Dunkirk PVWB, PWB Installation Instructions Manual
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
These instructions must be affixed on or adjacent to the boiler
MODEL PVWB
Continuous Pilot
PLPL
PL
PLPL
YMOUTHYMOUTH
YMOUTH
YMOUTHYMOUTH
WW
W
WW
AA
TERTER
A
TER
AA
TERTER
SERIES 2
Gas-FirGas-Fir
Gas-Fir
Gas-FirGas-Fir
Hot-WHot-W
Hot-W
Hot-WHot-W
BoilerBoiler
Boiler
BoilerBoiler
These Gas-Fired Water Boilers are low pressure, sectional
cast iron boilers Designed Certified by C.S.A. (Canadian
Standards Association) for use with Natural and Propane
Gases. They are constructed and hydrostatically tested for a
maximum working pressure of 50 psi (pounds per square
inch) in accordance with A.S.M.E. (American Society of
Mechanical Engineers) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code
Section IV Standards for cast iron heating boilers.
aa
terter
a
ter
aa
terter
eded
ed
eded
ss
s
ss
MODEL PWB
Electronic
Intermittent Ignition
Warning: Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service or maintenance can cause injury or
property damage. Refer to this manual. For assistance or additional information consult a qualified
installer, service agency or the gas supplier
DUNKIRK BOILERS
DUNKIRK, NEW YORK 14084 • AREA CODE 716 366-5500
MEMBER: The Hydronics Institute
1
V
r
V
r
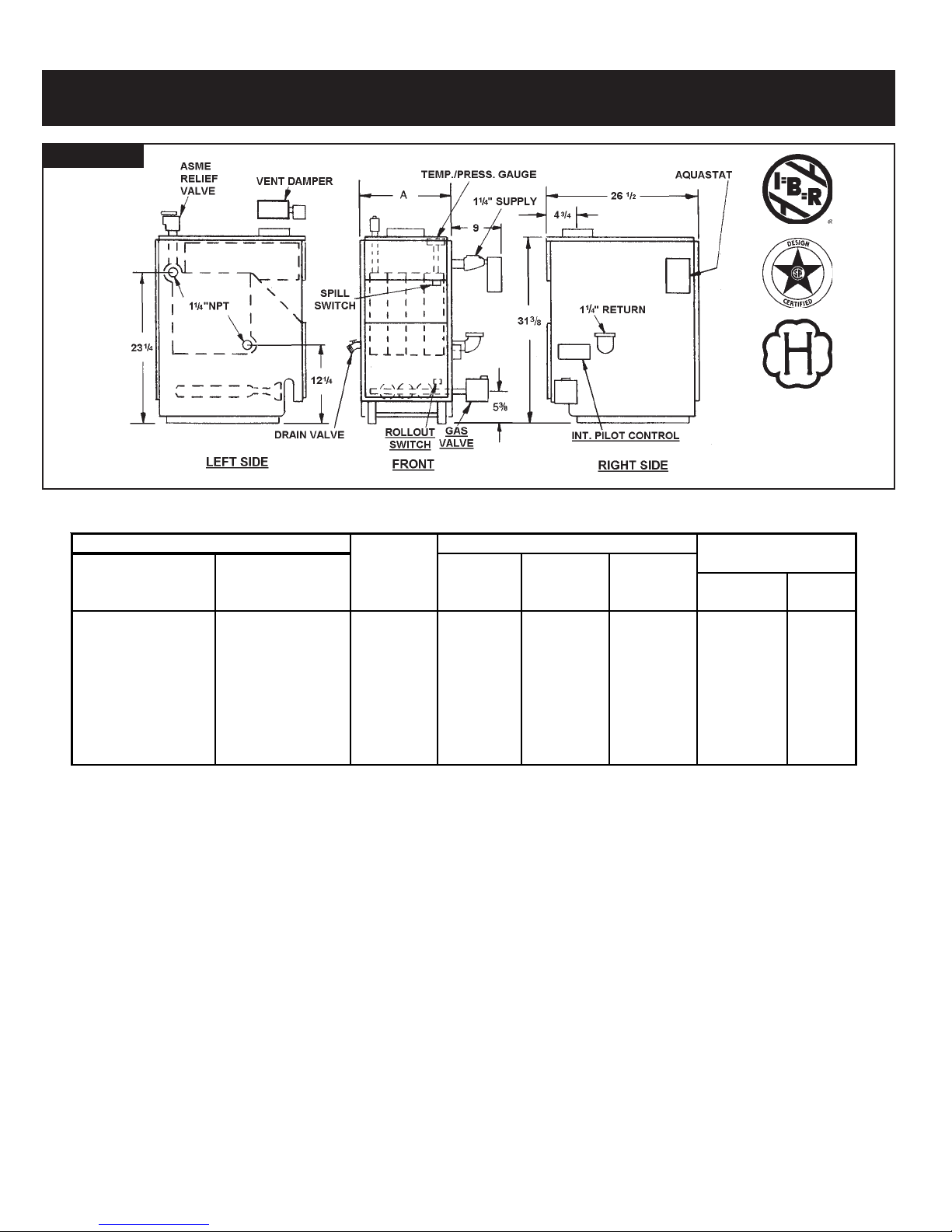
FIG. 1
Boiler Ratings and Capacities
GAS-FIRED HOT WATER BOILERS
BASIC BOILER UNIT NO. DIMENSIONS
Electronic Ignition Continuous Pilot NO. OF AGA/CGAHEATING NET I=B=R
With With SECTIONS INPUT CAPACITY RATING FLUE "A"
ent Dampe
PWB-2D PVWB-2D 2 37.5 30 26 4‡ 8
PWB-3D PVWB-3D 3 70 57 50 5 11¼
PWB-4D PVWB-4D 4 105 85 74 6 14½
PWB-5D PVWB-5D 5 140 113 98 6 17¾
PWB-6D PVWB-6D 6 175 142 123 7 21
PWB-7D PVWB-7D 7 210 170 148 7 24¼
PWB-8D PVWB-8D 8 245 198 172 7 27½
PWB-9D PVWB-9D 9 280 226 197 7 30¾
* MBH = 1,000 Btuh = British Thermal Unit Per Hour
Boilers are equipped for altitudes up to 2,000 feet only
U.S.A. Only - For altitudes above 2,000 feet, ratings should be reduced at the rate of 4% for each 1,000 feet above sea level.
Canada Only - Boilers may be used at high altitude by using a certified field conversion kit, resulting in a 10% derate.
+ Heating Capacity based on D.O.E. (Department of Energy) test procedure. Add 5½” to height when vent damper is used.
‡ 2 section boilers are equipped with a 3” diameter flue collar on the draft diverter, and use a furnished 3” x 4” increaser fitting to install
the furnished 4” vent damper.
ent Dampe
New York City MEA Number 39-86-E Vol. IV.
The Ratings marked “Net 1=B=R Ratings” indicate the amount
of remaining heat input that can be used to heat the radiation
or terminal units. The Net 1=B=R Ratings shown are based on
an allowance of 1.15 in accordance with the factors shown on
the 1=B=R Standard as published by The Hydronics Institute.
Selection of boiler size should be based upon “Net 1=B=R
Rating” being equal to or greater than the calculated heat loss
of the building.
The manufacturer should be consulted before selecting a boiler
for installations having unusual piping and pickup requirements.
These boilers must stand on a non-combustible floor. If in
NATURAL AND PROPANE GAS
(Inches)
*MBH *MBH *MBH DIAMETER WIDTH
stalled on a combustible floor, use Combustible Floor Base
Number 42135-1 or 146-14-031 (2-6 section boilers) or
42135-2 or 146-14-032 (7-9 section boilers).
BOILERS FOR USE AT HIGH ALTITUDE
This boiler is factory equipped for use at altitudes of 0-2,000
feet above sea level. For use at altitudes above 2,000 feet
above sea level, the input ratings are reduced by a change in
main burner orifice size.
U.S.A. Only - For altitudes above 2,000 feet above sea
level, input ratings should be reduced at the rate of 4% for
each 1,000 feet above sea level. Consult the National Fuel
2
Before You Start
Gas Code (NFPA54/ANSI Z223.1-latest edition), or the
manufacturer for correct orifice sizing information. High
altitude orifices are available from the boiler manufacturer.
Canada Only - For altitudes in the range of 2,000-4,500
feet above sea level, boilers may be field equipped for use
at high altitude by using a certified field conversion kit. The
change in main burner orifice size results in the boiler’s
input rating being reduced by 10%. The conversion shall
be carried out by a manufacturer’s authorized
representative, in accordance with the requirements of the
manufacturer, provincial or territorial authorities having
jurisdiction and in accordance with the requirements of the
CSA-B149.1 and CSA-B149.2 Installation Codes. The
certified field conversion kit includes a conversion data
plate, which must be attached to the boiler adjacent to the
rating plate, indicating that the boiler has been converted
for high altitude use. The conversion data plate must be
filled in with the correct conversion information.
Check to be sure you have the right size boiler before starting
the installation. _ See rating and capacity table on previous
page. Also be sure the new boiler is or the type of gas you are
using. Check the rating plate on the right side of the boiler.
You must see that the boiler is supplied with the correct type
of gas, fresh air for combustion, and a suitable electrical supply.
Also, the boiler must be connected to a suitable venting system
and an adequate piping system. Finally, a thermostat, properly
located, is needed for control of the heating system. If you
have any doubts as to the various requirements, check with
local authorities and obtain professional help where needed.
Take the time to complete all of the steps for SAFE and
PROPER operation of the heating system.
If this boiler is installed in a building under construction,
special care must be taken to insure a clean combustion
air supply during the construction process. Airborne
particulates such as from drywall dust and from fiberglass
insulation can clog the burner ports and cause incomplete
combustion and sooting.
Where required by the authority having jurisdiction, the
installation must conform to American Society of Mechanical
Engineers Safety Code for Controls and Safety Devices for
Automatically Fired Boilers, No. CSD-1.
The installation must conform to the requirements of the
authority having jurisdiction or, in the absence of such
requirements, to the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1latest revision.
In Canada, the boiler shall be installed according to CSA-
13149.1 and .2, Installation Code for Gas Burning
Appliances and Equipment.
Installers - Follow local regulations with respect to
installation of CO detectors. Follow maintenance
recommendations in this instruction manual.
Techniciens - Veuillez vous conformer a la
réglementation en vigueur concernant I’ installation des
détecteurs d’oxyde de carbone. Suivre les consignes
d’entretien figurant dans le manuel dínstruction ci-joint.
KEEP BOILER AREA CLEAN AND FREE FROM COMBUSTIBLE MATERIALS,
GASOLINE AND OTHER FLAMMABLE VAPORS AND LIQUIDS
3
Locating the Boiler
r
r
V
V
1. Select level location as centralized with piping system, and
as near chimney, as possible.
2. Place crated boiler at selected location, remove crate
by pulling crate sides from top and bottom boards.
Combustible floors: When boiler is to be installed on a
combustible floor, a Special Base Plate must be used 146-14-031 (2-6 Section) or 146-14-032 (7-9 Section).
This boiler must not be installed on carpeting.
3. Boiler is to be level. Metal shims may be used under
base legs for final leveling.
4. Additional clearances for service may exceed clearances
for fire protection. Always comply with the minimum fire
protection clearances shown on the boiler. An 18 inch
clearance should be maintained on any side where
passage is required to access another side for cleaning,
servicing, inspection or replacement of any part that may
need attention. An 18-inch clearance is recommended
on the control side for servicing.
Figure 2 shows minimum clearances to combustible
construction. Rooms that are large in comparison with
the size of the boiler are defined as rooms having a
volume equal to or greater than 16 times the volume of
the boiler. Where the actual ceiling height of a room is
greater that 8', the volume of a room shall be figured on
the basis of a ceiling height of 8'. Determination of room
size should be based do the total volume of all gas fired
equipment installed in the room. Consult section 6.3.1
of the National Fuel Gas Code for further information,
including approved methods for reducing clearances in
large rooms.
5. Equipment shall be installed in a location in which the
facilities for ventilation permit satisfactory combustion
of gas, proper venting, and maintenance of ambient
temperature at safe limits under normal conditions of use.
Equipment shall be located so as not to interfere with
proper circulation of air. When normal infiltration does
not provide the necessary air, outside air shall be
introduced (See Page 4 - “Fresh Air for Combustion”).
6. Advise owner to keep air passages free of obstructions.
Ventilating and combustion air must enter boiler room
without restrictions.
7. The boiler shall be installed such that the automatic gas
ignition system components are protected from water
(dripping, spraying, rain, etc.) during appliance operation
and service (condensate trap, control replacement, etc.).
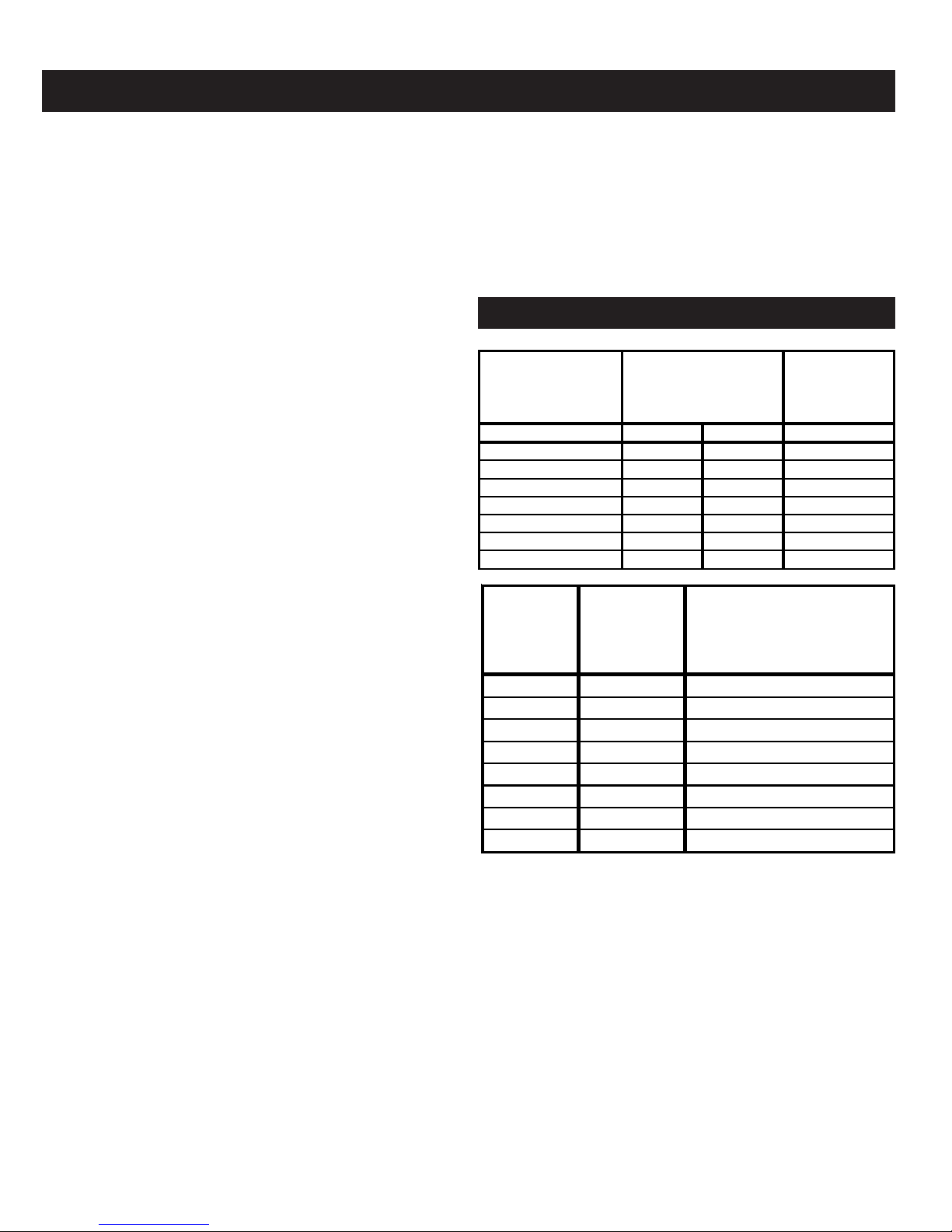
FIG. 2 - MINIMUM CLEARANCE DIMENSIONS
Alcove, or Room Not
Large in Comparison
With Boiler
2-5 SECT. 6-9 SECT. 2-9 SECT.
Top 6" 6" 6"
Rear 6" 6" 6"
Control Side 8" 24" 6"
Opposite Side 6" 24" 6"
Front 18" 18" 18"
Flue/Vent Connector 6" 6" 6"
Near Boiler Piping 1" 1" 1"
Room Large In
Comparison
With Boiler
Minimum Room
Boile
Size
Boile
olume Required
olume To Be Large
(Cu. Ft.) Room (Cu. Ft)*
2 sect. 3.8 61.6
3 sect. 5.4 86.6
4 sect. 7.0 111.6
5 sect. 8.5 136.6
6 sect. 10.1 161.7
7 sect. 11.7 186.7
8 sect. 13.2 211.7
9 sect. 14.8 236.7
* FOR ROOM WITH SINGLE BOILER ONLY THIS UNIT MUST
BE SET ON A CONCRETE OR OTHER NON-COMBUSTIBLE
MATERIAL BASE OR FLOOR.
4
Fresh Air for Combustion
Provision for combustion and ventilation air must be in accordance with Section 5.3, Air for Combustion and Ventilation,
of the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1-latest revision, or applicable provisions of the local building codes.
WARNING
Be sure to provide enough fresh air for combustion. Enough
air insures proper combustion and assures that no hazard
will develop due to the lack of oxygen.
Y ou must provide for enough fresh air to assure proper combustion. The
fire in the boiler uses oxygen. It must have a continuous supply . The air in
a house contains only enough oxygen to supply the burner for a short
time. Outside air must enter the house to replace that used by the burner.
Study following examples 1 and 2 to determine your fresh air requirements .
EXAMPLE 1: Boiler Located in Unconfined Space
An unconfined space is defined as a space whose volume is not less
than 50 cubic feet per 1,000 Btu per hour of the total input rating of all
appliances installed in that space.
If your boiler is in an open area (unpartitioned basement) in a
conventional house, the air that leaks through the cracks around doors
and windows will usually be adequate to provide air for combustion.
The doors should not fit tightly. Do not caulk the cracks around the
windows.
Equipment located in buildings of unusually tight construction shall be
provided with air for combustion, ventilation, and dilution of flue gases
using the methods described in example 2B or shall be specially
engineered. The authority having jurisdiction must approve specially
engineered installations.
EXAMPLE 2: Boiler Located in Confined Space
A. All Air from Inside the Building: The confined space shall be
provided with two permanent openings communicating directly with
an additional room(s) of sufficient volume so that the combined
volume of all spaces meets the criteria for an unconfined space.
The total input of all gas utilization equipment installed in the
combined space shall be considered in making this determination.
Each opening shall have a minimum free area of one square inch
per 1,000 Btu per hour of the total input rating of all gas utilization
equipment in the confined space, but not less that 100 square
inches. One opening shall be within 12 inches of the top and one
within 12 inches of the bottom of the enclosure. The minimum
dimension of air openings shall not be less than 3 inches.
B. All Air from Outdoors: The confined space shall communicate
with the outdoors in accordance with methods 1 or 2. The minimum
dimension of air openings shall not be less than 3 in. Where ducts
are used, they shall be of the same cross-sectional area as the
free area of the openings to which they connect.
1. Two permanent openings, one commencing within 12 inches of
the top. and one commencing within 12 inches of the bottom,
of the enclosure shall be provided. The openings shall
communicate directly, or by the ducts, with the outdoors or
spaces (crawl or attic) that freely communicate with the outdoors.
a) Where directly communicating with the outdoors or where
communicating to the outdoors through vertical ducts. each
opening shall have a minimum free area of 1 sq. in. per 4000
Btu per hour of total input rating of all equipment in the enclosure.
(See Figure 3B)
b) Where communicating with the outdoors through horizontal ducts.
each opening shall have a minimum free area of 1 sq. in. per
2000 Btu per hour of total input rating of all equipment in the
enclosure. (See Figure 38.)
If you use a fireplace or a kitchen or bathroom exhaust fan,
you should install an outside air intake. These devices will
rob the boiler and water heater of combustion air.
2. One permanent opening commencing with 12 inches of
a) 1 sq. inch per 3000 Btu per hour of the tatal input of all
b) Not less than the sum of the areas of all vent connectors
5
NOTE
the top of the enclosure, shall be permitted where the
equipment has clearance of at least 1 inch from the sides
and back and 6 inches from the front of the appliance. The
opening shall directly communicate with the outdoors or
shall communicate through a vertical or horizontal duct to
the outdoors or spaces (crawl or attic) that freely
communicate with the outdoor, and shall have a minimun
free area of:
equipment located in the enclosure ( See Figure 4), and
in theconfined space.
Figure 3A - FRESH AIR DUCT CAPACITIES (Btuh)
1 Square Inch per 4,000 Btuh
100% Free 75% Free 25% Free
Area Area Area
Fresh Air ¼" Wire Metal Wood
Duct Size Mesh Louvers Louvers
3" x 12" 144,000 108,000 36,000
8" x 8" 256,000 192,000 64,000
8" 12" 384,000 288,000 96,000
8½" x 16" 512,000 384,000 128,000
Figure 3B - FRESH AIR DUCT CAPACITIES (Btuh)
1 Square Inch per 2,000 Btuh
100% Free 75% Free 25% Free
Area Area Area
Fresh Air ¼" Wire Metal Wood
Duct Size Mesh Louvers Louvers
3" x 12" 72,000 54,000 18,000
8" x 8" 128,000 96,000 32,000
8" 12" 192,000 144,000 48,000
8½" x 16" 256,000 192,000 64,000
Figure 4 - FRESH AIR DUCT CAPACITIES (Btuh)
1 Square Inch per 3,000 Btuh
100% Free 75% Free 25% Free
Area Area Area
Fresh Air ¼" Wire Metal Wood
Duct Size Mesh Louvers Louvers
3" x 12" 108,000 81,000 27,000
8" x 8" 192,000 144,000 48,000
8" 12" 288,000 216,000 72,000
8½" x 16" 384,000 288,000 96,000

Installation - System Piping
1. Place boiler in the selected location (as near chimney as
possible.) Your boiler is shipped assembled. You need only
to install the Relief Valve and a drain line to carry any water
or steam to a drain.
2. Install Relief Valve into the 3/4" pipe on the top of the boiler.
See Figure 5. Use 3/4” Pipe and an elbow (not furnished) to
carry the water or steam to a nearby drain. Do not connect
directly to a drain but leave an air gap. No shutoff of any
description shall be placed between the safety relief valve
and the boiler, or on discharge pipes between such safety
valves and the atmosphere. Installation of the safety relief
valve shall conform to the requirements of the ANSI/ASME
Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section IV. The
manufacturer is not responsible for any water damage. Install
Drain Valve in lower left side of boiler as marked.
3. Connect Supply and Return Lines to boiler. The connections
may require certain additional fittings and parts, as shown
on diagram (Figs. 5 and 6).
4. This boiler is equipped with 1 1/4" supply and return
connections on both the left and right sides of the boiler.
In connecting the cold water supply to the water inlet valve,
make sure that a clean water supply is available. When the
water supply is from a well or pump, a sand strainer should be
installed at the pump.
A hot water boiler installed above radiation level must be
equipped with a low water cutoff device. A periodic inspection
is necessary, as is flushing of float type devices, per
manufacturers specific instruction.
The minimum design return water temperature to the boiler to
prevent condensation in the boiler and venting is 120° F. The
minimum high limit setting is 140° F.
CAUTION
THE ISOLATION BALL VALVES CONTAIN TEFLON
SEATS AND SEALS. OVERHEATING THIS VALVE MAY
CAUSE PREMATURE FAILURE.
FIG. 5 - TYPICAL HOT WATER PIPING
FOR USE WITH COOLING UNITS
A. This boiler, when used in connection with chilled water
systems, must be installed so that the chilled water is piped
in parallel with the heating boiler. Appropriate valves must
be used to prevent the chilled water from entering the heating
boiler (Fig. 6).
B. When this boiler is connected to heating coils located in air
handling units where they may be exposed to refrigerated
air circulation, the piping system shall be equipped with flow
control valves or other automatic means to prevent gravity
circulation of the boiler water during the cooling cycle.
LOW DESIGN WATER TEMPERATURE
SYSTEMS (BELOW 140°)
If the boiler is to be used in a heating system where design
water temperatures below 140° F are desired (e.g. radiant floor
heating), a 3-way or 4-way mixing valve or suitable alternative
is required to prevent low temperature return water from
entering the boiler. Follow the mixing valve manufacturer’s
installation instructions.
FIG. 6 - CHILLED WATER PIPING
6

Chimney and Vent Pipe Connection
For boilers for connection to gas vents or chimneys, vent installations shall be in
accordance with Part 7, Venting of Equipment, of the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI
Z223.1-latest revision and applicable provisions of the local building codes.
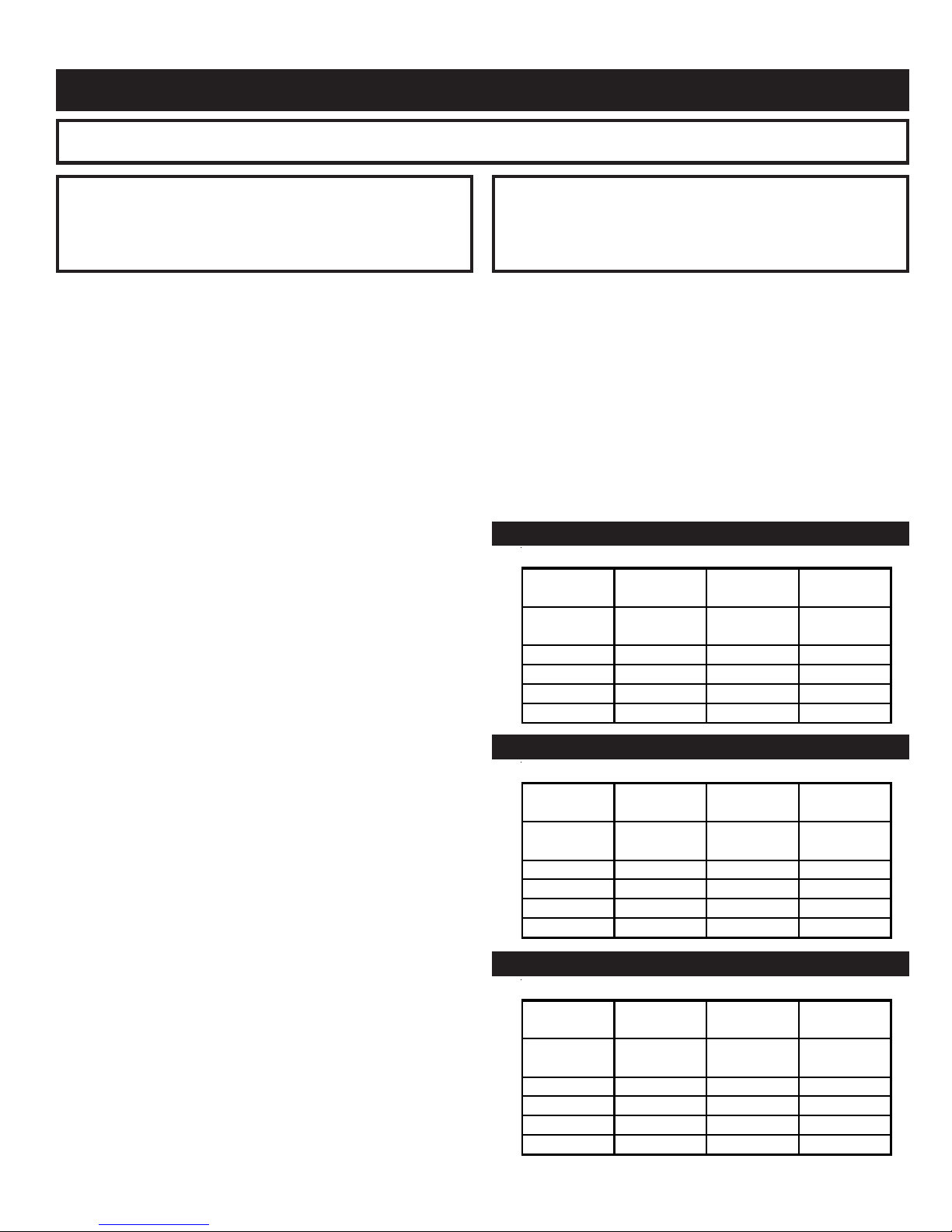
CHECK YOUR CHIMNEY
This is a very important part of your heating system. It must be
clean, the right size, properly constructed and in GOOD
CONDITION. No boiler can function properly with a bad
chimney. Fig. 7 gives typical chimney sizes. Fig. 8 gives you
an idea how a boiler might be vented to a chimney. Note that
the height (HT) is measured from the vent pipe to the top.
CHIMNEY SIZING
Chimney sizing, and all other aspects of the vent installation
must be in accordance with Part 7 of the National Fuel Gas
Code, ANSI Z223.1 latest revision, and applicable provisions
of the local building codes.
In Canada, follow CAN/CGA B149.1 and B149.2, Installation
Codes for Gas Burning Appliances and Equipment.
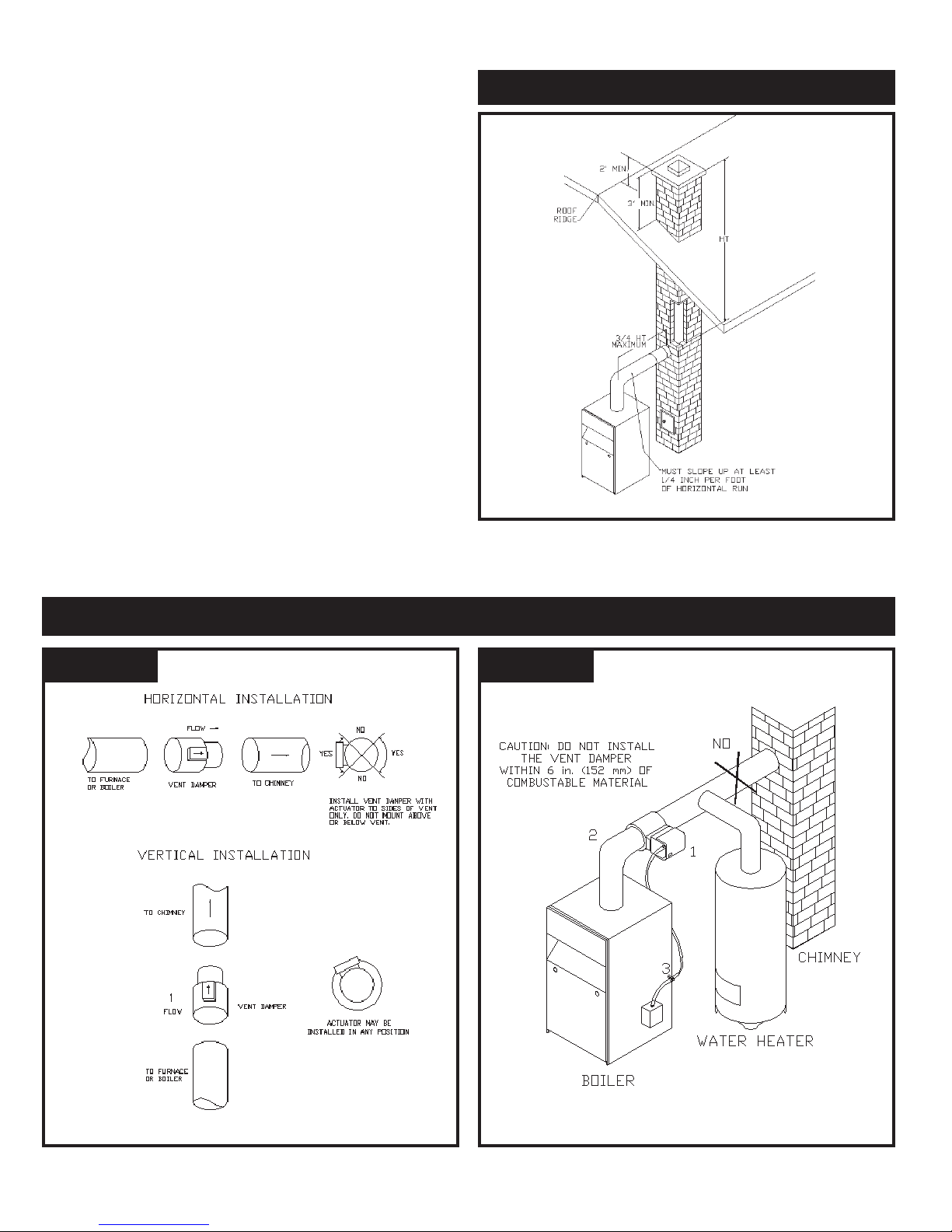
CONNECTING THE VENT DAMPER AND VENT
CONNECTOR
Refer to Fig. 1 flue diagram for the size and location of the vent
(flue opening). Use a 28 gauge (minimum) galvanized pipe to
connect to the chimney.
IMPORTANT - The damper blade on the furnished vent damper
has a 1/2 square inch hole (approximately3/4 diameter). On
boilers equipped with standing pilot, the hole must be left open.
On boilers equipped with intermittent ignition, the hole should
be plugged by using the plug supplied with the vent damper.
1. Position furnished vent damper on top of flue outlet collar.
Fasten damper securely to flue outlet collar with sheet
metal screws. Make sure damper blade has clearance to
operate inside of diverter.
On 2 section boilers equipped with vent damper, the
supplied 4-inch vent damper is equipped with a 3- to 4inch adapter so that the 4-inch vent damper may be
installed on the boiler’s 3-inch flue outlet collar. Fasten all
fittings securely.
As An Option (U.S.A. Only)
The damper may be installed in any horizontal or vertical
position, closer to the flue outlet collar preferred. Follow
the diagrams - Figures 9, 10 and 11.
2. Install the vent damper to service only the single boiler for
which it is intended. The damper position indicator shall
be in a visible location following installation. Locate the
damper so that it is accessible for servicing.
3. The damper must be in the open position when appliance
main burners are operating.
4. The boiler is equipped with a factory wired harness that
plugs into the vent damper.
5. Vent pipe must be same size as the flue outlet collar, except
2 section boilers with vent damper as noted above.
6. Slope pipe up from boiler to chimney not less than 1/4” per foot.
7. Run pipe as directly as possible with as few elbows as
possible.
8. Do not connect to fireplace flue.
9. End of vent pipe must be flush with inside face of chimney
flue. Use a sealed-in thimble for the chimney connection.
10. Horizontal run should not be longer than 3/4 the
chimney height (HT) (Fig, 8).
The sections of vent pipe should be fastened with sheet metal
screws to make the piping rigid. Horizontal portions of the vent
system must be supported to prevent sagging. Use stovepipe
wires every 5' to support the pipe from above If the vent pipe
must go through a crawl space, double wall vent pipe should
be used Where vent pipe passes through a combustible wall
or partition, use a ventilated metal thimble. The thimble should
be 4 inches larger in diameter than the vent pipe.
FIG. 7 - TYPICAL CHIMNEY SIZES
FLUE AREA IN INCHES
Boiler Input *HT. *HT. *HT.
Btuh 10-15 Ft. 10-25 Ft. 25 Ft. UP
Up to 100,000 6 x 6 6 x 5 5 x 5
Up to 155,000 6 x 7 6 x 6 6 x 5
Up to 230,000 7 x 8 7 x 7 6 x 7
Up to 350,000 9 x 9 8 x 9 8 x 8
* HT = top of thimble to top of flue. See Fig. 8
For boiler input refer to table, page 2.
For information only - not meant to imply minimum sizes.
MINIMUM VENT PIPE CLEARANCE
Wood and other combustible materials must not be closer than
6" from any surface of single wall metal vent pipe. Listed Type
B vent pipe or other listed venting systems shall be installed in
accordance with their listing.
REMOVING EXISTING BOILER FROM
COMMON VENTING SYSTEM
When an existing boiler is removed from a common venting
system, the common venting system is likely to be too large
for proper venting of the appliances remaining connected to it.
At the time of removal of an existing boiler, the following steps
shall be followed with each appliance remaining connected to
the common venting system placed in operation, while the other
appliances remaining connected to the common venting system
are not in operation.
1. Seal any unused openings in the common venting system.
2. Visually inspect the venting system for proper size and
horizontal pitch and determine there is no blockage or
restriction, leakage, corrosion and other deficiencies which
could cause an unsafe condition.
7
3. Insofar as is practical, close all building doors and windows
and all doors between the space in which the appliances
remaining connected to the common venting system are
located and other spaces of the building. Turn on clothes
dryers and any appliance not connected to the common
venting system. Turn on any exhaust fans, such as range
hoods and bathroom exhausts, so they will operate at
maximum speed. Do not operate a summer exhaust fan.
Close fireplace dampers.
4. Place in operation the appliance being inspected. Follow
the lighting instructions. Adjust thermostat so appliance
will operate continuously.
5. Test for spillage at the draft hood relief opening after 5
minutes of main burner operation. Use the flame of a match
or candle, or smoke from a cigarette, cigar or pipe.
6. After it has been determined that each appliance remaining connected to the common venting system properly
vents when tested as outlined above, return doorswindows,
exhaust fans, fireplace dampers and any other gas-burning
appliance to their previous conditions of use.
7. Any improper operation of the common venting system
should be corrected so the installation conforms with the
National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1-latest revision.
When resizing any portion of the common venting system,
the common venting system should be resized to approach
the minimum size as determined using the appropriate
tables in Part 11 in the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI
Z223.1-latest revision.
FIG. 8 TYPICAL MASONRY CHIMNEY REQUIREMENTS
Vent connectors serving appliances vented by natural draft
shall not be connected into any portion of mechanical draft
systems operating under positive pressure.
FIG. 9
Vent Damper Operation
FIG. 10
8
 Loading...
Loading...