Page 1
doepfer
A-178
Theremin Volt. Source
Antenna
CV Out
Offset
+
-
System A - 100
1. Introduction
Module A-178 (Theremin Voltage Source) produces
a
variable control voltage
closer your hand gets to its antenna.
You can use this control voltage in any modulation or
control process, and thus have access to an extra
system of real-time control in the synthesis process.
You use the Offset control to set the null point (zero)
of the control voltage output. Two LEDs give a visual
indication of the voltages produced.
The module also produces a gate signal at the
output: the signal goes "high" as soon as a voltage is
sensed which is above the threshold set with the
Threshold control
of the presence of a gate signal.
Theremin
which gets bigger the
. An LED gives a visual indication
A-178
gate
Gate Out
Threshold
This gives you the ability to produce a gate signal
simply by moving your hand.
1
Page 2
A-178
Theremin
System A - 100
doepfer
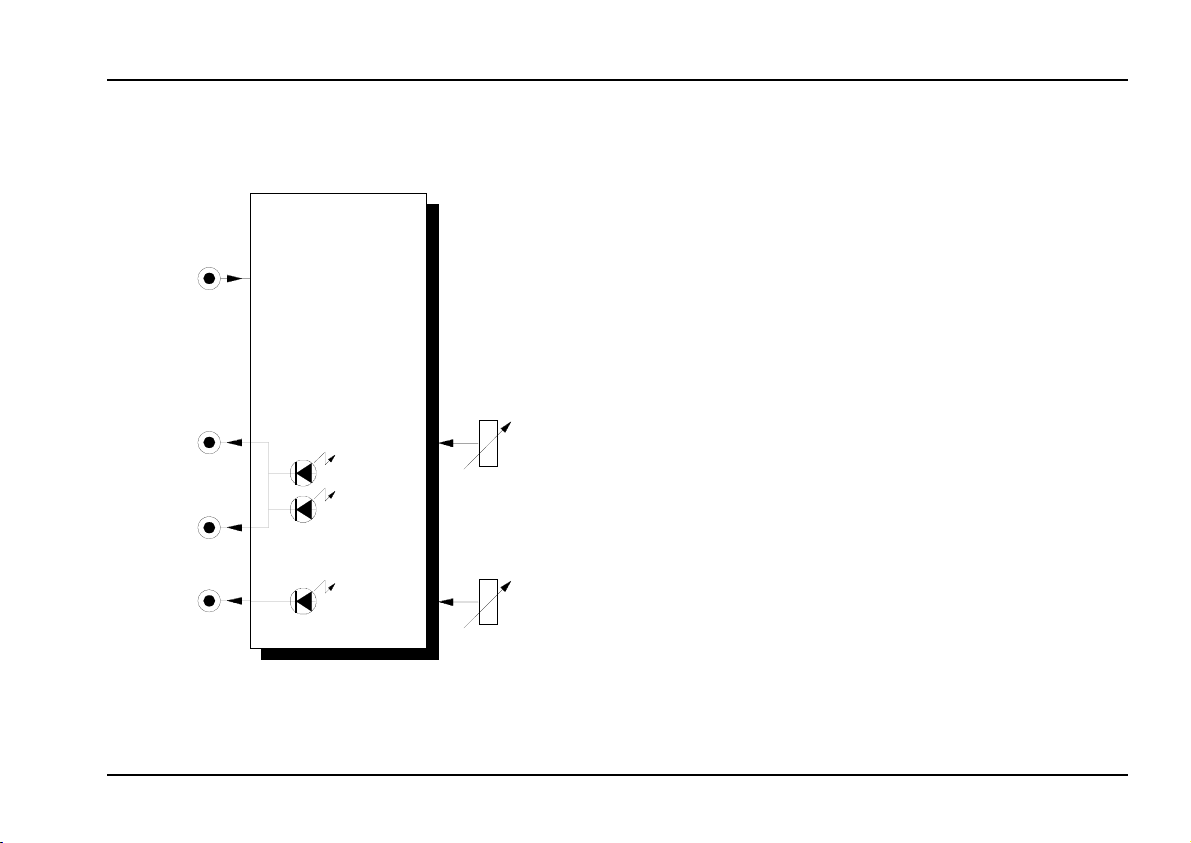
2. Overview
A-178
Theremin Volt. Source
Antenna
CV Out
Gate Out
THER
Offset
10
0
+-
10
0
Threshold
➀
➁
➂
➃
Controls:
Offset : control for setting the null (zero) point
1
2 LEDs : LEDs to give a visual indication of the
voltage present at output
LED : LED to give a visual indication of the
3
presence of a gate signal at output $
Threshold : control for setting the gate threshold
4
"
In / Outputs:
! Antenna : antenna input
CV Out
", §
Gate Out : gate output
$
: CV outputs (internally linked)
2
Page 3

doepfer
System A - 100
Theremin
A-178
3. Basic principles
The theremin acts as one plate of a capacitor and a
human body as the other plate. Moving the hand
towards and away from the antenna produces tiny
changes in capacitance (so tiny that they’re measured
in the picoFarad range). The electronics within the
theremin measure this change in the following way:-
The signal from an oscillator (whose frequency can be
subtly adjusted with the offset control 1) is compared
with the signal in another oscillating circuit, whose
capacitor is made up of the antenna and an external
object like the human body. If the capacitance is
changed (by, e.g., moving your hand) the circuit’s
resonant frequency changes. This is measured, and
converted into a control voltage.
Depending on the oscillator frequency, we may hit
either the rising or the falling edge of the oscillating
circuit’s resonance - and thus produce respectively
either rising or falling voltage as the hand gets closer
to the antenna. The module is factory adjusted so that
as the hand gets closer to the antenna, the voltage
rises. This can be reversed if required, though.
4. Controls
1 Offset
Control 1 is used to adjust the null point, so that the
control voltage at output " is at 0 V, when the hand is
some distance away from the antenna (more than
about 30 cm).
H Because this module, like all theremins, is
very sensitive to fluctuations in humidity,
temperature changes, etc., it’s necessary to
check adjustment each time you use it.
In addition to the offset control on the front
panel, there’s also an internal trim inductor
for
coarse adjustment
quency - see appendix on p. 8.
Using this trim pot for coarse adjustment may
be necessary if, for instance, you install
another antenna, and it’s then no longer
possible to set the null point with the front
panel offset control; or you want to use the
falling edge of the circuit resonance, so that
the control voltage generated gets lower as
you approach the antenna.
of this offset fre-
3
Page 4

A-178
Theremin
System A - 100
doepfer
2 LEDs
The LEDs 2 indicate the state of the voltage at CV
outputs " and §.
3 LED
LED 3 shows the presence of a gate signal at gate
output $.
4 Threshold
Using control 4 you set a threshold voltage for the CV
output, above which a gate signal will be produced at
output $.
5. In / Outputs
! Antenna
Use socket ! to connect the
H
If you use any other antenna than the telescopic one provided, and find that it’s not
longer possible to set the null point with the
offset control 1, then it may be necessary to
use the internal trim pot (see page 3, and
appendix, page 8).
antenna
" CV Out • § CV Out
CV outputs " and § (internally linked) put out the
theremin’s voltage.
$ Gate Out
Socket $ puts out the gate signal, whenever the
voltage created by the theremin is greater than the
threshold set with control 4. This gate signal can be
used as a noise-gate or as a source of manuallytriggered gates for other modules (see user examples).
.
4
Page 5

doepfer
6. User examples
System A - 100
Theremin
A-178
Theremin module A-178 provides a further source of
control for real-time sound manipulation and creation
(so see also the suggestions in the manual for the
Foot Controller, module A-177).
The change in voltage produced by your hand getting
closer to the antenna can be used for all sorts of
control or modulation:
• VCO pitch control
• VCA gain
VCF cut-off frequency
•
VCF resonance (with the A-121, 122 or 123)
•
VC-LFO frequency
•
LFO modulation depth
•
Standard Theremin
Fig. 1 shows how to use two A-178 modules to create
a standard theremin. One hand controls the pitch of
the VCO, and one controls the
of the VCA.
gain
A-178
: A standard theremin, using two A-178 modules
fig. 1
If you want to use two or more theremin modules, you
need to think carefully about the best positioning for
them in the rack relative to each other, so that each
can be controlled by hand movements without affecting the other/s.
It’s useful, with one or more theremin module, to place
them high in your rack, so that there’s less chance of
patch cables hanging down and affecting performance
(see fig. 2).
cv
VCO
cv
A-178
VCA
5
Page 6

A-178
A-178
THER
Theremin Volt. Sourc e
Antenna
Offset
CV Out
010
+
-
010
Gate Out
Threshold
Theremin
System A - 100
In the patch in fig. 3, just a quick movement of one
A-178
Theremin Volt. Source
Antenna
CV Out
Gate Out
Threshold
THER
Offset
010
+
-
010
hand can control both the frequency of the VCO, and a
rapid repeat of the envelope controlling the VCA, and
thus produce tremolo.
A-178
VCO
CV
Gate
doepfer
VCA
ADSR
fig. 2: Recommended positioning of two A-178s
Using the gate function
The gate function in the A-178 gives you the facility to
have remote switching of events in real time, simply
by moving your hand towards the antenna.
The function can be used as a noise gate, using the
gate signal to switch a VCA on and off, either directly
or via an ADSR or slew limiter. Whenever the signal is
underneath a certain voltage, the VCA simply shuts
down.
6
: User example for the gate function
fig. 3
An alternative to the patch in fig. 3 would be to use the
ADSR to control a filter as well.
Other possible uses: Start / Stop on a sequencer,
"one-shots" (ADSR-triggered noises, like thunder),
switching filter characteristics, etc. (see also the user
examples in the A-177 Foot Controller manual).
Page 7

doepfer
System A - 100
7. Patch-Sheet
The following diagrams of the module can help you
recall your own Patches. They’re designed so that
a complete 19” rack of modules will fit onto an A4
sheet of paper.
Photocopy this page, and cut out the pictures of
this and your other modules. You can then stick
them onto another piece of paper, and create a
diagram of your own system.
A-178
Theremin Volt. Source
Antenna
THER
Theremin
A-178
Make multiple copies of your composite diagram,
and use them for remembering good patches and
set-ups.
P • Draw in patchleads with colored
pens.
• Draw or write control settings in the
little white circles.
CV Out
Gate Out
Offset
0
+-
0
Threshold
10
10
7
Page 8

A-178
Theremin
System A - 100
doepfer
8. Appendix
On the board a trimming inductor resp. trimming
potentiometer is available with which the offset can
be adjusted internally. Use it if, for instance, you
connect a different antenna, and find that the frontpanel control 1 can’t adjust the offset sufficiently to
reach the null point, or if you want to reverse the
standard polarity of the theremin module, and change
its response so that it works on the falling edge of the
internal resonanct hf circuit
lower CV the closer your hand gets to the antenna).
Version 1:
The diagram on the right side shows the layout of the
A-178’s printed circuit board version 1. The trimming
inductor is encircled.
Versions 2 and 3:
For the versions 2 and 3 the circuit has been modified
and the inductor is replaced by a
meter. For version 2 it is labelled "Frequency Offset"/
P5 and located behind the offset front panel control.
For version 3 the potentiometer is labelled P3 and
located between the antenna socket and the offset
front panel control (close to the capacitor labelled "C1
150p").
(and thus produces a
trimming potentio-
The different pcb versions can be distinguished by the
pcb printings:
V1: no version imprint
V2: imprint "Theremin Controller Version 2 / 1998"
V3: imprint "Theremin A-178
V3
"
8
 Loading...
Loading...