DTI HV-500 Technical Description

HV-500 TECHNICAL
DESCRIPTION
B ETA VE R S I ON
www.drivetraininnovation.com
V1.31

HV-500 TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION (BETA VERSION)
2
Revision 1.31
CONTENTS
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................... 3
History ......................................................................................................................................................... 3
Related documents ..................................................................................................................................... 3
Liability and safe use of this unit ..................................................................................................................... 4
Main features .................................................................................................................................................. 5
Specifications................................................................................................................................................... 5
Current limit reduction .................................................................................................................................... 6
Power loss ....................................................................................................................................................... 6
Efficiency ......................................................................................................................................................... 7
physical description ......................................................................................................................................... 8
Mounting options ........................................................................................................................................ 9
Connections ................................................................................................................................................... 10
Harness connector pinout (H) ................................................................................................................... 10
Motor sensor connector pinout (M) ......................................................................................................... 11
Incremental encoder + SSI ..................................................................................................................... 11
Hall sensors ........................................................................................................................................... 12
High power connection ............................................................................................................................. 12
Liquid cooling connection ......................................................................................................................... 12
PC connection and control ............................................................................................................................ 13
Wiring ............................................................................................................................................................ 13
Harness connector wiring.......................................................................................................................... 14
Input supply ........................................................................................................................................... 15
Analog input .......................................................................................................................................... 15
Digital input ........................................................................................................................................... 15
Digital output......................................................................................................................................... 15
CAN periphery ....................................................................................................................................... 15
RS 232 pheriphery ................................................................................................................................. 16
Motor sensor connector wiring ................................................................................................................. 16
Encoder ................................................................................................................................................. 16
Hall sensor ............................................................................................................................................. 17
High voltage wiring .................................................................................................................................... 18

HV-500 TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION (BETA VERSION)
3
Revision 1.31
OVERVIEW
Read the manual carefully and thoroughly before using the controller. If you have
any questions, please contact us. info@drivetraininnovation.com
History
07/2016
IGBT and IGBTdriver testing
09/2016
Seventh version final box design
05/2017
Second version prototype hardware testing
11/2017
Using and testing the FOC algorithm for the third version prototype hardware
12/2017
Testing in an automotive environment
02/2018
Final construction
04/2018
Testing in an aerospace environment
05/2018
Adding the resolver and Sin/Cos encoder
07/2018
V1.0 User manual basic specifications
09/2018
Field oriented control with hall sensor improvement
01/2019
V1.1 User interface. Digital I/O and low power wiring diagrams added
Developing field weakening.
03/2019
V1.2 Adding efficiency measurement grap
04/2019
V1.3 High voltage wiring description
Related documents
• DTI Tool user manual
• Motor calibration description
• Analog input setup description
• Can communication description
• Wiring example

HV-500 TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION (BETA VERSION)
4
Revision 1.31
_________________________________________________
LIABILITY AND SAFE USE OF THIS UNIT
DTI Controller hardware, DTI Tool and the DTI firmware are experimental products designed to develop
and test electrical systems incorporating electric motors or actuators. Electrical systems can cause danger
to humans, property and nature; therefore precautions shall be taken to avoid any risk. Under no
circumstances shall the device be used where humans or property are put to risk without thoroughly
validating and testing the whole system. Software and hardware interact in various ways, and developers
cannot foresee all possible combinations of hardware used together with software, nor problems that can
occur in these different combinations. Tool and the DTI firmware are experimental software designed to
develop and test. Electrical systems can cause danger to humans, property and nature; therefore
precautions shall be taken to avoid any risk.
Things that can happen, even when using the correct settings, are
• electrical failure
• fire
• electric shock
• hazardous smoke
• overheating motors and actuators
• overstrained power sources, causing fire or explosions (e.g.
Lithium Ion Batteries)
• motors or actuators stopping from spinning/moving
• motors or actuators locking in, acting like a brake (full stop)
• motors or actuators losing control over torque production (uncontrolled acceleration or braking)
• interferences with other systems
• other non-intended or unforeseeable behavior of the system
DTI Tool and the DTI firmware are developer tools that for safety reasons may only be used
• by experts and experienced users, knowing exactly what they do.
• following safety standards applicable in the area of usage.
• under safe conditions where software or hardware malfunction will not lead to death, injuries or
severe property damage.
• keeping in mind that software and hardware failures can happen. We can't give any warranty
because every system is unique and we cannot make sure its safety. Although we design our
products to minimize such issues, you should always operate with the understanding that a
failure can occur at any point of time and without warning. As such, you shall take the
appropriate precautions to minimize danger in case of failure.
DTI does not assume any responsibility for difficulties, which are the result of inappropriate configuration,
electric system structure and settings that are not in accordance with the latest version of the manual for
DTI inverters.
Every inverter is tested before shipping. DTI assumes no liability in case a customer uses components for
the purposes for which they have not been developed or tested.
DTI reserves the right to change any information included this manual. All connection circuitry described
is meant for general information purposes and is not mandatory. DTI does not assume any liability,
expressively or inherently, for the information contained in this manual, for the functioning of the device
or its suitability for any specific application.
HV-500 TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION (BETA VERSION)
5
Revision 1.31
MAIN FEATURES
• Sensored FOC motor control
• Analog and digital inputs for control
• CAN (ISO 11898-2), UART communication
• Duty-cycle, speed or torque control
• Regenerative braking
• Hand brake function
• Motor angle positioning
• Motor sensors: UVW Hall sensors, SSI, resolver or ABI encoder
• Hardware and Software overcurrent and overvoltage protection
• Undervoltage limitation and protection
• IGBT and motor overtemperature protection
• Encoder wire damage protection
• Maximum motor speed limitation
• Maximum power limitation
• DC and AC current limitation
• Different setup for reverse operation
• Adjustable non-linear or linear analog input caracteristics
• Adjustable reverse switch or centerized analog input for reverse operation
• Simplified motor setup for perfect current control
Awaiting completion…
SPECIFICATIONS
Maximum operating voltage:
700 V
Continuous/peak AC current:
400 A / 500 A depending on the temperature
Maximum power dissipation:
6000 W
Maximum electric RPM:
100.000 (10.000 physical RPM with 10 pole pair motor)
Maximum operating temperature:
100°C
Switching frequency:
8-14 Khz
Dimension (h/w/l):
77/213/420mm
Weight:
6,7 kg
Integrated liquid cooler
IP65 waterproof design
HV-500 TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION (BETA VERSION)
6
Revision 1.31
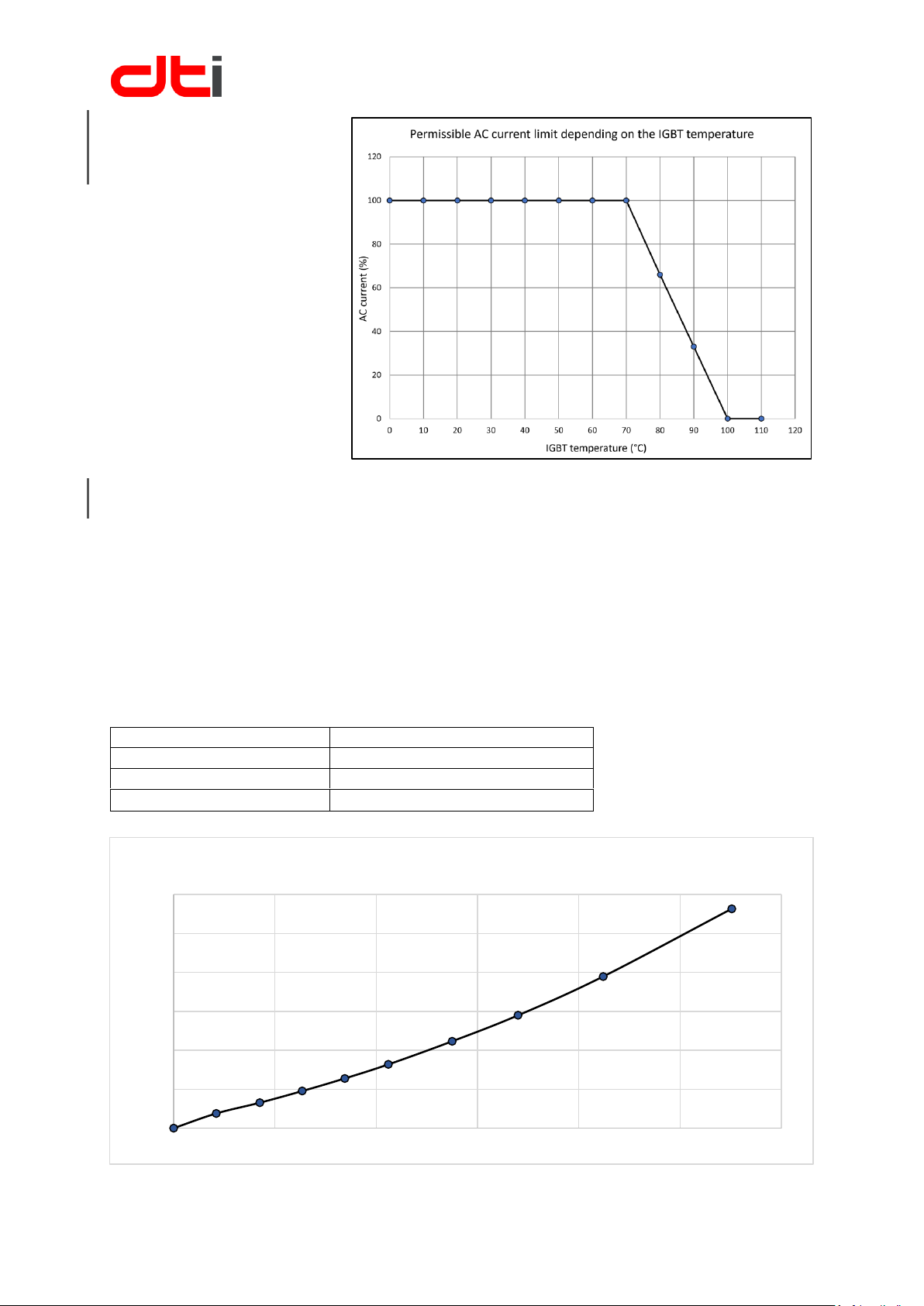
CURRENT LIMIT
REDUCTION
Maximum stepless AC current
limit depending on the IGBT
temperature in order to protect
them from damage.
POWER LOSS
The dissipated power depends on:
• PWM switching frequency
• AC frequency (motor rotation frequency)
• AC current
• AC voltage
• DC voltage
With a calculated example we demonstrate the power loss of the inverter. Power loss can be seen
compared to AC current.
Power loss calculated with the following inputs:
DC voltage:
370 V
Motor KV:
13 [RPM/V]
PWM switching frequency:
10.000 Hz
AC electric frequency:
20.000 Hz (2000 RPM with EMRAX)
0W
500W
1000W
1500W
2000W
2500W
3000W
0A 100A 200A 300A 400A 500A 600A
Total power loss
 Loading...
Loading...