
D
Dyy
n
naa
m
miixx
D
D
W
W--0011//
H
H
D
Dyy
n
naa
m
miixx
D
D
W
W--0022//
H
H
D
Dyy
n
naa
m
miixx
D
D
W
W--0044//
H
H
UUsseerr M
Maannuuaall

Table of Contents
TABLE OF CONTENTS ...................................................................................................................II
LIST OF FIGURES..........................................................................................................................V
LIST OF TABLE .........................................................................................................................VIII
PREFACE .................................................................................................................................... IX
VOIP GATEWAY OVERVIEW ...................................................................................................1
CHAPTER 1 VOIP GATE WA Y OVERVIEW .......................................................................................2
1.1 VoIP Gateway Overview....................................................................................................2
1.2 Features of The VoIP Gateway ..........................................................................................2
1.3 Default Settings..................................................................................................................3
1.4 Front Panels ......................................................................................................................3
1.5 Back Panel Ports ...............................................................................................................4
1.6 Hardware Specifications....................................................................................................4
1.7 Additional Installation Requirements ................................................................................9
1.8 Setting Up the TCP/IP Protocol ........................................................................................9
1.9 Power Up Your VoIP Gateway .........................................................................................10
WEB CONFIGURATION WITH VOIP GATEWAY ..............................................................12
CHAPTER 2 WEB CONFIGURATION WITH FXS INTRODUCTION ...................................................13
2.1 Web Configuration with FXS Overview...........................................................................13
2.2 Accessing the Web Configuration ....................................................................................13
2.3 Login and welcome screen...............................................................................................13
2.4 Welcome Screen ...............................................................................................................13
2.5 Saving Your Configuration ..............................................................................................15
2.6 Navigating the Web Configuration ..................................................................................16
CHAPTER 3 INITIAL CONFIGURATION..........................................................................................17
3.1 Initial Configuration Overview .......................................................................................17
3.2 General Configuration ....................................................................................................17
3.3 Static IP address ..............................................................................................................17
3.4 DHCP mode.....................................................................................................................19
3.5 PPPoE mode....................................................................................................................20
3.6 IP Sharing Configuration ................................................................................................22
3.7 PPPoE (NAT) mode (1A-FXS).........................................................................................24
CHAPTER 4 MAKING A VOIP CALL.............................................................................................27
4.1 Configure the gateway into the Peer-to-Peer mode ........................................................27
4.2 Configure the gateway into the GK routed mode ............................................................30
CHAPTER 5 UPGRADE ROM VERSION........................................................................................33
5.1 Before you start downloading..........................................................................................33
Table of Connect
II

5.2 Update Application Version .............................................................................................33
5.3 Update Boot2m Version ...................................................................................................35
CHAPTER 6 NETWORK INTERFACE SCREEN ................................................................................39
6.1 Network Interface Overview............................................................................................39
6.2 Network Interface Screen.................................................................................................39
CHAPTER 7 H323 CONFIGURATION SCREEN ...............................................................................42
7.1 H323 Configuration Overview ........................................................................................42
7.2 H323 Configuration Screen.............................................................................................42
CHAPTER 8 LINE CONFIGURATION SCREEN ................................................................................45
8.1 Line Configuration Overview ..........................................................................................45
8.2 Line Configuration Screen...............................................................................................45
CHAPTER 9 PHONE BOOK CONFIGURATION SCREEN...................................................................47
9.1 Phone Book Configuration Overview..............................................................................47
9.2 Phone Book Configuration Screen ..................................................................................47
CHAPTER 10 SUPPORT CONFIGURATION SCREEN........................................................................49
10.1 Support Configuration Overview...................................................................................49
10.2 Support Configuration Screen .......................................................................................49
CHAPTER 11 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION SCREEN .........................................................................51
11.1 System Configuration Overview ....................................................................................51
11.2 System Configuration Screen .........................................................................................51
CHAPTER 12 VOICE CONFIGURATION SCREEN ............................................................................53
12.1 Voice Configuration Overview.......................................................................................53
12.2 Voice Configuration Screen ...........................................................................................53
C
HAPTER 13 PHONE CONFIGURATION SCREEN ...........................................................................55
13.1 Phone Configuration Overview .....................................................................................55
13.2 Phone Configuration Screen..........................................................................................55
CHAPTER 14 RTP PAY LO A D TYPE CONFIGURATION SCREEN ......................................................57
14.1 RTP Payload Type Configuration Overview .................................................................57
14.2 RTP Payload Type Configuration Screen......................................................................57
C
HAPTER 15 IP PACKET TOS CONFIGURATION SCREEN .............................................................59
15.1 IP Packet ToS Overview.................................................................................................59
15.2 IP Packet ToS Configuration Screen .............................................................................59
CHAPTER 16 DDNS DEVICE CONFIGURATION SCREEN ..............................................................61
16.1 DDNS Device Configuration Overview.........................................................................61
16.2 DDNS Device Configuration Screen .............................................................................61
CHAPTER 17 PREFIX DROP/INSERT CONFIGURATION SCREEN.....................................................63
17.1 Prefix Drop/Insert Configuration Overview ..................................................................63
17.2 Prefix Drop/Insert Configuration Screen ......................................................................63
Table of Connect
III

CHAPTER 18 PASSWORD CONFIGURATION SCREEN.....................................................................65
18.1 Password Configuration Overview................................................................................65
18.2 Password Configuration Screen ....................................................................................65
CHAPTER 19 VERSION AND INFORMATION SCREEN ....................................................................67
19.1 Version and Information Overview................................................................................67
19.2 Version and Information Screen ....................................................................................67
CHAPTER 20 ROM UPGRADE SCREEN .......................................................................................68
20.1 ROM Configuration Overview.......................................................................................68
20.2 ROM Configuration Screen ...........................................................................................68
CHAPTER 21 FLASH CLEAN SCREEN...........................................................................................70
21.1 Flash Clean Overview ...................................................................................................70
21.2 Flash Clean Screen........................................................................................................70
CHAPTER 22 COMMIT DATA SCREEN ..........................................................................................71
22.1 Commit Configuration Data Overview..........................................................................71
22.2 Commit Configuration Data Screen ..............................................................................71
CHAPTER 23 REBOOT SYSTEM SCREEN ......................................................................................72
23.1 Reboot VoIP Gateway Overview....................................................................................72
23.2 Reboot VoIP Gateway Screen ........................................................................................72
COMMAND WITH VOIP GATEWAY .....................................................................................73
CHAPTER 24 COMMAND LIST .....................................................................................................74
24.1 Hyper Terminal Setting..................................................................................................74
24.2 Power Up Your Gateway ...............................................................................................75
24.3 Command Structure with Gateway ................................................................................77
24.4 Application modes .........................................................................................................78
24.5 How to upgrade .............................................................................................................89
24.6 Commands with Gateway ..............................................................................................92
24.7 System Commands Overview.........................................................................................93
Table of Connect
IV

List of Figures
Figure 1-1 Dynamix DW-01/H Gateway Front Panel .........................................................4
Figure 1-3 Dynamix DW-02/H Gateway Front Panel .........................................................4
Figure 1-4 Dynamix DW-04/H Gateway Front Panel .........................................................4
Figure 1-5 Dynamix DW-01/H Gateway Back Panel Ports ................................................4
Figure 1-7 Dynamix DW-02/H Gateway Back Panel Ports ................................................4
Figure 1-8 Dynamix DW-04/H Gateway Back Panel Ports ................................................4
Figure 2-2 VoIP Gateway web configuration welcome screen..........................................14
Figure 2-3 Network Interface Screen ................................................................................16
Figure 3-1 Network Interface ............................................................................................18
Figure 3-2 Commit Configuration Data ............................................................................18
Figure 3-3 Reboot VoIP Gateway ......................................................................................19
Figure 3-4 Network Interface ............................................................................................20
Figure 3-5 PPPoE Device Configuration...........................................................................21
Figure 3-6 Enable the IP sharing function.........................................................................24
Figure 3-7 PPPoE Device Configuration...........................................................................25
Figure 4-1 H323 Configuration – Peer to Peer mode Screen ............................................28
Figure 4-2 Phone Book......................................................................................................28
Figure 4-3 Phone Book – New Record..............................................................................29
Figure 4-4 Phone Book......................................................................................................29
Figure 4-5 Configure the GK info .....................................................................................31
Figure 5-1 ROM Configuration.........................................................................................33
Figure 5-2 ROM File Upgrade ok .....................................................................................34
Figure 5-3 Flash Clean ......................................................................................................34
Figure 5-4 Flash Clean OK................................................................................................35
Figure 5-5 ROM File Upgrade ok .....................................................................................36
Figure 5-6 Flash Clean ......................................................................................................37
Figure 5-7 Flash Clean OK................................................................................................37
Figure 6-1 Network Interface ............................................................................................40
Figure 7-1 H323 Configuration .........................................................................................43
Figure 8-1 Line Configuration Information.......................................................................45
Figure 9-1 Phone Book......................................................................................................47
Figure 10-1 Support Configuration ...................................................................................49
Figure 11-1 System Configuration ....................................................................................51
Figure 12-1 Voice Configuration.......................................................................................53
Figure 13-1 Phone Configuration ......................................................................................55
Figure 14-1 RTP Payload Type Configuration ..................................................................57
Figure 15-1 IP Packet ToS Configuration..........................................................................59
List of Figure
V

Figure 16-1 DDNS Device Configuration.........................................................................61
Figure 17-1 Prefix Drop/Insert Configuration...................................................................63
Figure 18-1 Password Configuration.................................................................................65
Figure 19-1 Version and Information ................................................................................67
Figure 20-1 ROM Configuration.......................................................................................68
Figure 21-1 Flash Clean ....................................................................................................70
Figure 22-1 Commit Configuration Data ..........................................................................71
Figure 23-1 Reboot VoIP Gateway ....................................................................................72
Figure 24-1 Connection Description .................................................................................74
Figure 24-2 Connection Description .................................................................................74
Figure 24-3 Connect To .....................................................................................................75
Figure 24-4 Com Properties ..............................................................................................75
Figure 24-5 Initial Screen ..................................................................................................76
Figure 24-6 Login Screen ..................................................................................................77
Figure 24-7 password –set command ................................................................................77
Figure 24-8 quit commend ................................................................................................94
Figure 24-9 debug commend list .......................................................................................94
Figure 24-10 debug –status commend...............................................................................95
Figure 24-11 reboot commend...........................................................................................95
Figure 24-12 flash commend list .......................................................................................96
Figure 24-13 flash –clean commend .................................................................................97
Figure 24-14 commit commend ........................................................................................97
Figure 24-15 ifaddr commend list .....................................................................................98
Figure 24-16 ifaddr –print command...............................................................................100
Figure 24-17 time commend list......................................................................................100
Figure 24-18 ping commend list......................................................................................101
Figure 24-19 sysconf commend list.................................................................................102
Figure 24-20 sysconf -print commend.............................................................................103
Figure 24-21 h323 commend list.....................................................................................105
Figure 24-22 h323 -print commend (Gatekeeper mode) .................................................107
Figure 24-23 h323 -print commend (Peer to Peer mode)................................................107
Figure 24-24 line commend list.......................................................................................108
Figure 24-25 line -print commend...................................................................................109
Figure 24-26 prefix commend list ...................................................................................109
Figure 24-27 prefix –print commend...............................................................................110
Figure 24-28 pbook commend list...................................................................................111
Figure 24-29 pbook -print commend...............................................................................112
Figure 24-30 voice commend list ....................................................................................114
List of Figure
VI

Figure 24-31 voice –print commend ...............................................................................115
Figure 24-32 support commend list.................................................................................116
Figure 24-33 support –print commend ............................................................................117
Figure 24-34 sysinfo commend list .................................................................................118
Figure 24-35 phone commend list ...................................................................................119
Figure 24-36 phone –print rbt commend.........................................................................120
Figure 24-37 phone –print rbt commend.........................................................................120
Figure 24-38 phone –print bt commend ..........................................................................121
Figure 24-39 phone –print dt commend ..........................................................................121
Figure 24-40 phone –print flash commend......................................................................121
Figure 24-41 tos commend list ........................................................................................122
Figure 24-42 tos -print commend ....................................................................................122
Figure 24-43 ddns commend list .....................................................................................123
Figure 24-44 ddns -print commend .................................................................................124
Figure 24-45 pt commend List ........................................................................................125
Figure 24-46 pt -print commend......................................................................................125
Figure 24-47 rom commend List .....................................................................................126
Figure 24-48 rom –print commend..................................................................................126
Figure 24-49 passwd commend List................................................................................127
Figure 24-50 passwd –set commend ...............................................................................127
Figure 24-51 passwd –clean commend ...........................................................................127
List of Figure
VII

List of Table
Table 1-1 Dynamix DW-01/H LEDs Descriptions..............................................................4
Table 1-3 Dynamix DW-02/H LEDs Functions ..................................................................5
Table 1-4 LEDs Functions ...................................................................................................6
Table 2-1 Navigation Panel Links .....................................................................................14
Table 6-1 Network Interface ..............................................................................................40
Table 7-1 H323 Configuration...........................................................................................43
Table 8-1 Line Status Information.....................................................................................45
Table 9-1 Phone Book .......................................................................................................47
Table 10-1 Support Configuration .....................................................................................49
Table 11-1 System Configuration......................................................................................51
Table 12-1 Voice Configuration.........................................................................................53
Table 13-1 Phone Configuration........................................................................................55
Table 14-1 RTP Payload Type Configuration List.............................................................57
Table 15-1 IP Packet ToS Configuration ...........................................................................59
Table 16-1 DDNS Device Configuration ..........................................................................61
Table 17-1 Prefix Drop/Insert Configuration ....................................................................63
Table 18-1 Password Configuration ..................................................................................65
Table 19-1 Version and Information ..................................................................................67
Table 20-1 ROM Configuration.........................................................................................68
Table 21-1 Flash Clean ......................................................................................................70
Table 22-1 Commit Configuration Data ............................................................................71
Table 23-1 Reboot VoIP Gateway......................................................................................72
Table 24-1 Commands with Gateway................................................................................93
List of Table
VIII

Preface
Congratulations on your purchase of the VoIP Gateway.
About this User’s Manual
This user’s guide gives hardware specifications and explains web configuration and
command line configuration for the Dynamix DW-01/H, Dynamix DW-02/H, and Dynamix
DW-04/H.
General Syntax Conventions
Mouse action sequences are denoted using a comma. For example, click start, Settings,
Control Panel, Network means first you click Start, Click or move the mouse pointer over
Settings the click or move the mouse pointer over Control Panel and finally click (or
double-click) Network.
“Enter” means for your to type one or more characters.
Naming Conventions
“Dynamix DW-01/H” Gateway provides one Phone port and four Ethernet Port.
“Dynamix DW-02/H” Gateway provides two Phone port and two Ethernet Port.
“Dynamix DW-04/H” Gateway provides four Phone port and two Ethernet Port.
Related Documentation
This user’s guide provides hardware connection details and configuration and
management instruction for the managements VoIP Gateway.
IX

:
Part I:
VoIP Gateway Overview
This part introduces the general features default settings and hardware of the VoIP Gateway.
- 1 -

Chapter 1
VoIP Gateway Overview
The chapter introduces the VoIP Gateway general feature, factory default settings and hardware.
1.1 VoIP Gateway Overview
VoIP Gateway, which based on ITU-T H.323 v3, provides voice and fax over IP networks. Its
simplified operation and configuration features are the most suitable for residential and SOHO
application. There are four models for VoIP Gateway, which are Dynamix DW-01/H, Dynamix
DW-02/H, and Dynamix DW-04/H. One more added switch hub for A series is the only
difference. User can choose 2 ports or 4 ports as request in A series. Just an IP address and 2/4
phone sets bring you to Voice over IP world.
1.2 Features of The VoIP Gateway
VoIP Gateway Features
ITU-T H.323 v4 compliance
Ethernet:
Dynamix DW-01/H: Four 10/100 Base-T Ethernet RJ45 ports (Auto LAN MDI/
MDIX).
Dynamix DW-02/H /Dynamix DW-04/H: Two 10/100 Base-T Ethernet ports
Configuration interface: RS-232, TELNET and HTTP web management
Automatic Gatekeeper Discovery
Dimensions:
Dynamix DW-01/H: 165(W) x 29(H) x 139mm(D)
Dynamix DW-02/H/Dynamix DW-04/H: 222(W) x 34(H) x 143mm(D)
Transmit Voice and T.38 fax simultaneously
Support T.38 ECM function (Error Correction in high speed fax Mode)
Provides call progress tone
E.164 Common Dial Plan
DTMF Dialing
Inband/Outband DTMF
TFTP/FTP software upgrade
Remote configuration/reset
LED indication for system status
Support Static IP, DHCP and PPPoE
Set the ring back tone from the IP or local
FAX redundancy support
RAS and Signal port exchangeable
GK id support and GK auto discovery
- 2 -

Audio feature
Codec: G.711 a/µlaw, G.723.1 (6.3kbps), G.729A, G.729B, G.729AB
VAD (Voice Activity Detection)
CNG (Comfort Noise Generate)
G.168/165-compliant adaptive echo cancellation
Dynamic Jitter Buffer
Bad Frame Interpolation
Voice/DTMF Gain Settings
Generate Caller ID (DTMF or FSK)
Provide In-band or Out-band DTMF generation/detection
Provide Progress tone
System Monitoring
System status (Link, Ready, Status, TEL, Power).
Remote Firmware Upgrade
You can use FTP/TFTP to perform configuration backup/restore and firmware upgrade for
the VoIP Gateway from a remote location.
Security
Password protection for system management
VLAN
1.3 Default Settings
The following are the settings of the defualt profile
Login: root
Password: Null (default)
1.3.1 IP Parameters
IP Address = 10.1.1.3
Subnet mask = 255.0.0.0
Default gateway = 10.1.1.254
LAN IP address = 192.168.123.123 (Only Dynamix DW-01/H)
1.3.2 Telnet and Web Login Password
Login = root
Password = Null (default)
1.4 Front Panels
The LEDs on the front panel indicate the operational status of the Gateway.
- 3 -

Figure 1-1 Dynamix DW-01/H Gateway Front Panel
The LEDs on the front panel indicate the operational status of the Gateway.
Figure 1-2 Dynamix DW-02/H Gateway Front Panel
Figure 1-3 Dynamix DW-04/H Gateway Front Panel
1.5 Back Panel Ports
Figure 1-4 Dynamix DW-01/H Gateway Back Panel Ports
Figure 1-5 Dynamix DW-02/H Gateway Back Panel Ports
Figure 1-6 Dynamix DW-04/H Gateway Back Panel Ports
1.6 Hardware Specifications
These are the hardware details of the Dynamix DW-02/H, Dynamix DW-04/H.
1.6.1 Dynamix DW-01/H LEDs
The following table describes the LED functions:
Table 1-1 Dynamix DW-01/H LEDs Descriptions
LEDs Functions Indicator
Status
Active Description
Power Power Green On The Power adapter is connected to the
Gateway.
Off The system is off or not receiving power.
TEL TEL Red On The Telephone is Off-Hook.
- 4 -

LEDs Functions Indicator
Status
Active Description
Off The Telephone is On-Hook.
Ready Ready Green Slow
Blinking
The VoIP Gateway is in normal mode.
Fast Blinking The VoIP Gateway is in downloading
mode.
Status Status Green Off The VoIP Gateway is in Peer-to-Peer
Mode.
On The VoIP Gateway has successfully
registered to Gatekeeper when it is in
Gatekeeper mode.
Blinking The VoIP Gateway is not registered to
Gatekeeper when it is in Gatekeeper
mode.
The VoIP Gateway is in downloading
mode.
Active Blinking Ethernet data is being
transmitted/received.
100/10 LAN Green On The 100M LAN is connected.
Off The 10M LAN is connected.
Link LAN Green On The VoIP Gateway is physically
connected to the Ethernet correctly.
Full/HLF
DPX
Full/HLF
DPX
Green On Light on means current transmitting
mode is full duplex.
Off Light off means half-duplex.
1.6.2 Dynamix DW-02/H LEDs
The following table describes the LED functions:
Table 1-2 Dynamix DW-02/H LEDs Functions
LEDs Functions Indicator
Status
Active Description
LAN Switch to another device, such as PC
Link/ACT Link/ACT Green Blinking While plugging on the Ethernet cable, it
must light on and the flash if some data is
being TX/RX.
OFF The Ethernet cable is not connected.
10/100M LAN Green Off The 10M LAN is connected.
- 5 -

LEDs Functions Indicator
Status
Active Description
On The 100M LAN is connected.
WAN Uplink to the HUB/Router directly.
Link/ACT Link/ACT Green Blinking While plugging on the Ethernet cable, it
must light on and the flash if some data is
being TX/RX.
OFF The Ethernet cable is not connected.
10/100M WAN Green Off The 10M WAN is connected.
On The 100M WAN is connected.
Ready Ready Green Slow
Blinking
The VoIP Gateway is in normal mode.
Fast Blinking The VoIP Gateway is in downloading
mode.
Status Status Green Off The VoIP Gateway is in Peer-to-Peer
Mode.
On The VoIP Gateway has successfully
registered to Gatekeeper when it is in
Gatekeeper mode.
Blinking The VoIP Gateway is not registered to
Gatekeeper when it is in Gatekeeper
mode.
The VoIP Gateway is in downloading
mode.
TEL(1-2) TEL Red On The Telephone is Off-Hook.
Off The Telephone is On-Hook.
Power Power Green On The Power adapter is connected to the
Gateway.
Off The system is off or not receiving power.
1.6.3 Dynamix DW-04/H LEDs
Table 1-3 LEDs Functions
LEDs Functions Indicator
Status
Active Description
LAN Switch to another device, such as PC
Link/ACT Link/ACT Green Blinking While plugging on the Ethernet cable, it
must light on and the flash if some data is
being TX/RX.
- 6 -
LEDs Functions Indicator
Status
Active Description
OFF The Ethernet cable is not connected.
10/100M LAN Green Off The 10M LAN is connected.
On The 100M LANis connected.
WAN Uplink to the HUB/Router directly.
Link/ACT Link/ACT Green Blinking While plugging on the Ethernet cable, it
must light on and the flash if some data is
being TX/RX.
OFF The Ethernet cable is not connected.
10/100M WAN Green Off The 10M WAN is connected.
On The 100M WAN is connected.
Ready Ready Green Slow
Blinking
The VoIP Gateway is in normal mode.
Fast Blinking The VoIP Gateway is in downloading
mode.
Status Status Green Off The VoIP Gateway is in Peer-to-Peer
Mode.
On The VoIP Gateway has successfully
registered to Gatekeeper when it is in
Gatekeeper mode.
Blinking The VoIP Gateway is not registered to
Gatekeeper when it is in Gatekeeper
mode.
The VoIP Gateway is in downloading
mode.
TEL(1-4) TEL Red On The Telephone is Off-Hook.
Off The Telephone is On-Hook.
Power Power Green On The Power adapter is connected to the
Gateway.
Off The system is off or not receiving power.
1.6.4 Back Panel Port
Ethernet Port:
Ethernet port is for connecting VoIP Gateway to network, transmit rate supports 10/100
Base-T.
- 7 -

Ethernet connector LAN
COM Port:
RS232 console port (DB-9pin male connector)
Note: use straightforward cable to connect to your computer.
PINOUTS
Pin Name Dir Description
2 RXD Receive Data
3 TXD Transmit Data
5 GND System Ground
TEL Port:
RJ-11 connector, FXS interface. To connect analog phone sets or trunk line of PABX.
12V DC Port:
DC Power supply.
1.6.5 Back Panel Connections
This section outlines how to connect your VoIP Gateway to the LAN and the WAN. In the
case of connecting a Cable Modem you must connect the coaxial cable from your cable service
to the threaded coaxial cable connect on the back of the cable modem.
Step 1. Connecting the Console Port
For the initial configuration of your VoIP Gateway, you need to use terminal emulator
software on a workstation and connect it to the VoIP Gateway the console port. Connect the 9-pin
end of the console cable to the console port of the VoIP Gateway and the other end to a serial port
- 8 -

(COM1, COM2 or other COM port) of your workstation. You can use an extension RS-232 cable
if the enclosed one is too short. After the initial setup, you can modify the configuration remotely
through telnet connections.
Step 2. Connect the VoIP Gateway to the WAN port
Connect the WAN port (silver) on the VoIP Gateway to the Ethernet port on the cable
modem using the cable that came with your cable modem. The Ethernet port on the cable modem
is sometimes labeled “PC” or “Workstation”.
Step 3. Connecting the PC to the LAN
If you have more than one PC, you must use an external hub. Connect the 10/100M LAN
Port (gold) on the VoIP Gateway to a port on the hub using a straight through Ethernet cable. If
you only have one PC, you can connect the VoIP Gateway to the PC directly without a hub. For a
single PC, connect the 10/100M LAN port on the VoIP Gateway to the Network Adapter on the
PC using a crossover cable (red tag).
Step 4. Connecting the Power Adapter to your VoIP Gateway
Connect the power adapter to the port labeled POWER on the rear panel VoIP Gateway.
Caution: To prevent damage to the VoIP Gateway, first make sure you have the correct
AC power adapter. Please see the Appendices for AC power adapter specifications for
your region.
Step 5. Grounding the VoIP Gateway
If you want to ground the VoIP Gateway then connect a grounded wire to the F.G. (Frame
Ground) of the VoIP Gateway.
1.7 Additional Installation Requirements
In addition to the contents of your package, there are other hardware and software
requirements you need before you can install and use your VoIP Gateway. These requirements
include:
1. A computer with an Ethernet NIC (Network Interface Card) installed.
connections
2. A computer equipped with communications software configured to the following
parameters:
VT100 terminal emulation.
9600 Baud.
No parity, 8 Data bits, 1 stop bit, Flow Control set to None.
3. Use Internet Explorer 5.5 and later or Netscape Navigator 6 and later versions.
4. Analog telephone set
5. Software tools: Gatekeeper (optional)
After the VoIP Gateway is properly set up, you can make future changes to the
configuration through telnet
1.8 Setting Up the TCP/IP Protocol
If you are not sure whether the TCP/IP Protocol has been installed, follow these setups to
- 9 -

check, and if necessary, install TCP/IP onto your PCs.
Step 1. Click the [Start] button, Choose [Settings], then [Control Panel]. Double-click the
[Network] icon. Your Network window should appear as follows.
Step 2. Select the [Configuration] tab.
Import:
For Windows 2000 & Windows XP Setting, you will find that they differs with Windows
98/ME/NT slightly. See the Following for reference.
Status] windows, click the [Properties] button the your
Step
Protocol an be installed for a computer’s Dial-Up Adapter
as well as for the Ethernet cad.
Step Protocol] in the Select Network Component Type or highlight [Protocol]
Step window. The TCP/IP Protocol
Step tton. The TCP/IP Properties windows consist of several tabs.
Step
255.0.0.0]. Note than no two computers on the same LAN
Step ck on the [DNS Configuration] tab and select [Enable DNS]. Then click the [Add]
Step ay default
.
11 o complete the TCP/IP installation.
1.9
ely after the Status LED come on, if
Click the “Local Area Connection” icon on the lower right hand side of your desktop
screen.
In the [Local Area Connection
Network windows will appear.
There is only one tab, [General], in the Network window.
3. Click whether the TCP/IP Protocol has already been installed onto your computer’s
Ethernet card. Note that TCP/IP
- If yes, go to set 7.
- If no, click the [Add] button
4. Double-click [
then click [Add].
Step 5. Highlight [Microsoft] under the list of manufactures
6. After a new second, you will be returned to the Network
should now be on the list of installed network components.
7. Click the [Properties] bu
Choose the [IP Address] tab.
8. Select [Specify an IP Address] and enter [10.1.1.1] in the [IP Address] location (where
xxx is a number between 2 and 254 used by the VoIP Gateway to identify each computer),
and the default [Subnet Mask:
can have the same IP address.
9. Cli
button.
10. Click on the [Gateway] tab and enter the High-Performance VoIP Gatew
gateway value 10.1.1.254 in the [new gateway] field, then click [Add] Button
Step . Click [OK] button, Restart your PC t
Power Up Your VoIP Gateway
At this point, you should have connected the console port, the LAN Port, the WAN port and
the power port to the appropriate devices or lines. Plug the power adapter into a wall outlet. The
Power LED should be on. The Status LED will come on after the system tests are complete. The
WAN LED and one of the LAN LEDs come on immediat
- 10 -

connections have been made to the LAN and WAN ports.
- 11 -

:
Part II:
Web Configuration with VoIP Gateway
This part tells how to access and navigate the web configurator and perform initial configuration. It
also describes the Getting Started web configuration when you use the VoIP Gateway.
- 12 -

Chapter 2
Web Configuration with FXS Introduction
This Chapter describes how to login into the WEB and navigate through it.
2.1 Web Configuration with FXS Overview
The embedded web configuration allows you to use a web browser to manage the VoIP
Gateway.
2.2 Accessing the Web Configuration
You will need a computer with and Ethernet 10BaseT, 100Base-TX Network Interface Card
(NIC). Connect to the LAN port in the FXS.
Use Internet Explorer 5.5 and later or Netscape Navigator 6 and later versions.
Use the following instructions to login on to the web configuration.
2.3 Login and welcome screen
Step 1. Start your web browser.
Step 2. Launch your web browser and enter [10.1.1.3] (the default IP address of the VoIP
Gateway) in the Location or Address field. Press Enter.
Step 3. The Password screen now appears. Type [root] in the user name field (it may display
automatically for you) and your password (default [Null]) in the password field.
Step 4. Click OK.
Step 5. After a successful login, you will see the welcome screen show next.
2.4 Welcome Screen
This is the web configuration welcome screen. Click a link on the navigation panel to go to
the corresponding screen.
- 13 -

Figure 2-1 VoIP Gateway web configuration welcome screen
The following table describes the screen.
Table 2-1 Navigation Panel Links
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Network Interface This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the VoIP Gateway
Network Interface Information.
- 14 -

LABEL DESCRIPTION
H323 Information This link takes you to a screen where you can setup up H323 Information.
Line Status This link takes you to a screen. When will set hotline, no answer forward;
understand Line registration and use status of the VoIP Gateway.
Phone Book This link takes you to a screen where you can set up Phone Book
Information.
Support Configuration This link takes you to a screen where you can set up Support Functions
Configuration.
System Configuration This link takes you to a screen where you can set up System Configuration.
Voice Setting This link takes you to a screen where you can set up Voice Configuration.
Phone Configuration This link takes you to a screen. When will set phone patterns of the VoIP
Gateway.
RTP Payload Type
configuration
This link takes you to a screen. When will set RTP Payload Type patterns
of the VoIP Gateway.
IP Packet ToS This link takes you to a screen. When will set IP Pack ToS of the VoIP
Gateway.
DDNS Configuration This link takes you to a screen. When will use DDNS of the VoIP Gateway.
Prefix Configuration This link takes you to a screen. When will set prefix number of the VoIP
Gateway.
Version and
Information
This link takes you to a screen. When will understand Version and
Information of the VoIP Gateway.
Password This link takes you to a screen. When will change passwords.
ROM Upgrade This link takes you to a screen. When will change ROM Upgrade
configuration.
Flash Clean This link takes you to a screen. When will clean flash memory information
back to factory setting.
Commit Data This link takes you to a screen. When will save your changes to the
non-volatile memory.
Reboot System This link takes you to a screen. When will reboot VoIP Gateway.
FXSO Gateway Only FXO Gateway special setting. Only use FXO port can set.
Route Table This link takes you to a screen. When will set Routing Table is a rule to
define the destination of the calls you make (FXO Gateway only).
Tone Configuration This link takes you to a screen. When will set Tone pattern (FXO Gateway
only).
FXO Password This link takes you to a screen. When will set use FXO password (FXO
Gateway only).
2.5 Saving Your Configuration
Click OK to save your changes back to the VoIP Gateway volatile memory. The VoIP
- 15 -

Gateway loses these changes if it is turned off or loses power, so use the Commit Data link on the
navigation panel to the left to save your changes to the non-volatile memory when your are done
configuring.
2.6 Navigating the Web Configuration
The web configuration uses one level. For example, to configure [Network Interface], click
the link on the navigation panel to open the configuration screen.
Figure 2-2 Network Interface Screen
- 16 -
Chapter 3
Initial Configuration
This Chapter covers the basic configuration needed to set up and use the VoIP Gateway. Refer to
the other part describes about individual fields within screens.
3.1 Initial Configuration Overview
This chapter describes the procedure for the initial configuration of the VoIP Gateway.
Refer to the relevant chapters in this User’s Guide for descriptions of the fields and buttons
within individual screens.
3.2 General Configuration
The VoIP Gateway the factory with a default IP address of 10.1.1.3 and a subnet mask of
255.0.0.0, default gateway of 10.1.1.254.
3.3 Static IP address
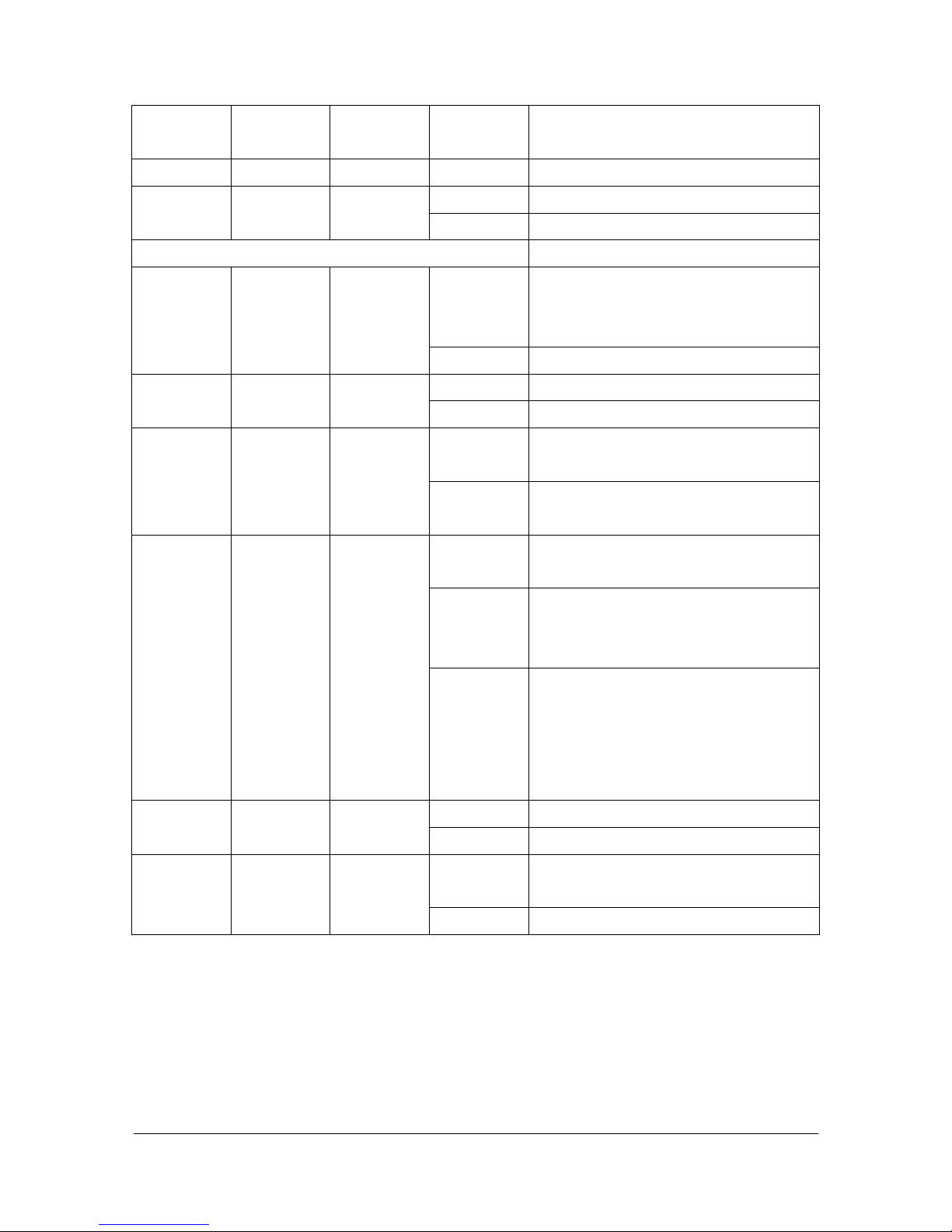
Step 1. Configuration the VoIP Gateway IP address. Click [Network Interface] on the
navigation panel. In the Network Interface screen, type a new IP address, subnet mask and
the default routing gateway (e.g. IP Address: 192.168.13.80, Subnet mask: 255.255.248.0,
Default routing gateway: 192.168.8.254) and click the OK button.
- 17 -

Figure 3-1 Network Interface
Step 2. Click [Commit Data] on the navigation panel. In the Commit Configuration Data
screen, click the [Commit] button. In the Commit Configuration Data screen to Display
[Commit to Flash OK!], When the Commit Data Ok.
Figure 3-2 Commit Configuration Data
Step 3. Click [Reboot System] on the navigation panel. In the VoIP Gateway screen, click the
- 18 -

[Reboot] button. It will take 40 seconds to reboot.
Figure 3-3 Reboot VoIP Gateway
Step 4. Close the current browser windows and launch your web browser again. Enter the new
IP address in the Location or Address field.
3.4 DHCP mode
Step 1. Configuration the VoIP Gateway IP address for DHCP Mode. Click [Network
Interface] on the navigation panel. In the Network Interface screen, enable the DHCP
function if you are using the cable modem or DHCP server and click the [OK] button.
- 19 -

Figure 3-4 Network Interface
Step 2. Click [Commit Data] on the navigation panel. In the Commit Configuration Data
screen, click the Commit button. In the Commit Configuration Data screen to Display
[Commit to Flash OK!], When the Commit Data Ok.
Step 3. Click [Reboot System] on the navigation panel. In the VoIP VoIP Gateway screen,
click the [Reboot] button. It will take 40 seconds to reboot.
Step 4. Close the current browser windows and launch your web browser again. Enter the new
IP address in the Location or Address field.
3.5 PPPoE mode
Step 1. Configuration the VoIP Gateway IP address for PPPoE Mode. Click [Network
Interface] on the navigation panel. In the Network Interface screen, Select IP mode: PPPoE,
- 20 -

and put the info of the PPPoE User Name, password, and Reboot After Remote Host
Disconnection: Enable (e.g. User: 123456@hinet.net, password: 123456) and click the [OK]
button.
Figure 3-5 PPPoE Device Configuration
Step 2. Click [Commit Data] on the navigation panel. In the Commit Configuration Data
screen, click the Commit button. In the Commit Configuration Data screen to Display
- 21 -

[Commit to Flash OK!], When the Commit Data Ok.
Step 3. Click [Reboot System] on the navigation panel. In the VoIP VoIP Gateway screen,
click the [Reboot] button. It will take 40 seconds to reboot.
Step 4. Close the current browser windows and launch your web browser again. Enter the new
IP address in the Location or Address field. .
3.6 IP Sharing Configuration
The function is only for the user who is using the IP Sharing device. It is said Gateway is
connected to the IP Sharing device.
The IP Sharing Device must support the DMZ or Virtual server functions
An e.g. such as ADSL network is in the following.
- 22 -

Step 1. The WAN IP Address obtained from ADSL has two kinds of methods.
Step 2. One is fixed IP Address, while user applies for one or more fixed IP Addresses.
Step 3. Another is dynamic IP Address while user applies for dial-up connection way. The
LAN IP Address of User’s PC can be set as DHCP client in order to gain a valid one.
Step 4. Another IP Address for Gateway must be set as an fixed one in order for that IP
Sharing device pass forwarding the relevant information from WAN to LAN. Besides, a
valid IP Address meets the IP Sharing device (LAN site) is the element.
Step 5. VoIP Gateway must enable the IP Sharing function for the fixed/dynamic WAN IP
Address.
Note:
IP
With Dynamic WAN IP Address, a valid Gatekeeper for VoIP Gateway to get register
on is a must. In other word, it is not workable in Peer-to-Peer mode while dynamic WAN
Address.
Step 6. IP Sharing device must have a function to do IP/Port mapping. Some is named as DMZ,
some is named as virtual server whatever. The VoIP messages from WAN have to
completely pass forward to the LAN. It is said if the VoIP Gateway is assigned a virtual
fixed IP Address such as 192.168.1.5, IP Sharing device must forward the VoIP message to
192.168.1.5.
Step 7. Configuration the VoIP Gateway IP address for IP Sharing Mode. Click [Network
Interface] on the navigation panel. In the Network Interface screen, enter the IP address,
Subnet mask and the default gateway in the network table. Please follow up your IP Sharing
device
Step 8. Enable the IP sharing function and put the static IP address in the IP Sharing server
address (e.g. 210.59.163.198) and click the OK button.
- 23 -

Figure 3-6 Enable the IP sharing function
Step 9. Click [Commit Data] on the navigation panel. In the Commit Configuration Data
screen, click the Commit button. In the Commit Configuration Data screen to Display
[Commit to Flash OK!], When the Commit Data Ok.
Step 10. Click [Reboot System] on the navigation panel. In the VoIP Gateway screen, click the
[Reboot] button. It will take 40 seconds to reboot.
Step 11. Close the current browser windows and launch your web browser again. Enter the new
IP address in the Location or Address field.
3.7 PPPoE (NAT) mode (1A-FXS)
- 24 -

Step 1. Configuration the VoIP Gateway IP address for PPPoE Mode. Click PPPoE
Configuration on the navigation panel. In the PPPoE Configuration screen, On the Device
and put the info of the PPPoE User Name and password (e.g. User: 123456@hinet.net,
password: 123456) and click the OK button.
Figure 3-7 PPPoE Device Configuration
Step 2. Click Commit Data on the navigation panel. In the Commit Configuration Data screen,
- 25 -

click the Commit button. In the Commit Configuration Data screen to Display Commit to
Flash OK!, When the Commit Data Ok.
Step 3. Click [Reboot System] on the navigation panel. In the VoIP Gateway screen, click the
[Reboot] button. It will take 40 seconds to reboot.
Step 4. Close the current browser windows and launch your web browser again. Enter the new
IP address in the Location or Address field.
Step 5. Setup PC use LAN IP connection Network
Select [Specify an IP Address] and enter [192.168.123.111] in the [IP Address] location
(where xxx is a number between 2 and 254 used by the VoIP Gateway to identify each
computer), and the default [Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0]. Note than no two computers on
the same LAN can have the same IP address. VoIP Gateway default gateway value
192.168.123.123 in the [new gateway] field. Then save your change.
- 26 -

Chapter 4
Making a VoIP Call
This Chapter covers the basic configuration the gateway for making VoIP calls. One is the
Peer-to-Peer mode, another is GK routed mode. The configurations and functions are different.
Please make sure about the mode you want and follow up the step to configure your gateway.
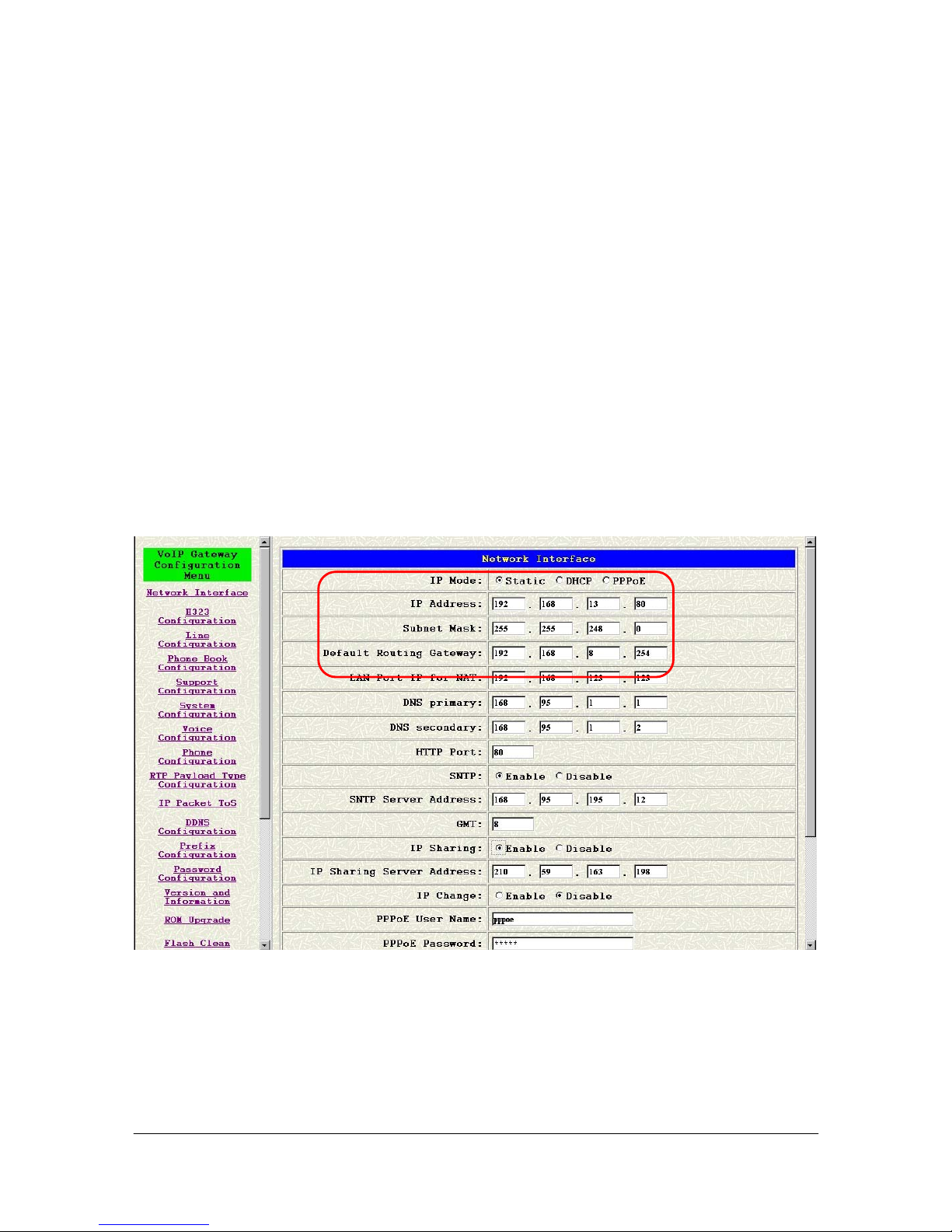
4.1 Configure the gateway into the Peer-to-Peer mode
Step 1. Configuration the VoIP Gateway H323 Configuration. Click [H323 Configuration] on
the navigation panel. In the H323 Configuration screen, select Peer-to-Peer Mode function,
set line number (e.g. Line1 Number 3001, Line2 Number: 3002) and click the [OK] button.
- 27 -

Figure 4-1 H323 Configuration – Peer to Peer mode Screen
Step 2. Configuration the VoIP Gateway Phone Book. Click [Phone Book] on the navigation
panel. In the Phone Book screen, enter the Index, Name, IP address and e164 (phone
number) of the destination and click the Add Data button.
Figure 4-2 Phone Book
Step 3. E.g. enter the Index: 1, Name: test1, e164 No.: 20, IP address: 192.168.13.80 and of
- 28 -

the destination and click the [Add Data] button.
Figure 4-3 Phone Book – New Record
Step 4. On table will display on the first index.
Figure 4-4 Phone Book
Step 5. Click [Commit Data] on the navigation panel. In the Commit Configuration Data
screen, click the [Commit] button. In the Commit Configuration Data screen to Display
- 29 -

[Commit to Flash OK!], When the Commit Data Ok.
Step 6. Click [Reboot System] on the navigation panel. In the VoIP VoIP Gateway screen,
click the [Reboot] button. It will take 40 seconds to reboot.
4.2 Configure the gateway into the GK routed mode
4.2.1 Gateway Type: Gateway
Step 1. Configuration the VoIP Gateway H323 Configuration. Click [H323 Configuration] on
the navigation panel. In the H323 Configuration screen, select GK routed Mode function.
Step 2. To change the GK information from your service provider Gatekeeper IP, 2nd
Gatekeeper IP, Gateway Type, Registered Prefix, Line1 Number, Line 2 Number, Line 3
Number and Line 4 Number (e.g. Gatekeeper IP: 192.168.13.71, 2nd Gatekeeper IP:
192.168.13.71, Gateway Type: Gateway, Registered Prefix: 300, Line1 Number: 3001,
Line2 Number: 3002, Line3 Number: 3003, Line 4 Number: 3004), and click the [OK]
button.
- 30 -

Figure 4-5 Configure the GK info
Step 3. Click Commit Data on the navigation panel. In the Commit Configuration Data screen,
click the Commit button. In the Commit Configuration Data screen to Display [Commit to
Flash OK!], When the Commit Data Ok.
Step 4. Click [Reboot System] on the navigation panel. In the VoIP VoIP Gateway screen,
click the [Reboot] button. It will take 40 seconds to reboot.
4.2.2 Gateway Type: Terminal
Step 1. Configuration the VoIP Gateway H323 Configuration. Click [H323 Configuration] on
the navigation panel. In the H323 Configuration screen, select GK routed Mode function.
Step 2. To change the GK information from your service provider Gatekeeper IP, 2nd
Gatekeeper IP, Gateway Type, Line1 Number, Line 2 Number (e.g. Gatekeeper IP:
192.168.13.71, 2nd Gatekeeper IP: 192.168.13.71, Gateway Type: Terminal, Line1
Number: 3001, Line2 Number: 3002, Line3 Number: 3003, Line 4 Number: 3004), and
click the [OK] button.
- 31 -

Step 3. Click Commit Data on the navigation panel. In the Commit Configuration Data screen,
click the Commit button. In the Commit Configuration Data screen to Display [Commit to
Flash OK!], When the Commit Data Ok.
Step 4. Click [Reboot System] on the navigation panel. In the VoIP VoIP Gateway screen,
click the [Reboot] button. It will take 40 seconds to reboot.
- 32 -

Chapter 5
Upgrade ROM Version
This Chapter covers the basic how to upgrade VoIP Gateway ROM Version.
5.1 Before you start downloading
Step 1. Please confirm Host PC, which is installed as TFTP / FTP server and device is in
available network.
Step 2. Remember the current configuration, such as [H323 Configuration] [Line
configuration], [Phone Book].
5.2 Update Application Version
Step 1. Update the VoIP Gateway ROM Version. Click [ROM Upgrade] on the navigation
panel. In the [ROM Configuration] screen, type a Server IP address, Target File Name,
Method, Target File Type (e.g. Server IP Address: 192.168.4.71, Target File Name:
Dynamix DW-04/H.204, Method: TFTP, Target File Type: Application image) and click the
[OK] button.
Figure 5-1 ROM Configuration
Step 2. In the screen to Display [Please issue FLASH CLEAN to consist software version.]
information. When the ROM Upgrade file ok.
- 33 -

Figure 5-2 ROM File Upgrade ok
Step 3. Click [Flash Clean] on the navigation panel. In the Flash Clean screen, click the
[CLEAN] button.
Figure 5-3 Flash Clean
Step 4. In the Flash Clean screen to Display [Flash cleaned!! Please reboot your system!!],
When the Flash Clean Ok.
- 34 -

Figure 5-4 Flash Clean OK
Step 5. Click [Reboot System] on the navigation panel. In the Reboot VoIP Gateway screen,
click the [Reboot] button. It will take 40 seconds to reboot.
Step 6. Close the current browser windows and launch your web browser again. Enter the IP
address in the Location or Address field.
5.3 Update Boot2m Version
Step 1. Update the VoIP Gateway 2mROM Version. Click [ROM Upgrade] on the navigation
panel. In the [ROM Configuration] screen, type a Server IP address, Target File Name,
Method, Target File Type (e.g. Server IP Address: 192.168.4.71, Target File Name:
2mDynamix DW-04/H.204, Method: FTP, FTP Login name: totoro, passwd: totoro, Target
File Type: 2m Boot image) and click the [OK] button.
- 35 -

Step 2. In the screen to Display [Please issue FLASH CLEAN to consist software version]
information. When the ROM Upgrade file ok.
Figure 5-5 ROM File Upgrade ok
Step 3. Click [Flash Clean] on the navigation panel. In the Flash Clean screen, click the
[CLEAN] button.
- 36 -

Figure 5-6 Flash Clean
Step 4. In the Flash Clean screen to Display [Flash cleaned!! Please reboot your system!!],
When the Flash Clean Ok.
Figure 5-7 Flash Clean OK
Step 5. Click [Reboot system] on the navigation panel. In the Reboot VoIP Gateway screen,
click the [Reboot] button. It will take 40 seconds to reboot.
- 37 -

Step 6. Close the current browser windows and launch your web browser again. Enter the IP
address in the Location or Address field.
- 38 -

Chapter 6
Network Interface Screen
This Chapter covers setup Network Interface identification information for VoIP Gateway.
6.1 Network Interface Overview
The web configuration provides Network Interface screen.
6.2 Network Interface Screen
Click [Network Interface] in the navigation panel and open the Network Interface Screen.
Use this screen to setup Network Interface identification information for the VoIP Gateway.
- 39 -

Figure 6-1 Network Interface
The following table describes this screen.
Table 6-1 Network Interface
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Mode Select use defines the networking type for this gateway. It could support
the Static, DHCP and PPPoE function.
IP Address Enter the IP Address of the VoIP Gateway in dotted decimal notation for
e.g. 192.168.4.92. Range of IP Address setting (0.0.0.0~255.255.55.255).
Subnet Mask Enter the IP Subnet Mask of your VoIP Gateway in dotted decimal notation
for e.g. 255.255.0.0.
Default Routing
Gateway
Enter the IP Address of the default-outgoing gateway of your VoIP
Gateway in dotted decimal notation for e.g. 192.168.1.254.
LAN Port IP for NAT Specify LAN port IP address for NAT function (Dynamix DW-01/H only).
HTTP Port Set VoIP Gateway HTTP Port Number e.g. 80.
DNS primary Enter the DNS IP Address in dotted decimal notation for e.g. 168.95.1.1
DNS Secondary Enter the DNS secondary IP Address in dotted decimal notation for e.g.
168.95.1.1
SNTP Select enable/disable Simple Network Time Protocol.
SNTP Server Address Set specifies a SNTP Server as network time source in dotted decimal
notation for e.g. 168.95.192.12.
GMT Set local time zone according to GMT e.g. 8.
- 40 -

LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Sharing Select enable IP Sharing function, when you specify usage of and IP
Sharing device.
IP Sharing Server
Address
Enter specify a global fixed IP Address, user can add this IP Address in
dotted decimal notation for e.g. 210.11.22.33. However, dynamic IP
Address is not working in Peer-to-Peer mode.
PPPoE User Name Set the PPPoE connection account in this table. Please get this info from
your ISP.
PPPoE Password Set the PPPoE connection password in this table. Please get this info from
your ISP.
PPPoE IP Address The field display the IP address. When VoIP Gateway after the connection
success, which the gateway got from the ISP.
PPPoE Destination The field display the default gateway address. When VoIP Gateway after
the connection success, which the gateway got from the ISP.
PPPoE DNS primary The field display the DNS IP address. When after the connection success,
will show you the DNS ip address from the ISP.
Reboot After Remote
Host Disconnection
Select enable or disable this function will make the gateway restart
automatically if the PPPoE connection is disconnected or the IP address
was taken back by the ISP.
OK [button] Click [OK] button to save your changes back to the VoIP Gateway volatile
memory.
- 41 -
Chapter 7
H323 Configuration Screen
This Chapter covers setup H.323 related parameters.
7.1 H323 Configuration Overview
The web configurator provides H.323 Configuration screen.
7.2 H323 Configuration Screen
Click [H323 Configuration] in the navigation panel and open the [H323 Configuration]
Screen.
- 42 -

Figure 7-1 H323 Configuration
The following table describes this screen.
Table 7-1 H323 Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Mode Select Gatekeeper routed mode or Peer-to-Peer mode.
GateKeeper IP
Address
Set Gatekeeper IP Address in dotted decimal notation e.g.192.168.4.71.
2nd GateKeeper IP Set redundancy second 2 Gatekeeper IP Address in dotted decimal notation
e.g.192.168.4.71.
Default Gateway IP All the calls will be routed to this destination if the destination couldn’t be
found in the Phone Book configuration. Support the Peer-to-Peer mode
only.
Gateway Type Select registration Gateway Type is Gateway mode or Terminal mode.
Registered Prefix Set Prefix number while registration Gateway Type is Gateway example
60 (max 20 digits).
Line1 Number Set Line1 number e.g.601 (1~20 digits).
Line2 Number Set Line2 number e.g.602 (1~20 digits).
Line3 Number Set Line3 number e.g.603 (1~20 digits).
Line4 Number Set Line4 number e.g.604 (1~20 digits).
Registered Alias Set IP side Registration alias as h323 ID.
Display Information Set string representing display information for repertory to the called party.
- 43 -

LABEL DESCRIPTION
Gatekeeper ID The name of the GK. It has used with the Gatekeeper Discovery function.
Support the GK mode only.
Gatekeeper Discovery Select Gatekeeper auto Discovery is enable/disable.
Time To Live (TTL) Set RAS TTL Time, example 60 (0~3600 second).
RTP Port Set RTP port number, example 16384 (1024 to 65532).
Gatekeeper finding
port
Set Gatekeeper finding port e.g.1718 (1024 to 65535).
Gatekeeper RAS Port Set Gatekeeper RAS Port e.g.1719 (1024 to 65535).
H225 RAS Port Set H225 Call RAS Port e.g.1024 (1024 to 65535).
H225 Call Signal Port Set H225 Call Signal Port e.g.1720 (1024 to 65535).
Destination H225 Call
Signal Port
The destination Call Signal Port. Support the GK and Peer-to-Peer mode
both (1024 to 65535).
Allocate Port Range
Start
The port range for this gateway (1024 to 19999).
Allocate Port Range
End
The port range for this gateway (1024 to 19999).
Response Timeout Set max waiting time for 1st response to a new call e.g.15 (1~200).
Connection Timeout Set max waiting times for call establishment after receiving 1st response of
a new all e.g.200 (1~20000).
H.235 Security Token Support H235 security password for the registration (1~20 digits).
OK [button] Click [OK] button to save your changes back to the VoIP Gateway volatile
memory.
Note:
Line1 & Line2 number must follow the prefix number if device is configured as Gateway
type. For example, if prefix number is 999, the line1 & line2 number are 9991 & 9992.
Line number field auto display data follow VoIP Gateway line port number, if you see Line
number field display [-1], you can’t set it.
- 44 -

Chapter 8
Line Configuration Screen
This chapter explains the Line Status Information Screen.
8.1 Line Configuration Overview
The web configurator provides Line Status Information screen.
8.2 Line Configuration Screen
Click [Line Configuration] in the navigation panel to open the Line Configuration]
Information screen.
Figure 8-1 Line Configuration Information
The following table describes this screen.
Table 8-1 Line Status Information
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Line Number This field Display the Line Number.
Type This field Display the port type. There is only display FXS Type. It couldn’t
be changed.
Hunting Group Define the group number of this port. When the port is busy, the call could
be transferred to another port in the same group. Only the same type could
be configured in the same group.
Hotline Set the hotline number, the hotline mode will be enabled if you enter the
hotline number. The default setting is disabled.
- 45 -

LABEL DESCRIPTION
No Answer Forward Set the port no answer will be forward other number. This is only for the
E164 number or the phone numbers you want to transfer.
Registration This field Display the VoIP Gateway registered on the GK or not.
Status This field Display line status is Ready or Busy.
OK [button] Click [OK] button to save your changes back to the VoIP Gateway volatile
memory.
Note:
Hunting Group field auto display data follow VoIP Gateway line port number, if you see
Hunting Group field display [Null], you can’t set it.
- 46 -

Chapter 9
Phone Book Configuration Screen
This Chapter covers Phone Book function allows users to define their own numbers, which
mapping to real IP address. It is effective only in peer-to-peer mode. When adding a record to
Phone Book, users do not have to reboot the machine, and the record will be effective
immediately.
9.1 Phone Book Configuration Overview
The web configuration allows you to Set up Phone Book that tell the VoIP Gateway how to
call management traffic when you configuration P2P mode.
9.2 Phone Book Configuration Screen
Click [Phone Book Configuration] in the navigation panel and open the [Phone Book]
Screen.
Figure 9-1 Phone Book
The following table describes this screen.
Table 9-1 Phone Book
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Index The field displays the index number.
Name The field displays the descriptive name.
E164 The field displays the descriptive E164 number.
IP Address The field displays the IP Address or Domain name.
- 47 -

LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port The field displays the call signal port of the destination (default: 1720).
Drop Prefix The filed display the drop function.
Insert Prefix The field displays the insert digits number.
New Record
Index Set up an Index number from 1 to 100, to the parameter to show specific
phone number.
Name Set up a descriptive name (max 20 byte).
IP Address Set up IP Address or Domain Name.
E164 Set up e164 (telephone) number (max 20 digits)
Port Set up the call signal port of the destination (default: 1720).
Drop Prefix Select enable or disable drop prefix function. The function is enable means
to drop e.164 number when dialing out. The function is disable means to
keep e 164 number.
Insert Prefix Set up the insert digits number (1~20 digits).
Add Data [button] Click [Add Data] button to insert the information table.
Delete Date [button] Input the index number on index filed, and then click [Delete Data] button
will to delete the record from the table.
Note:
The e164 number defined in phone book will fully carry to destination. It is not just a
representative number for destination’s IP Address. In other words, user dial this e164 number to
reach destination, destination will receive the number and find out if it is matched to its e164,
including Line number in some particular device.
- 48 -

Chapter 10
Support Configuration Screen
This Chapter provides some extra functions that might be needed by users.
10.1 Support Configuration Overview
The web configuration provides Support Configuration screen.
10.2 Support Configuration Screen
Click [Support configuration] in the navigation panel and open the [Support Configuration]
Screen.
Figure 10-1 Support Configuration
The following table describes this screen.
Table 10-1 Support Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
T.38 FAX Select enable/disable for T.38 FAX function. When T.38 ability is on, VoIP
Gateway will automatically defer codec (G.723 or G.729a) to T.38 when
FAX signal is detected.
T.38 FAX ECM Select enable/disable for T.38 FAX ECM function. Support the error
correction in the high speed fax mode
T.38 FXS ASN.1 Select enable/disable for T.38 FXS ASN.1. Support the ASN.1 function.
Fax Redundancy
Depth
Select enable/disable for Fax Redundancy Depth. This support function
could make the data for the FAX sending for twice. But this will take more
- 49 -
LABEL DESCRIPTION
bandwidth (0~2).
Fast Start Select enable/disable for Fast Start function. Fast Start function can
shorten the connection time if the opposite party also supports Fast Start.
H.245 Tunneling Select enable/disable for H.245 Tunneling function. If the function is on,
VoIP Gateway will send H.245 (Call Control messages) via H.225’s (Call
Signal messages) link. The function is effective only when both side
support h245 tunnel.
H.245 Message After
Fast Start
Select enable/disable for H.245 Message After Fast Start function. If the
function is ON, VoIP Gateway will send H.245 messages after Fast Start.
Early H.245 Select enable/disable for Early H.245 Message. The function is effective
only when both sides support early H.245.
H.450 Select enable/disable for H450 related features, which include transfer,
hold and forward.
OK [button] Click [OK] button to save your changes back to the VoIP Gateway volatile
memory.
Note:
It is not recommended to change the value in this web, only if users do know well the
application. This might cause incompatibility with other devices.
- 50 -

Chapter 11
System Configuration Screen
This Chapter covers System Information and configuration.
11.1 System Configuration Overview
The web configuration provides System Configuration screen.
11.2 System Configuration Screen
Click [System Configuration] in the navigation panel and open the [System Configuration]
Screen.
Figure 11-1 System Configuration
The following table describes this screen.
Table 11-1 System Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Inter Digit Time The call will be sent out if user didn’t enter the digits after this timer. From
1 to 10.
Forward time It supports the No Answer Forward function. If users configure it for 10,
the call will be forwarded when it rings about 10 seconds. From 5 to 65535.
Keypad Type Select In-Band: The DTMF signal sending by RTP. Out-Band: The DTMF
signal sending not by RTP. Including the H.245 (Alpha), H.245 (Signal),
Q.931 and RFC 2833.
User defined Prefix Select on/off for User defined local zone prefix switch. If user enables
- 51 -
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Switch prefix function, once user dials out, gateway will automatically add prefix
number before number user dialed.
User defined Prefix
Disable
Disable the defined prefix after press the selected digit (0,1~9, *)
User defined Prefix This will be added in the first digits of the numbers that users had dialed.
Can also define IP address here in P2P mode, once user press “#”, Gateway
will call out this IP address.
Ring Time
(FXS+FXO)
It for the ring detection from the PSTN. The ring detection will be failed if
users configure it too long (FXO Only).
Ring Before Answer
(FXS+FXO)
This will help the users to answer the calls from PSTN into this gateway
quickly. The call will be connected by one time ring if users configure this
for 1. From 1 to 10 (FXO Only).
Codec Select Method This could support that the codec will follow the MSD (Master Slave
Determination) or the caller side. Master: Follow the result from the
Master Slave Determination. Caller: Follow the caller side.
Local Generate Ring
Back Tone
To enable or disable the ring back tone generation from the local side.
End of Dial To enable or disable the end of dial function. This function key will be the
digit “#”.
Gateway Prefix To keep or drop the prefix number of this gateway. This only support the
Gateway type in the GK routed mode.
FXO Type
(FXS+FXO)
Users could configure the entire calls need the 2nd stage dialing or not.
Normal: The 1st or 2nd stage dialing will depend on the dialing plan from
the users. If user dial the number of the FXO port, that will be the 2nd stage
dialing. Force 2nd dial: Every call will need the 2nd stage dialing type
(FXO Only).
Hardware Type
(FXS+FXO)
Set the hardware detection type, select auto detect/ 1FXS+1FXO/
2FXS+2FXO mode (FXO Only).
OK [button] Click [OK] button to save your changes back to the VoIP Gateway volatile
memory.
Note:
The default value is to auto detect hardware type. Usually it is not necessary to change this
setting. Please make sure about your Hardware Type, Gateway may be not functional if set
wrong hardware type.
- 52 -

Chapter 12
Voice Configuration Screen
This Chapter covers voice is associated with the audio setting information.
12.1 Voice Configuration Overview
The web configuration provides Voice Configuration screen.
12.2 Voice Configuration Screen
Click [Voice Configuration] in the navigation panel and open the [Voice Configuration]
Screen.
Figure 12-1 Voice Configuration
The following table describes this screen.
Table 12-1 Voice Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Codec Priority Set priority preference of installed codes, G.723, G.711A, G.711U, G.729,
G.729A, G.729B, G.729AB.
Frame Size Set Specify sending packet size, G.723: 30/60/90, G.711A, G.711U, G.729,
G.729A, G.729B, G.729AB: 20/40/60ms.
The smaller the packet size, the shorter the delay time. If network is in
good condition, smaller sending packet size is recommended.
Line1/
TEL1 Volume
Set voice volume stands for volume, which can be heard from VoIP
Gateway side (0~63, default: 28).
- 53 -

LABEL DESCRIPTION
Set input gain stands for volume, which the opposite party hears (0~38,
default: 28).
Set dtmf volume stands for DTMF volume/level (0~31, default: 23).
Line2/
Line1 Volume
Set voice volume stands for volume, which can be heard from VoIP
Gateway side (0~63, default: 28).
Set input gain stands for volume, which the opposite party hears (0~38,
default: 28).
Set dtmf volume stands for DTMF volume/level (0~31, default: 23).
Line3/
TEL2 Volume
Set voice volume stands for volume, which can be heard from VoIP
Gateway side (0~63, default: 28).
Set input gain stands for volume, which the opposite party hears (0~38,
default: 28).
Set dtmf volume stands for DTMF volume/level (0~31, default: 23).
Line4/
Line2 Volume
Set voice volume stands for volume, which can be heard from VoIP
Gateway side (0~63, default: 28).
Set input gain stands for volume, which the opposite party hears (0~38,
default: 28).
Set dtmf volume stands for DTMF volume/level (0~31, default: 23).
G723 Silence
Suppression
Select enable/disable for G723 silence suppression and comfort noise
generation setting.
Echo Canceller Setting enable/disable of echo canceller.
Jitter Buffer Setting of jitter buffer min/max delay.
OK [button] Click [OK] button to save your changes back to the VoIP Gateway volatile
memory.
Note:
Well the application before you change voice parameters, because this might cause
incompatibility.
- 54 -

Chapter 13
Phone Configuration Screen
This Chapter covers VoIP Gateway progress tone is configurable. Default tone value is set
according to U.S. tone specification. Users may adjust the values according to their own
country’s tone specification or users-defined tone specification.
13.1 Phone Configuration Overview
The web configurator provides [Phone Configuration] screen.
13.2 Phone Configuration Screen
Click [Phone Configuration] in the navigation panel and open the [Phone Configuration]
Screen.
Figure 13-1 Phone Configuration
The following table describes this screen.
Table 13-1 Phone Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ring Cadence Setting the played tone type, when VoIP Gateway is receiving a call.
Ring Back Tone Setting the played tone type, when VoIP Gateway receives a Q.931
Alerting message. In condition that VoIP Gateway is the originate side.
Busy Tone Setting the played tone type, when destination is busy.
Dial Tone Setting the played tone type, when hook off a phone set of workable VoIP
Gateway.
- 55 -

LABEL DESCRIPTION
2nd Dial Tone To configure the value of the local 2nd dial tone (FXO only).
Flash Timer Setting the detective flash range in ms, for example, 300-500 ms.
OK [button] Click [OK] button to save your changes back to the VoIP Gateway volatile
memory.
Note:
For tone simulation, VoIP Gateway adopts dual frequencies as traditional telephone does. If
users want to have their own call progress tone, they can change the value of tones. High and
Low frequency/level/cadence can be configured respectively.
ringing frequency: 15 ~ 100 (Unit: Hz)
ringing ring ON/OFF: 0 ~ 8000 (Unit: ms)
ringing level: 0 ~ 94 (Unit: V)
tone frequency: 0 ~ 65535 (Unit: Hz)
tone freqLevel: 0 ~ 65535 (Unit: mVrms)
tone Tone ON/OFF: 0 ~ 8000 (Unit: ms)
- 56 -

Chapter 14
RTP Payload Type Configuration Screen
This Chapter covers RTP Payload Type information and configuration
14.1 RTP Payload Type Configuration Overview
The web configurator provides Speed Dialing screen.
14.2 RTP Payload Type Configuration Screen
Click [RTP Payload Type Configuration] in the navigation panel and open the [RTP Payload
Type Configuration] Screen.
Figure 14-1 RTP Payload Type Configuration
The following table describes this screen.
Table 14-1 RTP Payload Type Configuration List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
RFC2833 Payload
Type
Set the payload type for RFC2833 type.
DTMF Payload Type Set the payload for the DTMF type.
FAX Payload Type Set the payload for the FAX type.
FAXByPass Payload
type
Set the payload for the FAX by Pass type.
MODEMByPass
Payload Type
Set the payload for the Modem by Pass type. (This is no use for the
hardware as so far.)
- 57 -

LABEL DESCRIPTION
Redundancy Payload
Type
Set the payload for the Redundancy type.
MODEMRelay
Payload Type
Set the payload for the FAX by Pass type. (This is no use for the hardware
as so far.)
OK [button] Click [OK] button to save your changes back to the VoIP Gateway volatile
memory.
- 58 -

Chapter 15
IP Packet ToS Configuration Screen
This Chapter covers IP Packet ToS configuration.
15.1 IP Packet ToS Overview
The web configuration provides TOS Configuration screen.
15.2 IP Packet ToS Configuration Screen
Click [IP Packet ToS] in the navigation panel and open the [IP Packet ToS Configuration]
Screen.
Figure 15-1 IP Packet ToS Configuration
The following table describes this screen.
Table 15-1 IP Packet ToS Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Signaling Packet
DSCP Code
Set the Signaling Packet DSCP code value, the value of is from 0 to 63
e.g.0.
Media Packet DSCP
Code
Set the Media Packet DSCP Code, the value of is from 0 to 63 e.g.0.
OK [button] Click [OK] button to save your changes back to the VoIP Gateway volatile
memory.
Note:
- 59 -

It’s working if it supported by your network.
According to the RFC 1349 document, the TOS value as following:
1000 – minimize delay
0100 – maximize throughput
0010 – maximize reliability
0001 – minimize monetary cost
0000 – normal service
These values are the Binary format. Please change to the Decimal and put these values in to
the correct table.
- 60 -

Chapter 16
DDNS Device Configuration Screen
This Chapter covers Display DDNS related information.
16.1 DDNS Device Configuration Overview
The web configuration provides DDNS Device Configuration screen.
16.2 DDNS Device Configuration Screen
Click [DDNS Configuration] in the navigation panel and open the [DDNS Device
Configuration] Screen.
Figure 16-1 DDNS Device Configuration
The following table describes this screen.
Table 16-1 DDNS Device Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Status Select enable or disable to use DDNS device function.
Server Enter the server address of your DDNS server.
Host Name Your Dynamic DNS name.
ID Your Dynamic DNS Login account.
Password Your Dynamic DNS Login password.
Check IP Select On or Off to check IP function. If use IP Sharing machine will use
check IP function. Then will get this information from your DDNS server.
IP Check Server 1 Set check the endpoints IP address.
- 61 -

LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Check Server 2 Set check the endpoints IP address.
Check Every Set on/off function will check the server after a period. Set how long will
check it (0~59) minutes or (1~24) hours check it.
OK [button] Click [OK] button to save your changes back to the VoIP Gateway volatile
memory.
Note:
Support DDNS Server: www.dyndns.org.
- 62 -

Chapter 17
Prefix Drop/Insert Configuration Screen
This Chapter covers to set Hotline function must be under Peer-to-Peer mode and switch to
hotline mode.
17.1 Prefix Drop/Insert Configuration Overview
The web configurator provides Bureau screen.
17.2 Prefix Drop/Insert Configuration Screen
Click [Prefix configuration] in the navigation panel and open the [Prefix Drop/Insert
Configuration] Screen.
Figure 17-1 Prefix Drop/Insert Configuration
The following table describes this screen.
Table 17-1 Prefix Drop/Insert Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Index This field refers to the index number.
Prefix This field refers to the numbers that could be into VoIP gateway.
Drop This field refers to the enable/disable drop function.
Insert This field refers to the want to insert in this number.
New Prefix
Index Setting the index number for prefix record (max 100 record).
Prefix Setting the prefix number of the whole numbers that could be into this
- 63 -

LABEL DESCRIPTION
VoIP gateway (1~20 digits).
Drop Select enable or disable drop prefix function. The function is enable means
to drop prefix number when dialing out. The function is disable means to
keep prefix number.
Insert Setting the digits that you want to insert in this number (1~30 digits).
Add Data [button] Click [Add Data] button to insert the information table.
Delete Date [button] Input the index number on index filed, and then click [Delete Data] button
will to delete the record from the table.
Note:
This function is just like the Phone Book configuration. But it will make the drop and insert
function in the GK routed mode. All the numbers into this gateway will check out the prefix table
first.
- 64 -

Chapter 18
Password Configuration Screen
This Chapter explains how to change the VoIP Gateway password.
18.1 Password Configuration Overview
The Password screen allows you to configure the administrator password.
18.2 Password Configuration Screen
Click [Password configuration] in the navigation panel to open the [Password Configuration]
screen.
Use the [Password Configuration] to set root and administrator password for the VoIP
Gateway.
It is highly recommended that you change the default password ([Null)).
Figure 18-1 Password Configuration
The following table describes this screen.
Table 18-1 Password Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Username Select root or administrator different options from the drop-down list box.
Current Password Type the existing system password ([Null] is the default password when
shipped).
New Password Type your new system password.
- 65 -

LABEL DESCRIPTION
Confirm New
Password
Confirm your new system password for confirmation.
CHANGE [button] Click [CHANGE] to save your change back to the VoIP Gateway volatile
memory.
ABORT [button] Click [ABORT] to clean type data this page afresh.
- 66 -

Chapter 19
Version and Information Screen
This chapter explains the Version and Information Screen.
19.1 Version and Information Overview
The web configuration provides Version and Information screen to allow you to see VoIP
Gateway Version Information.
19.2 Version and Information Screen
Click [Version and Information] in the navigation panel to open the [Version and Information]
screen.
Figure 19-1 Version and Information
The following table describes this screen.
Table 19-1 Version and Information
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Boot Rom This field refers to the Boot Rom Version.
Application Rom This field refers to the Application Rom Version.
DSP Application This field refers to the DSP Application Version.
DSP Kernel This field refers to the DSP Kernel Version.
DSP Test Code This field refers to the DSP Test Code Version.
Greeting This field refers to the Greeting file. (FXO only)
ASK Pin This field refers to the ASK Pin file. (FXO only)
- 67 -

Chapter 20
ROM Upgrade Screen
This Chapter explains how to Update VoIP Gateway Version.
20.1 ROM Configuration Overview
The web configuration provides Update VoIP Gateway ROM Version.
20.2 ROM Configuration Screen
Click [ROM Upgrade] in the navigation panel and open the [ROM Configuration] Screen.
Figure 20-1 ROM Configuration
The following table describes this screen.
Table 20-1 ROM Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server IP Address Enter the FTP or TFTP Server IP Address.
Target File Name Enter the file name prepared to upgrade.
Method Select download method as FTP or TFTP.
FTP Login Name Enter the FTP Login name (max 20 byte)
FTP Login Password Enter the FTP Login password (max 20 byte)
Target File Type Select download Target File Type on 2M Boot Image, DSP Application
Image, DSP Core Image, DSP Test Image different options from the
drop-down list box.
OK [button] Click [OK] to save your change back to the VoIP Gateway volatile memory.
- 68 -

Note:
Most of all, the Rom file needed to get upgrade is App or Boot2m. Please check the exactly
Rom file before doing download procedure.
- 69 -

Chapter 21
Flash Clean Screen
This Chapter covers save change and clean the entire user defined value in factory default mode.
21.1 Flash Clean Overview
The web configuration provides Flash Clean screen.
21.2 Flash Clean Screen
Click [Flash Clean] in the navigation panel and open the [Flash Clean] Screen.
Figure 21-1 Flash Clean
The following table describes this screen.
Table 21-1 Flash Clean
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Clean [button] Clean all configuring VoIP Gateway stored.
Note:
User whose login name is root only executes it. All configurations in [Network Interface]
will be kept.
- 70 -

Chapter 22
Commit Data Screen
This Chapter covers save change after configuring VoIP Gateway.
22.1 Commit Configuration Data Overview
The web configuration provides Commit Configuration Data screen.
22.2 Commit Configuration Data Screen
Click [Commit Data] in the navigation panel and open the [Commit Configuration Data]
Screen.
Figure 22-1 Commit Configuration Data
The following table describes this screen.
Table 22-1 Commit Configuration Data
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Commit [button] Save changes after configuring VoIP Gateway.
- 71 -

Chapter 23
Reboot System Screen
This Chapter covers reboot to reload VoIP Gateway in new configuration.
23.1 Reboot VoIP Gateway Overview
The web configuration provides Reboot VoIP Gateway screen.
23.2 Reboot VoIP Gateway Screen
Click [Reboot System] in the navigation panel and open the [Reboot VoIP Gateway] Screen.
Figure 23-1 Reboot VoIP Gateway
The following table describes this screen.
Table 23-1 Reboot VoIP Gateway
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Reboot [button] After commit command, type reboot to reload VoIP Gateway in new
configuration. The procedure is as below:
- 72 -

Command with FXS Gateway
Part III:
Command with VoIP Gateway
This part gives information on commands to use.
- 73 -

Command with FXS Gateway
Chapter 24
Command List
This section introduces the command line interface and lists all of the commands.
24.1 Hyper Terminal Setting
A terminal emulator is needed when using RS-232 port to configure Gateway. There are
kinds of terminal emulator software. Here, we use Microsoft HyperTerminal to depict how to set
up terminal emulator:
Step 1. Execute the Hyper Terminal program, and then the following windows will pop-up on
the screen (STARTProgram filesAccessories Communication Hyper Terminal).
Figure 24-1 Connection Description
Step 2. Define a name such as [3502] for this new connection, after pressing [OK] button.
Figure 24-2 Connection Description
Step 3. The next windows appear, and then choose COM1/2 Port, which you are going to use.
- 74 -

Command with FXS Gateway
Figure 24-3 Connect To
Step 4. Configure the COM Port Properties as following: Bits per second: 9600, Flow control:
None, Press [OK] button, and then start to configure Gateway.
Figure 24-4 Com Properties
24.2 Power Up Your Gateway
At this point, you should have connected the console port, the LAN Port, the WAN port and
the power port to the appropriate devices or lines. Plug the power adapter into a wall outlet. The
Power LED should be on. The [Status LED] will come on after the system tests are complete.
The WAN LED and one of the LAN LED come on immediately after the [Status LED] come on,
if connections have been made to the LAN and WAN ports.
Initial Screen
When you power on your Gateway it performs server internal tests as well as line
initialization.
After the tests, the Gateway asks you to enter the Login, as shown.
....Attached TCP/IP interface to cpm unit 0
Attaching interface lo0...done
Hardware Type : 4FXS
- 75 -

Command with FXS Gateway
HTTPD initialized...
AC4804[0] is ok
AC4804[1] is ok
successful 2 2
Initialize OSS libraries...OK!
VP v1.44 stack open sucessfully.
cmInitialize succeed!
Ras port:1024
CallSignal port:1720
login:
Figure 24-5 Initial Screen
Entering Login
For you first login, enter the login [root] and default password [Null]. As you type the
password, the screen displays and (*) for each character you type.
....Attached TCP/IP interface to cpm unit 0
Attaching interface lo0...done
Hardware Type : 4FXS
HTTPD initialized...
AC4804[0] is ok
AC4804[1] is ok
successful 2 2
Initialize OSS libraries...OK!
VP v1.44 stack open sucessfully.
cmInitialize succeed!
Ras port:1024
CallSignal port:1720
login: root
Welcome to Terminal Configuration Mode
Please enter your configuration item
usr/config$
- 76 -

Command with FXS Gateway
Figure 24-6 Login Screen
Note:
Login account [root] or [administrator] is the default login account and there is no password
needed.
Set Password
To set your own password in root login name, just input command [passwd –set root ****].
For example, if password of root account is prepared as [voip], configuration it. When set
password ok, you can see ok message.
usr/config$ passwd -set root voip
Setting
Login: root
Password: voip
OK
usr/config$
Figure 24-7 password –set command
24.3 Command Structure with Gateway
24.3.1 Setup IP Address
Use command [ifaddr] to configure Gateway IP Address and related information.
For example:
Step 1. Setting ip address
usr/config$ ifaddr –ip 192.168.1.11 –mask 255.2555.255.0 –gate 192.168.1.254
Description:
This is to configure Gateway IP Address as [192.168.1.11], subnet mask as [255.255.255.0],
default router gateway as [192.168.1.254].
Step 2. Ather the configuration [commit] and [reboot] the device.
usr/config$ commit
usr/config$ reboot
Note:
After configured the IP Address and input the [commit], then [reboot] process, user can start
to do other configurations via HTTPD.
Application Version 200 supports PPPoE function for user to set up the login ID and
password to connect to Internet. Please refer to PPPoE mode for how to set up PPPoE.
- 77 -

Command with FXS Gateway
24.3.2 Application Mode Configuration
It is including Basic mode, such as Gatekeeper and Peer-to-Peer, and Advanced mode, such
as Hotline mode and IP-Sharing mode. It will be detailed in the next Chapter.
24.3.3 Saving Your Configuration
Save the change of configurations for Gateway and apply the new configurations by
rebooting the device.
Step 1. Confirm the changed configurations, input [commit] and press [enter] key to save it.
Step 2. Input [reboot] then press [enter] key to restart Gateway.
Step 3. After around 40 seconds, Gateway will take effect in new configurations.
These commands save all system configuration into nonvolatile memory. Nonvolatile
memory refers to the Gateway storage that remains even if the Gateway power is turned of. Run
Time (memory) is lost when the Gateway power is turned off. You must use the command to
save any configuration that you make, otherwise the Gateway will return to its default setting
when it is restarted.
Do not turn off your Gateway or remove the Gateway
while saving your configuration.
24.4 Application modes
This Chapter will introduce the four application modes users often use. Particularly the
Gatekeeper and Peer-to-Peer mode are the basic application mode. User would like to set as
advanced application mode, such as Hotline Mode and Behind IP-Sharing mode, please refer to
the basic application mode for more information.
24.4.1 Gatekeeper mode
User has to prepare a Gatekeeper Program. To assign a gatekeeper address for Gateway, and
define it’s own registered ID and phone number. For detail, please refer to [h323] command.
Several important H323 parameters are listed below when setting gatekeeper mode: [–gk],
[gwtype], [-prefix], [–line1], [–line2], [–line3], and [–line4].
Step 1. Setting gatekeeper mode, and line number
usr/config$ h323 –mode 0 (default gatekeeper mode)
usr/config$ h323 –gk 192.168.1.1 –prefix 1 –line1 11 –line2 12 –line3 13 –line4 14
For example:
usr/config$ h323 -print
H.323 stack relate information
RAS mode : GK mode
Gatekeeper IP address : 192.168.13.71
Second Gatekeeper IP : 192.168.13.71
- 78 -

Command with FXS Gateway
Gateway Type : Gateway
Registered prefix number : 1
Line1 : 11
Line2 : 12
Line3 : 13
Line4 : 14
H.235 security token : *
Registered alias : 4FXS-0015db
Display Information : 4FXS
Gatekeeper discovery : Off
Gatekeeper ID : GK
RAS TTL time : 60
RTP port : 16384
Gatekeeper finding port : 1718
GK RAS port : 1719
H225 RAS port : 1024
H225 Call signal port : 1720
Allocated port range :
start port : 1024
end port : 1043
Response timeOut : 15
Connect timeOut : 200
usr/config$
Note:
This is to set gatekeeper IP address as [192.168.1.1], prefix as [1], line 1 number as [11],
line 2 number as [12], line 3 number as [13], and line 4 number as [14]. The gateway type is
kept as default value as Gateway Type.
Step 2. Ather the configuration [commit] and [reboot] the device.
usr/config$ commit
usr/config$ reboot
24.4.2 Peer-to-Peer Mode
Peer-to-Peer Mode allows users to call other VoIP devices without using a gatekeeper. When
in Peer-To-Peer mode, Gateway will send SETUP message directly to the destination IP address
once the dial is finished. Users have 2 methods of dial. One is IP Address dialing, and the other is
[Phone Book] dial, which we will describe later. When using IP address as destination phone
- 79 -

Command with FXS Gateway
number, press [*] as [.] in IP address expression, and press [#] when dial is finished.
When using Phone Book, users can dial predefined phone number, and press [#] as end of
dial.
To configure Peer-To-Peer Mode in Gateway, follow the steps below:
Step 1. Set Peer-To-Peer Mode, using [h323] command
usr/config$ h323 –mode 1 (Peer To Peer mode)
For example:
usr/config$ h323 –print
H.323 stack relate information
RAS mode : Peer-to-Peer
Default Gateway : x
Line1(TEL 1) : 1001
Line2(LINE 1) : 1002
Line3(TEL 2) : 1003
Line4(LINE 2) : 1004
Alias(H323-ID) : 4FXS-0015db
Display Information : 4FXS
RTP port : 16384
H225 Call signal port : 1720
Destination H225 call signal port : 1720
Allocated port range :
start port : 1024
end port : 1043
Response timeOut : 15
Connect timeOut : 200
usr/config$
Step 2. Configure Phone Book, using [pbook] command.
Users can refer to [pbook] command for more information.
usr/config$ pbook –add name TEST1 ip 192.168.1.20 e164 20
Memo:
The command is to add a record onto PhoneBook. After the command completed, you
can type [pbook –print] to see if the input record is correct.
Step 3. Ather the configuration [commit] and [reboot] the device.
usr/config$ commit
usr/config$ reboot
- 80 -

Command with FXS Gateway
24.4.3 Hotline Mode
The Hotline Mode is applied in limited two peers. User just picks up the phone set and then
hears ring back tone or dial tone depended on configurations of destination device.
Gatekeeper Mode
Step 1. Set gateway under Gatekeeper mode.
Step 2. Create a Hotline table with [line] command.
Usr/config$ line –config 1 hotline 1001
In this example means: if user picks up phone set of FXS Line1, gateway will automatically
dial out [1001].
Step 3. Ather the configuration [commit] and [reboot] the device.
Usr/config$ commit
usr/config$ reboot
P2P Mode Usage:
Step 1. Set gateway under P2P mode.
Step 2. Create phone book table with [pbook] command.
Step 3. Create a Hotline table with [line] command.
usr/config$ h323 –mode 1
usr/config$ pbook –add name test ip 10.1.1.1 e164 1001
usr/config$ line –config 1 hotline 1001
In this example means: if user picks up phone set of FXS Line1, gateway will automatically
dial out IP address of [1001].
Step 4. Ather the configuration [commit] and [reboot] the device.
usr/config$ commit
usr/config$ reboot
24.4.4 Forward Mode
Set no answer forward table provides No Answer Forward function. For call forward
function, it can works under GK or P2P mode.
GK Mode Usage:
Step 1. Setting Line1 busy forward Line2
usr/config$ line –config 1 forward 1002
In this example means: if user calls in FXS Line and hasn’t been answered in forward time
(please refer to [sysconf -forwardtime] command), gateway will automatically forward this call
to phone number [1002].
Step 2. Ather the configuration [commit] and [reboot] the device.
- 81 -

Command with FXS Gateway
usr/config$ commit
usr/config$ reboot
P2P Mode Usage:
Step 1. Setting Line1 busy forward Line2
usr/config$ line –config 1 forward 1002
In this example means: if user calls in FXS Line1 when Line1 is busy, gateway will
automatically forward this call to IP address of [1002] in Phone book.
Step 2. Ather the configuration [commit] and [reboot] the device.
usr/config$ commit
usr/config$ reboot
24.4.5 Behind IP-Sharing Mode
The function is for user whose network environment is behind IP Sharing device. It is said
Gateway is connected to the IP Sharing device.
An example such as ADSL network is in the following.
Step 1. The WAN IP Address obtained from ADSL has two kinds of methods. One is fixed IP
Address, while user applies for one or more fixed IP Addresses. Another is dynamic IP
Address while user applies for dial-up connection way.
Step 2. The LAN IP Address of User’s PC can be set as DHCP client in order to gain a valid
one.
Step 3. Another IP Address for Gateway must be set as an fixed one in order for that IP
Sharing device pass forwarding the relevant information from WAN to LAN. Besides, a
- 82 -

Command with FXS Gateway
valid IP Address meets the IP Sharing device (LAN site) is the element.
Step 4. Gateway must enable the IP Sharing function for the fixed/dynamic WAN IP Address.
Fixed IP Address:
usr/config$ ifaddr –ipsharing 1 210.11.22.33
Dynamic IP Address:
usr/config$ ifaddr –ipsharing 1
Note:
With Dynamic WAN IP Address, a valid Gatekeeper for Gateway to get register on is a
must. In other word, it is not workable in Peer-to-Peer mode while dynamic WAN IP
Address.
Step 5. Ather the configuration [commit] and [reboot] the device.
usr/config$ commit
usr/config$ reboot
Step 6. IP Sharing device must have a function to do IP/Port mapping. Some is named as DMZ,
some is named as virtual server whatever. The VoIP messages from WAN have to
completely pass forward to the LAN. It is said if the Gateway is assigned a virtual fixed IP
Address such as 192.168.1.5, IP Sharing device must forward the VoIP message to
192.168.1.5.
Important Notes:
For some IP-Sharing devices do not support DMZ or virtual server function, but allowed user
to allocate some particular TCP/UDP port range.
While a complete H.323 communication is established, the following ports are possibly to be
used:
TCP port:
Q.931/H.225 1720
H.245 Dynamic,
But range 1025 ~ 1029 (not in use if Fast Start or Tunnel mode is
activated)
UDP port:
RAS Device: 1024,
Gatekeeper: 1719
RTP/ RTCP Adj u s t a b l e ,
Default: 16384 ~ (16384 + 4*Line Numbers)
Note:
- 83 -

Command with FXS Gateway
The port number allocation is for reference only. RTP/RTCP port may allocate on unexpected
port. It is better to define the port in wider range than limited range
24.4.6 PPPoE Mode
Step 1. Set PPPoE mode, using [ifaddr]
usr/config$ ifaddr –mode 2 (PPPoE mode)
Step 2. Input the user id & password provided by your ISP, using [ifaddr]
usr/config$ ifaddr –id 123@hinet.net
(PPPoE login account)
usr/config$ ifaddr –pwd 123 (PPPoE login Passowd)
Step 3. Reboot the device once after disconnection, using [ifaddr]
usr/config$ ifaddr –reboot 1 (Enable)
For example:
usr/config$ print
IP mode : PPPoE
PPPoE adapter information
Status : Not initialized
DNS primary : 168.95.1.1
DNS secondary : 168.95.1.2
HTTP port : 80
SNTP : mode=1
server 168.95.195.12
time zone : GMT+8
cycle=1024 mins
IPSharing : no IPSharing device.
IP change : Disable
PPPoE user name : 84460791@hinet.net
PPPoE password : ********
- 84 -

Command with FXS Gateway
PPPoE reboot : Yes
usr/config$
Step 4. Ather the configuration [commit] and [reboot] the device.
usr/config$ commit
usr/config$ reboot
Step 5. When Gateway connection success.
For example:
usr/config$ ifaddr -print
IP mode : PPPoE
PPPoE adapter information
Status : Ready
IP address : 61.216.36.6
Destination : 61.216.36.254
DNS primary : 168.95.192.1
Subnet Mask : 255.255.255.255
Authenticate : PAP
Protocol : TCP/IP
Device : PPP/PPPoE
DNS primary : 168.95.1.1
DNS secondary : 168.95.1.2
HTTP port : 80
SNTP : mode=1
server 168.95.195.12
time zone : GMT+8
cycle=1024 mins
IPSharing : no IPSharing device.
IP change : Disable
PPPoE user name : 84460791@hinet.net
PPPoE password : ********
PPPoE reboot : Yes
usr/config$
- 85 -

Command with FXS Gateway
24.4.7 PPPoE (NAT) mode (Dynamix DW-01/H only)
Step 1. Set PPPoE mode, using [ifaddr]
usr/config$ ifaddr –mode 2 (PPPoE mode)
Step 2. Input the user id & password provided by your ISP, using [ifaddr]
usr/config$ ifaddr –id 123@hinet.net
(PPPoE login account)
usr/config$ ifaddr –pwd 123 (PPPoE login Passowd)
Step 3. Reboot the device once after disconnection, using [ifaddr]
usr/config$ ifaddr –reboot 1 (Enable)
For example:
usr/config$ print
IP mode : PPPoE
PPPoE adapter information
Status : Not initialized
DNS primary : 168.95.1.1
DNS secondary : 168.95.1.2
LAN port IP (for NAT): 192.168.123.123
HTTP port : 80
SNTP : mode=1
server 168.95.195.12
time zone : GMT+8
cycle=1024 mins
IPSharing : no IPSharing device.
IP change : Disable
- 86 -

Command with FXS Gateway
PPPoE user name : 84460791@hinet.net
PPPoE password : ********
PPPoE reboot : Yes
usr/config$
Step 4. Ather the configuration [commit] and [reboot] the device.
usr/config$ commit
usr/config$ reboot
Step 5. When Gateway connection success.
Step 6. Setup PC use LAN IP connection Network
Select [Specify an IP Address] and enter [192.168.123.111] in the [IP Address] location
(where xxx is a number between 2 and 254 used by the VoIP Gateway to identify each
computer), and the default [Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0]. Note than no two computers on
the same LAN can have the same IP address. Gateway default gateway value
192.168.123.123 in the [new gateway] field. Then save your change.
Note:
One Group only use only LAN IP address, if have two gateway on this group, you must
change second gateway LAN IP Address different first gateway.
Gateway First:
usr/config$ ifaddr -lanip 192.168.124.124
Gateway Second:
usr/config$ ifaddr -lanip 192.168.124.125
Important Note:
This command function only Dynamix DW-01/H (FXS-01) VoIP Gateway used. So, other mode
VoIP Gateway not sees it.
For example:
usr/config$ ifaddr -print
IP mode : PPPoE
PPPoE adapter information
Status : Ready
IP address : 61.216.36.6
Destination : 61.216.36.254
LAN port IP (for NAT): 192.168.123.123
DNS primary : 168.95.192.1
Subnet Mask : 255.255.255.255
Authenticate : PAP
- 87 -

Command with FXS Gateway
Protocol : TCP/IP
Device : PPP/PPPoE
DNS primary : 168.95.1.1
DNS secondary : 168.95.1.2
HTTP port : 80
SNTP : mode=1
server 168.95.195.12
time zone : GMT+8
cycle=1024 mins
IPSharing : no IPSharing device.
IP change : Disable
PPPoE user name : 84460791@hinet.net
PPPoE password : ********
PPPoE reboot : Yes
usr/config$
24.4.8 H.450 Call Hold, Transfer and Forward Mode
Gateway provides H.450 function including call hold, transfer and forward. Please be noted
that both calling and called site have to support H.450 feature. For call forward function, it only
works under GK mode. Of course, GK must support H.450 feature.
To enable H.450 feature, it is better for user to prepare a telephone set supported [FLASH]
function on keypad. If telephone set does not support [FLASH] function on keypad, user is
possible to click the Hook quickly by sending FLASH message. The default FLASH value for
Gateway is between 100ms to 300 ms. It is said the value of Gateway is subject to the telephone
set.
Call Hold – press [FLASH]
By pressing the FLASH after making a call, both site shall hear the 2nd dial tone generated
by Gateway. To retrieve the call back, just press the FLASH again.
Call Transfer – press [FLASH], then [transferring number]
For example, A call B, B transfer to C
A make call to B, B press FLASH. A and B hear 2nd dial tone. B presses the C’s number. C
ringing and A hear the RingBack tone. B Hang up its call. A and C Make call.
Call Forward:
Activate - *147#
Deactivate - *258#
Busy Forward – [Forward No.] *#
- 88 -

Command with FXS Gateway
No response/ Answer – [Forward No.]*1#
Unconditional – [Forward No.]*2#
It is important to send an activate/deactivate call forward message before setting up the
forward number. This function is only available under GK mode, and the GK supports H.450
Call Forward function. There are three conditions for user to set a forwarding number.
Step 1. Busy Forward – while line is engaged or phone set is off-hook.
Step 2. No response/Answer – while no one answer the call.
Step 3. Unconditional – forward it unconditionally.
24.5 How to upgrade
Before you start downloading
Step 1. Please confirm Host PC, which is installed as TFTP / FTP server and device is in
available network.
Step 2. Remember the current configuration, such as [h323], [line], [pbook], and you change
configuration data.
Step 3. It will list current version and default download method. Please check the Application
Rom in particular, it is showed version list, as well as the most common one you have to
upgrade.
Step 4. General speaking, App Rom is named including product name and version and size is
under 1MB, such as 2fxs.115a. 2MB Rom is named such as 2m2fxs.115a. Please be very
careful of the prepared Rom file while upgrading.
Step 5. Check Application Rom Version, input [rom –print] command
For example:
usr/config$ rom –print
Download Method : TFTP
Boot Rom : sdboot.200
Application Rom : 4afxs.203a
DSP App : 48302ce3.140
DSP Kernel : 48302ck.140
DSP Test Code : 483cbit.bin
usr/config$
Step 6. Prepare FTP or TFTP server ready.
Upgrade steps: FTP Mode (Application Rom)
- 89 -

Command with FXS Gateway
Step 1. Choose Download Method: FTP method
1. [-method]: Choose download method: FTP method,
2. input the FTP Login name and password
3. [rom -print]: check configuration data
usr/config$ rom –method 1
usr/config$ rom –ftp id password
usr/config$ rom –print
For example:
usr/config$ rom -print
Download Method : FTP
FTP username : test
FTP password : test
Boot Rom : sdboot.200
Application Rom : 4afxs.203a.bin
DSP App : 48302ce3.140
DSP Kernel : 48302ck.140
DSP Test Code : 483cbit.bin
usr/config$
Step 2. Application Rom upgrade
1. [-app]: Choose means the prepared upgrade Rom.
2. [-s]: input the FTP Server IP Address.
3. [-f]: input the Rom files name
usr/config$ rom –app –s 192.168.1.1 –f 4afxs.204
Step 3. flash –clean
Command [flash -clean] to clear old configurations. It will keep all configurations in
[ifaddr].
usr/config$ flash –clean
Note:
Old version: such as 115a, will only keep IP Address and MAC Address.
Upgrade steps: TFTP Mode (Boot2m)
Step 1. Choose Downlaod Method: TFTP method (default)
1. [-method]: Choose download method: TFTP method,
- 90 -

Command with FXS Gateway
2. [rom -print]: check configuration data
usr/config$ rom –method 0
usr/config$ rom –print
For example:
usr/config$ rom –print
Download Method : TFTP
Boot Rom : sdboot.200
Application Rom : 4afxs.203a
DSP App : 48302ce3.140
DSP Kernel : 48302ck.140
DSP Test Code : 483cbit.bin
usr/config$
Step 2. Boot2m upgrade
1. [-boot2m]: Choose means the prepared upgrade Rom.
2. [-s]: input the FTP Server IP Address.
3. [f]: input the Rom files name
usr/config$ rom –boot2m –s 192.168.1.1 –f 2m4afxsH.204
Note:
If the version list is older than 113, all configurations will be back to default value,
including IP Address. In other word, user has to set IP Address and MAC Address before
[reboot] the device; otherwise, user cannot access to device any more via Telnet.
The version 200 and above support to keep every configurations after upgrade. If you
upgrade version 200 over and above you check step 6.
Step 3. Find out MAC Address:
There are 12 digits on label on the back panel of the device, or command as [ifaddr -ifshow]
(find the list information of Ethernet address, it is MAC Address).
usr/config$ ifaddr –ifshow
For example:
usr/config$ ifaddr -ifshow
cpm (unit number 0):
Flags: (0x8063) UP BROADCAST MULTICAST ARP RUNNING
Type: ETHERNET_CSMACD
Internet address: 192.168.13.80
Broadcast address: 192.168.15.255
- 91 -
 Loading...
Loading...