Page 1

iii
Page 2

iv
Page 3

Preface
Copyright
This publication, including all photographs, illustrations and software, is protected under
international copyright laws, with all rights reserved. Neither this manual, nor any of the
material contained herein, may be reproduced without written consent of the author.
Version 1.0b
Disclaimer
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The manufacturer
makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents hereof and specifically
disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose.
The manufacturer reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from
time to time in the content hereof without obligation of the manufacturer to notify any
person of such revision or changes.
Trademark Recognition
Microsoft, MS-DOS and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corp.
MMX, Pentium, Pentium-II, Pentium-III, Celeron are registered trademarks of Intel Cor-
poration.
Other product names used in this manual are the properties of their respective owners and
are acknowledged.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which
can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to
correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver
• Connect the equipment onto an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help
Shielded interconnect cables and a shielded AC power cable must be employed with this
equipment to ensure compliance with the pertinent RF emission limits governing this
device. Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the system’s manufacturer
could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Preface
Page 4

ii
Declaration of Conformity
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following
conditions:
• This device may not cause harmful interference, and
• This device must accept any interference received, including interference
that may cause undesired operation
Canadian Department of Communications
This class B digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-causing
Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B respecte toutes les exigences du Réglement sur le
matériel brouilieur du Canada.
About the Manual
The manual consists of the following:
Chapter 1
Introducing the Motherboard
Describes features of the motherboard.
Go to
H
page 1
Chapter 2
Installing the Motherboard
Chapter 3
Using BIOS
Chapter 4
Using the Motherboard Software
Chapter 5
SIS965/SIS965L SA TA RAID Setup
Guide
Describes installation of motherboard
components.
Go to
Provides information on using the BIOS
Setup Utility.
Go to
Describes the motherboard software
Go to
Provides information about SATA RAID
Setup
Go to
H
H
H
H
page 7
page 27
page 49
page 53
Preface
Page 5

TT
ABLE OF CONTENTSABLE OF CONTENTS
T
ABLE OF CONTENTS
TT
ABLE OF CONTENTSABLE OF CONTENTS
Preface i
iii
Chapter 1
Introducing the Motherboard 1
Introduction.................................................................................................1
Feature..........................................................................................................2
Motherboard Components........................................................................4
1
Chapter 2
Installing the Motherboard 7
Safety Precautions......................................................................................7
Choosing a Computer Case.......................................................................7
Installing the Motherboard in a Case......................................................7
Checking Jumper Settings.........................................................................8
Setting Jumpers..............................................................................8
Checking Jumper Settings..............................................................9
Jumper Settings..............................................................................9
Connecting Case Components...............................................................10
Front Panel Header.....................................................................12
Installing Hardware...................................................................................13
Installing the Processor...............................................................13
Installing Memory Modules.........................................................15
Installing a Hard Disk Drive/CD-ROM/SATA Hard Drive........17
Installing a Floppy Diskette Drive...............................................19
Installing Add-on Cards..............................................................20
Connecting Optional Devices......................................................21
Connecting I/O Devices..........................................................................25
7 7
7
7 7
Chapter 3
Using BIOS 27
About the Setup Utility............................................................................27
The Standard Configuration........................................................27
Entering the Setup Utility..............................................................27
Updating the BIOS.......................................................................29
Using BIOS................................................................................................29
Standard CMOS Features...........................................................30
Advanced BIOS Features.............................................................32
Advanced Chipset Features.........................................................35
27 27
27
27 27
Page 6

iv
Integrated Peripherals.................................................................37
Power Management Setup...........................................................40
PNP/PCI Configurations.............................................................43
PC Health Status..........................................................................44
Frequency/Voltage Contr ol..........................................................45
Load Fail-Safe Defaults................................................................46
Load Optimized Defaults.............................................................46
Set Password...............................................................................46
Save & Exit Setup Option.............................................................47
Exit Without Saving......................................................................47
Chapter 4
49 49
49
49 49
Using the Motherboard Software 49
About the Software CD-ROM................................................................49
Auto-installing under Windows 98/ME/2000/XP................................49
Running Setup..............................................................................50
Manual Installation..................................................................................52
Utility Software Reference......................................................................52
Chapter 5
53 53
53
53 53
SIS965/SiS965L SAT A RAID Setup Guide 53
Introduction for SiS965/SiS965L SA TA RAID Function.....................53
Features......................................................................................................53
Support Operating Systems....................................................................53
What is RAID............................................................................................53
Installing Software Drivers......................................................................54
BIOS Utility Operation.............................................................................55
Multi-Language Translation
Page 7

Chapter 1
Introducing the Motherboard
Introduction
Thank you for choosing the 649-M2 motherboard. This motherboard is a high
performance, enhanced function motherboard that supports LGA775 socket for the
latest Intel Pentium 4/Celeron processors for high-end business or personal desktop
markets.
The motherboard incorporates the SiS649 Northbridge (NB) and SiS965/SiS965L
Southbridge (SB) chipsets. The SiS649 Northbridge chipset features the AGTL & AGTL+
compliant bus driver technology with integrated on-die termination to support Intel
Pentium 4 series processors up to FSB 800/533 MHz. The memory controller supports
DDR SDRAM only, supporting up to 2GB in maximum size with DDR400/333/266. It
can offer maximum memory bandwidth up to 3.2 GB/s under DDR 400. One 16-lane PCI
Express slot, intended for Graphics Interface, is fully compliant to the PCI Express Base
Specification revision 1.0a.
The SiS965/SiS965L Southbridges support Hi-Precision Event Timer (HPET) for Microsoft
Windows with multiple DMA bus architecture that supports isochronous request and
continuous packet transmission. It implements an EHCI compliant interface that provides
480Mb/s bandwidth for eight USB 2.0 ports, integrates AC’97 v2.3 compliant audio
controller that features a 6-channel audio speaker out and HSP v.90 modem support.
With PCI 2.3 specification compliant, this motherboard supports three PCI slots. The
Southbridge integrates a Serial ATA host controller with four onboard SATA ports (SiS965L
features two SATA ports) that is SATA v1.0 compliant, supporting Ultra DMA 150 and
LAN controller supporting 10/100Mbit/s ethernet. In addition, the Southbridge comes
with dual independent IDE channels, supporting PIO mode 0,1,2,3,4 and Multiword DMA
mode 0,1,2 and UltraDMA 133/100/66.
1
The 649-M2 motherboard is equipped with advanced full set of I/O ports in the rear panel,
including PS/2 mouse and keyboard connectors, COM1, LPT1, four USB ports, one
optional LAN port, one optional 1394 port, and audio jacks for microphone, line-in and
line-out.
Introducing the Motherboard
Page 8

2
Feature
Processor
The motherboard uses a LGA775 socket that has the following features:
• Accommodates Intel P4/Celeron Processors
• Supports a system bus of 800/533MHz
• Supports Dual Core CPU
• Supports “Hyper-Threading” technology CPU
“Hyper-Threading” technology enables the operating system into thinking it’s hooked
up to two processors, allowing two threads to be run in parallel, both on separate
“logical” processors within the same physical processor.
Chipset
The SiS649 Northbridge (NB) and SiS965 Southbridge (SB) chipset are based on an
innovative and scalable architecture with proven reliability and performance.
SiS649
(NB)
SiS965/965L
(SB)
Memory
• Supports DDR up to 400/333/266 MHz SDRAM memory module
• Accommodates two DDR 184-pin un-buffered DIMM sockets
• Each slot supports up to 1GB with a total maximum capacity of 2GB
• Supports 12 Outstanding Transactions and Quasi-Synchro-
nous Host to DRAM timing
• Accommodates High Throughput SiS MuTIOL connecting to
SiS965 MuTIOL media I/O with bi-directional 16-bit data bus
to perform 1GB/s bandwidth in 133 MHz x 4 mode
• Supports PCI-Express X16 Graphic Port
• Supports DDR400/333/266 or DDR2-533/400 SDRAM
• Supports up to 2 unbuffered DDR2-533 DIMMs or 2 unbuffered DDR400 DIMMs up to 2 GB
• Concurrent servicing of all DMA Devices: Dual IDE Controllers, SATA controller, three USB 1.1 host controllers and
one USB 2.0 host controller, LAN MAC Controller and Audio/Modem DMA Controller
• Integrated MuTIOL 1G to PCI Express x1 Bridge, compliant
with PCI Express 1.0a
• Compliant with PCI 2.3 specificaiton
• Compliant with Serial ATA 1.0 specification, supports up to
four independent ports (SiS965 only)
• Compliant with AC’97 v2.3 supporting 8 Channels of audio
outputs and V.90 HSP-Modem
• Integrated USB 2.0/1.1 Controller sopporting up to eight
USB ports
Expansion Options
The motherboard comes with the following expansion options.
• One PCI Express x16 slot
• Three 32-bit PCI slots
• Two IDE connectors which support four IDE channels
• A floppy disk drive interface
The motherboard supports UltraDMA bus mastering with transfer rates of 133/100
66MB/s
1394a FireWire (optional)
• Compliant Single Chip PCI Host Controller for IEEE1394-1995 Release 1.0
and IEEE 1394a-2000
• Provides two 1394a fully compliant cable ports at 100/200/400 Mbit per
second
Introducing the Motherboard
Page 9

• Supports 3.3V power supply with 5V tolerant inputs
• Supports 32-bit power-managed PCI Bus interface
Audio
• Compliant with the AC’97 v2.3 CODEC
• Supports 6-channel audio CODEC designed for PC multimedia systems
• Provides three analog line-level stereo inputs with 5-bit volume control:
Line-in, CD, AUX
• Supports S/PDIF output function
• Compliant with Azalia specification, supporting 8 channel DACs with
SNR.100dB
• Capabilities: 192/96/48/44.1 KHz with 24/20/16 bits
• 8 Smart Jack I/O port support
• Extensive jack detection via RNM (resistors network method) that can be
used to monitor the plugging status of each jack
• Digital S/PDIF OUT & IN support
Onboard LAN (optional)
• Supports 100/10 Mb/s N-Way Auto negotiation operation
• Half/Full duplex capability
• Supports Wake-On-LAN(WOL) function and remote wake-up
• Integrate 10/100/1000 transceiver
• Supports PCI v2.3, 32-bit, 33/66MHz
• Supports fully with IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u and IEEE802.3ab
•(Please note that only SiS965 supports Giga LAN)
• Supports 10/100Mbps operation
• Half/full duplex operation
• Supports 802.3/802.3u compliant
Integrated I/O
The motherboard has a full set of I/O ports and connectors:
• Two PS/2 ports for mouse and keyboard
• Two serial ports (COM1)
• One parallel port
• Four USB ports
• One LAN port (optional)
• One 1394 port (optional)
• Audio jacks for microphone, line-in and line-out
BIOS Firmware
This motherboard uses Award BIOS that enables users to configure many system
features including the following:
• Power management
• Wake-up alarms
• CPU parameters
• CPU and memroy timing
The firmware can also be used to set parameters for different processor clock speeds.
3
Some hardware specifications and software items are subject to change
with out prior notice.
Introducing the Motherboard
Page 10
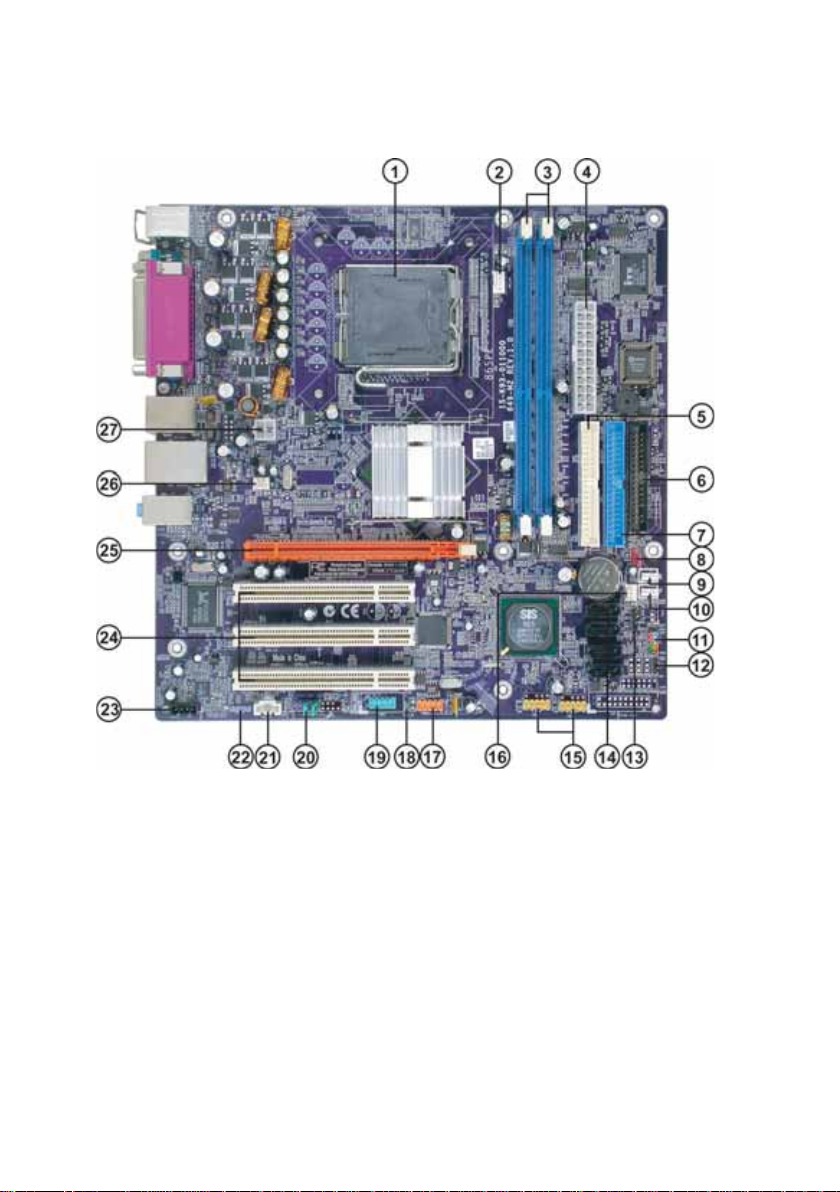
4
Motherboard Components
Introducing the Motherboard
Page 11

Table of Motherboard Components
LABEL COMPONENT
1 CPU Socket LGA775 socket for Pentium 4/Celeron CPUs
2 CPU_FAN CPU cooling fan connector
3 DIMM1~DIMM2 184-pin DDR SDRAM slots
4 ATX_POWER Standard 24-pin ATX power connector
5 IDE2 Secondary IDE channel
6 FDD Floppy diskette drive connector
7 IDE1 Primary IDE channel
8 CLR_CMOS Clear CMOS jumper
9 WOM Wake on Modem wakeup connector
10 WOL Wake on LAN wakeup connector
11 PANEL1 Front panel switch/LED header
12 SJ1* Single-colored LED header
13 IRDA Infrared header
14 SATA1~SATA4 FourSerial ATA connectors(SiS965 supports )
15 USB3~4 Front Panel USB headers
16 PWR_FAN* Power cooling fan connector
17 1394A2* Onboard IEEE 1394a connector
18 BIOS_WP BIOS Flash Protect jumper
19 COM2 Onboard serial port connector
20 AUDIO1 Front panel audio header
21 AUX_IN Auxiliary In connector
22 SPDIFO1 SPDIF out header
23 CD_IN Analog audio input connector
24 PCI1~PCI3 Three 32-bit add-on card slots
25 PCIEX16 PCI Express x16 slot for graphic card
26 SYS_FAN System cooling fan connector
27 ATX12V Auxiliary 4-pin power connector
“*” stands for optional components.
This concludes Chapter 1. The next chapter explains how to install the motherboard.
5
Introducing the Motherboard
Page 12

6
Memo
Introducing the Motherboard
Page 13

Chapter 2
Installing the Motherboard
Safety Precautions
• Follow these safety precautions when installing the motherboard
• Wear a grounding strap attached to a grounded device to avoid damage from
static electricity
• Discharge static electricity by touching the metal case of a safely grounded
object before working on the motherboard
• Leave components in the static-proof bags they came in
• Hold all circuit boards by the edges. Do not bend circuit boards
Choosing a Computer Case
There are many types of computer cases on the market. The motherboard complies with
the specifications for the Micro ATX system case. First, some features on the motherboard
are implemented by cabling connectors on the motherboard to indicators and switches on
the system case. Make sure that your case supports all the features required. Secondly, 649M2 supports one or two floppy diskette drives and four enhanced IDE drives. Make sure
that your case has sufficient power and space for all drives that you intend to install.
Most cases have a choice of I/O templates in the rear panel. Make sure that the I/O
template in the case matches the I/O ports installed on the rear edge of the motherboard.
This motherboard carries an Micro ATX form factor of 244 x 244 mm. Choose a case that
accommodates this form factor.
7
Installing the Motherboard in a Case
Refer to the following illustration and instructions for installing the motherboard in a case.
Most system cases have mounting brackets installed in the case, which correspond the holes
in the motherboard. Place the motherboard over the mounting brackets and secure the
motherboard onto the mounting brackets with screws.
Ensure that your case has an I/O template that supports the I/O ports and expansion slots
on your motherboard.
Installing the Motherboard
Page 14
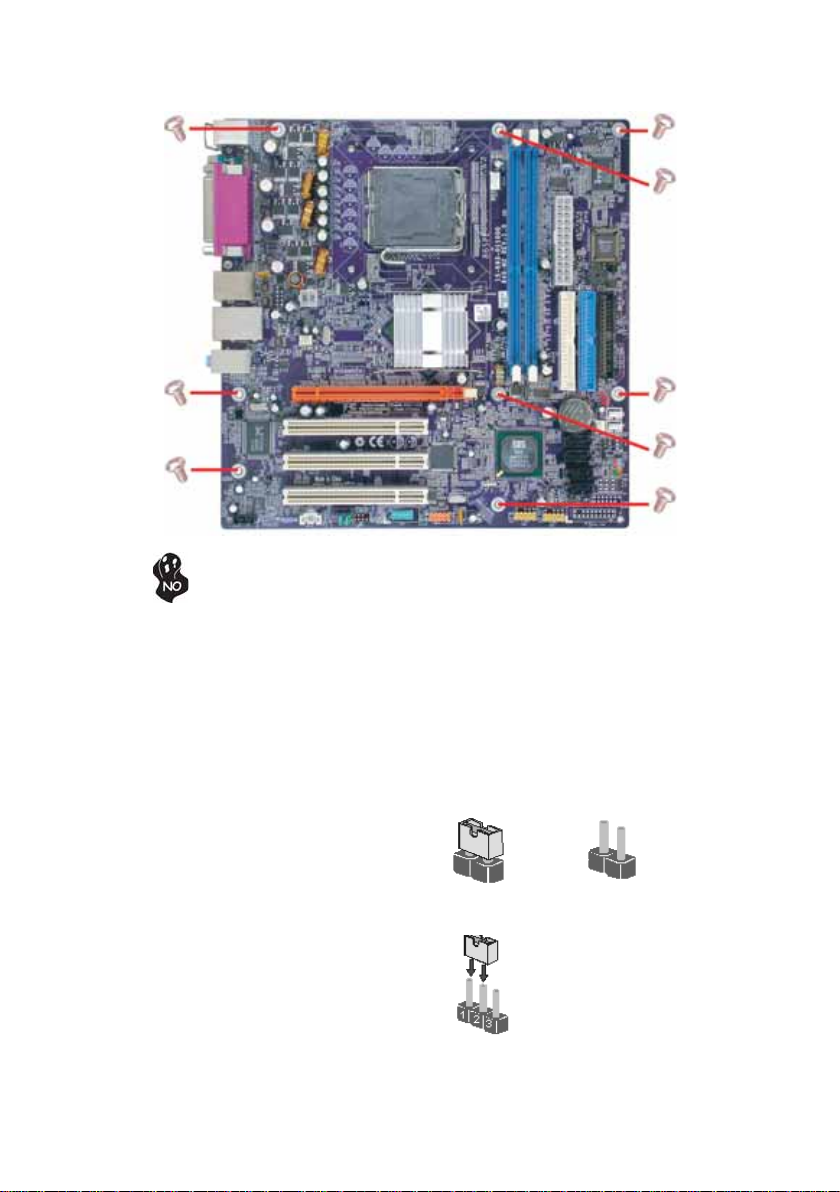
8
Do not over-tighten the screws as this can stress the motherboard.
Checking Jumper Settings
This section explains how to set jumpers for correct configuration of the motherboard.
Setting Jumpers
Use the motherboard jumpers to set system configuration options. Jumpers with more than
one pin are numbered. When setting the jumpers, ensure that the jumper caps are placed on
the correct pins.
The illustrations show a 2-pin jumper. When
the jumper cap is placed on both pins, the
jumper is SHORT. If you remove the jumper
cap, or place the jumper cap on just one pin,
the jumper is OPEN.
This illustration shows a 3-pin jumper. Pins
1 and 2 are SHORT
SHORT OPEN
Installing the Motherboard
Page 15

Checking Jumper Settings
The following illustration shows the location of the motherboard jumpers. Pin 1 is labeled.
9
Jumper Settings
Jumper
CLR_CMOS
BIOS_WP
Type
3-pin
2-pin
Description
CLEAR CMOS
BIOS Protect
Setting (default)
1-2: CLEAR
2-3: NORMAL
Before clearing the CMOS,
make sure to turn off the system.
Open: Disable
Short: Enable
Installing the Motherboard
Clear CMOS
1
BIOS_WP
Page 16

10
Connecting Case Components
After you have installed the motherboard into a case, you can begin connecting the motherboard components. Refer to the following:
1 Connect the CPU cooling fan cable to CPU_FAN.
2 Connect the power cooling fan connector to PWR_FAN.(optional)
3 Connect the system cooling fan connector to SYS_FAN.
4 Connect the case switches and indicator LEDs to the PANEL1. If there is a 3-
pin LED cable, connect it to SJ1.(optional)
5 Connect the standard power supply connector to ATX_POWER.
6 Connect the auxiliary case power supply connector to ATX12V.
Installing the Motherboard
Page 17

Connecting 20/24-pin power cable
Users please note that the 20-pin and 24-pin power cables can both be connected to the ATX_POWER connector. With the 20-pin power cable, just
align the 20-pin power cable with the pin 1 of the ATX_POWER connector.
However, using 20-pin power cable may cause the system to become unbootable
or unstable because of insufficient electricity. The minimum recommend power
is 300W for a fully-configured system.
20-pin power cable
24-pin power cable
CPU_FAN: CPU Cooling Fan Connector
Pin Signal Name Function
1 GND System Ground
2 +12V Power +12V
3 Sense Sensor
4 Control FAN Control Signal
11
With ATX v1.x power supply, users please
note that when installing 20-pin power cable,
the latche of power cable falls on the left
side of the ATX_POWER connector latch,
just as the picture shows.
With ATX v2.x power supply, users please
note that when installing 24-pin power cable,
the latches of power cable and the
ATX_POWER match perfectly.
Users please note that the fan connector supports the CPU cooling fan of
1.1A~2.2 (26.4W max.) at +12V.
SYS_FAN/PWR_F AN: F AN Power Connectors
Pin Signal Name Function
1 GND System Ground
2 +12V Power +12V
3 Sense Sensor
ATX12V : A TX 12V Power Connector
Pin Signal Name
1 Ground
2 Ground
3 +12V
4 +12V
Installing the Motherboard
Page 18
12
ATX_PWR: A TX 24-pin Power Connector
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 +3.3V 13 +3.3V
2 +3.3V 14 -12V
3 Ground 15 COM
4 +5V 16 PS_ON
5 Ground 17 COM
6 +5V 18 COM
7 Ground 19 COM
8 PWRGD 20 -5V
9 +5VSB 21 +5V
10 +12V 22 +5V
11 +12V 23 +5V
12 +3.3V 24 COM
SJ1: Single-color LED header (optional)
Pin Signal Name
1 ACPI LED
Pin Signal Name
2 ACPI LED
3 5VSB
ACPI LED function
SJ1
S0 S1 S3 S4/S5
Light Blinking Blinking Dark
1
Front Panel Header
The front panel header (PANEL1) provides a standard set of switch and LED headers
commonly found on ATX or Micro ATX cases. Refer to the table below for information:
Pin Signal Function Pin Signal Function
1 HD_LED_P Hard disk LED(+) 2 F P PWR/SLP *MSG LED(+)
3 HD_LED_N Hard disk LED(-)
5 RST_SW_N Reset Switch(-)
7 RST_SW_P Reset Switch(+)
9 RSVD Reserved
* MSG LED (dual color or single color)
4 FP PWR/SLP *MSG LED(-)
6 PWR_SW_P Power Switch(+)
8 PWR_SW_N Power Switch(-)
10 Key No pin
Installing the Motherboard
Page 19

Hard Drive Activity LED
Connecting pins 1 and 3 to a front panel mounted LED provides visual indication that data
is being read from or written to the hard drive. For the LED to function properly, an IDE
drive should be connected to the onboard IDE interface. The LED will also show activity
for devices connected to the SCSI (hard drive activity LED) connector.
Power/Sleep/Message waiting LED
Connecting pins 2 and 4 to a single or dual-color, front panel mounted LED provides power
on/off, sleep, and message waiting indication.
Reset Switch
Supporting the reset function requires connecting pin 5 and 7 to a momentary-contact
switch that is normally open. When the switch is closed, the board resets and runs POST.
Power Switch
Supporting the power on/off function requires connecting pins 6 and 8 to a momentarycontact switch that is normally open. The switch should maintain contact for at least 50 ms
to signal the power supply to switch on or off. The time requirement is due to internal debounce circuitry. After receiving a power on/off signal, at least two seconds elapses before
the power supply recognizes another on/off signal.
Installing Hardware
13
Installing the Processor
Caution: When installing a CPU heatsink and cooling fan make sure that
you DO NOT scratch the motherboard or any of the surface-mount
resistors with the clip of the cooling fan. If the clip of the cooling fan
scrapes across the motherboard, you may cause serious damage to the
motherboard or its components.
On most motherboards, there are small surface-mount resistors near the
processor socket, which may be damaged if the cooling fan is carelessly
installed.
Avoid using cooling fans with sharp edges on the fan casing and the clips.
Also, install the cooling fan in a well-lit work area so that you can clearly
see the motherboard and processor socket.
Before installing the Processor
This motherboard automatically determines the CPU clock frequency and system bus
frequency for the processor. You may be able to change these settings by making changes
to jumpers on the motherboard, or changing the settings in the system Setup Utility. We
strongly recommend that you do not over-clock processors or other components to run
faster than their rated speed.
Installing the Motherboard
Page 20

14
Warning: Over-clocking components can adversely affect the reliability
of the system and introduce errors into your system. Over-clocking can
permanently damage the motherboard by generating excess heat in
components that are run beyond the rated limits.
This motherboard has a LGA775 processor socket. When choosing a processor, consider
the performance requirements of the system. Performance is based on the processor design,
the clock speed and system bus frequency of the processor, and the quantity of internal
cache memory and external cache memory.
CPU Installation Procedure
The following illustration shows CPU installation components.
A. Unload the cap
· Use thumb & forefinger to hold the
lifting tab of the cap.
· Lift the cap up and remove the cap
completely from the socket.
B. Open the load plate
· Use thumb & forefinger to hold the
hook of the lever, pushing down and pulling
aside unlock it.
· Lift up the lever.
· Use thumb to open the load plate. Be
careful not to touch the contacts.
C. Install the CPU on the socket
· Orientate CPU package to the socket.
Make sure you match triangle marker
to pin 1 location.
D. Close the load plate
· Slightly push down the load plate onto the
tongue side, and hook the lever.
· CPU is locked completely.
E. Apply thermal grease on top of the CPU.
F. Fasten the cooling fan supporting base onto
the CPU socket on the motherboard.
G. Make sure the CPU fan is plugged to the
CPU fan connector. Please refer to the CPU
cooling fan user’s manual for more detail
installation procedure.
To achieve better airflow rates and heat dissipation, we suggest that you use
a high quality fan with 3800 rpm at least. CPU fan and heatsink installation procedures may vary with the type of CPU fan/heatsink supplied. The
form and size of fan/heatsink may also vary.
Installing the Motherboard
Page 21

Installing Memory Modules
This motherboard accommodates two memory modules. It can support two 184-pin 2.5V
unbuffered DIMM, DDR400/333/266. The total memory capacity is 2GB.
DDR SDRAM memory module table
Memory module Memory Bus
DDR266
DDR333
DDR400
You must install at least one module in any of the three slots. Each module can be installed
with 128 MB to 1 GB of memory; total memory capacity is 2GB.
Do not remove any memory module from its antistatic packaging until you
are ready to install it on the motherboard. Handle the modules only by
their edges. Do not touch the components or metal parts. Always wear a
grounding strap when you handle the modules.
133MHz
166MHz
200MHz
Installation Procedure
Refer to the following to install the memory modules.
1 This motherboard supports unbuffered DDR SDRAM only.
2 Push the latches on each side of the DIMM slot down.
3 Align the memory module with the slot. The DIMM slots are keyed with
notches and the DIMMs are keyed with cutouts so that they can only be
installed correctly.
4 Check that the cutouts on the DIMM module edge connector match the notches
in the DIMM slot.
5 Install the DIMM module into the slot and press it firmly down until it seats
correctly. The slot latches are levered upwards and latch on to the edges of
the DIMM.
6 Install any remaining DIMM modules.
15
Installing the Motherboard
Page 22

16
Table A: DDR (memory module) QVL (Qualified V endor List)
The following DDR400 memory modules have been tested and qualified for use with this
motherboard.
Size Vendor Model Name
NANYA NT128D64SH4B1G-5
128MB
Infineon HYS64D16301GU-5-B
NANYA NT128D64SH4B1G-5T
Micron MT16VDDT3264AG-403B2
Infineon HYS64D32300GU-5-B
NANYA NT256D64S88B1G-5T
256MB
Infineon HYS64D32300HU-5-C
Ramaxel HYB25D256800CE-5C
SAMSUNG M368L3223DTM-CC4
Micron MT8VDDT3264AG-40BC4
SAMSUNG M368L6423DTM-CC4
NANYA NT512D64S8HB1G-5T
Apacer HYB25D256800BT-5B
512 MB
Apacer V58C2256804SAT5
Infineon HYS64D64320HU-5-C
SAMSUNG M368L6423ETM-CCC
Apacer A2S56D30ATP
Installing the Motherboard
Page 23

Installing a Hard Dish Drive/CD-ROM/SA T A Hard Drive
This section describes how to install IDE devices such as a hard disk drive and a CD-ROM
drive.
About IDE Devices
Your motherboard has a primary and secondary IDE channel interface (IDE1 and IDE2).
An IDE ribbon cable supporting two IDE devices is bundled with the motherboard.
You must orient the cable connector so that the pin1 (color) edge of the
cable correspoinds to the pin 1 of the I/O port connector.
IDE1: Primary IDE Connector
The first hard drive should always be connected to IDE1.
17
IDE2: Secondary IDE Connector
The second drive on this controller must be set to slave mode. The cinfiguration is the same
as IDE1.
IDE devices enclose jumpers or switches used to set the IDE device as MASTER or SLAVE.
Refer to the IDE device user’s manual. Installing two IDE devices on one cable, ensure that
one device is set to MASTER and the other device is set to SLAVE. The documentation of
your IDE device explains how to do this.
Installing the Motherboard
Page 24

18
About SAT A Connectors
This motherboard features four SATA connectors supporting a total of four drives. SATA
refers to Serial ATA (Advanced Technology Attachment) is the standard interface for the
IDE hard drives which are currently used in most PCs. These connectors are well designed
and will only fit in one orientation. Locate the SATA connectors on the motherboard (see
page 20) and follow the illustration below to install the SATA hard drives.
Installing Serial A T A Hard Drives
To install the Serial ATA (SATA) hard drives, use the SATA cable that supports the Serial
ATA protocol. This SATA cable comes with an SATA power cable. You can connect either
end of the SATA cable to the SATA hard drive or the connector on the motherboard.
SATA cable (optional)
Refer to the illustration below for proper installation:
1 Attach either cable end to the connector on the motherboard.
2 Attach the other cable end to the SATA hard drive.
3 Attach the SATA power cable to the SATA hard drive and connect the other
end to the power supply.
This motherboard does not support the “Hot-Plug” function.
SATA power cable (optional)
Installing the Motherboard
Page 25

Installing a Floppy Diskette Drive
The motherboard has a floppy diskette drive (FDD) interface and ships with a diskette drive
ribbon cable that supports one or two floppy diskette drives. You can install a 5.25-inch
drive and a 3.5-inch drive with various capacities. The floppy diskette drive cable has one
type of connector for a 5.25-inch drive and another type of connector for a 3.5-inch drive.
You must orient the cable connector so that the pin 1 (color) edge of the
cable corresponds to the pin 1 of the I/O port connector.
FDD: Floppy Disk Connector
This connector supports the provided floppy drive ribbon cable. After connecting the single
end to the onboard floppy connector, connect the remaining plugs on the other end to the
floppy drives correspondingly.
19
Installing the Motherboard
Page 26

20
Installing Add-on Cards
The slots on this motherboard are designed to hold expansion cards and connect them to the
system bus. Expansion slots are a means of adding or enhancing the motherboard’s features
and capabilities. With these efficient facilities, you can increase the motherboard’s capabilities by adding hardware that performs tasks that are not part of the basic system.
PCIEx16
Slot
PCI1~3
Slots
The PCI Express x16 slot is used to install an external PCI Express graphics
card that is fully compliant to the PCI Express Base Specification revision
1.0a.
This motherboard is equipped with two standard PCI slots. PCI stands for
Peripheral Component Interconnect and is a bus standard for expansion
cards, which for the most part, is a supplement of the older ISA bus standard.
The PCI slots on this board are PCI v2.3 compliant.
Before installing an add-on card, check the documentation for the card
carefully. If the card is not Plug and Play, you may have to manually
configure the card before installation.
Installing the Motherboard
Page 27

Follow these instructions to install an add-on card:
1 Remove a blanking plate from the system case corresponding to the slot you
are going to use.
2 Install the edge connector of the add-on card into the expansion slot. Ensure
that the edge connector is correctly seated in the slot.
3 Secure the metal bracket of the card to the system case with a screw.
For some add-on cards, for example graphics adapters and network adapters, you have to install drivers and software before you can begin using the
add-on card.
Connecting Optional Devices
Refer to the following for information on connecting the motherboard’s optional devices:
21
Installing the Motherboard
Page 28

22
SPDIFO1: SPDIF out header
This is an optional header that provides an S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) output
to digital multimedia device through optical fiber or coaxial connector.
Pin Signal Name
Function
1 SPDIF SPDIF digital output
2 +5VA 5V analog Power
3 Key No pin
4 GND Ground
AUDIO1: Front Panel Audio header
This header allows the user to install auxiliary front-oriented microphone and line-out ports
for easier access.
Pin Signal Name
Pin Signal Name
Function
1 AUD_MIC Front Panel Microphone input signal
2 AUD_GND Ground used by Analog Audio Circuits
3 AUD_MIC_BIAS Microphone Power
4 AUD_VCC Filtered +5V used by Analog Audio Circuits
5 AUD_F_R Right Channel audio signal to Front Panel
6 AUD_RET_R Right Channel Audio signal to Return from Front Panel
7 REVD Reserved
8 Key No Pin
9 AUD_F_L Left Channel Audio signal to Front Panel
10 AUD_RET_L Left Channel Audio signal to Return from Front Panel
CD_IN: Analog audio input connector
Pin Signal Name
1 CD in_L CD In left channel
2 GND Ground
3 GND Ground
4 CD in_R CD In right channel
Function
SAT A1~SA T A4: Serial AT A connectors
These connectors are use to support the new Serial ATA devices for the highest date transfer
rates (150 MB/s), simpler disk drive cabling and easier PC assembly. It eliminates limitations
of the current Parallel ATA interface. But maintains register compatibility and software
compatibility with Parallel ATA.
Pin Signal Name
Pin Signal Name
1 Ground 2 TX+
3 TX- 4 Ground
5 RX- 6 RX+
7 Ground - -
Users please note that SiS965L supports 2 Serial ATA conenctors only.
Installing the Motherboard
Page 29

USB3~USB4: Front Panel USB connectors
The motherboard has four USB ports installed on the rear edge I/O port array. Additionally,
some computer cases have USB ports at the front of the case. If you have this kind of case,
use the onboard USB connectors to connect the front-mounted ports to the motherboard.
23
Pin Signal Name
1 USBPWR Front Panel USB Power
2 USBPWR Front Panel USB Power
3 USB_FP_P0- USB Port 0 Negative Signal
4 USB_FP_P1- USB Port 1 Negative Signal
5 USB_FP_P0+ USB Port 0 Positive Signal
6 USB_FP_P1+ USB Port 1 Positive Signal
7 GND Ground
8 GND Ground
9 Key No pin
10 USB_FP_OC0 Overcurrent signal
Please make sure that the USB cable has the same pin assignment as
indicatged above. A different pin assignment may cause damage or system
hang-up.
Function
AUX_IN: Auxiliary In connector
This connector is an additional line-in audio connector. It allows you to attach a line-in
cable when your rear line-in jack is set as line out port for 4-channel function.
Pin Signal Name
1 AUX_L AXU In left channel
2 GND Ground
3 GND Ground
4 AUX_R AXU In right channel
Function
COM2: Onboard serial port header
Connect a serial port extension bracket to this header to add a second serial port to your
system.
Pin Signal Name
1 NDCDB Data carry detect
2 NSINB Serial Data In
3 NSOUTB Serail Data Out
4 NDTRB Data terminal ready
5 GND Ground
6 NDSRB Date set ready
7 NRTSB Request to send
8 NCTSB Clear to send
9 NRIB Ring Indicator
10 KEY Key
Function
Installing the Motherboard
Page 30

24
IRDA: Infrared header
The motherboard supports an Infrared data port. Infrared ports allow the wireless exchange
of information between your computer and similarly equipped devices such as printers,
laptops, Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs), and other computers.
Pin Signal Name
1 VCC IR power
2 KEY No pin
3 IRRX IrDA serial input
4 GND Ground
5 IRTX IrDA serial output
Function
WOM: Wake On Modem connector
If you have installed a modem, use the cable provided with the modem to plug into the
WOM connector onboard. This enables the Wake On Modem (WOM) feature. When your
system is in a power-saving mode, any modem signal automatically resumes the system. Yo u
must enable this item using the Power Management page of the Setup Utility in the BIOS.
See Chapter 3 for more information.
Pin Signal Name Function
1 5VSB +5V stand by power
2 GND Ground
3 Ring# Wake up signal (low acti ve)
WOL: Wake On LAN connector
If you have installed a LAN card, use the cable provided with the card to plug into the WOL
connector onboard. This enables the Wake On LAN (WOL) feature. When your system is
in a power-saving mode, any LAN signal automatically resumes the system. You must
enable this item using the Power Management page of the Setup Utility in the BIOS. See
Chapter 3 for more information.
Pin Signal Name Function
1 5VSB +5V stand by power
2 GND Ground
3 Ring# Wake up signal (low acti ve)
Installing the Motherboard
Page 31

1394A2: Onboard IEEE 1394a connector (optional)
Connect this header to any device with IEEE 1394a interface.
25
Pin Signal Name
Pin Signal Name Function
1 TPA+ 2 TPA-
3 GND 4 GND
5 TPB+ 6 TPB-
7 Cable-Power 8 Cable-Power
9 Key Pin 10 GND
Users please note that “1394A2” shares with “USB1394A1”. That is, only
either of them can function at one time!
Pin Signal Name
Connecting I/O Devices
The backplane of the motherboard has the following I/O ports:
PS2 Mouse Use the upper PS/2 port to connect a PS/2 pointing device.
PS2 Keyboard Use the lower PS/2 port to connect a PS/2 keyboard.
Parallel Port (LPT1) Use LPT1 to connect printers or other parallel communications
devices.
Serial Port Use the COM1 port to connect serial devices such as mice or
(COM1) fax/modems.
LAN Port (optional) Connect an RJ-45 jack to the LAN port to connect your computer
1394a Port (optional) Use the 1394a port to connect to any firewire device.
USB Ports Use the USB ports to connect USB devices.
Audio Ports Use the three audio ports to connect audio devices. The first jack
This concludes Chapter 2. The next chapter covers the BIOS.
to the Network.
is for stereo line-in signal. The second jack is for stereo line-out
signal. The third jack is for microphone.
Installing the Motherboard
Page 32

26
Memo
Installing the Motherboard
Page 33

Chapter 3
Using BIOS
About the Setup Utility
The computer uses the latest Award BIOS with support for Windows Plug and Play. The
CMOS chip on the motherboard contains the ROM setup instructions for configuring the
motherboard BIOS.
The BIOS (Basic Input and Output System) Setup Utility displays the system’s configuration status and provides you with options to set system parameters. The parameters are
stored in battery-backed-up CMOS RAM that saves this information when the power is
turned off. When the system is turned back on, the system is configured with the values you
stored in CMOS.
The BIOS Setup Utility enables you to configure:
• Hard drives, diskette drives and peripherals
• Video display type and display options
• Password protection from unauthorized use
• Power Management features
The settings made in the Setup Utility affect how the computer performs. Before using the
Setup Utility, ensure that you understand the Setup Utility options.
This chapter provides explanations for Setup Utility options.
27
The Standard Configuration
A standard configuration has already been set in the Setup Utility. However, we recommend
that you read this chapter in case you need to make any changes in the future.
This Setup Utility should be used:
• when changing the system configuration
• when a configuration error is detected and you are prompted to make changes
to the Setup Utility
• when trying to resolve IRQ conflicts
• when making changes to the Power Management configuration
• when changing the password or making other changes to the Security Setup
Entering the Setup Utility
When you power on the system, BIOS enters the Power-On Self Test (POST) routines.
POST is a series of built-in diagnostics performed by the BIOS. After the POST routines are
completed, the following message appears:
Using BIOS
Page 34

28
Press DEL to enter SETUP
Pressing the delete key accesses the BIOS Setup Utility:
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility:
Standard CMOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Advanced Chipset Features Load Optimized Defaults
Integrated Peripherals Set Password
Power Management Setup Save & Exit Setup
PnP/PCI Configurations Exit Without Saving
PC Health Status
Esc: Quit
F10: Save & Exit Setup
Time, Date, Hard Disk Type...
Frequency/Voltage Control
BIOS Navigation Keys
The BIOS navigation keys are listed below:
KEY FUNCTION
ESC Exits the current menu
Scrolls through the items on a menu
+/-/PU/PD Modifies the selected field’s values
F10 Saves the current configuration and exits setup
F1 Displays a screen that describes all key functions
F5 Loads previously saved values to CMOS
F6 Loads a minimum configuration for troubleshooting
F7 Loads an optimum set of values for peak performance
: Select Item
Using BIOS
Page 35

Updating the BIOS
You can download and install updated BIOS for this motherboard from the manufacturer’s
Web site. New BIOS provides support for new peripherals, improvements in performance,
or fixes for known bugs. Install new BIOS as follows:
1 If your motherboard has a BIOS protection jumper, change the setting to allow
BIOS flashing.
2 If your motherboard has an item called Firmware Write Protect in Advanced
BIOS features, disable it. (Firmware Write Protect prevents BIOS from being
overwritten.
3 Create a bootable system disk. (Refer to Windows online help for information
on creating a bootable system disk.)
4 Download the Flash Utility and new BIOS file from the manufacturer’s Web
site. Copy these files to the system diskette you created in Step 3.
5 Turn off your computer and insert the system diskette in your
computer’s diskette drive. (You might need to run the Setup Utility and change
the boot priority items on the Advanced BIOS Features Setup page, to force
your computer to boot from the floppy diskette drive first.)
6 At the A:\ prompt, type the Flash Utility program name and press <Enter>.
7 Type the filename of the new BIOS in the “File Name to Program” text box.
Follow the onscreen directions to update the motherboard BIOS.
8 When the installation is complete, remove the floppy diskette from the diskette
drive and restart your computer. If your motherboard has a Flash BIOS jumper ,
reset the jumper to protect the newly installed BIOS from being overwritten.
Using BIOS
When you start the Setup Utility, the main menu appears. The main menu of the Setup
Utility displays a list of the options that are available. A highlight indicates which option is
currently selected. Use the cursor arrow keys to move the highlight to other options. When
an option is highlighted, execute the option by pressing <Enter>.
29
Some options lead to pop-up dialog boxes that prompt you to verify that you wish to
execute that option. Other options lead to dialog boxes that prompt you for information.
Some options (marked with a triangle
values for the option. Use the cursor arrow keys to scroll through the items in the submenu.
In this manual, default values are enclosed in parenthesis. Submenu items are denoted by a
triangle
.
) lead to submenus that enable you to change the
Using BIOS
Page 36

30
Standard CMOS Features
This option displays basic information about your system.
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Standard CMOS Features
Date (mm:dd:yy) Wed, Jan 19 2005
Time (hh:mm:ss) 9 : 33 : 26
IDE Channel 0 Master
IDE Channel 0 Slave
IDE Channel 1 Master
IDE Channel 1 Slave
IDE Channel 2 Master
IDE Channel 2 Slave
IDE Channel 3 Master
IDE Channel 3 Slave
Drive A [1.44M, 3.5 in.]
Drive B [None]
Floppy 3 Mode Support [Disabled]
Video [EGA/VGA]
Halt On [All Errors]
Base Memory 640K
Extended Memory 65535K
Tot al Memory 1024K
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Date and Time
The Date and Time items show the current date and time on the computer. If
you are running a Windows OS, these items are automatically updated whenever you make
changes to the Windows Date and Time Properties utility.
IDE Devices (None)
Your computer has two IDE channels (Primary and Secondary) and each channel can be
installed with one or two devices (Master and Slave). Use these items to
configure each device on the IDE channel.
This motherboard features four SATA connectors supporting four SATA drives. SATA
refers to Serial ATA (Advanced Technology Attachment), the standard interface for the
IDE hard drives which are currently used in most PCs.
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
IDE Channel 0 Maser
IDE HDD Auto-Detection [Press Enter]
IDE Prinmary Master [Auto]
Access Mode [Auto]
Capacity 0MB
Cylinder 0
Head 0
Precomp 0
Landing Zone 0
Sector 0
Item Help
Menu Level
Change the day, month,
year and century
Item Help
Menu Level
To auto-detect the
HDD’s size, head... on
this channel
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Using BIOS
Page 37

IDE HDD Auto-Detection
Press <Enter> while this item is highlighted to prompt the Setup Utility to automatically
detect and configure an IDE device on the IDE channel.
If you are setting up a new hard disk drive that supports LBA mode, more
than one line will appear in the parameter box. Choose the line that lists
LBA for an LBA drive.
IDE Channel 0/1 Master/Slave IDE/Extended IDE Drives (Auto)
Leave this item at Auto to enable the system to automatically detect and configure
IDE devices on the channel. If it fails to find a device, change the value to Manual and
then manually configure the drive by entering the characteristics of the drive in the
items described below. Please noted that if you choose IDE Channel 2/3 Master, the
item may change to Extended IDE Drive.
Refer to your drive’s documentation or look on the drive casing if you need to obtain
this information. If no device is installed, change the value to None.
Before attempting to configure a hard disk drive, ensure that you have the
configuration information supplied by the manufacturer of your hard drive.
Incorrect settings can result in your system not recognizing the installed hard
disk.
Access Mode (Auto)
This item defines ways that can be used to access IDE hard disks such as LBA (Large
Block Addressing). Leave this value at Auto and the system will automatically decide
the fastest way to access the hard disk drive. If you choose IDE Channel 2/3 Master,
the item only have Large and Auto.
Press <Esc> to return to the Standard CMOS Features page.
31
Drive A/Drive B (1.44M, 3.5 in./None)
These items define the characteristics of any diskette drive attached to the system.
You can connect one or two diskette drives.
Floppy 3 Mode Support (Disabled)
Floppy 3 mode refers to a 3.5-inch diskette with a capacity of 1.2 MB. Floppy 3 mode
is sometimes used in Japan.
Video (EGA/VGA)
This item defines the video mode of the system. This motherboard has a built-in VGA
graphics system; you must leave this item at the default value.
Halt On (All Errors)
This item defines the operation of the system POST (Power On Self Test) routine. You
can use this item to select which types of errors in the POST are sufficient to halt the
system.
Base Memory, Extended Memory, and Total Memory
These items are automatically detected by the system at start up time. These are
display-only fields. You cannot make changes to these fields.
Press <Esc> to return to AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility page.
Using BIOS
Page 38

32
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
Advanced BIOS Features
This option defines advanced information about your system.
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Advanced BIOS Features
CPU Feature [Press Enter]
Hard Disk Boot Priority [Press Enter]
CPU L1 & L2 Cache [Enabled]
CPU L3 Cache [Enabled]
Hyper-Threading Technology [Enabled]
Quick Power On Self Test [Enabled]
First Boot Device [Floppy]
Second Boot Device [Hard Disk]
Third Boot Device [CDROM]
Boot Other Device [Enabled]
Swap Floppy Drive [Disabled]
Boot Up Floppy Seek [Disabled]
Boot Up NumLock Status [On]
BIOS Bootblock Protect [Disabled]
AT A 66/100 IDE Cable Msg [Enabled]
Typematic Rate Setting [Disabled]
x
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec0 6
x
Typematic Delay (Msec) 25 0
Security Option [Setup]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
CPU Feature (Press Enter)
Users please note that this function is only available for Prescott CPUs. Scroll to this
item and press <Enter> to view the following screen:
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
CPU Feature
Item Help
Menu Level
Thermal Management [Thermal Monitor 1]
TM2 Bus Ratio [0 X]
TM2 Bus VID [0.8375V]
Limit CPUID MaxVal [Disabled]
C1E Function [Disabled]
Execute Disable Bit [Enabled]
Virtualization T echnology [Enabled]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6”Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized
Item Help
Menu Level
Thermal Monitor 1 (On die
throtting)
Thermal Monitor 2 Ratio
& VID transition
Thermal Management (Thermal Monitor 1)
This item displays CPU’s temperature and enables you to set a safe temperature to Prescott
CPU.
TM2 Bus Ratio (0X)
This item represents the frequency (bus ratio) of the throttled performance state that will
be initiated when the on-die sensor goes from not hot to hot).
TM2 Bus VID (0.8375V)
This item represents the voltage of the throttled performance state that will be initiated
when the on-die sensor goes from not hot to hot.
Using BIOS
Page 39

Limit CPUID MaxVal (Disabled)
This item can support Prescott CPUs for old OS. Users please note that under NT 4.0, it
must be set “Enabled”, while under WinXP, it must be set “Disabled”.
C1E Function (Disabled)
This item allows you to further reduce the total power consumption while in C1. When C1E
is enabled, and all logical processors in the physical processor have entered the C1 state, the
processor will reduce the core clock frequency to system bus ratio and VID.
Execute Disable Bit (Enabled)
This item is a security feature that helps you protect your CPU and operating system
against malicious software executing code. This item is available when CPU supports the
feature.
Virtualization Technology (Enabled)
When enabled, a VMM can utilize the additional hardware capabilities provided by Vandor
pool Technology.
Hard Disk Boot Priority (Press Enter)
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the following screen:
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Hard Disk Boot Priority
1. Pri.Master:
2. Pri.Slave:
3. Sec. Master:
4. Sec. Slave:
5. USBHDD0:
6. USBHDD1:
7. USBHDD2:
8. Bootable Add-in Cards
Item Help
Menu Level
Use < > or < >
to select a device, then
press <+> to move it
up, or <-> to move it
down the list. Press
<ESC> to exit this
menu.
33
: Move PU/PD+/-/:Change Priority F10:Save ESC:Exit
CPU L1&L2 Cache (Enabled)
All processors that can be installed in this mainboard use internal level 1 (L1) and external
level 2 (L2) cache memory to improve performance. Leave this item at the default value
for better performance.
CPU L3 Cache (Enabled)
This item is only available when processors support L3. Some high-end processors support
L3. If the CPU do support L3, you may set this item to enable or disable. Leave this item
at the default value for better performance.
Hyper-Threading Technology (Enabled)
This item is only available when the chipset supports Hyper-Threading and you are using a
Hyper-Threading CPU.
Quick Power On Self Test (Enabled)
Enable this item to shorten the power on testing (POST) and have your system start up
faster. You might like to enable this item after you are confident that your system hardware
is operating smoothly.
First/Second/Third Boot Device (Floppy/Hard Disk/CDROM)
Use these three items to select the priority and order of the devices that your system
searches for an operating system at start-up time.
Using BIOS
Page 40

34
Boot Other Device (Enabled)
When enabled, the system searches all other possible locations for an operating system if
it fails to find one in the devices specified under the First, Second, and Third boot devices.
Swap Floppy Drive [Disabled]
If you have two floppy diskette drives in your system, this item allows you to swap the
assigned drive letters so that drive A becomes drive B, and drive B becomes drive A.
Boot Up Floppy Seek (Disabled)
If this item is enabled, it checks the size of the floppy disk drives at start-up time. You
don’t need to enable this item unless you have a legacy diskette drive with 360K capacity.
Boot Up NumLock Status (On)
This item defines if the keyboard Num Lock key is active when your system is started.
BIOS Bootblock Protect (Disalbed)
This item enables or disables the BIOS bootblock rom to be protected from overwritten.
ATA 66/100 IDE Cable Msg. (Enalbed)
This item enables or disables the ATA 66/100 IDE Cable Msg. This message will appear
during reboot when you use 40-pin cable on your 66/100 hard disks.
Typematic Rate Setting (Disabled)
If this item is enabled, you can use the following two items to set the typematic rate and the
typematic delay settings for your keyboard.
• Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec): Use this item to define how many characters
per second are generated by a held-down key.
• Typematic Delay (Msec): Use this item to define how many milliseconds
must elapse before a held-down key begins generating repeat characters.
Security Option (Setup)
If you have installed password protection, this item defines if the password is required at
system start up, or if it is only required when a user tries to enter the Setup Utility.
APIC Mode (Enabled)
This item allows you to enable or disable the APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt
Controller) mode. APIC provides symmetric multi-processing (SMP) for systems, allowing
support for up to 60 processors.
OS Select For DRAM > 64 MB (Non-OS2)
This item is only required if you have installed more than 64 MB of memory and you are
running the OS/2 operating system. Otherwise, leave this item at the default.
HDD S.M.A.R.T Capability (Disabled)
The S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) system is a diagnostics technology that monitors and predicts device performance. S.M.A.R.T. software
resides on both the disk drive and the host computer.
Video BIOS Shadow (Enabled)
This item determines whether the BIOS will be copied to RAM for faster execution.
Small Logo (EPA) Show (Disabled)
This item enables or disables the display of the EPA logo during boot.
Press <Esc> to return to Advanced BIOS Features screen.
Using BIOS
Page 41

Advanced Chipset Features
These items define critical timing parameters of the motherboard. You should leave the
items on this page at their default values unless you are very familiar with the technical
specifications of your system hardware. If you change the values incorrectly, you may
introduce fatal errors or recurring instability into your system.
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Advanced Chipset Features
DRAM Clock/Drive Control [Press Enter]
System BIOS Cacheable [Disabled]
Video RAM Cacheable [Disabled]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Item Help
Menu Level
DRAM Clock/Drive Control (Press Enter)
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the following screen:
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
DRAM Clock/Timing Control
35
DDR CAS Latency [By SPD]
DRAM Timing Control [Auto]
x
RAS to CAS Delay (tRCD) 2T
x
Precharge Time (tRP) 2T
RAS Active Time (tRAS) 15T
x
Write Recovery Time (tWR) 1T
x
Command Bypass [Disabled]
Data Bypass [Disabled]
UMC0 MA Timing [Auto]
UMC0 Read Data Ready [Auto]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Item Help
Menu Level
DDR CAS Latency (SPD)
This item controls the timing delay (in clock cycles) before the DRAM starts a read
command after receiving it.
DRAM Timing Control (Auto)
Enables you to select the CAS latency time in HCLKs of 2, 2.5, or 3. The value is set at
the factory depending on the DRAM installed. Do not change the values in this field
unless you change specifications of the installed DRAM or the installed CPU.
• RAS to CAS Delay (tRCD) (2T): This is the amount of time a CAS is performed after a RAS. The lower the better, but some DRAM does not support
low figures.
Using BIOS
Page 42

36
• Precharge Time (tRP) (2T): This is the duration of the time interval during
which the Row Address Strobe signal to a DRAM is held low during normal
Read and Write Cycles. This is the minimum interval between completing one
read or write and starting another from the same (non-page mode) DRAM.
Techniques such as memory interleaving, or use of Page Mode DRAM are
often used to avoid this delay. Some chipsets require this parameter in order
to set up the memory configuration properly. The RAS Precharge value is
typically about the same as the RAM Access (data read/write) time.
• RAS Active Time (tRAS) (15T) : This item allows you to set the amount of
time a RAS can be kept open for multiple accesses. High figures will improve
performance.
• Write Recovery Time (tWR)(1T): This item defines DRAM internal write to
read command delay in the same device.
Command Bypass(Disabled)
When enabled, request will bypass the command queue if the queue is empty.
Data Bypass (Disabled)
When enabled, the latency of read data from DRAM back to CPU will be lower.
UMC0 MA Timing (Auto)
This option allows you to set the lead off DRAM read and write cycles. When set to Delay
1T, memory read/write commands are sent one clock cycle behind the memory address.
When set to Normal, read/write and memory address commands are sent simultaneously.
UMC0 Read Data Ready (Auto)
This item defines the channel A DRAM read data latency.
Press <Esc> to return to the Advanced Chipset Features page.
System BIOS Cacheable (Disabled)
This item allows the system to be cached in memory for faster execution. Enable this item
for better performance.
Video RAM Cacheable (Disabled)
These items allow the video BIOS and RAM to be cached in memory for faster execution.
Enable these items for better performance.
Using BIOS
Page 43

Integrated Peripherals
These options display items that define the operation of peripheral components on
the system’s input/output ports.
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Integrated Peripherals
OnChip IDE Device [Press Enter]
OnChip PCI Device [Press Enter]
Onboard SuperIO Device [Press Enter]
Onboard 1394 Device [Enabled]
Onboard LAN Device [Enabled]
Onboard LAN Boot ROM [Disabled]
IDE HDD Block Mode [Enabled]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
OnChip IDE Device (Press Enter)
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the following screen:
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
SiS OnChip IDE Device
InternalPCI/IDE [Both]
IDE Primary Master PIO [Auto]
IDE Primary Slave PIO [Auto]
IDE Secondary Master PIO [Auto]
IDE Secondary Slave PIO [Auto]
Primary Master UltraDMA [Auto]
Primary Slave UltraDMA [Auto]
Secondary Slave UltraDMA [Auto]
Secondary Slave UltraDMA [Auto]
IDE DMA Transfer Access [Enabled]
Item Help
Menu Level
Item Help
Menu Level
37
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Internal PCI/IDE (Both)
Use these items to enable or disable the internal PCI IDE channels that are integrated on the
mainboard.
IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave PIO (Auto)
Each IDE channel supports a master device and a slave device. These four items let you
assign which kind of PIO (Programmed Input/Output) is used by IDE devices. Choose Auto
to let the system auto detect which PIO mode is best, or select a PIO mode from 0-4.
IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave UltraDMA (Auto)
This mainboard supports UltraDMA technology, which provides faster access to IDE devices. If you install a device that supports UltraDMA, change the item on this list to Auto.
You may have to install the UltraDMA driver supplied with this mainboard in order to use
an UltraDMA device.
Using BIOS
Page 44

38
IDE DMA Transfer Access (Enabled)
This item allows you to enabled the transfer access of the IDE DMA.
Press <Esc> to return to the Integrated Peripherals page.
OnChip PCI Device (Press Enter)
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the following screen:
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
SiS OnChip PCI Device
USB Controller [Enabled]
USB 2.0 Supports [Enabled]
USB Legacy Support [Enabled]
USB Mouse Support [Enabled]
AC97 AUDIO [Enabled]
Serial AT A Controller [Enabled]
Serial AT A Mode [IDE]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Item Help
Menu Level
USB Controller (Enabled)
Enables or disables the onboard USB controller. We recommend users keep the dafault value.
Disabling it might cause the USB devices not to work properly.
USB 2.0 Supports (Enabled)
This item enables or disables the onboard USB 2.0.
USB Legacy Support (Enabled)
Enable this item if you plan to use a keyboard connected through the USB port in a legacy
operating system (such as DOS) that does not support Plug and Play.
USB Mouse Support (Enabled)
Enable this item if you plan to use a mouse connected through the USB port in a legacy
operating system (such as DOS) that does not support Plug and Play.
AC97 AUDIO (Enabled)
Enables or disables the onboard AC 97 audio function. Disable this item if you are going to
install a PCI audio add-on card.
Serial ATA Controller (Enabled)
Enables or disables the onboard Serial ATA controller. Enable this item if you are to install
SATA devices onboard.
Serial ATA Mode (IDE)
Use this item to define the onboard SATA mode. Set this item to RAID if you are to activate
the RAID function of the SATA devices.
Using BIOS
Page 45

Onboard SuperIO Device (Press Enter)
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the following screen:
Onboard FDC Controller [Enabled]
Onboard Serial Port 1 [3F8/IRQ4]
Onboard Serial Port 2 [2F8/IRQ3]
UART Mode Select [Normal]
UR2 Duplex Mode [Half]
Onboard Parallel Port [378/IRQ7]
Parallel Port Mode [ECP]
ECP Mode Use DMA [3]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
SuperIO Device
Item Help
Menu Level
Onboard FDC Controller (Enabled)
This option enables the onboard floppy disk drive controller.
Onboard Serial Port 1/2 (3F8/IRQ4)(2F8/IRQ3)
This option is used to assign the I/O address and interrupt request (IRQ) for onboard serial
port 1/2 (COM1/COM2).
UART Mode Select (Normal)
This field is available if the Onboard Serial Port 2 field is set to any option but Disabled.
UART Mode Select enables you to select the infrared communication protocol-Normal
(default), IrDA, or ASKIR. IrDA is an infrared communication protocol with a maximum
baud rate up to 115.2K bps. ASKIR is Sharp’s infrared communication protocol with a
maximum baud rate up to 57.6K bps.
UR2 Duplex Mode (Half)
This field is available when UART 2 Mode is set to either ASKIR or IrDA. This item enables
you to determine the infrared function of the onboard infrared chip. The options are Full
and Half (default).
Full-duplex means that you can transmit and send information simultaneously. Half-duplex
is the transmission of data in both directions, but only one direction at a time.
Onboard Parallel Port (378/IRQ7)
This option is used to assign the I/O address and interrupt request (IRQ) for the onboard
parallel port.
Parallel Port Mode (ECP)
Enables you to set the data transfer protocol for your parallel port. There are four options:
SPP (Standard Parallel Port), EPP (Enhanced Parallel Port), ECP (Extended Capabilities
Port) and ECP+EPP.
SPP allows data output only. Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) and Enhanced Parallel Port
(EPP) are bi-directional modes, allowing both data input and output. ECP and EPP modes
are only supported with EPP- and ECP-aware peripherals.
ECP Mode Use DMA (3)
When the onboard parallel port is set to ECP mode, the parallel port can use DMA 3 or
DMA 1.
Press <Esc> to return to the Integrated Peripherals page.
39
Using BIOS
Page 46

40
Onboard 1394 Device (Enabled)
Enable this item if you plan to use the 1394 device.
Onboard LAN Device (Enabled)
Use this item to enable and disable the onboard LAN function.
Onboard LAN Boot ROM (Disabled)
Use this item to enable or disable the booting from the onboard LAN or a network add-in
card with a remote boot ROM installed.
IDE HDD Block Mode (Enabled)
Enable this field if your IDE hard drive supports block mode. Block mode enables BIOS to
automatically detect the optimal number of block read and writes per sector that the drive
can support. It also improves the speed of access to IDE devices.
Power Management Setup
This option lets you control system power management. The system has various powersaving modes including powering down the hard disk, turning off the video, suspending
to RAM, and software power down that allows the system to be automatically resumed
by certain events.
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Power Management Setup
ACPI Suspend Type [S3(STR)]
Suspend Mode [Disabled]
Video Off Option [Susp, Stby -> Off]
Video Off Method [DPMS Supported]
MODEM Use IRQ [Auto]
HDD Off After [Disabled]
Power Button Override [Instant Off]
Power On After Power Fail [Off]
PM Wake Up Events [Press Enter]
Item Help
Menu Level
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
ACPI Suspend Type (S3(STR))
Use this item to define how your system suspends. In the default, S3 (STR), the suspend
mode is suspend to RAM, i.e., the system shuts down with the exception of a refresh current
to the system memory.
Suspend Mode (Disabled)
The CPU clock will be stopped and the video signal will be suspended if no Power Management events occur for a specified length of time. Full power function will return when a
Power Management event is detected.
Video Off Option (Susp, Stby —> Off)
This option defines if the video is powered down when the system is put into suspend mode.
Video Off Method (DPMS Supported)
This item defines how the video is powered down to save power. This item is set to DPMS (Display
Power Management Software) by default.
Using BIOS
Page 47

MODEM Use IRQ (Auto)
If you want an incoming call on a modem to automatically resume the system from a powersaving mode, use this item to specify the interrupt request line (IRQ) that is used by the
modem. You might have to connect the fax/modem to the motherboard Wake On Modem
connector for this feature to work.
HDD Off After (Disabled)
The IDE hard drive will spin down if it is not accessed within a specified length of time.
Options are from 1 Min to 15 Min and Disable.
Power Button Override (Instant Off)
Under ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power management Interface) you can create a
software power down. In a software power down, the system can be resume by Wake Up
Alarms. This item lets you install a software power down that is controlled by the power
button on your system. If the item is set to Instant-Off, then the power button causes a
software power down. If the item is set to Delay 4 Sec. then you have to hold the power
button down for four seconds to cause a software power down.
Power On After Power Fail (Off)
This item enables your computer to automatically restart or return to its last operationg
status after power returns from a power failure.
PM W ake Up Events (Press Enter)
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
PM Wake Up Events
IRQ [3-7, 9-15], NMI [Enabled]
IRQ 8 Break Suspend [Disabled]
Resume By WOL/WOM/RING [Disabled]
Resume By MACPME [Enabled]
Resume By PCI PME [Enabled]
Resume By USB (S3) [Disabled]
PS2 KB Wakeup from S3
PS2 MS Wakeup from S3
Month Alarm Na
Day of Month Alarm 0
Time (hh:mm:ss) Alarm 0 : 0 : 0
**Reload Global Timer Events**
Primary IDE [Disabled]
Secondary IDE [Disabled]
FDD, COM, LPT Port [Disabled]
PCI PIRQ[A-D]# [Disabled]
Item Help
Menu Level
41
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
IRQ [3-7, 9-15], NMI (Enabled)
This option determines whether any activity for IRQ 3-7/9-15 will cause the system to
wake from a power saving mode.
IRQ 8 Break Suspend (Disabled)
Determines whether the system will monitor IRQ 8 activity and wake the system from a
power saving mode when IRQ 8 is activated.
Resume By WOL/WOM/RING (Disabled)
Use this item to enable LAN or modem activity to wakeup the system from a power saving
mode.
Using BIOS
Page 48

42
Resume By MACPME (Enabled)
Use this item to enable MAC activity to wake up the system from a power saving mode.
Resume By PCI PME (Enabled)
This item allows users to enable or disable PCI activity to wakeup the system from a power
saving mode.
Resume By USB (S3) (Disabled)
This item allows users to enable or disable USB activity to wakeup the system from a power
saving mode.
PS2 KB/MS Wakeup from S3 (Disabled)
This option enables or disables you to allow mouse or keyboard activity to awaken the
system from power saving mode.
** Reload Global Timer Events **
Global Timer (power management) events are I/O events whose occurrence can prevent the
system from entering a power saving mode or can awaken the system from such a mode. In
effect, the system remains alert for anything that occurs to a device that is configured as
Enabled, even when the system is in a power-down mode.
Primary/Secondary IDE 1/0 (Disabled)
When these items are enabled, the system will restart the power-saving timeout counters
when any activity is detected on any of the drives or devices on the primary or secondary
IDE channels.
FDD, COM, LPT Port (Disabled)
When this item is enabled, the system will restart the power-saving timeout counters when
any activity is detected on the floppy disk drive, serial ports, or the parallel port.
PCI PIRQ[A-D]# (Disabled)
When disabled, any PCI device set as the Master will not power on the system.
Press <Esc> to return to Power Management Setup page.
Using BIOS
Page 49

PNP/PCI Configurations
These options configure how PnP (Plug and Play) and PCI expansion cards operate in
your system. Both the the ISA and PCI buses on the motherboard use system IRQs
(Interrup ReQuests) and DMAs (Direct Memory Access). You must set up the IRQ and
DMA assignments correctly through the PnP/PCI Configurations Setup utility for the
motherboard to work properly. Selecting PnP/PCI Configurations on the main program
screen displays this menu:
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
PnP/PCI Configurations
43
Reset Configuration Data [Disabled]
Resources Controlled By [Auto(ESCD)]
X
IRQ Resources Press Enter
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop [Disabled]
Assign IRQ For USB [Enabled]
INT Pin 1 Assignment [Auto]
INT Pin 2 Assignment [Auto]
INT Pin 3 Assignment [Auto]
INT Pin 4 Assignment [Auto]
INT Pin 5 Assignment [Auto]
INT Pin 6 Assignment [Auto]
INT Pin 7 Assignment [Auto]
INT Pin 8 Assignment [Auto]
** PCI Express relatvie items**
Maximum ASPM supported [L0s&L1]
Maximum Payload Size [4096]
Init Display First [PCI Slot]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Item Help
Menu Level
Default is Disabled. Select
Enabled to reset Extended
System Configuration Data
ESCD) when you exit Setup if
you have installed a new addon and the system
reconfiguration has caused
such a serious conflict that
the OS cannot boot
Reset Configuration Data (Disabled)
If you enable this item and restart the system, any Plug and Play configuration data stored in the
BIOS Setup is cleared from memory.
Resources Controlled By Auto (Auto(ESCD))
You should leave this item at the default Auto (ESCD). Under this setting, the system dynamically
allocates resources to Plug and Play devices as they are required.
If you cannot get a legacy ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) expansion card to work properly,
you might be able to solve the problem by changing this item to Manual, and then opening up the
IRQ Resources submenu.
• IRQ Resources:In the IRQ Resources submenu, if you assign an IRQ to
Legacy ISA, then that Interrupt Request Line is reserved for a legacy ISA
expansion card. Press <Esc> to close the IRQ Resources submenu.
In the Memory Resources submenu, use the first item Reserved Memory Base
to set the start address of the memory you want to reserve for the ISA
expansion card. Use the section item Reserved Memory Length to set the
amount of reserved memory. Press <Esc> to close the Memory Resources
submenu.
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop (Disabled)
This item is designed to overcome problems that can be caused by some non-standard VGA
cards. This board includes a built-in VGA system that does not require palette snooping so
you must leave this item disabled.
Using BIOS
Page 50

44
Assign IRQ For USB (Enabled)
Names the interrupt request (IRQ) line assigned to the USB on your system. Activity of the
selected IRQ always awakens the system.
Maximum ASPM supported (L0s&L1)
This item controls the maximum level of ASPM supported on the given PCI Express links
on the system.
Maximum Payload Size (4096)
This item specifies the maximum TLP payload size for the PCI Express devices. The unit
is byte.
INT Pin 1-8 Assignment (Auto)
Identifies the interrupt request (IRQ) line assigned to a device connected to the PCI interface of your system.
PC Health Status
On motherboards that support hardware monitoring, this item lets you monitor the
parameters for critical voltages, temperatures and fan speeds.
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
PC Health Status
Shutdown T emperature [Disabled]
Warning T emperature [Disabled]
CPU Core Voltage
DDR Voltage
Vcc 3.3V
Vcc 5.0V
+12V
Voltage Battery
CPU T emperature
System T emperature
CPU FAN Speed
SYS FAN Speed
PWR FAN Speed
Item Help
Menu Level
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Shutdown Temperature (Disabled)
Enables you to set the maximum temperature the system can reach before powering down.
Warning Temperature (Disabled)
This item allows users to set the CPU warning temperature. The default setting is Disabled.
Users may change it to 60°C/140°F, 65°C/149°F, 70°C/158°F, 75°C/167°F, or 80°C/176°F
System Component Characteristics
These fields provide you with information about the systems current operating status. You
cannot make changes to these fields.
• CPU Core Volt age
• DDR Volt age
• 3.3V
• 5.0V
• 12V
• Voltage Battery
• CPU T emperature
• System Temperature
• CPU FAN S peed
• SYS FAN Speed
• PWR FAN S peed
Using BIOS
Page 51

Frequency/Voltage Control
This item enables you to set the clock speed and system bus for your system. The clock
speed and system bus are determined by the kind of processor you have installed in your
system.
Phoenix-AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Frequency/Voltage Control
45
CPU Clock Ratio [ 0 X]
Auto Detect PCI Clk [Enabled]
Spread Spectrum [Enabled]
Colck Control By [Auto]
x
Async PCI Clock control Disabled
x
CPU Clock 100
x
CPU:DRAM Frequency Ratio SPD
DRAM Frequency
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1: General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Item Help
Menu Level
CPU Clock Ratio (0 X)
Use the CPU Host/SDRAM/PCI Clock to set the frontside bus frequency for the installed
processor (usually 133 MHz, 100 MHz or 66 MHz). Then use CPU Clock Ratio Jumpless to
set a multiple. The multiple times the frontside bus must equal the core speed of the installed
processor e.g., 3.5 (multiple) x 100 MHz (frontside bus) = 350 MHz (installed
processor clock speed).
Auto Detect DIMM/PCI Clk (Enabled)
When this item is enabled, BIOS will disable the clock signal of free DIMM/PCI slots.
Spread Spectrum (Enabled)
If you enable spread spectrum, it can significantly reduce the EMI (Electro-Magnetic
Interference) generated by the system.
Clock Control By (Auto)
Use this item to set the CPU Host Clock frequency to Auto or by manual setting. Select
“Manual” to activate the following items and set each item manually.
• Async PCI Clock control (Disabled): This item allows you to select the
fixed clock to generate the output to PCI frequency.
• CPU Clock (100): Use the CPU Host Clock to set the fronside bus frequency
for the installed processor (usually 200MHz, 133 MHz or 100 MHz).
• CPU:DRAM Frequency Ratio (SPD): This item determines if the DRAM frequency is controlled by SPD or by manually. Do not change the value in this
field unless you know the specification of the installed DRAM orthe installed
CPU quite well.
DRAM Frequency
Use this item to set the frequency of the installed DRAM. We strongly recommend users
leave this item at its default value. Inappropriate value may cause the system to be unbootable
or crash.
Using BIOS
Page 52

46
Load Fail-Safe Defaults Option
This option opens a dialog box that lets you install fail-safe defaults for all appropriate
items in the Setup Utility: Press <Y> and the <Enter> to install the defaults. Press
<N> and then <Enter> to not install the defaults. The fail-safe defaults place no great
demands on the system and are generally stable. If your system is not functioning
correctly, try installing the fail-safe defaults as a first step in getting your system working
properly again. If you only want to install fail-safe defaults for a specific option, select
and display that option, and then press <F6>.
Load Optimized Defaults Option
This option opens a dialog box that lets you install optimized defaults for all appropriate
items in the Setup Utility. Press <Y> and then <Enter> to install the defaults. Press
<N> and then <Enter> to not install the defaults. The optimized defaults place demands on the system that may be greater than the performance level of the components,
such as the CPU and the memory. You can cause fatal errors or instability if you install
the optimized defaults when your hardware does not support them. If you only want to
install setup defaults for a specific option, select and display that option, and then press
<F7>.
Set Password
When this function is selected, the following message appears at the center of the screen
to assist you in creating a password.
ENTER PASSWORD
Type the passw ord, up to eight characters , and press <Enter>. The password typed now
will clear any previously entered password from CMOS memory. You will be asked to
confirm the password. Type the passw ord again and press <Enter>. You may also press
<Esc> to abort the selection.
To disable password, just press <Enter> when you are prompted to enter password. A
message will confirm the password being disabled. Once the password is disabled, the
system will boot and you can enter BIOS Setup freely.
P ASSWORD DISABLED
If you have selected “System” in “Security Option” of “BIOS Features Setup” menu,
you will be prompted for the password every time the system reboots or any time you try
to enter BIOS Setup.
If you have selected “Setup” at “Security Option” from “BIOS Features Setup” menu,
you will be prompted for the password only when you enter BIOS Setup.
Supervisor Password has higher priority than User Password. You can use Supervisor
Password when booting the system or entering BIOS Setup to modify all settings. Also
you can use User Password when booting the
system or entering BIOS Setup but can not modify any setting if Supervisor Password
is enabled.
Using BIOS
Page 53

Save & Exit Setup
Highlight this item and press <Enter> to save the changes that you have made in the
Setup Utility and exit the Setup Utility. When the Save and Exit dialog box appears,
press <Y> to save and exit, or press <N> to return to the main menu.
Exit Without Saving
Highlight this item and press <Enter> to discard any changes that you have made in the
Setup Utility and exit the Setup Utility. When the Exit Without Saving dialog box
appears, press <Y> to discard changes and exit, or press <N> to return to the main
menu.
If you have made settings that you do not want to save, use the “Exit
Without Saving” item and press <Y> to discard any changes you have
made.
This concludes Chapter 3. Refer to the next chapter for information on the software
supplied with the motherboard.
47
Using BIOS
Page 54

48
Memo
Using BIOS
Page 55

Chapter 4
Using the Motherboard Software
About the Software CD-ROM
The support software CD-ROM that is included in the motherboard package contains all the
drivers and utility programs needed to properly run the bundled products. Below you can find
a brief description of each software program, and the location for your motherboard
version. More information on some programs is available in a README file, located in the
same directory as the software.
Never try to install all software from folfer that is not specified for use with your
motherboard.
Before installing any software, always inspect the folder for files named README.TXT,
INSTALL.TXT, or something similar. These files may contain important information that
is not included in this manual.
Auto-installing under Windows 98/ME/2000/XP
The Auto-install CD-ROM makes it easy for you to install the drivers and software for your
motherboard.
If the Auto-install CD-ROM does not work on your system, you can still install
drivers through the file manager for your OS (for example, Windows Explorer). Refer to the Utility Folder Installation Notes later in this chapter.
49
The support software CD-ROM disc loads automatically under Windows 98/ME/2000/XP.
When you insert the CD-ROM disc in the CD-ROM drive, the autorun feature will automatically bring up the install screen. The screen has three buttons on it, Setup, Browse CD and
Exit.
If the opening screen does not appear; double-click the file “setup.exe” in
the root directory.
Using the Motherboard Software
Page 56

50
Setup Tab
Setup
Browse CD
Exit The EXIT button closes the Auto Setup window.
Application Tab
Lists the software utilities that are available on the CD.
Read Me Tab
Displays the path for all software and drivers available on the CD.
Click the Setup button to run the software installation program. Select
from the menu which software you want to install.
The Browse CD button is the standard Windows command that allows
you to open Windows Explorer and show the contents of the support
CD.
Before installing the software from Windows Explorer, look for a file
named README.TXT, INSTALL.TXT or something similar. This file
may contain important information to help you install the software
correctly.
Some software is installed in separate folders for different operating
systems, such as DOS, WIN NT, or WIN98/95. Always go to the correct
folder for the kind of OS you are using.
In install the software, execute a file named SETUP.EXE or INSTALL.EXE
by double-clicking the file and then following the instructions on the
screen.
Running Setup
Follow these instructions to install device drivers and software for the motherboard:
1. Click Setup. The installation program begins:
The following screens are examples only. The screens and driver lists will be
different according to the motherboard you are installing.
The motherboard identification is located in the upper left-hand corner.
Using the Motherboard Software
Page 57

2. Click Next. The following screen appears:
3. Check the box next to the items you want to install. The default options are recommended.
4. Click Next run the Installation Wizard. An item installation screen appears:
51
5. Follow the instructions on the screen to install the items.
Drivers and software are automatically installed in sequence. Follow the onscreen instructions, confirm commands and allow the computer to restart a few times to complete the
installation.
Using the Motherboard Software
Page 58

52
Manual Installation
Insert the CD in the CD-ROM drive and locate the PATH.DOC file in the root directory.
This file contains the information needed to locate the drivers for your motherboard.
Look for the chipset and motherboard model; then browse to the directory and path to
begin installing the drivers. Most drivers have a setup program (SETUP.EXE) that automatically detects your operating system before installation. Other drivers have the setup
program located in the operating system subfolder.
If the driver you want to install does not have a setup program, browse to the operating
system subfolder and locate the readme text file (README.TXT or README.DOC) for
information on installing the driver or software for your operating system.
Utility Software Reference
All the utility software available from this page is Windows compliant. They are provided
only for the convenience of the customer. The following software is furnished under license
and may only be used or copied in accordance with the terms of the license.
These software(s) are subject to change at anytime without prior notice.
Please refer to the support CD for available software.
AMI/AWARD Flash Memory Utility
This utility lets you erase the system BIOS stored on a Flash Memory chip on the motherboard,
and lets you copy an updated version of the BIOS to the chip. Proceed with caution when
using this program. If you erase the current BIOS and fail to write a new BIOS, or write a
new BIOS that is incorrect, your system will malfunction. Refer to Chapter 3, Using BIOS for
more information.
WinFlash Utility
The Award WinFlash utility is a Windows version of the DOS Award BIOS flash writer utility.
The utility enables you to flash the system BIOS stored on a Flash Memory chip on the
motherboard while in a Windows environment. This utility is currently available for
WINXP\ME\2000\98SE. To install the WinFlash utility, run WINFLASH.EXE from the
following directory: \UTILITY\WINFLASH 1.51.
This concludes Chapter 4.
Using the Motherboard Software
Page 59

Chapter 5
SiS965/SiS965L SA TA RAID Setup Guide
Introduction for SiS965/SiS965L SA T A RAID Function
The SiS965 S-ATA Host controller supports up to four serial ATA on four independent
ports, but the SiS965L S-ATA controller only supports two SATA ports of up to two Serial
ATA drives. The Serial ATA RAID is designed to provide a cost-effective, high performance
RAID solution that adds performance and/or reliability to PC desktops and/or servers using
Serial ATA/150 hard disks.
Serial ATA RAID function supports striping (RAID 0), mirroring (RAID 1), striping+mirroring
(RAID0+1) and span (JBOD). Please note that the function supports hard disk drives only.
With striping, identical drives can read and write data in parallel to increase performance.
Mirroring increases read performance through load balancing and elevator sorting while
creating a complete backup of your files. Span would increase the logic hard disk space.
Serial ATA RAID striped arrays can double the sustained data transfer rate of Serial ATA/
150. Serial ATA RAID fully supports Serial ATA/150 specification of up to 150MB/sec per
drive, depending on individual drive specifications.
Features
• The SiS965 controller supports up to four Serial A TA (Serial AT A RAID) drivers,
but SiS965L controller suppotrs up to two Serial ATA drives.
• Support RAID function: RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1, JBOD. (SiS965L does not
support RAID 0+1)
• Support bootable disk.
• Windows-based RAID Utility software tool (only support Windows XP and
2000).
• BIOS Utility.
Support Operating Systems
Support Microsoft Windows 98/98SE/ME/2000 Professional and Server/XP.
What is RAID?
This section will give you an overview about the RAID system and introduce the basic
background and glossary which you need to know before using “SiS RAID Controller Application”.
1 RAID: (Redundant Array of Independent Disk Drives) use jointly several hard
drives to increase data transfer rates and data security. It depends on the
number of drives present and RAID function you select to fulfill the security
or performance purposes or both.
2 RAID 0: Also known as “Stripping”. All of the data are distributed evenly to all
of the existing drives. You gain benefits on performance because the data
transfer rate is multiplied by the number of drives. However, RAID 0 has high
risks of data security. All of the stored data will be lost if even any one drive
in the RAID set crashes.
3 RAID 1: Also known as “Mirroring”. Two hard drives are required. The goal of
RAID 0 is to ensure data security. Data is written to two or more drives
synchronously. That is, 100% duplication of data from one drive to another.
53
SiS965/SiS965L SAT A RAID Setup Guide
Page 60

54
4 RAID 0+1: Also known as “Stripe-Mirror”. At least four hard drives are re-
quired. RAID 0+1 is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1. Data is striped into
two drives then mirrored. It provides high performance and high data protection. This is a costly solution as RAID 1 because the two mirrored drives
represent an expensive insurance.
5 JBOD: (Just a Bunch of Drives). Also known as “Spanning”. Two or more hard
drives are required. Several hard disk types configured as a single hard disk.
The hard drives are simply hooked up in series. This expands the capacity of
your drive and results in a useable total capacity. However, JBOD will not
increase any performance or data security.
Installing Software Drivers
SiS RAID driver support Microsoft Windows XP/2000/Me/98SE.
1 For RAID function, SiS965 support RAID0, RAID1, RAID 0+1 and JBOD by
software RAID driver.
2 For RAID function, SiS965L support RAID0, RAID1 and JBOD by software
RAID driver.
3 Support the function of installing windows to RAID array.
New Windows 2000/XP Installation
1 Start the installation:
Boot from the CD-ROM. Press F6 when the message “Press F6 key if you
need to install third party SCSI or RAID driver” appears.
2 When the Windows 2000/XP Setup window is generated, press S key to
specify an Additional Device(s).
3 Insert the driver diskette into drive A: and press Enter.
4 Choose one of the following items:
“Windows 32bit SiS Raid/IDE Controller”,
“Windows 64bit SiS Raid/IDE Controller”,
that appears on screen, and then press the Enter key.
5 Press Enter to continue with installation or if you need to specify any addi-
tional devices to be installed, do so at this time. Once all devices are speci-
fied, Press Enter to continue with installation.
6 From the Windows 2000/XP Setup screen, press the Enter key. Setup will
now load all device files and then continue the Windows 2000/XP instal-
lation.
7 Please install the driver package again (ex. SiS RAID driver v2.01) while the
operation system has been setup.
If you would like to install windows to any RAID set, you should create
RAID from BIOS utility or SiS965/SiS965L RAID Utility first and then
follow the steps above.
Existing Windows 2000/XP/98/Me Installation
1 Install the driver by executing SiS driver setup utility.
2 The drivers will be automatically installed.
Confirming Windows 2000/XP Driver Installation
1 From Windows 2000/XP, open the Control Panel from “My Computer” followed
by the System icon.
2 Choose the “Hardware” tab, then click the “Device Manager” tab.
3 Click the “+” in front of “SCSI and RAID Controllers” hardware type. The driver
“SiS182 Raid Controller” should appear.
SiS965/SiS965L SAT A RAID Setup Guide
Page 61

Confirming Windows 98/Me Driver Installation
1 From Windows 98/Me, open the Control Panel from “My Computer” followed
by the System icon.
2 Choose the “Device Manager” tab.
3 Click the “+” in front of “IDE ATA/ATAPI Controllers” hardware type. The driver
“SiS965 IDE/Raid Controller” should appear.
BIOS Utility Operation
BIOS Utility supports windows 2000/XP/98/Me.
St arting BIOS Utility
1 Boot your system. If this is the first time you have booted with the SiS965 or
SiS965L and the drives installed, the BIOS will display the following:
Silicon Integrated Systems Corp. RAID BIOS Setting Utility v0.XX
(c) 2003-2005 Silicon Integrated Systems Corp. All Rights Reserved.
Press <Ctrl.<S> to run BIOS Setting Utility
2 Press <Ctrl-S> keys to display the SiS965/SiS965L Utility Main Menu.
55
3 You can press <B> key to select the boot disk on the SiS965 controller. The
yellow highlight will show on the disk and you can switch it to select the disk
you wanted. Press “Enter” key to select it and the selected boot device will be
marked by “*”. The default boot device will be set as Disk 1.
4 Press <R> to display the RAID setup menu below. This is the fastest and
easiest method to creating your first array.
SiS965/SiS965L SAT A RAID Setup Guide
Page 62

56
Create RAID
• SIS965 controller support RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1 and JBOD.
• SIS965L controller support RAID 0, RAID 1 and JBOD.
• The selection of RAID 0+1 will appear when 4 single HDD existing
Creating a RAID 0 (Stripe) Array for Performance
• SiS965 enables users to create striped arrays with 2, 3, or 4 drives.
• SiS965L enables users to create striped arrays with 2 drives.
To create an array for best performance, follow these steps:
1 Press <A> to start creating a RAID array.
2 Press <2> and <Enter> to select RAID 0.
3 You will have two selections to create a RAID 0 array. The default value is
<1>. If you select <1>Auto Create, you can create a RAID 0 array faster and
easier. The Blocksize will be selected by its default value “64K”. The result
after creating will be show on step 8. Besides, you also can select <2>Manual
Create, see following steps.
4 Press <1>-<5> keys and <Enter> to select Block Size. (Default:64K)
SiS965/SiS965L SAT A RAID Setup Guide
Page 63

5 Use <↑ > < ↓ > to select disk, and press <Enter> to select disk, <Q> to exit.
When you press <Enter> on the disk you wanted, the RAID Type will be
changed from Single to RAID 0. An the disk you select first will be the SOURCE
disk.
6 Next, you will see a message “Split the SOURCE(DISK x) data to RAID disks?”.
Press <N> and <Enter> to create RAID 0 array only or press <Y> and <Enter>
to split the data from source disk to other disks.
57
7 Starting splitting action, the following frame will be shown.
8 After all steps finished, press ,<Q> until escape the setup menu and RAID 0
array will be show on the top of the main frame.
SiS965/SiS965L SAT A RAID Setup Guide
Page 64

58
9 Press <Q> again to exit this BIOS utility and the red message frame will show.
Press <Y> and <Enter> to save changes.
10 Once the array has been created, you will need to FDISK and format the array
as if it were a new single hard drive.
Creating a RAID 1 (Mirror) Array
• SIS965/SiS965L enables users to create a Mirror array with a pair of drives
only.
• SIS965 enables users to create one or two Mirror arrays.
• SiS965L enables users to create one Mirror array only.
To create a Mirror array, follow these steps:
1 Press <A> to start creating a RAID array.
2 Press <3> and <Enter> to select Mirror.
3 You will have two selections to create a RAID 1 array. The default value is
<1>. If you select <1>Auto Create, you can create a RAID 1 array faster and
easier. The result after creating will be show on step 7. Besides, you also
can select <2>Manual Create, see following steps.
SiS965/SiS965L SAT A RAID Setup Guide
Page 65

4 Use <↑ > < ↓ > to select disk, and press <Enter> to select disk, <Q> to exit.
When you press <Enter> on the disk you wanted, the RAID Type will be
changed from Single to RAID 1. The same as RAID 0, the disk you select first
will be the SOURCE disk.
5 Next, you will see a message “Duplicate the SOURCE (DISK x) data to RAID
disks?”. Press <N> and <Enter> to create RAID 1 array only or press <Y> and
<Enter> to duplicate the data from source disk to mirror disk.
59
6 Starting duplicating action, the following frame will be showing.
7 After all steps finished, press <Q> until escape the setup menu and RAID 1
array will be show on the top of the main frame.
SiS965/SiS965L SAT A RAID Setup Guide
Page 66

60
8 Press <Q> again to exit this BIOS utility and the red message frame will show
as the same as the creation of the RAID 0 array. Press <Y> and <Enter> to
save changes.
9 Once the array has been created, you will need to FDISK and format the array
as if it were a new single hard drive.
Creating a RAID 0+1 (Stripe-Mirror) Array
• Only SiS965 controller can support RAID 0+1 function
• The selection of RAID 0+1 will appear when 4 single HDD existing.
• For user’s convenience, RAID 0+1 will be auto created.
• For best performance, the sequence of RAID 0+1 is forced to set as Disk1->
Disk 3-> Disk 2-> Disk 4.
To create an a Stripe-Mirror array, follow these steps:
1 Press <A> to start creating a RAID array.
2 Press <4> and <Enter> to select RAID 0+1.
3 After step 2, RAID 0+1 array will be shown on the top of the main frame.
4 Press <Q> until exit this BIOS utility RAUID Setup menu and the red message
frame will show as the same as the creation of the RAID 0 array. Press <Y>
and <Enter> to save changes.
SiS965/SiS965L SAT A RAID Setup Guide
Page 67

5 Once the array has been created, you will need to FDUSK and FORMAT the
array as if it were a new single hard drive.
Creating a JBOD Array
• SiS965 enables users to create a JBOD array with 2, 3, or 4 drives.
• SiS965L enables users to create a JBOD array with 2 drives.
To create an JBOD array, follow these steps:
1 Press <A> to start creating a RAID array.
2 Press <1> and <Enter> to select JBOD.
3 You will have two selections to create a JBOD array. The default value is
<1>. If you select <1>Auto Create, you can create a JBOD array faster and
easier. The result after creating will be show on step 5. Besides, you also
can select <2>Manual Create, see following steps.
4 Use <↑> < ↓ > to select disk, and press <Enter> to select disk, <Q> to exit.
When you press <Enter> on the disk you wanted, the RAID Type will be
changed from Single to JBOD.
61
5 After all steps finished, press <Q> until escape the setup menu and JBOD
array will be show on the top of the main frame.
SiS965/SiS965L SAT A RAID Setup Guide
Page 68

62
6 Press <Q> again to exit this BIOS utility and the red message frame will show
as the same age as the creation of the RAID 0 array. Press <Y> and <Enter>
to save changes.
7 Once the array has been created, you will need to FDISK and format the array
as if it were a new single hard drive.
This concludes Chapter 5.
SiS965/SiS965L SAT A RAID Setup Guide
Page 69

Caractéristiques
Processeur
La carte mère utilise un socket LGA775 ayant les caractéristiques suivantes :
• Reçoit des processeurs Intel P4/Celeron
• Support un bus système (FSB) de 800/533 MHz
• Prend en charge les CPU à double noyau
• Supporte le CPU de technologie “Hyper-Threading”
La technologie “Hyper-Threading” permet au système d’exploitation de penser qu’il
est connecté à deux processeurs, permettant d’exécuter deux threads en parallèle, à la fois sur des
processeurs ‘logiques’ dans le même processeur physique.
Chipset
La SiS 649 Northbridge (NB) et SiS965 Southbridge (SB) sont basés sur une architecture novatrice et
dimensionnable avec une fiabilité et des performances prouvées.
SiS649
(NB)
SiS965/965L
(SB)
• Prend en charge 12 Transactions Remarquables et la synchroni-
sation Quasi-Synchrone d’Hôte à DRAM
• Intègre le SiS MuTIOL Haut Débit s’interconnectant au média
d’E/S SiS965 MuTIOL avec bus de données bidirectionnel 16 bits
pour atteindre une bande passante de 1Go/s en mode 133 MHz x
4.
• Prend en charge le Port Graphique PCI-Express X16
• Supporte les DDR400/333/266 ou SDRAM DDR2-533/400
• Prend en charge jusqu’à 2 DIMM DDR2-533 sans tampon ou 2
DIMM DDR400 sans tampon jusqu’à 2 Go
• Entretien simultané pour tous les Périphériques DMA : Contrôleurs
IDE Doubles, contrôleur SATA, trois contrôleurs d’hôte USB 1.1 et
un contrôleur d’hôte USB 2.0, Contrôleur MAC LAN et Contrôleur
DMA Audio/Modem.
• Pont MuTIOL 1G vers PCI Express x1 integre, conforme a PCI
Express 1.0a
• Conforme aux spécifications PCI 2.3.
• Conforme aux spécifications Serial ATA 1.0, prend en charge
jusqu’à quatre ports indépendants (SiS965 seulement).
• Conforme à AC’97 v2.3 supportant 8 Canaux de sorties audio et
Modem V.90 HSP.
• Contrôleur USB 2.0/1.1 intégré prenant en charge jusqu’ à huit
USB ports .
Mémoire
• Supporte le module mémoire DDR SDRAM 400/333/266 MHz
• Peut recevoir deux sockets DIMM sans tampon DDR 184 broches
• Chaque logement prend en charge jusqu’à 1Go avec une capacité maximum totale
de 2Go
Options d’Extensions
La carte mère est livrée avec les options d’extensions suivantes:
• Un logement PCI Express x16
• Trios logement conforme PCI 32 bits
• Deux connecteurs IDE prenant en charge quatre canaux IDE
• Une interface de lecteur de disquette
Cette carte mère prend en charge la maîtrise de bus Ultra DMA avec des vitesses de transfert de
133/100/66 Mo/s.
Français
1394a FireWire (optionnel)
• Conforme au Contrôleur d’hôte PCI à simple puce pour IEEE1394-1995 version
1.0 et IEEE 1394a-2000
• Offre deux ports câbles entièrement compatibles 1394a à 100/200/400 Mbits par
seconde
Multi-Language Translation
Page 70

Français
Audio
LAN Interne (Optionnel)
• Prend en charge une alimentation de 3.3V avec entrées tolérant jusqu’à 5V
• Prend en charge l’interface de BUS PCI à alimentation gérée de 32 bits
• Conforme au CODEC AC’97 V2.3
• Prend en charge le CODEC audio 6 canaux destiné aux systèmes multimédia
PC
• Offre trois entrées stéréo de niveau de ligne analogique avec contrôle de
volume 5 bits: Ligne d’entrée, CD, AUX
• Prend en charge la fonction de sortie S/PDIF
• Conforme à la spécification Azalia, prenant en charge 8 canaux DAC avec
SNR.100dB
• Capacités : 192/96/48/44.1 KHz avec 24/20/16 bits
• Prise en charge du port d’E/S à 8 prises intelligentes
• Détection de prise étendue via RNM (resistors network method) pouvant
être utilisée pour surveiller l’état de branchement de chaque prise
• Prise en charge de SORTIE & ENTRÉE S/PDIF numérique
• Supporte le fonctionnement en Auto-négociation N-way en 100/10Mb/s
• Supporte le fonctionnement en half/full duplex
• Supporte la fonction Wake-On-LAN (WOL) -réveil par appel réseau et le réveil
à distance
• Emetteur-récepteur intégré 10/100/1000
• Prend en charge PCI v2.3, 32 bits, 33/66 MHz
• Prise en charge totale de IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u et IEEE802.3ab
(Remarquez que seul SiS965 prend en charge Giga LAN)
• Prend en charge l’auto-négociation 10/100Mbps
• Prend en charge le fonctionnement en half/full duplex
• Conforme IEEE 802.3/802.3u
E/S intégrées
La carte mère comporte un ensemble complet de connecteurs et de ports E/S :
• Deux ports PS/2 pour souris et clavier
• Un port série (COM1)
• Un port parallèle
• Quatre ports USB
• Un port LAN (optionnel)
• Un port 1394 (optionnel)
• Prise audio pour micro, entrée de ligne et sortie de ligne
Microprogramme BIOS
La carte mère utilise Award BIOS qui permet à l’utilisateur de configurer bon nombre de fonctions
du système, dont :
• Gestion d’alimentation
• Alertes de réveil
• Paramètres de CPU
• Synchronisation de CPU et de mémoire
Le micro-programme peut également être utilisé pour définir les paramètres pour différentes vitesses
d’horloge de processeur.
Certaines spécifications matérielles et certains éléments logiciels sont susceptibles de
modification sans préavis.
Multi-Language Translation
Page 71

Feature
Prozessor
Dieses Mainboard verwendet einen LGA775-Sockel mit den folgenden Eigenschaften:
• Nimmt Intel P4/Celeron Prozessoren auf
• Unterstützt einen Systembus (FSB) mit 800/533 MHz
• Unterstützt Dual-Core-CPU
• Unterstützt CPU mit “Hyper-Threading”-Technologie
“Hyper-Threading”-Technologie läßt das Betriebssystem glauben, es sei an zwei Prozessoren ang
eschlossen, was zwei parallele Threads auf separaten ‘logischen’ Prozessoren im selben physischen
Prozessor erlaubt.
Chipsatz
Die SiS649 Northbridge (NB) und SiS965 Southbridge (SB) basieren auf einer innovativen und
skalierbaren Architektur mit bewiesener Zuverlässigkeit und Leistung.
SiS649
(NB)
SiS965/965L
(SB)
• Unterstützt 12 Outstanding-Transactions und quasi-syn
chrones Host-zu-DRAM-Timing
• Nimmt High-Throughput-SiS MuTIOL auf, für die Verbindung
zu SiS965 MuTIOL Medien I/O mit bidirektionalem 16-Bit
Datenbus, um 1GB/s Bandbreite im 133 MHz x 4 Modus zu
liefern
• Unterstützt PCI-Express X16 Grafik-Port
• Unterstützt DDR400/333/266 oder DDR2-533/400 SDRAM
• Unterstützt bis zu 2 ungepufferte DDR2-533 DIMMs oder 2
ungepufferte DDR400 DIMMs, bis zu 2 GB
• Gleichzeitige Bedienung aller DMA-Geräte: Dual IDE-Controller,
SATA-Controller, drei USB 1.1 Host-Controller und ein USB 2.0
Host-Controller, LAN MAC-Controller und Audio/Modem DMAController
• Integrierte MuTIOL 1G zu PCI Express x1 Bridge, entspricht PCI
Express 1.0a
• Gemäß Spezifikationen von PCI 2.3.
• Entspricht der Serial ATA 1.0 Spezifikation, unterstützt bis zu
vier unabhängige Ports (nur SiS965).
• Gemäß AC’97 v2.3 welcher 8 Audio-Output-Kanäle und ein V.90
HSP-Modem unterstützt.
• Onboard-USB 2.0/1.1-Controller acht USB Port.
Speicher
• Unterstützt DDR400/333/266 MHz SDRAM-Speichermodule
• Nimmt zwei DDR 184-Pin ungepufferte DIMM-Sockel auf
• Jeder Slot unterstützt bis zu 1GB mit einer Gesamtkapazität von 2GB
Erweiterungsmöglichkeiten
Das motherboard bietet die folgenden Erweiterungsoptionen:
• Ein PCI Express x16 Slot
• Drei 32-bit PCI-Slot
• Zwei IDE-Stecker, die vier IDE-Kanäle unterstützen
• Eine Schnittstelle für ein Floppydiskettenlaufwerk
Das Motherboard unterstützt UltraDMA Bus Mastering mit einer Übertragungsrate von133/100/66
MB/Sek.
1394a FireWire (optional)
• Single-Chip PCI Host-Controller entspricht IEEE1394-1995 Release 1.0 und
IEEE 1394a-2000
• Bietet zwei vollständig 1394a entsprechende Kabelports bei 100/200/400 Mbit
pro Sekunde
Multi-Language Translation
-
Deutsch
-
Page 72

• Unterstützt 3.3V Netzteil mit 5V-toleranten Eingängen
• Unterstützt 32-Bit power-managed PCI Bus-Interface
Deutsch
Audio
Onboard LAN (Optional)
Integrierte I/O
BIOS-Firmware
• Entspricht AC' 97 V2.3 CODEC
• Unterstützt 6-Kanal Audio CODEC, entwickelt für Multimedia PC-Systeme
• Stellt drei analoge Line-Level Stereoeingänge mit 5-bit Lautstärkeregelung
zur Verfügung:
• Unterstützt S/PDIF Ausgangsfunktion
• Entspricht Azalia Spezifikation, unterstützt 8-Kanal DACs mit SNR.100dB
• Fähigkeiten: 192/96/48/44.1 KHz mit 24/20/16 Bits
• Unterstützung für 8 Smart Jack I/O-Port
• Weitreichende Steckererkennung via RNM (Resistors Network Method),
kann zur Überwachung des Anschlussstatus für jeden Stecker verwendet
werden.
• Unterstützung für Digital S/PDIF OUT & IN
• Unterstützt den Betrieb bei 100/10Mb/s N-Way Auto-Negotiation
• Halb-/Vollduplexfähigkeit
• Unterstützt Wake-On-LAN(WOL) Funktion und Remote-Wake-up
• Integrierter 10/100/1000 Transceiver
• Unterstützt PCI v2.3, 32-Bit, 33/66MHz
• Vollständige Unterstützung für IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u und IEEE802.3ab
• (Bitte beachten Sie, dass Giga LAN nur von SiS965 unterstützt wird)
• Unterstützt 10/100Mbps Auto-Negotiation
• Unterstützt Halb-/Vollduplexbetrieb
• IEEE 802.3/802.3u Entsprechung
Das Motherboard hat einen vollständigen Satz von I/O-Schnittstellen bzw. -Anschlüssen:
• Zwei PS/2-Anschlüsse für Maus und Tastatur
• Eine serielle Schnittstelle (COM1)
• Eine parallele Schnittstelle
• Vier USB-Anschlüsse
• Ein LAN-Anschluss (optional)
• Ein 1394-Anschluss (optional)
• Audiobuchse für Mikrofon, Line-In und Line-Out
Das Motherboard verwendet Award BIOS, das es Benutzern gestattet, viele Systemfunktionen inkl.
der Folgenden zu konfigurieren:
• Energieverwaltung
• Aufweckfunktionen
• CPU-Parameter
• CPU- und Arbeitsspeicherfrequenz
Die Firmware kann auch zur Einstellung von Parametern für verschiedene Prozessortaktgeschwind
igkeiten verwendet werden.
Manche Hardwarespezifikationen und Softwareelemente können ohne Ankündigung
geändert werden.
Line-in, CD, AUX
-
Multi-Language Translation
Page 73

Caratteristiche
Processore
La scheda madre utilizza una presa LGA775 che offre le seguenti caratteristiche:
• Alloggia processori Intel P4/Celeron
• Supporta un bus di sistema (FSB) fino a 800/533 MHz
• Supporto di CPU a doppio core
• Supporta CPU con tecnologia “Hyper Threading”
La tecnologia “Hyper-Threading” (HT) abilita il sistema operativo a credere di essere collegato a due
processori, consentendo di eseguire in parallelo due Thread, entrambi su processori “logici” separati,
all’interno dello stesso processore fisico.
Chipset
I chipset SiS649 Northbridge (NB) e SiS965 Southbridge (SB) sono basati su un’architettura innovativa
e scalabile di provata affidabilità e di eccellenti prestazioni.
SiS649
(NB)
SiS965/965L
(SB)
• Supporto di 12 transazioni in sospeso e di temporizzazione da host
a DRAM quasi sincrona
• Compatibile con SiS MuTIOL a elevato volume di dati connesso
al supporto I/O SiS965 MuTIOL con bus dati a 16 bit bidirezionale
per larghezza di banda di 1 GB/s in modalità 133 MHz x 4
• Supporto di porta grafica PCI-Express X16
• Supporta DDR400/333/266 o DDR2-533/400 SDRAM
• Supporto di fino a 2 DIMM DDR2-533 senza buffer o a 3 DIMM400
senza buffer per un massimo di 2 GB
• Supporto simultaneo di tutti i componenti DMA: doppio controller
IDE, controller SATA, tre host controller USB 2.0/1.1 e un host
controller USB 2.0, controller LAN MAC e controller DMA Audio/
Modem
• Bridge MuTIOL 1G/PCI Express x1 integrato conforme a PCI
Express 1.0a
• Conforme alle specifiche PCI 2.3.
• Conforme alla specifica Serial ATA 1.0, supporto di fino a quattro
porte indipendenti (solo SiS965)
• Conforme alle specifiche AC’97 v2.3 con il supporto di 6 canali
audio in uscita e HSP-Modem V.90.
• Controller USB 2.0/1.1 integrati con supporto di un massimo di otto
USB porte
Memoria
• Supporta un modulo di memoria SDRAM con DDR fino a 400/333/266 MHz
• Compatibile con due prese DIMM per DDR a 184 pin prive di buffer
• Ogni slot supporta fino a 1 GB per una capacità massima totale di 2 GB
Opzioni d’espansione
La scheda madre è dotata delle seguenti opzioni di espansione
• Uno slot PCI Express x16
• Tre slots PCI 32 bit
• Due connettori IDE per il supporto di 4 canali IDE
• Una interfaccia floppy disk
La scheda madre supporta il bus mastering Ultra DMA con transfer rate 133/100/66 MB/sec.
FireWire 1394a (Opzionale)
• Host controller PCI Single Chip conforme con IEEE1394-1995 versione 1.0 e
IEEE 1394a-2000
• Dotata di due porte per cavo pienamente conformi con 1394a a 100/200/400
Mbit per secondo
• Supporto di alimentazione a 3,3 V con ingressi dotati di tolleranza di 5 V
iano
Ital
Multi-Language Translation
Page 74

Ital
iano
• Supporto di interfaccia bus PCI a 32 bit con gestione dell’alimentazione
Audio
• Conforme alla specifica AC’97 v2.3 CODEC
• Supporto di CODEC audio a 6 canali per sistemi PC multimediali
• Tre ingressi analogici stereo lineari con controllo volume a 5 bit: Line-In, CD,
AUX
• Supporto di funzionalità S/PDIF in uscita
• Conforme con la specifica Azalia, con supporto di DAC a 8 canali con SNR
di 100 dB
• Capacità: 192/96/48/44,1 KHz con 24/20/16 bit
• Supporto di 8 porte I/O Smart Jack
• Estesa rilevazione di jack tramite RNM (Resistors Network Method) che può
essere utilizzato per monitorare lo stato di collegamento di ciascun jack
• Supporto di IN e OUT di S/PDIF digitale
LAN su scheda (Opzionale)
• Supporta operazioni di auto-negoziazione N-way a 100/10Mb/s
• Supporto operazioni half/full duplex
• Supporto funzione WOL (Wake on Lan) e wake up remoto
• Transceiver 10/100/1000 integrato
• Supporto di PCI v2.3, a 32 bit, 33/66 MHz
• Supporto completo degli standard IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u e IEEE802.3ab
(Solo SiS965 offre il supporto di Giga LAN)
• Supporto di auto-negotiation a 10/100 Mb/s
• Supporto di funzionalità half/full duplex
• Conforme a IEEE 802.3/802.3u
I/O integrato
La scheda madre ha una serie completa di porte e connettori I/O:
• Due porte PS/2 per mouse e tastiera
• Una porta seriale
• Una porta parallela
• Quattro porte USB
• Una porta LAN (opzionale)
• Una porta 1394 (opzionale)
• Connettori audio per microfono, ingresso linea ed uscita linea
Firmware BIOS
La scheda madre impiega il software Award BIOS che abilita gli utenti a configurare molte carat
teristiche de sistema, tra cui sono incluse le seguenti:
• Risparmio energetico
• Allarmi di riattivazione
• Parametri CPU
• Temporizzazione di CPU e memoria
Il Firmware può anche essere utilizzato per impostare i parametri di diverse velocità di temporizzazione del processore.
Alcune specifiche hardware ed elementi software sono soggetti a modifica senza
preavviso.
Multi-Language Translation
-
Page 75

Multi-Language Translation
Español
Chipset
Los chipsets Northbridge SiS649 (NB) y Southbridge SiS965 (SB) están basados en una arquitectura
innovadora y escalable con fiabilidad y rendimiento comprobados.
SiS649
(NB)
• Soporta 12 Transacciones Sobresalientes y Anfitrión Casi
Sincrónico al cronometraje de DRAM
• Acomoda Sis MuTIOL de Alto Rendimiento que conecta al I/O
de media SiS965 MuTIOL con bus de datos de 16-bit bidireccional para realizar la ancha de banda de 1GB/s en el modo
133 MHz x 4
• Soporta Puerto de Gráficas PCI-Express X16
• Soporta DDR400/333/266 o DDR2-533/400 SDRAM
• Soporta hasta 2 DIMMs DDR2-533 sin buffer o 2 DIMMs
DDR400 sin buffer hasta 2 GB
SiS965/965L
(SB)
• Servicio concurrente de todos los Dispositivos DMA: Controla-
dores IDE Dual, controlador SATA, tres controladores anfitriones
USB 1.1 y un controlador anfitrión USB 2.0, Controlador LAN
MAC y Controlador DMA Audio/Módem
• MuTIOL 1G a PCI Express x1 Bridge Integrado, conforme
con PCI Express 1.0a
• Conforme con la espec. PCI 2.3.
• Conformidad de la especificación Serial ATA 1.0, soporta
hasta cuatro puertos independientes (SiS965 solamente)
• Conforme con AC’97 v2.3 que soporta 8 Canales de salidas de
sonido y V.90 HSP-Modem.
• Controladores Anfitriones USB 2.0/1.1 integrados que soporta
hasta ocho USB puertos
Memoria
• Soporta DDR hasta módulo de memoria 400/333/266 MHz SDRAM
• Acomoda dos zócalos DIMM sin buffer DDR de 184-pin
• Cada ranura soporta hasta 1GB con una capacidad máxima total de 2GB
Características
Procesador
Esta placa principal usa un tipo LGA775 de Pentium 4 que lleva las sigtes. características:
• Acomoda procesadores Intel P4/Celeron
• Soporta un sistema de bus (FSB) de 800/533MHz
• Soporte CPU de Centro Dual
• Soporta CPU de tecnología “Hyper-Threading”
La tecnología “Hyper-Threading” habilita el sistema operativo para que piense como si estuviera
conectado a dos procesadores, que permite dos hilos a correr en paralelo, ambos en procesadores
“lógicos” dentro del mismo procesador físico.
Opciones de expansión
La placa principla viene con las sigtes. opciones de expansión:
• Una ranura PCI Express x16
• Tres ranuras conforme con 32-bit PCI
• Dos conectores IDE que soporta cuatro canales IDE
• Una interfaz de lector de floppy
La placa principal soporta mastering de bus Ultra DMA con índices de transferencia de 133/100/66
MB/s.
1394a FireWire (optativo)
• Conformidad con el Controlador Anfitrión PCI de Chip Singular para IEEE13941995 Versión 1.0 e IEEE 1394a-2000
Page 76

Multi-Language Translation
Sonido
Español
LAN en abordo (Optativo)
• Provee dos puertos de cable con conformidad completa de 1394a en
100/200/400 Mbit por segundo
• Soporta suministro de cable de 3.3V con entradas tolerantes de 5V
• Soprota interfaz de Bus PCI administrado a 32-bit
• Conforme con el CODEC AC’97 v2.3
• Soporta CODEC de audio de 6 canales diseñaods para los sistemas multimedia
• Provee tres entradas en estéreo a nivel de línea análogicas con control de
volumen de 5-bit: LINE-iIN CD, AUX
• Soporta la función de salida S/PDIF
• Conformidad de la especificación Azalia, que soporta 8 canales de DACs con
SNR.100dB
• Habilidades: 192/96/48/44.1 KHz con 24/20/16 bits
• Soporta 8 puertos I/O Smart Jack
• Detección de clavija extensiva vía RNM (resistors network method/método de
redes de resistores) que se la puede usar para monitorear el estado de conexión
de cada clavija
• Soporte Digital S/PDIF OUT & IN
• Soporta operación de Autonegociación N-Way de 100/10Mb/s
• Capacidad Medio/Completo duplex
• Soporta la función Wake-On-LAN(WOL) y despertar remoto
• Transreceptor 10/100/1000 integrado
• Soporta PCI v2.3, 32-bit, 33/66MHz
• Soporte total de IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u y IEEE802.3ab
(Observe que solamente SiS965 soporta Giga LAN)
• Soporta autonegociación en 10/100Mbps
• Soporta operación de duplex medio/completo
• Conformidad IEEE 802.3/802.3u
I/O integrado
La placa base tiene un conjunto completo de puertos I/O y conectores:
• Dos puertos PS/2 para ratón y de teclado
• Un puerto serie (COM1)
• Un puerto paralelo
• Cuatro puertos USB
• Un puerto LAN (optativo)
• Un puerto 1394 (optativo)
• Clavijas de audio para micrófono, entrada de línea y salida de línea
Firmware de BIOS
La placa base utiliza Award BIOS que permite a los usuarios configurar muchas funciones del sistema,
incluyendo las siguientes:
• Administración de energía
• Alarmas de encendido
• Parámetros CPU
• Temporización de memoria y CPU
El firmware también puede utilizarse para ajustar los parámetros para diversas velocidades del reloj
del procesador.
Algunas especificaciones de hardware y elementos de software están sujetos a cambios
sin previo aviso.
Page 77

Multi-Language Translation
Português
Chipset
O SiS649 Northbridge (NB) e o SiS965 Southbridge (SB) baseia-se numa inovadora arquitectura
escalável, com confiança e desempenho comprovados.
SiS649
(NB)
• Suporta Transacções Fora de Série 12 e Host Quase-Síncrona para
temporização DRAM
• Acomoda Produtividades Elevadas SiS MuTIOL ligando para SiS965
MuTIOL media I/O com bus de dados de 16 bits bi-direccional para
executar largura de banda de 1GB/seg. no modo 4 x 133 MHz
• Suporta PCI-Express X16 Porta de Gráficos
• Suporta DDR400/333/266 ou DDR2-533/400 SDRAM
• Suporta até 2 DDR2-533 DIMMs sem buffers até 2 GB ou 2 DDR2400 DIMMs sem buffers até 2 GB
SiS965/965L
(SB)
• Manutenção concorrente de todos os Dispositivos DMA: Controladores IDE Duplos, controlador SATA, três controladores
host 1.1 USB e um controlador host 2.0 USB, Controlador LAN
MAC e Controlador DMA de Modem/Áudio
• MuTIOL 1G Integrado para PCI Express x1 Bridge, compatí-
vel com PCI Express 1.0a
• Em conformidade com a especificação PCI 2.3
• Cumpre com a especificação de Série 1.0 da ATA, suporta
até quatro portas independentes(somente SiS965)
• Compatível com AC’97 v2.3, suporta 8 canais de saída de áudio
e a norma V.90 HSPModem
• Controladores USB 2.0/1.1 integrados suportando até oito
USB portas
Memória
• Suporta o módulo de memória DDR400/333/266 MHz SDRAM
• Acomoda duas fichas DIMM sem buffers de 184 pinos DDR
• Cada ranhura suporta até 1GB com uma capacidade máxima total de 2GB
Características
Processador
A motherboard usa uma ficha LGA775 que possui as seguintes características:
• Acomoda processadores Intel Intel P4/Celeron
• Suporta um bus sistema (FSB) de 800/533MHz
• Suporta CPU com Núcleo Duplo
• Suporta CPU de tecnologia “Hyper-Threading”
A tecnologia “Hyper-Threading” permite que o sistema operativo “pense” que está ligado a dois proces
-
sadores, permitindo que sejam executados dois threads em paralelo, ambos em processadores
Opções de expansão
A placa principal vem equipada com as seguintes opções de expansão:
• Uma ranhura PCI Express x16
• Três ranhuras PCI de 32 bit
• Dois conectores IDE que suportam quatro canais IDE
• Uma interface da unidade de disquete
Esta motherboard suporta mastering bus Ultra DMA com taxas de transferência de 133/100/66MB/
s.
1394a FireWire (opcional)
• Compatível com Controlador Host PCI com um Único Chip para Versão
IEEE1394-1995 1.0 e IEEE 1394a-2000
• Fornece duas portas para cabo completamente compatíveis 1394a a
100/200/400 Mbit por segundo
Page 78

Multi-Language Translation
Áudio
Português
LAN integrada (Opcional)
• Suporta fonte de alimentação 3.3V com entradas tolerantes de 5V
• Suporta Interface Bus PCI gerido a energia de 32 bits
• Cumpre com o AC’97 v2.3 CODEC
• Suporta CODEC áudio com 6 canais concebido para sistemas multimédia
para PC
• Fornece três entradas estéreo nível de linha analógicas com controlo de
volume de 5 bits: LIne-in, CD, AUX
• Suporta uma função de saída S/PDIF
• Compatível com a especificação Azalia, suportando 8 DACs com canal com
SNR.100dB
• Capacidades: 192/96/48/44.1 KHz com 24/20/16 bits
• Suporta 8 portas Smart Jack I/O
• Detecção extensiva de fichas via RNM (método de rede de resistores) que
podem ser usados para monitorizar o estado de ligação de cada ficha
• Suporte IN & OUT S/PDIF Digital
• Suporta operação de Auto-negociação N-Way 100/10Mb/s
• Capacidade de duplex na totalidade/pela metade
• Suporta função Wake-On-LAN(WOL) e wake-up remoto
• Transmissor 10/100/1000 integrado
• Suporta PCI v2.3, de 32 bits, 33/66MHz
• Suporta na totalidade IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u e IEEE802.3ab
(Tenha em atenção que somente o SiS965 suporta Giga LAN)
• Suporta auto-negociação 10/100Mbps
• Suporta operação de duplex pela metade/na totalidade
• Compatível com IEEE 802.3/802.3u
E/S integradas
A placa principal conta com um conjunto completo de portas e conectores E/S:
• Duas portas PS/2 para o rato e o teclado
• Uma porta de série(COM1)
• Uma porta paralela
• Quatro portas USB
• Uma porta LAN (opcional)
• Uma porta 1394 (opcional)
• Tomadas de áudio para microfone, linha de entrada e linha de saída
Firmware do BIOS
A placa principal usa o Award BIOS que permite aos usuários configurar vários recusos do sistema,
como:
• Gerenciamento de energia
• Alarmes de reativação
• Parâmetros da CPU
• Sincronização da CPU e memória
O firmware também pode ser usado para definir os parâmetros de diferentes velocidades de clock
do processador.
Alguns itens de software e especificação de hardware estão sujeitos a alterações
sem prévio aviso.
Page 79

Multi-Language Translation
日本語
チップセット
SiS649 Northbridge(NB)およびSiS965 Southbridge(SB)チップセットは、実証された信頼
性と性能を持つ革新的で拡張性のあるアーキテクチャに基づいています。
SiS649
(NB)
• 12つOutstanding Transaction機能と、準同期ホスト対DRAMタイミン
グ機能とをサポート
• 高性能SiS MuTIOLを、SiS965 MuTIOL メディア I/Oに双方向16ビッ
トバスを介して接続することにより、133 MHz x 4 モードでの1GB/秒の
帯域幅を実現
• PCI-Express X16 グラフィックポートに対応済み
• DDR400/333/266 あるいは DDR2-533/400 SDRAMをサポート
• 最大2つまでの非バッファーDDR2-533 DIMMあるいはDDR400
DIMM をサポートで、2 GBまでのメモリーの取り付けが可能
SiS965/965L
(SB)
• すべてのDMA 装置の同時サービスを可能に、それらの装置としてデュ
アルIDEコントローラと、SATA コントローラ、三つのUSB 1.1 ホストコ
ントローラや1つのUSB 2.0 ホストコントローラ、LAN MAC コントロー
ラ、オーディオ/モデムDMAコントローラとがある
• PCI Express x1 BridgeのMuTIOL 1Gを内蔵し、PCI Express
1.0aに対応
• PCI 2.3仕様に準拠
• Serial ATA 1.0規格に対応済みで、最大4つまでの独立ポートをサポー
ト可能(SiS965のみ)
• AC' 97 v2.3に準拠し、8チャネルオーディオ出力と V.90 HSP-モデム
をサポート
• 内蔵のUSB 2.0/1.1 コントローラーで、8つのポートを提供
メモリー
• 400 /333/266 MHz SDRAMまでのDDRメモリモジュールに対応
• 2つのDDR 184ピン非バッファーDIMMソケットを搭載
• おのおののスロットに1GB まで、2つのスロットで最大2GBまでのメモリの取り付けが
可能
機能
プロセッサ
本マザーボードに取り入れた LGA775 ソケットは、次の特徴があります:
• Intel P4/Celeronプロセッサに対応
• 800/533 MHzのシステムバス(FSB)をサポート
• デュアルコアプロセッサ対応済み
• 塔nイパースレッド 技術をサポート
"Hyper-Threading"技術というのは、事実上1つのプロセッサ(物理上のプロセッサ)を、2つの
プロセッサ(論理上のプロセッサ)が存在するかのようにオペレーションシステムに認識させるこ
とで、同一の物理上のプロセッサで2つの電算スレッドを同時に執行させる技術です。
拡張オプション
このメインボードには次の拡張オプションがあります:
• PCI Express x16 スロットが1つ
• 32ビットPCIスロットが3つ
• IDE コネクタが2つで、IDE チャネルを4つまでサポート可能
• フロッピーディスクインターフェースが1つ
このマザーボードは、133/100/66MB/秒の転送速度でのUltra DMAバスマスタリングをサポ
ートします。
1394a FireWire (オプション)
• Single Chip PCI Host Controller for IEEE1394-1995 Release 1.0 and IEEE
1394a-2000基準に準拠
Page 80

日本語
オーディオ
• AC’97 v2.3仕様に適合
• PCマルチメディアシステムの6チャネルオーディオCODECをサポート
• 5ビット音声コントロール可能のアナログラインレベルのステレオ入力が3つ:ライ
ンイン、CD、およびAUX
• S/PDIF出力をもサポート
• Azalia 規格に対応し、 SNR.100dBでのDACを8チャネルサポート
• 作動能力: 24/20/16 ビットで192/96/48/44.1 KHz
• 8 つのSmart Jack I/O ポートを搭載
• RNM (resistors network method)方式の外付けジャック認識で、各ジャックの
接続状態をモニタ可能
• デジタルS/PDIF 入出力をサポート
• 1394a 完全対応ののポートが2つで、おのおの秒毎100/200/400 Mbit の転
送率に対応
• 5V許容電圧仕様の3.3V 電源サプライをサポート
• 32ビット電源管理式PCIバスインターフェースをサポート
オンボードLAN (オプション)
• 100/10Mb/s N-way自動ネゴシエーション操作をサポート
• 半/全二重動作可能
• Wake-On-LAN(WOL)機能と遠隔Wake-up機能をサポート
• 10/100/1000 トランシーバーを内蔵
• PCI v2.3( 32ビット、33/66MHz仕様)に対応
• IEEE802.3、IEEE802.3u、およびIEEE802.3abに完全対応
(注意: Giga LAN機能はSiS965のみ)
• 10/100Mbps 自動折衝機能をサポート
• 半/全二重動作可能
• IEEE 802.3/802.3uに対応済み
統合I/O
マザーボードには、次のI/Oポートやコネクタを揃えています
• マウスとキーボード用のPS/2ポートが2つ
• シリアルポート が1つ(COM1)
• パラレルポート が1つ
• USBポート が4つ
• LANポート が1つ(オプション)
• 1394ポート が1つ(オプション)
• マイク、ラインイン、ラインアウト用オーディオジャック
BIOSファームウェア
本マザーボードはAward BIOSを採用することにより、次の機能を含めた多様なシステム構成
を可能にしました
• 電源管理
• ウェークアップアラーム
• CPUパラメータ
• CPUおよびメモリのタイミング
さらに、所定のパラメータを設定することによって、プロセッサのクロック速度を変更すること
もできます。
一部のハードウェア仕様とソフトウェアアイテムは、予告なしに変更すること
がありますので、ご了承ください。
Multi-Language Translation
Page 81

특징
프로세서
본 마더보드는 LGA775 소켓을 사용하여 다음의 특징을 지닌다:
• Intel P4/Celeron프로세서 사용
• 800/533 MHz시스템 버스(FSB) 지원
• 듀얼 코어 CPU 지원
• " Hyper-Threading "기술 CPU 지원
"Hyper-Threading(HT)" 기술은 운영체제로 하여금 두 개의 프로세서에 연결된 것으로 인
식하게 하여 동일한 물리적 프로세서 내의 각기 분리된 논리적 프로세서에서 두 개의 스레드
를 병렬로 실행할 수 있게 합니다.
칩셋
SiS649 Northbridge (NB) 와 SiS965 Southbridge (SB) 칩셋은혁신적이고 범위성을 지닌
아키텍쳐를 바탕으로 인정된 신뢰성과 성능을 지닌다.
SiS649
(NB)
SiS965/965L
(SB)
• 12 Outstanding Transactions 및 DRAM 타이밍을 위한
Quasi-Synchronous Host 지원
• 쌍방향 16 비트 데이터 버스로 SiS965 MuTIOL media I/O 에
연결한 고 쓰루풋 SiS MuTIOL 사용, 133 MHz x 4 모드에서
1GB/s 대역폭 실행
• PCI-Express X16 그래픽 포트 지원
• DDR2-533/400 SDRAM또는 DDR400/333/266 지원
• 최대 2 개의 unbuffered DDR2-533 DIMMs 또는 2 개의
unbuffered DDR400 DIMMs 최대 2 GB 지원
• 모든 DMA 장치의 동시 사용: 듀얼 IDE 컨트롤러, SATA 컨트
롤러, 3 개의 USB 1.1 호스트 컨트롤러 및 1 개의 USB 2.0 호스
트 컨트롤러, LAN MAC 컨트롤러 및 오디오/모뎀 DMA 컨트
롤러
• 통합 MuTIOL 1G to PCI Express x1 Bridge, PCI Express
1.0a 부합
• PCI 2.3 사양 호환.
• Serial ATA 1.0 사양 부합, 최대 4 개의 독립 포트 지원(SiS965
경우에 한함)
• 8채널의 오디오 출력과V.90 HSP-모뎀을 지원하는 AC’97 v2.3
호환.
• 최대 8 개의 USB포트를 지원하는 통합 USB 2.0/1.1 컨트롤러
메모리
• DDR 400/333/266 MHz SDRAM 메모리 모듈 지원
• 2 개의 DDR 184 핀 un-buffered DIMM 소켓 사용
• 각 슬롯은 최대 1GB , 총 용량 2GB 지원
확장 옵션
마더보드에는 다음과 같은 확장 옵션이 있습니다.
• PCI Express x16 슬롯 1 개
• 32비트 PCI 슬롯 3 개
• 4 개의 IDE 채널을 지원하는 IDE 커넥터 2 개
• 플로피 디스크 드라이브 인터페이스 1 개
메인보드는 전송 속도 133/100/66 MB/s 의 Ultra DMA bus mastering 을 지원한다
한 국 어
1394a FireWire (선택사항)
• IEEE1394-1995 Release 1.0 및 IEEE 1394a-2000 을 위한 싱글 칩 PCI 호스트
컨트롤러 부합
• 1394a 케이블 포트 2 개 제공, 초당 100/200/400 Mbit
Multi-Language Translation
Page 82

한
국
어
• 5V 용인 입력의 3.3V 파워 써플라이 지원
• 32 비트 전원 관리 PCI 버스 인터페이스 지원
오디오
• AC’ 97 v2.3 코덱 부합
• PC 멀티미디어 시스템을 위해 디자인 된 6 채널 오디오 코덱 지원
• 5 비트 볼륨 컨트롤의 아날로그 라인 레벨 스테레오 입력 3개 : Line-in, CD,
AUX
• S/PDIF 출력 기능 지원
• Azalia 사양 부합, SNR.100 dB 의 8 채널 DACs 지원
• 용량: 192/96/48/44.1 KHz, 24/20/16비트
• 8 스마트 잭 I/O 포트 지원
• RNM (resistors network method) 을 통한 뛰어난 잭 감지로 각 잭의 플러깅
상태를 모니터할 수 있다.
• 디지털 S/PDIF 출력 및 입력 지원
온보드 LAN(선택 품목)
• 100/10Mb/s N-Way Auto-negotiation 작업 지원
• Half/Full 듀플렉스 성능
• Wake-On-LAN(WOL) 기능 및 원격 wake-up 지원
• 통합 10/100/1000 트랜시버
• PCI v2.3, 32-bit, 33/66MHz 지원
• IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u 및 IEEE802.3ab 지원
(SiS965의 경우에만 Giga LAN 지원)
• 10/100Mbps auto-negotiation 지원
• half/full 듀플렉스 오퍼레이션 지원
• IEEE 802.3/802.3u 부합
통합 I/O
마더보드에는 충분한 수의 I/O 포트 및 커넥터가 있습니다.
• 마우스 및 키보드용 PS/2 포트 2개
• 시리얼 포트 1개(COM1)
• 병렬 포트 1개
• USB 포트 4개
• LAN 포트 1개(선택 품목)
• 1394 포트 1개(선택 품목)
• 마이크, 라인 인 및 라인 아웃용 오디오 단자
바이오스 펌웨어
마더보드는 다음의 기능은 물론 많은 시스템 기능을 설정할 수 있게 하는 Award 바이오스
를 사용합니다.
• 전원 관리
• 웨이크업(Wake-up) 경보
• CPU 매개 변수
• CPU 및 메모리 타이
펌웨어를 사용하여 다른 프로세서 클록 속도에 대한 매개 변수를 설정할 수도 있습니다.
일부 하드웨어 사양 및 소프트웨어 항목은 사전 통보 없이 변경될 수 있습
니다.
Multi-Language Translation
Page 83

功能
處理器
本主機板採用LGA775 插座,該插座具有如下功能:
• 支援Intel P4/Celeron 處理器
• 支援高達800/533 MHz之系統匯流排(FSB)
• 支援雙核心處理器
• 支援使用高速執行緒(Hyper-Threading)技術之CPU
利用"超執行緒(HT)"技術,可使作業系統在相當於裝上了兩具處理器的狀態下運作:
利用一個實體處理器模擬出兩個獨立的"邏輯"處理器,同時執行兩個工作緒。
晶片組
SiS649北橋及SiS965南橋晶片組,採用了獨創且具有擴充功能的架構,能夠發揮最佳
的穩定性及功能。
SiS649
(NB)
SiS965/965L
(SB)
• 支援12 組待傳功能及準同步(Quasi-Synchronous)主控至
DRAM 時序功能
• 配備高效能 SiS MuTIOL ,介以雙向16位元資料匯流排連接
於SiS965 MuTIOL 媒體輸出入單元,藉此在133MHz x 4模式
中實現1GB/秒的頻寬
• 支援 PCI-Express X16 繪圖埠
• 支援DDR400/333/266 或 DDR2-533/400 SDRAM
• 支援2個非緩衝DDR2-533 DIMM或2個非緩衝DDR400 DIMM,可
安裝記憶體容量達2 GB
• 所有DMA 裝置可同時提供服務,此等裝置包含:雙IDE控制
器、SATA 控制器、三個USB 1.1 主控器及1個USB 2.0 主控
器、LAN MAC 控制器、及音訊/數據機DMA控制器
• 內建PCI Express x1 Bridge 用MuTIOL 1G,相容於PCI
Express1.0a規格
• 符合 PCI 2.3規格
• 相容於Seria l ATA 1.0 規格,支援高達4個獨立埠(僅
SiS965)
• 符合AC' 97 v2.3規格,支援8聲道音訊輸出及V.90 HSP數據
機
• 內建USB 2.0/1.1控制器,提供8個連接埠
記憶體
• 支援DDR高達400/333/266 MHz 之SDRAM記憶體模組
• 配備2個DDR 184針非緩衝DIMM插槽
• 各插槽支援1GB,兩個合計支援2GB的記憶體容量
繁體中文
擴充選項
主機板機載有下列擴充選項功能:
• 1個PCI Express x16 插槽
• 3個32位元PCI插槽
• 2個IDE 連接器,藉此支援4個IDE通道
• 1個軟體機介面
主機板也支援Ultra DMA 匯流排主控功能,可提供133 / 100 / 66 MB/sec之傳輸速
率。
1394a FireWire(選配)
• 相容於”Single Chip PCI Host Controller for IEEE1394-1995 Release
1.0 and IEEE 1394a-2000”規格
• 提供2個與1394a 完全相容之連接埠,具每秒100/200/400 Mbit 傳輸率
Multi-Language Translation
Page 84

音效
機載LAN(選項)
繁體中文
• 支援3.3V 電源供應,輸入容限電壓為5V
• 支援32位元電源管理PCI 匯流排介面
• 相容於AC’97 2.3版CODEC規格
• 支援為個人電腦多媒體系統設計的6聲道音訊CODEC功能
• 提供具有5位元音量控制功能的3種類比線級立體音效輸入:LINE-IN、
CD、及AUX
• 支援S/PDIF輸出功能
• 相容於Azalia規格,支援SNR.100dB規格之 8通道 DAC
• 功能:24/20/16 位元下之192/96/48/44.1 KHz
• 支援8 個Smart Jack 輸出入埠
• 採RNM(resistors network method)技術之外延插槽識別功能,藉此可識
別各插槽的插入狀態
• 支援數位S/PDIF輸出入功能
• 支援 100/10Mb/s N-way 自動協調作業
• 半/全雙工功能
• 支援Wake-On-LAN(WOL)功能及遠距 wake-up功能
• 整合有10/100/1000 收發器
• 支援 PCI v2.3(32位元33/66MHz規格)
• 完全支援IEEE802.3、IEEE802.3u 及IEEE802.3ab
(請注意:僅SiS965 支援 Giga LAN功能)
• 支援 10/100Mbps 自動協商功能
• 支援半/全雙工作業
• IEEE 802.3/802.3u 相容
整合 I/O
主機板具有一組齊全的 I/O 連接埠及連接頭:
• 2 個 PS/2 埠,供滑鼠與鍵盤使用
• 1 個串列埠(COM1)
• 1 個平行埠
• 4 個USB埠
• 1 個區域網路埠 (
• 1 個1394埠 (
• 麥克風音頻插座、線級輸入及線級輸出
選項)
選項)
BIOS 韌體
本主機板使用 Award BIOS,使用者可以組態設定許多系統功能,包括如下:
• 電源管理
• 喚醒警鈴
• CPU 參數
• CPU 及記憶體的時脈定時
此外,也可藉由參數的設定,調整處理器的時脈速度。
部份硬體規格和軟體內容可能會在未經通知的情況下更動,敬請見諒。
Multi-Language Translation
Page 85

功能
处理器
此主板使用一个 LGA775 插座,此插座具有以下特点:
• 支持 Intel P4/Celeron 处理器
• 支持 800/533 MHz 系统总线 (FSB)
• 支持 双核心 处理器
• 支持“多线程”技术 CPU
“多线程”技术可以让操作系统认为自己连接了两个处理器,允许两个线程并行运行,
每个线程位于同一处理器中的单独“逻辑”处理器中。
芯片组
SiS649 北桥 (NB) 和 SiS965 南桥 (SB) 芯片组是基于一种新型的、可扩展的架构,能
提供已经证明的可靠性和高性能。
SiS649
NB)
SiS965/965L
(SB)
内存
• 支持 DDR400/333/266 MHz SDRAM 内存模块
• 支持 2 个 DDR 184 线非缓冲 DIMM 插槽
• 每个插槽最大支持 1GB,总共可支持 2GB
扩展选项
此主板提供如下扩展选项:
• 1 个 PCI Express x16 插槽
• 3 个 32 位 PCI 扩展槽
• 2 个 IDE 接口,可支持 4 个 IDE 通道
• 1 个软驱接口
此主板支持 Ultra DMA 总线控制,传输速率可达 133 / 100 / 66 MB/sec。
• 支持 12 个未决事务处理准同步主机到 DRAM 定时
• 支持高吞吐量 SiS MuTIOL 1G 与 SiS965 MuTIOL 媒体
I/O 互连(带双向 16 位数据总线,在 133 MHz x 4 模式
下提供 1GB/s 带宽)
• 支持 PCI-Express X16 图形端口
• 支持 DDR400/333/266 或 DDR2-533/400 SDRAM
• 支持 2 个非缓冲 DDR2-533 DIMM 或 2 个非缓冲 DDR400
DIMM 内存模块,最大支持 2 GB
• 所有 DMA 设备的并发服务:双 IDE 控制器、SATA 控制
器、3 个 USB 1.1主控器和 1 个 USB2.0 主机控制器、LAN
MAC 控制器和音频/调制解调器 DMA 控制器
• 集成 MuTIOL 1G 到 PCI Express x1 桥路,符合 PCI
Express 1.0a 标准
• 符合 PCI 2.3 规格
• 符合串行 ATA 1.0 规格,支持 4 个独立端口(仅SiS965)
• 符合AC’97 v2.3(支持 AC’97 扬声器 8 通道输出)标准和
V.90 HSP 标准
• 集成 USB 2.0/1.1 控制器,最多支持 8 个端口
简体中文
1394a 火线(可选)
• 用于 IEEE1394-1995 Release 1.0 和 IEEE 1394a-2000 的兼容单芯片 PCI
主机控制器
• 提供 2 个 1394a 全兼容的电缆端口,传输速率达 100/200/400 Mbit/秒
• 支持 3.3V 电源,可承受 5V 输入
• 支持 32 位电源管理 PCI 总线接口
Multi-Language Translation
Page 86

音频
Onboard LAN (可选)
简体中文
集成 I/O
• 符合AC’97 v2.3 编解码器规格
• 支持为PC多媒体系统设计的 6 声道音频编解码器
• 提供 3 路带 5 位音量控制的模拟线路电平立体声输入:线入、CD 和
AUX
• 支持 S/PDIF 输出功能
• 符合 Azalia 规格,支持 100dB 信噪比的 8 通道 DAC
• 兼容:192/96/48/44.1 KHz,24/20/16 位
• 支持 8 个智能插孔 I/O 端口
• 通过 RNM(电阻网络方法)的全面插孔检测,用于监视每个插孔的插入
状态
• 支持数字量 S/PDIF OUT & IN
• 支持 100/10Mb/s N 路自协商工作
• 半双工/全双工功能
• 支持 LAN 唤醒 (WOL) 功能和远程唤醒功能
• 集成 10/100/1000 收发器
• 支持 PCI v2.3,32-位,33/66-MHz
• 完全支持 IEEE 802.3、IEEE802.3u 和 IEEE802.3ab
(注意仅 SiS965 支持千兆 LAN)
• 支持 10/100Mbps auto-negotiation
• 支持半双工/全双工工作
• 符合 IEEE 802.3/802.3u 标准
此主板具有完整的 I/O 端口和插孔:
• 2 个用于连接鼠标和键盘的 PS/2 端口
• 1 个串口(COM1)
• 1 个并口
• 4 个 USB 端口
• 1 个 LAN 端口(可选)
• 1 个 1394 端口(可选)
• 麦克风、线入和线出声音插孔
BIOS
此主板使用 Award BIOS,可以让用户自己配置以下系统功能:
• 电源管理
• 唤醒报警
• CPU 参数
• CPU 和记忆定时
还可用于设置不同处理器时钟速度的参数
某些硬件规格和软件项目若有更改恕不另行通知。
Multi-Language Translation
Page 87

Multi-Language Translation
Русский
Чипсеты SiS649 «Северный мост» (Northbridge, NB) и SiS965 «Южный мост» (Southbridge, SB)
построены с использованием инновационной масштабируемой архитектуры, обеспечивающей
высокую надежность и производительность.
SiS649
(NB)
• Обслуживает 12 одновременных операций с квазисинхронным
одращением хоста к памяти DRAM
• Размещает скоростное соединение SiS MuTIOL со входом/
выходом для медиа на SiS965 MuTIOL и двусторонней 16битной шиной со скоростью передачи данных 1 ГБ/с в режиме
133 MГц x 4
• Поддерживает графическую технологию PCI-Express X16
Graphic Port
• Поддерживает DDR400/333/266 или DDR2-533/400 SDRAM
• Поддерживает до 2 модулей небуферируемой памяти DDR2533 DIMM или 2 модулей небуферируемой памяти DDR400
DIMM общим объемом до 2 ГБ
Память
• Поддерживает модули памятиDDR400/333/266 MГц SDRAM
• Размещает два 184-пиновых сокета небуферируемой памяти DDR DIMM
• Каждый слот поддерживает до 1 ГБ памяти с максимальным объемом до 2 ГБ
Чипсет
SiS965/965L
(SB)
• Одновременно обслуживает все уствройства DMA: двойные
контроллеры IDE, контроллер SATA, три контроллера хоста
USB 1.1 и один контроллер хоста USB 2.0, контроллер LAN
MAC и контроллер аудио/модем DMA
• Встроенный мостик MuTIOL 1G - PCI Express x1, совместимый
с PCI Express 1.0a
• Совместимость с PCI 2.3
• Совместимость со спецификацией Serial ATA 1.0, поддержка
до четырех независимых портов (SiS965 ТОЛЬКО)
• Совместимо с AC’97 v2.3б поддерживает 8 – канальный
аудиовыход AC’97 и модем V.90 HSP
• Интегрированный хост-контроллер USB 2.0/1.1 с поддержкой
до 8 USB портов
Характеристики
Процессор
Технология “Hyper-Threading” «убеждает» операционную систему в том, что в машине имеется два
процессора; это позволяет параллельно обслуживать два процесса, причем каждый из процессов
обслуживается отдельным «логическим» процессором в пределах одного физического процессора.
Материнская плата использует сокет LGA775 и обладает следующими характеристиками:
• Размещает процессоры Intel P4/Celeron
• Поддерживает системные шины (FSB) с частотой 800/533MHz
• Обслуживает двухъядерные (Dual Core) процессоры
• Поддерживает технологию CPU “Hyper-Threading”
Плата поддерживает захват управления шиной Ultra DMA со скоростью передачи 133/100/66 MБ/с.
Существуют следуюшие опции расширения данной материнской платы:
• Один слот PCI Express x16
• Три 32-битных слотов PCI
• Два коннектора IDE с поддержкой четырех каналов IDE
• Один разъем для накопителя на гибких дисках
Возможности расширения
1394a FireWire (опционально)
• Совместимость с технологией Single Chip PCI-контроллера хоста для
IEEE1394-1995 в версии 1.0 и IEEE 1394a-2000
Page 88

Русский
• Совместимость с AC’97 V2.3 CODEC
• Поддержка 6-канального аудио-CODEC для компьютерных
мультимедиальных систем
• Три аналоговых стереовхода с 5-битной регуляцией громкости: LINE-IN, CD,
AUX
• Поддержка выхода S/PDIF
• Совместимость со спецификацией Azalia, поддержка 8 каналов DACs при
SNR.100 дБ
• Возможности: 192/96/48/44.1 KГц при 24/20/16 бит
• Поддержка восьми портов входа/выхода типа Smart Jack
• Активное распознавание занятых гнезд технологией RNM (resistors network
method), что позволяет контролировать статус каждого гнезда
• Поддержка цифрового входа/выхода S/PDIF
Аудио
• Два порта полностью совместимые с 1394a на скорости 100/200/400
мегабит в секунду
• Поддерживает электропитание 3.3V при допустимом входном уровне 5V
• Поддерживает 32-битный интерфейс шины PCI с управлением
электропитанием
Встроенный сетевой адаптер LAN (опционально)
• Поддерживает автоматическое определение скорости и режима соединения
100/10Mb/s
• Возможность половинного/полного дуплекса
• Поддерживает функции Wake-On-LAN(WOL) и remote wake-up
• Встроенный трансивер 10/100/1000
• Поддерживает PCI v2.3, 32-бит, 33/66 MГц
• Поддерживает IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u и IEEE802.3ab
(Внимание: поддержка Giga LAN возможна только в случае SiS965)
• Поддержка 10/100Mbps в режиме auto-negotiation
• Поддержка режимов половинный/полный дуплекс
• Совместимость с IEEE 802.3/802.3u
Интегрированный вход/выход
Плата снабжена полным набором портов входа/выхода и разъемов:
• Два порта PS/2 для подключения мыши и клавиатуры
• Один серийный порт (COM1)
• Один параллельный порт
• Четыре порта USB
• Один порт LAN (опционально)
• Один порт 1394 (опционально)
• Гнездо для подключения микрофона, гнезда аудио-входа и выхода
BIOS
Плата работает под Award BIOS, который позволяет пользователю конфигурировать различные
характеристики системы:
• Управление питанием
• Сигналы пробуждения системы
• Параметры CPU
• Время доступа для CPU и памяти
BIOS допускает также установку параметров для различных частот процессора.
Некоторые параметры платы и характеристики ее программного
обеспечения могут быть изменены без предварительного уведомления.
Multi-Language Translation
Page 89

Cechy
Procesor
Płyta główna posiada gniazdo procesorowe LGA775 które zapewnia następujące właściwości:
• Przystosowana do obsługi procesorów Intel P4/Celeron
• Obsługuje szynę systemowa (FSB) 800/533MHz
• Obsługuje procesory o podwójnym rdzeniu (Dual Core)
• Zabezpiecza technologię CPU “Hyper-Threading”
Technologia “Hyper-Threading” powoduje, że system "myśli”, że posiada dwa procesory i
wykonuje równolegle dwa procesy; za wykonanie każdego procesu odpowiedzialny jest jeden z
dwuch "logicznych" procesorów w ramach jednego fizycznego procesora
Chipset
Mostek północny (NB) SiS649 i mostek południowy (SB) SiS965 chipsetu oparty jest na nowatorskiej
i skalowalnej architekturze o sprawdzonej niezawodności i funkcjonalności.
SiS649
(NB)
SiS965/965L
(SB)
Pamięć
• Obsługuje pamięć DDR400/333/266 MHz SDRAM
• Przystosowana do obsługi dwu 184-nóżkowych gniazd pamięci niebuforowanej
DDR DIMM
• Każde gniazdo obsługuje 1 GB pamięć, a całkowicie 2 GB.
• Obsługuje 12równoległych procesów i quasi-synchroniczny taimer
DRAM
• Przystosowany do obsługi wysokowydajnego SiS MuTIOL
połączonego z dwukierunkowym We/Wy SiS965 MuTIOL
oraz 16-bitowej szyny danych zapewniającej przesył 1 GB/s z
częstotliwością w trybie 133 MHz x 4
• Obsługuje złącze graficzne PCI-Express X16
• Obsługuje DDR400/333/266 lub DDR2-533/400 SDRAM
• Obsługuje do 2 banków niebuforowanej pamięci DDR2-533 DIMM
lub niebuforowanej pamięci DDR400 DIMM o pojemności do 2 GB
• Współdziała ze wszystkimi urz ądz eniami DMA: podwójnym
kontrolerem IDE, kontrolerem SATA, trzema kontrolerami hosta USB
1.1 i jednym kontrolerem hosta USB 2.0, kontrolerem LAN MAC oraz
kontrolerem Audio/Modem DMA
• Zintegrowany MuTIOL 1G do mostka PCI Express x1, zgodny z PCI
Express 1.0a
• Zgodny z PCI w wersji 2.3
• Zgodny z Serial ATA w wersji 1.0, obsługuje do czterech
niezależnych złączy (tylko SiS965)
• Zgodny z AC’97 w wersji 2.3, obsługuje 8 kanałowe wyjście AC’97
audio oraz HSP-modem V.90.
• Zcalony kontroler USB 2.0/1.1 obsługuje do ośmiu portów USB
Polski
Możliwości rozbudowy
Płyta głwna wyposażona jest w następujące gniazda:
• Jedno gniazdo PCI Express x16
• Trzy 32-bitowe gniazda PCI
• Dwa złącza IDE, które obsługują cztery kanały IDE
• Jedno złącze obsługujące stacje dyskietek
Płyta głwna obsługuje magistralę Ultra DMA o szybkościach przesyłu 133/100/66MB/s.
FireWire typu 1394a (opcjonalnie)
• Kontroler hosta Single Chip PCI zgodny z IEEE1394-1995 w wersji 1.0 oraz
IEEE 1394a-2000
• Zapewnia dwa całkowicie zgodne złącza do kabli 1394a o przepustowości
100/200/400 Mbit na sekundę
• Obsługuje zasilanie 3,3 V z akceptacją 5 V wejscia
Multi-Language Translation
Page 90

• Obsługuje 32-bitowy interfejs szyny PCI
Audio
• Zgodność z AC’97 V2.3 CODEC
• Obsługa 6-kanałowego audio-CODEC dla multimedialnych systemów komputerowych
• Trzy analogowe linie wejścia stereo z 5-bitową regulacją głosnoći:
LINE-IN, CD, AUX
• Obsługa funkcji wyjścia S/PDIF
• Zgodny z protokołem Azalia, obsługuje 8 kanałowy DACs z SNR.100dB
• Zgodność z: 192/96/48/44.1 KHz oraz z 24/20/16 bitami
• Obsługuje 8 gniazd We/Wy Smart Jack
• Aktywna detekcja gniazd typu jack przez RNM (resistors network method),
która pozwala na monitoring podłączeń do każdego z gniazd.
• Obsługuje cyfrowe Wej/Wyj S/PDIF
Zintegrowana obsługa sieci LAN (opcjonalnie)
• Obsluguje N-drożne automatycznie ustalane operacje z szybkościami
100/10Mb/s
• Możliwość Half/Full duplex
• Obsługuje funkcję Wake-On-LAN(WOL) I zdalne wake-up
• Zintegrowany transceiver LAN 10/100/1000
• Obsługuje PCI wersja 2.3, 32-bit, 33/66MHz
• Całkowicie zgodny z IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u and IEEE802.3ab
(Uwaga: Giga LAN obsługuje tylko chipset SiS965)
• Obsługuje szybkości przesyłania 10/100Mbps z opcją auto-wyboru
• Obsługuje operacje half/full duplex
• Zgodny ze standardem IEEE 802.3/802.3u
Polski
Zintegrowane We/Wy
Płyta głwna wyposażona jest w pełny zestaw gniazd i złączy We/Wy:
• Dwa gniazda PS/2 dla myszy i klawiatury
• Jedno gniazdo szeregowe (COM1)
• Jedno gniazdo równoległe
• Cztery gniazda USB
• Jedno gniazdo LAN (opcjonalnie)
• Jedno gniazdo 1394 (opcjonalnie)
• Gniazdo wejściowe mikrofonowe, gniazdo wejściowe i wyjściowe dzwięku
(audio)
Firmowy BIOS
Płyta głwna wyposażona jest w BIOS firmy Award, który pozwala użytkownikowi konfigurować
wiele cech systemu włączając w to następujące właściwości:
• Zarządzanie poborem mocy
• Alarmy typu Wake-up
• Parametry pracy procesora
• Ustalenia szybkoœci pracy procesora i pamiêci
BIOS może być używany do ustalania parametrów wpływających na szybkości pracy zegara
procesora.
Niektóre parametry dotyczące płyty i jej oprogramowania mogą ulec zmianie bez
uprzedniego powiadomienia.
Multi-Language Translation
Page 91

Multi-Language Translation
Česky
SiS649
(NB)
• Podpora 12 nevyřešených transakcí a kvazi synchronního časování
mezi hostitelem a DRAM
• Podpora vysoké průchodnosti SiS MuTIOL s propojením na mediální
vstup/výstup SiS965 MuTIOL 1G s obousměrnou 16bitovou datovou
sběrnicí k zajištění šířky pásma 1 GB/s na frekvenci 133 MHz x 4.
• Podporuje grafický port PCI Express X16
• Podpora paměťových modulů DDR400/333/266 nebo DDR2-533/400
SDRAM
• Podporuje až 2 moduly DDR2-533 DIMM bez vyrovnávací paměti
nebo 2 moduly DDR400 DIMM bez vyrovnávací paměti, do celkové
kapacity 2 GB
Paměť
• Podporuje paměťové moduly SDRAM, DDR400/333/266 MHz
• Systém je vybaven dvěma 184kolíkovými paticemi pro paměťové moduly DDR
DIMM bez vyrovnávací paměti
• Každý slot podporuje adresování paměti 1 GB až do celkové kapacity 2 GB
Čipová sada
SiS965/965L
(SB)
• Současná obsluha všech zařízení DMA: Duální řadiče IDE, řadič
SATA, tři hostitelské řadiče USB 1.1 a jeden hostitelský řadič USB
2.0, řadič LAN MAC a řadič audio/modemu DMA
• Integrovaný můstek MuTIOL 1G na PCI Express x1, podle standardu
PCI Express 1.0a
• Splňuje požadavky standardu PCI 2.3
• Splňuje požadavky standardu Serial ATA 1.0, podporuje až čtyři
nezávislé porty (Pouze SiS965)
• Splňuje požadavky standardu AC’97 v2.3 s podporou 8kanálového
zvuku AC’97 a modemu V.90 HSP
• Integrované řadiče USB 2.0/1.1 podporující až osm USB portů
Vlastnosti
Procesor
Tato základní deska využívá patici LGA775 nabízející následující vlastnosti:
• Použití pro procesory Intel P4/Celeron s jádrem
• Podporuje taktování systémové sběrnice (FSB) na frekvenci 800/533 MHz
• Podpora procesorů s duálním jádrem
• Podporuje technologii CPU „Hyper-Threading“
Technologie „Hyper-Threading“ umožňuje operačnímu systému pracovat tak, jako by byl připojen
ke dvěma procesorům, protože je možné pracovat se dvěma toky programového kódu (vlákny)
paralelně najednou, přičemž jsou k dispozici samostatné „logické“ procesory umístěné v rámci
jednoho fyzického procesoru.
Čipová sada SiS649 s northbridge (NB) a southbridge (SB)SiS965 je založena na inovativní a
škálovatelné architektuře s ověřenou spolehlivostí a výkonem.
Základní deska je dodávána s následujícími možnostmi rozšíření
• Jedna patice PCI Express x16
• Tři 32bitové patice PCI
• Dva konektory IDE, podporující připojení až 4 zařízení IDE
• Jedno rozraní pro disketovou mechaniku
Možnosti rozšíření
Základní deska podporuje řízení sběrnice Ultra DMA s přenosovými rychlostmi 133/100/66 MB/s.
1394a FireWire (volitelné)
• Splňuje požadavky jednočipového hostitelského řadiče PCI pro IEEE13941995, vydání 1.0 a IEEE 1394a-2000
• Poskytuje dva plně slučitelné porty 1394a pro připojení kabelů s přenosovou
rychlostí 100/200/400 Mbit
Page 92

Multi-Language Translation
Česky
• Podporuje napájení 3,3 V s tolerancí vstupu 5 V
• Podporuje 32bitové rozhraní sběrnice PCI s řízením spotřeby
Audio kodek
• Splňuje požadavky standardu kodeku AC’97 v2.3
• Podpora 6kanálového zvukového kodeku určeného pro multimediální PC systémy
• Nabízí tří analogové linkové stereo vstupy s 5bitovým řízení hlasitosti:
LINE-IN, CD, AUX
• Podpora výstupní funkce S/PDIF
• Zvuková sada splňuje specifikace standardu Azalia, který podporuje 8 kanálový
převodník DAC s odstupem signál/šum 100 dB
• Možnosti: 192/96/48/44,1 kHz s 24/20/16bitovým vzorkováním
• Podpora 8 I/O portů Smart Jack
• Rozsáhlá detekce konektorů prostřednictvím RNM (metoda odporové sítě), kterou
lze využít pro monitorování stav připojených konektorů v každé zdířce
• Podpora digitálního vstupního/výstupního rozhraní S/PDIF
Vestavění síťové rozhraní LAN (volitelně)
• Podpora 100/10Mb/s N–cestného automatického přepínání provozu
• Možnost polovičního a plného duplexu
• Podpora funkce Wake–On–LAN a aktivace na dálku
• Integrovaný přijímač/vysílač 10/100/1000
• Podpora rozhraní PCI v2.3, 32bitové, 33/66 MHz
• Plná podpora IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u a IEEE802.3ab
(Povšimněte si, že pouze SiS965 podporuje Giga LAN)
• Podpora provozu 10/100 Mbps s automatickým vyjednáváním
• Podpora plného/polovičního duplexního provozu
• Splňuje požadavky standardu IEEE 802.3/802.3u
Integrovaný vstup/výstup
Základní deska je vybavena kompletní sadou vstupních portů a konektorů I/O:
• Dva porty PS/2 pro myš a klávesnici
• Dva sériový porty (COM1)
• Jeden paralelní port
• Čtyři porty USB
• Jeden port LAN (volitelně)
• Jeden port 1394 (volitelně)
• Zvukové konektory pro mikrofon, zvukový vstup a výstup
Firmware BIOS
Základní deska využívá BIOS formy Award, který uživateli umožňuje nakonfigurovat mnoho
systémových parametrů, včetně následujících:
• Řízení spotřeby
• Alarmy při spouštění systému
• Parametry CPU
• Časování CPU a paměti
Firmware může být rovněž použit k nastavení parametrů pro různé taktovací frekvence procesoru.
Některé technické parametry hardware a software se mohou měnit bez
předchozího upozornění.
Page 93

Caracteristici
Procesorul
Placa de bază utilizează un soclu LGA775 cu următoarele proprietăţi:
• Funcţionează cu procesoare Intel P4/Celeron
• Funcţionează cu bus sistem (FSB) de 800/533 MHz
• Suporta procesoare dual-core
• Este compatibilă cu unităţi centrale dotate cu tehnologia „Hyper-Threading”
Tehnologia „Hyper-Threading” permite sistemului de operare să funcţioneze ca şi cum ar exista
două procesoare, putând fi rulate în paralel două fire, fiecare pe câte un procesor „logic” separat,
aflate pe acelaşi procesor fizic.
Setul de chipuri
Seturile de chipuri SiS649 Northbridge (NB) şi SiS965 Southbridge (SB) se bazează pe o arhitectură
inovatoare şi scalabilă, care s-a impus deja prin fiabilitate şi performanţă.
SiS649
(NB)
• Suportă 12 tranzacţii nesoluţionate şi gazdă cvasi-sincronă pentru
temporizare DRAM
• Funcţionează cu SiS MuTIOL de mare capacitate pentru conectarea
cu I/O SiS965 MuTIOL, pentru suporturi cu bus sistem bidirecţional
pe 16 biţi, cu lăţime de bandă de 1 GB/s în modul 133 MHz x4
• Suportă port grafic PCI-Express X16
• Suportă module DDR400/333/266 sau SDRAM DDR2-533/400
• Suportă până la cel mult 2 module DIMM DDR2-533 fără zonă
tampon sau 2 module DIMM DDR400 fără zonă tampon
SiS965/965L
(SB)
Memoria
• Suportă module de memorie SDRAM DDR400/333/266 MHz
• Este echipată cu două module DIMM DDR fără zonă tampon cu 184 ace
• Fiecare soclu suportă module de până până la 1 GB, cu o capacitate totală
maximă de 2 GB
• Deservire concurentă a tuturor dispozitivelor DMA: controleri IDE
duali, controler SATA, trei controleri gazdă USB 1.1 şi un controler
gazdă USB 2.0, un controler LAN MAC şi un controler Audio/Modem
DMA
• MuTIOL 1G integrat pentru PCI Express x1 Bridge, compatibil cu
PCI Express, versiunea 1.0a
• Compatibil cu specificaţia PCI 2.3
• Compatibilitate cu Serial ATA specificaţia 1.0, suportând până la
patru porturi independente (numai SiS965)
• Compatibilă cu AC’97, versiunea 2.3, suportând 6 canale pentru
ieşiri difuzor AC’97 şi modem HSP V.90
• Controleri gazdă USB 2.0/1.1 integraţi, care suportă cel mult opt
porturi
Opţiuni de extindere
Placa de bază este dotată următoarele posibilităţi de extindere:
• Un soclu PCI Express x16
• Trei sloturi PCI de 32 biţi
• Două conectoare IDE care suportă patru canale IDE
• O interfaţă pentru unitate floppy
Această placă de bază suportă Ultra DMA bus mastering cu viteza de transfer de 133/100/66MB/s.
1394a FireWire (opţional)
• Controler gazdă PCI cu un singur cip pentru IEEE1394-1995, versiunea 1.0 şi
IEEE 1394a-2000
• Oferă două porturi de cablu total compatibile cu 1394a, la viteze de
100/200/400 Mb/s
Multi-Language Translation
Română
Page 94

• Suportă sursă de alimentare de 3,3V cu intrări cu toleranţă de 5 V
• Suportă interfaţă PCI Bus pe 32 biţi cu control electric
Audio
• Compatibil cu CODEC AC’97, versiunea 2.3
• Suportă CODEC audio de 6 canale, destinat sistemelor multimedia ale
calculatoarelor
• Asigură trei linii intrare stereo analoge, cu control al volumului pe 5 biţi:
LINE-IN, CD, AUX
• Suportă funcţia de ieşire S/PDIF
• Compatibilă cu specificaţia Azalia, supotând DAC-uri cu 8 canale cu SNR de
100 dB
• Posibilităţi: 192/96/48/44.1 KHz cu 24/20/16 biţi
• Suport pentru 8 porturi Smart Jack I/O
• Detectare avansată mufă prin RNM (metoda reţelei de rezistori) care poate fi
utilizată pentru a monitoriza starea de conectare a mufelor
• Suport pentru S/PDIF IEŞIRE şi INTRARE digitale
Onboard LAN (opţional)
• Suportă operaţii de autonegociere N-way de 100/10 Mb/s
• Capacitate semi-duplex/duplex complet
• Suportă funcţia Wake-On-LAN(WOL - activare în caz de conectare LAN) şi
trezire de la distanţă
• Emiţător-receptor 10/100/1000 integrat
• Suport pentru PCI vers. 2.3, pe 32 biţi, la 33/66 MHz
• Compatibilitate deplină cu IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u şi IEEE802.3ab
(Reţineţi că doar SiS965 suportă Giga LAN)
• Suportă reglare automată 10/100Mbps
• Suportă modul de operare duplex total/semi-duplex
• Compatibilitate cu IEEE 802.3/802.3u
Română
I/O integrată
Placa de bază este dotată cu un set complet de porturi şi conectoare I/O:
• Două porturi PS/2, pentru mouse şi tastatură
• Un port serial (COM1)
• Un port paralel
• Patru porturi USB
• Un port LAN (opţional)
• Un port 1394 (opţional)
• Mufe audio pentru microfon, intrare şi ieşire audio
Firmware BIOS
Această placă de bază utilizează Award BIOS, care permite utilizatorului să configureze mai mulţi
parametri ai sistemului, cum ar fi:
• Gestionarea energiei
• Alarme de trezire
• Parametri CPU
• Temporizare CPU şi memorie
Acest firmware poate fi utilizat şi pentru a seta parametrii diferitelor frecvenţe de comandă ale
procesorului.
Anumite specificaţii hardware şi elemente de software pot fi modificate fără
înştiinţare prealabilă.
Multi-Language Translation
Page 95

Multi-Language Translation
Български
Чŕпсетът със северен мост SiS649 и южен мост SiS965 е изграден на базата на оригинална
архитектура с възможност за надстройка с доказана надеждност и производителност.
SiS649
(NB)
• Поддръжка на 12 изчакващи транзакции и квази-синхронно
Host-to-DRAM синхронизиране
• Високопроизводителен интерфейс SiS MuTIOL към SiS965
MuTIOL media I/O с двупосочна 16 битова шина за данни и
скорост 1GB/s в режим 133 MHz x 4
• поддръжка на графичен порт PCI-Express X16
• Поддръжка на модули памет DDR400/333/266 или DDR2533/400 SDRAM
• поддръжка до два небуферирани модула памет DDR2533 или два небуферирани модула памет DDR400 с общ
капацитет до 2 GB
Памет
• Поддръжка на модули памет DDR400/333/266 MHz SDRAM
• поддръжка на два небуферирани слота DDR 184-pin DIMM
• всеки слот поддържа до 1 GB с общ максимален капацитет 2GB
Чипсет
SiS965/965L
(SB)
• Равностойно обслужване на всички DMA устройства: Два IDE
контролера, SATA контролер, три USB 1.1 host контролера и един
USB 2.0 host контролер, LAN MAC контролер и Audio/Modem DMA
контролер
• Интегриран мост MuTIOL 1G към PCI Express x1 съвместим с
PCI Express 1.0a
• поддръжка на шината PCI 2.3
• Съвместимост със спецификацията Serial ATA 1.0, с
поддръжка до четири независими порта (само SiS965)
• Съвместимост със спецификацията AC’97 v2.3 с поддръжка на
6-канално аудио и модем V.90 HSP
• интегрирани USB 2.0/1.1 контролери, поддържащи до осем
USB порта
Спецификация
Процесор
Тази дънна платка използва сокет LGA775 със следните спецификации:
• поддръжка на процесори Intel P4/Celeron
• поддръжка на системна шина със скорост 800/533MHz
• Поддръжка на двуядрени процесори
• поддръжка на процесори с технология “Hyper-Threading"
Технологията “Hyper-Threading" позволява да се “излъже” операционната система, че работи
на два процесора, което дава възможност за паралелното изпълнение на две задачи на два
отделни “логически” процесора в един и същ физически процесор.
Дънната платка поддържа шина Ultra DMA 133/100/66/33MB/s.
Дънната платка има следните разширителни възможности:
• един слот PCI Express x16
• Три слота 32-bit PCI
• два IDE конектора с поддръжка на четири IDE канала
• един конектор за флопидисково устройство
Възможности за разширяване
1394a FireWire (опция)
• PCI Host контролер (на един чип) съвместим със спецификациите
IEEE1394-1995 Release 1.0 и IEEE 1394a-2000
• Два кабелни порта (100/200/400 Mbit/sec) напълно съвместими със
стандарта 1394a
Page 96

Multi-Language Translation
• поддръжка на захранване 3.3V с толеранс до 5V
• поддръжка на 32-битов интерфейс на PCI шината с управление на
захранването
Audio
• съвместимост с AC’97 V2.3 CODEC
• п оддръжка на 6-канален аудио CODEC специално създа ден за
мултимедийни системи
• Включва три аналогови линейни стерео входа с 5-битов контрол на силата
на звука: LINE-IN, CD, AUX
• поддръжка на функцията S/PDIF Out
• Съвместимост със спецификацията Azalia с поддръжка на 8 канала
цифрово-аналогови преобразователи (8 channel DACs) при SNR 100 dB
• Възможности: 192/96/48/44.1 KHz с 24/20/16 bits
• поддръжка 8 Smart Jack I/O порта
• Разширено определяне на гнездата чрез RNM (resistors network method)
с възможности за мониторинг на статуса на включване на всяко гнездо
• Поддръжка на Digital S/PDIF OUT & IN
Интегриран мрежов контролер (опция)
• поддръжка на 100/10Mb/s, N-Way Auto-negotiation operation
• Half/Full duplex режими
• Поддръжка на режими Wake-On-LAN (WOL) и remote wake-up
• Интегриран трансивер 10/100/1000
• Поддръжка на PCI v2.3, 32-bit, 33/66MHz
• Пълна съвместимост с IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u и IEEE802.3ab
(Моля отбележете, че Giga LAN се поддържа само от SiS965)
• Поддръжка на автосъгласуване 10/100Mbps
• Поддръжка на режими half/full duplex
• Съвместимост със спецификацията IEEE 802.3/802.3u
Български
Интегриран Вход/Изход контролер
Дънната платка има пълен набор от I/O портове и конектори:
• два PS/2 порта за мишка и клавиатура
• един сериен порт (COM1)
• един паралелен порт
• четири USB порта
• един LAN порт (опция)
• един 1394 порт (опция)
• Аудио жакове за микрофон, линеен вход и линеен изход
BIOS Firmware
Дънната платка използва Award BIOS с възможност за различни системни настройки,
включително
• управление на захранването
• Wake-up аларми
• параметри на процесора
• синхронизиране на процесора и паметта
настройка на скоростта на часовника на процесора
Хардуерните и софтуерни спецификации и параметри могат да бъдат изменени
без предупреждение.
Page 97

Multi-Language Translation
Magyar
Az SiS649 Northbridge (NB) és SiS965 Southbridge (SB) lapkakészletek egy újító és méretezhető,
nagy megbízhatóságú és teljesítőképességű architektúrára épülnek.
SiS649
(NB)
• 12 elintézetlen műveletet és kvázi szinkronizált gazdát támogat
DRAM időzítéshez
• Nagy teljesítményű SiS MuTIOL, amely a SiS965 MuTIOL I/O
hordozóhoz egy kétirányú, 16 bites adatbusszal csatlakozik, 1 GB/
s sávszélesség elérésére 133 MHz x 4 módban.
• PCI-Express X16 grafikus portot támogat
• DDR2-533/400SDRAM vagy DDR400/333/266 modulokkal
kompatibilis
• Maximum 2 puffer nélküli DDR2-533 DIMM vagy 2 puffer nélküli
DDR400 DIMM modult támogat, 2 GB maximális kapacitással
Memória
Lapkakészlet
SiS965/965L
(SB)
• Minden DMA eszköz egyidejű kiszolgálása Duál IDE vezérlők, SATA
vezérlők, három USB 1.1 gazda vezérlő és egy USB 2.0 gazda
vezérlő, LAN MAC vezérlő és Audio/Modem DMA vezérlő
• Beépített MuTIOL 1G a PCI Express x1 híd, amely a PCI Express
1.0a változatával kompatibilis
• Kompatibilis a PCI 2.3-as specifikációjával
• Kompatibilis a Soros ATA 1.0 változatával, maximum négy
független portot támogat (csak SiS965)
• Kompatibilis az AC’97 2.3-as verziójával, amely 8 csatornás AC’97
hangszóró kimenetet és V.90 HSP modemet támogat
• Beépített USB 2.0/1.1 gazda vezérlők, legtöbb nyolc portot
támogatnak
Jellemző
Processzor
Ez az alaplap LGA775 foglalattal rendelkezik, ennek jellemzői pedig a következők:
• Intel P4/Celeron processzorokkal működik
• 800/
533 MHz sebességű rendszerbuszt (FSB) támogat
• Kétmagos processzor támogatása
• Támogatja a „Hyper-Threading” technológiát használó központi egységeket
A „Hyper-Threading” technológia által az operációs rendszer úgy működik, mintha két
processzorral rendelkezne, ami két szál párhuzamos futását teszi lehetővé két független, ugyanazon
fizikai processzoron található „logikai” processzoron.
• DDR400/333/266 MHz-es SDRAM memóriamodulokat támogat
• Két 184 tűs puffer nélküli DDR DIMM foglalattal rendelkezik
• Mindkét foglalat maximum 1 GB-os modult képes befogadni, a maximális
kapacitás 2 GB
Ez az alaplap a 133/100/66 MB/s átviteli sebességű Ultra DMA ’bus mastering’ megoldást is
támogatja.
Az alaplap a következő bővítési lehetőségekkel rendelkezik:
• Egy 16-szoros PIC Express foglalat
• Három 32 bites PCI foglalat
• Két IDE csatlakozó, amelyek négy IDE csatornát tudnak kiszolgálni
• Egy hajlékonylemez meghajtó interfész
Bővítési lehetőségek
1394a FireWire (opcionális)
• Az IEEE1394-1995 1.0 és az IEEE 1394a-2000 szabványokkal kompatibilis
egylapkás PCI gazda vezérlő
• Két az 1394a szabvánnyal teljesen kompatibilis kábelportot bocsát rendelkezésre, 100/200/400 Mbit/s sebességen
Page 98

Multi-Language Translation
Magyar
Audio
• Kompatibilis az AC’97 2.3-as CODEC változatával
• A számítógép multimédiás rendszereinek szánt hat csatornás audio CODEC-et
támogat
• Három analóg sztereo bemenetet biztosít 5 bites hangerő vezérléssel:
AUDIO BEMENET, CD, AUX
• Támogatja az S/PDIF kimeneti funkciót
• Kompatibilis az Azalia specifikációval, 8 csatornás, 100 dB-es SNR értékű DAC
támogatása
• Lehetőségek: 192/96/48/44,1 KHz, 24/20/16 biten
• 8 Smart Jack I/O port támogatása
• Átfogó dugaszérzékelés RNM (ellenállás-hálózat módszer) segítségével, amely a
dugaszok csatlakozási állapotának követésére használható
• Digitális S/PDIF BE és KI támogatása
• 3,3V-os tápforrást támogat, 5 V-ot toleráló bemenetekkel
• 32 bites tápvezérelt PCI Bus interfészt támogat
Alaplapon levő LAN (választható)
• 100/10Mb/s N-Way automatikus beállítással
• Teljes/fél duplex lehetőség
• Támogatja a Wake-On-LAN funkciót és a távoli ébresztést
• Beépített 10/100/1000 adó-vevõ
• Támogatja a 32 bites, 33/66 MHz-es PCI 2.3-as változatát
• Teljesen megfelel az IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u és IEEE802.3ab szabványoknak
(Jegyezze meg, hogy csak a SiS965 támogatja a Giga LAN-t)
• 10/100Mbps automatikus beállítás támogatása
• Fél, illetve teljes duplex üzemmód támogatása
• IEEE 802.3/802.3u kompatibilitás
Beépített I/O
Az alaplapot az I/O portok és csatlakozók teljes készletével szerelték fel:
• Két PS/2 port az egér és a billentyűzet számára
• Egy soros port (COM1)
• Egy párhuzamos port
• Négy USB port
• Egy LAN port (választható)
• Egy 1394 port (választható)
• Audio csatlakozók mikrofon, bemenet és kimenet számára
BIOS Firmware
Az alaplapon levő Award BIOS segítségével a felhasználó a rendszer sok paraméterét állíthatja be,
például:
• Energiagazdálkodás
• Ébresztési riasztások
• CPU paraméterek
• CPU és memória időzítés
A firmware segítségével a processzor órajel-frekvenciáinak paramétereit is beállíthatják.
Bizonyos hardverjellemzők és szoftverelemek előzetes bejelentés nélkül
módosulhatnak.
 Loading...
Loading...