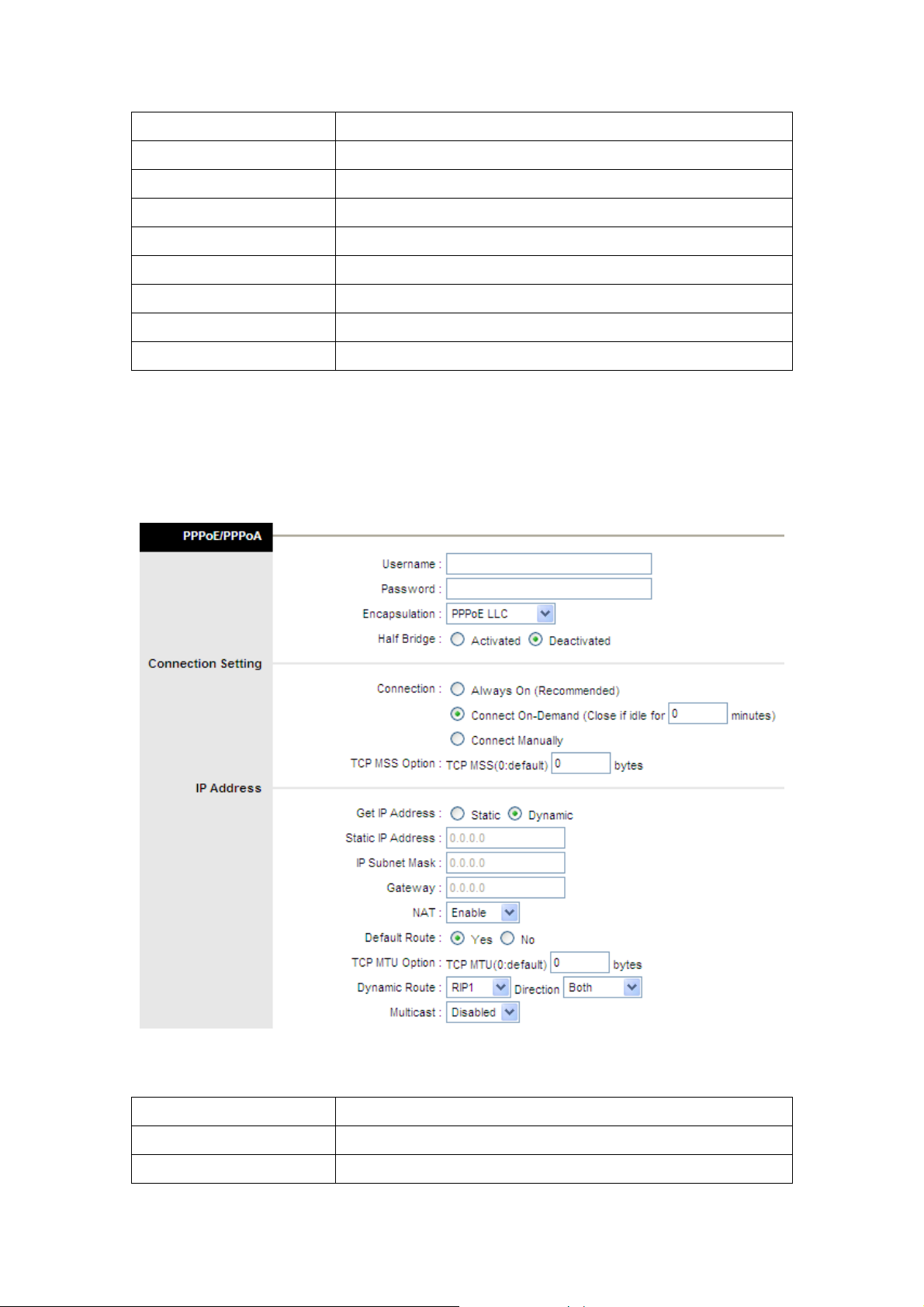
4.2.2.3 PPPoE/PPPoA
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Username Enter your username here.
Password Enter your password here.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 25 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008

Encapsulation Select your encapsulation type from the dropdown list.
Bridge interface Select whether Bridge interface is activated or deactivated.
Connection Select whether your connection is always on or if it connects on
demand. If on demand, specify how many minutes the connection may
be idle before it disconnects.
TCP MSS Option Enter the TCP MSS you wish to use here.
Get IP Address Choose whether the TC3162 EVM obtains the IP address statically or
dynamically.
Static IP Address Enter the static IP address here. Only if you chose Static above.
IP Subnet Mask Enter the IP subnet mask here. Only if you chose Static above.
Gateway Enter the gateway here. Only if you chose Static above.
NAT Select whether NAT is Enabled or Disabled.
Default Route Select whether this PVC will be the default route for Internet data.
TCP MTU Option Enter you TCP MTU bytes here. (Default is 0 bytes)
Dynamic Route Select the RIP type and direction from the dropdown lists.
Multicast Select the multicast protocol you wish to use from the dropdown list.
Your ISP should provide the above information. Note that you must enter the user name
exactly as your ISP assigned it. If the assigned name is in the form of user@domain where
domain identifies a service name, enter it exactly as given.
4.2.2.4 Bridge Mode
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Encapsulation Select your encapsulation type from the dropdown list.
4.3 The LAN Screen
The LAN screen allows you to set up how your DSL-2120/2120W connects to your LAN.
When you are done making changes, click on SAVE to save your changes or CANCEL to reset
the fields to their original states.
Proprietary & Confidential Page 26 of 86
Revision: V1.0 Apr. 23, 2008
 Loading...
Loading...