Page 1
Bulletin F-41-STFLO
4-1/32
[102.25]
2-11/16
[68.07]
IN
10-21/32
[270.78]
LABEL, SEE
DETAIL 1
3/4 NPT CONNECTION
O
UT
2
-13/16
[
71.37]
LABEL
SEE
DETAIL 2
2-3/4
[69.95]
Ø1-11/32
[34.29]
3/4 NPT
1
5-21/32
[
397.28]
LABEL SEE
DETAIL 1
LABEL, SEE
DETAIL 2
IN
OUT
4
-1/2
[
114.38]
3-23/32
[94.23]
5
-11/16
[
144.65]
1
-1/2 NPT
Ø2-15/32
[62.99]
Ø4
[101.85]
1-1/2 NPT CONNECTION
3
[76.20]
LABEL, SEE
DETAIL 1
L
ABEL, SEE
DETAIL 2
5
[127.00]
4-31/32
[125.98]
5
[127.00]
6
-13/16
[
172.97]
3
-1/2
[
88.91]
Ø3-7/8
[Ø98.55]
Ø2-3/4
[Ø69.85]
2-1/8
[53.59]
3
[76.20]
4-1/2
[114.30]
LABLE, SEE
DETAIL 1
LABEL, SEE
DETAIL 2
3-11/16
[93.73]
3-9/16
[90.43]
3-7/8
[98.55]
3/4 FLANGE CONNECTION
1-1/2 FLANGE CONNECTION
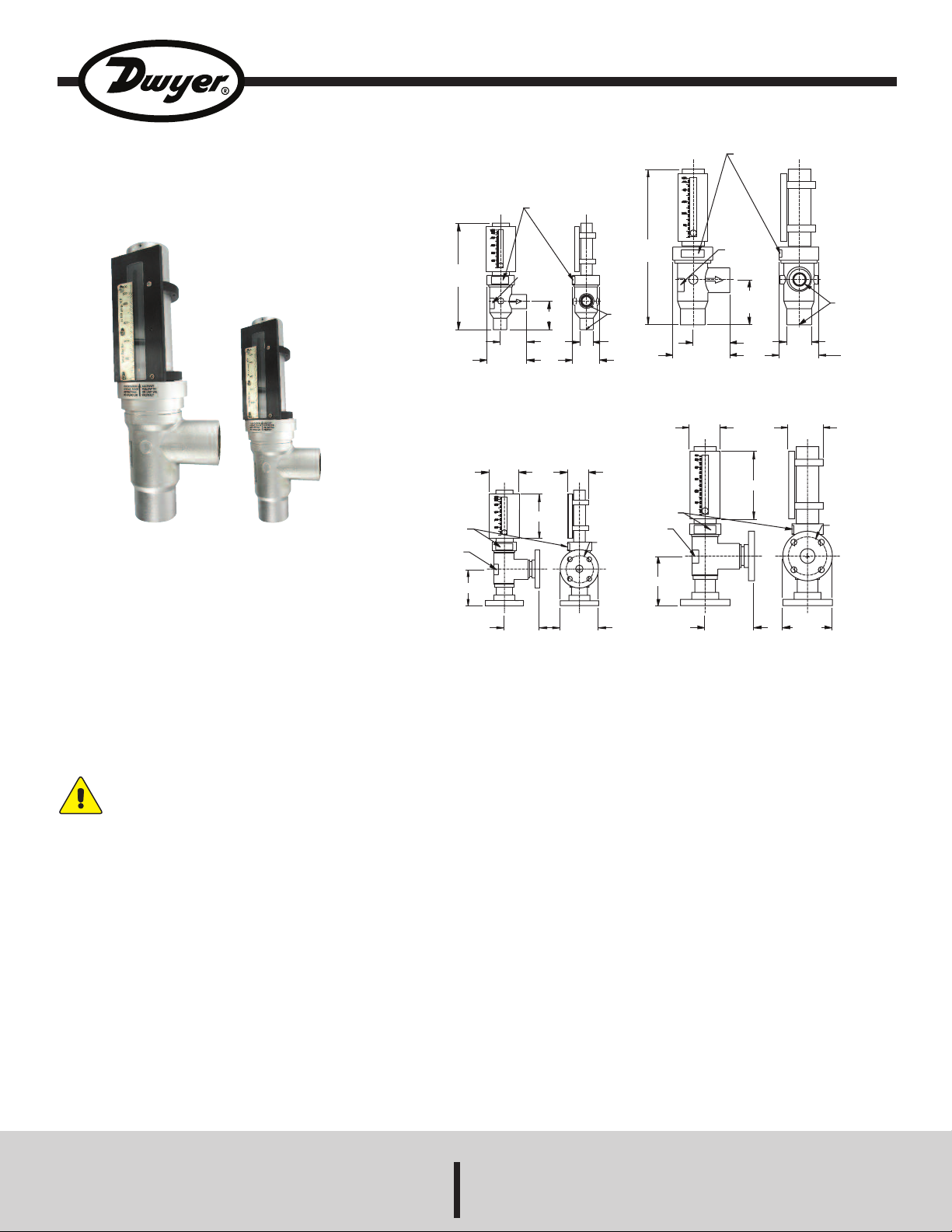
Series STFLO Stainless Steel Flowmeters
Specifications - Installation and Operating Instructions
Series STFLO Stainless Steel Flowmeters are ideal for dirty or
opaque fluids, high temperature and high pressure service and harsh
environments, specifically steam applications.The direct reading scale
provides ±2% accuracy. Flowmeters can quickly be disassembled
without removing the body from the pipeline for easy cleaning.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Personnel safety should be considered before pressurizing and
operating the system. There are numerous possibilities for
error in system operation and maintenance as well as
component installation. Because human eyes must necessarily
come into close proximity with the flowmeter to read it, Dwyer
SPECIFICATIONS
Service: Compatible with liquids and gases.
Wetted Material: T316 SS, Alnico magnet, PTFE.
Temperature Limits: See chart on page 7.
Pressure Limits: See chart on page 7.
Accuracy: ±2% FS.
Repeatability: ±0.5% of indicated flow rate.
Process Connections: 3/4˝ or 1-1/2˝ female NPT, optional flange
connections.
Scale Length: 3/4˝ models: 3.2˝ (8 cm); 1-1/2˝ models: 5.2˝ (13 cm).
Weight: 3/4˝ NPT models: 5.75 lb (2.6 kg); 1-1/2˝ NPT models: 14 lb (6.4
kg). 3/4˝ Flange: 9.75 lb (4.4 kg); 1-1/2˝ Flange: 22 lb (10 kg).
Instruments, Inc. recommends that safety shielding such as a
sheet of transparent, high impact material be used in front of
the meter. If hazardous, toxic, or flammable fluids are being
metered, recommended safeguard should include methods to
protect personnel from splash or rebound. A method of quick,
safe removal of dangerous fluids should also be included.
INSTALLATION
PREPARATION: Series STFLO Stainless Steel Flowmeters are ready to
install as-is, although the reading scales may need repositioning so the
scale is visible after installation. First, remove the protective caps from
the connection ports. Also, remove the plastic tubing above the inlet cap
in the meter core tube! This tubing blocks the float assembly in place
during shipment. Check that the float moves freely within the core tube,
and that no packing materials are in the meter.
DWYER INSTRUMENTS, INC.
P.O. BOX 373 • MICHIGAN CITY, INDIANA 46360, U.S.A. Fax: 219/872-9057 e-mail: info@dwyer-inst.com
Phone: 219/879-8000 www.dwyer-inst.com
Page 2
RECOMMENDED PIPING
SEC A-A, TOP VIEW
METAL
PRESSURE
TUBE
PHENOLIC
RACEWAY
A
A
MAGNET
BALL
INDICATOR
SNORKELGUIDE
READING
SCALES
Series STFLO Stainless Steel Flowmeters generally have no special
straight run or other piping requirements. Inlet piping should be the same
size as the meter connection. Some effect on meter accuracy may occur
at high flow velocities if inlet piping guidelines are violated. Please refer
to the table on the next page. When installing on different size pipe, use
standard pipe adapters and come into the meter inlet with a nipple 8
diameters long of the same size for greatest accuracy. Control valves
should be mounted on the outlet side of the meter. The use of a three
valve manifold around the meter is suggested, as it allows uninterrupted
process flow while the meter is being cleaned.
STARTUP
System flow should be started with the bypass valve open and meter
inlet and outlet valves closed. After the system is operating, open the
meter inlet valve gradually to equalize internal pressure. Then slowly
crack meter outlet valve and wait for float to stabilize. Finally, slowly
open the meter outlet and/or flow regulating valve all the way and close
the system by-pass valve.
AVOID SUDDEN SURGES THAT CAUSE THE METER
FLOAT TO SLAM INTO THE TOP OF THE READING
SCALES!
PLUMBING-IN
While the flowmeters should be vertical, exact plumbness is not
necessary. A general rule is that if the meter appears plumb, it is close
enough (even if off by 10º, the predictable reading error is usually less
than 1%). Pipe should be cut to proper lengths to avoid stress on the
meter. Avoid over-tightening, and do no use wrenches on the body or
reading scales. If using solvents in the vicinity of reading scales, the
scales should be removed until fumes clear.
SURGE & WATER HAMMER PREVENTION
Operating Limits are for non-shock conditions only. Flowmeters are more
accurate and less likely to be damaged when the fluid flow is smooth.
Water hammer is a hazardous phenomenon and should be eliminated
from any fluid system. Water hammer is a series of pressure shocks
create by a sudden change in the flow velocity of liquid in a pipe. This
sudden change, often caused by a fast acting valve or starting, stopping,
or change in speed of a pump, generates an immediate rise in pressure
that sometimes makes a noise similar to striking the pipe with a hammer.
The pressure wave is transmitted from the source throughout the
system, subjecting every component to the sudden shock. Pressure
returns to normal only when a larger vessel or pipe section is reached,
the energy dissipated thru friction and pipe expansion, or some
component ruptures. Rupture of piping, valves, flowmeters, or other
components have obvious safety ramifications that must be addressed.
SURGE CHAMBERS & ACCUMULATORS
Flowmeters are more accurate and less likely to be damaged when the
fluid flow is smooth. If the meter must be installed on a line where
reciprocating pumps causing pulsation are used, surge chambers,
accumulators, or desurgers are strongly suggested to dampen the shock
wave. This is a good, general practice for all flowmeters.
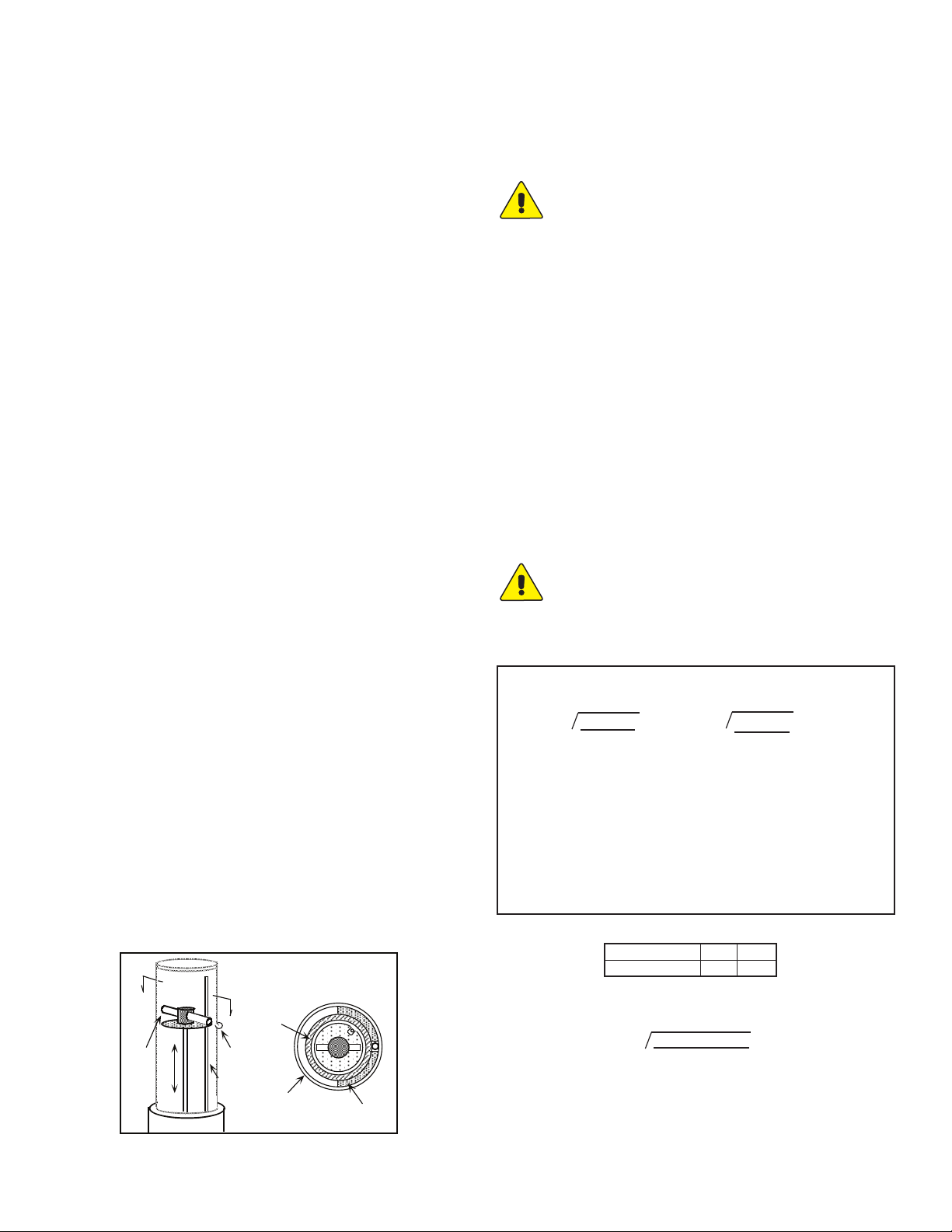
READING SCALES ROTATION
Series STFLO Stainless Steel Flowmeters use magnetically-linked ball
indicators and the scale may be positioned over approximately a 300 ˚
range. However, the magnet position must also be changed accordingly,
requiring removal of the reading scales (see “Disassembly”). On
standard STFLO Stainless Steel Flowmeters as depicted in Figure 1, the
magnet slides out of the carrier at the top of the float assembly. The
screw holding the carrier to the float may be loosened to allow rotation
of the carrier toward the desired scale location. Re-tighten the screw
(thread sealant is recommended), replace magnet, and reassemble the
meter (see “Assembly”). Verify that the ball indicator has been “captured”
by the magnet. If not, rotate the reading scales until the ball is “grabbed”
by the float magnet.
Although not essential, the meter reading scales should be filled to a
level above the float on liquid systems. The snorkel tube (present in most
standard models) allows escape of entrapped gases except for a small
pocket in the upper end which helps cushion hydraulic shock. To assure
proper filling and to flush any foreign particles from the meter, operate
the system at full flow briefly at startup.
READING FLOW
Read flow directly from the scale as the number nearest to the center of
the ball indicator.
COMPENSATING FOR SYSTEM CHANGES
To find the correct flow reading for a system whose fluid conditions vary
from those for which the meter is scaled, use the conversion equations
provided. The most practical method of applying the formulae is to
calculate a conversion factor for the new system condition and
multiplying the scale reading by that factor. In the problems to the right,
“Q’s” has been assigned a value of “1” to determine the conversion
factor. (Dwyer Instruments, Inc. can provide special scales at additional
cost for other fluids and/or units.)
CAUTION: DO NOT OPERATE THE FLOWMETER ON A
SYSTEM EXCEEDING THE OPERATING LIMITS OF THE
UNIT. WHEN CHANGING OPERATING CONDITIONS, MAKE
SURE THAT THE NEW SYSTEM CONDITIONS ARE WITHIN
THE FLOWMETER OPERATING LIMITS, AND ALL WETTED
MATERIALS ARE COMPATIBLE WITH THE FLUID.
CORRECTING READINGS FOR NEW LIQUID CONDITIONS
Qa= Q
s
√
Ps(Pf-Pa)
Pa(Pf-Ps)
or Qa= Q
s
√
ds(df-da)
da(df-ds)
Where:
Qa=Actual flow, GPM (or same units as scale)
Qs=Meter reading from scale, (scale units)
ps=Specific gravity of calibration liquid related to water in std.
atmosphere at 70˚F being 1.00
pa=Specific gravity of metered liquid, same base
ds=Density of calibration liquid, lbs/ft3
da=Density of metered liquid, lbs/ft3
pf=Specific gravity of meter float
df=Density of the meter float as per Table below
FLOAT SPECIFIC GRAVITIES/DENSITIES
Material
Stainless Steel
pf
8.05
df
501.1
EXAMPLE: Using a standard stainless steel meter scaled for water (ps
= 1.00), what is the conversion factor for an oil with a specific gravity of
0.85?
Qa= 1.00
FIGURE 1
Thus, actual flow of the oil would be the observed scale reading times
1.00 (8.05 - 0.85)
x
√
0.85 (8.05 - 1.00)
=1.11
Page 3

MAXIMUM FLOWS (WITHOUT EFFECTING ACCURACY)
SPIRAL RETAINING
RING
INNER FLANGE
RING
READING
SCALE
SIGHT TUBE
ASSEMBLY
STATIC O-RING
SEAL
MAGNET(S)
CORE TUBE / FLOAT
ASSEMBLY
FOR UNDERSIZED PIPES CONNECTED DIRECTLY TO
FLOWMETER INLETS
DATA
PIPE
NPS
1/4
3/8
1/2
3/4
1
1-1/4
1-1/2
2
2-1/2
3
ata per Cameron Hydraulic Data. Based on 5 FPS max. liquid velocity having
D
*
no effect on flowmeters accuracy if the inlet pipe is smaller than the meter
connections.
†
CFM=0.445 x (psig + 14.7) x (ID)
S
o effect on flowmeters accuracy if the inlet pipe is smaller than the meter
n
connections.
(ID)
0.132
0.243
0.387
0.679
1.100
1.904
2.592
4.272
6.096
9.413
2
MAX. *
GPM LIQ.
1.72
2.98
4.74
8.31
13.47
23.32
31.74
52.29
74.56
115.2
ATMOS.
0.864
1.59
2.53
4.44
7.20
12.5
17.0
28.0
39.9
61.6
MAX. SCFM AIR @ †
50 PSIG
3.80
7.00
11.1
19.5
31.7
58.8
74.6
123
176
271
2
Based on 20 FPS max. air velocity having
.
100 PSIG
6.74
12.4
19.8
34.7
56.1
97.2
132
218
311
480
CORRECTING READINGS FOR NEW GAS CONDITIONS
s
√
Psx Tgx P
Pg x Tsx P
s
g
Qg= Q
Where:
Qg=SCFM, corrected to new conditions
Qs=SCFM read on meter scale
Pg=Operating pressure, psia (psig + 14.7)
Qs=Pressure stated on scale, psia (psig + 14.7)
Tg=Operating temperature, absolute (˚F +460)
Ts=Temperature stated on scale, absolute (˚F + 460)
Pg=Specific gravity of metered gas
Ps=Specific gravity stated on scale
200 PSIG
12.6
23.2
37.2
64.9
105
182
248
408
582
804
VISCOSITY CONSIDERATIONS
Each liquid flowmeter has so-called “Viscosity Immunity Ceiling” (V.I.C.).
Usually, if the viscosity of the metered liquid is less than the V.I.C., the
meter will be influenced significantly, and must be calibrated for that
viscosity. Effects of viscosity on a given flowmeter are not always
predictable. Two apparently similar liquids with comparable densities
and viscosities may impact meter calibrations quite differently. The table
below provides general guidelines for the typical maximum viscosity for
meter models without affecting accuracy.
AVERAGE V.I.C., CENTISTOKES, FOR
STANDARD “THRU VIEW”FLOWMETERS
100% GPM,
3/4˝ METERS
0.54-0.80
1.20-2.60
3.80-7.00
10.0-23.0
100% GPM,
CTS
1-1/2˝ METERS
3
11.0-15.0
7
21.0-35.0
15
50.0
25
70.0-120
CTS
50
100
250
500
MAINTENANCE
Upon final installation of the Series STFLO Stainless Steel Flowmeters,
no routine maintenance is required. A periodic check of the system
calibration is recommended. The Series STFLO Stainless Steel
Flowmeters are not field serviceable and should be returned if repair is
needed (field repair should not be attempted and may void warranty). Be
sure to include a brief description of the problem plus any relevant
application notes. Contact customer service to receive a return goods
authorization number before shipping.
METER DISASSEMBLY
EXAMPLE: If using a standard meter scaled for SCFM Dry Air @ 100
psig, 70˚F on argon (SP. GR.=1.378) at 50 psig, 100˚F, what would the
conversion factor be?
Qa= 1.00
64.7 x1.00 x530
√
114.7 x1.378 x560
= 0.622
Thus, actual flow of the argon would be the observed scale reading
times 0.622.
STEAM
Series STFLO flowmeters are recommended for use with vapors,
especially steam. The conversion factor may be determined with the
following formula:
Where:
Mfh=Actual flow, lbs/hr.
Qm=Meter scale reading, Std. (SCFM Dry Air @ 100 psig, 70˚F)
M
= Qm _______
fh
5.879
√S
v
Sv=Specific volume of media (from steam table)
EXAMPLE: When using a standard gas meter scaled from SCFM Dry Air
@ 100 psig, 70˚F, what is the conversion factor for lbs/hr. steam at 50
psig, 300˚F?
Mfh=
5.879
√6.727
Thus, actual flow of steam in lbs/hr. would be the observed scale reading
times 2.267.
FIGURE 2: PARTIALLY EXPLODED DRAWING OF SERIES STFLO
STAINLESS STEEL FLOWMETERS
It is not necessary to remove the flowmeters from the pipeline for
cleaning or replacing parts. The body remains plumbed into the pipe,
allowing easy service and even installation of the different sensing
elements to accommodate new flow rates or fluids. Figure 2 shows some
of the major components. Step by step disassembly and reassembly
instructions and photos are included in the following.
Page 4

CAUTION: BE SURE PRESSURE IS FULLY VENTED AND FLUIDS
COMPLETELY DRAINED BEFORE DISASSEMBLING THE
FLOWMETER. DISCONNECT POWER TO ELECTRONIC
ACCESSORIES. WEAR SAFTEY GLASSES AND PROTECTIVE
CLOTHING IF THERE IS A CHANCE OF EXPOSURE TO
HAZARDOUS FLUIDS!
1. Remove the reading scale by removing the two set screws in the black
rings attaching the reading scale to the sight tube. Lift the reading scale up
and off of the meter. Set the screws aside where they will not be lost.
2. Using a screwdriver, carefully pry the notched end of the spiral retaining
ring out of the body groove. Move the screwdriver blade under the ring- the
action is very much like putting a key on a key ring. Continue until the entire
spiral ring has been removed from the groove (please see the photo
below).
FLOWMETER ASSEMBLY
In general, replace all parts in reverse order of the disassembly.
1. Place the slotted meter tube into the body, aligning the “key” at the
bottom of the tube with the keyslot in the bottom of the body.
2. Place the spider over the meter tube with the “notched leg over the
snorkel tube or guide rod. Slide the spider down to the meter tube’s
shoulder.
3. Place the meter float in the meter tube, aligning the notch in the indicator
disk with the snorkel.
3. Using hands only, pull the sight tube straight up out of the body with a
slight twisting motion, lifting it clear of the body and snorkel. The inner
flange ring will lift off with the sight tube.
4. Remove the float assembly by lifting it up and away from the snorkel.
The core tube assembly may then be lifted out. If stuck, CAREFULLY pry
at the top of the slot with a brass rod, taking care not to damage the body
or core tube. The spider ring and O-ring will come out with the core tube. If
the core tube is stuck, try removing the metal spider ring first (please see
the photo below).
INSPECTION & CLEANING
Inspect parts for nicks, scratches, chips, wear, and contaminant build-up.
The edges of the core tube slot, ID of the core tube and OD of the piston
(largest section at the float assembly bottom) are precision machined.
Damage to these areas can destroy the meter’s accuracy. Also inspect the
O-ring, the bottom section of the sight tube, and the inside of the upper
body section. Damage to these areas may result in leaking. Clean, rinse,
and dry all parts carefully, including the O-ring, preferably with a mild
detergent and water and a soft cloth or soft tube brush. If solvents are
used, make sure they are compatible with meter parts.
CAUTION: DO NOT SCRAPE OR USE ABRASIVE
MATERIALS FOR CLEANING!
4. Seat the O-ring on the sight tube, lubricating it with a small amount of
service-compatible silicone grease or petroleum jelly to facilitate
replacement.
Page 5

5. Using hands only, press the sight tube firmly down into the meter body
with a twisting motion. Be careful not to rock the sight tube side to side and
bend the snorkel tube/guide inward where it might interfere with float
movement. Rotate sight tube as necessary for scale visibility and/or
alignment of the raceway screw.
6. Slide the inner flange ring over the sight tube. When properly seated, the
top of the flange ring should be flush with the bottom edge of the snap ring
groove.
If new flow internals are used, the scale may have to be remounted on the
sight tube. Depending on the model type, this can be done either by
loosening the mounting screw, or reattaching the scale with double sided
adhesive (new flow internals are shipped with a new scale).
REPLACEMENT PARTS
Under proper care, there should be no need to stock replacement parts. If
the service or environment is quite harsh, or frequent meter disassembly
dictated, a spare O-ring may be desirable.
Otherwise, parts only need to be replaced if damaged. Any visible damage
to the entire surface of the O-ring or sight tube (particularly from the bottom
edge) indicates need for replacement. To insure accuracy, the inside
surface of the meter core tube, slot edges, and OD of the float piston
should be free of nicks, chips, with no visible erosion of any surfaces. If
abrasive particles are suspended in the meter fluid, it may be desirable to
keep replacement core tube/float assemblies on hand (Dwyer Instruments,
Inc. may also be able to recommend a more abrasive-resistant
construction).
To order parts, include the model and serial number of the units involved,
and description of the part ordered. If converting the meter to a new
application, in addition to the model and serial numbers, SEND DWYER
INSTRUMENTS, INC. COMPLETE APPLICATION DATA INCLUDING
FLUID, MAXIMUM FLOW RATE, MAXIMUM AND OPERATING
PRESSURES AND TEMPERATURES, AND APPLICATION
PARTICULARS OR FLUID CHARACTERISTICS. This information is
essential for Dwyer Instruments, Inc. to provide proper items, and verify
that the new application is within the operating limits of the flowmeter.
7. Separate the coils of the spiral retaining ring, and insert one end into the
body groove. Wind the ring into the groove, making sure the ring is properly
seated. Then replace the ball indicator (the tip of a screwdriver can be used
to help locate the magnet), and replace the raceway and raceway cover.
Slide the reading scale over the sight tube, aligning the top of the black
metal of the reading scale with the screw hole on the sight tube. The
reading scale should read zero. Use the set screws to secure the reading
scale in place. Verify that the indicator ball moves with the magnet.
TEMPERATURE VS. PRESSURE, OPERATING LIMITS, SERIES STFLO STAINLESS STEEL FLOWMETERS*
METER SIZE
& MATERIAL
3/4” NPT
1-1/2” NPT
0˚F (-18°C)
1000 (68.9)
800 (55)
70˚F (21°C)
1000 (68.9)
800 (55)
MAXIMUM NON-SHOCK WORKING PRESSURE, PSIG @ ˚F
300˚F (148°C)
1000 (68.9)
800 (55)
350˚F (176°C)
990 (68.2)
790 (54.4)
400˚F (204°C)
970 (66.8)
780 (53.7)
450˚F (232°C)
950 (65.5)
770 (53)
500˚F (260°C)
930 (64.1)
760 (52.4)
600˚F (315°C)
900 (62)
750 (51.7)
*OPERATING LIMITS GIVEN ARE BASED ON WATER OR AIR. FOR MORE SEVERE SERVICE, CORROSIVE, AND OTHER MEDIA AND/OR ENVIRONMENTAL
FACTORS, AN ADDITIONAL CORRECTION FACTOR DOWN-RATING THESE LIMITS MAY BE REQUIRED. LIMITS ARE BASED ON TESTING AND PRACTICAL
EXPERIENCE. POSSIBLE EXTREME APPLICATIONS CONDITIONS CANNOT BE FORESEEN. THUS, DATA OFFERED ONLY AS A GUIDE. IT IN NO WAY
CONSTITUTES A SPECIFIC RECOMMENDATION OR WARRANTY EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED.
Page 6

TROUBLESHOOTING
SYMPTOM
FLOAT HANG-UP:
FLOAT BOUNCE:
LOSS OF BALL
INDICATOR:
APPARENT FALSE
READINGS, LIQUID
METERS:
APPARENT METER
READING MIGRATION
(reading changes but flow
appears constant):
LEAKAGE:
NOTE: Flowmeters are hydrostatically pressure tested before they are shipped. Dwyer Instruments, Inc. encourages you to contact your Dwyer Instruments, Inc.
representative or the factory with any questions regarding proper installation and operation of our flowmeters.
Caused by particles, sludge, etc. (including failure to remove
the plastic tubing used to block meter float during shipment)
inside the core tube and/or sight tube holding float. A bent
snorkel tube/guide rod (usually caused by careless
disassembly or violent surges) may also be causing float to
stick. Violent surges may also unseat the internals in
extreme cases.
Caused by pumping/compressor surges or other pulsation
sources, loose valve disks or similar mechanical
components, extreme violation of inlet piping
recommendations, or for gas applications, harmonics
commonly found in systems with low pressure, low density
gas.
Caused either by rotating the sight tube without realigning
the float magnet, or sudden flow surges or shocks.
Liquid density not according to calibration data (different
temperature or new liquid or liquid mixture), excessive
dissolved or suspended solids or gases, partial clogging of
core tube slot or foreign matter interfering with float
movement, or viscosity levels above the meter’s immunity
index (V.I.C.)
NOTE: If the meter is suspected of giving false readings, and
none of the causes mentioned is found, please advise
Dwyer Instruments, Inc. as to the method used in
determining the suspected flow “error”. Each Flowmeter is
individually calibrated by traceable methods, and carefully
inspected. There may be some error in checking the meter
against another standard.
Frequently caused by use of soft disc type valves, which
may need to be replaced with a valve more suited to flow
control. Can also be indicative of changing fluid conditions
(density, viscosity, etc.). Problems with other elements of the
flow system, including leaks, clogged filters,
pump/compressor wear, etc. may first appear as a change in
meter reading-one of the functions of a flowmeter.
If at the junction of the body and sight tube, it is indicative of
either (a) damaged O-ring (most common); (b) damaged
sight tube; or (c) damage to the gland section of the body. It
may also be caused by improper reassembly of the
flowmeter in the field.
If there is leakage at the pipe connections to the meter, it is
probably caused from over-tightening pipes on a prior
installation (or the initial installation).
USUAL CAUSE
Remedies include tapping the meter gently to temporarily
dislodge the float, but if problem reoccurs, meter should be
disassembled & cleaned, and/or snorkel/guide rod
straightened. If hang-up caused by sludge or pipe scale,
clean lines & install a filter or other form of cleaner in
supply line. If surges have caused the internals to unseat,
install a desurger, accumulator, etc.
Modification of piping, such as addition of a desurger,
receiver, accumulator, vibration eliminators, loops, hoses,
etc. between the source and meter should remedy the
problem. Severe vibration may ultimately damage the
meter, and should be avoided. If “bounce” seems to be
from some other source, or shocks such as “water
hammer” (a potentially dangerous condition), discontinue
using the meter and contact Dwyer Instruments, Inc.
Check the ball alignment to magnet by removing the
raceway cover and using the tip of a small screwdriver to
locate the float magnet. Rotate the sight tube as required,
and replace raceway (or disassemble meter to change
magnet position if required). If the alignment is okay,
eliminate system shock or surges with desurgers or
accummulators.
By determining the actual density (due to changes in
mixture, temperature, etc.), the correction formulae may be
applied. If dissolved gases are in the liquid, some
elimination means should be provided on the supply side
(also recheck all piping, as improper seals at connection
points are common sources of air in the liquid). If the
metered liquid is near the boiling point producing partial
“flash gas” at the meter, relocate the meter to point of lower
temperature and/or higher pressure, or cool lines and/or
increase system pressure. Note: It is potentially dangerous
to meter near the “flash point” of any fluid, and this practice
should be avoided. Consult Dwyer Instruments, Inc. for
recommendations. The previous recommendations
regarding cleaning the meter and/or filtration will also solve
problems due to dirt. If metering liquids with high
viscosities, consult Dwyer Instruments, Inc. (may require
special calibration). If none of these causes seem to be
present, contact Dwyer Instruments, Inc. for assistance.
Verifying the proper fluid conditions are known and
applying correction formulae as needed will remedy
problems associated with changing fluids. Cleaning,
servicing, and replacement and/or repair of other system
components may be required.
Replace any damaged parts immediately, using the proper
assembly procedures indicated in this instruction and the
assembly detail drawings.
Remove the body and inspect for damage-if none is
visible, check pipe threads, reapply proper thread
lubricant/sealant, and reinstall. If leak persists, replace
meter body.
SUGGESTED REMEDY
©Copyright 2012 Dwyer Instruments, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. 12/12 FR# R1-443701-00 Rev.1
DWYER INSTRUMENTS, INC.
Phone: 219/879-8000 www.dwyer-inst.com
P.O. BOX 373 • MICHIGAN CITY, INDIANA 46360, U.S.A. Fax: 219/872-9057 e-mail: info@dwyer-inst.com
 Loading...
Loading...