Page 1
DX810 v3.3
8x10 Digital Matrix Mixer and Signal Processor
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
OL
OL
OL
OL
OL
2
2
2
4
4
7
7
10
10
15
15
20
20
25
25
30
30
35
35
40
40
50
50
2
4
4
7
7
10
10
15
15
20
20
25
25
30
30
35
35
40
40
50
50
OL
2
2
4
4
7
7
10
10
15
15
20
20
25
25
30
30
35
35
40
40
50
50
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
23456781
DX810 DIGITAL MIXER
100–240V , 50/60Hz, 1A MAX
LISTED COMMERCIAL
AUDIO EQUIPMENT
R
DIRECT OUTPUTS
U
U
+20-20
+20-20
TRIM
TRIM
BUS A
BUS B
MIC
+
G
POWER
–
INPUT
LINE
-
28V DC,
22
+
–
G
3A MAX
–
+
9Z39
U
U
G
G
A
A
C
C
I
I
N
N
I
I
M
M
60
60
0
0
-
-
30dB+30dB
30dB+30dB
TRIM2TRIM3TRIM4TRIM5TRIM6TRIM7TRIM
TRIM
1
MIC
MIC
LINELINELINE
LINE
I
M
0
-
30dB+30dB
OL
2
4
7
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
50
U
G
A
C
I
I
N
N
I
M
60
60
0
-
30dB+30dB
8
MIC
PHANTOM POWER
48V DC
ON
12345678
LINE
DX810 DIGITAL MIXER
ABLOCK
MODE
G
–
+
•
10
e
G
–
+
INPUTS
12 1 +5V
OUTPUTS
11G1
LOGIC I/O
A
B
RECORD
COMM PORT
J I H G
C D E F
+
–
G
REMOTE BUS
OUTPUTS
+
–
G
A
COMM PORT
B
G
POWER
+
–
M
0
-
30dB+30dB
15
12
9
6
3
0
3
6
9
12
15
HILO EQ BA MASTER
MANUFACTURING DATE
SERIAL NUMBER
U
U
U
G
A
C
I
N
I
60
MIC
LINE
M
0
-
30dB+30dB
G
G
A
A
C
C
I
N
I
I
M
60
0
-
30dB+30dB
MIC
MIC
LINE
LINE
OL
2
4
7
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
50
U
U
G
G
A
A
C
C
I
I
N
N
I
M
60
60
0
-
30dB+30dB
MIC
MIC
LINE
LINE
Page 2
2 – DX810
-
CAUTION AVIS
RISK OF ELECTRIC
RISQUE DE
CAUTION: TO REDUCE THE RISK OF ELECTRIC SHOCK
DO NOT REMOVE COVER (OR BACK)
NO USER-SERVICEABLE PARTS INSIDE
REFER SERVICING TO QUALIFIED PERSONNEL
ATTENTION: POUR EVITER LES RISQUES DE CHOC
ELECTRIQUE, NE PAS ENLEVER LE COUVERCLE. AUCUN
ENTRETIEN DE PIECES INTERIEURES PAR L'USAGER. CONFIER
L'ENTRETIEN AU PERSONNEL QUALIFIE.
AVIS: POUR EVITER LES RISQUES D'INCENDIE OU
D'ELECTROCUTION, N'EXPOSEZ PAS CET ARTICLE
A LA PLUIE OU A L'HUMIDITE
The lightning flash with arrowhead symbol within an equilateral triangle is
intended to alert the user to the presence of uninsulated "dangerous voltage"
within the product's enclosure, that may be of sufficient magnitude to constitute
a risk of electric shock to persons.
Le symbole éclair avec point de flèche à l'intérieur d'un triangle équilatéral est
utilisé pour alerter l'utilisateur de la présence à l'intérieur du coffret de "voltage
dangereux" non isolé d'ampleur suffisante pour constituer un risque d'éléctrocution.
The exclamation point within an equilateral triangle is intended to alert the user
of the presence of important operating and maintenance (servicing) instructions
in the literature accompanying the appliance.
Le point d'exclamation à l'intérieur d'un triangle équilatéral est employé pour
alerter les utilisateurs de la présence d'instructions importantes pour le fonction
nement et l'entretien (service) dans le livret d'instruction accompagnant l'appareil.
SHOCK
CHOC
NE PAS OUVRIR
• DO NOT OPEN
ELECTRIQUE
Table of Contents
1. SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS ............................................................... 2
2. INTRODUCTION .............................................................................. 3
Key Features ................................................................................. 4
Front Panel Features .....................................................................5
Rear Panel Features ..................................................................... 5
3. INSTALLATION ................................................................................ 7
Connections .................................................................................. 7
AC Power Considerations .............................................................8
4. OPERATION .................................................................................... 9
Quick Start .................................................................................... 9
Using Inputs 1-8 ......................................................................... 10
Using the BUS A and B Inputs ....................................................10
Using the DIRECT OUTPUTS ....................................................... 11
Using OUTPUTS A Through J ..................................................... 11
Using the RECORD Output .......................................................... 11
Using the REMOTE Controls .......................................................11
Using the LOGIC I/O ................................................................... 11
Password Protection ................................................................... 13
5. DX-810-PC SOFTWARE (v 3.3) .................................................... 13
Installing the Software ............................................................... 13
Upgrading the Software ............................................................. 13
Connecting a PC ......................................................................... 14
Upgrading the Firmware ............................................................. 14
Overview .................................................................................. 14
Top Section ................................................................................. 15
Menu Bar ............................................................................... 15
Indicators/Presets/Control .....................................................18
Button Section ....................................................................... 19
Crosspoint Matrix Section .......................................................... 26
Input Section .............................................................................. 27
Output Section ............................................................................ 27
Group Section ............................................................................. 28
Exclusive Enable Program Selection ...................................... 28
6. SPECIFICATIONS .......................................................................... 29
DX810 Block Diagram ................................................................. 29
DX810 Specifications ................................................................. 30
7. SERVICE INFORMATION ............................................................. 32
Appendix A: Logic Input Functions ................................................... 33
Appendix B: Logic Output Functions .................................................33
Appendix C: Selection Remote Predefined Functions ...................... 34
Appendix D: Level Remote Predefined Functions ............................. 35
WARNING — To reduce the risk of fire or
electric shock, do not expose this appliance to
rain or moisture.
CAUTION — Internal lithium battery. Danger
of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or equivalent type.
1. SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
1. Read Instructions — Read all the safety and operation instructions before
operating the DX810.
2. Retain Instructions — The safety and operating instructions should be
kept for future reference.
3. HEED ALL WARNINGS — Follow all warnings on the DX810 and in these
operating instructions.
4. FOLLOW ALL INSTRUCTIONS — Follow all operating and other
instructions.
5. Water and Moisture — Do not use the DX810 near water – for example,
near a bathtub, washbowl, kitchen sink, laundry tub, in a wet basement,
near a swimming pool, etc.
6. Ventilation — This DX810 should be situated so that its location or
position does not interfere with its proper ventilation. For example, it
should not be situated on a bed, sofa, rug, or similar surface that may block
any ventilation openings, or placed in a built-in installation such as a
bookcase or cabinet that may impede the flow of air through ventilation
openings.
7. Heat — Locate the DX810 away from heat sources such as radiators, or
other devices which produce heat.
8. Power Sources — Connect the DX810 to a power supply only of the type
described in these operation instructions or as marked on the rear panel. If
using an external DC power supply or battery pack, be sure the voltage
corresponds to the range indicated on the rear panel, and that it is
connected with the correct polarity.
9. Power Cord Protection — Route power supply cords so that they are not
likely to be walked upon or pinched by items placed upon or against them,
paying particular attention to cords at plugs, convenience receptacles, and
the point where they exit the DX810.
10. Object and Liquid Entry — Do not drop objects into or spill liquids into the
inside of the DX810.
11. Damage Requiring Service — The DX810 should be serviced only by
qualified service personnel when:
A. The power-supply cord or the plug has been damaged; or
B. Objects have fallen, or liquid has spilled into the DX810; or
C. The DX810 has been exposed to rain; or
D. The DX810 does not appear to operate normally or exhibits a marked
change in performance; or
E. The DX810 has been dropped, or its chassis damaged.
12. Servicing — The user should not attempt to service the DX810 beyond
those means described in this operating manual. All other servicing should
be referred to the EAW Commercial Service Department.
13. To prevent electric shock, do not use this polarized plug with an extension
cord, receptacle or other outlet unless the blades can be fully inserted to
prevent blade exposure.
Pour prévenir les chocs électriques ne pas utiliser cette fiche polariseé
avec un prolongateur, un prise de courant ou une autre sortie de courant,
sauf si les lames peuvent être insérées à fond sans laisser aucune pariie à
découvert.
14. Grounding or Polarization — Precautions should be taken so that the
grounding or polarization means of the DX-810 is not defeated.
15. This apparatus does not exceed the Class A/Class B (whichever is
applicable) limits for radio noise emissions from digital apparatus as set
out in the radio interference regulations of the Canadian Department of
Communications.
ATTENTION —Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de bruits
radioélectriques dépassant las limites applicables aux appareils
numériques de class A/de class B (selon le cas) prescrites dans le
règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique édicté par les ministere des
communications du Canada.
Page 3

2. INTRODUCTION
The DX810 is our popular DX8 stereo digital audio
mixer with the DX10e Expansion Kit installed. This
adds eight more balanced outputs and converts it
into a powerful matrix mixer/processor. It is
designed for use in a variety of installations such as
churches, courtrooms, convention centers, and
hotels. With eight inputs, ten outputs, and a toolbox
full of DSP, the DX810 fits most any installed sound
reinforcement application.
Each of the 10 outputs represents a discrete mix
of the eight inputs, resulting in a true 8x10 mixing
matrix with virtual faders at each crosspoint. It has
the ability to group any combination of gain
elements to one of 32 groups.
A new software interface provides intuitive
setup and operation via a PC. 31-band third-octave
graphic or eight-band parametric EQs are available
on each output. There is also a three band
sweepable high and low shelving EQ with a fully
parametric mid-range control on each input.
The processing power provided by the DX810
permits inserting a gate on each input, as well as a
compressor on each input and output. It also
permits inserting signal delay on each output, and
creating crossover groups with custom high, low, or
bandpass filters applied to each output. Up to five
outputs can be assigned to a crossover group.
Each of the eight input channels is terminated to
two Phoenix-type detachable connectors. Each
connector is optimized to accept either microphone
or line-level signals. Microphone preamplifiers
employ XDR™ technology to offer studio-class
audio performance. Phantom power of 48 VDC is
switchable individually on each input. Two auxiliary
line-level inputs with trim are provided, allowing
analog signals to be mixed with the A and B master
mixes. All main outputs deliver balanced line-level
signals to detachable Phoenix-type connectors. The
main A and B outputs also deliver buffered
unbalanced signals to RCA connectors intended for
recording.
The DX810 offers an intuitive front panel user
interface for the A and B outputs. It consists of
dual-function LED bar graph meters for each input
and the A and B outputs. Input meters indicate the
presence of signal before signal processing (pre-
fader). Output meters indicate the actual level at
output (post-fader). Levels are set by means of UP/
DOWN pushbuttons dedicated to each input and
output. A MODE button is used to select between
Mix A and B. This allows adjustment of levels to
both mix outputs from the same set of input
controls. A third function of the MODE button
allows the user to LOCK the front panel controls
until a security unlock code is entered.
The DX810 offers flexible interface options
through dedicated inputs and outputs for control
and programming purposes. Two independent
RS232 connectors are provided, one on the front
panel and one on the rear, for connection to a
computer or control system. A multi-pin (DB25F)
connector on the rear panel allows interface among
the 10 Logic Inputs and 10 Logic Outputs. This
interface connects to switches, LEDs, and other
devices, enabling hardware control and indication
from custom control panels. All logic inputs and
outputs are programmable in software. A
proprietary remote control bus allows connection of
the optional wired remotes over three-conductor
cable. Remotes are available in Volume Control
(DX-RVC) and 4-Switch (DX-SW4) versions and may
be combined in any configuration.
The DX810 is supplied with DX-810-PC software
that allows access to all of the system’s settings
and configurations. The software provides access to
the 3-band input EQ, 31-band graphic EQ, eightband parametric EQ, compressors, gates, delays,
and crossover configuration. Group assignments
and room combining are also configured in the
software application. In addition, it allows saving
and recalling up to 24 presets, configuration for
input force on/force off functions with priority, and
for the logic input and output connections. All
settings and text labels are retained in the DX810,
and can be saved on the computer’s local drive.
The DX810 is UL and CE approved and designed
for continuous use in professional fixed installation
systems. An internal auto-ranging power supply
allows connection to mains voltages from 90-240
VAC at 50/60 Hz. This is without requiring jumper or
switch setting changes. A 24 VDC input is provided
for applications where backup power is required.
Switchover to backup power is automatic and silent.
Part No. SW0096 Rev. A 01/04
© 2004 LOUD Technologies Inc. All Rights Reserved.
DX810 – 3
Page 4
10
e
KEY FEATURES
• 32-bit DSP and 24-bit Analog/Digital Conversion
• 8 balanced XDR™ Mic/Line inputs with trim
• 2 balanced Line inputs direct to mix buses A and B
• 10 Independent Mix Buses and balanced Outputs
• 2 unbalanced Record Outputs
• 8 unbalanced Direct Channel Outputs
• Individual Level/Peak (PPM) metering on each
Input
• 2-band sweepable shelving EQ with a parametric
mid on each Input
• Gating on each Input
• Solo button on each Input
• 31-band Graphic EQ or 8-band Parametric EQ on
each Output
• Fully variable Compressor on each Input and
Output
• Variable delay on each Output
• Configurable crossover for up to five bands
• Butterworth, Bessel, and Linkwitz-Riley filter
selections in Crossover window
• Direct link to DSP controls from the Input and
Output Processor View
• Room Combining with up to 16 different
combinations available
• 10 Programmable Logic Inputs
• 10 Programmable Logic Outputs
• 2 independent RS-232 interface ports
• 48 VDC Phantom Power switch per input
• 24 VDC Backup Power input
• Hardware Expansion Port accepts optional
modules
• PC Software application included
• Two levels of password protection
• Powerup Preset
• Enable and Exclusive Enable
• Group priority assignments
• Preset names now appear in Preset box
• User adjustable ramp time between presets
• Global Output fader assign overrides presets
• Force On/Off Group and Combine selection added
to remote control
• Remote Mapping feature provides individual
button assignments for the DX-SW4 remote control
OL
2
4
7
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
50
OL
2
4
7
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
50
OL
2
4
7
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
50
OL
2
4
7
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
50
OL
2
4
7
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
50
OL
2
4
7
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
50
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
23456781
DX810 DIGITAL MIXER
100–240V , 50/60Hz, 1A MAX
LISTED COMMERCIAL
AUDIO EQUIPMENT
R
9Z39
DIRECT OUTPUTS
U
+20-20
TRIM
BUS A
MIC
POWER
INPUT
-
28V DC,
22
3A MA X
–
+
+
–
LINE
+
G
U
+20-20
TRIM
BUS B
G
–
U
G
C
I
M
0
-
30dB +30dB
TRIM
1
MIC
LINELINELINE
A
60
U
G
A
C
I
M
0
-
30dB +30dB
TRIM
2
MIC
LINE
I
N
60
I
N
U
C
I
M
0
-
30dB +30dB
TRIM
3
MIC
LINE
A
I
N
60
15
12
9
6
3
0
3
6
9
12
15
SERIAL NUMBER
U
G
A
C
I
M
0
-
30dB +30dB
TRIM
6
MIC
LINE
HILO EQ A MASTE
MANUFACTURING DATE
C
I
N
I
M
60
0
-
30dB +30dB
TRIM
MIC
LINE
U
G
A
I
N
60
7
OL
2
4
7
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
50
G
A
60
U
G
A
C
I
M
0
-
30dB +30dB
TRIM
4
MIC
LINE
I
60
I
N
U
G
C
N
I
M
0
-
30dB +30dB
TRIM
5
MIC
LINE
U
G
C
I
M
0
-
30dB +30dB
TRIM
8
MIC
LINE
OL
2
4
7
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
50
A
I
N
60
4 – DX810
Page 5
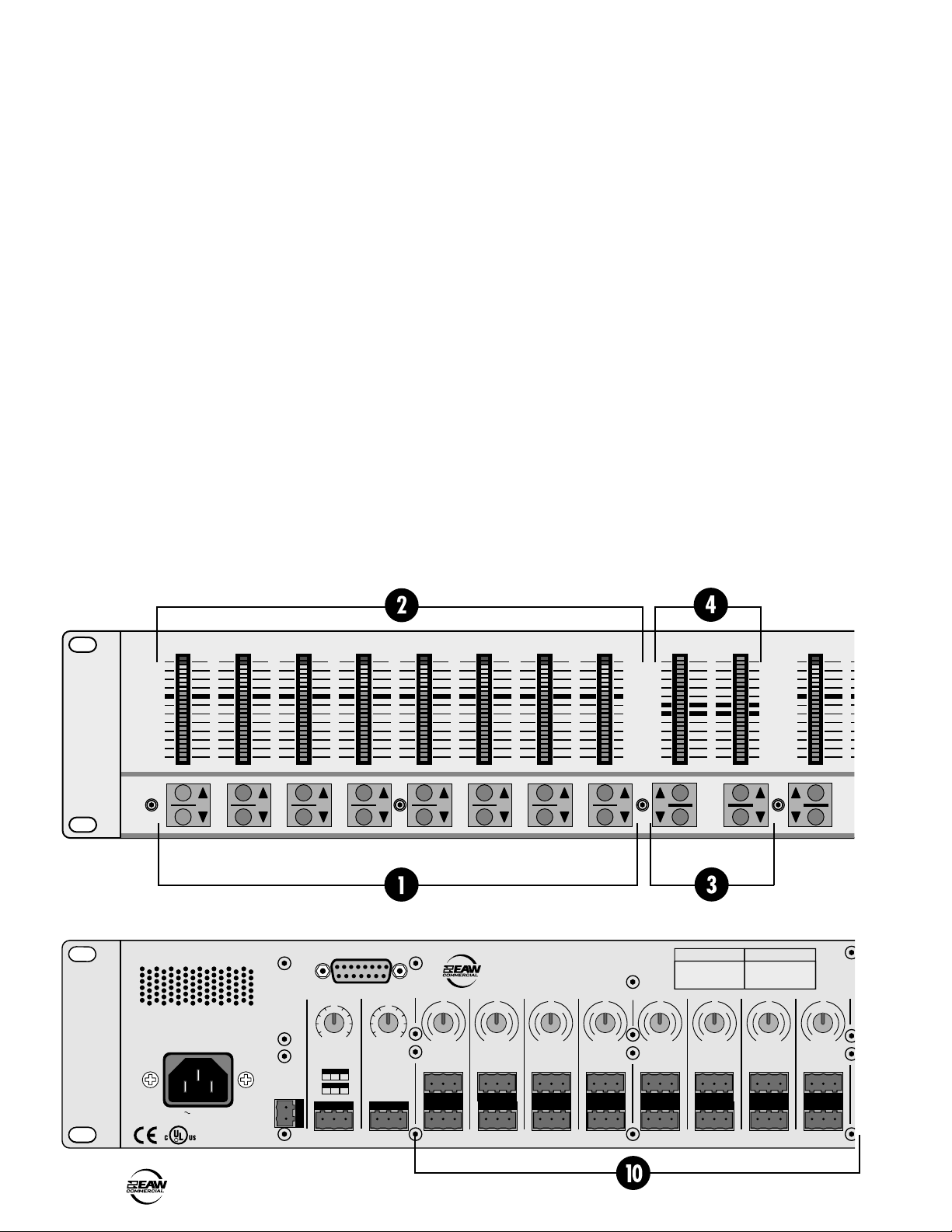
FRONT PANEL FEATURES
Note: The front panel controls only apply to the A
and B outputs. Outputs C through J are controlled
with the DX-810-PC software interface.
INPUT UP/DOWN BUTTONS
Use these buttons to adjust the mix level for each
input channel.
INPUT LED DISPLAY
This indicates the signal level after the mic preamp
stage, just after the A/D converter, but prior to any
digital signal processing. When any input UP/
DOWN button is pressed, all the meters (except
EQ) switch from level metering to level setting
indication. After five seconds, the meters switch
back to normal peak program metering (PPM).
When the 10 and 7 LEDs are both lit, the gain is set
to unity (0 dB).
EQ LO/HI UP/DOWN BUTTONS
These buttons are disabled in the DX810 (they are
for DX8 use only).
EQ LED DISPLAY
This display is disabled in the DX810 (it is for DX8
use only).
MASTER A/B UP/DOWN BUTTONS
These buttons adjust the output level for the A and
B output buses.
MASTER OUTPUT LED DISPLAY
This indicates the signal level after the digital signal
processing and MASTER A and B gain stage, just
prior to the D/A converter. When any MASTER UP/
DOWN button is pressed, all the meters switch
from level metering to level setting indication. After
five seconds, the meters switch back to normal
peak program metering (PPM).
MODE
This switch changes the front panel operation
between Bus A and Bus B operation. In addition,
the LOCK position disables the front panel controls
to prevent unauthorized changes to the settings. A
security code must be entered to enable the front
panel controls when the DX810 is locked. See page
13 for more information on locking and unlocking
the DX810.
URING DATE
dB
U
G
C
I
M
0
-
30dB +30dB
TRIM
8
MIC
LINE
A
I
N
60
OL
2
4
7
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
50
BA MASTER
PHANTOM POWER
48V DC
ON
12345678
DX810 DIGITAL MIXER
A B LOCK
MODE
J I H G
G
–
+
•
10
e
G
–
+
INPUTS
12 1 +5V
OUTPUTS
11G1
LOGIC I/O
A
RECORD
C D E F
B
OUTPUTS
A
COMM PORT
+
–
G
REMOTE BUS
+
–
G
POWER
COMM PORT
G
B
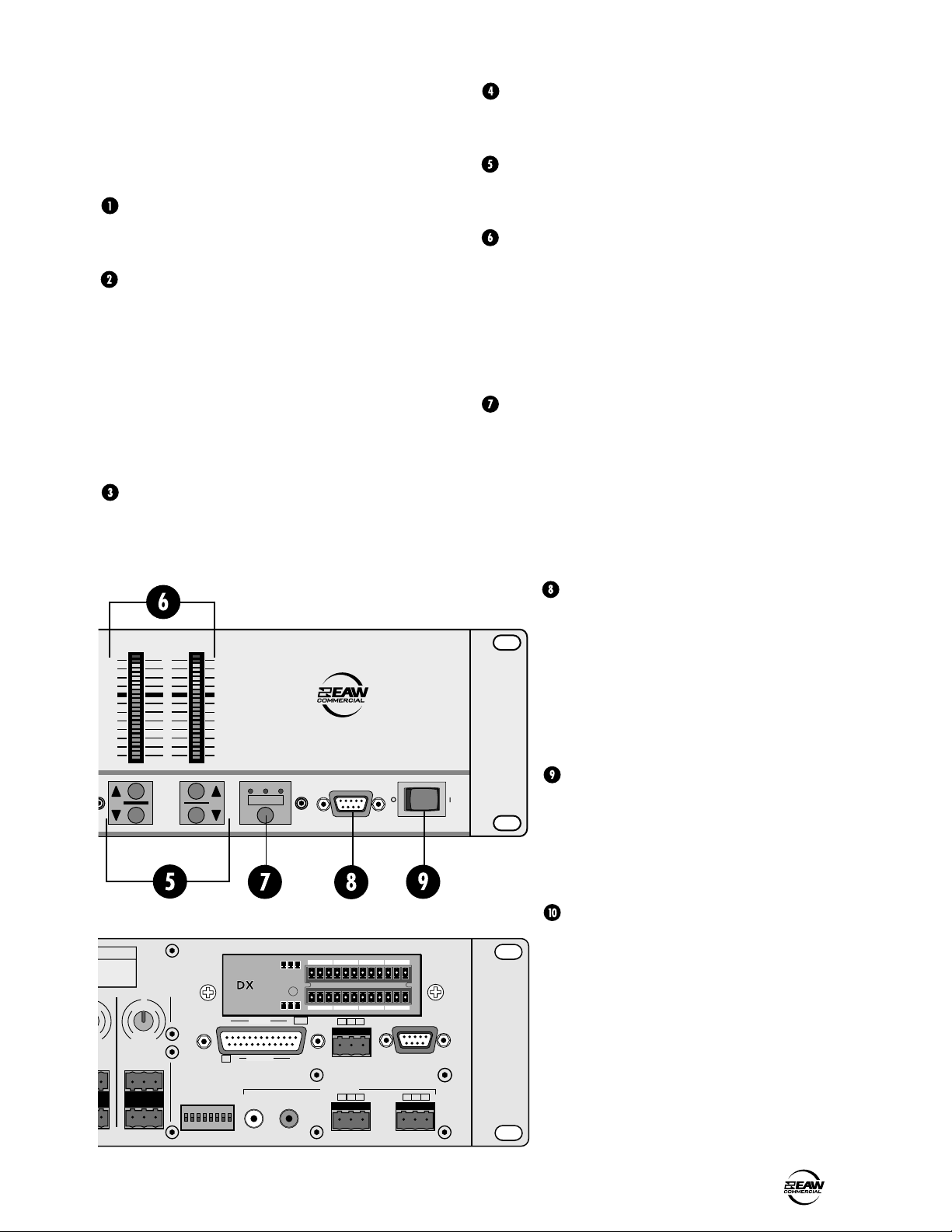
COMM PORT
This is an RS-232 port on a 9-pin D-Sub
connector. It connects to a personal
computer or other compatible control
system for external control of the DX810
settings. A second COMM port on the rear
panel duplicates this function, for
permanent connection to an installed
controller.
POWER
Use the POWER switch to turn the DX810
on and off.
REAR PANEL FEATURES
INPUTS 1-8
Each of the eight analog inputs has
separate balanced mic and line input
connectors that use XDR mic preamps.
These are 3-pin Phoenix-type connectors.
Use either the MIC or LINE input, but only
one can be used per channel.
+
–
DX810 – 5
Page 6
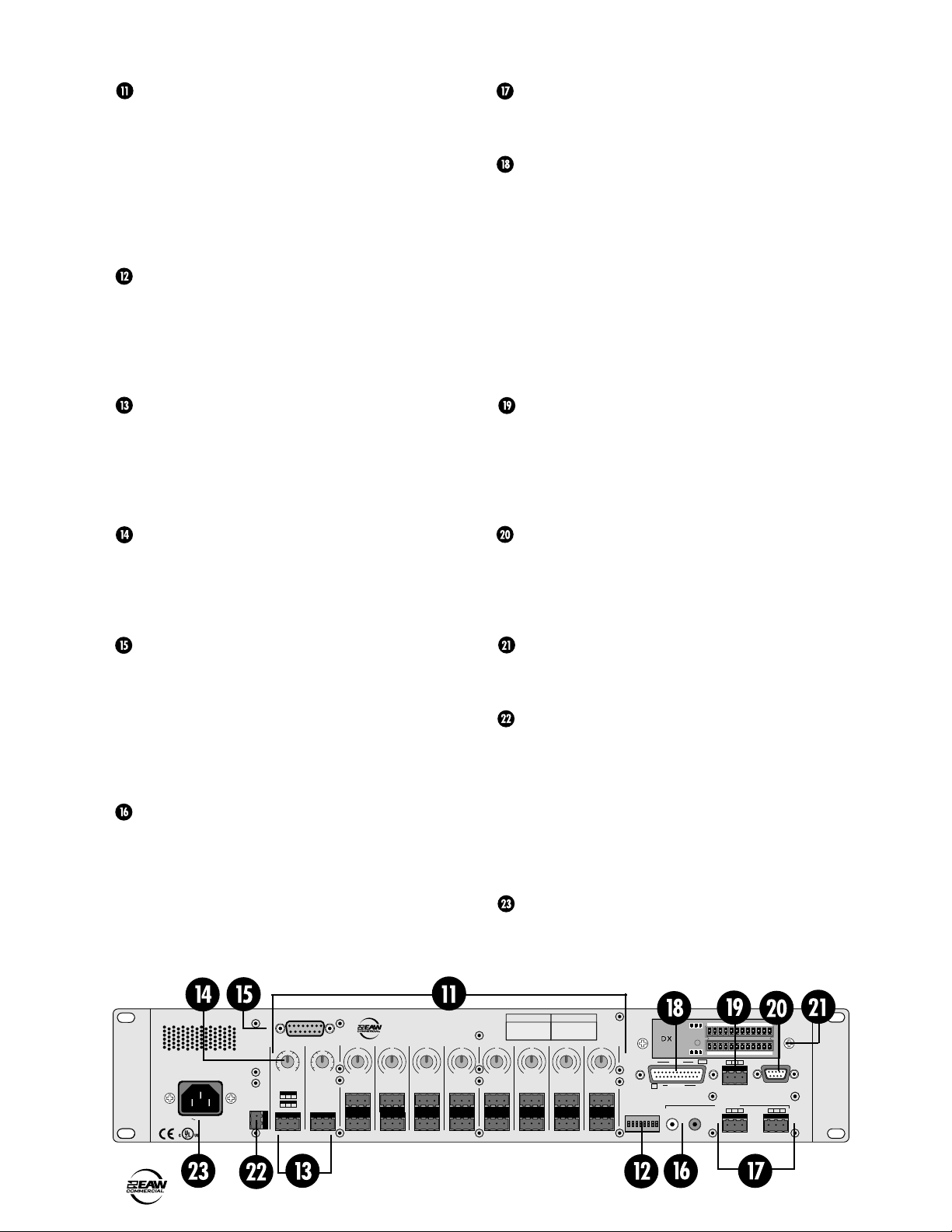
TRIM
This rotary analog control is used to trim the gain of
the input signal for optimum signal-to-noise ratio in
the preamp stage. For mic-level signals, it provides
from 0 to +60 dB of gain. For line-level signals, it
provides from –30 dB to +30 dB of gain. Unity (0 dB)
is at the center position. This control accepts a
maximum input signal of +18 dBu before clipping
(at unity gain).
PHANTOM POWER
These switches apply phantom power (+48 VDC) to
pins 2 and 3 of the selected mic input connectors.
Put the PHANTOM POWER switch in the UP
position for an individual channel when using a
condenser microphone.
OUTPUTS A/B
These 3-pin Phoenix-type connectors supply a
balanced line-level signal from OUTPUTS A and B.
LOGIC I/O
This 25-pin D-Sub connector provides 10 logic control
inputs and 10 logic control outputs (open-collector).
These inputs can be used to control a wide variety of
DX810 functions via external switching. The outputs
can be used to provide logic for external indicators for
a number of internal settings and conditions. They can
also control switching to external devices. The function
of each logic input and output can be programmed via
software to suit individual applications. In addition, logic
output 11 is dedicated to the "System OK" function.
See page 8 for the Logic I/O pinouts.
BUS A/B INPUTS
These analog inputs accept balanced line-level
signals and route the signal to the internal A and B
buses. These inputs may serve as additional zone
inputs for program devices. There is no DSP
processing on these inputs.
BUS A and B TRIM
These rotary analog controls are used to trim the
gain of the inputs to the A and B buses. This trim
control provides from –20 dB to +20 dB of gain,
with unity (0 dB) at the center-detent position.
DIRECT OUTPUTS
This 15-pin D-Sub connector supplies an analog,
unbalanced line-level signal from each of the eight
program inputs, post-preamp and pre-processing.
Use these outputs to connect to another mixing
console for additional zone coverage, a telephone
system for music-on-hold, or a multi-track recorder.
See page 7 for the Direct Output pinouts.
RECORD Out
These RCA connectors supply unbalanced line-level
signals from the A and B outputs. Use these
outputs to connect to the inputs of a recorder. They
can also act as additional line-level outputs to
connect to an external power amplifier. The signals
are the same as the main outputs.
REMOTE BUS
This 3-pin Phoenix-type connector can be used to
attach optional remote controls to the DX810.
Several remote controls can be connected to each
other in a daisy-chain fashion to extend the remote
control functionality of the DX810.
COMM PORT
This is identical to the COMM PORT on the front
panel. Use this to connect to an RS-232 serial port
on a personal computer or third-party controller (i.e.,
show controller) for external control of the DX810.
DX10e Expansion Panel
The DX10e provides eight additional independent
balanced output mixes, (C-J).
24 VDC POWER
The DX810 can be powered using a 24 VDC power
supply. This can serve as the primary power supply
for the DX810, or as a backup supply in case of an
AC power failure. The DX810 seamlessly switches
to the backup supply if there’s a power loss. When
both AC power and 24 VDC power are connected,
the AC power is used and no current is drawn from
the DC supply.
IEC AC Socket
Connect the supplied AC linecord to the IEC AC socket.
6 – DX810
100–240V , 50/60Hz, 1A MAX
LISTED COMMERCIAL
AUDIO EQUIPMENT
R
23456781
DIRECT OUTPUTS
U
U
+20-20
+20-20
TRIM
TRIM
BUS A
BUS B
MIC
+
G
POWER
–
INPUT
LINE
-
28V DC,
22
+
–
G
3A MAX
–
+
9Z39
DX810 DIGITAL MIXER
U
U
U
U
M
0
-
30dB+30dB
TRIM
U
G
A
C
I
N
I
60
1
MIC
LINELINELINE
G
G
A
A
C
C
I
I
N
N
I
I
M
M
60
60
0
0
-
-
30dB+30dB
30dB+30dB
TRIM2TRIM3TRIM4TRIM5TRIM6TRIM7TRIM
MIC
MIC
LINE
LINE
M
0
-
30dB+30dB
G
G
A
A
C
C
I
I
N
N
I
I
M
60
60
0
-
30dB+30dB
MIC
MIC
LINE
LINE
SERIAL NUMBER
U
G
C
I
M
0
-
30dB+30dB
MIC
LINE
A
I
N
60
MANUFACTURING DATE
U
G
A
C
I
N
I
M
60
0
-
30dB+30dB
MIC
LINE
C
I
M
0
-
30dB+30dB
MIC
LINE
J I H G
G
–
+
•
10
U
G
A
I
N
60
8
PHANTOM POWER
ON
12345678
e
12 1 +5V
INPUTS
11G1
OUTPUTS
LOGIC I/O
48V DC
A
RECORD
G
–
+
B
C D E F
+
–
G
REMOTE BUS
OUTPUTS
+
–
G
A
COMM PORT
G
B
+
–
Page 7
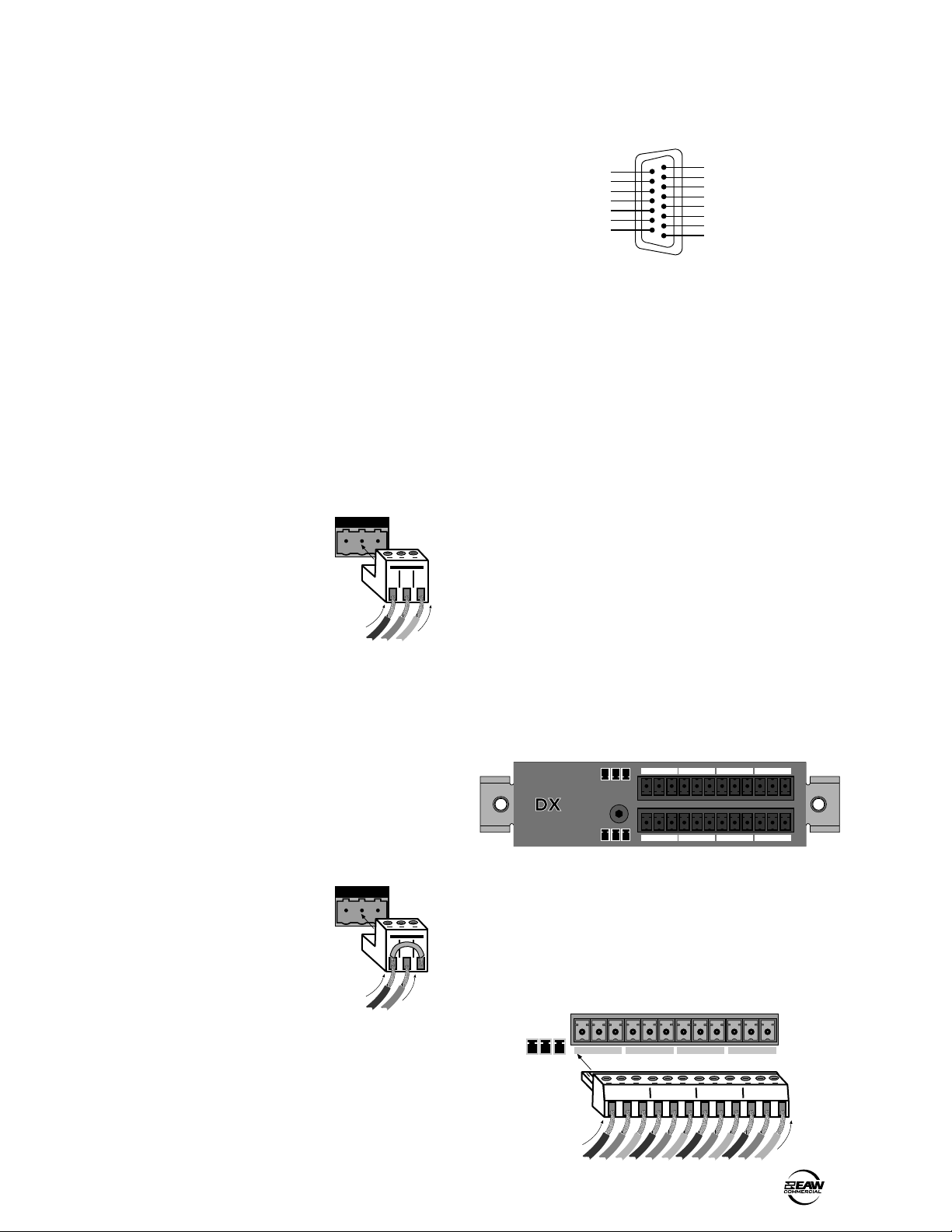
3. INSTALLATION
The DIRECT OUTPUT connector is wired as
follows:
CONNECTIONS
Connecting Balanced Sources
Use high-quality three-conductor cable for balanced
connections, such as Star Quad by Belden, Canare,
or Mogami, etc. The better the shield, the better
the audio signal is protected from induced EMI and
RFI.
Note: With screw-down connectors, it’s best to
use stranded wire that is not tinned. Solder can
“flow” under the pressure of the screw-down
terminal and cause the connection to become loose.
To connect a balanced mic or line-level signal:
Strip the wire back about 1/4" inch. Insert the
wire as far as it will go into the appropriate hole in
the supplied Phoenix-type connector. Tighten down
the screw with a small slot-head screwdriver. It is
recommended that you use 20 or 22 gauge wire
with the Phoenix-type connectors. The connectors
are wired as follows:
Pin 1 = Ground (Shield)
Pin 2 = Hot (+)
Pin 3 = Cold (–)
Balanced Connection (Line Input Shown)
Note: To connect to the MIC inputs, turn the
connector upside-down relative to the LINE input
connector. Double check the wiring with the wiring
graphics indicated on the rear panel.
Connecting Unbalanced Sources
It may be necessary to connect a 2-conductor
unbalanced input to a balanced input on the DX810.
123
Gnd + –
DIRECT OUTPUTS
8
SIGNAL RETURN
SIGNAL RETURN
SIGNAL RETURN
SIGNAL RETURN
SIGNAL RETURN
SIGNAL RETURN
SIGNAL RETURN
15
9
INPUT 1 HOT (+)
INPUT 2 HOT (+)
INPUT 3 HOT (+)
INPUT 4 HOT (+)
INPUT 5 HOT (+)
INPUT 6 HOT (+)
INPUT 7 HOT (+)
INPUT 8 HOT (+)
1
DIRECT OUTPUTS Pinout Connection
Connecting the RECORD Outputs
These are RCA-type unbalanced connectors. Use
high-quality shielded cable with RCA-type plugs for
these connections.
Connecting the Bus A and B Outputs
These are 3-pin Phoenix-type connectors that
provide a balanced line-level output signal from Bus
A and Bus B. Use high-quality, three-conductor
shielded cable for these connections.
Strip the wire back about 1/4" inch. Insert the
wire as far as it will go into the appropriate hole in
the supplied Phoenix-type connector. Then tighten
down the screw with a small slot-head screwdriver.
It is recommended that you use 20 or 22 gauge
wire with the Phoenix-type connectors. The
OUTPUT connectors are wired as follows:
Pin 1 = Ground (Shield)
Pin 2 = Hot (+)
Pin 3 = Cold (–)
Connecting the Bus C-J Outputs
Outputs C-J are on the DX•10e connector panel.
J I H G
G
–
+
•
10
e
To connect an unbalanced line-level signal:
Follow the instructions for connecting a balanced
line-level signal above, but wire the connector
as follows:
Pin 1 = Ground (Shield)
Pin 2 = Hot (+)
Pin 3 = Ground
Unbalanced Connection
123
Gnd +
Connecting the DIRECT OUTPUTS
This is a 15-pin D-Sub connector. The signals on the
DIRECT OUTPUT are unbalanced. Use shielded,
twisted pairs for the DIRECT OUTPUT cable to ensure
the best rejection of external noise (EMI and RFI).
G
–
+
C D E F
The DX•10e Expansion Kit includes two 12position Phoenix-type connectors for connecting to
the DX•10e connector panel. These are wired as
indicated on the connector panel. Notice that the
top connector is wired the same way as the bottom
connector; however, it is turned upside-down when
it is plugged into the unit.
G
–
+
C D E F
G+– G+– G+– G+–
+ – + – + – + –
Gnd
Gnd
Gnd
Gnd
DX810 – 7
Page 8
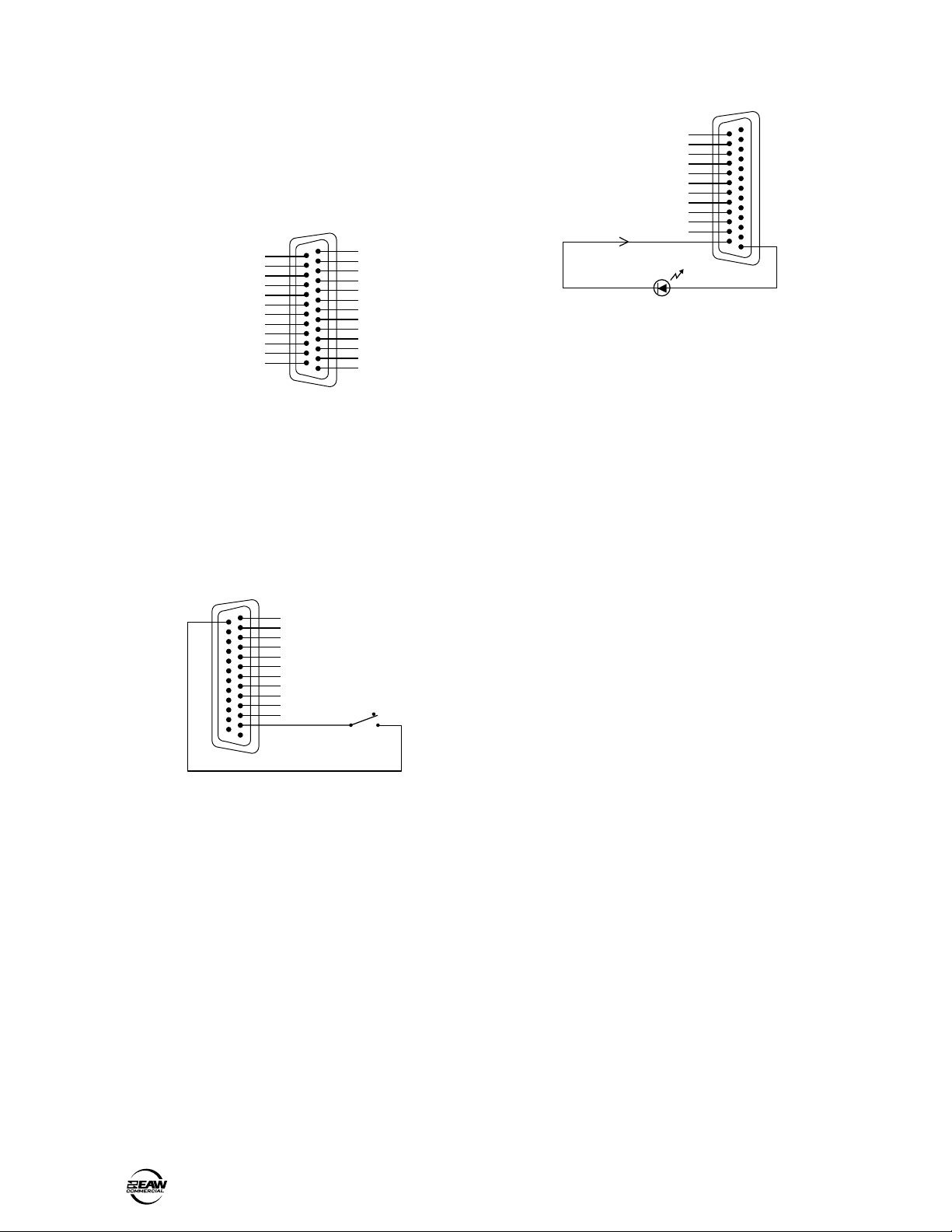
Connecting the LOGIC I/O
This is a 25-pin D-Sub connector. There are 10
programmable logic inputs and 10 programmable
logic outputs. In addition, there is an 11th fixed logic
output to indicate "System OK." They are all activelow circuits. Use 22 gauge wire for these connections.
LOGIC I/O
13
SYSTEM OK LOGIC OUT 11
GROUND
LOGIC OUT 10
LOGIC OUT 9
LOGIC OUT 8
LOGIC OUT 7
LOGIC OUT 6
LOGIC OUT 5
LOGIC OUT 4
LOGIC OUT 3
LOGIC OUT 2
LOGIC OUT 1
25
14
LOGIC I/O Pinout Connection
The logic inputs are active-low with internal pull-
up resistors connected to +5 VDC. Use a normally
open switch connected between the logic input and
ground (pin 25). When the switch is closed, the
logic input is active. Depending on the function
assigned to the logic input, a toggle switch or a
momentary switch may be used.
LOGIC INPUT
13
25
GROUND
14
N/C
N/C
LOGIC IN 10
LOGIC IN 9
LOGIC IN 8
LOGIC IN 7
LOGIC IN 6
LOGIC IN 5
LOGIC IN 4
LOGIC IN 3
LOGIC IN 2
LOGIC IN 1
1
LOGIC INPUT Connection
The logic outputs are active-low, open-collector
outputs with internal pull-up resistors. Connect the
indicator or activation circuit between the logic
output and +5 VDC (pin 1). When the output is
active, the output is 0 VDC. The logic outputs can
supply up to 10 mA of current each.
N/C
N/C
LOGIC IN 10
LOGIC IN 9
LOGIC IN 8
LOGIC IN 7
LOGIC IN 6
LOGIC IN 5
LOGIC IN 4
LOGIC IN 3
LOGIC IN 2
LOGIC IN 1
+5VDC
1
LOGIC OUT
13
25
+5VDC
14
1
10mA Maximum
SYSTEM OK LOGIC OUT 11
GROUND
LOGIC OUT 10
LOGIC OUT 9
LOGIC OUT 8
LOGIC OUT 7
LOGIC OUT 6
LOGIC OUT 5
LOGIC OUT 4
LOGIC OUT 3
LOGIC OUT 2
LOGIC OUT 1
LOGIC OUTPUT Connection
Note: Pins 12 and 13 are not used at this time.
They are reserved for future updates.
Do not
connect anything to these pins.
Connecting the REMOTE BUS
This is a 3-pin Phoenix-type connector specifically
for connecting the optional remote control
peripherals. Use a high-quality three-conductor
shielded cable to make this connection, such as
Belden 8451, 9451, or equivalent. The lower the
nominal capacitance of the wire, the more distance
you can have between the remote control and the
DX810. This is in order to avoid transmission losses.
Strip the wire back about 1/4" inch. Insert the
wire as far as it will go into the appropriate hole in
the supplied Phoenix-type connector. Then tighten
down the screw with a small slot-head screwdriver.
It is recommended that you use 18, 20, 22, or 24
gauge wire for the remote control connections. The
guage used depends on the distance between the
DX810 and the remotes.
The REMOTE BUS connector is wired as
follows:
Pin 1 = Ground (Shield)
Pin 2 = Data + (with +24 VDC power)
Pin 3 = Data – (with +24 VDC power)
Note: See the instructions with the remote
control for more information.
AC POWER CONSIDERATIONS
8 – DX810
The DX810 can accept an AC voltage ranging from
90 V to 240 V without having to reconfigure the
primary wiring. This is due to the sophisticated
design of the switching power supply. Each DX810
draws an average of 1 amp of AC line current at
120 VAC.
Warning: Always use a 3-conductor AC power
cord with a safety ground connection. Never
remove the ground pin or attempt to bypass it. This
is very dangerous.
Page 9

4. OPERATION
QUICK START
Reading the instruction manual is the only way to
fully understand the features and functions of the
DX810. However, this Quick Start section provides
a quick overview to get the DX810 set up and
working fast.
Make sure the power switch is off while setting
up and making connections to the DX810.
Make the Connections
Determine which inputs to use for
program sources and which to use for
microphones. Follow the wiring
diagram on the rear panel to make
the connections.
Make use of the PHANTOM
POWER switches if any of the
microphones require phantom power. Phantom
power is present when the switch is in the UP
position.
Make use of the supplied Phoenix connectors
with appropriate wiring to connect the DX810
outputs to the amplifier inputs. Connect the power
amplifier outputs to speakers appropriate for the
amplifier’s specified output power.
Connect a personal computer loaded with the
DX-810-PC control software to the COMM PORT
on the DX-810. This is for maximum control and
ease of use. The RS-232 serial port from the
computer can be connected to either COMM PORT
on the DX-810 (front or rear panels).
Start Up
Before turning on the DX810, set the TRIM controls
all the way down.
Turn on the DX810 power switch. Open the DX810-PC control software on the computer and click
On Line. This begins the communication between
the DX810 and the computer.
Configure the DX810 for the current application.
Download the appropriate plug-ins, if installed. Set
all the EQ controls flat. Adjust the input faders and
the output faders all the way down.
Tip: To speed things up, select Output A and set
all the Input faders down. Select Copy Mix Levels
from the Edit menu. Select Output B and select
Paste Mix Levels from the Edit menu. Repeat for
outputs C-J.
MIC
+
G
–
LINE
+
–
G
Set the Levels
MIC and LINE Input Trim
The analog trim controls on the rear panel are not
adjustable via the control software. This is because
these are in the analog domain, prior to the A/D
converters. To adjust the MIC and LINE TRIM
controls:
1. Start the program source playback for Input 1 or, if
a microphone is connected, have someone speak
into the microphone at a normal volume.
2. Adjust the Input 1 TRIM control so the meter
indication is at or around –10 dB. The peaks should
regularly hit, and occasionally exceed the –10 dB
level. This provides plenty of headroom for
transient peaks.
Input Mix Levels
After setting the MIC and LINE TRIM controls as
instructed above, adjust the input mix levels to unity
gain (Ctrl + click on the fader to set it to unity gain).
Adjust the input faders on the eight input channels
individually to achieve a balanced mix.
Output Levels
Before adjusting the output faders, turn on the
power amplifier.
If the power amplifier has level controls:
1. Turn the amplifier level controls all the way down.
2. Adjust the output faders to unity “U” on-screen.
Have the program sources playing. The peaks on
the master output meter should regularly hit, and
occasionally exceed the –10 dB level. This provides
a nominal +4 dBu level at the OUTPUTS.
3. Slowly increase the amplifier level controls to
attain the volume level desired. If the volume gets
too loud too fast, adjust the output level controls to
–15 dB or –20 dB. If the volume level isn’t loud
enough, adjust the output faders to –5 or –10. Be
careful that the peak level doesn’t hit the OL
(overload) indicator on the meter, as this may run
the risk of driving the output into clipping.
If the power amplifier doesn’t have level controls:
1. Slowly adjust the output faders until the –10 and –7
dB LED indicators light (or to unity “U” on-screen).
They may also be adjusted until the desired
volume level is attained. If the volume level isn’t
loud enough, adjust the output faders to –5 or –10.
Be careful that the peak level doesn’t hit the OL
(overload) indicator on the meter, as this may run
the risk of driving the output into clipping.
DX810 – 9
Page 10

USING INPUTS 1-8
Bus A and B Input Trim
There is no metering after the BUS A and B input
TRIM controls. These controls must be adjusted by
ear. Start the program source playback for all
sources connected to the BUS A or BUS B input.
Slowly increase the TRIM control to the center
position (12 o’clock), which is unity gain. Then
adjust the TRIM control up or down to attain a
balance within the total mix at the A and B outputs.
Accessing the Digital Signal Processors
The DX810 has five powerful floating-point 32-bit
digital signal processors (DSPs) to implement the
digital audio processing functions. Access the
processing windows by clicking on their buttons in
the Button Section, or double-clicking on the DSP
name in the Input Proc or Output Proc windows.
• Input 3-Band Shelving EQ With Parametric
Mid-Range Control
• Output 8-Band Parametric EQ
or
• Output 31-Band 1/3 Octave Graphic EQ
• Input/Output Compressors
• Input Gate
• Output Delay
• Crossover
Connect the microphones or program sources to
Inputs 1-8. Examples of program sources include a
CD player, tape deck, tuner, satellite feed, TV audio,
jukebox, or other audio source. Each input has a
separate Phoenix-type connector for a mic or linelevel input.
TRIM
Use the TRIM control to adjust the gain of the input
preamp stage according to the level of the input signal.
Refer to the “Quick-Start” section (Set the Levels) for
instructions on how to set the TRIM controls.
LEVEL
The up/down arrow buttons on each channel are
used to adjust the mix level for each channel going
to the A and B outputs (use the on-screen faders for
outputs C-J). Use these to fine tune the mix or
relative loudness of each input signal that is
connected to the DX810.
When adjusting these buttons, the channel
meter indicates the gain of the channel relative to
the maximum gain of +10 dB. After 5 seconds, the
meter reverts back to indicating the actual input
signal level of the channel. This metering is pre-EQ
and pre-LEVEL control.
Unity gain is indicated when the –10 and –7 dB
LEDs are both lit on the meter (or “U” on-screen).
Software Updates
Check the EAW Commercial website at
www.eawcommercial.com for new information and
updates to the DX810 software and firmware.
EQ
Each Input 1-8 has a 3-band shelving EQ with a
parametric mid. This is adjustable from the PC only.
It provides 15 dB of boost or cut with user selectable
corner and center frequencies (LO: 20 Hz-500 Hz;
MID: 20 Hz-20 kHz HI: 500 Hz-20 kHz).
USING THE BUS A AND B INPUTS
These inputs provide a direct analog connection to
the BUS A and B buses. These input points are post-
DSP and post-D/A converter, and accept a balanced
analog line-level signal. Use these to connect an
additional program source to a zone, or to connect
the Zone A and B outputs from another DX810.
TRIM
Use the TRIM control to adjust the signal level at
the BUS A and B inputs. Typically, this control
would be set to the center detent position (unity
gain). However, it can be adjusted up or down by 20
dB to achieve a balance between the signal at the
BUS A and B inputs, and the signal on the internal
A and B buses.
10 – DX810
Page 11
USING THE DIRECT OUTPUTS
The DIRECT OUTPUTS provide an unbalanced line-
level signal from each of the 8 Input channels. This
signal comes from the output of the preamplifier
stage on each input channel, prior to the A/D
converter and subsequent digital signal processing.
Use the DIRECT OUTPUTS to connect a
continuous music source (e.g., satellite feed,
prerecorded background music, or multi-disc CD
player). This may connect to a telephone system
music-on-hold input. It may provide a feed to a
multi-track recorder (for recording), or a mixing
console (for additional zone coverage).
USING OUTPUTS A THROUGH J
Refer to Appendix C for a list of the predefined
functions available for the Selection Remote Control.
Refer to "Remotes" on page 21 for instructions on
custom programming the DX-SW4.
DX-RVC Level Remote (2-Button/12-LED)
These outputs provide a balanced line-level signal.
Connect these outputs to the inputs of a power amp.
USING THE RECORD OUTPUT
The A and B output signals are provided at the
RECORD output jacks, which are industry standard
unbalanced RCA connectors. Connect these to the
Tape Input jacks on a tape deck or other recording
device to record the mix at the A and B outputs.
USING THE REMOTE CONTROLS
Connect one or up to nine remote controls to the
REMOTE BUS connection. Each remote control has
an 8-position DIP switch that must be set to a
unique ID. When the DX810 is first turned on, it
polls the REMOTE BUS and identifies the remote
controls connected to it by each unique ID.
There are two remote control versions available:
DX-SW4 Selection Remote (4-Button/4-LED)
This remote device can control a level, preselected
via the 8-position DIP switch, and display the
selected level on the LED meter. The predefined
functions include INPUT 1A-8J level, OUTPUT A
through J, and Group 1-32 level. Note that the
remote control indicates the gain setting of the
channel, and not the signal level in real time.
Refer to Appendix D for a list of the predefined
functions available for the Level Remote Control.
Connecting One or More Remote Controls
The remote control devices are connected to the
DX810 using a 3-wire half-duplex interface with +24
VDC phantom power. The REMOTE BUS connection
can provide power for up to nine remotes. Provision
is made to connect local power to the remote
controls if required in certain applications.
The maximum distance between the DX810 and
the remotes depends on the type of cable selected
and type of remote controls used. Generally, with
22 gauge wire (at 0.014 Ω/ft. and 34 pF/ft), one
remote can be up to 3000 feet away. Five remotes can
be up to 2500 feet away, and eight remotes can be up
to 500 feet away. This is to prevent transmission
losses from becoming a factor. (See the instructions
with the remote control for more information).
This remote device is designed to select functions
such as preset selection, mute, and force-on/off.
Each of the four buttons controls a single function
and its associated LED displays the current state of
the function.
USING THE LOGIC I/O
The DX810 has 10 programmable general-purpose
logic inputs, 10 programmable general-purpose
logic outputs, and one preconfigured logic output
(System OK). The inputs are active low with internal
pull-up resistors. The outputs are active low opencollectors with internal pull-up resistors. With the
inputs or outputs unconnected or inactive, the logic
voltage level is high (+5 V). The active state is
defined as voltage low (0 V or ground).
DX810 – 11
Page 12

The logic functions assigned to each individual
logic input and output are configured using the DX810-PC application. In addition, each logic input and
output can be assigned a descriptive name (up to
32 characters) for easier identification within the PC
application.
Note: Logic I/O functions are set from the PC
application only.
Logic Inputs
The following functions can be activated by the
logic inputs:
Force On
Force Off
Input Mute/Enable
Output Mute/Enable
Group Mute/Enable
Preset Recall
Combine On
Force-on/Force-off
This provides a means to temporarily increase or
decrease the gain of an input channel or group with
an external switch, remote control, or through the
priority function. This is defined in the Force
Control window in the DX-810-PC software
application. It forces the input fader level to the
Force On Level or Force Off Level selected for that
channel (relative to the current setting). It forces the
group fader level (when selected under Affected I/O
in the Logic Input window) to its current fader level
(Force On) or completely off (Force Off). See “Force
Ctrl” on page 19 for more information about the
Force-on and Force-off function.
This function can be activated in one of four
ways, and is active when the logic input pin is
active (held low):
• Momentary: The force function is continuously
active while the logic input is continuously active.
• Latch On: The force function is activated when the
logic input goes from inactive to active.
• Latch Off: The force function is deactivated when
the logic input goes from inactive to active.
• Toggling: The force function toggles its state when
the logic input goes from inactive and active.
Mute/Enable
An input, output, or group can be muted or enabled
with a Logic Input (see page 28 for information on
changing between mute or enable operation). This
function can be activated in one of four ways:
• Momentary: The mute/enable function is
continuously active while the logic input is
continuously active.
• Latch On: The mute/enable function is activated
when the logic input goes from inactive to active.
• Latch Off: The mute/enable function is deactivated
when the logic input goes from inactive to active.
• Toggling: The mute/enable function toggles its
state when the logic input goes from inactive and
active.
Preset Recall
This function can be activated as a momentary
function or as a latching function. When activated
as a momentary function, the preset state is
recalled only when the logic input is active. When
the logic input is inactive, the DX810 returns to its
base state as long as no other momentary function
is in force. Normally, the base state is the state the
DX810 was in prior to activating the preset state.
When activated as a latching function, the preset
state is recalled when the logic input goes from
inactive to active. See “Presets” on page 18 for
more information about the preset recall function.
Combine
This function can be activated as a momentary
function, a latching function, or a toggling function.
When activated as a momentary function, the
selected combination is activated only when the
logic input is active. When the logic input is inactive,
the combination is deactivated.
When activated as a latching function, the
combination is activated when the logic input goes
from inactive to active (Latch On), or the
combination turns off when the logic input goes
from inactive to active (Latch Off).
When activated as a toggling function, the
combine state changes from its current state when
the logic input goes from inactive to active.
See “Combine” on page 21 for more information
about the room combining function.
Logic Outputs
The logic outputs indicate the state of the following
conditions, selectable in software:
Input Mute/Enable
Output Mute/Enable
Group Mute/Enable
Output Signal Present
Preset Active
Force On Active
Priority Active
Combine Active
Gate Status
Mute/Enable
A logic output can indicate when the mute or
enable for a particular input, output, or group is
active. See page 28 for information on changing
between mute or enable operation.
Output Signal Present
A logic output can indicate when a signal greater
than –40 dBFS is present on an output.
12 – DX810
Page 13

Preset Active
A logic output can indicate when a particular preset
is active.
Force On
A logic output can indicate when a particular input
or group is being forced on.
Priority active
A logic output can indicate when a particular input
or group force-on priority is active.
Combine active
A logic output can indicate when a particular
combination (combine) is active.
Gate Status
A logic output can indicate when a particular Input
Gate is open.
Note: An input gate that is disabled (off) is
always open.
Administrator Level
Administrator Level provides access to all of the
DX-810-PC software application functions. When
you click the On Line button in the application to
begin communication between the application and
the DX810, the Enter Pass Code window opens.
Entering the four-digit User Pass Code limits you to
fader control only. Entering the four-digit
Administrator Pass Code (previously defined in the
Set Lock Code window under the Advanced menu)
allows you full access to the software controls.
Note: The default administrator code is “1234.”
5. DX-810-PC SOFTWARE (v 3.3)
INSTALLING THE SOFTWARE
PASSWORD PROTECTION
There are two levels of password protection, User
and Administrator.
User Level
User level provides access to the front panel
controls and the fader controls in the DX-810-PC
application.The MODE button on the front panel is
used to disable the front panel controls by selecting
LOCK. The LOCK LED blinks for about five seconds
before it engages. When the LED lights steadily, the
front panel controls are disabled.
To unlock the DX810 from the front panel, press
the bottom “Down” buttons on the front panel in
the correct numerical sequence. Use the following
chart:
Input 1 Down = 1
Input 2 Down = 2
Input 3 Down = 3
Input 4 Down = 4
Input 5 Down = 5
Input 6 Down = 6
Input 7 Down = 7
Input 8 Down = 8
Low EQ Down = 9
Hi EQ Down = 0
A PC-based Windows-style graphical interface
software application is provided on a CD-ROM. This
is to control and configure the DX810 at the point of
installation.
Check our website at www.eawcommercial.com
for software upgrades as they become available.
To install the software on a PC:
It is necessary to install the DX-810-PC software
on your PC.
1. Make sure no other applications are running.
2. Insert the DX810 CD into your PC’s CD drive, or
download the software from
www.eawcommercial.com.
3. The CD should begin the installation automatically.
If not, click Start, then click Run.
4. Type <drive>:\DX-810-PC\Setup in the command
line (where <drive> is the letter assigned to the CD
drive, i.e., D drive, or the location on your hard
drive where the file was downloaded).
5. Setup will install the DX-810-PC application onto
your PC. You can accept the default directory, or
specify a different location to install the
application.
UPGRADING THE SOFTWARE
Note: The default User Lock Code is “1234.”
The buttons must be pressed in rather rapid
sequence in order to unlock the front panel (no
more than about 1 second between key presses).
From time to time, EAW Commercial will release
upgrades for the internal operating software in the
DX810. This can be downloaded from our website
(www.eawcommercial.com) to a PC-compatible
computer. Use the serial port on the computer to
connect to the COMM PORT on the DX810. Then
transfer the data to the on-board flash memory with
the DX-810-PC software.
DX810 – 13
Page 14

CONNECTING A PC
Use a standard DB9 (male/female) computer cable
to connect a PC to the DX810. The DX-810-PC
application uses COM1 on the PC by default. You
can select a different COM port by clicking on
Advanced in the top menu bar and selecting
Configure COM Ports. Refer to “Configure COM
Ports” on page 16 for more information. Connect
the COM port on the PC to one of the COMM
PORTs on the DX810 (front or rear).
Important!
Note: Due to software reallocation necessary to
provide new features in Version 3.x, files from
previous DX810 (DX-10e) versions are not
compatible with version 3.x. You will need to
create new version 3.x sessions and manually
reload all settings from previous versions.
OVERVIEW
UPGRADING THE FIRMWARE
Before attempting to go "Online" with the DX810,
you must upgrade the firmware in the DX810's
flash memory.
1. Connect the PC to the DX810 as described above.
2. Open the DX810 v3.3 software. DO NOT click the
On Line button yet.
3. Click Advanced in the top menu bar and select
Firmware Upgrade.
4. Click Select File in the Firmware Upgrade window
and the Select OS Upgrade File dialog box opens.
Browse to the location of the OS upgrade file (with
a .pkt extension) on your hard drive, CD, or floppy
drive and click Open, then click Upgrade. You can
monitor the progress in the Firmware Upgrade window.
5. Upgrade Successful appears in the Status window
when it is complete.
6. Close the Firmware Upgrade window and click the
On Line button to connect to the DX810.
The DX-810-PC software application provides real
time control and configuration editing for the DX810
using a laptop or other PC-compatible computer.
The graphical user interface is divided into six
sections:
1. Top Section
2. Button Section
3. Crosspoint Matrix Section
4. Input Section
5. Output Section
6. Group Section
Caution: To adjust a fader, click on the fader knob
to select it. Ctrl+click to set the fader to unity. If you
click above or below the knob, it will jump to the
point where you clicked. This is useful to move the
fader quickly to where you want it to be. However,
be careful not to inadvertently click above a fader
knob. A sudden jump in volume will occur.
Top
14 – DX810
Crosspoint
Matrix
Section
Input
Section
Button
Section
Output
Section
Group
Section
Page 15

TOP SECTION
The Top Section includes the Menu bar, the Active
Logic Input and Output indicators, and Preset, On
Line, and Panel Lock controls.
Menu Bar
The following menus are available in the Menu
bar at the top of the screen:
File
Open (Ctrl+O)
Opens a previously saved session. The Select
Workspace File dialog box opens and allows you to
select a session to open. Select a file and click
Open, or double-click on the file to open it.
When offline, this loads the new settings into
the application only, allowing you to edit and save
them without being connected to the DX810.
When online, this loads the new settings into
the application and the connected DX810,
overwriting the existing settings in the DX810.
Caution:
amplifiers and powered speakers from the
DX810 are OFF before loading new settings from
a file into the DX810.
Save As
Saves the current session. Use this to save the
session when you have made a change to it or to
create a new session file. The Save the Session
As... dialog box opens and allows you to save the
settings under the current session name, or enter a
new file name. Enter the new name and click Save.
Note: The extension (.dx8) is automatically
appended to the filename. Use up to 20
alphanumeric characters.
Quit (Ctrl+Q)
Closes the DX-810-PC application. The DX810 will
continue to operate with the current settings.
Make sure all downstream power
Edit
Copy Crosspoint (Ctrl+C)
Copies the gain setting of the selected crosspoint
to the clipboard. Click the (S) in the crosspoint box
to select it, then select Copy Crosspoint.
Copy Mix Levels (Ctrl+M)
Copies the gain settings of all the inputs for the
selected output to the clipboard. Click the
associated letter button (A-J) in the Output Section
to select an output.
Paste Crosspoint (Ctrl+P)
Pastes the gain setting from the clipboard to the
selected crosspoint. Click the (S) in the crosspoint
box to select it, then select Paste Crosspoint.
Paste Mix Levels (Ctrl+L)
Pastes the input gain settings from the clipboard to
the selected output. Click the associated letter
button (A-J) in the Output Section to select an
output, then select Paste Mix Levels.
Advanced
DX810 Unit Info
This opens a dialog box that contains the following
information about the DX810 that is currently
connected:
DX810 – 15
Page 16

Firmware Upgrade
This allows you to select an OS upgrade file to
upload to the DX810 as they become available.
Click Select File in the Firmware Upgrade window
and the Select OS Upgrade File dialog box opens.
Browse to the location of the OS upgrade file (with
a .pkt extension) on your hard drive or floppy drive
and click Open, then click Upgrade. You can monitor
the progress in the Firmware Upgrade window.
Set Lock Code
Select this to view and change the four-digit
Administrator Pass Code or User Pass Code for the
DX810. The code must consist of four digits. Use
the Panel Lock button in the Top Section to lock and
unlock the front panel controls (User level), or use
the MODE button on the front panel to lock the
controls. Refer to page 13 for more information on
using the Lock mode and password protection.
Note: The DX–810–PC application defaults to
COM1 whenever it is restarted. This is regardless
of whether another COM port was selected in a
previous session. To permanently change the
default COM port setting, you must open the file
named DX8.ini (located in the System folder where
the DX–810–PC application is located) with
NotePad. Change the line “dspport:0” to
“dspport:1” to change to COM2, “dspport:2” to
change to COM3, and so on.
The DX–810–PC application uses 115.2k baud
transmission speed for both COMM PORTS. Some
third-party control systems require a lower baud
rate. If using one of these systems, the DX810 rear
COMM PORT baud rate can be changed in the
COM Port Setup window. The front panel COMM
PORT always operates at 115.2k baud.
Note that when the rear COMM PORT baud rate
is changed from 115.2k baud, the PC application
can no longer communicate with the DX810 via this
port. You must use the front COMM PORT with the
PC application in this case.
Set Temperature
Select this to open the Delay/Distance Parameters
window. The temperature value entered here is
used to calculate the delay time in the Delay Line
output processor (the Delay button). The speed of
sound varies with air temperature, so it is necessary
to enter the ambient air temperature here to
calculate the time delay required as a function of
distance traveled.
Click and drag up or down in the Set
Temperature box to change the temperature
setting from –40.0° F to 122° F (–40° C to 50° C).
Change from Fahrenheit (US Units) to Celsius
(Metric) in the Set Units box. This also changes the
distances in the Delay Line window to Metric.
16 – DX810
Configure COM Ports
The DX–810–PC application uses COM1 on the PC
by default. If necessary, you can change the COM
port used by the application. Click the PC Com Port
pull-down box in the COM Port Setup window and
select the desired COM port.
Set Ramp Time
Select this to open the Preset Ramp Time window.
This controls the transition time for the input,
output, and group faders when changing from one
preset to another. The range is Off to 30 seconds.
Page 17

Note: When changing presets, the faders
change position quickly on-screen, but the audio
actually ramps according to the Ramp Time setting.
Set Powerup Preset
Select this to open the Powerup Preset Selection
window. When None (last state) is selected, the
DX810 returns to its state when it was last turned
off. Click in the Select Powerup Preset box and
drag up or down to select one of the 24 presets to
load on powerup.
Windows
About
This provides information about the DX–810–PC
software application, including the version and
personnel credits.
Set Global Faders
Select this to open the Global Output Faders
window. Click in the Output Faders are stored: box
to choose whether the output fader settings are
saved with each preset, or the output fader settings
are global and remain at their current settings
regardless of the preset selected.
Close Window (Esc)
This closes the window that is currently selected
(front-most) on-screen.
Close All (Ctrl+/)
This closes sub-windows that are currently open on
the screen, leaving just the main window open.
Combine
This toggles the Combine view with the Crosspoint
Matrix view. It duplicates the function of the
Combine button in the Button Section.
Input EQ
This toggles the Input EQ window open and closed.
It duplicates the function of the Input EQ button in
the Button Section.
DX810 – 17
Page 18

Output EQ
This toggles the Output EQ window open and
closed. It duplicates the function of the Output EQ
button in the Button Section.
Compressor
This toggles the Compressor window open and
closed. It duplicates the function of the Compress
button in the Button Section.
Gate
This toggles the Gate window open and closed. It
duplicates the function of the Gate button in the
Button Section.
Delay
This toggles the Delay window open and closed. It
duplicates the function of the Delay button in the
Button Section.
XOver
This toggles the Crossover window open and
closed. It duplicates the function of the X-Over
button in the Button Section.
Options
The Options window is reserved for future
upgrades.
Force Control
This toggles the Force Control window open and
closed. It duplicates the function of the Force Ctrl
button in the Button Section.
Logic Input
This toggles the Logic Input window open and
closed. It duplicates the function of the Logic In
button in the Button Section.
Logic Output
This toggles the Logic Output window open and
closed. It duplicates the function of the Logic Out
button in the Button Section.
Remote Mapping
This toggles the Remote Mapping window open
and closed. It duplicates the function of the
Remotes button in the Button Section.
Indicators/Presets/Control
Active Logic Inputs
These light to indicate when a logic input is active
(e.g., contact closure).
Active Logic Outputs
These light to indicate when a logic output is active.
Presets
The DX–810–PC stores up to 24 presets, which can
be selected via the Presets pull-down box. Select a
preset in the pull-down box and the settings are
instantly recalled from memory.
Save To Preset
Click this button to save the current mixer,
processor, and group assignment settings to a
preset.
The Save To Preset window opens. Enter a
name for the preset, then click the Save To Preset
button next to it to save it.
Clear Edits
If changes are made to a stored preset, and you
want to return to the original settings, click this
button. This restores the settings for the currently
selected preset.
On Line
Click this button to initiate communication with the
DX810. This button lights to indicate when there is
active communication between the DX810 and the
DX–810–PC application. Click this button again to
terminate communication.
Panel Lock
Indicates front panel lock status. Click this button to
lock and unlock front panel control. Note that the
lock code is not required to use this control. It
doesn’t affect the PC application’s controls.
18 – DX810
Page 19

Button Section
The Button Section includes the assignment
buttons (Force Ctrl, Logic In, Logic Out, Groups,
Input Proc, Out Proc, Mute Ind) and the DSP
buttons (Combine, Input EQ, Output EQ, Compress,
Gate, Delay, X-Over).
Assignments
Force Ctrl
Click this button to open the Force Control window.
Input Name:
with the keyboard. It will accept up to 32 characters.
Force On Level:
input, from OFF to +10 dB. Click and drag in the
Force On Level box to change the force-on level
setting. The force-on action is always relative to the
current mix level.
Activate:
activate the Force On or Force Off function. When
Logic In is selected, an input can be forced on or
forced off by configuring the Logic Input window, or
by a remote control configured to force on or off an
input. When Gate is selected, an input can be
forced on or forced off when its Gate is open.
Force On Priority:
(highest) to 8 (lowest) for each channel’s force-on
function. The default setting is None. A higher priority
input can force on or off a lower priority input to its
assigned relative force-on or force-off level (see next).
Force Off Level:
can be adjusted from OFF to +10 dB. Click and drag
in the Force Off Level box to change the force-off
level setting. The force-off action is always relative
to the current mix level (e.g., a 0 dB force-off level
means the level will not change).
Enter a name for each channel
Assign a force-on level to each
Choose between Logic In or Gate to
Assign a priority level from 1
A force-off level to each input
Grp Name:
the keyboard. It will accept up to 32 characters.
Priority:
to 8 (lowest) for each group. The default setting is
None. Assigning priority to groups is useful if you
need to have, for example, a paging microphone
force off background music in some zones, but not
in others. In this case, assign the paging mic input
to a Control Group with Priority 1 level, and a
Control Group of designated outputs a Priority 2 or
lower level. Note that Input Priority and Group
Priority are separate functions, and the force-off
level for groups is completely off.
Logic In
Click this button to open the Logic Input window.
Make the following settings and assignments in the
Logic Input window:
Name:
32 characters.
Function:
this drop-down box. The functions include Inactive,
Force-on, Force-off, Mute Input, Mute Output,
Mute Group, Preset Recall, and Combine.
Enter a name for each group with
Assign a priority level from 1 (highest)
Enter a name for each Logic Input, up to
Select one of 8 different functions in
Action:
function selected is momentary, latch
on, latch off, or toggling. The selections
will vary depending on the function
selected for the Logic Input.
Affected I/O:
Output, or other parameter that is
affected by the Logic function. The
selections will vary depending on the
function and action selected for the
Logic Input.
See Appendix A for a chart of the
Logic Input functional combinations
available.
Select whether the particular
Select the Input,
DX810 – 19
Page 20

Logic Out
Click this button to open the Logic Output window.
Make the following settings and assignments in the
Logic Output window:
assigned to a group by clicking this button. If it is, and
the group fader is turned down, you won’t get a signal!
Input Proc
Click this button to view the processors (Gate,
Compressor, Input EQ) that are active for each input
(over the Crosspoint Matrix Section). Lit buttons
show processors that are turned on. Click the
buttons to turn the processors on and off for each
individual input. Ctrl+click on a button to open the
processor window and make adjustments.
Name:
to 32 characters.
Function:
this drop-down box. These functions include
Inactive, Input/Mute Enable, Output Signal Present,
Preset Active, Output/Mute Enable, Group/Mute
Enable, Force On, Priority Active, Combine Active,
and Gate Status.
Parameter:
parameter that is monitored by the Logic Output.
The selections will vary depending on the function
selected for the Logic Output.
Condition:
must be satisfied for the Logic Output to become
active. The condition will vary depending on the
function and parameter selected for the Logic Output.
See Appendix B for a chart of the Logic Output
functional combinations available.
Groups
Click this button to view group assignments for
crosspoints and outputs. The gain readout boxes
change and display the assigned group for the
crosspoint or output. This is true of the Crosspoint
Matrix and Output Sections.
Enter a name for each Logic Output, up
Select one of 10 different functions in
Select the input, output, or other
Displays the particular condition that
Out Proc
Click this button to view the processors that are
active for each output (over the Crosspoint Matrix
Section). These processors include Output EQ, XOver, Delay, and Compressor. Lit buttons show
processors that are turned on. Click the buttons to
turn processors on and off for each individual
output. Ctrl+click on a button to open the processor
window and make adjustments.
20 – DX810
Tip: If you have an input and output turned up,
but you are not hearing the signal in the output,
check to see if that input or output (or crosspoint) is
Note that if two or more outputs are linked via
the Crossover window, only one button appears.
This is true of the Output EQ (Graphic or Parametric),
X-Over, and Delay output processors, as shown in
outputs A through E in the previous output
processor view.
Page 21

Mute Ind
Click this button to view the Active Mute Groups
indicator in the upper left corner of the screen. If a
group mute button is active, the associated indicator
lights up in the Active Mute Group indicator.
Remotes
Click this button to open the Remote Mapping window.
possible to assign any of these listed functions to
any of the four DX-SW4 selection buttons.
See Appendix C for the switch settings for the
DX-SW4.
DSP
Combine
Click this button to view the Combine buttons,
superimposed over the Crosspoint Matrix Section.
The combine function allows increased flexibility
when providing audio for multiple rooms that need
to be reconfigured for different events. Up to sixteen
different combinations can be created (C1–C16).
Four buttons along the top of this window allow
selecting 16 DX-SW4 remotes in groups of four.
The four selected remotes (addresses 41-44, 45-48,
49-52, and 53-56) appear in the Remote Mapping
window. Drop-down menus for each of the four
buttons on the remote are provided for selecting
the Function and the Affected I/O.
The following chart indicates the Function and
Affected I/O selections available:
Function Affected I/O
Force On Inputs 1-8
Force Off Inputs 1-8
Mute/Enable Input Inputs 1-8
Mute/Enable Output Outputs A-J
Mute/Enable Group Groups 1-32
Preset Recall Presets 1-24
Combine Combine 1-16
With the DIP switches on the DX-SW4 set for
the appropriate address (41 through 56), it is now
It is important to understand that combining is
implemented through control groups. Once you
become familiar with this concept, configuring and
using the combine feature is actually quite simple.
When using room combining, levels are adjusted
through groups, so crosspoints and outputs are assigned
to groups. Once this has been set up, use the combine
buttons to group outputs in up to 16 combinations. Note
that when a "combine" (combination) is active, combining
rules overide some settings.
Combine Rules
1. Combining only affects groups. No other controls
are affected.
2. When two or more mixes (outputs) are combined:
a. All crosspoints in a column assigned to a
control group will be reassigned to the same
control group as the first assigned crosspoint in
the same column.
b. All control groups present in a column of
crosspoints will be linked together such that
any operation on one control group will affect
the others as well.
c. These two rules (a and b) apply for each
crosspoint column in the combined mix, and
also for the combined mix outputs.
DX810 – 21
Page 22

3. Combining only affects crosspoints and outputs
that are assigned to control groups (see rule 1).
Any crosspoint or output that is part of a
combination, but is not assigned to a control
group, will be muted when the combination is
inactive, and audible when the combination is
active.
4. Multiple combinations can be activated at the
same time.
5. Outputs that are not assigned to any combinations
are not affected by these rules.
This means that:
• Control groups controlling the outputs to the
combined rooms will be linked together. All these
control groups will have the same level. The actual
output level of each output is the basic level adjusted
by this group level. Any of the controls that previously
controlled the group level for each output can now
adjust the level to all the combined outputs. Mute/
enable controls for these groups are also linked.
• Groups that previously controlled the relative level
of a single source input to each room will now be
linked together to control the relative level of that
input to all combined rooms. All the groups for the
same input will always have the same level. The
actual relative level of the input to each combined
output is the basic level to each room adjusted by
this group level. Any of the controls that previously
controlled the group for the relative level for an
input can now adjust the relative level of this input
to the combined outputs. Mute/enable controls for
these groups are also linked.
• Combining also works with crossover outputs. In
this case, as with crosspoints, the crossover looks
like a single output for mixing/combining.
Now let’s look at an example to see how the
rules apply in a practical application.
A Three Room Combination
In this example, Outputs A, B, and C provide
separate mixes for three rooms, which are
separated by dividing walls that can be folded back
to create one large room.
Initial Setup
1. A microphone from Room A is connected to
Input 1, a microphone from Room B is connected to
Input 2, and a microphone from Room C is
connected to Input 3.
2. Input 1 is routed to Output A (Room A) via
crosspoint 1A.
3. Input 2 is routed to Output B (Room B) via
crosspoint 2B.
4. Input 3 is routed to Output C (Room C) via
crosspoint 3C.
So far we have one mic in each room that is
routed to its room only. Now set the inputs and
outputs to nominal levels appropriate for the gain
structure of the system.
Secondary Setup for Room Combining
We want to be able to fold the walls back and
combine rooms A and B, rooms B and C, or
combine all three rooms into one large room. We
will create two combinations: C1 will combine rooms
A and B, and C2 will combine rooms B and C. To
combine all three rooms, activate both C1 and C2.
5. Assign each output A, B, and C to its own control
group. Let’s use groups 1, 2, and 3.
6. Assign each crosspoint to its own control group.
For this example, let’s use the following:
Crosspoint Group
1A 4
2B 5
3C 6
Tip: Don’t forget to deselect the group select
button when you are finished assigning the outputs
and crosspoints to the groups! You can click the
Group button to verify that you have assigned the
outputs and crosspoints correctly.
7. Set the group levels to a nominal level (or unity
gain).
Now we have assigned each crosspoint and
output to a control group, to satisfy one of the
combine rules (rule number 1).
Next we will add the inputs that we want to appear
at each output when each combination is active.
8. Select Output A and adjust crosspoints 2A and
3A so they can be heard in Output A. This puts
Room B and Room C mics into Room A output.
9. Select Output B and adjust crosspoints 1B and
3B so they can be heard in Output B. This puts
Room A and Room C mics into Room B output.
10. Select Output C and adjust crosspoints 1C and
2C so they can be heard in Output C. This puts
Room A and Room B mics into Room C output.
Notice that we haven’t assigned these crosspoints
to groups. This ensures that the extra inputs added to
each output will only be heard when the combination
is active (rule number 3). Note that the added inputs
can be heard in all the outputs until the combination
22 – DX810
Page 23

is created, activated, and then deactivated. That is
when the combine rules take effect.
Assign Combinations
Now we’ll create the combination to allow the
inputs for rooms A and B to be heard in both A and B
outputs when C1 is active.
11. Open the combine view by clicking on the
Combine button.
Tip: Each row of combine buttons (C1-C16) is
associated with the output at the end of the row.
There is no association with the inputs or input
faders at the bottom (vertically). Each output can be
assigned to none, one, or more combinations. The
last row of reddish colored combine buttons are
used to activate individual combinations.
12. Create Combination 1 by clicking on C1 for
Outputs A and B.
13. Click on C1 in the last row of reddish combine
buttons to activate Combination 1.
Now Mics 1 and 2 room will be heard in rooms A
and B outputs.
• Groups 1 and 2 are linked and control the output
level into A and B outputs.
• Group 6 controls the volume of mic #3 into B and
C outputs.
18. Finally, activate both C1 and C2, and all three
inputs can be heard in all three outputs.
• Groups 1, 2, and 3 are linked and control the
output level into A, B, and C outputs.
• Group 4 controls the volume of mic #1 into all
three outputs.
• Group 5 controls the volume of mic #2 into all
three outputs.
• Group 6 controls the volume of mic #3 into all
three outputs.
Input EQ
Click this button to view the Input 3-band EQ
controls, superimposed over the Crosspoint Matrix
Section.
• Group 4 controls the volume of mic #1 into A and
B outputs.
• Group 5 controls the volume of mic #2 into A and
B outputs.
Note: All the control group faders adjust the
volume levels relative to the individual output and
crosspoint level settings made previously.
Next we’ll create the combination to allow the
inputs for rooms B and C to be heard in both B and C
outputs when C2 is active.
14. Open the combine view by clicking on the
Combine button.
15. Click on C1 to deactivate Combination 1.
16. Create Combination 2 by clicking on C2 for
Outputs B and C.
17. Click on C2 in the last row of reddish combine
buttons to activate Combination 2.
Now Mics 2 and 3 will be heard in both rooms B
and C outputs.
• Groups 2 and 3 are linked and control the output
level into B and C outputs.
• Group 5 controls the volume of mic #2 into B and
C outputs.
Each input strip has a 3-band EQ comprised of:
1. A high-frequency shelving EQ with adjustable gain
(±15 dB) and frequency (500 Hz–20 kHz).
2. A mid-frequency parametric EQ with adjustable
gain (±15 dB), frequency (20 Hz–20 kHz), and
bandwidth (0.1–6.0 octaves).
3. A low-frequency shelving EQ with adjustable gain
(±15 dB) and frequency (20 Hz–500 Hz).
4. An ON button to turn the EQ on and off.
Click and drag up and down on the control knob
to change the setting.
Note: You can not directly enter a numeric value
with the mouse and keyboard. The EQ settings apply
to all the outputs to which the input is assigned.
Use the arrow keys on the keyboard to make fine
adjustments to a selected control, and the Page Up/
Down keys to make course adjustments. Use the Tab
key to quickly move the selection to adjacent controls.
DX810 – 23
Page 24

Output EQ
Click this button to view the Output EQ controls.
Click the output letter buttons (A-J) to select an
output after the Output EQ window is open.
Select either a 31-band Graphic EQ or an 8-band
Parametric EQ.
Note: When switching between the 31-band
Graphic EQ and the 8-band Parametric EQ, a
warning will appear: "This will reset all EQ
parameters!" Click Cancel to retain the current EQ
settings, or OK to change EQ modules.
31-band Graphic EQ
With an output selected, click the 31b button to
view the Graphic EQ controls.
Click the On button to activate the Graphic EQ
for the selected output. The Reset button returns all
the sliders to their center (0 dB) positions.
Each band is on an ISO center frequency ranging
from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, with ±15 dB gain on each band.
Click and drag on a slider knob to adjust the EQ.
Use the arrow keys on the keyboard to make fine
adjustments to a selected control. Use the Page
Up/Down keys to make course adjustments. The
selected band’s GAIN and BAND (frequency) are
displayed at the top of the window.
Click the right mouse button over the processor
display. This brings up a menu allowing you to cut,
copy, or paste the processor settings to another output.
8-band Parametric EQ
With an output selected, click the 8b button to view
the 8-band Parametric EQ controls.
Click the On button to activate the Parametric
EQ for the selected output. The Reset button
returns all the controls to their center positions.
Each band has adjustable gain (±15 dB), frequency
(20 Hz–20 kHz), and bandwidth (0.1–6.0 octaves).
Click the right mouse button over the processor
display. This brings up a menu allowing you to cut,
copy, or paste the processor settings to another output.
Compress
Click this button to view the Compressor for a
selected input or output. Click an input SELECT
button to select an input. Click the output letter
buttons (A-J) to select an output.
Click the On button to activate the Compressor
for the selected input or output. The Reset button
returns all the controls to their default positions.
The Compressor has five knobs: Attack,
Release, Output, Threshold, and Ratio. Click and
drag on the individual knobs to adjust each
parameter. An analog-style meter indicates the
amount of compression applied in decibels.
Click the right mouse button over the processor
display. This brings up a menu allowing you to cut,
copy, or paste the processor settings to another channel.
About Compression:
A compressor is used to reduce or limit transient
peaks in a signal. As the input level to the
compressor increases, the output level increases
linearly until the threshold point is reached. After
that point, the output level no longer increases
linearly. Instead, it increases at a reduced rate
determined by the ratio setting.
This compressor features ‘soft-knee’
compression. As the input signal level approaches
and crosses the threshold, the compressor gradually
starts compressing. The compression ratio gradually
increases to the required setting smoothly.
• Threshold: This control determines the level around which the
compressor begins to act on the incoming signal. It is calibrated
in decibels, with a range from –60.0 dBFS to –1.0 dBFS.
• Attack: This determines how fast the compressor reacts once the
threshold has been exceeded. It is calibrated in milliseconds,
with a range from 0.1 ms to 2500 ms (2.5 seconds) per 20 dB of
gain change.
• Release: This determines how fast the compressor turns off once
the signal falls below the threshold. It is calibrated in milliseconds,
with a range from 10 ms to 2500 ms (2.5 seconds) per 20 dB of
gain change.
24 – DX810
Page 25

• Ratio: This determines the change in output level. It is a function
of the change in input level (at full compression), once the
threshold has been fully exceeded. It is calibrated in decibels,
with a range from 1.0:1 (off) to 20:1. Thus, if it is set to 10:1, an
increase in input level of 10 dB results in a 1 dB increase in
output level. This assumes the input is above the threshold
level.
Generally, use ratio settings from 1.5:1 to 5.0:1 for compressor
use. Settings from 10:1 to 20:1 are more useful for limiting
purposes. This is because in that range the output level changes
very little as the input increases.
• Output: This determines the overall gain of the compressor from
input to output (as measured with the signal below the
threshold level). You can use this control to compensate for the
loss of gain caused by the action of the compressor. It is
calibrated in decibels, with a range from 0 dB (unity) to +20.0 dB.
• Range: This determines the amount of attenuation of the input
signal when the gate is closed. It is calibrated in decibels,
ranging from –100 dB to –1 dB.
Delay
Click this button to view the Delay settings for a
selected output. Click the output letter buttons (A-J)
to select an output.
Gate
Click this button to view the Gate for a selected input.
Click an input SELECT button to select an input.
Click the On button to activate the Gate for the
selected input. The Reset button returns all the
knobs to their default settings.
The Gate has four knobs: Hold, Release,
Threshold, and Range. Click and drag on the
individual knobs to adjust each parameter. An
analog-style meter indicates the input signal level
for the selected channel.
Click the right mouse button over the processor
display to bring up a menu that allows you to cut, copy,
or paste the processor settings to another channel.
About Gating:
A gate is used to duck or mute a channel when
the signal level drops below a certain point. This can
reduce the overall noise level in your mix by muting
unused or noisy channels.
Note: When we say the gate opens, it means
the gate is not acting on the signal and the signal is
allowed to pass. When the gate closes, the gate
acts on the signal by attenuating it.
• Threshold: This determines the level below which the gate
closes (and above which it opens). It is calibrated in decibels,
ranging from –60 dBFS to –1 dBFS.
• Hold: This determines how long the gate remains open after the
input signal has fallen below, and remains below, the threshold
before closing. It is calibrated in milliseconds, ranging from 0 ms
to 2550 ms (2.55 sec).
• Release: This determines how fast the gate closes after the hold
time has expired. It is calibrated in milliseconds, ranging from
10 ms to 2500 ms (2.5 sec) per 20 dB of gain change.
Click the On button to activate the Delay Line.
The Delay Line has two knobs: Coarse, and
Fine. Click and drag on the individual knobs to
adjust each parameter.
Coarse:
This control adjusts the delay in 1
millisecond increments, with a range from 0 ms to
200 ms. The equivalent distance the sound travels
in the selected amount of time is displayed. Use
this control when setting up a delay between two
speakers, as in a delay tower.
Fine:
This control adjusts the delay in small
increments (22.7 µs), with a range from 0 µs to 997 µs.
The equivalent distance the sound travels in the
selected amount of time is displayed. Use this
control to adjust for offsets between drivers in a
stack. For example, use this control to time-align a
horn’s compression driver and a woofer’s voice coil.
In addition, it is necessary to enter the ambient
air temperature in the Delay/Distance Parameters
window (click Advanced in the top menu bar and
select Set Temperature). The speed of sound
varies with air temperature, and this value is
needed to accurately calculate the time delay
required as a function of distance traveled (see "Set
Temperature" on page 16). You can also choose
between US units (Fahrenheit/Feet/Inches) and
Metric units (Celsius/Meters/Millimeters) in the
Delay/Distance Parameters window.
Click the right mouse button over the processor
display. This brings up a menu allowing you to cut, copy,
or paste the processor settings to another channel.
X-Over
Click this button to view the 1 to 5-Band Crossover.
The crossover window has a graphic display to
indicate the number of bands and crossover points
selected. Up to five outputs can be selected, which
become linked to a single row of inputs. In other
words, each of the eight inputs has just one mix level
to the combined outputs in the crossover. This is
DX810 – 25
Page 26

reflected in the Crosspoint Matrix Section by “blanking
out” all but the top row of crosspoints for the linked
crossover outputs. Note that only contiguous outputs
may be linked to create a crossover.
Linking outputs together for the crossover
automatically links those outputs in Output EQ
processors. The Output EQ defaults to the setting
for the first output in the crossover (i.e., Output A).
The equalizers are located prior to the crossover in
the signal chain, so all the outputs assigned to the
crossover are affected by the EQ settings.
With the first band active (red active button lit),
click the On button to turn the crossover on and off.
When the crossover is turned off, all the outputs
assigned to the crossover pass a full-range signal.
Click the Reset button to return all the knobs for the
currently active band to their default settings.
Output:
(A-J). Click the arrow next to the box to select an
output in the pull-down list. It appears in the first
Output box. Repeat for up to five bands in a single
crossover system.
To deselect an output once you've selected one,
click the arrow next to the box and select the
"blank" line under the J output. This removes the
output selection from the crossover.
Polarity:
polarity of the output by 180°.
Edit:
the settings for the selected output. Then use the
Filter Type, Filter Slope, Alignment, Frequency,
and Delay Time controls.
Filter Type:
(HP), low-pass (LP), or band-pass (BP) filters for the
selected output. Notice that the Frequency control
selection changes to High Freq and Low Freq
when BP is selected.
Filter Slope:
curve for the frequencies above or below the cutoff
frequency. When Butterworth or Bessel alignment is
selected, 12, 18, and 24 dB/octave slopes are
Select the first output for the crossover
The Polarity button reverses the
Click the Active button under Edit to adjust
Use this control to select high-pass
Use this control to choose the roll-off
available. When Linkwitz-Riley is selected, 12 and
24 dB/octave are available (18 dB can’t be selected).
Alignment:
Riley, Butterworth, or Bessel characteristics for the
selected Filter Type.
Frequency:
the selected filter, with a range from 20 Hz to 20
kHz. When a bandpass filter is selected, High Freq
and Low Freq controls are available.
Delay Time:
the selected output in small increments (22.7 µs),
with a range from 0 µs to 997 µs. The equivalent
distance the sound travels in the selected amount
of time is displayed.
Note: This control is provided in the Crossover
window because the Delay Line DSP (the Delay
button) is situated prior to the crossover in the signal
chain. When the crossover is active, use this delay
control to adjust for offsets between drivers in a
stack. For example, use this control to time-align a
horn’s compression driver and a woofer’s voice coil.
Option
This button is reserved for future upgrades.
This switch selects either Linkwitz-
This selects the cutoff frequency for
This control adjusts the delay for
CROSSPOINT MATRIX SECTION
This section provides a view of all the input-tooutput crosspoints in the mixing matrix. It has a
numerical and graphical indication of the gain
setting for each crosspoint.
Click the associated letter button (A-J) in the
Output Section to select an output and the
horizontal row of input crosspoints is highlighted.
The input faders in the Input Section now control
the gain settings and mix for the selected output.
Either click on the fader or click on the horizontal
mini-fader indicator bar in the crosspoint to adjust
the gain for the input.
Click the select (S) button to select the
crosspoint for copying or pasting the level.
Otherwise, when a group is selected, use it to
assign the crosspoint to the selected group.
26 – DX810
Page 27

INPUT SECTION
OUTPUT SECTION
This section includes the eight input faders along
with their associated bargraph input level meters,
Select and Mute buttons, and name box.
The fader adjusts the mix level from the input to
the output selected in the Crosspoint Matrix Section
(indicated by the highlighted row). The numerical
display for the level is shown at the crosspoint in the
Crosspoint Matrix section. Use the arrow keys on the
keyboard to make fine adjustments to the level. Use
the Page Up/Down keys to make course adjustments.
The input level meter indicates the level of the
input signal as it comes out of the analog to digital
converters and shows the level in dBFS. If the red
0 dB portion is lit, then the signal level is above
–2 dBFS and close to clipping. Note that the meter
indicates the signal level before any processing or
digital gain stages. If the signal is clipping, or is too
low, adjust the signal level at the source, or use the
trim controls on the rear panel of the DX810.
When a group is selected, click the SELECT
button to assign the input to the selected group.
The assigned group fader then affects the signal
level for that input to all ten outputs. Click the
SELECT button when the gate or compressor
windows are showing to adjust the processing
options for that input.
Click the mute (M) button to mute the input
signal to all ten outputs.
Ctrl+click the (M) button to engage the enable
function. The blue (M) button changes to a gray (E)
to indicate the enable function is active. This mutes
the input signal normally, and unmutes it when the
enable button is active. Ctrl-click the enable (E)
button to change back to the mute function.
Note: When the enable function is engaged,
logic inputs, outputs, and remotes that are
programmed to activate/deactivate/indicate the
mute function now control (or are controlled by) the
enable function.
Click the solo (S) button to isolate the input
signal in the mix. When an input solo button is
engaged, the remaining inputs are automatically
muted. This is useful for troubleshooting and
listening to each input individually.
Use the name box at the bottom of the Input
Section to enter a name for the input (e.g., CD Left,
CD Right, Vocal, Guitar, etc.), up to 32 characters.
The Output Section includes the ten output faders
along with their associated bargraph output level
meters. This section also includes numerical gain
display, mute and solo buttons, and name box.
Use the output faders to adjust the final output
level of the signal. Adjust the output faders so that
the associated output meter indicates around the
–10 and –7 dB positions when a normal signal is
going to that output. This provides the best signalto-noise ratio for the output stage. It is okay for the
–4 and –2 LEDs to blink occasionally on musical
peaks. However, avoid allowing the red 0 dB
indicator to light, which indicates that the signal is
within 2 dB of clipping.
Note that the meter indicates the signal level
after the output signal processing (i.e., Graphic EQ
or Parametric EQ, Compressor, Crossover). If
adjustments are made to the output processors, the
output fader may need to be readjusted. This is to
compensate for an increase or decrease in gain
through the processors.
Click the mute (M) button to mute the output signal.
Ctrl+click the (M) button to engage the enable
(E) function. This mutes the output signal normally,
and unmutes it when the enable button is on
(active). Ctrl+click the enable (E) button to change
back to the mute function.
Note: When the enable function is engaged,
logic inputs, outputs, and remotes that are
programmed to activate/deactivate/indicate the
mute function now control (or are controlled by) the
enable function.
Click the (S) button to solo the output. This
mutes all the outputs except the soloed output.
This is useful for troubleshooting and listening to
each output individually.
Click the letter button (A-J) when a group is
selected to assign the output to the selected group.
DX810 – 27
Page 28

Click the letter button when a processing window
is showing (except Gate and Input EQ) to adjust the
processing options for that output.
Use the box to the right of the Output Section to
enter a name for the output (e.g., Main Left,
Control R), using up to 32 characters.
GROUP SECTION
This section includes the 32 control groups. Eight
groups are displayed at one time. However, the
horizontal fader at the bottom allows you to scroll
through all the control groups.
unmutes it when the enable button is on (active).
Ctrl+click the enable (E) button to change back to
the mute function.
Exclusive Enable Program Selection
Control Groups can be enabled exclusively; that is,
when one group is enabled, other groups are
automatically disabled so that only one group is
active at a time. Use this feature to configure a zone
so that one input at a time can be selected in the
mix. Up to eight programs (inputs) can be selected
individually in a room using two DX-SW4 remote
control units configured to select (force on) groups.
To configure groups for Exclusive Enable:
1. For this example, use Groups 1-4. Ctrl+click the (M)
button on Groups 1-4 to engage the enable
function. The (M) will change to an (E).
2. Click the select button (S) for the first group. For
this example, use Groups 1-4.
3. Ctrl+click the select button for the second group.
The button will start blinking.
4. Ctrl+click the select button for the remaining
groups (3-4) that you want to associate with the
exclusive enable function.
There is a mute and select button associated
with each Control Group.
To assign or unassign a crosspoint or output to a group:
1. Click the select (S) button for the desired group. If
any crosspoints or outputs are assigned to the
selected group, their select buttons light.
2. Click the select (S) button for the crosspoints you
want to assign to the selected group. The group
fader affects the mix level for each crosspoint to a
single output.
3. Click the SELECT button in the Input Section to
assign the input fader to the selected group. The
group fader affects the mix level for each input to
all the outputs.
4. Click the associated letter button (A-J) in the Output
Section to assign an output to the selected group.
The group fader affects a single output level.
5. Click the Groups button in the Top Section to view
and verify group assignments.
Group assignments are saved in each preset.
This allows different combinations of crosspoints,
inputs, and outputs to be assigned to the same
group number in separate presets.
Click the (M) button to mute the group. This
mutes all crosspoints, inputs, and outputs assigned
to the group. Click the Mute Ind button to view the
Active Mute Groups indicator.
Ctrl+click the (M) button to engage the enable
(E) function. This mutes the group normally, and
5. Click the select button for the first group to turn it
off. The other three select buttons stop blinking.
6. Click the select button for the second group.
7. Ctrl+click the select buttons for the first, third, and
fourth groups.
8. Click the select button for the second group to turn
it off.
9. Click the select button for the third group, and
Ctrl+click the select buttons for the first, second,
and fourth groups. Click the select button for the
third group to turn it off.
10.Click the select button for the fourth group, and
Ctrl+click the select buttons for the first, second,
and third groups. Click the select button for the
fourth group to turn it off.
Now when you click on the enable buttons for
Groups 1-4, only one at a time can be selected.
The group fader controls the relative level for all
the crosspoints, inputs, and outputs assigned to it.
At the unity gain position (U), all the levels are at
their assigned values and the group fader has no
effect. Reduce the group fader 10 dB, and all the
levels assigned to that group are reduced 10 dB,
relative to their assigned value. Note that the group
fader can increase the level 10 dB. However, if an
assigned level is already at +10 dB, it will not
change. The maximum overall gain available for any
crosspoint, input, or output is +10 dB.
Use the box at the bottom of the Group Section
to enter a name for the group (e.g., Voc,
Drum), using up to 32 characters.
28 – DX810
Page 29

DIRECT
OUTPUT
CHANNEL 1
32-BIT DSP
CHANNELS 2-8
(IDENTICAL TO CH 1)
3-BAND INPUT EQGATE
INPUT METER
INTERNAL DIGITAL
BUSES
ADC
24-BIT
PHANTOM POWER
+48 VDC
MUTE/ENABLE
TRIM
+5V
PC
OR OTHER
CONTROL
DEVICE
(OPTIONAL)
PC
OR OTHER
CONTROL
DEVICE
(OPTIONAL)
REMOTE
CONTROL
(OPTIONAL)
MIC
LINE
ABCDE FGHI J
LOGIC
IN
(1 OF 10)
FRONT PANEL
COMM PORT
REMOTE
CONTROL
+5V
LOGIC
OUT
(1 OF 10)
CONTROL
PROCESSING
REMOTE
CONTROL
(OPTIONAL)
TO ADDITIONAL
REMOTE CONTROLS
(OPTIONAL)
REAR PANEL
COMM PORT
COMPRESSOR
DAC
24-BIT
8-BAND PARAMETRIC EQ
BUSES E-J
(IDENTICAL TO A-D)
MUTE/ENABLE
X-OVER
31b
8b
31b
8b
31b
8b
31b
8b
DELAY
A
B
C
D
INTERNAL ANALOG
BUSES
ABCDEFGHI J
31-BAND GRAPHIC EQ
DAC
24-BIT
COMPRESSOR
COMPRESSOR
OUTPUT METER
OUTPUT METER
RECORD
OUTPUTS
A
OUTPUT
B
OUTPUT
C-F
OUTPUTS
A
–
+
G
–
+
G
–
+
G
–
+
G
–
+
G
–
+
G
G-J
OUTPUTS
–
+
G
–
+
G
–
+
G
–
+
G
B
BUS A
INPUT
BUS B
INPUT
TRIM
TRIM
EAW COMMERCIAL
DX810 (v3.3)
BLOCK DIAGRAM
(6/30/03 DF)
MUTE/ENABLE
X-OVER
DELAY
MUTE/ENABLE
X-OVER
DELAY
MUTE/ENABLE
X-OVER
DELAY
DAC
24-BIT
DAC
24-BIT
COMPRESSOR
COMPRESSOR
OUTPUT METER
OUTPUT METER
8-BAND PARAMETRIC EQ
31-BAND GRAPHIC EQ
8-BAND PARAMETRIC EQ
31-BAND GRAPHIC EQ
8-BAND PARAMETRIC EQ
31-BAND GRAPHIC EQ
6. SPECIFICATIONS
DX810 BLOCK DIAGRAM
DX810 – 29
Page 30

DX810 SPECIFICATIONS
INPUTS / OUTPUTS
Inputs 1-8: Balanced, Phoenix-type terminals
Bus A and B: Balanced, Phoenix-type terminals, Direct to
Mix Buses
Outputs A-J: Balanced, Phoenix-type terminals
Record Outputs A/B: Unbalanced, RCA
Direct Outputs 1-10: Unbalanced on DB15
(bottom row is signal return)
Logic Inputs: 10 Inputs on DB25
Series resistance: 570Ω
Internal pull-up: 47 kΩ to +5 VDC
Input voltage: +5.5 VDC maximum
Active voltage: +1.0 VDC maximum
Logic Outputs: 10 open-collector Outputs on DB25
Series resistance: 550 Ω
Internal pull-up: 10 kΩ to +5 VDC
Active current: 10 mA maximum
Active voltage: +0.8 VDC max @ 1 mA
Serial Ports: 2 RS-232C on DB9 (COMM PORTS)
PANEL CONTROLS
Input Trim: 8 Rotary Potentiometers
Input Gain: 2 Pushbuttons per Input
EQ: 2 Pushbuttons for Low, 2 for High
Master Output Gain: 2 Pushbuttons per Output
Mode Select: 1 Pushbutton
Power: Rocker Switch
Phantom Power Select: 8 DIP Switches
PANEL INDICATORS
Input Levels: 12-segment LEDs per ch.
Output EQ Levels: 12-segment LEDs per ch.
Mode Status: 3 LEDs; A/B/LOCK
Output Levels: 12-segment LEDs per ch.
Volume Setting: 12-segment LED Bar Graph
SIGNAL PROCESSING
General: Five 32-bit floating-point DSPs
24-bit A/D and D/A converters
512Kx16 Flash ROM
128Kx32 SRAM (with battery backup)
Inputs: 3-band shelving EQ with parametric mid
Gain: ±15 dB
Corner Frequency:
LO: 20 Hz-500 Hz variable
HI: 500 Hz-20 kHz variable
Center Frequency:
MID: 20 Hz-20 kHz variable
Gate on each Input
Threshold: –60 dBFS to –1 dBFS
Hold: 0 ms to 2500 ms
Release: 10 ms to 2500 ms
Range: –100 dB to –1 dB
Outputs: Delay on each Output
Te mp : –40ºF to 122ºF
(40ºC to 50ºC)
Coarse: 0 ms to 200 ms
Fine: 0 µs to 997 µ s
Crossover
Polarity: 0º, 180º
Filter Type: High-Pass, Low-Pass,
Band-Pass
Alignment: Linkwitz-Riley,
Butterworth, Bessel
Filter Slope: 12 dB/oct, 18 dB/oct,
24 dB/oct (Butterworth only)
Frequency: 20 Hz-20 kHz
1/3-Octave Graphic EQ on each Output
Gain: ±15 dB
ISO-Centered Frequencies: 20, 25,
31.5, 40, 50, 63, 80, 100, 125, 160,
200, 250, 315, 400, 500, 630, 800, 1 k,
1.25 k, 1.6 k, 2 k, 2.5 k, 3.15 k, 4 k,
5 k, 6.3 k, 8 k, 10 k, 12.5 k, 16 k, 20 k
8-Band Parametric EQ on each Output
Gain: ±15 dB
Center Frequency:
20 Hz-20 kHz variable
Bandwidth: 0.1 octave to 6 octaves
30 – DX810
LED METER VALUES
1. Red (scale: OL): > –2 dB full-scale (> 16 dBu)
2. Yellow (scale: 2): > –4 dB full-scale (> 14 dBu)
3. Yellow (scale: 4): > –7 dB full-scale (> 11 dBu)
4. Yellow (scale: 7): > –10 dB full-scale (> 8 dBu)
5. Green (scale: 10): > –15 dB full-scale (> 3 dBu)
6. Green (scale: 15): > –20 dB full-scale (> –2 dBu)
7. Green (scale: 20): > –25 dB full-scale (> –7 dBu)
8. Green (scale: 25): > –30 dB full-scale (> –12 dBu)
9. Green (scale: 30): > –35 dB full-scale (> –17 dBu)
10. Green (scale: 35): > –40 dB full-scale (> –22 dBu)
11. Green (scale: 40): > –50 dB full-scale (> –32 dBu)
12. Green (scale: 50): > –60 dB full-scale (> –42 dBu)
Compressor/Limiter on each Input and Output
Threshold: –60.0 dB to –1.0 dB
Attack: 1 ms to 2500 ms
Release: 10 ms to 2500 ms
Ratio: 1:1 to 20:1
Output: 0 dB to +20.0 dB
Page 31

AUDIO
Noise
(20 Hz-20 kHz bandwidth, Master Out, channel Trims @ unity gain,
channel EQs flat, all odd channels panned left, even channels
panned right):
Master level @ unity, channel levels @ unity: –82 dBu
Single channel to Master Out: –100 dBu
(referenced to 1% THD+N)
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD+N)
(1 kHz @ +10 dBu (unity level) 20 Hz-20 kHz):
Mic in to Master Out: < 0.005%
Crosstalk
(1 kHz relative to 0 dBu, 20 Hz-20 kHz bandwidth, any line input to
adjacent Direct Out):
Trim to unity: < –90 dB
Frequency Response
Mic input to any output: 20 Hz–20 kHz, ±0.5 dB
Equivalent Input Noise (EIN)
Mic in to Direct out, max gain, 150 ohm termination:
–129.5 dBm unweighted
Common Mode Rejection (CMR)
Mic in to Direct out, max gain, 1 kHz signal: better than 80 dB
Maximum and Nominal Levels and Ranges
Mic inputs: +18 dBu, +4 dBu,
0 to 60 dB gain
Line inputs: +18 dBu, +4 dBu,
–30 to +30 dB gain
Bus A/B inputs: +18 dBu, +4 dBu,
–20 to +20 dB gain
All outputs: +18 dBu, +4 dBu
Impedances
Mic inputs: 1.3K ohms
Line inputs: 40K ohms
All other inputs: 10K ohms or greater
All outputs: 120 ohms
PHYSICAL
Dimensions (HxWxD): 3.5"/2 RU (89mm) x 19" (483mm) x
13.25" (337mm)
Net Weight: 12.9 lbs. (5.9 kg)
ELECTRICAL
AC Power: 90–240 VAC, 50/60 Hz, 1.0 A
DC Power: 24 VDC, 3 A
Phantom Power: +48 VDC, current limited to 7 mA
per input channel
Fuse Ratings: 1.6 A Slo Blo, 250 V
PC SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
OS: Windows® 95, 98, NT®, 2000, XP
Processor: Pentium® or faster
RAM: 16 MB minimum
32 MB recommended
Storage: 10 MB free disk space
Display: 800x600 pixels, 256 colors minimum
DX810
DX810 DIGITAL MIXER
DX810 – 31
Page 32

DISCLAIMER
7. SERVICE INFORMATION
EAW Commercial continually engages in
research related to product improvement, new
materials, and production methods. Design
refinements are introduced into existing products
without notice as a routine expression of that
philosophy. For this reason, any current EAW
Commercial product may differ in some respect
from its published description, but will always equal
or exceed the original design specifications unless
otherwise stated.
EAW Commercial is a trademark of LOUD
Technologies Inc.
All other brand names mentioned are
trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective holders, and are hereby acknowledged.
© 2004 All Rights Reserved.
LOUD Technologies Inc.
In the event that your DX810 should require
servicing, please follow these instructions:
1. Call EAW Commercial Tech Support at 1-888-3377404, 8 am to 5 pm PST (Monday-Friday). Verify
the problem and obtain a Return Authorization
(RA) Number. Be sure to have the serial number of
the unit when you call. You must have a Return
Authorization Number in order to obtain warranty
service at the factory or at an authorized service
center.
2. Pack the unit in its original packaging.
important.
any damage that occurs during shipping due to
non-conventional packaging. Original packaging
helps to minimize the possibility of shipping
damage.
3. Include a legible note stating your name, return
shipping address (no P.O. boxes), daytime phone
number, and Return Authorization Number. Give
us a detailed description of the problem, including
how we can duplicate it.
4. Write the Return Authorization Number in BIG
BOLD PRINT on the top of the box.
EAW Commercial is not responsible for
This is very
5. Tech Support will tell you where to ship the unit
when you call for an RA Number. We suggest
insurance for all forms of cartage.
32 – DX810
Page 33

Appendix A: Logic Input Functions
Logic Input
Function Action Affected I/O
Inactive None None
Force-On Momentary Input 1-8; Group 1-32
Force-Off Momentary Input 1-8; Group 1-32
Mute/Enable Input Momentary Input 1 to Input 8
Mute/Enable Output Momentary Output A to J
Mute/Enable Group Momentary Group 1 to Group 32
Preset Recall Momentary Preset 1 to Preset 24
Combine Momentary Combine 1 to Combine 16
Latch On Input 1-8; Group 1-32
Latch Off Input 1-8; Group 1-32
Toggling Input 1-8; Group 1-32
Latch On Input 1-8; Group 1-32
Latch Off Input 1-8; Group 1-32
Toggling Input 1-8; Group 1-32
Latch On Input 1 to Input 8
Latch Off Input 1 to Input 8
Toggling Input 1 to Input 8
Latch On Output A to J
Latch Off Output A to J
Toggling Output A to J
Latch On Group 1 to Group 32
Latch Off Group 1 to Group 32
Toggling Group 1 to Group 32
Latch On Preset 1 to Preset 24
Latch On Combine 1 to Combine 16
Latch Off Combine 1 to Combine 16
Toggling Combine 1 to Combine 16
Appendix B: Logic Output Functions
Logic Output
Function Parameter Condition
Inactive None None
Inp Mute/Enable Input 1-8 Input Muted or Enabled
Out Sig Present Output A-J Output A Signal > –40 dB
Preset Active Preset 1-24 Preset Active
Out Mute/Enable Output A-J Output Muted or Enabled
Group Mute/Enable Group 1-32 Group Muted or Enabled
Force On Input 1-8;
Priority Active Input Priority 1-8;
Combine Active Combine 1-16 Combine Active
Gate Status Input 1-8 Gate Open
Group 1-32 Force On Active
Group Priority 1-8 Priority Active
DX810 – 33
Page 34

Appendix C: Selection Remote Predefined Functions
DX-SW4 Remote Switch Control (4-button/4-LED) for DX-810 v3.3 (Firmware v7.06)
Switch Positions
ID 1 through 8 Function Control 1 Control 2 Control 3 Control 4
0 00000000 Mute Input 1-4 Mute Input 1 Mute Input 2 Mute Input 3 Mute Input 4
1 10000000 Mute Input 5-8 Mute Input 5 Mute Input 6 Mute Input 7 Mute Input 8
2 01000000 Mute Output A-D Mute Output A Mute Output B Mute Output C Mute Output D
3 11000000 Mute Output E-H Mute Output E Mute Output F Mute Output G Mute Output H
4 00100000 Mute Output G-J Mute Output G Mute Output H Mute Output I Mute Output J
5 10100000 Mute Group 1-4 Mute Group 1 Mute Group 2 Mute Group 3 Mute Group 4
6 01100000 Mute Group 5-8 Mute Group 5 Mute Group 6 Mute Group 7 Mute Group 8
7 11100000 Mute Group 9-12 Mute Group 9 Mute Group 10 Mute Group 11 Mute Group 12
8 00010000 Mute Group 13-16 Mute Group 13 Mute Group 14 Mute Group 15 Mute Group 16
9 10010000 Mute Group 17-20 Mute Group 17 Mute Group 18 Mute Group 19 Mute Group 20
10 01010000 Mute Group 21-24 Mute Group 21 Mute Group 22 Mute Group 23 Mute Group 24
11 11010000 Mute Group 25-28 Mute Group 25 Mute Group 26 Mute Group 27 Mute Group 28
12 00110000 Mute Group 29-32 Mute Group 29 Mute Group 30 Mute Group 31 Mute Group 32
13 10110000 Preset Recall 1-4 Preset Recall 1 Preset Recall 2 Preset Recall 3 Preset Recall 4
14 01110000 Preset Recall 5-8 Preset Recall 5 Preset Recall 6 Preset Recall 7 Preset Recall 8
15 11110000 Preset Recall 9-12 Preset Recall 9 Preset Recall 10 Preset Recall 11 Preset Recall 12
16 00001000 Preset Recall 13-16 Preset Recall 13 Preset Recall 14 Preset Recall 15 Preset Recall 16
17 10001000 Preset Recall 17-20 Preset Recall 17 Preset Recall 18 Preset Recall 19 Preset Recall 20
18 01001000 Preset Recall 21-24 Preset Recall 21 Preset Recall 22 Preset Recall 23 Preset Recall 24
19 11001000 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
20 00101000 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
21 10101000 Force On Group 1-4 Force On Grp 1 Force On Grp 2 Force On Grp 3 Force On Grp 4
22 01101000 Force On Group 5-8 Force On Grp 5 Force On Grp 6 Force On Grp 7 Force On Grp 8
23 11101000 Force On Group 9-12 Force On Grp 9 Force On Grp 10 Force On Grp 11 Force On Grp 12
24 00011000 Force On Group 13-16 Force On Grp 13 Force On Grp 14 Force On Grp 15 Force On Grp 16
25 10011000 Force On Group 17-20 Force On Grp 17 Force On Grp 18 Force On Grp 19 Force On Grp 20
26 01011000 Force On Group 21-24 Force On Grp 21 Force On Grp 22 Force On Grp 23 Force On Grp 24
27 11011000 Force On Group 25-28 Force On Grp 25 Force On Grp 26 Force On Grp 27 Force On Grp 28
28 00111000 Force On Group 29-32 Force On Grp 29 Force On Grp 30 Force On Grp 31 Force On Grp 32
29 10111000 Force Off Group 1-4 Force Off Grp 1 Force Off Grp 2 Force Off Grp 3 Force Off Grp 4
30 01111000 Force Off Group 5-8 Force Off Grp 5 Force Off Grp 6 Force Off Grp 7 Force Off Grp 8
31 11111000 Force Off Group 9-12 Force Off Grp 9 Force Off Grp 10 Force Off Grp 11 Force Off Grp 12
32 00000100 Force Off Group 13-16 Force Off Grp 13 Force Off Grp 14 Force Off Grp 15 Force Off Grp 16
33 10000100 Force Off Group 17-20 Force Off Grp 17 Force Off Grp 18 Force Off Grp 19 Force Off Grp 20
34 01000100 Force Off Group 21-24 Force Off Grp 21 Force Off Grp 22 Force Off Grp 23 Force Off Grp 24
35 11000100 Force Off Group 25-28 Force Off Grp 25 Force Off Grp 26 Force Off Grp 27 Force Off Grp 28
36 00100100 Force Off Group 29-32 Force Off Grp 29 Force Off Grp 30 Force Off Grp 31 Force Off Grp 32
37 10100100 Combine Group 1-4 Combine 1 Combine 2 Combine 3 Combine 4
38 01100100 Combine Group 5-8 Combine 5 Combine 6 Combine 7 Combine 8
39 11100100 Combine Group 9-12 Combine 9 Combine 10 Combine 11 Combine 12
40 00010100 Combine Group 13-16 Combine 13 Combine 14 Combine 15 Combine 16
41 10010100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
42 01010100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
43 11010100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
44 00110100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
45 10110100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
46 01110100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
47 11110100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
48 00001100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
49 10001100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
50 01001100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
51 11001100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
52 00101100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
53 10101100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
54 01101100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
55 11101100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
56 00011100 Assignable in Remote Mapping Window
57-255 For Future Updates
34 – DX810
Page 35

Appendix D: Level Remote Predefined Functions
DX-RVC Remote Volume Control (2-button/12-LED)
Switch Positions
ID 1 through 8 Function In/Out
0 00000000 Input Level 1A
1 10000000 Input Level 1B
2 01000000 Input Level 1C
3 11000000 Input Level 1D
4 00100000 Input Level 1E
5 10100000 Input Level 1F
6 01100000 Input Level 1G
7 11100000 Input Level 1H
8 00010000 Input Level 1I
9 10010000 Input Level 1J
10 01010000 Input Level 2A
11 11010000 Input Level 2B
12 00110000 Input Level 2C
13 10110000 Input Level 2D
14 01110000 Input Level 2E
15 11110000 Input Level 2F
16 00001000 Input Level 2G
17 10001000 Input Level 2H
18 01001000 Input Level 2I
19 11001000 Input Level 2J
20 00101000 Input Level 3A
21 10101000 Input Level 3B
22 01101000 Input Level 3C
23 11101000 Input Level 3D
24 00011000 Input Level 3E
25 10011000 Input Level 3F
26 01011000 Input Level 3G
27 11011000 Input Level 3H
28 00111000 Input Level 3I
29 10111000 Input Level 3J
30 01111000 Input Level 4A
31 11111000 Input Level 4B
32 00000100 Input Level 4C
33 10000100 Input Level 4D
34 01000100 Input Level 4E
35 11000100 Input Level 4F
36 00100100 Input Level 4G
37 10100100 Input Level 4H
38 01100100 Input Level 4I
39 11100100 Input Level 4J
40 00010100 Input Level 5A
41 1001010 Input Level 5B
42 01010100 Input Level 5C
43 11010100 Input Level 5D
44 00110100 Input Level 5E
45 10110100 Input Level 5F
46 01110100 Input Level 5G
47 11110100 Input Level 5H
48 00001100 Input Level 5I
49 10001100 Input Level 5J
50 01001100 Input Level 6A
51 11001100 Input Level 6B
52 00101100 Input Level 6C
53 10101100 Input Level 6D
54 01101100 Input Level 6E
55 11101100 Input Level 6F
56 00011100 Input Level 6G
57 10011100 Input Level 6H
58 01011100 Input Level 6I
59 11011100 Input Level 6J
60 00111100 Input Level 7A
Switch Positions
ID 1 through 8 Function In/Out
61 10111100 Input Level 7B
62 01111100 Input Level 7C
63 11111100 Input Level 7D
64 00000010 Input Level 7E
65 10000010 Input Level 7F
66 01000010 Input Level 7G
67 11000010 Input Level 7H
68 00100010 Input Level 7I
69 10100010 Input Level 7J
70 01100010 Input Level 8A
71 11100010 Input Level 8B
72 00010010 Input Level 8C
73 10010010 Input Level 8D
74 01010010 Input Level 8E
75 11010010 Input Level 8F
76 00110010 Input Level 8G
77 10110010 Input Level 8H
78 01110010 Input Level 8I
79 11110010 Input Level 8J
80 00001010 Output Level A
81 10001010 Output Level B
82 01001010 Output Level C
83 11001010 Output Level D
84 00101010 Output Level E
85 10101010 Output Level F
86 01101010 Output Level G
87 11101010 Output Level H
88 00011010 Output Level I
89 10011010 Output Level J
90 01011010 Group Level 1
91 11011010 Group Level 2
92 00111010 Group Level 3
93 10111010 Group Level 4
94 01111010 Group Level 5
95 11111010 Group Level 6
96 00000110 Group Level 7
97 10000110 Group Level 8
98 01000110 Group Level 9
99 11000110 Group Level 10
100 00100110 Group Level 11
101 10100110 Group Level 12
102 01100110 Group Level 13
103 11100110 Group Level 14
104 00010110 Group Level 15
105 10010110 Group Level 16
106 01010110 Group Level 17
107 11010110 Group Level 18
108 00110110 Group Level 19
109 10110110 Group Level 20
110 01110110 Group Level 21
111 11110110 Group Level 22
112 00001110 Group Level 23
113 10001110 Group Level 24
114 01001110 Group Level 25
115 11001110 Group Level 26
116 00101110 Group Level 27
117 10101110 Group Level 28
118 01101110 Group Level 29
119 11101110 Group Level 30
120 00011110 Group Level 31
121 10011110 Group Level 32
122-255 Reserved for future
updates
DX810 – 35
Page 36

EAW Commercial A LOUD Technologies Inc. Company
EAW Commercial | Bldg 11 | One Main Street | Whitinsville, MA 01588 USA | TEL toll free within US/Canada 888.337.7404
TEL outside US 425.892.6503 | FAX 425.485.1152 | www.eawcommercial.com
© 2004 LOUD Technologies Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...