
Model LKP-8024
DIRECT CURRENT METERING SYSTEMS
Installation, Operation and Service Instructions
Manual Item No. 041837
Rev. H
DynAmp, LLC 3735 Gantz Road Phone +1 614.871.6900 www.dynamp.com
Grove City, Ohio 43123 USA Fax +1 614.871.6910 help@dynamp.com

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
This Page is Intentionally Blank
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page ii
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
DynAmp, LLC WARRANTY
Items and components manufactured by Seller for permanent installation are warranted for
two (2) years from the date of shipment.
Items and components manufactured by Seller for portable and temporary use in more than
one location are warranted to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period
of eighteen (18) months from the date of shipment.
Items and components not manufactured and resold by Seller are warranted by their
manufacturer.
Warranty repair shall be, at DynAmp’s option, in the form of repair or replacement of the
defective items or components. Concerning warranty repairs, DynAmp will be responsible
for DynAmp provided time, material and transportation costs (shipping or travel). Actual
method of warranty repair / correction will be determined by DynAmp at DynAmp’s sole
option. Such warranty repair shall constitute a fulfillment of all DynAmp, LLC liabilities in
respect to said items and components. In no event shall DynAmp, LLC be liable for
consequential damages.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2004, 2005, 2008, 2011 DynAmp, LLC. All rights reserved.
Reproduction for purposes other than operation and service without written permission of DynAmp, LLC
is strictly forbidden.
This manual includes detailed drawings, installation, operation, service and maintenance. Users should
evaluate the information in the manual and their particular application. DynAmp assumes no liability for
any incidental, indirect, or consequential damages arising fro the use of this documentation.
While all information presented is believed to be reliable and in accordance with accepted engineering
practices, DynAmp makes no warranties as to the completeness of the information.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page iii
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
This Page is Intentionally Blank
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page iv
041837 H
Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
Hazard Warning!
GENERAL
HAZARDOUS
VOLTAGE
INSTALLATION
Symbol
Identification:
All installation, maintenance and service must be performed by qualified
technicians who are familiar with the warnings and instructions of this manual.
The enclosure doors must remain closed at all times during operation to ensure
safety of personnel. A set of keys may be provided for locking the doors. Only
General definitions of safety symbols used on equipment and manual
authorized personnel or technicians should open and service the unit.
Disconnect power to the system before servicing or replacing fuses.
Use of the equipment in a manner not specified by the manufacturer can impair
the protection provided within.
DynAmp does not assume liability for the customer’s failure to comply with the
rules and requirements provided in this manual.
This equipment is designed to be connected to hazardous electric voltages.
Ignoring the installation precautions and warnings can result in severe personal
injury or equipment damage.
To avoid the risk of electrical shock or fire, the safety instructions and guidelines
in this manual must be followed. The electrical specifications must not be
exceeded and the unit must be installed according to directions provided.
These instructions apply only to retrofit kits installed on standard systems as
originally supplied by Halmar Electronics or DynAmp. Customer is responsible to
verify that the units are standard and do not have non-standard, customer
modifications installed. Before installing the upgrade kit, document any
modifications and contact DynAmp, LLC Service Department for further written
instructions to deal with the non-standard circumstances.
The installer is responsible for any damages resulting from improper installation
of upgrade kit.
This equipment is intended for indoor use only. It should be mounted in a wellventilated area, away from high heat, dust, and corrosive atmosphere. The
ambient temperature must not exceed 55°C.
For mounting considerations that fall outside the recommended specifications
provided in this manual, the factory should be contacted for approval.
Caution/Warning: Refer to accompanying documents for instructions.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page v
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
This Page is Intentionally Blank
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page vi
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
DynAmp, LLC Customer Support
For further assistance, contact DynAmp Customer Support at:
Americas:
Telephone: +1 614.871.6900 Fax: +1 614.871.6910
8:00 AM to 5:00 PM USA Eastern Time
From first Sunday in November to second Sunday in March – 13:00 GMT to 22:00 GMT
From second Sunday in March to first Sunday in November – 12:00 GMT to 21:00 GMT
Europe:
Telephone: +41 22.706.1446 Fax: +41 22.706.1311
8:30 AM to 5:00 PM Central European Time
From last Sunday in October to last Sunday in March – 7:30 GMT to 16:00 GMT
From last Sunday in March to last Sunday in October – 6:30 GMT to 15:00 GMT
After Hours Critical Service Emergency:
Telephone: +1 614.871.6906
5:00 PM to 8:00 AM USA Eastern Time
From first Sunday in November to second Sunday in March – 22:00 GMT to 13:00 GMT
From second Sunday in March to first Sunday in November – 21:00 GMT to 12:00 GMT
Central e-mail:
help@dynamp.com
DynAmp web:
www.dynamp.com
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page vii
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
This Page is Intentionally Blank
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page viii
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
REVISION PAGE
Page Change Reason For Revision Date
all Rev NEW 12/99
all A Warranty, Hazard Warning, Calibration Intervals, add
Technical Bulletin List, update drawing to current revision
19 B Deleted text regarding Hall Sensor power supply.
18, 24 C Updated Accuracy Diagnostics & Spare Parts section 04/02
all Rev D Update to DynAmp, LLC 12/04
22 Rev E Update per ECR-1245 – Remove 6-3. “Five Year Service”
and revised 6.2 (F.)
v, 1, 22,
24
29 G ECO 3166 update accuracy diagnostics drawings/list 09/08
Rev F Update fuse precautions per ECR 1304 07/06
12/00
3/01
11/05
all H
PAR 10245 – Handling & Storage, ECR 1440- Calibration
Intervals / New Manual Format
06/11
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page ix
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
This Page is Intentionally Blank
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page x
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Par. Title Page
1. SAFETY _____________________________________________________________ 1
1-1. OVERVIEW ..............................................................................................................................1
2. HANDLING AND STORAGE _____________________________________________ 3
3. DESCRIPTION ________________________________________________________ 5
3.1 APPLICATION.........................................................................................................................5
3.2 SIGNAL CONVERTER RETROFIT KIT ..................................................................................5
3.3 ELECTRICAL ..........................................................................................................................5
4. SPECIFICATIONS _____________________________________________________ 7
5. INSTALLATION _______________________________________________________ 9
5.1 WARNING ...............................................................................................................................9
5.2 HANDLING PRECAUTIONS ...................................................................................................9
5.3 EQUIPMENT NEEDED ...........................................................................................................9
5.4 PRELIMINARY PRECAUTIONS .............................................................................................9
5.5 CONVERSION PROCEDURE...............................................................................................10
5.6 INITIAL SYSTEM CHECKOUT..............................................................................................11
6. THEORY OF OPERATION______________________________________________ 15
6.1 GENERAL .............................................................................................................................15
6.2 MAGNETIC SENSOR (NULL DETECTOR) ..........................................................................15
6.3 SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONS....................................................................................................15
6.4 CIRCUIT FUNCTIONS ..........................................................................................................16
6.5 METERING UNIT ..................................................................................................................17
6.6 POWER SUPPLIES ..............................................................................................................17
6.7 SYNC, PLL, AND RAMPS.....................................................................................................17
6.8 ERROR AMPLIFIERS ...........................................................................................................17
6.9 COMPARATORS AND PULSE GENERATOR .....................................................................17
6.10 PULSE TRANSFORMER DRIVERS .....................................................................................18
6.11 ACCURACY DIAGNOSTICS.................................................................................................18
7. MAINTENANCE & SPARE PARTS ______________________________________ 21
7.1 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE ..................................................................................................21
7.2 ANNUAL MAINTENANCE.....................................................................................................21
7.3 CALIBRATION INTERVALS..................................................................................................22
7.4 SPARE PARTS ORDERS - ROUTINE OR EMERGENCY ...................................................22
7.5 RECOMMENDED SPARE PARTS........................................................................................23
7.6 SERVICE ASSISTANCE .......................................................................................................24
8. RELATED TECHNICAL BULLETINS _____________________________________ 25
9. DRAWINGS _________________________________________________________ 27
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page xi
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
DRAWINGS & TABLES
Figure #
Title ................................................................................................. Page
Figure 6.1 Magnetic Null Detector Diagram ............................................................................15
Figure 6.2 Functional Diagram of Four-Channel System .................................................... 16
Table #
Table 4.1 LKP-8024 Specifications ...........................................................................................7
Table 5.1 Measuring Head Resistance Chart -LKP-8024 .......................................................13
Table 5.2 Form for Recording Channel Voltage Measurements ............................................. 14
Table 7.1 Spare Parts List* ...................................................................................................23
Table 8.1 Technical Bulletins List............................................................................................ 25
Table 9.1 Drawing List............................................................................................................27
Title ................................................................................................. Page
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page xii
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
1. SAFETY
1-1. OVERVIEW
This equipment is designed to be connected to hazardous electric voltages. Ignoring the
installation precautions and warnings can result in severe personal injury or equipment
damage. Also, the equipment may be heavy and require special handling procedures to
ensure the safety of both personnel and equipment itself. The following are general
guidelines that should be followed when installing, operation and servicing the meter unit
and head.
•
All installation, maintenance and service must be performed by qualified technicians
who are familiar with the warnings and instructions of this manual.
•
Always follow all local and plant safety procedures.
•
These instructions apply only to retrofit kits installed on standard systems as originally
supplied by Halmar Electronics or DynAmp. Customer is responsible to verify that the
units are standard and do not have non-standard, customer modifications installed.
Before installing the upgrade kit, document any modifications and contact DynAmp, LLC
Service Department for further written instructions to deal with the non-standard
circumstances.
•
The installer is responsible for any damages resulting from improper installation of
upgrade kit.
•
The enclosure doors must remain closed at all times during operation to ensure safety
of personnel. A set of keys is provided for locking the doors. Only authorized
personnel or technicians should be allowed to open and service the unit.
•
Make sure that the cables are disconnected from the head during installation.
•
Replace fuses with correct type, size and value. All channel fuses are Type MDA time
delay fuses 3AB style, 1/4” x 1-1/4” (6.3mm x 32mm). Refer to the servicing
instructions or spare parts list for more information on replacement fuses. Do not
bypass the fuses or modify the electronics. Disconnect power to the system before
replacing fuses. Failure to follow these instructions will result in intermittent operation
and premature failure and will void the warranty.
•
Service must be performed by qualified technicians only. If use of an oscilloscope
becomes necessary during servicing, the scope must be floating and not grounded.
The meter unit is isolated from the mains via the power transformers. If a grounded
scope is used, a hazardous condition is created since current will flow through the
probe to ground.
•
If the installation is to be made on a "live" bus, the measuring head cables must be
disconnected from the head. A condition hazardous to the measuring head and any
person handling un-insulated cable-lead terminals will result if metal parts of the head
contact the bus, or sudden changes in the bus current occur.
•
Bus current must be zero when taking resistance measurements.
•
Use wire and fuse (slow-blow) size adequate for the maximum burden of 20 VA/kA of
measured current. The wire should have an insulation rating of 1000Vac and 80 - 105°
C temperature rating.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 1
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
•
Units are not intrinsically safe. Do not place in explosive atmospheres
•
Do not place in the rain, or under water, or submerge any part of the head or meter unit.
•
Use of the equipment in a manner not specified by the manufacturer can impair the
protection provided within.
DynAmp does not assume liability for the customer’s failure to comply with the rules and
requirements provided in this manual.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 2
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
2. HANDLING AND STORAGE
DynAmp products are engineered and manufactured for use in industrial environments.
However, they contain sensitive electronic and mechanical components which may be
damaged and fail if not handled and stored properly. All products must be handled and
stored with the same care as any precision measurement instrument. Severe bumps or
jolts may damage internal parts and cause malfunction or premature failure. DynAmp
products are designed and assembled with conformal coating, shock mounting, and
environmental seals, when appropriate or when specified. However, this protection
requires that the product must be properly installed and operational before the protection is
fully functional. Therefore, adequate protection from humidity, shock, and temperature
must be provided during handling and storage prior to installation.
The handling and storage of equipment must be sufficient to meet the storage temperature
and humidity specifications of the product and to prevent any condensation or contact with
water or any other liquid. The storage location and container or crate must provide
adequate protection from precipitation (rain, snow, ice) and direct water contact. Adequate
shelter must be provided to prevent the accumulation of precipitation (rain, snow, ice) and
water which can lead to the deterioration or failure of shipping containers or crates and
cause water ingress. Storage in coastal or industrial areas subject to salt-laden or
corrosive air or areas of wind-driven sand or other abrasive dust must be adequate to
prevent the deterioration or failure of shipping containers or crates and cause ingress.
Frequent inspection of storage areas and storage containers or crates is required to ensure
proper storage conditions are being maintained.
If the shipping container or crate is opened and/or the equipment is removed for inspection
prior to installation, the equipment must be repackaged in the original undamaged container
or crate in the same manner as it was shipped to prevent environmental damage or placed
in a storage location that meets the required environmental and storage conditions.
General product storage temperature and humidity requirements:
Storage Temperature: -40 to 70°C
-40 to 158°F
Storage Humidity: 85%, non-condensing
DynAmp, LLC does not assume liability for the customer’s failure to comply with handling
and storage requirements.
For further assistance, contact DynAmp customer support.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 3
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
This Page is Intentionally Blank
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 4
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
3. DESCRIPTION
3.1 APPLICATION
The LKP-8000 Series Replacement Signal Converter Kits permits an economical field
conversion and upgrade of an existing FM system. This conversion makes it possible to
get many of the benefits of the new DynAmp LKP design, while keeping the existing
enclosure, cables, and measuring head.
3.2 SIGNAL CONVERTER RETROFIT KIT
The LKP-8024 Retrofit Kit comes with step-by-step instructions, which affords easy
conversion and minimum time off-line. The kit contains two LKP-8000 modules and a kit of
parts required to complete installation. The modules replace the existing 24FM Metering
Unit modules, and the remaining components are mounted along with existing system
components.
3.3 ELECTRICAL
Four outputs are provided by the system:
1.) A standard voltage output 1mV/kA.
2.) An optional secondary voltage output (typically 1 volt at full scale).
3.) A current output of 1 Adc per 5 kA of bus current - Do not
the system is energized. Maximum allowable voltage drop across the terminals is 15
Vdc at maximum bus current.
4.) A normally closed relay contact for accuracy diagnostics output.
5.) LED indicators for accuracy diagnostics.
open the current loop while
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 5
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
This Page is Intentionally Blank
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 6
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
4. SPECIFICATIONS
TABLE 4.1
LKP-8024 SPECIFICATIONS
Ambient Temperature Range Of
Signal Converter Location
-20°C to 55°C
Humidity (head and signal converter) 85% maximum
AC Line Voltage at 50 or 60 Hz ±5Hz* 120, 240 Vac +10%, -15%
Burden on ac Line (maximum) 20 VA/kA
Maximum Allowable Burden
of Output Circuit
15 volts
Linearity Error ±0.03% of full scale from 5% to
100% of bus current.
Repeatability Error Limits ±0.02% of full scale plus zero error.
Temperature Sensitivity ±0.002%/V@120V ac
Line Voltage Sensitivity ±0.001%/V @ 120V ac
±0.0005%/V @ 240V ac
OUTPUTS
Current output 1 A/5 kA, ±0.5% full scale
Voltage output 1mV per kA of bus current, ±0.1% full scale**
Voltage output 1V at full scale bus current+ 0.1% full scale**
Accuracy Diagnostics Relay Normally closed. 60 VDC @ 2A
or 30 Vrms AC @ 2A
PHYSICAL
Overall Dimensions, in. (mm):
LKP Signal Converter Module
20.5 (521)H x 12.25 (311)W x 7.5 (191)D
Weight, lb. (kg):
Signal Converter Module 13.0 (6.0)
* The LKP systems are factory-set for the correct voltage and frequency (50 or 60 Hz) per customer
order. To operate an LKP system at a different line frequency than was ordered, move jumper JP1
(located on the control board inside each module) to the desired frequency. Refer to the wiring
diagrams for changing the input voltage.
** When calibrated with at DynAmp, LLC factory after retrofit kit installation. May be 0.5% if not
recalibrated. May be 0.2% if calibrated on site with a DynAmp portable measurement system.
When tested at 120 Vac, less than 1 V burden, 24°C ambient.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 7
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
This Page is Intentionally Blank
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 8
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
5. INSTALLATION
5.1 WARNING
These instructions apply only to retrofit kits installed on standard systems as originally
supplied by Halmar Electronics or DynAmp. Customer is responsible to verify that the units
are standard and do not have non-standard, customer modifications installed. Before
installing the upgrade kit, document any modifications and contact DynAmp, LLC Service
Department for further written instructions to deal with the non-standard circumstances.
The installer is responsible for any damages resulting from improper installation of upgrade kit.
5.2 HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
Review plant safety regulations, and make sure that personnel involved are aware of the
hazards involved in working with and around high voltages.
The system should be inspected for shipping damage at the earliest opportunity. Visible
damage must be reported to the carrier immediately. Concealed damage (not evident until
the system is operated) must be reported to DynAmp, LLC immediately.
5.3 EQUIPMENT NEEDED
The following items are included in the LKP-8024 Retrofit Kit
a. 1 each - LKP-8000 High Range Module 1
b. 1 each - LKP-8000 High Range Module 2
c. 1 each - LKP-8024 Installation Parts Kit
Tools Required:
a. Flat blade screwdriver
b. 1 each - Wire strippers
c. 1 each - Digital Multimeter
1 each – OPTIONAL - 1.25 inch hole punch or steel-cutting 1.25 inch hole saw electric
d.
drill and bits
NOTE
The drawings listed in the rear of this manual should be readily available during the
24FM Metering Unit conversion.
5.4 PRELIMINARY PRECAUTIONS
DynAmp, LLC recommends that all work be done on a de-energized bus. If this is not
possible at your location, shut down the mains power to the 24FM, and observe the
WARNINGS and NOTES that follows.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 9
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
WARNING
1.)
An electrical shock hazard exists at the barrier strips, even with the ac line power
removed. To prevent possible personal injury and/or damage to the equipment,
remove all wires from each FM modular unit, one wire at a time, and tape the ends
of each wire.
Disclaimer: These instructions apply only to retrofit kits installed on standard
systems as originally supplied by Halmar Electronics or DynAmp, LLC. Customer is
responsible to verify that the units are standard and do not have non-standard,
customer modifications installed. Before installing the upgrade kit, document any
modifications and contact DynAmp, LLC Service Department for further written
instructions to deal with the non-standard circumstances.
2.)
Disclaimer: Installed is responsible for any damages resulting from improper
installation of upgrade kit.
NOTE
IN THE EVENT THAT WORK IS DONE ON A LIVE BUS, ANY WARRANTY,
EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED MAY BE AFFECTED. CHECK WITH DynAmp, LLC FOR
SPECIFIC DETAILS.
5.5 CONVERSION PROCEDURE
Conversion from the old 24FM Metering System to the new LKP-8024 is described in the
following steps.
Prior to shutting down the old system, record the “As Found” channel voltages for
comparison later to the “After Conversion” voltages.
a. Refer to Assembly Drawing. Observing the WARNING (above), remove all of the old
FM modular units from the enclosure, and install the new LKP-8024 modular units per
drawing.
b. Disconnect (or cut) all wires from transformer TX-1, and cap the ends for safety. The
connections going to the head Hall plate supply terminals should also be removed
and capped.
c. (Optional) Punch hole in enclosure door as shown in LKP-8024 Assembly drawing
Detail “1”. Use care to avoid damaging existing wiring on panel door.
d. Refer to Wiring Diagram. After the LKP-8024 modules are in place, connect wires
shown as dashed lines in wiring diagram.
e. Align wiring on top of existing wiring harness. Use cable ties to secure added wires to
existing harness.
f. If fault alarm indicator will NOT be installed, cut and cap wires routed to “power on”
and fault alarm panel lights.
g. Reconnect the main power to the signal converter, and close the circuit breaker. With
a digital Multimeter or equivalent, monitor the channel voltages on the main terminal
strip to verify correct operation.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 10
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
5.6 INITIAL SYSTEM CHECKOUT
Recheck all wiring connections against the drawings to ensure proper installation. When
they are satisfactory, turn on the system by first closing the external breaker or disconnect
(if used), and then the LKP-8024 circuit breaker. Close the Signal Converter enclosure
door, and confirm that the white POWER lamp is ON.
With the bus energized, the LKP-8024 outputs in use should accurately measure the bus
current. However, it is now necessary to take a complete set of channel voltage readings to
verify that all channels are operating properly. With the bus current operating at its highest
operating level, take two sets of readings, the first set taken immediately (to verify no
condition exists that may cause damage to the LKP-8024), and the second set after a 24hour period of time (to thermally stabilize the head). Proceed as follows:
a. Compare the “After Conversion” channel voltages to the “As Found” voltages. They
should closely match except for heating effects as the head warms up.
b. The dc voltage range may be as high as 75 Vdc. Make certain the voltmeter being
used is set to measure dc volts in this range.
c. The measured bus and all other high current buses in the vicinity (or in the facility)
should be operating at or near their highest levels. Note: All magnetic field sources will
affect the channel voltage readings.
d. Make a photocopy of the “Form for Recording Channel Voltage Measurements” (table
5.2). The initial readings are made as instructed on the form, and are recorded in the
individual blocks, which correspond to channel locations shown for the measuring head.
e. Excluding the effects of external magnetic sources and assuming a bus current of 100
kA, each channel is expected (by calculation) to measure approximately 18 V to 30 Vdc.
In practice, channel readings should be more on the order of 10 V to 30 Vdc, but may
not be achievable. A channel failure will
usually
be indicated by either a full-ff (near
zero), half-on (35-38 V) or full- on (70-75 V) condition.
f. Monitor the green alarm indicator LEDs. All LEDs should be turned on indicating that all
channels are working properly. The fault light is a push-to-test assembly and should
light up when pressed. Continue to monitor the alarm LEDs for proper operation. As
bus current is dropped to a minimum, the alarm relays will click off and one or more
channel LEDs will extinguish (usually this occurs after a few seconds since there is a
short delay designed into the alarm circuit). The fault light should turn on. As the bus
current is increased, the relays should click on and the channel LEDs should turn on.
The fault light should extinguish. Note that at low currents near zero, the channels are
not fully switched on and the alarm LEDs’ status can be arbitrary. The alarm circuit will
operate properly when bus current reaches 500A to 1kA, when channels are balanced.
The alarm relay connection terminals should be checked using an ohmmeter for proper
opening and closure of the contacts and also to ensure that the relays are wired
according to the wiring diagrams and labels.
CAUTION
Avoid operating the unit for an extended time with any channel output over 40 V. This will
permanently damage the system. For voltages over 40 V (only if the unit has an
interconnection cable length greater than 30 feet), consult the factory.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 11
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
NOTES
1.) Low Readings: A very low amplifier output voltage may be normal for certain
channels; however, ripple can be as high as 3 V on a non-operating (full-off) channel.
Thus, a very low reading (i.e., 2 V to 3 V, should be suspected as a possible
problem;
subsequent head movement or other magnetic change may show that the channel is
good. A blown channel fuse can cause a low reading.
2.) High Readings: The maximum allowable channel output of 40 V relates to the
maximum heat dissipation that the channel can safely handle. A reading of 30 V to 40 V
makes a change in head position highly desirable. A reading exceeding 40 V makes a
head position change necessary. A reading of 70-75 V indicates a full-on channel
condition, and requires immediate action to resolve the problem. A reading of 35-38 V
when immediately adjacent channels are significantly different may indicate that one of
the two SCRs in the channel has failed.
NOTE
You cannot get good ohmmeter readings if the head is on a live bus. The coils pick
up induced voltages from any rectifier ripple. The Hall plate resistance changes in a
high magnetic field.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 12
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
TABLE 5.1
MEASURING HEAD RESISTANCE CHART -LKP-8024
Measure Between Leads: Desired Value Circuit
(Ohms)
CABLE TO “1” HALF OF HEAD
25 & 26 25-30 Hall Current - Channels 1, 2. 3
1 & 4 3-6 Hall Signal - Channel #1
5 & 6 3-6 Hall Signal - Channel #2
7 & 10 3-6 Hall Signal - Channel #3
27 & 34 10-12 Coil Circuit - Channel #1
28 & 35 10-12 Coil Circuit - Channel #2
29 & 36 10-12 Coil Circuit - Channel #3
39 & 40 Open Over temperature Thermostat
CABLE TO “2” HALF OF HEAD
25 & 26 25-30 Hall Current - Channels 4, 5, 6
11 & 12 3-6 Hall Signal - Channel #4
13 & 16 3-6 Hall Signal - Channel #5B
17 & 18 3-6 Hall Signal - Channel #6
30 & 34 10-12 Coil Circuit - Channel #4
31 & 35 10-12 Coil Circuit - Channel #5
32 & 36 10-12 Coil Circuit - Channel #6
39 & 40 Open Hall Current - Channels 5B through 1A
NOTES:
1. BUS CURRENT MUST BE ZERO when taking resistance measurements!
2. Use R x 1 ohmmeter scale. Measurements are made between cable leads listed, at Signal Converter
end of Cable and with leads disconnected from TS1.
3. The resistance readings will be slightly higher if the cable is over 30 feet in length. These resistance
readings are the room temperature values of the copper channel coils.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 13
041837 H
Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
TABLE 5.2
FORM FOR RECORDING CHANNEL VOLTAGE MEASUREMENTS
The following table is for the customer's convenience in keeping accurate records on his
unit's performance.
If the channel voltages are measured and recorded at least two hours after the system is
energized has been properly "centered" electrically, the information may prove valuable in
the event of any future malfunction.
It is a good idea to take an additional set of readings at the hottest time of the year,
especially if the equipment is exposed to outdoor temperatures; space is provided for the
recording of three sets of readings. NOTE: Although the channel voltages may vary widely
with temperature extremes, the accuracy will remain unaffected so long as each channel
voltage falls within the limits of +3V to +40Vdc.
Channel voltages are measured between terminals at the Signal converter terminal block
with the LKP meter unit in service on an energized bus.
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Record the channel measurements for every channel (make additional copies of this
form as needed).
2. Supply the information called for below.
CHANNEL VOLTAGES READINGS
FROM
TERMINAL
TS1-
27
28 “ 2
29 “ 3
30 “ 4
31 “ 5
32 “ 6
33 “ 7
34 “ 8
[ ] LOOP BURDEN (TS1 -37 & 38)
[ ] LINE VOLTAGE: (TS1 -52 & 53)
[ ] BUS CURRENT (kA):
TO COMMON
TERMINAL
TS1-35 OR
TS1-36
CHANNEL
NUMBER
1
DATE
____/____/___
_
VOLTS VOLTS VOLTS
DATE
____/____/____
Serial Number: ________________________
DATE
____/____/____
NOTE: The channel voltages should be between +3V and +40Vdc
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 14
041837 H
Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
6. THEORY OF OPERATION
6.1 GENERAL
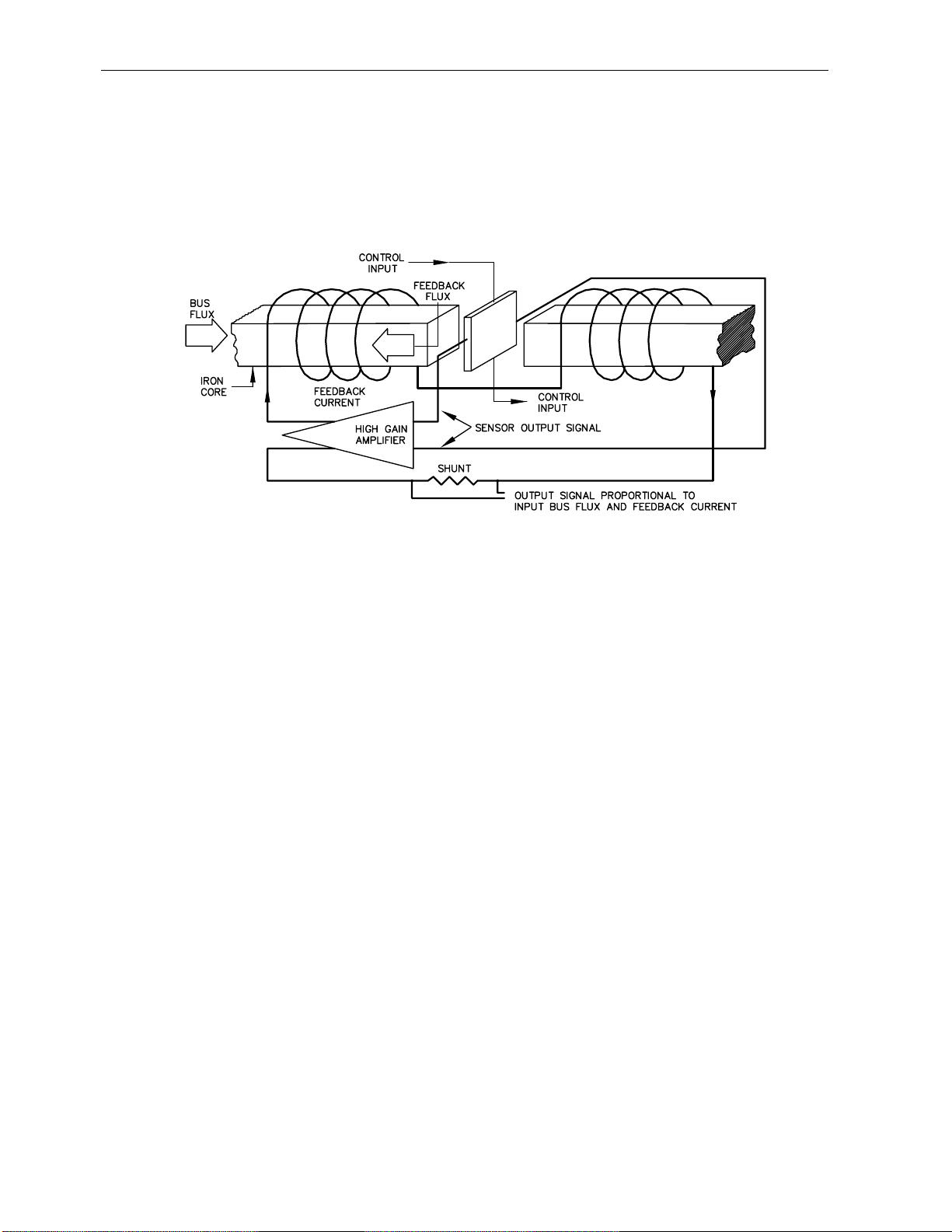
Figure 6.1
Magnetic Null Detector Diagram
A thorough knowledge of the LKP system theory of operation is essential for efficient
troubleshooting. In figure 6.1, a portion of the measuring head is shown to illustrate the
magnetic-null principle used in all Series LKP current measuring equipment.
6.2 MAGNETIC SENSOR (NULL DETECTOR)
The magnetic sensor produces a voltage output proportional to the difference between the
bus field and the feedback field. The sensor output is amplified and is returned to the
magnetic circuit in the form of feedback current. This current is passed through 5000 turns
to produce the feedback field.
The measuring head contains many magnetic sensors and feedback coils. Each set of
sensors and the adjacent coils plus the associated amplifying section of the Signal
converter is termed a channel. Each channel responds nearly independently of the other
channels to null the bus field in its own section of magnetic core. However, after passing
through their respective coil groups, all channel currents are summed to produce the output
current. This current, which is always in the ratio of 1 A to 5000 A of bus current, is passed
through resistors or shunts to develop voltages for the meter and proportional outputs. The
output current itself is also available at the output terminals, which are jumpered if not used.
6.3 SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONS
Effects of stray fields are nullified by joining a number of magnetic assemblies like the one
just described in a closed path around the bus. Figure 6.2 shows four such assemblies
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 15
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
(referred to as a 4-channel assembly). A 4-channel system is used here as an illustration
to simplify the drawing and explanation.
Functional Diagram of Four-Channel System
A magnetic null detector (sensor), high-gain current amplifier, and feedback coil are
combined to form one channel, or current feedback loop. The function of each current loop
(current I
, I2, I3, or I4) is to maintain a state of zero flux in its related segment of the iron
1
core. A burden shunt placed in series with the total current (I
, proportional to It. The common side of the shunt is returned to the four high-gain current
E
o
amplifiers.
Since the bus current is directly proportional to the total current I
bus current can be measured accurately by summing the independent feedback currents (I
+ I2 + I3 + I4). Therefore, the bus current is equal to 5000It. Moving the measuring head
= I
1
with respect to the bus will cause the values of the individual feedback currents to change
but will not affect the total current nor the accuracy of the measurement.
6.4 CIRCUIT FUNCTIONS
For the following discussion refer to the “High Range Module Schematic” and system
schematic drawings as appropriate. These drawings are located in the back of the manual.
Figure 6.2
), develops an output voltage
t
by a ratio of 5000:1, the
t
t
Before discussing the various circuit functions, a general description of the metering unit
will be helpful. A metering unit may consist of one or more modular units. Each modular
unit contains the necessary circuitry for four channels of amplification. The metering unit
also contains one main power transformer, circuit breaker, and the resistors or shunts to
develop output voltages. A 4-channel system is used here as an illustration to simplify the
explanation.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 16
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
Beginning at a magnetic sensor in the measuring head, we can trace the signal path. To
achieve a signal output in the presence of a magnetic field, the sensor (Hall plate) must be
supplied a small exciting current. This current is called the control
approximately 6 mAdc for each sensor. The control current is derived from the 12 Vdc
power supply in the Signal converter. Since the sensor resistance is low (about 200 ohm),
the sensor current is limited by two 1500-ohm resistors (one on each side of the sensor).
These resistors are located in the measuring head.
With a constant dc control current applied to a sensor in the presence of a dc magnetic
field, the sensor output is a dc voltage proportional to the dc field. The sensor output
voltage is conducted via the interconnecting cable to the Signal converter, where it
becomes the signal input.
current (Ic), and it is
6.5 METERING UNIT
Although each modular unit contains only two circuit boards, it is comprised of several subcircuits. Each of these circuits is described in the remaining paragraphs.
6.6 POWER SUPPLIES
The LKP module contains a ±15 Vdc power supply, which powers only the on-board
circuitry. The first module in the meter unit (also referred to as Module “1”) includes a 12
Vdc power supply for the Hall devices.
6.7 SYNC, PLL, AND RAMPS
The Signal converter employs phase locked loop circuitry for synchronization of the firing
pulses of the SCRs. This particularly is an advantage when there is a high noise level
present on the line voltage. The PLL circuitry consists of U101, U102, and associated
circuitry. The line voltage is sensed at TP-4. It is then filtered and sent to U112 to be
converted into a square wave, and then to the PLL circuitry. The output of the PLL is a
square wave and is present at TP-2. This signal is sent to U104, U105, and RP101, which
constitutes the ramp generator. The ramp generator output consists of two downward
sloping ramps, each 180 degrees out of phase from one another. Both ramps are sent to
the quad comparators (U110 and U111), which are used to generate the firing pulses for
the SCRs.
6.8 ERROR AMPLIFIERS
The error amplifier circuitry consists of U106 through U109 and associated circuitry. The
error amplifiers serve two purposes, to amplify the Hall error signal and to filter it before
sending it to the comparators.
6.9 COMPARATORS AND PULSE GENERATOR
The comparators consist of U110 and U111. They compare the amplified and filtered
output of the error amplifiers to the two ramps generated by PLL and ramp generators. Two
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 17
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
square waves are generated at the output of these comparators, one for the positive half
cycle and one for the negative half, (pins 1 and 2 of U110 for channel #1). One square
wave will be used to trigger an SCR on the positive half of the waveform, and the other will
be used for the other half cycle. Since these square waves are too long in duration, they
cannot be used directly to drive the pulse transformer drivers. The comparator output is
"ANDed" (the mathematical product of a logic AND gate) with several pulses generated by
the PLL. The output, (pins 3 and 4 on U113 for channel #1) will be a pulse train which will
be used to drive the pulse transformer drivers. Pulse train triggering is an advantage when
noise on the line turns off an SCR. The SCR is retriggered allowing a minimum off time.
Since these pulses are fixed and do not move, if they alone were used to drive the SCRs,
the output would be very jumpy. This was smoothed by also ANDing the comparator with
an integrated output of itself to give the output pulse train infinite resolution.
6.10 PULSE TRANSFORMER DRIVERS
The pulse transformer drivers consist of U203, U204, and associated circuitry. A pulse
train signal is sent into the drivers (pin 2 and 1 of U203 for channel #1). These drivers are
open collector outputs, which drive the pulse transformers (T203A and T203B for channel
1). The secondary of the pulse transformer develops a current pulse which drives the
associated SCRs (SCR pack #1 for channel #1).
6.11 ACCURACY DIAGNOSTICS
“ACCURACY DIAGNOSTICS” (AD) is a system that assures the user that most internal
circuits are operating properly and it is also a diagnostic tool. It is made up of a number of
circuits, monitoring conditions of many of the critical components, circuits and connections
within the current monitoring system. The AD subsystem provides relay contacts for the
user to connect to his remote warning indicator. The AD diagnostic light emitting diodes
on each meter unit module indicates proper operation of associated circuits. On some
larger systems a red warning light mounted on the enclosure door provides a simple visual
warning (refer to wiring diagram for this feature).
The AD indicates the feedback circuits are functioning properly and the system’s power
supplies are within specifications. More specifically, this indicates the following conditions
exist:
1. All channels have a core magnetic flux null:
a. All components in the circuits appear to be operating normally.
b. Input fields are of the expected polarity.
c. Input magnetic flux appears balanced by feedback flux.
2. Power supplies are operating within acceptable ranges.
a. Mains input power is on.
b. Hall plate sensor power supply output is correct.
With unidirectional LKP measurement systems, it is possible that the AD circuits will give a
warning indication when the system is operated at low rectifier current level, even though all
circuits and components are functioning properly. This warning at low levels is most likely
to occur if the metering system is associated with one of several rectifiers in the area.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 18
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
The AD outputs indicate the present condition, having only a short time delay from an
instantaneous condition. Although the AD does not monitor every possible error condition,
it is an effective means of giving the user continual assurance of signal reliability.
A.) If the “Diagnostics Relay” is O.K. and the green LED indicators are all on: Continue
operating normally.
B.) If the “Diagnostics Relay” indicates a warning and one or more green indicators are
off:
This indicates there may be measurement errors. Consequently the metering system
should not be in full, automatic control of the rectifier. The AD relay contact output is not
intended to be the only monitor protecting the power rectifiers. Primarily, it is expected that
the customer wants to take immediate action to prevent unsafe operation. Unsafe
operation could result if the metering system is in the rectifier control loop and it
erroneously produces a significantly lower output than is true. This might cause the
rectifier control circuit to inappropriately increase the power output, perhaps to overload
levels for either the power supply or the process. So, if the metering system is in the
control loop and the “Accuracy Diagnostics” indicates a potential problem, the following
actions are recommended: FIRST- Lock out control actions that could drive the rectifier
output higher and SECOND-alert the operator.
Basically, each module inside the metering unit has four channel LEDs and 2 power supply
monitoring LEDs. The following is a description of their functionality:
A.) Line: This LED indicates whether the supply voltage to the meter unit falls within the
specified limit of +10%, -15% of nominal. Significant changes from these values will
cause this LED to turn off and trip the relay.
B.) Hall P.S.: This LED indicates whether the Hall plate supply voltage supply voltages fall
with the specified operating limits. A failed Hall plate power supply or a line voltage out
of specification will extinguish this LED and trip the relay.
C.) Channel LEDs: Each channel LED indicates the status of the corresponding channel to
aid quick troubleshooting. An extinguished channel LED can be caused by the
following:
a. A blown channel fuse;
b. a bad connection between the cable and the metering unit or cable and measuring
head;
c. a bad Hall device in the head;
d. an open /or shorted coil in the head;
e. a primary current that exceeds the dynamic measuring range of the metering unit;
f. the primary current is too low to activate all channels properly;
g. a strong external magnetic field causing a channel reversal.
Notes on items f and g above:
1.) Under certain conditions, external magnetic fields can reverse one or more
channels in the head. The accuracy indicators will show an error in those channels
until the bus current level rises high enough to effectively turn on all channels (23Vdc is the minimum reliable channel voltage). This condition can cause false
alarms. For more information on this, please refer to technical bulletin TEC9908,
“Resolving External Magnetic Field Errors”.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 19
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
2.) In some installations, when the channel voltages are balanced, the channel LEDs
will remain on, even though the bus is turned down to zero. In this case, the
accuracy diagnostics circuit is in an unstable condition and alarm faults, as indicated
by the channel LEDs, should be ignored. Note that, in general, the metering unit’s
0.1% accuracy is only guaranteed when the primary bus current is above 5% of the
full scale rating of the unit.
A relay contact output is available to connect to a remote warning system. The relay is
closed under normal operating conditions and opens when a fault condition occurs. The
output connections are available via Terminal Strip TS1 (see appropriate interconnection
diagram for location).
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 20
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
7. MAINTENANCE & SPARE PARTS
7.1 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
As is true with any electronic circuitry, proper maintenance will prolong the service life.
DynAmp, LLC recommends the following program be performed at the recommended
interval to prevent or detect damage to the LKP system and to ensure continuing highaccuracy performance. Always use appropriate measures to correct any problems found.
Following the suggested maintenance schedule may assist in early diagnosis of problem(s)
to minimize repairs and down time.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Keep organized, accurate recorded data (forms, etc.) from each Periodic
Maintenance. This information may be invaluable in troubleshooting a malfunctioning
LKP system.
7.2 ANNUAL MAINTENANCE
Perform the following steps at least once per year. If LKP system equipment is exposed to
outdoor temperatures, DynAmp, LLC recommends these steps be performed during the
hottest time of the year.
The following procedures should be performed at the recommended interval to prevent or
detect damage to the LKP system and to ensure continuing high-accuracy performance.
Use appropriate measures to correct any problems found.
A.) Repeat voltage measurements given in "Magnetic Centering" procedure to ensure that
no significant change has occurred from the data recorded at startup. A large change in
the amplifier output voltage of a given channel (compared to other channels) may
indicate trouble in the channel. If all channels change proportionally, then that might
indicate a change in the bus current. Remember that channel voltages will vary slightly
depending on the ambient temperature of the head.
B.) Measure and record the Hall device dc power supply voltage.
C.) Visually inspect measuring head and interconnection cable for evidence of severe
overheating, excessive corrosion, or possible leaks in the RTV rubber seal around the
aperture. Record any suspect conditions.
D.) Visually inspect Signal converter and signal converter(s) for evidence of severe
overheating, or excessive corrosion. Record any suspect conditions and take
appropriate action.
E.) Clean the following items:
1.) Cables and external surfaces of measuring head and Signal converter:
2.) Clean as necessary; remove any oil or grease with a mild detergent or cleaner
solvent. Do not use strong chemical solvents as they may damage the cables or
erase the silk-screening from the Signal converter.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 21
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
Signal converter interior (should only be performed after disconnecting power to the
Signal converter): Dust and dirt can be removed by gently vacuum cleaning the
unit. Be careful not damage the internal shunt. Solvents should never be used on
any of the PC boards. The boards are coated with a protective conformal coating,
which can be stripped away by certain solvents.
F.) Check the electrolytic filter capacitors for seals that have been popped (degassed), are
leaking electrolytic fluid or have excessive bulging. Contact DynAmp for repair options.
G.) If the unit is equipped with a cooling fan and filter, then the filter should be cleaned or
replaced according to the manufacturer instructions.
CAUTION
To avoid the risk of shock and electrocution, always disconnect the AC power and
head cables from the head before performing any cleaning or service operation on the
Signal converter.
Disconnect power to the system before servicing or replacing fuses.
7.3 CALIBRATION INTERVALS
DynAmp does not specify required intervals of calibration for its products.
The end user of the product is responsible for identifying the appropriate interval between
calibrations. The intervals should be determined based on the following factors:
•
Requirements of a Quality Management System
•
Accuracy and permissible limits of errors
•
Purpose and usage
•
Experience with similar products
•
Manufacturer's recommendations
•
Stability of the product
•
Past history
•
Other characteristics of the product
Reference: "ISO/IEC 17025:2005, General requirements for the competence of testing and
calibration laboratories" and Laboratory Accreditation Bureau "Guidance for Documenting
and Implementing ISO/IEC 17025:2005 and Laboratory Guidance."
As a guideline, DynAmp recommends a 24-month interval of calibration for all permanently
installed products and a 12-month interval of calibration for all products used in portable
applications.
7.4 SPARE PARTS ORDERS - ROUTINE OR EMERGENCY
Requests for spare parts should be directed to "Service" at DynAmp, LLC during normal
hours. When contacting us, please present as much information as possible - the related
equipment Model and Serial Numbers (available on the equipment tag); the required part
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 22
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
name; its DynAmp, LLC item number (and other identifying or vendor number(s); and your
time needs. An approved Purchase Order Number should be given with your order.
7.5 RECOMMENDED SPARE PARTS
The following table lists the minimum recommended quantities* for spare parts for the LKP
meter unit. As spares are used, replacements should be ordered. Since continuous
operation of high-current measurement systems is usually critical, stocking spare parts
should be given high priority.
TABLE 7.1
SPARE PARTS LIST*
DESCRIPTION ITEM NO. QTY
Signal converter
Kit, Spare Parts, LKP-8024 43808 1
Kit includes Module, Power supply, lamps & fuses as one package.
Module, LKP (4) channel electronics 41350 1
Power Supply 12V 19658 1
Bulb, “Fault” light 42405 1
Bulb, POWER ON light 26673 2
**Fuse, MDA1 Slo-blo (AC Primary) 12590 1 box
**Fuse, MDA3 Slo-blo (5 per box) Ch 1, 2, 3,4, 5, 6 12591 2 box
PC Board Assembly, Accuracy Diagnostics 40355 1
PC Board Assembly, Accuracy Diagnostics, (2) channel 40402 1
* For one to five units, stock the quantities shown. For six or more units, a complete system
(Head, cable, and Signal converter) should be kept on hand.
** All Fuses are Time lag MDA style (3AB) ¼” by 1 ¼” (6.3 mm x 32mm), 250 Volt
Disconnect power to the system before servicing or replacing fuses.
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 23
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
7.6 SERVICE ASSISTANCE
For further assistance, contact DynAmp Customer Support at:
Americas:
Telephone: +1 614.871.6900 Fax: +1 614.871.6910
8:00 AM to 5:00 PM USA Eastern Time
From first Sunday in November to second Sunday in March – 13:00 GMT to 22:00 GMT
From second Sunday in March to first Sunday in November – 12:00 GMT to 21:00 GMT
Europe:
Telephone: +41 22.706.1446 Fax: +41 22.706.1311
8:30 AM to 5:00 PM Central European Time
From last Sunday in October to last Sunday in March – 7:30 GMT to 16:00 GMT
From last Sunday in March to last Sunday in October – 6:30 GMT to 15:00 GMT
After Hours Critical Service Emergency:
Telephone: +1 614.871.6906
5:00 PM to 8:00 AM USA Eastern Time
From first Sunday in November to second Sunday in March – 22:00 GMT to 13:00 GMT
From second Sunday in March to first Sunday in November – 21:00 GMT to 12:00 GMT
Central e-mail:
help@dynamp.com
DynAmp web:
www.dynamp.com
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 24
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
8. RELATED TECHNICAL BULLETINS
The following is a list of available technical bulletins that contain relevant information in
regards to high current measurements and the use of LKP systems. The technical bulletins
are available upon request from DynAmp, LLC. Always consult the factory for a list of the
latest technical bulletins.
TABLE 8.1
TECHNICAL BULLETINS LIST
Number Subject Title / Description
9908 External Fields Resolving External Magnetic Field Errors (replaces
TEC727)
9907 LKP/ LKB LKP and LKB Sensor Mounting Guidelines and
Restrictions
9905 LKP/ LKB Recommended Calibration Intervals for LKP or LKB High
Current Systems
9904 Diagnostics Self Diagnostics for DynAmp High Current Measurement
systems (Accuracy Diagnostics)
987 LKP/ LKB Ferromagnetic Materials near LKP or LKB High Current
Measurement Systems
749 Bus Analysis Computer Analysis of Measuring Head Locations In High
Current Measurement systems
748 LKP/ LKB Guidelines for locations of LKP or LKB High Current
Systems Heads on Busses
747 kWH Volt-hours times Ampere-Hours is NOT equal to Watt-
hours
941 Bus Analysis Data required for Bus Analysis of High Current
Measurement Systems
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 25
041837 H

Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
This Page is Intentionally Blank
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 26
041837 H
Installation, Operation and Service Manual LKP Series
9. DRAWINGS
TABLE 9.1
DRAWING LIST
DRAWING TITLE NUMBER
Schematic: LKP-8024 Power Input 05B108413
Schematic: LKP High Range Module 05B108074
Schematic: CM 4CH Alarm PC Board 05A107144
Schematic: CM 2CH Alarm PC Board 05A107147
Schematic: LKP-8024 Calibration Network 05B108412
Assembly: LKP-8024 Retrofit 84B108417
Assembly: Control PC Board 75A108104
Assembly: Supply & SCR Drive 75B108106
Assembly: Accuracy Diagnostics 07A109083
Assembly CM 4 Ch Alarm PC Board 26A107145
Assembly CM 2 Ch Alarm PC Board 26A107146
Interconnection: LKP-8024 Metering System 02B108418
Wiring Diagram: LKP Module 83C108030
Wiring Diagram: LKP-8024 83B108414
Wiring Diagram: LKP-8000 To FM Conversion - High Range 83B108232
Outline & Mounting, Module “1” 02D108221
Outline & Mounting, Module “2” 02D108222
© 2011 DynAmp, LLC Page 27
041837 H
 Loading...
Loading...