Page 1

F - UFM
UFM
Ultrasonic Flowmeter
User Manual
Issue 1.4 Page 1
Page 2

F - UFM
Table of Contents
1 General Description ........................................................................................................................ 4
2 How does it work? .......................................................................................................................... 5
3 User interface .................................................................................................................................. 6
3.1 Key switches ............................................................................................................................ 6
4 Installing the UFM ........................................................................................................................... 7
4.1 Preparation ............................................................................................................................. 8
4.2 Sensor separation ................................................................................................................... 8
4.3 Adaptors for small pipes ....................................................................................................... 10
4.4 Attaching the UFM to the pipe ............................................................................................. 11
4.5 UFM interface cable .............................................................................................................. 12
4.6 Connecting the UFM to the Supply ....................................................................................... 12
4.7 Pulse Output connection ...................................................................................................... 12
4.8 Current Output ...................................................................................................................... 13
4.9 Cable Screen .......................................................................................................................... 13
5 Powering up for the first time ....................................................................................................... 14
5.1 How to enter the Pipe ID ...................................................................................................... 15
5.2 Pulse output .......................................................................................................................... 16
5.2.1 Volumetric mode .......................................................................................................... 16
5.2.2 Frequency mode ........................................................................................................... 16
5.3 4-20 mA Current output........................................................................................................ 16
6 Subsequent Power-ON Sequence ................................................................................................. 17
7 Password Controlled Menus ......................................................................................................... 17
7.1 General procedure for changing menu settings ................................................................... 17
7.1.1 Selection menus ............................................................................................................ 17
7.1.2 Data entry menus .......................................................................................................... 18
7.2 User Password controlled menu structure ........................................................................... 18
8 Diagnostics Menu .......................................................................................................................... 23
9 Relocation of guide rail ................................................................................................................. 24
10 Appendix I – UFM Specification ................................................................................................ 25
11 Appendix II – Default values ..................................................................................................... 26
12 Appendix III – Error and Warning Messages ............................................................................. 27
Issue 1.4 Page 2
Page 3

F - UFM
12.1 System errors ........................................................................................................................ 27
12.2 Warnings ............................................................................................................................... 27
13 Maintenance/Repair ................................................................................................................. 28
14 Warranty /Return ...................................................................................................................... 28
Issue 1.4 Page 3
Page 4

F - UFM
1 General Description
The UFM is a fixed installation, clamp-on flowmeter that is easy to install and requires
minimum information to be entered by the user. Both the electronics and guide rail housings
form an integral unit that is attached to the pipe using the supplied jubilee clips. Power to the
unit is provided by an external 12 – 24 V ac/dc power supply. The UFM is intended to operate
on steel, copper and plastic pipes with OD’s in the range 0.98 inches (24.9 mm) to 4.62 inches
(117.4 mm).
Compact, rugged and reliable, the UFM has been designed to provide sustained performance
in industrial environments.
UFM standard features include:
2 line x 16 character LCD with backlight
4-key keypad
Isolated pulse output
4-20 mA current output
Simplified guide rail and transducer assembly
Continuous signal monitoring
Password protected menu operation for secure use
Operates from external 12 to 24 V ac/dc power supplies
Small pipe adaptors
Typical applications
Hot water metering and flow measurement
Flow measurement for heat metering
Chilled water metering and flow measurement
Potable water metering and flow measurement
Process water metering and flow measurement
Ultra pure water metering and flow measurement.
Issue 1.4 Page 4
Page 5
F - UFM
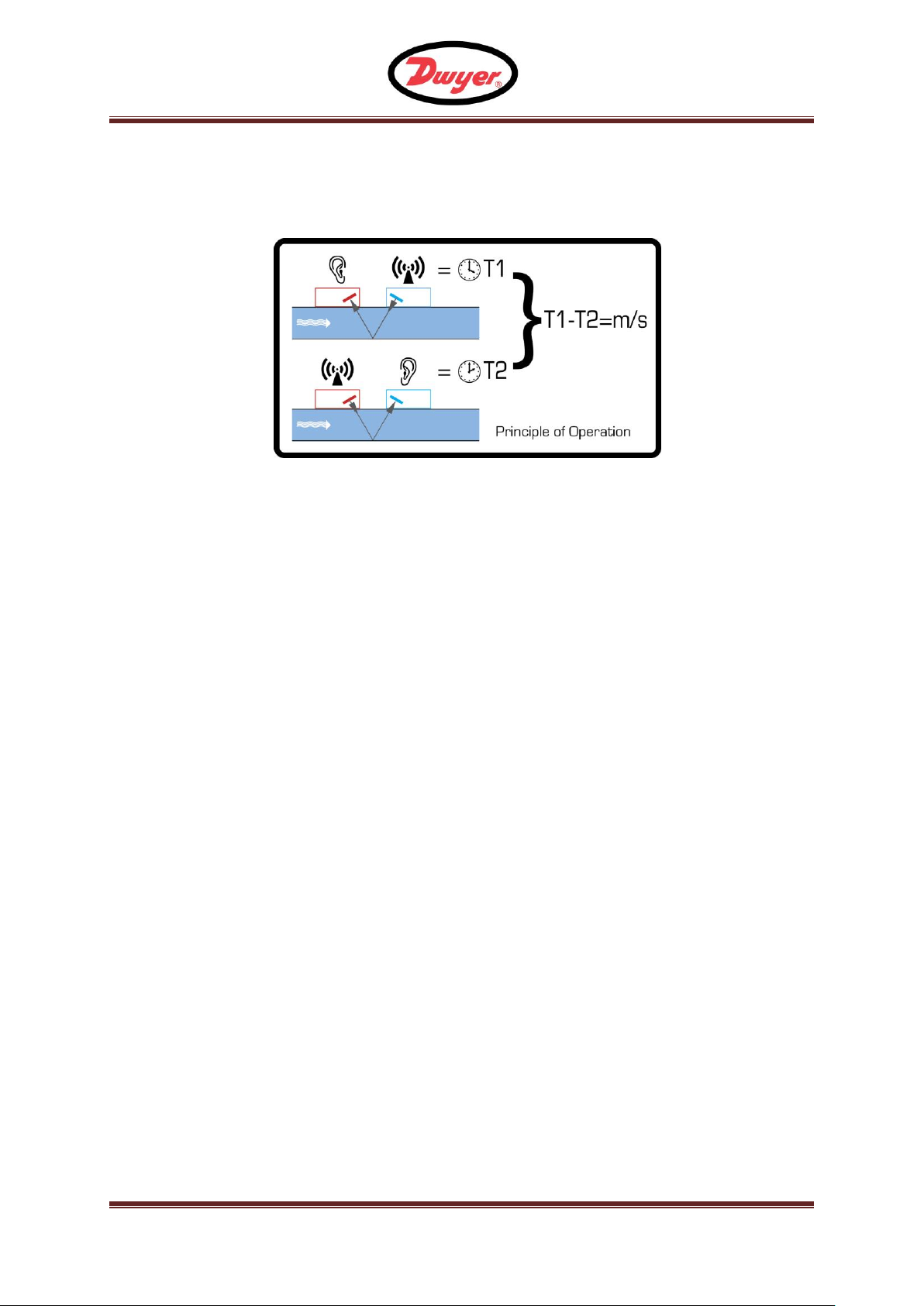
Figure 1 Principle of Transit-Time operation
2 How does it work?
The UFM is a clamp-on, ultrasonic flowmeter that uses a multiple slope transit time algorithm
to provide accurate flow measurements.
An ultrasonic beam of a given frequency is generated by applying a repetitive voltage pulse to
the transducer crystals. This transmission goes first from the Downstream transducer to the
Upstream transducer (red) as shown in the upper half of Figure 1. The transmission is then
made in the reverse direction, being sent from the Upstream transducer (red) to the
Downstream transducer (blue) as shown in the lower half of Figure 1. The speed at which the
ultrasound is transmitted through the liquid is accelerated slightly by the velocity of the liquid
through the pipe. The subsequent time difference T1 – T2 is directly proportional to the liquid
flow velocity.
Issue 1.4 Page 5
Page 6
F - UFM
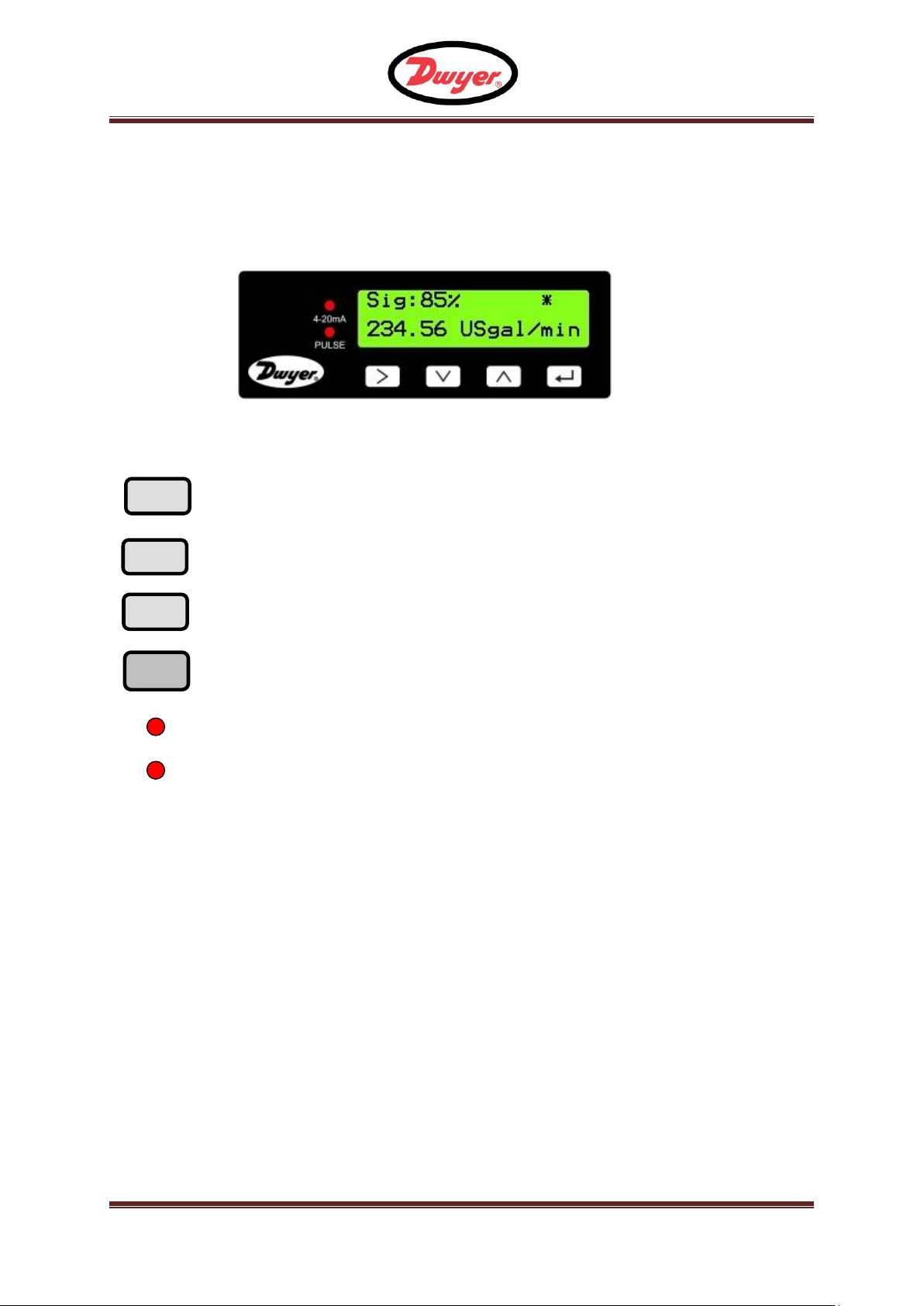
Figure 2 UFM User Interface
Selection key. Allows the user to select between options on the
display.
Used to increment the value of each digit in numeric entry fields.
Used to decrement the value of each digit in numeric entry fields.
Used to enter the selection displayed or terminate the data entry.
Pressing this key will take the user to another menu or to the Flow
Reading screen.
V
Λ
3 User interface
Figure 2 illustrates the UFM user interface comprising of :
One 2 line x 16 character LCD with backlight
Four tactile key switches
Two LED’s
3.1 Key switches
4-20 mA LED is illuminated when the 4-20 mA output is ON
Pulse LED is illuminated when the Pulse output is ON
Issue 1.4 Page 6
Page 7
F - UFM
Possible Air
Possible
sludge
Guide
rail
Uniform Flow Profile
Distorted Flow Profile
Flow
Flow
Valid transducer location
20 x Diameter
10 x Diameter
45°
4 Installing the UFM
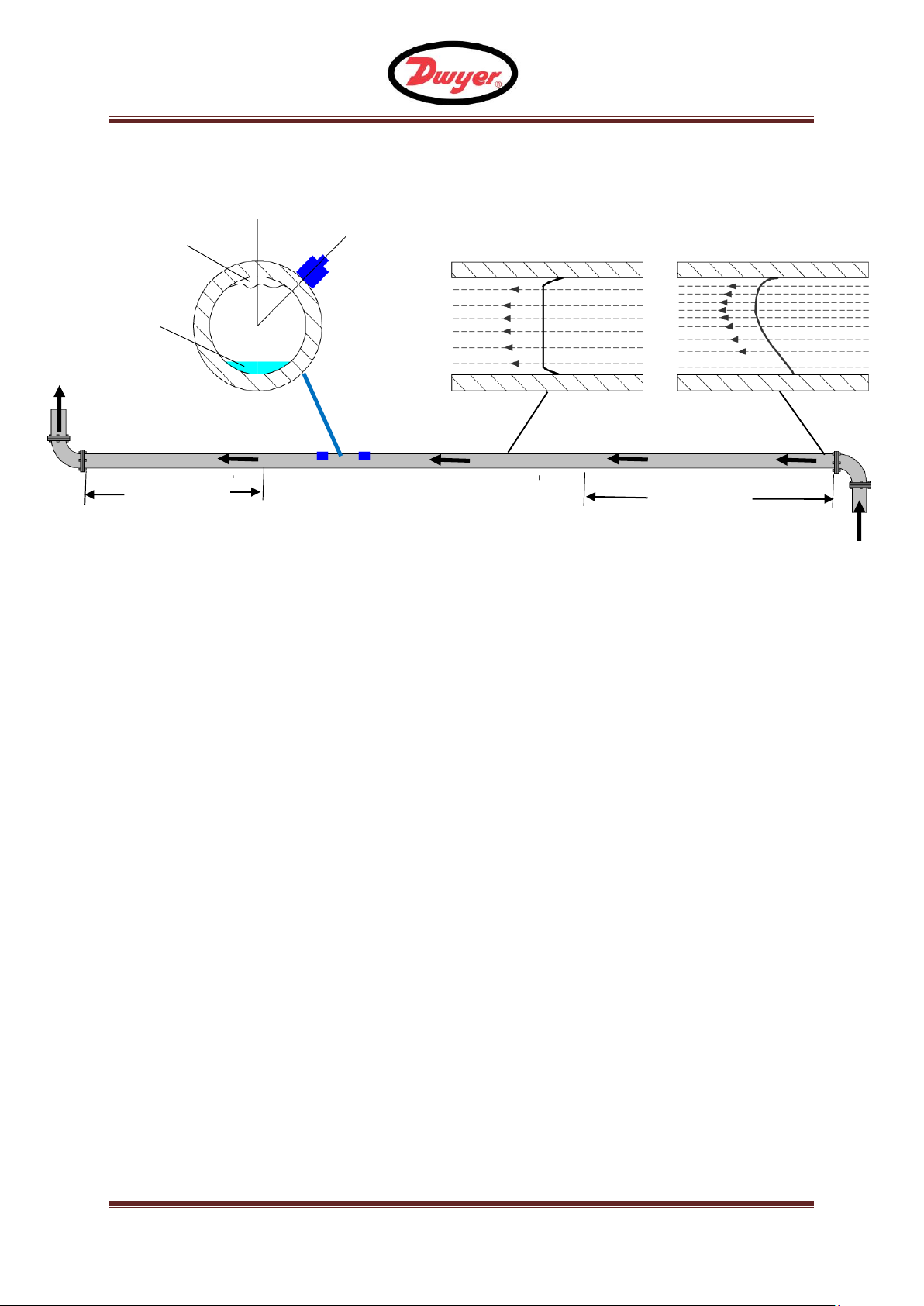
Figure 3 Location of Transducers
In many applications an even flow velocity profile over a full 360° is unattainable due to the
presence of air turbulence at the top of the flow and possibly sludge at the bottom of the pipe.
Experience has shown that the most consistently accurate results are achieved when the
transducer guide rails are mounted at 45° with respect to the top of the pipe.
The UFM equipment expects a uniform flow profile, as a distorted flow will produce
unpredictable measurement errors. Flow profile distortions can result from upstream
disturbance such as bends, tees, valves, pumps and other similar obstructions. To ensure a
uniform profile the transducers must be mounted far enough away from any cause of distortion
such that it no longer has an effect.
To obtain the most accurate results the condition of both the liquid and the pipe must be
suitable to allow ultrasound transmission along the predetermined path. It is important that
liquid flows uniformly within the length of pipe being monitored, and that the flow profile is not
distorted by any upstream or downstream obstructions. This is best achieved by ensuring
there is a straight length of pipe upstream of the transducers of at least 20 times the pipe
diameter, and 10 times the pipe diameter on the downstream side, as shown in Figure 3. Flow
measurements can be made on shorter lengths of straight pipe, down to 10 diameters
upstream and 5 diameters downstream, but when the transducers are mounted this close to
any obstruction the resulting errors can be unpredictable.
Key Point: Do not expect to obtain accurate results if the transducers are positioned close to
any obstruction that distorts the uniformity of the flow profile.
Issue 1.4 Page 7
Page 8
F - UFM
Pipe Material
Plastic & Copper
Steel
Minimum
Maximum
Minimum
Maximum
B1
0.98 inches (24.9 mm)
1.22 inches (31.0 mm)
A2
1.22 inches (31.0 mm)
1.50 inches (38.1 mm)
0.98 inches (24.9 mm)
1.18 inches (30.0 mm)
C1
1.50 inches (38.1 mm)
1.69 inches (42.9 mm)
1.18 inches (30.0 mm)
1.42 inches (36.1 mm)
B2
1.69 inches (42.9 mm)
1.97 inches (50.0 mm)
1.42 inches (36.1 mm)
1.69 inches (42.9 mm)
A3
1.97 inches (50.0 mm)
2.20 inches (55.9 mm)
1.69 inches (42.9 mm)
1.93 inches (49.0 mm)
C2
2.20 inches (55.9 mm)
2.44 inches (62.0 mm)
1.93 inches (49.0 mm)
2.17 inches ( 55.1 mm)
B3
2.44 inches (62.0 mm)
2.68 inches (68.1 mm)
2.17 inches ( 55.1 mm)
2.40 inches (61.0 mm)
D2
2.68 inches (68.1 mm)
2.91 inches (73.9 mm)
2.40 inches (61.0 mm)
2.64 inches (67.0 mm)
C3
2.91 inches (73.9 mm)
3.15 inches (80.0 mm)
2.64 inches (67.0 mm)
2.87 inches (72.9 mm)
E2
3.15 inches (80.0 mm)
3.39 inches (86.1 mm)
2.87 inches (72.9 mm)
3.11 inches (79.0 mm)
D3
3.39 inches (86.1 mm)
3.66 inches (93.0 mm)
3.11 inches (79.0 mm)
3.35 inches (85.1 mm)
C4
3.66 inches (93.0 mm)
3.90 inches (99.0 mm)
3.35 inches (85.1 mm)
3.58 inches (90.9 mm)
E3
3.90 inches (99.0 mm)
4.13 inches (104.9 mm)
3.58 inches (90.9 mm)
3.82 inches (97.0 mm)
D4
4.13 inches (104.9 mm)
4.37 inches (111.0 mm)
3.82 inches (97.0 mm)
4.06 inches (103.1 mm)
F3
4.37 inches (111.0 mm)
4.53 inches (115.0 mm)
4.06 inches (103.1 mm)
4.29 inches (109.0 mm)
E4
4.53 inches (115.0 mm)
4.62 inches (117.3 mm)
4.29 inches (109.0 mm)
4.53 inches (115.0 mm)
D5
4.53 inches (115.0 mm)
4.62 inches (117.3 mm)
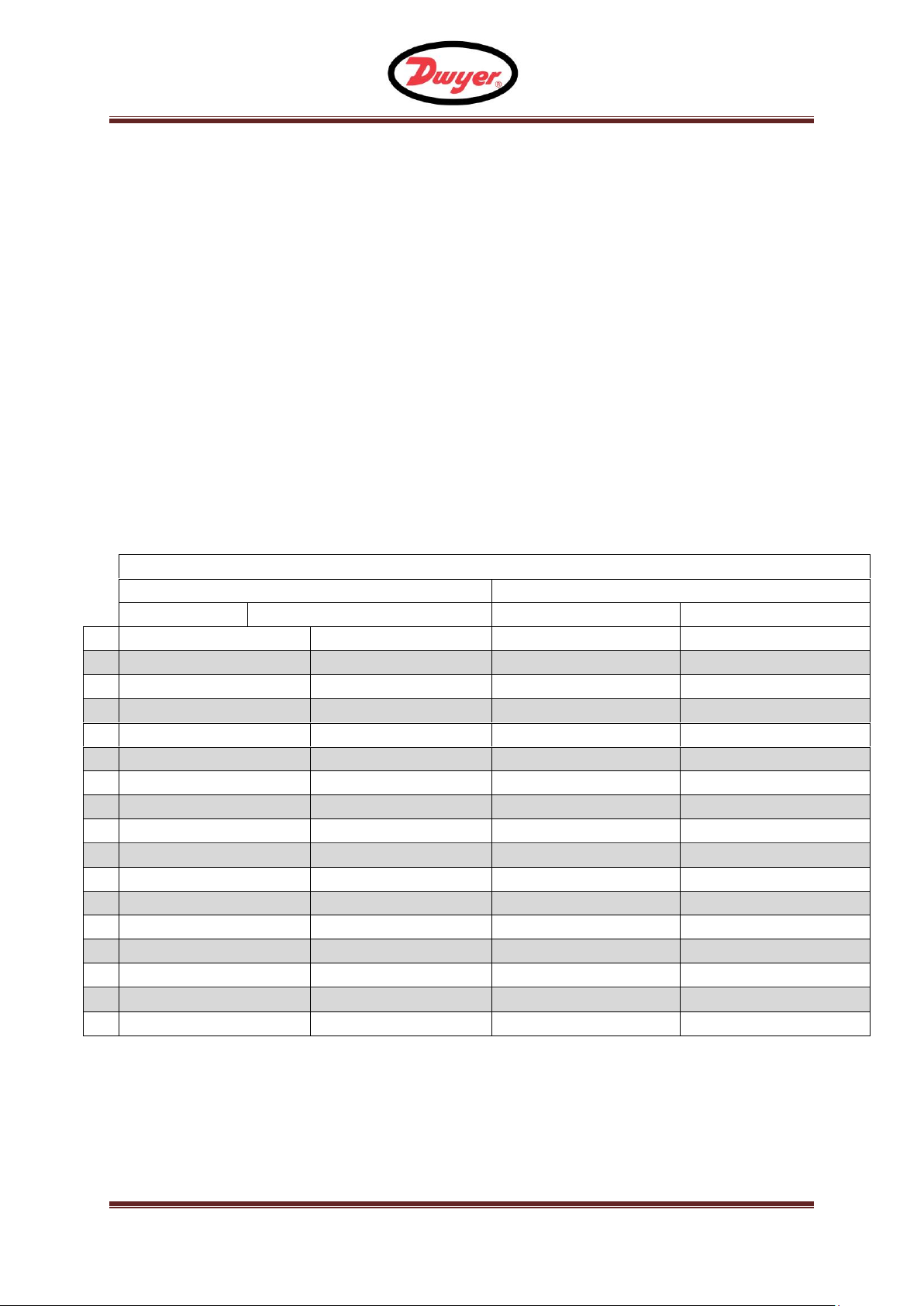
Pipe OD range (inches)
4.1 Preparation
1. Before attaching the transducers first ensure that the proposed location satisfies the
distance requirements shown in Figure 3 otherwise the resulting accuracy of the flow readings
may be affected.
2. Prepare the pipe by degreasing it and removing any loose material or flaking paint in order
to obtain the best possible surface. A smooth contact between pipe surface and the face of
the transducers is an important factor in achieving a good ultrasound signal strength and
therefore maximum accuracy.
4.2 Sensor separation
The sensor must be positioned at the correct distance for the pipe size and type they will be
used on. The table shown in Figure 4 gives the separation code for a given pipe material and
outside diameter. This code will be displayed whenever the pipe inside diameter and material
are prompted for.
Issue 1.4 Page 8
Figure 4 Separation Table
Page 9
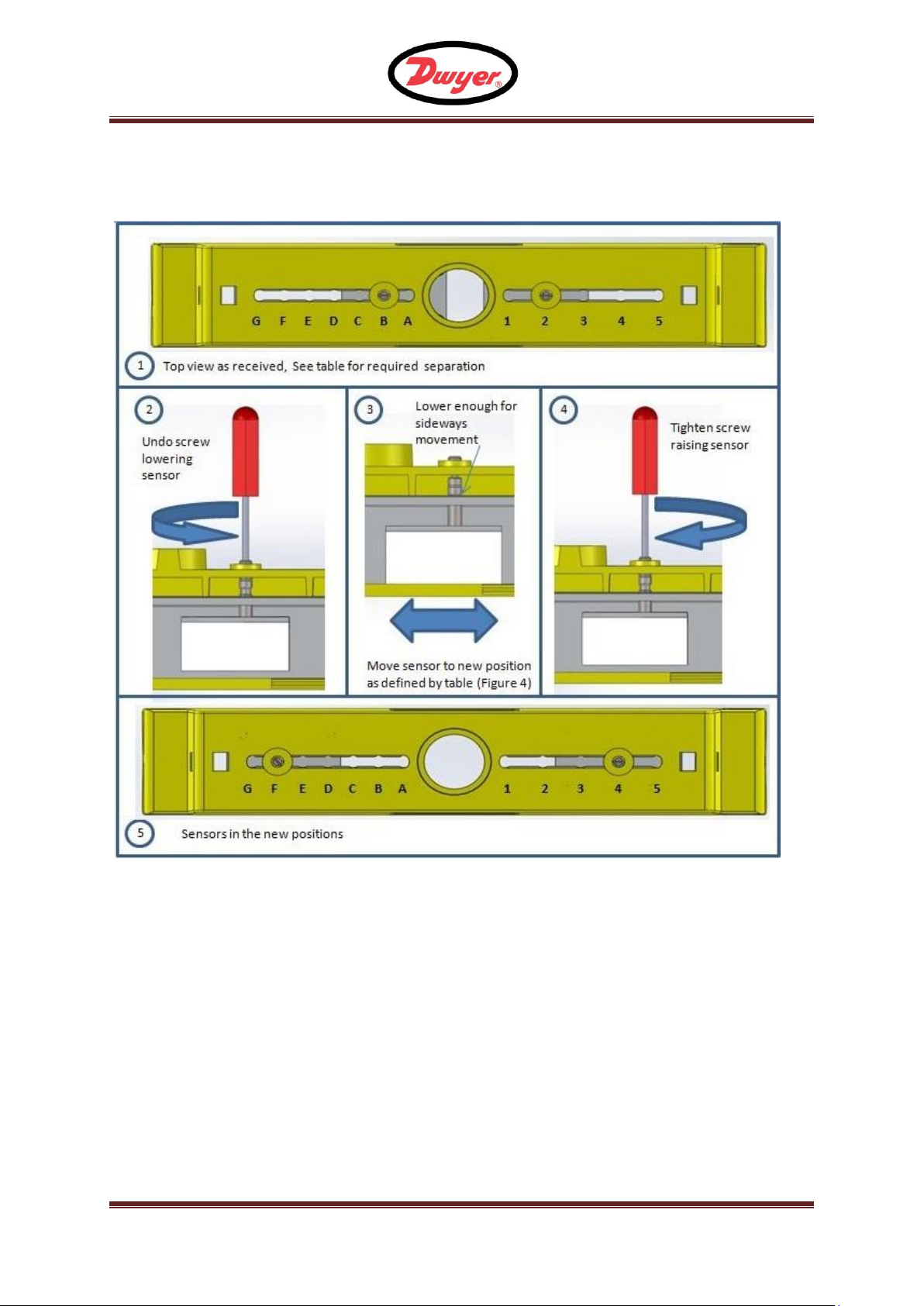
F - UFM
The diagram in figure 5 shows how to adjust the separation of the sensors
Figure 5 Separation Setting
Issue 1.4 Page 9
Page 10

F - UFM
Less than 1.6 inches (40.6 mm) outside diameter
1.6 to 2.4 inches (40.6 to 61 mm) outside diameter
Greater than 2.4 inches (61.0 mm) outside diameter
4.3 Adaptors for small pipes
Figure 6 Pipe Adaptors
Adaptors are supplied for use on small pipes. The diagrams in figure 6 show how these are fitted
around the pipe. The top pipe adaptor clips into the ends of the guide rail.
Issue 1.4 Page 10
Page 11

F - UFM
The grease provided in the syringe is applied to the
center of the sensors as shown above.
Clamp guide rail and sensor assembly to pipe,
using the supplied banding, and release sensor
locking screws.
Connect power and sensors to the electronics
assembly. Sensor leads can be connected either
way round.
4.4 Attaching the UFM to the pipe
Follow the five steps shown in Figure 7 below to attach the UFM to the pipe.
Click electronic assembly onto guide rails and sensor assembly
Figure 7 Simple Steps to Attaching the UFM on the Pipe
The locking screws and washers should be kept in case it is necessary to change the location of the
guide rail and sensors. See the relocation instructions in section 9 for the procedure to do this.
Issue 1.4 Page 11
Page 12

F - UFM
Power
Pulse
4-20 mA
Figure 8 UFM Interface Cable
12/24 V Input (+)
12/24 V Return (-)
Pulse Output
Pulse Return
4-20 mA Output (+) (Polar Sensitive)
4-20 mA Return (-) (Polar Sensitive)
Un-insulated screen
4.5 UFM interface cable
The UFM interface cable supplied is a 6-core cable and is shown in Figure 8.
The polarity of the wires is as follows:
The un-insulated wire is the connection to the screen of the cable and should be earthed for full
immunity to electrical noise.
4.6 Connecting the UFM to the Supply
The UFM will operate within the voltage range 12 – 24 V ac/dc. Connect the external power
supply to the Brown and Blue wires of the six core cable. For full compliance with EMC
regulation a 12 V supply is recommended for domestic and light industrial applications.
4.7 Pulse Output connection
The isolated pulse output is provided by a SPNO MOSFET relay which has a maximum load
current of 500 mA and maximum load voltage of 48 V ac. The relay also provides 2500 V
isolation.
The pulse output is available at the White and Green wires. Electrically this is a volt free
contact closure.
Issue 1.4 Page 12
Page 13

F - UFM
4.8 Current Output
The isolated 4-20 mA is a current source and can drive into a maximum load of 620 Ω.
The 4-20 mA current output is available at the Red and Black wires. The polarities are shown
in Figure 8.
The alarm current due to a flow outside the range specified or due to a loss of signal is set at
3.5 mA.
4.9 Cable Screen
For full immunity to electrical interference the screen of the cable should be connected to
Earth.
Issue 1.4 Page 13
Page 14

F - UFM
5 Powering up for the first time
Powering up for the first time will initiate the sequence shown in Figure 9:
Figure 9 Powering the Unit Up
1. The startup screen is displayed for 5 seconds
2. The user enters the pipe ID and then the material by scrolling through the available list.
(refer to section 5.1)
3. The UFM checks for a valid signal
4. If a valid signal is found, signal strength and flow magnitude are displayed. The direction of
flow when powered up will be set as that for positive flow. The current output and pulse output
will relate to the flow in this direction. If the flow is reversed then the flow rate will still be
displayed but the activity indication will change from an asterisk to an exclamation mark. No
pulses will be generated, and the current will go to the 3.5 mA alarm state if the flow is
reversed.
Issue 1.4 Page 14
Page 15

F - UFM
Press the
key to increment the inches digit (1.964) in the sequence 0, 1. Press once
to increment digit, or hold key down to automatically scroll between 0 and
4.
Press the
key to decrement the inches digit in the sequence 4 to 0. Press once to
decrement digit, or hold key down to automatically scroll between 4 and
0.
Press the
key to move to the 0.1 inch digit (1.964). The 0.1 inch digit should now
blink.
Increment the 0.1 inch digit in the sequence 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0 using
the
key. Press once to increment digit or hold down to scroll
through the numeric sequence. Decrement the 0.1 inch digit in the
sequence 9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0,9 using the key. Press once to
increment digit or hold down to scroll through the numeric sequence.
Press the
key to move to the 0.01 inch and 0.001 inch digits. The selected digit
should now blink. Increment or decrement the digit in an identical manner
to the 0.1 inch digit described above.
Press the
Use
Press the
key to enter the Pipe ID numerical value, and move to the next screen.
and
keys to scroll through the pipe materials.
To select the material and complete the setup
procedure.
V
Figure 10 Enter Pipe ID Screen (Metric)
V
Pipe material
Plastic
V
5.1 How to enter the Pipe ID
Figure 10 shows the Enter Pipe ID screen after an initial power up.
Initially, the inches digit (1.964) will blink.
Issue 1.4 Page 15
Page 16

F - UFM
If any of the parameters need to be changed from the default values, for example different
units are required, then the menu system must be activated via the password (see section 7).
5.2 Pulse output
Pulse output can be set up to operate in two modes, namely volumetric and frequency.
5.2.1 Volumetric mode
In Volumetric mode, each pulse output represents a measured volume of 10 gallons (default
value). In Volumetric mode, with the Vol per Pulse set to 1 and the pulse width set to 25 ms,
the maximum number of pulses that can be output (without storage) is 1/(0.025*2) = 20 pulses
per second. If the flow rate in the pipe is such that more than 20 pulses per second are
generated, a Pulse Overflow error may eventually occur if the stored number of pulses
exceeds 1000. To avoid this, set the Vol per Pulse to 100 gallons.
5.2.2 Frequency mode
In Frequency mode, the pulse output frequency is proportional to the flow rate within a
specified frequency range of 0 – 200 Hz.
5.3 4-20 mA Current output
The default 4-20 mA output setting will be ON, and the 4-20 mA LED on the keypad will be
illuminated. The default flow for 20 mA output will be automatically set depending on the pipe
size. The default flow for 4 mA is 0. This can be changed, see section 7.
If the flow reading is greater than that set as the 20 mA value, or there is negative flow, or no
flow signal can be detected, then an alarm current of 3.5 mA will generated.
Note: The 4-20 mA current output is factory calibrated.
Issue 1.4 Page 16
Page 17

F - UFM
Figure 11 Flow Units menu
6 Subsequent Power-ON Sequence
If the power supply is cycled OFF then ON after the pipe ID has been entered, all subsequent
start-ups will use the same configuration as was previously entered. If the configuration needs
to be changed for any reason, the user can make use of the password-controlled menu as
described in section 7.
7 Password Controlled Menus
The password controlled menu allows the user some flexibility to change the default settings:
User Password (71360):
Change the dimensions from mm to inches or vice-versa.
Change from Flow to Velocity Measurement
Change the system units liters/m3 or Impgal/USgal
Change the flow units l/s, l/min or gal/s, gal/min or USgals/s, USgals/min
Change the default value for Flow at Maximum Current
Change the default setting for Flow at Minimum Current
Change the Pulse Output type
Change the Pulse output parameters
Press the to get to the screen prompting for the password, which is entered using the
method shown in 7.1.2. To exit the password controlled menu navigate to the Exit screen and
press . To exit the password entry screen without entering a password wait until the flow
screen is displayed.
7.1 General procedure for changing menu settings
7.1.1 Selection menus
When a password controlled menu is selected the procedure for changing the default setting
is the same for all menus. For example, consider the Flow Units menu shown in Figure 11.
The default value ‘USgal/m’ will blink to indicate that this is the current setting. To change to
‘USgal/h’, press the key. Now the ‘USgal/h’ units will blink to indicate that this is now the
selected units. Press the key to confirm the change.
Issue 1.4 Page 17
Page 18

F - UFM
Press the
key twice to select the hundreds unit (01000.0) which will now blink
Press the
Press the key twice to increment the hundreds unit from 0 to 2
(01200.0)
Press the
key once to select the tens unit (01200.0) which will now blink
Press the
key five times to increment the tens unit from 0 to 5 (01250.0)
Press the
key once to select units (01250.0) which will now blink
Press the
key twice to decrement the units from 0 to 8 (01258.0)
Press the
key to confirm the change
Figure 12 Example of a Data entry screen
V
7.1.2 Data entry menus
Menus containing a numeric value can be altered using the following procedure. For example,
consider changing the Flow at maximum current from the default setting 1000 gallons as
indicated in Figure 12. to 1258 gallons.
All numeric data menus can be changed in this way.
7.2 User Password controlled menu structure
Ensure that the instrument is in Flow Reading mode then press the key to go to the user
password menu. Enter 71360 using the procedure explained in section 7.1.2. to enter the
password.
The flow chart shown in Figure 13 shows the user password menu structure. To skip over any
menu item that should remain unchanged, simply press the key.
Issue 1.4 Page 18
Page 19

F - UFM
Sig: 87% *
1245 USgal/min
Enter Password:
*****
71360 MENU
Invalid & OR No
input for 10 seconds
User Menu:
Pulse Output
User Menu:
Current Output
User Menu:
Calibration
User Menu:
Setup
User Menu:
Totals
Checking Signals
******
Sig: 87% *
1245 USgal/min
Setup Menu
Totalizer Menu
Pulse Output Menu
Current Output Menu
User Menu:
Exit
v v v
v
v
Calibration Menu
v
Issue 1.4 Page 19
Figure 13 Main Menu
Page 20

F - UFM
Select Dimensions:
mm | inches
Enter Pipe ID:
050.0 mm
Enter Pipe ID:
2.000 inches
Select Reading:
Flow | Vel
Select Reading:
Flow | Vel
System Units:
liters | m3
System Units:
Impgal | USgal
Flow Units
m3/min | m3/hr
Flow Units
l/min | l/s
Flow Units
gal/min | gal/hr
Flow Units
USgal/min | USgal/hr
Range 20 – 110mm
050.0 mm
SETUP MENU
Inches &
Invalid
range
&
mm &
Invalid range
&
Valid &
Valid &
Vel & (m/s)
m3 &
Flow &
Liters &
Valid &
Flow &
Impgal &
USgal &
Vel &
(ft/s)
Range 0.79 – 4.33
2.000 inches
Pipe material
Plastic
Set Separation
B 2
Issue 1.4 Page 20
Figure 14 Setup Menu
Page 21

F - UFM
Select Pulse:
ON | OFF
Volume per Pulse:
10.0 gal
Pulse Width
25 ms
PULSE OUTPUT MENU
Valid &
Valid &
On &
Volume &
Max Pulse Freq:
200
Max Flow @ Freq:
9999.0
Valid &
Valid &
Off &
Invalid &
Valid &
Freq &
Pulse Type:
VOLUME | FREQ
Range 3 - 99
25 ms
Range 1 – 200
200
Invalid &
Valid &
Test mode, press V or Λ to
generate a pulse
Select Totals
ON|OFF
On &
Reset + Total
NO |YES
Off &
TOTALIZER MENU
Valid &
Figure 15 Pulse Output & Totalizer Menus
Issue 1.4 Page 21
Page 22

F - UFM
Select 4-20 mA:
ON | OFF
Flow @ 20mA
1000.0
Flow @ 4mA
0000.0
OFF &
ON &
CURRENT OUTPUT MENU
Valid &
Valid &
Damping Time [s]:
20
Zero Cut-off:
0.10 m/s
Zero Offset
0.000 USgal/min
Range 0.00 – 0.50
0.10 m/s
Done
Zero Offset:
Averaging…9
^ To Clear
v To Set
Valid &
Invalid &
Calibrat. Factor:
1.000
Range 0.500–1.500
1.000
CALIBRATION MENU
Invalid &
Valid &
Set Zero cut-off to
0.00 before using
Zero Offset and
restore to 0.05 or
more afterwards
If the Total is turned on then the display will alternate between the flow reading and the total.
Either display can be held for 30 seconds by pressing the key.
Issue 1.4 Page 22
Figure 16 Current Output & Calibration Menus
Page 23

F - UFM
V
The Estimated TA (Time of Arrival) and Actual TA show the
theoretical and measured transit times. These values should
be within several per cent of each other.
The gain on line one is an indicator of the signal strength. A
good signal should have a gain of between 600 to 970. The
number in parentheses is the switch setting and should be x1.
The second line shows the current time differential between
the upstream and downstream signals.
Line 1: Software version
Line 2: Serial number.
If the Frequency pulse option is enabled this screen displays
the current pulse output frequency. This is proportional to the
flow rate.
Press
To exit the Diagnostics menu
Please note the key board is less responsive in
the Diagnostics Menu and longer key presses
are required.
Sig: 87% *
1245 USgal/min
Est.TA 85.64
Act .TA 86.77
Gain 845 (x1)
DT 125 ns
Rev: 05.00.001
S/N: 12547 11/13
Pulse Frequency
124
>
>
>
v
Pipe Material
Plastic
The Selected pipe material
Figure 17 Diagnostics Menu
>
Separation
D-4
The separation setting based on the pipe material and inside
diameter.
>
8 Diagnostics Menu
The diagnostics menu provides some additional information about the flowmeter and its setup. The
menu can be accessed by pressing the key from the main flow-reading screen. The menu shown
below describes the various diagnostics items.
DIAGNOSTICS MENU
Issue 1.4 Page 23
Page 24

F - UFM
9 Relocation of guide rail
If it is necessary to relocated the guide rail and sensor assembly use the following procedure
1. Remove complete assembly from the pipe
2. Insert a small screwdriver in the hole at the end of the guide rail moulding and lever
up the clip holding the electronics assembly by pressing down on the screwdriver as
shown in figure 18.
3. Repeat 2 on the other end and then pull off the electronics unit.
Figure 18
4. Disconnect the sensors
5. Remove the original grease from the sensors
6. Push the sensor blocks into the guide rail so that the washers and locking screws
can be refitted.
7. Place a bead of grease down the center of the sensor block using the syringe
provided. See illustration on fitting the guide rail to the pipe for recommended bead
size.
8. Follow the original procedure for installing the guide rail on the pipe.
Issue 1.4 Page 24
Page 25

F - UFM
General
Measuring Technique
Transit time
Measurement channels
1
Timing Resolution
±50 ps
Turn down ratio
200:1
Flow velocity range
0.1 to 10 m/s
Applicable Fluid types
Clean water with < 3% by volume of particulate content.
Accuracy
±3% of flow reading for flow rate >0.3 m/s
Repeatability
±0.5% of measured value
Selectable units
Velocity: m/s, ft/s
Flow Rate:l/s, l/min, gal/s, gal/min, USgal/s, USgal/min,
m3/min, m3/hr
Volume: liters, m3, gals, USgals
Languages supported
English only
Power input
12 – 24 V ac or dc
Power consumption
7 VA maximum
Cable
5 m screened 6 core
Pulse Output
Output
Opto-isolated MOSFET volt free normally open contact.
Isolation
2500V
Pulse width
Default value 25 ms; programmable range 3 – 99 ms
Pulse repetition rate
Up to 166 pulses/sec (depending on pulse width)
Frequency mode
200 Hz maximum
Maximum load voltage/current
48V AC / 500mA
Current Output
Output
4 – 20 mA
Resolution
0.1% of full scale
Maximum load
620 Ω
Isolation
1500 V opto-isolated
Alarm current
3.5 mA
Enclosure
Material
Plastic Polycarbonate
Fixing
Pipe mountable
Degree of Protection
IP54
Flammability Rating
UL94 V-0
Dimensions
10 inches x 2 inches x 3.6 inches (electronics + guide rail)
Weight
1.1 lb
Environmental
Pipe temperature
32°F to 185°F (0°C to 85°C)
Operating temperature (Electronics)
32°F to 122°F (0°C to 50°C )
10 Appendix I – UFM Specification
Table 1 lists the UFM Product Specification.
Issue 1.4 Page 25
Page 26

F - UFM
Storage temperature
14°F to 140 °F (-10°C to 60°C)
Humidity
90% RH at 122°F Max
Display
LCD
2 line x 16 characters
Viewing angle
Min 30°, Max 40°
Active area
3.27 inches (W) x 0.74 inches(H)
Keypad
Format
4 key tactile feedback membrane keypad
Parameter
Default Value
Dimensions
mm
Flow Rate
l/min
Pipe size
50 (mm)
4-20 mA
On, 4-20 mA selected
Flow at Max Current
Equivalent to 2m/s
Flow at Min Current
0
Pulse Output
On
Volume per Pulse
10 liters
Pulse Width
25 ms
Damping
20 seconds
Calibration Factor
1.000
Zero Cut-off
0.10 m/s
Zero Offset
0.000 l/min
Parameter
Default Value
Dimensions
inches
Flow Rate
USgal/min
Pipe size
2 (inches)
4-20 mA
On, 4-20 mA selected
Flow at Max Current
Equivalent to 6.5 ft/s
Flow at Min Current
0
Pulse Output
On
Volume per Pulse
10 US gallons
Pulse Width
25 ms
Damping
20 seconds
Calibration Factor
1.000
Zero Cut-off
0.10 m/s ( 0.3 ft/s)
Zero Offset
0.000 gal/min
11 Appendix II – Default values
The settings will be configured at the factory for either metric or imperial units. Table 2 lists
the metric default values.
Table 2 System Default Values
Table 3 lists the default values when Imperial dimensions are selected.
Table 3 System Default Values
Issue 1.4 Page 26
Page 27

F - UFM
Range 0.79 – 4.33
0.000 inches
Range 0 - 99999
0000.0
Range 1 - 200
200Hz
12 Appendix III – Error and Warning Messages
12.1 System errors
There are three possible ‘System Error’ messages that can be displayed. They are:
1. Poor Signal. The unit is unable to detect a signal from one or both transducers. If this
message persists the sensors will need to be relocated.
2. Pulse Overflow. The value for the ‘Vol per pulse’ is set too low. Increase the Vol per
Pulse setting in the password-controlled menu.
3. No BBME: This indicates a unit failure. Reset the unit by turning the power on and off.
Contact Dwyer Instruments, Inc. if the problem persists.
12.2 Warnings
These generally advise the user that the data entered is out of the specified range.
1. When an invalid Pipe ID is entered, the warning message shown below is displayed,
prompting the user to enter a value between 0.79 and 4.33 inches.
2. When the 4-20 mA current output is turned ON, the Flow at Maximum and Minimum current
can be changed under password control. The valid range is 0 – 99999.0 If an invalid value is
entered the following warning message is displayed:
3. When programming a Frequency Pulse output the frequency is limited to the range 1 to 200
Hz. If an invalid value is entered then the following warning message is displayed.
Issue 1.4 Page 27
Page 28

F - UFM
Range 3 - 99
00ms
Range 0.00 – 0.50
0.00
Range 0.50 – 1.50
0.000
4. When programming a Volume Pulse output the pulse width is limited to the range 3 to 99
ms. If an invalid value is entered then the following warning message is displayed.
5. When programming the Zero Cut -off this is limited to the range 0.000 to 0.500 m/s. If an
invalid value is entered then the following warning message is displayed.
6. When programming the Calibration Factor this is limited to the range 0.5 to 1.5. If an invalid
value is entered then the following warning message is displayed.
13 Maintenance/Repair
Upon final installation of the model UFM, no routine maintenance is required. The model UFM
is not field serviceable and should be returned if repair is needed. Field repair should not be
attempted and may void warranty.
14 Warranty /Return
Refer to “Terms and Conditions of Sale” in our catalog or on our website. Contact customer
service to receive a Return Goods Authorization number before shipping you product back for
repair. Be sure to include a brief description of the problem plus any relevant application notes.
Issue 1.4 Page 28
 Loading...
Loading...