Dwyer SCD-8 User Manual

TYPE device and therefore should be installed in an enclosure free of airborne dust,
the device (e.g. key or specific tools are required for opening the enclosure) in case danger and damage on the
OFF
AL-H
OFF
AL-H
OFF
AL-H
AL-L
AL-H
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
SCD8000/8100 Temperature Controller
Instruction Sheet
Thank you very much for choosing SCD8000/8100 series temperature controller. Please read this instruction sheet carefully
before using your SCD8000/8100 to ensure proper operation. Keep this instruction sheet handy for quick reference.
!
1
!
DANGER! CAUTION! ELECTRIC SHOCK!
SCD8000/8100 is an OPENhumidity, electric shock and vibration. The enclosure should prevent non-maintenance staff from operating
device may occur.
1. Prevent dust or metallic debris from falling into the device and cause malfunctions. DO NOT
board of SCD8000/8100 without being permitted. DO NOT use empty terminals.
2. Keep away from high-voltage and high-frequency environment during the installation in case of interference. Prevent using
the device in premises which contain:
(a) dust or corrosive gas; (b) high humidity and high radiation; (c) shock and vibration.
3. The power has to be switched off when wiring or changing the temperature sensor.
4. When installing the circuit board of the accessory, please make sure the power of the main unit is switched off and insert
the accessory into the correct slot on the main unit.
5. Make sure to use compensation wire which matches the thermocouple or platinum resistance when extending or
connecting the thermocouple or platinum resistance.
6. Keep the wire as short as possible when wiring a sensor to the controller. Separate the power cable and load wire in order
to prevent interference and induced noise.
7. Make sure the power cables and signal device are installed correctly before switching on the power; otherwise serious
damage may occur.
8. DO NOT
9. Please wait for 1 minute after the power is switched off to allow the capacitor to discharge and DO NOT
wiring within this period.
10. DO NOT
11. Please place SCD8000/8100 with other heating objects (e.g. power supply) within proper distance while installing
SCD8000/8100.
2
Power input DC 24V, isolated switching power supply
Voltage range 90% ~ 110% rated voltage
Power consumption Max. 10W + 3W × number of SCD2000 controllers connected in parallel (Max. 7)
Input sensor
Sampling cycle Thermocouple or platinum resistance: 1.0 second/all input
Control method PID, PID programmable, manual, ON/OFF
Output accessories
(optional)
Output functions
Alarm modes 12 alarm modes available
Communication RS-485 digital communication; supports baud rate 2,400bps ~ 115,200bps
Communication
protocol
Extension port
Vibration resistance 10 ~ 55Hz 10m/s
Shock resistance Max. 300m/s2 3 axes 6 directions, 3 times each
Ambient temperature 0°C ~ +50°C
Storage temperature -20°C ~ +65°C
Operation altitude < 2,000m
Ambient humidity 35% to 85% RH (non-condensing)
Pollution degree 2
3
touch the terminal or repair the device when the power is on; otherwise an electric shock may occur.
touch the internal terminal when SCD8000/8100 is either switched on or off in case you may damage the circuit.
Functions & Electrical Specifications
Thermocouple: K, J, T, E, N, R, S, B, L, U, TXK
Platinum resistance: Pt100, JPt100, Cu50
Relay output: SPST, Max. AC 250V load, 3A resistive load
Voltage pulse output: DC 24V, Max. 40mA current output
Current output: DC 4 ~ 20mA output (resistive load < 500Ω); for OUT1 and OUT2 only
Analog voltage output: 0 ~ 10V (resistive load > 1,000Ω); for OUT1 and OUT2 only
Control output, alarm output or proportional output (proportional output is only applicable in the
model with linear voltage and current output for OUT1, OUT2)
Supports Modbus ASCII/RTU
The extension port transmits 24V power supply and communication signals to extension module
SCD2000.
2
3 axes 10mins
Product Profile & Outline
Precaution
modify or uninstall the circuit
touch the internal
SCD8000/8100
1 I/O terminals
2 Status LED
3 Display and setup unit
4 DIN rail clip
5 Power input port
6 RS-485 communication port
7 Extension module fixing clip
8 Extension port
4
5
The standard SCD8000/8100 main unit is attached with 4 channels of inputs. You can purchase additional SCD-4T or SCD-4R
to expand the number of input channels. SCD8000/8100 supports maximum 8 channels of inputs which belong to group INA
and group INB. Each group possesses 4 input channels.
SCD8000/8100 series supports the following input sensors:
Input Sensor Type Register Value Range
Temperature measurement resistance (Cu50) 13 -50 ~ 150°C
Platinum resistance (Pt100) 12 -200 ~ 600°C
Platinum resistance (JPt100) 11 -20 ~ 400°C
Thermocouple TXK type 10 -200 ~ 800°C
Thermocouple U type 9 -200 ~ 500°C
Thermocouple L type 8 -200 ~ 850°C
Thermocouple B type 7 100 ~ 1,800°C
Thermocouple S type 6 0 ~ 1,700°C
Thermocouple R type 5 0 ~ 1,700°C
Thermocouple N type 4 -200 ~ 1,300°C
Thermocouple E type 3 0 ~ 600°C
Thermocouple T type 2 -200 ~ 400°C
Thermocouple J type 1 -100 ~ 1,200°C
Thermocouple K type 0 -200 ~ 1,300°C
Note: The default setting in SCD8000 is “thermocouple K type”. The default setting in SCD8100 is “Pt100".
Communication address: Input sensor types at H10A0 ~ H10A7; input upper limits at H1010 ~ H1017; input lower limits at
H1018 ~ H101F.
6
SCD8000/8100 supports maximum 16 channels of outputs, belonging to output groups OUT1, OUT2, SUB1 and SUB2, each
group with 4 channels. See the explanations below for how input channels correspond to output groups.
Without group INB (4 channels of input): Every channel corresponds to 2 groups of output and 2 groups of alarms. OUT1 and
SUB1 are for control output, and OUT1 can be used for proportional output. OUT2 and SUB2 are fixed for alarm output.
With group INB (8 channels of input): Every channel is paired with 2 groups of outputs. OUT1 and OUT2 are used for control
output or proportional output of CH1 ~ CH8. SUB1 and SUB2 are used for control output or alarm output.
See Table 1 for the relations between input and output.
Output Group
OUT1
OUT2 Alarm 1 output No corresponding output
SUB1 Control output Control output or alarm output No corresponding output
SUB2 Alarm 2 output No corresponding output Control output or alarm output
4 channels of input 8 channels of input
INA (CH1 ~ CH4) INA (CH1 ~ CH4) INB (CH5 ~ CH8)
Main control output or proportional
output
Note: SUB1 and SUB2 do not support SCD-46 and SCD-45. Please install the optional output modules you purchase into
the correct slot.
Communication Address of Output & How to Set up Parameters:
See Table 2 for the communication addresses of output and Table 3 for the definition of the value in the address.
CH1 CH2 CH3 CH4 CH5 CH6 CH7 CH8
OUT1, OUT2 H10A8 H10A9 H10AA H10AB H10AC H10AD H10AE H10AF
SUB1, SUB2 H10B0
INA INB
H10B1 H10B2
Panel Layout
Input
For SCD8100 / SCD-4R
For SCD8000 / SCD-4T
Output
Main control output or proportional
output
Table 1
H10B3 H10B4
Table 2
No corresponding output
Main control output or proportional
H10B5
output
H10B6
H10B7
Val ue = 0 Val ue = 1 Val ue = 2 Val ue = 3
OUT1, OUT2** Heating control Cooling control Proportional output Disable output
SUB1, SUB2** Heating control Cooling control Alarm output* Disable output
Table 3
*When there are only 4 channels of inputs, SUB1 cannot be used for alarm output but heating/cooling control only.
**When there are only 4 channels of inputs, OUT2 and SUB2 cannot be set up by the user but set up automatically as "alarm
output” by the controller.
Control Output:
SCD8000/8100 offers PID control, ON/OFF control, manual control and programmable PID control. Control output methods are
set at address H10B8 ~ H10BF (default = 0: PID), PID parameters at H1028 ~ H105F, ON/OFF parameters at H1058 ~ H106F,
and manual control parameters at H1070 ~ H107F.
Alarm Output:
SCD8000/8100 offers 12 alarm modes. The alarm modes are set up at address H10C0 ~ H10C7, upper limits at H1080 ~
H1087 and lower limits at H1088 ~ H108F.
SV Alarm Mode Alarm Output Operation
0 No alarm Off
Alarm output is enabled when the temperature reaches upper and lower
1
limits: The alarm will be enabled when PV exceeds SV + AL-H or falls below
SV – AL-L.
Alarm output will be enabled when the temperature reaches the upper limit:
2
The alarm will be enabled when the PV exceeds SV + AL-H.
Alarm output will be enabled when the temperature reaches the lower limit:
3
The alarm will be enabled when the PV falls below SV – AL-L.
Alarm output will be enabled when the PV is between SV + AL-H and SV –
4
AL-L.
Alarm output will be enabled when the temperature reaches the absolute
5
value of the upper and lower limits: The alarm will be enabled when the PV
exceeds AL-H or falls below AL-L.
Alarm output will be enabled when the temperature reaches the absolute
6
value of the upper limit: The alarm will be enabled when the PV exceeds
AL-H.
Alarm output will be enabled when the temperature reaches the absolute
7
value of the lower limit: The alarm will be enabled when the PV falls below
AL-L.
Upper/lower limit standby alarm: The alarm will be enabled when the PV
8
reaches SV and further exceeds SV + AL-H or falls below SV – AL-L.
Upper limit standby alarm: The alarm will be enabled when the PV reaches
9
SV and further exceeds SV + AL-H.
Lower limit standby alarm: The alarm will be enabled when the PV reaches
10
SV and further falls below SV – AL-L.
Upper limit hysteresis alarm: The alarm will be enabled when the PV exceeds
11
SV + AL-H. The alarm will be disabled when the PV falls below SV + AL-L.
Lower limit hysteresis alarm: The alarm will be enabled when the PV falls
12
below SV – AL-H. The alarm will be disabled when the PV exceeds SV –
AL-L.
7
LED Display
PWR: On B SCD8000/8100 is powered.
RUN: On B Any of the channel is executing.
COM: Flashing B Communication in progress
ERR: Indicating errors (red)
ERR LED is on indicates one of the following errors occur, and the output has to be disabled.
1. Memory EEPROM error.
2. Any of the input points is not connected.
3. Any of the input points exceeds the setup range.
4. Any of the input temperatures has not been stabilized.
8
Synchronous Communication Protocol & Auto ID Setup
This function allows the auto setup of communication protocol in extension module SCD2000 following the communication
protocol set in the SCD8000 main unit. The station IDs of SCD2000 decrease. See below for the steps.
1. Set the auto communication ID of SCD8000 as “1” (communication address: H10F8).
2. Switch off SCD8000. Connect SCD8000 with extension module SCD2000 and switch on SCD8000 again.
3. Default communication protocol: 9,600bps, 7 bits, Even, 1 stop bit, communication address = 01.
4. This function will consume 3 ~ 5 seconds more when you switch on SCD8000.
9
RS-485 Communication
1. SCD8000/8100 supports baud rates 2,400/4,800/9,600/19,200/38,400/57,600/115,200 bps and does not support
communication format 7, N, 1/8, E, 2/8, O, 2. Communication protocol = Modbus ASCII or RTU.
2. Function codes: H03 = read maximum 8 words in the register; H06 = write 1 word into the register.
3. Address and contents: Every parameter has 2 communication addresses. One is numbered by the function of the parameter,
and the other is by the order of channel (as shown in the table below).
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
AL-L SV AL-H
SV
AL-L
SV
SV
SV AL-H
AL-L
AL-L
AL-H
AL-H
AL-L SV
AL-L
AL-L
AL-L SV
AL-H
Disabled when higher
H10F3
H10F4
H10F5
H10F6
H10F7
INA INB
Content Explanation CH1 CH2 CH3 CH4 CH5 CH6 CH7 CH8
Present
temperature
value/input error
Unit; 0.1
See Table 5
H1000
(H1100)
H1001
(H1200)
H1002
(H1300)
H1003
(H1400)
H1004
(H1500)
H1005
(H1600)
H1006
(H1700)
code
Set temperature
value
Unit: 0.1
Max. temperature
value
Min. temperature
value
Error temperature
value
Proportional band
value (Pb)
than default value
Disabled when lower
than default value
-999 ~ +999
Unit: 0.1°C
0 ~ 9,999
Unit: 0.1
Ti value 0 ~ 9,999
Td value 0 ~ 9,999
Integration default
Proportional control
offset error value,
when Ti = 0
Proportional band
coefficient of output
1 and output 2
0.0 ~ 100.0%
Unit: 0.1%
0.0 ~ 100.0%
Unit: 0.1%
0.01 ~ 99.99
Unit: 0.01
Dead band of
control output 1 &
-99.9 ~ 999.9
output 2.
Hysteresis for
output 1
Hysteresis for
output 2
Read/write output
1 value
Read/write output
2 value
Upper limit for
alarm output
0 ~ 9,999
Unit: 0.1%
0 ~ 9,999
Unit: 0.1%
Unit: 0.1 %
Unit: 0.1 %
Alarm enabled
when temperature
exceeds upper limit
H1008
(H1101)
H1010
(H1102)
H1018
(H1103)
H1020
(H1104)
H1028
(H1105)
H1030
(H1106)
H1038
(H1107)
H1040
(H1108)
H1048
(H1109)
H1050
(H110A)
H1058
(H110B)
H1060
(H110C)
H1068
(H110D)
H1070
(H110E)
H1078
(H110F)
H1080
(H1110)
H1009
(H1201)
H1011
(H1202)
H1019
(H1203)
H1021
(H1204)
H1029
(H1205)
H1031
(H1206)
H1039
(H1207)
H1041
(H1208)
H1049
(H1209)
H1051
(H120A)
H1059
(H120B)
H1061
(H120C)
H1069
(H120D)
H1071
(H120E)
H1079
(H120F)
H1081
(1210)
H100A
(H1301)
H1012
(H1302)
H101A
(H1303)
H1022
(H1304)
H102A
(H1305)
H1032
(H1306)
H103A
(H1307)
H1042
(H1308)
H104A
(H1309)
H1052
(H130A)
H105A
(H130B)
H1062
(H130C)
H106A
(H130D)
H1072
(H130E)
H107A
(H130F)
H1082
(H1310)
H100B
(H1401)
H1013
(H1402)
H101B
(H1403)
H1023
(H1404)
H102B
(H1405)
H1033
(H1406)
H103B
(H1407)
H1043
(H1408)
H104B
(H1409)
H1053
(H140A)
H105B
(H140B)
H1063
(H140C)
H106B
(H140D)
H1073
(H140E)
H107B
(H140F)
H1083
(H1410)
H100C
(H1501)
H1014
(H1502)
H101C
(H1503)
H1024
(H1504)
H102C
(H1505)
H1034
(H1506)
H103C
(H1507)
H1044
(H1508)
H104C
(H1509)
H1054
(H150A)
H105C
(H150B)
H1064
(H150C)
H106C
(H150D)
H1074
(H150E)
H107C
(H150F)
H1084
(H1510)
H100D
(H1601)
H1015
(H1602)
H101D
(H1603)
H1025
(H1604)
H102D
(H1605)
H1035
(H1606)
H103D
(H1607)
H1045
(H1608)
H104D
(H1609)
H1055
(H160A)
H105D
(H160B)
H1065
(H160C)
H106D
(H160D)
H1075
(H160E)
H107D
(H160F)
H1085
(H1610)
H100E
(H1701)
H1016
(H1702)
H101E
(H1703)
H1026
(H1704)
H102E
(H1705)
H1036
(H1706)
H103E
(H1707)
H1046
(H1708)
H104E
(H1709)
H1056
(H170A)
H105E
(H170B)
H1066
(H170C)
H106E
(H170D)
H1076
(H170E)
H107E
(H170F)
H1086
(H1710)
Alarm enabled
Lower limit for
alarm output
when temperature
falls below lower
H1088
(H 1111)
H1089
(H1211)
H108A
(H1311)
H108B
(H1411)
H108C
(H1511)
H108D
(H1611)
H108E
(H1711)
limit
Tuning for upper
limit of analog
output
Tuning for lower
limit of analog
output
Input sensor type See “Input” section
Current (4 ~ 20mA)
or voltage output
tuning
Current (4 ~ 20mA)
or voltage output
tuning
H1090
(H1112)
H1098
(H1113)
H10A0
(H1114)
H1091
(H1212)
H1099
(H1213)
H10A1
(H1214)
H1092
(H1312)
H109A
(H1313)
H10A2
(H1314)
H1093
(H1412)
H109B
(H1413)
H10A3
(H1414)
H1094
(H1512)
H109C
(H1513)
H10A4
(H1514)
H1095
(H1612)
H109D
(H1613)
H10A5
(H1614)
H1096
(H1712)
H109E
(H1713)
H10A6
(H1714)
0: heating
Output function
for output 1
1: cooling
2: proportional
H10A8
(H1115)
H10A9
(H1215)
H10AA
(H1315)
H10AB
(H1415)
H10AC
(H1515)
H10AD
(H1615)
H10AE
(H1715)
output
Output function
for output 2
0: heating (default)
1: cooling
2: alarm
H10B0
(H1116)
H10B1
(H1216)
H10B2
(H1316)
H10B3
(H1416)
H10B4
(H1516)
H10B5
(H1616)
H10B6
(H1716)
0: PID
Control method
1: ON-OFF
2: manual
3: PID
H10B8
(H1117)
H10B9
(H1217)
H10BA
(H1317)
H10BB
(H1417)
H10BC
(H1517)
H10BD
(H1617)
H10BE
(H1717)
programmable
Alarm 1 output
mode
Alarm 2 output
mode
Heating/cooling
cycle for output 1
Heating/cooling
cycle for output 2
See “Alarm Output”
section
See “Alarm Output”
section
1 ~ 99 seconds
0 = 0.5 second
1 ~ 99 seconds
0 = 0.5 second
H10C0
(H1118)
H10C4
(H1518)
H10C8
(H1119)
H10D0
(H 111A)
H10C1
(H1218)
H10C5
(H1618)
H10C9
(H1219)
H10D1
(H121A)
H10C2
(H1318)
H10C6
(H1718)
H10CA
(H1319)
H10D2
(H131A)
H10C3
(H1418)
H10C7
(H1818)
H10CB
(H1419)
H10D3
(H141A)
H10C4
(H1518)
H10C5
(H1618)
H10C6
(H1718)
H10CC
(H1519)
H10D4
(H151A)
H10CD
(H1619)
H10D5
(H161A)
H10CE
(H1719)
H10D6
(H171A)
0: stop
Run/Stop the
control
1: executing
2: program stops
H10D8
(H 111B)
H10D9
(H121B)
H10DA
(H131B)
H10DB
(H141B)
H10DC
(H151B)
H10DD
(H161B)
H10DE
(H171B)
3: program pauses
Status of PID
auto-tuning
Positive/negative
proportional
0: stop
1: executing
0: positive
1: negative (slope)
H10E0
(H 111C)
H10E8
(H 111D)
H10E1
(H121C)
H10E9
(H121D)
H10E2
(H131C)
H10EA
(H131D)
H10E3
(H141C)
H10EB
(H141D)
H10E4
(H151C)
H10EC
(H151D)
H10E5
(H161C)
H10ED
(H161D)
H10E6
(H171C)
H10EE
(H171D)
H1007
(H1800)
H100F
(H1801)
H1017
(H1802)
H101F
(H1803)
H1027
(H1804)
H102F
(H1805)
H1037
(H1806)
H103F
(H1807)
H1010
(H1808)
H104F
(H1809)
H1057
(H180A)
H105F
(H180B)
H1067
(H180C)
H106F
(H180D)
H1077
(H180E)
H107F
(H180F)
H1087
(H1810)
H108F
(H1811)
H1097
(H1812)
H109F
(H1813)
H10A7
(H1814)
H10AF
(H1815)
H10B7
(H1816)
H10BF
(H1817)
H10C7
(H1818)
H10CF
(H1819)
H10D7
(H181A)
H10DF
(H181B)
H10E7
(H181C)
H10EF
(H181D)
INA INB
Content Explanation CH1 CH2 CH3 CH4 CH5 CH6 CH7 CH8
output
Other statuses Other statuses
Communication
specifications
See Table 4
H10F0
Temperature
unit
H10F8
Auto ID
setup
H10F1
Open special
function
(H1234)
H10F9
Reserved
H10F2
Return to
default
(H1357)
H10FA
Baud rate
Reserved
H10FB
ASCII = 0
RTU = 1
Reserved
H10FC
8 bits=0
7 bits=1
Reserved
H10FD
2 stop=0
1 stop=1
Reserved
H10FE
Parity
Reserved
H10FF
Address
1 ~ 247
Communication Parameter Setting:
Content 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Baud rate 2,400bps 4,800bps 9,600bps 19,200bps 38,400bps 57,600bps 115,200bps
Parity bit None (N) Even (E) Odd (O)
Tabl e 4
Error Codes:
The error codes can be read from address H1000 ~ H1007. When the input operation is in normal status, H1000 ~ H1007 are
for input values. When input error occurs (except for stable status and input exceeding the range), SCD8000/8100 will read
error codes in H8001 ~ H8002.
H1000 Error description
H8001 EEPROM cannot be written in.
H8002 Input sensor is not connected.
H8003 Group INB is not connected.
Table 5
Analog output current tuning scale: 1μA/scale
Analog output voltage tuning scale: 1mV/scale
Returning to Default Value: Write H1234 into address H10F1 and H1357 into address H10F2. Restart SCD8000/8100.
Programmable Communication Parameter Setting:
INA INB
Content Explanation CH1 CH2 CH3 CH4 CH5 CH6 CH7 CH8
Read remaining time of the step Unit: sec H111E H121E H131E H141E H151E H161E H171E H181E
Read remaining time of the step Unit: min H111F H121F H131F H141F H151F H161F H171F H181F
Read the NO. of the current
pattern
0 ~ 7 H1120
H1220 H1320 H1420 H1520 H1620 H1720 H1820
Read the NO. of the current step 0 ~ 7 H1121 H1221 H1321 H1421 H1521 H1621 H1721 H1821
NO. of start pattern 0 ~ 7 H1122 H1222 H1322 H1422 H1522 H1622 H1722 H1822
NO. of start step 0 ~ 7 H1123 H1223 H1323 H1423 H1523 H1623 H1723 H1823
Programmable Parameter Setting:
Content Explanation
Max. number of
steps in the pattern
Number of cycles of
pattern 0 ~ 7
execution
NO. of current link
pattern
0 ~ 7 = N: The pattern
executes from step 0 to
N.
0 ~ 199: The pattern
has been executed for 1
~ 200 times
0 ~ 8: 8 refers to end of
program; 0 ~ 7 refer to
the NO. of next pattern
Pattern 0 Pattern 1 Pattern 2 Pattern 3 Pattern 4 Pattern 5 Pattern 6 Pattern
7
H2068
H2070
H2078
H2069 H206A H206B H206C H206D H206E H206F
H2071 H2072 H2073 H2074 H2075 H2076 H2077
H2079 H207A H207B H207C H207D H207E H207F
Address Default Content Explanation
2000H ~ 203FH 0
2080H ~ 20BFH 0
Target temperatures for pattern 0 ~ 7
Pattern 0: 2000H ~ 2007H
Execution time for pattern 0 ~ 7
Pattern 0: 2080H ~ 2087H
Unit: 0.1°C
Time: 0 ~ 900 (Unit: 1 min)
4. Communication format: H03 = read bit data; H06 = write bit data
ASCII Mode:
Read Command Read Response Message Write Command Write Response Message
Start word ’:’
Start word ’:’ Start word ’:’ Start word ’:’
Machine address 1 ‘0’ Machine address 1 ‘0’ Machine address 1 ‘0’ Machine address 1 ‘0’
Machine address 0 ‘1’ Machine address 0 ‘1’ Machine address 0 ‘1’ Machine address 0 ‘1’
Command 1 ‘0’
Command 0 ‘3’
Read start address of
data/bit
Read length of data/bit
(word/bit)
‘1’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
Command 1 ‘0’
Command 0 ‘3’
Length of response
data (byte)
Data content in H1000
‘0’
‘4’
‘0’
‘1’
‘F’
Write data content
‘4’
Command 1 ‘0’
Command 0 ‘6’
Data address
‘1’
‘0’
‘0’
‘1’
‘0’
Write data content
‘3’
Command 1 ‘0’
Command 0 ‘6’
Data address
‘1’
‘0’
‘0’
‘1’
‘0’
‘3’
Read Command Read Response Message Write Command Write Response Message
‘0’
‘2’
LRC1 check ‘E’
Data content in H1001
LRC0 check ‘A’
End word 1 CR
End word 0 LF
LRC1 check ‘0’
LRC0 check ‘3’
End word 1 CR
End word 0 LF
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘E’
‘8’
LRC1 check ‘F’
LRC0 check ‘D’
End word 1 CR
End word 0 LF
LRC1 check ‘F’
LRC0 check ‘D’
End word 1 CR
End word 0 LF
LRC Check:
Sum up the contents from “machine address” to “data content”, e.g. H01 + H03 + H10 + H00 + H00 + H02 = H16. Obtain
2’scomplement H EA.
RTU Mode:
Read Command Read Response Message Write Command Write Response Message
Machine address H01 Machine address H01 Machine address H01 Machine address H01
Command H03
Read start address of
data
Read length of data
(bit/word)
H10
H00
H00
H02
CRC low byte HC0
CRC high byte HCB
CRC low byte HBB
CRC high byte H15
Command H03 Command H06 Command H06
Length of response
data (byte)
Data content 1
Data content 2
H04 Write data address
H01 H03 H03
HF4
Write data content
H03 CRC low byte HDD
H20 CRC high byte HE2
H10 H10
Write data address
H01
Write data content
H20
CRC low byte HDD
CRC high byte HE2
CRC (Cyclical Redundancy Check) is obtained by the following steps:
unsigned int reg_crc = 0xffff;
i = 0;
while (length--)
{ reg_crc ^= RTUData[i];
i ++;
for (j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{ if (reg_crc & 0x01) reg_crc = (reg_crc >> 1) ^ 0xA001;
else reg_crc = reg_crc >> 1;
}
}
return(reg_crc);
Software for Setting up Communication on PC: Download the free software on Dwyer’s website.
10
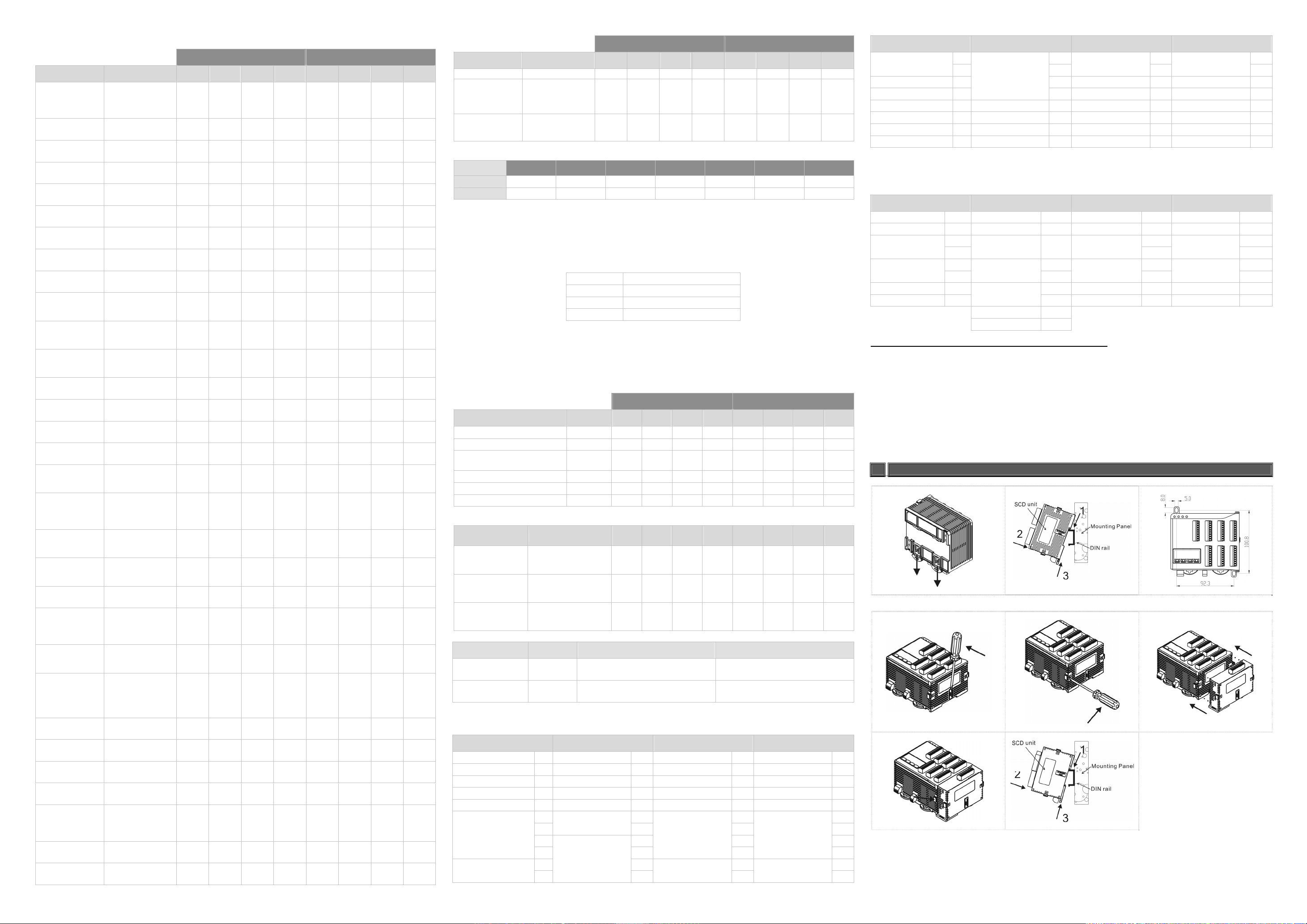
How to Mount & DIN Rail Size
Connect maximum 7 SCD2000 controllers to SCD8000 by using DIN rail.
‘E’
‘8’
H01
H20
 Loading...
Loading...