Page 1

Page 2

VigorSwitch P2280
24 Ports + 4 Combo UTP/SFP Ports
PoE L2 Managed Gigabit Switch
User’s Guide
Version: 1.0
Firmware Version: V2.2.1
(For future update, please visit DrayTek web site)
Date: March 6, 2018
ii
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 3

Copyrights
© All rights reserved. This publication contains information that is protected by copyright. No part may be
reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language without
written permission from the copyright holders.
Trademarks
The following trademarks are used in this document:
Microsoft is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corp.
Windows, Windows 95, 98, Me, NT, 2000, XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10 and Explorer are trademarks of Microsoft Corp.
Apple and Mac OS are registered trademarks of Apple Inc.
Other products may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective manufacturers.
Caution
Circuit devices are sensitive to static electricity, which can damage their delicate electronics. Dry weather
conditions or walking across a carpeted floor may cause you to acquire a static electrical charge.
To protect your device, always:
Touch the metal chassis of your computer to ground the static electrical charge before you pick up the circuit
device.
Pick up the device by holding it on the left and right edges only.
Warranty
We warrant to the original end user (purchaser) that the device will be free from any defects in workmanship or
materials for a period of one (1) year from the date of purchase from the dealer. Please keep your purchase
receipt in a safe place as it serves as proof of date of purchase. During the warranty period, and upon proof of
purchase, should the product have indications of failure due to faulty workmanship and/or materials, we will, at
our discretion, repair or replace the defective products or components, without charge for either parts or labor,
to whatever extent we deem necessary tore-store the product to proper operating condition. Any replacement
will consist of a new or re-manufactured functionally equivalent product of equal value, and will be offered solely
at our discretion. This warranty will not apply if the product is modified, misused, tampered with, da maged by an
act of God, or subjected to abnormal working conditions. The warranty does not cover the bundled or licensed
software of other vendors. Defects which do not significantly affect the usability of the product will not be
covered by the warranty. We reserve the right to revise the manual and online documentation and to make
changes from time to time in the contents hereof without obligation to notify any person of such revision or
changes.
Be a Registered Owner
Web registration is preferred. You can register your Vigor router via http://www.DrayTek.com.
Firmware & Tools Updates
Due to the continuous evolution of DrayTek technology, all routers will be regularly upgraded. Please consult the
DrayTek web site for more information on newest firmware, tools and documents.
More update, please visit www.draytek.com.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
iii
Page 4

v
TTaabbllee ooff CCoonntteennttss
Part I Introduction..............................................................................................................1
I-1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................... 2
I-1-1 Key Features....................................................................................................................... 2
I-1-2 Specifications ...................................................................................................................... 3
I-1-3 Packing List......................................................................................................................... 4
I-1-4 LED Indicators and Connectors .......................................................................................... 4
I-2 Installation..................................................................................................................................... 6
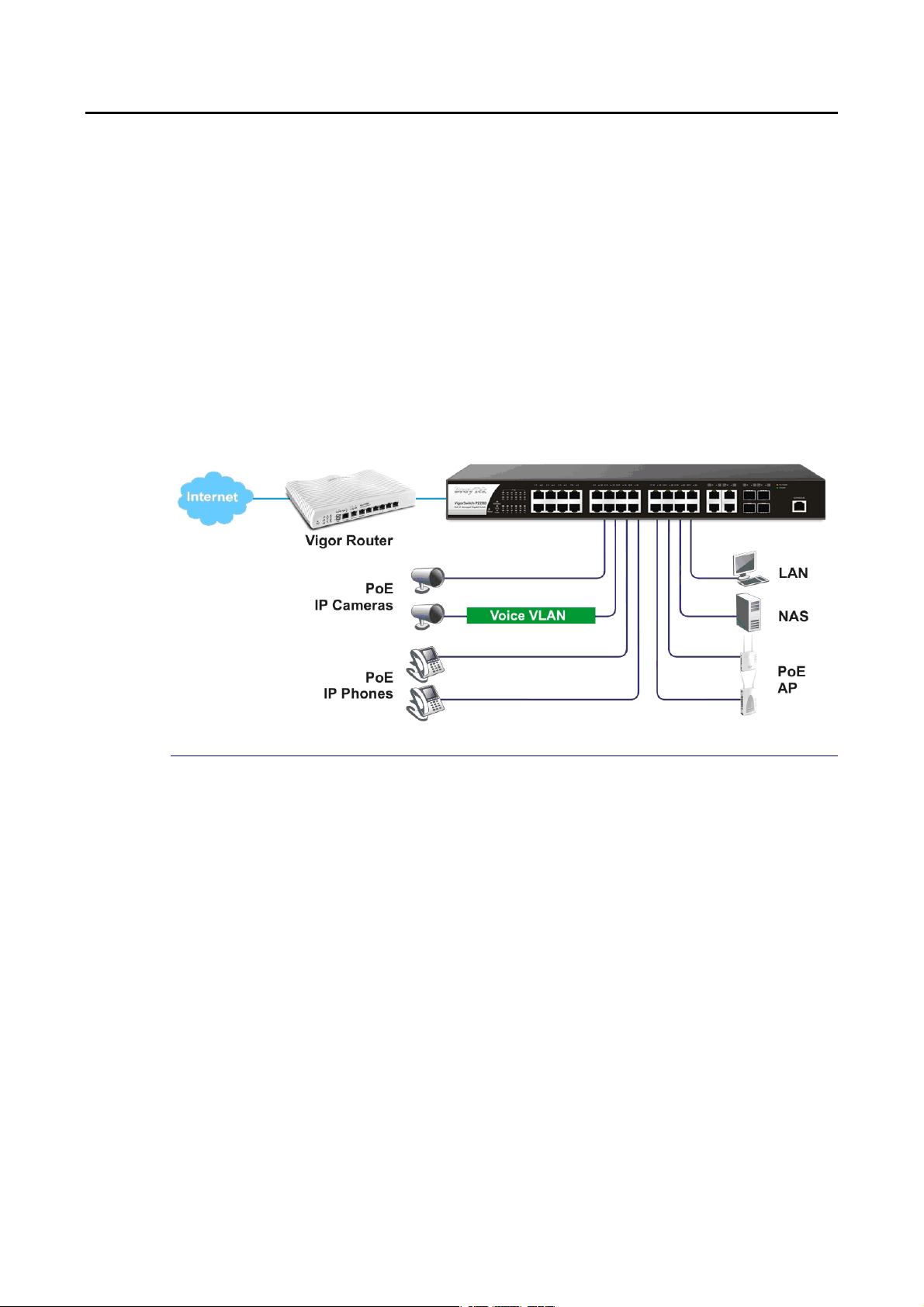
I-2-1 Typical Applications............................................................................................................. 6
I-2-2 Installing Network Cables.................................................................................................. 10
I-2-3 Configuring the Management Agent of Switch.................................................................. 10
I-2-4 Managing VigorSwitch P2280 through Ethernet Port........................................................ 10
I-2-5 IP Address Assignment.....................................................................................................11
I-3 Accessing Web Page of VigorSwitch.......................................................................................... 14
I-4 Dashboard................................................................................................................................... 15
I-5 Status..........................................................................................................................................16
I-5-1 Port Bandwidth Utilization ................................................................................................. 16
I-5-2 LLDP Statistics.................................................................................................................. 16
I-5-3 GVRP Statistics................................................................................................................. 17
I-5-4 MLD Snooping Statistics ...................................................................................................17
Part II Switch LAN............................................................................................................19
II-1 General Setup............................................................................................................................ 20
II-1-1 IP Address........................................................................................................................ 20
II-1-2 IPv6 Address.................................................................................................................... 21
II-1-3 Management VLAN..........................................................................................................22
II-2 Port Setting ................................................................................................................................ 23
II-3 Mirror.......................................................................................................................................... 25
II-4 Link Aggregation........................................................................................................................ 26
II-4-1 LAG Setting...................................................................................................................... 26
II-4-2 LAG Management ............................................................................................................ 27
II-4-3 LAG Port Setting............................................................................................................... 28
II-4-4 LACP Setting.................................................................................................................... 29
II-4-5 LACP Port Setting ............................................................................................................ 30
II-5 VLAN Management.................................................................................................................... 31
II-5-1 Create VLAN .................................................................................................................... 31
II-5-2 Interface Settings.............................................................................................................. 32
II-5-3 Voice VLAN...................................................................................................................... 34
II-5-3-1 Properties.................................................................................34
II-5-3-2 Telephony OUI Setting ..................................................................35
II-5-3-3 Port Setting...............................................................................36
i
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 5

v
II-5-4 MAC VLAN....................................................................................................................... 37
II-5-4-1 MAC Group................................................................................37
I-5-4-3 Group Binding .............................................................................37
II-5-5 Protocol VLAN.................................................................................................................. 39
II-5-5-1 Protocol Group ...........................................................................39
II-5-5-2 Group Binding ............................................................................40
II-5-6 Surveillance VLAN............................................................................................................ 42
II-5-6-1 Property...................................................................................42
II-5-6-1 Surveillance OUI..........................................................................43
II-5-7 GVRP ............................................................................................................................... 45
II-5-7-1 Property...................................................................................45
II-5-7-2 Membership...............................................................................46
II-6 EEE............................................................................................................................................ 47
II-7 Multicast..................................................................................................................................... 48
II-7-1 Properties......................................................................................................................... 48
II-7-2 IGMP Snooping................................................................................................................ 50
II-7-2-1 IGMP Setting..............................................................................50
II-7-2-2 IGMP Querier Setting....................................................................52
II-7-2-3 IGMP Static Group .......................................................................53
II-7-2-4 IGMP Group Table........................................................................54
II-7-2-5 IGMP Router Table.......................................................................55
II-7-2-6 Forward All ...............................................................................56
II-7-2-7 Throttling .................................................................................57
II-7-2-8 Filtering Profile..........................................................................58
II-7-2-9 Filtering Binding .........................................................................59
II-7-3 MVR.................................................................................................................................. 61
II-7-3-1 Property...................................................................................61
II-7-3-2 Port Setting...............................................................................62
II-7-3-3 Group Address............................................................................63
II-7-4 MLD Snooping.................................................................................................................. 64
II-7-4-1 MLD Setting...............................................................................64
II-7-4-2 MLD Static Group ........................................................................66
II-7-4-3 MLD Group Table.........................................................................68
II-7-4-4 MLD Router Table........................................................................69
II-7-4-5 Forward All ...............................................................................70
II-7-4-6 Throttling .................................................................................71
II-7-4-7 Filtering Profile..........................................................................72
II-7-4-8 Filtering Binding .........................................................................73
II-8 Jumbo Frame............................................................................................................................. 75
II-9 STP............................................................................................................................................ 76
II-9-1 Properties......................................................................................................................... 76
II-9-2 Port Setting....................................................................................................................... 77
II-9-3 Bridge Setting................................................................................................................... 79
II-9-4 Port Advanced Setting...................................................................................................... 80
II-9-5 Statistics........................................................................................................................... 81
II-9-6 MST Instance ................................................................................................................... 82
II-9-7 MST Port Setting.............................................................................................................. 83
II-10 MAC Address Table.................................................................................................................. 85
II-10-1 Static MAC Setting ......................................................................................................... 85
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 6

II-10-2 Dynamic Address Setting............................................................................................... 86
II-10-3 Dynamic Learned ........................................................................................................... 86
II-11 Blocked Port Recover............................................................................................................... 88
Part III Security.................................................................................................................89
III-1 RADIUS..................................................................................................................................... 90
III-2 T ACACS+.................................................................................................................................. 92
III-3 Management Access Authentication......................................................................................... 93
III-3-1 Method Profile ................................................................................................................. 93
III-3-2 Application Authentication............................................................................................... 94
III-4 Management Access Control.................................................................................................... 95
III-4-1 Management Access Control Profile (ACL)..................................................................... 95
III-4-2 Management Access Control Entries (ACE)................................................................... 95
III-5 802.1X/MAC Authentication...................................................................................................... 98
III-5-1 Properties........................................................................................................................ 98
III-5-1-1 Global Settings ..........................................................................98
III-5-1-2 Port Authentication Setting...........................................................99
III-5-2 Port Control/Settings ..................................................................................................... 100
III-5-3 MAC-Based Local Account ........................................................................................... 102
III-5-4 Authenticated Hosts ...................................................................................................... 103
III-6 Port Security............................................................................................................................ 104
III-7 Protected Ports ....................................................................................................................... 106
III-8 Storm Control.......................................................................................................................... 107
III-8-1 Properties...................................................................................................................... 107
III-1-2 Port Setting.................................................................................................................... 108
III-9 DoS......................................................................................................................................... 109
III-9-1 Properties...................................................................................................................... 109
III-9-2 DoS Port Setting............................................................................................................ 111
III-10 Dynamic ARP Inspection .......................................................................................................112
III-10-1 Properties.................................................................................................................... 112
III-10-1-1 Global Property Settings ........................................................... 112
III-10-1-2 Per Port Property Settings ......................................................... 113
III-10-2 Statistics...................................................................................................................... 114
III-11 DHCP Snooping.....................................................................................................................115
III-11-1 Properties.................................................................................................................... 115
III-11-1-1 Global Property Settings ........................................................... 115
III-11-1-2 Per Port Property Settings ......................................................... 116
III-11-2 Statistics...................................................................................................................... 117
III-11-3 Option82 Property ....................................................................................................... 117
III-11-3-1 Global Option82 Property Settings ............................................... 117
III-11-3-2 Per Port Option82 Property Settings ............................................. 118
III-11-4 Option82 Circuit ID...................................................................................................... 119
III-12 IP Source Guard ................................................................................................................... 120
vi
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 7

III-12-1 Port Settings................................................................................................................ 120
III-12-2 IMPV Binding............................................................................................................... 121
III-12-3 Save Database............................................................................................................ 122
Part IV ACL Configuration.............................................................................................125
IV-1 Create ACL............................................................................................................................. 126
IV-1-1 MAC .............................................................................................................................. 126
IV-1-2 IPv4............................................................................................................................... 126
IV-1-3 IPv6............................................................................................................................... 127
IV-2 Create ACE............................................................................................................................. 129
IV-2-1 MAC .............................................................................................................................. 129
IV-2-2 IPv4............................................................................................................................... 130
IV-2-3 IPv6............................................................................................................................... 132
IV-3 ACL Binding ............................................................................................................................ 134
Part V QoS Configuration..............................................................................................135
V-1 General....................................................................................................................................136
V-1-1 Properties....................................................................................................................... 136
V-1-1-1 QoS General Setting................................................................... 136
V-1-1-2 Trust Ports.............................................................................. 137
V-1-2 Port Settings................................................................................................................... 138
V-1-3 Queue Settings .............................................................................................................. 139
V-1-4 CoS Mapping ................................................................................................................. 140
V-1-5 DSCP Mapping .............................................................................................................. 141
V-1-6 IP Precedence Mapping................................................................................................. 142
V-2 Bandwidth................................................................................................................................143
V-2-1 Ingress Rate Limit.......................................................................................................... 143
V-2-2 Egress Shaping Rate..................................................................................................... 144
V-2-3 Egress Shaping Per Queue........................................................................................... 145
Part VI PoE Configuration.............................................................................................147
VI-1 Properties ............................................................................................................................... 148
VI-2 Status...................................................................................................................................... 149
VI-3 Device Check.......................................................................................................................... 150
VI-4 Schedule................................................................................................................................. 151
VI-4-1 Schedule Profile............................................................................................................ 151
VI-4-2 Port Scheduling............................................................................................................. 152
Part VII System Maintenance........................................................................................153
VII-1 LLDP...................................................................................................................................... 154
VII-1-1 Properties..................................................................................................................... 154
VII-1-2 LLDP Port Setting ........................................................................................................ 155
VII-1-3 LLDP Local Device....................................................................................................... 156
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
vii
Page 8

VII-1-4 MED Network Policy .................................................................................................... 157
VII-1-5 LLDP MED Port Settings ............................................................................................. 158
VII-1-6 LLDP Remote Device................................................................................................... 159
VII-1-7 LLDP Overloading........................................................................................................ 160
VII-2 SNMP .................................................................................................................................... 161
VII-2-1 View ............................................................................................................................. 162
VII-2-2 Group........................................................................................................................... 163
VII-2-3 Community................................................................................................................... 164
VII-2-4 User.............................................................................................................................. 165
VII-2-5 Engine ID ..................................................................................................................... 167
VII-2-5-1 Local Engine ID........................................................................ 167
VII-2-5-2 Remote Engine ID..................................................................... 168
VII-2-6 Trap Event.................................................................................................................... 169
VII-2-7 Notification ................................................................................................................... 170
VII-3 Access Manager.................................................................................................................... 172
VII-4 Time and Date....................................................................................................................... 173
VII-4-1 System Time Zone....................................................................................................... 173
VII-4-2 Time............................................................................................................................. 174
VII-5 Backup Manager.................................................................................................................... 175
VII-6 Upgrade Manager.................................................................................................................. 176
VII-7 Firmware Information............................................................................................................. 177
VII-8 Account Manager................................................................................................................... 178
VII-9 Factory Default ...................................................................................................................... 180
VII-10 Reboot Switch...................................................................................................................... 181
Part VIII Diagnostics......................................................................................................183
VIII-1 Cable Diagnostics................................................................................................................. 184
VIII-2 Ping Test............................................................................................................................... 185
VIII-3 SysLog.................................................................................................................................. 186
VIII-3-1 SysLog Explorer.......................................................................................................... 186
VIII-3-2 SysLog Settings.......................................................................................................... 187
VIII-3-2-1 SysLog Service........................................................................ 187
VIII-3-2-2 Local SysLog .......................................................................... 188
VIII-3-2-3 Remote SysLog ....................................................................... 189
Appendix: Reference.....................................................................................................191
A-1 What’s the Ethernet................................................................................................................. 191
A-2 Media Acce ss Control (MAC).................................................................................................. 194
A-3 Flow Control............................................................................................................................. 198
Index ...............................................................................................................................201
viii
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 9

Paarrtt II II
P
nttrr
n
o
o
d
uccttii
d
u
o
o
n
n
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
1
Page 10
II--11 IInnttrroodduuccttiioonn
VigorSwitch P2280, 24 Ports + 4 Combo UTP/SFP Ports PoE L2 Managed Gigabit Switch, is a
standard switch that meets all IEEE 802.3/u/x/z Gigabit, Fast Ethernet specifications. The
switch has 24 10/100/1000Mbps TP ports. It supports telnet, http, https, SSH and SNMP
interface for switch management. The network administrator c an login the switch to monit or,
configure and control each port’s activity. In addition, the switch implements the QoS
(Quality of Service), VLAN, and Trunking. It is suitable for office application.
Vigor switch supports IEEE 802.3az, Energy-Efficient Ethernet, and provides power saving
feature. It can efficiently save the switch power with auto detect the client idle and cable
length to provide different power.
1000Mbps SFP Fiber port fully complies with all IEEE 802.3z and 1000Base-SX/LX standards.
II--11--11 KKeeyy FFeeaattuurreess
Below shows key features of this device:
QQooSS
The switch offers powerful QoS function. This function supports 802.1p V LAN tag pri ority an d
DSCP on Layer 3 of network framework.
VVLLAANN
Support Port-based VLAN and IEEE802.1Q Tag VLAN. Support 24 active VLANs an d VLA N ID
1~4094.
PPoorrtt TTrruunnkkiinngg
Allows one or more links to be aggregated together to form a Link Aggregation Group by the
static setting.
PPoowweerr SSaavviinngg
The Power saving using the IEEE 802.3az, Energy-Efficient Ethernet to detect the client idle
and cable length automatically and provides the different power. It could efficient to save
the switch power and reduce the power consumption.
2
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 11

II--11--22 SSppeecciiffiiccaattiioonnss
The VigorSwitch P2280, a standalone off-the-shelf switch, provides the comprehensive
features listed below for users to perform system network administration and efficiently and
securely serve your network.
HHaarrddwwaarree
24 10/100/1000Mbps Auto-negotiation Gigabit Et hernet TP ports with PoE+
Jumbo frame support 9KB
4 UTP/SFP Combo Ethernet Ports
Programmable classifier for QoS (Layer 2/Layer 3)
8K MAC address and support VLAN ID(1~4094)
Per-port shaping, policing, and Broadcast Storm Control
Power Saving with IEEE 802.3az, Energy-Efficient Ethernet
Full-duplex flow control (IEEE802.3x) and half-duplex backpressure
Extensive front-panel diagnostic LEDs; Power, System, PoE fail and PoE/link activity
Hardware reset button for resetting configuration to factory default by pressing over 5
seconds
MMaannaaggeemmeenntt
Supports per port traffic monitoring counters
Supports a snapshot of the system Information when you login
Supports port mirror function
Supports the static trunk function
Supports 802.1Q VLAN
Supports user management and limits three users to login
Maximal packet length can be up to 9600 bytes for jumbo frame application
Supports Broadcasting Suppression to avoid network suspended or crashed
Supports to send the trap event while monitored events happened
Supports default configuration which can be restored to overwrite the current
configuration which is working on via Web UI and Reset button of the switch
Supports on-line plug/unplug SFP modules
Supports Quality of Service (QoS) for real time applications based on the information
taken from Layer 2 to Layer 3
Built-in web-based management and CLI management, providing a more convenient UI
for the user
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
3
Page 12
II--11--33 PPaacckkiinngg LLiisstt
Before you start installing the switch, verify that the package contains the following:
VigorSwitch P2280
AC Power Cord
Quick Start Guide
Rubber feet
Rack mount kit
Please notify your sales representative immediately if any of the aforementioned items is
missing or damaged.
II--11--44 LLEEDD IInnddiiccaattoorrss aanndd CCoonnnneeccttoorrss
Before you use the Vigor device, please get acquainted with the LED indicators and
connectors first. There are 8 Ethernet ports and SFP ports on the front panel of the switch.
LED display area, locating on the front panel, contains an ACT, Power LED and ports working
status of the switch.
LLEEDD EExxppllaannaattiioonn
Combo Port
SFP LNK/ACT
RJ45 LNK/ACT Port 1 to Port 24 / PoE for Port 1 to Port 24
LED Color Explanation
On (Green) Connected over the PoE maximum power budget. PoE /Max
Off Connected within the PoE maximum power
budget.
The switch finishes system booting and the system
is ready.
The switch is powered on and starts system
booting.
The power is off or the system is not ready /
malfunctioning.
SYS
PWR
PoE 1~24
On (Green)
Blinking (Green)
Off
On (Green) The device is powered on and running normally.
Off The device is not ready or is failed.
On (Green) The port is supplied with PoE power.
Off No PoE power is supplied on the port.
On (Green) The device is connected with 1000Mbps. RJ 45
LNK/ACT
4
On (Amber) The device is connected with 10/100Mbps.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 13

Port 1 ~ 24
Combo for
Port 25 ~ 28
(RJ 45
LNK/ACT)
SFP LNK/ACT
CCoonnnneeccttoorr EExxppllaannaattiioonn
Interface Description
RJ 45 LNK/ACT Port 1 ~ 24
PoE for Port 1 ~ 24
Blinking The system is sending or receiving data through
the port.
Off The port is disconnected or the link is failed.
On (Green) The device is connected with 1000Mbps.
On (Amber) The device is connected with 10/100Mbps.
Blinking The system is sending or receiving data through
the port.
Off The port is disconnected or the link is failed.
On (Green) The device is connected with 1000Mbps.
On (Amber) The device is connected with 10/100Mpps.
Blinking The system is sending or receiving data through
the port.
Off The port is disconnected or the link is failed.
Port 1 to Port 24 can be used for Ethernet
connection and PoE connection, depending on the
device connected
.
SFP LNK/ACT Port 25 ~ 28
Console
Port 25 to Port 28 are used for fiber connection.
Used to perform telnet command control.
Power inlet for AC input (100~240V/AC, 50/60Hz).
Note:
Power Output –
IEEE 802.3af Max. 15.4W Output Supported
IEEE 802.3at Max. 30W Output Supported
PoE Power Budget--
340 Watts (Max)
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
5
Page 14
II--22 IInnssttaallllaattiioonn
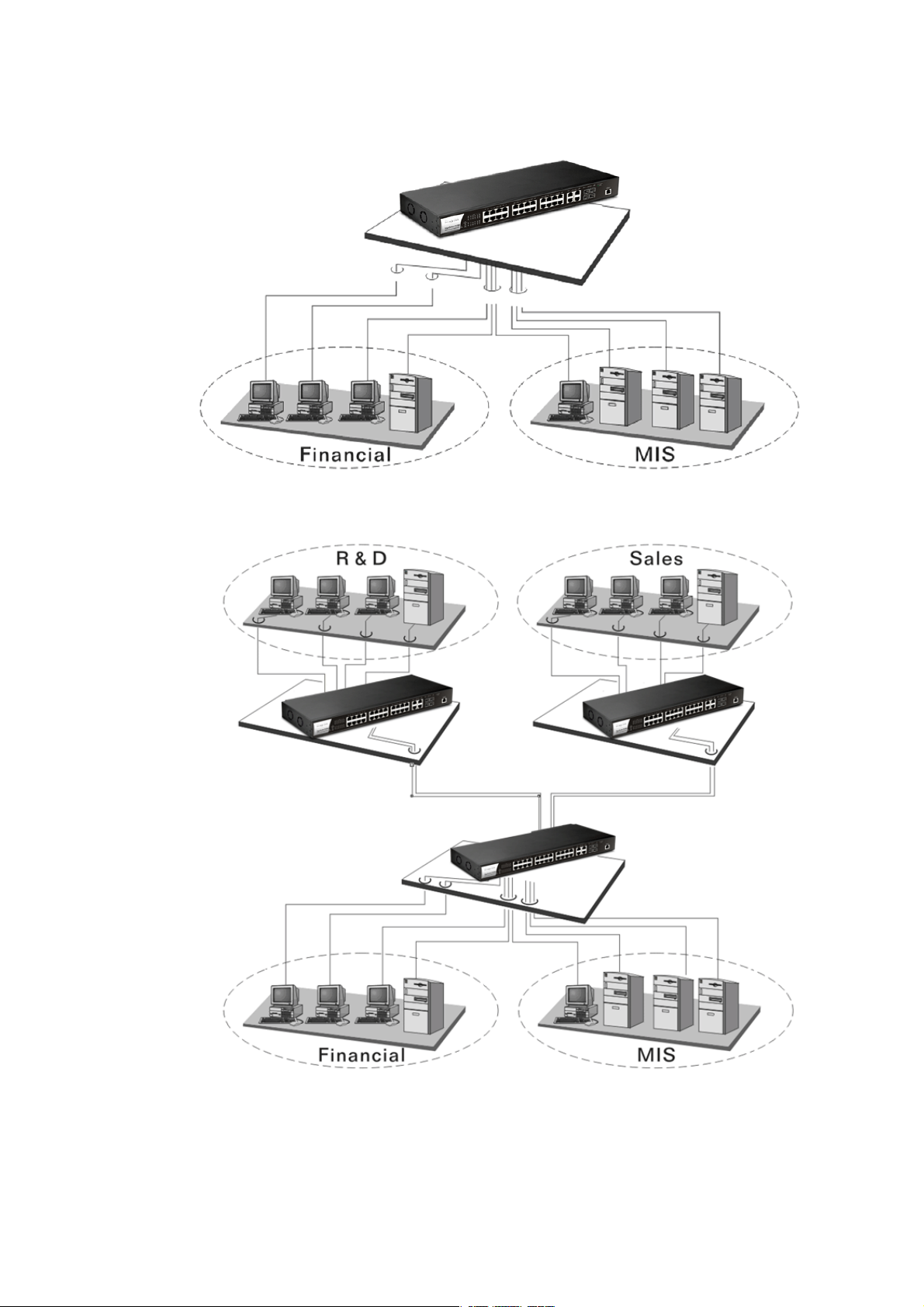
II--22--11 TTyyppiiccaall AApppplliiccaattiioonnss
The VigorSwitch implements 24 Gigabit Ethernet TP ports with auto MDIX and four slots for
the removable module supporting comprehensive fiber types of connection, including LC and
BiDi-LC SFP modules. The switch is suitable for the following applications:
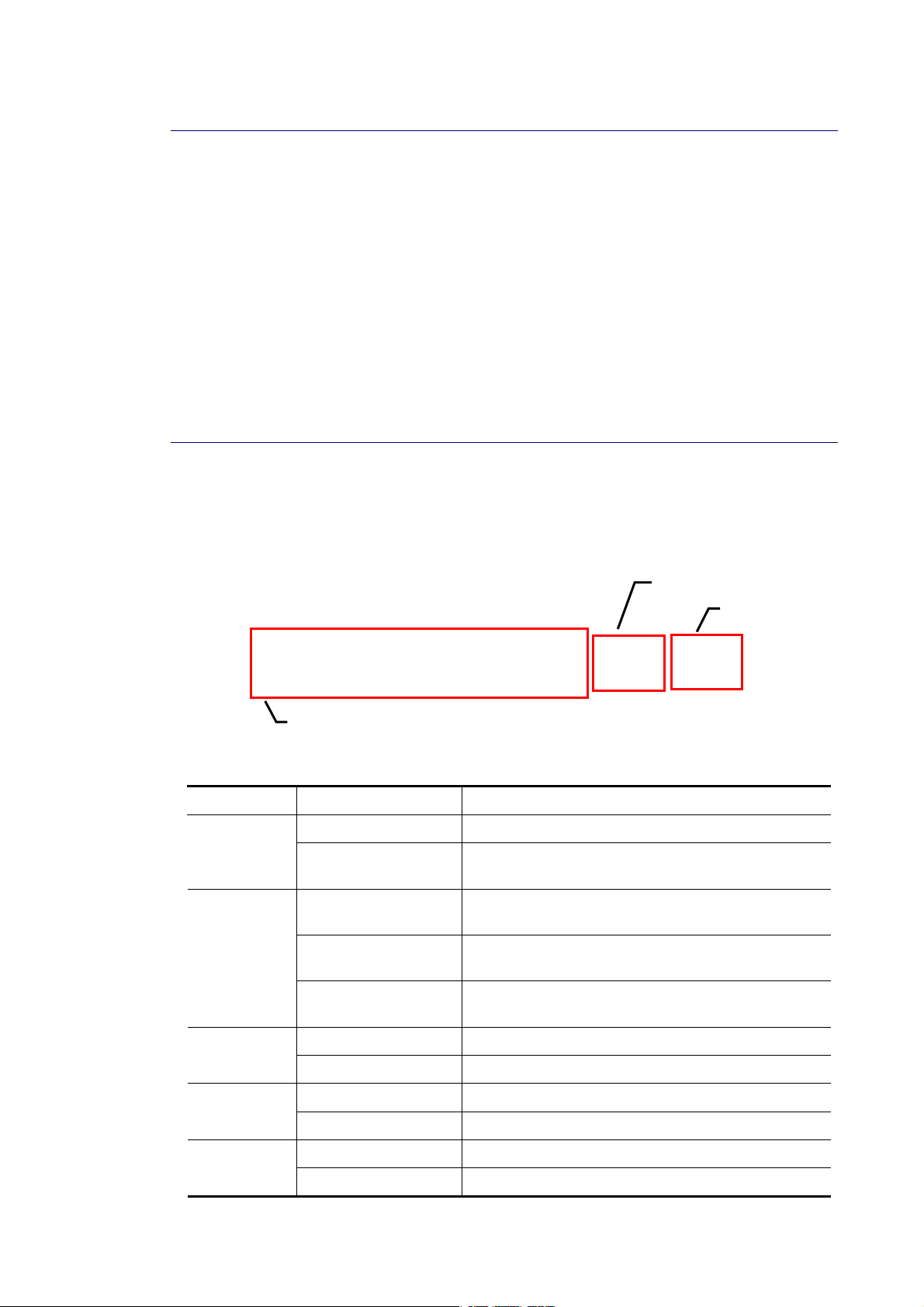
CCaassee 11:: AAllll sswwiittcchh ppoorrttss aarree iinn tthhee ssaammee llooccaall aarreeaa nneettwwoorrkk..
Every port can access each other. (*The switch image is sample only.)
If VLAN is enabled and configured, each node in the network that can communicate each
other directly is bounded in the same VLAN area.
Here VLAN area is defined by what VLAN you are using. The switch supports both port-based
VLAN and tag-based VLAN. They are different in practical deployment, especially in physical
location. The following diagram shows how it works and what the difference they are.
CCaassee 22:: PPoorrtt--bbaasseedd VVLLAANN --11 ((**TThhee sswwiittcchh iimmaaggee iiss ssaammppllee oonnllyy..))
6
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 15

7
The same VLAN members could not be in different switches.
Every VLAN members could not access VLAN members ea ch other.
The switch manager has to assign different names for each VLAN groups at one switch.
CCaassee 33:: PPoorrtt--bbaasseedd VVLLAANN -- 22
VLAN1 members could not access VLAN 2, VLAN3 and VLAN4 members.
VLAN2 members could not access VLAN1 and VLAN3 members, but they could access
VLAN4 members.
VLAN3 members could not access VLAN 1, VLAN2 and VLAN4.
VLAN4 members could not access VLAN1 and VLAN3 members, but they could access
VLAN2 members.
CCaassee 44:: TThhee ssaammee VVLLAANN mmeemmbbeerrss ccaann bbee aatt ddiiffffeerreenntt sswwiittcchheess wwiitthh tthhee ssaammee VVIIDD
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 16
CCaassee 55:: DDeesskkttoopp IInnssttaallllaattiioonn
1. Install the switch on a level surface that can support the weight of the unit and the
relevant components.
2. Plug the switch with the female end of the provided power cord and plug the male end
to the power outlet.
CCaassee 66:: RRaacckk--mmoouunntt IInnssttaallllaattiioonn
The switch may be standalone, or mounted in a rack. Rack mounting facilitate to an orderly
installation when you are going to install series of networking devices.
Procedures to Rack-mount the switch:
1. Disconnect all the cables from the switch before continuing.
2. Place the unit the right way up on a hard, flat surface with the front facing you.
3. Locate a mounting bracket over the mounting holes on one side of the unit.
4. Insert the screws and fully tighten with a suitable screwdriver.
5. Repeat the two previous steps for the other side of the unit.
6. Insert the unit into the rack and secure with suitable screws.
7. Reconnect all the cables.
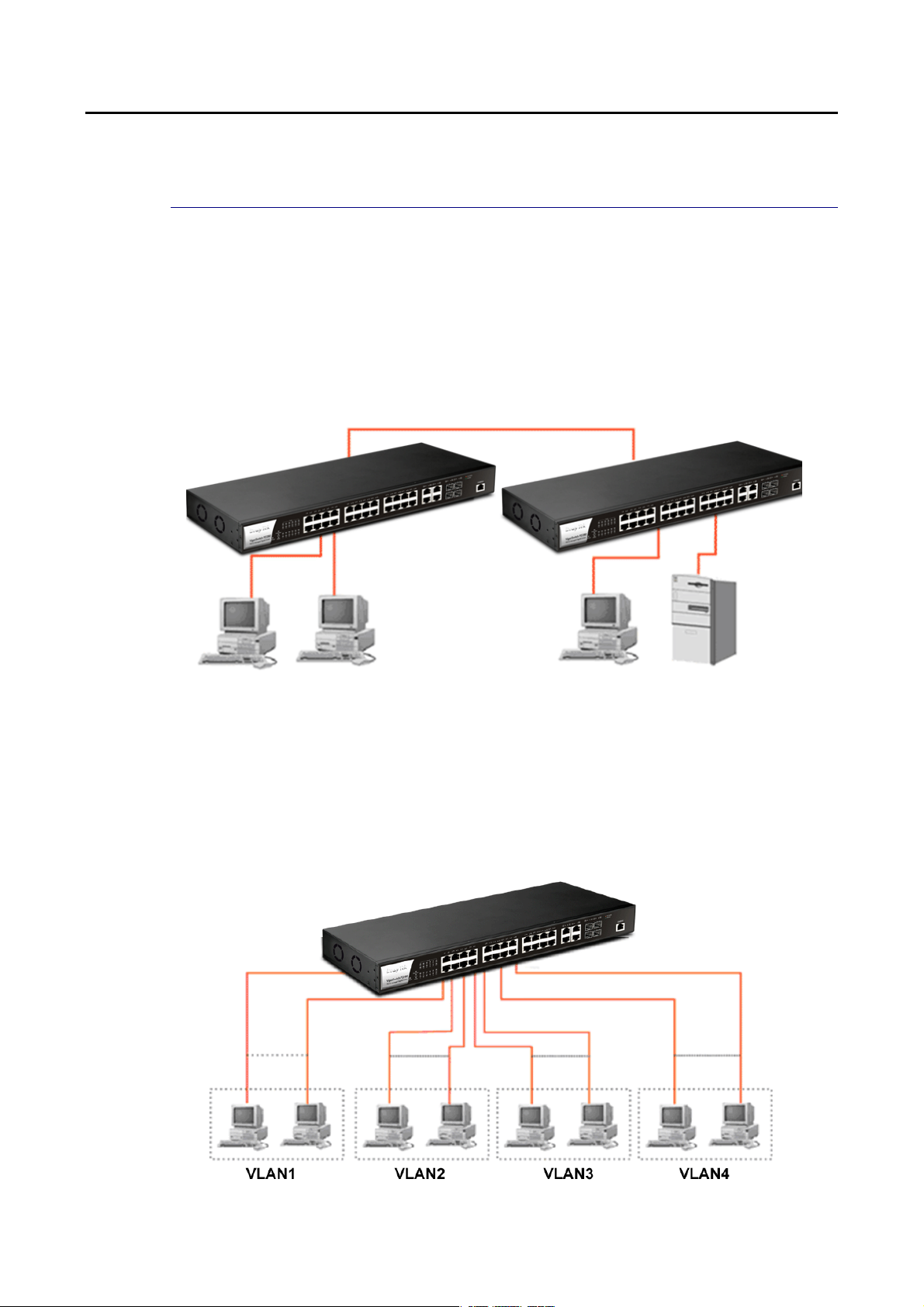
CCaassee 77:: CCeennttrraall SSiittee//RReemmoottee ssiittee aapppplliiccaattiioonn iiss uusseedd iinn ccaarrrriieerr oorr IISSPP
8
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 17
9
CCaassee 88:: PPeeeerr--ttoo--ppeeeerr aapppplliiccaattiioonn iiss uusseedd iinn ttwwoo rreemmoottee ooffffiicceess
CCaassee 99:: OOffffiiccee nneettwwoorrkk
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 18
0
II--22--22 IInnssttaalllliinngg NNeettwwoorrkk CCaabblleess
Crossover or straight-through cable: All the ports on the switch support Auto-MDI/MDI-X
functionality. Both straight-through or crossover cables can be used as the media to connect
the switch with PCs as well as other devices like switches, hubs or router.
Category 3, 4, 5 or 5e, 6 UTP/STP cable: To make a valid connection and obtain the optimal
performance, an appropriate cable that corresponds to different transmitting/receiving
speed is required. To choose a suitable cable, please refer to the following table.
Media Speed Wiring
10 Mbps Category 3,4,5 UTP/STP
10/100/1000
Mbps copper
100Mbps Category 5 UTP/STP
1000 Mbps Category 5e, 6 UTP/STP
II--22--33 CCoonnffiigguurriinngg tthhee MMaannaaggeemmeenntt AAggeenntt ooff SSwwiittcchh
Users can monitor and configure the switch through the following procedures.
Configuring the Management Agent of VigorSwitch P2280 through the Ethernet Port.
There are several ways to configure and monitor the switch through Ethernet port, includes
Web-UI and SNMP.
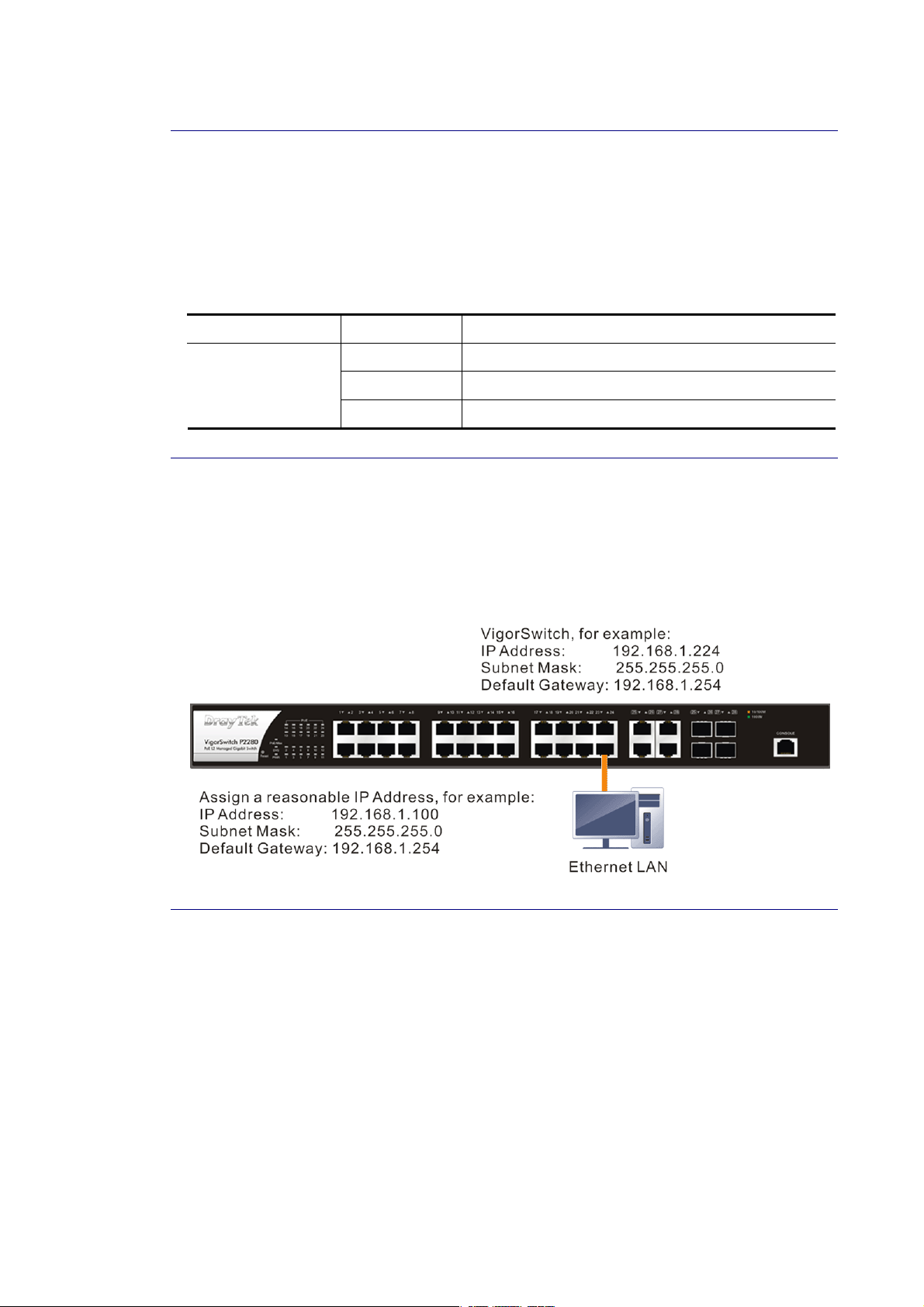
II--22--44 MMaannaaggiinngg VViiggoorrSSwwiittcchh PP22228800 tthhrroouugghh EEtthheerrnneett PPoorrtt
Before start using the switch, the IP address setting of the switch should be done, then
perform the following steps:
1. Set up a physical path between the configured the switch and a PC by a qualified UTP Cat.
5e cable with RJ-45 connector.
Note: If PC directly connects to the switch, you have to setup the same subnet mask
between them. But, subnet mask may be different for the PC in the remote site. Please
refer to the above figure about the Web Smart Switch default IP address information.
2. After configuring correct IP address on your PC, open your web browser and access
switch's IP address.
Default system account is "admin", with password "admin" in default. Switch IP address is
"192.168.1.224" by default with DHCP client enabled.
1
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 19
II--22--55 IIPP AAddddrreessss AAssssiiggnnmmeenntt
For IP address configuration, there are three parameters needed to be filled in. They are IP
address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway and DNS.
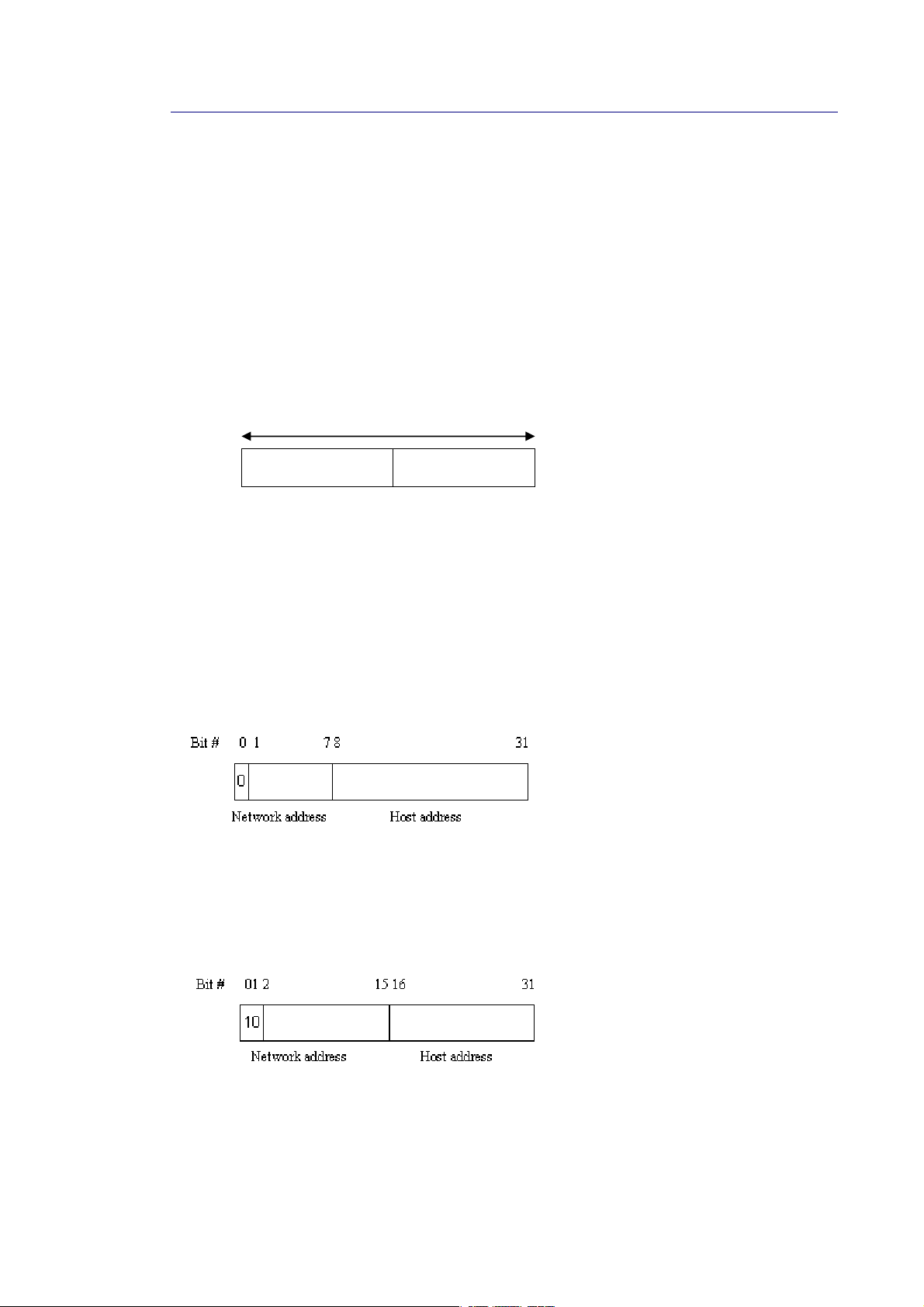
IP address:
The address of the network device in the network is used for internetworking communication.
Its address structure looks is shown below. It is “classful” because it is s p lit into predefined
address classes or categories.
Each class has its own network range between the network identifier and host identifier in the
32 bits address. Each IP address comprises two parts: network ide n tifier (address) and host
identifier (address). The former indicates the network where the addressed host resides, and
the latter indicates the individual host in the network which the address of host refers to. And
the host identifier must be unique in the same LAN. Here the term of IP address we used is
version 4, known as IPv4.
Network identifier Host identifier
32 bits
With the classful addressing, it divides IP address into three classes, class A, class B and class
C. The rest of IP addresses are for multicast and broadcast. The bit length of the network
prefix is the same as that of the subnet mask and is denoted as IP address/X, for example,
192.168.1.0/24. Each class has its address range described below.
Class A:
Address is less than 126.255.255.255. There are a total of 126 networks can be defined
because the address 0.0.0.0 is reserved for default route and 127.0.0.0/8 is reserved for
loopback function.
Class B:
IP address range between 128.0.0.0 and 191.255.255.255. Each cl ass B network has a 16-bit
network prefix followed 16-bit host address. There are 16,384 (2^14)/16 networks able to be
defined with a maximum of 65534 (2^16 –2) hosts per network.
Class C:
IP address range between 192.0.0.0 and 223.255.255.255. Each class C network has a 24-bit
network prefix followed 8-bit host address. There are 2,097,152 (2^ 21)/24 networks able to
be defined with a maximum of 254 (2^8 –2) hosts per network.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
11
Page 20
Class D and E:
Class D is a class with first 4 MSB (Most significance bit) set to 1-1-1-0 and is used for IP
Multicast. See also RFC 1112. Class E is a class with first 4 MSB set to 1-1-1-1 and is used for I P
broadcast.
According to IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority), there are three specific IP address
blocks reserved and able to be used for extending internal network. We call it Private IP
address and list below:
Class A 10.0.0.0 --- 10.255.255.255
Class B 172.16.0.0 --- 172.31.255.255
Class C 192.168.0.0 --- 192.168.255.255
Please refer to RFC 1597 and RFC 1466 for more information.
Subnet mask:
It means the sub-division of a class-based network or a CIDR block. The subnet is used to
determine how to split an IP address to the network prefix and the host address in bitwise
basis. It is designed to utilize IP address more efficiently and ease to manage IP network.
For a class B network, 128.1.2.3, it may have a subnet mask 255.255.0.0 in default, in which
the first two bytes is with all 1s. This means more than 60 thousands of nodes in flat IP
address will be at the same network. It’s too large to manage practically. Now if we divide it
into smaller network by extending network prefix from 16 bits to, say 24 bits, that’s using it s
third byte to subnet this class B network. Now it has a subnet mask 255.255.255.0, in which
each bit of the first three bytes is 1. It’s now clear that the first two bytes is used to identify
the class B network, the third byte is used to identify the subnet within this class B network
and, of course, the last byte is the host number.
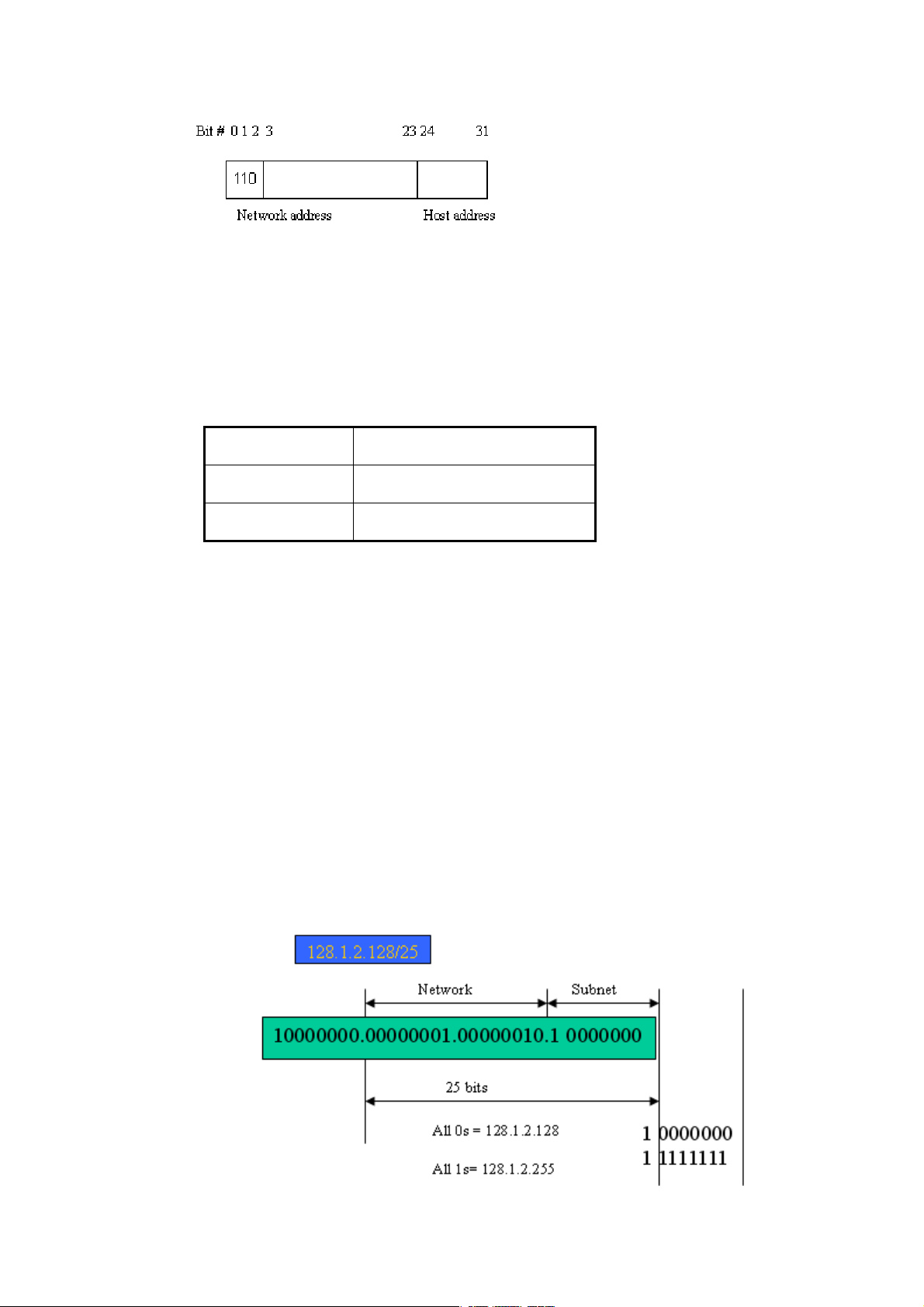
Not all IP address is available in the sub-netted network. Two special addresses are reserved.
They are the addresses with all zero’s and all one’s host number. For example, an IP address
128.1.2.128, what IP address reserved will be looked like? All 0s mean the network itself, a nd
all 1s mean IP broadcast.
12
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 21
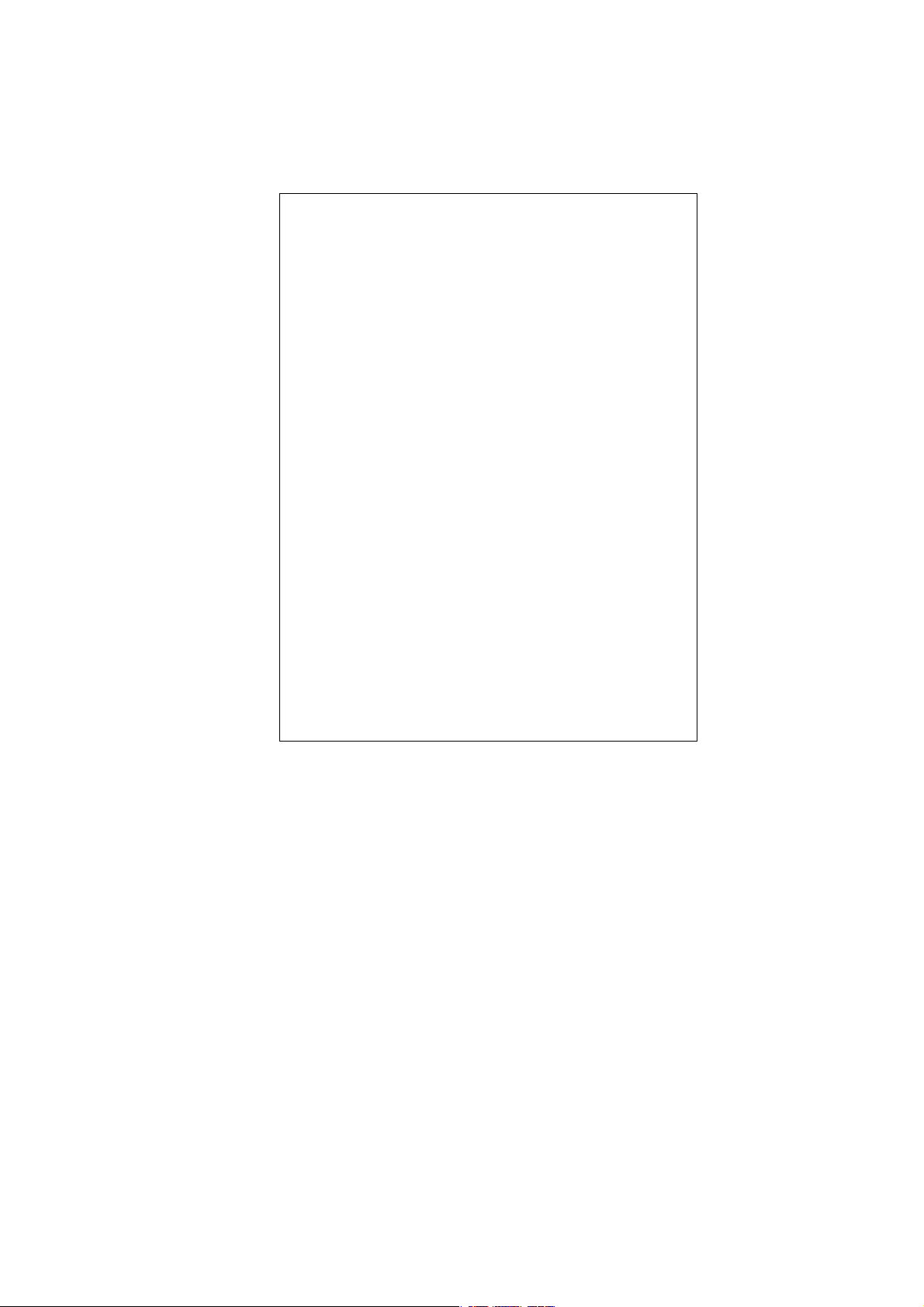
In this diagram, you can see the subnet mask with 25-bit long, 255.255.255.1 28, contain s 126
members in the sub-netted network. Another is that the length of network prefix equals the
number of the bit with 1s in that subnet mask. With this, you can easily count the number of
IP addresses matched. The following table shows the result.
Prefix Length No. of IP matched No. of Addressable IP
/32 1 /31 2 /30 4 2
/29 8 6
/28 16 14
/27 32 30
/26 64 62
/25 128 126
/24 256 254
/23 512 510
/22 1024 1022
/21 2048 2046
/20 4096 4094
/19 8192 8190
/18 16384 16382
/17 32768 32766
/16 65536 65534
According to the scheme above, a subnet mask 255.255.255.0 will partition a network with
the class C. It means there will have a maximum of 254 effective nodes existed in this
sub-netted network and is considered a physical network in an autonomous network. So it
owns a network IP address which may looks like 168.1.2.0.
With the subnet mask, a bigger network can be cut into small pieces of network. If we want to
have more than two independent networks in a worknet, a partition to the network must be
performed. In this case, subnet mask must be applied.
For different network applications, the subnet mask may look like 255.255.255.240. This
means it is a small network accommodating a maximum of 15 nodes in the network.
For assigning an IP address to the switch, you just have to check what the IP address of the
network will be connected with the switch. Use the same network address and append your
host address to it.
First, IP Address: as shown above, enter “192.168.1.224”, for instance. For sure, an
IP address such as 192.168.1.x must be set on your PC.
Second, Subnet Mask: as shown above, enter “255.255.255.0”. Choose a subnet mask
suitable for your network.
Note: The DHCP Setting is enabled in default. Therefore, if a DHCP server presented on
network connected to the switch, check before accessing your switch is essential.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
13
Page 22
4
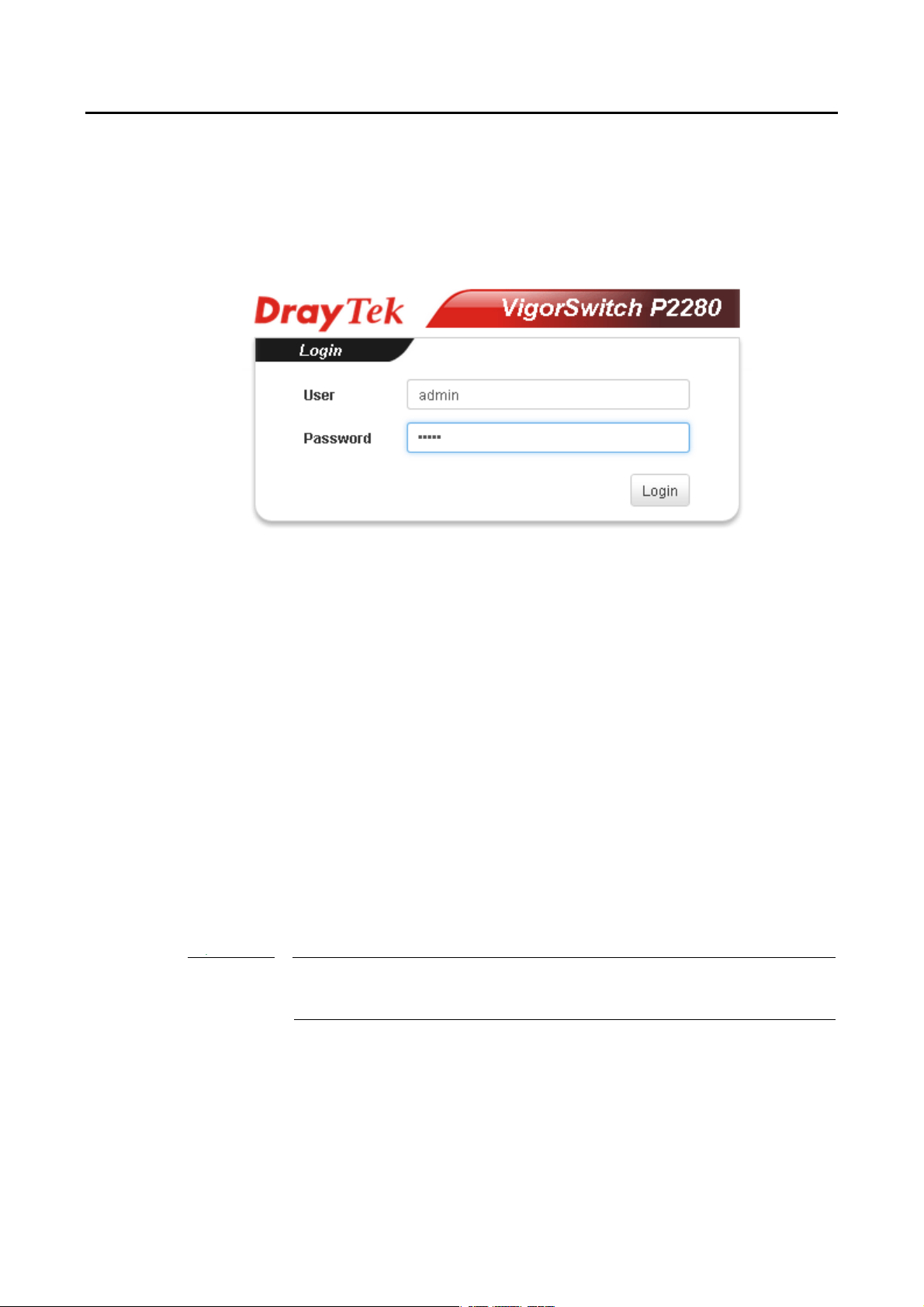
II--33 AAcccceessssiinngg WWeebb PPaaggee ooff VViiggoorrSSwwiittcchh
1. Open any browser (e.g., Firefox) and type “192.168.1.224” as URL.
2. Please type “admin/admin” as the Username/Password and click Login.
3. Now, the Main Screen will appear.
Info
1
The DHCP Setting is enabled in default. Therefore, if a DHCP server presented on
network connected to VigorSwitch, checking before accessing VigorSwitch is
essential.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 23
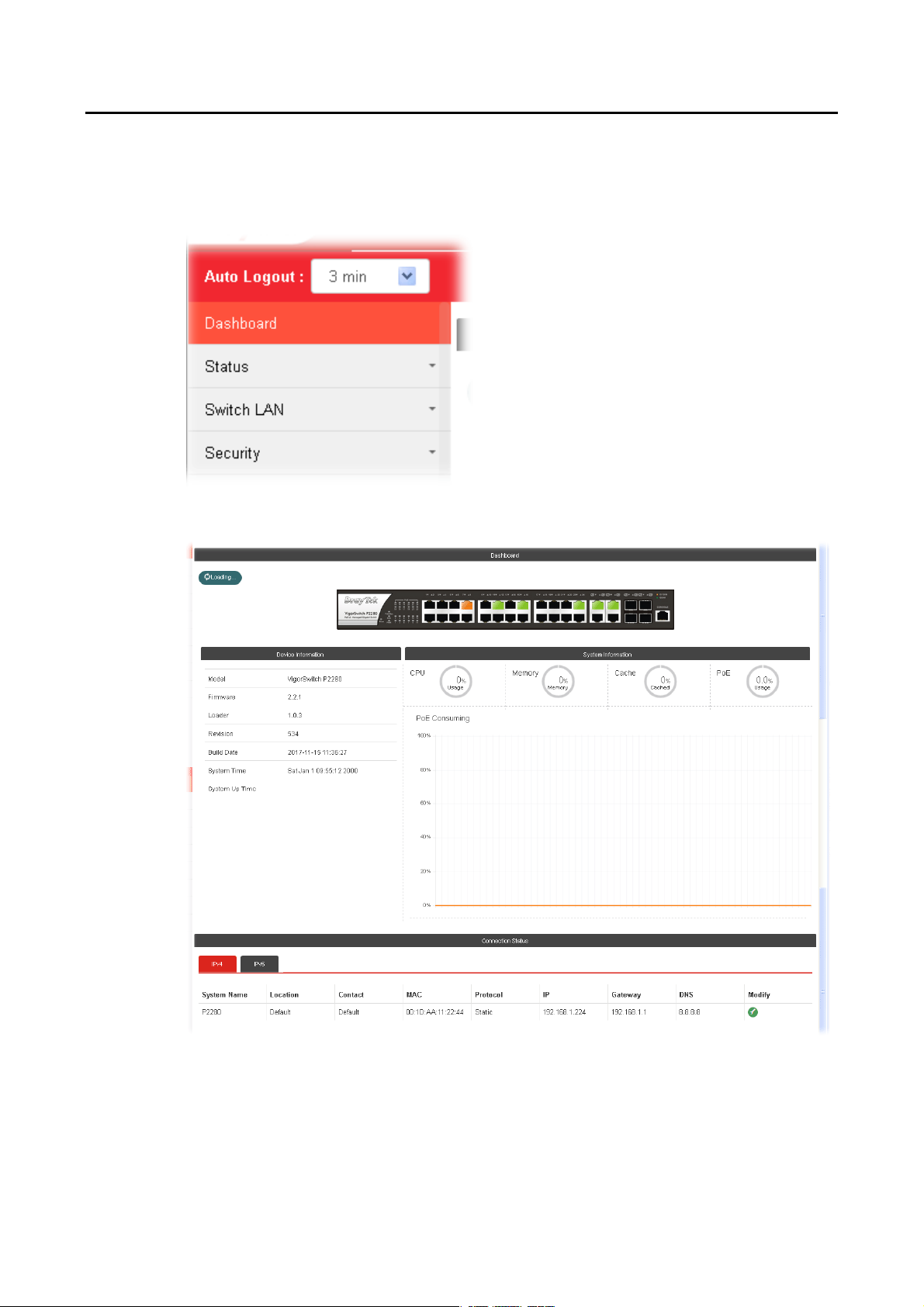
II--44 DDaasshhbbooaarrdd
Click Dashboard from the main menu on the left side of the main page.
A web page with default selections will be displayed on the screen. Refer to the following
figure:
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
15
Page 24

II--55 SSttaattuuss
II--55--11 PPoorrtt BBaannddwwiiddtthh UUttiilliizzaattiioonn
This page offers the traffic statistics inlcuding data information and data of interframe gap
for each port (GE1 to GE28). In which, data of interframe gap can be displayed or hidden by
choose Enable / Disable for IFG.
II--55--22 LLLLDDPP SSttaattiissttiiccss
This page offers the statistics of LLDP packets (in, out and error) of each port (GE1 to GE28).
16
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 25

7
II--55--33 GGVVRRPP SSttaattiissttiiccss
GVRP (Generic Attribute Registration Protocol) is used automatically for exchanging
information for VLAN membership between switches. This page counts the GVRP inform ation
received on each port.
II--55--44 MMLLDD SSnnooooppiinngg SSttaattiissttiiccss
This page counts the MLD messages received or transmitted on the network.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
1
Page 26

This page is left blank.
18
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 27

9
Paarrtt IIII SS
P
wiittcc
w
h LL
h
A
A
N
N
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
1
Page 28
0
IIII--11 GGeenneerraall SSeettuupp
General setup is used to configure settings for the switch network interface and offers how
the switch connects to a remote server to get services.
IIII--11--11 IIPP AAddddrreessss
Use the IP Address screen to configure the switch IP address and the default gateway device.
The gateway field specifies the IP address of the gateway (next hop) for outgoing traffic.
The switch needs an IP address for it to be managed over the network. The factory default IP
address is 192.168.1.224. The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP
address. The factory default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
Info
If VigorSwitch has connected to Vigor router, it will use the IP address obtained from
the DHCP server on Vigor router. Thus, the user must type the assigned IP as URL for
accessing into the web user interface of VigorSwitch. If not, 192.168.1.224 shall be
the default IP.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Mode Select the mode of network connection.
Static- Use static IPv4 address.
DHCP – Use DHCP provisioned IP address and Gateway if
feasible.
IP Address It is available when Static is selected as Mode.
Enter the IP address of your switch in dotted decimal notation
for example 192.168.1.224. If static mode is enabled, enter IP
address in this field.
Subnet Mask It is available when Static is selected as Mode.
Enter the IP subnet mask of your switch in dotted decimal
2
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 29

notation for example 255.255.255.0. If static mode is enabled,
enter subnet mask in this field.
Gateway It is available when Static is selected as Mode.
Enter the IP address of the gateway in dotted decimal
notation. If static mode is enabled, enter gateway address in
this field.
DNS Server 1 It is available when Static is selected as Mode.
If static mode is enabled, enter primary DNS server address in
this field.
DNS Server 2 It is available when Static is selected as Mode.
If static mode is enabled, enter secondary DNS server address
in this field.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
IIII--11--22 IIPPvv66 AAddddrreessss
Use the IPv6 Address screen to configure the switch IPv6 address and the default gateway
device. The gateway field specifies the IPv6 address of the gateway (next hop) for outgoing
traffic.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Auto Configuration Enable - Check it to let switch automatically configure IPv6
address.
IPv6 Address It is available when Auto Configuration is set as Disable.
Enter the IPv6 address of your switch. If auto configuration
mode is disabled, enter IPv6 address in this field.
Link Local Address Display link local address.
Gateway It is available when Auto Configuration is set as Disable.
Enter the IPv6 address of the router as your default IPv6
gateway to access IPv6 Internet or other IPv6 network.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
21
Page 30
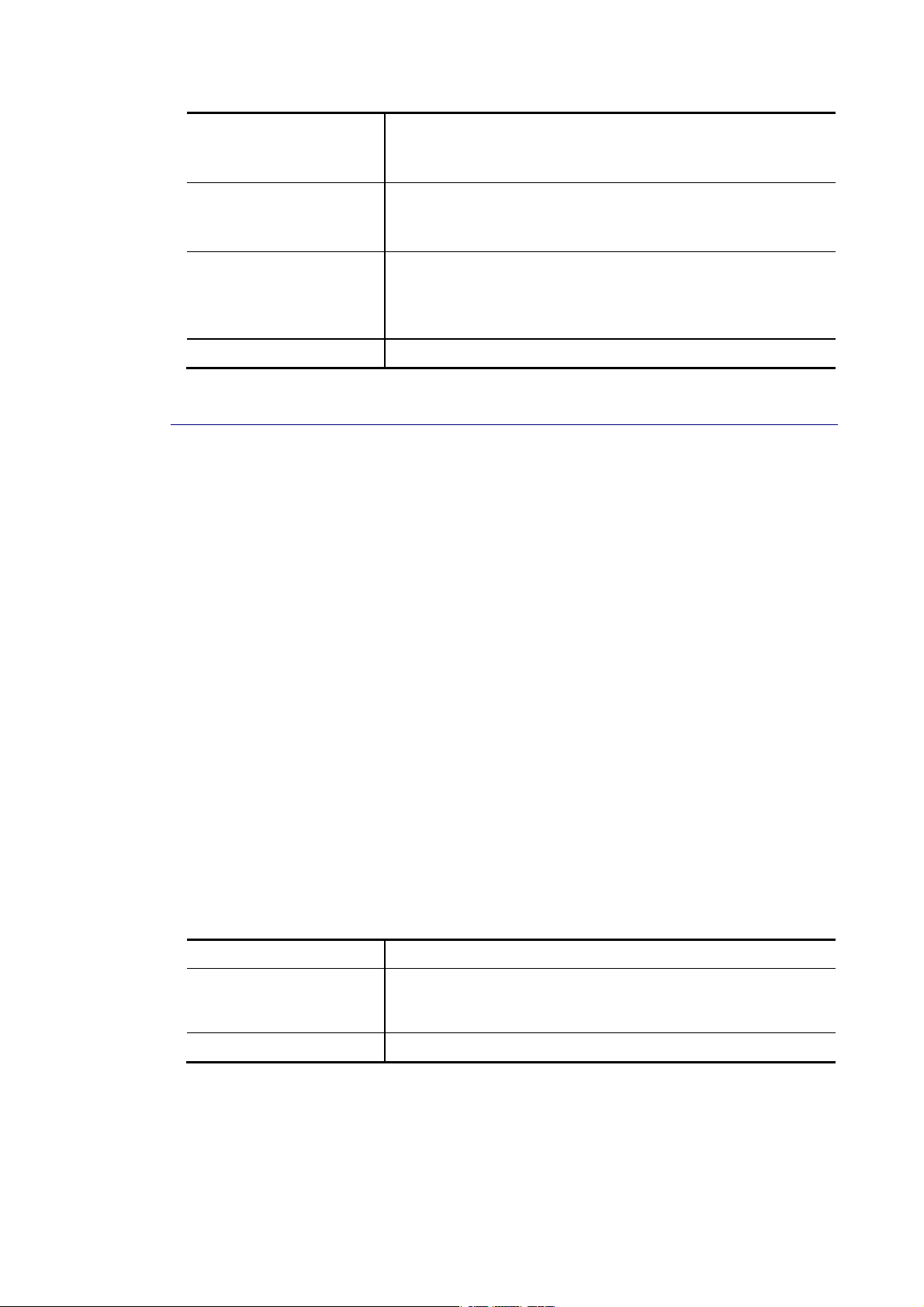
DNS Server 1 It is available when Auto Configuration is set as Disable.
If static mode is enabled, enter primary DNS server address in
this field.
DNS Server 2 It is available when Auto Configuration is set as Disable.
If static mode is enabled, enter secondary DNS server address
in this field.
DHCPv6 Client It is available when Auto Configuration is set as Enable.
Enable this feature if there is a DHCPv6 server on your network
for assigning IPv6 Address, instead of using Router
Advertisement.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
IIII--11--33 MMaannaaggeemmeenntt VVLLAANN
This page allows the network administrator to change the VLAN ID of manage ment access.
Management access protocols such as http, https, SNMP and etc., are only accessible from the
VLAN specified as management VLAN.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Management VLAN Select the VLAN ID as management VLAN. You can create
additional VLAN profiles by Switch LAN>>VLAN
management>> Create VLAN.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
22
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 31

IIII--22 PPoorrtt SSeettttiinngg
Port Setting is used to configure settings for the switch ports, trunk, Layer 2 protocols and
other switch features.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Ports Use the drop down list to selelct one or more LAN port(s).
Enable State Enable –Click it to enable the port.
Disable – Click it to disable the port.
Speed Port speed capabilities:
Auto: Auto speed with all capabilities.
Auto-10M: Auto speed with 10M ability only.
Auto-100M: Auto speed with 100M ability only.
Auto-1000M: Auto speed with 1000M ability only.
Auto-10/100M: Auto speed with 10/100M ability.
10M: Force speed with 10M ability.
100M: Force speed with 100M ability.
1000M: Force speed with 1000M ability.
Selecting Auto (auto-negotiation) allows one port to negotiate
with a peer port automatically to obtain the connection speed
and duplex mode that both ends support. When
auto-negotiation is turned on, a port on the switch negotiates
with the peer automatically to determine the connection
speed and duplex mode. If the peer port does not support
auto-negotiation or turns off this feature, the switch
determines the connection speed by detecting the signal on
the cable and using half duplex mode. When the switch’s
auto-negotiation is turned off, a port uses the pre-configured
speed and duplex mode when making a connection, thus
requiring you to make sure that the settings of the peer port
are the same in order to connect.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
23
Page 32

4
For SFP fiber module, you might need to manually configure
the speed to match fiber module speed.
Duplex Port duplex capabilities:
Auto: Auto duplex with all capabilities.
Half: Auto speed with 10/100M ability only.
Full: Auto speed with 10/100/1000M ability only.
Flow Control A concentration of traffic on a port decreases port bandwidth
and overflows buffer memory causing packet discards and
frame losses. Flow Control is used to regulate transmission of
signals to match the bandwidth of the receiving port. The
switch uses IEEE802.3x flow control in full duplex mode and
backpressure flow control in half duplex mode. IEEE802.3x
flow control is used in full duplex mode to send a pause signal
to the sending port, causing it to temporarily stop sending
signals when the receiving port memory buffers fill. Back
Pressure flow control is typically used in half duplex mode to
send a "collision" signal to the sending port (mimicking a state
of packet collision) causing the sending port to temporarily
stop sending signals and resend later.
Enable – Click it to enable such function.
Disable – Click it to disable such function.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Modify It is used to manually enter the description, state, speed,
duplex, flow control for the port.
2
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 33

IIII--33 MMiirrrroorr
This section provides ability to mirror packets coming in or going out on any port to a
destination port. Through the packet duplication in the destination port, this feature is
convinent for system administrator to monitor / understand the traffic operation.
Session ID 1 to 4 can be enabled simultaneously and operate independently.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Session ID Select the session ID (profile 1 to 4) of mirror operation you
wish to configure.
Monitor Session State Enable – Enable specified mirror session.
Disable - Disable specified mirror session.
Destination Port Specify the port where you wish to observe the mirrored
packets.
Allow Operation as
Normal Port
Sniff Ports (RX) / (TX) Select the port(s) which you wish to mirror the traffic, Rx for
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Enable – The destination port is able to function as a port
connecting to network, communicating with other network
devices.
Disable - Only observe the mirrored packets.
mirror the packets into the port, Tx for mirror the packets
going out from the port.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
25
Page 34

IIII--44 LLiinnkk AAggggrreeggaattiioonn
LAG means Link Aggregation Group which groups some physical ports together to make a
single high-bandwidth data path. Thus it can implement traffic load sharing among the
member ports in a group to enhance the connection reliability.
IIII--44--11 LLAAGG SSeettttiinngg
This page allows to configure Load Balance Algorithm for Link Aggregation.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Load Balance Algorithm Select your Load balance algorithm.
MAC address - Aggregated group will balance the traffic based
on different MAC addresses. Therefore, the packets from
different MAC addresses will be sent to different links.
IP/Mac Address - Aggregated group will balance the traffic
based on MAC addresses and IP addresses. Therefore, the
packets from same MAC addresses but different IP addresses
will be sent to different links.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
26
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 35

7
IIII--44--22 LLAAGG MMaannaaggeemmeenntt
There are eight LAG profiles allowed to group different physical ports (GE1 to GE28). The
system will assign certain port(s) as Active Member and Standby Member according to the GE
selections.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Description Display the port description.
Port Type Display the type of the LAG.
Link Status Display LAG port link status.
Active Member Display active member ports of the LAG.
Standby Member Display inactive or candidate member ports of the LAG.
Modify It is used to edit the name, type and port number for each link
aggregation profile.
Name- Enter a string as LAG name.
Type – Use the drop down menu to specify the type for LAG.
Static- The static aggregated port sends packets over
active member without detecting or negotiating with
remote aggregated port.
LACP- The LACP aggregated ports place member into
active only after negotiated with remote aggregated port
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
2
Page 36

for best reliability.
IIII--44--33 LLAAGG PPoorrtt SSeettttiinngg
This page defines port setting for each LAG profile (LAG1 to LAG8), including data speed and
enabling/disabling the flow control.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
LAG Use the drop down list to selelct one or more LAG profiles.
Enable Enable –Click it to enable the profile.
Disable – Click it to disable the profile.
Speed Port speed capabilities:
Auto: Auto speed with all capabilities.
Auto-10M: Auto speed with 10M ability only.
Auto-100M: Auto speed with 100M ability only.
Auto-1000M: Auto speed with 1000M ability only.
Auto-10/100M: Auto speed with 10/100M ability.
10M: Force speed with 10M ability.
100M: Force speed with 100M ability.
1000M: Force speed with 1000M ability.
Selecting Auto (auto-negotiation) allows one port to negotiate
with a peer port automatically to obtain the connection speed
and duplex mode that both ends support. When
auto-negotiation is turned on, a port on the switch negotiates
with the peer automatically to determine the connection
speed and duplex mode. If the peer port does not support
auto-negotiation or turns off this feature, the switch
determines the connection speed by detecting the signal on
the cable and using half duplex mode. When the switch’s
auto-negotiation is turned off, a port uses the pre-configured
speed and duplex mode when making a connection, thus
requiring you to make sure that the settings of the peer port
are the same in order to connect.
28
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 37

For SFP fiber module, you might need to manually configure
the speed to match fiber module speed.
Flow Control A concentration of traffic on a port decreases port bandwidth
and overflows buffer memory causing packet discards and
frame losses. Flow Control is used to regulate transmission of
signals to match the bandwidth of the receiving port. The
switch uses IEEE802.3x flow control in full duplex mode and
backpressure flow control in half duplex mode. IEEE802.3x
flow control is used in full duplex mode to send a pause signal
to the sending port, causing it to temporarily stop sending
signals when the receiving port memory buffers fill. Back
Pressure flow control is typically used in half duplex mode to
send a "collision" signal to the sending port (mimicking a state
of packet collision) causing the sending port to temporarily
stop sending signals and resend later.
Enable – Click it to enable such function.
Disable – Click it to disable such function.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Modify It is used to edit status, speed, and flow control for the LAG.
IIII--44--44 LLAACCPP SSeettttiinngg
This page allows the network administrator to enable or disable the LACP function.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
LACP Enable – Click it to enable such function.
Disable – Click it to disable the function.
System Priority The priority is used to determine which switch (local or
remote) on the LAG connection is able to decide LACP
activities. The lower the number is, the higher the priority for
Vigorwitch will be. Therefore, the switch with the highest
system priority (e.g., 1) can make decisions about which ports
actively participate in LAG at a given time.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
29
Page 38

Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
IIII--44--55 LLAACCPP PPoorrtt SSeettttiinngg
This section provides few detailed configuration regarding to Ports under LACP protocol.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Ports Use the drop down list to specify LAN Port.
Priority Enter a port priority number for the port.
Timeout The timeout option decides how local switch of LAG
connection determines connection to be lost. Switch would
also notify the remote switch about this setting value, so that
remote switch can send LACP PDU in correct timing.
Long - LACP PDU will be sent every 30 seconds. If port member
is not seen over 90 seconds, it will cause port member
timeout.
Short - LACP PDU will be sent per second. If port member is
not seen over 3 seconds, it will cause port member timeout.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Modify It is used to edit settings (priority and timeout) for LACP port.
30
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 39

IIII--55 VVLLAANN MMaannaaggeemmeenntt
A virtual local area network, virtual LAN or VLAN, is a group of hosts with a common set of
requirements that communicate as if they were attached to the same broadcast domain,
regardless of their physical location. A VLAN has the same attributes as a physical local area
network (LAN), but it allows for end stations to be grouped together even if they are not
located on the same network switch. VLAN membership can be configured through software
instead of physically relocating devices or connections.
IIII--55--11 CCrreeaattee VVLLAANN
This page allows a user to add, edit or delete VLAN settings.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Action Select which action to perform, add VLANs or delete VLANs.
Add – Create a new VLAN profile.
Delete – Delete an existed VLAN profile.
VLAN ID Enter the number as VLAN ID to be created or deleted. If you
want to create / delete multiple VLAN profiles, simply enter
multiple VLAN ID separated by comma, and/or range of VLAN
ID using hyphen.
VLAN Name Enter the prefix you wish to add followed by VLAN ID as VLAN
name. Leave it empty for using default "VLAN".
After clicking Apply, you will see:
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
31
Page 40

Modify
- Modify the name of the selected VLAN ID.
New Name - Type a name for such VLAN profile.
OK - Apply the settings to the switch.
Cancel - Close the page and return to previous page.
- Delete the selected VALN ID.
IIII--55--22 IInntteerrffaaccee SSeettttiinnggss
This page allows a user to configure interface setting related to VLAN.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Port Select Select LAN ports to configure VLAN Settings.
Interface VLAN Mode Select the VLAN mode of the interface.
Hybrid – Support all functions as defined in IEEE 802.1Q
specification.
Access – Accept only untagged frames and join an untagged
VLAN.
32
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 41

Trunk - An untagged member of one VLAN at most, and is a
tagged member of zero or more VLANs.
PVID A PVID (Port VLAN ID) is a tag that adds to incoming untagged
frames received on a port so that the frames are forwarded to
the VLAN group that the tag defines.
For port under Access Mode, VLAN ID provided as PVID would
automatically be selected as the untagged VLAN.
Accepted Type Specify the acceptable-frame-type of the specified interfaces.
It’s only available with Hybrid mode.
All - Accept frames regardless it's tagged with 802.1q or not.
Tag Only - Accept frames only with 802.1q tagged.
Untag Only - Accept frames untagged.
Ingress Filtering Enable the ingress filtering to filter out any packets not belong
to any VLAN members of this port. It is enabled automatically
while operating in Access and Trunk mode.
Enabled – Click it to enable the function.
Disabled - Click it to disable the function.
Tagged VLAN Specify the VLAN profile tagged in the VLAN.
Untagged VLAN Specify the VLAN profile untagged in the VLAN.
Forbidden VLAN Specify the VLAN profile forbidden in the VLAN.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Modify
- It is used to edit settings for the selected port.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
33
Page 42

4
IIII--55--33 VVooiiccee VVLLAANN
With such feature, a VLAN will be created temporarily and when the specified OUI device
delivers protocol packets related to “VoIP”, VigorSwitch will guide these packets into the
specified Voice LAN with specified priorioty tag to speed up the packet transmission. Such
voice VLAN is only active inside VigorSwitch for packet transmission. After these packets
leave VigorSwitch, the Voice VLAN tag will be removed immediately.
IIII--55--33--11 PPrrooppeerrttiieess
This page allows a user to configure global and per interface setting of voice VLAN.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Voice VLAN State Enabled – Click it to enable Voice VLAN.
Disabled - Click it to disable Voice VLAN.
Voice VLAN Id Check the box of Enable first and then select Voice VLAN ID
profile.
Remark CoS/802.1p Click Enabled / Disabled to enable or disable 1p remarking. If
enabled, qualified packets will be remarked by this value.
Remark Value Specify the number of packets to be remarked.
Specify the CoS/802.1p number you wish ingress VoIP packets
be tagged with, so that QoS can prioritize it correctly.
Aging Time Select value of aging time (30~65536 min).
Default is 1440 minutes. A voice VLAN entry will be age out
after this time if without any packet pass through.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
3
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 43

IIII--55--33--22 TTeelleepphhoonnyy OOUUII SSeettttiinngg
This page allows a user to add, edit or delete OUI MAC addresses. Default has 8 pre-defined
OUI MAC.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
OUI Address Type OUI address.
Description Enter a description of the specified MAC address to the voice
VLAN OUI table.
Add Click it to create a new voice OUI based on the settings
configured above.
Modify
- Modify OUI setting for voice VLAN.
- Click it to remove the selected OUI entry.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
35
Page 44

IIII--55--33--33 PPoorrtt SSeettttiinngg
This page allows a user to specify LAN port(s) as Voice LAN port.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Port Use the drop down list to specify one or more LAN ports.
State Enabled – Click it to enable the port settings for Voice LAN.
Disabled – Click it to disable the port settings for Voice LAN.
Cos Mode If Remark CoS/802.1p is enabled in Voice VLAN>>Properties,
settings in this page shall be applied. Otherwise, this option
will not take effect.
All - Once this port is identified as Voice VLAN by frame with
matched OUI, remark CoS/802.1p shall tag for all ingress
frame regardless of remarked frame matched with
pre-configured OUI or not.
Src (Source) - Once this port is identified as Voice VLAN by
frame with matched OUI, remark CoS/802.1p shall tag for only
the matched ingress frame with pre-configured OUI.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Edit Click the icon under Edit for one entry to modify port settings
(State, Cos Mode) for voice VLAN.
36
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 45

7
IIII--55--44 MMAACC VVLLAANN
IIII--55--44--11 MMAACC GGrroouupp
The MAC VLAN allows you to statically assign a VLAN ID to a host with specific MAC address(es).
VigorSwitch allows you configure multiple groups with configured MAC address and mask to be
active on ports and to be bound with VLAN ID. This page allows the network administrator to
define groups with specific MAC addresses for later binding with VLAN and Port.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Group ID It is a number for identification later, while chosen to be
bound with VLAN/Port.
MAC Address Enter the MAC address you wish to be classified in this group
Mask The mask is the length of matching prefix you wish to have on
MAC address.
For example, configure mask in 10. It means a host with
beginning of the 10-digit of MAC address will be checked, and
classified into this group if matched.
Add Click it to create a new MAC group profile based on the
settings configured above.
Edit Click the icon under Edit for one entry to modify settings for
group ID.
II--55--44--33 GGrroouupp BBiinnddiinngg
The MAC VLAN allows you to statically assign a VLAN ID to a host with specific MAC address(es).
VigorSwitch allows you to configure multiple groups with configured MAC address and mask to
be active on ports and to be bound with VLAN ID. This page allows the network administrator
to bind the group of specified MAC addresses with VLAN and Port.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
3
Page 46

Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Ports Select the ports you wish to be bound with specified MAC
address group.
Group ID Choose the group ID you have created in earlier section, which
specified a group of host by MAC address and its mask.
VLAN Enter the VLAN ID that you wish to be bound with.
Add Click it to create a new MAC group binding profile based on the
settings configured above.
Edit Click the icon under Edit for one entry to modify settings for
selected port profile.
38
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 47

9
IIII--55--55 PPrroottooccooll VVLLAANN
VigorSwitch offers protocol VLANs which allows Network Ad ministrator to filter out untagged
traffic of certain protocol and then assign them a specific VLAN ID.
IIII--55--55--11 PPrroottooccooll GGrroouupp
Up to eight protocol groups can be defined, each of them can have a unique filtering criteria
such as frame type and protocol value.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Group ID It is a number for identification while bounding with
VLAN/Port.
Frame Type Use the drop-down list to specify the frame type which you
would like to filter.
Ethernet_II - Packet will be mapped based on Ethernet version
2.
IEEE802.3_LLC_Other –Packet will be mapped based on 802.3
packet with LLC other header.
RFC_1042 - Packet will be mapped based on RFC 1042.
Protocol Value Input a value (ranging from 0x600 ~0xFFFE). Packets match
with such value will be classified into this group.
Add Click it to create a new protocol group profile based on the
settings configured above.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
3
Page 48

Edit
- Modify setting for selected group.
- Click it to remove the group.
IIII--55--55--22 GGrroouupp BBiinnddiinngg
This page is for setting up the ports and protocol group that we would like to filter, and the
VLAN ID we would like to assign.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Ports Use the drop-down list to select one or more ports for applying
protocol-based VLAN. Note that protocol-based VLAN can only
be applied to the ports of which Interface VLAN Mode (at VLAN
Management >> Interface Settings) is set to “Hybrid”.
Group ID Select the protocol group defined in Protocol Group setup.
VLAN Use drop down list to choose a value as VLAN number.
Add Add the above settings to the switch.
Before using Add, open Switch LAN>>VLAN
Management>>Interface Settings to specify Hybrid as
40
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 49

Interface VLAN Mode for the GE ports first. Otherwise, the
following error message will appear.
Edit
- Modify setting for the selected group.
- Click it to remove the selected group.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
41
Page 50

IIII--55--66 SSuurrvveeiillllaannccee VVLLAANN
Surveillance VLAN can be configured for VigorSwitch to identify the packets coming from an IP
camera automatically and assign those traffics to a specific VLAN ID and CoS/8 02.1p value,
this helps you to prioritize those traffics and improve video quality.
IIII--55--66--11 PPrrooppeerrttyy
This page is for setting up the VLAN to which the video traffic should be assigned and to
enable/disable Surveillance VLAN on each port.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
State Enabled – Click it to enable the port settings for such VLAN.
Disabled – Click it to disable the port settings for such VLAN.
VLAN ID Choose a VLAN profile (created in Switch LAN>>VLAN
Management>>Create Vlan) as Surveillance VLAN.
CoS/802.1p Remarking Specify the CoS/802.1p number you wish ingress packets be
tagged with, so that QoS can prioritize it correctly.
Enable - If enabled, qualified packets will be remarked by this
value.
Aging Time Unit is second.
Select value of aging time (30~65536 seconds).
Default is 1440 seconds. VLAN entry will be aged out after this
time if no packet passes through.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Edit
- Click it to modify port setting status.
42
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 51

State –Set it to enable surveillance VLAN function of interface.
Mode –Select port surveillance VLAN mode.
Auto: Surveillance VLAN auto detect packets that match
OUI table and add received port into surveillance VLAN ID
tagged member.
Manual: User need add interface to VLAN ID tagged
member manually.
QoS Policy - Select port QoS Policy mode.
Video Packet: QoS attributes are applied to packets with
OUI in the source MAC address.
All: QoS attributes are applied to packets that are
classified to the Surveillance VLAN.
OK - Apply the settings to the switch.
Cancel - Abandon the changes and return to previous page.
IIII--55--66--11 SSuurrvveeiillllaannccee OOUUII
Filtering Surveillance traffic is based on the OUI of the IP cameras. Users can add, edit, and
delete OUI on this page.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
43
Page 52

4
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
OUI Address Enter OUI MAC address of monitored IP camera. It can’t be
edited in edit dialog.
Description Enter a description of the specified MAC address to the
surveillance VLAN OUI table.
Add Click it to create a new voice OUI based on the settings
configured above.
Edit
- Modify OUI setting for surveillance VLAN.
- Click it to remove the selected OUI entry.
4
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 53

IIII--55--77 GGVVRRPP
IIII--55--77--11 PPrrooppeerrttyy
This page allows the network administrator to configure registration mode (e.g., Normal,
Fixed or Forbidden) of GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Prot ocol) for each GE port.
Such function can eliminate unnecessary network traffic and prevent any attempt to transmit
information to unregistered users.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
State Enabled – Click it to enable the port settings for such VLAN.
Disabled – Click it to disable the port settings for such VLAN.
Timeout Display the current time status for GVRP.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Edit
- Click it to modify settings for the selected port.
State – Select Enabled or Disabled for such port.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
45
Page 54

VLAN Creation –Select Enabled or Disabled.
Mode – There are three modes to be specified.
Normal – Default setting. All packets can pass through
the selected GE port.
Fixed – The selected GE port only sends static VLAN
information to neighboring device and allows static VLAN
packet to pass through.
Forbidden – The selected GE port only allows default
VLAN packet to pass through.
IIII--55--77--22 MMeemmbbeerrsshhiipp
This page display information about membership for GVRP.
46
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 55

7
IIII--66 EEEEEE
This page allows a user to enable or disable port EEE (Energy Efficient Ethernet) function.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Port Select one or multiple ports to configure (GE1 to GE28).
Enable Enable –Click it to enable the EEE function.
Disable - Click it to disable the EEE function.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Modify
- Click it to modify port setting status.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
4
Page 56

IIII--77 MMuullttiiccaasstt
IP multicast is a technique for one-to-many communication over an IP infrastructure in a
network.
To avoid the incoming data broadcasting to all GE ports, multicast is useful to transfer the
data/message to specified GE ports for IGMP snooping. When VigorSwitch receives a message
“subscribed” by the client, it must decide to transfer the data to specified GE ports according
to the location of the client (subscribed member).
IIII--77--11 PPrrooppeerrttiieess
For the multicast packets, This page allows the network administrator to choose actions for
processing the unknown muliticast packets and for handling known packets with MAC address,
IP address and VLAN ID.
48
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Unknown Multicast
Action
IPv4 Forward Method Set the IPv4 multicast forward method.
IPv6 Forward Method Set the IPv6 multicast forward method.
Select an action for switch to handle with unknown multicast
packet.
Drop: Drop the unknown multicast data.
Flood: Flood the unknown multicast data.
Forward to Router port: Forward the unknown multicast data
to router port.
Dst. MAC & VID: Forward using destination multicast MAC
address and VLAN IDs.
Dst. IP & VID: Forward using destination multicast IP address
and VLAN ID.
Dst. MAC & VID: Forward using destination multicast MAC
address and VLAN IDs.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 57

9
Dst. IP & VID: Forward using destination multicast IPv6 address
and VLAN ID.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
4
Page 58

0
IIII--77--22 IIGGMMPP SSnnooooppiinngg
IGMP snooping is the process of listening to Internet Group Manag e ment Protocol (IGMP)
network traffic. The feature allows a network switch to listen in on the IGMP conversation
between hosts and routers. By listening to these conversations the switch maintains a ma p of
which links need which IP multicast streams. Multicasts may be filtered from the links which
do not need them and thus controls which ports receive specific multicast traffic.
IIII--77--22--11 IIGGMMPP SSeettttiinngg
This page allows the network administrator to enable/disable IGMP function, select snooping
version, and enable/disable snooping report suppression.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
IGMP Snooping State Enable – Click it to set enabling IGMP function.
5
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 59

Disable - Click it to disable IGMP function.
IGMP Snooping Version Set the IGMP snooping version.
v2 - Only support process IGMP v2 packet.
v3 (BISS) - Support v3 basic and v2.
IGMP Snoopign Report
Suppression
Click Enable to allow the switch to handle IGMP reports
between router and host, suppressing bandwidth used by
IGMP.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Modify
- Click it to modify IGMP settings for selected profile.
However, if IGMP Snooping State is not set as Enable, such
option will be disabled.
IGMP Snooping State –Choose Enable to enable IGMP snooping
function.
Router Ports Auto Learn – Set the enabling status of IGMP
router port learning. Choose Enable to learn router port by
IGMP query.
Query Robustness – Set a number which allows tuning for the
expected packet loss on a subnet.
Query Interval – Set the interval of querier send general
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
51
Page 60

query.
Query Response Interval – It specifies the maximum allowed
time before sending a responding report in units of 1/10
second.
Last Member Query Counter – After quering for specified
times (defined here) and still not receiving any response from
the subscribed member, VigorSwitch will stop transmitting
data to the related GE port(s).
Last Member Query Interval – The maximum time interval
between counting each member query message with no
responses from any subscribed member.
Immediate Leave – Leave the multicast group immediately on
the port & VLAN where leave message is sent from, regardless
there is still a subscribed member or not. Click Enable to
enable Fastleave function.
OK - Apply the settings to the switch.
Cancel - Close the page and return to previous page.
IIII--77--22--22 IIGGMMPP QQuueerriieerr SSeettttiinngg
This page allows a user to configure querier settings on specific VLAN of IGMP Snooping.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
VLAN ID Use the drop down list to specify a VLAN profile as IGMP
Snooping querier.
Querier State Enable – Click Enable to set the enabling status of IGMP
Querier on the chosen VLAN profile.
Disable – Click it to disable the function.
Querier Version Set the query version of IGMP Querier Election on the chosen
VLANs.
v2 - Querier version 2.
v3 - Querier version 3.
Note: For maximum compatibility, it is suggested to use
querier version lower than IGMP snooping version, for there is
possibile network mixed with IGMP v2/v3 client and v2 query
message is widerly understandable for those clients.
52
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 61

Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
IIII--77--22--33 IIGGMMPP SSttaattiicc GGrroouupp
The IGMP static group is allowed to assign a VLAN/port as a specific IPv4 multicast member.
Every IPv4 multicast stream that belongs to the specified group IP address will be forwarded
to the specified port/VLAN member.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
VLAN ID Use the drop down list to specify a VLAN profile as IGMP Static
Group.
Group IP Address It is an identifier for the group member. Packets sent to such
address will be transferred to all interfaces defined in Member
Ports.
Specify the IPv4 multicast address you wish to assign for the
static group (defined in VLAN ID).
Member Ports Specify the port(s) that static group with given IPv4 multicast
address shall include.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Modify
- Click it to modify settings.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
53
Page 62

4
IIII--77--22--44 IIGGMMPP GGrroouupp TTaabbllee
This page shows currently known and dynamically learned by IGMP snooping or shows the
assigned IPv4 multicast address group in operation.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
VLAN ID Display the VLAN of this multicast group belongs to.
Group IP Address Display the multicast address of this multicast group.
Member Ports Display the port(s) where subscribing member of this multicast
group belongs to.
Type Display if it is dynamically learned or statically assigned.
Life(sec.) Display the life time of this multicast member left if no
membership report sent again.
5
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 63

IIII--77--22--55 IIGGMMPP RRoouutteerr TTaabbllee
This page shows the IGMP querier router known to this switch.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
VLAN ID Use the drop down list to specify a VLAN profile (created in
Switch LAN>>VLAN Management>>Create Vlan) that the MLD
querier belongs to.
Type Static - Specify LAN Port (GE/LAG) to send out query to
remote host.
Forbidden - Use the drop down list to specify forbidden LAN
Port (GE/LAG).
Member Ports Use the drop down list to choose the uplink ports where
querier router exists.
Add Click it to display the result based on the settings configured
above.
Port Display the static port member specified in Member Ports.
Expire Time (sec.) Display the time before querier is considered no longer
existed.
Edit Click the icon under Edit to modify the settings for the
selected VLAN profile.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
55
Page 64

IIII--77--22--66 FFoorrwwaarrdd AAllll
This page is allowed to determine which port(s) would like to receive the data (multicast
packets) that forwarded by VigorSwitch.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Available VLAN To display all of the available VLAN, the State must be set as
Enabled in MLD Setting first.
Use the drop down list to specify a VLAN profile (created in
Switch LAN>>VLAN Management>>Create Vlan) that
multicast packets will be forwarded to.
Static Ports Use the drop down list to specify LAN Port (GE/LAG).
Later, the multicast packets will be delivered to the network
device connected by these ports.
Forbidden Ports Use the drop down list to specify forbidden LAN Port
(GE/LAG).
Later, the multicast packets will not be delivered to the
network device connected by these ports.
Add Click it to display the result based on the settings configured
above.
Edit
- Click it to modify port setting (static port and forbidden
port).
- Click it to remove the selected entry.
56
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 65

7
IIII--77--22--77 TThhrroottttlliinngg
The administrator can configure the user on a switch port (GE/LAG port) belonging to which
multicast group and restrict the number of multicast group that the user on the switch can
join. Then the administrator is able to control the network service (e.g, IP/TV service) that
the user can enjoy.
The Throttling page is used for configuring the maximum number (0~255) of IGMP group that a
user on a switch port can join
interface can be set to deny the IGMP join report or set to replace randomly selected
multicast interface with received IGMP join report.
. After defined the maximum number, each switch port
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Ports Use the drop down list to specify LAN Port (GE/LAG).
Max Group Define the maximum number of IGMP group profile that a user
on the switch can join. If “0” is selected, then such interface
(port) can join all of the IGMP group profiles (defined in
Filtering Profile).
Exceed Action VigorSwitch will perform the action defined below when the
number of IGMP join report for the specified interfa ce exceeds
value defined in Max Group.
Deny – It is default setting. The IGMP join report (for multicast
service) received by such interface will be discarded.
Replace – When it is selected, a new group with IGMP report
received will replace the existing group.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Edit
- Click it to modify port setting (max group and exceed
action).
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
5
Page 66

IIII--77--22--88 FFiilltteerriinngg PPrrooffiillee
The administrator can configure the user on a switch port (GE/LAG port) belonging to which
multicast group and restrict the number of multicast group that the user on the switch can
join. Then the administrator is able to control the network service (e.g, IP/TV service) that
the user can enjoy.
The filtering profile page allows to configure up to 128 IP-group (for multicast servie) pr ofiles
(starting and ending point within an IP range shall be specified). Each IP group profile can be
set for permission of / denial of network service respectively.
In addition, such filtering profile is only effective for controlling the query for multicast. It
has nothing to do with the general IGMP query.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Profile ID Use the drop down list to select one filtering profile (1~128)
for IGMP snooping.
Start Address Enter an IP address as the starting point for the IP range.
End Address Enter an IP address as the ending point for the IP range.
Action Deny – It is default setting. The forwarding request of
multicast traffic will be discarded.
Allow – When it is selected, the request for multicast traffic
will be forwarded to the multicast group normally.
Add Click it to display the result based on the settings configured
above.
Edit
- Click it to modify port setting (max group and exceed
action).
58
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 67

IIII--77--22--99 FFiilltteerriinngg BBiinnddiinngg
This page allows the network administrator to select a filtering profile for LAN/GE port to
process multicast traffic.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Ports Use the drop down list to specify LAN Port (GE/LAG).
Profile ID Use the drop down list to choose the filtering profile for the
select port/interface.
Enable – Check this box first to make profile ID selection be
available for choosing.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Edit
- Click it to modify port setting (enabling / disabling filter
function and choosing a profile for such interface).
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
59
Page 68

60
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 69

IIII--77--33 MMVVRR
Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR) can route packets received in a multicast source VLAN to
one or more desination VLANs. LAN users are in the destination VLANs and the multicast
server is in the source VLAN.
MVR can continuously send multicast stream for traffic in the multicast VLAN, but isolate the
streams from the source VLANs for bandwidth and security reasons.
In general, MVR is able to:
Identify the MVR IP multicast streams and their associated IP multicast group.
Intercept the IGMP messages
IIII--77--33--11 PPrrooppeerrttyy
This page allows the network administrator to configure general settings for MVR, such as
enabling function, selecting VLAN ID (as source VLAN) and specify IP address(es) for
receiver/LAN users.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
State Enabled – Click it to enable the MVR function.
VLAN ID
Mode There are two modes offered for MVR operation.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Disabled – Click it to disable the MVR function.
Choose one VLAN profile from the drop down list as multicast
source VLAN which will receive multicast data. All source
ports must belong to this VLAN. The default is VLAN 1.
Note: Each VLAN ID shall be configured with group address
and member port (defined in MVR>>Group Address page).
Comaptible – Multicast data received by MVR hosts
(multicast server) will be forwarded to all MVR receiver
ports.
Dynamic – Multicast data received by MVR hosts (multicast
server) on Vigor switch will be forwarded from those MVR
data and client ports grouped under MVR server.
61
Page 70

Group Start Enter an IP address. Any multicast data sent to this IP
address will be sent to all source ports on Vigor switch; and
all receiver ports will accept /receive data from that
multicast address.
Group Count Select a number to configure a contiguous series of MVR
group addresses (the range for count is 1 to 128; the default
is 1).
Query Time Use the drop down list to define the maximum time (1 - 10
seconds) to wait for IGMP report members on a rece iv er port
before the port is removed from multicast group.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Operation Group Display group information for MVR operation.
IIII--77--33--22 PPoorrtt SSeettttiinngg
It is necessary to specify destination port and source port (GE/LAG) for Vigor system to
perform MVR operation.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Ports Use the drop down list to select LAN Port (GE/LAG). Later,
each port can be set as Recevier or Source port respectively. If
you do not satisfy with the port setting, simply click the Edit
button to make the modification.
Role None – Noting will be happed to the selected LAN port in MVR
operation.
Receiver – The selected port will be treated as destination
port which will receive multicast data from the multicast
server.
Source – The selected port will be treated as source port
which will send multicast data to the receiver port.
Immediate Leave Enabled – Enable the function fo immediate leave. When the
port (with the role of receiver) receives the leave message, it
will be removed from multicast group to speed up leave
latency.
Disabled – Disable the function of immediate leave.
62
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 71

Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Edit
- Click it to modify port setting (role and immediate
leave).
IIII--77--33--33 GGrroouupp AAddddrreessss
This page allows the network administrator to configure IP address and specify port member
for VLAN selected in MVR>>Property page.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
VLAN ID Display the ID number of the VLAN.
Group Address Define a range of IP address(es) with the format of
“xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx – xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx”.
Member Choose GE/LAG port to be grouped under the selected VLAN.
Add Click it to display the result based on the settings configured
above.
Edit
- Click it to modify the settings.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
63
Page 72

IIII--77--44 MMLLDD SSnnooooppiinngg
MLD snooping does the same thing as IGMP snooping. The difference is that IGMP snooping
acts on IPv4 packets; MLD snooping acts on IPv6 packets. MLD snooping is the process of
listening to Multicast Listener Discovery network traffic. It can examine IPv6 packets and
forward these packets to designate location via VLAN port members.
IIII--77--44--11 MMLLDD SSeettttiinngg
This page allows the network administrator to enable/disable MLD Snooping function, select
snooping version, and enable/disable snooping report suppression.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
State Enabled – Click it to enable the MLD snooping function.
64
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 73

Disabled – Click it to disable the MLD snooping function.
Version VigorSwitch supports two versions of MLD snooping.
MLDv1 – When it is selected, VigorSwitch will detect packets
controlled by MLDv1 and bridge the traffic to IPv6 destination
defined with multicast address(es).
MLDv2 - When it is selected, VigorSwitch will detect packets
controlled by MLDv1 and forward the traffic to destination
defined with multicast address(es).
Report Suppression Enabled – Click it to allow the switch to handle MLD reports
between router and host, suppressing bandwidth used by MLD.
Disabled – Click it to disable the function.
Apply Click it to display the result based on the settings configured
above.
Edit
- Click it to modify the settings for the selected VLAN ID
(GE/LAG port).
MLD Snooping State – Enable/disable the MLD snooping
function for the selected port.
Router Ports Auto Learn –Set the enabling status of IGMP
router port learning. Choose Enable to learn router port by
MLD query.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
65
Page 74

Query Robustness – Set a number which allows tuning for the
expected packet loss on a subnet.
Query Interval – Specify the time interval for VigorSwitch to
send out general MLD query to the host (responsible for
responding). Later, based on the response, VigorSwitch can
forward the traffic through ports in VLAN.
Query Response Interval – Specify the time interval for
VigorSwitch to receive the query response from the host. If
time is up and no response received, the packets will be
blocked and discarded.
Last Member Query Counter – After quering for specified
times (defined here) and still not receiving any response from
the subscribed member, VigorSwitch will stop transmitting
data to the related GE port(s).
Last Member Query Interval – The maximum time interval
between counting each member query message with no
responses from any subscribed member.
Immediate Leave – Click Enable to enable the function of
immediate leave. When the GE/LAG port receives the leave
message, it will be removed from multicast group to speed up
leave latency.
OK - Apply the settings to the switch.
Cancel - Close the page and return to previous page.
IIII--77--44--22 MMLLDD SSttaattiicc GGrroouupp
The MLD static group is allowed to assign a VLAN/port as a specific IPv6 multicast member.
Every IPv6 multicast stream that belongs to the specified group IP address will be forwarded
to the specified port/VLAN member.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
VLAN ID Use the drop down list to specify a VLAN profile (created in
Switch LAN>>VLAN Management>>Create Vlan) as MLD
Static Group.
However, if State in MLD Setting is not set as Enabled, such
option will be disabled and no ID can be selected.
Group IP Address It is an identifier for the group member. Packets sent to such
66
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 75

7
address will be transferred to all interfaces defined in Member
Ports.
Specify the IPv6 multicast address you wish to assign for the
static group (defined in VLAN ID).
Member Ports Use the drop down list to specify interaces (GE/LAG) for
receiving the packets from group IP address.
Add Click it to display the result based on the settings configured
above.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
6
Page 76

IIII--77--44--33 MMLLDD GGrroouupp TTaabbllee
This page shows currently known and dynamically learned by MLD snooping or shows the
assigned IP6 multicast address group in operation.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
VLAN ID Display the name of VLAN configured in MLD Static Group.
Group IP Address Display the IP adderss defined in MLD Static Group.
Member Ports Display all of the interfaces defined in MLD Static Group.
Type Display if it is dynamically learned or statically assigned.
Life(sec.) Display the life time of this multicast member left if no
membership report sent again.
68
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 77

9
IIII--77--44--44 MMLLDD RRoouutteerr TTaabbllee
This page is allowed to configure VLAN profile by specifying static/forbidden ports for the
router (MLD querier).
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
VLAN ID Use the drop down list to specify a VLAN profile (created in
Switch LAN>>VLAN Management>>Create Vlan) that the MLD
querier belongs to.
Type Static - Specify LAN Port (GE/LAG) to send out query to
remote host.
Forbidden - Use the drop down list to specify forbidden LAN
Port (GE/LAG).
Member Ports Use the drop down list to choose the uplink ports where
querier router exists.
Add Click it to display the result based on the settings configured
above.
Port Display the static port member specified in Member Ports.
Expire Time (sec.) Display the time before querier is considered no longer
existed.
Edit
- Click it to modify the settings for the selected entry.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
6
Page 78

0
IIII--77--44--55 FFoorrwwaarrdd AAllll
This page is allowed to determine which port(s) would like to receive the data (multicast
packets) that forwarded by VigorSwitch.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Available VLAN To display all of the available VLAN, the State must be set as
Enabled in MLD Setting first.
Use the drop down list to specify a VLAN profile (created in
Switch LAN>>VLAN Management>>Create Vlan) that
multicast packets will be forwarded to.
Static Ports Use the drop down list to specify LAN Port (GE/LAG).
Later, the multicast packets will be delivered to the network
device connected by these ports.
Forbidden Ports Use the drop down list to specify forbidden LAN Port
(GE/LAG).
Later, the multicast packets will not be delivered to the
network device connected by these ports.
Add Click it to display the result based on the settings configured
7
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 79

above.
Edit
- Click it to modify port setting (static port and forbidden
port).
- Click it to remove the selected entry.
IIII--77--44--66 TThhrroottttlliinngg
The administrator can configure the user on a switch port (GE/LAG port) belonging to which
multicast group and restrict the number of multicast group that the user on the switch can
join. Then the administrator is able to control the network service (e.g, IP/TV service) that
the user can enjoy.
The Throttling page is used for configuring the maximum nu mber (0~255) of M LD group that a
user on a switch port can join
interface can be set to deny the MLD join report or set to replace randomly selected multicast
interface with received MLD join report.
. After defined the maximum number, each switch port
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Ports Use the drop down list to specify LAN Port (GE/LAG) for
applying throttling feature.
Max Group Define the maximum number of MLD group profile that a user
on the switch can join. If “0” is selected, then such interface
(port) can join all of the MLD group profiles (defined in
Filtering Profile).
Exceed Action VigorSwitch will perform the action defined below when the
number of MLD join report for the specified interface exceeds
value defined in Max Group.
Deny – It is default setting. The MLD join report (for multicast
service) received by such interface will be discarded.
Replace – When it is selected, a new group with MLD report
received will replace the existing group.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Edit
- Click it to modify the settings for the selected entry.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
71
Page 80

IIII--77--44--77 FFiilltteerriinngg PPrrooffiillee
The administrator can configure the user on a switch port (GE/LAG port) belonging to which
multicast group and restrict the number of multicast group that the user on the switch can
join. Then the administrator is able to control the network service (e.g, IP/TV service) that
the user can enjoy.
The filtering profile page allows to configure up to 128 IP-group (for multicast servie) pr ofiles
(starting and ending point within an IP range shall be specified). Each IP group profile can be
set for permission of / denial of network service respectively.
In addition, such filtering profile is only effective for controlling the query for multicast
traffic. It has nothing to do with the general MLD query.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Profile ID Use the drop down list to select one filtering profile (1~128)
for MLD snooping.
Start Address Enter an IP address as the starting point for the IP range.
End Address Enter an IP address as the ending point for the IP range.
Action Deny – It is default setting. The forwarding request of
multicast traffic will be discarded.
Allow – When it is selected, the request for multicast traffic
will be forwarded to the multicast group normally.
Add Click it to display the result based on the settings configured
above.
Edit
- Click it to modify the settings for the selected entry.
72
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 81

IIII--77--44--88 FFiilltteerriinngg BBiinnddiinngg
This page allows the network administrator to select a filtering profile for LAN/GE port to
process multicast traffic.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Ports Use the drop down list to specify LAN Port (GE/LAG).
Profile ID Use the drop down list to choose the filtering profile for the
select port/interface.
Enable – Check this box first to make profile ID selection be
available for choosing.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
Edit
- Click it to modify port setting (enabling / disabling filter
function and choosing a profile for such interface).
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
73
Page 82

4
7
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 83

IIII--88 JJuummbboo FFrraammee
This page allows a user to configure switch port jumbo frame settings.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Jumbo Frame (Bytes) Enter Jumbo frame size. The valid range is 1526 bytes – 9216
bytes.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
75
Page 84

IIII--99 SSTTPP
IIII--99--11 PPrrooppeerrttiieess
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that ensures a loop-free topology for
any bridged Ethernet local area network.
Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) are frames that contain information about the Spanning
Tree Protocol (STP). Switches send BPDUs using a unique MAC address from its origin port and
a multicast address as destination MAC (01:80:C2:00:00:00, or 01:00:0C:CC:C C:CD for Per
VLAN Spanning Tree).
For STP algorithms to function, the switches need to share inf ormation about t hemsel ves an d
their connections. What they share are bridge protocol data units (BPDUs).
BPDUs are sent out as multicast frames to which only other layer 2 switches or bridges are
listening. If any loops (multiple possible paths between switches) are found in the network
topology, the switches will co-operate to disable a port or ports to ensure that there are no
loops; that is, from one device to any other device in the layer 2 network, only one path can
be taken.
This page allows a user to configure and display Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) property
configuration.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
STP Mode Set the operating mode of Spanning Tree (STP).
Disabled – Disable the STP operation.
STP - Enable the Spanning Tree (STP) operation.
RSTP - Enable the Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP) operation.
MSTP – Enable the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
operation.
BPDU Handling Specify the BPDU forward method when the STP is disabled.
Filtering - Filter the BPDU when STP is disabled.
Flooding - Flood the BPDU when STP is disabled.
76
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 85

7
PathCost Method Specify the path cost method.
Long - Specifies that the default port path costs are within the
range: 1~200,000,000.
Short - Specifies that the default port path costs are within
the range: 1~65,535.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
IIII--99--22 PPoorrtt SSeettttiinngg
This page allows the user to configure and display Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) port settings.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Ports Use the drop down to specify the interface ID or the list of
interface IDs.
Path Cost (0=Auto) Path cost is the cost of transmitting a frame on to a LAN
through that port. It is recommended to assign this value
according to the speed of the bridge. The slower the media,
the higher the cost. Entering 0 means the switch will
automatically assign a value.
Priority Specify a priority value for the switch. The smaller the priority
value, the higher the priority and greater chance of becoming
the root.
Edge Port In the edge mode, the interface would be put into the
Forwarding state immediately upon link up. If the edge mode
is enabled for the interface and there are BPDUs received on
the interface, the loop might be occurred in the short time
before the STP state change.
Yes – Enable the function.
No – Disable the function.
P2P Option Auto – VigorSwitch determines the STP of link type for this
port automatically.
Yes – It means the STP of link type on this port is full-duplex
and directly connect to another switch or host.
No - It means the STP of link type on this port is “not”
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
7
Page 86

full-duplex and “does not” directly connect to another switch
or host.
BPDU Filter Yes – Drop all BPDU packets and no BPDU will be sent.
BPDU Guard Yes – BPDU Guard further protects your switch by turning this
port into error state and shutdown if any BPDU received from
this port. Check it to enable such function.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
After clicking it, the settings configured above will be shown
on the table below.
Ports Use the drop down to specify the interface(s) for applying the
function of Migrate.
Migrate Click it to force the port(s) specified above to send one RSTP
BPDU (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data
Unit).
Admin Enable YES – Such port is managed by VigorSwitch.
Edit Click it to modify the settings for the selected GE port.
78
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 87

9
IIII--99--33 BBrriiddggee SSeettttiinngg
This page allows the network administrator to configure required information to negotiate
with other VigorSwitch for determining the bridge switch.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Priority Specify the bridge priority. The valid range is from 0 to 61440,
and the value should be the multiple of 4096. It ensures the
probability that the switch is selected as the root bridge, and
the lower value has the higher priority for the switch to be
selected as the root bridge of the topology.
Forward Delay Specify the STP forward delay time, which is the amount of
time that a port remains in the Listening and Learning states
before it enters the Forwarding state. Its valid range is from 4
to 10 seconds.
Max Age Specify the time interval in seconds for a switch to wait the
configuration messages, without attempting to redefine its
own configuration.
Tx Hold Count Specify the tx-hold-count used to limit the maximum numbers
of packets transmission per second. The valid range is from 1
to 10.
Hello Time Specify the STP hello time in second to broadcast its hello
message to other bridge by Designated Ports. Its valid range is
from 1 to 10 seconds.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
7
Page 88

0
IIII--99--44 PPoorrtt AAddvvaanncceedd SSeettttiinngg
This page allows user to edit general setting of STP CIST port and browser CIST port status.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Port Display the interface number for GE and LAG.
Indentifier(Priority/ID) Display the spanning tree port identifier.
Path Cost Conf/Oper Display current path cost of given port.
Designated Root Bridge Display the identifier of designated root bridge.
Root Path Cost Display the operational root path cost.
Designated Bridge Display the identifier of next bridge on this port.
Edge Port Conf/Oper Display if this port is configured as Edge of STP network, for
speed up link up.
P2P MAC Conf/Oper Display if this port is configured as point to point link to
another switch or host.
Port Role Display current port role on the specified port. The possible
values will be: “Disabled”, “Root”, “Designated”,
“Alternative”, and “Backup”.
Port State Display current port state on the specified port. The possible
values will be: “Disabled”, “Discarding”, “Learning”, and
“Forwarding”.
Edit Click it to modify the priority setting for the selected GE port /
LAG port.
8
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 89

IIII--99--55 SSttaattiissttiiccss
This page displays STP statistics.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Port Display the port number (GE / LAG).
Configure BPDUs Rx. Display the counts of the received CONFIG BPDU.
TCN BPDUs Rx. Display the counts of the received TCN BPDU.
Configure BPDUs Tx. Display the counts of the transmitted CONFIG BPDU.
TCN BPDUs Rx Display the counts of the transmitted TCN BPDU.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
81
Page 90

IIII--99--66 MMSSTT IInnssttaannccee
MSTP allows traffic of different VLAN to be mapped into different MST Instances. VigorSwitch
supports up to 16 independent MST instances (0~15) with which the VLAN can be associated.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
MSTI Display the index number of MST Instance. Each MSTI can have
one or multiple VLANs.
Edit
- Click it to modify the priority setting for the selected GE
port / LAG port.
VLAN – Enter the ID (1-4094) of the VLAN which should be
82
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 91

associated with this MSTI.
Priority – The switch priority for this MST instance. A lower
number gives the switch higher chance to be chosen as the
root bridge.
Bridge Identifiter – Display the priority of MSTI instance
number + MAC address of the switch.
Designated Root Bridge – Display the Bridge Identifier of the
root bridge.
Root Port – Display the port toward the root.
Root Path Cost – Display the path cost toward the root.
Remaining Hop – Display the remaining hop count in BPDU.
OK – Save the modifications.
IIII--99--77 MMSSTT PPoorrtt SSeettttiinngg
MST Port Settings is used to configure the GE port / LAG group settings for each MST instance.
The table displays the MST parameters for each port.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
MSTI Select one of the MST instances.
Edit
- Click it to modify the path cost and priority setting for
the port.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
83
Page 92

4
MSTI – Display the selected MST instance.
Path Cost – Set path cost value for the port. A port with lowest
value will be used as the forwarding port by spanning tree.
Default value was set according to the bandwidth of the port.
Priority – Among the ports with same path cost, port with
lower priority will have higher chance to be used as the
forwarding port by spanning tree. Use the drop down list to
choose desired priority value.
8
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 93

IIII--1100 MMAACC AAddddrreessss TTaabbllee
This section allows user to view the dynamic MAC address entries in the MAC table, change
related setting, and assign MAC address into MAC table.
IIII--1100--11 SSttaattiicc MMAACC SSeettttiinngg
This section allows user to manually assign MAC address into MAC table. The configuration
result will be displayed on the table listed on the lower side of this web page.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
MAC Address Enter the MAC address that will be forwarded.
VLAN This is the VLAN group to which the MAC address belongs.
Port Select the port where received frame of matched destination
MAC address will be forwarded to.
Add Click it to add any port into the static MAC table.
Delete Click it to remove the selected port from the static MAC table.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
85
Page 94

IIII--1100--22 DDyynnaammiicc AAddddrreessss SSeettttiinngg
This page allows a user to configure aging time for dynamic MAC address.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Aging Time Enter the Dynamic MAC address aging out value (5-32767
seconds).
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
IIII--1100--33 DDyynnaammiicc LLeeaarrnneedd
This page displays the MAC address and port number automatically learned by VigorSwitch.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
MAC Address Display the MAC address that will be forwarded.
86
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 95

7
VLAN Display the VLAN group to which the MAC address belongs.
Type Display whether the MAC address is Dynamic (learned by the
Switch) or Static Unicast (manually entered in the Static MAC
Forwarding screen).
Port Display the port to which this MAC address belongs.
Add to Static Click this button to add any port into the static MAC table.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
8
Page 96

IIII--1111 BBlloocckkeedd PPoorrtt RReeccoovveerr
This page is used for configuring settings to recover the port which is being blocked by the
following functions after a defined period of time.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Recovery Interval The port being blocked will be able to receive and send traffic
after the time period configured here.
BPDU Guard Enable – Recover the port being blocked by BPDU Guard after
the time set in Recovery Interval.
Self Loop Enable – Recover the port being blocked by self loop Guard
after the time set in Recovery Interval.
Broadcast Flood Enable –Recover the port being blocked by broadcast flood
after the time set in Recovery Interval.
Unknown Multicast Flood Enable – Recover the port being blocked by unknown multicast
flood after the time set in Recovery Interval.
Unicast Flood Enable – Recover the port being blocke d by unicast flood after
the time set in Recovery Interval.
ACL Enable – Recover the port being blocked by ACL after the time
set in Recovery Interval.
Port Security Enable – Recover the port being blocked by port security after
the time set in Recovery Interval.
DHCP Rate Limit Enable – Recover the port being blocked by DHCP rate limit
after the time set in Recovery Interval.
ARP Rate Limit Enable – Recover the port being blocked by ARP rate limit
after the time set in Recovery Interval.
Apply Apply the settings to the switch.
88
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 97

9
Paarrtt IIIIII SSeecc
P
urriittyy
u
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
8
Page 98

0
IIIIII--11 RRAADDIIUUSS
This page allows the network administrator to add and configure multiple RADIUS servers.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Use Default Parameters Retries - The retry time before this server being considered
not-reachable.
Timeout for Reply – Set the time (in seconds) before this
server being considered lost connection.
Key String – Enter the string used to encrypt and authenticate
with RADIUS server.
Apply - Save the settings.
Add RADIUS Server Address Type – Specify whether switch uses a hostname to
resolve address by DNS to connect to server, or directly
connect using IPv4 address.
Sever Address – Enter the server’s address corresponding with
address type given.
Server Port – Enter the port number used by RADIUS server.
Priorty - Specify the priority that switch uses this server. The
higher number, the lower priority. Switch will start with server
with lowest priority.
Retry – Set the time before this server being considered
not-reachable
Timeout – Set the time (in seconds) before this server being
considered lost connection.
Key String – Enter the key string used for encrypting and
authenticating with server. Unless Key String is specified here,
the default string will be used.
Usage –Specify whether you would like to use this server for
switch login authentication or 802.1x access port
authentication, or both.
9
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
Page 99

Add – Click it to add a new RADIUS server and display in this
page.
under Edit- Click it to modify the priority setting for the
selected GE port / LAG port.
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
91
Page 100

IIIIII--22 TTAACCAACCSS++
This page allows the network administrator to add and configure multiple T AC ACS+ server.
Available settings are explained as follows:
Item Description
Use Default Parameters Timeout –Set the time (in seconds) before this server being
considered lost connection.
Key String – Enter the string used to encrypt and authenticate
with TACACS+ server.
Apply - Save the settings.
Add TACACS+ Server Address Type – Specify whether switch use a hostname to
resolve address by DNS to connect to server, or directly
connect using IPv4 address.
Sever Address – Enter the server’s address corresponding with
address type given.
Server Port – Enter the port number used by TACACS+ server.
Priorty - Specify the priority that switch uses this server. The
higher number, the lower priority. Switch will start with server
with lowest priority.
Timeout –Set the time (in seconds) before this server being
considered lost connection.
Key String – Enter the key string used for encrypting and
authenticating with server. Unless Key String is specified here,
the default string will be used.
Add – Click it to add a new RADIUS server and display in this
page.
under Edit- Click it to modify the priority setting for the
selected GE port / LAG port.
92
VigorSwitch P2280 User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...