Page 1

Page 2

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1
Introduction..............................................................................................1-1
Package Check List..................................................................................1-1
Feature Summary......................................................................................1-2
Special Features........................................................................................1-3
Major Components...................................................................................1-5
Headers and Connectors...........................................................................1-7
Jumpers.....................................................................................................1-11
Rear Panel................................................................................................1-12
CHAPTER 2
Installing the CPU...................................................................................2-1
Installing the CPU cooling FAN...............................................................2-1
Installing Memory Module.......................................................................2-1
Connecting IDE, Floppy and SATA cable..................................................2-3
Installing Motherboard in a case...............................................................2-3
Connecting IDE, Floppy & SATA Device..................................................2-4
Installing Expansion cards........................................................................2-4
Connecting the Power supply cable...........................................................2-5
Powering up..............................................................................................2-5
CHAPTER 3
Entering the BIOS Setup Menu.................................................................3-1
Updating and Recovering the BIOS...........................................................3-1
Using AWARD Flash to update your BIOS..........................................3-1
Using ECS EZ Flash to update your BIOS.........
.................................3-2
Using ECS Top-Hat Flash to recover your BIOS.
.................................3-3
The Main Menu.......................................................................................3-3
Standard CMOS Features............................................................3-3
Advanced BIOS Features............................................................3-5
Advanced Chipset Features.........................................................3-7
Integrated Peripherals.................................................................3-10
Power Management Setup.................................................................3-13
PNP/PCI Configurations..................................................................3-16
PC Health Status............................................................................3-17
Page 3

Frequency/Voltage Control................................................................3-18
Load Performance Defaults...............................................................3-19
Load Optimized Defaults..................................................................3-19
Set Supervisor/User Password...........................................................3-19
Save & Exit Setup...........................................................................3-20
Exit Without Saving.........................................................................3-20
CHAPTER 4
Software CD Information.........................................................................4-1
Running the Software CD.........................................................................4-1
Setup Tab..................................................................................................4-1
Application Tab........................................................................................4-2
Read Me Tab............................................................................................4-2
Software Utilities Introduction.................................................................4-2
CHAPTER 5
VIA RAID Configurations........................................................................5-1
Install the Serial ATA (SATA) hard disks.............................................5-1
Entering VIA Tech RAID BIOS Utility.................................................5-2
Create Array..................................................................................5-3
RAID 0 for performance...................................................................5-3
RAID 1 for data protection...............................................................5-4
Delete Array...................................................................................5-5
Select Boot Array............................................................................5-5
Serial Number View.........................................................................5-6
Duplicate Critical RAID 1 Array.......................................................5-6
Rebuild Broken RAID 1 Array...........................................................5-7
Installing RAID Software & Drivers........................................................5-8
Install Driver in Windows OS..........................................................5-8
Using VIA RAID Tool...........................................................................5-10
Introduction for SiS180 RAID Function................................................5-13
Serial/UltraATA RAID Interfaces......................................................5-13
Features.................................................................................................5-13
Support Operating Systems....................................................................5-13
Page 4

What is RAID.......................................................................................5-14
Installing Software Drivers....................................................................5-14
New Windows 2000/XP Installation.................................................5-14
Existing Windows 2000/XP/98/ME Installation..................................5-15
Confirming Windows 2000/XP Driver Installation..............................5-15
Confirming Windows 98/ME Driver Installation.................................5-15
BIOS Utility Operation.........................................................................5-15
Starting BIOS Utility......................................................................5-15
Creating RAID..............................................................................5-16
Creating a RAID 0 (Stripe) Array for Performance.............................5-16
Creating a JBOD Array..................................................................5-20
Creating a RAID 0+1 (Stripe-Mirror) Array......................................5-21
Multi-Language Translation
Legal Notices
Page 5
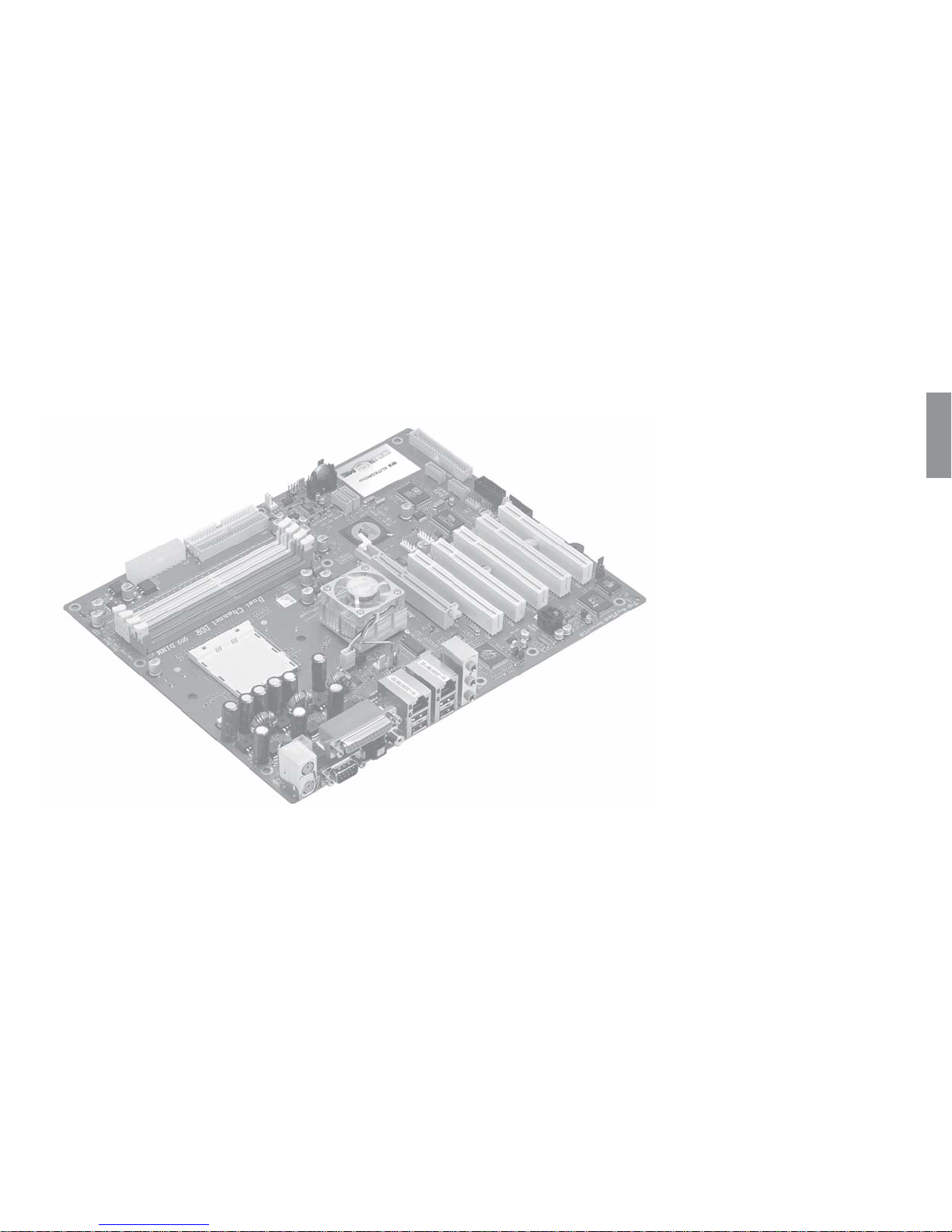
Chapter 1
This chapter entails the newest technology and rich
features on the Photon Extreme motherboard.
Page 6

1.1 Introduction....................................................1-1
1.2 Package Check List...........................................1-1
1.3 Feature Summary...........................................1-2
1.4 Special Features.............................................1-3
1.5 Major Components........................................1-5
1.6 Headers and Connectors................................1-7
1.7 Jumpers........................................................1-11
1.8 Rear Panel...................................................1-12
Reference
Page 7

1-1
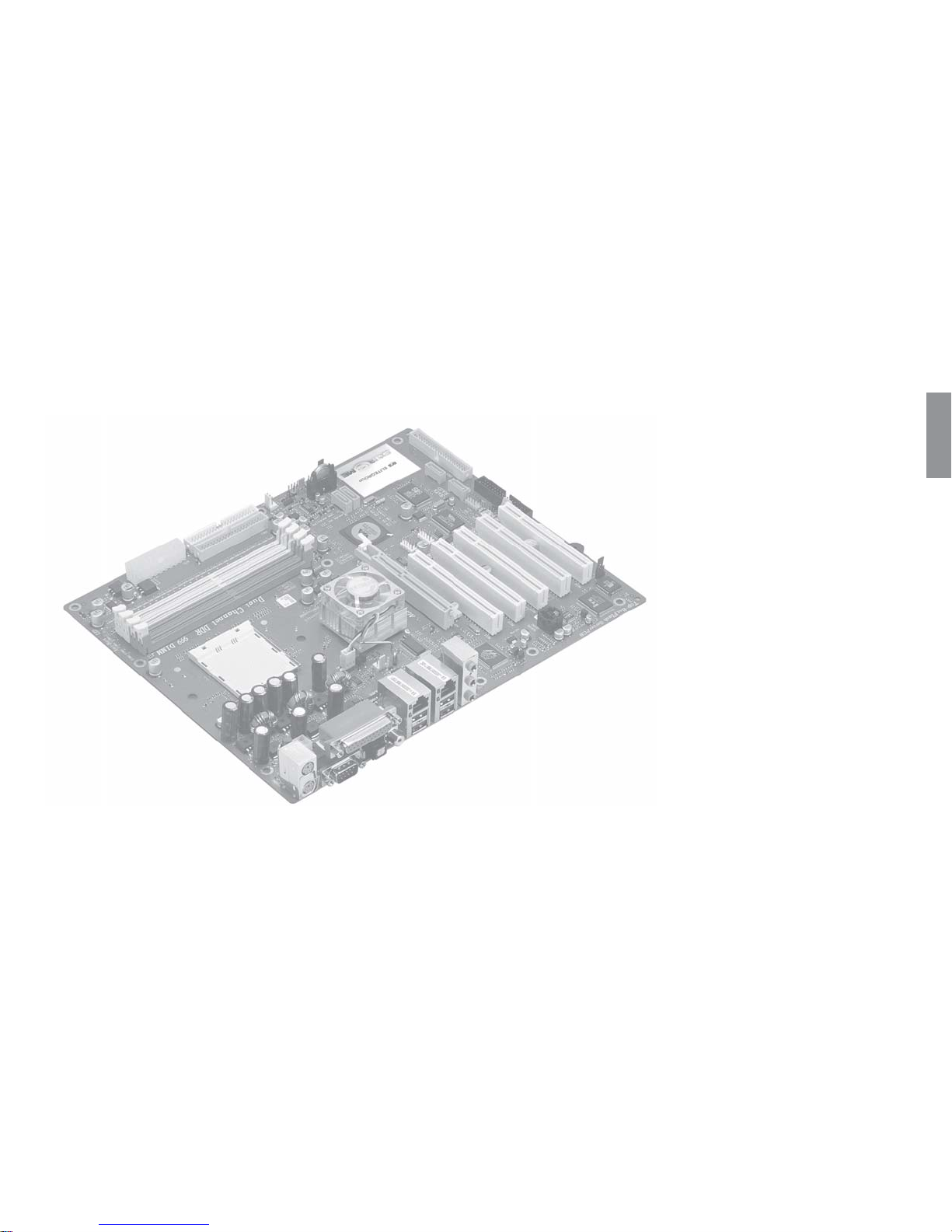
1.1 Introduction
Thank you for choosing the ECS KV2 Extreme motherboard.
The KV2 Extreme is the next generation of high performance motherboard
designed to support the AMD K8 processors.
This motherboard has an ATX form factor that uses a 6-layer printed circuit
board and measures 305 mm x 244 mm.
The KV2 Extreme motherboard is based on the VIA K8T800 PRO
Northbridge and VT8237 chipset to set a new benchmark for the best
desktop platform solution. Supporting up to 4 GB of system memory with
PC3200/2700/2100/1600 DDR DIMMs, high resolution graphics via an
AGP8X slot, Dual LAN, USB 2.0, 6-channel audio, Digital S/PDIF out
and SATA support and RAID function.
1.2 Package Check List
Motherboard User’s Guide Installation CD
Two Streamlined IDE &
FDD Ribbon Cable
USB+1394 PCI
Bracket & housing
Top Hat Flash I/O ShieldSATA Power Cable
Two SATA Cable Cross Over Cable
All pictures are for reference only.
Page 8
1-2
1.3 Feature Summary
CPU
Chipset
• VIA K8T800 PRO & 8237
• North Bridge: VIA K8T800 PRO
• South Bridge: VIA 8237
Memory
Expansion
Slots
• 1 x AGP 8X/4X slot
• 5 x PCI slots
Storage
• Supported by VIA8237
- 4 x Ultra DMA133/100/66 devices
- 2 x SATA devices
- RAID 0 and RAID 1 configuration
• Supported by SiS180
- 2 x Ultra DMA133/100/66 devices
- 2 x SATA devices
- RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1 configuration
IEEE 1394a
• VIA VT6307 IEEE1394a controller
• Supports 2 x IEEE1394a connectors
Audio
• Realtek ALC655 6-channel audio CODEC
• Compliant with AC’97 2.3 specification
Dual LAN
• Marvel 88E8001 Gigabit LAN Controller
• VIA VT6103L 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet PHY
Rear panel
I/O
• 1 x PS/2 keyboard
• 1 x PS/2 mouse connector
• 4 x USB ports
• 2 x RJ45 LAN connectors
• 1 x Parallel port (LPT1)
• 1 x Serial port (COM1)
• 2 x Digital SPDIF (Optical & Coaxial) out
• 1 x Audio port (Line-in, Line-out, Mic-in)
• Socket 939 for AMD Athlon 64 FX processor
• High-performance Hyper Transport CPU Interface
• Transfer rate of 2000/1600/1200/800/400 MT/s
• Dual-channel DDR memory architecture
• 4 x 184-pin DDR DIMM socket support up to 4 GB
• Support DDR400/333/266/200 unbuffered DDR
SDRAM
BIOS features
• Award BIOS with 4Mb Flash ROM
• Supports Plug and Play 1.0A, APM 1.2, Multi Boot, DMI
• Supports ACPI revision 1.0B specificaion
Page 9
1-3
1.4 Special Features
Extreme PowerExtreme Power
Extreme PowerExtreme Power
Extreme Power
Extreme GuardianExtreme Guardian
Extreme GuardianExtreme Guardian
Extreme Guardian
PC protection toolkit!
A ‘time machine’ to
protect and restore files!
Become your own BIOS
‘doctor’!
• 1 x 20-pin ATX Power Supply Connector & 4-pin 12 V
Connector
• 1 x Floppy connector- supports 360K ~ 2.88M Bytes, 3
Mode FDDs or LS120
• 3 x IDE connectors
• 4 x Serial ATA connectors
• 2 x USB 2.0 header support additional 4 USB ports
• 2 x 1394a headers
• 1 x EZ-Watcher header (optional)
• 1 x SMBus header
• 1 x Front panel switch/LED header
• 1 x Front panel audio header
• CD in/AUX in header
• CPUFAN/NB_FAN/CASFAN connectors
• ATX size
• 305mm x 244mm
Form Factor
Internal I/O
The best aluminum
capacitors empowering!
Uncompromising DVD
audio quality!
One-key boot device
selection!
Play complex 3D games
without compromise!
Slash memory access time!
Device plug with USB-like
ease!
6-layer PCB!
Auto restart after power
loss!
Page 10

1-4
Extreme LinkExtreme Link
Extreme LinkExtreme Link
Extreme Link
SATA RAID!
Extreme GeniusExtreme Genius
Extreme GeniusExtreme Genius
Extreme Genius
Dust proof auto shutter!
Clear & Clean!
PC ‘health’ monitor!
Memory module alert!
Dr. LED!
Know your AGP!
PCI 2.3 support!
Add peripherals and
consumer electronics
devices!
Smart LAN!
All the USB 2.0
connectivity you’ll ever
need!
More port options!
Industrial-strength LAN
power!
Auto-negotiate your 10/
100M LAN!
Server class dual LAN
for both Internet &
Intranet!
Double digital audio!
Let your PC as a
fileserver!
Color-coding for easy
connections!
Customize your start-up
screen!
Rounded corners for
strength and safety!
Flash BIOS from
Windows!
Cool operations, cool
appearance!
Eliminate data highway
roadblocks!
Ultra sound quality!
Overclock CPU quickly
and easily!
Page 11
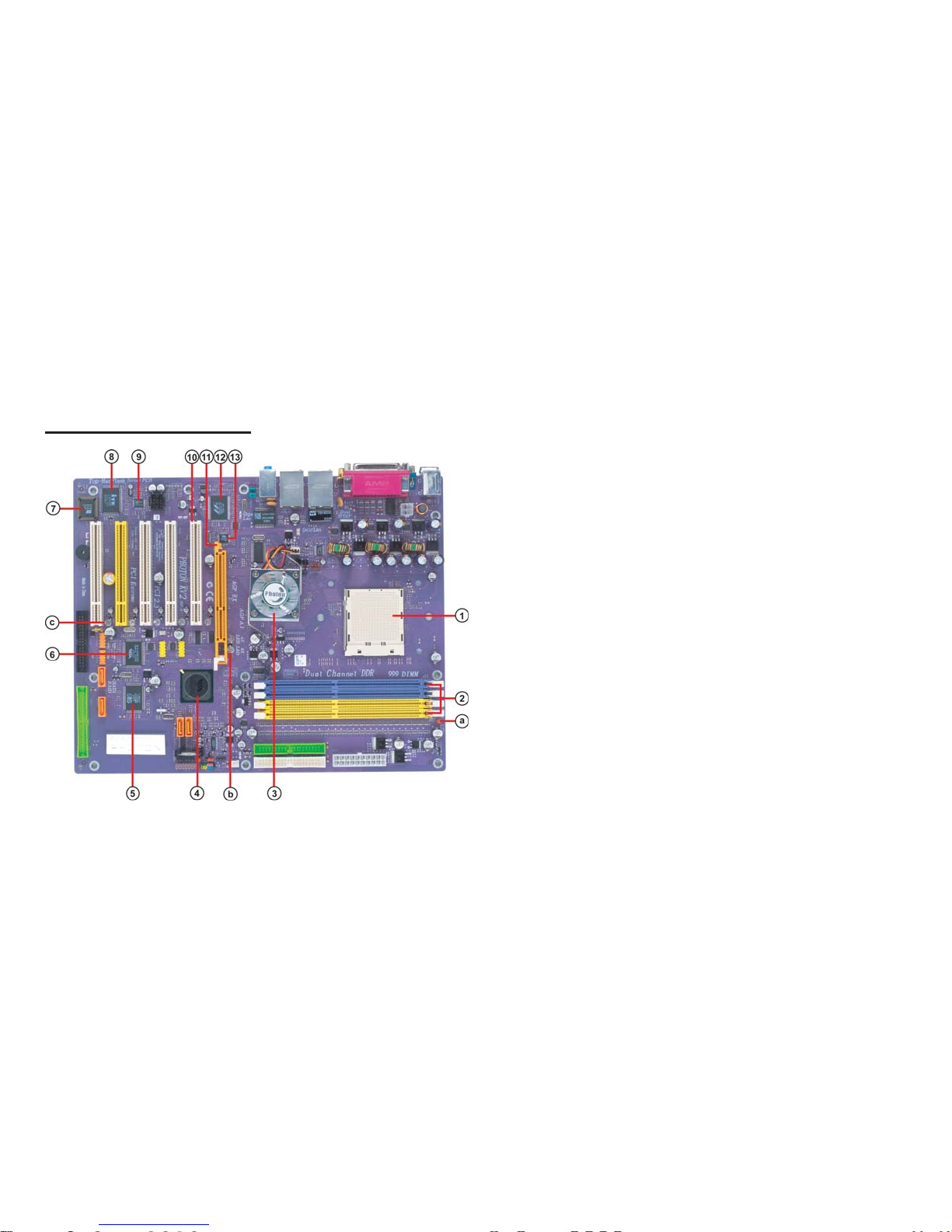
1-5
1.5 Major Components
1. CPU socket
2. Dual channel DDR DIMM sockets
These four 184-pin DIMM sockets support up to 4GB system
memory using unbuffered PC3200/2700/2100/1600 DDR DIMMs.
3. Northbridge controller
Socket 939 surface mount, Zero Insertion Force socket for AMD K8
Athlon 64 FX Processor support FSB 1000/800/600/400/200 MHz
that allows up to 8 GB/s data transfer rates.
5. SiS 180 Serial ATA controller
This motherboard incorporates the high performance SiS 180 IDE RAID
controller, which supports RAID 0, RAID 1 and RAID 0+1 configuration.
The VIA VT8237 integrated peripheral controller supports various I/O
functions including two Serial ATA ports, dual channel UltraDMA133/100/66/33 master mode EIDE controller, up to eight USB 2.0
ports, AC’97 2.1 interface, and PCI 2.2 interface.
4. Southbridge controller
The VIA K8T800 PRO links with AMD 64 processor through a 16-bit/
1 GHz data transfer rate for a total bandwidth of 8 GB/s Hyper-Transport interface. It also supports AGP 3.0 specification.
Page 12

1-6
6. IEEE 1394a controller
The IEEE 1394a controller provides high-speed and flexible
PC connectivity to a wide range of peripherals and devices compliant
to IEEE 1394a standards. The IEEE 1394a interface allows up to
400Mbps tranfer rates.
7. Flash ROM
This 4Mb ROM contains the programmable BIOS program.
12. Gigabit LAN controller
The Gigabit LAN controller delivers transfer rates up to 10/100/
1000Mbps Ethernet connection. Ideal for handling large amounts of
data such as video, audio and voice.
13. 10/100Mbps LAN PHY
A. Anti-Burn LED indicator
When this LED is light up, do not remove the memory module from
your DIMM slot or else your memory module will be damaged.
B. AGP A.I indicator
C. PCI LED indicator
8. Super I/O (ITE 8705F) controller
This Super I/O provides the commonly used functionality. The chipset
supports a high performance floppy disk controller, a multimode parallel
port, one serial port, a game port, the mouse and keyboard interface.
11. AGP Slot
This Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) slot supports AGP 8X
and 4X mode graphic cards for 3D graphical applications.
The 10/100Mbps LAN PHY delivers a transfer rates up to 10/100
Mbps.
These two LEDs indicate which type of graphics card you have installed.
4X- Yellow LED; 8X-Blue LED
The blinking PCI LED indicates the PCI slot activity. These LEDs will
stop blinking when add card has been installed. Blinking means no add
card installed or add card was not properly installed.
9. Audio CODEC
The audio CODEC is compliant with AC’97 v2.3 spec and supports
6-channel audio.
10. PCI slots
These five 32-bit PCI 2.2 expansion slots support bus master PCI
cards like SCSI or LAN cards with 133MB/s maximum throughput.
Page 13
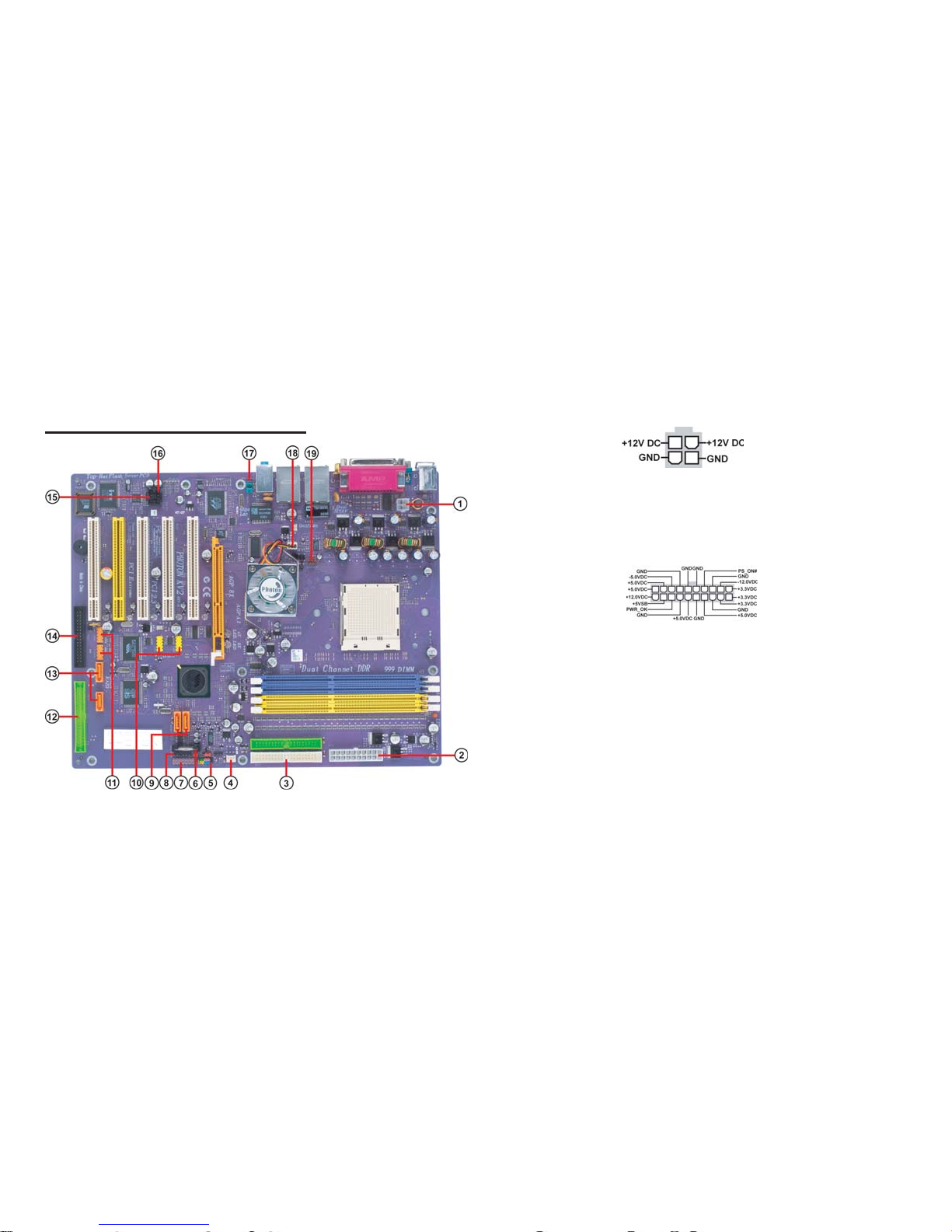
1-7
1.6 Headers and Connectors
1. ATX12V
This connector supplies the CPU operation voltage (Vcore). Don’t
forget to connect the 4-pin ATX 12V connector, otherwise the
system cannot boot up.
AC power cord should only be connected to your power supply until
after ATX power cable and other related devices are firmly connected to
the motherboard. Make sure that your ATX12V power supply could
provide 8A of 12V and at least 1A on the +5V standby. The minimum
recommended voltage is 230W or 300W. If not, the system may become
unstable or may not even boot up.
2. ATX 1 (ATXPWR, 20 pin)
Page 14
1-8
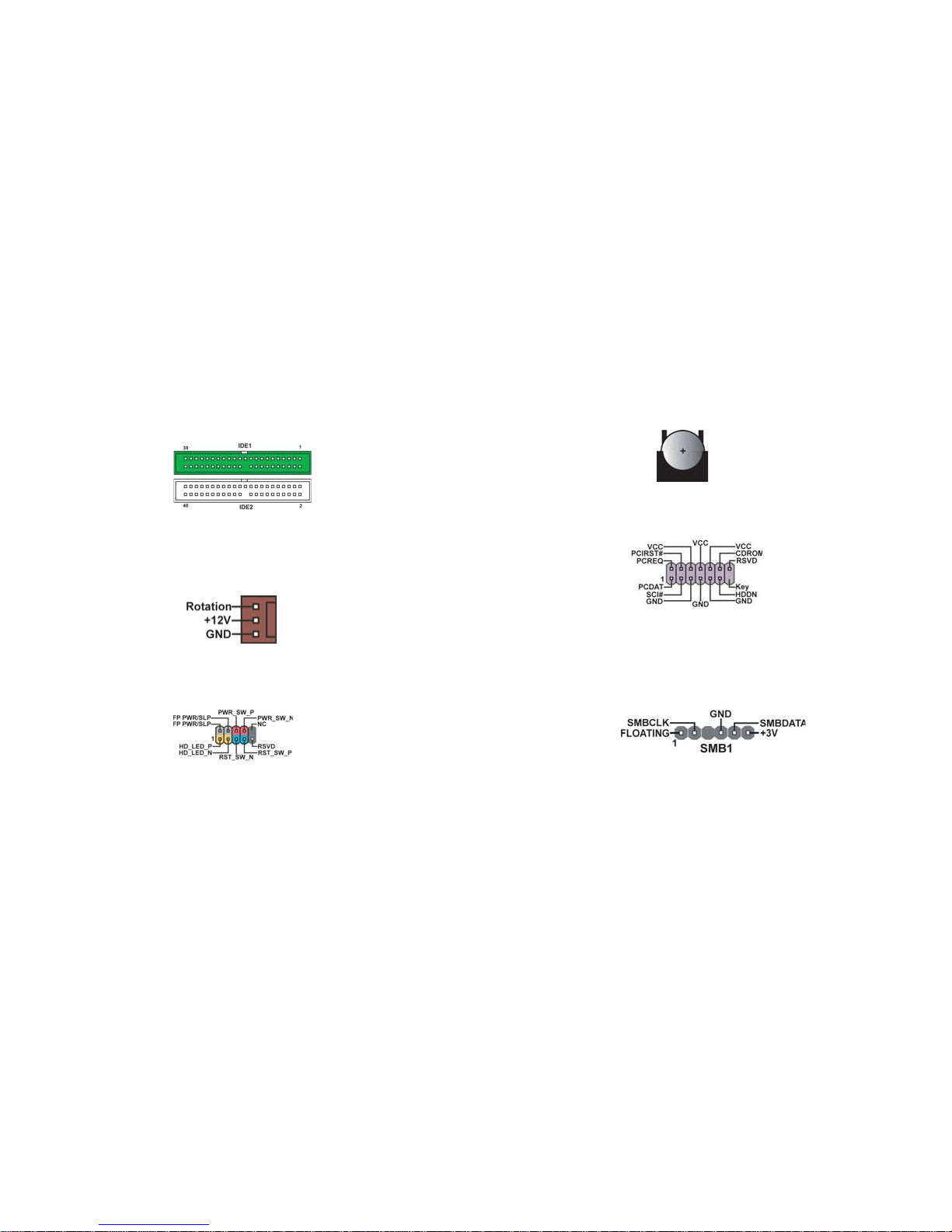
3. IDE 1/2 (IDE1/IDE2 Connectors, 40-1 pin, Green and White)
These are supported by VIA8237 South Bridge. Please connect the first
hard disk to IDE 1 and connect the CD-ROM to IDE 2. The streamline
IDE cable must be the same side with the Pin 1.
4. CASFAN1 (Case Fan Connector, 3 pin)
This connector allows you to link with the cooling fan on the system case
to lower the system temperature.
The front panel connector provides a standard set of switch and LED
connectors commonly found on ATX or micro-ATX cases.
5. Panel1 (Front Panel Header, 10-1 pin)
6. Battery
Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with
the same of equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer.
8. SMBus1 (SMBus Header, 6-1 pin)
This connector allows you to connect SMBus (System Management Bus)
devices. Devices communicate with an SMBus host and/or other SMBus
devices using the SMBus interface.
7. EZJ1 (EZ-Watcher Interface Header, 14-1 pin) (optional)
This connector is for use with EZ-Watcher interface only. The EZWatcher allows you to adjust the CPU frequency according to your desire.
Note: EZ-Watcher is an optional device, please contact your nearest dealer for the device.
Page 15
1-9
9. SATA 1/2 (Serial ATA Connectors, 7 pin, Orange)
These next generation connectors are delivered by VIA 8237 South
Bridge support the thin Serial ATA cables for Serial ATA hard disks. The
current Serial ATA interface allows up to 150MB/s data transfer rate,
faster than the standard parallel ATA with 133MB/s (UltraATA 133)
10. USB 3/4 (Front USB Headers, 10-1 pin, Yellow)
If the USB ports on the rear panel are inadequate, two USB headers are
available for additional USB ports. The USB header complies with USB
2.0 specification that supports up to 480 Mbps connection speed. This
speed advantage over the conventional 12 Mbps on USB 1.1.
11. 1394A1/A2 (10-1 pin Headers, Orange)
Attach the 10-1 pin 1394 cable plug from the device to this connector.
You may also connect a 1394-compliant internal hard disk to this connector.
12. IDE 3 (IDE RAID ATA133 Connector, 40-1 pin, Green)
This connector supports either RAID 0 or RAID 1 configuration through
the onboard SiS180 controller. You can connect two UltraATA 133
hard disks to this connector and set up a disk array configuration. You
may also set up the UltraATA 133 hard disks with the Serial ATA hard
disks on the Serial ATA RAID connectors to create a multi-RAID configuration.
13. SATA 3/4 (Serial ATA RAID Connectors, 7 pin, Orange)
Page 16

1-10
17. Audio1 (Front Panel Audio Header, 10-1 pin)
This is an interface for the Intel front panel audio cable that allows
convenient connection and control of audio devices. By default, the
pins labeled LINE OUT_R/BLINE_OUT_R and the pins LINE
OUT_L/BLINE_OUT_L are shorted with jumper caps. Remove the
caps only when you are connecting the front audio cable.
18. NBFAN1 (Northbridge Fan Connector, 3 pin)
If you installed wrong direction, the chip fan will not work. Sometimes
will damage the chip fan.
19. CPUFAN1 (CPU Fan Connector, 3 pin)
Please note, a proper installation of the CPU cooler is essential to prevent the CPU from running under abnormal condition or damaged by
overheating. The CPU fan connector supports maximum current up to
600 mA.
These Serial ATA connectors support SATA hard disks that you may
configure as a RAID set. Through the onboard SiS180 RAID controller
you may create a RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1, or multiRAID configuration together with the RAID ATA133 connector.
14. FDD1 (Floppy Connector, 34-1 pin, Black)
Please connect the floppy drive ribbon cables to FDD. It supports
360K, 12M, 720K, 1.44M and 2.88M bytes floppy disk types.
15. CDIN1 (CD In Connector, 4 pin)
Connect CD-ROM or DVD-ROM audio out to the connector.
16. AUXIN1 (AUX In Connector, 4 pin)
Connect other device (such as PCI TV Tuner audio out) to the connector.
Page 17
1-11
1.7 Jumpers
1. JP1 (Clear CMOS)
This jumper allows you to clear the Real Time Clock (RTC) RAM in
CMOS. You can clear the CMOS memory of date, time, and system
setup parameters by erasing the CMOS RTC RAM data. Before
clearing the CMOS data, make sure to turn the system off.
Page 18

1-12
mode, the function of this jack becomes Rear Speaker Out.
6. Line out jack
This jack connects a headphone or a speaker. In 6-channel mode, the
function of this jack becomes Front Speaker Out.
7. Microphone jack
This jack connects a microphone. In 6-channel mode, the function of
this jack becomes Basss/Center Speaker Out.
8. USB 2.0 ports 3 and 4
These Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports are available for connecting
USB 2.0 devices.
9. USB 2.0 ports 1 and 2
These Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports are available for connecting
USB 2.0.
10. Coaxial S/PDIF output port
This jack connects to external digital audio output devices.
11. Optical S/PDIF output port
This jack connects to external digital audio output devices
12. Serial port
This 9-pin COM1 port is for serial devices.
13 PS/2 keyboard port
This 6-pin connector is for connecting PS/2 keyboard.
1. PS/2 mouse port
This 6-pin connector is for connecting PS/2 mouse.
2. Parallel port
This 25-pin port connects a parallel printer, a scanner, or other
devices.
3. RJ-45 port
This port allows connection to a Local Area Network (LAN)
through a network hub. It supports up to 10/100Mbps transfer rate.
4. RJ-45 port
This port allows connection to a Local Area Network (LAN)
through a network hub. It supports up to Gigabit tranfer rate.
5. Line in jack
This jack connects a tape player or other audio sources. In 6-channel
1.8 Rear Panel
Page 19
Chapter 2
This chapter explains the hardware setup procedure
for this motherboard, such as installing the CPU,
memory modules, expansion cards, as well as the
jumpers
Page 20

2.1 Installing the CPU..............................................2-1
2.2 Installing the CPU cooling F AN.........................2-1
2.3 Installing Memory Module.................................2-1
2.4 Connecting IDE, Floppy and SA T A cable...........2-3
2.5 Installing Motherboard in a case.........................2-3
2.6 Connecting IDE, Floppy & SA T A Device...........2-4
2.7 Installing Expansion cards...................................2-4
2.8 Connecting the Power supply cable...................2-5
2.9 Powering up.......................................................2-5
Reference
Page 21
2-1
2.2 Installing the CPU cooling FAN
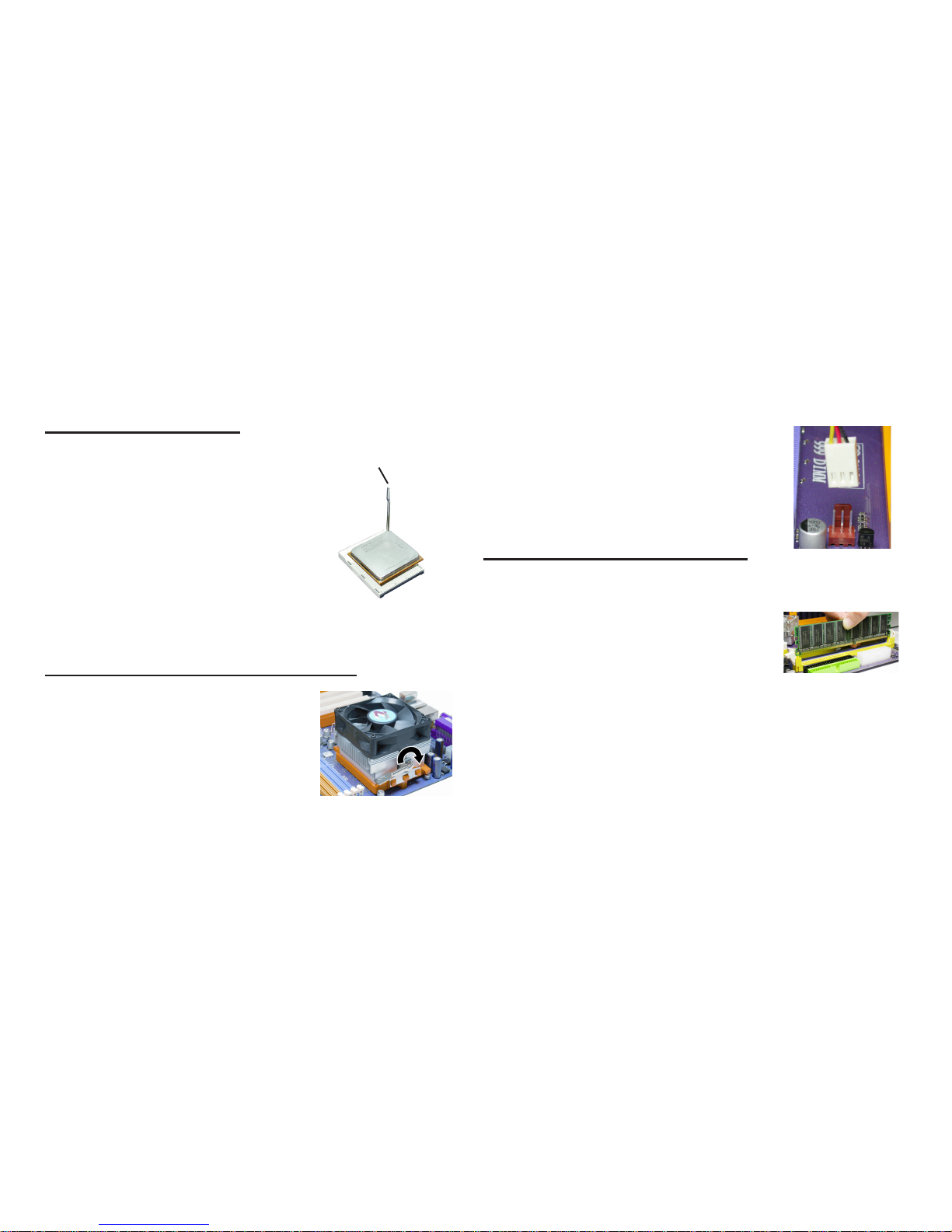
2.1 Installing the CPU
2. Make sure the CPU fan is plugged to the
CPU fan connector. Please refer to the CPU
cooling fan user’s manual for more detail
installation procedure.
Warning: We recommend you to apply the thermal tape to
provide better heat conduction between your
CPU and cooling fan.
2.3 Installing Memory Module
1. Push the latches on each side of the DIMM
slot down.
2. Check that the cutouts on the DIMM module
edge connector match the notches in the
DIMM slot.
3. Install the DIMM module into the slot and
press it firmly down until it seats correctly.
The slot latches are levered upwards and latch
on to the edges of the DIMM.
Warning: If the CPU does not fit, please change the insert orientation. Do not force the
CPU into the socket.
3. Close the socket by lowering and locking the lever.
1. Angling the rod to 65-degree may feel
tight, continue to pull the rod to 90degree angle.
2. Position the CPU above the socket
such that its notched or marked corner
matches the socket corner near the base
of the lever, while making sure that the
CPU is parallel to the socket. Then insert the CPU into the socket.
Actual angle
1. Fasten the cooling fan supporting
base onto the CPU socket on the
motherboard.
Page 22
2-2
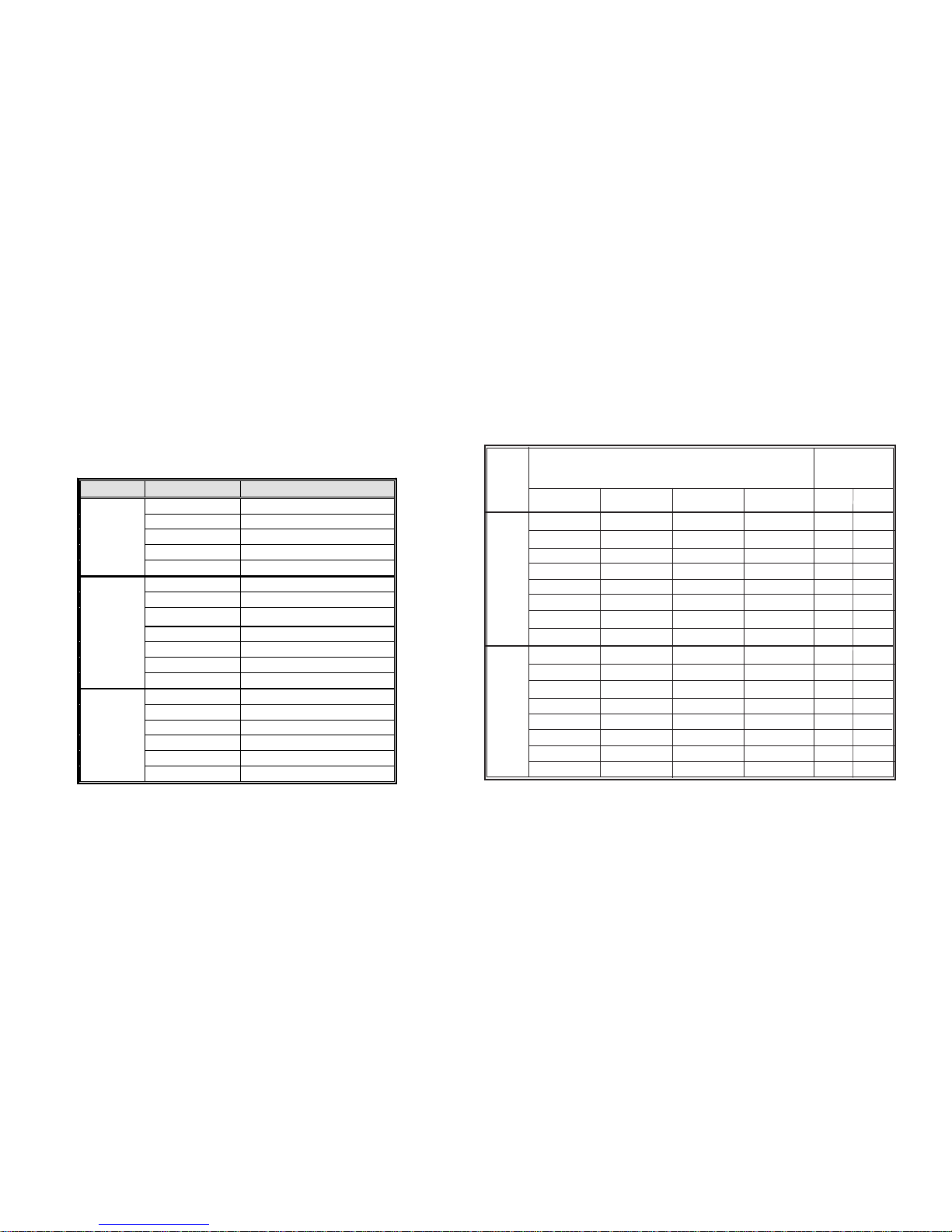
Table A: DDR (memory module) QVL (Qualified Vendor List)
The following DDR400 memory modules have been tested and qualified
for use with this motherboard.
Size Vendor Module Name
128MB
SAMSUNG M368L1713DTM-CC4
Micron MT8VDDT1664AG-403B2
NANYA NT128D64SH4B1G-5
Infineon
HYS64D16301GU-5-B
NANYA NT128D64SH4B1G-5T
256MB
SAMSUNG M368L3223DTM-CC4
NANYA NT256D64S88B1G-5
Micron MT16VDDT3264AG-403B2
Infineon
HYS64D32300GU-5-B
Micron MT8VDDT3264AG-40BC4
NANYA NT256D64S88B1G-5T
Infineon
HYS64D32300HU-5-C
512MB
SAMSUNG M368L6423DTM-CC4
NANYA NT512D64S8HB1G-5
Micron MT16VDDT6464AG-40BC4
NANYA NT512D64S8HB1G-5T
SAMSUNG M368L6423ETM-CC4
Infineon HYS64D64320HU-5-C
Table B: Unbuffered DIMM Support for 939-pin
N/A
N/A
Single rank
Double rank
Single rank
Double rank
Single rank
Double rank
Chip Selects
Data
Bus
128bits
Maximum
DRAM Speed
MEMCS_1L_L* MEMCS_2H_L* MEMCS_2L_L* MEMCS_2H_L*
1T 2T
64bits
Single rank
Double rank
N/A
N/A
Single rank
Single rank
Double rank
Double rank
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Single rank
Double rank
Single rank
Double rank
Single rank
Double rank
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Single rank
Double rank
N/A
N/A
Single rank
Single rank
Double rank
Double rank
Single rank
Double rank
N/A
N/A
Single rank
Single rank
Double rank
Double rank
N/A
N/A
Single rank
Double rank
Single rank
Double rank
Single rank
Double rank
DDR400 DDR400
DDR400 DDR400
DDR400 DDR400
DDR400 DDR400
DDR333 DDR400
DDR200 DDR400
DDR200 DDR400
DDR200 DDR333
DDR400 DDR400
DDR400 DDR400
DDR400 DDR400
DDR400 DDR400
DDR333 DDR400
DDR200 DDR400
DDR200 DDR400
DDR200 DDR333
Note for “*”: Memory types must be set to values consistent with system hardware.
Page 23
2-3
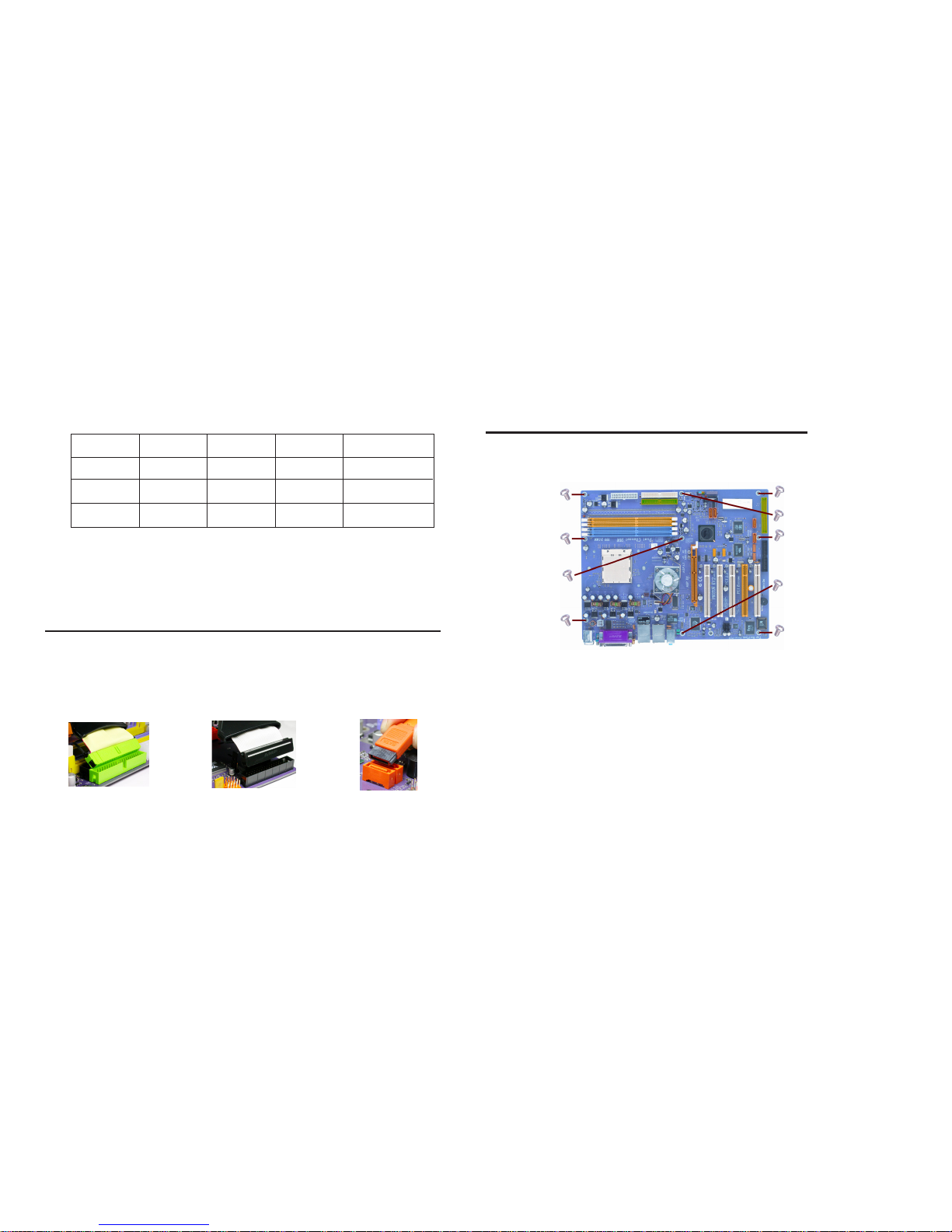
2.4 Connecting IDE, Floppy and SATA cable
1. Connect the IDE/Floppy disk ribbon cable. Make sure the side of
the cable with the red stripe on it is plugged into pin 1 side of the
disk connector.
2. Connect the SATA cable to the SATA hard drive or the connector
on the motherboard.
IDE connector FDD connector SATA connector
Notes: 1. When using dual channel mode, install only same (same density, DRAM
technology and DRAM bus width) module for each deal channel.
2. Please note that those types not in the Table B will not boot up.
3. The KV2 Extreme doesn’t support three memory modules. If three memory modules
are inserted, the system will not boot.
2.5 Installing Motherboard in a case
1. Place the motherboard over the mounting brackets.
2. Secure the motherboard with screws where appropriate.
3. Double check to make sure that the underside of the motherboard is
not touching the case or else shorting may occur and make sure that
the slots and I/O connectors line up with the holes on the back of
the case.
4. Case LED leads are labeled, connect the leads to the panel header on
the motherboard.
Table C: Recommended dual-channel DDR configurations
DDR1 DDR2 DDR3 DDR4 Dual Channel
√
√
√
√
√√
√√
√
√
√
Page 24

2-4
2.6 Connecting IDE, Floppy & SATA Device
1. If installing two IDE devices on the same
ribbon cable, one device must be set to
“master” and the other to “slave.” Check
the accompanying documents for the
master/slave settings of IDE Devices, ie.:
the hard disk and CD-ROM drives and then
set their jumper caps accordingly.
2. Mount the drives in the case.
3. Connect the floppy disk ribbon cable and
power cable.
4. Connect the IDE ribbon cable and power
cable.
IDE Hard Disk
Floppy Disk Device
SATA Hard Disk
2.7 Installing Expansion cards
1. Remove the slot covers from the case where you will be installing
the expansion cards.
2. Install your graphics card in the proper slot if your motherboard does
not have integrated graphics.
3. Press the card firmly into the slot
4. Secure the card with the screw from step 1.
5. Install other expansion cards using the same procedure.
Graphics card
PCI card
Page 25

2-5
2.8 Connecting the Power supply cable
The ATX power connector is keyed for proper insertion. There are two
connectors 4-pin and 20-pin ATX power cable. The plastic clip on the
power connector should lock over the plastic tab on the motherboard
power connector.
20-pin ATX
power connector
4-pin ATX
power connector
2.9 Powering up
Turn on the power to the monitor and the computer. If necessary,
format your hard disk drive and install an operating system.
Page 26
Chapter 3
In this chapter, you will learn how to adjust the BIOS
(Basic Input and Output System) setup menus. It
provides information on the system’s configuration
status and options to setup system parameters.
Page 27

3.1 Entering the BIOS Setup Menu..........................3-1
3.2 Updating and Recovering the BIOS....................3-1
3.2-1 Using A W ARD Flash to update your BIOS............3-1
3.2-2 Using ECS EZ Flash to update your BIOS...........3-2
3.2-3 Using ECS T op-Hat Flash to r ecover your BIOS..3-3
3.3 The Main Menu.................................................3-3
3.3-1 Standard CMOS Features........................................3-3
3.3-2 Advanced BIOS Features.........................................3-5
3.3-3 Advanced Chipset Features.....................................3-7
3.3-4 Int egr ate d Pe rip her als .. ............................................3-10
3.3-5 Power Management Setup..................................3-13
3.3-6 PNP/PCI Configurations..........................................3-16
3.3-7 PC Health Status.......................................................3-17
3.3-8 Frequency/V oltage Contr ol....................................3-18
3.3-9 Load Performance Defaults.....................................3-19
3.3-10 Load Optimized Defaults........................................3-19
3.3-11 Set Supervisor/User Password...............................3-19
Reference
3.3-12 Save & Exit Setup....................................................3-20
3.3-13 Exit Without Saving.................................................3-20
Page 28
3-1
3.1 Entering the BIOS Setup Menu
When you power on the system, BIOS enters the Power-On Self Test
(POST) routines. POST is a series of built-in diagnostics performed by the
BIOS. After the POST routines are completed, the following message
appears:
Press DEL to enter SETUP
Pressing the delete key accesses the BIOS Setup Utility:
3.2 Updating and Recovering the BIOS
A standard configuration has already been set in the Setup Utility. However,
if you encounter a configuration error or you need a better performance.
You could attempt to update or recover your system BIOS.
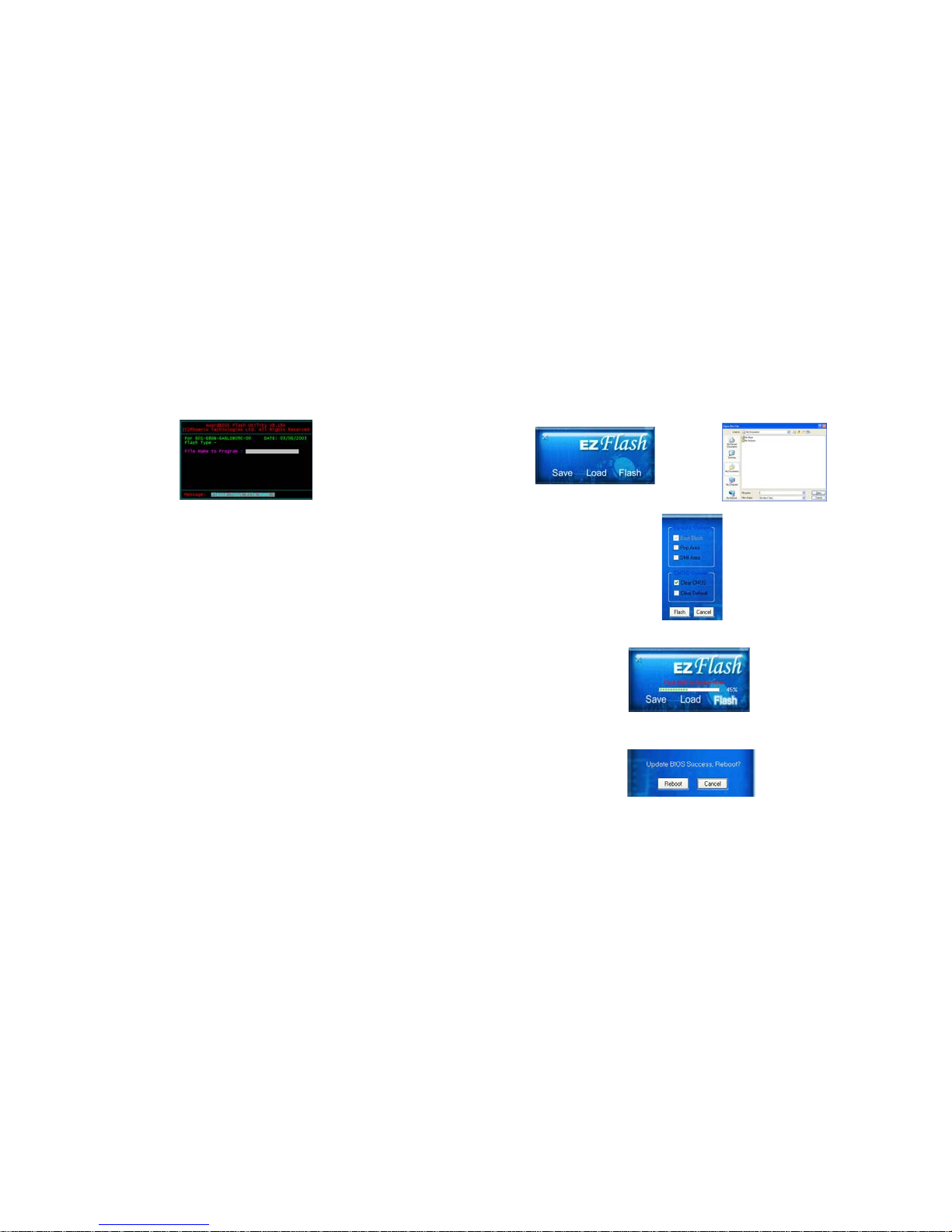
3.2-1 Using AWARD Flash to update your BIOS
1. If your motherboard has an item called Firmware Write Protect in
Advanced BIOS features, disable it. (Firmware Write Protect prevents
BIOS from being overwritten).
2. Create a bootable system disk. (Refer to Windows online help for
information on creating a bootable system disk.)
3. Use the Award Flash Utility from the ECS support CD and download
the last BIOS file for this motherboard from ECS web site
(www.ecs.com.tw). Copy these files to the system diskette you created
in step 2.
4. Turn off your computer and insert the system diskette in your computer’s
diskette drive. (You might need to run the Setup Utility and change the
boot priority items on the Advanced BIOS Features Setup page, to
force your computer to boot from the floppy diskette drive first.)
5. At the A:\ prompt, type the Flash Utility program name and press
<Enter>. You see a screen similar to the following:
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility:
Standard CMOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features
Advanced Chipset Features
Integrated Peripherals
Power Mangement Setup
PnP/PCI Configurations
PC Health Status
Frequency/Voltage Control
Load Performance Defaults
Load Optimized Defaults
Set Supervisor Password
Set User Password
Save & Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
Esc: Quit F9: Menu in BIOS
: Select Item
F10: Save & Exit Setup
Time, Date , Hard Disk Type...
Page 29
3-2
6. Type the filename of the new BIOS in the “File Name to Program” text
box. Follow the onscreen directions to update the motherboard BIOS.
7. When the installation is complete, remove the floppy diskette from the
diskette drive and restart your computer. If your motherboard has a
Flash BIOS jumper, reset the jumper to protect the newly installed
BIOS from being overwritten.
3.2-2 Using ECS EZ Flash to update your BIOS
The ECS EZ Flash feature allows you to easily update the BIOS without
having to go through the long process of booting from a diskette and using
a DOS-based utility.
Note: EZ Flash only supports Windows 2000/XP.
1. Download the last BIOS file for this motherboard from ECS web site
(www.ecs.com.tw). Copy these files to any storage device that you
have.
2. Enable the utility from ECS support CD, then click the “Load” button
and select the BIOS that you have downloaded in advance.
3. Select the “Flash” button.
4. The Utility will update the new BIOS into the motherboard Flash
ROM.
5. Click the “Reboot” button if you want to adopt the new BIOS or
choose the “Cancel” button if you still want to use the previous BIOS.
Page 30

3-3
3.2-3 Using ECS Top-Hat Flash to recover your BIOS
The ECS Top-Hat Flash kit allow you to restore BIOS from ECS website
(www.ecs.com.tw) or ECS support CD, in case you current BIOS on the
motherboard or get corrupted, please follow the procedures below to recover
your BIOS.
1. Please find the BIOS ROM located on your motherboard. (Figure A)
2. Find the cut edge corner on the Flash ROM. (Figure B)
3. Find the cute edge corner on the Top Hat Flash. (Figure C)
4. Orient the cut edge Top Hat Flash to BIOS ROM’s and press the flash
ROM into the lower socket of Top Hat Flash. (Figure D & E)
5. Then, power on your computer.
6. After the computer boots up, remove the Top Hat Flash.
7. Download the BIOS file from ECS web site (www.ecs.com.tw) or
ECS support CD and use Flash Utility to reflash the original Flash
ROM.
8. You can choose either AWARD Flash utility in DOS mode or ECS “EZ
Flash Utility” in windows to reflash the BIOS.
Figure A Figure B Figure C Figure D Figure E
3.3 The Main Menu
The main menu of the Setup Utility displays a list of the options that are
available. A highlight indicates which option is currently selected. Use the
cursor arrow keys to move the highlight to other options. When an option
is highlighted, execute the option by pressing <Enter>.
3.3-1 Standard CMOS Features
This option displays basic information about your system.
Date and Time
The Date and Time items show the current date and time on the computer. If you are
running a Windows OS, these items are automatically updated whenever you make
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Standard CMOS Features
Date (mm:dd:yy) Wed, Feb 25 2004
Time (hh:mm:ss) 9 : 33 : 26
IDE Channel 0 Master
IDE Channel 0 Slave
IDE Channel 1 Master
IDE Channel 1 Slave
Drive A [1.44M, 3.5 in.]
Drive B [None]
Video [EGA/VGA]
Halt On [All, But Keyboard]
Base Memory 640K
Extended Memory 65535K
Total Memory 1024K
Item Help
Menu Level
Change the day, month,
year and century
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
Page 31

3-4
IDE Channel 0/1 Master/Slave
Leave this item at Auto to enable the system to automatically detect and
configure IDE devices on the channel. If it fails to find a device, change the
value to Manual and then manually configure the drive by entering the
characteristics of the drive in the items described below.
Note: Before attempting to configure a hard disk drive, ensure that you have the
configuration information supplied by the manufacturer of your hard drive.
Incorrect settings can result in your system not recognizing the installed hard
disk.
Access Mode
This item defines ways that can be used to access IDE hard disks such as LBA
(Large Block Addressing). Leave this value at Auto and the system will automatically
decide the fastest way to access the hard disk drive.
Press <Esc> to return to the Standard CMOS Features page.
Drive A/Drive B [1.44M, 3.5in./None]
These items define the characteristics of any diskette drive attached to the system.
You can connect one or two diskette drives.
Video [EGA/VGA]
Thsi item defines the video mode of the system. This motherboard has a built-in
VGA graphics system; you must leave this item at the default value.
changes to the Windows Date and Time Properties utility.
IDE Devices [None]
Your computer has two IDE channels (Primary and Secondary) and each channel
can be installed with one or two devices (Master and Slave). Use these items to
configure each device on the IDE channel.
Press <Enter> to display the IDE submenu:
IDE HDD Auto-Detection
Press <Enter> while this item is highlighted to prompt the Setup Utility to automatically
detect and configure an IDE device on the IDE channel.
Note: If you are setting up a new hard disk drive that supports LBA mode, more than one
line will appear in the parameter box. Choose that lists LBA for an LBA drive.
IDE HDD Auto-Detection [Press Enter]
IDE Channel 0 Slave [Auto]
Access Mode [Auto]
Capacity 0MB
Cylinder 0
Head 0
Precomp 0
Landing Zone 0
Sector 0
Item Help
Menu Level
To auto-detect the
HDD’s size, head... on
this channel
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
IDE Channel 0 Slave
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
Page 32

3-5
Halt On [All, But Keyboard]
This item defines the operation of the system POST (Power On Self Test) routine.
You can use this item to select which types of errors in the POST are sufficient to
halt the system.
Base Memory, Extended Memory and Total Memory
These items are automatically detected by the system at start up time. These are
display-only fields. You cannot make chanages to these fields.
3.3-2 Advanced BIOS Features
This option defines advanced information about your system.
ATA 66/100 IDE Cable Msg (Enabled)
Enables or disables the A TA 66/100 IDE Cable Msg. This message will appear during
reboot when you use 40-pin cable on your 66/100 hard disks.
Hard Disk Boot Priority
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the following screen:
1. Pri.Master:
2. Pri.Slave:
3. Sec. Master:
4. Sec. Slave:
5. USBHDD0:
6. USBHDD1:
7. USBHDD2:
8. Bootable Add-in Cards
Item Help
Menu Level
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Hard Disk Boot Priority
: Move PU/PD+/-/:Change Priority F10:Save ESC:Exit
Use <
> or < > to
select a device, then press
<+> to move it up, or <-> to
move it down the list. Press
<ESC> to exit this menu.
Quick Power On Self Test (Enabled)
Enable this item to shorten the power on testing (POST) and have your system start
up faster. You might like to enable this item after you are confident that your system
hardware is operating smoothly.
First/Second/Third Boot Device (Floppy/Hard Disk/CDROM)
Use these three items to select the priority and order of the devices that your system
ATA 66/100 IDE Cable Msg. [Enabled]
Hard Disk Boot Priority [Press Enter]
Quick Power On Self Test [Enabled]
First Boot Device [Floppy]
Second Boot Device [Hard Disk]
Third Boot Device [CDROM]
Boot Other Device [Enabled]
Swap Floppy Drive [Disabled]
Boot Up Floppy Seek [Disabled]
Boot Up NumLock Status [On]
Typematic Rate Setting [Disabled]
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec0 6
Typematic Delay (Msec) 25 0
Security Option [Setup]
APIC Mode [Enabled]
HDD S.M.A.R.T. Capability [Disabled]
VIdeo BIOS Shadow [Enabled]
Small Logo(EPA) Show [Disabled]
Item Help
Menu Level
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Advanced BIOS Features
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
X
X
Page 33

3-6
Boot Other Device [Enabled]
When enabled, the system searches all other possible locations for an operating
system if it fails to find one in the devices specified under the First, Second, and
Third boot devices.
Swap Floppy Drive [Disabled]
If you have two floppy diskette drives in your system, this item allows you to swap
the assigned drive letters so that drive A becomes drive B, and drive B becomes
drive A.
Boot Up Floppy Seek [Disabled]
If this item is enabled, it checks the size of the floppy disk drives at start-up time.
You don’t need to enable this item unless you have a legacy diskete drive with 360K
capacity.
Boot Up NumLock Status [On]
This item defines if the keyboard Num Lock key is active when your system is
started.
Typematic Rate Setting [Disabled]
If this item is enabled, you can use the following two items to set the typematic rate
and the typematic delay settings for your keyboard.
Security Option [Setup]
If you have installed password protection, this item defines if the password is
required at system start up, or if it is only required when a user tries to enter the
Setup Utility.
APIC Mode [Enabled]
This item allows you to enable or disable the APIC (Advanced Programmable
Interrupt Controller) mode. APIC provides symmetric multi-processing (SMP) for
systems, allowing support for up to 60 processors.
HDD S.M.A.R.T Capability [Disabled]
The S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) system is a
diagnostics technology that monitors and predicts device performance S.M.A.R.T.
software resides on both the disk drive and the host computer.
The disk drive software monitors the internal performance of the motors, media,
heads and electronics of the drive. The host software monitors the overall reliability
status of the drive. If a device failure is predicted, the host software, through the
Client WORKS S.M.A.R.T applet, warns the user of the impending condition and
advises appropriate action to protect the data.
searches for an operating system at start-up time.
♦ Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec): Use this item to define how many characters
per second are generated by a held-down key.
♦ Typematic Delay (Msec): Use this item to define how many milliseconds
.
must elapse before a held-down key begins generating repeat characters
Video BIOS Shadow (Enabled)
This item determines whether the BIOS will be copied to RAM for faster execution.
Small Logo (EPA) Show [Disabled]
Enables or disables the display of the EPA logo during boot.
Page 34

3-7
3.3-3 Advanced Chipset Features
These items define critical timing parameters of the mainboard. You
should leave the items on this page at their default values unless you are
very familiar with the technical specifications of your system hardware.
If you change the values incorrectly, this may cause fatal errors or
instability into your system.
AGP & P2P Bridge Control [Press Enter]
DRAM Clock/Drive Control [Press Enter]
LDT & PCI Bus Control [Press Enter]
VLink Data Rate [8X]
Init Display First [PCI Slot]
Item Help
Menu Level
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Advanced Chipset Features
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
AGP & P2P Bridge Control (Press Enter)
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the following screen:
AGP Aperture Size [128M]
This item defines the size of aperture if you use an AGP graphics adapter. The AGP
aperture refers to a section of the PCI memory address range used for graphics
memory. We recommend that you leave this item at the default value.
AGP 2.0 Mode (4X)
This item allows you to enable or disable the caching of display data for the
processor video memory. Enabling AGP-8X Mode can greatly improve the display
speed. Disable this item if your graphics display card does not support this feature.
AGP Aperture Size [128M]
AGP 2.0 Mode [4X]
AGP Driving Control [Auto]
AGP Driving Value [DA]
AGP Fast Write [Dis abled]
AGP Master 1 WS Write [ Disa bled]
AGP Master 1 WS Read [ Dis abled]
AGP 3.0 Calibration [Enabled]
Item Help
Menu Level
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Advanced Chipset Features
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
X
Page 35

3-8
Current CPU Frequency
Current DRAM Frequency
Max Memclock (Mhz) [Auto]
1T/2T Memory Timing [Auto]
CAS# latency (Tcl) [Auto]
RAS# to CAS# delay(Trcd) [Auto]
Min RAS# active time (Tras) [Auto]
Row precharge Time (Trp) [Auto]
Item Help
Menu Level
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
DRAM Clock/Drive Control
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
Places an artificial memory
clock limit on the system.
Memory is prevented from
running faster than this
frequency
Current CPU Frequency/Current DRAM Frequency
These two items show the CPU and DRAM frequency.
Max Memclock (Mhz)(Auto)
When DDR Timing Setting by is set to Manual, use this item to set the DRAM
frequency.
1T/2T Memory Timing (Auto)
Press <Esc> to return to the Advanced Chipset Features page.
AGP Driving Control (Auto)
This item is used to signal driving current on AGP cards to auto or manual. Some
AGP cards need stronger than normal driving current in order to operate. We
recommend that you set this item to the default.
• AGP Driving Value: When AGP Driving Control is to set Manual, use
this item to set the AGP current driving value.
AGP Fast Write (Disabled)
This item lets you enable or disable the caching of display data for the video
memory of the processor. Enabling this item can greatly improve the display speed.
Disable this item if your graphics display card does not support this feature.
AGP Master 1 WS Write (Disabled)
This implements a single delay when writing to the AGP Bus. By default, two-wait
states are used by the system, providing greater stability.
AGP Master 1 WS Read (Disabled)
This implements a single delay when reading to the AGP Bus. By default, two-wait
states are used by the system, allowing for greater stability
AGP 3.0 Calibration cycle(Enabled)
This item is used to implement dynamic compensation to recalibrate the AGP bus
over time for AGP 3.0 compatible chipset.
DRAM Clock/Timing Control
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the following screen:
(Press Enter)
CAS# latency (Tcl) (Auto)
This item enables you to specify the waiting time for the CPU to issue the next
command after issuing the command to the DDR memory. We recommend that you
leave this item at the default value.
This item determines the operation of SDRAM memory CAS (column address
Page 36

3-9
Press <Esc> to return to the Advanced Chipset Features page.
strobe). It is recommended that you leave this item at the default value. The
2T setting requires faster memory that specifically supports this mode.
Upstream/Downstream LDT Bus Width (16 bit)
The LDT bus (Lighting Data Transport) is the bus between the North and South
Bridge, and boosts no less that 6.4 GB/sec on a 16 bit upstream and a 16 bit
downstream dataflow.
LDT Bus Frequency (1 GHz)
This option allows you to specify the maximum operating frequency for the LDT
transmitter clock.
PCI/2 Master 0 WS Write (Enabled)
When enabled, writes to the PCI bus are executed with zero wait states, providing
faster data transfer.
PCI/2 Post Write (Enabled)
When enabled, writes from the CPU to PCU bus are buffered, to compensate for
the speed differences between the CPU and PCI bus. When disabled, the writes are
not buffered and the CPU must wait until the write is complete before starting
another write cycle.
PCI Delay Transaction (Disabled)
The motherboard’s chipset has an embedded 32-bit post write buffer to support
delay transactions cycles. Select Enabled to support compliance with PCI
specification version 2.1.
Press <Esc> to return to the Advanced Chipset Features page.
VLink Data Rate (8X)
This option allows you to select the data transfer rate between the Northbridge and
Southbridge chipsets.
LDT & PCI Bus Control (Press Enter)
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the following screen:
Upstream LDT Bus Width [16bit]
Downstream LDT Bus Width [16bit]
LDT Bus Frequency [1 GHz]
PCI Master 0 WS Write [Enabled]
PCI2 Master 0 WS Write [Enabled]
PCI Post Write [Enabled]
PCI2 Post Write [Enabled]
PCI Delay Transaction [Disabled]
Item Help
Menu Level
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
LDT & PCI Bus Control
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
RAS# to CAS# delay (Trcd)(Auto)
This item specifies the RAS# to CAS# delay to Rd/Wr command to the same bank.
Min RAS# active time (Tras)(Auto)
This item specifies the minimus RAS# active time.
Row Precharge Time (Trp)(Auto)
This item specifies the Row precharge to Active or Auto-Refresh of the same bank.
Page 37

3-10
OnChip VIA SATA (Enabled)
This option allows you to enable or disable the onboard Serial ATA device.
SATA Mode (IDE)
Use this item to select the mode of Serial ATA
IDE DMA transfer access (Enabled)
This item allows you to enable the transfer access of the IDE DMA then burst onto
the PCI bus and nonburstable transactions do not.
On-Chip IDE Channel 0/1 (Enabled)
Use these items to enable or disable the PCI IDE channels that are integrated on the
motherboard.
OnChip VIA SATA [Enabled]
SATA Mode [IDE]
IDE DMA transfer access [Enabled]
OnChip IDE Channel0 [Enabled]
OnChip IDE Channel1 [Enabled]
IDE Prefetch Mode [Enabled]
Primary Master PIO [Auto]
Primary Slave PIO [Auto]
Secondary Master PIO [Auto]
Secondary Slave PIO [Auto]
Primary Master UDMA [Auto]
Primary Slave UDMA [Auto]
Secondary Master UDMA [Auto]
Secondary Slave UDMA [Auto]
IDE HDD Block Mode [Enabled]
Item Help
ff
Menu Level
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
VIA OnChip IDE Device
mnlk
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
These options display items that define the operation of peripheral
components on the system’s input/output ports.
Init Display First (PCI Slot)
Use this item to specify whether your graphics adapter is installed in one of the PCI
slots or is integrated on the motherboard
3.3-4 Integrated Peripherals
VIA OnChip IDE Device (Press Enter)
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the following screen:
X
VIA OnChip IDE Device [Press Enter]
VIA OnChip PCI Device [Press Enter]
SuperIO Device [Press Enter]
Onboard Giga LAN Device [Enabled]
Onboard Giga LAN Boot ROM [Disabled]
Onboard 1394 Device [Enabled]
Item Help
ff
Menu Level
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Integrated Peripherals
f
f
f
mnlk
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
Page 38

3-11
IDE Prefetch Mode (Enabled)
The onboard IDE drive interface supports IDE prefetching, for faster drive access.
If you install a primary and secondary add-in IDE interface, set this field to
Disabled if the interface does not support prefetching.
Primary/Secondary Master/Slave PIO (Auto)
Each IDE channel supports a master device and a slave device. These four items
let you assign the kind of PIO (Programmed Input/Output) was used by the IDE
devices. Choose Auto to let the system auto detect which PIO mode is best, or
select a PIO mode from 0-4.
Primary/Secondary Master/Slave UltraDMA (Auto)
Each IDE channel supports a master device and a slave device. This motherboard
supports UltraDMA technology, which provides faster access to IDE devices.
If you install a device that supports UltraDMA, change the appropriate item on this
list to Auto. Y ou may have to inst all the UltraDMA driver supplied with this motherboard
in order to use an UltraDMA device.
IDE HDD Block Mode (Enabled)
Enable this field if your IDE hard drive supports block mode. Block mode enables
BIOS to automatically detect the optimal number of block read and writes per sector
that the drive can support and improves the speed of access to IDE devices.
Press <Esc> to return to the Integrated Peripherals page.
AC97 Audio (Auto)
Enables and disables the onboard audio chip. Disable this item if you are going to
install a PCI audio add-in card.
OnChip VIA LAN Device (Enabled)
Enables and disables the onboard LAN.
VIA OnChip PCI Device (Press Enter)
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the following screen:
OnChip VIA LAN Boot ROM (Disabled)
Enables and disables the booting from the onboard LAN or a network add-in card with
a remote boot ROM installed.
AC97 Audio [Auto]
Onchip VIA LAN Device [Enabled]
Onchip VIA LAN Boot ROM [Disab led ]
OnChip USB Controller [All Enabled]
USB 2.0 Support [Enabled]
USB Legacy Support [Enabled]
USB Mouse Support [Enabled]
Item Help
Menu Level
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
VIA OnChip PCI Device
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
Page 39

3-12
OnChip USB Controller (All Enabled)
Enable this item if you plan to use the Universal Serial Bus ports on this motherboard.
USB 2.0 Support (Enabled)
Enable this item if your system supports USB 2.0.
USB Legacy Support (Enabled)
This item allows the BIOS to interact with a USB keyboard or mouse to work with MSDOS based utilities and non-Windows modes.
USB Mouse Support (Enabled)
Enables this item if you plan to use a mouse connected through the USB port in a
legacy operating system (such as DOS) that does not support Plug and Play.
Press <Esc> to return to the Integrated Peripherals page.
SuperIO Device (Press Enter)
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the following screen:
Onboard FDC Controller [Enabled]
Onboard Serial Port 1 [3F8/IRQ4]
Onboard Parallel Port [378/IRQ7]
Parallel Port Mode [ECP ]
ECP Mode Use DMA [3]
Item Help
Menu Level
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
SuperIO Device
Onboard FDC Controller (Enabled)
This option enables the onboard floppy disk drive controller.
Onboard Serial Port 1 (3F8/IRQ4)
This option is used to assign the I/O address and interrupt request (IRQ) for onboard
serial port 1 (COM1).
Onboard Parallel Port (378/IRQ7)
This option is used to assign the I/O address and interrupt request (IRQ) for the
onboard parallel port.
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
Page 40

3-13
Onboard Giga LAN Device (Enabled)
Enables and disables the onboard LAN chip.
Onboard GIGA LAN Boot ROM (Disabled)
Use this item to enable and disable the booting from the onboard LAN or a network addin card with a remote boot ROM installed.
Onboard 1394 Device (Enabled)
Enable this item if you plan to use the 1394 device.
Parallel Port Mode (ECP)
Enables you to set the data transfer protocol for your parallel port. There are four
options: SPP (Standard Parallel Port), EPP (Enhanced Parallel Port), ECP (Extended
Capabilities Port) and ECP+EPP.
SPP allows data output only. Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) and Enhanced Parallel
Port (EPP) are bi-directional modes, allowing both data input and output. ECP and EPP
modes are only supported with EPP- and ECP-aware peripherals.
ECP Mode Use DMA (3)
When the onboard parallel port is set to ECP mode, the parallel port can use DMA 3 or
DMA 1.
Press <Esc> to return to the Integrated Peripherals page.
3.3-5 Power Management Setup
This option lets you control system power management. The system has
various power-saving modes including powering down the hard disk, turning
off the video, suspending to RAM, and software power down that allows
the system to be automatically resumed by certain events.
ACPI Suspend Type [S3(STR)]
Use this item to define how your system suspends. In the default, S3 (STR), the
suspend mode is a suspend to RAM, i.e., the system shuts down with the exception
of a refresh current to the system memory. If you select S1 (POS), the suspend
mode is equivalent to a software power down.
ACPI Suspend Type [S3(STR)]
HDD Power Down [Disable]
Suspend Mode [Disable]
Video Off Option [Suspend -> Off]
Video Off Method [V/H SYNC+Blank]
MODEM Use IRQ [3 ]
Soft-Off by PWRBTN [Instant-Off]
Run VGABIOS if S3 Resume [Auto]
Power on After Power fail [Off]
AMD K8 Cool’n’Quiet control [Auto]
IRQ/Event Activity Detect [Press Enter]
Item Help
f
Menu Level
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Power Management Setup
mnlk
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
f
Page 41

3-14
HDD Power Down [Disabled]
The IDE hard drive will spin down if it is not accessed within a specified length of
time.
Suspend Mode [Disabled]
The CPU clock will be stopped and the video signal will be suspended if no Power
Management events occur for a specified length of time. Full power function will
return when a Power Management event is detected.
Video Off Option (Suspend —> Off)
This option defines if the video is powered down when the system is put into suspend
mode.
Video Off Method (V/H SYNC+Blank)
This selection will cause the system to turn off the vertical and horizontal synchronization ports and write blanks to the video buffer.
MODEM Use IRQ (3)
If you want an incoming call on a modem to automatically resume the system from a
power-saving mode, use this item to specify the interrupt request line (IRQ) that is
used by the modem. You might have to connect the fax/modem to the motherboard
Wake On Modem connector for this feature to work.
Soft-Off by PWRBTN (Instant-Off)
Under ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power management Interface) you can
create a software power down. In a software power down, the system can be resumed
by Wake Up Alarms. This item lets you install a software power down that is controlled
by the power button on your system. If the item is set to Instant-Off, then the power
button causes a software power down. If the item is set to Delay 4 Sec. then you have
to hold the power button down for four seconds to cause a software power down.
Run VGABIOS if S3 Resume [Auto]
This item allows the system to initialize the VGA BIOS from S3 (Suspend to RAM)
sleep state.
Power on After Power-fail (Off)
This item enables your computer to automatically restart or return to its last operating.
AMD K8 Cool’n’Quiet control (Auto)
IRQ/Event Activity Detect (Press Enter)
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the following screen:
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
IRQ/Event Activity Detect
PS2KB Wakeup Select [Hot key]
PS2KB Wakeup from S1-S3 [Dis abled ]
Power Button Lock for S3 Disabled
PS2MS Wakeup from S1-S3 [Di sabl ed]
USB Resume from S3 [Disab led]
VGA [OFF]
LPT & COM [LPT/COM]
HDD & FDD [ON]
PCI Master [OFF]
PowerOn by PCI Card [Enabled]
Modem Ring Resume [Disa bled]
RTC Alarm Resume [Disa bled]
Date (of Month) 0
Resume Time (hh: mm: ss) 0: 22: 0
IRQs Activity Monitoring [Press Enter]
Item Help
Menu Level
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
X
X
X
When Select Password,
Please press ENTER key to
change Password Max 8
numbers.
This item helps the system to lower the frequency when CPU idles. When the
frequency decreases, the temperature will drop automatically as well.
Page 42

3-15
USB Resume from S3 (Disabled)
When set to Enabled, the system power will resume the system from a power
saving mode if there is any USB port activity.
VGA (Off)
When set to On, the system power will resume the system from a power saving
mode if there is any VGA activity.
LPT & COM (LPT/COM )
When this item is enabled, the system will restart the power-saving timeout counters
when any activity is detected on the serial ports, or the parallel port.
HDD & FDD (ON)
When this item is enabled, the system will restart the power-saving timeout counters
when any activity is detected on the hard disk drive or the floppy diskette drive.
PCI Master (OFF)
When set to Off, any PCI device set as the Master will not power on the system.
PowerOn by PCI Card (Enabled)
Use this item to enable PCI activity to wakeup the system from a power saving
mode.
Modem Ring Resume (Disabled)
Use this item to enable modem activity to wakeup the system from a power saving
mode.
• Power Button Lock for S3 (Disabled): When this item is disabled,
power button will not be locked.
PS2KB Wakeup Select (Hot key)
This option allows you to set hot key combination to turn on the system by
keyboard.
PS2KB/MS Wakeup from S1-S3 (Disabled)
This option enables you to allow keyboard or mouse activity to awaken the system
from power saving mode.
RTC Alarm Resume (Disabled)
When set to Enabled, additional fields become available and you can set the date
(day of the month), hour, minute and second to turn on your system. When set to
0 (zero) for the day of the month, the alarm will power on your system every day at
the specified time.
Press <Esc> to return to the Integrated Peripherals page.
Page 43

3-16
3.3-6 PNP/PCI Configurations
These options configure how PnP (Plug and Play) and PCI expansion cards
operate in your system. Both the the ISA and PCI buses on the motherboard
use system IRQs (Interrup ReQuests) and DMAs (Direct Memory Access).
You must set up the IRQ and DMA assignments correctly through the
PnP/PCI Configurations Setup utility for the motherboard to work properly.
Selecting PnP/PCI Configurations on the main program screen displays this
menu:
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
PnP/PCI Configurations
Reset Configuration Data [Disa bled]
Resources Controlled By [Auto(ESCD)]
IRQ Resources Press Enter
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop [Di sabled]
Assign IRQ For USB [Enabled]
Item Help
Menu Level
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
X
Default is Disabled. Select
Enabled to reset Extended
System Configuration Data
ESCD) when you exit Setup if
you have installed a new addon and the system
reconfiguration has caused
such a serious conflict that
the OS cannot boot
Reset Configuration Data [Disabled]
If you enable this item and restart the system, any Plug and Play configuration data
stored in the BIOS Setup is cleared from memory.
IRQs Activity Monitoring (Press Enter)
This screen enables you to set IRQs that will resume the system from a power saving
mode.
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
IRQs Activity Monitoring
Primary INTR [ON]
IRQ4 (COM1) [Enabled]
IRQ5 (LPT2) [Enabled]
IRQ6 (Floppy Disk) [Enabled]
IRQ7 (LPT1) [Enabled]
IRQ8 (RTC Alarm) [Disabled]
IRQ9 (IRQ2 Redir) [Disabled]
IRQ10 (Reserved) [Disabled]
IRQ11 (Reserved) [Disabled]
IRQ12 (PS/2 Mouse) [Enabled]
IRQ13 (Coprocessor) [Enabled]
IRQ14 (Hard Disk) [Enabled]
IRQ15 (Reserved) [Disabled]
Item Help
Menu Level
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
Set any IRQ to Enabled to allow activity at the IRQ to wake up the system from a
power saving mode.
Press <Esc> to return to the IRQ/Event Activity Detect pages
Page 44

3-17
Resources Controlled By [Auto(ESCD)]
You should leave this item at the default Auto (ESCD). Under this setting, the
system dynamically allocates resources to Plug and Play devices as they are
required.
If you cannot get a legacy ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) expansion card to
work properly, you might be able to solve the problem by changing this item to
Manual, and then opening up the IRQ Resources submenu.
IRQ Resources [Press Enter]
In the IRQ Resources submenu, if you assign an IRQ to Legacy ISA, then that
Interrupt Request Line is reserved for a legacy ISA expansion card. Press <Esc> to
close the IRQ Resources submenu.
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop [Disabled]
This item is designed to overcome problems that can be caused by some nonstandard VGA cards. This board includes a built-in VGA system that does not require
palette snooping so you must leave this item disabled.
Assign IRQ For USB [Enabled]
Names the interrupt request (IRQ) line assigned to the USB on your system.
Activity of the selected IRQ always awakens the system.
3.3-7 PC Health Status
On motherboards that support hardware monitoring, this item lets you
monitor the parameters for critical voltages, temperatures and fan speeds.
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
PC Health Status
Shutdown Temperature [Dis abled]
CPU Vcore
3.30 V
5.00 V
+12 V
Voltage Battery
Current System Temp
Current CPU Temp
CPUFAN1 Speed
CASFAN1 Speed
Item Help
Menu Level
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
Shutdown Temperature [Disabled]
Enables you to set the maximum temperature the system can reach before powering
down.
System Component Characteristics
These fields provide you with information about the systems current operating
status. You cannot make changes to these fields.
Page 45

3-18
Auto Detect PCI/DIMM Clk (Enabled)
When this item is enabled, BIOS will disable the clock signal of free DIMM and PCI
slots.
Spread Spectrum (Enabled)
If you enable spread spectrum, it can significantly reduce the EMI (Electro-Magnetic
Interference) generated by the system.
Async AGP clock control (Disabled)
This item allows you to set the AGP clock in asynchronous status.
Hammer Fid control (StartUp)
This item allows you to adjust CPU frequency ID.
Hammer Vid control (StartUp)
This item allows you to adjust CPU voltage ID.
CPU Clock(200MHz)
This item allows you to adjust the CPU clock to 200Mhz to 511MHz. You can key-in the
numbers within the range to make a precise and ideal adjustment.
Turbo Performance (Disabled)
This function only works when loading performance Defaults setting.
3.3-8 Frequency/Voltage Control
This item enables you to set the clock speed and system bus for your system.
The clock speed and system bus are determined by the kind of processor
you have installed in your system.
DIMM Voltage Adjust [2.60V]
AGP Voltage Regulator [1.53V]
Auto Detect PCI Clk [Enabled]
Spread Spectrum [Enabled]
Async AGP clock control [Disabl ed]
Hammer Fid control [StartUp]
Hammer Vid control [StartUp]
CPU Clock [200MHz]
Turbo Performance [Di sabled]
Item Help
Menu Level
F5:Previous Values F6:Performance Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Frequency/Voltage Control
DIMM Voltage Adjust (2.60V)
This item adjusts the voltage delivered to the DIMM memory.
AGP Voltage Regulator (1.53V)
This item regulates the voltage delivered to the AGP.
Page 46

3-19
3.3-9 Load Performance Defaults
This option opens a dialog box that lets you install performance defaults for
all appropriate items in the Setup Utility: Press <Y> and the <Enter> to
install the defaults. Press <N> and then <Enter> to not install the defaults.
If you want to make your system for greater effectiveness, then install the
performance defaults. If you only want to install performance defaults for
a specific option, select and display that option, and then press <F6>.
3.3-10 Load Optimized Defaults
This option opens a dialog box that lets you install optimized defaults for all
appropriate items in the Setup Utility. Press <Y> and then <Enter> to
install the defaults. Press <N> and then <Enter> to not install the defaults. The optimized defaults place demands on the system that may be
greater than the performance level of the components, such as the CPU
and the memory. You can cause fatal errors or instability if you install the
optimized defaults when your hardware does not support them. If you only
3.3-11 Set Supervisor/User Password
When this function is selected, the following message appears at the center
of the screen to assist you in creating a password.
ENTER P ASSWORD
Type the password, up to eight characters, and press <Enter>. The password
typed now will clear any previously entered password from CMOS memory.
You will be asked to confirm the password. Type the password again and
press <Enter>. You may also press <Esc> to abort the selection.
To disable password, just press <Enter> when you are prompted to enter
password. A message will confirm the password being disabled. Once the
password is disabled, the system will boot and you can enter BIOS Setup
freely.
PASSWORD DISABLED
If you have selected “System” in “Security Option” of “BIOS Features
Setup” menu, you will be prompted for the password every time the system
reboots or any time you try to enter BIOS Setup.
If you have selected “Setup” at “Security Option” from “BIOS Features
Setup” menu, you will be prompted for the password only when you enter
BIOS Setup.
want to install setup defaults for a specific option, select and display that
option, and then press <F7>.
Notes: To load performance defaults may make system unstable or unbootable.
Page 47

3-20
Supervisor Password has higher priority than User Password. You can use
Supervisor Password when booting the system or entering BIOS Setup to
modify all settings. Also you can use User Password when booting the
system or entering BIOS Setup but can not modify any setting if
Supervisor Password is enabled.
3.3-12 Save & Exit Setup
Highlight this item and press <Enter> to save the changes that you have
made in the Setup Utility and exit the Setup Utility. When the Save and
Exit dialog box appears, press <Y> to save and exit, or press <N> to
return to the main menu.
3.3-13 Exit Without Saving
Highlight this item and press <Enter> to discard any changes that you have
made in the Setup Utility and exit the Setup Utility. When the Exit Without
Saving dialog box appears, press <Y> to discard changes and exit, or press
<N> to return to the main menu.
Note: If you have made settings that you do not want to save, use the “Exit Without Saving”
item and press <Y> to discard any changes you have made.
Page 48

Chapter 4
This chapter delivers contents of the ECS support CD.
Page 49

4.1 Software CD Information...................................4-1
4.2 Running the Software CD..................................4-1
4.3 Setup T ab..........................................................4-1
4.4 Application Tab..................................................4-2
4.5 Read Me T ab....................................................4-2
4.6 Software Utilities Introduction............................4-2
Reference
Page 50

4-1
4.1 Software CD Information
The support software CD-ROM that is included in the motherboard package
contains all the drivers and utility programs needed to properly run the
bundled products. Below you can find a brief description of each software
program, and the location for your motherboard version. More information
on some programs is available in a README file, located in the same
directory as the software.
Note: Never try to install software from a folder that is not specified for use with your
motherboard.
4.3 Setup Tab
The setup tab shows three buttons - Setup, Browse CD, Exit.
Setup button: Click the Setup button to run the software installation
program. Select from the menu which software you want
to install.
1. Click
Setup
. The installation program begins:
4.2 Running the Software CD
To begin using the software CD, simply insert the CD into your CD-ROM
drive. The CD automatically display the multimedia if auto run is enable in
your computer.
Note: The following screens are examples only. The screens and driver lists will be different
according to the motherboard you are installing.
The motherboard identification is located in the upper left-hand
corner.
Page 51

4-2
2. Click
Next
. The following screen appears:
3. Check the box next to the items you want to install. The default options are
recommended.
4. Follow the instructions on the screen to install the items.
Drivers and software are automatically installed in sequence. Follow
the onscreen instructions, confirm commands and allow the computer
to restart a few times to complete the installation.
Browse CD button: The Browse CD button is the standard Windows
command that allows you to open Windows
Explorer and show the contents of the support
CD.
Exit button: The Exit button closes the Auto Setup window.
4.4 Application Tab
Lists the software utilities that are available on the CD.
4.6 Software Utilities Introduction
4.5 Read Me Tab
Displays the path for all software and drivers available on the CD.
AWARD Flash Memory Utility
This utility lets you erase the system BIOS stored on a Flash Memory
chip on the motherboard, and lets you copy an updated version of the
BIOS to the chip. Proceed with caution when using this program. If you
Page 52

4-3
erase the current BIOS and fail to write a new BIOS, or write a new
BIOS that is incorrect, your system will malfunction. Refer to Chapter 3
“Using BIOS” for more information.
WinFlash Utility
The AWARD WinFlash utility is a Windows version of the DOS Award
BIOS flash writer utility. The utility enables you to flash the system BIOS
stored on a Flash Memory chip on the motherboard while in a Windows
environment. This utility is currently available for WINXP\ME\2000\
98SE. To install the WinFlash utility, rin WINFLASH.EXE from the
following directory: \UTILITY\WINFLASH
MediaRing Talk - Telephony Software
Go to \UTILITY\MEDIARING EZ NET and run SETUP 331.EXE to
install the MediaRing Talk voice modem software for the built-in
modem.
WinCinema
WinDVD Creator Plus
WinDVD Creator Plus is designed for people who want to make their own
DVDs but who don’t want to learn complicated programs. By taking you
through 4 DVD-making steps, WinDVD Creator Plus walks you through
capturing video, editing it, adding titles, transitions, effects, music, DVD
menus and finally burning the finished product. User also can direct-burn
to DVD when DVD burner is available.
WinDVD
WinDVD is the world’s most popular DVD player and supports over 30 new
features and enhancements such as improved picture quality, easier-to-use
Time-Stretching, MP3 playback, and Video Desktop - which lets you watch
movies under your desktop icons while you work or check email.
WinRIP
WinRIP lets you record, store, organize, and enjoy you music collection on your PC, CD player, and portable player. Organize your Music Galleryand
create your own playlists. You can switch between simple Player mode or
full-featured Jukebox mode.
Page 53

4-4
Pro Magic
This amazing software not only provides users with convenient and instant
restoration of your computer, but also restores within seconds important
data back to the preferred state at a specific point in time. Pro Magic also
combines several other functions including anti-virus, backup, uninstall
software and multi-booting to satisfy all your system protection needs.
DPU (Data Process Utility)
Specially designed for file protection, security and management this DPU
or data processing utility insures the safety of important data through
complete file restoration, eliminating file damage even in case of improper
operation. User can freely edit original files after a set restore time point.
The DPU can even restore even deleted files.
Adobe Reader
This item install the Adobe Acrobat Reader. The Acrobat Reader software
is for viewing files saved in Portable Document Format (PDF).
Show Shifter
ShowShifter, the award winning software, combines viewing TV, video,
CD, MP3 and digital pictures into one easy to use application. With a little
help from Showshifter your PC will be the ultimate home media center.
Extreme Utilities
Omni-Guardian
Omni-Guardian is a self-diagnostic utility for PC system. It will protect PC
hardware by monitoring several critical items including power supply voltage, CPU Fan speed, and CPU & System temperature. These are all impor-
tant to Windows System. Some errors maybe result in permanent hurt of
your system. User could set the reasonable range. Once when system monitors some being out of range, an obvious warning or beeping message will
remind users to make a proper treatment. Omni-Guardian only supports
under Window 2000/XP.
Fuzzy Over Clocking
Fuzzy Over Clocking is a utility that allow users to over clock your CPU
speed. It only supports under Windows 2000/XP.
EZ-Flash
EZ-Flash provide users an easy-to-use tool which can maintain the BIOS
easily. Also, it has two major functions, one is to save the current BIOS, the
Smart LAN
The motherboard support Marvell Virtual Cable Tester (VCT) technology.
It enables end users to remotely diagnose the quality and characteristics of
the attached cable. With this feature it is possible to detect and report
potential cabling issues such as cable opens, cable shorts, and impedance
mismatches. The distance of the fault can be reported within one meter.
Page 54

4-5
other is to update a new BIOS. EZ-Flash only supports under Windors
2000/XP.
MyPic
User can build their own BIOS image which will display a customized
picture at the boot-up time. MyPic only supports Windows 2000/XP which
is an application to make a rom file.
Page 55

Chapter 5
In this chapter, you will learn how to create Serial
ATA/Ultra RAID and the type of RAID we support.
Page 56

5.1 VIA RAID Configurations.................................5-1
5.1-1 Install the Serial ATA (SATA) hard disks.............5-1
5.1-2 Entering VIA T ech RAID BIOS Utility ...................5-2
5.1-3 Create Array ..............................................................5-3
5.1-4 RAID 0 for performance...........................................5-3
5.1-5 RAID 1 for data protection.....................................5-4
5.1-6 Delete Array...............................................................5-5
5.1-7 Select Boot Array ......................................................5-5
5.1-8 Serial Number V iew ..................................................5-6
5.1-9 Duplicate Critical RAID 1 Array ...........................5-6
5.1-10Rebuild Broken RAID 1 Array ................................5-7
5.2 Installing RAID Software & Drivers..................5-8
5.2-1 Install Driver in W indows OS.................................5-8
5.3 Using VIA RAID Tool................................5-10
5.4 Introduction for SiS180 RAID Function..........5-13
5.4-1 Serial/Ultra AT A RAID Interfaces..........................5-13
5.5 Features.........................................................5-13
Reference 5.6 Support Operating Systems.............................5-13
5.7 What is RAID.................................................5-14
5.8 Installing Software Drivers...............................5-14
5.8-1 New W indows 2000/XP Installation...................5-14
5.8-2
5.8-3
5.8-4
5.9 BIOS Utility Operation...................................5-15
5.9-1 Starting BIOS Utility..............................................5-15
5.9-2 Creating RAID........................................................5-16
5.9-3
5.9-4 Creating a RAID 1 (Mir ror) Array ......................5-19
5.9-5 Creating a JBOD Array .........................................5-20
5.9-6 Creating a RAID 0+1 (Stripe-Mirror) Array....5-21
Existing Windows 2000/XP/98/Me
Installation..............................................................5-15
Confirming Windows 2000/XP Driver Installa-
tion............................................................................5-15
Confirming Windows 98/Me Driver Installa-
tion............................................................................5-15
Creating a RAID 0 (Stripe) Array for Perfor-
mance........................................................................5-16
Page 57

5-1
5.1 VIA RAID Configurations
The motherboard includes a high performance Serial ATA RAID controller
integrated in the VIA VT8237 Southbridge chipset. It supports RAID 0,
RAID 1 and JBOD with two independent Serial ATA channels.
RAID: (Redundant Array of Independent Disk Drives) use jointly several
hard drives to increase data transfer rates and data security. It depends on the
number of drives present and RAID function you select to fulfill the seurity
or performance purposes or both.
RAID 0: (called data striping) optimizes two identical hard disk drives to
read and write data in parallel, interleaved stacks. Two hard disks perform
the same work as a single drive but at a sustained data transfer rate, double
that of a single disk alone, thus improving data access and storage.
RAID 1: (called data mirroring) copies and maintains an identical image of
data from one drive to a second drive. If one drive fails, the disk array
management software directs all applications to the surviving drive as it
contains a complete copy of the data in the other drive. This RAID
configuration provides data protection and increases fault tolerance to the
entire system.
JBOD: (Just a Bunch of Drives) Also known as “Spanning”. Two or more
hard drives are requried. Several hard disk types configured as a single hard
disk. The hard drives are simply hooked up in series. This expands the
capacity of your drive and results in a useable total capacity. However,
♦ If you are creating a RAID 0 (striping) array of performance, use two
new drives.
♦
5.1-1 Install the Serial ATA (SATA) hard disks
The VIA VT8237 Southbridge chipset supports Serial ATA hard disk drives.
For optimal performance, install identical drives of the same model and
capacity when creating a RAID set.
If you are creating a RAID 1 (mirroring) array for protection, you can
use two new drives or use an existing drive and a new drive (the new
drive must be of the same size or larger than the existing drive). If you
use two drives of different sizes, the smaller capacity hard disk will be
the base storage size. For example, one hard disk has an 80GB storage
capacity and the other hard disk has 60GB storage capacity, the maximum storage capacity for the RAID 1 set is 60GB. The SATA hard disks
only support data backup, not support boot device.
JBOD will not increase any performance or data security.
Both the data and power SATA cables are new cables. You cannot use
older 40-pin 80-conductor IDE or regular IDE power cables with Serial
ATA drives. Installing Serial ATA (SATA) hard disks require the use of
ii
Follow these steps to install the SATA hard disks for RAID configuration.
i
Before setting up your new RAID array, verify the status of your hard
disks. Make sure the Master/Slave jumpers are configured properly.
Page 58

5-2
5.1-2 Entering VIA Tech RAID BIOS Utility
1 Boot-up your computer
2 During POST, press <TAB> to enter VIA RAID configuration util-
ity. The following menu options will appear.
Note: The RAID BIOS information on the setup screen shown is for reference only. What
you see on your screen may not by exactly the same as shown.
On the upper-right side of the screen is the message and legend box. The
keys on the legend box allow you to navigate through the setup menu options. The message describes the function of each menu item. The following
lists the keys found in the legend box with their corresponding functions.
new Serial ATA cable (4-conductor) which supports the Serial ATA
protocol and a Serial ATA power cable.
Either end of the Serial ATA data cable can be connected to the SATA
hard disk or the SATA connector on the motherboard.
iii
1 Install the Serial ATA hard disks into the drive bays.
2 Connect one end of the Serial ATA cable to the motherboard’s
primary Serial ATA connector (SATA1).
3 Connect the other end of Serial ATA cable to the master Serial ATA
hard disk.
4 Connect one end of the second Serial ATA cable to the motherboard’s
secondary Serial ATA connector (SATA2)
5 Connect the other end of Serial ATA cable to the secondary Serial
ATA hard disk.
Note: Please note that SiS180 does not support hot plug function.
6 Connect the Serial ATA power cable to the power connector on
each drive.
7 Proceed to section “Entering VIA Tech RAID BIOS Utility” for the
next procedure.
Page 59

5-3
2 Select RAID 0 for performance from the menu and press <En-
ter>. From this point, you may choose to auto-configure the RAID
array by selecting Auto Setup for Performance or manually configure the RAID array for stripped sets. If you want to manually
configure the RAID array continue with next step, otherwise, proceed to step #5.
3 Select Select Disk Drives, then press <Enter>. Use arrow keys to
select disk drives, then press <Enter> to mark selected drive. An
asterisk is placed before the selected drive.
4 Select Block Size, then press <Enter> to set array block size. Lists
of valid array block sizes are displayed on a pop-up menu.
Tip For server system, it is recommended to use a lower
array block size. For multimedia computer system
used mainly for audio and video editing, a higher array
block size is recommended for optimum performance.
F1 View Array
↑↓
Move to the next item
Enter Confirm the selection
ESC Exit
5.1-3 Create Array
1 In the VIA RAID BIOS utility main menu, select Create Array
then press the <Enter> key. The main menu items on the upperleft corner of the screen are replaced with create array menu options.
5.1-4 RAID 0 for performance
1 Select the second option item Array Mode, then press the <Enter>
key. The RAID system setting pop-up menu appears.
Page 60

5-4
2 Select RAID 1 for data protection from the menu and press <En-
ter>. Select next task from pop-up menu. The task Create only
creates the mirrored set without creating a backup. Create and
duplicate creates both mirrored set and backup.
3 Select task and press <Enter>. The screen returns to Create Array
menu items. From this point, you may choose to auto-configure
the RAID array by selecting Auto Setup for Data Security or manually configure the RAID array for mirrored sets. If you want to
manually configure the RAID array continue with next step, otherwise, proceed to step #5.
4 Select Disk Drives, then press <Enter>. Use arrow keys to select
disk drive/s, then press <Enter> to mark selected drive. (An asterisk is placed before a selected drive.)
5 Select Start Create Process and press <Enter> to setup hard disk for
RAID system. The following confirmation message appears:
The same confirmation message appears when
the Auto Setup for Performance option is selected.
5 Select Start Create Process and press <Enter> to setup hard disk for
RAID system. The following confirmation appears:
The same confirmation message appears when
the Auto Setup for Performance option is selected.
Press “Y” to confirm or “N” to return to the configuration options.
5.1-5 RAID 1 for data protection
1 Select the second option item Array Mode, then press the <Enter>
key. The RAID system setting pop-up menu appears.
Use arrao keys to move selection bar on items and press <Enter> to select.
Page 61

5-5
Press “Y” to confirm or “N” to return to the configuration options.
5.1-6 Delete Array
Press “Y” to confirm or “N” to return to the configuration options.
1 In the VIA RAID BIOS utility main menu, select Delete Array
then press the <Enter> key. The focus is directed to the list of
channel used for IDE RAID arrays.
2 Press the <Enter> key to select a RAID array to delete. The
following confirmation message appears.
5.1-7 Select Boot Array
1 In the VIA RAID BIOS utility main menu, select Boot Array then
press the <Enter> key. The focus is directed to the list of channel
used for IDE RAID arrays.
2 Press the <Enter> key to select a RAID array for boot. The Status
of the selected array will change to Boot. Press <ESC> key to go
return to menu items. Follow the same procedure to deselect the
boot array.
Page 62

5-6
.
5.1-9 Duplicate Critical RAID 1 Array
When booting up the system, BIOS will detect if the RAID 1 array has any
inconsistencies between user data and backup data. If BIOS detects any
inconsistencies, the status of the disk array will be marked as critical, and
BIOS will prompt the user to duplicate the RAID 1 in order to ensure the
backup data consistency with the user data.
If user selects Continue to boot, it will enable duplicating the array after
booting into OS.
5.1-8 Serial Number View
1 In the VIA RAID BIOS utility main menu, select Serial Number View
then press the <Enter> key. The focus is directed to the list of
channel used for IDE RAID arrays. Move the selection bar on each
item and the serial number is displayed at the bottom of the screen.
This option is useful for identifying same model disks.
Page 63

5-7
5.1-10 Rebuild Broken RAID 1 Array
When booting up the system, BIOS will detect if any member disk drives of
RAID has failed or is absent. If BIOS detects any disk drive failures or
missing disk drives, the status of the array will be marked as broken.
If BIOS detects a broken RAID 1 array but there is a spare hard drive
available for rebuilding the broken array, the spare hard drive will automatically become the mirroring drive. BIOS will show a main interface just like
a duplicated RAID 1. Selecting Continue to boot enables the user to
duplicate the array after booting into operating system.
If BIOS detects a broken RAID 1 array but there is no spare hard drive
available for rebuilding the array, BIOS will provide several operations to
solve such problems.
1. Power off and Check the Failed Drive:
This item turns off the computer and replaces the failed hard drive with a
good one. If your computer does not support APM, you must turn off your
computer manually. After replacing the hard drive, boot into BIOS and
select Choose replacement drive and rebuild to rebuild the broken
array.
Page 64

5-8
2. Destroy the Mirroring Relationship:
This item cancels the data mirroring relationship of the broken array. For
broken RAID 1 arrays, the data on the surviving disk will remain after the
destroy operation. However, Destroy the Mirroring Relationship is not
recommended because the data on the remaining disk will be lost when the
hard drive is used to create another RAID 1 array.
3. Choose Replacement Drive and Rebuild:
This item enables users to select an already-connected hard drive to rebuild
the broken array. After choosing a hard drive, the channel column will be
activated.
Highlight the target hard drive and press <Enter>, a warning message will
appear. Press Y to use that hard drive to rebuild, or press N to cancel. Please
note selecting option Y will destroy all the data on the selected hard drive.
4. Continue to boot:
This item enables BIOS to skip the problem and continue booting into OS.
5.2 Installing RAID Software & Drivers
5.2-1 Install Driver in Windows OS
New Windows OS (2000/XP/NT4) Installation
The following details the installation of the drivers while installing Windows XP.
1 Start the installation:
Boot from the CD-ROM. Press F6 when the message “Press F6 if
you need to install third party SCSI or RAID driver’ appears.
2 When the Windows Setup window is generated, press S to specify
an Additional Device(s).
3 Insert the driver diskette VIA VT8237 Disk Driver into drive A: and
press <Enter>.
4 Depending on your operation system, choose VIA Serial ATA RAID
Controller (Windows XP), VIA Serial ATA RAID Controller
(Windows 2000) or VIA Serial ATA RAID Controller (Windows NT4)
Page 65

5-9
Existing Windows XP Driver Installation
1 Insert the ECS CD into the CD-ROM drive.
2 The CD will auto-run and the setup screen will appear.
3 Under the Driver tab, click on VIA SATA RAID Utility.
4 The drivers will be automatically installed.
Confirming Windows XP Driver Installation
1 From Windows XP, open the Control Panel from My Computer
followed by the System icon.
2 Choose the Hardware tab, then click the Device manager tab.
3 Click the “+” in front of the SCSI and RAID Controllers hard-
ware type. The driver VIA IDE RAID Host Controller should
appear.
from the list that appears on Windows XP Setup screen, press the
<Enter> key.
5 Press <Enter> to continue with installation or if you need to specify
any additional devices to be installed, do so at this time. Once all
devices are specified, press <Enter> to continue with installation.
6 From the Windows XP Setup screen press the <Enter> key. Setup
will now load all device files and the continue the Windows XP
installation.
Installation of VIA SATA RAID Utility
The VIA SATA RAID Utility is the software package that enables high-performance RAID 0 arrays in the Windows*XP operating system. This version of
VIA SATA RAID Utility contains the following key features:
• Serial ATA RAID driver for Windows XP
• VIA SATA RAID utility
• RAID0 and RAID1 functions
Insert the ECS CD and click on the Setup to install the software.
Page 66

5-10
The InstallShield Wizard will begin automatically for installation. Click
on the Next button to proceed the installation in the welcoming window.
5.3 Using VIA RAID Tool
Put a check mark in the check box to install the feature you want. Then click
Next button to proceed the installation.
Once the installation is complete, go to Start---> Programs---> VIA--->
raid_tool.exe to enable VIA RAID Tool.
After the software is finished installation, it
will automatically started every time Windows
is initiated. You may double-click on the
icon shown in the system tray of the tool
bar to launch the VIA RAID Tool utility.
Page 67

5-11
The main interface is divided into two windows and the toolbar above
contain the main functions. Click on these toolbar buttons to execute their
specific functions. The left windowpane displays the controller and disk
drives and the right windowpane displays the details of the controller or disk
drives. The available features are as following:
View by Controller
View by Devices
View Event log
Help Topics
It means that VT8237 SATA RAID only has the feature of monitoring
the statuses of RAID 0 and RAID 1.
Click on or button to determine the viewing type of left
windowpane. There are two viewing types: By controllers and by device.
Click on the object in the left windowpane to display the status of the object
in the right windowpane. The following screen shows the status of Array 0RAID 0.
Click on the plus (+) symbol next to Array 0--RAID 0 to see the details of
each disk.
Page 68

5-12
You may also use the same or button to view the statuses of
Array 0--RAID 1.
Click on the plus (+) symbol next to Array 0; RAID 1 to see the details of
each disk.
Page 69

5-13
5.4 Introduction for SiS180 RAID Function
The 180 S-ATA controller is a hybrid solution that combines two
independent SATA ports and one Ultra ATA port for support of up to two
Serial ATA (Serial ATA RAID) and two Ultra ATA (Ultra ATA RAID)
drives.
5.4-1 Serial/Ultra ATA RAID Interfaces
The Serial/Ultra ATA RAID is designed to provide a cost-effective, high
performance RAID solution that adds performance and/or reliability to PC
desktops and/or servers using Serial ATA/150, Ultra ATA/133, Ultra
ATA/100, Ultra ATA/66 hard disks.
Serial/Ultra ATA RAID function supports striping (RAID 0), mirroring
(RAID 1), striping + mirroring (RAID 0+1) and span (JBOD). Please note
that the function supports hard disk drives only and the 964 S-ATA controller
don’t support Striping + mirroring (Raid 0+1).
With striping, identical drives can read and write data in parallel to increase
performance. Mirroring increases read performance through load balancing
and elevator sorting while creating a complete backup of your files. Span
would increase the logic hard disk space.
Serial/Ultra ATA RAID striped arrays can double the sustained data transfer
rate of Serial ATA/150 and Ultra ATA/133 drives. Serial/Ultra ATA
RAID fully supports Serial ATA/150 and Ultra ATA/133 specification of
up to 150MB/sec per drive, depending on individual drive specifications.
5.5 Features
♦ The SiS 180 controller support two Serial ATA (Serial ATA RAID)
and two Ultra ATA (Ultra ATA RAID) drives.
♦ Support RAID function: RAID 0, RAID 1, JBOD and RAID 0+1.
(RAID 0+1 function can be used by 180 controller with all hard
drivers on it.)
♦ Support bootable disk except for RAID 0+1.
♦ Windows-based RAID Utility software tool (only support Windows
XP and 2000).
♦ BIOS Utility.
5.6 Support Operating Systems
Support Microsoft Windows 98/98SE/ME/2000 Professional and Server/
XP.
Note: Please note that RAID 0+1 use 4 devices. (2 parallel devices and 2 SATA deviecs. )
Page 70

5-14
5.7 What is RAID?
This section will give you an overview about the RAID system and introduce
the basic background and glossary which you need to know before using
“SiS RAID Controller Application”.
1. RAID: (Redundant Array of Independent Disk Drives) use jointly
several hard drives to increase data transfer rates and data security. It
depends on the number of drives present and RAID function you
select to fulfill the security or performance purposes or both.
2. RAID 0: Also known as “Stripping”. All of the data are distributed
evenly to all of the existing drives. You gain benefits on performance
because the data transfer rate is multiplied by the number of drives.
However, RAID 0 has high risks of data security. All of the stored
data will be lost if even any one drive in the RAID set crashes.
3. RAID 1: Also known as “Mirroring”. Two hard drives are required.
The goal of RAID 0 is to ensure data security. Data is written to two
or more drives synchronously. That is, 100% duplication of data
from one drive to another.
4. RAID 0+1: Also known as “StripeMirror”. At least four hard drives
are required. RAID 0+1 is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1.
Data is striped into two drives then mirrored. It provides high
performance and high data protection. This is a costly solution as
RAID 1 because the two mirrored drives represent an expensive
insurance.
5. JBOD: (Just a Bunch of Drives). Also known as “Spanning”. Two or
more hard drives are required. Several hard disk types configured as a
single hard disk. The hard drives are simply hooked up in series. This
expands the capacity of your drive and results in a useable total
capacity. However, JBOD will not increase any performance or data
security.
5.8 Installing Software Drivers
SiS provides RAID driver for SiS180 SATA with RAID function.
1. For RAID function, SiS180 support RAID0, RAID1, RAID 0+1
and JBOD.
5.8-1 New Windows 2000/XP Installation
1. Start the installation:
Boot from the CD-ROM. Press F6 when the message “Press F6 key
if you need to install third party SCSI or RAID driver” appears.
2. When the Windows 2000/XP Setup window is generated, press S
key to specify an Additional Device(s).
3. Insert the driver diskette into drive A: and press Enter.
4. Choose one of the following items:
“WinXP SiS Raid/IDE Controller”
,
“Win2000 SiS Raid/IDE Controller”
,
Page 71

5-15
that appears on screen, and then press the Enter key.
5. Press Enter to continue with installation or if you need to specify
any additional devices to be installed, do so at this time. Once all
devices are specified, Press Enter to continue with installation.
6. From the Windows 2000/XP Setup screen, press the Enter key.
Setup will now load all device files and then continue the Windows
2000/XP installation.
7. Please install the driver package again (ex. SiS RAID driver v1.00)
while the operation system has been setup.
Remark: If you would like to install windows to any RAID set, you should create RAID
from BIOS utility or SiS180 RAID Utility first and then follow the steps
above.
5.8-2 Existing Windows 2000/XP/98/Me Installation
1. Install the driver by executing SiS driver setup utility.
2. The drivers will be automatically installed.
5.8-3 Confirming Windows 2000/XP Driver Installation
1. From Windows 2000/XP, open the Control Panel from “My
Computer” followed by the System icon.
2. Choose the “Hardware” tab, then click the “Device Manager” tab.
3. Click the “+” in front of “SCSI and RAID Controllers” hardware
type. The driver “SiS 180 Raid Controller” should appear.
5.8-4 Confirming Windows 98/Me Driver Installation
1. From Windows 98/Me, open the Control Panel from “My Computer” followed by the System icon.
2. Choose the “Device Manager” tab.
3. Click the “+” in front of “IDE ATA/ATAPI Controllers” hardware
type. The driver “SiS 180 IDE Dual Channel” and “SiS 180 IDE/
RAID Controller” should appear.
5.9 BIOS Utility Operation
BIOS Utility supports windows 2000/XP/98/Me.
5.9-1 Starting BIOS Utility
1. Boot your system. If this is the first time you have booted with the
SiS180 and the drives installed, the BIOS will display the
following:
2. Press <Ctrl-S> keys to display the SiS 964/180 Utility Main Menu.
Silicon Integrated Systems Corp. RAID BIOS Setting Utility v0.XX
(c) 2003-2005 Silicon Integrated Systems Corp. All Rights Reserved.
Press <Ctrl.<S> to run BIOS Setting Utility
Page 72

5-16
3. You can press <B> key to select the boot disk on the 180 controller.
The yellow highlight will show on the disk and you can switch it to
select the disk you wanted. Press “Enter” key to select it and the
selected boot device will be marked by “*”. The default boot device
will be set as Disk 1.
4. Press <R> to display the RAID setup menu below. This is the fastest
and easiest method to creating your first array.
5.9-2 Create RAID
♦ SIS 180 controller support RAID 0, RAID 1, JBOD and RAID 0+1.
5.9-3 Creating a RAID 0 (Stripe) Array for Performance
♦ SIS 180 enables users to create striped arrays with 2, 3, or 4 drives.
To create an array for best performance, follow these steps:
1. Press <A> to start creating a RAID array.
2. Press <2> and <Enter> to select RAID 0.
3. You will have two selections to create a RAID 0 array. The default
value is <1>. If you select <1>Auto Create, you can create a
RAID 0 array faster and easier. The Blocksize will be selected by its
default value “64K”. The result after creating will be show on step
Page 73

5-17
5. Use <> <> to select disk, and press <Enter> to select disk, <Q>
to exit. When you press <Enter> on the disk you wanted, the RAID
Type will be changed from Single to RAID 0. An the disk you select
first will be the SOURCE disk.
6. Next, you will see a message “Split the SOURCE(DISK x) data to
RAID disks?”. Press <N> and <Enter> to create RAID 0 array only
or press <Y> and <Enter> to split the data from source disk to
other disks
4. Press <1>-<5> keys and <Enter> to select Block Size.
(Default:64K)
8. Besides, you also can select <2>Manual Create, see following
steps.
Page 74

5-18
.
9. Press <Q> again to exit this BIOS utility and the red message frame
will show. Press <Y> and <Enter> to save changes.
10. Once the array has been created, you will need to FDISK and format
the array as if it were a new single hard drive.
7. Starting splitting action, the following frame will be shown.
8. After all steps finished, press ,<Q> until escape the setup menu and
RAID 0 array will be show on the top of the main frame.
Page 75

5-19
5.9-4 Creating a RAID 1 (Mirror) Array
♦ SIS180 enables users to create Mirror arrays with 2 drives only.
To create a Mirror array, follow these steps:
1. Press <A> to start creating a RAID array.
2. Press <3> and <Enter> to select Mirror.
3. You will have two selections to create a RAID 1 array. The default
value is <1>. If you select <1>Auto Create, you can create a
RAID 1 array faster and easier. The result after creating will be show
on step 7. Besides, you also can select <2>Manual Create, see
following steps.
4. Use <> <> to select disk, and press <Enter> to select disk, <Q>
to exit. When you press <Enter> on the disk you wanted, the RAID
Type will be changed from Single to RAID 1. The same as RAID 0,
the disk you select first will be the SOURCE disk.
5. Next, you will see a message “Duplicate the SOURCE (DISK x) data
to RAID disks?”. Press <N> and <Enter> to create RAID 1 array
only or press <Y> and <Enter> to duplicate the data from source
disk to mirror disk.
Page 76

5-20
8. Press <Q> again to exit this BIOS utility and the red message frame
will show as the same as the creation of the RAID 0 array. Press <Y>
and <Enter> to save changes.
9. Once the array has been created, you will need to FDISK and format
the array as if it were a new single hard drive.
5.9-5 Creating a JBOD Array
♦ SIS180 enables users to create JBOD arrays with 2, 3, or 4 drives.
To create an JBOD array, follow these steps:
1. Press <A> to start creating a RAID array.
2. Press <1> and <Enter> to select JBOD.
3. You will have two selections to create a JBOD array. The default
value is <1>. If you select <1>Auto Create, you can create a
JBOD array faster and easier. The result after creating will be show
7. After all steps finished, press <Q> until escape the setup menu and
RAID 1 array will be show on the top of the main frame.
6. Starting duplicating action, the following frame will be showing.
Page 77

5-21
on step 5. Besides, you also can select <2>Manual Create, see
following steps.
5. After all steps finished, press <Q> until escape the setup menu and
JBOD array will be show on the top of the main frame.
6. Press <Q> again to exit this BIOS utility and the red message frame
will show as the same age as the creation of the RAID 0 array. Press
<Y> and <Enter> to save changes.
7. Once the array has been created, you will need to FDISK and format
the array as if it were a new single hard drive.
5.9-6 Creating a RAID 0+1 (Stripe-Mirror) Array
♦ SIS180 supports Stripe-Mirror array with 4 drives.
To create an Stripe-Mirror array, follow these steps:
1. Press <A> to start creating a RAID array.
2. Press <4> and <Enter> to select RAID 0+1.
4. Use <> <> to select disk, and press <Enter> to select disk, <Q>
to exit. When you press <Enter> on the disk you wanted, the RAID
Type will be changed from Single to JBOD.
Page 78

5-22
3. You will have two selections to create a RAID 0+1 array. The
default value is <1>. If you select <1>Auto Create, you can
create a RAID 0+1 array faster and easier. The result after creating
will be show on step 6. Besides, you also can select <2>Manual
Create, see following steps.
4. Use <1>-<5> keys and <Enter> to select Block Size. (Default: 64K)
5. Use <> <> to select disk, and press <Enter> to select disk. <Q>
to exit. When you press <Enter> on the disk you wanted, the RAID
Type will be changed from Single to RAID 0+1.
6. After all steps finished, press <Q> until escape the setup menu and
RAID 0+1 array will be show on the top of the main frame.
Page 79

5-23
7. Press <Q> again to exit this BIOS utility and the red message frame
will show as the same as the creation of the RAID 0 array. Press <Y>
and <Enter> to save changes.
Remark: On DOS, it can’t support RAID 0+1 function. So you can’t use FDISK to format
the array as if it were a new single hard driver. If you want to format this single
hard driver, you must need to use disk manager of OS to format it.
Page 80

Français
Résumé des caractéristiques
CPU
Chipset
• VIA K8T800 PRO & 8237
• North Bridge: VIA K8T800 PRO
• South Bridge: VIA 8237
Mémoire
Options
d’extension
• 1 x logement AGP 8X/4X
• 5 x logements PCI
Stockage
• Pris en charge par VIA8237
- 4 x périphériques Ultra DMA133/100/66
- 2 x périphériques SATA
- Conguration RAID 0 et RAID 1
• Pris en charge par SiS180
- 2 x périphériques Ultra DMA133/100/66
- 2 x périphériques SATA
- Conguration RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1
IEEE 1394a
• Contrôleur VIA VT6307 IEEE1394a
• Prend en charge 2 x connecteurs IEEE1394a
Audio
• CODEC audio Realtek ALC655 6-canaux
• Conforme aux spécications AC’97 2.3
LAN Double
• Contrôleur LAN Gigabit Marvel 88E8001
• PHY Fast Ethernet VIA VT6103L 10/100 Mbps
E/S du
panneau
arrière
• 1 x Clavier PS/2
• 1 x connecteur souris PS/2
• 4 x ports USB
• 2 x connecteurs LAN RJ45
• 1 x Port Parallèle (LPT1)
• 1 x port Série (COM1)
• 2 x sorties SPDIF numériques (Optique & Coaxiale)
• 1 x port Audio (Entrée de ligne, sortie de ligne, entrée Micro)
• Socket 939 pour processeur AMD Athlon 64 FX
• Interface de CPU HyperTransport de Haute performance
• Vitesse de transfert de 2000/1600/1200/800/400 MT/s
• Architecture mémoire DDR double canal
• 4 x sockets DIMM DDR 184 broches prenant en charge jusqu’à
4 Go
• Prend en charge les SDRAM DDR sans mémoire tampon
DDR400/333/266/200
Caractéristiques du BIOS
• Award BIOS avec ROM Flash de 4Mb
• Prend en charge Plug & Play 1.0A, APM 1.2, Multi Boot, DMI
• Prend en charge les spécications 1.0B révision ACPI
Page 81

Français
• 1 x Connecteur d’alimentation ATX 20 broches & Connecteur 12
V 4 broches
• 1 x connecteur de lecteur de disquette- prenant en charge 360K
~ 2,88M octets, 3 Lecteurs de disquettes Modes ou LS120
• 3 x connecteurs IDE
• 4 x connecteurs ATA Série
• 2 x embases USB 2.0 supportant 4 ports USB supplémentaires
• 2 x embases 1394a
• 1 x embase EZ-Watcher (optionnelle)
• 1 x embase SMBus
• 1 x embase de commutateur/LED de panneau avant
• 1 x embase audio de panneau avant
• Embase entrée CD/entrée AUX
• Connecteurs CPUFAN/NB_FAN/CASFAN
• Taille ATX
• 305mm x 244mm
Facteur de
Forme
E/S interne
Page 82

Deutsch
Zusammenfassung der Merkmale
CPU
Chipsatz
• VIA K8T800 PRO & 8237
• North Bridge: VIA K8T800 PRO
• South Bridge: VIA 8237
Arbeitsspeicher
Erweiterungsmöglichkeiten
• 1 x AGP 8X/4X Steckplatz
• 5 x PCI Steckplätze
Speicher
• Unterstützt durch einen VIA8237
- 4 x Ultra DMA133/100/66 Geräte
- 2 x SATA Geräte
- RAID 0 und RAID 1 Konguration
• Unterstützt durch einen SiS180
- 2 x Ultra DMA133/100/66 Geräte
- 2 x SATA Geräte
- RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1 Konguration
IEEE 1394a
• VIA VT6307 IEEE1394a Controller
• Unterstützt 2 x IEEE1394a Anschlüsse
Audio
• Realtek ALC655 6-Kanal Audio CODEC
• Entspricht AC’97 2.3 Spezikation
Dual LAN
• Marvel 88E8001 Gigabit LAN Controller
• VIA VT6103L 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet PHY
Rear panel
I/O
• 1 x PS/2 Tastatur
• 1 x PS/2 Mausanschluss
• 4 x USB Ports
• 2 x RJ45 LAN Anschlüsse
• 1 x Parallelanschluss (LPT1)
• 1 x Seriellanschluss (COM1)
• 2 x Digital SPDIF (optischer & Koaxial)-Ausgang
• 1 x Audio Anschluss (Line-in, Line-out, Mic-in)
• Sockel 939 für AMD Athlon 64 FX Prozessor
• Hochleistungs-HyperTransport-CPU-Schnittstelle
• Übertragungsgeschwindigkeiten: 2000/1600/1200/800/400 MT/s
• Dual-Kanal DDR Speicherarchitektur
• 4 x 184-Pin DDR DIMM Sockel, unterstützt bis zu 4 GB
• Unterstützt DDR400/333/266/200 ungepufferter DDR SDRAM
BIOS
Merkmale
• Award BIOS mit 4Mb Flash ROM
• Unterstützt Plug und Play 1.0A, APM 1.2, Multi Boot, DMI
• Unterstützt ACPI Revision 1.0B Spezikation
Page 83

Deutsch
• 1 x 20-Pin ATX Netzteilanschluss & 4-Pin 12 V Anschluss
• 1 x Floppylaufwerkanschluss, unterstützt 360K ~ 2.88M Bytes, 3
Modus Festplatten oder LS120
• 3 x IDE Anschlüsse
• 4 x Seriell ATA Anschluss
• 2 x USB 2.0 Anschluss, unterstützt zusätzlich 4 USB Anschlüsse
• 2 x 1394a Anschlüsse
• 1 x EZ-Watcher Anschluss (Optional)
• 1 x SMBus Anschluss
• 1 x Schalter in der Frontabdeckung/LED-Anschluss
• 1 x Audioanschluss in der Frontabdeckung
• CD-Eingang-/AUX-Einganganschluss
• CPUFAN/NB_FAN/CASFAN Anschlüsse
• ATX-Größe
• 305mm x 244mm
Formfaktor
Internes I/O
Page 84

Italiano
Indice delle caratteristiche
CPU
Chipset
• VIA K8T800 PRO & 8237
• North Bridge: VIA K8T800 PRO
• South Bridge: VIA 8237
Memoria
Opzioni
d’espansione
• 1 x slot AGP 8X/4X
• 5 x slot PCI
Deposito
• Supportato da VIA8237
- 4 x dispositivi Ultra DMA133/100/66
- 2 x dispositivi SATA
- congurazione RAID 0 e RAID 1
• Supportato da SiS180
- 2 x dispositivi Ultra DMA133/100/66
- 2 x dispositivi SATA
- congurazione RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1
IEEE 1394a
• Controller VIA VT6307 IEEE1394a
• Supporta 2 xconnettori IEEE1394a
Audio
• Realtek ALC655 6- canale audio CODEC
• Conforme alle speciche AC’97 2.3
Doppia LAN
• Controller LAN Marvel 88E8001 Gigabit
• VIA VT6103L 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet PHY
Pannello
posteriore
I/O
• 1 x tastiera PS/2
• 1 x connettore mouse PS/2
• 4 x porte USB
• 2 x connettori RJ45 LAN
• 1 x porta Parallela (LPT1)
• 1 x porta Seriale (COM1)
• 2 x output SPDIF digitali (ottico e coassiale)
• 1 x porta audio (Line-in, Line-out, Mic-in)
•
Presa 939 per processore AMD Athlon 64 FX
•
Interfaccia per CPU HyperTransport ad elevata prestazione
•
Velocità di trasferimento 2000/1600/1200/800/400 MT/s
• Dual-channel DDR memory architecture
• 4 x 184-pin DDR DIMM socket che supportano sino a 4 GB
• Supporta DDR400/333/266/200 unbuffered DDR SDRAM
Caratteristiche BIOS
• BIOS Award con 4Mb Flash ROM
• Supporta plug and play 1.0A, APM 1.2, Multi Boot, DMI
• Supporta speciche di revisione ACPI 1.0B
Page 85

Italiano
• 1 x connettore di alimentazione 20-pin ATX e connettore 4-pin
da 12 V
• 1 x connettore oppy - supporta 360K ~ 2.88M Byte, 3 Mode
FDDs o LS120
• 3 x connettori IDE
• 4 x connettori seriali ATA
• 2 x supporti header USB 2.0 con 4 porte USB supplementari
• 2 x headers 1394a
• 1 x EZ-Watcher header (opzionale)
• 1 x SMBus header
• 1 x interruttore del pannello frontale /LED header
• 1 x pannello frontale header audio
• CD in/AUX in header
• Connettori CPUFAN/NB_FAN/CASFAN
• Dimensione -ATX
• 305mm x 244mm
Form Factor
I/O interno
Page 86

Español
Resumen de Características
CPU
Chipset
• VIA K8T800 PRO & 8237
• North Bridge: VIA K8T800 PRO
• South Bridge: VIA 8237
Memoria
Opciones de
expansión
•
1 x ranura AGP 8X/4X
•
5 x ranuras PCI
Almacenaje
•
Soportado por VIA8237
- 4 x dispositivos Ultra DMA133/100/66
- 2 x dispositivos SATA
- Conguración RAID 0 y RAID 1
•
Soportado por SiS180
- 2 x dispositivos Ultra DMA133/100/66
- 2 x dispositivos SATA
- Conguración RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1
IEEE 1394a
•
Controlador VIA VT6307 IEEE1394a
•
Soporta 2 x conectores IEEE1394a
Audio
•
Realtek ALC655 6-channel audio CODEC
•
Conforme con la especicación AC’97 2.3
Dual LAN
•
Controlador Marvel 88E8001 Gigabit LAN
•
VIA VT6103L 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet PHY
I/O del panel
trasero
•
1 x teclado PS/2
•
1 x conector de ratón PS/2
•
4 x puertos USB
•
2 x conectores RJ45 LAN
•
1 x puerto Paralelo (LPT1)
•
1 x Puerto Serial (COM1)
•
2 x salidas de SPDIF Digital (Óptico & Coaxial)
•
1 x puerto Audio (Line-in, Line-out, Mic-in)
• Socket 939 para procesador AMD Athlon 64 FX
• Interfaz HyperTransport CPU de Alto Rendimiento
• Índice de transferencia de 2000/1600/1200/800/400 MT/s
• Arquitectura de memoria DDR Canal Dual
•
4 x zócalos 184-pin DDR DIMM soporta hasta 4 GB
•
Soporta DDR SDRAM de DDR400/333/266/200 sin buffer
Características de BIOS
•
Award BIOS con 4Mb Flash ROM
•
Soporta Plug and Play 1.0A, APM 1.2, Multi Boot, DMI
•
Soporta especicación ACPI revisión 1.0B
Page 87

Español
•
1 x Conector de Suministro 20-pin ATX & Conector 4-pin 12 V
•
1 x conector Floppy - soporta 360K ~ 2.88M Bytes, FDD de 3
Modos o LS120
•
3 x conectores IDE
•
4 x conectores Serial ATA
•
2 x cabezales USB 2.0 soporta 4 puertos USB adicionales
•
2 x cabezales 1394a
•
1 x cabezal EZ-Watcher (optativo)
•
1 x cabezal SMBus
•
1 x interruptor del panel frontal/cabezal LED
•
1 x cabezal de audio del panel frontal
•
Cabezal CD in/AUX in
•
Conectores CPUFAN/NB_FAN/CASFAN
• Tamaño de ATX
• 305mm x 244mm
Factor de
Forma
I/O Interno
Page 88

Português
Sumário de Características
CPU
Chipset
• VIA K8T800 PRO & 8237
• North Bridge: VIA K8T800 PRO
• South Bridge: VIA 8237
Memória
Opções de
expansão
• 1 x Ranhura AGP 8X/4X
• 5 x Ranhuras PCI
Armazenamento
• Suportado por VIA8237
- 4 x Dispositivos ultra DMA133/100/66
- 2 x Dispositivos SATA
- Conguração RAID 0 e RAID 1
• Suportado por SiS180
- 2 x Dispositivos ultra DMA133/100/66
- 2 x Dispositivos SATA
- Conguração RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1
IEEE 1394a
• Controlador VIA VT6307 IEEE1394a
• Suporta 2 x conectores IEEE1394a
Áudio
• CODEC 6 canais áudio Realtek ALC655
• Cumpre com a especicação AC’97 2.3
LAN duplo
• Controlador Marvel 88E8001Gigabit LAN
• VIA VT6103L 10/100 Mbps Internet Rápida PHY
Painel
traseiro I/O
• 1 x teclado PS/2
• 1 x conector de rato PS/2
• 4 x portas USB
• 2 x conectores RJ45 LAN
• 1 x porta Paralela (LPT1)
• 1 x porta de Série (COM1)
• 2 x Saída digital SPDIF (Óptica & Coaxial)
• 1 x Porta áudio (Line-in, Line-out, Mic-in)
• Tomada de parede 939 para processador AMD Athlon 64 FX
• Interface CPU HyperTransport de alta performance
• Taxa de transferência de 2000/1600/1200/800/400 MT/s
• Arquitectura de memória DDR bicanal
• 4 x Tomada de parede 184 pinos DDR DIMM suporta até 4
GB
• Suporta DDR400/333/266/200 sem buffers DDR SDRAM
Características BIOS
• Award BIOS com 4Mb Flash ROM
• Suporta dispositivo Plug e Play 1.0A, APM 1.2, Multi Boot, DMI
• Suporta especicação da revisão 1.0B ACPI
Page 89

Português
• 1 x Conector de Fonte de Alimentação 20 pinos ATX &
Conector 4 pinos 12 V
• 1 x Conector exível - suporta 360K ~ 2.88M Bytes, FDDs de 3
Modos ou LS120
• 3 x Conectores IDE
• 4 x Conectores de série ATA
• 2 x Colector USB 2.0 suporta 4 portas USB adicionais
• 2 x Colectores 1394a
• 1 x Colector EZ-Watcher (opcional)
• 1 x Colector SMBus
• 1 x Colector com interruptor/LED do painel traseiro
• 1 x Colector de áudio do painel traseiro
• Entrada para CD/Colector com entrada para AUX
• Conectores CPUFAN/NB_FAN/CASFAN
• Tamanho ATX
• 305mm x 244mm
Coeciente de
Forma
I/O interno
Page 90

日本語
特徴概要
プロセッサ
チップセット
• VIA K8T800 PRO & 8237
• North Bridge: VIA K8T800 PRO
• South Bridge: VIA 8237
メモリ
拡張スロット
• 1つのAGP 8X/4X スロット
• 5つのPCI スロット
保存装置
• VIA8237チップセットがサポートするのは
- 4つのUltra DMA133/100/66 デバイス
- 2つのSATA デバイス
- RAID 0とRAID 1 構成
• SiS180がサポートするのは
- 2つのUltra DMA133/100/66 デバイス
- 2つのSATA デバイス
- RAID 0、RAID 1、および RAID 0+1の 構成
IEEE 1394a
• VIA VT6307 IEEE1394a コントローラ
• 2つのIEEE1394a コネクタをサポート
オーディオ
• Realtek ALC655の6チャネル・オーディオCODEC
• AC’97 2.3 規格に準拠
デュアルLAN
• Marvel 88E8001 ギガバイトLAN コントローラ
• VIA VT6103L 10/100 Mbps 高速イーサーネットPHY
背面パネル入
出力
• 1つのPS/2 キーボードコネクタ
• 1 つのPS/2 マウスコネクタ
• 4 つのUSBポート
• 2 つのRJ45 LAN コネクタ
• 1 つのパラレルポート(LPT1)
• 1 つのシリアルポート(COM1)
• 2 つのデジタルSPDIF (光ケーブルと同軸ケーブル) 出力
• 1つのオーディオポート(ラインイン、ラインアウト、マイクイ
ン)
• AMD Athlon 64 FXプロセッサ用のSocket 939
• 高性能HyperTransport CPU インターフェース
• 転送率が2000/1600/1200/800/400 MT/s
• デュアルチャネルDDRメモリのアーキテクチャ
• 4つの184ピンDDR DIMMソケットで最大4 GBまでサ
ポート
• DDR400/333/266/200 非バッファーDDR
SDRAMをサポート
BIOSの諸
機能
• 4 Mb Flash ROM のAward BIOS
• Plug&Play 1.0A、APM 1.2、Multi Boot、および
DMIをサポート
• ACPI revision 1.0B 規格に準拠
Page 91

日本語
• 1 つの20ピンATX 電源サプライコネクタと4ピン12 V コネ
クタ
• 1つのフロッピーディスクドライブコネクタ、360Kから
2.88Mバイトの3 Mode FDDとLS120をサポート
• 3つのIDEコネクタ
• 4つのシリアルATAコネクタ
• 2つのUSB 2.0ヘッダーでさらなる4つのUSBポートを増設
可能
• 2つの1394a ヘッダー
• 1つEZ-Watcher ヘッダー(オプション)
• 1 つのSMBusヘッダー
• 1 つの前面パネルスイッチ/LED ヘッダー
• 1つのフロントパネルオーディオヘッダー
• CD入力/AUX 入力ヘッダー
• CPUFAN/NB_FAN/CASFAN コネクタ
• ATXサイズ
• 305mm x 244mm
寸法
内部入出力
Page 92

한 국 어
특성 요약
CPU
칩셋
• VIA K8T800 PRO & 8237
• North Bridge: VIA K8T800 PRO
• South Bridge: VIA 8237
메모리
확장 옵션
• 1 x AGP 8X/4X 슬롯
• 5 x PCI 슬롯
저장
• VIA8237 지원
- 4 x Ultra DMA133/100/66 장치
- 2 x SATA 장치
- RAID 0 및 RAID 1 구성
• SiS180 지원
- 2 x Ultra DMA133/100/66 장치
- 2 x SATA 장치
- RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1 구성
IEEE 1394a
• VIA VT6307 IEEE1394a 컨트롤러
• 2 x IEEE1394a 커넥터 지원
오디오
• Realtek ALC655 6 채널 오디오 코덱
• AC’97 2.3 사양 부합
듀얼 랜
• Marvel 88E8001 기가바이트 랜 컨트롤러
• VIA VT6103L 10/100 Mbps 패스트 이더넷 PHY
뒷 패널 I/O
• 1 x PS/2 키보드
• 1 x PS/2 마우스 커넥터
• 4 x USB 포트
• 2 x RJ45 LAN 커넥터
• 1 x 패러럴 포트 (LPT1)
• 1 x 시리얼 포트 (COM1)
• 2 x 디지털 SPDIF (선택 및 동축) 출력
• 1 x 오디오 포트 (라인 입력, 라인 출력, 마이크 입력)
• AMD 애슬론 64 FX 프로세서를 위한 소켓 939
• 고성능의 HyperTransport CPU 인터페이스
• 전송 속도 2000/1600/1200/800/400 MT/s
• 듀얼 채널 DDR 메모리 아키텍처
• 4 x 184 핀 DDR DIMM 소켓, 최대 4 GB 지원
• DDR400/333/266/200 unbuffered DDR SDRAM 지원
BIOS 특성
• 4Mb 플래시 ROM의 Award BIOS
• 플러그 앤 플레이 1.0A, APM 1.2, Multi Boot, DMI 지원
• ACPI 1.0B 사양 지원.
Page 93

한 국 어
• 1 x 20 핀 ATX 파워 써플라이 커넥터 및 4 핀 12 V 커넥터
• 1 x 플로피 커넥터- 360K ~ 2.88M Bytes, 3 모드 FDD 또
는 LS120 지원
• 3 x IDE 커넥터
• 4 x 시리얼 ATA 커넥터
• 2 x USB 2.0 헤더, 추가적으로 4 개의 USB 포트 지원s
• 2 x 1394a 헤더
• 1 x EZ-Watcher 헤더 (선택)
• 1 x SMBus 헤더
• 1 x 앞 패널 스위치/LED 헤더
• 1 x 앞 패널 오디오 헤더
• CD 입력/AUX 입력 헤더
• CPUFAN/NB_FAN/CASFAN 커넥터
• ATX 사이즈
• 305mm x 244mm
규격
내부 I/O
Page 94

繁體㆗文
功能摘要
㆗央處理器
晶片組
• VIA K8T800 PRO & 8237
• 北橋晶片: VIA K8T800 PRO
• 南橋晶片: VIA 8237
記憶體
擴充槽
‧ 1個AGP 8X/4X 槽
‧ 5個PCI槽
儲存裝置
‧ 以VIA8237晶片支援
- 4個Ultra DMA133/100/66 裝置
- 2個SATA 裝置
- 支援RAID 0及RAID 1 設定
‧以 SiS180支援
- 2個Ultra DMA133/100/66 裝置
- 2個 SATA 裝置
- 支援RAID 0、RAID 1、及 RAID 0+1 設定
IEEE 1394a
• VIA VT6307 IEEE1394a 控制器
• 支援2個IEEE1394a 連接器
音訊
• 採Realtek ALC655 6-聲道音訊CODEC
• 相容於 AC’97 2.3 規格
雙LAN
• Marvel 88E8001 Gigabit LAN 控制器
• VIA VT6103L 10/100 Mbps 高速㆚太網路PHY
背面板
輸出入介面
• 1個PS/2 鍵盤連接埠
• 1個PS/2 滑鼠連接埠
• 4個USB埠
• 2個RJ45 LAN 插孔
• 1個平行埠 (LPT1)
• 1個序列埠(COM1)
• 2個數位SPDIF (光纖及同軸電纜)輸出端子
• 1個音訊埠(線級輸入、線級輸出、夾克風插孔)
• AMD Athlon 64 FX 處理器用Socket 939
• 高效能HyperTransport CPU介面
• 傳輸速率2000/1600/1200/800/400 MT/s
‧ 雙通道DDR 記憶體架構
‧ 4個184針DDR DIMM 插槽支援㉃4 GB
‧ 支援DDR400/333/266/200 無緩衝DDR SDRAM
BIOS功能
• 採4Mb Flash ROM的Award BIOS
• 支援Plug and Play 1.0A、 APM 1.2、 Multi Boot、
及 DMI
• 支援ACPI 修訂版1.0B 規格
Page 95

繁體㆗文
• 1個20針ATX 電源供應器連接器及1個4針12 V連接器
• 1個軟碟機連接器,可支援360K㉃2.88M位元組之3
Mode 軟碟機及LS120軟碟機
• 3個IDE連接器
• 4個序列ATA 連接器
• 2個USB 2.0接頭,可支援4個額外的USB埠
• 2個1394a接頭
• 1個EZ-Watcher接頭(可選)
• 1個SMBus接頭
• 1個前面板開關及1個LED 接頭
• 1個前面板音訊接頭
• CD音源輸入/AUX音源輸入接頭
• 處理器冷卻風扇/北橋晶片風扇/機殼風扇連接器
• ATX 尺寸
• 305mm x 244mm
主機板尺寸
內部輸出入
介面
Page 96

简体中文
功能摘要
CPU
芯片组
• VIA K8T800 PRO & 8237
• 北桥:VIA K8T800 PRO
• 南桥:VIA 8237
内存
扩展选项
• 1 个 AGP 8X/4X 插槽
• 5 个 PCI 插槽
存储
• 支持 VIA8237
- 4 个 Ultra DMA133/100/66 设备
- 2 个 SATA 设备
- RAID 0 和 RAID 1 配置
• 支持 SiS180
- 2 个 Ultra DMA133/100/66 设备
- 2 个 SATA 设备
- RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1 配置
IEEE 1394a
• VIA VT6307 IEEE1394a 控制器
• 支持 2 个 IEEE1394a 接口
音頻
• Realtek ALC655 6 声道音频编解码器
• 符合 AC’97 2.3 规格
双 LAN
• Marvel 88E8001 千兆 LAN 控制器
• VIA VT6103L 10/100 Mbps 高速以太网 PHY
后面板 I/O
• 1 个 PS/2 键盘接口
• 1 个 PS/2 鼠标接口
• 4 个 USB 端口
• 2 个 RJ45 LAN 接口
• 1 个并口 (LPT1)
• 1 个串口 (COM1)
• 2 个数字量 SPDIF(光纤和同轴)输出
• 1 个音频端口(线入、线出、麦克风入)
• 用于AMD Athlon 64 FX 处理器的 Socket 939 插座
• 高性能超级传输(HyperTransport)CPU 接口
• 传输速率 2000/1600/1200/800/400 MT/s
• 双通道 DDR 内存架构
• 4 个 184 线 DDR DIMM 插槽,内存最大可支持 4
GB
• 持 DDR400/333/266/200非缓冲DDR SDRAM
BIOS 功能
• Award BIOS (4Mb Flash ROM)
• 支持即插即用 1.0A、APM 1.2、Multi Boot、DMI
• 支持 ACPI Revision 1.0B 规格
Page 97

简体中文
• 1 个 20 针 ATX 电源接口和 1 个 4 针 12 V 接口
• 1 个软驱接口- 支持 360K ~ 2.88M 字节,3 Mode
FDD 或 LS120
• 3 个 IDE 接口
• 4 个串行 ATA 接口
• 2 个 USB 2.0 接头,支持另外 4 个 USB 端口
• 2 个 1394a 接头
• 1 个 EZ-Watcher 接头(可选)
• 1 个 SMBus 接头
• 1 个前面板开关/LED 接头
• 1 个前面板音频接头
• CD 输入/AUX 输入接头
• CPUFAN/NB_FAN/CASFAN 接口
• ATX 尺寸
• 305mm x 244mm
外形
集成 I/O
Page 98

Русский
Характеристики
CPU
Чипсет
• VIA K8T800 PRO и 8237
• Северный мост: VIA K8T800 PRO
• Южный мост: VIA 8237
Память
Возможности
расширения
• 1 разъем AGP 8X/4X
• 5 разъемов PCI
Массовая
память
• Поддерживаемая VIA8237
- 4 устройства Ultra DMA133/100/66
- 2 устройства SATA
- Конфигураци RAID 0 и RAID 1
• Поддерживаемая SiS180
- 2 устройства Ultra DMA133/100/66
- 2 устройства SATA
- Конфигураци RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1
IEEE 1394a
• Контроллер VIA VT6307 IEEE1394a
• Поддержка 2 разъемов IEEE1394a
Aудиo
• 6-канальный аудио CODEC Realtek ALC655
• Совместимость с технологией AC’97 2.3
Dual LAN
• Контроллер Marvel 88E8001 Gigabit LAN
• Карта VIA VT6103L 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet PHY
Гнезда
входа/
выхода на
тыльной
панели
• 1 гнездо клавиатуры PS/2
• 1 гнездо мыши PS/2
• 4 порта USB
• 2 гнезда RJ45 LAN
• 1 параллельный порт (LPT1)
• 1 серийный порт (COM1)
• 2 гнезда выхода Digital SPDIF (оптическое и
коаксиальное)
• Гнездо для подключения микрофона, гнезда аудио-входа
и выхода
• Разъем 939 для процессоров AMD Athlon 64 FX
• Интерфейс HyperTransport CPU с высокой пропускной
способностью
• Скорость передачи данных 2000/1600/1200/800/400 MT/сек
• Архитектура памяти Dual-channel DDR
• 4 184-штырьковых разъема DDR DIMM с поддержкой
до 4 ГБ памяти
• Поддержка DDR400/333/266/200 и небуферизуемой памяти
DDR SDRAM
Особенности
BIOS'а
• Award BIOS с 4Mб Flash ROM
• Поддержка Plug and Play 1.0A, APM 1.2, Multi Boot, DMI
• Поддержка ACPI вер.1.0B
Page 99

Русский
Стандарт
• 1 20-штырьковое гнездо питания ATX и 4-штырьковое
гнездо 12 V
• 1 гнездо подключения накопителя НГМД с поддержкой
форматов 360K ~ 2.88MБ, 3 формата FDD или LS120
• 3 гнезда IDE
• 4 гнезд Serial ATA
• 2 гнезда USB 2.0 с поддержкой 4 дополнительных портов
USB
• 2 гнездо 1394a
• 1 гнездо EZ-Watcher (опционально)
• 1 гнездо SMBus
• 1 гнездо выключателя/индикатора передней панели
• 1 аудио гнездо передней панели
• Гнездо CD in/AUX in
• Разъемы вентиляторов CPU, северного моста и CASFAN
• Стандарт ATX
• 305мм x 244мм
Габариты
Внутренние
гнезда входа/
выхода
Page 100

Polski
Cechy
CPU
Chipset
• VIA K8T800 PRO & 8237
• Mostek północny: VIA K8T800 PRO
• Mostek południowy: VIA 8237
Pamięć
Możliwości
rozbudowy
• 1 złącze AGP 8X/4X
• 5 złącz PCI
Urządzenia
pamięc
masowej
• Obsługiwane przez VIA8237
- 4 urządzenia Ultra DMA133/100/66
- 2 urządzenia SATA
- Konguracje RAID 0 i RAID 1
• Obsługiwane przez SiS180
- 2 urządzenia Ultra DMA133/100/66
- 2 urządzenia SATA
- Konguracje RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1
IEEE 1394a
• Kontroler VT6307 IEEE1394a rmy VIA
• Obsługa 2 złącz IEEE1394a
Audio
• 6-kanałowy audio CODEC Realtek ALC655
• Zgodne z AC’97 2.3
Dual LAN
• Kontroller Marvel 88E8001 Gigabit LAN
• VIA VT6103L 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet PHY
Gniazda We/
Wy na tylnym
panelu
• 1 gniazdo klawiatury PS/2
• 1 gniazdo myszy PS/2
• 4 gniazda USB
• 2 złącza RJ45 LAN
• 1 port równoległy (LPT1)
• 1 port szeregowy (COM1)
• 2 gniazda Digital SPDIF (wyjście optyczne i koaksialne)
• 1 gniazdo wejściowe i 1 wyjściowe audio, 1 gniazdo wejściowe
mikrofonowe
• Gniazdo 939 dla procesorów AMD Athlon 64 FX
• Złącze szybkiego transpotu danych HyperTransport CPU
Interface
• Szybkość przesyłania danych 2000/1600/1200/800/400 MT/s
• Architektura pamięci dwukanałowej DDR
• Cztery 184 nóżkowe złącza DDR DIMM obsługujące do 4
GB pamięci
• Obsługa pamięci typu DDR400/333/266/200 i niebuforowanej
pamięci DDR SDRAM
Cechy BIOSu
• Award BIOS, zaopatrzony w 4Mb Flash ROM
• Obsługuje technologie Plug and Play 1.0A, APM 1.2, Multi Boot,
DMI
• Obsługuje technologię ACPI w wersji 1.0B
 Loading...
Loading...