Page 1

GPRS TRANSMITTER
EPX400
Installation and
programming manual
Issue:
1.7
Release date:
30.10.2017
Firmware version:
2.3.0
GPRS transmitter configurator version:
1.3.76.3
OSM server version:
1.3.68.2
Page 2

DECLARATION OF COMPLIANCE
We, EBS Sp. z o.o., declare with full responsibility that the present
product meets all requirements provided for in the Directive 1999/5/EC
of European Parliament and Council dated 9 March 1999. The copy of
the “Declaration of Compliance” can be found at
http://www.ebs.pl/en/certificates/ .
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Crossed symbol of a trash bin means that at the territory of European
Union, the product, after finishing its useful life, shall be disposed of in
a separate, specially dedicated collection point. It refers to the
equipment itself and its accessories marked with that symbol. The
products shall not be disposed of together with non-sortable municipal
waste.
The content of the document is presented “as is”. The present
document shall not be deemed to be providing any warranties, either express or
implicit, including but not limited to, any implied warranties of merchantability or
fitness for a particular purpose, unless it is required by relevant law. The
manufacturer reserves the right to amend the present document or withdraw it any
time, without notice.
The manufacturer of the equipment promotes the sustainable development policy. It
reserves the right to modify and improve any functions of the product described in
the present document without previous notice.
The availability of particular functionalities will depend on the software version of the
equipment. Details can be found at the nearest dealer of the equipment.
In no event, the Manufacturer shall be held liable for any loss of data or loss of
profits or any specific, incidental, consequential or indirect damages caused in any
way.
MANUFACTURER
EBS Sp. z o.o.
59 Bronislawa Czecha St.
04-555 Warsaw, POLAND
E-mail : sales@ebs.pl
Technical support: support@ebs.pl
Webpage : www.ebs.pl
Page 3

EPX400 – Manual
Page 3 / 71
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION ..................................................................................... 5
2. FUNCTIONAL AND TECHNICAL PARAMETERS ......................................... 6
3. ASSEMBLY AND WIRING ........................................................................ 8
3.1. EPX400 TRANSMITTER ...................................................................... 8
3.2. PCB VERSION .................................................................................... 9
3.3. INPUT CONFIGURATION ................................................................. 10
4. QUICK START PROCEDURE ................................................................... 11
5. OPERATION ......................................................................................... 13
6. PRE-CONFIGURATION VIA ETHERNET PORT ........................................ 14
6.1. LOGGING IN .................................................................................... 14
6.2. DESCRIPTION ................................................................................. 15
6.3. CONFIGURATION ............................................................................ 15
6.3.1. Server parameters ....................................................................... 16
6.3.1.1. Server address ...................................................................... 16
6.3.1.2. Server port ............................................................................ 16
6.3.2. APN parameters ........................................................................... 16
6.3.2.1. APN ...................................................................................... 16
6.3.2.2. User ID ................................................................................. 16
6.3.2.3. User password ....................................................................... 17
6.3.2.4. DNS ..................................................................................... 17
6.3.3. Access Parameters ....................................................................... 17
6.3.3.1. Service code .......................................................................... 17
6.3.3.2. SIM card PIN ......................................................................... 17
6.4. UPDATE FIMWARE ........................................................................... 17
6.5. CONTACT ......................................................................................... 18
7. CONFIGURATION PROGRAM ................................................................ 20
7.1. INITIAL REMARKS ........................................................................... 20
7.2. COMPUTER – REQUIREMENTS ......................................................... 20
7.3. PROGRAM FUNCTIONS .................................................................... 20
7.3.1. File -> New ................................................................................. 21
7.3.2. File -> Open ................................................................................ 21
7.3.3. File -> Save ................................................................................ 21
7.3.4. File -> Language.......................................................................... 22
7.3.5. File -> Connections ...................................................................... 22
7.3.5.1. Local connection .................................................................... 22
7.3.5.2. Remote connection ................................................................. 23
7.3.6. File-> Automatic device settings backup ......................................... 25
7.3.7. File -> Exit .................................................................................. 25
7.3.8. Operations -> Read ...................................................................... 25
7.3.9. Operations -> Send ...................................................................... 25
7.3.10. Operation -> Device monitor ......................................................... 26
7.3.11. Operation -> System events history ............................................... 26
7.3.12. Operation -> Restore default settings ............................................. 26
7.3.13. Help -> About program ................................................................. 26
8. PROGRAMMABLE PARAMETERS ............................................................ 27
8.1. ACCESS ........................................................................................... 27
8.1.1. Transmitter ................................................................................. 27
8.1.1.1. Group: Access ....................................................................... 27
8.1.1.2. Group: SIM Cards .................................................................. 28
8.1.2. Server connection ........................................................................ 29
8.1.2.1. Ethernet parameters............................................................... 29
8.1.2.2. GPRS parameters ................................................................... 30
Page 4

EPX400 – Manual
Page 4 / 71
8.1.2.3. SMS Parameters .................................................................... 31
8.1.3. Communication ............................................................................ 32
8.2. TRANSMISSION .............................................................................. 35
8.3. INPUTS/OUTPUTS ........................................................................... 35
8.3.1. Inputs configuration ..................................................................... 35
8.3.2. Partitions .................................................................................... 37
8.3.3. Outputs ...................................................................................... 39
8.3.4. Advanced outputs control .............................................................. 40
8.4. MONITORING .................................................................................. 42
8.4.1. Ethernet ..................................................................................... 42
8.4.2. GPRS .......................................................................................... 42
8.4.3. SMS ........................................................................................... 43
8.4.4. Skip initial state ........................................................................... 43
8.4.5. Power loss................................................................................... 43
8.4.6. Event: CLIP ................................................................................. 43
8.4.7. Sleep when the battery voltage less than ........................................ 43
8.5. RESTRICTIONS ................................................................................ 44
8.5.1. SMS and data calls (CSD) ............................................................. 44
8.6. SMS NOTIFICATIONS ...................................................................... 46
8.6.1. Phone numbers ............................................................................ 46
8.6.2. Events ........................................................................................ 47
8.6.3. Status ........................................................................................ 49
8.6.4. SMS Forward ............................................................................... 50
8.7. RS232 ............................................................................................. 51
8.7.1. Serial port settings ....................................................................... 52
8.7.2. Buffer flushing ............................................................................. 52
8.7.3. Advanced port options .................................................................. 53
8.8. LINK CONTROL ................................................................................ 53
8.8.1. Watchdog ................................................................................... 54
8.9. PHONE LINE .................................................................................... 55
8.9.1. Phone line settings ....................................................................... 55
8.9.2. First and Second phone number ..................................................... 56
8.10. FIRMWARE ...................................................................................... 58
8.11. DEVICE MONITOR ........................................................................... 59
8.12. EVENTS HISTORY ............................................................................ 60
9. DEVICE PROGRAMMING ....................................................................... 62
9.1. LOCAL PROGRAMMING .................................................................... 62
9.2. REMOTE PROGRAMMING ................................................................. 62
9.2.1. The first programming of device .................................................... 63
9.2.2. Reprogramming of device ............................................................. 63
10. RECEIVING OF SMS MESSAGE .............................................................. 64
10.1. REMOTE COMMANDS DESCRIPTION ................................................ 64
11. LED DIODES INDICATION .................................................................... 67
11.1. LOGGING TO GSM NETWORK ........................................................... 67
11.2. GSM RANGE ..................................................................................... 67
11.3. DATA TRANSMISSION ..................................................................... 68
11.4. RECEIVING OF DTMF DATA ............................................................. 68
11.5. PROGRAMMING ............................................................................... 69
11.6. FIRMWARE UPDATING .................................................................... 69
11.7. SIM CARD ERROR ............................................................................ 70
11.8. SYSTEM ERROR ............................................................................... 70
12. CHANGELOG ......................................................................................... 71
Page 5

EPX400 – Manual
Page 5 / 71
1. INTRODUCTION
EPX400 Transmitter is a modern, microprocessor device for data transmission in
real time, capable of simulating a telephone line (PSTN). In case of telephone line
failure or by selecting the appropriate prefix, the device is able to perform a
connection to the monitoring station, allowing you to transfer data from the control
panel via Contact ID (DTMF) or SIA (FSK) protocol.
EPX400 Transmitter provides the highest security of data transmission through up
to five channels of transmission: ETHERNET, GPRS, SMS, PSTN.
The primary purpose is to use the device as a security systems transmission module
in ETHERNET, GPRS and PSTN. The transmitter works with all most popular alarm
systems. Ethernet connection and packet data transmission (GPRS), can reduce the
operating cost of the alarm systems. This device provides an opportunity to send text
messages to private mobile phones.
An advanced encoding methods like a 256 bits encoding key and AES (Advanced
Encryption Standard) provides for security of data transmission. As a result reception
of this transmission is possible with OSM.Server monitoring receiver system.
Furthermore there is possibility to transmit not coded messages that are to be
comprehensible by reception solutions and also by GPRS Server software.
EPX400 transmitter depending on model can be equipped with 2G or 3G modem.
Programming of receiver is possible:
o Locally: - with computer and “GPRS Transmitters Configurator”
software
- with computer and web browser via Ethernet connection
o Remotely : - via GPRS connection (or SMS)
- via SMS commands
- via transmission on CSD channel
Page 6
EPX400 – Manual
Page 6 / 71
2. FUNCTIONAL AND TECHNICAL PARAMETERS
Transmission channels
*transparent, PSTN dialer required in a CP
ETH, GPRS, SMS, PSTN*
Backup server
YES (GPRS, SMS, ETH)
User notifications
SMS (5 phone numbers)
Communication watchdog
YES
Inputs
9 (NO/NC/EOL-NO/EOL-NC/DEOL-NO/DEOL-NC)
Partitions
2
Simulated PSTN Line
YES
Protocols supported on the phone input
SIA, ContactID
Control panel dialer bypass
NO (optional)
Voice gateway functions
NO (optional)
Outputs
2 (OC, max. load 100mA)
1 relay output (NO/NC, max. load 1A/30VDC or
0,5A/125VAC)
Output functions
- unavailable GSM signal or ETH channel
- GSM jamming (only for BGS2-W module)
- from server or through SMS
- incoming CLIP
- in reaction on events and inputs
RC Receiver: 434 MHz
NO (optional)
Max.number supported keyfobs
-
Power output +12V
YES (max. load 200mA)
Serial interface
RS232 / RS485 (lines: RxD, TxD, RTS, CTS)
transmission speed up to 115200bps
Alarm events buffer size
-
Quantity of system events stored in history
min. 5000
Event's timestamps
-
GPRS/SMS transmission security
AES encryption
Status LEDs
(functions)
4 LEDs (GSM signal level, device state, DTMF
communication)
Configuration
Remote: GPRS, SMS, CSD, ETHERNET cable via Web
Browser
Local: PC through RS232 (required cable: GD-PROG or
SP-PROG)
Remote firmware update
YES
Remote access to the control panels
NO (optional)
Phone line protection circuit
NO (optional)
Dual SIM
NO (optional)
Multiantenna steering output
NO (optional)
Supported modems
model EPX400-50: Cinterion BGS2-W (Quad-Band GSM:
850, 900, 1800, 1900 MHz)
model EPX400-60: Cinterion EHS6 (Five Bands UMTS:
800, 850, 900, 1900, 2100 MHz; Quad-Band GSM: 850,
900, 1800, 1900 MHz)
Ethernet
- 10BaseT/100Base-TX IEEE 802.3 compliant
- speed and duplex auto-negotiation
- auto-detection of correct cable connections
(cross/straight)
Power supply parameters
- PCB
Voltage supply
18VAC (acceptable: 16-20VAC)
Power consumption
DC (AKU)
(average / max)
100mA/170mA@13,8VDC*
* Measured with full charged battery, modem BGS2-W
Cinterion
120mA/205mA@13,8VDC*
* Measured with full charged battery, modem EHS6-A
Cinterion
Power consumption
AC (AC)
(average / max)
125mA/185mA@18VAC*
* Measured with full charged battery, modem BGS2-W
Cinterion
156mA/235mA@18VAC*
* Measured with full charged battery, modem EHS6-A
Cinterion
Power supply parameters
- PCB in EBS plastic casing
Voltage supply
230VAC (acceptable: 190-250VAC)
Power consumption
(average / max)
3W/13W@230VAC (recommended transformer 20W)
Page 7

EPX400 – Manual
Page 7 / 71
Charging module functions
- protection against reverse battery connection
- AC failure signalization
- low battery/no battery signalization
- protection against short circuit battery output
- polymer fuse
Backup battery connection
YES, lead-acid 12V
Battery charging current
max. 220mA
Threshold of signaling low AC voltage (at
secondary / at primary)
13.5VAC / 160V
AC
(with EBS transformer)
Threshold of signaling low battery voltage
11VDC
Cut-off battery voltage level
-
Dimension
PCB: 159 x 73 x 35mm
Working temperature
-10ºC … +55ºC
Working humidity
5% … 93%
Standards
- CE
- according with EN 50136-1-1 Grade 3 ATS Class 5
Page 8
EPX400 – Manual
Page 8 / 71
3. ASSEMBLY AND WIRING
Transmitter is delivered along with a power supply (see below). The manufacturer
provides necessary wiring linking a power supply with the transmitter, and described
procedures relate to wiring of a transmitter printed circuit board.
Switch power off to perform any connection.
Length of the wires connecting between the transmitter and control panel must not
exceed 3 m.
3.1. EPX400 TRANSMITTER
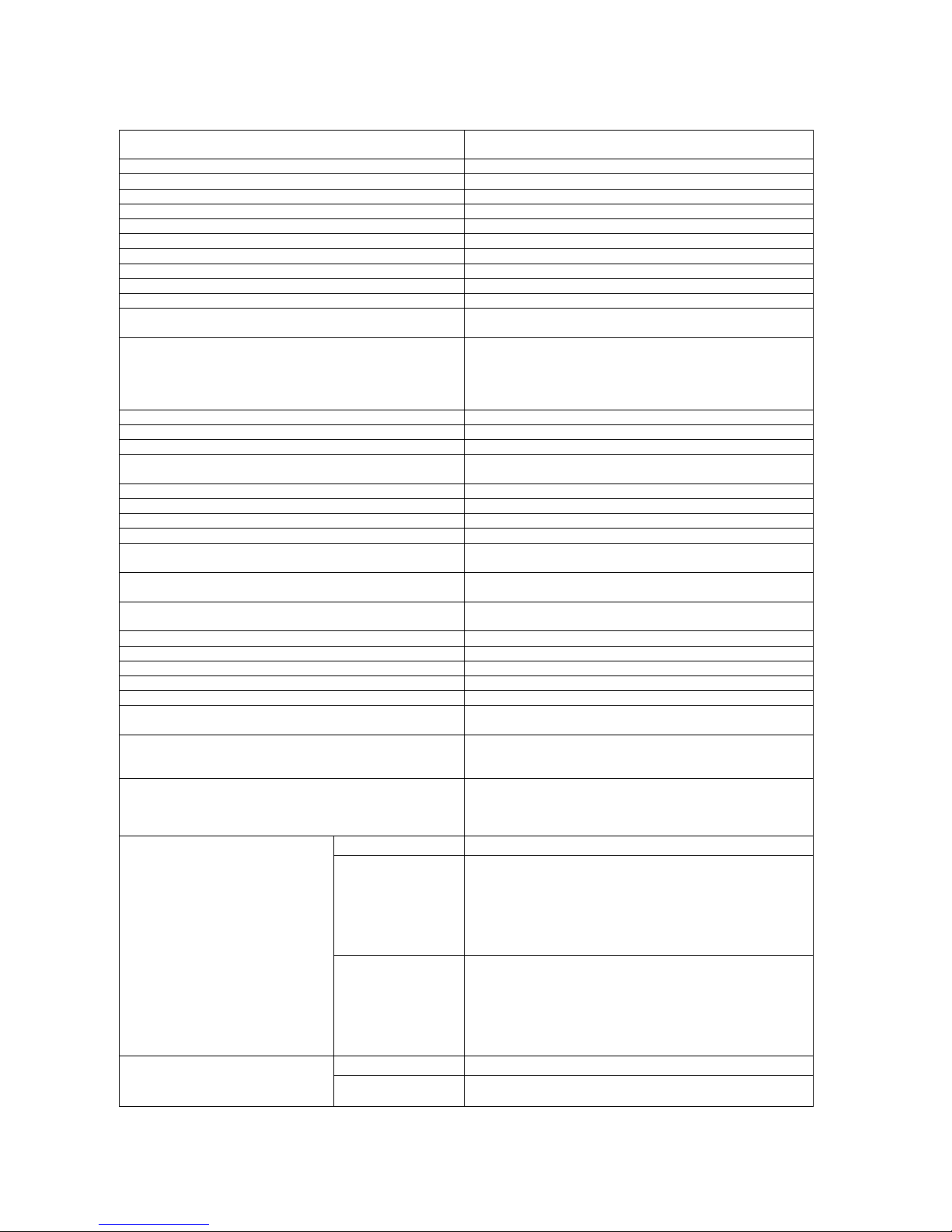
Figure 1. Connecting the EPX400 transmitter
Connections of wires shall be made with due care to prevent any faults or dead
shorts. Places of connections shall be protected against weather conditions. For
safety reasons, on AC supply lines must be mounted fuse 400mA/250VAC and double
Page 9

EPX400 – Manual
Page 9 / 71
pole switch that provides the ability to quickly disconnect the external power supply
from the transmitter.
According to the figure 1 terminals of transmitter shall be connected to:
Terminal
Connection description
AC, AC
Two terminals for AC power supply (output from AC
transformer)
GND
Device ground, common for other input and output
+ACU
Positive terminal of the battery
IN1 – IN9
Signal inputs. Possible connection of detectors contacts or
alarm control panel outputs. GND terminal is common for
all inputs.
OUT1, OUT2
Type OC outputs. It may control external device. Provides
ground during activation.
NC3, NO3,
C3
Additional output relay. It may control external device.
During activation disconnects C terminal from NC, and
connects C to NO terminal.
AUX1+
Supply voltage output. Provides up to 100mA.
R1, T1
Connection to alarm control panel phone communicator
R2, T2
Connection to the phone
RING, TIP
Terminals for a PSTN telephone
PGND
Ground line for protecting an external phone line
GSM
Connector for external GSM antenna
NOTES:
OUT1 and OUT2 outputs can sink up to 100mA. Don’t short this outputs to
power supply because it can cause permanent damage of the output.
Don’t connect power supply when GSM antenna isn’t connected, because it
can cause permanent damage of GSM/GPRS modem.
After careful connections examination a battery may be connected (to +ACU and
GND terminals) and then power may be switched on for transformer and
programming procedure of transmitter may begin (See chapter 7.).
3.2. PCB VERSION
The customer may choose to purchase only PCB version of transmitter. In this case,
is required to connect the appropriate power to the AC connectors.
NOTE !
MANUFACTURER RESERVES THE RIGHT TO AMEND APPEARANCE OF PRINTED CIRCUIT WITH
NO EFFECT ON FUNCTIONALITY OF DEVICE.
Page 10
EPX400 – Manual
Page 10 / 71
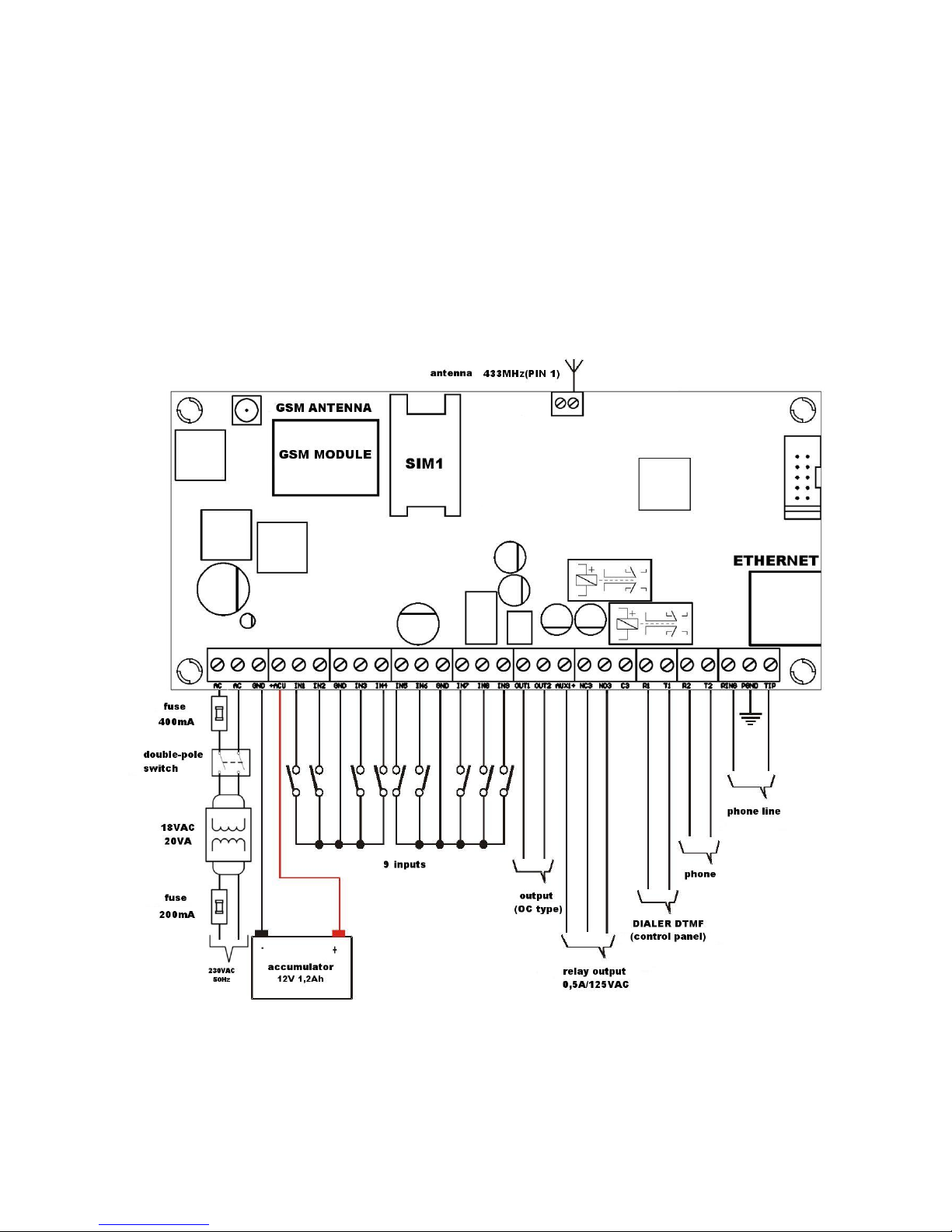
3.3. INPUT CONFIGURATION
Inputs IN1 – IN9 might work as normally closed (NC) or normally open (NO).
Additionally inputs might be configured as end of line (EOL-NO or EOL-NC) with
resistors 2.2kΩ or as double end of line (DEOL-NO or DEOL-NC) with resistor 1.1kΩ.
Examples of connecting sensors to the inputs in various configurations are shown in
figure 2.
Figure 2. Configuration of input lines
Page 11

EPX400 – Manual
Page 11 / 71
4. QUICK START PROCEDURE
NOTE:
Do not insert SIM card before the first programming of transmitter as it may
block the card if PIN code is required for the card.
This chapter is purposed for users that possess experience regarding GPRS
data transmission systems and who work with OSM.Server server. Other
users shall skip this chapter and go to chapter 5. of this Manual.
As many users possess protected facilities spread at vast locations, local
programming of transmitter is not always available (with computer keyboard and
programming cable).
Two phases comprise programming in this option:
a) sending to transmitter of main parameters (with SMS) that enable GPRS
connection to communication server (OSM.Server system).
b) full configuration of device with remote programming (GPRS transmitters
configurator and OSM.Server).
Quick start procedure:
a) insert into device SIM card with PIN code 1111 or without PIN code.
b) connect power supply for module,
c) send to SIM card number with SMS parameters related to connection of device
to communication server (OSM.Server)
d) waiting for moment, when device indicates connection to server
Note: Connection to server is possible if the device was registered into it.
Registration procedure has been described in OSM.Server Operation Manual.
e) complete, remote programming with GPRS transmitters configurator.
SMS text message shall provide the following information:
<transmitter’s service code>█SERVER=<server address>█PORT=<server port>█
APN=<access point name>█UN=<user ID number>█
PW=<user password>
Where:
█: space (every parameter shall be separated with space – blank character)
<transmitter’s service code>: factory settings – 1111.
<server address>: address of communication server purposed for collection of
transmitter signals e.g. 89.123.115.8. In case address is provided as domain e.g.
block.autostrada.com, SMS message shall include DNS1 parameter (address of main
DNS server)
<server port>: Number of port in server that receives messages from a device
<access point name>: defines access point name to GSM network.
If private network is used, SMS message shall provide the following parameters:
UN=<user ID number> and PW=<user password>.
Exemplary SMS to set the parameters of the GPRS connection is as follows (if we use
public network and provide server address as IP):
Page 12

EPX400 – Manual
Page 12 / 71
1111█SERVER=89.123.115.8█PORT=6780█APN=general.t-mobile.uk█
UN=█PW=
Where:
█: space character
Page 13

EPX400 – Manual
Page 13 / 71
5. OPERATION
EPX400 device is able to transmit data via channel over GSM network, via GPRS, via
SMS messages and via Ethernet.
Communication mode is configurable – see chapter 8. Programmable parameters for
more information. As a result the transmitter may be used only at the territory
covered with mobile phone operator network or with wired Ethernet network.
If status of inputs is the same as programmed one (NO/NC, EOL-NO/NC, DEOLNO/NC) a device stays in a rest. Change of status on any input results in signal
transmitting of this event by the device.
In case of voice channel communication mode there is possibility to choose 2
signalling formats: ContactID or SIA.
Note:
Each input (IN1 – IN9) may be individually defined as normally open (NO) or
normally closed (NC). It means that when input was defined as NO, input shorting
will be an active state, and when input was defined as NC, input opening will be an
active state. EOL and DEOL (parametrized and double parametrized) are options
where you use 1 or 2 resistors to distinguish alarm from sabotage.
To avoid an excessive cost of use related in particular to false alarms a device
possesses a programmable analysis of inputs.
All inputs respond only to states change which means that transmitting will follow
only if an active state is on input and maintains during programmed minimum time.
Maintenance of active state longer than a minimum time will result in single
indicating. Another input activation (another transmitting) is possible only after input
reached based state.
Number of messages sent in SMS mode is limited (limit includes also text massages
or answers to orders sent by user).This function provides for cost reduction by
limiting messages e.g. in case of damage of sensor connected to any input. After
passage of programmed time new messages will be sent but only in a number
determined by the user.
Text message on events sent to private phone numbers may be edited.
All programmable parameters are saved in memory and in case of voltage drop that
are not lost. Supply of power starts the transmitter with saved settings.
Page 14
EPX400 – Manual
Page 14 / 71
6. PRE-CONFIGURATION VIA ETHERNET PORT
To enable the EPX400 to communicate properly, you need to provide basic server
connection parameters. The simplest way to do this is via the built-in web server
WWW.
To access the server, connect the EPX400 using an Ethernet cable to a PC that has
an RJ-45 Ethernet port and a web browser.
The device is equipped with Auto MDI-MDIX function – supports straight-through and
crossover cable. Connection does not require network switch.
The default settings of the device is IP=192.168.7.7 , mask = 255.255.255.0 and the
following description applies to such settings.
6.1. LOGGING IN
You must configure the Ethernet interface to which the device is connected, you need
to manually set the appropriate IP address for example. 192.168.7.42 (Control Panel
\ Network and Internet \ Network and Sharing Center -> Connections-> Properties->
Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP / IPv4) -> Properties - for Windows 10) and the
mask of 255.255.255.0. In the Web browser, enter the device address
http://192.168.7.7
There will appear the home page described below. Service code is the password.
NOTE: The address of the EPX400 network and the computer to which the device is
connected should be the same, and the IP addresses should be different.
Page 15
EPX400 – Manual
Page 15 / 71
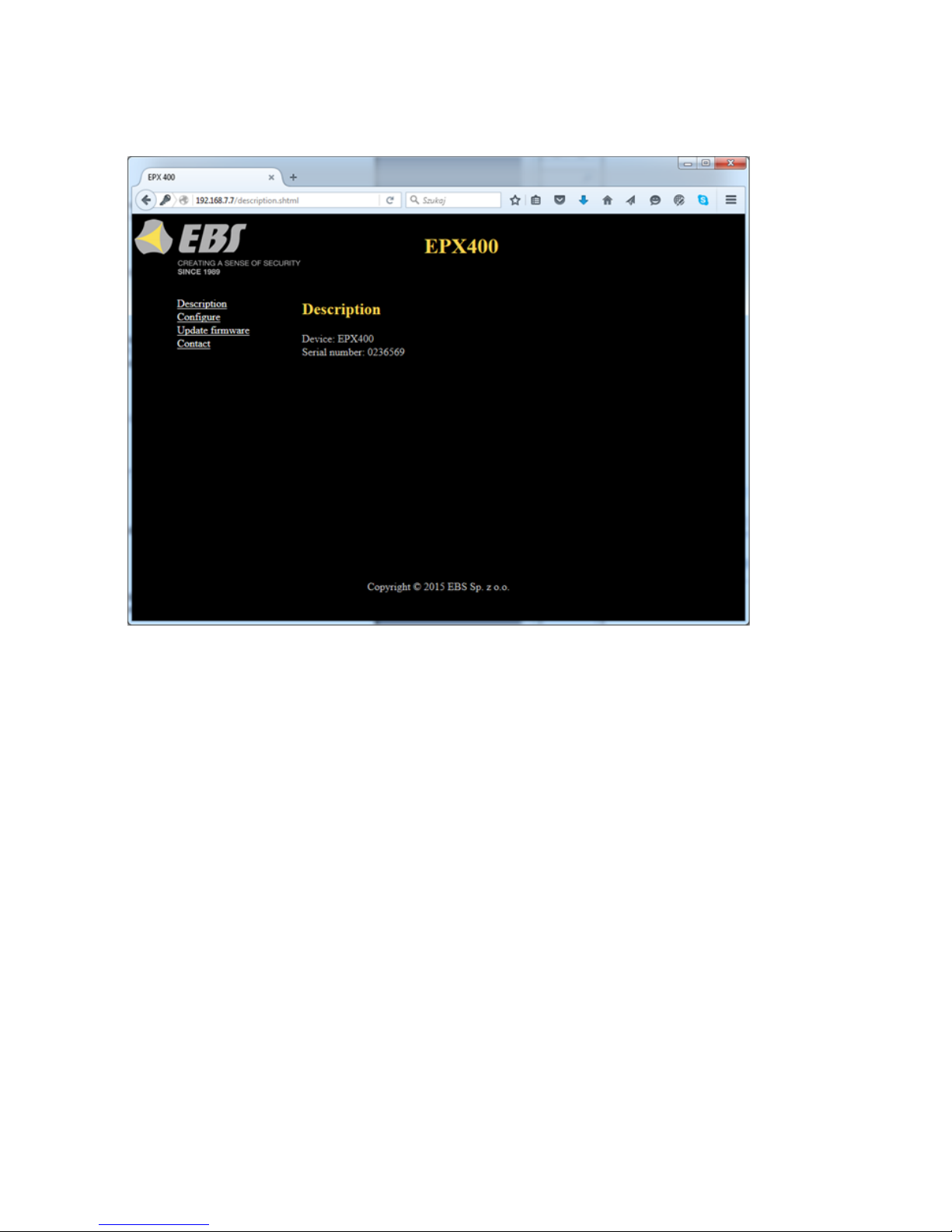
6.2. DESCRIPTION
“Description” item.
Displays information about the type of device and its serial number.
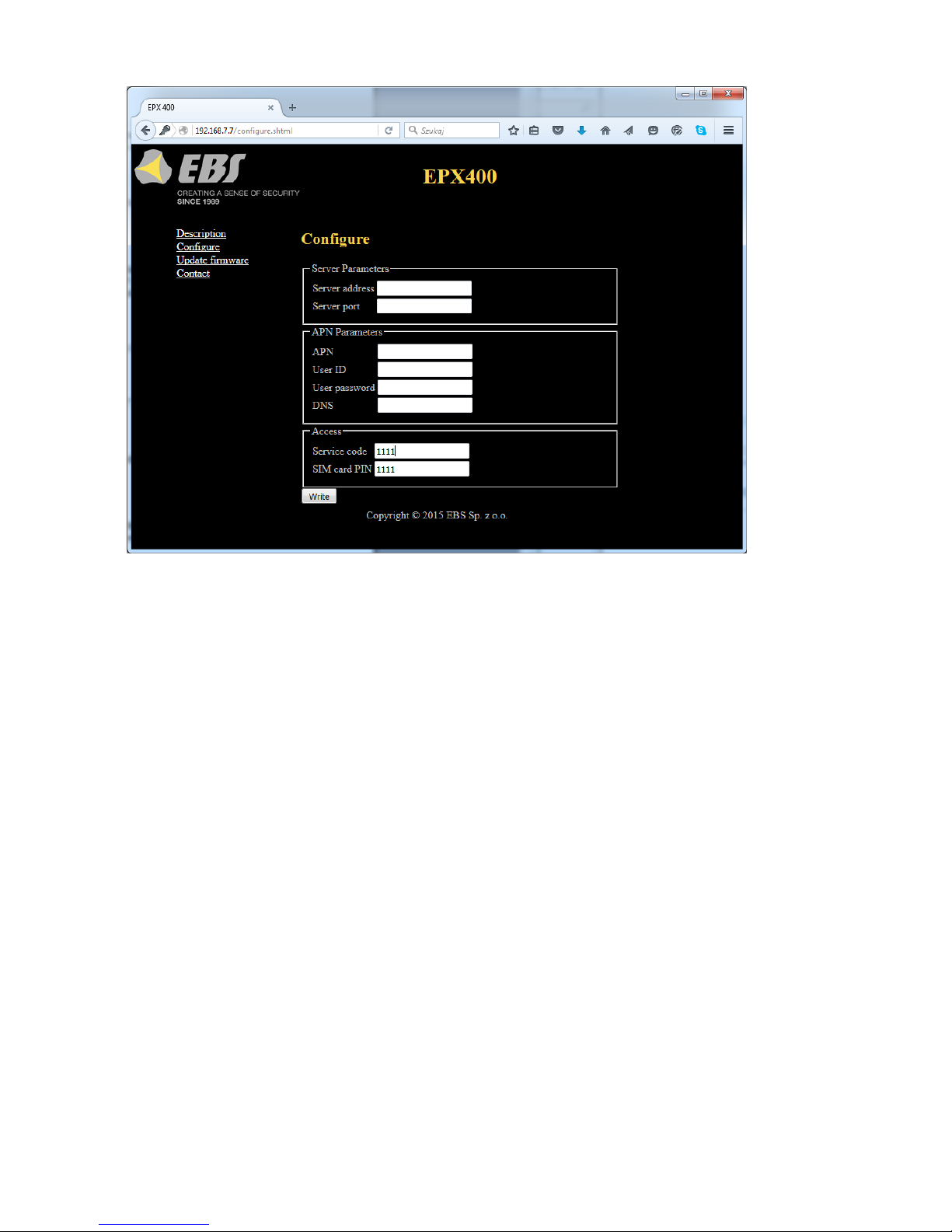
6.3. CONFIGURATION
“Configure” item.
Page 16
EPX400 – Manual
Page 16 / 71
6.3.1. Server parameters
In this section we define the server parameters in the monitoring station.
6.3.1.1. Server address
This is the IP address of the monitoring system receiver (OSM.Server), e.g.
“89.123.115.8”. The address can be specified as a domain name of the server, e.g.
“module.gprs.com”.
For domain name addresses, a DNS sever address is also required.
6.3.1.2. Server port
Specifies the server port assigned to receive data from the transmitter.
6.3.2. APN parameters
In this section we define the APN parameters needed for GPRS connection.
6.3.2.1. APN
In “APN” field you can enter the APN name. This parameter depends on the GSM
network provider whose services you are going to use. It specifies the name of the
access point to the GPRS network. It is possible to use a private access point. In this
case, the name of the access point will be provided by your GSM network provider.
This is usually not required with public APNs.
6.3.2.2. User ID
In this field you can enter the user name required to connect to the GPRS network.
This is usually not required with public APNs. If you have a private APN, you should
ask your provider for this parameter.
Note: Using a private APN increases the security of the system.
Page 17

EPX400 – Manual
Page 17 / 71
6.3.2.3. User password
In this field you can enter the user password required to connect to the GPRS
network. This is usually not required with public APNs. If you have a private APN, you
should ask your provider for this parameter.
Note: Using a private APN increases the security of the system.
6.3.2.4. DNS
Identifies the address of the primary DNS server (Domain Name System). If you
provided the server's address as a domain, at least one DNS address must be
specified.
6.3.3. Access Parameters
In this section we define the parameters of access to the device.
6.3.3.1. Service code
Protects the device against unauthorized access. It is used during the device
programming process and for remote control of the device (in TCP/IP or SMS mode).
The code is factory set to 1111. You should change this code at the first
programming the device. It may contain up to seven alphanumeric characters.
6.3.3.2. SIM card PIN
As the device works in a GSM network, you need a SIM card from a mobile telephone
network provider. Before first use, you need to enter the PIN code of the SIM card
that will be used with the particular transmitter. This is required for automatic system
start-up. If you have a SIM card without PIN code protection, you can enter any
value, e.g. 0000.
If the PIN you enter is incorrect, SIM card may be blocked after you insert the card
and power on the transmitter. To unblock the SIM card you will need to enter the
PUK code (using any GSM phone) before you can use the card again.
Factory PIN number in EPX400 is set to 1111.
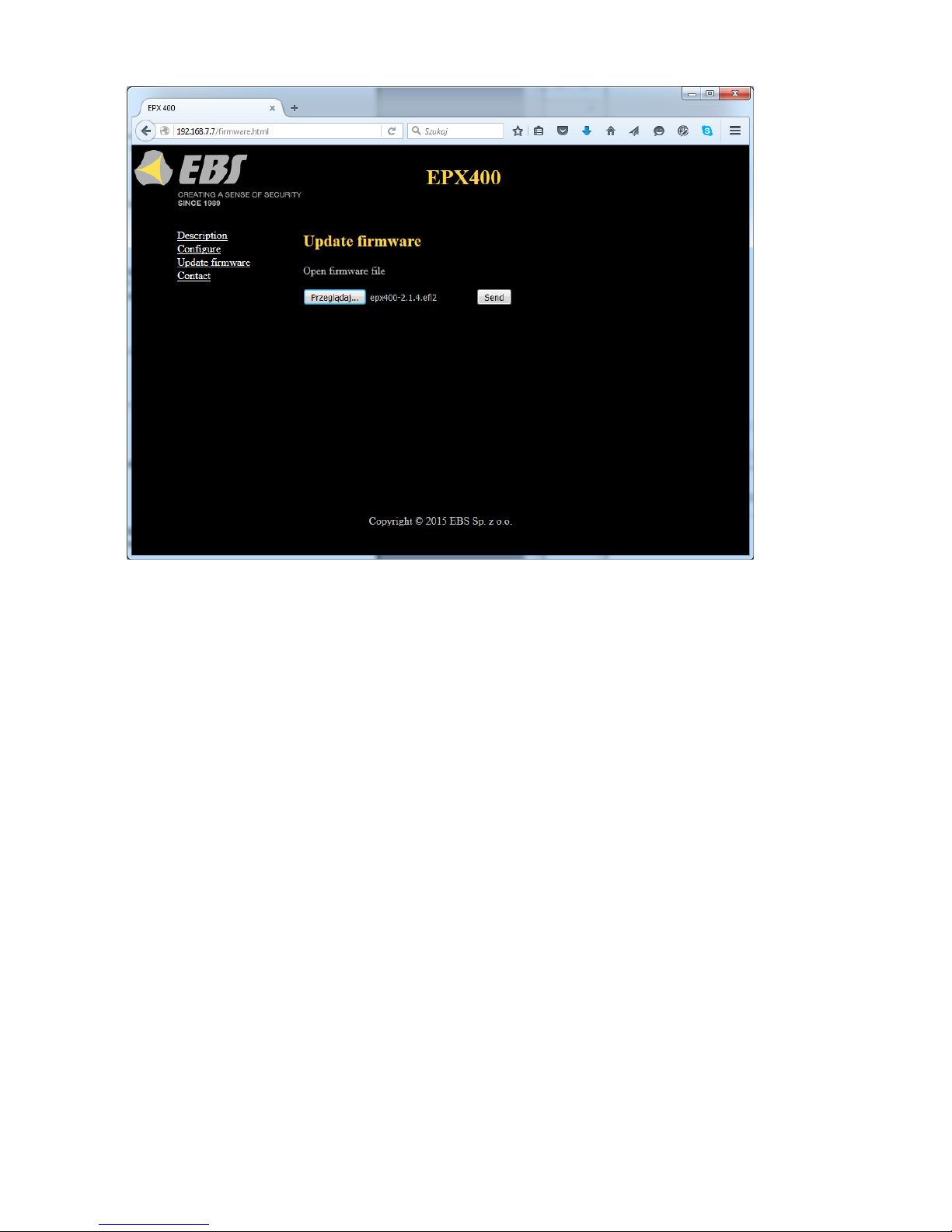
6.4. UPDATE FIMWARE
The device features a firmware update mechanism.
Page 18
EPX400 – Manual
Page 18 / 71
To flash new firmware, follow these steps:
a) Open the file with the new firmware (click [Browse] to locate the file,
which should have the extension “.efi2”, e.g. epx400-2.1.7.efi2).
b) Click [Send]. The firmware update process will start.
c) After the process is complete, you will see the update status
success: “The firmware has been updated successfully.”
error: “This operation has been cancelled.”
To activate the new firmware, power on the device again or restart it.
Note: this procedure should be performed with the utmost care, as any
error, especially due to loss of power supply during the update, can result in
improper operation of the device.
6.5. CONTACT
“Contact” item – displays the manufacturer's contact details.
Page 19
EPX400 – Manual
Page 19 / 71
Page 20

EPX400 – Manual
Page 20 / 71
7. CONFIGURATION PROGRAM
7.1. INITIAL REMARKS
“GPRS transmitters configurator” software may be downloaded from
http://www.ebs.pl (login: ebs, password: ebs).
To install program an installation wizard shall be started that performs installation in
default place C:\Program Files\EBS\. During installation process shortcuts on screen
and Windows menu are created.
If device is to be used for the first time it shall be programmed with the above
program and after this procedure the SIM card may be inserted into the device.
Otherwise SIM card may be blocked if wrong PIN code is entered. Alternatively SIM
card may be used along with switched off PIN code.
In case of remote programming it is necessary to insert SIM card prior to
sending configuration settings. In this situation SIM card with switched off PIN code
shall be used or before card inserting, PIN code shall be changed with mobile phone.
Default PIN code in transmitter is 1111.
7.2. COMPUTER – REQUIREMENTS
Minimum requirements for computer system where configuration software
(Configurator from 1.3.69.022 version) is to be installed are the following:
Hardware:
Processor 1GHz or faster,
1 GB RAM,
4GB HDD,
Software:
Operating system: Windows 7 or newer,
.NET Framework 4,5 software
7.3. PROGRAM FUNCTIONS
After installation and program starting a main view shall be displayed on screen.
Thanks to this view an access to program or programmable parameters of device is
possible.(See chapter 8.).
Main window of program is divided into some fields.
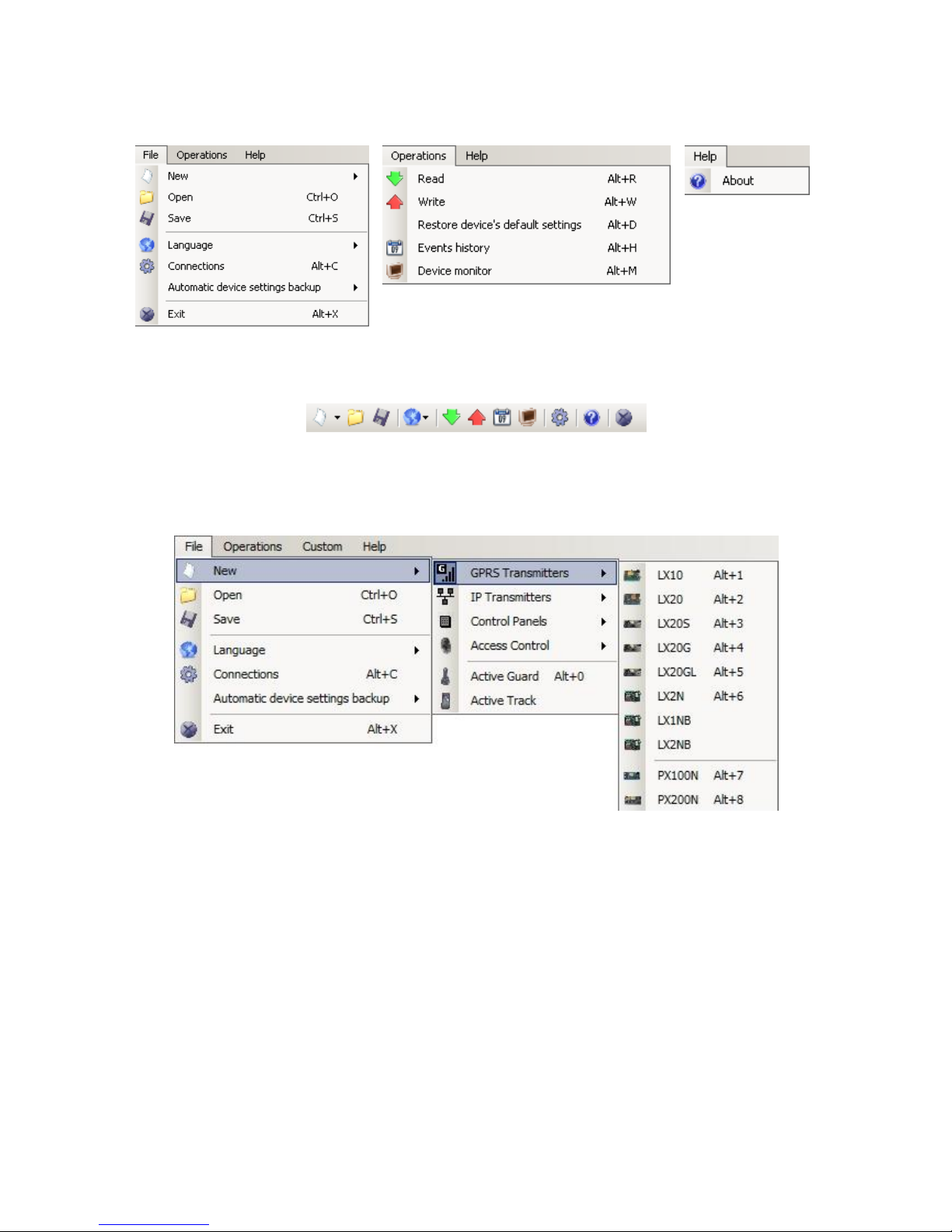
Main menu at upper part of window, contains control and configuration options.
Page 21
EPX400 – Manual
Page 21 / 71
Main menu contents:
Main menu is available as icons on fast access bar:
7.3.1. File -> New
Opens new set of parameters. Editing of configuration parameters is possible.
Select type of device – EPX400.
7.3.2. File -> Open
If file contains saved settings, they may be used to program next device. Firstly a
folder where file has been saved shall be chosen and then name of file shall be
provided. Obtained data collection may be modified by the user. Any amendments
are effective if send to device.
7.3.3. File -> Save
During programming many devices in different configurations, it is not necessary to
have in mind each one as it may be saved on hard disc under any name and it may
be loaded later. This function save on disc any information from configuration wizard
window. After activation of function a dialog window appears with request to provide
file name. Default data is saved with .cmi extension.
Page 22
EPX400 – Manual
Page 22 / 71
7.3.4. File -> Language
Allows for selection of any available languages (determined in attached exterior
language files).
7.3.5. File -> Connections
Before programming of devices, a connection type shall be defined. It is possible to
do it with two methods:
- locally
- remotely.
7.3.5.1. Local connection
Local connection means that configuration software (or, in fact, a computer, on which
it is installed) is directly connected to proper terminal of transmitter via special wire
and through RS-232 serial port (GD-PROG) or USB port or Bluetooth (MINI-PROG-BT,
SP-PROG-BT). All channel connection (also USB and Bluetooth) "open" virtual COM
serial ports used in communication control panel-Configurator.
To program device or make any other operations (e.g. reading of device settings,
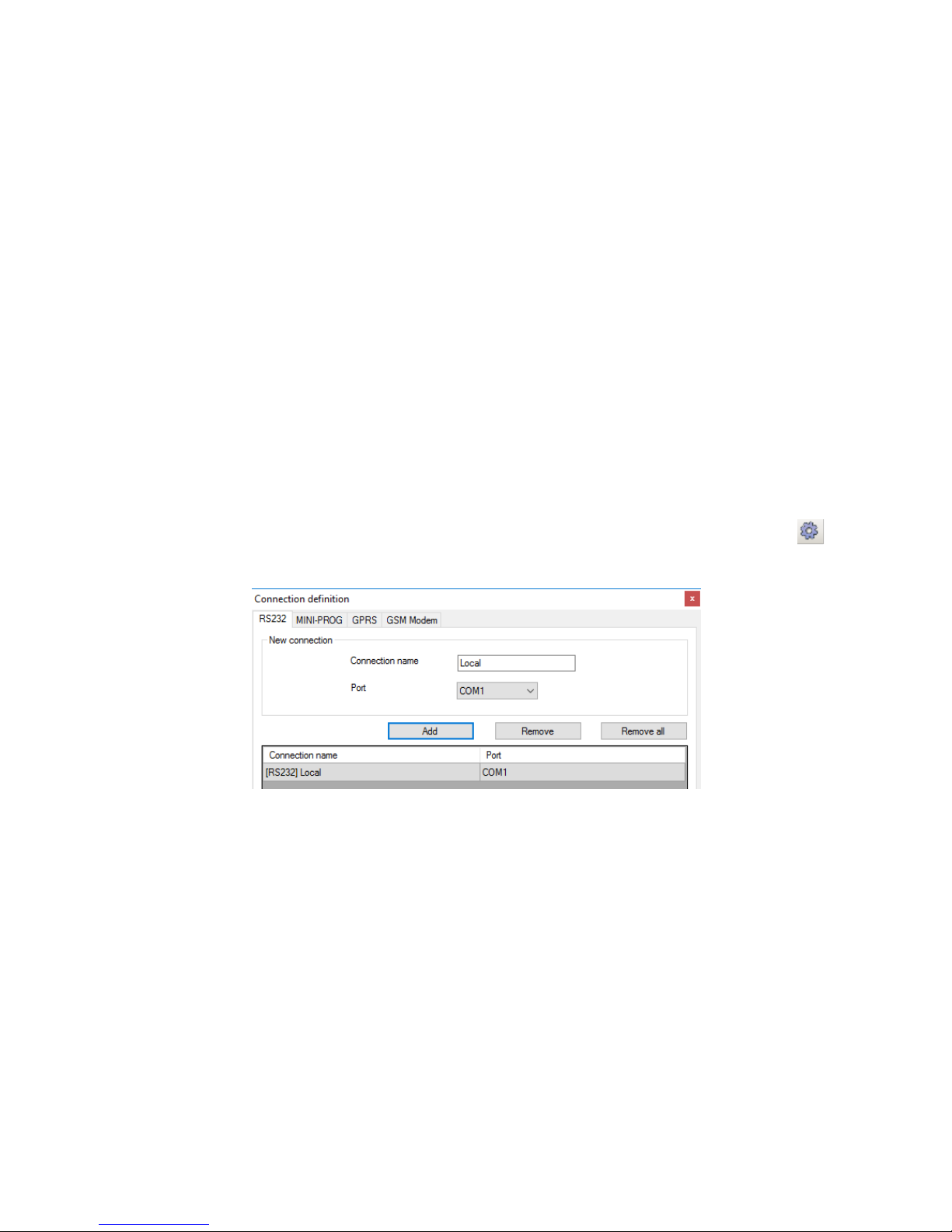
firmware amendments, etc.) it is necessary firstly to define connection parameters.
For the above purpose you shall use the following window, available after activating
File option from the Main Menu and selecting Connection function or after clicking
icon on a taskbar and opening RS232 tab.
Define:
Name of connection e.g. Local
Choose serial port e.g. COM 1
Click on [Add] button to confirm settings. Connections shall be saved (and inserted in
table). From this time on program shall enable wires connection with device and
reading, and saving of parameters in memory will be possible.
In the next tab "MINI-PROG" (the name derived from the programmer) you have to
also define the connection parameters.
Page 23

EPX400 – Manual
Page 23 / 71
Operations are the same as with the "RS232" tab. Specify the name, the correct COM
port and add a connection.
Programmers MINI-PROG-BT and SP-PROG-BT have microUSB ports, through which
we can connect to the computer using the USB port, but also have built-in Bluetooth
interface.
7.3.5.2. Remote connection
As provided above the device and software makes for complete configuration with
GPRS link or CSD channel. This programming mode requires definition of linking
parameters.
GPRS linking
Activate file in Main menu and select Connection function (or after clicking on
icon on fast access bar) and click on GPRS tab to carry out configuration of this
mode.
On screen the following window shall appear:
Define:
Name of connection e.g.: Remote
Select name of analyzer e.g.: Primary
Enter analyzer address e.g.: www.ebs.pl
Enter port on which analyzer operates e.g. 9000
Click on [Add] button to confirm settings. Connections shall be saved (and inserted in
table). From this time on program shall enable remote connection to device and
reading and saving of parameters in memory shall be possible.
Page 24

EPX400 – Manual
Page 24 / 71
Notice: The following parameters: analyzer name, analyze address, port
relate to settings of OSM.Server receiver of monitoring system. Remote
programming is available only if above mentioned device (or software) is
used.
CSD connection
Activate file in Main Menu and select Connection function (or after clicking on
icon on fast access bar) and click on GSM Modem tab to carry out configuration of
this mode.
On screen the window shall appear where it is possible to define:
Name of connection e.g. Remote CSD
Serial port where GSM modem is connected (e.g. Wavecom Fastrack)
PIN code of SIM card installed in GSM modem e.g. 1111
Serial port parameters: amount of bytes/sec. (e.g. 115200), data bytes (8),
parity (none), stop bytes (1).
Click [Add] button to confirm settings and save connection (settings are inserted into
table). Since that time a remote connection to device, reading and saving of
parameters in transmitter memory is possible.
Note: Remote configuration with CSD canal is possible if option of CSD data sending
has been activated both for SIM card inserted into a device and SIM card installed in
GSM modem. Beside, transmitter must enable to pick up data calls (see 8.5.1.2. GSM
modems authorized phones).
Programming with CSD is also possible if OSM.Server system has been installed, and
minimum one GSM modem is connected. If device has been entered onto server list
(factory number and SIM card telephone number –See OSM.Server Operation Manual
– chapter 3.1.3.1. Settings and chapter 3.1.3.2. Adding and modyfying devices) it is
possible to use link via OSM. It is possible if device is not connected to the
OSM.Server via GPRS. During programming procedure (with GPRS link- See above) a
question will be displayed if user want to use a modem connected to the server. After
confirmation procedure will follow as in case of other programming channels.
Page 25

EPX400 – Manual
Page 25 / 71
7.3.6. File-> Automatic device settings backup
All configuration settings including reread from devices and saved on devices are to
be automatically saved on hard disc. If during installation on configuring tool settings
have not been changed, files will be saved as follows:
C:\Program Files\ EBS\KonfiguratorLX\configs\EPX400_20000
Folder “EPX400_20000” contains all files associated with programming of the EPX400
with factory number 20000. The name contains date and time of operation and its
type (saving/reading). Files have .cmi extension.
7.3.7. File -> Exit
Finishes program operation.
7.3.8. Operations -> Read
Function reads data saved in memory of GPRS module. Exchange of data follows on
port selected in section “Select Connection Type” (See below description of option
”Configuration”). Correct reading is confirmed with message on a screen. Data
downloaded from device may be saved on file (see clause 7.3.3.) and use for other
devices.
To use this function it is necessary to define type and parameters of connection. E.g.
for local connection the following view is displayed:
where:
Connection kind – serial port to which module is connected
Access code – service code of transmitter
Detailed description of connections configuration is included in clause 7.3.5.
7.3.9. Operations -> Send
This function is analogical to the above one, at the same time it enables data saving
into EEPROM module. Correct saving is confirmed with message on a screen.
Page 26

EPX400 – Manual
Page 26 / 71
7.3.10. Operation -> Device monitor
Function provides real-time information on device state. See chapter 8.11. Device
monitor.
7.3.11. Operation -> System events history
Function provides information about last events stored in EPX400 device memory.
See chapter 8.12. Events history.
7.3.12. Operation -> Restore default settings
If operation “Read” finishes with error message (e.g. if access code is unknown) it is
possible to come back to default settings by selecting “Restore default settings”. e
“Do you want to overwrite current configuration with default values?”. After
confirming the following window shall appear:
This operation is possible only with local connection. After operation completing
device parameters shall come back to default settings.
7.3.13. Help -> About program
Select this information to view additional information about program.
Page 27

EPX400 – Manual
Page 27 / 71
8. PROGRAMMABLE PARAMETERS
Parameters available in configuration program are divided into groups: Access,
Transmission, Inputs/Outputs, Monitoring, Restrictions, SMS Notifications, RS232,
Link control, Phone line and Firmware. Every from these groups will be described in
detail in next part of this manual.
8.1. ACCESS
8.1.1. Transmitter
This tab contains parameters for access to the transmitter and SIM cards.
8.1.1.1. Group: Access
Service Code
It provides security against unauthorized access. It is being used during
programming of device and during remote controlling (in TCP/IP or SMS mode).
Factory setting is 1111. During the first starting of device (programming) it shall be
changed. Code may consist of up to seven alpha numerical characters.
Installer code
Allows restricted access to the parameters of device. When installer code is used
following groups of parameters are unavailable: Access, Transmission, Restrictions,
Page 28

EPX400 – Manual
Page 28 / 71
SMS notifications, RS232, Link control, and Phone line. An unauthorized attempt to
access to this parameters causes error notification.
Default installer code: 2222.
8.1.1.2. Group: SIM Cards
SIM Card PIN
As a device operates via GSM network, SIM card is indispensable and it may be
received from phone operator. Before the first use PIN code of SIM card shall be
programmed for operation in given transmitter. PIN code is indispensable for
automatic system launching. In case of card without PIN code, it is possible to enter
any value e.g. 0000.
If you enter wrong PIN number after inserting card and switching on transmitter, the
system will not launch and you may be able to use card after entering PUK card only
(with use of any GSM mobile phone).
Factory setting of PIN in transmitter is 1111.
8.1.1.3. Option: Embedded HTTP server
Selecting this option allows to configure the basic parameters for the EPX400
connection to the server through a Web browser. The method of this configuration is
described in chapter "6. Pre-configuration via Ethernet port"
NOTE: To avoid unauthorized tampering with the device, the manufacturer
recommends that you disable this option when you install the GPRS Transmitter
Configurator (This option is factory-set on).
Page 29

EPX400 – Manual
Page 29 / 71
8.1.2. Server connection
In “Server Connection” tab you can set the basic parameters of Ethernet, GPRS and
SMS connections
8.1.2.1. Ethernet parameters
Primary Server Address
It is address of receiver of monitoring system (OSM.Server) or computer where
“Communication Server” software has been installed , e.g. 89.123.115.8. This
address may be provided in domain name of server, e.g. modul.gprs.com. In this
case it is required to provide minimum one address of DNS server.
Primary Server Port
It determines server port that was selected in server for collection of data from
transmitter.
Backup Server Address
It is address of second (backup) receiver of monitoring system (OSM.Server) or
computer where “Communication Server” software has been installed , e.g.
Page 30

EPX400 – Manual
Page 30 / 71
89.130.125.82. This address may be provided in domain name of server, e.g.
monitor.gprs.com. In this case it is required to provide minimum one address of DNS
server.
Backup Server Port
It determines server port that was selected in backup server for collection of data
from transmitter.
IP
Option “DHCP”: address of the device and other network settings can be assigned by
the DHCP server (default setting).
Option “Static”: allows you to define your own settings. The remaining fields form
described below will be activated.
Address
The IP address of the device for the LAN to which you want to work.
Mask
Subnet mask, default mask is "255.255.255.0".
Gate
The IP address of the computer on the local network that routes the traffic from the
device to the outside network and the communication server.
DNS1, DNS2
It determines address of main and backup DNS server (Domain Name System).
If IP server address has been entered in form of domain, it is required to provide
minimum one DNS address.
8.1.2.2. GPRS parameters
Primary Server Address
It is address of receiver of monitoring system (OSM.Server) or computer where
“Communication Server” software has been installed , e.g. 89.123.115.8. This
address may be provided in domain name of server, e.g. modul.gprs.com. In this
case it is required to provide minimum one address of DNS server.
Primary Server Port
It determines server port that was selected in server for collection of data from
transmitter.
Page 31

EPX400 – Manual
Page 31 / 71
Backup Server Address
It is address of second (backup) receiver of monitoring system (OSM.Server) or
computer where “Communication Server” software has been installed , e.g.
89.130.125.82. This address may be provided in domain name of server, e.g.
monitor.gprs.com. In this case it is required to provide minimum one address of DNS
server.
Backup Server Port
It determines server port that was selected in backup server for collection of data
from transmitter.
APN
Parameter depending on GSM network operator that supplies GPRS (SMS) services.
It provides GSM network access point name.
It possible to obtain a private access point. In this case a name will be provided by
GSM network operator.
User ID
When using public APN, user ID is mostly not required. For private APN this
parameter shall be obtained from operator (it is impossible to be granted access to
GPRS network without it).
User password
When using public APN, user ID is mostly not required. For private APN this
parameter shall be obtained from operator (it is impossible to be granted access to
GPRS network without it).
Note: Private APN provides for higher system security.
DNS1 and DNS2
It determines address of main and backup DNS server (Domain Name System).
If IP server address has been entered in form of domain it is required to provide
minimum one DNS address.
8.1.2.3. SMS Parameters
Server Phone Number
If GSM modem is connected to server application (e.g. OSM.Server) enter in this field
its number. Any SMS will be sent to this number if transmitter has got problems with
GPRS transmission.
If this field is left blank or 0 was entered, the transmitter will not be operating in
SMS mode.
Page 32

EPX400 – Manual
Page 32 / 71
8.1.3. Communication
Channel Role (Channel Priority)
By the term channel we mean the data transmission channel to the monitoring
center. This can be Ethernet, GPRS or SMS. The transmitter while connecting to the
monitoring station is trying to select main channel first, then a backup one, and
emergency channel at last. If there is an address and port of backup server provided,
then we try to take advantage of this connection before switching to another
transmission channel. When in the result of the disconnection in the main channel, a
channel with lower priority is used, then the availability of primary channel is being
checked periodically. If the connection to main channel returns, the transmitter will
switch over to it and will try to stay on it. You can set channel role as “unused” – so
the communication in this way will not be possible.
There are four settings possible:
Unused
Main
Backup
Emergency
Page 33

EPX400 – Manual
Page 33 / 71
8.1.3.1. Ethernet and GPRS Parameters
Channel Role (Channel Priority)
By the term channel we mean the data transmission channel to the monitoring
center. This can be Ethernet, GPRS or SMS. The transmitter while connecting to the
monitoring station is trying to select main channel first, then a backup one, and
emergency channel at last. If there is an address and port of backup server provided,
then we try to take advantage of this connection before switching to another
transmission channel. When in the result of the disconnection in the main channel, a
channel with lower priority is used, then the availability of primary channel is being
checked periodically. If the connection to main channel returns, the transmitter will
switch over to it and will try to stay on it. You can set channel role as “unused” – so
the communication in this way will not be possible.
There are four settings possible:
Unused
Main
Backup
Emergency
Test Events Period
The device sends message “Test” with determined interval that informs monitoring
station that the device is in operation mode. In this field you can determine how
often this message will be sent (in seconds).
Primary Server Parameters
Interval between subsequent connection attempts
Configured and equipped with SIM card device will try to make automatic connection
with server. In this field you define interval (in seconds) after which next connection
attempt will follow if the previous attempt failed.
Number of connections attempts before switching to backup server
In this filed you determine how many times the device will try to make connection to
primary server. If connection fail, after execution of some connections, device will
start connecting to backup server.
Always try to connect to primary server at first
Mark this check box means, that the device will try in first order to connect to
primary server, without regard on definition of parameters for backup server
(especially number of connection attempts).
Page 34

EPX400 – Manual
Page 34 / 71
Backup Server Parameters
Interval between subsequent connection attempts
In this field you define the period (in seconds) after which next attempt of connection
to backup server will follow if the previous attempt failed.
Number of connections attempts before switching to primary server
In this filed you determine how many times the device will try to make connection to
backup server. If connection fail, after execution of some connections, device will
start connecting to primary server.
Disconnect after
If you mark this field the device will disconnect from backup server after defined
time. If this option is active the device reconnects to the primary server. If this
option is not active the device firstly completes connection to backup server
procedure and if this fails, the device will try to connect to the primary server.
8.1.3.2. SMS Parameters
Channel Role (Channel Priority)
There are four settings:
Unused
Main
Backup
Emergency
Test Events Period
The device sends message “Test” with determined interval that informs monitoring
station that the device is in operation mode. In this field you can determine how
often this message will be sent (in minutes). Usually it is undesirable to send text as
SMS so often as with GPRS or Ethernet transmission. Parameter this allow for
significant extension of distance between tests (time in minutes) or completely
disabling this option.
Fast events mode
Selecting this option will immediately send the monitored events (considered as
more important) if other transmission channels had not established communication
with the server. This means that potentially events can be sent by more expensive
and less optimal channels like SMS, but we have greater confidence that the
notification arrives as quickly as possible. If this option is disabled, the device stops
sending events until it connects to the server.
Page 35

EPX400 – Manual
Page 35 / 71
8.2. TRANSMISSION
For the purpose of maximum security of transmission, data is encrypted with AES
key. This option may be used for GPRS and SMS transmission.
After selection of encrypted transmission you may use your own code (256 bits –
signs 0-9 and A-F) or use default settings.
8.3. INPUTS/OUTPUTS
Transmitter has got 9 inputs, two OC type outputs and one relay ouput. The
"Input/Output" option allows to configure the transmitter in accordance with the
requirements of the user.
8.3.1. Inputs configuration
For every input the following settings shall be determined respectively.
8.3.1.1. Input mode
The parameter describes input configuration and stable state of input. Any change of
that state causes alarm message to be sent. The following configuration types are
available: NO / NC / EOL-NO / EOL-NC / DEOL-NO / DEOL-NC. NC type input must be
closed for the whole time. Line interruption causes its induction. NO type input
remains open. It activates when closed. EOL and DEOL (single end-of-line resistor
and double end-of-line resistor) differ with 1 or 2 resistors allowing distinguishing
alarm from sabotage. Electric diagrams for all configuration types were described in
chapter 3.3. Input configuration.
Page 36

EPX400 – Manual
Page 36 / 71
8.3.1.2. Sensitivity
This parameter means minimum time for change maintenance at input so that it
would be detected by transmitter.. Default setting is 400ms.
8.3.1.3. Locks
With this option you can lock any input of module, and as a result condition changes
on this input will be ignored and will not be reported to monitoring station. Lock may
be persistent or temporary.
In case of temporary lock – user can set lock time and number of input state changes
after which lock occurs. Lock time is counted from first input state change. More
detailed information about input locks is shown on a diagram.
Page 37

EPX400 – Manual
Page 37 / 71
Event: automatic input lock
Event: automatic input unlock
Limit: N = 2 input changes during Tb time (3rd change activates input lock)
Tb
Tb Tb Tb Tb
Input activation and deactivation
Input activation and deactivation – no reaction
Temporary input lock
Events send to server
Event: input active
Event: input not active
- Locally there can be 2 x N – 1 input activations. In summary average number of activations during defined period of time will be preserved.
- N and Tb parameters may be set per input
Temporary lock may be deactivated by SMS or GRPS command (RLIMIT command).
8.3.2. Partitions
Partitions are configured using Partitions tab.
Using partitions you may configure which inputs will be monitored depending on
state of one of the inputs (arming). If arming input is not active then all changes of
the state of the input assigned to partition will be ignored. For the active arming
input all changes of the state of the input assigned to partition will be monitored and
processed in a normal way.
Page 38

EPX400 – Manual
Page 38 / 71
8.3.2.1. Partition arming input
Using this, partition arming input can be selected. To selected input, arming device
(remote controller receiver output or electronic keyboard NO/NC output for instance)
is connected. When this input is armed, partition is armed (after Exit Time, see
below). When arming input is disarmed, partition is disarmed.
8.3.2.2. Inputs assigned to partitions
Assigning input to partition means that it is monitored only when partition to which
input belongs is armed. Input can be assigned up to one partition. Arming inputs can
not be assigned to any partition. If input is not assigned to any partition, it acts as 24
hours input – it is monitored regardless of partitions state.
8.3.2.3. Delayed inputs
Here, delayed inputs can be selected. Delayed input switches on associated output,
ie. generates alarm, after expiry of Entry time, but only when partition to which input
belongs will not be disarmed before Entry time period.
8.3.2.4. Exit time
Partition exit time. Partition inputs will be monitored when this configured time
elapses after partition input had been armed.
8.3.2.5. Entry time
Time after which alarm will be generated after delayed input had been armed and
partition to which delayed input belongs will not be disarmed.
Page 39

EPX400 – Manual
Page 39 / 71
8.3.3. Outputs
Tabs "Output 1 (OUT1)", "Output 2 (OUT2)" and "Output 3 (NC-NO-C)" define the
outputs parameters. The options for the outputs are common and are described in a
single section.
8.3.3.1. Activation mode and timing
Thanks to this option you may choose output operation mode. There are two
operation modes available:
o bistable – connection follows for indefinite time – up to the moment of
disconnection of power for module or remote command which switches output
off,
o monostable – connection follows for time defined by user – every 100ms.
8.3.3.2. Conditions
Defines conditions for activating both of outputs. User can set following conditions:
No connection to server (immediately after detection);
No GSM signal (immediately after detection);
Detection of incoming call from defined telephone number;
After selecting this option can be generated CLIP event, if appropriate position
in the “Monitoring” group is set (see item 8.4.6. Event: CLIP). You can enter
full phone number or only a part of number. The device will detect all
numbers with specified sequence. E.g. if entered number is 1234, the output
will activate after incoming call from number 123456789 or 600123456.
Note: The phone number must be entered without country code (e.g. without
prefix 0048 and +48).
Page 40

EPX400 – Manual
Page 40 / 71
Dependent on state transitions from non-active to active of one of the inputs.
Outputs can be also activated by internal watchdog (see 8.8. Link control).
8.3.3.3. Additional conditions
If option “Dependent on state transitions from non-active to active of one of the
inputs” is chosen, we might configure additional conditions for output activations:
o Never: input disturbance does not cause operation of the output,
o No network: input disturbance causes actuation of the output if sending of
information to server is impossible.
o Always: every input disturbance causes actuation of the output.
o Available network: input disturbance causes actuation of the output if
sending of information to server is possible.
Note: The outputs may be controlled by SMS commands.
The outputs can also be activated by the watchdog that can be configured in tab
"8.8. Link control”.
8.3.4. Advanced outputs control
The user is able to determine an alternative course of action to go over basic outputs
configuration function described in 8.3.3. Outputs.
In the “Advanced outputs control” you may define separately the behavior of each of
the outputs, depending on events taking place. “Advanced outputs control” differs
from the existing basic “Outputs configuration” by:
o it is possible not only to turn on but also to turn off the output
o output can be activated temporarily for specified amount of time
o there is a complete list of events for which you can define the behavior of the
output.
Note: Do not use at the same time the basic configuration of outputs (8.3.3
Outputs) and the “Advanced outputs control”!
In particular, the basic configuration of existing options: “No GSM signal
(immediately after detection)” and “Dependent on state transitions from non-active
to active of one of the inputs” should not be used with their replacements “[Off]
GSM” and “[On] Input x”. The use the basic configuration of outputs and “Advanced
outputs control” at the same time, may cause unexpected behavior of the
transmitter.
Page 41

EPX400 – Manual
Page 41 / 71
8.3.4.1. Output 1 / Output 2 / Output 3
These columns define which events are to influence the status of a specific output.
Possible choices are:
o Do Nothing – output status will be not changed (default action)
o Turn on output – output will be permanently turned on
o Turn on output temporarily – output will be turned on for an amount of time
specified by parameter 8.3.4.2. Time of output activation
o Turn off output – output will be turned off
Press the [Reset] button to assign the action “Do Nothing” for each event.
The output state does not change if the current state of the output coincides with the
result of the action.
8.3.4.2. Time of output activation
Parameter defining amount of time for which the output is to be turned on for the
functions of advanced outputs control.
8.3.4.3. Event: CLIP
Incoming call from the number defined in option: Inputs/Outputs –> Output 1 /
Output 2 / Output 3. The phone number is entered at option: “When incoming call
detected from number” (see item 8.3.3.2.).
Page 42

EPX400 – Manual
Page 42 / 71
8.4. MONITORING
Thanks to this option you may determine which of available events generated by the
device shall be transmitted to monitoring station.
NOTE: “Configuration changed” event refer to configuration changes made
by SMS or GPRS commands.
8.4.1. Ethernet
In this columns you define events that are to be reported to monitoring station with
Ethernet transmission. There is possibility to send information on alarms (violation of
input) and on returns of inputs state to normal (inactive) state. To transmit any
event you should only click it (proper square on your right).
Click on [Clear] button to remove all marked events.
Click on [Invert] button to change markings to contrary.
8.4.2. GPRS
In this columns you define events that are to be reported to monitoring station with
GPRS transmission. There is possibility to send information on alarms (violation of
input) and on returns of inputs state to normal (inactive) state. To transmit any
event you should only click it (proper square on your right).
Click on [Clear] button to remove all marked events.
Click on [Invert] button to change markings to contrary.
Page 43

EPX400 – Manual
Page 43 / 71
8.4.3. SMS
In this columns you define events that may be reported at monitoring station with
SMS messages – when there is no connection with server over GPRS. There is
possibility to send information on alarms (violation of input) and on returns of inputs
state to normal (inactive) state. To transmit any event you should only click it
(proper square on your right).
Click on [Clear] button to remove all marked events.
Click on [Invert] button to change markings to contrary.
8.4.4. Skip initial state
This option allow for locking of sending of information on status of active inputs at
power connection. Information on inputs will be sent to server after the first change
from inactive to active status.
For the events “Power” and “Battery” no selection “Skip initial state” will cause
sending information about the power supply / battery on boot device regardless of
the power supply / battery state.
8.4.5. Power loss
One of device additional options is monitoring of power supply voltage. As short
voltage drop may follows at some facilities, it is possible to avoid reporting by
entering time after which information will be sent.
Value of this parameter means that voltage drop shall follow within this determined
time so that device recognizes it as real voltage drop and that information might be
sent.
8.4.6. Event: CLIP
Incoming call from the number defined in options: “Inputs/Outputs –>Output 1 /
Output 2 / Output 3”. The phone number is entered at option: “When incoming call
detected from number” (see item 8.3.3.2.).
8.4.7. Sleep when the battery voltage less than
If you check an option “Sleep when the battery voltage less than” battery voltage
threshold field becomes available. The threshold is used when the transmitter goes
into Sleep mode. Due to the characteristics of the battery Sleep mode ensures
reliable operation of the device when the battery is the only source of power at the
time. If the option “Sleep when the battery voltage less than” will remain unchecked
transmitter will work as long as it allows the battery. This may adversely affect the
capacity of the battery for a further period of use as well as cause a generation of
false alarms.
Transition to Sleep mode occurs when the battery voltage falls below the defined
threshold (taken into account the 3 consecutive measurements performed in 10second interval). The following steps are then performed:
1. “Too low voltage – sleep” event is generated
2. Transmitter for up to 30 seconds is trying to send “Too low voltage – sleep”
event to the software
3. Device switches to Sleep mode, i.e. the modem goes to off, inputs are not
being monitored, outputs are turned off, an external telephone line is attached
Sleep mode is indicated by alternating lighting and off LEDs: OK and ERR.
Page 44

EPX400 – Manual
Page 44 / 71
Exit from Sleep mode occurs when one of the following situations takes place:
Main power supply is connected and the battery voltage exceeded a value of
“threshold of sleep” + 0.6 V
Overall disconnect power and re-connect the battery and/or AC power
For transmitter inputs are reported only changes in relation to the state before sleep.
8.5. RESTRICTIONS
8.5.1. SMS and data calls (CSD)
In this section, you can define the restriction for the phone numbers from which
incoming data calls and SMS commands are received. You can also specify SMS
validity period and outgoing SMS limits.
8.5.1.1. SMS authorized phones
User may restrict remote access to the device (via SMS) for determined phone
numbers. A list of numbers (up to 5 numbers) determines which numbers are
allowed to connect with transmitter.
Available options:
o Deny all: means no available telephone communication.
o Allow all: means that telephone communication is possible from any phone.
Page 45

EPX400 – Manual
Page 45 / 71
o Allow chosen: means that telephone communication is possible only from
these numbers that are on the list. It is possible to list up to 5 phone numbers.
Select “Allow chosen” to get access to edition window. Enter another numbers and
click on [Add] button to send them to the below table. Position cursor on line with
number and click on “Remove” to remove number from table.
Click on “Remove all” to remove all numbers from table.
Note:
a) Authorizing of coming SMS comes through comparing number of oncoming
SMS with numbers from table. It is allowable to enter only a part of number
e.g. 1234. As a result all numbers with this sequence will be authorized
e.g.600123456 or 601234567.
b) If modem connected to OSM.Server server will be used to send SMS, its
number have to be entered on the list.
8.5.1.2. GSM modems authorized phones
For connections on CSD channel the user may limit remote access to device from
GSM modems. Only numbers on the list (up to 5) allow for communication with
transmitter.
Available options:
o Deny all: means no available telephone communication.
o Allow all: means that telephone communication is possible from any phone.
o Allow chosen: means that telephone communication is possible only from these
numbers that are on the list. It is possible to list up to 5 phone numbers.
Po wyborze Pozwól wybranym uzyskuje się dostęp do pola edycji. Kolejne numery
należy wpisać w pole, po czym kliknięcie przycisku [Dodaj] przeniesie numer do
tabeli poniżej. Ustawienie kursora na danej linii z numerem i kliknięcie przycisku
„Usuń” spowoduje usunięcie numeru z tabeli.
Opcja „Usuń wszystkie” wyczyści całą zawartość tabeli.
Note:
a) Authorizing of coming CSD comes through comparing of number from which it
was sent with numbers from table. It is allowable to enter only a part of
number e.g. 1234. As a result all numbers with this sequence will be
authorized e.g.600123456 or 601234567.
b) If modem connected to OSM.Server server will be used to make connections
CSD, its number have to be entered on the list.
8.5.1.3. Validity period of outgoing SMS messages
User may limit time for the GSM operator to deliver information via SMS when
recipient is unavailable due to out of GSM signal coverage for example. Time limit is
defined separately for the following groups of information:
o SMS test to server
o SMS events sent to server
o SMS events sent to user
o Answers to commends
Selection is to be made from scrolled down values by clicking on arrow besides
selection area. Allowable options: 5, 10, 15, 30 minutes; 1, 2, 6, 12 hours; 1, 7
days, MAX (meaning no specified time).
8.5.1.4. SMS limits
Page 46

EPX400 – Manual
Page 46 / 71
User may limit number of SMS sending by transmitter. As the main way of
transmission should be Ethernet and GPRS, this limitation is essential to reduce
costs.
Mark field [Turn on SMS limits] to activate access to information groups that
shall subject to limitation:
o SMS test to server
o SMS event s sent to server
o SMS events sent to user
o Answers to commends
Limitation are defined by providing two values:
SMS maximum number: determines maximum number of sent SMS messages per
time unit (see SMS counter reset). This option protects user against sending too
much of SMS messages e.g. in case of failure.
SMS counter reset: This parameter determines time schedule (in minutes) according
to which counter of sent SMS messages will be zeroed.
8.6. SMS NOTIFICATIONS
User may define messages that in case of any event (e.g. input state change) will be
sent to private phone numbers. At the same time it is worth to remember about
limitation in this respect.
8.6.1. Phone numbers
One way to limit amount of sent information (by SMS) is to define a list of 5 private
phone numbers. This list means that only telephones listed on it will receive
messages sent by transmitter.
To edit you shall follow this procedure:
o Enter due telephone number into edition field.
o Click on [Add] button to transfer number to the below table.
o Repeat procedure (up to 5 phone numbers).
Page 47

EPX400 – Manual
Page 47 / 71
Position cursor on line with phone number and click on “Remove” button to remove
number from table.
Click on “Remove all” button to remove all numbers from table.
8.6.2. Events
This tab is to configure and edit SMS messages to be sent to listed phone numbers.
You may define SMS text message with reference to any event from the list (Input 1:
Activation, Restore; Input 2: Activation, Restore; etc.) that will be sent if this event
follows. To define use edition field on the right of events list.
Follow the procedure:
a) Select event to edit from the list
b) Mark square next to phone number that SMS is to sent to
c) Enter message text of SMS when field is active
d) If the “Copy the contents from first message” will be marked then selection
and text content will be automatically copied from the first message, otherwise
you may copy one text and paste to other field manually
Page 48

EPX400 – Manual
Page 48 / 71
Note:
o The total number of characters for all SMS messages shall not exceed 2000.
o Mark any mistake and delete by pressing [Del] button.
o You may copy one text and paste to other field.
8.6.2.1. SMS user tests
SMS user tests sent to specified phone numbers are carried out independently of the
operating mode of the device (GPRS / SMS / GRPS & SMS / Serverless). To enable
the cyclic tests provide up to 5 phone numbers in “SMS Notifications” tab.
Then, for the event “Test message”, type your message and provide a period of the
test message. To do this, mark “Send test every” and indicate the period of the test
set out in the next field. The format of the test period field is “the total number of
days, number of hours:the number of minutes”. No selection in the “Send test every”
will disable SMS user tests.
Page 49

EPX400 – Manual
Page 49 / 71
8.6.3. Status
The device provides for remote enquiry about the status. Edit in this field message
text that is to be sent to the user as a reply to command regarding status checking.
Telephone numbers authorized to send enquiry about status are defined in option
Restrictions > Authorized SMS phones.
Reply from device shall be sent at number, from which enquiry was sent.
In reply about status a device shall send one SMS message containing proper text
defining actual output , input state and power supply.
Note: Counter “Allowed characters” informs about the total number of characters
that may be inserted into the table.
Page 50

EPX400 – Manual
Page 50 / 71
8.6.4. SMS Forward
The device is able to forward received SMS messages according to the specified rules.
This function may be helpful for example when GSM operator sends messages with
account state to SIM card installed within device. In this window you may provide up
to 5 rules.
Each rule contains a pair: part of sender phone number and correct recipient phone
number. In some cases a part of sender phone number may be an empty string
which means that any phone number matches to the rule. All rules are processed
with given order. It means that in some cases one SMS message may be forwarded
to more than one recipients and/or some of them may be forwarded more than once
to the same recipient. The second case may occur when there are at least two rules
with the same recipient phone number and their part of sender phone number
matches with message sender phone number.
Note: It is a user’s responsibility to provide correct rules which will not create loops
of forwarded SMS messages.
Page 51

EPX400 – Manual
Page 51 / 71
8.7. RS232
In order to provide additional capabilities for sending information, EPX400 transmitter
is equipped with serial port RS-232, 3.3V TTL level. To connect devices equipped with
a standard RS-232 or RS-485 the appropriate cables and converters are needed.
Page 52

EPX400 – Manual
Page 52 / 71
8.7.1. Serial port settings
The selected parameters shall correspond to RS-232 port settings in device which will
be connected to the transmitter. Available parameters are shown in the table below:
Parameter
Value
Baud rate (bits/sec)
1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400,
57600, 115200
Data bits
8
Parity
None, Even, Odd
Stop bits
1, 2
Flow control
None, RTS, CTS, RTS/CTS
If RS232 checkbox will not be enabled, data to the Event monitor will be sent on
device’s serial port. With this setting, GD-PROG cable can be used to observe device
state using GPRS transmitters configurator application and Monitor option described
in point 8.11.
8.7.2. Buffer flushing
Data received from connected device are stored in transmitter buffer. Buffer capacity
is 511 bytes. Define criteria that meeting shall mean data transmission to monitoring
system transmitter. The following options are available:
- After receiving defined ASCII character
- After expiry of defined time
- After receiving defined amount of characters
Page 53

EPX400 – Manual
Page 53 / 71
For every option list of available values are provided, and they me be scrolled down
after clicking on adequate arrow.
The transmitter controls buffer contents in respect of meeting of determined criteria.
It is performed with the following order: selected character, time, number of
characters.
Discharge of buffer (transmission) follows if one criteria is fulfilled.
8.7.3. Advanced port options
8.7.3.1. Disable data receiving
This option allow for lock of data received from device connected to RS-232 port of
transmitter. It is used in case of failure or situation when transmitter is being used to
control the another device.
8.7.3.2. Disable data sending
This option allow for lock of data sending to device connected to RS-232 port of
transmitter. This prevent accidental or unauthorized controlling of the device.
8.7.3.3. Half duplex mode
This option provides for automatic lock of data receiving (via RTS) if transmitter
begin to send data to the device.
8.7.3.4. Check tests send by device connected to the port
If the device connected to transmitter port generates periodical connection tests,
these tests may be under control. To provide for that (after this option activation)
enter text message and define frequency (in “Test presence every [s]” option).
Additionally user may determine if text messages will be sent to server. If this option
was not selected it is required to make sure that while the device connected to
transmitter port is not sending text message to transmitter, then transmitter sends
to server due message (See chapter 8.11. Device monitor – option “RS232 tests”).
8.8. LINK CONTROL
By using the options described in this section, you can set the device to react
automatically when the connection with the monitoring station is lost. This applies to
situations where the device has lost GSM connectivity, GPRS transmission is not
possible or the Ethernet link is not working.
Page 54

EPX400 – Manual
Page 54 / 71
8.8.1. Watchdog
In this section, you can enable the watchdog, a system that monitors the
transmitter's operation. It can control the status of 3 transmission channels:
Ethernet, GPRS and GSM.
The watchdog can be enabled for each transmission channel separately by checking
the box “Turn watchdog on” in the respective column.
In the [React after inactivity time] box, specify the amount of time that must elapse
from the loss of connectivity before the transmitter attempts to reconnect. The time
should be specified in minutes.
If connectivity in a channel is lost, the device will wait for the specified amount of
time from the moment of registering the loss of connectivity and then execute
pre-defined actions.
The following actions are available:
o Reset submodule
o Reset transmitter
o Turn on output 1
o Turn on output 2
o Turn on output 3
To enable an action, check the corresponding box next to its name.
“Reset submodule” means restarting the communication module of the respective
channel: PHY module for the Ethernet channel or GSM/GPRS modem for the GPRS
and GSM channels.
Enabling the “Reset transmitter” setting is not recommended, but it may be
necessary in special situations.
Page 55

EPX400 – Manual
Page 55 / 71
8.9. PHONE LINE
The device is equipped with a PSTN phone line connector. It may be used to transmit
data from an alarm control panel. Additionally transmitter may collect information
from an control panel using its a phone communicator, and next transmit them via
PSTN/GPRS/SMS link. For proper operation, define the parameters described below.
8.9.1. Phone line settings
This tab is provided to determine settings of telephone line.
8.9.1.1. Use external phone line
If this function has been chosen (Activation) the transmitter will be cooperating with
PSTN line. This way data transmission is possible from an alarm control panel with
two ways: via GPRS link and standard telephone line.
8.9.1.2. Disconnect external phone when server connected
If enabled, PSTN line will be disconnected from T1-R1 port when connection with the
server is established. If events registered by the alarm control panel are supposed to
be sent by GPRS, this option can be used to separate external line from the alarm
control panel.
8.9.1.3. Monitor external phone line voltage
Page 56

EPX400 – Manual
Page 56 / 71
If transmission with two ways follows, it is necessary that operator of monitoring
system received information on access to an external telephone line. Choice of this
option will result in voltage drop on telephone line (longer that defined minimal time
of decay) that will be signalized with an adequate message sent via GPRS.
Note: The transmitter is to simulate a telephone line access if:
o A PSTN line is not connected
o A PSTN line is connected but has not been activated – option from clause
8.9.1.1. Use external phone line
o Options from clause 8.9.1.1. and clause Błąd! Nie można odnaleźć źródła
odwołania.. are active and voltage on terminals TIP-RING decreased below
8V.
8.9.1.4. Report off-hook condition
If a phone set is connected in parallel output of control panel communicator (to
terminals T1-R1 of transmitter), picking up of a phone prevent from exchange of data
between an control panel and a transmitter. There is possibility to control this
situation. Choice of this option result in sending a report to monitoring station if time
of picking up the phone exceeds determined time limit.
8.9.1.5. Report intervals between dialled digits
This option is being used if in configuration “PSTN line – EPX400 – Alarm Control
Panel” there are not other telecommunication devices. If such device will be
connected and telephone number will be dialled (and a call will follow) after expiry
defined time limit (counted since conclusion of last digit dialling) the transmitter
sends a message. This operation prevents unauthorised installation of additional
devices.
8.9.1.6. Generate dial tone
Some alarm control panels require that during a receiver picking up a tone of dialling
was actuated. To enable cooperation with a transmitter it is possible to make a
transmitter to generate such tone.
8.9.1.7. Detect off-hook after
The default value for the delay detection off-hook is 100ms. You can define your own
delay value by choosing option "After" and giving the number in milliseconds.
8.9.2. First and Second phone number
To provide for proper cooperation between a transmitter and a control panel in DTMF
mode determination of some parameters is required. The below described functions
are analogous to the both telephone numbers that may be saved in the device
memory.
8.9.2.1. DTMF phone number
This is a number that has been saved in memory of an alarm control panel. If the
panel is to transmit information on an event it shall dialled this number. Transmission
of this information via GSM (GPRS) will be possible if this number will be identical as
a number entered into the transmitter.
8.9.2.2. Handshake delay
Page 57

EPX400 – Manual
Page 57 / 71
This defines time after which a transmitter generates confirmation to an alarm
control panel for correct phone number dial. Default setting is 2.0 sec. European
Standard determines this value at 0.5 to 12.5 sec.
8.9.2.3. Protocol
Select protocol of data transmission used by an alarm control panel and that is
acceptable for monitoring station. Available options: ContactID and SIA.
Note:
1) For all protocols you may use following options:
o [Enable SMS sending] which means that in case of no GPRS connection,
data will be sent via SMS (if this mode will be accessible).
o [Don’t transmit data when external phone line is available] which means
that when the external PSTN line is available then it will be used during
transmission from the control panel.
2) [Disable CRC checking] option may be used for ContactID format. Some control
panel generate improper messages regarding a control sum for transmitted data, the
device is not able to confirm collection of data, and as a result the panel tries to send
them again (until execution of all determined trials). Select this option to avoid the
above mentioned.
Page 58

EPX400 – Manual
Page 58 / 71
8.10. FIRMWARE
The device is equipped with built in bootloader that allow for updating and change of
firmware. During programming all information is displayed in respect of carried out
operation.
Follow the following procedure:
a) Launch configuration program.
b) Open “Firmware” option of configuration wizard.
c) Open file with new firmware (click [Open] button to locate where file is).
d) Select file transmission mode: local or remote.
Note: Procedure of assigning firmware to a device is analogous to
programming a device. For procedure refer to chapter 9. Device
programming.
e) Click [Start] button to start software exchange.
f) Loading course is displayed on special window.
g) Close the window after completed saving.
From this time on the device will work under control of new firmware.
Note: The above procedure shall be carry out with due care to avoid
improper device operation.
Page 59

EPX400 – Manual
Page 59 / 71
8.11. DEVICE MONITOR
“Device Monitor” provides real-time information on device state. To use this function
device must be connected to PC computer with GD-PROG cable (the switch in position
DEBUG). Correct RS232 port must be chosen in “Port” field. “Device monitor”
provides following information:
o AC power indication
o Battery power indication
o PSTN line indication
o GSM network signal level indication
o Bit-Error-Rate level measuring
o Inputs and outputs state monitoring
o Type or serial number of device
o Firmware and hardware revision
o Device time
These parameters are also shown in LOG window in text style. All data can be saved
to file.
Note: Relay output “NC-NO-C” in the Device Monitor window are presented as OUT3.
Page 60

EPX400 – Manual
Page 60 / 71
8.12. EVENTS HISTORY
„Events history” provides information about last events stored in EPX400 device
memory. EPX400 transmitter is able to save at least 5000 events. It is possible to
read the history using a GPRS or RS232 connection. In the second case data can be
send to PC via GD-PROG cable (the switch in position PROG). Correct RS232 port or
GPRS connection must be chosen in “Choose connection kind” field. After providing
Service code and clicking “Open” button events data will be downloaded from EPX400
memory. After properly reading access to features such as the "Filtering" and
"Charts" becomes possible. Both of them may be used to quickly diagnose the
device.
Page 61

EPX400 – Manual
Page 61 / 71
Page 62

EPX400 – Manual
Page 62 / 71
9. DEVICE PROGRAMMING
Programming of device is possible with “GPRS transmitters configurator”
configuration program described in chapter 7. CONFIGURATION PROGRAM. To
program the device establish connection with a device.
Depending on connection mode there are two ways for programming.
9.1. LOCAL PROGRAMMING
To program a device locally follow the procedure:
a) Connect PROG joint (on printed circuit) with COM computer port by way of
service wire, defined in option -> RS-232.
b) Connect power supply to terminals +12V and GND. After connection and
detection of programming wire a module shall signal this with LED diodes: a
green one shall flash and red one shall flicker.
c) Launch software and define device options (description is in chapter 3. of this
Manual ). Provide right PIN code for SIM card.
d) Save settings into memory of device. Saving course is displayed in special
window.
e) After saving disconnect power supply and disassembly service wire.
f) Insert SIM card. Connect module wiring pursuant to guidelines from chapter 3.
Turn power supply on.
g) The device is ready to transmit data.
9.2. REMOTE PROGRAMMING
Remote programming of device is possible if:
o user uses GPRS transmitters configurator and GSM modem connected to PC
o user uses OSM.Server monitoring system receiver
In first case remote programming is possible on CSD channel and its procedure is
analogous to local programming, remembering that “Modem GSM” shall be selected
from connection options (See chapter 7.3.5.2. Remote connection – CSD connection).
Note: Remote configuration with use of CSD canal is possible only if transmission of
CSD data is active both for SIM card inserted in the device, and for SIM card installed
in GSM modem.
In second case according to description in chapter 7.3.5.2. Remote connection –
GPRS linking, it is required to define remote link on grounds of OSM.Server
parameters. As OSM.Server collects (and transmits) information exclusively from
Page 63

EPX400 – Manual
Page 63 / 71
devices saved in data base, the first operation during remote programming is proper
registration of the device. This procedure has been described in OSM.Server
Operation Manual.
9.2.1. The first programming of device
As the device does not have defined access parameters in respect of GPRS network
and OSM.Server, programming shall be begun with providing parameters.
Irrespectively of providing these parameters the first operation shall be registration
of device in OSM.Server data base.
Before remote programming user shall check that the device is furnished with SIM
card (with reservations provided in chapter 8.1.1.2.) and is connected to power
supply. User shall know serial number of device and phone number for SIM card.
Follow the procedure:
a) With the use of OSM.Server console position cursor on proper device in
“Devices” tab.
b) Click “Config.” option and then select “Set Configuration” function to display lit
of parameters.
c) Enter server address, server port and APN. Click OK and system shall send to
device provided parameters (SMS).
d) Wait till device addresses server (in “Devices” tab it will be marked with green
colour).
e) Launch software and define options of device (description is provided in
chapter 8. of this Manual).
f) Select “Send” to display a new window and select remote connection (GPRS
tab). Save settings in memory of device. Saving course is displayed on special
window.
g) After saving completion close Configuration Wizard.
h) The device is ready to transmit data.
9.2.2. Reprogramming of device
As the device has defined access parameters in respect of GPRS network and
OSM.Server, it is possible to program device at any time.
If device is installed in secured object and is furnished with SIM card and connected
to power supply follow the procedure:
a) Launch configuration wizard and define options of device (description is
provided in chapter 8. of this Manual).
b) Select “Send” to display a new window and select remote connection (GPRS
tab). Save settings in memory of device. Saving course is displayed in special
window.
c) After saving completion close Configuration Wizard
d) The device is ready to transmit data according to new settings.
Page 64

EPX400 – Manual
Page 64 / 71
10. RECEIVING OF SMS MESSAGE
GPRS module receives specially prepared SMS. If received SMS is not correct it will
be automatically cancelled and device will not operate any action. The device uses an
encrypted protocol for transmission.
10.1. REMOTE COMMANDS DESCRIPTION
The following format of message is acceptable allowing to send some commends with
one SMS (every command shall be separated with SPACE ):
SERVICE CODE█COMMAND█COMMAND█………
Where:
SERVICE CODE
- device service code
█
- SPACE
COMMAND
- order (see the table below)
List of commands:
DISC
Disconnects active TCP connection.
KILL
Reset modem; after execution of command a confirmation is
sent.
RESET
Reset device. Note: all unsent events will be lost.
OUT=outNr, state
Turn on or turn off outputs. outNr specifies output number
(0 for OUT1, 1 for OUT2, 2 for OUT3), state specifies
requested output state (0 – switched off, 1 – switched on).
Examples:
OUT=0,0 – switches off output OUT1
OUT=2,1 – switches on output OUT3
CMD= [timeout], command
Issues AT command to GSM modem and sends response
back. Optional timeout parameter defines time for modem
response. Time determined in seconds and ranges from 1-30
seconds. If timeout isn’t specified, 3 seconds is assumed.
DESC
Returns device description, serial number (hexadecimal
number) and firmware version.
GETSTATUS
Download device status. Command sends text back
according to definition from chapter 8.6.3. Status.
GETPARAM=
parameter_name
Gets inquired parameter :SERVER, PORT, APN, UN, PW,
DNS1, DNS2, SMS, SMSPERIOD
GETCFG
Gets primary communication parameters of device in form:
SERVER:PORT,APN UN PW,DNS1
APN=apn
Access point to GPRS network. Parameter should be
obtained from mobile network operator. If APN address
contain space sign put it with “”, e.g. “my apn”.
UN=un
APN user name. Parameter should be obtained from mobile
network operator. If APN user name contain space sign put it
with “”, e.g. “my user name”.
PW=pw
APN password. Parameter should be obtained from mobile
network operator. If APN password contain space sign put it
with “”, e.g. “my password”.
SERVER=server address
If the role of the GPRS channel is sets as "Unused", this
command sets the address of the server and the role GPRS
channel as "Backup."
If the role of the GPRS channel is DIFFERENT than "Unused"
(it’s mean turned on), this command sets only the address
of the server.
Page 65

EPX400 – Manual
Page 65 / 71
SERVER=
(empty string, without the
parameter)
Clears the server address.
NOTE: The Transmitter will not attempt communication with
the server via GPRS.
PORT=port
Server port number.
DNS1=dns1
Specifies primary DNS server address (only needed when
domain name address is used as SERVER address)
DNS2=dns2
Specifies secondary DNS server address (only needed when
domain name address is used as SERVER address)
SMS=phone number
SMS=
(empty string, without the
parameter)
If the role of the SMS channel is set as "Unused", this
command sets the phone number of the server and the role
of SMS channel as "Emergency". When there is GPRS failure,
SMS with events will be sent to this number.
Clears the phone number.
NOTE: The Transmitter will not go into SMS mode.
SMSPERIOD=time
Defines in minutes time between SMS test messages
sending to the server.
RLIMIT
Removes automatic temporary locks on all inputs
RLIMIT=inputs_mask
Removes selected automatic temporary locks. Parameter is
decimal number made from 10-bit word: A10 … A2, A1,
where A1 always equals 0, A2 means INPUT 1, A3 means
INPUT 2, and A10 means INPUT9.
EXAMPLE:
RLIMIT=6 removes locks on inputs:IN1, IN2
RLIMIT=2 remove lock on input IN1
DT=YY/MM/DD,hh:mm:ss
Sets date and time in the transmitter; must be putted in a
specific format (see the table on the left)
FLUSH=x
Flushes events buffer, where x is:
2 – system events history
ETHSERVER=server_addres
s:port
ETHSERVER=
(tzw. empty string)
Server address and port which the transmitter EPX will
connect. If the role of the channel ETHERNET was set as
"Unused" is now set to "Main".
Example:
ETHSERVER = 89.123.115.8: 9000
The command returns:
EOK - entered correctly value;
EFORMAT - incorrect format of the command;
EINVALID - if incomplete (e.g. the lack of port), or entering
other characters after “:” than numbers.
Deleting the set server address.
Page 66

EPX400 – Manual
Page 66 / 71
ETHCONFIG=parameter
It is used to configure the Ethernet interface where the
parameter can be set to:
DHCP - ETH interface set in DHCP mode;
IP, MASK, GATEWAY [, DNS1, DNS2] - command sets the
static IP MASK, GATEWAY, and optional server DNS1 and
DNS2 (if the address is given in the form of domain e.g.
black.autostrada.com)
Example:
ETHCONFIG = 192.168.7.7,255.255.255.0,192.168.7.5
The command returns:
EOK - entered correctly value;
EINVALID - if the parameters do not correspond to the
format of the IP address;
EFORMAT - when the values of the parameters is not
enough.
Notes:
1. DESC, CMD, GETSTATUS, GETPARAM, GETCFG commands require separate
SMS, so one command with only one SMS.
2. SERVER and SMS commands are not used to setting the priorities of the
channel, but only for setting up a backup (or emergency) transmission channel
in case of loss of communication with the monitoring system via main channel.
Samples of commands and device reaction:
Parameters setting:
1111█APN=general.t-mobile.uk█SERVER=89.112.43.78█PORT=6670█
SMS=500445566█SMSPERIOD=25
Parameters verification:
Inquiry: 1111█GETCFG
Answer: 89.112.43.78:6670,general.t-mobile.uk██,
Inquiry: 1111█GETPARAM=SMS
Answer:: 500445566
Page 67

EPX400 – Manual
Page 67 / 71
11. LED DIODES INDICATION
LED diodes (4), mounted directly on printed circuit, are purposed to show current
condition of the device.
11.1. LOGGING TO GSM NETWORK
Once SIM card has been inserted into the device and power supply was turned on
logging to GSM system follows.
Description
LED Diodes
Green
Red
Logging to GSM
11.2. GSM RANGE
Flickering of a green diode indicates GSM signal (1-8 flickers).
Device operation mode is signalled with a green diode on during 2 seconds once the
range was detected. If after signalling range diode will not flash for 2 seconds the
device is in SMS mode. Range indication is interrupted during data transmission, and
after sending of data again GSM range is being indicated.
Description
LED Diodes
Green
Red
GSM range = 8
GPRS mode
GSM range = 6
GPRS mode
DTMF ERR OK STATUS
DTMF ERR OK STATUS
Page 68

EPX400 – Manual
Page 68 / 71
11.3. DATA TRANSMISSION
During data transmission a green diode indicates data transmitting.
Description
LED Diodes
Green
Red
GPRS Transmission
SMS Transmission
11.4. RECEIVING OF DTMF DATA
STATUS LED (blue) and DTMF LED (yellow) indicate actual condition during
receiving data from a control panel.
Dioda LED
Signalling
STATUS
DTMF
(HandShake)
(KissOff)
6 digits of phone 16 digits ContactID
DTMF ERR OK STATUS
DTMF ERR OK STATUS
DTMF ERR OK STATUS
Page 69

EPX400 – Manual
Page 69 / 71
11.5. PROGRAMMING
After detection of programming cable, diodes indicate programming mode.
Description
LED Diodes
Green
Red
Connected
service
cable
Programming
in CSD mode
11.6. FIRMWARE UPDATING
During programming bootloader operating is indicated. If error follows during
updating there is bootloader in device and another programming of device is
possible.
Description
LED Diodes
Green
Red
No program
in device
(1/sek)
Software
updating
Received firmware
decoding
10 sek
DTMF ERR OK STATUS
DTMF ERR OK STATUS
Page 70

EPX400 – Manual
Page 70 / 71
11.7. SIM CARD ERROR
In case of SIM card problems, device states this with ERROR LED (red) and OK LED
(green).
LED diode
Signalling
OK
(Green)
ERROR
(Red)
11.8. SYSTEM ERROR
Errors may occure during device operation. An error is indicated by a permanent
lighting of red LED. In most cases it means a communication problem with the
modem or SIM card.
DTMF ERR OK STATUS
Page 71

EPX400 – Manual
Page 71 / 71
12. CHANGELOG
Date / Version
Description
30.11.2015 / v1.0
First version of the manual
03.12.2015 / v1.1
Minor changes
15.01.2016 / v1.2
Expanded Ethernet description
08.07.2016 / v1.3
Removing few features
09.03.2017 / v1.4
Expansion of remote commands SMS and SERVER, added
ETHSERVER and ETHCONFIG commands.
16.03.2017 / v1.5
Updating information about GPRS Transmitter
Configurator
27.03.2017 / v1.6
Added information about “Embedded HTTP server”
30.10.2017 / v1.7
Update requirements for the computer in reference to
configurator; replacement of OSM.2007 with OSM.Server
 Loading...
Loading...