Page 1

For Microsoft™ Windows XX™, Windows ME™, and Windows NT™
“Your Partners in Network Alarm Management”
T/KdaW
USER MANUAL
UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001
Firmware: 3.1A
Page 2

Revision History
10/23/01 - UM00C.08103 Split Quick Start UM01A.22100) and User Manual.
Added BAS function.
Supports firmware version 3.1A.
This document contains proprietary information which is protected by copyright. All rights are reserved. No part of this document may be photocopied without prior written consent of DPS Telecom.
All software and manuals are copyrighted by DPS Telecom. Said software and manuals may not be reproduced, copied, transmitted or used
to make a derivative work, by either mechanical, electronic or any other means, in whole or in part, without prior written consent from DPS
Telecom, except as required by United States copyright laws.
© Copyright 2001, DPS Telecom
Notice
The material in this manual is for information purposes and is subject to change without notice. DPS Telecom shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this manual.
Page 3

D-SW-709 UM00C.08102
March 2, 2001 www.dpstelecom.com
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Section 1-Software Details
Site Definition, Hardware Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.2-1.3
Primary Docking Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.6-1.11
Secondary Docking Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.12-1.13
Base and Satellite Units, Alarms and Relays . . . . . . .1.14-1.16
Base Ports and Polling Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.16-1.17
Connecting to the KDA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.18-1.19
First Time Satellite Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.19
Monitoring the KDA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.20-1.25
Section 2-Troubleshooting
LAN Traffic and Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.2
Spy Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.2-2.3
Display Protocol and Connecting Software . . . . . . . . . . . .2.4
Help and Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.4
Section 3-Expansion Cards
4 and 8 Channel TBOS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.2
8 and 16 Channel Analog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.3
Analog Scaling Worksheet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.4-3.5
Exp 832 Alarms and Relays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.6-3.7
LR-24 and SR-24 Relays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.8
Building Access Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.9
Section 4-Appendix
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.3-4.8
Terms and Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.2
Index
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5.1-5.4
Page 4

SOFTWARE DETAILS
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Software
Details
Page 5
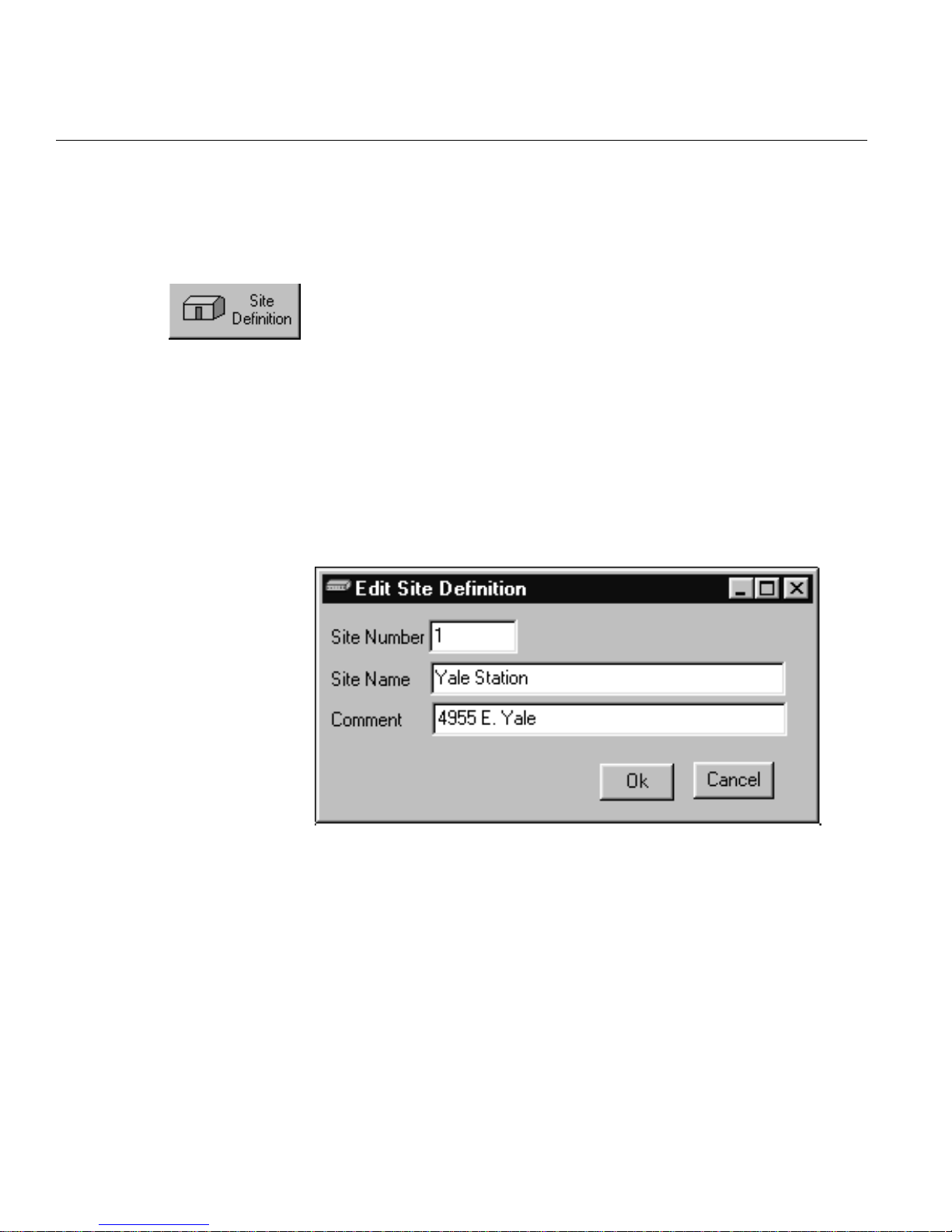
1.2
SOFTWARE DETAILS • EDIT SITE DEFINITION
SOFTWARE DETAILS
Edit Site Definition
Site Number
Arbitrary number 1-9999999 used for reporting alarms to T/Mon
masters.
Site Name
Up to 24 characters. Descriptive only, does not affect system operation in any way.
Comment
Up to 30 characters. Descriptive only, does not affect system operation in any way.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 6

EDIT HARDWARE SETUP • SOFTWARE DETAILS
This screen describes the physical
configuration of a KDA shelf
assembly, which is made up of
interconnected boards and modules
and is usually established when the
unit is purchased. Entries on this
page inform T/KdaW of this hardware configuration, and affect how
it communicates with all elements
of the system. It also determines
what will be displayed on other
T/KdaW screens, so it is essential
to fill this page out accurately
before proceeding to the Docking
Ports, Base and Satellite editing
screens, or connecting with a KDA
device.
Firmware Type
T/KdaW supports the following firmware type and versions:
• Standard versions 2.1G and later
• Timestamp version 1.4B and later
• KDA-E2A version 1.0B and later
• KDA832-T8 version 2.0 and later
Certain features may not be available in all versions; any ver-
sion limitations will be noted. T/KdaW detects the firmware type
and version of a particular KDA device when it connects to it, and
will notify the user of any incompatibilities.
The program installed on the base KDA processor chip may be
identified through the KDA part number or the version number
inscribed on the chip:
Standard
• Part Number KDA-864-01, 05 or 11
• Chip Version 2.1x. or 2.2x
TimeStamp
• Part Number KDA-864-03, 08 or 09
KDA-E2A
• Part Number KDA-864-E2-01
Hardware Setup
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 7
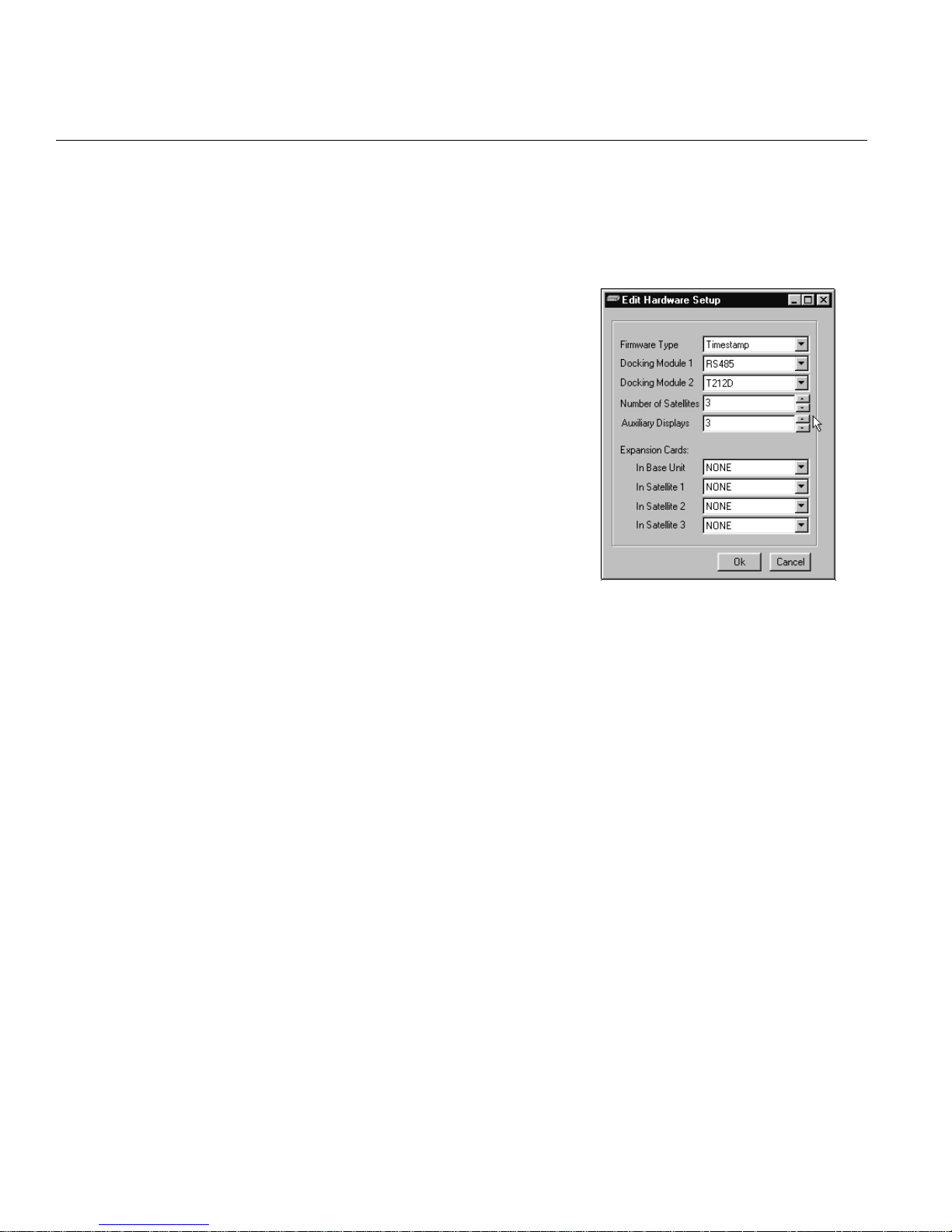
1.4
SOFTWARE DETAILS • EDIT HARDWARE SETUP
Docking Modules
Docking Module 1
Piggyback board plugged into the
left rear corner of the base KDA,
usually used for communicating
with an alarm monitoring device
such as T/Mon via a dedicated
line. May be identified through the
part number inscribed on the
assembly:
• RS-232: Part Number
D-PC-635-10A-00
• T202: Part Number
D-PC-635-10A-00
• RS422/RS 485: Part Number
D-PC-655-10A-00
• RS-232 to NIA: uses fixed connection from RS-232
docking module to a DPS Network Interface Adapter (NIA): Part
Number D-PC-770-10A-0V.
• For Dual RS422 and 212 pad, select RS422 for Docking Module
1 and T212 for Docking Module 2.
Note: The NIA
may be used only
with Standard
firmware versions
2.1i and later, or
Timestamp version 1.4m and
later.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 8
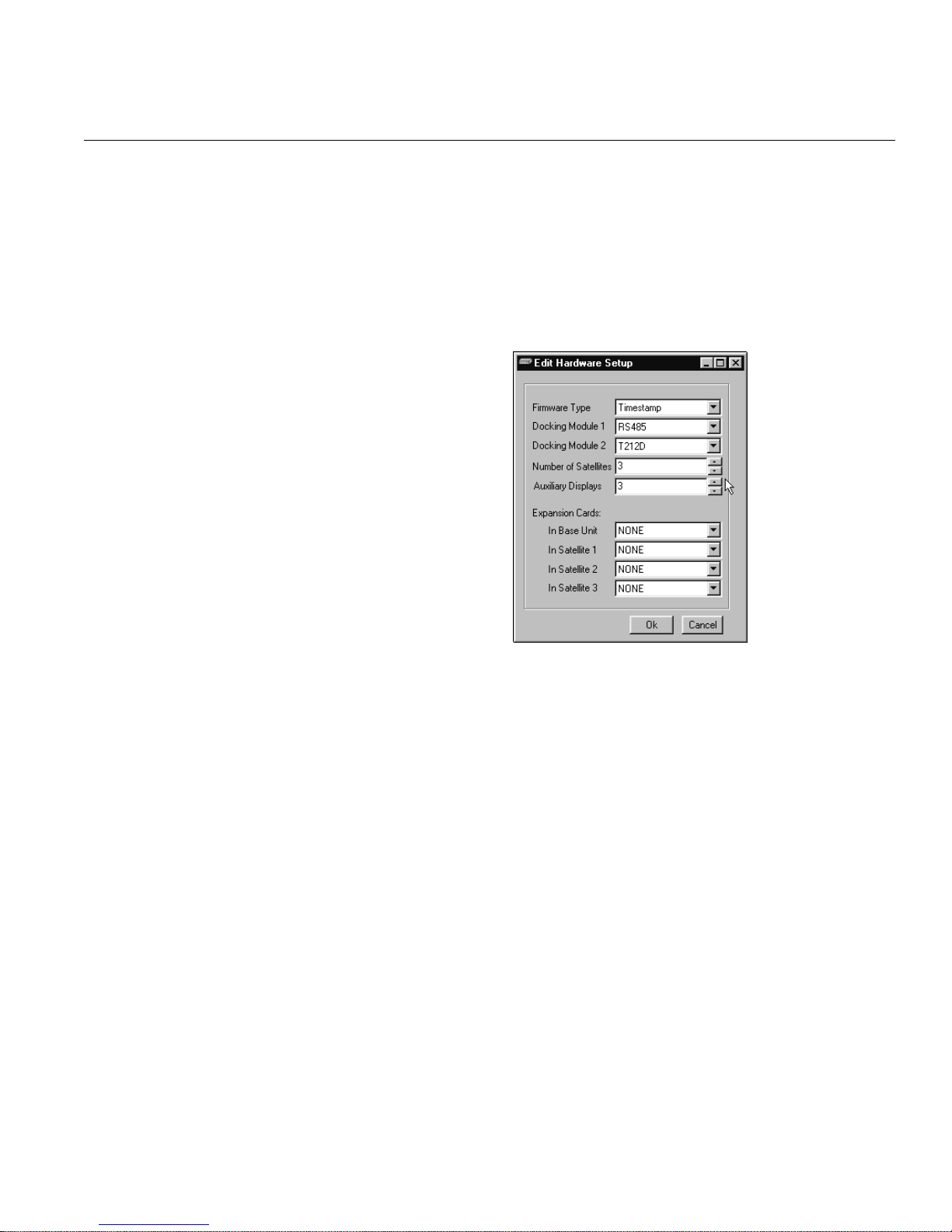
EDIT HARDWARE SETUP • SOFTWARE DETAILS
Docking Module 2
Piggyback board plugged into the left rear corner of the base KDA,
usually used for communicating via a dialup phone line with T/Mon
or T/KdaW. May be identified through the part number inscribed on
the assembly:
T212: Part Number
D-PC-640-10A-00
Modem Types:
• T212: dialup modem
• T212D: dialup modem
and DTMF decoder
• T212X: external modem
Number of Satellites
Number of satellite KDAs
installed.
Auxiliary Displays
Number of General LCD
Display (GLD) units and LED
Bars installed.
Expansion Cards
• In Base Unit
Type of expansion card
installed in base, if any.
• In Satellites
Type of expansion card
installed in satellites, if any. Only the relay cards LR24 and
SR24 are supported in satellites.
Note: a Network Interface
Adapter (NIA) is not considered
an expansion card, but is a communications device set up under
Docking Module.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 9
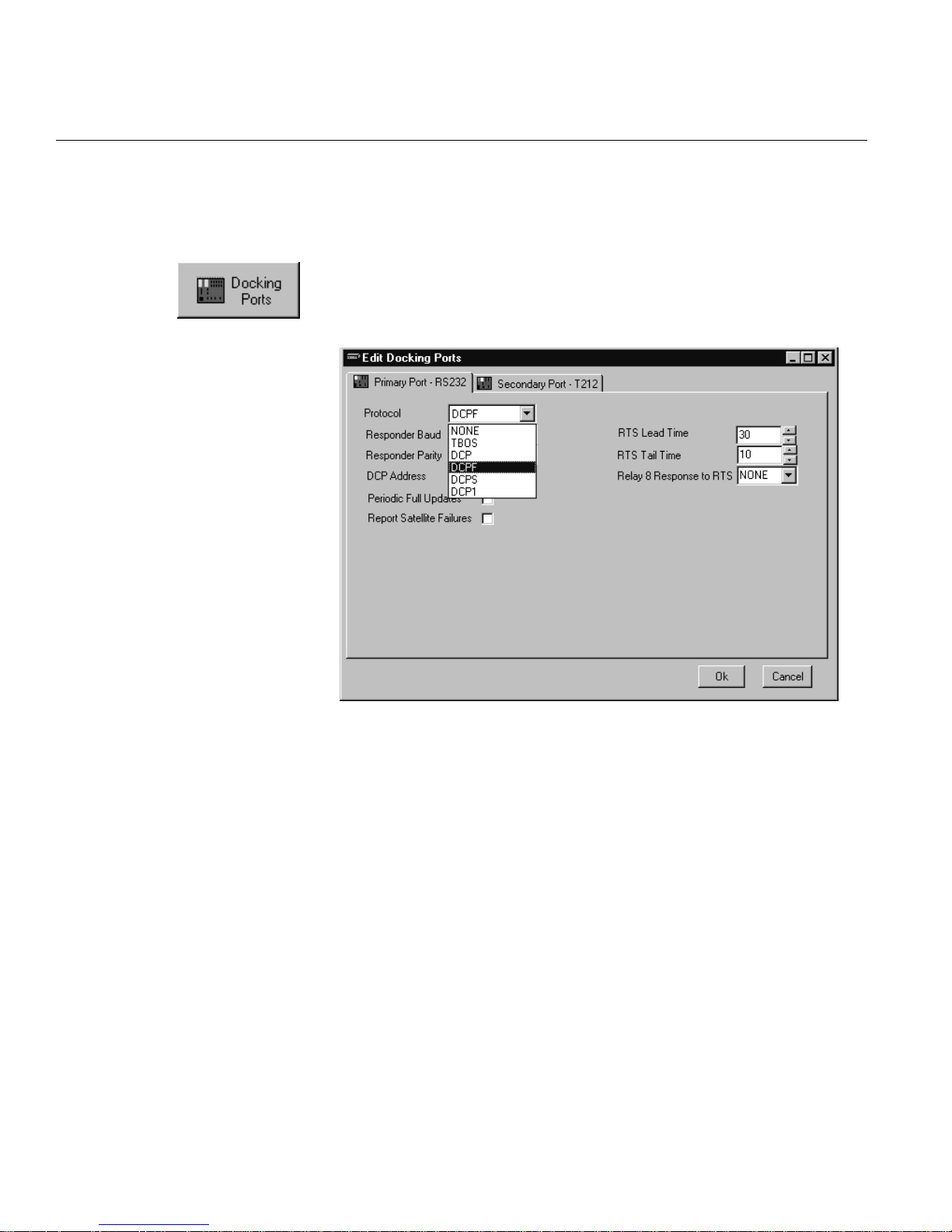
SOFTWARE DETAILS • PRIMARY DOCKING PORT
1.6
Edit Docking Ports
Primary Docking Port
This screen defines detailed parameters for docking modules specified on the Hardware Setup screen. Available fields depend upon
the module type installed. Available protocols depend upon
firmware type.
Docking Modules
RS-232, RS-422, RS-485, T202 or T202F
Protocol Options:
• DCPF is normally used when reporting to a T/Mon master. Other
DCP-type protocols would only be used in special application.
• TBOS may be used when reporting to third-party TBOS masters.
• E2A is used only when reporting to E2A masters.
• ClrChan is used only when the KDA is being used as a communications link into an external serial device. The external device is
plugged into the primary port. All alarm reporting is through the
secondary port. The Clear Channel is established by calling into
the secondary port, which establishes a pass-through connection
to the primary port.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 10

PRIMARY DOCKING PORT • SOFTWARE DETAILS
DCP-Type Protocol Settings
Responder Baud Must match interrogator port setting, nor-
mally 9600.
Responder Parity Must match interrogator port setting, nor-
mally NONE.
DCP Address Must match the base address being polled
by the master.
Periodic Full Updates When checked, the KDA will generate a
full alarm status report every 250 polls, as
opposed to the normal report that only
gives changes. The polling master may
also request full status reports. DPS recommends leaving this unchecked, let the
master take care of it.
Report Satellite Failures When the KDA is monitored by a T/Mon
Workstation, the T/Mon will monitor the
status of KDA and its alarms. When and if
a unit fails, the Report Satellite Failure
option will report which unit has the failure. Satellite failures are reported on
display 33. Satellite 1 is reported on point
25, satellite 2 on point 26, and satellite 3
on point 27.
RTS Lead Time Time, in milliseconds, after serial port
RTS handshaking is asserted that data bits
start to be transmitted. Ordinarily does not
have to be changed, but may be adjusted if
communications timing problems are
encountered or delay is needed for relay
keying.
RTS Tail Time Time, in milliseconds, after serial port data
transmission stops that RTS handshaking
is cleared. Ordinarily does not have to be
changed, but may be adjusted if communications timing problems are encountered
or delay is needed for relay keying.
Relay 8 Response to RTS When checked, on-board relay 8 closes
when RTS is asserted. This may be used to
key an external radio transmitter, etc.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 11

SOFTWARE DETAILS • PRIMARY DOCKING PORT
1.8
TBOS Protocol Settings
Responder Baud Must match interrogator port setting,
normally 2400.
Responder Parity Must match interrogator port setting,
normally ODD.
Report Satellite Failures When checked, reports satellite failures
in bit 65.
RTS Lead Time Time, in milliseconds, after serial port
RTS handshaking is asserted that data
bits start to be transmitted. Ordinarily
does not have to be changed, but may be
adjusted if communications timing problems are encountered or delay is needed
for relay keying.
RTS Tail Time Time, in milliseconds, after serial port
data transmission stops that RTS handshaking is cleared. Ordinarily does not
have to be changed, but may be adjusted
if communications timing problems are
encountered or delay is needed for relay
keying (see below).
Relay 8 Response to RTS When checked, on-board relay 8 closes
when RTS is asserted. This may be used
to key an external radio transmitter, etc.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 12

PRIMARY DOCKING PORT • SOFTWARE DETAILS
E2A Protocol Settings
E2A Address The address entered here is effective only
if DIP switches on the KDA board are all
set OFF. Address must match the base
address being polled by the master.
(Satellite E2A addresses are set up automatically.)
Respond with relay status Check for yes, leave unchecked for no.
Display number is 5 when Respond with
relay status box is no.
Generate COS on Clear Yes indicates the KDA will issue a
Change of State (COS) report when an
alarm clears. No indicates it will not
issue a report when an alarm clears.
ClrChan Protocol Settings
Baud Data rate to use with the craft port inter-
face, normally 1200.
Parity Use with the craft port interface on the
primary docking pad, normally NONE.
Word Length Use with the craft port interface on the
primary docking pad, normally 8.
Password Up to 15 characters.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 13

1.10
SOFTWARE DETAILS • PRIMARY DOCKING PORT
Docking Module
RS-232 to NIA
SNMP Protocol Settings
Unit IP Address Enter the IP address of the KDA, ranging
from 000.000.000.000 to
255.255.255.255.
Subnet IP Mask Enter the Subnet IP Mask of the KDA,
ranging from 000.000.000.000 to
255.255.255.255.
Gateway IP Address Enter the Gateway IP Address of the
KDA, ranging from 000.000.000.000 to
255.255.255.255.
Trap Manager IPAddress Enter the IP address for TRAP reporting,
ranging from 000.000.000.000 to
255.255.255.255.
Unit ID Assign an ID number from 1 to 255 if
there are other units on the net.
Community Names • Get* Enter the numbers or letters as
assigned by the network administrator.
• Set* Enter the numbers or letters as
assigned by the network administrator.
• Trap* Enter the numbers or letters as
assigned by the network administrator.
Granular Trapping When checked, reports system status
using unique identification for each
alarm or relay.
Pass-Through Baud Rate Enter the pass-through baud rate, default
is OFF. Use when connecting to an
external device through the pass-through
port.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
* The Get, Set, and Trap community names create a method of security for responding to SNMP
requests. The SNMP Manager will only respond to those SNMP requests that possess the community name defined here. Refer to your SNMP Manager for any SNMP Community names being used.
Page 14

PRIMARY DOCKING PORT • SOFTWARE DETAILS
UDP Protocol Settings
Unit IP Address Enter the IP address of the KDA,
ranging from 000.000.000.000 to
255.255.255.255.
Subnet IP Mask Enter the Subnet IP Mask of the
KDA, ranging from 000.000.000.000
to 255.255.255.255.
Gateway IP Address Enter the Gateway IP Address of the
KDA, ranging from 000.000.000.000
to 255.255.255.255.
Unit ID Assign an ID number from 1 to 255 if
there are other units on the net.
Pass-Through Baud Rate Enter the pass-through baud rate,
default is OFF. Use when connecting
to an external device through the
pass-through port.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 15
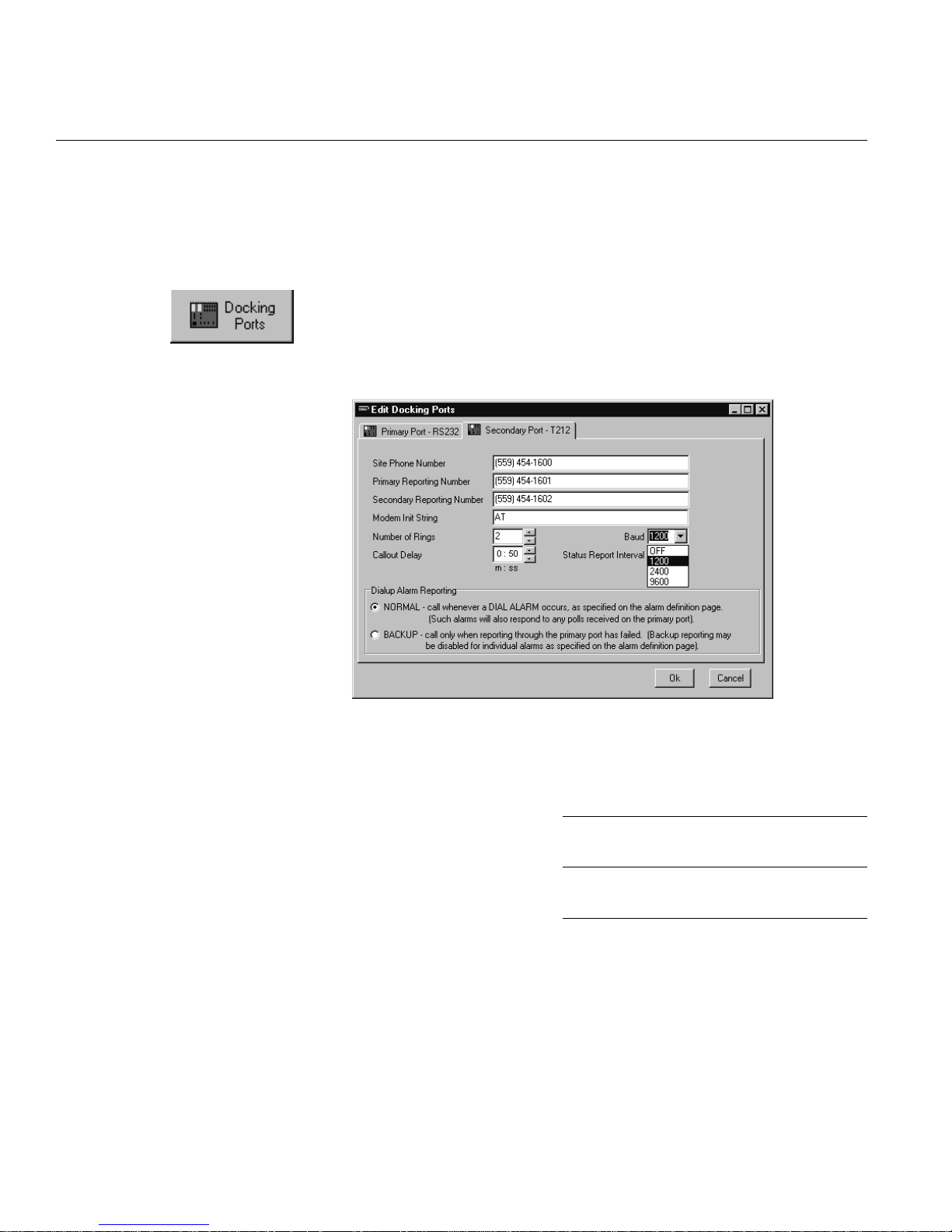
1.12
SOFTWARE DETAILS • SECONDARY DOCKING PORT
Secondary Docking Port
This screen defines detailed parameters of the docking
module 2 specified on the Hardware Setup screen. Defaults vary
depending upon the modem type installed.
Secondary Port Configuration
Site Phone Number Enter the phone number to dial to call
into the KDA.
Primary Reporting Number Enter the primary phone number the
KDA should call to report alarms.
Secondary Reporting Number Enter the secondary phone number the
KDA should call to report alarms.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 16

SECONDARY DOCKING PORT • SOFTWARE DETAILS
Modem Unit String Number of Rings enter the number of
rings that the KDA should wait before
answering an incoming call.
Callout Delay Sets the minimum time that the KDAwill
wait after a previous dialout attempt to
either call in a new alarm or call an alternate number if a previous alarm was not
acknowledged.
Baud Select from OFF, 1200, 2400 or 9600,
normally set to 1200.
Status Report Interval The time period between periodic alarm
status reports dialed from the KDA to
T/Mon. A value of 0 for both hours and
minutes disables periodic status reporting.
Dialout Alarm Reporting Determines when the KDA will use the
dialup link to report alarms (as opposed
to normal reporting via fixed connection
on the primary port). This entry works in
conjunction with an entry on the Alarms
definition page for each individual alarm:
• When NORMAL, calls whenever a
DIALALARM occurs, as specified on
the Alarms page.
• When BACKUP, calls only when the
primary port has failed, may be
enabled-or disabled for individual
alarms on the Alarms page.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 17

SOFTWARE DETAILS • BASE AND SATELLITE UNITS
1.14
Alarms, Relays and Expansion Cards
This page defines the alarms, relays and expansion cards on a base or
satellite board that will be monitored and reported by the KDA. Screens
will vary depending upon hardware setup.
See section 3 for expansion cards.
Base and Satellite Units
Alarms
Description Any useful name that may be attached to the
alarm, up to 21 characters. This name is
copied to KDA internal memory when connected to standard firmware versions and
later, or Timestamp firmware version. It is
used only in the T/KdaW program itself. If
alarms are being reported via SNMP, alarm
descriptions are obtained from this entry. It
otherwise has no effect on system operation.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 18

BASE AND SATELLITE UNITS • SOFTWARE DETAILS
Normally Closed Alarms are essentially detected as
changes in the position of a switch. The
KDA assumes that conditions are normal
when a switch is open and triggers an
alarm when it closes. In some applications
this is reversed and the alarm occurs when
the switch opens. Check Normally Closed
if you have any alarms that are wired up
this way.
Normal Dialout Dial Alarms if NORMAL dialup alarm
reporting has been selected under Edit
Docking Ports - Secondary Port, alarms
checked here will be dialed when they
occur (they will also respond to any polls
received on the primary port).
Backup Dialout Enable Dial Backup if BACKUP dialup
alarm reporting has been selected under
Edit Docking Ports - Secondary Ports,
alarms checked here will be dialed when
they occur if communication fails on the
primary port.
When Firmware Qual Time is the time period that an
alarm must be active before the KDA will
consider it to be valid and start to report it.
Range and resolution depends upon
Qualification Units.
Qual Units time units — tenths of seconds, seconds or minutes — referred to
by the Qualification Time entry. Units
apply to groups of eight consecutive
alarms.
Use Alarm 1 If you are physically located near a KDA,
you can acknowledge alarms directly to
the device. Wire up a switch(usually a
push button) as Alarm 1, and check this
entry to tell the KDA to treat it as an ack.
Activate Relay 1 When checked, closes Relay 1 whenever
an alarm on COS occurs and keeps it
closed until it is ack'ed. This is
often used to sound a buzzer, etc.
Type is Timestamp or E2A
for local ack
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 19

SOFTWARE DETAILS • BASE AND SATELLITE UNITS
1.16
Relays
Description Optional identifying information, shows on monitor dis-
play.
Momentary Time (0.1 seconds to 25.5 seconds) that a relay Activation
Period stays closed when issued a Momentary command.
Base Ports
Port ID Physical port located on the KDA
Protocol Select the Protocol to be used (TBOS or TELTRAC)for
communicating with devices connected to that port.
Select None if the port is not used.
Baud Rate Select the baud rate of the port here. Select from 1200 or
2400 for TBOS. TELTRAC ports must be 1200 baud and
have no selectable options for baud rate.
Parity Select the parity setting from None, Odd or Even. Odd
is the default selection.
Stop Bits Select 1 or 2 Stop Bits.
RTS lead Time, in milliseconds, after serial port RTS handshaking
is asserted that data bits start to be transmitted.
Ordinarily does not have to be changed, but may be
adjusted if communications timing problems are
encountered or delay is needed for relay keying.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 20

SOFTWARE DETAILS • BASE PORTS AND POLLING MAP
RTS tail Time, in milliseconds, after serial port data trans-
mission stops that RTS handshaking is cleared.
Ordinarily does not have to be changed, but may
be adjusted if communications timing problems
are encountered or delay is needed for relay keying (see below).
Polling Map
Ports (T8 Displays) This column defines the physical KDA
ports. Their DCPF output display mapping is shown in parenthesis.
Polling TELTRAC
Address/TBOS Display Enter the TELTRAC addresses and
TBOS displays to be shown on the KDA
Ports. TBOS displays are selected from
the range of 1-8 and must be sequential.
(T/kdaW will automatically adjust if
TBOS displays are entered into an incorrect field.) TELTRAC addresses are
selected from the range of 0-126. Any
eight may be selected and entered in any
order. Duplicate addresses are not
allowed.
There are eight
TELTRAC
addresses per
port with one display per address
(Points 1-63).
Device failures
appear on point
64, 65, and 66 of
each display.
Note:
To preserve TELTRAC mapping
on DPS masters,
always append
new TELTRAC
addresses to the
first available
address slot on
the port.
TELTRAC mapping example:
Port 2, TELTRAC Addresses: 2 9 5 6 7
Map to displays: 9 10 11 12 13
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 21

SOFTWARE DETAILS • CONNECTING TO THE KDA
1.18
CONNECTING TO THE KDA
Connect Direct
After setting your KDA and expansion card configurations, go to the
Connect menu and set up this screen.
Note: Only
com ports that
are installed
and available
will appear on
your KDA software screen.
Line Name Select the serial port that will be used to connect to
the KDA.
Line Properties Select to edit the baud rate, data bits, parity and stop
bits of the connection device.
Connect To
Shelf You may select the Shelf option once the base and
satellite units have been initially configured. Then,
plug into the base KDA. Both the base and all satellites are accessible through this connection.
Base Select the Base option to connect to just the base
unit. Then, plug into the base KDA.
Note:
Each satellite
must be initially
downloaded
individually
from its own
craft port. (See
the First Time
Satellite
Configuration
section on the
following page.)
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 22

SOFTWARE DETAILS • FIRST TIME SATELLITE CONFIGURATION
Sat 1-2-3 Select the appropriate satellite that corresponds
to the serial cable connection. Only that satellite
and any expansion card installed in it may be
accessed through this connection. Then, plug
into that satellite. This option is used for the initial download of each satellite in order to tell the
KDA that it is a Satellite KDA and not a Base
and also which Satellite address it is to use. This
is accomplished after connecting to the appropriate KDA and then writing the configuration to
it by selecting the “Write To KDA button (See
Writing and Reading section).
Use Terminal N/A
Server
To configure satellites for the first time, go through the hardware setup
screens as described earlier in the manual. A satellite KDA needs to be
told that it is a satellite and not a base unit. This is done by connecting
to each Satellite KDA individually at its own front panel craft port.
1. Create a database specifying the satellite count. See Hardware
Setup menu.
2. Connect your computer to the craft port of the satellite
3. Click the Connect menu at the top of the screen to access the
Connect options window.
4. In the Connect To portion of the window, select the radio but
ton of the satellite number that you are connecting to.
5. Click the Connect button to connect to the KDA.
6. Write the information to the KDA by clicking the Write to
KDA button (See the Writing and Reading section page 2.25)
Repeat these steps for each satellite KDA until they all have been provisioned as satellites. Once this has been done, further changes cal all be
done from the base KDA’s craft port with the Connect To radio button
set to Shelf.
First Time Satellite Configuration
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 23

SOFTWARE DETAILS
1.20
Warning:
Monitoring
KDA alarm
points through
T/KdaW prevents normal
alarm reporting. This should
only be used as
a turn-up diagnostic.
After connecting to a base unit or satellite, click on the monitor button from the Connect to KDA tool bar.
Alarms
Alarm Acknowledgement
Use this screen to acknowledge alarms. When an alarm is in a
change of state (COS) mode, a red alarm button will be displayed on
the Monitor KDA Alarms screen. First, click on the red Ack button
to acknowledge the alarm. Then, the red Ack will turn green and the
KDA will activate a relay.
Monitoring the KDA
Relays
Released Relay open
Latch Relay closed
Mom (Momentary) Close the relay for a pre-deter-
mined time
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Indicates current state.
Indicates change of site.
Red=Has gone into alarm.
Green=Has cleared.
Click to acknowledge change
of state.
Page 24

SOFTWARE DETAILS • MONITOR KDA
Note to NIA
Card and
SNMP users:
Alarm descriptions are used
by your SNMP
manager,
otherwise the
alarm descriptions are
ignored by the
KDA.
Housekeeping
Applicable to Timestamp version firmware only
Power Up System has been re-powered
Watchdog Reset Watch dog reset has occurred
Points Locked One or more points locked
Lost Provisioning Download configuration lost
Memory Diag Fail There has been a CPU failure
Exp Card Error There has been an expansion card error
Reserved
Modem Response Modem not getting a response
No Dialtone Modem not getting a dialtone
Time Stamp Time stamp buffer memory has filled and
“wrapped around” deleting some records.
Over Flow
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 25

1.22
MONITOR KDA • TUNE MODEM • SOFTWARE DETAILS
Tune Modem
This feature is only available when a 202 modem is installed on the
primary docking port. To access this screen, click on the Monitor
button and select the Tune Modem tab.
Signal
Mark Transmit high tone
Space Transmit low tone
Square Transmit high/low square wave
Off Transmitter off
Level
Coarse Up Level up 10 steps
Fine Up Level up 1 step
Fine Down Level down 1 step
Coarse Down Level down 10 steps
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 26

SOFTWARE DETAILS • TUNE MODEM • MONITOR KDA
Tuning optimizes the signal quality of the 202 tone modem interface. The receive level is automatically adjusted over a 20 dB range.
A “pad” on the input can be set for an input range of -43 to -23 dB
or for a range of -23 -3 dB. The modem transmit level is software
adjustable and, therefore, does not require the unit to be opened.
The modems are shipped from the factory with the transmit level set
a t approximately -13dBm. The transmit level is stored in NV RAM,
making it unaffected by power removal.
Tuning Procedures
1) Connect a Level Meter across the modem transmit leads. If the
modem is not connected to any terminating equipment, place a
620 ohm resistor across the leads. (A resistor is not necessary if
the modem is connected to a VF line or other terminating
device.)
2) Place transmitter on Mark (High Tone).
3) Click the appropriate signal keys to achieve a desirable transmit
level range.
4) When the level is correct, return to the monitor screen by
selecting another tab from the Monitor KDA toolbar, or select
Exit Monitor to return to the Connect to KDA screen.
Warning:
Tuning a
modem above
-2 Dbm will
cause wave
form distortion.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 27

1.24
MONITOR KDA • TBOS • SOFTWARE DETAILS
Tbos
This screen shows the state of all 64 Tbos alarm points.
Any active alarms
are shown in red
with an alarm
number displayed
vertically.
The channel number is shown in
yellow if invalid
information is
being received.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 28

SOFTWARE DETAILS • CONNECTING • WRITING AND READING
Write to KDA
This feature transmits
device properties in
the current system
record to the KDA. If
a connection has been
made to the KDA
Shelf and satellites
have been installed
and initialized, configuration data will also
be written to the satellites.
Read from KDA
This feature replaces
the current system
record with device
properties retrieved
from the KDA. A message window also
appears, showing
progress and any
exceptional conditions
that may arise. If a
connection has been
made to the KDA
Shelf, and satellites have been installed and initialized, configuration data will also be retrieved from the satellites.
How to Terminate Writing or Reading
A write- or read-in-progress may be terminated by clicking Cancel.
However, it is not recommended since it leaves the KDA with a
mixture of two configuration records. Clicking Done after the write
is complete closes the Write window and the system remains connected.
Writing and Reading
Note: The Write to KDA/Read From KDA
progress window depicts the internal memory of the KDA.
Green = Unchanged
Blue = Changed
Yellow = Unused
Note: New
information
written to the
KDA does not
take effect
until you have
disconnected,
which causes
the KDA to
reboot.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 29

NOTES
1.26
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 30

TROUBLESHOOTING
2.1
Troubleshooting
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 31

2.2
TROUBLESHOOTING • LAN TRAFFIC AND COMMANDS
T
ROUBLESHOOTING
Primary, Satellite, LAN Traffic and LAN Commands
Spy mode will allow examination of the protocol between a host
KDA and its associated expansion card when being polled from the
T/MonXM master. By plugging in a lap top or other DOS computer
at the craft port you can view the protocol in either ASCII or
Hexadecimal. This allows on-the-spot analysis of the communications between the KDA and the polling master to quickly isolate
communication problems.
The query and response is indicated by the color of the data
bytes: the host data in green and the expansion card response in red.
Spy LAN Traffic and LAN Commands applies to expansion
card. Spy Primary applies to primary docking pad. Spy Satellite
to base satellite communications.
Notes: Spy
modes work
only in direct
mode, requiring
the computer to
be connected
directly to the
craft port.
‘LAN’ here
refers to communications
between a host
and satellite
card.
LAN protocol is
DCPF. Please
refer to your
KDA user manual for information on
DCPF protocol.
See page 3.3 for screen definitions.
Spy Mode
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 32

2.3
SPY SECONDARY • TROUBLESHOOTING
Spy Options
Pause Causes display to temporarily stop. (Button will tog-
gle to Resume once selected.)
Clear Refreshes screen by erasing all data bytes and start-
ing with clean window.
Capture Captures protocol analyzer display to a file in the
TCONFIG directory. File name appears at lower
right corner of analyzer window. In File name
includes a sequence number. The 000 increments
001, 002, etc. each time a capture is executed.
Deleting the files from the directory will return the
counter to 000.
Hex, Ascii, Dec View data bytes in any one of three forms.
Scroll Check this box to use automatic scrolling.
Primary, Satellite,Select desired unit or items to view.
Spy Secondary
Access the Spy Secondary screen
under the Tools item under the main
T/KdaW menu. This screen will allow
the user to view and capture the activity on the docking module installed in
the KDA secondary docking pad, usually a modem.
Lan Traffic or
LanCommands
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 33

2.4
TROUBLESHOOTING • DISPLAY PROTOCOL • CONNECTING • SOFTWARE
This screen reveals the data bytes communicated between the KDA
software and hardware. It shows communications between the
TKdaW program and the KDA itself. Red is read (received) from
KDA, Green is written (transmitted) to KDA.
Scroll
Check this box for data to automatically scroll. Allows you to view the
most current code without manually
using the scroll bar.
Clear
Click this button to erase information from the Protocol screen.
Pause
Click to pause the protocol viewing.
Re-click to resume.
Close
Click close to return to the main
connect window.
Help and
Technical Support
The Help screen may be accessed by clicking the Help button or F1
at any time. If you need further assistance, contact our technical
support staff at (800) 622-3314, or check our web site Tech Support
FAQ at www.dpstele.com.
Display Protocol
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 34

3.1
EXPANSION CARDS
Expansion
Cards
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 35

EXPANSION CARDS
3.2
Provides 4 or 8 TBOS polling ports. Each port may poll up to 8 displays
(512 alarm points).
Edit Expansion Ports Screen
for the 4- and 8-Port Scanner
Enabled Only the ports that are currently connected to
active TBOS sources should be enabled. Check to
enable, leave blank to disable.
Baud Select 1200 or 2400, normally 2400.
Displays to Poll Click on the number to enable. Select only displays
available in the interrogated TBOS device. Leave
out unavailable displays to save polling time and to
prevent unnecessary failed display alarms.
DCP Address Must match the base address being polled by the
master. Any range from 1-255 or 0 to disable.
[When using a DCP-type
protocol]
EXPANSION CARDS
4- and 8-Channel TBOS
Note: The
TBOS portion
of the 8-analog
6-TBOS card
uses the same
screen.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 36

3.3
EXPANSION CARDS
8- and 16-Channel Analog
Enabled Check to activate a particular channel. A chan-
nel cannot be edited until it is enabled.
Description Enter the point description, up to 13 characters.
Label Enter a 3-character name or abbreviation for
the native units being measured (e.g., F OR C
for degrees).
Unit Thresholds Enter the numeric boundaries for threshold
alarms (major over, minor over, major under,
minor under).
Dial Alarms Enter NONE for no alarms reported; enter MJ for
only Major Over or Major Under to be reported;
enter MJ+MN for all cases reported.
Dial Clear When checked, a dialed alarm will also be
dialed when it clears.
Qual Period and Enter the time period an alarm must be
Qual Units active before the KDA will validate it to be
reported.
Scale Click the “Scale” button to acces the analog
scaling worksheet. This enables monitoring in
native units, rather than volts or milliamps.
(8- and 16-Channel Analog continued)
DCP Address Must match the base address being polled by the
master. Any range from 1-255 or 0 to disable.
Note: The
Analog portion
of the 8-analog
4-TBOS card
uses this same
screen.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 37

EXPANSION CARDS
3.4
Analog Scaling Worksheet
Access the worksheet by clicking on the elipses following the analog
channel number on the analog editing page or the “scale” button.
Analog scaling assumes that there is a positive straight-line relationship between the native quantity being measured, such as degrees of
temperature and the corresponding voltage (or current) that is applied
to the analog card.
Native Units Same as Native Unit Label on the main analog
page — a 3-character name or abbreviation for the
native units being measured (e.g., RH for relative
humidity or F for Fahrenheit).
Analog Units Volts or Current. (Current actually measures the
voltage drop across a standard 250-ohm shunt that
is inserted by a PC board jumper.)
Native Value 1 A value in native units such as degrees.
Analog Value 1 The voltage (or current) corresponding to Native
Value 1.
Native Value 2 A value in native units such as degrees.
Analog Value 2 The voltage (or current) corresponding to Native
Value 2.
Report Threshold Check if only threshold alarms are to be reported,
Only not analog values.
[When using a DCP-type
protocol]
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 38

EXPANSION CARDS
3.5
Analog Scaling Worksheet
Note: Scaling is automatically calculated in
Volts (or Milli-amps) = Native Units x Scale + Offset
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 39

EXPANSION CARDS
3.6
Exp 832 Alarms
Description Enter the point description, up to 13 characters.
Normally Closed Alarms are essentially detected as changes in the
position of a switch. The KDA assumes that conditions are normal when a switch is open and
triggers an alarm when it closes. In some applications this is reversed and the alarm occurs when
the switch opens. Check Normally Closed if you
have any alarms that are wired up this way.
Dial Alarms Check to dial upon occurrence of an alarm. If
left unchecked, alarm will be held until
polled by the master.
DCP Address Must match the base address being polled by
the master. Any range from 1-255 or 0 to disable.
[When using a DCP-type
protocol]
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 40

3.7
EXPANSION CARDS
Exp 832 Relays
Description Enter the point description, up to 13 characters.
Momentary Enter the time period in seconds that the
Period control point will remain activated when a
momentary operate command is sent.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 41

3.8
EXPANSION CARDS
LR-24 and SR-24 Relays
Description Any useful name up to 13 characters.
Momentary Enter the time period in seconds that the
Period control point will remain activated when a
momentary operate command is sent.
Momentary periods apply to groups of 6
relays.
DCP Address Must match the base address being polled by
the master. Any range from 1-255 or 0 to disable.
[When using a DCPtype protocol]
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 42

3.9
EXPANSION CARDS
Building Access Controller (BAC)
Turn-Up Password Enter a password for each door point being
used. The passwords entered here are for
turn-up and test procedures only and are only
effective until the BAC provisioning information is downloaded from an IAM or
T/MonXM master.
Note: If there is no information downloaded
from the IAM or T/MonXM regarding a door
point with a T/KdaW password, the T/KdaW
password will continue to be valid.
DCP Address Must match the base address being polled by
the master. It must be different than the DCP
address set for the KDA. Any range from 1255 is acceptable or enter zero to disable.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 43

APPENDIX
Appendix
4.1
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 44

APPENDIX • TERMS AND CONDITIONS
4.2
Warranty
DPS Telecom warrants, to the original purchaser only, that its products a) substantially conform to DPS’published specifications and b) are substantially free from defects in material and workmanship. This warranty expires two years from
the date of product delivery with respect to hardware and ninety days from the date of product delivery with respect to
software. If the purchaser discovers within these periods a failure of the product to substantially conform to the specifications or that the product is not substantially free from defects in material and workmanship, the purchaser must promptly
notify DPS. Within reasonable time after notification, DPS will endeavor to correct any substantial non-conformance with
the specifications or substantial defects in material and workmanship, with new or used replacement parts. All warranty
service will be performed at the company’s office in Fresno, California at no charge to the purchaser, other than the cost
of shipping to and from DPS, which shall be the responsibility of the purchaser. If DPS is unable to repair the product to
conform to the warranty, DPS will provide at its option one of the following: a replacement product or a refund of the purchase price for the non-conforming product. These remedies are the purchaser’s only remedies for breach of warranty.
Prior to initial use the purchaser shall have determined the suitability of the product for its intended use.
DPS does not warrant a) any product, components or parts not manufactured by DPS, b) defects caused by the purchaser’s
failure to provide a suitable installation environment for the product, c) damage caused by use of the product for purposes
other than those for which is was designed, d) damage caused by disasters such as fire, flood, wind or lightening unless
and to the extent that the product specification provides for resistance to a defined disaster, e) damage caused by unauthorized attachments or modifications, f) damage during shipment from the purchaser to DPS, or g) any abuse or misuse
by the purchaser.
THE FOREGOING WARRANTIES ARE IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
In no event will DPS be liable for any special, incidental, or consequential damages based on breach of warranty, breach
of contract, negligence, strict tort, or any other legal theory. Damages that DPS will not be responsible for include but are
not limited to, loss of profits; loss of savings or revenue; loss of use of the product or any associated equipment; cost of
capital; cost of any substitute equipment, facilities or services; downtime; claims of third parties including customers; and
injury to property.
The purchaser shall fill out the requested information on the Product Warranty Card and mail the card to DPS. This card
provides information that helps DPS make product improvements and develop new products.
For an additional fee DPS may, at its option, make available by written agreement only an extended warranty providing
an additional period of time for the applicability of the standard warranty.
Technical Support
If a purchaser believes that a product is not operating in substantial conformance with DPS’ published specifications or there
appear to be defects in material and workmanship, the purchaser should contact our technical support representatives. If the
problem cannot be corrected over the telephone and the product and problem are covered by the warranty, the technical support representative will authorize the return of the product for service and provide shipping information. If the product is out
of warranty, repair charges will be quoted. All non-warranty repairs receive a 90-day warranty.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 45

4.3
APPENDIX
Alarm Levels -
Alarm Levels are indicators that correspond to a specified alarm. Alarm
Levels range from “A” to “D”, with “A” as the highest priority, often
designated “critical.”
Alarm Point -
A single discrete alarm input that requires a discrete (usually on-to-off
or off-to-on) change in current flow or voltage to indicate a change of
alarm condition from normal to alarm state. Assigned to a point number in a display and address. Usually reported to master as a single bit
in a data stream.
Alternate Path -
A backup route to the master via dial facility. The alternate path will be
selected by the remote unit when communications via the primary path
fail.
ASCII -
The abbreviation for American Standard Code for Information
Exchange. ASCII is a generic DOS text file. Most word processors can
read ASCII text.
Auxiliary Display (GLD) -
A unit providing remote alarm point descriptions. Time Stamp KDA
versions 1.7 and above will support up to 3 General LCD Displays
(GLDs).
Battery -
Facility DC power. Normally supplied from a battery plant inside the
office. Polarity is normally negative (positive ground) in a telecom
facility.
GLOSSARY OF TECHNICAL TERMS
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 46

APPENDIX
4.4
Baud -
The data transmission rate that the COM Port uses to talk to the equipment. Common data rates include: 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200 (19)
and 38400 (38).
BIOS -
Basic Input/Output Operating System. This is the network of components that gives a computer the ability to operate with external devices
and programs.
Change Of State -
This is the condition of a point when it is in transition from one state to
another. Change of State is abbreviated as COS.
Config. Sys File -
The CONFIG.SYS file is an ASCII text file that allows the user to configure certain aspects of the operating system. Aspects that can be configured include: the number of internal disk buffers allocated, the number of files that can be open at one time, the formats for date and time,
and the name and location of the executable command processor file.
Connectorized
Unit provides quick-mate type connectors on the rear panel, as opposed
to the more permanent wire-wrap connections. Connectorized units can
shorten time for installation and replacement.
Control Point -
Relay isolated output that is controlled by command from the master.
Normally-open (SPST) dry contacts are commonly used.
Com Port -
Abbreviation for Communication Port.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 47

4.5
APPENDIX
Communication Port -
Serial interfaces that can be used for additional devices such as
modems. Abbreviated as Com Port and normally referred to as COM1
& COM2.
COS -
This is the abbreviation for Change Of State.
Craft Port -
Serial port for connection of a computer or ASCII terminal to test and
modify configuration of the remote.
CTS -
This is the abbreviation for Clear To Send.
Database -
A file containing records of organized and related information.
Dial String -
A combined set of numeric and special characters used as the pager or
modem dial number. The Dial String is the phone number and special
characters that the KDA will use to dial out to master.
Displays -
Displays contain 64 points of data.
Docking Module -
Small plug-in circuit assembly that provides the electrical interface for
a communications port. Available interfaces are RS232, RS422/485,
202 Modem (for dedicated line) and 212 Modem (for dial line).
DOS Path -
This is the DOS search path used to find specified directories on specified drives.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 48

APPENDIX
4.6
Download -
The act of transferring a configuration file from a computer to the
KDA. Can be done remotely via the dial port (modem), if equipped, or
locally via the craft port.
DTMF -
The abbreviation for Dual Tone Multi-Frequency. This is a common
touch tone telephone.
Expansion Card -
Accessory card that fits into a slot at the right side of the KDA chassis.
Adds additional functions to the KDA, such as Analog Channels,
TBOS Ports, Control Points, Discrete Alarm Points and ASCII Serial
Ports.
General LCD Display (GLD) -
A unit providing remote alarm point descriptions. Time Stamp KDA
versions 1.7 and above will support up to 3 General LCD Displays
(GLDs).
Hexadecimal -
A numbering system having a range from “0” to “F”.
Interface -
The electrical standard used by a data transmission port (RS232,
RS422, RS485, 202 Modem, RJ11 etc.)
LED -
The abbreviation for Light Emitting Diode. The LED is used as an indicator of activity.
Live Alarms -
Live Alarms are indicated by a display of the number of standing
alarms on the system.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 49

4.7
APPENDIX
Modem -
The abbreviation for Modulator/Demodulator. Modems are used to transfer data over telephone lines.
Optically Isolated -
Electrical interface, such as a discrete alarm point input, that isolates the
external circuitry from the internal circuitry of the KDA with an optical
coupler. Optical Isolation reduces the possibility of electrical mis-match or
interference between the KDA and the alarm sources.
Point -
The smallest unit on the line that can be monitored. It is therefore an alarm
in itself.
Polarity -
The polarity of a point can be either Normal (NRM) or Reverse (RVS).
Normal polarity is current flow in a closed circuit for an alarm.
Primary Pad -
Location of the docking module for the primary communications port. The
Primary communications port will be used by the KDA to report all
alarms, unless it is unequipped. If the Primary port fails to communicate
properly, the KDA will switch to the secondary pad, if equipped. (see
Docking Module)
Protocol Analyzer -
A diagnostics mode in which the absolute hex bytes (hexadecimal), going
to and from a particular channel, are displayed.
@SUBHEAD II = Qualification Time -
The Qualification Time is the amount of time an alarm must stand in an
“alarm state” before the KDA will perform an action.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 50

4.8
APPENDIX
Rebuild Key Files -
This function rebuilds index key files that are associated with the data files.
RTS
The abbreviation for Request To Send.
RTU -
Remote Telemetry Unit. An RTU is a device that gathers alarm inputs and
communicates them to a master alarm station.
Satellite -
Additional KDA units at the same location and communicating with the
master through a “base” KDA. Up to three satellites can be associated with
a base KDA. Using satellites expands the use of a remote address, allowing greater system capacity.
Secondary Pad -
Location of the docking module for the secondary communications port.
The Primary communications port will be used by the KDA to report all
alarms, unless it is unequipped. If the Primary port fails to communicate
properly, the KDA will switch to the Secondary pad. The Secondary pad is
normally the location of the dial-up modem, if equipped. (see Docking
Module)
Stop Bits -
The trailing bit(s) in a byte of data that indicate the end of a transmitted
byte in RS232 communications.
String -
A combined set of characters.
TBOS -
Telemetry-Byte-Oriented-Serial protocol. A well-established alarm system
protocol used by many telco-oriented manufacturers. Normally embedded
in switches, channel banks and other equipment with many alarm points.
TBOS normally uses an RS422 serial port. A port has a capacity of 512
alarm points, divided into 8 “displays” of 64 points each.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 51

4.9
APPENDIX
Timeout -
A timeout action indicates a time limit was exceeded.
T/MonXM -
DPS interrogating master.
T/KDA -
Configuration software for the KDA.
Toggle -
A process of switching back and forth from one mode to another. The
enabling and disabling of switches and settings.
Traffic -
Activity on the line or channel.
Upload -
The act of transferring a configuration file from the KDA to a computer
using T/KDA software. Can be done remotely via the dial port
(modem), if equipped, or locally via the craft port.
Window -
Depending on the context, the term window can refer to an alarm monitoring widow or to a special mode window.
Wire-Wrap -
Wire connection points using a steel post that the connecting wire is
wrapped around using a special tool. Wire-wrap is a fast and compact
method of making lots of connections. It is commonly used on the KDA
for all inputs and outputs, except on connectorized units.
(See Connectorized.)
Word Length -
A communication port attribute that indicates how many bits are in a byte.
Typically is 8.
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 52

INDEX
NUMBERS
4- and 8-Channel TBOS: 4.2
4- and 8-Port Scanner: 4.2
Baud
DCP Address
Displays to Poll
Enabled
8- and 16-Channel Analog: 4.3-4.4
Description
Dial Alarms
Dial Clear
Enabled
Native Unit Label
Native Unit Thresholds
Qual Period and Qual Units
A
Ack:19
Alarm Acknowledgement: 2.19
Alarms: 2.14-2.15
Backup Dialout
Description
Normal Dialout
Normally Closed
Qual Time
Qual Units
Analog Scaling Worksheet: 4.4-5
Analog Units
Analog Value 1
Analog Value 2
Native Units
Native Value 1
Native Value 2
Auxiliary Display: 2.5, 2.7, 5.3
(See also Gen. LCD Display)
B
Base and Satellite Units: 2.14
Base Ports: 1.8, 2.16
Base Unit: 1.7
Building Access Controller (BAC): 4.9
C
ClrChan Protocol: 2.9
Baud
Parity
Password
Word Length
Comment: 1.3
Connect Direct: 2.17-2.18
Base
Connect To Shelf
Line Name
Line Properties
Sat 1-2-3
Connect Options: 1.9
D
DCP-Type Protocol: 2.7-2.8
DCP Address
Periodic Full Updates
Relay 8 Response to RTS
Report Satellite Failures
Responder Baud
Responder Parity
RTS Lead Time
RTS Tail Time
Dialup Alarm Reporting: 1.6
Display Protocol: 3.4
Docking Modules: 2.4-5, 2.10
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 53

INDEX
Docking Ports: 1.5, 6
Primary Docking Port: 2.6
Primary Port: 1.5
Secondary Docking Port: 2.12
Secondary Port: 1.6
DPS Network Interface Adapter (NIA): 2.4
E
E2A Protocol: 2.9
E2A Address
Generate COS on Clear
Respond with relay status
Exp 832 Alarms: 4.6
DCP Address
Description
Dial Alarms
Normally Closed
Exp 832 Relays: 4.7
Description
Momentary Period
Expansion Cards: 4.1-8
F
Firmware Type: 2.3
G
Gen. LCD Display: 2.5, 2.7, 5.6
H
Hardware Setup: 1.4, 2.3
Help and Technical Support: 3.4
Housekeeping: 2.20
Exp Card Error
Lost Provisioning
Memory Diag Fail
Modem Response
No Dialtone
Points Locked
Power Up
Reserved
Time Stamp
Watchdog Reset
I
Import a KDA Configuration Created with a
DOS T/config Program: 1.11
Install T/KdaW: 1.2
J
K
KDA-E2A: 2.3
KDA832-T8:
L
LR-24 and SR-24 Relays:4.8
DCP Address
Description
Momentary Period
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 54

INDEX
M
Modify an Existing KDA: 1.10
Monitor KDA: 2.19
N
O
P
Polling Map: 1.9, 2.17
Primary Reporting Number: 1.6
Protocol Options
ClrChan
DCPF
E2A
TBOS
Q
Quick Start:1.1-11
R
Read from KDA: 2.24
Relays: 2.16
RS-232 to NIA: 2.10
S
Satellites: 1.7
Secondary Port Configuration: 2.12-2.13
Baud
Callout Delay
Dialout Alarm Reporting
Modem Unit String
Primary Reporting Number
Secondary Reporting Number
Site Phone Number
Status Report Interval
Secondary Reporting Number: 1.6
Set Up a New KDA: 1.2
Site Definition: 1.3
Site Name: 1.3
Site Number: 1.3
Site Phone Number: 1.6
SNMP Protocol: 2.10
Community Names
Gateway IP Address
Granular Trapping
Pass-Through Baud Rate
Subnet IP Mask
Trap Manager IP Address
Unit ID
Unit IP Address
Software Details: 2.1-24
Docking Module 1
Docking Module 2
Hardware Setup
Site Definition
Spy Mode: 3.2
LAN Commands
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 55

INDEX
LAN Traffic
Primary
Satellite
Spy Options: 3.3
Capture
Clear
Hex, Ascii, Dec
Pause
Scroll
Spy Secondary: 3.3
Standard: 2.3
T
TBOS:1.9, 2.23
TBOS Protocol: 2.8
Relay 8 Response to RTS
Report Satellite Failures
Responder Baud
Responder Parity
RTS Lead Time
RTS Tail Time
TELTRAC: 1.9, 2.16-2.17
Terminate Writing or Reading: 2.24
TimeStamp: 2.3
Troubleshooting: 3.1
Tune Modem: 2.21
Tuning Procedures
U
UDP Protocol: 2.11
Gateway IP Address
Pass-Through Baud Rate
Subnet IP Mask
Unit ID
Unit IP Address
V
W
Write to KDA: 2.24
X
Y
Z
D-SW-709 UM00C.08103
October 22, 2001 www.dpstele.com
Page 56

Warranty
DPS Telecom warrants, to the original purchaser only, that its products a) substantially conform to DPS’ published
specifications and b) are substantially free from defects in material and workmanship. This warranty expires two
years from the date of product delivery with respect to hardware and ninety days from the date of product delivery
with respect to software. If the purchaser discovers within these periods a failure of the product to substantially conform to the specifications or that the product is not substantially free from defects in material and workmanship, the
purchaser must promptly notify DPS. Within reasonable time after notification, DPS will endeavor to correct any
substantial non-conformance with the specifications or substantial defects in material and workmanship, with new or
used replacement parts. All warranty service will be performed at the company’s office in Fresno, California at no
charge to the purchaser, other than the cost of shipping to and from DPS, which shall be the responsibility of the purchaser. If DPS is unable to repair the product to conform to the warranty, DPS will provide at its option one of the
following: a replacement product or a refund of the purchase price for the non-conforming product. These remedies
are the purchaser’s only remedies for breach of warranty. Prior to initial use the purchaser shall have determined the
suitability of the product for its intended use. DPS does not warrant a) any product, components or parts not manufactured by DPS, b) defects caused by the purchaser’s failure to provide a suitable installation environment for the
product, c) damage caused by use of the product for purposes other than those for which is was designed, d) damage
caused by disasters such as fire, flood, wind or lightening unless and to the extent that the product specification provides for resistance to a defined disaster, e) damage caused by unauthorized attachments or modifications, f) damage
during shipment from the purchaser to DPS, or g) any abuse or misuse by the purchaser.
THE FOREGOING WARRANTIES ARE IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITYAND FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
In no event will DPS be liable for any special, incidental, or consequential damages based on breach of warranty,
breach of contract, negligence, strict tort, or any other legal theory. Damages that DPS will not be responsible for
include but are not limited to, loss of profits; loss of savings or revenue; loss of use of the product or any associated
equipment; cost of capital; cost of any substitute equipment, facilities or services; downtime; claims of third parties
including customers; and injury to property.
The purchaser shall fill out the requested information on the Product Warranty Card and mail the card to DPS. This
card provides information that helps DPS make product improvements and develop new products.
For an additional fee DPS may, at its option, make available by written agreement only an extended warranty providing an additional period of time for the applicability of the standard warranty.
Technical Support
If a purchaser believes that a product is not operating in substantial conformance with DPS’ published specifications
or there appear to be defects in material and workmanship, the purchaser should contact our technical support representatives. If the problem cannot be corrected over the telephone and the product and problem are covered by the
warranty, the technical support representative will authorize the return of the product for service and provide shipping information. If the product is out of warranty, repair charges will be quoted. All non-warranty repairs receive a
90-day warranty.
Page 57

“...Dependable, Powerful Solutions
that allow users to monitor larger,
more complicated networks with a
smaller, less trained staff.”
“Your Partners in Network Alarm Management”
www.dpstele.com
4955 E. Yale Avenue • Fresno, CA 93727
(559) 454-1600 • (800)622-3314 • (559) 454-1688 fax
 Loading...
Loading...