Page 1

DrayTek Telnet Commands
Reference Guide
Version: 1.11
Date: 2009/02/03
Page 2

Copyright Information
Copyright
Declarations
Trademarks
Copyright 2006 All rights reserved. This publication contains information that is
protected by copyright. No part may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed,
stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language without written
permission from the copyright holders.
The following trademarks are used in this document:
z Microsoft is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corp.
z Windows, Windows 95, 98, Me, NT, 2000, XP and Explorer are
trademarks of Microsoft Corp.
z Apple and Mac OS are registered trademarks of Apple Computer Inc.
z Other products may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective manufacturers.
ii
Page 3

TTaabbllee ooff CCoonntteennttss
1. Introduction.................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Accessing Telnet................................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Valid Commands .................................................................................................................................. 2
2. Commands Descriptions...............................................................................................3
2.1 upnp...................................................................................................................................................... 3
2.1.1 upnp off ..................................................................................................................................... 3
2.1.2 upnp on ..................................................................................................................................... 3
2.1.3 upnp nat .................................................................................................................................... 4
2.1.4 upnp service.............................................................................................................................. 4
2.1.5 upnp subscribe.......................................................................................................................... 5
2.1.6 upnp tmpvs................................................................................................................................ 6
2.2 ddns...................................................................................................................................................... 7
2.2.1 ddns log..................................................................................................................................... 7
2.2.2 ddns time................................................................................................................................... 7
2.3 exit........................................................................................................................................................ 7
2.4 ip........................................................................................................................................................... 8
2.4.1 ip 2ndsubnet.............................................................................................................................. 8
2.4.2 ip 2ndaddr ................................................................................................................................. 9
2.4.3 ip 2ndmask.............................................................................................................................. 10
2.4.4 ip aux....................................................................................................................................... 11
2.4.5 ip addr ..................................................................................................................................... 12
2.4.6 ip arp ....................................................................................................................................... 13
2.4.7 ip dhcpc................................................................................................................................... 14
2.4.8 ip ping...................................................................................................................................... 15
2.4.9 ip tracert .................................................................................................................................. 16
2.4.10 ip telnet (for 2950 Series only).............................................................................................. 17
2.4.10 ip rip....................................................................................................................................... 18
2.4.11 ip route .................................................................................................................................. 19
2.4.12 ip igmp_proxy........................................................................................................................ 20
2.4.13 ip wanaddr............................................................................................................................. 21
2.4.14 ip wan2addr........................................................................................................................... 22
2.4.16 ip dmz (for 2700/2950 series only)........................................................................................ 23
2.4.17 ip dmzswitch (for 2700 series) .............................................................................................. 24
2.4.19 ip session .............................................................................................................................. 25
2.4.20 ip bandwidth.......................................................................................................................... 26
2.4.21 ip bindmac............................................................................................................................. 27
2.5 ipf........................................................................................................................................................ 28
2.5.1 ipf view .................................................................................................................................... 28
2.5.2 ipf set (for 2950 series only).................................................................................................... 29
2.5.3 ipf flowtrack (for 2950 series only) .......................................................................................... 31
2.6 p2p...................................................................................................................................................... 32
2.7 im........................................................................................................................................................ 33
2.8 csm (for 2910/2950 series)................................................................................................................. 34
2.9 ddos.................................................................................................................................................... 36
2.10 urlf..................................................................................................................................................... 37
2.10.1 urlf blist.................................................................................................................................. 37
2.10.2 urlf setdefault......................................................................................................................... 38
iii
Page 4

2.10.3 urlf esubnet............................................................................................................................ 39
2.10.4 urlf webf................................................................................................................................. 40
2.10.5 urlf tschedule......................................................................................................................... 41
2.1 1 isdn................................................................................................................................................... 42
2.11.1 isdn blknum........................................................................................................................... 42
2.11.2 isdn dial................................................................................................................................. 43
2.11.3 isdn drop................................................................................................................................ 44
2.11.4 isdn vci .................................................................................................................................. 44
2.11.5 isdn overlap........................................................................................................................... 44
2.12 log..................................................................................................................................................... 45
2.13 quit.................................................................................................................................................... 46
2.14 srv..................................................................................................................................................... 47
2.14.1 srv dhcp................................................................................................................................. 47
2.14.1.1 srv dhcp fixip............................................................................................................ 47
2.14.1.2 srv dhcp gateway..................................................................................................... 47
2.14.1.3 srv dhcp ipcnt........................................................................................................... 48
2.14.1.4 srv dhcp off .............................................................................................................. 48
2.16.1.6 srv dhcp startip......................................................................................................... 48
2.14.1.7 srv dhcp status......................................................................................................... 48
2.14.1.8 srv dhcp leasetime................................................................................................... 49
2.14.1.9 srv dhcp frcdnsmanl................................................................................................. 49
2.14.1.10 srv dhcp dns1.........................................................................................................50
2.14.1.11 srv dhcp dns2.........................................................................................................50
2.14.1.12 srv dhcp relay......................................................................................................... 50
2.14.1.14 srv dhcp public.......................................................................................................51
2.14.2 srv nat.................................................................................................................................... 52
2.14.2.1 srv nat dmz .............................................................................................................. 52
2.14.2.2 srv nat openport.......................................................................................................52
2.14.2.3 srv nat portmap........................................................................................................53
2.14.2.4 srv nat status............................................................................................................ 54
2.14.3 srv vta.................................................................................................................................... 55
2.15 show................................................................................................................................................. 56
2.15.1 show lan1.............................................................................................................................. 56
2.15.2 show lan2.............................................................................................................................. 56
2.15.3 show dhcp............................................................................................................................. 56
2.15.4 show dmz.............................................................................................................................. 56
2.15.5 show dns............................................................................................................................... 57
2.15.6 show openport....................................................................................................................... 57
2.15.7 show nat................................................................................................................................ 57
2.15.8 show session......................................................................................................................... 58
2.15.9 show adsl ..............................................................................................................................58
2.16 mngt.................................................................................................................................................. 59
2.16.1 mngt ftpport........................................................................................................................... 59
2.16.2 mngt httpport......................................................................................................................... 59
2.16.3 mngt httpsport .......................................................................................................................60
2.16.4 mngt telnetport ...................................................................................................................... 60
2.16.5 mngt ftpserver .......................................................................................................................61
2.16.6 mngt noping........................................................................................................................... 62
2.16.7 mngt defenseworm................................................................................................................ 63
2.16.8 mngt rmtcfg ...........................................................................................................................64
2.16.9 mngt echoicmp...................................................................................................................... 65
2.16.10 mngt accesslist.................................................................................................................... 66
2.17 sys.................................................................................................................................................... 67
2.17.1 sys admin.............................................................................................................................. 67
iv
Page 5

2.17.2 sys cfg................................................................................................................................... 68
2.17.3 sys cmdlog ............................................................................................................................69
2.17.4 sys ftpd.................................................................................................................................. 70
2.17.5 sys domainname................................................................................................................... 71
2.17.6 sys iface ................................................................................................................................ 72
2.17.7 sys name............................................................................................................................... 73
2.17.8 sys passwd............................................................................................................................ 74
2.17.9 sys reboot.............................................................................................................................. 75
2.17.10 sys commit ..........................................................................................................................76
2.17.11 sys tftpd............................................................................................................................... 77
2.17.12 sys cc .................................................................................................................................. 77
2.17.13 sys version ..........................................................................................................................78
2.17.14 sys qrybuf............................................................................................................................ 79
2.17.15 sys pollbuf ...........................................................................................................................80
2.17.16 sys sip_alg........................................................................................................................... 81
2.18 register.............................................................................................................................................. 82
2.19 vpn.................................................................................................................................................... 83
2.19.1 vpn l2lset............................................................................................................................... 83
2.19.2 vpn 2ndsubnet....................................................................................................................... 84
2.20 wan................................................................................................................................................... 85
2.20.1 wan ppp_ipcp_vso ................................................................................................................ 85
2.20.2 ppp_mru................................................................................................................................ 85
2.20.3 wan ppp_mss........................................................................................................................ 86
2.20.4 wan DF_check....................................................................................................................... 86
2.20.5 wan disable ........................................................................................................................... 86
2.21 adsl................................................................................................................................................... 87
2.21.1 adsl txpct............................................................................................................................... 87
2.21.2 adsl rxpct............................................................................................................................... 88
2.21.3 adsl status............................................................................................................................. 89
2.21.4 adsl ppp................................................................................................................................. 90
2.21.5 adsl bridge (for 2700 series) .................................................................................................91
2.21.6 adsl idle................................................................................................................................. 92
2.21.7 adsl reboot............................................................................................................................. 92
2.21.8 adsl oamlb............................................................................................................................. 93
2.21.9 adsl vcilimit............................................................................................................................ 94
2.21.10 adsl showbins(for 2800 series)........................................................................................... 95
2.21.11 adsl codinggain (for 2800 series))....................................................................................... 96
2.21.12 adsl maxdnrate(for 2800 series).........................................................................................97
2.21.13 adsl duallatency (for 2800 series)....................................................................................... 98
2.21.14 adsl annex (for 2700 series)................................................................................................ 99
2.21.15 adsl savecfg ........................................................................................................................ 99
2.21.16 adsl atm (for 2700 series) ................................................................................................... 99
2.22 wl.................................................................................................................................................... 100
2.22.1 wl set (for 2910 series)........................................................................................................ 100
2.22.2 wl act (for 2910 series)........................................................................................................ 101
2.22.3 wl wpa ................................................................................................................................. 102
2.22.4 wl pwrtst (for 2900 series)................................................................................................... 103
2.22.5 wl emi (for 2900 series)....................................................................................................... 104
2.23 voip................................................................................................................................................. 105
2.23.1 voip block ............................................................................................................................ 105
2.23.2 voip debug........................................................................................................................... 106
2.23.3 voip dial_plan ......................................................................................................................107
2.23.4 voip rtp................................................................................................................................. 108
2.23.4.1 voip rtp codec......................................................................................................... 108
v
Page 6

2.23.4.2 voip rtp dtmf........................................................................................................... 109
2.23.4.3 voip rtp port............................................................................................................ 110
2.23.4.4 voip rtp symmetric.................................................................................................. 110
2.23.4.5 voip rtp tos ............................................................................................................. 111
2.23.5 voip sip................................................................................................................................ 112
2.23.5.1 voip sip acc............................................................................................................ 112
2.23.5.2 voip sip calllog........................................................................................................ 114
2.23.5.3 voip sip ep.............................................................................................................. 115
2.23.5.4 voip sip misc (for 2800 series)............................................................................... 117
2.23.5.5 voip sip nat............................................................................................................. 118
2.23.6 voip dsp............................................................................................................................... 119
2.23.6.1 voip dsp countrytone.............................................................................................. 119
2.23.6.2 voip dsp dialtonepwr.............................................................................................. 120
2.23.6.4 voip dsp ringfeq...................................................................................................... 120
2.23.6.5 voip dsp cidtype..................................................................................................... 121
2.23.6.6 voip dsp micgain.................................................................................................... 121
2.23.6.7 voip dsp spkgain.................................................................................................... 122
2.23.6.8 voip dsp timer......................................................................................................... 122
2.24 port (for 2910 series only) ..............................................................................................................123
2.25 wol.................................................................................................................................................. 124
2.26 vigbrg.............................................................................................................................................. 125
2.26.1 vigbrg on.............................................................................................................................. 125
2.26.2 vigbrg off.............................................................................................................................. 126
2.26.3 vigbrg status........................................................................................................................ 127
2.26.4 vigbrg cfgip.......................................................................................................................... 128
2.26.5 vigbrg wanstatus ................................................................................................................. 129
2.26.6 vigbrg wlanstatus ................................................................................................................ 130
2.27 portmaptime (for 2800 Series)........................................................................................................ 131
vi
Page 7
11.. IInnttrroodduuccttiioonn
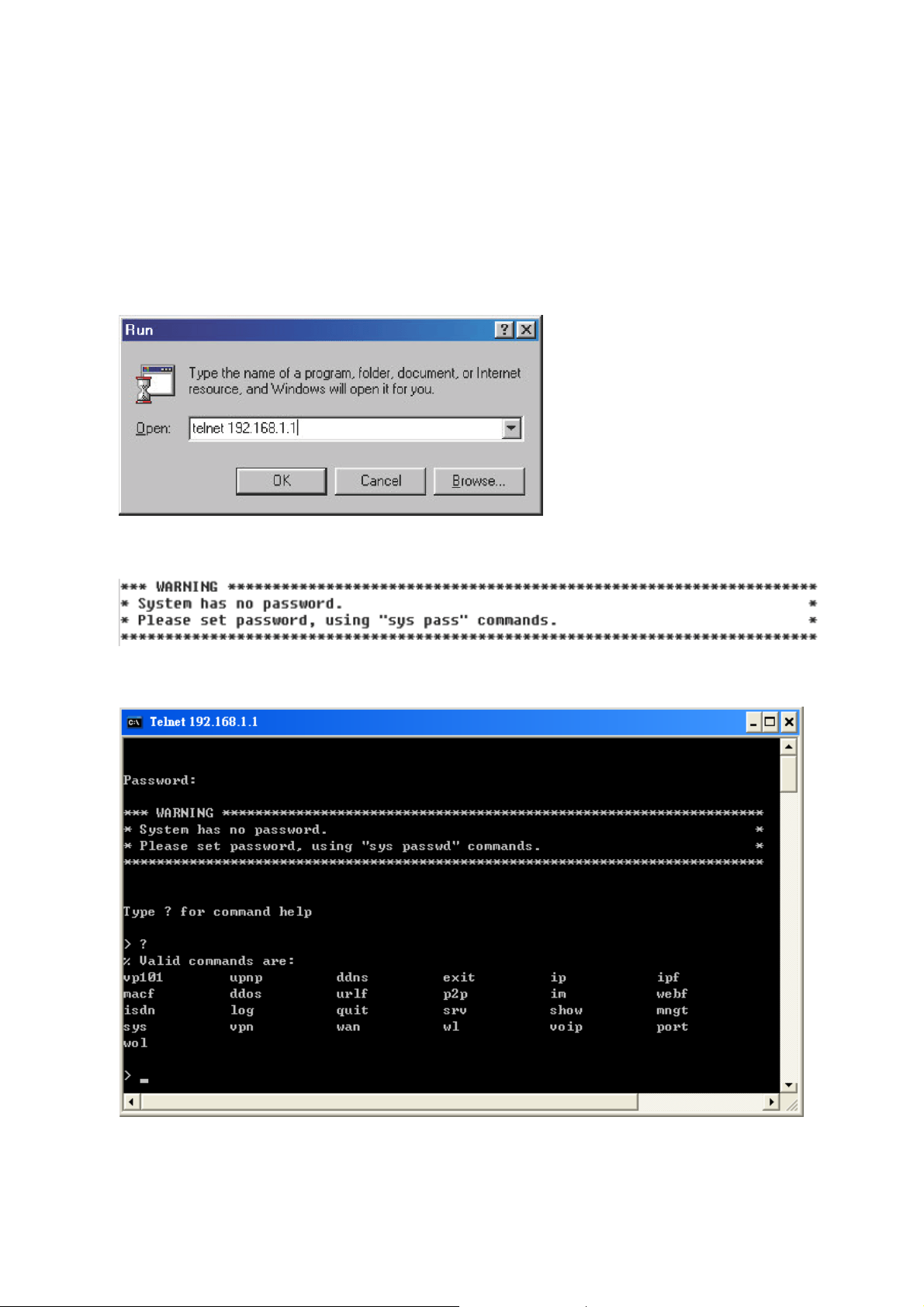
1.1 Accessing Telnet
Click Start > Run and type Telnet 192.168.1.1 in the Open box as below. Note that the IP
address in the example is the default address of the router. If you have changed the default,
enter the current IP address of the router.
Click OK. The Telnet terminal will be open. If an administrator password has not already been
assigned, follow the on-screen instructions to assign one.
After assigning a password, type ?. You will see a list of valid/common commands depending
on the router that your use.
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
1
Page 8

1.2 Valid Commands
The valid commands will differ according to the router and the firmware version that you have.
At present, commands explained in this manual are for Vigor 2700 Series, Vigor 2800 Series
Vigor2910 Series and 2950 Series.
Valid Command Types for Vigor 2700 Series (F/W: V2.6.3_RC1)
upnp ddns exit ip ipf p2p
Im ddos urlf isdn log quit
srv sys register show mngt vpn
wan adsl voip port wol vigbrg
Valid Command Types for Vigor 2800 Series (F/W: V2.7.1_B4_Y01)
upnp ddns exit ip ipf p2p
Im ddos urlf isdn log quit
srv sys register show mngt vpn
wan adsl wl voip port wol
vigbrg portmaptime
Valid Command Types for Vigor 2910 Series (F/W: V3.0.2_RC1a)
upnp ddns exit ip ipf csm
ddos urlf isdn log quit srv
sys register show mngt vpn wan
wl voip port wol
Valid Command Types for Vigor 2950 Series (F/W: V3.0.0)
upnp ddns exit ip ipf csm
ddos urlf log quit srv sys
register show mngt vpn wan wl
wol
2
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 9

22.. CCoommmmaannddss DDeessccrriippttiioonnss
2.1 upnp
2.1.1 upnp off
This command can close UPnP function.
Example
>upnp off
UPNP say bye-bye
2.1.2 upnp on
This command can enable UPnP function.
Example
>upnp on
UPNP start.
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
3
Page 10
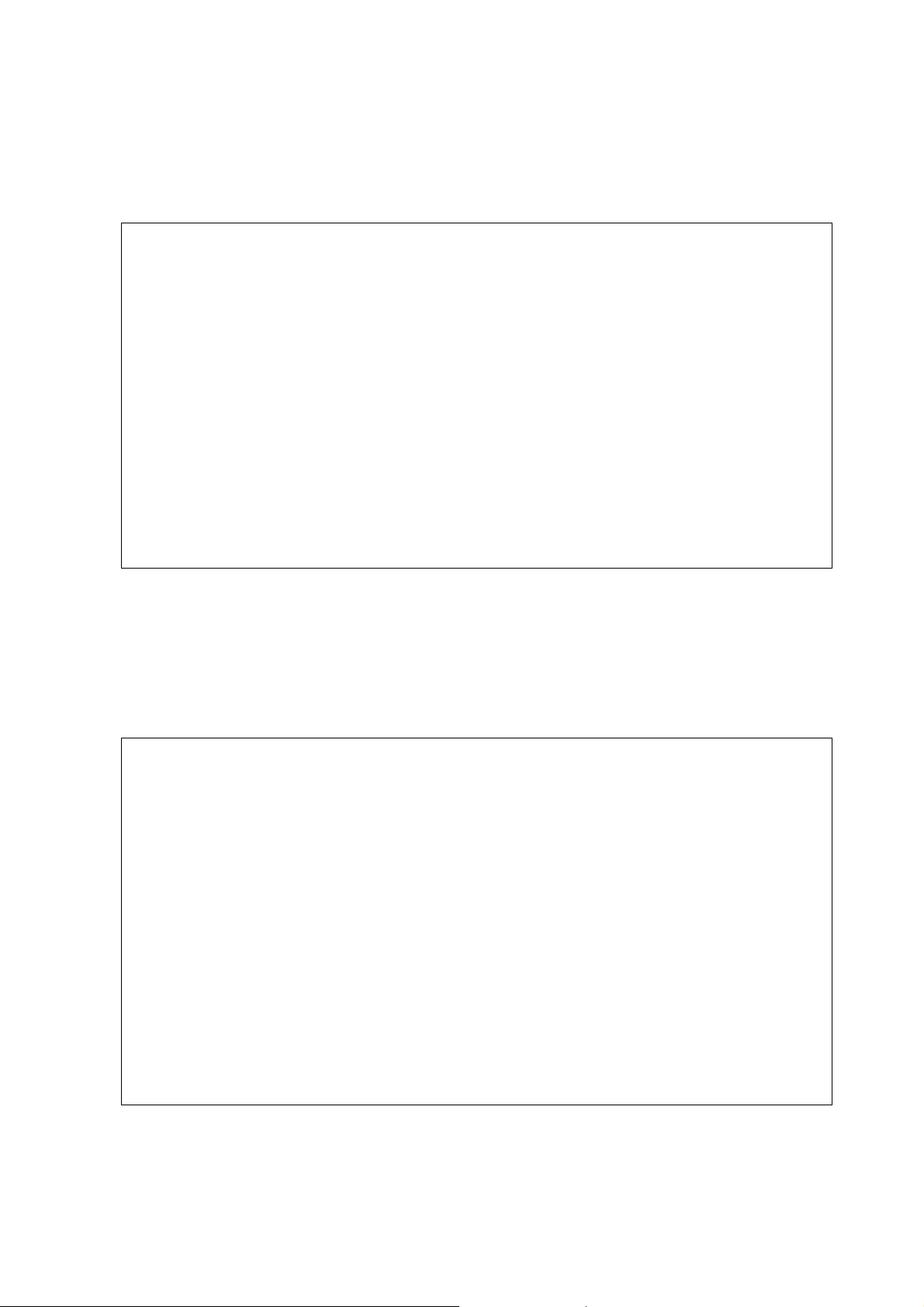
2.1.3 upnp nat
This command can display IGD NAT status.
Example
> upnp nat
****************** IGD NAT Status ****************
((0))
InternalClient >>202.168.1.0<<, RemoteHost >>0.0.0.0<<
InternalPort >>21<<, ExternalPort >>21<<
PortMapProtocol >>TCP<<
The tmpvirtual server index >>0<<
PortMapLeaseDuration >>0<<, PortMapEnabled >>0<<
Ftp Example [MICROSOFT]
((1))
InternalClient >>0.0.0.0<<, RemoteHost >>0.0.0.0<<
InternalPort >>0<<, ExternalPort >>0<<
PortMapProtocol >>*<<
The tmpvirtual server index >>0<<
PortMapLeaseDuration >>0<<, PortMapEnabled >>0<<
2.1.4 upnp service
This command can display the information of the UPnP service.
Example
> upnp service
>>>>> SERVICE TABLE1 <<<<<
serviceType urn:schemas-microsoft-com:service:OSInfo:1
serviceId urn:microsoft-com:serviceId:OSInfo1
SCPDURL /upnp/OSInfo.xml
controlURL /OSInfo1
eventURL /OSInfoEvent1
UDN uuid:f858949e-a0c6-4e4c-9eac-00507fd484f0
>>>>> SERVICE TABLE2 <<<<<
serviceType urn:schemas-upnp-org:service:WANCommonInterfaceConfig:1
serviceId urn:upnp-org:serviceId:WANCommonIFC1
SCPDURL /upnp/WComIFCX.xml
controlURL /upnp?control=WANCommonIFC1
eventURL /upnp?event=WANCommonIFC1
UDN uuid:aeadf384-d05a-429c-9f5f-d6e6f0591c43
4
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 11
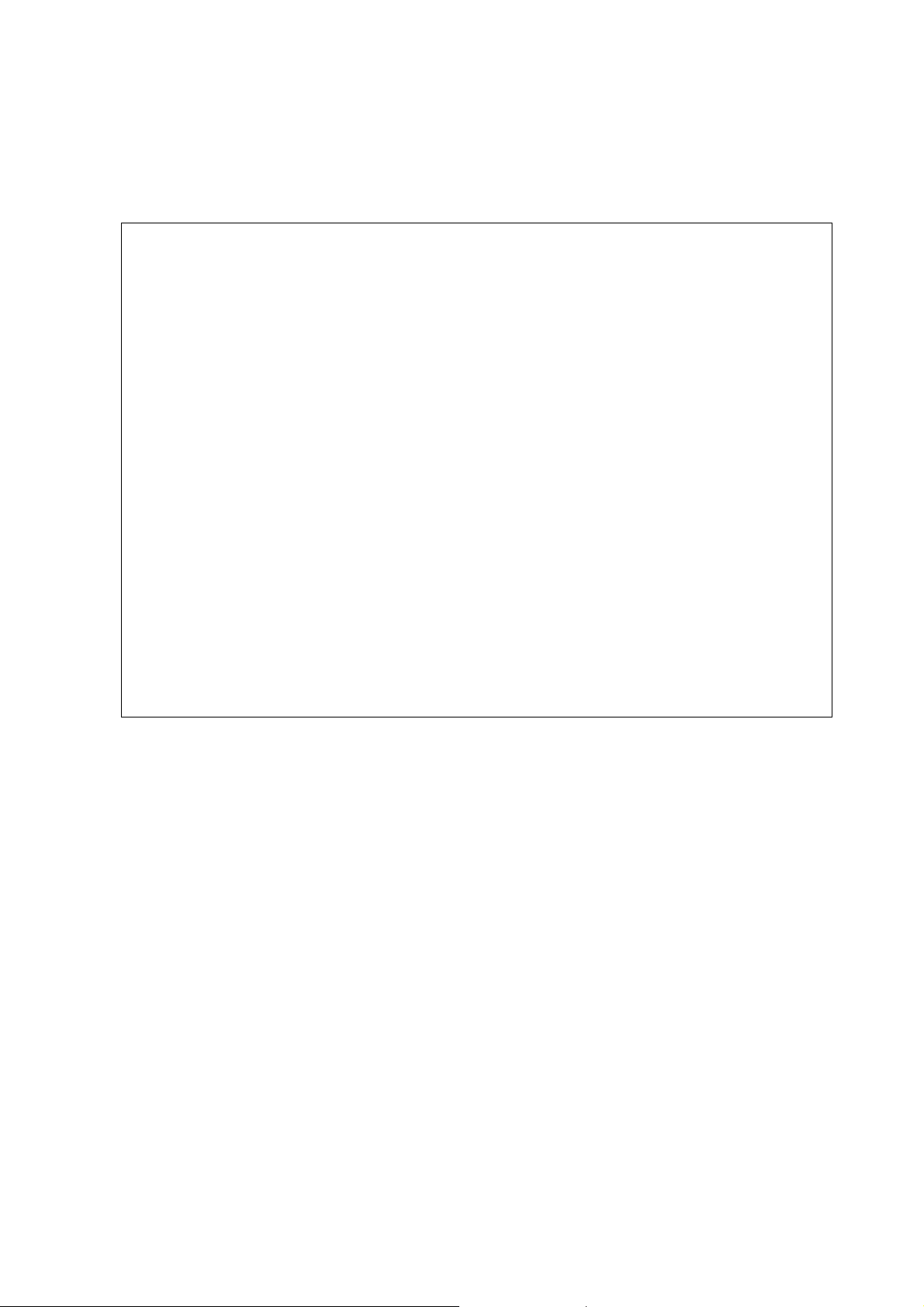
2.1.5 upnp subscribe
This command can show all subscribers of UPnP services.
Example
> upnp subscribe
>>>> (1) serviceType urn:schemas-microsoft-com:service:OSInfo:1
----- Subscribtion1 ------ sid = b6ebf734-bb66-4fcb-9481-ec12f852768c
eventKey =1, ToSendEventKey = 1
expireTime =85736
active =1
DeliveryURLs =<http://192.168.1.10:5000/notify>
>>>> (2) serviceType urn:schemas-upnp-org:service:WANCommonInterfaceConfig:1
----- Subscribtion1 ------ sid = b3bed84b-c49c-4caf-8da7-88691e5c38ea
eventKey =1, ToSendEventKey = 1
expireTime =85737
active =1
DeliveryURLs =<http://192.168.1.10:5000/notify>
>>>> (3) serviceType urn:schemas-upnp-org:service: WANDSLLinkConfig:1
>>>> (4) serviceType urn:schemas-upnp-org:service:WANPPPConnection:1
----- Subscribtion1 ------ sid = 789aab3a-e35f-487f-b7c5-5c19a26b2428
eventKey =1, ToSendEventKey = 1
expireTime =85738
active =1
DeliveryURLs =<http://192.168.1.10:5000/notify>
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
5
Page 12

2.1.6 upnp tmpvs
This command can display current status of temp Virtual Server of your router.
Example
****************** Temp virtual server status ****************
((0))
real_addr >>192.168.1.10<<, pseudo_addr >>172.16.3.229<<
real_port >>0<<, pseudo_port >>0<<
hit_portmap_index >>0<<
The protocol >>TCP<<
time >>0<<
((1))
real_addr >>0.0.0.0<<, pseudo_addr >>0.0.0.0<<
real_port >>0<<, pseudo_port >>0<<
hit_portmap_index >>0<<
The protocol >>0<<
time >>0<<
6
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 13

2.2 ddns
2.2.1 ddns log
Displays the DDNS log.
Example
>ddns log
01:07:38.0 >>>>> DDNS is updating. <<<<<
2.2.2 ddns time
Sets and displays the DDNS time.
ddns time <update in minutes>
Syntax Description
Update in minutes Type the value as DDNS time. The range is from 1 to 1440.
Example
> ddns time
ddns time <update in minutes>
Valid: 1 ~ 1440
%Now: 1440
> ddns time 1000
ddns time <update in minutes>
Valid: 1 ~ 1440
%Now: 1000
2.3 exit
Type this command will leave telnet window.
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
7
Page 14
2.4 ip
2.4.1 ip 2ndsubnet
This command allows users to enable or disable the second subnet for your router.
ip 2ndsubnet <Enable/Disable>
Syntax Description
Enable Enable the second subnet.
Disable Disable the second subnet.
Example
>ip 2ndsubnet Disable
2nd subnet disabled!
>ip 2ndsubnet Enable
2nd subnet enabled!
8
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 15
2.4.2 ip 2ndaddr
This command allows users to set the second IP address for your router.
ip 2ndaddr ?
ip 2ndaddr <2nd subnet IP address>
Syntax Description
? Display an IP address which allows users set as second subnet IP
address.
2nd subnet IP address Specify an IP address. The system will set the one that you specified
as the second subnet IP address.
Example
>ip 2ndaddr 192.168.2.1
% Set 2nd subnet IP address done!!!
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
9
Page 16
2.4.3 ip 2ndmask
This command allows users to set the second IP address for your router.
ip 2ndmask ?
ip 2ndmask <2nd subnet mask>
Syntax Description
? Display a subnet mask address which allows users set as second
subnet mask.
2nd subnet IP address Specify a subnet mask. The system will set the one that you specified
as the second subnet mask.
Example
>ip 2ndmask 255.255.255.0
% Set 2nd subnet mask done!!!
10
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 17

2.4.4 ip aux
This command allows users to set a specified WAN IP for joining into the NAT Pool. Basically,
the WAN IP has been added in WAN IP Alias but not joined to NAT Pool yet.
ip aux add [IP] [Join to NAT Pool]
ip aux remove [index]
Syntax Description
IP It means the auxiliary WAN IP address.
Join to NAT Pool 0 (disable) or 1 (enable)
[index] Type the index number of the table displayed on your screen.
Example
>ip aux 172.16.3.113 1
>
When you type ip aux?, the current auxiliar WAN IP Address table will be shown as the
following:
Index no. Status IP address NAT IP pool
----------------------------------------------
1 Enable 172.16.3.229 Yes
2 Enable 172.16.3.56 No
3 Enable 172.16.3.113 No
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
11
Page 18
2.4.5 ip addr
This command allows users to set/add a specified LAN IP your router.
ip addr [IP address]
Syntax Description
IP address It means the LAN IP address.
Example
>ip addr 192.168.50.1
% Set IP address OK !!!
Note: When the LAN IP address is changed, the start IP address of DHCP server are still the
same. To make the IP assignment of the DHCP server being consistent with this new IP address
(they should be in the same network segment), the IP address of the PC must be fixed with the
same LAN IP address (network segment) set by this command for accessing into the web
configurator of the router. Later, modify the start addresses for the DHCP server.
12
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 19

2.4.6 ip arp
ARP displays the matching condition for IP and MAC address.
ip arp add [IP address] [MAC address] [LAN or WAN]
ip arp del [IP address] [LAN or WAN]
ip arp flush
ip arp status
In which, arp add allows users to add a new IP address into the ARP table; arp del allows
users to remove an IP address; arp flush allows users to clear arp cache; arp status allows
users to review current status for the arp table.
Syntax Description
IP address It means the LAN IP address.
MAC address It means the MAC address of your router.
LAN or WAN It indicates the direction for the arp function.
Example
>ip arp status
[ARP Table]
Index IP Address MAC Address
1 192.168.1.10 00-0E-A6-2A-D5-A1
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
13
Page 20
2.4.7 ip dhcpc
This command is available for WAN DHCP.
ip dhcpc option
ip dhcpc release
ip dhcpc renew
ip dhcpc status
Syntax Description
option It is an optional setting for DHCP server.
release It means to release current WAN IP address.
renew It means to renew the WAN IP address and obtain another new one.
status It displays current status of DHCP client.
Example
>ip dhcpc status
I/F#3 DHCP Client Status:
DHCP Server IP : 172.16.3.7
WAN Ipm : 172.16.3.40
WAN Netmask : 255.255.255.0
WAN Gateway : 172.16.3.1
Primary DNS : 168.95.192.1
Secondary DNS : 0.0.0.0
Leased Time : 259200
Leased Time T1 : 129600
Leased Time T2 : 226800
Leased Elapsed : 259194
Leased Elapsed T1 : 129594
Leased Elapsed T2 : 226794
14
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 21
2.4.8 ip ping
This command allows users to ping IP address of WAN1 or WAN2 for verifying if the WAN
connection is OK or not.
ip ping [IP address] [WAN1/WAN2]
Syntax Description
IP address It means the LAN IP address.
WAN1/WAN2 It means the WAN port that the above IP address passes through.
Example
>ip ping 172.16.3.229 WAN1
Pinging 172.16.3.229 with 64 bytes of Data:
Receive reply from 172.16.3.229, time=0ms
Receive reply from 172.16.3.229, time=0ms
Receive reply from 172.16.3.229, time=0ms
Packets: Sent = 5, Received = 5, Lost = 0 <0% loss>
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
15
Page 22

2.4.9 ip tracert
This command allows users to trace the routes from the router to the host.
ip tracert [Host/IP address] [WAN1/WAN2]
Syntax Description
IP address It means the target IP address.
WAN1/WAN It means the WAN port that the above IP address passes through.
Example
>ip tracert 22.128.2.62 WAN1
Traceroute to 22.128.2.62, 30 hops max
1 172.16.3.7 10ms
2 172.16.1.2 10ms
3 Request Time out.
4 168.95.90.66 50ms
5 211.22.38.134 50ms
6 220.128.2.62 50ms
Trace complete
16
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 23

2.4.10 ip telnet (for 2950 Series only)
This command allows users to telnet another server (terminal) in the LAN or WAN side.
ip telnet [IP address] [Port]
Syntax Description
IP address It means the target IP address.
Port It means the LAN port that the above IP address passes through.
Example
>ip telnet 192.168.1.1 3
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
17
Page 24
2.4.10 ip rip
This command allows users to set the RIP (routing information protocol) of IP.
ip rip [0/1/2]
Syntax Description
0/1/2 0 means disable; 1 means first subnet and 2 means second subnet.
Example
>ip rip 1
%% Set RIP 1
st
subnet.
18
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 25
2.4.11 ip route
This command allows users to set static route.
ip route add [dst] [netmask][gateway][iface][rtype]
ip route del [dst] [netmask][rtype]
ip route status
Syntax Description
add It means to add an IP address as static route.
del It means to delete specified IP address.
status It means current status of static route.
dst It means the IP address of the destination.
netmask It means the netmask of the specified IP address.
gateway It means the gateway of the connected router.
iface It means the connection interface., 0 : LAN; 3: WAN1; 4: WAN2
rtype It means the type of the route, default : default route; static: static
route.
Example
> ip route add 172.16.2.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.2.4 3 static
> ip route status
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, * - default, ~ - private
C~ 192.168.1.0/ 255.255.255.0 is directly connected, IF0
S 172.16.2.0/ 255.255.255.0 via 172.16.2.4, IF3
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
19
Page 26

2.4.12 ip igmp_proxy
This command allows users to set
ip igmp_proxy [set|rset|status]
Syntax Description
set It means
reset It means
status it means
Example
>ip igmp_proxy status
%% ip igmp_proxy [set|rset|status], IGMP Proxy is ON
%%% igmp_proxy LAN:
239.255.255.250 state=1
igmp_proxy WAN:
%%%
224.0.0.9 timer=0
239.255.255.250 timer=0
20
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 27
2.4.13 ip wanaddr
This command allows users to set WAN address for the router.
ip wanaddr [IP address][IP netmask][gateway ip]
Syntax Description
IP address It means the WAN IP address.
IP netmask It means the netmask of the specified IP address.
gateway ip It means the IP address for gateway.
Example
>ip wanaddr 172.16.2.4 255.255.255.0
% Set WAN IP address OK!!!
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
21
Page 28
2.4.14 ip wan2addr
This command allows users to set second WAN address for the router.
ip wan2addr [IP address][IP netmask]
Syntax Description
IP address It means the WAN IP address.
IP netmask It means the netmask of the specified IP address.
gateway ip It means the IP address for gateway.
Example
>ip wan2addr 172.16.2.4 255.255.255.0
% Set WAN IP address OK!!!
22
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 29
2.4.16 ip dmz (for 2700/2950 series only)
Specify MAC address of certain device as the DMZ host.
ip dmz [mac]
Syntax Description
mac It means the MAC address of the device that you want to specify.
Example
>ip dmz ?
% ip dmz <mac>, now : 00-00-00-00-00-00
> ip dmz 11-22-33-44-55-66
> ip dmz ?
% ip dmz <mac>, now : 11-22-33-44-55-66
>
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
23
Page 30
2.4.17 ip dmzswitch (for 2700 series)
This command allows users to set DMZ mode.
ip dmzswitch off
ip dmzswitch private
ip dmzswitch active_trueip
Syntax Description
off It means to turn off DMZ function.
private It means to set DMZ as private IP.
active_truei It means to set the DMZ as active true IP DMZ.
Example
>ip dmzswitch off
24
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 31

2.4.19 ip session
This command allows users to set maximum session limit number for the specified IP.
ip session on
ip session off
ip session default num
ip session status
ip session show
ip session [add/del][IP1-IP2][num]
Syntax Description
on It means to turn on session limit for each IP.
off It means to turn off session limit for each IP.
default num It means to set the default number of session num limit.
status It means to display the current settings.
show It means to display all session limit settings in the IP range.
add It means to add the session limits in an IP range.
del It means to delete the session limits in an IP range.
IP1-IP2 It means the range of IP address specified for this command.
num It means the number of the session limits, e.g., 100.
Example
>ip session default 100
>ip session add 192.168.1.5. – 192.168.1.100 100
>ip session status
IP range:
192.168.1.50-192.168.1.100 : 100
Current ip session limit is turn on
Current default session number is 100
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
25
Page 32

2.4.20 ip bandwidth
This command allows users to set maximum bandwidth limit number for the specified IP.
ip bandwidth on
ip bandwidth off
ip bandwidth default [tx_rate][rx_rate]
ip bandwidth status
ip bandwidth show
ip bandwidth [add/del] [IP1-IP2][tx][rx]
Syntax Description
on It means to turn on the IP bandwidth limit.
off It means to turn off the IP bandwidth limit.
default [tx_rate][rx_rate] It means to set default tx and rx rate of bandwidth limit. The range is
from 0 – 65535 Kpbs.
status It means to display the current settings.
show It means to display all the bandwidth limits settings within the IP
range.
add It means to add the bandwidth within the IP range.
del It means to delete the bandwidth within the IP range.
IP1-IP2 It means the range of IP address specified for this command.
tx It means to set transmission rate for bandwidth limit.
rx It means to set receiving rate for bandwidth limit.
Example
>ip bandwidth default 200 800
>ip bandwidth add 192.168.1.50 - 192.168.1.100 10 60
>ip bandwidth status
IP range:
192.168.1.50 – 192.168.1.100 : Tx:10 Rx:60
Current ip Bandwidth limit is turn on
Current default Bandwidth rate is Tx:200 Rx:800 Kbps
26
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 33

2.4.21 ip bindmac
This command allows users to set IP-MAC binding for LAN host.
ip bandmac on
ip bandmac off
ip bandmac strict_on
ip bandmac show
ip bandmac add [IP][MAC]
ip bandmac del [IP]/all
Syntax Description
on It means to turn on IP bandmac policy. Even the IP is not in the
policy table, it can still access into network.
off It means to turn off all the bindmac policy.
strict_on It means that only those IP address in IP bindmac policy table can
access into network.
show It means to display the IP address and MAC address of the pair of
binded one.
add It means to add one ip bindmac.
del It means to delete one ip bindmac.
IP It means to type the IP address for binding with specified MAC
address.
MAC It means to type the MAC address for binding with the IP address
specified.
All It means to delete all the IP bindmac settings.
Example
>ip bindmac add 192.168.1.46 00:50:7f:22:33:55
>ip bindmac show
ip bind mac function is turned ON
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
27
Page 34

2.5 ipf
This command allows users to view the version of the IP filter, to view/set the log flag, to view
the running IP filter rules.
2.5.1 ipf view
ipf [-VzZ][-1 block]
ipf [-VzZ][-1 pass]
ipf [-VzZ][-1 nomatch]
ipf [-VzZ][-1 none]
ipf view [-cdfhrtz]
Syntax Description
V It means to show the version of this IP filter.
z It means to clear a filter rule’s statistics.
Z It means to clear IP filter’s gross statistics.
-1 It means to set the log flag.
block It means to log the packet which will be blocked by IP filter.
pass It means to log the packet that passes through IP filter.
nomatch It means to log the packet that doesn't match any rule in IP filter.
none It means logging or not depends on filter rule setting.
-c It means to show the running call filter rules.
-d It means to show the running data filter rules.
-f It means to show IP fragment states.
-h It means to show the hit-number of the filter rules.
-r It means to show the running call and data filter rules.
-t It means to display to the end.
-z It means to clear the statistics of IP filter rules.
Example
>ipf –V -1 pass
Ipf: IP Filter: v3.3.1 <416>
Kernel: IP Filter: v3.3.1
Running: yes
Log Flags: 0x0 = none set
Default: pass all, Logging: available
>ipf view –c
------ Call Filter Rules -----[Set 1 Rule 1]
Schedule:
Source IP : any
Destination IP: any
Service Type: TCP/UDP port from 137-139 to any
Fragments: Don’t Care
Action: Block immediately
28
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 35

2.5.2 ipf set (for 2950 series only)
This command is used to set filter rule for firewall.
ipf set [SET_NO] rule [RULE_NO] [Options]
ipf set [Options]
Syntax Description
SET_NO It means to specify the index number (from 1 to 12) of filter set.
RULE_NO It means to specify the index number (from 1 to 7) of filter rule set.
Options There are several options provided here, such as -v, -c [SET_NO], -d
[SET_NO], -l [VALUE], - p [VALUE], -C [CSM_NO], -i [VALUE]
and -f [VALUE].
-v Type “-v” to view the configuration of general set
-c [SET_NO] It means to setup Call Filter, e.g., -c 2. The range for the index
number you can type is “0” to “12” (0 means “disable).
-d [SET_NO] It means to setup Data Filter, e.g., -d 3. The range for the index
number you can type is “0” to “12” (0 means “disable).
-l [VALUE] It means to setup Log Flag, e.g., -l 2
Type “0” to disable the log flag.
Type “1” to display the log of passed packet.
Type “2” to display the log of blocked packet.
Type “3” to display the log of non-matching packet.
- p [VALUE] It means to setup actions for packet not matching any rule. e.g., -p 1
Type “0” to let all the packets pass;
Type “1” to block all the packets.
-C [CSM_NO] It means to setup CSM for packet not matching any rule. Type the
index number of CSM profile (0 to 32, 0=None), e.g., -C 32
-i [VALUE] It means to apply IP filter to VPN incoming packets.
Type “0” to disable; type “1” to enable, e.g., -i 1
-f [VALUE] It means to accept large incoming fragmented UDP or ICMP packets.
Type “0” to disable; type “1” to enable, e.g., -f 0
Example
> ipf set 2 rule 1 -p 0
Setting saved.
> ipf set 2 rule 1 -v
Filter Set 2 Rule 1:
Status : Enable
Comments : xNetBios -> DNS
Index(1-15) in Schedule Setup: <null>, <null>, <null>, <null>
Direction : LAN -> WAN
Source IP : Any
Destination IP : Any
Service Type : TCP/UDP, Port: from 137~139 to 53
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
29
Page 36

Fragments : Don't Care
Pass or Block : Pass Immediately
Branch to Other Filter Set : None
Content Management : None
Log : Disable
> ipf set -v
Call Filter : Enable (Start Filter Set = 1)
Data Filter : Enable (Start Filter Set = 2)
Log Flag : None
Actions for packet not matching any rule:
Pass or Block : Pass
Content Management : None
Apply IP filter to VPN incoming packets : Disable
Accept large incoming fragmented UDP or ICMP packets : Enable
30
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 37

2.5.3 ipf flowtrack (for 2950 series only)
This command is used to set and view flowtrack sessions.
ipf flowtrack set [-r]
ipf flowtrack view [-f]
Syntax Description
-r It means to refresh the flowstate.
-f It means to show all sessions state of flowtrack.
Example
> ipf flowtrack set -r
Refresh the flowstate ok
> ipf flowtrack view -f
Start to show the flowtrack sessions state:
ORIGIN>> 192.168.1.10 : 4771 -> 207.46.3.2 : 80 ,ifno=0
REPLY >> 207.46.3.2 : 80 -> 172.16.3.229 :54357 ,ifno=3
proto=6, age=7532140(2620), flag=4033
End to show the flowtrack sessions state
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
31
Page 38

2.6 p2p
This command allows users to block Peer-to-Peer file-sharing applications.
p2p [-a | -d | -s | -b P2P_P | -p P2P_P | -t]
Syntax Description
-a It means to activate the Peer-to-Peer blocking system.
-d It means to deactivate the Peer-to-Peer blocking system.
-s It means to view the configuration of Peer-to-Peer blocking system.
-b It means to enable blocking function for a specific protocol.
-p It means to disable blocking function for a specific protocol.
-t It means to set the time schedule that P2P applications will be
blocked.
P2P_P It means to specifies one or more of the following P2P protocol(s)
eDonkey: protocol of eDonkey and eMule applications
Upload: restrict upload of eDonkey and eMule applications only
FastTrack: protocol of KazaA, iMesh and Grokster applications
Gnutella: protocol of BearShare, Gnucleus and Limewire
applications
BitTorrent: protocol of BitTorrent application
Example
> p2p -s
Peer-to-Peer Blocking system: Deactived
eDonkey protocol blocking status: Disable
FastTrack protocol blocking status: Disable
Gnutella protocol blocking status: Disable
BitTorrent protocol blocking status: Disable
Time schedule:
32
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 39
2.7 im
This command allows users to block IM (Instant Messenger) applications.
im [-a | -d | -s | -b IM_APP | -p IM_APP]
Syntax Description
-a It means to activate Instant Messenger blocking function.
-d It means to deactivate Instant Messenger blocking function.
-s It means to view the configuration of Instant Messenger blocking
function.
-b It means to enable blocking function for a specific application.
-p It means to disable blocking function for a specific application.
-t It means to set the time schedule that IM applications will be
blocked.
IM_APP It means to specify one or more of the following IM applications, i.e.,
MSN, Yahoo, ICQ.
Example
> im -s
Instant Messenger Blocking function: Deactived
MSN messenger blocking status: Disable
Yahoo Messenger blocking status: Disable
ICQ/AOL blocking status: Disable
Time schedule:
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
33
Page 40

2.8 csm (for 2910/2950 series)
This command allows you to set CSM profile to define policy profiles for different policy of
IM (Instant Messenger)/P2P (Peer to Peer) application.
csm -i INDEX [-v | -n NAME | -e AP | -d AP]
Syntax Description
INDEX It means to specify the index number of CSM profile, from 1 to 32.
- v It means to view the configuration of the CSM profile.
- n It means to set a name for the CSM profile.
NAME It means to specify a name for the CSM profile, less then 15
characters.
- e It means to enable the blocking for specific application.
- d It means to disable the blocking for specific application.
AP It means to specify one or more of the following CSM applications:
MSN: MSN
YM: Yahoo Messenger
ICQ: ICQ
AIM: AIM
QQ: QQ
iChat: iChat
GT: Google Talk
WIM: Web IM (http://www.e-messenger.net/)
WMSN: Web MSN (http://webmessenger.msn.com/)
jajah: jajah
Skype: Skype
SoulSeek: SoulSeek protocol
eDonkey: eDonkey protocol
FastTrack: FastTrack protocol
Gnutella: Gnutella protocol
BitTorrent: BitTorrent protocol
Example
> csm -i 1 -n downloadbad
The name of csm profile 1 was set.
> csm -i 1 -v
CSM Profile 1:
Profile name: downloadbad
Block MSN : Disable
Block Yahoo Messenger : Disable
Block ICQ : Disable
Block AIM : Disable
Block QQ : Disable
Block iChat : Disable
Block Google Talk : Disable
Block Web IM : Disable
34
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 41

Block Web MSN : Disable
Block jajah : Disable
Block Skype : Disable
Block SoulSeek protocol : Disable
Block eDonkey protocol : Disable
Block FastTrack protocol : Disable
Block Gnutella protocol : Disable
Block BitTorrent protocol : Disable
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
35
Page 42
2.9 ddos
This command allows users to configure the settings for DoS defense system.
ddos [-V | D | A]
ddos [-s ATTACK_F [THRESHOLD][ TIMEOUT]]
ddos [-a | e [ATTACK_F][ATTACK_0] | d [ATTACK_F][ATTACK_0]]
Syntax Description
-V It means to view the configuration of DoS defense system.
-D It means to deactivate the DoS defense system.
-A It means to activate the DoS defense system.
-s It means to enable the defense function for a specific attack and set
its parameter(s).
ATTACK_F It means to specify the name of flooding attack(s) or portscan, e.g.,
synflood, udpflood, icmpflood, or postscan.
THRESHOLD It means the packet rate (packet/second) that a flooding attack will
be detected. Set a value larger than 20.
TIMEOUT It means the time (seconds) that a flooding attack will be blocked.
Set a value larger than 5.
-a It means to enable the defense function for all attacks listed in
ATTACK_0.
-e It means to enable defense function for a specific attack(s).
ATTACK_0 It means to specify a name of the following attacks: ip_option,
tcp_flag, land, teardrop, smurf, pingofdeath, traceroute, icmp_frag,
syn_frag, unknow_proto, fraggle.
-d It means to disable the defense function for a specific attack(s).
Example
>ddos –A
The Dos Defense system is Activated
>ddos –s synflood 50 10
Synflood is enabled! Threshold=50 <pke/sec> timeout=10 <pke/sec>
36
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 43

2.10 urlf
2.10.1 urlf blist
This command allows users to set the URL access control.
urlf blist [noip]
urlf blist [on|off]
urlf blist [status]
urlf blist [INDEX –e |d [KEYWORD[SYMBOL KEYWORD]]
urlf blist [white | black]
Syntax Description
noip It means to prevent web access from the IP address.
on It means to activate the functionality of the URL access control.
off It means to deactivate the functionality of the URL access control.
status It means to show the current configuration of the URL access
control.
INDEX It means the number of the specific item (e.g., 1-8).
-e It means to enable the specific item with user’s configuration.
-d It means to disable the specific item for URL.
KEYWORD It means the blocking keyword(s). The maximum length is 32.
SYMBOL It means the space, comma or semicolon.
white It means to block all packets except the ones that match the keyword
in the list.
black It means to pass all packets except the ones that match the keyword
in the list.
Example
>urlf blist on
The functionality of the URL access control is activated!!
>urlf blist 1 –e news
The blocking keyword list valued with news and numbered with 1 has been enabled.
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
37
Page 44
2.10.2 urlf setdefault
This command will reset all the configuration data for the contenet filtering.
Example
>urlf setdefault
All configuration data of the content filtering function is reset!!
38
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 45
2.10.3 urlf esubnet
This command allows users to deal with the exempt subnets.
urlf esubnet [on|off]
urlf esubnet [status]
urlf esubnet [INDEX –e |d [IP_ADDRESS SUBNET_MASK]]
Syntax Description
on It means to activate the functionality of the exempt subnets.
off It means to deactivate the functionality of the exempt sunbnets.
status It means to show the current configuration of the exempt subnets.
INDEX It means the number of the specific item (e.g., 1-4).
-e It means to enable the specific item with the user’s configuration.
-d It means to disable the specific item.
Example
>urlf esubnet on
The functionality of the exceptional subnet is activated!!
>urlf esubnet 1 –e 192.168.1.55 255.255.255.0
The exceptional subnet list 192.168.1.55/255.255.255.0 and numbered with 1 has
been enabled
>urlf esubnet status
[V]Enable the functionality of the exceptional Subnets!!
1.[V]192.168.1.55/255.255.255.0
2.[ ]0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
3.[ ]0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
4.[ ]0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
39
Page 46
2.10.4 urlf webf
This command allows users to restrict the web filter features.
urlf webf [on|off]
urlf webf [status]
urlf webf [-e|d [java][zip][exe][mms][cookie][proxy]]
Syntax Description
on It means to activate the functionality of the restricted web features.
off It means to deactivate the functionality of the restricted web features.
status It means to show the current configuration of the restricted web
features.
-e It means to enable the specific item.
-d It means to disable the specific item.
Example
>urlf webf on
The functionality of restricted web features is activated!!
>urlf webf –e java mms
Java is enabled!
mms is enabled!
>urlf webf status
[V]Enable restrict web feature!!
[V]java [ ]activex [ ]zip [ ]exe [V]mms
[ ]cookie [ ] proxy
>
40
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 47

2.10.5 urlf tschedule
This command allows users to choose the call schedule for URL access control. You can
choose up to four sets of call schedule profiles.
urlf tschedule Schedule1[,Schedule2][, Schedule3][, Schedule4]
Syntax Description
Schedule1~4 It means the index of the profile for the call schedule setup (1-15).
You can set 4 schedules in this command from the 15 sets of call
schedules. Action/Idle Timeout settings in the Call Schedule setting
page will be ignored. Set “0” to clear current settings.
Example
>urlf tschedule 1
New URL Filter time schedule: 1
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
41
Page 48
2.11 isdn
2.11.1 isdn blknum
This command allows users to block MSN number.
isdn blknum add [index][BlockNumber]
isdn blknum del [index]
isdn blknum status
Syntax Description
add It means to add one MSN number for block.
del It means to delete one existing MSN block number.
index It means item number (from 0 to 4) of MSN number.
blockNumber It means the specified MSN number which is not allowed to be
dialed out by the router.
Status It means to show the setting of blocked ISDN MSN number.
Example
>isdn blknum add 0 10
42
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 49

2.11.2 isdn dial
This command allows users to specify the ISP name if you want to access the Internet via a
single ISP connection.
isdn dial [Dest Name]
Syntax Description
Dest Name It means the ISP name that you want to dial through ISDN
connection.
Example
>isdn dial prima
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
43
Page 50

2.11.3 isdn drop
This command allows users to cut off the ISDN connection (B1/B2).
isdn drop [B1 or B2]
Syntax Description
B1 or B2 It means channel B1 (first channel) and B2 (second channel).
Example
>isdn drop B1
2.11.4 isdn vci
This command allows users to specify remote ISDN number as ISDN voice call. For example,
isdn vci 10 represents to dial ISDN number by using “10” .
isdn vci <dial number>
Syntax Description
dial number It means the remote ISDN phone number.
Example
> isdn vci 20
2.11.5 isdn overlap
This command allows users to make an ISDN voice call with overlap sending or en-bloc
sending.
isdn overlap [on/off]
isdn overlap [status]
Syntax Description
on It means to turn on the ISDN Overlap sending. The ISDN phone
number will be sent out digit by digit.
off It means to turn off the ISDN Overlap sending. The ISDN phone
number will be sent out after collecting all the digits completely.
(En-bloc Sending).
status It means to show the status of ISDN overlap sending.
Example
>isdn overlap on
% Overlap sending ON.
44
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 51

2.12 log
This command allows users to view log for WAN, ISDN interface such as call log, IP filter log,
flush log buffer, etc.
log [-cfhiptwx?] [-F a| c | f | w]
Syntax Description
-c It means to show the latest call log.
-f It means to show the IP filter log.
-F It means to show the flush log buffer.
a: flush all logs
c: flush the call log
f: flush the IP filter log
s: flush the IP state log
w: flush the WAN(ISDN and PPP) log
-h It means to show this usage help.
-i It means to show all the exchange message on ISDN interface.
-p It means to show PPP/MP log.
-t It means to show all logs saved in the log buffer.
-w It means to show WAN (ISDN and PPP) log.
-x It means to show packet body hex dump.
Example
>log –w
0:12:23.690---- >DHCP Len=300 Release XID = 0x5261da
Client IP =10.0.0.211
Your IP = 0.0.0.0
Next server IP = 0.0.0.0
Relay agent IP = 0.0.0.0
Option 53: Message Type = 7
Option 61: Client Identifier = 01 00 50 7f 31 9d 70
Option 54: Server Identifier = 10.0.0.2
0:12:24.920---- >DHCP Len=300 Release XID = 0x80a6f950
………………
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
45
Page 52

2.13 quit
This command can exit the telnet command screen.
46
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 53

2.14 srv
2.14.1 srv dhcp
This command allows users to set relational settings for DHCP server.
2.14.1.1 srv dhcp fixip
srv dhcp fixip add [IP Addr][MAC Addr XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX][Host ID]
srv dhcp fixip clr
srv dhcp fixip del [IP Addr]
Syntax Description
add It means to add a new specified dhcp client.
IP Addr It means the IP address of the specified client.
MAC Addr It means the MAC address of the specified client.
Host ID It means to specify the ID name of local host.
clr It means to clear all the fixed IP addresses.
del [IP Addr] It means to delete the specified IP address.
Example
> srv dhcp fixip add 192.168.1.56 22-33-44-55-66-77
> srv dhcp fixip clr
> srv dhcp fixip add 192.168.1.68 33-44-55-66-77-88
> srv dhcp fixip del 192.168.1.68
2.14.1.2 srv dhcp gateway
This command allows users to specify gateway address for DHCP server.
srv dhcp gateway [?]
srv dhcp gateway [Gateway]
Syntax Description
? It means to display current gateway that you can use.
Gateway It means to specify a gateway address used for DHCP server.
Example
> srv dhcp gateway 192.168.1.1
This function need rebooting router, please type "sys reboot" command to reboot
router.
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
47
Page 54

2.14.1.3 srv dhcp ipcnt
This command allows users to specify IP counts for DHCP server.
srv dhcp ipcnt [?]
srv dhcp ipcnt [IP counts]
Syntax Description
? It means to display current used IP count number.
IP counts It means the number that you have to specify for the DHCP server.
Example
> srv dhcp ipcnt 50
This function need rebooting router, please type "sys reboot" command to reboot
router.
2.14.1.4 srv dhcp off
This function allows users to turn off DHCP server. It needs rebooting router, please type "sys
reboot" command to reboot router.
2.16.1.5 srv dhcp on
This function allows users to turn on DHCP server. It needs rebooting router, please type "sys
reboot" command to reboot router.
2.16.1.6 srv dhcp startip
srv dhcp startip [?]
srv dhcp startip [IP address]
Syntax Description
? It means to display current used start IP address.
IP address It means the IP address that you can specify for the DHCP server as
the starting point.
Example
> srv dhcp startip 192.168.1.53
This function need rebooting router, please type "sys reboot" command to reboot
router.
2.14.1.7 srv dhcp status
This command can display general information for the DHCP server, such as IP address, MAC
address, leased time, host ID and so on.
Example
> srv dhcp status
48
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 55

DHCP server: Running
Default gateway: 192.168.1.1
Index IP Address MAC Address Leased Time HOST ID
1 192.168.1.1 00-50-7F-00-00-00 ROUTER IP
2 192.168.1.10 00-0E-A6-2A-D5-A1 4:09:33.300 ok-lccgjyiy075u
2.14.1.8 srv dhcp leasetime
This command can set the lease time for the DHCP server.
srv dhcp leasetime [?]
srv dhcp leasetime [Lease Time (sec)]
Syntax Description
? It means to display current leasetime used for the DHCP server.
Lease Time (sec) It means the lease time that DHCP server can use. The unit is
second.
Example
> srv dhcp leasetime ?
% srv dhcp leasetime <Lease Time (sec.)>
% Now: 259200
> srv dhcp leasetime 25900
2.14.1.9 srv dhcp frcdnsmanl
This command can force the router to invoke DNS Server IP address.
srv dhcp frcdnsmanl [on]
srv dhcp frcdnsmanl [off]
Syntax Description
? It means to display the current status.
on It means to use manual setting for DNS setting.
Off It means to use auto settings acquired from ISP.
Example
> srv dhcp frcdnsmanl on
% Domain name server now is using manual settings!
> srv dhcp frcdnsmanl off
% Domain name server now is using auto settings!
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
49
Page 56

2.14.1.10 srv dhcp dns1
This command allows users to set primary DNS setting.
srv dhcp dns1 [?]
srv dhcp dns1 [DNS IP address]
Syntax Description
? It means to display current IP address of DNS 1 for the DHCP
server.
DNS IP address It means the IP address that you want to use as DNS1.
Example
> srv dhcp dns1 168.95.1.1
>
2.14.1.11 srv dhcp dns2
This command allows users to set secondary DNS setting.
srv dhcp dns2 [?]
srv dhcp dns2 [DNS IP address]
Syntax Description
? It means to display current IP address of DNS 2 for the DHCP
server.
DNS IP address It means the IP address that you want to use as DNS2.
Example
> srv dhcp dns2 168.95.1.10
>
2.14.1.12 srv dhcp relay
This command allows users to set DHCP relay setting.
srv dhcp relay servip [server ip]
srv dhcp relay subnet [index]
Syntax Description
server ip It means the IP address that you want to used as DHCP server.
Index It means subnet 1 or 2. Please type 1 or 2. The router will invoke this
function according to the subnet 1 or 2 specified here.
Example
> srv dhcp relay servip 192.168.1.46
> srv dhcp relay subnet 2
>
50
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 57

2.14.1.14 srv dhcp public
This command allows users to configure DHCP server for second subnet.
srv dhcp public start [IP address]
srv dhcp public cnt [IP counts]
srv dhcp public status
srv dhcp public add [MAC Addr XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX]
srv dhcp public del [MAC Addr XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX/all/ALL]
Syntax Description
start It means the starting point of the IP address pool for the DHCP
server.
IP address It means to specify an IP address as the starting point in the IP
address pool.
cnt It means the IP count number.
IP counts It means to specify the number of IP addresses in the pool. The
maximum is 10.
status It means the execution result of this command.
add It means creating a list of hosts to be assigned.
MAC Addr It means to specify MAC Address of the host.
del It means removing the selected MAC address.
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
51
Page 58

2.14.2 srv nat
2.14.2.1 srv nat dmz
This command allows users to set DMZ host. Before using this command, please set WAN IP
Alias first.
srv nat dmz mapping [Index][Private IP address]
srv nat dmz remove [Index]
Syntax Description
mapping It means to map selected WAN IP to certain host.
Index It means the number of the DMZ host.
Default setting is “1” (WAN 1). It is only available for Static IP
mode. If you use other mode, you can set 2 ~ 8 in this field.
Private IP address It means to specify the private IP address of the DMZ host.
remove It means removing DMZ host setting.
Example
> srv nat dmz mapping 1 192.168.1.66
>
2.14.2.2 srv nat openport
This command allows users to set open port settings for NAT server.
srv nat openport list
srv nat openport enable [index]
srv nat openport disable [index]
srv nat openport comment [index][Comment]
srv nat openport dstip [index][Destination local IP address]
srv nat openport add [Profile index][Subitem index] [WAN IP addr][Pvt IP
addr][Protocol][Start port][End port]
srv nat openport remove [Profile index] [Subitem index]
srv nat openport flush
Syntax Description
list It means a detailed list for open port settings.
enable [index] It means to activate the specified entry of open port settings.
disable [index] It means to inactivate the specified entry of open port settings.
comment [index] It means the entry number of the comment.
Comment It means to type the description for the defined network service.
dstip [index] It means to choose a index number for the destination.
52
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 59

[Destination local IP address] It means to type the destination IP address.
add It means creating a new open port setting.
Profile index It means to specify the number for this profile. The range is from 1
to 10.
Subitem index It means to specify the subitem number for this profile. The range is
from 1 to 10.
WAN IP addr It means to specify the public IP address for this profile.
Pvt IP addr It means to specify the private IP address of local computer.
protocol It means to specify TCP or UDP as the protocol.
start port It means to specify the starting port number of the service offered by
the local host.
endt port It means to specify the ending port number of the service offered by
the local host.
remove It means deleting the specified open port setting.
Profile index It means to specify the entry number of the profile.
subitem index It means to specify the entry number of subitem.
flush It means to clear all the open port settings.
Example
> srv nat openport flush
Ok.
>
2.14.2.3 srv nat portmap
This command allows users to set port redirection table for NAT server.
srv nat portmap add [idx][serv name][proto][pub port][pri ip][pri port]
srv nat portmap del [idx]
srv nat portmap disable [idx]
srv nat portmap enable [idx] [proto]
srv nat portmap flush
srv nat portmap table
Syntax Description
Add[idx] It means to add a new port redirection table with an index number.
Available index number is from 1 to 10.
serv name It means to type one name as service name.
proto It means to specify TCP or UDP as the protocol.
pub port It means to specify which port can be redirected to the specified
Private IP and Port of the internal host
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
53
Page 60
pri ip It means to specify the private IP address of the internal host
providing the service.
pri port It means to specify the private port number of the service offered by
the internal host.
del [idx] It means to remove the selected port redirection setting.
disable [idx] It means to inactivate the selected port redirection setting.
enable [idx] It means to activate the port mapping settings of the specified
flush It means to clear all the port mapping settings.
table It means to display NAT Port Redirection Configuration Table:
Example
> srv nat portmap add 1 game tcp 80 192.168.1.11 100
>> srv nat portmap table
NAT Port Redirection Configuration Table:
Index Service Name Protocol Public Port Private IP Private Port
1 game 6 80 192.168.1.11 100
2 0 0 0
3 0 0 0
4 0 0 0
5 0 0 0
6 0 0 0
7 0 0 0
8 0 0 0
9 0 0 0
10 0 0 0
Protocol: 0 = Disable, 6 = TCP, 17 = UDP
2.14.2.4 srv nat status
This command allows users to view NAT Port Redirection Running Table.
54
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 61
2.14.3 srv vta
This command allows users to turn upon or off the virtual TA.
isdn vat [on/off]
isdn vta [status]
Syntax Description
on It means the turn on virtual TA.
off It means to turn off virtual TA.
status It means to show current status of virtual TA.
Example
> srv vta on
>
> srv vta off
>
> srv vta status
% Remote CAPI server: Stop
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
55
Page 62

2.15 show
2.15.1 show lan1
This command displays current status of LAN1 settings.
Example
> show lan1
%% 1st subnet settings:
%% IP address: 192.168.1.1
%% Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
%% RIP : [Disable]
2.15.2 show lan2
This command displays current status of LAN2 settings.
Example
> show lan2
%% 2nd subnet settings:
%% Status: [Inactive]
%% IP address: 192.168.2.1
%% Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
%% RIP : [Disable]
2.15.3 show dhcp
This command displays current status of DHCP server.
Example
> show dhcp
%% DHCP settings:
%% Status: [Active]
%% Start IP address for offering: 192.168.1.10
%% Maximus offer IP address count: 50
%% Default gateway: 192.168.1.1
%% DHCP Relay: [Inactive]
2.15.4 show dmz
This command displays current status of DMZ host.
Example
> show dmz
%% DMZ mapping status:
Index Status WAN aux IP Private IP
------------------------------------------- 1 Disable 172.16.3.229
56
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 63

2.15.5 show dns
This command displays current status of DNS setting
Example
> show dns
%% Domain name server settings:
% Primary DNS: [Not set]
% Secondary DNS: [Not set]
2.15.6 show openport
This command displays current status of open port setting.
Example
> show openport
%% Openport settings:
Index Status Comment Local IP Address
********************************************************
No data entry.
2.15.7 show nat
This command displays current status of NAT.
Example
> show nat
NAT Port Redirection Running Table:
Index Protocol Public Port Private IP Private Port
1 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
2 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
3 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
4 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
5 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
6 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
7 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
8 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
9 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
10 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
11 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
12 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
13 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
14 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
15 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
16 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
17 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
18 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
19 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
20 0 0 0.0.0.0 0
--- MORE --- ['q': Quit, 'Enter': New Lines, 'Space Bar': Next Page] ---
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
57
Page 64

2.15.8 show session
This command displays current status of current session.
Example
> show session
% Maximum Session Number: 10000
% Maximum Session Usage: 1
% Current Session Usage: 1
2.15.9 show adsl
This command displays current status of ADSL.
Example
> show adsl
--------------------------- ATU-R Info (hw: annex B, f/w: annex B) ---------- Running Mode : T1.413 State : READY
DS Actual Rate : 0 bps US Actual Rate : 0 bps
DS Path Mode : Fast US Path Mode : Fast
NE Current Attenuation : 0 dB Cur SNR Margin : 0 dB
ADSL Firmware Version : 131812_B
-------------------------------- ATU-C Info -------------------------------- Far Current Attenuation: 0 dB Far SNR Margin : 0 dB
CO ITU Version[0] : 00000000 CO ITU Version[1] : 00000000
DSLAM CHIPSET VENDOR : < Alcatel >
>
58
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 65

2.16 mngt
2.16.1 mngt ftpport
This command allows users to set FTP port for management.
mngt ftpport [?]
mngt ftpport [FTP port]
Syntax Description
? It can display current FTP port number setting.
FTP port It means to type the number for FTP port. The default setting is 21.
Example
> mngt ftpport 21
% Set FTP server port to 21 done.
2.16.2 mngt httpport
This command allows users to set HTTP port for management.
mngt httpport [?]
mngt httpport [Http port]
Syntax Description
? It can display current HTTP port number setting.
Http port It means to enter the number for HTTP port. The default setting is
80.
Example
> mngt httpport 80
% Set web server port to 80 done.
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
59
Page 66
2.16.3 mngt httpsport
This command allows users to set HTTPS port for management.
mngt httpsport [?]
mngt httpsport [Https port]
Syntax Description
? It can display current HTTPS port number setting.
Https port It means to type the number for HTTPS port. The default setting is
443.
Example
> mngt httpsport 443
% Set web server port to 443 done.
2.16.4 mngt telnetport
This command allows users to set telnet port for management.
mngt telnetport [?]
mngt telnetport [Telnet port]
Syntax Description
? It can display current telnet port number setting.
Telnet port It means to type the number for telnet port. The default setting is 23.
Example
> mngt telnetport 23
% Set Telnet server port to 23 done.
60
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 67

2.16.5 mngt ftpserver
This command can enable/disable FTP server.
mngt ftpserver [?]
mngt ftpserver [Enable]
mngt ftpserver [Disable]
Syntax Description
? It can display current status of FTP server.
Enable It means to activate FTP server function.
Disable It means to inactivate FTP server function.
Example
> mngt ftpserver enable
%% FTP server has been enabled.
> mngt ftpserver disable
%% FTP server has been disabled.
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
61
Page 68

2.16.6 mngt noping
This command allows users to reject or accept PING packets from the Internet.
mngt noping [on]
mngt noping [off]
mngt noping [viewlog]
mngt noping [clearlog]
Syntax Description
on It means to reject all PING packets from the Internet.
off It means to accept all PING packets from the Internet.
viewlog It means to display a log of ping action, including source MAC and
source IP.
clearlog It means to remove the log of ping action.
Example
> mngt noping off
No Ping Packet Out is OFF!!
62
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 69

2.16.7 mngt defenseworm
This command can block specified port for passing through the router.
mngt defenseworm [?]
mngt defenseworm [on]
mngt defenseworm [off]
mngt defenseworm [add port]
mngt defenseworm [del port]
mngt defenseworm [viewlog]
mngt defenseworm [clearlog]
Syntax Description
? It means to display current status. The default setting for Block TCP
port includes 135, 137, 138, 139 and 445.
on It means to activate the function of defense worm packet out.
off It means to inactivate the function of defense worm packet out.
add port It means to add a new TCP port for block.
del port It means to delete a TCP port for block.
viewlog It means to display current log of
clearlog It means the
viewlog It means to display a log of defense worm packet, including source
MAC and source IP.
clearlog It means to remvoe the log of defense worm packet.
Example
> mngt defenseworm add 21
Add TCP port 21
Block TCP port list: 135, 137, 138, 139, 445, 21
> mngt defenseworm del 21
Delete TCP port 21
Block TCP port list: 135, 137, 138, 139, 445
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
63
Page 70
2.16.8 mngt rmtcfg
This command can allow the system administrators to login from the Internet. By default, it is not
allowed.
mngt rmtcfg [?]
mngt rmtcfg [Enable]
mngt rmtcfg [Disable]
Syntax Description
? It can display current setting for your reference.
Enable It means to allow the system administrators to login from the Internet.
Disable It means to deny the system administrators to login from the Internet.
Example
> mngt rmtcfg enable
%% Remote configure function has been enabled.
64
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 71
2.16.9 mngt echoicmp
This command allows users to activate/inactivate echo ICMP packet function.
mngt echoicmp [?]
mngt echoicmp [Enable]
mngt echoicmp [Disable]
Syntax Description
? It can display current setting for your reference.
Enable It means to activate the function of echo ICMP packet.
Disable It means to inactivate the function of echo ICMP packet.
Example
> > mngt echoicmp enable
%% Echo ICMP packet enabled.
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
65
Page 72

2.16.10 mngt accesslist
This command allows you to specify that the system administrator can login from a specific
host or network. A maximum of three IPs/subnet masks is allowed.
mngt accesslist list
mngt accesslist add [index][ip addr][mask]
mngt accesslist remove [index]
mngt accesslist flush
Syntax Description
list It can display current setting for your reference.
add It means adding a new entry.
index It means to specify the number of the entry.
ip addr It means to specify an IP address.
mask It means to specify the subnet mask for the IP address.
remove It means to delete the selected item.
flush It means to remove all the settings in the access list.
Example
> mngt accesslist add 1 192.168.1.89 255.255.255.0
%% Set OK.
66
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 73

2.17 sys
2.17.1 sys admin
This command allows users to add a name for administrator.
sys admin [?]
sys admin [ASCII string]
Syntax Description
? It means to display current name of administrator.
ASCII string It means the name specified for the administrator, maximum 23
characters.
Example
> sys admin BBQ
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
67
Page 74

2.17.2 sys cfg
This command reset the router with factory default settings. When a user types this command,
all the configuration will be reset to default setting.
sys cfg default
sys cfg status
Syntax Description
default It means to reset current settings with default values.
status It means to display current profile version and status.
Example
> sys cfg status
Profile version: 0x2 Status: 1 (0x273cb001)
> sys cfg default
68
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 75

2.17.3 sys cmdlog
This command displays the history of the commands that you have typed.
Example
> >> sys cmdlog
% Commands Log: (The lowest index is the newest !!!)
[1] sys cmdlog
[2] sys ?
[3] sys version
[4] sys tftpd off
[5] sys tftpd ?
[6] sys tftpd
[7] sys tftpd on
[8] sys passwd ?
[9] sys name
[10] sys name >
[11] sys name clear
[12] sys name clear clear
[13] sys name ?
[14] sys name
[15] sys name
[16] sys name clear
[17] sys name routera
[18] sys name router a
[19] sys name ?
[20] sys iface
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
69
Page 76
2.17.4 sys ftpd
This command displays current status of FTP server.
sys cfg on
sys cfg off
Syntax Description
on It means to turn on the FTP server of the system.
off It means to turn off the FTP server of the system.
Example
> sys ftpd on
% sys ftpd turn on !!!
70
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 77

2.17.5 sys domainname
This command can set and remove the domain name of the system.
sys domainname[Domain Name Suffix]
Syntax Description
Domain Name Suffix It means the name for the domain of the system. The maximum
character that you can set is 40.
clear It means to remove the domain name of the system.
Example
> sys domainname clever
> sys domainname ?
% sys domainname <Domain Name Suffix (max. 40 characters)>
% sys domainname clear
% Now: clever
> sys domainname clear
>
> sys domainname ?
% sys domainname <Domain Name Suffix (max. 40 characters)>
% sys domainname clear
% Now:
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
71
Page 78

2.17.6 sys iface
This command displays the current interface connection status (UP or Down) with IP address,
MAC address and Netmask for the router.
Example
> sys iface
Interface 0 Ethernet:
Status: UP
IP Address: 192.168.1.1 Netmask: 0xFFFFFF00 (Private)
IP Address: 0.0.0.0 Netmask: 0xFFFFFFFF
MAC: 00-50-7F-D5-D4-40
Interface 3 PPPoE:
Status: UP
IP Address: --- Netmask: 0xFFFFFFFF
MAC: 00-50-7F-D5-D4-41
>
72
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 79

2.17.7 sys name
This command can set and remove the name for the router.
sys name [ASCII string]
Syntax Description
ASCII It means the name for router. The maximum character that you can
set is 20.
Example
> sys name >
>>
Note: Such name can be used to recognize router’s identification in SysLog dialog.
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
73
Page 80

2.17.8 sys passwd
This command allows users to set password for the administrator.
sys passwd [ASCII string]
Syntax Description
ASCII string It means the password for administrator. The maximum character
that you can set is 23.
Example
> sys passwd 1234
>
74
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 81
2.17.9 sys reboot
This command allows users to restart the router.
Example
> sys reboot
>
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
75
Page 82

2.17.10 sys commit
This command allows users to save current settings to FLASH. Usually, current settings will be
saved in SRAM. Yet, this command will save the file to FLASH.
Example
> sys commit
>
76
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 83
2.17.11 sys tftpd
This command can turn on TFTP server.
Example
> sys tftpd on
% TFTP server enabled !!!
2.17.12 sys cc
This command can display current code and wireless region of this device.
Example
> sys cc
Country Code : 0x 0 [International]
Wireless Region Code: 0x30
>
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
77
Page 84

2.17.13 sys version
This command can display current version for the system.
Example
> sys version
Router Model: XXXXX series Version: 2.7_RC13_Y01 English
Profile version: 0x2 Status: 1 (0x189a82e1)
Router IP: 192.168.1.1 Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Firmware Build Date/Time: Tue Jun 6 15:1:54.84 2006
Revision: 2426 v2.6
ADSL Firmware Version: Y.1.28.187 Annex A
78
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 85

2.17.14 sys qrybuf
This command can display the system memory status and leakage list.
Example
> sys qrybuf
System Memory Status and Leakage List
# of free L-Buffer=128, minimum=126, leak num:0
# of free M-Buffer=32, minimum=32, leak num:0
# of free Nc-Buffer=42, minimum=17
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
79
Page 86

2.17.15 sys pollbuf
This command can turn on or turn off polling buffer for the router.
sys pollbuf [on]
sys pollbuf [off]
Syntax Description
On It means to turn on pulling buffer.
Off It means to turn off pulling buffer.
Example
> sys pollbuf on
% Buffer polling is on!
> sys pollbuf off
% Buffer polling is off!
80
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 87
2.17.16 sys sip_alg
This command can turn on/off SIP ALG (Application Layer Gateway) for NAT traversal.
sys sip_alg [1]
sys sip_alg [0]
Syntax Description
1 It means to turn on SIP ALG.
0 It means to turn off SIP ALG.
Example
> sys sip_alg ?
usage: sys sip_alg [value]
0 - disable SIP ALG
1 - enable SIP ALG
current SIP ALG is disabled
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
81
Page 88

2.18 register
This command allows users to register to VigorView. It is only available for VigorView user.
register ems <server> [key]
Syntax Description
server It means VigorView server URL.
key It means the key of authentication for VigorView access.
Example
> register 172.176.2.220 1234
82
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 89

2.19 vpn
2.19.1 vpn l2lset
This command allows users to set advanced parameters for LAN to LAN function.
vpn l2lset [list index] peerid [peerid]
vpn l2lset [list index] localid [localid]
vpn l2lset [list index]main [auto/proposal index]
vpn l2lset [list index] aggressive [g1/g2]
vpn l2lset [list index]pfs [on/off]
vpn l2lset [list index] phase1[lifetime]
vpn l2lset [list index] phase2[lifetime]
Syntax Description
list index It means the index number of L2L profile.
peerid It means the peer identity for aggressive mode.
localid It means the local identity for aggressive mode.
main It means to choose proposal for main mode.
auto index It means to choose default proposals.
proposal index It means to choose specified proposal.
aggressive It means the chosen DH group for aggressive mode.
pfs It means “perfect forward secresy”.
on/off It means to turn on or off the PFS function.
phase1 It means phase 1 of IKE.
lifetime It means the lifetime value (in second) for phase 1 and phase 2.
phase2 It means phase 2 of IKE.
Example
> VPN l2lset 1 peerid 10226
>
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
83
Page 90

2.19.2 vpn 2ndsubnet
This command allows users to enable 2ndsubnet IP as VPN server ID.
vpn 2ndsubnet on
vpn 2ndsubnet off
Syntax Description
on/off It means to enable or disable second subnet.
Example
> vpn 2ndsubnet on
%Enable second subnet IP as VPN server IP!
84
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 91
2.20 wan
2.20.1 wan ppp_ipcp_vso
This command allows users to enable or disable PPP IPCP VSO (Vendor Specific Option)
function. It is used for specific network.
wan ppp_ipcp_vso [on]
wan ppp_ipcp_vso [off]
wan ppp_ipcp_vso [default]
Syntax Description
on/off It means to enable or disable PPP IPCP VSO.
default It means to recover to the default setting.
Example
> wan ppp_ipcp_vso default
>
2.20.2 ppp_mru
This command allows users to adjust the size of PPP LCP MRU. It is used for specific network.
wan ppp_mru [value]
Syntax Description
value It means the number of PPP LCP MRU. The available range is from
1400 to 1600.
Example
> wan ppp_mru 1450
wan ppp_mru ?
>
% wan ppp_mru <MRU size: 1400 ~ 1600>
% Now: 1450
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
85
Page 92

2.20.3 wan ppp_mss
This command allows you to adjust the parameters for TCP protocol, MSS (maximum section
size) for WAN side. The more the size is, the more the packets of payload will be.
wan ppp_mss [MSS size]
Syntax Description
MSS size It means to set suitable size for MSS. The available range for this
setting is 1000 to 1500.
Example
> wan ppp_mss 1442
2.20.4 wan DF_check
This command allows you to enable or disable the function of DF (Don’t fragment)
wan DF_check [on]
wan DF_check [off]
Syntax Description
on/off It means to enable or disable DF.
Example
> wan DF_check on
%DF bit check enable!
2.20.5 wan disable
This command allows you to disable wan connection.
Example
> wan disable
%WAN diabled.
86
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 93

2.21 adsl
2.21.1 adsl txpct
This command allows users to set the percentage of the transmission rate.
adsl txpct [auto]
adsl txpct [percent]
Syntax Description
auto It means to determine the transmission rate by the router
automatically.
percent It means to specify the percentage of the transmission rate. The
range is 10 ~ 100.
Example
>adsl txpct 70
tx percentage : 70
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
87
Page 94

2.21.2 adsl rxpct
This command allows users to set the percentage of the data receiving rate.
adsl rxpct [auto]
adsl rxpct [percent]
Syntax Description
auto It means to determine the transmission rate by the router
automatically.
percent It means to specify the percentage of the transmission rate. The
range is 10 ~ 100.
Example
>adsl rxpct 80
rx percentage : 70
88
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 95

2.21.3 adsl status
This command can display the link status of the ADSL router and the basic information
between router and CO.
Example
>adsl status
--------------------------- ATU-R Info (annex A) --------------------------- Running Mode : T1.413 State : HANDSHAKE
DS Actual Rate : 0 bps US Actual Rate : 0 bps
DS maximum Rate : 0 bps US maximum Rate : 0 bps
DS Path Mode : Interleave US Path Mode : Interleave
NE Current Attenuation : 0.0 dB Cur SNR Margin : 0.0 dB
DS actual PSDM(C) : 00000000 US actual PSDM(R) : 00000000
ADSL Firmware Version : E.38.2.23
-------------------------------- ATU-C Info -------------------------------- Far Current Attenuation : 0.0 dB Far SNR Margin : 0.0 dB
CO ITU Version[0] : 00000000 CO ITU Version[1] : 00000000
DSLAM CHIPSET VENDOR : < Unknown >
---------------------------------------------------------------------------- INTL, DSTREAM bytes/depth= 0, symbols/codewords = 0, latency= 0*0.25ms.
, USTREAM bytes/depth= 0, symbols/codewords = 0, latency= 0*0.25ms.
CODE, DSTREAM fast parity bytes= 0, fast codeword= 0.
DSTREAM intl parity bytes= 0, intl codeword= 0.
CODE, USTREAM fast parity bytes= 0, fast codeword= 0.
USTREAM intl parity bytes= 0, intl codeword= 0.
Setting>>
FDQ : Enable, TCM : Enable, EC : Disable, Framing Mode : 3.
Running>>
FDQ : Off, TCM : Off, EC : Off.
DS : Framing Mode 3, US : Framing Mode 3.
ADI ADSL Firmware Version: E.38.2.23
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
89
Page 96

2.21.4 adsl ppp
This command can set the Internet Access mode for the router.
adsl ppp [ ? | pvc_no vci vpi Encap Proto modu acqIP idle [Username Password]
Syntax Description
pvc_no It means pvc number and must be between 0(Channel 1) to
7(Channel 8).
Encap 0 : VC_MUX,
1: LLC/SNAP,
2: LLC_Bridge,
3: LLC_Route,
4: VCMUX_Bridge,
5: VCMUX_Route.
Proto It means the protocol used to connect Internet.
0: PPPoA; 1: PPPoE; 2: MPoA.
Modu 0: T1.413, 1: G.Lite, 2: G.dmt, 4: Multi, 5: ADSL2, 8:ADSL2+.
acqIP It means the way to acquire IP address.
0 : fix_ip, 1: dhcp_client/PPPoE/PPPoA (acquire IP method)
idle -1: always on, else idle timeout. This parameter is used only for
PPPoE/PPPoA.
Username This parameter is used only for PPPoE/PPPoA.
Password This parameter is used only for PPPoE/PPPoA.
Reboot the system when you set it on Route mode.
Example
> adsl ppp o 35 8 1 1 4 1 -1 draytek draytek
pvc no.=0
vci=35
vpi=8
encap=LLC(1)
proto=PPPoE(1)
modu=MULTI(4)
AcquireIP: Dhcp_client(1)
Idle timeout:-1
Username=draytek
Password=draytek
90
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 97

2.21.5 adsl bridge (for 2700 series)
This command can specify a LAN port for mapping to certain PVC, and the mapping port/PVC
will be operated in bridge mode.
adsl bridge [pvc_no/status] [on/off/clear] [px ... ]
Syntax Description
pvc_no It means pvc number and must be between 0(Channel 1) to
7(Channel 8).
status It means to shown the whole bridge status.
on/off It means to turn on/off bridge mode for the specific channel.
clear It means to turn off all the PVC settings.
px It means the number of LAN port (x=2~4). Port 1 is locked for NAT.
Example
support pure bridge mode in PVC y and map it to lan port x (x=2~4).
status : show whole bridge status.
pvc_no : pvc number and it must be between 4(Channel-5) to 7(Channel-8)
on/off : turn on/off bridge mode for the specific channel.
clear : turn off and clear ports.
ex: adsl bridge 4 on p2 p3 p4
PVC 4 will map to lan port 2/3/4 in bridge mode.
> adsl bridge 4 on p2 p3
PVC Bridge p1 p2 p3 p4
--------------------------------- 4 ON 0 1 1 0
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
91
Page 98

2.21.6 adsl idle
This command can make the router accessing into the idle status. If you want to invoke the
router again, you have to reboot the router by using “reboot” command.
Example
> adsl idle
%Idle Mode!
You has to use {adsl reboot} to restart booting.
2.21.7 adsl reboot
This command can wake up the idle router.
Example
> adsl reboot
% Adsl is Rebooting...
92
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
Page 99

2.21.8 adsl oamlb
This command is used to test if the connection between CPE and CO is OK or not.
adsl oamlb [n][type]
Syntax Description
n It means the total number of transmitted packets.
type It means the protocol that you can use.
1 – for F4 Seg-to-Seg (VP level)
2 – for F4 End-to-End (VP level)
4 – for F5 Seg-to-Seg (VC level)
5 – for F5 End-to-End (VC level)
Example
>adsl oamlb 10 2
Tx cnt=10
Rx Cnt=10
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
93
Page 100

2.21.9 adsl vcilimit
This command can cancel the limit for vci value.
Some ISP might set the vci value under 32. In such case, we can cancel such limit manually by
using this command. Do not set the number greater than 254.
Example
> adsl vcilimit 33
change VCI limitation from 32 to 33.
94
Telnet Command Reference Guide V1.1
 Loading...
Loading...