Page 1
Bulletin H-12-A
Series 160E Modified Ellipsoidal Pitot Tubes
Specifications - Installation and Operating Instructions - Flow Curves
Series 160E Pitot tubes conform to ISO 3966 for National Physics Laboratory type
Modified Ellipsoidal Tip Pitot tubes. They are constructed of 304 stainless steel
materials for use in corrosive environments to 1500°F (815°C). Orientation can be
visually determined by observing the alignment arm which is parallel to the tip.
These Pitot tubes provide an alternative to the Series 160 hemispherical design. All
Series 160 accessories can be used with Series 160E units.
Note: The ellipsoidal tip provides improved accuracy over the hemispherical tip when
alignment is maintained within 2° of flow. However this design is more prone to
damage, so extra care should be taken to avoid rough handling.
INTRODUCTION
The total pressure of a flowing air stream in a duct or pipe is the sum of the static
or bursting pressure exerted on the sidewalls and the velocity or impact pressure
of the moving air. The difference between total and static pressures is called
velocity pressure which can be used to determine the linear rate of air movement
expressed in FPM or feet per minute. A Pitot tube has two tubes, one inside the
other, to sense both pressures simultaneously. By connecting these two tubes
differentially to a manometer, velocity pressure is indicated directly and the
corresponding air velocity can be calculated after applying the appropriate correction
factor.
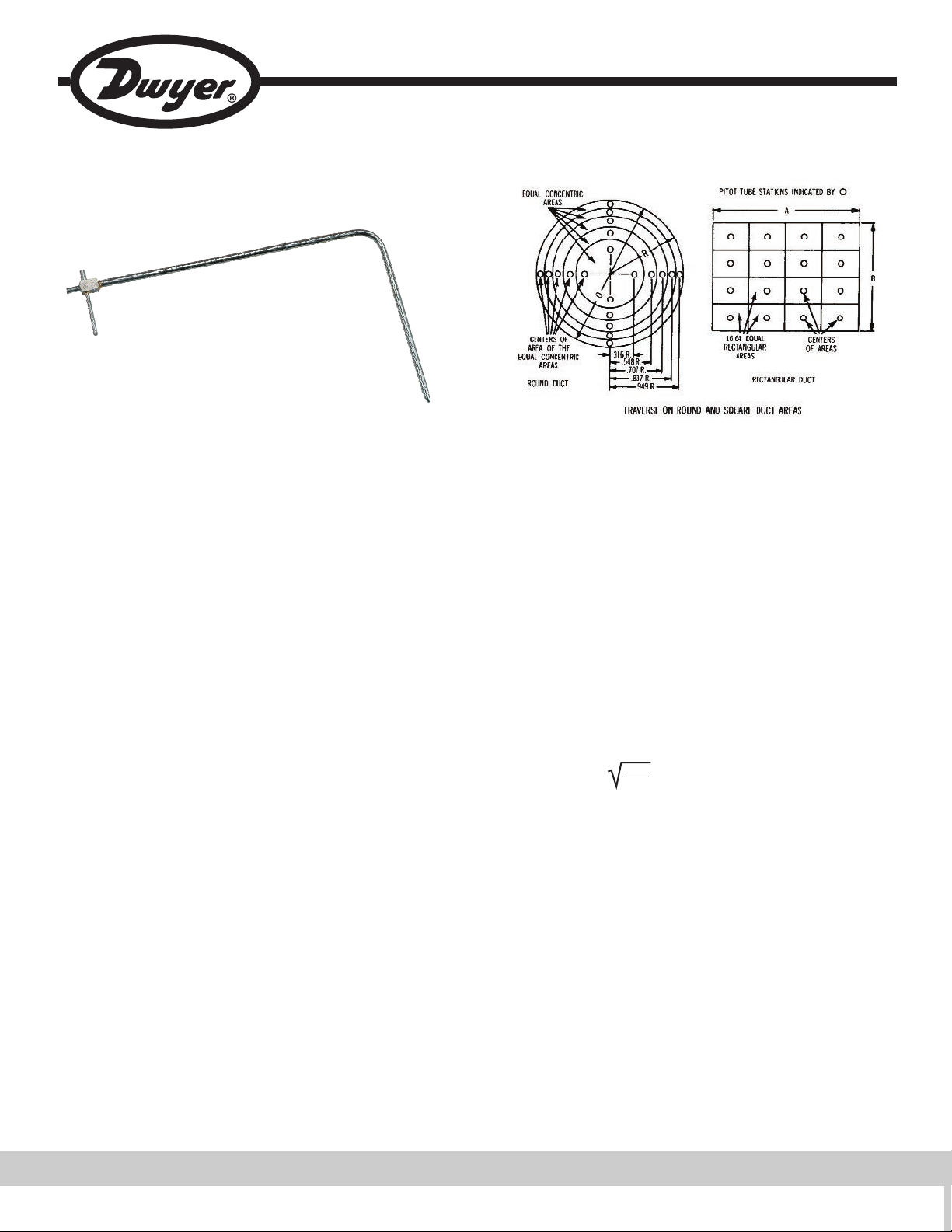
For maximum accuracy of ±2% as in laboratory applications, care is required and
the following recommendations should be followed.
1. Duct diameter should be 4˝ or larger.
2. Point tip upstream facing flow.
3. Make an accurate traverse per drawings, calculate the velocities at each point
and average them.
4. Take readings in a smooth, straight duct section a minimum of 8-1/2 duct
diameters in length upstream and 1-1/2 diameters downstream from the Pitot
tube.
5. Provide an egg crate type straightener upstream from the Pitot tube.
TAKING AIR VELOCITY READINGS
To measure air velocity with a Series 160E Pitot tube, make a 3/8˝ (9.5 mm) diameter
hole on the side of the duct. Insert Pitot tube to the required depth and connect to a
manometer or pressure gage with an appropriate range. The total pressure tap
should be connected to the high pressure side of the manometer and the static
pressure tap to the low pressure side. If reading is negative, reverse connections.
Make a series of readings traversing the duct in horizontal and vertical planes. Using
velocity pressures recorded at each location, calculate velocities and average
them for final velocity value.
If circumstances do not permit or require an accurate traverse, center the Pitot tube
in the duct, determine the pressure differential (velocity pressure), calculate actual
center velocity and multiply this value by 0.9. Tests run in this manner should be
accurate within ±5%.
CALCULATING VELOCITY
Follow instructions printed on the Dwyer Air Velocity Slide Chart included with each
Pitot tube or use the following equations:
Air Velocity = 1096.7
where P
Air Density = 1.325 x P
where P
Flow in cubic feet per minute equals duct cross sectional area in square feet x air
velocity in feet per minute.
With dry air at 29.9 inches mercury, air velocity can be read directly from temperature
correction charts on reverse.
V = Sensed pressure difference (velocity pressure) in inches of water
column
D=Air density in pounds/cubic foot (dry air = .075)
C=Pitot tube coefficient - 1.0
B = Barometric pressure in inches of mercury
T=Absolute temperature (indicated temperature in°F plus 460)
PV C
D
B T
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 2

AIR velocIty In feet peR mInute
GAGe ReADInG WItH pItot tuBe (velocIty pReSSuRe) In IncHeS of WAteR
AIR velocIty In feet peR mInute
GAGe ReADInG WItH pItot tuBe (velocIty pReSSuRe) In IncHeS of WAteR
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
 Loading...
Loading...