DSG InterPBX Blaze5000, InterPBX Blaze1200, InterPBX Savanna8000 Installation And Configuration Manual

InterPBX Communication System
Blaze5000/Blaze1200/Savanna8000
Administrator
Installation and Configuration Guide
08IPBXM.BZ/BA/BC2.00h.EN16

DSG, DSG logo, InterPBX, Blaze, Savanna, VG5000, VG6000, VG7000, IP590, IP580, IP500, IP510, InterConsole,
DSG SoftPhone, DSG SoftConsole, DSG SIP Proxy Server, DSG NAT Proxy Server, SIP1200, Blaze Logger,
BlazeLink, and S300X are trademarks of DSG Technology. Windows and Outlook Express are trademarks of
Microsoft Inc. Other names used here are trademarks of their respective owners.
Copyright © DSG Technology Inc. All rights reserved.
7F, 222 Cheng-Teh Road, Sec. 4, Taipei, Taiwan 111
Tel:886x2x88615558
Fax:886x2x88615557
E-mail:sales@dsg.com.tw
http://www.dsgtechnology.com

Table of Contents 3
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 InterPBX Communication System Overview...............................................................7
IP-Based Business Telephone System.......................................................................................8
Advantages of InterPBX..............................................................................................................8
Key Components .........................................................................................................................9
InterServer...........................................................................................................................9
VMS Server..........................................................................................................................9
Conference Server ..............................................................................................................9
Recording Servers ..............................................................................................................9
Voice Gateways ..................................................................................................................9
SIP Proxy Server...............................................................................................................10
NAT Proxy Server............................................................................................................10
CTI Solutions ....................................................................................................................10
Extension Types................................................................................................................10
Web-based Management Tools ......................................................................................11
SH2500 PoE Switching Hub............................................................................................12
Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System.................................................................13
Before You Start .........................................................................................................................14
Prepare Your Telephone Numbering Plan ...................................................................14
Installing PBX Server.................................................................................................................15
Installing and Configuring PBX Server.........................................................................16
Connecting PBX Server via Console Port......................................................................19
Installing VG5000 Voice Gateway...........................................................................................20
Connecting VG5000 via Telnet.......................................................................................24
Connecting VG5000 via Console Port ...........................................................................25
Installing IP Phones...................................................................................................................26
Create IP Phones via Auto Discovery ...........................................................................27
Create IP Phones Manually.............................................................................................32
Chapter 3 System Configuration.......................................................................................................35
General Parameters ...................................................................................................................36
Basic IP Settings................................................................................................................36
Email Settings ...................................................................................................................37
NAT Settings.....................................................................................................................37
Set QoS...............................................................................................................................38
Music on Hold ..................................................................................................................38
Ringing Patterns ...............................................................................................................39
Company Information...............................................................................................................39
Business Hours...........................................................................................................................39
Holidays......................................................................................................................................41
System Speed Dialing................................................................................................................41
Call Restriction ...........................................................................................................................42
Route............................................................................................................................................43
Function Code ............................................................................................................................44
Password Management.............................................................................................................45
Set System Date/Time ..............................................................................................................46
Miscellaneous.............................................................................................................................46
Timeout Settings...............................................................................................................46
Authorization Code .........................................................................................................47
Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration....................................................................................................49
Analog Gateways.......................................................................................................................50
Creating Analog Gateway List .......................................................................................50
Editing Analog Gateways ...............................................................................................51

4 Table of Contents
Configuring CO Line Ports.............................................................................................52
Configuring SLT Ports.....................................................................................................55
Off-Premises Gateways.............................................................................................................56
Creating Off-Premises Gateway List .............................................................................57
Configuring Off-Premises CO Line Ports .....................................................................58
Configuring Off-Premises SLT Ports.............................................................................59
Recording System ......................................................................................................................60
Setting Store-on-Demand (Available on Blaze5000 Series) ........................................60
Setting Record-on-Demand (Available on Blaze5000 and Blaze1200 Series)...........63
Setting Professional Recording System.........................................................................65
Digital Line Gateways...............................................................................................................66
Adding Digital Gateway .................................................................................................66
Modifying a Digital Gateway.........................................................................................68
Setting Trunk Parameters................................................................................................68
Setting Trunk Port Parameters .......................................................................................69
CTI Gateway...............................................................................................................................72
NAT Proxy..................................................................................................................................73
SIP Proxy.....................................................................................................................................74
Add SIP Proxy ..................................................................................................................74
Add SIP Trunks ................................................................................................................75
Create SIP Trunk ARS .....................................................................................................77
Add SIP Extensions..........................................................................................................79
Chapter 5 Extension Management....................................................................................................80
Configuring IP Phone, SoftPhone and SoftConsole..............................................................81
Extension No., Phone Type and MAC Address...........................................................81
User Information ..............................................................................................................81
User Password..................................................................................................................81
Off-Hook Access to ..........................................................................................................82
Class of Service .................................................................................................................82
Button Mapping Group...................................................................................................82
CODEC ..............................................................................................................................82
Jitter Buffer Depth ............................................................................................................83
Silence Suppression .........................................................................................................83
Conference Disabled........................................................................................................83
Paging Disabled................................................................................................................84
Enable/Disable Extension...............................................................................................84
Apply Settings ..................................................................................................................84
Button Mapping ...............................................................................................................85
Station Speed Dialing ......................................................................................................89
Answer Option .................................................................................................................90
Mailbox..............................................................................................................................91
Notification .......................................................................................................................93
Distribution List ...............................................................................................................95
Virtual Extensions............................................................................................................95
Analog Extensions .....................................................................................................................97
Off-Premises Extensions ...........................................................................................................98
SIP Phone List...........................................................................................................................100
InterConsole List......................................................................................................................101
Chapter 6 Group Management........................................................................................................103
CO Line Groups .......................................................................................................................104
Creating CO Line Groups .............................................................................................104
Assigning Members to CO Line Groups.....................................................................105
Extension Groups ....................................................................................................................105
Creating Extension Groups...........................................................................................106
Hunting Method.............................................................................................................107
Wrap Up Time ................................................................................................................107
Group Administrator Password...................................................................................107

Table of Contents 5
Set Sec. of Rings..............................................................................................................107
Queuing...........................................................................................................................108
Login to Group ...............................................................................................................108
Assigning Members to Extension Groups ..................................................................109
Group Answering Option.............................................................................................110
Group Mailbox ...............................................................................................................111
Message Notification for Extension Groups...............................................................113
Button Mapping Groups.........................................................................................................115
Class of Service.........................................................................................................................119
Creating a Class of Service............................................................................................119
Setting Allow and Disallow Table ...............................................................................121
Setting CO Priority.........................................................................................................122
Automatic Route Selection (ARS) ................................................................................123
Automatic Alternate Route (AAR) ..............................................................................124
Operator....................................................................................................................................125
Authorization Code.................................................................................................................126
Boss and Secretary...................................................................................................................127
Chapter 7 Voice Mail Configuration...............................................................................................129
Voice Mail Parameters ............................................................................................................130
Language .........................................................................................................................130
Name Directory ..............................................................................................................130
Inter-Digit and AA Timeout .........................................................................................130
Messages Storage Settings.............................................................................................131
Ring Notification ............................................................................................................131
Adjust Gain Level...........................................................................................................132
Transfer Options Settings .......................................................................................................132
Transfer Announcement ...............................................................................................132
Leave Message Directly.................................................................................................133
Transfer Options.............................................................................................................133
Before Leaving Message Timeout................................................................................135
AA Management......................................................................................................................135
Planning Your Auto Attendant Tree ...........................................................................135
Planning an AA Menu...................................................................................................136
Recording AA Menu Greetings....................................................................................138
CO Priority of Notification .....................................................................................................140
Tel. Programming Mode.........................................................................................................140
Chapter 8 Operation Management .................................................................................................141
General Information ................................................................................................................142
Check Software Version ................................................................................................142
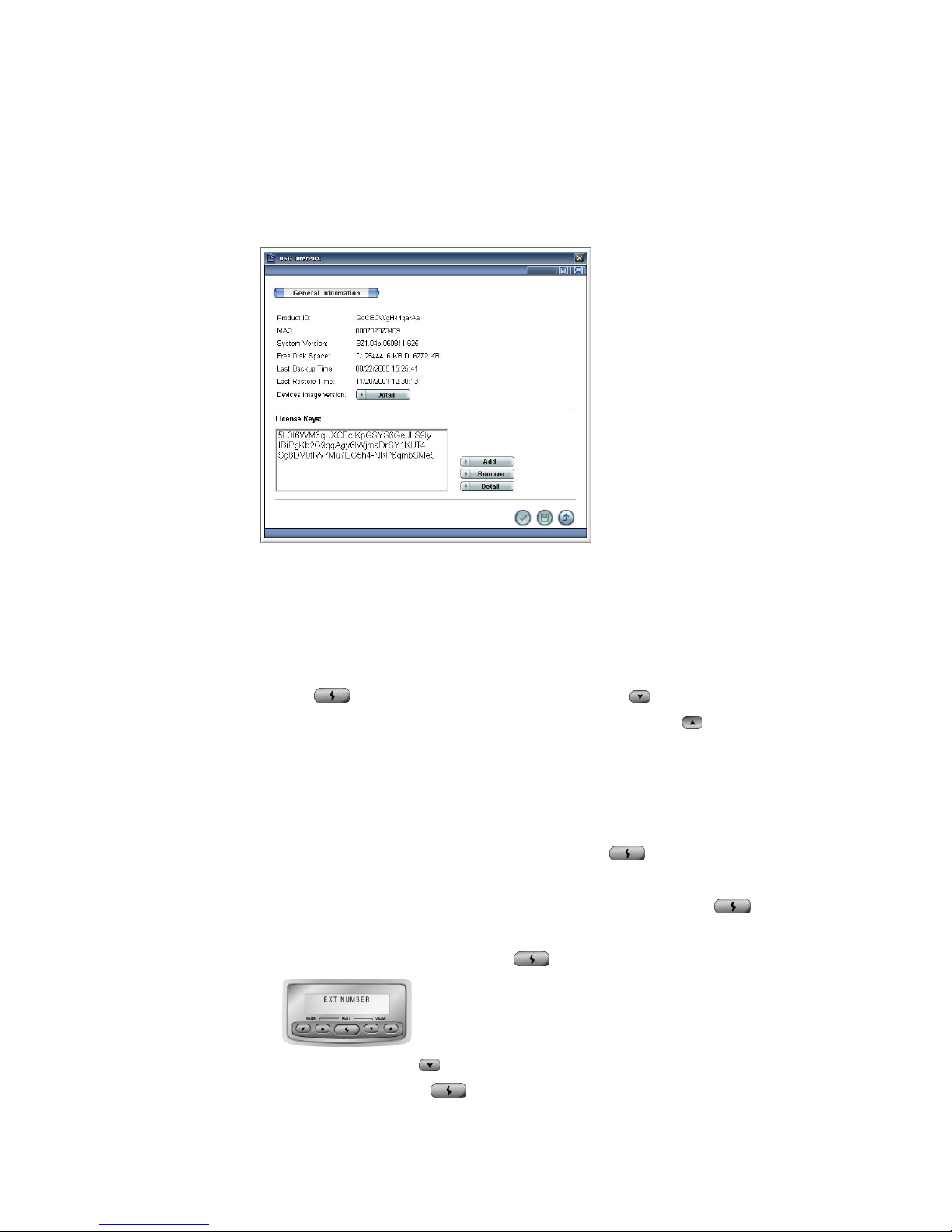
License Key .....................................................................................................................143
Auto Discovery ........................................................................................................................143
Setting Default Class of Service....................................................................................144
Enable/Disable Auto Discovery ..................................................................................144
Backup System Files................................................................................................................144
Restore System Files................................................................................................................145
Application Upgrades.............................................................................................................146
CDR ...........................................................................................................................................146
Billing System .................................................................................................................148
Reboot........................................................................................................................................148
Reset to Default........................................................................................................................149
Chapter 9 Report Management .......................................................................................................151
System Summary Report ........................................................................................................152
System Log................................................................................................................................152
Extension Report......................................................................................................................153
Chapter 10 Multi-Server Management...........................................................................................155
Server Information...................................................................................................................156

6 Table of Contents
Redundant Server....................................................................................................................156
Assigning Slave PBX Server..........................................................................................157
Installing and Setting Slave PBX Server......................................................................157
Joint Server ...............................................................................................................................158
Creating Joint Server......................................................................................................158
Setting Joint Server CO Lines Access Control............................................................160
Setting Links with Joint Server.....................................................................................160
Setting Joint Server Extension List ...............................................................................161
Joint Server Status ..........................................................................................................162
Appendix A: Function Code List ....................................................................................................163
Appendix B: Retrieving Voice Messages and Recordings...........................................................167
Appendix C: InterPBX Management Website...............................................................................171
Appendix D: Terminologies ............................................................................................................173
Appendix E: Default Values ............................................................................................................175
Appendix F: DTMF Programming..................................................................................................177
Appendix G: System Capacity.........................................................................................................183
Index ...................................................................................................................................................185

Chapter 1 InterPBX Communication System Overview 7
Chapter 1
InterPBX Communication System Overview
InterPBX Communication System is a new generation business phone system
that employs a data network for terminal connectivity and voice transport.
Contrary to traditional business phone systems that carry voice over legacy
TDM networks, InterPBX delivers voice in digitized packets over LAN or
Internet networks.

8 Chapter 1 InterPBX Communication System Overview
IP-Based Business Telephone System
Packet switching telephony technology allows enterprises to work upon their
existing data network infrastructure for implementing advanced applications
and to save costs on long distance and international calls. As a nature of
IP-based communication systems, the InterPBX brings significant savings on
call tolls, simplifies wiring, improves management and maintenance, and
provides advanced voice applications to enterprises’ needs.
Advantages of InterPBX
y Feature-rich – InterPBX supports an abundant number of features, including
Auto Attendant, built-in Messaging System, Automated Call Distribution
(ACD), Conference, Unified Messaging, Recording System, Auto discovery,
Contact Center applications, and other new generation business
applications.
y Flexibility – The capacity of InterPBX is not limited to a fixed system chassis.
InterPBX provides flexible structure for growing businesses. It can be set up
to meet the needs of enterprises from small to large or single to multiple
sites. Enterprises can connect each location by VPN or Internet.
y Reliability – InterPBX employs a unique distributed NeuralServer
architecture that allows multiple servers to coexist and communicate with
one another in a single system. Through synchronization and backup
mechanisms, InterPBX provides redundancy in the event of server failure
and therefore drastically enhances the reliability of the system.
y Management – Browse-based management tool provides administrators and
users a user-friendly interface to set, control, and maintain the system.

Chapter 1 InterPBX Communication System Overview 9
Key Components
DSG’s InterPBX Communication System supports flexible components. They
could either be integrated as an embedded system or work individually.
y Blaze 5000 Series: It contains InterServer, VMS Server, Conference Server,
Voice Gateway, and Recording Server.
y Blaze 1200 Series: It contains InterServer, VMS Server, Conference Server,
Recording Server and Voice Gateway.
y Savanna 8000 Series: It contains InterServer, VMS Server and Conference
Server.
InterServer
InterServer is the brain (central administration) of InterPBX Communication
System. It is a software-based switching solution that handles call signals, call
control and voice processing activities and manages all the extensions, voice
gateway and other applications within the system.
VMS Server
VMS Server works seamlessly with PBX Server and provides Auto Attendant,
Voice Mail, Automated Call Distribution (ACD) and Unified Messaging
features.
Conference Server
Conference Server improves communications among employees by providing
conference function.
Recording Servers
Recording Server helps enterprises record, monitor and search recording files.
It can be integrated seamlessly with users’ IP phones bringing more efficiency
for customer service representatives, banking officers or attorneys.
Note: Blaze 5000 provides built-in Record-on-Demand and Store-on-Demand
functions and Blaze200 provides built-in Record-on-Demand. Savanna 8000
Series requires a stand-alone Recording Server.
Voice Gateways
Voice Gateway connects PSTN and IP networks and allows voice packets to be
transferred between Internet and traditional PSTN network. VG5000 Voice

10 Chapter 1 InterPBX Communication System Overview
Gateway supports CO Line and/or SLT interfaces, which are able to connect
CO lines or analog phones. VG6000 and VG7000 Voice Gateway supports
T1/E1 ISDN network.
Note: The Savanna 8000 Series doesn’t provide built-in Voice Gateway.
SIP Proxy Server
DSG's SIP Proxy is a full-featured proxy server. It allows your Blaze or Savanna
Series IP-PBX to get connected to operators' softswitch and to enjoy the
provided SIP Trunk services. DSG SIP Proxy can register the IP-PBX to your
service provider. All the extensions under the system, including DSG IP
extensions or third parties' SIP phones, can access the SIP Trunks to make
long-distance or international calls.
NAT Proxy Server
DSG NAT Proxy is a complete solution to solve complicated network problems
that may happen when enterprises use the IP PBX Communication System.
With DSG NAT Proxy, Blaze or Savanna IP PBX Communication Systems and
Off-Premises Phones can traverse more than 95% of NAT or firewall
successfully without creating other service ports, and therefore enterprises can
communicate via IP-PBX Communication System with pure and stable voice
quality.
CTI Solutions
DSG BlazeLink is a CTI solution enables business to develop applications to
optimize workforce in a call center or contact center. Applications developed on
BlazeLink for call control, monitoring, or managing are able to connecting DSG
IP-PBX System to the data processing environment. With the supported tools
and resources, developers are able to deliver a comprehensive solution for
effective communications and better interactive experiences.
Extension Types
InterPBX Communication System supports various types of extensions – IP
phones, analog phones, software phones and SIP phones. Administrators may
set up any types of the phones as users’ needs.
IP Phone: IP phones offer various business telephone features. They could be
installed on LAN or on remote sites.

Chapter 1 InterPBX Communication System Overview 11
SoftPhone: DSG’s SoftPhone is an application software installed on PCs
offering telecommuters or business travelers full-featured extension functions.
Users can adopt their own headsets or use DSG S300X USB Phones when
utilizing the SoftPhone.
Off-premises Phone: Off-premises IP phones, SoftPhones or analog phones on
off-premises gateways are all able to connect to a company’s InterPBX
Communication System via Internet or VPN and perform the same way as the
extensions in the head office.
Analog Phone: Analog extensions are connected to the FXS ports of Voice
Gateway like VG5000.
Attendant Console: Both software attendant console and hardware DSS
console are supported.
Web-based Management Tools
InterPBX provides administrators and extension users a management tool with
a GUI interface that allows administrators and extension users to set the
preferences of InterPBX or extension via browser. The suggested browser is
Internet Explorer 5.0 or later.
Administrator: The Administrator web site provides a web-based GUI interface
allowing administrators to configure the InterPBX Communication System
through the web browser. It helps administrators to manage and maintain the
system easily.

12 Chapter 1 InterPBX Communication System Overview
Extension User: Extension users log in to user’s section to customize personal
settings on phones like Button Mapping, Speed Dial, Message Option, Answer
Option, Password and Phone Book.
SH2500 PoE Switching Hub
SH2500 is the recommended switching hub for InterPBX Communication
System. It supports 802.3af PoE (Power-over-Ethernet), which offers IP
extensions the current power over network cables. Users do not need additional
power socket when using IP phones.

Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System 13
Chapter 2
Installing InterPBX Communication System
This chapter guides you through the preparation, installation and basic
configuration of InterPBX Communication System.

14 Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System
Before You Start
The component of InterPBX Communication System contains servers, gateways
and IP phones. Please follow the recommendations below when you install or
operate your system in order to avoid any injury and damage.
Safety Recommendation
Always use ESD-preventive tools when you plug the power cord. Do not
disassemble or remove chassis cover of any components of your InterPBX
Communication System. If there is any problem of your system, please contact
our service representatives.
Environmental Prerequisite
InterPBX Communication System needs to be installed in clean, dry, adequately
ventilated areas. The server, gateway, and switching hub can be placed in a
control room or on a rack. Please remain the control room in a suitable
temperature and adequately ventilated environment.
Local Telecommunications Service
You have to apply for the local phone service in your area. The trunk lines of
the central office need to be connected to Voice Gateways. DSG VG5000 Voice
Gateway supports CO Line interface. Please make sure if your trunk lines
support analog interface.
Prepare Your Telephone Numbering Plan
If you are going to replace your traditional telephony system with InterPBX
Communication System, you can retain the old dialing plan. InterPBX
Communication System supports flexible extension number lengths. The
maximum extension number length is “5 digits”. The telephone numbering
plan must not overlap or conflict with other numbers that are on your system or
on Joint Server’s system.
You need to prepare the followings before you install InterPBX Communication
System.
y CO Line Extension Number: Prepare an extension number for each CO Line
port so that the associated extension number can reach each trunk line that
is connected to it.

Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System 15
y SLT Extension Number: Prepare an extension number for each SLT port so
that the associated extension number can reach each analog phone that is
connected to it.
y IP Phone: Prepare an extension number for each IP phone.
y Group Number: If you plan to group specific trunk lines or extensions as a
group, prepare a Group Number for each CO Line Group and Extension
Group.
y AA Menu: Plan your AA procedure and prepare an access code for each AA
Menu.
y Routes: Plan your Routes, ARS and Class of Service to be uses when making
calls.
Installing PBX Server
Figure: Blaze 5000 Series Connection Diagram
Figure: Blaze 1200 Series Connection Diagram
Figure: Savanna 8000 Series Connection Diagram

16 Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System
Installing and Configuring PBX Server
1. Connecting to Power Cord
Plug one end of the power cord to the power connector on the rear panel of
PBX Server. Plug the other end of the power cord into a power outlet.
2. Connecting to LAN
You need to connect PBX Server to your existing Ethernet network. Connect an
Ethernet cable from the “Network” RJ45 port on PBX Server to any
10/100BaseT RJ45 port on a switching hub.
3. Connecting to CO Lines or Extension Lines (For Blaze Series Only)
With Blaze Series, the Server is integrated with Voice Gateway module. Voice
Gateway supports CO line or analog extension modules. Please plug a CO line
connector to a CO Line port or plug an analog extension to a SLT port. If you
would like to install other embedded analog or digital gateways, please refer to
the related manual.
Note: If you accidentally plug the equipment with CO Line interface to SLT
port, it may damage your equipment. Please make sure that your equipment
connects to an appropriate interface.
4. Connecting to External Audio Source (For Blaze Series Only)
The MOH (Music on Hold) port can connect to a radio or CD player for playing
music or your customized greetings for callers placed on hold.
You can also choose the pre-recorded audio files as the MOH on the PBX Server.
If you choose to use the pre-recorded audio files from the system, do not
connect the external audio source to the MOH port.
5. Connecting to External Paging Facility (For Blaze Series Only)
The “Paging” port allowing you to connect external paging equipment for
broadcasting.
6. Setting Power Failure Transfer (For Blaze Series Only)
When power failure occurs and there is no backup power, the C.O. lines
connected to port 1 will be switched to port 24. You can connect single line
phones to port 24 to pick up calls. The PFT function only works on port 1 with

Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System 17
FXO interface supported. Port 24 can be FXO, FXS or empty ports. When power
is supplied, the PFT function is not available.
7. Preparing a Computer
Prepare a computer with web browser and be sure it is on the same subnet as of
your PBX Server. Change the computer’s IP settings if necessary. The suggested
web browser is Internet Explorer version 5.0 or later.
The default values of PBX Server are as follows:
y Default IP Address: 192.168.1.200:88 (The service port is 88)
y Default Gateway: 192.168.1.254
y Default Subnet Mask: 255.255.0.0
8. Login PBX Server
y Launch the web browser. On the address bar, type in the PBX Server’s
default IP address 192.168.1.200:88 to access PBX Server.
y You will be connected to InterPBX Administration Website. Please click the
Administrator icon.
y When you login the InterPBX Administration for the first time, you will see
the following picture. Please enter your user name and password and then
save the settings. Please remember your user name and password in order
to login again in the future. The password shall not exceed 8-character
alphanumeric. The user name and password are case sensitive.

18 Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System
When you login the InterPBX Administration next time, you will see the
following picture. Please enter your user name and password to login.
y After you login the InterPBX Administration successfully, the screen will
display the main menu of InterPBX Administration website as follows:
9. Basic Settings
There are some basic items you need to configure allowing the system to work
properly.
y PBX Server IP Settings: Go to Main Menu>System Configuration>General
Parameters to set your PBX’s IP. If you have more than one PBX server, go
to Main Menu>Multi-Server Management to assign each an ID and set the
Joint Server connection.

Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System 19
y License Keys: Go to Main Menu>Operation Management>General
Information. Input the license keys you purchased.
y Trunks: Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration. Depending on the voice
gateway you purchased, add your gateways and assign CO line extension
numbers. In addition, you many go to Main Menu>Group
Management>CO Line Group to group CO lines for better managing your
trunks.
y Extensions: Go to Group Management>Class of Service to set CoS for
providing different call permissions to extensions applied. Go to Main
Menu>Extension Management to add your extensions or turn on the Auto
Discovery allowing the system to detect connected extensions automatically.
y AA Menu: Go to Main Menu>System Configuration>Business Hours to set
your company operating hours. Then go to Main Menu>VM
Configuration>AA Management to set AA trees. And make sure the Ring
Assignment of CO lines is set to the appropriate AA Menu Access Code.
y Accessing CO Lines: Each CoS will have its CO priority. Or you may go to
Main Menu>System Configuration>Route to set routes and go to Main
Menu>Group Management>Class of Service to further assign ARS for better
using your trunk resource.
You may change your computer IP setting to the original values after you finish
setting up the Blaze/Savanna Server. You will need to enter the new IP address
to connect to the Blaze/Savanna Server next time.
If you encounter any problem or have questions during installation or
operation, click on the Help icon from the web setting page for assistance.
Connecting PBX Server via Console Port
When you forget the IP address of the PBX Server, you can connect a computer
to the console port of the PBX Server in order to check the current IP address,
gateway address, and subnet mask.
1. Connect one end of the RS232 transmission line to the computer’s COM
port and the other end to the Console port of PBX Server.
2. Open the Hyper Terminal program. Enter the connection name and set the
baud rate to 9600 bps.
3. Turn off the power of PBX Server. Wait for a while and then turn on the
power again. The computer can start to connect to the PBX Server.

20 Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System
4. You can see the IP address from the “Hyper Terminal” page. You can also
change the IP address here. If you are going to change the IP address,
please press any key within 3 seconds to setup.
Note: The RS-232 DB-9 connector enclosed with the package is with pin 2/3,
pin 4/6, and pin 7/8 shorted.
Installing VG5000 Voice Gateway
Figure: VG5000 Voice Gateway Connection Diagram
This section will guide you through the installation and configuration of
VG5000. For more details, please refer to VG5000 Operation Manual. For other
model Voice Gateways, please refer to their respective manuals.
1. Connecting to Power Cord
Plug one end of the power cord to the power connector on the rear panel of the
VG5000. Plug the other end of the power cord into a power outlet. After you
turn on the power switch on the rear panel, you can verify the function by
checking if the LED labeled Power is on.

Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System 21
2. Connecting to LAN
You can connect VG5000 to your existing Ethernet network. Please connect one
end of the Ethernet cable to the network RJ45 port of VG5000 and connect the
other end of the Ethernet cable to any 10/100BaseT RJ45 port on DSG SH2500
Switching Hub or your existing switching hub.
3. Connecting to Trunk Lines or Analog Extensions
VG5000 supports trunk lines and analog extensions. Please plug the trunk line
from the Central Office to the CO Line port or plug the analog extension to the
SLT port.
Note: Misplacing FXO equipment into FXS interface and vice versa may
damage your VG5000 Voice Gateway. Be sure that the FXO/FXS interfaces of
VG5000 are connected to suitable telephone lines and equipment.
4. Connecting to External Audio Source (Optional)
InterPBX Communication System supports external and internal MOH (Music
on Hold). VG5000 Voice Gateway provides a “MOH” port for connecting to the
radio or CD player. When callers are placed on hold, the system will play the
music from the radio or CD player. Please insert the plug of your music source
to the MOH port to enable this function.
You can also choose the pre-recorded audio files as the MOH on the PBX Server.
If you choose to use the pre-recorded audio files from the system, do not
connect the external audio source to the MOH port.
5. Connecting to External Paging Facility (Optional)
VG5000 Voice Gateway provides a “Paging” port allowing you to connect
external paging equipment for broadcasting to co-workers. Each VG5000
supports a paging port. If you have more than one VG5000, you can separate
them into different paging zones.
6. Setting Power Failure Transfer (Optional)
VG5000 Voice Gateway provides PFT (Power Failure Transfer) function. When
power failure occurs and there is no backup power, the C.O. lines connected to
port 1 will be switched to port 24. You can connect single line phones to port 24
to pick up calls. The PFT function only works on port 1 with FXO interface

22 Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System
supported. Port 24 can be FXO, FXS or empty ports. When power is supplied,
the PFT function is not available.
7. Prepare a Computer
Prepare a computer with web browser and be sure it is on the same subnet as of
VG5000. Change the computer’s IP settings if necessary. The suggested web
browser is Internet Explorer version 5.0 or later.
The default settings of VG5000 are as follows:
y Default IP Address: 192.168.1.201:89 (The service port is 89)
y Default Gateway: 192.168.1.254
y Default Subnet Mask: 255.255.0.0
8. Login VG5000
y Launch the web browser. On the address bar, enter the VG5000 default IP
address http://192.168.1.201:89 to access the VG5000.
y After you access to the web page of the VG5000, click on the Login icon. On
the login page, please enter the password. The default password is “1234”.
y After you log into the system successfully, the screen will display the System
Information page of DSG VG5000 as below:

Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System 23
y Basic IP Settings: On the System Information page, please enter the IP
address, gateway address and subnet mask assigned for VG5000. And then
enter the IP address of the PBX Server in “PBX Server.”
y Upgrade VG5000 Software (Optional)
If you need to upgrade the software version of the VG5000 in the future,
please click “Upload Pack” item after you access to VG5000.
9. Settings on InterServer
After you install the VG5000 Voice Gateway, you need to set the VG5000
on the PBX Server.
y Enter License Key : Please login the PBX Server and go to Main
Menu>Operation Management>General Information. Click “Add” and
then enter your license key to make sure the system capacity fits your
needs.
y Creating Analog Gateway List: After you install VG5000, you need to
set VG5000 on the PBX Server. Each VG5000 has a MAC address. You
can see the MAC address from the label on the VG5000 or from the
VG5000 web or through Telnet. Please record your MAC address in
order to register to the PBX Server. Access the PBX Server and login to
the InterPBX Administration Website. Go to Main Menu>Gateway
Configuration>Analog Gateways. Click the Add button to create an

24 Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System
Analog Gateway.
y Editing Basic Gateway Data
On the “Add Analog Gateway” page, enter the name and the MAC
address of your gateway, and the range of CO Line/SLT ports. The
port number range starts from 1. For example, the CO Line port range
of a 24-port VG5000 with FXO interface is from 1 to 24.
y External Paging Setup: If you connect a paging amplifier to the
“PAGING” port on VG5000, select the “External Paging Enabled”
option to enable this function and assign a specific paging code at
“Paging Code” box. For example, if you assign “111” as the paging
code of your VG5000, please dial “111” to broadcast.
y Music On Hold (MOH) Setup: If the VG5000 Voice Gateway connects
to the external music source to play the Music On Hold, please go to
Main Menu>System Configuration>General Parameters and then
enable the “Music On Hold” function. For more details about MOH,
please refer to Chapter 3 System Configuration/System
Parameters/Music On Hold.
Connecting VG5000 via Telnet
Besides connecting VG5000 via the web browser, you can also connect VG5000
via Telnet.
1. Prepare a computer with Telnet program and be sure it is on the same
subnet as of VG5000.
2. Open the Telnet program and connect to the IP address of VG5000, or enter
C:\Telnet 192.168.1.201 90 (IP addresss+space+90) under DOS. In which
“192.168.1.201” is the default IP address of VG5000 and the communication
port is 90.

Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System 25
3. Enter the default password “1234” to login VG5000.
4. After you have logged into the VG5000 successfully, a window will be
shown as below. Please follow the instruction to edit the IP address,
Gateway IP, Subnet Mask, PBX IP, Off-premises items and Telnet password
of VG5000. After the editing, please save and exit.
Connecting VG5000 via Console Port
When you forgot the IP address for VG5000, you could connect a computer to
the console port of VG5000 to look up the current IP address, Gateway IP, and
Subnet Mask.
1. Please plug one end of the RS232 cable into the COM port of your
computer and the other end into the Console port of VG5000.
2. Open the Hyper Terminal program. Enter the profile name for the
connection and set the baud rate to 9600 bps.
3. Turn off the power of VG5000. Wait for a while and turn on the power
again. The computer will create a connection with VG5000.
4. You can see the IP address of the VG5000 from the window of Hyper
Terminal. You may also change the IP address in this window. If you want

26 Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System
to change the IP address, please press any key within 3 seconds.
Note: The RS-232 DB-9 connector enclosed with the package is with pin 2/3,
pin 4/6, and pin 7/8 shorted.
Installing IP Phones
InterPBX Communication System supports IP phones, such as IP590, IP580 or
IP500. IP phones provide various functions like Voice Mailbox, Message
indicator light, Auto-Answer, Mute, Replay, Hold, Transfer, DND, and
Speaker.
You may allow the system to automatically discover and register all the IP
phones connected LAN via Auto Discovery function. Strongly recommend you
to install IP phones via Auto Discovery at the first time. You can also create an
IP Phone manually.
Note: Please do not connect your IP phone to LAN before you start Auto
Discovery.

Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System 27
Figure: IP580 IP Phone
Create IP Phones via Auto Discovery
InterPBX Communication System provides Auto Discovery function that allows
PBX Server to automatically search and register IP phones. When you install
your IP phones at the first time, we recommend you to start Auto Discovery in
order to simplify the installation procedure. Please make sure the relevant
License Key has been added.
This section will guide you through the installation of IP580. For other types of
phones, please refer to the respective operation manuals.
1. Creating Default Class of Service
Specify a commonly used call limitation as the default Class of Service (CoS).
The default CoS will be applied to all IP extensions when registering with PBX
Server using Auto Discovery.
y Access the PBX Server and login to InterPBX Administration Website.
y Go to Main Menu>Group Management>Class of Service. And then click the
Add button to create a new Class of Service (CoS).
y Assign a name and select the call permissions. Click the Submit button to
save and exit. You can modify the CoS or create more entries later. See

28 Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System
Chapter 6 Group Management/Class of Service for more details.
2. Turn on Auto Discovery
y Go to Main Menu> Operation Management>Auto Discovery.
y Click the Turn On Auto Discovery button to enable the Auto Discovery
function. The Current Mode will display “Auto Discovery On.” After
the Auto Discovery is turned on, if you don’t turn off this function
manually, the system would automatically turn off the Auto Discovery
within 2 hours.
y You will find the Class of Service you have created from the list of “Set
Default CoS for Auto Discovery.” Select the one you would like to set
as the default value and click the Set Default button. You will see an
arrow sign pointed to the default CoS. Click the Submit button to save
and exit.
Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System 29
3. Enter License Key
Before installing the IP phones, be sure to enter the License Key on the PBX
Server set up page. Please login to the PBX Server and then go to Main
Menu>Operation Management>General Information. Click “Add” and then
enter your license key.
4. Settings on IP Phones
You will need to assign the Extension Number, IP Address, Gateway IP
Address, Subnet Mask and PBX Server IP to each IP phone. Please DO NOT
connect your IP phones to LAN before completing the above setups. Press the
middle
button to enter the setup menu. Press the downward button
next to the middle button to move to the next setting item or the upward
button next to the middle button to move to the previous setting item. Use the
keypad to input digits.
y Plug in the power cord of the IP phone and please DO NOT connect the IP
phone to LAN.
y After the system check, press and hold the middle button for 3
seconds to enter the setup menu.
y You will see “EXT NUMBER” shown on the LCD screen. Press the
button to start editing and use the keypad to input the extension number
assigned to the IP phone. Press the
button again to save.
y Press the downward button and the LCD screen will display “IP
ADDRESS.” Press the
button to start editing and use the keypad to

30 Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System
input the IP address assigned to the IP phone. Press the
button to
save.
y Follow the above procedures to assign the “GATEWAY IP” and “SUBNET
MASK” to the IP phone
y Keep pressing the downward button until the LCD displays “PBX
SERVER IP.” Press the
button to start editing and use the keypad to
input the IP address of your PBX Server. Press the
button to save.
y Keep pressing the downward button until the LCD displays “EXIT
SETUP”. Press the
button to exit.
The IP Phone will automatically search and download the latest version of
software from the PBX Server and then reboot with the latest version.
In DHCP Environment
If your LAN is under DHCP environment, you can skip the settings of IP
address, Gateway IP and Subnet Mask. Instead, you can move to “DHCP”
setup item and enable this function.
y Plug in the power cord of the IP phone and please DO NOT connect the IP
phone to LAN.
y After the system check, press and hold the middle button for 3
seconds to enter the setup menu.
y You will see “EXT NUMBER” shown on the LCD screen. Press the
button to start editing and use the keypad to input the extension number
assigned to the IP phone. Press the
button again to save.
y Keep pressing the downward button until the LCD displays “DHCP.”
Press the
button to start editing and then press the downward

Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System 31
button to change the selection to “On” Press the
button again to save.
y Keep pressing the downward button until the LCD displays “PBX
SERVER IP.” Press the
button to start editing and use the keypad to
input the IP address of your PBX Server. Press the
button to save.
y Keep pressing the downward button until the LCD displays “EXIT
SETUP”. Press the
button to exit.
Other Setting Items:
y MAC Address: MAC address shows the hardware address of an IP phone. It
is not editable.
y Image Version: Display the current software version of IP phones.
y Set Password: You may change the password for logging in to the phone. If
it is blank, the password will not be required when entering the setting
mode. The default password is “1234”.
y Echo Utility: You may input the PBX Server IP here and press Test. The
phone set will send testing packets to the assigned IP address and reply the
round trip time. This can help you test the connection status with the PBX
server.
5. Connect Your IP Phone to LAN
y Connect your IP phone to the Ethernet Network. Please connect one end of
the network cable to the “LAN” port on an IP phone and connect the other
end to the RF45 port of 10/100 BaseT switching hub or Hub on LAN. PBX
Server will automatically search the IP phones on LAN via Auto Discovery
and register them to the phone list.
y During the registration, the LCD screen will display “System Checking”,
“Server Searching”, “Authorizing”, “Load Setting”, and then “Extension
Number and Current Time.”
If the LCD on the phone displays “Server Searching” or “Server Not Found”, it
means there is a connection problem between this phone and PBX Server.
Please check the network settings of your phone or your network environment

32 Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System
again. Please also make sure the IP address and extension number are not used
by other extension accidently.
6. Turning Off Auto Discovery
Access PBX Server and login InterPBX Administration Website. Go to Main
Menu>Operation Management>Auto Discovery. On the “Auto Discovery”
page, click the “Turn Off Auto Discovery” icon to disable the Auto Discovery
function. This will prevent your InterPBX Communication System from being
accessed by unauthorized users.
After the Auto Discover was turned on, if you didn’t turn it off manually, the
system will automatically turn off the Auto Discovery function within 2 hours
in order to avoid unauthorized users using the system.
Create IP Phones Manually
Besides creating IP phones via Auto Discovery, you can also create IP phones
one by one manually. Please make sure the relevant License Key has been
added.
1. The Settings on the Administration Website
y Before installing the IP phones, be sure to enter the License Key on the
PBX Server set up page. Please login to the PBX Server and then go to
Main Menu>Operation Management>General Information. Click
“Add” and then enter your license key.
y Go to Main Menu>Extension Management>InterPhone List. Click the
Add button to create IP phones.
y Enter the IP phone’s extension number on “Extension No.”

Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System 33
y Select the phone type from the “Phone Type” list.
y Enter the password of the extension in order to edit the personal
options from the InterPBX Management Website. The password must
only be numbers. If you create IP phones via Auto Discovery, the
phone password is blank. You can set the password later.
y Enter the MAC address of the phone in “MAC Address.” MAC is the
hardware address of the IP phone. Each IP phone has a unique MAC
address. You can see the MAC address of each IP phone by the
following procedure. Press and hold
on the phone for 3 seconds
to enter the setup menu. And then keep pressing
until the LCD
screen displays “MAC ADDRESS.”
You may set the other items later. For other settings, please refer to Chapter
5 Extension Management/Set IP Phones, SoftPhones, and Virtual Phones.
2. Settings on IP Phones
Press and hold
button on the IP phone for 3 seconds. The LCD screen
will display “EXT NUMBER.” Please refer to the above IP phones settings to
enter the relevant Extension Number, IP Address, Gateway IP, Subnet Mask,
and the IP Address of PBX Server.
3. Connect IP Phones to LAN
y After you finish the above procedure, please connect your IP phone to LAN.
y During the registration, the LCD screen of IP phone will display “System
Checking”, “Server Searching”, Authorizing”, “Load Setting”, and finally
show the Extension Number and the Current Time.
y Login to InterPBX Administration website. Go to Main Menu>Extension
Management>InterPhone List. You will see the list of all the IP phones. You
can start to set the phone functions one by one.


Chapter 3 System Configuration 35 Chapter 3 System Configuration 35
Chapter 3
System Configuration
This chapter guides you through the initial and basic configuration of InterPBX
Communication System. The basic system settings include PBX Server IP
settings, your company information, your business hours, system-wide speed
dialing, call restriction, password management, and system date and time
settings.

36 Chapter 3 System Configuration
General Parameters
Please login to the InterPBX Administration Website. Go to Main Menu>System
Configuration>General Parameters. In this section, you can edit the basic IP
settings of your PBX Server.
Basic IP Settings
IP Address, Default Gateway, Subnet Mask
The PBX Server is shipped with default IP settings as below for your initial
configuration. You may edit the IP address, Gateway IP and Subnet Mask in
this section.
y Default IP Address: 192.168.1.200 (service port 88)
y Default Gateway IP: 192.168.1.254
y Default Subnet Mask: 255.255.0.0
The PBX Server requires a static IP address. Either real IP or pseudo IP can do.
The Gateway IP is for the destination host to route the IP packets addressed to a
host outside the local subnet. Notice that all the on-site IP extensions need to be
set in the same subnet of your PBX Server.
Host Name
Enter the Host Name of your PBX Server. If you have added the host name to
your name resolution systems (DNS), you could connect to your InterPBX
Communication Server by typing its name on a web browser. If you haven’t
added it to your DNS, you can still access PBX Server using its IP address.

Chapter 3 System Configuration 37
DNS 1 and DNS 2
Enter the Domain Name Server (DNS) IP address offered by your ISP. You can
enter up to 2 DNS IP addresses.
Email Settings
Please enter the SMTP Server IP address in the field SMTP Server and the
e-mail address in the field E-mail Account. When the Unified Messaging
function is enabled, the system can send the voice message file via e-mail
through the SMTP server to the extension user.
You may also enable the SMTP Authorization function if the SMTP Server
needs to verity the e-mail account and password. If you enable SMTP
Authorization, please be sure to enter the Account Name and Password.
NAT Settings
If your network environment is behind NAT, you can assign a virtual IP to the
PBX Server. If you have off-premises extensions or Joint Servers, you need to
enter the NAT information of the PBX Server to allow the off-premises
extensions to connect to your PBX Server which is behind NAT. Please check
the “Behind NAT” box and enter your real IP address of NAT equipment on
the “NAT IP Address” box. If there are no off-premises extensions or Joint
Servers in your InterPBX Communication System, you don’t need to edit the
settings of NAT.
Open a Communication Port: When there are off-premises extensions or Joint
Servers in your PBX Server that is behind NAT, besides the above settings, you
also need to open a service port on your NAT Equipment or Firewall in order to
allow the off-premises equipments to connect to your PBX Server.
Off-Premises Extensions: When you have off-premises extensions, please open
the UDP6046 port on your NAT equipment. If the off-premises extensions are
also behind NAT equipment, you also need to open the UDP6046 port for them.
Please refer to Chapter 5 Extension Management/ Off-Premises Extensions for
more details.
Joint Servers: When you have Joint Servers, please open the UDP6055 port on
your NAT equipment. If the Joint Servers are behind NAT, you need to turn on

38 Chapter 3 System Configuration
the NAT settings of the PBX Server and open the UDP6055 port on NAT
equipment.
NAT Proxy: If you have DSG NAT Proxy, you only need to register the PBX
Server to the NAT Proxy without opening the communication port for PBX
Server or off-premises extensions.
Set QoS
The InterPBX Communication System supports 802.1p/Q. You can put a check
on “QoS Enabled” box to activate the system’s QoS. You may set VLAN ID and
802.1p Priority. If you activate the QoS function, your settings need to be the
same as the settings of Switch.
The QoS of system only covers local IP extensions and Voice Gateway. You can
also set the individual QoS on Off-Premises Extensions, Off-Premise Voice
Gateway and Joint Server. For more information about QoS settings, please
refer to Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration/Off-Premises Gateways, Chapter 5
Extension Management/Off-Premises IP Extensions, and Chapter 10
Multi-Server Management/Joint Server.
Note: If the values of VLAN ID and 802.1p Priority are both set as “0”, the QoS
will be disabled.
Music on Hold
When a call is on hold, the system will provide music or prerecorded
announcements for callers. Select the check box of “Music on Hold” to enable
this function. You can select the Music on Hold (MOH) source from an external
audio source connected to a gateway or from a prerecorded file.
y You can play the music by selecting the prerecorded audio file. Please click
the check box of “From Files” and select a preferred file from the list.
y If you connect the system with a radio or CD player, you can click the check
box “From Gateways” and select the specific gateway from the gateway list.
Make sure the gateway is properly connected to the audio source before you
select the specific gateway.
You may also amplify the MOH volume if necessary.

Chapter 3 System Configuration 39
MOH Converter: DSG provides a MOH Converter program allowing you
convert your own music on hold or queue announcement files from WAV or
MP3 format to the format compatible to the PBX Server. To know to how
convert your own MOH files, please consult our dealers or sales
representatives.
Ringing Patterns
You can assign different ringing patterns to identify internal or external calls.
From the “Internal” list, select your preferable ringing pattern for Intercom calls.
From the “External” list, select one for calls from CO lines.
Company Information
Go to Main Menu>System Configuration>Company Information. In this section,
you can edit your company’s contact information.
Business Hours
Your office hour settings will affect the behaviors of Automated Attendant,
Class of Service (CoS) or Voice Mail System. Automated Attendant may play
different greetings when the office is open, close or during lunch breaks.
Permissions of making calls after office hour may be limited by the settings of
CoS.

40 Chapter 3 System Configuration
1. Go to Main Menu>System Configuration>Business Hours.
2. From the “Operating Mode” list, select your company’s operating mode.
y Auto: It will switch automatically according to the schedule you set
below.
y Business Hours: The open hours on workdays.
y Break Hours: The lunch breaks on workdays.
y After Hours: The hours after open hours on workdays.
y Closed: The hours of non-workdays.
3. When setting the business hours, select the check box of the workday and
enter the opening hours and lunch breaks. If your company doesn’t offer
lunch breaks or days off, you may enter “0”.
Ring Assignment: The Ring Assignment will follow the operating hours you
set to play different greetings for incoming calls. For more information about
Ring Assignment, please refer to Chapter 4 Gateway Configurations/Analog
Gateways.
Holidays: For holidays, you may go to Holiday to set hours and dates. For
more information about Holiday, please refer to Chapter 3 System
Configuration/Holiday.
Change Current Operating Mode: You may manually change your current
Operating Mode to be Business Hours, Break Hours, After Hours or Closed.
Select the preferable item from the “Operating Mode” list. Notice that your
operating mode will be permanently in the mode you selected. To let the
operating mode be switched automatically according to the business hours you
set, please select “Auto” again.

Chapter 3 System Configuration 41
Night Service: You may assign a specific programmable button as Night
Service. And press to switch the Operation Mode to Closed Hours. The AA
menu and operators will be changed accordingly. This function is available for
Extension Group Button Mapping. Please refer to Chapter 6 Group
Management/Button Mapping Groups for more details.
Holidays
In addition to the regular business hour schedule, you can set the holiday list so
that the system will play different greetings on holidays. For more information
about Business Hours, refer to Chapter 3/System Configuration/Business
Hours.
1. Go to Main Menu>System Configuration>Holiday.
2. Click the Add button to create an entry in the Holiday List.
3. Set the date range (month/day) of the holiday. If there is only one day off,
enter the same date on the Date range boxes.
4. Input the name of the holiday.
5. Select an AA Menu from the list. If you select the “Enable Holiday”
checkbox in CO Lines or the Ring Assignment setting of CO Line groups,
the system will play the greeting of AA Menu you assigned here during
holidays.
For more information about Ring Assignment, please refer to Chapter 4
Gateway Configuration/Analog Gateways.
System Speed Dialing
You can edit frequently dialed phone numbers in this section to be used
throughout the system.

42 Chapter 3 System Configuration
1. Go to Main Menu>System Configuration>System Speed Dialing.
2. On the “System Speed Dialing” list, select one entry.
3. Enter the destination phone number or extension number on the “New
Number” box.
4. Enter the name of the destination or other description on the “Comment”
box.
5. Click the Assign button to save.
Note: You could set up to 1000 sets of system speed dialing. If you would like
to set a Speed Dialing Number for an outgoing call, please remember to add the
CO line access code (e.g. 0). For long distance calls, please enter your long
distance access code (e.g. 1) followed by the area code and phone number. For
international calls, please enter your international access code (e.g. 011) and the
country code, area code, and phone number.
To make a call with System Speed Dialing:
1. Lift the handset or press the Speakerphone button.
2. Press the System Speed Dialing function code #20.
3. Press the System Speed Dialing number (e.g. 000) to call.
Call Restriction
You can set the long distance and international access codes in the “Call
Restriction” in order to help the PBX Server to identify the types of outgoing
calls (e.g. local, long distance or international calls). Call Restriction allows you
to create call restrictions, exceptions, and routing tables in Class of Service.

Chapter 3 System Configuration 43
1. Go to Main Menu>System Configuration> Call Restriction.
2. Set the “Country Code (e.g. 1 for US)” and “Area Code (e.g. 213 for L.A.)”
where PBX Server is located.
3. On the list of “Long Distance Call Prefixes”, select one entry and assign the
long distance call prefix plus the area code (e.g. 1310 for Beverly Hills) in
the “New Number” box. Press the Assign button to save. Repeat this
procedure to edit all the area codes of your country.
4. Follow the above-mentioned procedure to set the “International Call
Prefixes”.(e.g. 011)
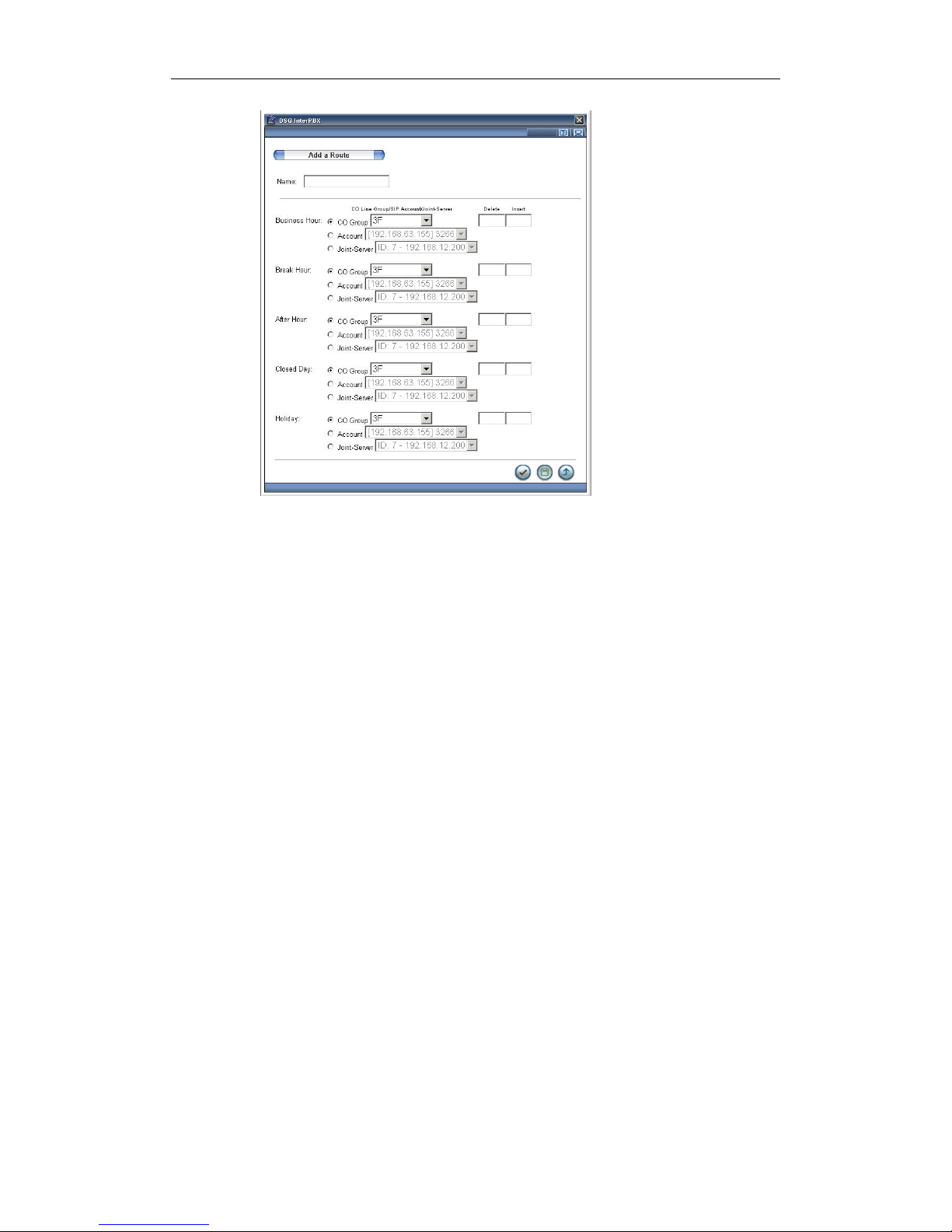
Route
If you want to activate the ARS function, please create the available routes for
selection. The route types for selection are CO Group, SIP Trunk, or Joint
Server.
44 Chapter 3 System Configuration
1. Go to Main Menu>System Configuration> Route. Click “Add” to create a
route.
2. Enter the name of the route.
3. Set the route in different time sections: Business Hour, Break Hour, After
Hour, Closed Hour, and Holiday. The route types for selection are as
follows:
● CO Group: Select the CO group from the list. For more information
about CO Group settings, please go to Main Menu>CO Line Groups.
● Account: Please select your SIP Account. For more information about
SIP Account settings, please refer to Set SIP Proxy.
● Joint Server: You may also make the phone call through another
InterPBX’s CO line. Please select your Joint Server here.
Function Code
The System provides Function Code for administrators to configure so that the
extension users can use multiple functions by entering the specified function
code directly on their extensions.

Chapter 3 System Configuration 45
Go to Main Menu>System Configuration>Function Code. You will see all the
function items available for configuration. Please enter a code for each function
and click the save button.
Password Management
This section allows the administrator to change Administrator’s Login Name
and Password and reset User Password to login the InterPBX Administration
website. The administrator will be authorized to edit all the administrative
features after login. For security reason, please change the Administrator
Password from time to time.
Go to Main Menu>System Configuration>Password Management. Input your
current password and new password. Re-enter the new password for
confirmation. Your password shall not exceed 8 characters. The password is
case sensitive.
Each user will be authorized to edit the user features after login. When users
forgot their passwords, you may reset their passwords to the default setting
(The default extension password is blank if created by Auto Discovery).

46 Chapter 3 System Configuration
You can connect VMS Server from a telephone remotely and edit the relevant
settings. The default remote Tel. Programming Password of VMS Server is
“1234”. For more information about DTMF remote control settings, please refer
to Appendix F.
Set System Date/Time
Go to Main Menu>System Configuration>Set System Date/Time in order to set
the current date and time of your time zone for your InterPBX Communication
System. The system date and time affect the play contents of business hours
and greetings. If you change the system Date and Time, the time display on the
phones will be updated after 8 seconds to 2 minutes.
Miscellaneous
Go to Main Menu>System Configuration>Miscellaneous. You could edit
system timeout settings and authorization code.
Timeout Settings

Chapter 3 System Configuration 47
y Forward Voice Mail Timeout: If an incoming call is not answered, the call
will be transferred to the voice mail system after the timeout.
y Call Park Timeout: When the call is parked, if no one picks up the call, it
will be bounced back to the original extension parked the call after the
timeout.
y Call Hold Timeout: When a call is placed on hold without any further action,
the call will ring back to the original extension after the timeout.
y Transfer Timeout : When a call is blind-transferred to a target extension but
no one answered or the extension is busy, the call will be transferred to the
Auto Attendant after the timeout. The Auto Attendant will guide the caller
to other selections according to the settings of Transfer Options. If the
personal forwarding is set on the target extension, the call will be forwarded
according to the personal forwarding setting.
y First-Digit Timeout: When a line is accessed, if the first digit is not
received within the period, the system will disconnect the call and release
the line.
y Inter-Digit Timeout : When entering digits, if the next number is not
received within the period, the system will see it as a typing ending signal
and use the numbers been input to make calls.
y Auth. Code Timeout: When entering authorization code, if the next digit is
not received before the timeout, the system will deem the input ends and
send out the numbers received.
y Max Trunk-to-Trunk Duration : The function allows CO line incoming calls
to be transferred out through the other CO lines. Please enter the call
duration limit time. When the period expires, the system will cut off the call
and release the CO line.
Authorization Code
Authorization Code function allows callers to make calls, such as long distance
or international calls, from an extension with limited call permissions.
Note: The Authorization Code function needs to be implemented with ARS.
1. Select the “Authorization Code Enable” check box.
2. Input the length of Authorization Code.
3. Input the Cancel Symbol allowing users to clear the authorization code
been input. This will help the user not to input the phone number again.

48 Chapter 3 System Configuration
Auth. Code Timeout: Please input the Authorization Code timeout at the above
Timeout Settings.
Assign Authorization Code: Please go to Main Menu>Group
Management>Authorization Code to assign Authorization Codes.

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 49
Chapter 4
Gateway Configuration
Voice Gateways are bridges between IP and traditional (PSTN) telephony
networks. Gateways connect the InterPBX Communication System to CO trunk
lines or analog extensions. InterPBX supports various gateway types including
analog gateways, digital gateways, and off-premises gateways. If you have
included Digital Gateway, Recording System, CTI Gateway, SIP Proxy or NAT
Proxy in your purchase, please consult their specific documentation for further
details on the settings.
Note: Savanna 8000 Series doesn’t include the Voice Gateway. If you would like
to add the Voice Gateway into the Savanna 8000 Series IP-PBX system, we offer
the VG5000 Voice Gateway or VG6000 Digital Gateway for your options.

50 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
Analog Gateways
InterPBX Communication System supports analog gateways such as VG5000.
VG5000 Voice Gateway provides up to 24 ports of FXO (for CO Lines), FXS (for
SLT), or mixture of both. Every unit of VG5000 also provides interfaces for
external music-on-hold and paging equipment.
Creating Analog Gateway List
After the installation of your gateway, you will need to incorporate it into the
PBX Server.
1. On the main screen go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration>Analog
Gateways.
2. Click the Add button to add a new gateway to PBX Server’s “Analog
Gateway List”.
3. Name this gateway and enter its MAC address. MAC address is the
hardware address of the gateway, you will find this information printed in
a label at the back of the gateway or alternatively, you may obtain this
information from the VG5000 Voice Gateway’s web page or Telnet. Please
see Chapter 2 “ Installing InterPBX Communication System “ for more
details.
4. Enter the range of CO Line and/or SLT ports of your gateway. Please note
the port number starts from 1, for example, if the VG5000 you purchased is
a 24-port FXO gateway, in the “CO Line Ports (From/To)” fields enter “1”
and “24” respectively.
5. At “CO Line Extension Base” input the starting number of CO Line
extension number. The CO Line extension numbers will be assigned
automatically. For example if you set it as 4000 for an 8-port FXO gateway,
the CO Line extension number of this gateway will be 4000-4007.

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 51
6. At “CO Line Index Base” input the starting number of the CO line display
number. For example if you set it as 1, when there is an incoming call from
port 1, the IP phones will display “Incoming Call CO 1” instead of the
extension number of the port, helping you to identify the CO lines being
used.
7. From “Jitter Buffer Depth” drop down menu, depending on your
bandwidth and CODEC, start with a Jitter Buffer with the minimum value.
Jitter Buffer will dynamically adjust its value according to the party you are
talking to and the bandwidth of the call but never below the value you
have set. The higher value of Jitter Buffer will reduce the chance of packet
loss during a call but might cause delays and the lower value will help to
transmit the voice packets faster but might cause packet loss problems.
8. Min. Loop Current Drop Time: Normally, when a telephone call terminates,
the telephone company sends a momentary drop in loop current to signal
the disconnect event. Please enter the minimum Loop Current Drop time in
this field to avoid the IP-PBX system detecting the disconnect signal
incorrectly. The value should not be too long or too short. Recommended
value is 400 ms.
Note: If later on your needs grow and you need to add more CO lines or
channels into an existing gateway, you will need to delete the existing gateway
from the list and create a new one with new trunk or channel numbers.
External Paging & MOH Functions
If you connect a paging facility to your gateway, click the “External Paging
Enabled” check box to enable the Paging function. Assign a specific paging
code to be used for announcement via this gateway.
Using External Paging
If you assign “111” as the paging code of your VG5000, you need to dial “111”
to page a person via the external paging facility on this VG5000. Refer to
Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX Communication System/Configuring VG5000
Voice Gateway for more details.
Editing Analog Gateways
After the addition of the new gateway, you may edit the settings to control the
input and output volume of the CO Line and SLT ports.
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration>Analog Gateways.

52 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
2. From the “Analog Gateway List” choose the gateway to edit then click on
the Modify button.
3. You will see the gateway type, software version running as well as the
ports that correspond to CO Line or SLT.
4. If needed, you may change in this screen the name of the gateway, MAC
address, CO Line Index Base, Jitter Buffer as well as to enable the Paging
feature. For more detailed information please see above section “Creating
Analog Gateway List”.
Configuring CO Line Ports
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration>Analog Gateways.
2. Select a gateway from the “Analog Gateway List” and click the Port Setting
button.
3. Select a CO Line port from the “Port List” and click the Port Parameters
button to configure the settings for this port.

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 53
Setting CO Line Extension Number
An extension number in InterPBX Communication System might represent a
CO line, an analog extension, an IP extension, a CO line group or an extension
group.
In “Extension Number” it will display the extension number of this CO Line
port automatically based on your settings under “CO Line Extension Base”, you
may also change the extension number from here. Please select “Enabled” to
activate this port. For maintenance purpose, you may click again on “Enabled”
to disable this port. In “Description” input the telephone number or other
information for this port.
CODEC
Choose the preferred CODEC from PCM, G.723.1 or G.729 supported by
InterPBX Communication System. PCM CODEC compresses and decompresses
voice conversation to 64 Kbps providing the best speech quality but consumes
larger bandwidths. G.723.1 CODEC uses 6.3 Kbps, the less bandwidth from the
three choices but may result in poorer call quality and finally G.729, which uses
8 Kbps.
Fax
Enter the extension number of the SLT port where the fax machine is connected.
When detecting fax tones, the fax will be automatically transported to the fax
machine. You may set all the CO Lines to the same fax extension or to different
fax extensions, as you need.
T.38 Fax: InterPBX system also support T.38 protocol allowing fax to be
transmitted across the IP networks. When selected, please also select the T.38
setting at SLT port. If you adopt T.38 fax, at the above Fax Ext Number, you
may set a local fax extension number, an off-premises fax machine or a fax of
Joint Server.
Ring Assignment
Ring Assignment allows you to assign a specific extension, extension group or
AA Menu to answer incoming calls from a specific CO line or CO Line Group.
In the Ring Assignment field, choose the option of “Local” or “From CO
Group”.

54 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
y If you select “Local”, input a specific extension number, extension group or
AA Menu access code to answer incoming calls for this port in Business
Hours, Break Hours, After Hours and Closed. The most usual setting is to
assign an AA Menu to answer phone calls, taking advantage of the
InterPBX’s VMS server. To learn more about AA Menu settings, please refer
to Chapter 7 Voice Mail Configuration. If you would like to play specific
greetings for holidays, select the “Enable Holiday” checkbox so that the
system will play the holiday greetings you assigned on the Holiday List. For
more details about Holiday settings, please refer to Chapter 3 System
Configuration/Holidays.
y If you select “From CO Group”, incoming calls will be answered according
to the Ring Assignment of the CO Line Group you have assigned. For more
details about CO Group’s Ring Assignment, please refer to Chapter 6 Group
Management/CO Group.
Silence Compression
The silence compression feature reduces network traffic whenever a period of
silence is detected during a conversation. When there is silence in a
conversation, silence indicator packets will be sent by the system instead of full
voice packets to reduce traffic. Select the check box of “Silence Compression
Enabled” to enable this function or uncheck to disable it.
Caller ID
InterPBX’s CO Line ports have the ability to detect either DTMF or FSK Caller
ID modes. You may select this item to enable this function. Please note that
your local telephone company must provide Caller ID service in order to
display the incoming party’s number.
Pickup After Rings
On the “Pickup After Rings” column, input the number of the ring count. If you
set the ring count as “2”, the system will pickup the incoming call after 2 rings.
Flash Timing
Under the application of Centrex, you can set the Flash Timing on the IP
phones through the system. The Flash function was set on the MENU button of
the IP phones. After you complete the Flash Timing setting, you can start to use
some of the Centrex functions. Please make sure the IP phone’s Flash Timing
must be within system’s Flash Timing.

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 55
Voice Gain Level
You may edit the input and output volume of:
y Transmit Gain: this field edits the TX Gain of the CO Line ports, or how loud
the external party hears your voice.
y Receive Gain: this field edits the RX Gain of the CO Line ports, or the volume
of incoming calls.
y DTMF Volume: this field edits the intensity of the DTMF tones in the CO
Line ports.
Apply Settings
After finalizing the settings in this port, if you want them to be identical as this
one, you may apply the settings to other CO Line ports present in the system,
saving you the hassles of configuring each port individually.
1. Click on “Apply Setting to” and a new window will appear displaying the
parameters you have entered.
2. Apply or change the settings, as you desire.
3. Enter in the field “Apply to Port” the first and the last CO Line port you
would like to be identical to the present settings. If the range selected
includes this port, the new settings, if any, will also be applied to this one.
Configuring SLT Ports
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration>Analog Gateways.
2. Select a gateway from the list then click the Port Setting button.
3. Select a SLT port and click the Port Parameters button.
Flash Time
You may set the Flash Timing of the SLT ports to check whether the Hook
action (quick press and release of the phone’s hook) on the analog phones

56 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
works fine. Analog extensions require the Hook action to transfer, answer call
waiting, or create a conference call. Make sure the phone set’s Flash Timing
must be within the system’s Flash Timing.
Caller ID
The SLT ports have the ability to detect either DTMF or FSK Caller ID modes.
You may this item to enable this function. Note that your local telephone
company must provide Caller ID service in order to display the incoming
party’s number.
T.38 Fax
T.38 is a fax relay protocol. It allows fax to be transported across IP networks
between fax machines. When selected, please be sure the T.38 is also enabled at
the CO line port setting.
Note: You may set the SLT port to get a CO line when off-hooked, without the
need to pressing the CO line access code first. Go to Main>Extension
Management>Analog Port list for more details.
Voice Gain Level
You may edit the input and output volume of:
y Transmit Gain: this field edits the TX Gain of the CO Line ports, or how loud
the external party hears your voice.
y Receive Gain: this field edits the RX Gain of the CO Line ports, or the volume
of incoming calls.
y DTMF Volume: this field edits the intensity of the DTMF tones in the CO
Line ports.
y Dial Tone Volume: this field edits the dialing volume of the SLT ports, or the
dial tone volume of analog phones.
Setting Analog Extension Numbers
Each of the SLT port in the InterPBX can be connected to an analog phone. After
setting up the Analog Gateway, go to Main Menu>Extension
Management>Analog Port List. You will see all your available SLT ports in this
window. Select a SLT port and click the Modify button to configure your analog
extension. For more details, please refer to Chapter 5 Extension Management.
Off-Premises Gateways

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 57
InterPBX Communication System supports Off-Premises Voice Gateways. By
installing Voice Gateways in remote offices or satellite offices, enterprises can
enjoy great savings on inter-office communication. Also, more savings can be
achieved through the remote gateways by utilizing it to place outgoing local
calls to local customers, saving this way the long distance charges since through
the remote gateway this call is now same as a local call.
Creating Off-Premises Gateway List
After installing your gateway in the remote office, you will need to add it to the
PBX Server.
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration>Off-Premises PSTNGW.
2. Click the Add button to add a new gateway to PBX Server’s “Off-Premises
Analog Gateway List”.
3. Refer to the section above “Analog Gateways” to configure the “Name”,
“MAC Address”, “Gateway Type”, “CO Line Ports”, “SLT Ports”, “CO
Line Index Base” and “Jitter Buffer Depth”.
4. For Off-Premises Gateways, you will need to enter its “IP Address”. The IP
Address assigned to this Off-Premises Gateways has to be a REAL
(PUBLIC) IP address. In the Signal Port, InterPBX will automatically preset
the port therefore you do not have to make any changes here.
5. Min. Loop Current Drop Time: Normally, when a telephone call terminates,
the telephone company sends a momentary drop in loop current to signal
the disconnect event. Please enter the minimum Loop Current Drop time in
this field to avoid the IP-PBX system detecting the disconnect signal
incorrectly. The value should not be too long or too short. Recommended
value is 400 ms.

58 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
6. If you have connected any type of paging device, select the “External
Paging Enabled” to activate this feature, then create and enter a code in the
Paging Code field to use this feature.
7. Lastly, if desired, you may activate the QoS feature from your Off-Premises
Gateway by enabling it here.
After finishing creating the gateways, you may edit the ports incoming and
outgoing volume as described in “Editing Analog Gateways” section above.
Configuring Off-Premises CO Line Ports
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration>Off-Premises PSTNGW.
2. Select a gateway from the list then click the Port Setting button.
3. Choose a CO Line port and click the Port Parameters button to edit the
settings to this port.
4. Refer to the sections above Editing Analog Gateway/Configuring CO Line
Ports to configure the “Extension Number”, “CODEC”, “Fax”, “Ring
Assignment”, “Silence Compression”, “Caller ID Detection” and “Voice
Gain Level” as well as how to duplicate the settings.
5. The system will automatically preset a port to the Media Port. Please do not
change this port number.
Make a call via off-premises CO Line port
To make a call via your off-premises CO Line port, pick up the phone, dial the
remote CO Line extension number then dial the phone number you need to call.
For long distance calls, please dial remote site’s long distance access code
followed by the phone number to be dialed.

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 59
Configuring Off-Premises SLT Ports
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration>Off-Premises PSTNGW.
2. Select a gateway from the list then click the Port Setting button.
3. Choose a SLT port and click the Port Parameters button to edit the settings
to this port.
4. Refer to the sections above Editing Analog Gateways/Analog Port to
configure this port.
5. Leave the Media Port as it is since it is assigned by the system
automatically.
6. Each off-premises SLT port can connect to an off-premises analog phone.
Go to Main Menu>Extension Management>Analog Port List and you will
see all your available SLT ports in this window. Select a SLT port and click
on Modify to configure your off-premises analog extension. For more
details, please refer to Chapter 5 Extension Management/Analog
Extensions.
Make a call to off-premises SLT port
To make a call to extensions connected on off-premises SLT ports, simply pick
up the phone and dial the remote SLT extension number normally as you
would for calling extensions in your office. You can make calls to remote
extensions as the way you do for calling extensions in the same office.

60 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
Recording System
The InterPBX System supports recording system to improve enterprise
productivity and enhance efficiency of business communication. InterPBX
Communication System supports two types of recording systems: the built-in
recording system which provides Record-on-Demand and/or
Store-on-Demand functions and the stand alone professional recording system.
y Blaze5000 Series: It provides built-in Record-on-Demand and
Store-on-Demand recording functions. When there is no one on the
Store-on-Demand list, Record-on-Demand will still be available. Up to 10
concurrent recording channels will be provided.
y Blaze1200 Series: It supports built-in Record-on-Demand with maximum
10 concurrent recording channels.
y Savanna8000 Series: It doesn’t support built-in recording function and an
additional recording system is required.
Note: The recording function does not apply to analog and off-premises
extensions.
Setting Store-on-Demand (Available on Blaze5000 Series)

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 61
The built-in Store on Demand function allows the system to record calls for
extensions on the Store on Demand list when conversation starts. The extension
user can save the recording at any time during a call by pressing the Record
button. Recordings will not be automatically saved for the concern of storage
space. User may also retrieve the recording when needed.
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration> Recording System.
2. Enter the IP address of the PBX Server in the field “IP Address”.
3. The default value of “Port Num” is “10”, which means the system can
record up to 10 extensions at the same time. You need to assign up to 10
extensions on the Store-on-Demand List.
4. Define the ”Storage Limitation” of the hard disk and the “Auto Purge
Days”. When exceeding the hard disk limit, the system will delete the
recordings of days as set on “Auto Purge Days”. For example, if the
Storage Limitation is “80%” and the Auto Purge Days is “7”, the system
will automatically delete previous 7-days recording data when it reaches
the storage limitation.
5. Put a check on the item of “Recording Beep” according to your company’s
requirement or the Government’s regulation. When the Recording Beep is
activated, the caller and the receiver will hear the beep sound every 15
seconds during a call.
6. Recording Flash: You can enable the Recording Flash function. After the
Recording Flash is enabled, the recording lamp on the recorded extension
will keep flashing until the call is hung up. If you need to record to an
extension confidentially, please do not enable this function.
Store on Demand List

62 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
You can add up to 10 extensions in the Store on Demand list. The system will
continuously record to these extensions during a call.
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration> Recording System.
2. From the ”Extension” list, move the extension number to the “Store on
Demand” list. The system can record to up to 10 extensions at once.
Activate the Recording
1. During a call, press the specific programmable button or Rec/Play button
to active the function.
2. After the call is hung up, the system will stop recording.
Note: The recording function does not apply to analog and off-premises
extensions.
Playing the Recording
The extension users can play the recording from their IP phones directly.
1. Press the specific programmable button or REC/Play button or function
code #42 to play recordings
2. Enter the password and then press #. (The password for the recording
system is same as your mailbox password. The default password is blank.)
3. Follow the system prompts, press 1 to play the latest recording or press 2 to
check the recording by entering date and time. Please follow the procedure
below to assist you in listening to the recording.
y In the recording system, you can press * anytime to return to the previous
menu or back to the main menu.
y When playing recordings, you can press 0 (zero) to skip the time stamp
announcement of the recording.

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 63
y If your UMS is enabled and the e-mail is set, after playing a recording, you
will be prompted to send the recording you just played to your email.
y For Store on Demand recording, you can only play the latest, previous or
next recording for the current day.
y When you input the time for searching recording, the system will play the
recent recording after the time.
Setting Record-on-Demand (Available on Blaze5000 and Blaze1200
Series)
The built-in Record on Demand allows the system to record calls after users
pressing the Record button. Calls will be recorded and saved after pressing the
Record button. User may also retrieve the recording when needed.
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration> Recording System.
2. Enter the IP address of the PBX Server in the field “IP Address”.
3. The default value of “Port Num” is “10”, which means the system can
record up to 10 extensions at the same time. You may set the permission
from extensions’ Class of Service.
4. Define the ”Storage Limitation” of the hard disk and the “Auto Purge
Days”. When exceeding the hard disk limit, the system will delete the
recordings of days as set on “Auto Purge Days”. For example, if the
Storage Limitation is “80%” and the Auto Purge Days is “7”, the system
will automatically delete previous 7-days recording data when it reaches
the storage limitation.
5. Select the “Recording Beep” checkbox according to your company’s
requirement or the government’s regulation. When the Recording Beep is
activated, the caller and the receiver will hear the beep sound every 15
seconds during a call.
6. Recording Flash: You can enable the Recording Flash function. After the
Recording Flash is enabled, the recording lamp on the recorded extension
will keep flashing until the call is hung up. If you need to record to an
64 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
extension confidentially, please do not enable this function.
Activate the Recording
1. During a call, press the specific programmable button or Rec/Play button
to active the function.
2. After the call is hung up, the system will stop recording.
Note: The recording function does not apply to analog and off-premises
extensions.
Playing the Recording
The extension users can play the recording from their IP phones directly.
1. Press the Play button to play the recording. On programmable button
supported phones, you can press a specific programmable button that is
assigned via Button Mapping to play the recording. Or press the
REC/PLAY button, if applicable.
2. Enter the password and then press #. (The password for the recording
system is same as your mailbox password. The default password is blank.)
3. Follow the system prompts, press 1 to play the latest recording or press 2 to
check the recording by entering date and time. Please follow the procedure
below to assist you in listening to the recording.

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 65
y In the recording system, you can press * anytime to return to the previous
menu or back to the main menu.
y When playing recordings, you can press 0 (zero) to skip the time stamp
announcement of the recording.
y If your UMS is enabled and the e-mail is set, after playing a recording, you
will be prompted to send the recording you just played to your email.
y For Store on Demand recording, you can only play the latest, previous or
next recording for the current day.
y When you input the time for searching recording, the system will play the
recent recording after the time.
Setting Professional Recording System
InterPBX Communication System can also work with the professional recording
system Blaze Logger that provides more powerful recording and searching
functions.
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration>Recording System.
2. On the “IP Address” field, enter the IP address of the recording system.
You don’t need to set the other items.
The Port Num will display the license numbers of your Blaze Logger. Please
refer to the Blaze Logger Administration Guide for more information.
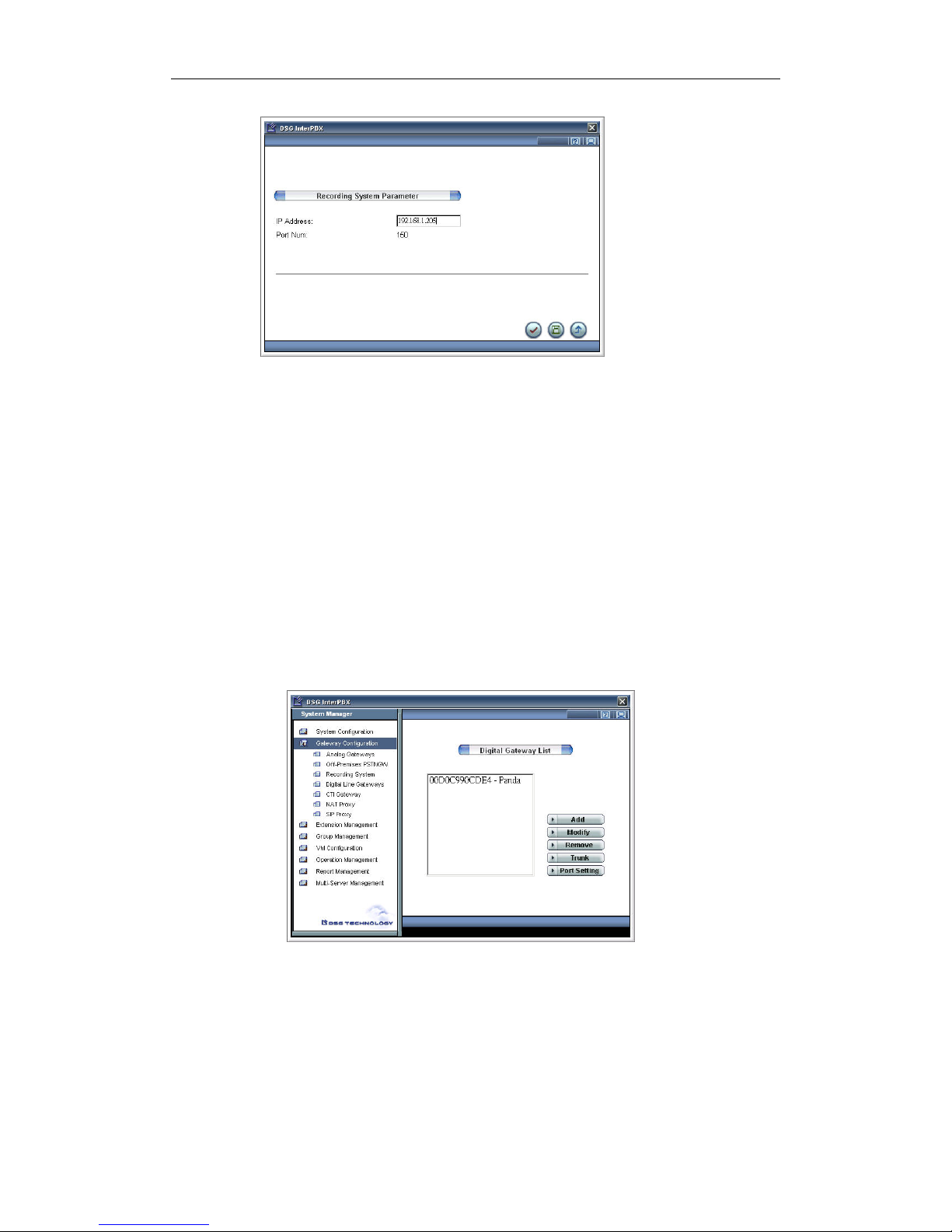
66 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
Digital Line Gateways
When adopting VG6000 or VG7000 Digital Gateway, your InterPBX IP
Communication System, including Blaze, Savanna series IP-PBX, needs to
enable the relevant function as well.
Adding Digital Gateway
You need to set the MAC address of Digital Gateway to the PBX Server.
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration>Digital Line Gateways,
the ”Digital Gateway” list will be displayed.
2. Click the Add button to create a Digital Gateway. Before you add a new
gateway, make sure the relevant License Keys has been added.

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 67
3. Input the required data of this gateway.
y
Name: Enter a name to describe this Digital Gateway.
y MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of the Digital Gateway. You
may find the MAC address from the device label.
y Trunk Number: Enter the available trunk numbers you may use or
purchase.
y CO Line per Trunk: Input the available channels of each trunk. For
example, input 32 for E1 or 24 for T1.
y CO Line Extension Base: Input the starting number of CO Line
extension number. The CO Line extension numbers will be assigned
automatically. For example if you set it as 4000 for an 8-port FXO
gateway, the CO Line extension number of this gateway will be
4000-4007.
y Jitter Buffer Depth: From “Jitter Buffer Depth” drop down menu,
depending on your bandwidth and CODEC, start with a Jitter Buffer
with the minimum value. Jitter Buffer will dynamically adjust its value
according to the party you are talking to and the bandwidth of the call
but never below the value you have set. The higher value of Jitter
Buffer will reduce the chance of packet loss during a call but might
cause delays and the lower value will help to transmit the voice
packets faster but might cause packet loss problems.
y Off-Premises and IP address: For Off-Premises Gateways, you will
need to select the check box and enter its “IP Address”. The IP Address
assigned to this Off-Premises Gateways needs to be a REAL (PUBLIC)
IP address.

68 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
Note: If later on your needs grow and you need to add more trunks or channels
into an existing gateway, you will need to delete the existing gateway from the
list and create a new one with new trunk or channel numbers.
Modifying a Digital Gateway
To modify, select a gateway from the list and click the Modify button. You may
change the name, MAC address or Jitter Buffer Depth. The software version of
the gateway will also be displayed here.
Setting Trunk Parameters
You can set the parameters of each trunk to adjust the voice quality and other
items.
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration>Digital Line Gateways.
2. Select a gateway you would like to edit from the list and click the Trunk
button to edit the trunk parameters.
y Trunk: Select a trunk you would like to edit from the list.

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 69
y CO Line Index Bass: Input the starting number of the CO line display
number. For example if you set it as 1, when there is an incoming call
from port 1, the IP phones will display “Incoming Call CO 1” instead
of the extension number of the port, helping you to identify the CO
lines being used.
y Transmit Gain: This field edits the TX Gain of the trunk, or how loud
the external party hears your voice. The value here should conform to
the one on Digital Gateway. The default value is 5.
y Receive Gain: This field edits the RX Gain of the trunk, or the volume
of incoming calls. The value here should conform to the one on Digital
Gateway. The default value is 5.
y DTMF Volume: This field edits the intensity of the DTMF tones in the
trunk. The value here should conform to the one on Digital Gateway.
The default value is 5.
y Tie Line: Select Tie Line check box if you would like to establish a tie to
connect the Digital Gateway to other PBX using this trunk.
Setting Trunk Port Parameters
You can edit the ring assignment and other settings for individual ports or
channels of a trunk.
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration>Digital Line Gateways.
2. Select a gateway from the list and click the Port Setting button.
3. Select a port from the port list and click the Port Parameters button to edit.
y Extension Number: The extension number will be displayed
automatically based on your settings under “CO Line Extension Base”.
You may also change the extension number here.

70 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
y Description: Input the telephone number or other information for this
port.
y Enable: For maintenance purpose, you may need to temporarily
disable some channels. Click the “Enable” check box to enable the
channel or uncheck to disable it.
y CODEC: Choose the preferred CODEC from PCM, G.723.1 or G.729
supported by InterPBX Communication System. PCM CODEC
compresses and decompresses voice conversation to 64 Kbps providing
the best speech quality but consumes larger bandwidths. G.723.1
CODEC uses 6.3 Kbps, the less bandwidth from the three choices but
may result in poorer call quality and finally G.729, which uses 8 Kbps.
y DID (Direct Inward Dialing): When selected, incoming calls will be
connected to extensions directly in stead of been picked up by Auto
Attendant. This function is available when you have subscribed the
DID service provided by your carrier. When you would like to set a
direct line between two PBXs connected by Tie Line, you may also
enable this function.
y Strip Prefix Digit: When the length of the number sent by DID is
longer than your extension numbers, set the digit that needs to be
removed. For example, if the DID prefix and adding number is
660x-xxxx, but you have 4-digit extension number, set “1” to delete the
first digit sent by your carrier. The default value is 0.
y Fax Ext. Number: The InterPBX System can detect the fax signal of CO
Line. Please enter the extension number of your fax machine here.
When the InterPBX System detects a fax signal, the fax will be
transferred to the fax machine.
y Ring Assignment: Ring Assignment allows you to assign a specific
extension, extension group or AA Menu to answer incoming calls from
a specific CO line or CO Line Group. In the Ring Assignment field,
choose the option of “Local” or “From CO Group”.
- Local: If you select “Local”, input a specific extension number,
extension group or AA Menu access code to answer incoming calls for
this port in Business Hours, Break Hours, After Hours and Closed. The
most common setting is to assign an AA Menu to answer phone calls.
If you would like to play special greetings for holidays, select the
“Enable Holiday” checkbox and the system will play the assigned
greeting from Holiday List. For more details about AA Menu, Voice
Mail and Holiday settings, please refer to InterPBX Administrator

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 71
Installation and Configuration Guide.
- From CO Group: If you select “From CO Group”, incoming calls will
be answered according to the Ring Assignment of the CO Line Group
you have assigned. For more details about CO Group’s Ring
Assignment, please refer to Administrator Installation and
Configuration Guide.
y Silence Compression Enable: Silence Compression reduces network
traffic whenever silence is detected during a conversation for a specific
amount of time. Silence indicator packets will be sent out instead of full
voice packets to reduce traffic.
y Caller ID Enabled: InterPBX’s CO Line ports can detect both DTMF
and FSK Caller ID. You may select or deselect it per your preference.
Please note that before using this function, the Caller ID service must
be provided by your local telephone company.
y Pickup After Rings: Please enter the Pickup After Rings times for the
CO Line port. If you set the ring times as 2, the system will pick up a
call after it rings twice and then transfer the call as settings.
y Flash Timing: You may set the Flash Timing of the SLT ports to check
whether the Hook action (quick press and release of the phone’s hook)
on the analog phones works fine. Analog extensions require the Hook
action to transfer, answer call waiting, or create a conference call. Make
sure the phone set’s Flash Timing must be within the system’s Flash
Timing.
Apply Settings
After finalizing the settings of this port, if you want the other ports to be
identical as this one, you may apply the settings to the others, saving you the
hassles of configuring each port individually.
1. Click on “Apply Setting to” and a new window will appear displaying the
parameters you have entered.
2. Apply or change the settings as you need.
3. Enter in the field “Apply to Port” the first and the last port you would like
to be identical to the present settings. If the range selected includes this port,

72 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
the new settings, if any, will also be applied to this one.
After you complete the installation of a new digital gateway, you need to set up
the associated Route and ARS. For more details, please refer to System
Configuration>Route and Group Management>Class of Service>ARS.
CTI Gateway
DSG BlazeLink is a CTI solution software enables business to develop
applications to optimize workforce in a call center or contact center.
Applications developed on BlazeLink for call control, monitoring, or managing
are able to connecting DSG IP-PBX System to the data processing environment.
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration> CTI Gateway.
2. In the field ”IP Address”, please enter the IP address of your CTI gateway.
3. Agent License: It displays the Agent License numbers you purchased. If
you purchase 100 Agent Licenses, the system will allow the 100 agents to
log in. This function will be released in a later version. The Agent License is

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 73
currently set at BlazeLink.
NAT Proxy
With DSG NAT Proxy, Blaze or Savanna IP PBX Communication Systems and
Off-Premises Phones can traverse more than 95% of NAT or firewall
successfully without creating other service ports, and therefore enterprises can
communicate via IP-PBX Communication System with pure and stable voice
quality.
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration> NAT Proxy.
2. On the field “IP Address of Master Proxy”, please enter the IP address of
the main NAT Proxy Server.
3. If you have the other NAT Proxy server, please also enter its IP address on
the field “IP Address of Slave Proxy”.
Note: When the NAT Proxy Server is activated successfully, a symbol
will be
shown beside the “IP Address of Master Proxy” field to represent that the NAT
Proxy Server is working.

74 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
For more information about the NAT Proxy Server’s settings and operation,
please refer to the NAT Proxy Administration Guide.
SIP Proxy
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) is a new generation multimedia communication
protocol. It enables voice and other media types such as video to be transmitted
over the IP networks. With DSG SIP Proxy, your Blaze or Savanna series IP-PBX
will be able to adopt the SIP Trunk services provided by ITSPs or deploy SIP
phones as your extensions.
Add SIP Proxy
You need to enroll the SIP Proxy IP address to the PBX Server.
1. Launch the web browser. On the address bar, enter your PBX Server’s IP
address. (Please use service port 88.)
2. Click on the Administrator icon and use your user name and password to
login.
3. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration>SIP Proxy, the ”SIP Proxy” list
will be displayed.

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 75
4. Click the Add button to create a SIP Proxy.
y Name: Enter a name to describe this SIP Proxy.
y MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of the SIP Proxy. You may find
the MAC address from SIP Proxy’s administration web site or from the
device.
y Port Number: Enter the available SIP channels you may use or
purchased.
y Extension Base: Input the starting number of SIP Trunks. The number
shall be a unique one from others on the system such as extension
numbers, group numbers or pickup codes. Notice that the SIP Trunk
numbers will not be displayed on the IP phone when accessed. Instead,
the associated SIP account number will be represented.
y Off-Premises: When SIP Proxy is not located in the LAN where PBX
Server is located and is deployed on the Internet, select the
“Off-Premises” check box and input its real IP address assigned to SIP
Proxy.
Add SIP Trunks
If you have subscribed the SIP Trunks service provided by your carrier, you can
input your account information at this section. Before you start, please prepare
the followings.
y Account and Password
y Registrar Server IP address
y Domain Name (In some cases, it is the same as the registrar Server)
y Specific service port used by your carrier
1. Go to Main Menu>Gateway Configuration>SIP Proxy.

76 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
2. Select a SIP Proxy from the list and click the Account button.
3. Click the Add button to create a SIP Account.
y Account Name: Assign a name for this SIP Trunk. When accessed, the
name will be displayed on IP phone.
y Phone Number: The account provided by your carrier.
y Registrar Server IP: The IP address of your carrier’s Registrar Server.
y Port: The service port provided by your carrier. The default setting is
5060.
y Domain Name: The domain name provided by your carrier. In some
cases, it is the same as the Registrar Server.
y User ID: The account provided by your carrier. In some cases, it is the
same as Phone Number.
y Password: The password provided by your carrier.
y Registrar Server Type: Depending on your carrier’s equipment, select
a type of Registrar Server from the list.
y Register Expire Time: Please input the expiring time of registration.
Once registration succeeds, the system will follow the required time of
your carrier to reset this item.
y CODEC: Select a CODEC supported by the SIP Trunk.
y Enabled: Click this item to enable the SIP Proxy.
y RTP Relay: When the network is behind NAT, select this item to
enable RTP Relay allowing voice packets to traverse NAT and firewall
automatically.
y DID and Strip Prefix Digit: If you have applied DID service provided
by your carrier, select the DID check box and input the digit of prefix
that needs to be deleted.

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 77
y Fax Ext Number: If you carrier supports SIP fax, you may input the
extension number connected to your fax machine. When a fax comes
from SIP Trunks, it will be transferred to the fax machine.
y Ring Assignment: You could assign a specific extension, extension
group or AA menu to answer incoming calls. In ring assignment, select
“Local” to set individual trunk line or select “From CO Group” to
allow this trunk referring to a CO Line Group. For more details about
ring assignment, please refer to InterPBX Administrator Installation
and Configuration Guide.
Create SIP Trunk ARS
After you add SIP Trunks to your system, you need to edit the associated ARS
(Automatic Route Selection) policies and procedures allowing extensions to
access those SIP Trunks for making calls. Notice that extensions are not able to
access SIP Trunk using the assigned extension number.
Creating Routes:
1. Go to Main Menu>System Configuration>Route.
2. Click the Add button to increase a route.
3. Input the description of this route.
4. In different business hours, click “Account” and select a SIP Proxy you
would like to use from the list.

78 Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration
Setting ARS:
1. Go to Main Menu>Group Management>Class of Service.
2. Select a Class of Service from the list and click the ARS button to apply the
route you just created to the selected CoS.
3. In “Dialed String”, define your policy and procedure. You may input the
commonly used international access code and country code, such as
“01144” for calls to UK, or long distance access code and area code, such as
“1212” for calls to New York. You may also set a specific number
representing the SIP Trunk code such as “7”. The digit length shall not
exceed 28 and the string shall be a unique one.
4. Set the Minimum and Maximum Digits length of dialed numbers.
5. From the “Route” list, select a SIP Trunk route you would like to adopt.
6. When editing SIP Trunk ARS, skip the ”Delete” and ”Insert” items.
7. Click the Add button to increase this policy and procedure to ARS list. To
remove, select one from the list and click the Remove button.
8. You may also click the “Copy from” button and increase one by modifying
others.
Making Calls via SIP Trunks
1. Lift the handset. Please make sure your Class of Service is allowed to access
SIP Trunk ARS.
2. Depending on the ARS policies and procedures you created, input the SIP
Trunk access code followed by the phone number, or simply input the
phone number. Press the # key to start dialing.

Chapter 4 Gateway Configuration 79
For example, if you set “7” in “Dialed String” as the SIP Trunk access code,
when you dial 7-44-2055551234#, the call to UK will get through your SIP
Trunk. If you set “01186” in “Dialed String”, when you dial
011-86-xxxxxxxxxxx#, all calls to China will get through the SIP Trunks.
Add SIP Extensions
SIP Proxy helps you to register third parties’ SIP phones to your InterPBX
System and they will be one of your extensions.
1. Go to Main Menu>Extension Management >SIP Phone List.
2. Click the Add button to increase SIP phones.
3. Assign an extension number in “Extension No.”.
4. Assign a password for this extension. Extension users can change the
password from InterClient. Password must be numbers.
5. From “SIP Proxy” list, select one for this SIP phone.
For more information about the SIP Proxy Server’s settings and operation,
please refer to the SIP Proxy Server Administration Guide.

80 Chapter 5 Extension Management 80 Chapter 5 Extension Management
Chapter 5
Extension Management
This chapter describes the installation and configuration of the various types of
extensions supported by InterPBX Communication System. These include IP
phones, soft-phones, virtual extensions, analog phones, and off-premises
extensions. You may at your own evaluation provide the appropriate type of
extension according to the user’s needs, whether they are at the head office,
branch offices or business travelers.

Chapter 5 Extension Management 81
Configuring IP Phone, SoftPhone and SoftConsole
You may create extensions via Auto Discovery or manually. For more
information about settings, please refer to Chapter 2 Installing InterPBX
Communication System.
Go to Main Menu>Extension Management>InterPhone List. Select one of the
extensions from the list and then click the Modify button to edit.
Extension No., Phone Type and MAC Address
If the extension is registered to the PBX server using Auto Discovery, these info
will be recorded automatically. You do not need to change them.
If you need to increase extensions manually, please set these info. For software
phone and console, the MAC address is the one of user’s PC.
User Information
Fill in the information about extension users, including First Name, Last Name,
Title, Location and Department. The user’s name will be displayed on the IP
phone’s LCD and the extension list. The information about extension users will
be applied to Caller ID of internal calls.
User Password
With User Password, administrators are allowed to modify the password for
logging in InterPBX Management Website. With Auto Discovery, the extension
password is blank. In case password is forgotten, the system allows setting
password back to default through Password Management. This is located at
Main Menu>System Configuration>Password Management.

82 Chapter 5 Extension Management
Off-Hook Access to
InterPBX provides extensions different Off-Hook selections that enable users
directly off-hook access to extension, CO line, operator, or hotline. Please select
a direct access port for your extension from the “Off-Hook Access to” list.
y Intercom: When you lift the headset, you can dial to an extension directly. To
dial the CO line number, you have to press the CO line access code first.
y CO Line: When you lift the headset, it will retrieve the CO line access code
automatically. To dial the extension number, you have to press the Intercom
button first.
y Operator: When you lift the headset, it will directly connect to the operator.
For the settings of operator, please refer to Chapter 6 Group Management.
y Hotline: When you lift the headset, it will automatically connect to a specific
extension or extension group. Please enter the hotline number in the field of
Hotline.
Class of Service
Assign one Class of Service to restrict extensions to make unnecessary calls.
With Auto Discovery, the settings in Class of Service will be applied to the
extension automatically.
Calling permission on Class of Service will be performed with top priority.
Please refer to Chapter 6 Group Management/Class of Service for more details
about call permission.
Button Mapping Group
Select a “Button Mapping Group” which supports programmable keys on IP
phone as feature access buttons to enable speed dialing, call park and to access
CO lines. You can set Button Mapping Group as a template to be adopted by
the IP phones.
For more information about Button Mapping, please refer to Chapter 6 Group
Management/IP Phone/Button Mapping and Chapter 5 Extension
Management/Button Mapping Groups for more details about Button Mapping
Extension.
CODEC

Chapter 5 Extension Management 83
From the CODEC list, select PCM format G.711 that compresses a call to 64
Kbps, providing higher call quality but using higher bandwidths. Other
alternatives include G.723.1 compressing to 6.3 Kbps consuming smaller
bandwidth, but with poorer voice quality and G.729 compressing to 8 Kbps.
Jitter Buffer Depth
From “Jitter Buffer Depth”, select “Low” based on the bandwidth and CODEC.
Jitter Buffer will be adjusted to accommodate the callers and bandwidth, but the
Depth will never be lower than the “Low” standard. The Depth of Jitter Buffer
can be specified as None, Low, Middle and High. The None buffer corresponds
to 0 packet, Low to 2 packets, Middle to 4 packets and High to 6 packets.
Higher Jitter Buffer Depth has more storage capacity when storing temporarily
the packets avoiding packets to be discarded, but additional delay may be
bothersome at times. On the contrary, smaller Depth offers faster transmission
but excessive number of packets might be lost during transmission. For
example, G.711 format transmits packets every 20 ms which probably leads to
40ms additional delay if you set the Jitter Buffer as Low.
Silence Suppression
Silence Suppression reduces network traffic whenever silence is detected
during a conversation for a specific amount of time. Furthermore, silence
indicator packets will be sent out instead of full voice packets to reduce traffic.
Select “Silence Suppression” to enable this function or uncheck to disable it.
Conference Disabled
Conference allows the extension making an outgoing call to initiate a
conference between three or more parties. Select the “Conference Disabled”
check box if the user does not need this function.
To initiate a conference call
1. During a call, press the Hold button to hold a party.
2. Call the second party where this can be an internal extension or an external
line. More parties can join this conference by pressing the Hold button to
hold the conversation and dialing to the next party. You can hold up to 4
parties.
3. After the call is connected, press the Transfer button and “#40” to start a
Conference.

84 Chapter 5 Extension Management
4. To invite more parties, hold this conference and dial to the new party.
When connected, press the Transfer button and “#40” to start.
Each conference allows for up to 18 parties in different sessions. But each
session requires one party to be a direct extension under the InterPBX.
Note: Off-premises extensions are not allowed to initiate a conference but can
be invited.
Paging Disabled
You may select “Paging Disabled” when this is not needed.
How to activate External Paging
1. Pick up the handset.
2. Dial the Paging Code assigned on the gateway where the Paging
equipment is connected.
3. Broadcast through the handset or the speakerphone on the phone.
4. After broadcasting, hang up the phone.
How to activate Internal Paging
1. Pick up the handset.
2. Dial #38.
3. Dial the pre-defined extension number or Extension Group Code for
internal paging.
4. Broadcast through the handset or the speakerphone on the phone.
5. After broadcasting, hang up the phone.
Enable/Disable Extension
For maintenance purpose, you may need to temporarily disable some
extensions. Click the “Enable” check box to enable the extension or uncheck to
disable it.
Apply Settings
After configuring one extension, apply the settings to other extensions to save
time on initial setups. Press “Apply Setting to” and a window will pop up
showing all your pre-defined settings. Apply or change the settings, as you
need. Enter the range of extensions in “Apply to Extension”. If the range

Chapter 5 Extension Management 85
selected includes the extension you are using, the new settings will also be
applied to this extension.
Button Mapping
Under Button Mapping, set programmable keys on IP phones as feature access
buttons to enable Speed Dialing, Call Park, Access CO Lines or Conference.
Depends on phone types, the available number of Programmable Buttons are
different.
1. Go to Main Menu>Extension Management>InterPhone List.
2. Select one of the extensions from the list and press Button Mapping to edit
the programmable keys. Please refer to Action List below, which lists
details about the action, numbers and functions required.
3. Select one programmable button and scroll down to the preferred Action.
4. After the action is selected, enter the correspondent number in the
“Number” field. For example, if you select “System Speed Dial” from the
“Action” drop down menu and enter a speed dial number. When you press
this programmable key, the system will dial the phone number assigned on

86 Chapter 5 Extension Management
this system speed dial number. If the “Number” field is left blank, press the
programmable key and followed by any speed dial number you desire.
Action Designated Number Description
Access Ext. An extension number
of a station, extension
group, CO line, CO
line group, or an
outside phone number
To make calls to the
assigned number. Please
note to add CO line access
code, e.g. 05551234 for an
outbound call. Notice that if
Trunk Group is set on a
button, when parts of
trunks are available, the
LED displays available
status for other people.
After Call Work - To allow agents to have a
period of after call work
time between two calls.
Ask Member Login An Extension Group
Number
Check the login status of
the extension group.
Hearing a dial tone means
members are logged-in
successfully and a busy
tone means not logged-in.
Auto Line Access - To get a CO Line
Auto-In - Agents’ extensions will pick
up the next call
automatically.
Auxiliary Time - Agents can enable this
function to notify the
system stop assigning
incoming calls to their
extensions so that the
agents can leave their seats
temporarily without
logging out the system.

Chapter 5 Extension Management 87
Action Designated Number Description
Call Appearance
-
Press to make or receive
calls. It functions similar to
intercom. When more than
one button is assigned,
buttons with lowest
number will take the first
call.
Call Hold Retrieve CO An extension number
of a CO line
To retrieve an incoming call
from a specific CO line
placed on hold. (You
should be able to see the
CO line extension number.
for using this function.) If
this CO line is set on the
programmable button,
users can directly press the
flashing button to retrieve
the incoming calls
Call Hold Retrieve Ext An extension number
of a station
To retrieve an internal call
placed on hold. If this
extension number is set on
the programmable button,
users can directly press the
flashing button to retrieve
the call.
Call Park A slot number (0-9) To park a call to a specific
slot.
Call Pickup CO Line - To answer the least recent
incoming call ringing on
the system.
Call Pickup Directed An extension number To answer a call ringing at
another extension.
Conference Call - Start Conference with the
callers placed on Hold.

88 Chapter 5 Extension Management
Action Designated Number Description
Forward All Calls An extension number
+ #
To forward all the incomin
g
calls to a specific extension
or an external phone
number automatically.
Press again to disable.
When setting external
number, please add the CO
line access code such as 0.
Headset - Press to allow voice been
transmitted from the
attached headset, instead of
the handset.
Internal Paging An extension number
or extension group
number
Broadcast for members
through the extension or
the extension group.
Manual-In - To allow agents to pick up
the next incoming call
manually by pressing the
specific button of
Manual-In function.
Member Login An Extension Group
Number
Login to be one of the
members in the Extension
Group.
Member Logoff An Extension Group
Number
Logout from the Extension
Group.
Personal Speed Dial
A personal speed dial
number(e.g. 00)
To dial a number defined
on the Personal Speed Dial
Number.
Record on Demand - Press to save the recording
or start recording. When
recording, the LED will be
flashing.
Retrieve Msg - To access mailbox.
Retrieve Record - To play the saved
recordings.
System Speed Dial A system speed dial
number(e.g. 000)
To dial a number defined
on the speed dial number.

Chapter 5 Extension Management 89
Action Designated Number Description
Transfer to Ext VM An extension number To transfer a call to the
extension’s voice mailbox.
Transfer to AA Tree An AA menu access
code
To transfer a call to the AA
menu.
Virtual Extension A virtual extension no. Press to act as the assigned
virtual extension to make
calls.
Note: A symbol “Lock” will show on the screen when the programmable keys
are assigned as Group’s Button Mapping and only the unlocked ones can be
used. Please refer to Chapter 6 Extension Management/Button Mapping for
more details about Button Mapping and Appendix A for Function Codes List.
Station Speed Dialing
InterPBX Communication System provides System Speed Dialing and Station
Speed Dialing functions. You can assign frequently dialed phone numbers at
“Station Speed Dialing” for individual use. For more details about System
Speed Dialing, please refer to Chapter 3 System Configuration/System Speed
Dialing.
1. Go to Main Menu>Extension Management>InterPhone List.
2. Select one of the extensions from the list and press Speed Dialing button.
3. From the "Station Speed Dialing" list, select one entry.
4. Enter the targeted phone number or extension number in the "New
Number" box.
5. Give details about New Number in the “Comment” box.
6. Click the Assign button to save.

90 Chapter 5 Extension Management
You can create up to 100 entries. If you would like to set an outside phone
number, please remember to add the CO line access code such as “0” in front of
the phone number (e.g. 05551234). For long distance calls, please add the long
distance code (e.g. 02125551234). For international calls, please add the
international code and country code (e.g. 001188628861558).
Making Calls using Personal Speed Dialing
1. Lift the handset or press the Speakerphone button.
2. Press #21.
3. Press the specific personal speed dialing number, such as “00”.
Answer Option
You can better manage the incoming calls by setting the forward targets for all
calls or when not available.
.
1. Go to Main Menu>Extension Management>InterPhone List, select an
extension from the list and click the Answer Option button to select Call
Forward.
2. Select All Calls, Busy or Ring-No-Answer as per your preference.
3. Select one of the targets to answer incoming calls.
y Extension: When selected, calls will be forwarded to the other
extension or an external phone number. Enter the target extension
number or phone number in the “Number” box.
Note: When setting an external phone number, remember to input
your CO line access code.
y Voice Mail: When selected, incoming calls will be sent to your voice
mailbox. Note: Notice that your administrator needs to set a DTMF
button in the Transfer Option menu allowing callers to leave messages.

Chapter 5 Extension Management 91
y Auto Attendant: When selected, incoming calls will be forwarded to
the voice mail system, but callers cannot leave messages.
4. Ring-No-Answer Timeout: When ring-no-answer, the incoming calls will
be redirected to the Ring-No-Answer forward target after the defined
timeout. The unit used here is in seconds.
5. Call Waiting: You may enable the “Call waiting” function to pick up the
second incoming call during a call. After Call Waiting is enabled, if your
line is busy, the second incoming caller will hear the normal ringing tone,
and you will hear the “beep” tone indicating that you have a call waiting.
The “Call Waiting” function can allow only one more incoming call to stay
on queue.
Note: If the forward destination is busy or no answer, the forwarded calls will
be redirected to the original destination’s busy or no answer setting.
If Personal Answering Option is not configured, the calls will be directed to
Auto Attendant when the requested extension is busy or not available. The
administrator needs to configure the Transfer Option of VMS for taking calls.
Please refer to Chapter 7 Voice Mail Configuration/Transfer Options for more
details.
Enable Call Forward from Phone: Users may also press #44 + forward
number +# from IP phone directly to enable Forward All Call function.
External Call Forward: To allow the External Call forward functioning well,
both internal callers and receivers’ COS need to support external calls. To allow
external calls been forwarded to external numbers, the administrator needs to
proper set the Trunk to Trunk Class of Service. For more details, please go to
Chapter 6 Group Management/Class of Service.
Mailbox
In Mailbox, users can select language options, Message Play Priority and
Message Forward.

92 Chapter 5 Extension Management
1. Go to Main Menu>Extension Management>InterPhone List, select an
extension from the list and click the Mailbox button to edit the mailbox
preferences.
2. Select a language from the “Language” list and the system prompts will be
announced in the language you have selected. InterPBX can support up to
4 languages, please consult your distributor regarding multiple language
options.
3. Set Message Play Priority which allows users to select “Last-In-First-Out”
for playback of the latest message first or “First-In-First-Out” to play the
oldest one first.
4. Enter the extension number in “Message Forward to” to allow the system
to forward messages to pre-defined mailboxes.
5. Play Time Stamp: If “Play Time Stamp” is enabled, the system will play the
message recorded time when you play the message.
6. Call Screen: This function allows you to filter callers before answering calls.
When enabled, the voice mail system will require callers to say the name,
hold the call, and then make calls to the receiver and announce the name of
the caller. Receivers will be offered options to answer or not to answer the
call. If the receiver chooses to answer, the call will be connected. If not, the
voice mail system will reply the caller that the receiver is not available.
7. External Forward: When you are not available, incoming calls will be
bounced back to the VMS. Depending on the Transfer Options settings,
callers can connect to the operator, voice mail or a desired external phone
number if this option is enabled by the Administrator. Set your external
forward number here allowing the VMS to forward your incoming calls.
You may also set the external forward number from your IP phone.
How to retrieve messages

Chapter 5 Extension Management 93
1. From a phone set, press the “Message” button or “##” if messages are
retrieved via an analog phone.
2. Enter the password of the voice mailbox followed by the “#” sign (on its
first initial use, no password is required as the default password is null).
3. To retrieve messages or modify personal options simply follow the voice
guidance prompts.
Notification
InterPBX provides options for message notification. Go to Main
Menu>Extension Management>InterPhone List, select an extension from the
list then click the Notification button.
Internal Notification
The Internal Notification is Ring Notification. When the extension receives new
messages, the system will notify the receiver by ringing the extension. This
function can be used on different kinds of extensions such as assistant
extensions, analog phones, and virtual extensions.
1. Internal Notification Method: Select “Extension” from the drop-down
menu to enable the internal notification.
2. Setting the Notification Target: If you enable the internal notification, input
the desired extension number. The system will ring the extension number
you assigned when receiving new messages. If you want to enable your
station’s notification function, please input your extension number or
simply leave it blank.

94 Chapter 5 Extension Management
External Notification
1. Click the “Enabled External Notification” check box to enable the External
Notification function, or click the “Urgent Messages Only” check box to
notify you only when receiving urgent messages. The notification of urgent
messages will be delivered even when you disable the external notification.
2. Set the “Notification Schedule” to deliver notification during business
hours or specified hours to avoid interruptions.
3. Set the notification sequence. Set the destination type and its associated
phone number or pager ID. You don’t need to add the CO line access code
such as “0” here.
4. Set the interval and trial times. The system will repeat the notification, if
failed, after the interval period.
The system will send notification to the destination’s phone/pager numbers
from 1 to 5. If the number in sequence 1 is busy or unavailable, the system will
retry after the interval time you set. If failed, the system will start from
sequence 2 and repeat until it reaches the “Try Times.”
Note: If the Answer Options of the destination’s phone or extension is set, the
notification will also follow the settings.
Note: Sending a notification via phone or pager is limited by your call
permission in the Class of Service. Please consult your administrator for your
Class of Service.
Unified Messaging
You may enable the unified messaging function allowing the system to forward
the voice messages to your e-mail. The new voice messages will be as saved as a
WAV file and sent to your e-mail address.
1. Select “Enable UMS”
2. Select “Keep as new” or “Save as old” after messages are forwarded to
e-mail.
3. Input the e-mail address in “E-mail”. You can input up to 3 different e-mail
addresses.
When the “Unified Messaging” is enabled, if you select “Save as old”, the
internal and external notifications won’t be delivered due to all new messages
will be switched to old messages.

Chapter 5 Extension Management 95
Note: If you are on the recording list, when Unified Messaging is enabled, you
will be prompted for asking if you want to send recordings to e-mail when
finish listening recordings.
Note: Set the SMTP Server when Unified Messaging is enabled. For more
details about SMTP, please refer to Chapter 3 System Configuration/General
Parameters/SMTP Server.
Distribution List
Users can record or forward voice messages to a personal voice mailbox or
members in Distribution List. Users can create the Distribution Lists based on
his preferences:
1. Go to Main Menu>Extension Management>InterPhone List.
2. Select an extension from the list and then click the Distribution List button.
3. Select a List ID from the list.
4. Select extensions from the Non-Member List and move to Members List.
InterPBX allows editing up to 9 groups for each extension in Distribution List
and each can hold up to 15 members.
Virtual Extensions
You can associate Virtual Extensions with regular extensions offering one
extension with multiple numbers to be used for different purpose. The regular
extensions to be applied need to have programmable buttons.
1. Creating Virtual Extension Number. Go to Main Menu>Extension
Management>InterPhone List. Click the Add button and assign the

96 Chapter 5 Extension Management
extension number and password. From the Phone Type drop down menu,
select “Virtual”. You do not need to set the MAC address. Refer to the
above Chapter 3 Extension Management/InterPhone to set other items.
2. Associating with Extensions. Go to Main Menu>Extension
Management>InterPhone List. Select one extension from the list and click
the Virtual Ext button. You will see available virtual extension number list.
Select one or more to be associated with the regular extension to the
Allowed Virtual Ext list. The amount of Virtual Extensions you could
assign should not exceed the number of programmable buttons on the
phone.
3. Button Mapping. Go to Main Menu>Extension Management>InterPhone
List. Select the extension you just edit and click the Button Mapping button.
Pick one programmable button and set its action as “Virtual Ext” and input
the correspondent virtual extension number. To access the Virtual
Extension, simply press the specific programmable button.

Chapter 5 Extension Management 97
Making Calls: To place calls, simply press the specific button and dial the
number.
Answering Calls: When the Virtual Extension receives calls, your phone will
ring and the specific programmable button will be flashing. You may simply
pick up the handset to answer calls.
Retrieving Voice Messages
You could listen to voice messages for Virtual Extensions in many ways.
y Set Virtual Ext message forward to a regular extension. When receiving new
message, the regular extension’s message lamp will be lit and a running
message will appear on the LCD display.
y Set Virtual Ext message UMS to an e-mail. You will be able to listen to the
new messages from e-mail.
y Accessing Voice Mail System. You can also access voice mail system to listen
to messages.
- Press the Message button or press ##, then press * to go back to the main
menu of VMS. Follow the prompt to enter the extension number and
password to listen to voice messages.
- Or you could access a specific AA Menu using the AA menu access code or
make calls to the company phone number. Select a pre-defined DTMF key to
access voice mailbox. Follow the prompt to enter the extension number to
retrieve messages. (The administrator need to assign a key functioning as
“Access Mailboxes”. Please refer to Chapter 7 Voice Mail
Configuration/Auto Attendant for more details.)
Analog Extensions
The analog extensions are connected to the analog ports of the gateway like
VG5000 Voice Gateway. When you install an Analog Gateway, if it provides
FXS interface, you have already created the Analog Extensions. For more details
about installing Analog Gateway, see Chapter 4 Analog Gateway/Creating
Analog Gateway List.
1. Go to Main Menu>Extension Management>Analog Port List.
2. Select a SLT port from the list and click Modify button.
3. You will find “Gateway Name”, “Gateway Port Number” and “MAC
Address” have already been entered when administrators configured the
gateway.

98 Chapter 5 Extension Management
4. Input the extension number of the SLT port in “Extension No.”.
5. Fill in information including Name, Title, Location, Department, Change
Password, Class of Service, CODEC, Silence Compression, Conference,
Paging, Off-Hook Access to CO Directly, Apply Setting to, Station Speed
Dialing, Answer Option, Mailbox, Notification and Distribution List. For
more details, please refer to Chapter 5 Extension Management/InterPhone.
Off-Premises Extensions
InterPBX is also applied to branches or the staff who work at home. Branches
can reach Headquarters via Internet, VPN or Ethernet instead of leased lines as
Off-Premises Extensions have the same functions as any other extension in the
Headquarters.
Make sure the remote site has a permanent Internet connection using xDSL,
Cable Modem or Leased Line. Ideally it is recommended that each of the
Off-Premises phones can be assigned with a Real IP address but this is often not
the case. If you are not able to assign a Real IP address to each of the
Off-Premises phone, you can assign it a virtual IP address and open specific
ports on the Off-Premises NAT device. Before you create extensions, make sure
the relevant License Keys has been added.

Chapter 5 Extension Management 99
1. Go to Main Menu>Extension Management>Off-Premises List. Click the
Add button to create a new Off-Premises extension.
2. Assign an “Extension No.” to this phone.
3. Create a password for this extension.
4. Input the “MAC Address” of this extension. Every IP phone or PC running
the SoftPhone have a unique MAC address to be entered into this field.
5. From the “Phone Type” drop down menu select a phone type.
6. Do not change the default Signal Port 6045 and Media Port 5000 provided
by the system. If more than one Off-Premises IP phone is used in a single
remote site, set the second phone’s Signal Port to 6046 and Media Port to
5001 and so on.
7. Select the “Static IP” will reinforce the system’s security and the system can
only be connected by the specified IP address. If a real IP is used on
off-premises phone, enter it in “IP Address”. If a virtual IP is used on
off-premises phone, enter the NAT equipment’s real IP of the remote site in
“IP Address”. If a fixed IP cannot be obtained (e.g. PPPoE) do not select the
“Static IP” option.
8. Make sure “Enabled” check box is selected
9. Activate QoS if applicable. All other settings you may leave to be set at a
later time. For other setting items, please refer to Chapter 3 Extension
Management/InterPhone.
Note: If the Off-Premises extension uses virtual IP, on remote NAT equipment,
you will have to open the Signal and Media Ports as well as setup their Port
Mapping.

100 Chapter 5 Extension Management
Note: If the PBX Server is also under NAT, please activate PBX Server’s NAT
setting then open the NAT equipment’s UDP port 6046. Please refer to Chapter
3 System Configuration/General Parameters/Behind NAT, NAT IP Address
for more detailed information. On the Off-Premises phone, input the NAT
device’s Real IP address in the “PBX Server IP” item.
Note: When the off-premises extension is registered to the NAT Proxy, input
the NAT Proxy’s IP address on phone’s “PBX Server IP” setting item.
Configuring Off-Premises Analog Phones
If the Off-Premises gateway you have installed supports FXS ports, you will see
under “Analog Port List” the Off-Premises SLT ports. Please refer to above
sections for information on how to install analog extensions. For Off-Premises
gateway information, please see Chapter 4 Gateway
Configuration/Off-Premises Gateways.
SIP Phone List
SIP Proxy helps you register third parties’ SIP phones to your InterPBX System
and they will be one of your extensions.
1. Go to Main Menu>Extension Management >SIP Phone List.
2. Click the Add button to increase SIP phones.
3. Assign an extension number in “Extension No.”.
4. Assign a password for this extension. Extension users can change the
password later. Password must be numbers.
5. From “SIP Proxy” list, select one applied for this SIP phone. For other
settings, please refer to Extension Management>InterPhone.
 Loading...
Loading...